Protective Effect of a Combined Glutamine and Curcumin Formulation on Alcoholic Gastric Mucosal Damage
-
摘要: 目的:旨在探讨谷氨酰胺、姜黄素组方对乙醇致大鼠胃粘膜损伤的保护作用及机制。方法:将50只SPF级健康SD雄性大鼠随机分为空白组、模型对照组、西米替丁组、高剂量组、低剂量组5组。连续30 d口服灌胃给药后,除空白组外,其余各组均在无水乙醇造模后处死。通过H&E染色观察胃粘膜组织病理学变化情况,采用试剂盒测定血清丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)、一氧化氮(NO)含量和谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(Glutathioneperoxidase,GSH-Px)活性,并测定组织中前列腺素E2(PGE2)含量水平和血红素加氧酶-1(heme oxygenase-1,HO-1)、NADPH醌氧化还原酶(NADPH Quinone Oxidoreductase 1,NQO1)、抗氧化相关基因核因子-E2相关因子2(Nuclear factor-E2 related factor2,Nrf2)、丝氨酸蛋白激酶-3β(Glycogen synthase kinase-3β,GSK-3β)的表达情况。结果:西米替丁组、高剂量给药组的胃粘膜出血等损伤情况较模型组(P<0.05)均有所缓解,高剂量给药组的效果更明显。此外,模型组MDA含量和GSH-PX活性明显增加,NO和PGE2含量明显下降(P<0.05),抗氧化相关基因HO-1、NQO1和Nrf2表达受到明显抑制,GSK-3β表达明显增加。与模型组相比,西咪替丁组和高剂量给药组MDA含量和GSH-Px活性显著下降,NO、PGE2含量显著上升(P<0.05),抗氧化相关基因HO-1、NQO1、Nrf2得到显著恢复(P<0.05),GSK-3β被抑制(P<0.05)。结论:组方对乙醇引起的急性胃黏膜损伤有抑制作用,其作用机制推测与Keap1-Nrf2-ARE氧化应激通路有关。Abstract: Objective: This study aimed to investigate the protective effect and underlying mechanism of a combined glutamine and curcumin formulation on ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage in rats. Method: A total of fifty SPF-grade healthy SD male rats were randomly partitioned into five groups: A normal group, a model control group, a cimetidine group, a high-dose treatment group, and a low-dose treatment group. After a period of 30 days marked by oral gavage administration, all groups, with the exception of the normal group, were euthanized post anhydrous ethanol-induced modeling. The histopathological alterations in the gastric mucosa were observed via hematoxylin & eosin (H&E) staining. Furthermore, serum levels of malondialdehyde (MDA), nitric oxide (NO), and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-PX) were ascertained using a specific reagent kit. Concurrently, the concentration of prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) within the tissue and the expression levels of heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1), NADPH quinone oxidoreductase (NQO1), the antioxidant-related nuclear factor-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) gene, and glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK-3β) were evaluated. Results: In the cimetidine and high-dose treatment groups, the incidence of gastric mucosal bleeding and other forms of injury were noticeably mitigated (P<0.05) compared to the model control group, with the high-dose treatment group demonstrating a more pronounced effect. Moreover, the model control group exhibited a significant elevation in MDA content and GSH-PX activity and a concurrent decline in NO and PGE2 levels (P<0.05). The expression of antioxidant-related genes, namely, HO-1, NQO1, and Nrf2, was significantly suppressed (P<0.05), whereas GSK-3β expression was markedly increased. In contrast, in comparison to the model control group, the cimetidine and high-dose treatment groups manifested a significant reduction in MDA content and GSH-PX activity, while NO and PGE2 levels notably increased (P<0.05). The expression of the antioxidant-related genes HO-1, NQO1, and Nrf2 was significantly returned to normal (P<0.05), and GSK-3β expression was suppressed (P<0.05). Conclusion: The combined formulation appears to exert an inhibitory effect on ethanol-induced acute gastric mucosal damage. This effect is hypothesized to be associated with the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE oxidative stress signaling pathway.
-
Keywords:
- glutamine /
- curcumin /
- gastric mucosal damage /
- oxidative stress
-
慢性胃炎在胃病类型中占比排名第一,初期临床表现上有腹痛、饱胀等,如果不加控制导致病情进一步发展,则会出现出血、穿孔、癌变等并发症[1−2]。多数慢性胃炎患者都有不同程度的胃粘膜损伤。作为“酒文化”盛行国家,我国由乙醇引发胃粘膜损伤进而演变为慢性胃炎患者不在少数[3]。乙醇具有脂溶性特性,在其进入体内被代谢时,能促进中性粒免疫细胞释放氧自由基的过程,导致胃黏膜出现组织损伤、微循环障碍、损伤愈合变慢等现象。接着通过呼吸爆发,使上述过程持续反复进行,最终导致胃粘膜损伤[4]。目前用于治疗胃粘膜损伤药物主要为质子泵抑制剂类、组胺H2受体阻滞剂,作用通路较为单一,且长期使用会出现耐药性情况。
通过检索国家市场监督管理总局特殊食品信息查询平台注册保健食品批件数据库[5],发现截至2022年7月,获得具有辅助胃粘膜保护功能批件保健食品共计77个。从使用原料来看,基本都为传统中药成分,其中砂仁、蜂胶、党参、葛根使用率较高,频率分别20%、17.6%、16.2%和16.2%;从主要功效成分来看,主要是粗多糖、总黄酮和总皂苷,占比分别为33.8%、31.1%和21.6%。整体来看,目前已有产品同质性较高,主要依据传统中医药理论设计。
传统中药靶点复杂,作用机制不够明确,且大多非药食两用;而西药则作用通路较为单一,且长期使用会出现耐药性情况。因此,从天然原料中寻找具有明确功效原料组方并将其应用于相关产品中,适用范围更为广泛。通过查询文献、咨询专家等方式确定谷氨酰胺与姜黄素搭配组方,推测其对由乙醇引发胃粘膜损伤发生有极佳抑制作用。谷氨酰胺能够增加防御因子粘液分泌,促进粘膜细胞连接紧密,加快上皮细胞修复和生长作用实现胃粘膜保护[6−8];姜黄素能增加胃粘膜血流量[9−10]、减少胃粘膜氧化应激和炎性因子表达[11−12],从而减轻胃粘膜损伤。根据国食药检保化[2012]107号《关于印发抗氧化功能评价等9个保健功能评价方法》中辅助胃粘膜保护功能动物实验要求,本文验证谷氨酰胺与姜黄素组方功效,并探索其作用机制,实现组方功效、靶点明确,为今后将其应用于功能食品或保健食品打好理论基石。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
SD大鼠 SPF级,健康雄性,体质量180~220 g,共50只,上海斯莱康实验动物有限责任公司提供,实验动物许可证号码:SCK(沪)2017-0005;谷氨酰胺 河北力维素科技有限公司提供;姜黄素 河南中大恒源生物科技股份有限公司提供; MDA、NO、GSH-Px、PGE2试剂盒 碧云天生物技术有限公司提供;PCR引物、逆转录酶试剂盒 由苏州金唯智生物技术有限公司提供。
HistoCore PEARL自动组织脱水机、HistoCore Arcadia全自动包埋机、Leica RM2125RTS手动轮转式切片机 美国徕卡公司;CX23生物显微镜 日本Olympus公司;7900HT Fast Real-Time PCR仪 美国ABI公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 分组及给药
SPF级SD大鼠50只,每组10只,随机分配,共5组,分别为空白组、模型对照组、西咪替丁组(阳性对照组)、高剂量给药组和低剂量给药组。给药方式和剂量:空白组、模型对照组每天口服灌胃生理盐水10 mL/kg;西咪替丁组灌胃给药65 mg/kg/d;将谷氨酰胺与姜黄素复配混合灌胃给药,其中高剂量组给药谷氨酰胺15 g/kg/d、姜黄素360 mg/kg/d;低剂量组给药谷氨酰胺2.5 g/kg/d、姜黄素60 mg/kg/d。杭州娃哈哈集团实验动物中心审查并批准实验程序(NO:2023010501)。
1.2.2 动物模型建立
根据国食药检保化[2012]107号《关于印发抗氧化功能评价等9个保健功能评价方法》中辅助胃粘膜保护功能动物实验要求,大鼠在连续灌胃服药30 d后禁食禁水24 h,除正常组大鼠外,其余各组用1 mL/只无水乙醇灌胃,1 h后用乙醚麻醉,主动脉取血并取胃部。
1.2.3 胃粘膜损伤评分标准
沿胃部大弯处切开,洗净胃内容物,将胃黏膜展开,用游标卡尺将出血点或出血带的长宽分别测定,并拍照记录[13]。观察等级分评定办法,见表1。按下列公式计算各组胃黏膜损伤程度:
表 1 急性酒精损伤肉眼观察分标准Table 1. Gross visual scorings of acute alcohol injury损伤程度 1分 2分 3分 4分 出血点 1个 − − − 出血带长度 1~5 mm 6~10 mm 10~15 mm >15 mm 出血带宽度 1~2 mm >2 mm 注:损伤总积分=出血点分值+长度分值+(宽度分值×2)。 损伤发生率(%)=某组出现出血或溃疡大鼠数/该组大鼠数×100
损伤积分指数=各组损伤总积分/组动物数量
损伤抑制率(%)=(A−B)/A×100
其中,A、B分别为模型组与实验组的损伤总积分。
1.2.4 病理组织学观察
根据官方动物评价方法对胃粘膜损伤进行评分后,取损伤严重相同部位组织固定于10%甲醛溶液制备成切片,将所制切片脱腊之后,严格按照H&E染色说明书进行染色操作,采用生物显微镜观察各组胃粘膜组织情况。
1.2.5 大鼠血清MDA、GSH-Px、NO水平
乙醚麻醉后,主动脉取血,将所取主动脉血液充分静置,两次离心后,取澄清上清液。按照试剂盒说明书操作流程测定各组大鼠血清MDA、NO含量以及GSH-Px活力[14−15]。
1.2.6 大鼠胃粘膜组织中PGE2含量
取损伤严重部位大鼠胃粘膜经过组织研磨、充分静置、离心后得组织上清液,按ELISA试剂盒操作方法测定胃粘膜组织中PGE2含量[16]。
1.2.7 大鼠胃粘膜组织抗氧化相关基因表达水平分析
采用Trizol法提取胃粘膜组织总RNA[17−18],严格按照逆转录酶试剂盒(MultiScribe Reverse Transcriptase;Applied Biosystems)说明书进行操作。首先,使用One-drop测定样品在260 nm和280 nm处RNA的纯度和浓度,样品的纯度即A260/A280的比值在1.8~2.0之间表示为纯的RNA。其次,将RNA逆转录成cDNA。然后将cDNA、引物和SYBR Green Master Mix充分混合至均匀,使用实时荧光定量PCR扩增并检测荧光强度,基因扩增程序如下:95 ℃,5 min循环1次;按照高温变性95 ℃,20 s;低温退火60 ℃,30 s,适温延伸72 ℃,20 s,循环45次,72 ℃终末延伸2 min。最后以β-actin作为参照基因,采用2−ΔΔCt方式计算四个基因相对表达水平[19]。实验所用基因引物的引物序列见表2[20−21]。
表 2 RT-PCR引物序列Table 2. Primers used in Real-time PCR基因 上游引物(5’→3’) 下游引物(5’→3’) β-actin GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT GSK-3β TGGCAGCAAGGTAACCACAG CGGTTCTTAAATCGCTTGTCCTG Nrf2 GCCGCTTAGAGGCTCATCTC TGGGCGGCGACTTTATTCTT HO-1 GGAAATCATCCCTTGCACGC TGTTTGAACTTGGTGGGGCT NQO1 AGGATGGGAGGTACTCGAATC AGGCGTCCTTCCTTATATGCTA 1.3 数据处理
统计学处理结果采用平均值±标准差(mean±SE)表示。用SPSS 26.0软件进行统计学分析,P<0.05表明差异具有统计学意义。采用Origin 2019软件作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 胃粘膜损伤评价结果
参照官方辅助胃粘膜保护功能评价方法对胃粘膜表面损伤评价,更客观展现胃粘膜损伤情况。各组胃粘膜组织损伤结果如表3所示。可以看出,无水乙醇造模,模型组损伤发生率为100%,显示造模成功。与模型组相比,西米替丁组和高剂量给药组SD大鼠损伤积分显著降低(P<0.01),低剂量给药组无差异。从损伤抑制率来看,高剂量给药组抑制作用最为明显,达到75%。结果表明西米替丁组、高剂量给药组都具有较好改善无水乙醇导致的胃粘膜损伤作用,且高剂量给药组效果更好。
2.2 胃粘膜组织病理学检查结果
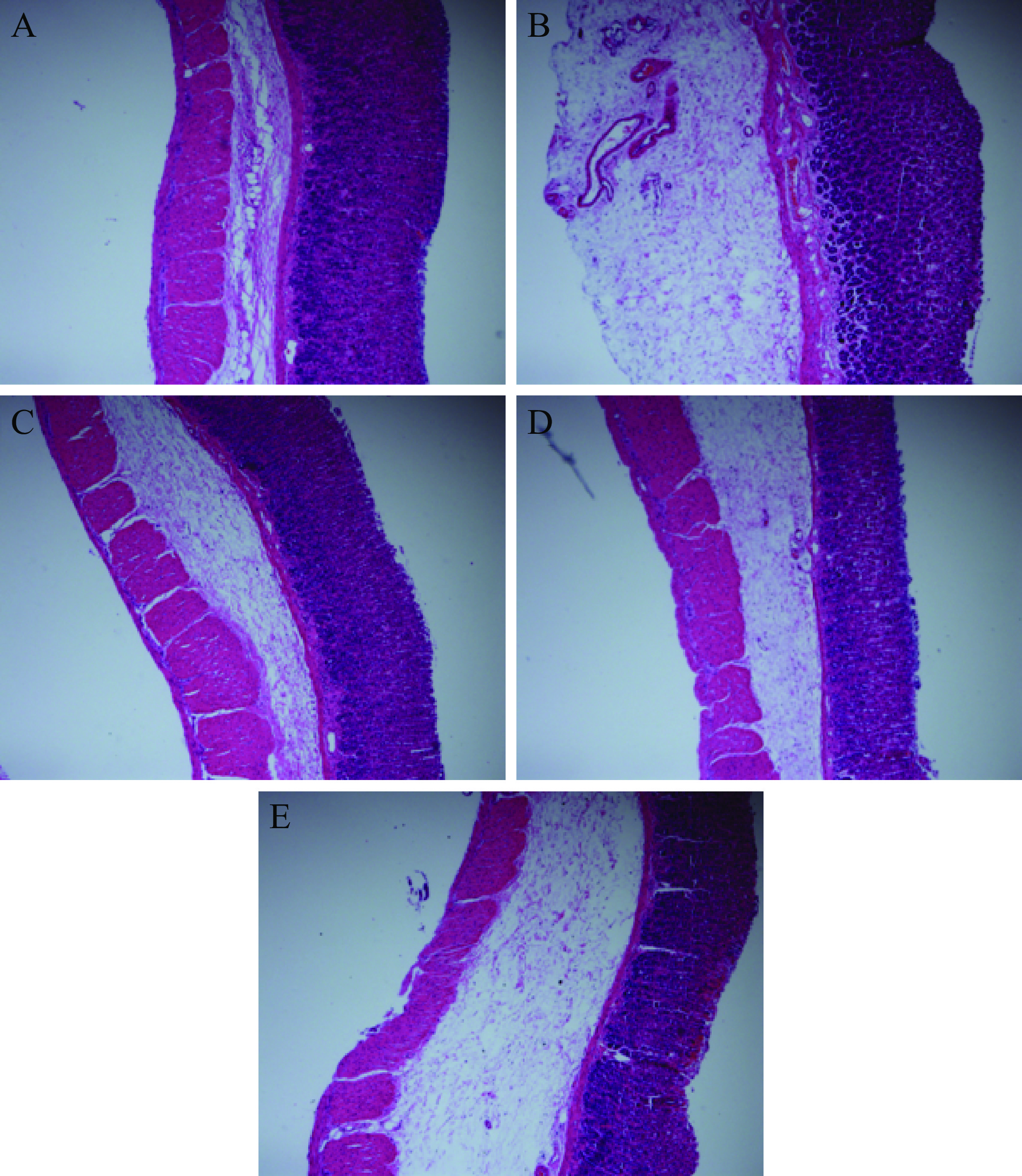
胃粘膜组织细胞是胃的天然保护屏障,即可以发挥胃保护作用又具有吸收功能[22]。通过H&E染色法观察大鼠胃黏膜情况(图1)。空白组大鼠胃粘膜组织结构完整且边界清晰(图1A);模型对照组大鼠胃黏膜组织细胞可见明显坏死、排列松散、结构不完整现象(图1B)。与模型对照组相较,西米替丁组与不同剂量的给药组中胃粘膜形态结构较为完整,排列相对整齐有规则,胃黏膜受损症状皆有所减轻(图1C),且给药组中高剂量给药组大鼠胃黏膜病理性损伤明显较轻。因此,组方可以帮助胃粘膜组织抵御乙醇带来的损伤,帮助胃粘膜组织细胞更好发挥屏障作用[23−24](图1D,图1E)。
2.3 大鼠血清MDA、GSH-Px、NO水平变化
GSH-Px、NO、MDA是反映组织器官氧化应激损伤的重要指标,NO、MDA升高显示氧化应激损伤发生和加重,GSH-Px活性降低意味着在受到氧化应激损伤后,胃粘膜组织细胞自我调节能力下降[13]。从表4大鼠血清检测结果可以发现模型对照组大鼠血清中GSH-PX活性较正常组有明显下降,MDA和NO水平均有明显上升(P<0.01),表明乙醇对胃黏膜的损伤与氧自由基有关。各给药组较模型对照组均能显著改善GSH-PX活性,降低MDA,NO水平(P<0.05),且高剂量组作用更显著(P<0.01)。因此,可以看出,组方改善了由乙醇引起的胃粘膜组织氧化应激损伤,增强了组织细胞自我调节能力[25−26]。
表 4 各组大鼠血清中MDA、GSH-Px和NO水平变化(n=10)Table 4. Changes of MDA, GSH-PX and NO levels in serum of rats in each group (n=10)组别 MDA含量(mmoL/L) GSH-Px(IU/mg) NO含量(μmol/ L) 正常组 7.9±1.4 52.3±7.5 32.5±2.3 模型对照组 13.1±2.3## 30.7±6.9## 15.2±2.8## 西米替丁组 9.1±2.8** 35.1±7.8** 48.9±5.4##** 高剂量给药组 8.5±4.5** 39.6±6.9** 61.7±4.2##** 低剂量给药组 10.7±5.1* 33.6±8.1#** 45.5±8.2##** 2.4 大鼠胃粘膜组织中PGE2 含量变化
PGE2是避免胃粘膜损伤无可替代的保护因子[27−28]。检测结果表明,与空白组相比,通过无水乙醇造模后,模型对照组大鼠胃粘膜组织中PGE2水平极显著降低(P<0.01)。各给药组与模型对照组相比,PGE2含量水平明显提高,高剂量组作用更显著(P<0.01)(表5),表明组方对胃黏膜组织的保护作用可通过提高PGE2水平而发挥作用。
表 5 各组大鼠胃粘膜组织PGE2水平(n=10)Table 5. PGE2 levels in gastric mucosal tissue of rats in each group (n=10)组别 PGE2水平(pg/mg) 正常组 275.6±6.7 模型对照组 142.1±7.2## 西米替丁组 248.1±5.4##** 高剂量给药组 259.3±6.3#** 低剂量给药组 214.6±8.7##* 2.5 大鼠胃粘膜组织中抗氧化相关基因表达水平变化
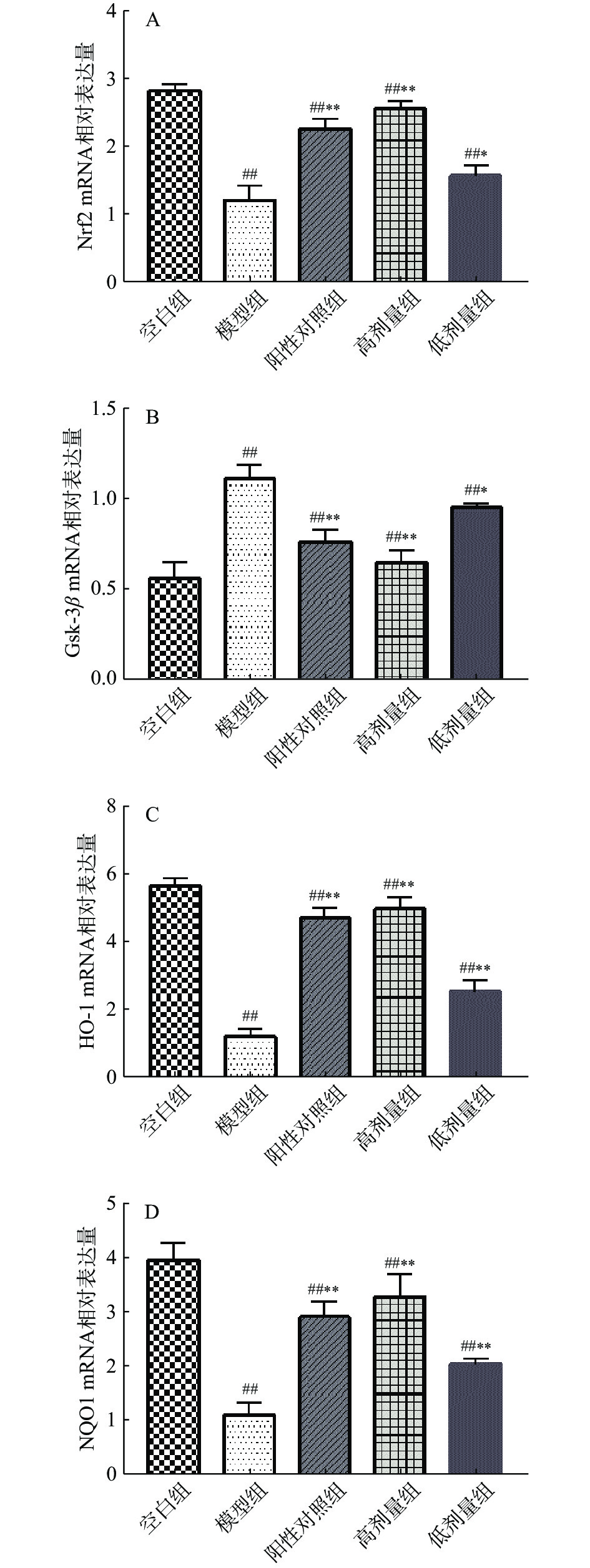
KEAP1-Nrf2-ARE是细胞内重要的抗氧化信号通路,机体的氧化应激激发NRF2/ARE信号通路的活化,使Nrf2与KEAP1解偶联,活化的Nrf2与ARE结合,刺激下游抗氧化酶相关基因(HO-1与NQO1)的表达。GSK-3β作为糖原合成激酶,通过推进Nrf2磷酸化降解过程,对下游抗氧化酶的表达进行抑制[29−30]。实验结果表明,各给药组与模型对照组相比,均可提升Nrf2、HO-1和NQO1的基因表达水平(P<0.05),抑制GSK-3β的表达(P<0.05),其中高剂量组给药效果极显著(P<0.01)(图2)。由此推测,组方保护酒精性胃黏膜损伤的作用与KEAP1-Nrf2-ARE信号通路有关。
3. 结论
本实验通过建立SD大鼠酒精性胃黏膜损伤模型,探究谷氨酰胺与姜黄素组方对胃粘膜损伤的保护作用。高剂量的谷氨酰胺和姜黄素组方灌胃SD大鼠后,在一定程度上降低了大鼠胃粘膜损伤积分指数,改善了大鼠胃黏膜组织病理损伤现象。同时,高剂量的谷氨酰胺和姜黄素组方使大鼠血清中的MDA含量得到了显著降低(P<0.01),GSH-Px的酶活性、NO含量和胃粘膜组织中PGE2水平均有显著提高(P<0.05),对酒精性胃粘膜损伤起到了保护作用。同时可以上调大鼠胃粘膜组织中抗氧化相关基因Nrf2、HO-1及NQO1的mRNA相对表达水平(P<0.05),下调了抑制抗氧化通路相关基因GSK-3β的mRNA相对表达水平(P<0.05),增强胃粘膜组织的抗氧化能力。
综合以上结果,谷氨酰胺和姜黄素组方具有抑制乙醇所致胃粘膜损伤的作用,其作用机制推测与调节抗氧化通路关键因子的基因表达,进而减轻氧化应激反应有关。虽然目前已有部分文献报道单一成分的谷氨酰胺或姜黄素具有修复胃粘膜损伤的功效,但是关于谷氨酰胺和姜黄素联用的组方对修复胃粘膜的文献少之又少,所以需要对其修复胃粘膜的机制进行深入研究。本研究阐明了谷氨酰胺和姜黄素组方对胃粘膜损伤的保护作用,为把其开发为安全有效的治疗酒精性胃粘膜损伤疾病的功能食品和保健食品提供了理论支持。
-
表 1 急性酒精损伤肉眼观察分标准
Table 1 Gross visual scorings of acute alcohol injury
损伤程度 1分 2分 3分 4分 出血点 1个 − − − 出血带长度 1~5 mm 6~10 mm 10~15 mm >15 mm 出血带宽度 1~2 mm >2 mm 注:损伤总积分=出血点分值+长度分值+(宽度分值×2)。 表 2 RT-PCR引物序列
Table 2 Primers used in Real-time PCR
基因 上游引物(5’→3’) 下游引物(5’→3’) β-actin GGCTGTATTCCCCTCCATCG CCAGTTGGTAACAATGCCATGT GSK-3β TGGCAGCAAGGTAACCACAG CGGTTCTTAAATCGCTTGTCCTG Nrf2 GCCGCTTAGAGGCTCATCTC TGGGCGGCGACTTTATTCTT HO-1 GGAAATCATCCCTTGCACGC TGTTTGAACTTGGTGGGGCT NQO1 AGGATGGGAGGTACTCGAATC AGGCGTCCTTCCTTATATGCTA 表 3 胃粘膜损伤评价(n=10)
Table 3 Evaluation of gastric mucosal injury (n=10)
表 4 各组大鼠血清中MDA、GSH-Px和NO水平变化(n=10)
Table 4 Changes of MDA, GSH-PX and NO levels in serum of rats in each group (n=10)
组别 MDA含量(mmoL/L) GSH-Px(IU/mg) NO含量(μmol/ L) 正常组 7.9±1.4 52.3±7.5 32.5±2.3 模型对照组 13.1±2.3## 30.7±6.9## 15.2±2.8## 西米替丁组 9.1±2.8** 35.1±7.8** 48.9±5.4##** 高剂量给药组 8.5±4.5** 39.6±6.9** 61.7±4.2##** 低剂量给药组 10.7±5.1* 33.6±8.1#** 45.5±8.2##** 表 5 各组大鼠胃粘膜组织PGE2水平(n=10)
Table 5 PGE2 levels in gastric mucosal tissue of rats in each group (n=10)
组别 PGE2水平(pg/mg) 正常组 275.6±6.7 模型对照组 142.1±7.2## 西米替丁组 248.1±5.4##** 高剂量给药组 259.3±6.3#** 低剂量给药组 214.6±8.7##* -
[1] 陈韶华, 厉有名. 酒精性胃粘膜损伤的研究进展[J]. 国际消化病杂志,2006,26(4):2−13. [CHENG S H, LI Y M. Advance of ethanol-induced gastric mucosa injury[J]. International Journal of Digestive Diseases,2006,26(4):2−13.] CHENG S H, LI Y M . Advance of ethanol-induced gastric mucosa injury[J]. International Journal of Digestive Diseases,2006 ,26 (4 ):2 −13 .[2] LIU Y, SUI D, FU W, et al. Protective effects of polysaccharides from Panax Ginseng on acute gastric ulcer induced by ethanol in rats[J]. Food & Function,2021,16(9):123−131.
[3] 罗永祥. 乙醇对胃粘膜损伤的机制研究概况[J]. 西南军医,2011,12(1):13−21. [LUO Y X. Overview of the mechanism of ethanol on gastric mucosal damage[J]. Journal of Military Surgeon in Southwest China,2011,12(1):13−21.] LUO Y X . Overview of the mechanism of ethanol on gastric mucosal damage[J]. Journal of Military Surgeon in Southwest China,2011 ,12 (1 ):13 −21 .[4] PANG S T, YU T, et al. Protective effect of camellia oil ( Camellia oleifera abel.) against ethanol-induced acute oxidative injury of the gastric mucosa in mice[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2017,65(24):4932−4938. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b01135
[5] 国家市场监督管理总局特殊食品信息查询平台网址[EB/OL]. http://ypzsx.gsxt.gov.cn/specialfood/#/food. [Website of the Special Food Information Query Platform of the State Administration for Market Regulation[EB/OL]. http://ypzsx.gsxt.gov.cn/specialfood/#/food.] Website of the Special Food Information Query Platform of the State Administration for Market Regulation[EB/OL]. http://ypzsx.gsxt.gov.cn/specialfood/#/food.
[6] SHAH A M, WANG Z, MA J. Animals glutamine metabolism and its role in immunity, a comprehensive review[J]. Animals,2020,10(326):25−29.
[7] MIN HYUN K, HYEYOUNG K. The roles of gutamine in the intestine and its implication in intestinal diseases[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2017,18(5):1051−1064. doi: 10.3390/ijms18051051
[8] 张宏伟, 张志广. 谷氨酰胺对非甾体抗炎药损伤胃黏膜的保护作用[J]. 医学综述,2010,1(37):41−51. [ZHANG H W, ZHANG Z G. The protective effect glutamine on the gastric mucosal damage by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug[J]. Medical Recapitulate,2010,1(37):41−51.] ZHANG H W, ZHANG Z G . The protective effect glutamine on the gastric mucosal damage by non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug[J]. Medical Recapitulate,2010 ,1 (37 ):41 −51 .[9] KIM J H, JIN S, KWON H J, et al. Curcumin blocks naproxen-induced gastric antral ulcerations through inhibition of lipid peroxidation and activation of enzymatic scavengers in rats[J]. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology,2016,26(8):1738−8872.
[10] KUADKAEW S, UNGPHAIBOON S, PHDOONGSOMBUT N, et al. Efficacy of a chitosan-curcumin mixture in treating indomethacininduced acute gastric ulcer in rats[J]. Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology,2021,22(14):1873−4316.
[11] SLAWOMIR, KWIECIEN, MARCIN, et al. Curcumin:A potent protectant against esophageal and gastric disorders[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2019,20(6):1422−1467. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061422
[12] CZEKAJ R, MAJKA J, MAGIEROWSKA K, et al. Mechanisms of curcumin-induced gastroprotection against ethanol-induced gastric mucosal lesions[J]. Journal of Gastroenterology,2017,53(9):1−13.
[13] AMIRSHAHROKHI K, KHALILI A R. The effect of thalidomide on ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage in mice:Involvement of inflammatory cytokines and nitric oxide[J]. Chemico-Biological Interactions,2015,225:63−69. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2014.11.019
[14] ZHAO H, ZHANG X, ZHANG B, et al. Gastroprotective effects of diosgenin against HCl/ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury through suppression of NF- κB and myeloperoxidase activities[J]. Open Life Sciences,2021,16(1):719−727. doi: 10.1515/biol-2021-0075
[15] WANG X, FU S, ZHANG C, et al. Gastroprotective effect of ethanol extracts from bark of magnolia officinalis on ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage in rats[J]. Bio Med Research International,2021,2021:6688414.
[16] LIM J S, OH J, BYEON S, et al. Protective effect of Dio scorea batatas peel extract against intestinal inflammation[J]. Journal of Medicinal Food,2018,21(12):57−65.
[17] FU X, HUANG X, LIN Z, et al. Protective effect of teprenone on gastric mucosal injury induced by dual antiplatelet therapy in rats[J]. American Journal of Translational Research, 2021, 13(4):2702-2709.
[18] QIN S, HUANG K, FANG Z, et al. The effect of astragaloside IV on ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury in rats:Involvement of inflammation[J]. International Immunopharmacology,2017,52:211−217. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2017.09.011
[19] RAHMAN Z, DWIVEDI D K, JENA G B. Ethanol-induced gastric ulcer in rats and intervention of tert-butylhydroquinone:Involvement of Nrf2/HO-1 signalling pathway[J]. Human & Experimental Toxicology,2020,39(4):547−562.
[20] BEIRANVAND M, BAHRAMIKIA S. Ameliorating and protective effects mesalazine on ethanol-induced gastric ulcers in experimental rats[J]. European Journal of Pharmacology,2020(888):1879−0712.
[21] LIU J, WANG F, LUO H, et al. Protective effect of butyrate against ethanol-induced gastric ulcers in mice by promoting the anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant and mucosal defense mechanisms[J]. International Immunopharmacology,2016,30:179−187. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2015.11.018
[22] 林晓春, 陈育尧, 白殊同, 等. 甘草总黄酮对慢性浅表性胃炎大鼠胃粘膜损伤的保护作用[J]. 南方医科大学学报,2013,33(2):145−150. [LING X C, CHENG X R, BAI S T, et al. Protective effect of licoflavone on gastric mucosa in rats with chronic superficial gastritis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University,2013,33(2):145−150.] LING X C, CHENG X R, BAI S T, et al . Protective effect of licoflavone on gastric mucosa in rats with chronic superficial gastritis[J]. Journal of Southern Medical University,2013 ,33 (2 ):145 −150 .[23] 王海杰, 戴正寿, 李大伟, 等. 食管胃粘膜线的解剖和胃镜观察[J]. 中国临床解剖学杂志,2004,22(3):273−276. [WANG H J, DAI Z S, LI D W, et al. Anatomic and gastroscopic examination of the esophagogastric mucosa line[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Anatomy,2004,22(3):273−276.] WANG H J, DAI Z S, LI D W, et al . Anatomic and gastroscopic examination of the esophagogastric mucosa line[J]. Chinese Journal of Clinical Anatomy,2004 ,22 (3 ):273 −276 .[24] 李卫星, 戈应滨, 杜军, 等. 慢性饮酒对大鼠胃粘膜细胞的凋亡与增殖的影响[J]. 右江医学,2002(1):1−12. [LI W X, GE Y B, DU J, et al. Apoptosis and cell proliferation of the gastric mucosa in chronic alcohol drinking rats[J]. Youjiang Medical Journal,2002(1):1−12.] LI W X, GE Y B, DU J, et al . Apoptosis and cell proliferation of the gastric mucosa in chronic alcohol drinking rats[J]. Youjiang Medical Journal,2002 (1 ):1 −12 .[25] 张朝阳, 杜婷, 谢姗, 等. 桂皮醛对酒精性胃粘膜损伤的防治研究进展[J]. 转化医学电子杂志,2018,5(9):59−62. [ZHANG C Y, DU T, XIE S, et al. Research progress of cinnamaldehyde on the prevention and treatment of alcoholic gastric mucosa injury[J]. Magazine Introduction,2018,5(9):59−62.] ZHANG C Y, DU T, XIE S, et al . Research progress of cinnamaldehyde on the prevention and treatment of alcoholic gastric mucosa injury[J]. Magazine Introduction,2018 ,5 (9 ):59 −62 .[26] 魏巍, 许晓燕, 余梦瑶, 等. 猴头菌对酒精造成的胃粘膜损伤和肝损伤保护作用的评价[J]. 中国食用菌,2015,34(4):72−75. [WEI W, XU X Y, YU M Y, et al. Protective effect study of hericium erinaceus on ethanol-induced gastric mucosal lesion and liver injury[J]. Edible Fungi of China,2015,34(4):72−75.] WEI W, XU X Y, YU M Y, et al . Protective effect study of hericium erinaceus on ethanol-induced gastric mucosal lesion and liver injury[J]. Edible Fungi of China,2015 ,34 (4 ):72 −75 .[27] 张建锋, 侯晓杰, 刘文, 等. 戊己丸对幽门结扎型胃溃疡大鼠GAS、MDA、SOD和PGE2含量分布影响[J]. 时珍国医国药, 2017, 28(5):1030-1048. [ZHANG W F, HOU X J, LIU W, et al. Effect of wuji pills onexpressions of GAS, MDA, SOD and PGE2 in rat ulcer model[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research, 2017, 28(5):1030-1048.] ZHANG W F, HOU X J, LIU W, et al. Effect of wuji pills onexpressions of GAS, MDA, SOD and PGE2 in rat ulcer model[J]. Lishizhen Medicine and Materia Medica Research, 2017, 28(5): 1030-1048.
[28] 刘颖, 代振振, 袁海峰, 等. 蜂胶对大鼠急性酒精性胃损伤保护作用[J]. 中国公共卫生,2016,32(10):1336−1339. [LIU Y, DAI Z Z, YUAN H F, et al. Protective effect of propolis on ethanol-induced acute gastric injury in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Public Health,2016,32(10):1336−1339.] LIU Y, DAI Z Z, YUAN H F, et al . Protective effect of propolis on ethanol-induced acute gastric injury in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Public Health,2016 ,32 (10 ):1336 −1339 .[29] ZHOU L, CHANG J, ZHAO W, et al. Proanthocyanidins regulate the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway and protect neurons from cypermethrin-induced oxidative stress and apoptosis[J]. Pesticide Biochemistry and Physiology,2021,177:1095−1204.
[30] YANG R, SONG C, CHEN J, et al. Limonin ameliorates acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity by activating Nrf2 antioxidative pathway and inhibiting NF- κB inflammatory response via upregulating Sirt1[J]. Phytomedicine,2020,69(153211):1618−1623.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 陈燕雨. 高光谱成像技术在食品掺假检测中的应用研究综述. 食品安全导刊. 2025(03): 144-147 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王冬,栾云霞,王欣然,贾文珅. 近红外光谱无损分析肉类品质的研究进展. 肉类研究. 2024(05): 61-70 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
