Effects of Different Exogenous Substances on the Protein Conformation and in Vitro Digestion Characteristics of Low-salt Tilapia Surimi
-
摘要: 以微波超声波辅助制备的低盐罗非鱼糜凝胶为研究对象,分析谷氨酰胺转氨酶(TGase)、羟丙基二淀粉磷酸酯(HDP)、结冷胶和三者的复配物(THG)对其水分分布及蛋白质构象的影响;并通过体外模拟消化实验,探究不同外源物质对微波超声波辅助制备的低盐罗非鱼鱼糕体外消化特性的影响。结果表明:添加THG后,鱼糜结合水和不易流动水较空白组分别增加98.71%和14.75%,自由水含量显著减少(P<0.05);THG促进了α-螺旋向β-折叠、β-转角和无规则卷曲结构转化。与空白组相比,添加0.4%TGase和THG对低盐罗非鱼糕的胃排空速度、蛋白体外消化率及蛋白水解度均有正面作用;其中THG可显著促进蛋白质分解成粒径较小的聚集体(P<0.05),经胃-十二指肠消化结束后的消化产物颜色更加透明清晰,从激光共聚焦显微镜可观察到THG组的红色荧光亮点显著减少,反映其蛋白被消化得较为完全。由此可见,在THG的作用下,鱼糜中水分子与蛋白质结合更紧密,相对于单一的外源物质,THG更加明显地改变了蛋白质的构象,且更有利于疏水蛋白基团的暴露和蛋白间的相互作用,且对鱼糕的消化有促进作用。本研究的结果为罗非鱼糜凝胶特性研究及罗非鱼糕类食品的开发与应用提供理论参考。Abstract: The effects of glutamine transaminase (TGase), hydroxypropyl distarch phosphate (HDP), gellan gum and their complex (THG) on the water distribution and protein conformation of low-salt tilapia surimi gel prepared with microwave and ultrasound were analyzed. In addition, the effects of different exogenous substances on the characteristics of low-salt tilapia fish cake were explored through in vitro digestion experiment. The results showed that compared with the control group, THG increased the bound water and immovable water of surimi to 98.71% and 14.75%, respectively, and significantly decreased the free water content (P<0.05). Moreover, THG promoted the transformation of α-helix to β-folding, β-turning and random curling structures. TGase and THG (0.4%) played important roles on gastric emptying rate, protein digestibility and protein hydrolysis degree of low-salt tilapia cake. THG significantly promoted protein decomposition into aggregates with smaller particle size (P<0.05). After the digestion of stomach and duodenum, color of the THG group products was more transparent and clear. And it could be observed by the laser confocal microscope that the red fluorescence highlights of the THG group were significantly reduced, indicating that proteins had been fully digested. Hence, compared with a single exogenous substance, THG not only promoted the binding of water molecules and proteins and induced the change of protein conformation, but also facilitated the exposure of hydrophobic protein groups and the interaction between proteins, and promoted the digestion and absorption of surimi products in the stomach and duodenum. This project provided a theoretical reference for the research on the gel properties of tilapia surimi and the development and application of tilapia fish cake.
-
罗非鱼(Oreochromis niloticus)是一种淡水鱼,具有生长速度快、产量高、肌肉加工性能好的特点,极具市场潜力,是鱼糜生产的主要淡水鱼来源之一[1]。但以罗非鱼为代表的淡水白肉鱼肌球蛋白含量较低,因此鱼糜凝胶弹性较弱[2],需通过优化加工工艺(超高压、微波、超声辅助等)[3−4]或添加合适的外源物质(如酶类蛋白质、非酶类蛋白质、淀粉类、非淀粉多糖类等)对其品质进行改良。
转谷氨酰胺酶(transglutaminase,TGase)可通过催化转酰基反应增强蛋白质间的交联程度,从而改善鱼糜的凝胶特性[5]。然而在低盐条件下,难以暴露足够数量的谷氨酰胺和赖氨酸残基作为 TGase 反应底物,从而不利于 TGase 催化交联反应的进行[6]。天然淀粉和变性淀粉是改善鱼糜制品质量最常用的添加剂[7]。羟丙基二淀粉磷酸酯是淀粉与磷酸化试剂和醚化剂伴同酯化制得的具有优异特性的复合变性淀粉,较普通淀粉糊化后膨润力、透明度显著提高,具有粘度稳定性好,保水性强及耐加工性好的特点[8−9];研究表明,羟丙基二淀粉磷酸酯的添加可以使鲅鱼鱼糜凝胶的持水性显著增大,提高不易流动水所占比例,使鲅鱼鱼糜的凝胶性能在1%添加量时达到最大值,当添加量为 1.5%时,鱼糜的硬度、粘聚性达到最大值,咀嚼度也处于较高的水平,且白度处于合适的感官区间[10]。羟丙基二淀粉磷酸酯对高温杀菌后鱼糜凝胶的破断力及凹陷距离的改善效果最好,能显著增强鱼糜的凝胶强度,且可不同程度提高鱼糜的持水力[11]。但添加过量的淀粉会使鱼糜制品产生一定的“粉感”[12]。亲水胶体是从植物和海藻中提取或由微生物合成的高分子多聚糖,也可以用来改善鱼糜制品的凝胶特性[13]。0.2%的卡拉胶可显著地提高白鲢鱼鱼糜凝胶强度、硬度、胶着性和咀嚼性,持水性和白度均达到最大值,凝胶网络结构变得更加致密,孔洞较少且分布均匀,然而大量的亲水胶体又会使鱼糜制品变脆[12],由此带来一定的局限性。为更好改善罗非鱼糜的品质,有必要将几种技术手段进行联合并优化合适比例以克服不同外源物的不足。然而,TGase、羟丙基二淀粉磷酸酯和结冷胶及其复配物是否会影响低盐罗非鱼糕的消化吸收特性,目前尚不明确。
本实验以微波超声波辅助制备的低盐罗非鱼糜凝胶为研究对象,分析谷氨酰胺转氨酶、羟丙基二淀粉磷酸酯、结冷胶以及三者的复配物(THG)对其水分分布及蛋白质构象的影响;并通过体外模拟消化实验,探究不同外源物质对微波超声波辅助制备的低盐罗非鱼鱼糕体外消化特性的影响,为外源添加物的应用前景及罗非鱼糕类食品的开发与应用提供理论参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
冷冻罗非鱼片 广东省茂名鸿业水产有限公司;氯化钠(NaCl)为食品级 广东省盐业集团有限公司;姜末、葱白、白砂糖、肥膘肉、鸡蛋 广州市滨江街市场;谷氨酰胺转氨酶(≥30000 U/g) 河南万邦实业有限公司;羟丙基二淀粉磷酸酯 泰威生物技术有限责任公司;结冷胶 高酰,深圳市星牧生物工程有限公司;尼罗蓝 上海阿拉丁试剂公司;唾液淀粉酶(500 U/mg)、胃蛋白酶(≥250 U/mg)、胰酶(~1500 U/mg)、α淀粉酶(~50 U/mg)、胆盐 上海Sigma-Aldrich贸易有限公司;碳酸氢钠、盐酸、氯化钾、磷酸二氢钾、氯化钠、氯化镁、氯化钙、碳酸铵、硼砂、十二烷基硫酸钠、邻苯二甲醛、1,4-二巯基苏糖醇、丝氨酸(serine)标准品 国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
XO-SM100超声波微波组合反应系统 南京先欧仪器制造有限公司; 碗状陶瓷模具(直径9 cm×高度5 cm×厚度0.1 mm) 广州雪诺陶瓷有限公司;MesoMR23-060H-1低场核磁共振成像分析仪 苏州纽迈仪器分析股份有限公司;Chirascan V100圆二色光谱 英国应用光物理公司;DHSI-IV体外仿生动态人胃肠消化系统 苏州晓东宜健仪器设备有限公司;85-2集热式恒温加热磁力搅拌器 北京大龙;移液枪 德国艾本德股份公司;MP512-01 pH计 上海三信仪表厂;UV-1600分光光度计 上海美谱达仪器有限公司;DHG-9070A鼓风干燥箱 上海精宏实验设备有限公司;LA960激光粒度仪 日本堀场公司;K9840凯氏定氮仪 济南海能仪器股份有限公司;Olympus FV10i 激光共聚焦显微镜 奥林巴斯中国有限公司;K600食品调理机 德国博朗电器公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 低盐罗非鱼糜凝胶的制备
样品制备主要参照陈燕婷等[14]的方法略作修改:将冷冻的罗非鱼片置于4 ℃解冻12 h,经漂洗后,切成约30 mm×30 mm×30 mm的方块(每组样品100 g)。先以20000 r/min空斩90 s;再加入1.5% NaCl,以23000 r/min盐斩120 s,然后按需求添加0.4%TGase、9%羟丙基二淀粉磷酸酯(HDP)、0.6%结冷胶,添加浓度由前期的工艺优化得到。以28000 r/min斩拌180 s;斩拌过程加入70 mL的冰水调节水分含量至75%左右,且使鱼糜的温度控制在10 oC以下。斩拌均匀的鱼糜倒入9 cm×5 cm×0.1 mm的碗状陶瓷模具中,用PE保鲜膜封口后密封。置于40 oC水浴加热30 min,而后置入微波超声波组合反应釜中,90 oC保温处理8 min,其中,微波功率620 W、超声功率330 W。然后立即放入4 oC冰箱,待测相关指标。5组罗非鱼糜凝胶样品的简称分别是:空白组、0.4%TGase组、9%HDP组、0.6%结冷胶组,以及0.4%TGase、9%HDP与0.6%结冷胶三者互作的处理组(THG组)。
1.2.2 低盐罗非鱼糕的制备
参考Ye等[15]方法。鱼糕的制备方法与鱼糜制备的区别在于,鱼糕的制备过程中,在盐斩后,除了按需求添加0.4%TGase、9%HDP、0.6%结冷胶之外,还加入姜末(5%)、葱白(5%)、料酒(0.3%)、蛋清(8%)、肥膘肉(10%)、味精(0.2%)、白砂糖(0.5%)等配料,添加浓度由前期的工艺优化得到。5组罗非鱼糕样品的简称分别是:空白组、0.4%TGase组、9%HDP组、0.6%结冷胶组,以及0.4%TGase、9%HDP与0.6%结冷胶三者互作的处理组(THG组)。
1.2.3 低场核磁共振(LF-NMR)分析
参考 Traffano等[16]的方法略作修改:鱼糜样品在室温条件下恒温30 min后,切成3 cm×1 cm×2 cm的长方体并置于核磁管中,使用CPMG(Carr-Purcell-Meiboom-Gill)脉冲序列进行自旋-自旋弛豫时间T2的测定。参数设定:SW=100 kHz,SF=21 MHz,RFD=0.002 ms,RG1=20.0 db,P1=10.0 μs,DRG1=2,TD=1024,PRG=1,TW=4000 ms,NS=2,回波个数NECH=5000。反演结果做归一化处理,每组样品3个平行,每个平行样测3次。
1.2.4 圆二色光谱分析
参考Guan等[17]的方法略作修改:用20 mmol PBS将样品稀释成0.1 g/mL溶液,将样品注入具有0.1 cm光程的石英比色皿,设置参数为:扫描波段190~260 nm,扫描速度:60 nm/min,带宽1 nm,步进1 nm,测其常温圆二色光谱。椭圆率取三次扫描的平均值,并扣除基线。利用CDNN软件,选择Net using 33 basespectra 进行二级结构拟合。
1.2.5 体外仿生动态人胃肠模拟消化
参考Minekus等[18]方法,消化液模拟液主要由电解质储备液、酶、CaCl2和水组成。唾液模拟液(SSF)、胃液模拟液(SGF)及肠液模拟液(SIF)中电解质的浓度推荐如表1所示。以100 mL为例,将α淀粉酶溶解在80 mL的SSF母液中,并加入0.5 mL的CaCl2 (H2O)2(0.3 mol/L)和19.5 mL的去离子水,得到α淀粉酶在SSF中的最终浓度为150 U/mL,并用1 mol/L HCl将SSF的pH调节至7.0,一次实验唾液用量是60 mL;同样在SGF中,将胃蛋白酶溶解于80 mL的母液,加入500 μL的CaCl2(H2O)2(0.3 mol/L)和19.95 mL的去离子水,得到胃蛋白酶在SGF中的最终浓度为4000 U/mL,用6 mol/L HCl调节SGF的pH 至1.6,一次实验胃液用量是296 mL;同样在SIF中,将胰酶和胆盐溶解于80 mL的母液,加入0.2 mL的CaCl2(H2O)2(0.3 mol/L)和19.8 mL的去离子水,得到胰酶在SIF中的最终浓度为200 U/mL、胆盐20 mmol/L,用6 mol/L HCl将SIF的pH调节至7.0,一次实验肠液用量是576 mL。
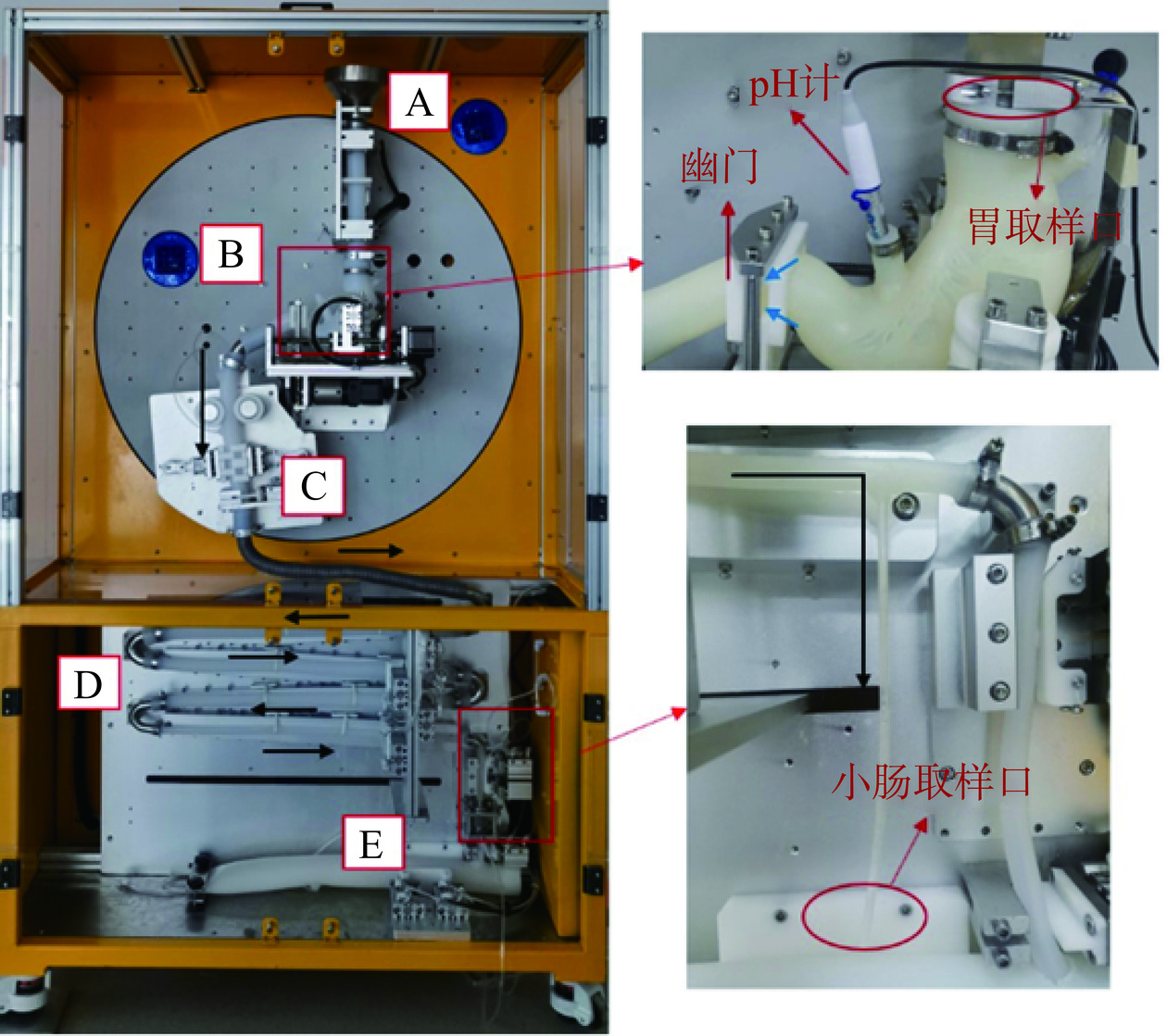
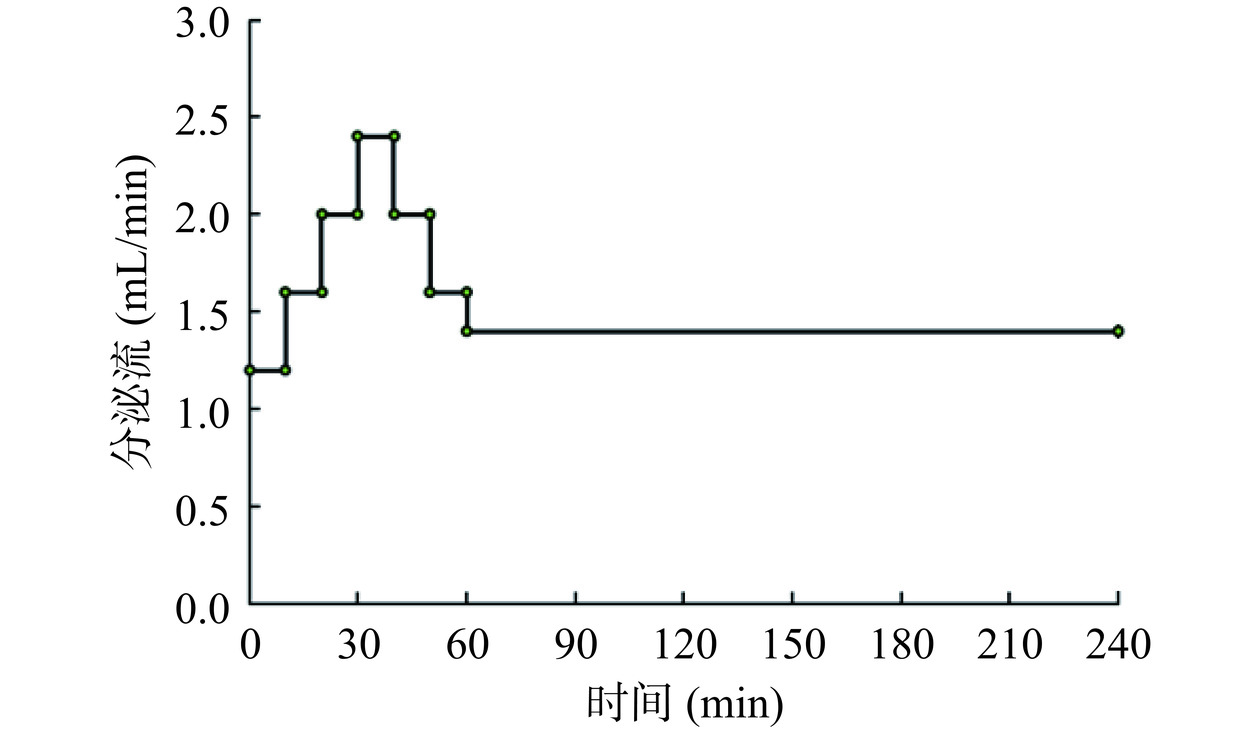
表 1 动态体外胃肠消化设备运行参数Table 1. Operating parameters of dynamic in vitro gastrointestinal digestion equipment需控制的指标 运行参数 实验方式 连续胃-十二指肠消化(见图1) 系统温度 37 ℃ 进样时间 30 min 胃部滚轮转速 12 r/min 胃蠕动频率 3次/min 幽门开口大小 0~2 mm 挤压板挤压频率和深度 5次/min和25 mm 幽门开口频率 1次/1 min(即胃蠕动2次,幽门打开1次) 空腹胃液 20 mL 胃液进液速度 1.2~2.4 mL/min 肠部滚轮转速 12 r/min 肠液进液速度 3.0 mL/min 0.5 mol/L HCl 0.5 mL/min 1 mol/L NaHCO3进液速度 0.5 mL/min 正确安装胃肠模型和一次性进液装置(如图1),并将当天配制的消化液模拟液吸入针筒内与模型正确连接。取150 g样品并将其放入食品调理机中,加入60 mL SSF并在10档下斩拌30 s以模拟口腔消化。然后将样品置于DHSI-IV仿生动态人胃肠消化系统胃模型中,进行180 min的连续胃肠消化。在消化过程中,先将296 mL模拟胃液注入空胃模型中20 mL,随后以可变流速模拟胃液分泌,流加速度变化趋势如图2所示;肠液模拟液匀速流加,流加速度为3.0 mL/min。消化完成后收集样品,在4 ℃、8000 r/min下离心20 min,将沉淀和上清液分离后,贮存于−80 ℃冰箱,备用。
1.2.6 蛋白质体外消化率的测定
参考张怡洁等[19]的方法,取消化物上清液部分采用凯氏定氮仪测定其中的总氮含量,代表已经消化了蛋白质量,计算蛋白质消化率,每组样品重复3次实验。
蛋白质消化情况用以下方式表示,公式如下:
180min的总蛋白质消化率(%)=M胃内剩余+M0-180−M0M总×100 (1) 式中,M胃内剩余=胃肠消化180 min胃内剩余物上清液中的总N量;M0-180=胃肠消化180 min肠消化产物上清液中的总N量;M0=消化液模拟液上清液中的总N量;M总=未消化样品中的总蛋白质含量。
1.2.7 蛋白水解度的测定
采用OPA(邻苯二甲醛)法测定蛋白质水解度[20];使用分光光度计测试所有样品的340 nm吸光值,空白对照为去离子水。在装有3 mL OPA试剂的试管中加入400 μL丝氨酸标准溶液或样品溶液,充分混匀(5 s)并静置 2 min,然后立即读取340 nm处的吸光度。在测量空白值和样品值之前测2个标准品,另2个标准品在测完空白和样品后再测。标准品的吸光值取4次的平均值,每组样品重复3次实验。
1.2.8 激光共聚焦显微镜观察微观结构
激光共聚焦显微镜观察(CLSM)微观结构的方法参考王嵬等[21]的方法略有修改,用无水乙醇制备0.1%的尼罗蓝染色剂,并在4 oC下避光保存。取消化后的样品上清液1 mL与尼罗蓝染色剂(40 μL)混合均匀,取1滴置于载玻片中央,从一侧盖上盖玻片,避免产生气泡,倒置在载物台上使用50倍观察。激发波长为633 nm,接收波长为680 nm。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验数据表示为结果平均值±标准差,采用Origin 2018和Excel 2010软件进行作图,实验数据采用SPSS 22.0软件进行方差分析,Duncan多重比较分析实验数据间的差异显著性(P<0.05)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 外源物质对低盐罗非鱼糜凝胶水分分布状态的影响
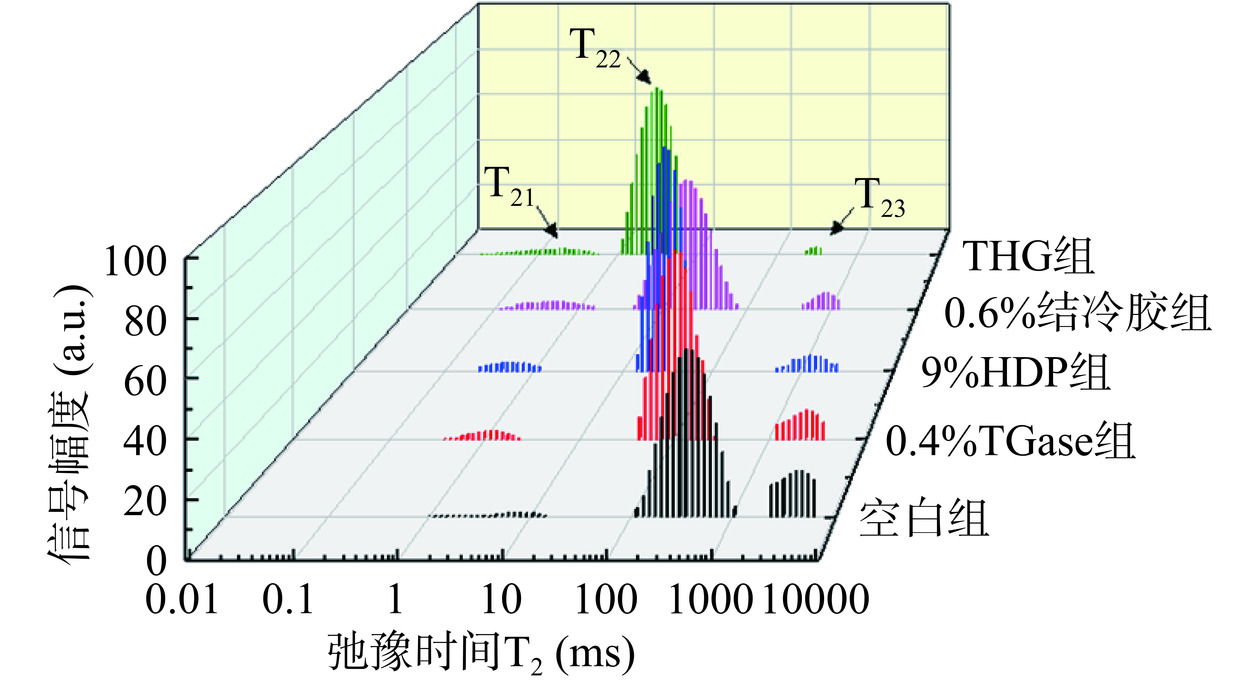
如图3所示,低盐罗非鱼糜凝胶的横向弛豫时间T2波谱图存在3个区间:T21(0~10 ms),T22(50~100 ms),T23(900~1300 ms);P21、P22、P23则分别代表鱼糜样品中结合水、不易流动水、自由水的相对含量。
表2结果表明,弛豫时间受添加物种类的作用影响较大。与空白组相比,添加0.4%TGase、9%HDP、0.6%结冷胶及THG组的弛豫时间均显著提前(P<0.05),其中THG组提前得最为明显,表明它们的结合水和不易流动水更加稳固。与空白组相比,THG 组的 T21、T22 及 T23 弛豫时间分别减小了约56.72%、13.03% 及 24.35%,表明复配物互作减弱自由水流动性的作用最显著。
表 2 低盐罗非鱼糜凝胶低场核磁共振自旋弛豫时间(T2)和峰比例(P)Table 2. LF-NMR spin-spin relaxation time (T2) and peak proportion (P) of low-salt tilapia surimi gels不同处理组 弛豫时间T2分布(ms) 弛豫时间T2峰面积所占比例(%) T21 T22 T23 P21 P22 P23 空白组 8.11±0.00d 86.98±0.03d 1232.85±0.00d 3.09±0.58a 80.25±0.69a 16.67±0.93e 0.4%TGase组 4.64±0.00b 85.29±0.11c 1072.27±0.07c 4.02±0.26b 84.97±0.47b 11.02±0.78d 9%HDP组 4.03±0.02b 83.65±0.06bc 1072.27±0.10c 4.48±0.43b 86.99±0.55c 8.83±0.59c 0.6%结冷胶组 6.14±0.01c 82.23±0.04b 985.30±0.22b 4.77±0.45bc 90.76±0.63d 4.48±0.82b THG组 3.51±0.03a 75.65±0.09a 932.60±0.05a 6.14±0.31c 92.09±0.39e 1.77±0.36a 注:同列不同字母表示样品之间差异显著(P<0.05)。 表2中的P21、P22和P23分别代表各弛豫时间所对应的峰面积比例,代表不同状态的水分含量。可以看出,添加单一外源物质和复配物后凝胶体系的结合水和不易流动水的含量均有所增多,而自由水的含量均减少。与空白组相比,0.4%TGase组、9%HDP组和0.6%结冷胶组的低盐鱼糜凝胶中P21、P22和P23均存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。此外,THG组P21和P22较空白组分别增加98.71%和14.75%,自由水(P23)含量远小于空白组,说明在复配物的作用下,自由水向结合水和不易流动水方向迁移,可能是由于复配物分子中游离的羟基在氢键的作用下结合成网状,锁住了一部分自由水,导致不易流动水含量增加,所以添加复配物后水分子与蛋白质结合更紧密[22]。
图4为低盐罗非鱼糜凝胶的水分质子密度伪彩图,鱼糜凝胶伪彩图的不同颜色可以更好地比较添加不同外源物质时鱼糜凝胶中水分的分布情况。伪彩图像越红,代表检测的信号强度越强,样品含有更多的水分子氢质子。伪彩图像越蓝,代表检测的信号强度越弱,样品含有的水分子氢质子较少[23]。从图中可以看出,相比于水分质子密度最低的空白组而言,0.4%TGase组、9%HDP组和0.6%结冷胶组的鱼糜凝胶水分质子密度相对较高;THG组的红色最深且分布最广泛,表明THG组鱼糜凝胶水分质子密度较高。有研究认为,持水率越高,鱼糜凝胶水分质子密度也相对提高[24]。本实验中几种外源物的添加,可能对鱼糜凝胶的持水率有正面影响。
2.2 外源物质对低盐罗非鱼糜凝胶二级结构的影响
在添加不同外源物质条件下,鱼糜肌原纤维蛋白的圆二色光谱如图5所示。从图5可以看出,空白组、0.6%结冷胶组及0.4%TGase组的鱼糜肌原纤维蛋白有两个明显的负峰在205 nm和225 nm附近,说明富含α-螺旋构象单元。THG组和9%HDP组的CD谱中两个负峰的强度减弱,表明α-螺旋含量下降。
从图6可得,与空白组相比,单一外源物质和复配物会影响肌原纤维蛋白的构象单元组成,可见α-螺旋相对含量减少,但β-折叠、β-转角和无规卷曲相对含量增加,这表明在单一外源物质和复配物的作用下,鱼糜蛋白的紧密螺旋结构向无规则状态转化。在5组样品中,THG组肌原纤维蛋白中含有相对含量最低的α-螺旋,以及相对含量最高的β-折叠、β-转角及无规卷曲,这表明:相对于单一的外源物质,THG更加明显地改变了蛋白质的构象,且更有利于疏水蛋白基团的暴露和蛋白间的相互作用。较低含量的α-螺旋和较高含量的无规则卷曲有助于蛋白质形成稳定的三维网络结构,在束缚水分的同时还能改善凝胶的品质[25]。THG对鱼糜凝胶品质的影响,需要进一步研究。
2.3 外源物质对低盐罗非鱼糕蛋白体外消化率的影响
蛋白体外消化率可用于评估鱼糜制品蛋白质的营养价值。如图7所示,在经过180 min的模拟消化过程后,不同外源物质的添加导致低盐罗非鱼糕呈现出的消化差异性较大(P<0.05),5组样品的消化率范围在52.75%到73.73%之间,蛋白体外消化率大小依次为:0.4%TGase组>THG组>9%HDP组>空白组>0.6%结冷胶组。
![]() 图 7 不同外源物质对低盐罗非鱼糕模拟体外消化后蛋白体外消化率的影响注:不同字母表示样品之间差异显著(P<0.05),图8同。Figure 7. Effects of different exogenous substances on protein digestibility of tilapia fish cakes after simulated digestion in vitro
图 7 不同外源物质对低盐罗非鱼糕模拟体外消化后蛋白体外消化率的影响注:不同字母表示样品之间差异显著(P<0.05),图8同。Figure 7. Effects of different exogenous substances on protein digestibility of tilapia fish cakes after simulated digestion in vitro目前有关研究报道[26]称鱼肉蛋白对消化酶的敏感性可能决定于蛋白质的结构,蛋白质的无规则卷曲含量与体外消化率呈正相关,从前期实验中不同外源物质对肌原纤维蛋白二级结构含量变化结果可知,THG组的无规则卷曲含量大,故体外消化率也会有所上升。关于 TGase 对蛋白质的消化特性影响,有的研究认为会有负面作用,比如酪蛋白分子因 TGase 的交联作用会形成高分子聚集体,对胃蛋白酶的消化产生抑制作用,并且在 20 h 的胃消化后消化液中会仍有高分子量的蛋白片段残留[27−29]。也有研究表明,TGase 会对蛋白质的消化没有抑制作用,甚至有促进作用。比如,Havenaar 等[29]的研究证实,添加 TGase 的酪蛋白在小肠中会被快速降解。同样,添加 TGase 甚至会在一定程度上提高β-伴大豆球蛋白对胰蛋白酶的敏感程度,使其更容易被降解[30]。张怡洁等[19]研究发现添加TGase的带鱼纯鱼肉重组制品样品中蛋白质体外消化率比对照组高。本研究表明,0.6%结冷胶组蛋白质消化率下降,其原因需要进一步研究。
2.4 不同外源物质对低盐罗非鱼糕蛋白水解度的影响
由图8可知,0.4%TGase组(28.74%)、9%HDP组(26.47%)、0.6%结冷胶组(27.68%)和THG组(30.15%)的蛋白水解度均显著高于仅有20.62%的空白组(P<0.05),但这4组样品之间相差不大,说明本实验中添加的外源物质均在一定程度上有助于蛋白质水解,且THG互作效果优于单一外源物质,以上外源物质的加入对低盐罗非鱼糕的蛋白水解度有正面作用,水解后的蛋白质较易消化吸收,因此推测适当添加外源物质可促进罗非鱼糕中大分子蛋白质分解为低分子量多肽,具体原因还需进一步研究。
2.5 激光共聚焦显微镜观察不同外源物质对低盐罗非鱼糕的消化作用
如图9所示,图中显示的红色荧光亮点为尼罗蓝试剂染色后的蛋白质颗粒。空白组中有许多红色荧光亮点甚至聚集成团,这表明大部分蛋白质没有被消化或消化不完全,而且还有大量的颗粒聚集体;0.4%TGase组、9%HDP组、0.6%结冷胶组以及THG组中红色荧光亮点均少于空白组,并且更加分散,特别是THG组的红色荧光亮点明显变少,从而推测THG复配物对蛋白质的消化分解不会产生不利影响甚至还起到促进作用。已有的研究认为,凝胶消化率与结构孔隙率和凝胶溶解率呈正相关性,与凝胶强度、硬度、弹性、持水率和凝胶形成作用力(二硫键、离子键、氢键)呈负相关性[31],低盐罗非鱼糕的消化率与哪些因素相关,需要进一步研究。
3. 结论
添加THG后,罗非鱼糜结合水和不易流动水较空白组分别增加98.71%和14.75%,自由水含量显著减少(P<0.05);鱼糜凝胶伪彩图的结果表明,THG组水分质子密度较高;THG促进了α-螺旋向β-折叠、β-转角和无规则卷曲结构转化。由此可见,在THG的作用下,鱼糜中水分子与蛋白质结合更紧密,相对于单一的外源物质,THG更加明显地改变了蛋白质的构象,且更有利于疏水蛋白基团的暴露和蛋白间的相互作用。
体外模拟消化实验结果表明,与空白组相比,添加0.4%TGase和THG对低盐罗非鱼糕的胃排空速度、蛋白体外消化率及蛋白水解度均有正面作用;其中THG可显著促进蛋白质分解成粒径较小的聚集体(P<0.05),经胃-十二指肠消化结束后的消化产物颜色更加透明清晰,从激光共聚焦显微镜可观察到THG组的红色荧光亮点显著减少,反映其蛋白被消化得较为完全。后续实验将从0.4%TGase和THG对鱼糜凝胶结构特性的影响角度分析,进一步分析其对体外消化率及蛋白水解度均有正面作用的机制,为罗非鱼糜凝胶特性研究及罗非鱼糕类食品的开发与应用提供理论参考。
-
图 7 不同外源物质对低盐罗非鱼糕模拟体外消化后蛋白体外消化率的影响
注:不同字母表示样品之间差异显著(P<0.05),图8同。
Figure 7. Effects of different exogenous substances on protein digestibility of tilapia fish cakes after simulated digestion in vitro
表 1 动态体外胃肠消化设备运行参数
Table 1 Operating parameters of dynamic in vitro gastrointestinal digestion equipment
需控制的指标 运行参数 实验方式 连续胃-十二指肠消化(见图1) 系统温度 37 ℃ 进样时间 30 min 胃部滚轮转速 12 r/min 胃蠕动频率 3次/min 幽门开口大小 0~2 mm 挤压板挤压频率和深度 5次/min和25 mm 幽门开口频率 1次/1 min(即胃蠕动2次,幽门打开1次) 空腹胃液 20 mL 胃液进液速度 1.2~2.4 mL/min 肠部滚轮转速 12 r/min 肠液进液速度 3.0 mL/min 0.5 mol/L HCl 0.5 mL/min 1 mol/L NaHCO3进液速度 0.5 mL/min 表 2 低盐罗非鱼糜凝胶低场核磁共振自旋弛豫时间(T2)和峰比例(P)
Table 2 LF-NMR spin-spin relaxation time (T2) and peak proportion (P) of low-salt tilapia surimi gels
不同处理组 弛豫时间T2分布(ms) 弛豫时间T2峰面积所占比例(%) T21 T22 T23 P21 P22 P23 空白组 8.11±0.00d 86.98±0.03d 1232.85±0.00d 3.09±0.58a 80.25±0.69a 16.67±0.93e 0.4%TGase组 4.64±0.00b 85.29±0.11c 1072.27±0.07c 4.02±0.26b 84.97±0.47b 11.02±0.78d 9%HDP组 4.03±0.02b 83.65±0.06bc 1072.27±0.10c 4.48±0.43b 86.99±0.55c 8.83±0.59c 0.6%结冷胶组 6.14±0.01c 82.23±0.04b 985.30±0.22b 4.77±0.45bc 90.76±0.63d 4.48±0.82b THG组 3.51±0.03a 75.65±0.09a 932.60±0.05a 6.14±0.31c 92.09±0.39e 1.77±0.36a 注:同列不同字母表示样品之间差异显著(P<0.05)。 -
[1] JIAN W J, WU H Y, WU L L, et al. Effect of molecular characteristics of konjac glucomannan on gelling and rheological properties of tilapia myofibrillar protein[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,150:21−31. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.05.001
[2] 米红波, 王聪, 赵博等. 6-姜酚对草鱼鱼糜凝胶特性及贮藏稳定性的影响[J]. 食品科学技术学报,2017,35(1):21−27. [MI H B, WANG C, ZHAO B, et al. Effects of 6-gingerol on gel properties and storage stability of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) surimi gels[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2017,35(1):21−27.] MI H B, WANG C, ZHAO B, et al. Effects of 6-gingerol on gel properties and storage stability of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) surimi gels[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2017, 35(1): 21−27.
[3] 秦影, 欧昌荣, 汤海青, 等. 鱼糜制品凝胶特性研究进展[J]. 核农学报,2015,29(9):1766−1773. [QIN Y, OU C R, TANG H Q, et al. Progress on gel properties of surimi products[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2015,29(9):1766−1773.] QIN Y, OU C R, TANG H Q, et al. Progress on gel properties of surimi products[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2015, 29(9): 1766−1773.
[4] 马海建. 超高压处理对草鱼鱼肉和鱼糜制品品质的影响[D]. 上海:上海海洋大学, 2016. [MA H J. Effects of high hydrostatic pressure (HHP) treatment on the quality of Lateolabrax japonicus during chilled storage and its antibactial mechanism[D]. Shanghai:Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2016.] MA H J. Effects of high hydrostatic pressure (HHP) treatment on the quality of Lateolabrax japonicus during chilled storage and its antibactial mechanism[D]. Shanghai: Journal of Shanghai Ocean University, 2016.
[5] MOTOKI M, KUMAZAWA Y. Recent research trends in transglutaminase technology for food processing[J]. Food Science and Technology Research,2000,6(3):151−160. doi: 10.3136/fstr.6.151
[6] LI C, XIONG Y, CHEN J. Protein oxidation at different salt concentrations affects the cross-linking and gelation of pork myofibrillar protein catalyzed by microbial transglutaminase[J]. Journal of Food Science,2013,78(6):C823−C831.
[7] KORMA S A, KAMAL A, NIAZI S, et al. Chemically modified starch and utilization in food stuffs[J]. International Journal of Nutrition and Food Sciences,2016,5(4):264−272. doi: 10.11648/j.ijnfs.20160504.15
[8] MEHFOOZ T, ALI T M, SHAIKH M, et al. Characterization of hydroxypropylated-distarch phosphate barley starch and its impact on rheological and sensory properties of soup[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,144:410−8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.142
[9] MI J, ZHAO X, HUANG P, et al. Effect of hydroxypropyl distarch phosphate on the physicochemical characteristics and structure of shrimp myofibrillar protein[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,125(4):107417.
[10] 王睿纯, 李义, 林松毅, 等. 不同类型变性淀粉对鲅鱼鱼糜凝胶特性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(20):85−92. [WANG R C, LI Y, LIN S Y, et al. Effects of different types of modified starch on gel properties of spanish mackerel surimi[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(20):85−92.] WANG R C, LI Y, LIN S Y, et al. Effects of different types of modified starch on gel properties of spanish mackerel surimi[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(20): 85−92.
[11] 孔文俊, 韦依侬, 张涛等. 淀粉对高温杀菌鱼糜凝胶特性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2016,37(5):78−81. [KONG W J, WEI Y N, ZHANG T, et al. Effects of starches on gelling properties of high-temperature sterilization surimi[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2016,37(5):78−81.] KONG W J, WEI Y N, ZHANG T, et al. Effects of starches on gelling properties of high-temperature sterilization surimi[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2016, 37(5): 78−81.
[12] 王聪. 淀粉和亲水胶体对白鲢鱼鱼糜凝胶特性的增效作用研究[D]. 锦州:渤海大学, 2019. [WANG C. Synergistic effect of starch and hydrocolloid on gel properties of silver carp surimi[D]. Jinzhou:Bohai University, 2019.] WANG C. Synergistic effect of starch and hydrocolloid on gel properties of silver carp surimi[D]. Jinzhou: Bohai University, 2019.
[13] RAMIREZ J A, URESTI R M, VELAZQUEZ G, et al. Food hydrocolloids as additives to improve the mechanical and functional properties of fish products:A review[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2011,25(8):1842−185225. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2011.05.009
[14] 陈燕婷, 林露, 高星, 等. 超高压对带鱼鱼糜凝胶特性及其肌原纤维蛋白结构的影响[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(21):115−120. [CHEN Y T, LIN L, GAO X, et al. Effect of ultra-high pressure on the myofibrillar protein structure and gel properties of hairtail surimi[J]. Food Science,2019,40(21):115−120.] CHEN Y T, LIN L, GAO X, et al. Effect of ultra-high pressure on the myofibrillar protein structure and gel properties of hairtail surimi[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(21): 115−120.
[15] YE Y H, LIU X Y, BAI W D, et al. Effect of microwave-ultrasonic combination treatment on heating-induced gel properties of low-sodium tilapia surimi during gel setting stage and comparative analysis[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2022,161:113386. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2022.113386
[16] TRAFFANO-SCHIFFO M V, LAGHI L, CASTRO-GIRALDEZ M, et al. Osmotic dehydration of organic kiwifruit pre-treated by pulsed electric fields and monitored by NMR[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,236:87−93. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.02.046
[17] GUAN A, MEI K, LV M, et al. The effect of electron beam irradiation on IgG binding capacity and conformation of tropomyosin in shrimp[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,264:250−254. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.05.051
[18] MINEKUS M, ALMINGER M, ALVITO P, et al. A standardised static in vitro digestion method suitable for food-an international consensus[J]. Food & Function,2014,5:1113−1124.
[19] 张怡洁, 何芳, 俞吉, 等. 带鱼纯鱼肉重组工艺以及制品蛋白质体外消化的研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2012,38(6):17−21. [ZHANG Y J, HE F, YU J, et al. Study on recombination technology of hairtail mackerel meat and the digestibility of protein in vitro[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2012,38(6):17−21.] ZHANG Y J, HE F, YU J, et al. Study on recombination technology of hairtail mackerel meat and the digestibility of protein in vitro[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2012, 38(6): 17−21.
[20] NIELSEN P M, PETERSEN D, DAMBMANN C. Improved method for determining food protein degree of hydrolysis[J]. Journal of Food Science,2001,66(5):642−646. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2001.tb04614.x
[21] 王嵬, 马兴胜, 仪淑敏, 等. 面筋蛋白和大米蛋白对鲢鱼鱼糜凝胶特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(11):46−51. [WANG W, MA X S, YI S M, et al. Effects of gluten and rice protein on gel properties of silver carp surimi[J]. Food Science,2017,38(11):46−51.] WANG W, MA X S, YI S M, et al. Effects of gluten and rice protein on gel properties of silver carp surimi[J]. Food Science, 2017, 38(11): 46−51.
[22] 王冬妮, 范馨茹, 祁立波, 等. 淀粉和蛋白类添加物对鱿鱼鱼糜凝胶特性的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2018,18(4):65−71. [WANG D N, FANG X R, QI L B, et al. Effect of starch and non-muscle protein on gel properties of squid (Illex argentinus) surimi[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2018,18(4):65−71.] doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2018.04.010 WANG D N, FANG X R, QI L B, et al. Effect of starch and non-muscle protein on gel properties of squid (Illex argentinus) surimi[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2018, 18(4): 65−71. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2018.04.010
[23] LI M, LI B, ZHANG W J. Rapid and non-invasive detection and imaging of the hydrocolloid-injected prawns with low-field NMR and MRI[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,242:16−21. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.08.086
[24] 姜鹏飞, 于文静, 朱凯悦, 等. 漂洗对罗非鱼鱼糜凝胶特性的影响[J]. 食品研究与开发,2022,43(2):10−18. [JIANG P F, YU W J, ZHU K Y, et al. Effect of rinsing on gelation behavior of tilapia surimi[J]. Food Research and Development,2022,43(2):10−18.] JIANG P F, YU W J, ZHU K Y, et al. Effect of rinsing on gelation behavior of tilapia surimi[J]. Food Research and Development, 2022, 43(2): 10−18.
[25] 于楠楠. 盐和多糖对鱼糜凝胶形成的影响与机制[D]. 无锡:江南大学, 2017. [YU N N. Effect of salts and polysaccharides on the formation of surimi gel and the mechanism[D]. Wuxi:Jiangnan University, 2017.] YU N N. Effect of salts and polysaccharides on the formation of surimi gel and the mechanism[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2017.
[26] 陈艾霖, 刘曼曼, 周春霞, 等. pH值对罗非鱼蛋白-大豆蛋白混合热凝胶特性及体外消化性的影响[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(5):38−45. [CHEN A L, LIU M M, ZHOU C X, et al. Effect of pH value on gelling properties and in vitro digestibility of heat-induced gel from tilapia protein-soy protein mixtures[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(5):38−45.] CHEN A L, LIU M M, ZHOU C X, et al. Effect of pH value on gelling properties and in vitro digestibility of heat-induced gel from tilapia protein-soy protein mixtures[J]. Food Research and Development, 2021, 42(5): 38−45.
[27] LUO Z L, ZHAO X H. The preparation and properties of three caseinate-hydrolyzed bovine gelatin composites generated by microbial transglutaminase[J]. CyTA-J Food,2014,12(4):340−346. doi: 10.1080/19476337.2014.882415
[28] MONOGIOUDI E, FACCIO G, LILLE M, et al. Effect of enzymatic cross-linking of β-casein on proteolysis by pepsin[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2011,25(1):71−81. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2010.05.007
[29] HAVENAAR R, DE J A, KOENEN M E, et al. Digestibility of transglutaminase cross-linked caseinate versus native caseinate in an in vitro multicompartmental model simulating young child and adult gastrointestinal conditions[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2013,61(31):7636−7644. doi: 10.1021/jf402824u
[30] TANG C H, LI L, YANG X Q. Influence of transglutaminase-induced cross-linking on in vitro digestibility of soy protein isolate[J]. Journal of Food Biochemistry ,2006,30(6):718−731. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-4514.2006.00092.x
[31] 游刚, 张自然, 李莹, 等. 钙离子对仙草胶-鱼糜凝胶特性和体外消化性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(21):100−106. [YOU G, ZHANG Z R, LI Y, et al. Effects of Ca2+ on the gel properties and in vitro digestibility of HG-added surimi gel[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(21):100−106.] YOU G, ZHANG Z R, LI Y, et al. Effects of Ca2+ on the gel properties and in vitro digestibility of HG-added surimi gel[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(21): 100−106.
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 雷美康,彭芳,陈瑶,许源,余琪,邓徐霞,祝子铜. 气相色谱-串联质谱法同时测定衢枳壳中多种农药残留. 质量安全与检验检测. 2024(01): 16-24 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈玉娇,江利兵,谢俊,郑婷,朱子健,许源. 固相萃取-高效液相色谱串联质谱法同时测定鱼子酱中12种磺胺类药物残留. 质量安全与检验检测. 2024(01): 25-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘迪,王会霞,黄坤,罗彤,曾妮,郭晓希,石梦玲,徐芬,柳迪. 同位素稀释-液相色谱-串联质谱法测定肉制品中氟苯尼考及代谢物氟苯尼考胺残留. 中南农业科技. 2024(07): 58-62 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 舒达,江敏,吴昊,王凌宇,李昊霖. 改良QuEChERs法联合超高效液相色谱-质谱法测定水产养殖池塘底泥中8种抗生素残留. 分析试验室. 2024(08): 1139-1145 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 罗嘉儿,欧佳灵. QuEChERS-高效液相色谱串联质谱法测定猪肉中氟苯尼考残留量. 食品安全导刊. 2024(31): 84-87 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张文华,吴媛,施雅梅,汪鹏,叶芮辰,徐可,谢文,徐敦明,伊雄海. 超高效合相色谱法测定鱼肉中氟苯尼考对映体及其代谢产物残留量. 食品科学. 2022(20): 321-327 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 解迎双,王新潮,刘兰霞,张欢,白兴斌,寇宗红,王波. DART-MS/MS快速筛查畜肉中氯霉素残留的应用研究. 中国口岸科学技术. 2022(11): 59-66 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 刘顺,关洪宣,刘军. 基于DNA酶-Mg催化显色反应快速检测食品中氯霉素. 食品科技. 2022(11): 284-289 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:
