Comprehensive Evaluation and Analysis of Dried Fruit Quality and Mineral Elements of 60 Different Germplasms of Lycium barbarum L.
-
摘要: 基于宁夏枸杞干果品质及矿物质元素含量差异与相关性研究,建立综合评价体系筛选优良种质,为枸杞品质育种提供理论基础。以60份种质的干果为材料,测定16项品质及矿物质元素指标含量,采用变异系数、相关性分析和因子分析筛选核心评价指标,利用层次分析、灰色关联分析和聚类分析构建枸杞干果品质综合评价体系。结果表明,不同种质营养成分、常量元素和微量元素含量存在显著性差异,总糖含量、甜菜碱含量与Zn含量,多糖含量与Fe含量,类胡萝卜素含量与Mg、Se含量,黄酮含量与B、Zn和Ca含量,脂肪含量与Se、Mg含量呈极显著正相关(P<0.01);总糖含量与类胡萝卜素含量,蛋白质含量与Zn含量呈极显著负相关(P<0.01);因子分析筛选出9项核心指标,前8个因子累积贡献率为85.591%;层次分析将这9项核心指标分成营养因子、常量元素因子和微量元素因子三类,核心指标综合权重分别为多糖(0.138)、类胡萝卜素(0.269)、黄酮(0.373)、脂肪(0.220)、Ca(0.474)、Mg(0.606)、Fe(0.394)、B(0.123)、Se(0.403);欧氏距离为8.63时将60份种质分为五大类,因子分析法和灰色关联分析法皆筛选出‘宁农杞3号’、‘宁农杞9号’、‘14-06-11-12’、‘14-02-03-21’和‘14-04-03-13’为优良种质。宁夏枸杞种质干果品质及矿物质元素综合评价分析,初步揭示了干果品质与常/微量元素含量间的关系,筛选出了5种优良种质。Abstract: Based on the differences and correlations of quality and mineral elements content in dried fruit of Lycium barbarum L., a comprehensive evaluation system was established to screen the excellent germplasms, also to provide theoretical basis for high quality breeding of Lycium barbarum L.. The 16 qualities and mineral elements content of dried fruit in 60 germplasms of Lycium barbarum L. were measured. The core evaluation indexes were screened by coefficient of variation, correlation analysis and factor analysis, and the comprehensive evaluation system of dried fruit quality of Lycium barbarum L. was constructed by analytic hierarchy process (AHP), grey correlation analysis (GCA) and cluster analysis (CA). The results showed that there were significant differences in nutritional components, constant element and trace element contents among different germplasms. There were significant positive correlations between total sugar content, betaine content and Zn content, polysaccharide content and Fe content, carotenoids content and Mg, Se content, flavonoids content and B, Zn, Ca content, fat content and Se, Mg content (P<0.01), while there were significant negative correlations between total sugar content and carotenoids content, protein content and Zn content (P<0.01). Nine core indexes were filtered out by factor analysis, and the accumulative contribution rate of the first eight factors was 85.591%. The AHP divided the nine core indicators into three categories, which were nutritional factors, constant element factors and trace element factors. The comprehensive weight of core indexes were polysaccharide (0.138), carotenoids (0.269), flavonoids (0.373), fat (0.220), Ca (0.474), Mg (0.606), Fe (0.394), B (0.123), Se (0.403). The 60 germplasms could be divided into five categories when the Euclidean distance was 8.63, and 'Ningnongqi No.3', 'Ningnongqi No. 9', '14-06-11-12', '14-02-03-21' and '14-04-03-13' were the relative excellent germplasms selected by both factor analysis and grey correlation analysis. The comprehensive evaluation and analysis of dried fruit quality and mineral elements of different Lycium barbarum L. germplasms revealed the relationship between dried fruit quality and the content of constant and trace elements, and 5 excellent germplasms were selected finally.
-
宁夏枸杞(Lycium barbarum L.)的干燥果实枸杞子是我国传统药食同源中药材,始载于《神农本草经》具有预防老年黄斑性病变、抗氧化、抗肿瘤、改善视力等作用[1−2]。枸杞子主要功效成分为枸杞多糖、甜菜碱、类胡萝卜素及类胡萝卜素酯、维生素C、多种氨基酸及微量元素K、Na、Ca、Mg、Cu、Fe、Mn、Zn、P等成分。甜菜碱、枸杞多糖、黄酮、氨基酸、总糖等物质决定着果实的营养及药用性,其含量是评价食品和中药药材品质的一项重要指标[3]。建立宁夏枸杞干果品质及矿物质元素评价体系,有助于明确矿物质元素与主要功效物质间关系,本研究将枸杞品质指标与矿物质元素指标结合完善补充宁夏枸杞质量标准体系,为枸杞品质遗传改良与种质创新奠定理论基础。
枸杞综合评价分析多以主栽品种在不同生态区品质差异研究为主,如张晓煜等[4]选取6省(区)多点‘宁杞1号’干果样品,选出4个药用和4个商品品质因子作为评价枸杞综合品质的因子,反映气候波动和年季变化对枸杞品质的影响;张波等[5]研究宁夏、青海、新疆3个产区的‘宁杞1号’、‘宁杞5号’和‘宁杞7号’宁夏枸杞外在品质和内在活性成分,发现干果枸杞总糖、多糖、甜菜碱等含量因产区而异;同时,也有对枸杞品质性状进行综合评价的研究;如王艳平等[6]以宁夏、内蒙产区‘宁杞1号’和‘宁杞7号’干果样品,基于灰色关联度法分析评价,建立了以多糖、黄酮、浸出物、抗氧化性、水分、灰分6个指标的评价模型,更科学、更全面反映枸杞子质量。赵建华等[7]针对不同果色枸杞鲜果品质性状指标间的相互关系,构建枸杞鲜果品质性状的综合评价体系,发现红色鲜果综合品质表现较优,黑色鲜果综合品质表现较差。
对于枸杞中矿物质元素的研究主要集中在其含量差异,如开建荣等[8]利用电感耦合等离子体质谱对宁夏枸杞中55种矿物元素在不同成熟阶段的含量进行跟踪测定,证明大部分矿物元素的吸收和积累存在时间差异。蒋金花等[9]建立了微波消解-电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS)同时测定枸杞中22种元素方法,对不同产地枸杞中无机元素的含量进行比较,K、P、Na含量最高,微量元素中Al、Zn、Cu、Mn、Ni、Ba、Se含量较高,有害元素含量均未超过其限量;还有相关施肥[10−11]、非生物胁迫对枸杞品质影响研究[12]的报道。现有研究不仅反映了相同的枸杞种质在不同生态产区品质存在差异,不同种质的枸杞或成熟度不同的同种质枸杞在相同的生态产区品质也存在差异,也反映了枸杞果实中各种矿物质含量的差异。
但目前研究大多是将品质指标和矿质营养分开分析,缺乏对枸杞主要品质指标和矿物质元素综合评价分析,未针对枸杞新品种选育方向和优良种质利用提出建议。矿物质的动态平衡会影响到功效活性成分的累积,本研究从不同品种(系)枸杞果实主要品质指标和主要矿物质元素着手,开展功效成分含量与主要矿物质元素的相关性研究与综合评价分析,筛选出品质优良的枸杞种质,以期为枸杞定向育种和遗传改良核心亲本选择提供理论支持。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
试验在宁夏农林科学院枸杞科学研究所进行,试材选用60份枸杞品种(系)皆来自宁夏农林科学院枸杞研究所资源圃,其中除了主栽品种外,很多为本课题组选育的优系。该资源圃位于宁夏回族自治区银川市西夏区芦花台试验地,东经106°09′,北纬38°39',为中温带干旱大陆性气候,干旱少雨、日照充足,年平均气温8.5 ℃左右,年平均日照时数2800~3000 h,年平均降水量200 mm,试验地土壤以淡灰钙土为主,其pH为8.2~8.7[13]。7月初选择不同种质健壮的枸杞树统一挂牌标记,7月中旬分别从枸杞树冠中部外围,围绕树体东西南北4个方向选择成熟度一致的枸杞鲜果,带果柄采摘,拣选出明显破裂、不成熟的枸杞鲜果,同时清除杂物,将清选后的枸杞鲜果浸泡在碱水中15~20 s后取出放置在烘盘上,枸杞入烘房后35~40 ℃保温2~3 h,升温到40~45 ℃保温8 h,升温到50~55 ℃保温8 h,取出放入自封袋中。品种(系)概况见表1;所用试剂均为分析纯。
表 1 实验材料编号与名称Table 1. Experimental material number and name实验
编号名称 拉丁名 实验
编号名称 拉丁名 G1 大麻叶 Lycium barbarum L.‘damaye’ G31 14-02-03-21 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-02-03-21’ G2 小麻叶 Lycium barbarum L.‘damaye’ G32 14-02-03-20 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-02-03-20’ G3 宁杞1号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningqi No.1’ G33 14-02-07-07 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-02-07-07’ G4 宁杞2号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningqi No.2’ G34 14-03-01-05 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-03-01-05’ G5 宁杞3号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningqi No.3’ G35 14-03-02-03 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-03-02-03’ G6 宁杞4号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningqi No.4’ G36 14-03-02-06 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-03-02-06’ G7 宁杞5号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningqi No.5’ G37 14-03-02-07 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-03-02-07’ G8 宁杞6号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningqi No.6’ G38 14-03-02-08 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-03-02-08’ G9 宁杞7号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningqi No.7’ G39 14-03-03-03 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-03-03-03’ G10 宁杞8号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningqi No.8’ G40 14-03-03-07 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-03-03-07’ G11 宁农杞9号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningnongqi No.9’ G41 14-03-03-11 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-03-03-11’ G12 宁农杞1号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningnongqi No.1’ G42 14-03-04-14 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-03-04-14’ G13 宁农杞2号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningnongqi No.2’ G43 14-03-09-05 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-03-09-05’ G14 宁农杞3号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningnongqi No.3’ G44 14-04-02-02 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-04-02-02’ G15 蒙杞1号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Mengqi No.1’ G45 14-04-03-13 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-04-03-13’ G16 09-06 Lycium barbarum L.‘09-06’ G46 14-06-03-04 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-06-03-04’ G17 09-03 Lycium barbarum L.‘09-03’ G47 14-06-10-17 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-06-10-17’ G18 16-16 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-16’ G48 14-06-10-22 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-06-10-22’ G19 中科绿川 Lycium barbarum L.‘Zhongkelvchuan’ G49 14-06-11-12 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-06-11-12’ G20 14-JC2 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-JC2’ G50 16-01-03-05 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-01-03-05’ G21 14-16 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-16’ G51 16-01-04-03 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-01-04-03’ G22 14-Z44 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-Z44’ G52 16-14-05-04 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-14-05-04’ G23 14-Z46 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-Z46’ G53 16-14-08-09 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-14-08-09’ G24 14-87 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-87’ G54 16-16-07-06 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-16-07-06’ G25 14-104 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-104’ G55 16-16-08-16 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-16-08-16’ G26 14-Z168 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-Z168’ G56 16-16-09-02 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-16-09-02’ G27 14-Z235 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-Z235’ G57 16-17-05-06 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-17-05-06’ G28 14-401 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-401’ G58 16-20-11-11 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-20-11-11’ G29 14-01-02-14 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-01-02-14’ G59 16-21-07-08 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-21-07-08’ G30 14-01-03-21 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-01-03-21’ G60 16-21-08-10 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-21-08-10’ 1260高效液相色谱仪、G6410液相色谱-质谱联用仪 美国安捷伦;RE-5286旋转蒸发器 上海亚荣生化仪器厂;UV755B紫外可见光分光光度计 上海精密科学仪器有限公司;ZX4涡旋混匀仪 意大利 VELP。
1.2 实验方法
枸杞总糖含量参照中华人民共和国国家标准GB/T18672-2014附录B-滴定法测定;多糖含量参照中华人民共和国国家标准GB/T18672-2014中附录A分光光度法测定;水分含量参照GB5009.3-2016减压烘干方法测定;脂肪含量参照GB/T5009.6-2016索氏抽提法测定;蛋白质含量参照GB5009.5-2016分光光度法测定[14];甜菜碱含量参考潘菲等[15]的液相色谱法测定;类胡萝卜素含量参考郑坚强等[16]的分光光度法测定;黄酮含量参考张自萍等[17]的微波提取法测定;氨基酸总量参考丁春瑞等[18]利用氨基酸自动分析仪测定;各元素成分含量参考王亚盟等[19]微波消解法测定。
1.3 数据处理
采用Excel计算各指标的均值、标准差、变异系数[20],根据平均值(X)和标准差(s)将测量性状分为10等级,1级<X-2s,2级<X-1.5s,3级<X-1s,......,10级≥X+2s,中间每级相差0.5s,通过计算每一级的相对频率(Pi)来计算Shannon’多样性指数(H')[21]。遗传多样性指数:H'=−ΣPilnPi,其中,Pi为某性状第i级别的种质份数占总种质材料的百分比即相对频率。
运用SPSSv20.0将原始数据标准化,进行因子分析;用Excel进行层次分析,运用SPSSv20.0构建因子分析评价体系,用SPSSAU构建灰色关联分析法评价体系,运用Origin Pro进行聚类分析与相关性分析[22−23]。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同种质枸杞相关指标的变异特征分析
宁夏枸杞相关指标的变化情况如表2所示,测定60份枸杞种质的16项指标,各指标变异系数较大,变异系数范围在6.917%~52.272%。其中,变异系数较高指标有Se、Zn、Ca、Mn,其变异系数分别为52.272%、48.780%、34.780%、31.578%;变异系数较低指标有总糖、氨基酸总量、B,其变异系数分别为6.917%、8.676%、10.540%。不同种质间鲜果品质性状存在较大变异,可为筛选优良枸杞种质创造选择空间。
表 2 枸杞干果主要品质指标与矿物质元素多样性分析Table 2. Main quality indexes and mineral elements diversity analysis of dried fruit of Lycium barbarum L.成分 极小值 极大值 极差 平均值 标准差 变异系数(%) 多样性指数 总糖(g/100 g) 40.130 52.330 12.200 46.396 3.209 6.917 1.970 多糖(g/100 g) 1.600 4.260 2.660 2.419 0.542 22.406 1.930 甜菜碱(g/100 g) 0.380 1.190 0.810 0.675 0.177 26.222 1.950 类胡萝卜素(g/100 g) 0.180 0.550 0.370 0.401 0.101 25.187 1.980 黄酮(g/100 g) 0.098 0.239 0.141 0.148 0.031 20.946 1.980 蛋白质(g/100 g) 5.840 16.230 10.390 10.176 1.797 17.659 0.10 脂肪(mg/kg) 1.780 5.590 3.810 3.369 0.835 24.785 1.980 水分(g/100 g) 1.830 15.700 13.870 12.623 1.717 13.602 1.560 氨基酸总量(mg/100 g) 8.170 13.250 5.080 10.443 0.906 8.676 1.950 Ca(mg/kg) 214.000 1051.000 837.000 416.295 144.788 34.780 1.580 Mg(mg/kg) 668.520 1518.000 849.480 1021.406 211.997 20.755 2.010 Mn(mg/kg) 4.650 14.210 9.560 7.651 2.416 31.578 1.810 Zn(mg/kg) 3.690 24.690 21.000 10.158 4.955 48.780 1.860 Fe(mg/kg) 37.620 122.600 84.980 59.508 18.398 30.917 1.820 B(mg/kg) 7.450 12.650 5.200 9.573 1.009 10.540 2.060 Se(mg/kg) 0.008 0.095 0.087 0.044 0.023 52.272 0.000 2.2 枸杞种质中各指标分布规律
60份枸杞种质品质指标的含量分布箱线图(图1)可以看出,总糖在45.0~46.0 g/100 g的品种数量最多,占总数量的18.3%,总糖含量较高的品种为‘宁农杞1号’、‘宁杞8号’和‘宁农杞2号’;多糖主要分布在2.0~2.5 g/100 g之间,约占总资源的48.3%,其中多糖含量较高的品种为‘14-02-03-21’和‘14-04-02-02’;甜菜碱主要分布在0.50~0.75 g/100 g之间,约占总资源的55%,甜菜碱含量较高的种质为‘宁杞7号’、‘宁杞3号’、‘宁杞8号’和‘09-03’;类胡萝卜素主要分布在0.4~0.5 g/100 g之间,约占总资源的40%,类胡萝卜素含量较高的为‘14-04-03-13’、‘14-06-11-12’、‘14-01-02-14’和‘14-03-01-05’;黄酮主要分布在1.0~1.5 g/100 g之间,约占总资源的55%,含量较高的种质为‘宁农杞3号’、‘宁农杞9号’、‘宁杞2号’、‘宁杞6号’、‘宁杞7号’和‘宁杞3号’;蛋白质主要分布在9.0~12.0 g/100 g之间,约占总资源的60%,含量较高的种质为‘14-04-03-13’和‘宁农杞3号’;脂肪主要分布在3.00~4.00 mg/kg之间,约占总资源的55%,含量较高的为‘14-04-03-13’、‘14-03-01-05’和‘宁农杞9号’;水分含量主要分布在12.15~13.27 g/100 g之间,约占总资源的47%,含量较高的为‘14-04-03-13’、‘14-06-11-12’和‘宁农杞9号’;氨基酸总量主要分布在9.7~10.5 mg/100 g之间,约占总资源的41.7%,含量较高的种质为‘14-01-03-21’、‘14-03-09-05’、‘14-04-03-13’。
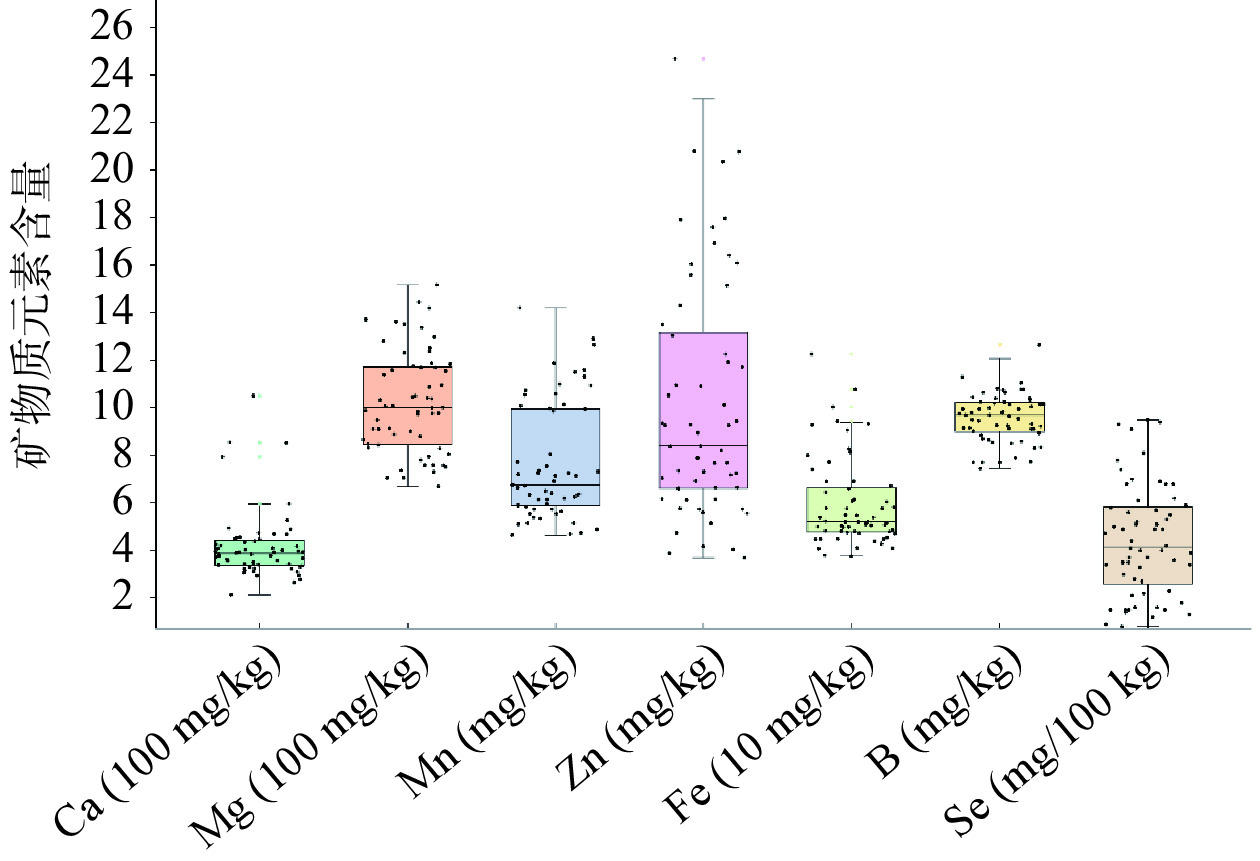
矿物质元素在60份枸杞种质中的分布情况箱线图(图2)可以看出,Mn元素含量范围4.65~14.21 mg/kg,含量由高到低依次为‘宁农杞3号’、‘14-87’和‘宁农杞9号’;Zn元素含量范围3.69~24.69 mg/kg,含量较高的种质为‘宁杞2号’、‘宁杞3号’、‘宁杞5号’和‘16-16’;Fe元素含量范围37.62~122.6 mg/kg,‘14-01-03-21’、‘14-06-11-12’和‘14-06-03-04’ 含量较高;Ca元素含量范围214.0~1051.0 mg/kg,‘宁农杞9号’、‘宁农杞1号’和‘宁农杞3号’含量较高;Mg元素含量范围668.52~1518.00 mg/kg,‘14-02-03-21’、‘14-04-03-13’和‘14-03-03-11’含量较高;B元素含量范围7.45~12.65 mg/kg,含量较高的种质为‘宁农杞9号’、‘14-03-03-11’、‘宁杞4号’;Se元素含量范围0.008~0.095 mg/kg,‘16-20-11-11’、‘小麻叶’、‘14-16’、‘宁农杞9号’和‘14-Z235’含量较高。
在各个单项指标含量较高的种质中有三种枸杞种质多个指标含量均高,分别是‘宁农杞9号’、‘宁农杞3号’和‘14-04-03-13’,在这60份材料中这三种种质为优良种质,将这个结果与后面的总和评价进行对比。
2.3 不同种质枸杞干果品质及矿物质元素综合评价分析
2.3.1 不同种质枸杞干果品质及矿物质元素相关性分析
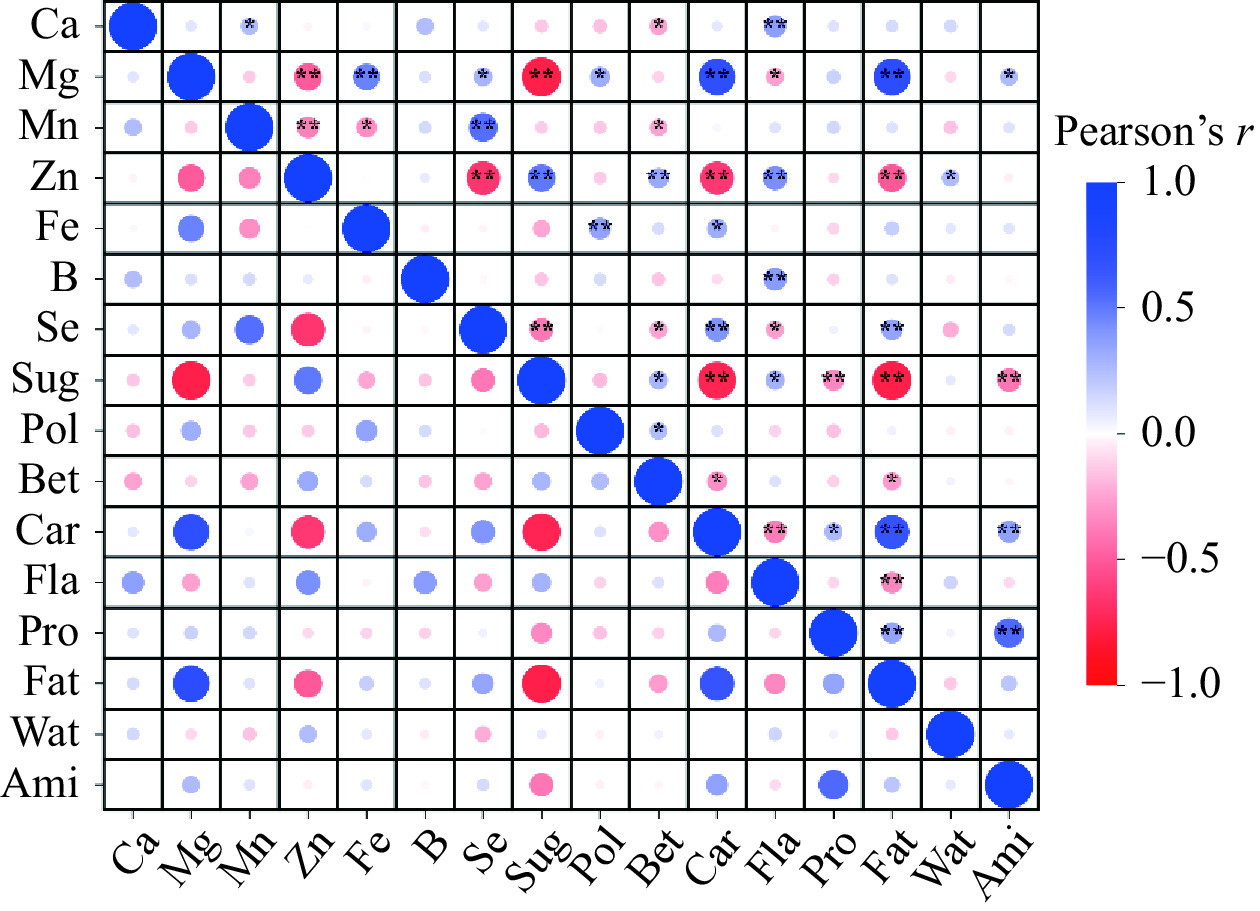
通过60份不同种质枸杞的16项果实性状指标相关性分析(图3),结果表明,品质性状指标间存在相关性,总糖含量与黄酮含量、甜菜碱含量呈显著正相关(P<0.05);多糖含量与甜菜碱含量呈显著正相关(P<0.05);甜菜碱含量与类胡萝卜素含量、脂肪含量呈显著性负相关(P<0.05);类胡萝卜素含量与黄酮含量呈极显著性负相关(P<0.01),与脂肪含量和氨基酸总量呈极显著正相关(P<0.01);黄酮含量与脂肪含量呈极显著负相关(P<0.01);蛋白质含量与脂肪含量、氨基酸总量呈极显著正相关(P<0.01)。同时,总糖含量与类胡萝卜素含量、蛋白质含量、氨基酸总量含量、脂肪含量呈极显著负相关(P<0.01)。
常量元素和微量元素指标也存在显著相关性,其中Ca含量与Mn含量呈显著正相关(P<0.05);Mg含量与Se含量呈显著正相关(P<0.05),与Fe含量呈极显著正相关(P<0.01);Mn含量与Se含量呈极显著正相关(P<0.01)。同时Mg含量与Zn含量呈极显著负相关(P<0.01);Mn含量与Fe含量呈显著负相关(P<0.05),与Zn含量呈极显著负相关(P<0.01);Zn含量与Se含量呈极显著负相关(P<0.01)。
品质性状指标与常量元素和微量元素指标也存在极显著相关性,总糖含量、甜菜碱含量与Zn含量,多糖含量与Fe含量,类胡萝卜素含量与Mg、Se含量,黄酮含量与B、Zn和Ca含量,脂肪含量与Se、Mg含量呈极显著正相关(P<0.01);总糖含量与类胡萝卜素含量,蛋白质含量与Zn含量呈极显著负相关(P<0.01);综上,Zn、Mg及Se含量与枸杞关键品质性状的含量存在极显著相关性,说明品质指标与矿物质元素指标间相互影响,抑制或促进代谢物的积累过程。
2.3.2 不同种质枸杞干果品质及矿物质元素指标因子分析
对16项枸杞果实功效成分指标进行因子分析(表3),前8个因子的累积贡献率为85.591%,即前8个因子所含信息量占总信息量的85.591%,表明前8个因子可以用于枸杞果实功效成分评价。根据这16个指标在8个因子中的总占比,选出的代表性指标分别为多糖、黄酮、类胡萝卜素、脂肪、Mg、Fe、Ca、B、Se,这9项指标为枸杞干果主要功效成分综合评价指标。
表 3 枸杞种质果实品质及矿物质元素指标因子分析Table 3. Factor analysis of fruit quality and mineral elements index on germplasm of Lycium barbarum L.成分 因子1 因子2 因子3 因子4 因子5 因子6 因子7 因子8 总占比(%) 总糖 −0.19 −0.033 −0.117 0.001 −0.057 0.095 0.099 −0.083 29.592 多糖 0.034 0.249 −0.009 0.258 0.348 0.216 −0.422 0.216 19.434 甜菜碱 −0.081 0.220 −0.038 −0.035 0.433 0.283 0.29 0.592 22.438 类胡萝卜素 0.187 0.063 0.023 −0.048 −0.176 0.084 −0.017 −0.112 29.802 黄酮 −0.098 −0.107 0.352 0.139 0.141 0.113 0.249 −0.072 27.068 蛋白质 0.08 −0.081 0.126 −0.428 0.231 −0.11 0.046 0.332 24.723 脂肪 0.179 0.014 0.061 0.001 −0.057 −0.27 0.059 0.4 26.41 水分 −0.037 0.062 0.24 −0.173 −0.367 0.515 −0.672 0.174 17.441 Mn 0.048 −0.34 −0.048 0.079 0.278 0.349 −0.028 0.018 23.885 Zn −0.162 0.086 0.206 −0.137 0.057 −0.158 0.075 −0.153 21.51 Fe 0.056 0.290 0.148 0.118 −0.097 0.268 0.445 −0.531 31.488 Ca 0.026 −0.188 0.340 0.112 −0.222 0.196 0.395 0.406 22.304 Mg 0.174 0.166 0.111 0.097 −0.01 −0.092 0.12 0.115 19.851 B 0.005 −0.089 0.296 0.318 0.266 −0.361 −0.429 −0.186 32.733 Se 0.128 −0.178 −0.178 0.127 0.091 0.392 0.069 −0.223 16.709 氨基酸总量 0.086 0.005 0.155 −0.366 0.383 0.121 −0.053 −0.58 29.304 特征值 4.655 2.237 1.802 1.628 1.087 0.934 0.736 0.615 贡献率(%) 29.096 13.984 11.26 10.174 6.795 5.84 4.6 3.842 85.591 2.3.3 不同种质枸杞干果品质及矿物质元素层次分析
将筛选的9项核心评价指标依据层次分析法,采用1~9标度法构建判断矩阵(表4~表5)[24]。对矩阵一致性进行检验,判断矩阵一致性比率(consistent ratio,CR)均小于0.1,通过一次性检验。将9项指标分成了营养因子、常量元素因子和微量元素因子三类,通过层次分析法最终确定多糖、黄酮、类胡萝卜素、脂肪、Mg、Fe、Ca、B、Se这9项核心评价指标权重分别为0.138、0.373、0.269、0.22、0.606、0.394、0.474、0.123、0.403。
表 4 准则层评价指标及类型Table 4. Criterion level evaluation index and type指标类型 品质评价指标 多糖(C1) 营养因子 黄酮(C2) 类胡萝卜素(C3) 脂肪(C4) 常量元素因子 Ca(C5) Mg(C6) 微量元素因子 B(C7) Fe(C8) Se(C9) 表 5 指标层评价指标判别矩阵及一致性检验Table 5. Discriminant matrix and consistency test for evaluation index of index layer判别矩阵 A B1 B2 B3 B1 C1 C2 C3 C4 B2 C5 C6 B3 C7 C8 C9 B1 1 1 1 C1 1 0.37 0.513 0.629 C5 1 1.538 C7 1 3.846 1.176 B2 1 1 C2 1 1.389 1.695 C6 1 C8 1 0.307 B3 1 C3 1 1.22 C9 1 C4 1 一致性比率CR 0 0 0 0 权重 0.333 0.333 0.333 0.138 0.373 0.269 0.22 0.606 0.394 0.474 0.123 0.403 综合权重 0.046 0.124 0.09 0.073 0.202 0.131 0.158 0.041 0.134 注:A 代表指标层;B1营养因子;B2常量元素因子;B3微量元素因子。 2.3.4 不同种质枸杞干果品质及矿物质元素综合评价
选择所筛选的9项核心评价指标作为综合评价的指标体系,前8个因子累计方差贡献率为85.591%,提取前8个因子信息进行分析,其中因子1主要代表类胡萝卜素、脂肪、Se和Mg;因子2主要代表多糖、Fe;因子3主要代表黄酮、Ca、B;因子4主要代表B;提取前8因子所对应的方差贡献率为权重,对60份枸杞种质材料完成基于因子分析法的枸杞干果品质评价,见表6。
表 6 枸杞种质干果品质及矿物质元素综合评价Table 6. Comprehensive evaluation on quality and mineral elements of dried fruit germplasm of Lycium barbarum L.排名 实验编号 因子1
得分因子2
得分因子3
得分因子4
得分因子5
得分因子6
得分因子7
得分因子8
得分综合
得分实验
编号关联度 1 G11 2.447 −0.931 −0.554 1.702 2.205 3.684 1.384 −1.085 126.44 G11 0.781 2 G31 0.266 0.911 2.473 1.074 1.137 −0.048 −0.378 0.265 68.21 G45 0.647 3 G14 0.323 −0.721 0.032 0.599 −0.014 2.696 1.835 1.204 65.27 G31 0.633 4 G49 0.221 2.300 1.285 0.267 −1.315 0.574 0.848 1.118 60.21 G49 0.628 5 G45 2.624 1.343 −0.612 −0.879 −0.538 −0.085 0.597 0.179 55.5 G29 0.62 6 G29 1.486 0.496 1.167 −0.524 0.439 0.268 −0.209 0.500 54.96 G14 0.616 7 G44 −0.065 1.439 3.145 −0.267 0.581 −0.274 0.261 −0.709 49.89 G44 0.598 8 G41 1.484 0.116 −0.892 −0.702 1.761 −0.830 0.482 0.707 36.07 G34 0.597 9 G30 0.019 2.344 −0.773 0.548 −0.495 −0.174 0.778 1.085 35.64 G41 0.588 10 G33 0.804 0.189 1.115 0.126 0.860 −1.014 1.411 −1.513 34.76 G30 0.586 11 G34 1.678 −0.978 0.607 0.443 0.117 −0.622 0.077 0.435 34.72 G46 0.586 12 G54 0.877 0.512 1.357 −0.572 0.343 0.050 −0.701 0.340 33.7 G54 0.578 13 G46 0.249 3.697 −0.438 0.772 −0.126 −0.250 −1.001 −1.440 26.81 G35 0.575 14 G35 0.899 1.942 −1.313 0.110 0.624 −0.328 −0.604 −0.068 24.87 G47 0.564 15 G38 −0.110 0.429 0.056 −0.309 0.196 0.009 0.583 1.429 20.24 G2 0.558 16 G39 1.093 −0.603 1.550 −0.354 −0.839 −0.010 −0.132 −0.019 18.67 G21 0.553 17 G1 −1.019 0.458 0.279 1.221 0.168 0.376 0.181 0.816 15.95 G48 0.553 18 G58 0.543 −0.367 −1.460 2.278 −0.069 −0.925 1.121 −0.558 12.56 G58 0.552 19 G2 −2.375 −0.141 0.078 2.461 −0.020 1.208 0.487 1.941 11.64 G22 0.548 20 G53 0.697 −0.851 0.852 0.059 −0.022 −0.364 −0.081 0.084 10.58 G38 0.547 21 G48 0.935 −0.694 0.028 −0.827 −0.499 0.104 −0.027 1.475 9.66 G39 0.547 22 G47 0.662 1.767 −0.751 −0.075 −1.530 0.044 −0.434 0.618 9.29 G33 0.545 23 G43 −0.019 0.153 1.081 −0.517 0.827 0.082 −1.150 0.310 8.61 G8 0.54 24 G8 −0.992 −0.739 −0.018 −1.078 0.659 0.067 2.752 1.456 7.1 G1 0.538 25 G27 0.059 −0.630 0.253 1.924 0.310 −0.854 0.720 −1.654 6.74 G40 0.533 26 G40 1.288 −1.252 0.358 −1.551 0.763 −0.080 −0.388 0.394 5.43 G43 0.533 27 G36 −0.238 0.900 1.452 −0.712 −0.981 0.432 −0.492 0.102 3.77 G53 0.532 28 G32 0.106 −0.630 0.043 0.522 −0.406 −0.199 0.091 0.764 1.56 G24 0.531 29 G5 −0.063 −0.561 0.406 −1.181 0.167 0.162 1.702 −0.574 0.26 G37 0.529 30 G22 −0.349 −1.058 1.349 0.885 1.455 −1.191 −1.640 0.913 −1.29 G36 0.526 31 G21 −0.171 −0.576 −0.272 2.023 −0.128 1.042 −1.774 −0.297 −1.58 G32 0.524 32 G6 −1.501 1.216 −0.948 −0.914 1.610 −0.055 0.765 0.350 −10.02 G27 0.519 33 G52 −0.205 −0.512 −1.067 0.164 0.398 −0.111 −0.307 1.320 −10.21 G52 0.519 34 G24 0.625 −0.335 −0.710 1.306 −2.046 −0.120 −0.494 −0.053 −14.29 G56 0.518 35 G57 −0.020 −0.854 1.780 0.530 −2.026 −0.151 −0.061 −0.611 −14.33 G42 0.515 36 G20 −0.122 0.006 −0.219 1.173 −0.126 −0.798 −0.514 −1.029 −15.96 G60 0.51 37 G42 −0.244 −0.215 −0.371 −0.694 −0.282 0.467 −0.851 1.343 −16.08 G6 0.506 38 G4 −1.164 0.886 −1.250 −0.964 0.432 0.077 1.455 0.235 −16.37 G5 0.503 39 G59 0.207 −0.845 −0.832 0.572 0.964 −0.755 −0.488 −0.687 −17.31 G50 0.503 40 G60 0.449 −0.510 −1.080 0.962 −1.146 −0.568 −0.035 −0.040 −18.23 G59 0.5 41 G56 1.057 0.333 −1.773 −0.638 1.147 −0.537 −1.841 −0.526 −18.56 G57 0.498 42 G3 −1.489 0.143 −0.633 0.276 0.997 −1.287 1.285 0.279 −21.24 G20 0.497 43 G50 −0.436 −1.410 0.325 0.170 −0.151 −0.025 −0.639 0.924 −21.76 G4 0.496 44 G12 −1.113 −0.288 0.022 −0.894 1.161 3.505 −1.763 −2.273 −21.93 G23 0.495 45 G51 0.556 −1.126 −0.602 0.311 −1.088 −0.232 0.182 −0.460 −21.97 G12 0.494 46 G37 0.397 −0.311 −1.752 −1.216 1.046 −0.196 −1.497 1.619 −22.72 G51 0.49 47 G9 −0.718 −0.450 0.161 −0.833 −1.395 −0.276 2.329 −0.635 −27.61 G3 0.488 48 G23 −0.984 −0.083 −0.086 0.026 0.222 −0.910 −0.644 1.107 −28.16 G26 0.488 49 G7 −0.034 −0.210 −0.699 −0.778 0.087 −0.346 0.448 −1.225 −28.52 G25 0.485 50 G26 −1.729 0.081 −0.144 1.449 0.031 −0.247 −1.511 0.329 −36.67 G9 0.475 51 G15 −1.553 0.077 −0.551 0.774 0.520 −0.815 0.506 −1.384 −38.79 G7 0.471 52 G25 0.361 −0.695 −0.682 0.044 −1.741 −0.115 −0.848 −0.212 −40.01 G17 0.467 53 G17 −1.342 −0.674 0.620 −1.255 1.310 −0.581 −0.195 −0.407 −40.95 G19 0.466 54 G16 −1.700 0.118 1.166 −0.877 0.335 −0.001 −0.560 −1.117 −42.63 G15 0.464 55 G18 −0.404 −0.472 −0.607 −1.081 0.722 −0.573 −0.292 −1.349 −46.24 G28 0.463 56 G19 −1.215 0.495 −0.894 −1.555 −1.970 3.108 −0.650 −0.497 −46.45 G55 0.461 57 G55 0.169 −1.084 0.045 −0.655 −1.898 −0.599 0.017 −0.304 −47.1 G16 0.46 58 G10 −0.173 −0.572 −0.428 −0.596 −0.990 −0.516 0.595 −2.074 −50.15 G18 0.456 59 G13 −0.588 0.153 −0.516 −0.855 −0.732 −0.550 0.434 −1.714 −50.43 G13 0.448 60 G28 −0.447 −1.124 −0.157 −1.415 −1.022 −0.342 −1.126 0.871 −61.51 G10 0.446 以9项核心评价指标作为灰色关联分析法的指标体系,结合层次分析法确定的指标权重,对60份枸杞种质材料利用灰色关联分析法进行综合评价。由表6可知,2种评价方法获得的综合排序差异小,排名前6的种质材料基本一致。‘宁农杞9号’、‘14-04-03-13’、‘14-02-03-21’、‘14-06-11-12’、‘14-01-02-14’和‘宁农杞3号’在因子分析法评价结果中得分明显较高,‘宁农杞9号’、‘14-02-03-21’、‘宁农杞3号’、‘14-06-11-12’、‘14-04-03-13’和‘14-01-02-14’在灰色关联分析法评价结果中与参考值关联度较高,‘宁农杞9号’在2种评价方法结果中得分和关联度值高于其他材料。以上结果说明,2种评价方法皆可筛选出果实品质优异的种质资源材料,其中‘宁农杞9号’、‘14-04-03-13’、‘宁农杞3号’、‘14-02-03-21’、‘14-01-02-14’和‘14-06-11-12’果实综合品质较高。
2.3.5 不同种质枸杞干果品质及矿物质元素聚类分析
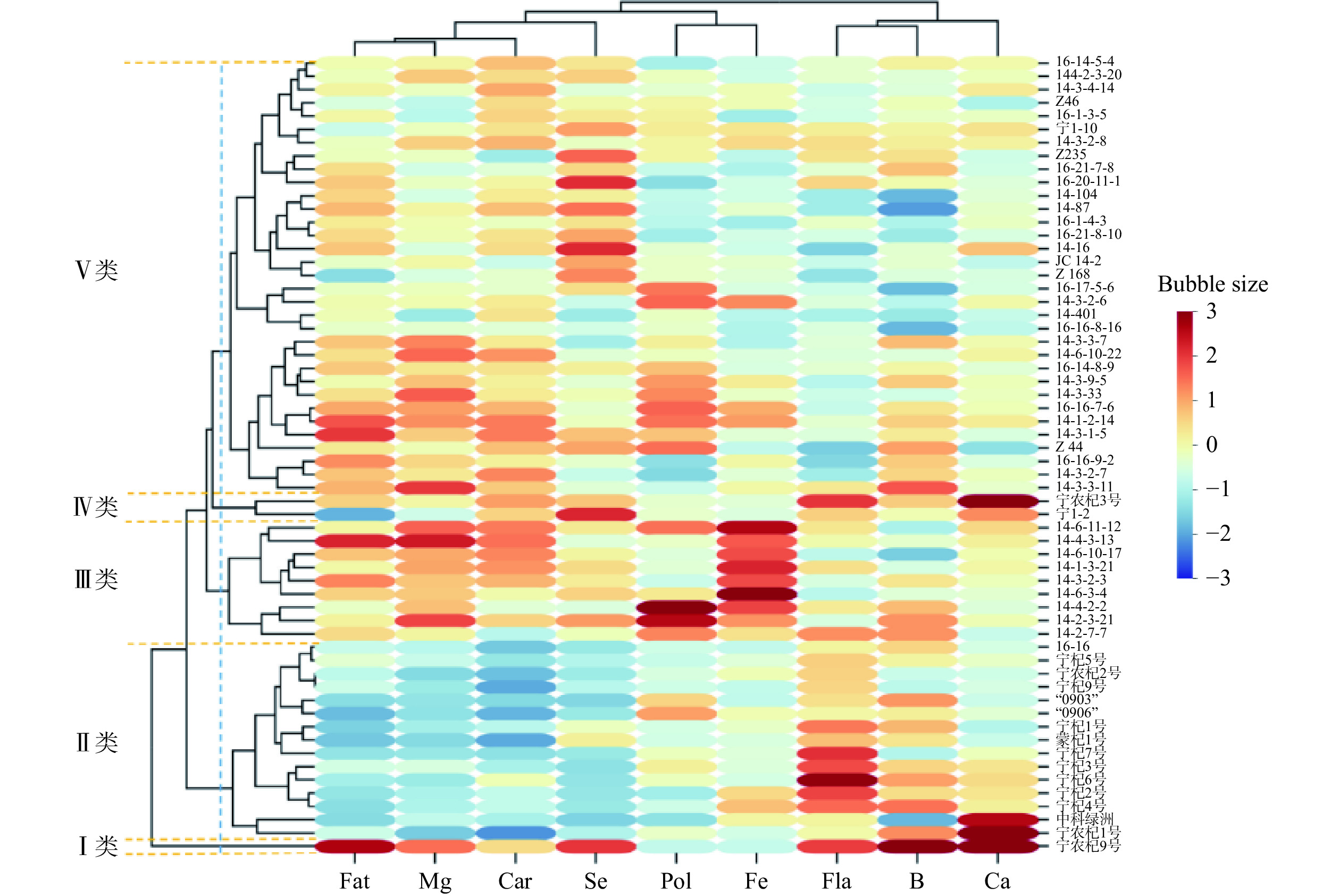
选择所筛选的9项核心评价指标作为依据,对60份枸杞种质进行热图聚类分析,将60份不同种质的枸杞中相似的分为一类,以便于利用核心种质作为亲本。分析结果如图4所示,越接近红色代表该指标数值越大,越接近蓝色代表该指标数值越小[25]。欧氏距离为8.63时全部种质材料可划分为五大类:
第Ⅰ类有1份材料为‘宁农杞9号’,此类种质黄酮和脂肪含量,Ca、Se和B含量高;
第Ⅱ类有15份材料分别为‘宁农杞1号’、‘中科绿州’、‘宁杞2号’、‘宁杞4号’、‘宁杞3号’、‘宁杞6号’、‘宁杞7号’、‘宁杞1号’、‘蒙杞1号’、‘09-06’、‘09-03’、‘宁杞8号’、‘宁农杞2号’、‘宁杞5号’和‘16-16’,此类种质黄酮和B含量高,类胡萝卜素、脂肪含量低;
第Ⅲ类含有9份材料分别为‘14-02-07-07’、‘14-02-03-21’、‘14-04-02-02’、‘14-03-02-03’、‘14-06-10-17’、‘14-06-11-12’、‘14-06-03-04’、‘14-01-03-21’和‘14-04-03-13’,此类种质多糖和Fe元素含量较高,黄酮含量低;
第Ⅳ类含有2份材料分别为‘宁1-2(小麻叶)’和‘宁农杞3号’,此类种质类胡萝卜素、黄酮含量较高,Ca、Se含量高;
第Ⅴ类含有33份材料分别为’16-14-5-4’、‘14-3-3-11’、‘14-3-2-7’、‘16-16-9-2’、‘14-Z44’、‘14-3-1-5’、‘14-1-2-14’、‘16-16-7-6’、‘14-3-33’、‘14-3-9-5’、‘16-14-8-9’、‘14-3-3-7’、‘14-6-10-22’、‘14-401’、‘16-16-8-16’、‘14-3-2-6’、‘16-17-5-6’、‘JC14-2’、‘Z168’、‘14-16’、‘16-1-4-3’、‘16-21-8-10’、‘14-87’、‘14-104’、‘16-20-11-11’、‘Z235’、‘16-21-7-8’、‘宁1-10(大麻叶)’、‘14-3-2-8’、‘Z46’、‘16-1-3-5’、‘14-3-4-14’和‘14-2-3-20’,此类种质类胡萝卜素、Mn、Se含量高,黄酮、B含量低。
9项核心评价指标分成三大类,第一类指标含有1项品质指标(黄酮),1项微量元素指标(B)和常量元素(Ca);第二类指标含有1项品质指标(多糖),1项微量元素指标(Fe);第三类指标含有2项品质指标(类胡萝卜素和脂肪),1项微量元素指标(Se),1项常量元素指标(Mg)。聚类结果显示黄酮含量与B含量,多糖含量和Fe含量,类胡萝卜素和Mg含量聚类关系较近,这与相关性分析的结果一致。
3. 讨论
3.1 枸杞干果品质评价方法的确定
作物品种评价方法已逐步由定性和单一指标发展到多指标定量综合评价,由此构建起来的综合评价体系较为客观、全面、科学。统计数学、灰色系统理论、系统科学等学科的发展为这种综合评价体系的构建奠定了基础[26]。作物品种评价方法主要包括层次分析法、百分制记分法、模糊数学法、灰色系统分析法、主成分分析、因子分析和聚类分析等[27],不同方法的数学原理不同,且各具特点。灰色关联度法是根据比较数列与参考数列的关联情况确定样本的质量级别的方法因子分析法是把一些具有错综复杂关系的变量归结为少数几个无关的新的综合因子的一种多变量统计分析方法[28−29]。郑国保等[30]针对不同生育期水分胁迫条件下宁夏枸杞果实的品质分析与综合评价,在盛果期和秋果期均进行中度胁迫处理可以提高果实的综合品质。王艳平等[6]通过灰色关联度法分析评价枸杞子质量,以6个指标(多糖、黄酮含量、浸出物、抗氧化性、水分、灰分)建立的评价模型能够更科学、更全面地反映枸杞子质量。赵建华等[7]针对不同果色枸杞鲜果品质性状指标间的相互关系,利用相关性分析、因子分析、层次分析法构建了枸杞鲜果品质性状的综合评价体系。本项研究所用评价方法都是大量用于品质评价中的方法,有些方法的科学性在枸杞品质评价中也被检验过,从方法选择上来说科学、客观,能够全面满足在本项研究的需要。
3.2 枸杞干果品质评价指标的选择
本研究参照国家标准枸杞GB/T18672-2014中所规定的理化指标进行测定,同时将甜菜碱、黄酮、类胡萝卜素、氨基酸总量,常量元素Ca、Mg和微量元素的Mn、Zn、Fe、B、Se等反映营养成分的指标纳入评价体系,综合反映枸杞果实品质。常量元素K、Na也是品质指标评价的重要矿质元素,由于枸杞在制干过程中需要添加碳酸钾或者碳酸钠作为破蜡剂,虽然在后期制备测定的过程中得到充分的洗脱,但是为避免对相关实验科学性的干扰,所以本研究未将K、Na作为矿质元素指标进行选择,对于微量元素Se的选择,主要由于宁夏中卫等地土壤富含Se元素,通过对Se元素的测定建立枸杞干果Se含量的标准值,为同类其他实验样品的测定提供参考依据。
3.3 枸杞干果品质评价结果的分析
宁夏枸杞种质干果品质及矿物质元素相关性分析与聚类热图结果显示具有较强的一致性。总糖含量与Zn含量,黄酮和Ca含量,多糖和Fe含量具有显著正相关关系,但也存在一些差异,黄酮和Ca含量、多糖和Fe含量、甜菜碱和总糖含量这三组指标在聚类热图中体现出相关性,但在相关性分析中并未显著相关。综合评价筛选出的5份优异种质优良种质‘宁农杞3号’、‘宁农杞9号’、‘14-06-11-12’、‘14-02-03-21’和‘14-04-03-13’,其中‘宁农杞9号’属于第Ⅰ类,其黄酮和脂肪含量,Ca、Se和B含量高;‘宁农杞3号’属于Ⅳ类,类胡萝卜素、黄酮含量较高,Ca、Se含量高;‘14-06-11-12’、‘14-02-03-21’和‘14-04-03-13’属于第Ⅲ类,此类种质多糖和Fe元素含量较高,黄酮含量低。所筛选出的5份优质种质均是这三个类群中的优异种质。
4. 结论
60份种质干果种质营养成分和矿物质元素含量存在显著性差异,总糖含量、甜菜碱含量与Zn含量,多糖含量与Fe含量,类胡萝卜素含量与Mg、Se含量,黄酮含量与B、Zn和Ca含量,脂肪含量与Se、Mg含量呈极显著正相关(P<0.01);总糖含量与类胡萝卜素含量,蛋白质含量与Zn含量呈极显著负相关(P<0.01);优良种质‘宁农杞3号’、‘宁农杞9号’、‘14-06-11-12’、‘14-02-03-21’和‘14-04-03-13’可作为枸杞定向育种和遗传改良核心亲本选择。宁夏枸杞种质干果品质及矿物质元素综合评价分析,初步揭示了干果品质与常/微量元素含量间的关系,为开展枸杞品质育种提供了参考依据。
-
表 1 实验材料编号与名称
Table 1 Experimental material number and name
实验
编号名称 拉丁名 实验
编号名称 拉丁名 G1 大麻叶 Lycium barbarum L.‘damaye’ G31 14-02-03-21 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-02-03-21’ G2 小麻叶 Lycium barbarum L.‘damaye’ G32 14-02-03-20 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-02-03-20’ G3 宁杞1号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningqi No.1’ G33 14-02-07-07 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-02-07-07’ G4 宁杞2号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningqi No.2’ G34 14-03-01-05 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-03-01-05’ G5 宁杞3号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningqi No.3’ G35 14-03-02-03 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-03-02-03’ G6 宁杞4号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningqi No.4’ G36 14-03-02-06 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-03-02-06’ G7 宁杞5号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningqi No.5’ G37 14-03-02-07 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-03-02-07’ G8 宁杞6号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningqi No.6’ G38 14-03-02-08 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-03-02-08’ G9 宁杞7号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningqi No.7’ G39 14-03-03-03 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-03-03-03’ G10 宁杞8号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningqi No.8’ G40 14-03-03-07 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-03-03-07’ G11 宁农杞9号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningnongqi No.9’ G41 14-03-03-11 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-03-03-11’ G12 宁农杞1号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningnongqi No.1’ G42 14-03-04-14 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-03-04-14’ G13 宁农杞2号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningnongqi No.2’ G43 14-03-09-05 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-03-09-05’ G14 宁农杞3号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Ningnongqi No.3’ G44 14-04-02-02 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-04-02-02’ G15 蒙杞1号 Lycium barbarum L.‘Mengqi No.1’ G45 14-04-03-13 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-04-03-13’ G16 09-06 Lycium barbarum L.‘09-06’ G46 14-06-03-04 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-06-03-04’ G17 09-03 Lycium barbarum L.‘09-03’ G47 14-06-10-17 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-06-10-17’ G18 16-16 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-16’ G48 14-06-10-22 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-06-10-22’ G19 中科绿川 Lycium barbarum L.‘Zhongkelvchuan’ G49 14-06-11-12 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-06-11-12’ G20 14-JC2 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-JC2’ G50 16-01-03-05 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-01-03-05’ G21 14-16 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-16’ G51 16-01-04-03 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-01-04-03’ G22 14-Z44 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-Z44’ G52 16-14-05-04 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-14-05-04’ G23 14-Z46 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-Z46’ G53 16-14-08-09 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-14-08-09’ G24 14-87 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-87’ G54 16-16-07-06 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-16-07-06’ G25 14-104 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-104’ G55 16-16-08-16 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-16-08-16’ G26 14-Z168 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-Z168’ G56 16-16-09-02 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-16-09-02’ G27 14-Z235 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-Z235’ G57 16-17-05-06 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-17-05-06’ G28 14-401 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-401’ G58 16-20-11-11 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-20-11-11’ G29 14-01-02-14 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-01-02-14’ G59 16-21-07-08 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-21-07-08’ G30 14-01-03-21 Lycium barbarum L.‘14-01-03-21’ G60 16-21-08-10 Lycium barbarum L.‘16-21-08-10’ 表 2 枸杞干果主要品质指标与矿物质元素多样性分析
Table 2 Main quality indexes and mineral elements diversity analysis of dried fruit of Lycium barbarum L.
成分 极小值 极大值 极差 平均值 标准差 变异系数(%) 多样性指数 总糖(g/100 g) 40.130 52.330 12.200 46.396 3.209 6.917 1.970 多糖(g/100 g) 1.600 4.260 2.660 2.419 0.542 22.406 1.930 甜菜碱(g/100 g) 0.380 1.190 0.810 0.675 0.177 26.222 1.950 类胡萝卜素(g/100 g) 0.180 0.550 0.370 0.401 0.101 25.187 1.980 黄酮(g/100 g) 0.098 0.239 0.141 0.148 0.031 20.946 1.980 蛋白质(g/100 g) 5.840 16.230 10.390 10.176 1.797 17.659 0.10 脂肪(mg/kg) 1.780 5.590 3.810 3.369 0.835 24.785 1.980 水分(g/100 g) 1.830 15.700 13.870 12.623 1.717 13.602 1.560 氨基酸总量(mg/100 g) 8.170 13.250 5.080 10.443 0.906 8.676 1.950 Ca(mg/kg) 214.000 1051.000 837.000 416.295 144.788 34.780 1.580 Mg(mg/kg) 668.520 1518.000 849.480 1021.406 211.997 20.755 2.010 Mn(mg/kg) 4.650 14.210 9.560 7.651 2.416 31.578 1.810 Zn(mg/kg) 3.690 24.690 21.000 10.158 4.955 48.780 1.860 Fe(mg/kg) 37.620 122.600 84.980 59.508 18.398 30.917 1.820 B(mg/kg) 7.450 12.650 5.200 9.573 1.009 10.540 2.060 Se(mg/kg) 0.008 0.095 0.087 0.044 0.023 52.272 0.000 表 3 枸杞种质果实品质及矿物质元素指标因子分析
Table 3 Factor analysis of fruit quality and mineral elements index on germplasm of Lycium barbarum L.
成分 因子1 因子2 因子3 因子4 因子5 因子6 因子7 因子8 总占比(%) 总糖 −0.19 −0.033 −0.117 0.001 −0.057 0.095 0.099 −0.083 29.592 多糖 0.034 0.249 −0.009 0.258 0.348 0.216 −0.422 0.216 19.434 甜菜碱 −0.081 0.220 −0.038 −0.035 0.433 0.283 0.29 0.592 22.438 类胡萝卜素 0.187 0.063 0.023 −0.048 −0.176 0.084 −0.017 −0.112 29.802 黄酮 −0.098 −0.107 0.352 0.139 0.141 0.113 0.249 −0.072 27.068 蛋白质 0.08 −0.081 0.126 −0.428 0.231 −0.11 0.046 0.332 24.723 脂肪 0.179 0.014 0.061 0.001 −0.057 −0.27 0.059 0.4 26.41 水分 −0.037 0.062 0.24 −0.173 −0.367 0.515 −0.672 0.174 17.441 Mn 0.048 −0.34 −0.048 0.079 0.278 0.349 −0.028 0.018 23.885 Zn −0.162 0.086 0.206 −0.137 0.057 −0.158 0.075 −0.153 21.51 Fe 0.056 0.290 0.148 0.118 −0.097 0.268 0.445 −0.531 31.488 Ca 0.026 −0.188 0.340 0.112 −0.222 0.196 0.395 0.406 22.304 Mg 0.174 0.166 0.111 0.097 −0.01 −0.092 0.12 0.115 19.851 B 0.005 −0.089 0.296 0.318 0.266 −0.361 −0.429 −0.186 32.733 Se 0.128 −0.178 −0.178 0.127 0.091 0.392 0.069 −0.223 16.709 氨基酸总量 0.086 0.005 0.155 −0.366 0.383 0.121 −0.053 −0.58 29.304 特征值 4.655 2.237 1.802 1.628 1.087 0.934 0.736 0.615 贡献率(%) 29.096 13.984 11.26 10.174 6.795 5.84 4.6 3.842 85.591 表 4 准则层评价指标及类型
Table 4 Criterion level evaluation index and type
指标类型 品质评价指标 多糖(C1) 营养因子 黄酮(C2) 类胡萝卜素(C3) 脂肪(C4) 常量元素因子 Ca(C5) Mg(C6) 微量元素因子 B(C7) Fe(C8) Se(C9) 表 5 指标层评价指标判别矩阵及一致性检验
Table 5 Discriminant matrix and consistency test for evaluation index of index layer
判别矩阵 A B1 B2 B3 B1 C1 C2 C3 C4 B2 C5 C6 B3 C7 C8 C9 B1 1 1 1 C1 1 0.37 0.513 0.629 C5 1 1.538 C7 1 3.846 1.176 B2 1 1 C2 1 1.389 1.695 C6 1 C8 1 0.307 B3 1 C3 1 1.22 C9 1 C4 1 一致性比率CR 0 0 0 0 权重 0.333 0.333 0.333 0.138 0.373 0.269 0.22 0.606 0.394 0.474 0.123 0.403 综合权重 0.046 0.124 0.09 0.073 0.202 0.131 0.158 0.041 0.134 注:A 代表指标层;B1营养因子;B2常量元素因子;B3微量元素因子。 表 6 枸杞种质干果品质及矿物质元素综合评价
Table 6 Comprehensive evaluation on quality and mineral elements of dried fruit germplasm of Lycium barbarum L.
排名 实验编号 因子1
得分因子2
得分因子3
得分因子4
得分因子5
得分因子6
得分因子7
得分因子8
得分综合
得分实验
编号关联度 1 G11 2.447 −0.931 −0.554 1.702 2.205 3.684 1.384 −1.085 126.44 G11 0.781 2 G31 0.266 0.911 2.473 1.074 1.137 −0.048 −0.378 0.265 68.21 G45 0.647 3 G14 0.323 −0.721 0.032 0.599 −0.014 2.696 1.835 1.204 65.27 G31 0.633 4 G49 0.221 2.300 1.285 0.267 −1.315 0.574 0.848 1.118 60.21 G49 0.628 5 G45 2.624 1.343 −0.612 −0.879 −0.538 −0.085 0.597 0.179 55.5 G29 0.62 6 G29 1.486 0.496 1.167 −0.524 0.439 0.268 −0.209 0.500 54.96 G14 0.616 7 G44 −0.065 1.439 3.145 −0.267 0.581 −0.274 0.261 −0.709 49.89 G44 0.598 8 G41 1.484 0.116 −0.892 −0.702 1.761 −0.830 0.482 0.707 36.07 G34 0.597 9 G30 0.019 2.344 −0.773 0.548 −0.495 −0.174 0.778 1.085 35.64 G41 0.588 10 G33 0.804 0.189 1.115 0.126 0.860 −1.014 1.411 −1.513 34.76 G30 0.586 11 G34 1.678 −0.978 0.607 0.443 0.117 −0.622 0.077 0.435 34.72 G46 0.586 12 G54 0.877 0.512 1.357 −0.572 0.343 0.050 −0.701 0.340 33.7 G54 0.578 13 G46 0.249 3.697 −0.438 0.772 −0.126 −0.250 −1.001 −1.440 26.81 G35 0.575 14 G35 0.899 1.942 −1.313 0.110 0.624 −0.328 −0.604 −0.068 24.87 G47 0.564 15 G38 −0.110 0.429 0.056 −0.309 0.196 0.009 0.583 1.429 20.24 G2 0.558 16 G39 1.093 −0.603 1.550 −0.354 −0.839 −0.010 −0.132 −0.019 18.67 G21 0.553 17 G1 −1.019 0.458 0.279 1.221 0.168 0.376 0.181 0.816 15.95 G48 0.553 18 G58 0.543 −0.367 −1.460 2.278 −0.069 −0.925 1.121 −0.558 12.56 G58 0.552 19 G2 −2.375 −0.141 0.078 2.461 −0.020 1.208 0.487 1.941 11.64 G22 0.548 20 G53 0.697 −0.851 0.852 0.059 −0.022 −0.364 −0.081 0.084 10.58 G38 0.547 21 G48 0.935 −0.694 0.028 −0.827 −0.499 0.104 −0.027 1.475 9.66 G39 0.547 22 G47 0.662 1.767 −0.751 −0.075 −1.530 0.044 −0.434 0.618 9.29 G33 0.545 23 G43 −0.019 0.153 1.081 −0.517 0.827 0.082 −1.150 0.310 8.61 G8 0.54 24 G8 −0.992 −0.739 −0.018 −1.078 0.659 0.067 2.752 1.456 7.1 G1 0.538 25 G27 0.059 −0.630 0.253 1.924 0.310 −0.854 0.720 −1.654 6.74 G40 0.533 26 G40 1.288 −1.252 0.358 −1.551 0.763 −0.080 −0.388 0.394 5.43 G43 0.533 27 G36 −0.238 0.900 1.452 −0.712 −0.981 0.432 −0.492 0.102 3.77 G53 0.532 28 G32 0.106 −0.630 0.043 0.522 −0.406 −0.199 0.091 0.764 1.56 G24 0.531 29 G5 −0.063 −0.561 0.406 −1.181 0.167 0.162 1.702 −0.574 0.26 G37 0.529 30 G22 −0.349 −1.058 1.349 0.885 1.455 −1.191 −1.640 0.913 −1.29 G36 0.526 31 G21 −0.171 −0.576 −0.272 2.023 −0.128 1.042 −1.774 −0.297 −1.58 G32 0.524 32 G6 −1.501 1.216 −0.948 −0.914 1.610 −0.055 0.765 0.350 −10.02 G27 0.519 33 G52 −0.205 −0.512 −1.067 0.164 0.398 −0.111 −0.307 1.320 −10.21 G52 0.519 34 G24 0.625 −0.335 −0.710 1.306 −2.046 −0.120 −0.494 −0.053 −14.29 G56 0.518 35 G57 −0.020 −0.854 1.780 0.530 −2.026 −0.151 −0.061 −0.611 −14.33 G42 0.515 36 G20 −0.122 0.006 −0.219 1.173 −0.126 −0.798 −0.514 −1.029 −15.96 G60 0.51 37 G42 −0.244 −0.215 −0.371 −0.694 −0.282 0.467 −0.851 1.343 −16.08 G6 0.506 38 G4 −1.164 0.886 −1.250 −0.964 0.432 0.077 1.455 0.235 −16.37 G5 0.503 39 G59 0.207 −0.845 −0.832 0.572 0.964 −0.755 −0.488 −0.687 −17.31 G50 0.503 40 G60 0.449 −0.510 −1.080 0.962 −1.146 −0.568 −0.035 −0.040 −18.23 G59 0.5 41 G56 1.057 0.333 −1.773 −0.638 1.147 −0.537 −1.841 −0.526 −18.56 G57 0.498 42 G3 −1.489 0.143 −0.633 0.276 0.997 −1.287 1.285 0.279 −21.24 G20 0.497 43 G50 −0.436 −1.410 0.325 0.170 −0.151 −0.025 −0.639 0.924 −21.76 G4 0.496 44 G12 −1.113 −0.288 0.022 −0.894 1.161 3.505 −1.763 −2.273 −21.93 G23 0.495 45 G51 0.556 −1.126 −0.602 0.311 −1.088 −0.232 0.182 −0.460 −21.97 G12 0.494 46 G37 0.397 −0.311 −1.752 −1.216 1.046 −0.196 −1.497 1.619 −22.72 G51 0.49 47 G9 −0.718 −0.450 0.161 −0.833 −1.395 −0.276 2.329 −0.635 −27.61 G3 0.488 48 G23 −0.984 −0.083 −0.086 0.026 0.222 −0.910 −0.644 1.107 −28.16 G26 0.488 49 G7 −0.034 −0.210 −0.699 −0.778 0.087 −0.346 0.448 −1.225 −28.52 G25 0.485 50 G26 −1.729 0.081 −0.144 1.449 0.031 −0.247 −1.511 0.329 −36.67 G9 0.475 51 G15 −1.553 0.077 −0.551 0.774 0.520 −0.815 0.506 −1.384 −38.79 G7 0.471 52 G25 0.361 −0.695 −0.682 0.044 −1.741 −0.115 −0.848 −0.212 −40.01 G17 0.467 53 G17 −1.342 −0.674 0.620 −1.255 1.310 −0.581 −0.195 −0.407 −40.95 G19 0.466 54 G16 −1.700 0.118 1.166 −0.877 0.335 −0.001 −0.560 −1.117 −42.63 G15 0.464 55 G18 −0.404 −0.472 −0.607 −1.081 0.722 −0.573 −0.292 −1.349 −46.24 G28 0.463 56 G19 −1.215 0.495 −0.894 −1.555 −1.970 3.108 −0.650 −0.497 −46.45 G55 0.461 57 G55 0.169 −1.084 0.045 −0.655 −1.898 −0.599 0.017 −0.304 −47.1 G16 0.46 58 G10 −0.173 −0.572 −0.428 −0.596 −0.990 −0.516 0.595 −2.074 −50.15 G18 0.456 59 G13 −0.588 0.153 −0.516 −0.855 −0.732 −0.550 0.434 −1.714 −50.43 G13 0.448 60 G28 −0.447 −1.124 −0.157 −1.415 −1.022 −0.342 −1.126 0.871 −61.51 G10 0.446 -
[1] 国家药典委员会. 中国药典2020年版[S]. 一部. 北京:中国医药科技出版社, 2020:132−133. [National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2020 edition[S]. A. Beijing:China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2020:132−133.] National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese Pharmacopoeia 2020 edition[S]. A. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2020: 132−133.
[2] ZHAO L Q, QIU Z Q, NARASIMHAMOORTHY B, et al. Development of a rapid, high-throughput method for quantification of zeaxanthin in Chinese wolfberry using HPLC–DAD[J]. Industrial Crops & Products,2013,47:51−57.
[3] 王益民, 张珂, 许飞华, 等. 不同品种枸杞子营养成分分析及评价[J]. 食品科学, 2014, 35(1):34−38. [WANG Y M, ZHANG K, XU F H, et al. Chemical analysis and nutritional evaluation of different varieties of goji berries (Lycium barbarum L.)[J]. Food Science, 2014, 35(1):34−38.] WANG Y M, ZHANG K, XU F H, et al. Chemical analysis and nutritional evaluation of different varieties of goji berries (Lycium barbarum L.)[J]. Food Science, 2014, 35(1): 34−38.
[4] 张晓煜, 刘静, 王来喜. 枸杞品质综合评价体系构建. 中国农业科学, 2004, 37(3):416−421. [ZHANG X Y, LIU J, WANG L X. A synthetic system established for assessing the quality of Lycium barbarum L J]. Scientia Agriculturae Sinica, 2004, 37(3):416−421.
[5] 张波, 罗青, 王学琴, 等. 不同产区宁夏枸杞品质分析比较[J]. 北方园艺,2014(15):165−168. [ZHANG B, LUO Q, WANG X Q, et al. Fruit quality comparison of Lycium barbarum L. from different producing areas[J]. Northern Horticulture,2014(15):165−168.] ZHANG B, LUO Q, WANG X Q, et al. Fruit quality comparison of Lycium barbarum L. from different producing areas[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2014(15): 165−168.
[6] 王艳平, 崔永蕾, 黄丽, 等. 基于灰色关联度法的枸杞子质量评价[J]. 中国现代中药,2020,22(11):1851−1856,1862. [WANG Y P, CUI Y L, HUANG L, et al. Quality evaluation of lycii fructus based on grey incidence degree method[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine,2020,22(11):1851−1856,1862.] WANG Y P, CUI Y L, HUANG L, et al. Quality evaluation of lycii fructus based on grey incidence degree method[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine, 2020, 22(11): 1851−1856,1862.
[7] 赵建华, 述小英, 李浩霞, 等. 不同果色枸杞鲜果品质性状分析及综合评价[J]. 中国农业科学,2017,50(12):2338−2348. [ZHAO J H, SHU X Y, LI H X, et al. Analysis and comprehensive evaluation of the quality of wolfberry (Lycium L.) fresh fruits with different fruit colors[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2017,50(12):2338−2348.] ZHAO J H, SHU X Y, LI H X, et al. Analysis and comprehensive evaluation of the quality of wolfberry (Lycium L.) fresh fruits with different fruit colors[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2017, 50(12): 2338−2348.
[8] 开建荣, 王彩艳, 石欣, 等. 中宁枸杞中矿物元素在生长期的动态变化研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(4):218−225. [KAI J R, WANG C Y, SHI X, et al. Study on dynamic changes of mineral elements in Zhongning Lycium barbarum L. during growing period[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(4):218−225.] KAI J R, WANG C Y, SHI X, et al. Study on dynamic changes of mineral elements in Zhongning Lycium barbarum L. during growing period[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2022, 48(4): 218−225.
[9] 蒋金花, 周安丽, 徐新忠, 等. ICP-MS测定枸杞中的22种无机元素[J]. 食品工业,2020,41(2):333−338. [JIANG J H, ZHOU A L, XU X Z, et al. Determination of 22 inorganic elements in Lycium barbarum L. by ICP-MS[J]. The Food Industry,2020,41(2):333−338.] JIANG J H, ZHOU A L, XU X Z, et al. Determination of 22 inorganic elements in Lycium barbarum L. by ICP-MS[J]. The Food Industry, 2020, 41(2): 333−338.
[10] 王亚雄, 常少刚, 王锐, 等. 不同有机肥对宁夏枸杞生长、产量及品质的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料, 2019(5):91−95. [WANG Y X, CHANG S G, WANG R, et al. Effects of different organic fertilizers on growth, yield and quality of Lycium barbarum L J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2019(5):91−95.
[11] 闫鹏科, 常少刚, 孙权, 等. 施用生物有机肥对枸杞产量、品质 及土壤肥力的影响[J]. 中国土壤与肥料,2019(5):112−118. [YAN P K, CHANG S G, SUN Q, et al. Effect of bio-organic fertilizer on yield, quality and soil fertility of wolfberry[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China,2019(5):112−118.] YAN P K, CHANG S G, SUN Q, et al. Effect of bio-organic fertilizer on yield, quality and soil fertility of wolfberry[J]. Soil and Fertilizer Sciences in China, 2019(5): 112−118.
[12] 赵建华, 李浩霞, 周旋, 等. 干旱胁迫对宁夏枸杞生长及果实糖分积累的影响[J]. 植物生理学报,2012,48(11):1063−1068. [ZHAO J H, LI H X, ZHOU X, et al. Inflfl uence of drought stress on plant growth and sugar accumulation in fruit of Lycium barbarum L J]. Plant Physiology Journal,2012,48(11):1063−1068.
[13] 张波, 戴国礼, 秦垦, 等. 42份枸杞种质资源的物候特征[J]. 经济林研究,2021,39(1):85−96. [ZHANG B, DAI G L, QIN K, et al. Phenological characteristics of 42 wolfberry germplasm resources[J]. Non-wood Forest Research,2021,39(1):85−96.] ZHANG B, DAI G L, QIN K, et al. Phenological characteristics of 42 wolfberry germplasm resources[J]. Non-wood Forest Research, 2021, 39(1): 85−96.
[14] GB/T18672 中华人民共和国国家标准(枸杞)[S]. 北京:中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 2014. [GB/T18672 National standard of the People's Republic of China (wolfberry)[S]. Beijing:General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, 2014.] GB/T18672 National standard of the People's Republic of China (wolfberry)[S]. Beijing: General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, 2014.
[15] 潘菲, 韩晓萍. 五产区间黑果枸杞甜菜碱的含量测定及比较研究[J]. 西南民族大学学报(自然科学版),2022,48(3):283−289. [PAN F, HAN X P. Determination and comparative study on the content of betaine in Lycium barbarum L J]. Journal of Southwest Minzu University (Natural Science Edition),2022,48(3):283−289.
[16] 郑坚强, 宋佳旭, 李红, 等. 陈年枸杞中类胡萝卜素含量的测定[J]. 食品工业,2018,39(6):121−125. [ZHENG J Q, SONG J X, LI H, et al. Determination of carotenoid content in aged Lycium chinense[J]. The Food Industry,2018,39(6):121−125.] ZHENG J Q, SONG J X, LI H, et al. Determination of carotenoid content in aged Lycium chinense[J]. The Food Industry, 2018, 39(6): 121−125.
[17] 张自萍, 黄文波, 王玉炯. 枸杞黄酮提取方法的比较研究[J]. 宁夏大学学报(自然科学版),2007(1):60−62. [ZHANG Z P, HUANG W B, WANG Y J. Comparative study between the microwave and conventional extractions of the total flavones from Lycium barbarum L J]. Journal of Ningxia University(Natural Science Edition),2007(1):60−62.
[18] 丁春瑞, 郭武军, 远辉. 新疆黑枸杞中氨基酸含量的测定及分析[J]. 食品工业,2016,37(12):151−152. [DING C R, GUO W J, YUAN H. Determination and analysis of the amino acid content of Lycium ruthenicum Murr. in Xinjiang[J]. The Food Industry,2016,37(12):151−152.] DING C R, GUO W J, YUAN H. Determination and analysis of the amino acid content of Lycium ruthenicum Murr. in Xinjiang[J]. The Food Industry, 2016, 37(12): 151−152.
[19] 王亚盟, 郭家平, 刘洁, 等. 不同产地黑果枸杞中主要矿物质元素含量比较及主成分分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(11):233−239. [WANG Y M, GUO J P, LIU J, et al. Comparison and principal component analysis of main mineral elements in Lycium ruthenicum Murray from different habitats[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(11):233−239.] WANG Y M, GUO J P, LIU J, et al. Comparison and principal component analysis of main mineral elements in Lycium ruthenicum Murray from different habitats[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(11): 233−239.
[20] 张叶, 叶蓓蕾, 邬静, 等. 77份文心兰种质资源表型性状遗传多样性分析[J]. 热带作物学报,2021,42(8):2183−2190. [ZHANG Y, YE P L, WU J, et al. Analysis of genetic diversity of phenotypic traits of 77 Oncidium germplasm resources[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops,2021,42(8):2183−2190.] ZHANG Y, YE P L, WU J, et al. Analysis of genetic diversity of phenotypic traits of 77 Oncidium germplasm resources[J]. Chinese Journal of Tropical Crops, 2021, 42(8): 2183−2190.
[21] 郭燕, 张树航, 李颖, 等. 中国板栗36个叶片表型性状的多样性[J]. 中国农业科学,2022,55(5):991−1009. [GUO Y, ZHANG S H, LI Y, et al. Diversity analysis of 36 leaf phenotypic traits of Chinese chestnut[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2022,55(5):991−1009.] GUO Y, ZHANG S H, LI Y, et al. Diversity analysis of 36 leaf phenotypic traits of Chinese chestnut[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(5): 991−1009.
[22] 王秀秀, 邢爱双, 杨茹, 等. 陆地棉种质资源表型性状综合评价[J]. 中国农业科学,2022,55(6):1082−1094. [WANG X X, XING A S, YANG R, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of phenotypic traits of upland cotton germplasm resources[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2022,55(6):1082−1094.] WANG X X, XING A S, YANG R, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of phenotypic traits of upland cotton germplasm resources[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(6): 1082−1094.
[23] 徐晓, 任根增, 赵欣蕊, 等. 中国高粱地方品种和育成品种穗部表型性状精准鉴定及综合评价[J]. 中国农业科学,2022,55(11):2092−2108. [XU X, REN G Z, ZHAO X R, et al. Accurate identification and comprehensive evaluation of panicle phenotypic characters of local and developed Sorghum cultivars in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2022,55(11):2092−2108.] XU X, REN G Z, ZHAO X R, et al. Accurate identification and comprehensive evaluation of panicle phenotypic characters of local and developed Sorghum cultivars in China[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2022, 55(11): 2092−2108.
[24] 李勋兰, 魏召新, 彭芳芳, 等. 35份果桑资源果实品质分析与综合评价[J]. 果树学报,2022,39(3):332−342. [LI X L, WEI S X, PENG F F, et al. Fruit quality analysis and comprehensive evaluation of 35 mulberry accessions[J]. Journal of Fruit Science,2022,39(3):332−342.] LI X L, WEI S X, PENG F F, et al. Fruit quality analysis and comprehensive evaluation of 35 mulberry accessions[J]. Journal of Fruit Science, 2022, 39(3): 332−342.
[25] 姜璐, 包怡红, 贾雨彤, 等. 18个品种蓝靛果营养成分分析及综合品质评价[J]. 农业工程学报,2022,38(7):326−335. [JIANG L, BAO Y H, JIA Y T, et al. Nutritional component analysis and comprehensive quality evaluation of 18 different varieties of Lonicera caerulea[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2022,38(7):326−335.] JIANG L, BAO Y H, JIA Y T, et al. Nutritional component analysis and comprehensive quality evaluation of 18 different varieties of Lonicera caerulea[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2022, 38(7): 326−335.
[26] 刘翔宇, 赵龙, 巴哈尔古丽·先木西, 等. 新疆陆地棉种质资源的综合评价[J]. 中国农业科学,2017,50(24):4679−4692. [LIU Xi Y, ZHAO L, BAHARGULI X M X, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of upland cotton germplasm resources in Xinjiang[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2017,50(24):4679−4692.] LIU Xi Y, ZHAO L, BAHARGULI X M X, et al. Comprehensive evaluation of upland cotton germplasm resources in Xinjiang[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica, 2017, 50(24): 4679−4692.
[27] 刘龙昌, 尚富德, 向其柏. 植物品种综合评价方法——以桂花为例[J]. 河南大学学报(自然科学版),2003(1):14−17. [LIU L C, SHANG F D, XIANG Q B. Comprehensive evaluation method of plant varieties—A case study of Osmanthus[J]. Journal of Henan University (Natural Science Edition),2003(1):14−17.] LIU L C, SHANG F D, XIANG Q B. Comprehensive evaluation method of plant varieties—A case study of Osmanthus[J]. Journal of Henan University (Natural Science Edition), 2003(1): 14−17.
[28] 孟宪林, 孙丽欣, 周定, 等. 灰色理论在环境质量评价中的应用与完善[J]. 哈尔滨工业大学学报,2002(5):700−702. [MENG X L, SUN L X, ZHOU D, et al. Application and improvement of grey theory in environmental quality evaluation[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology,2002(5):700−702.] MENG X L, SUN L X, ZHOU D, et al. Application and improvement of grey theory in environmental quality evaluation[J]. Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology, 2002(5): 700−702.
[29] 游家兴. 如何正确运用因子分析法进行综合评价[J]. 统计教育,2003(5):10−11. [YOU J X. How to correctly use factor analysis method for comprehensive evaluation[J]. Statistical Education,2003(5):10−11.] YOU J X. How to correctly use factor analysis method for comprehensive evaluation[J]. Statistical Education, 2003(5): 10−11.
[30] 郑国保, 马玲, 撖志明, 等. 不同生育期水分胁迫条件下宁夏枸杞果实的主成分分析与综合评价[J]. 节水灌溉,2022(1):47−51,57. [ZHENG G B, MA L, QIAN Z M, et al. Principal component analysis and comprehensive evaluation of Lycium barbarum fruits under water stress at different growth stages[J]. Water Saving Irrigation,2022(1):47−51,57.] ZHENG G B, MA L, QIAN Z M, et al. Principal component analysis and comprehensive evaluation of Lycium barbarum fruits under water stress at different growth stages[J]. Water Saving Irrigation, 2022(1): 47−51,57.
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 姜坤,李玉国,张道志,徐恒伟,冯丹萍,孟小茜,郑春英. 微生物发酵对刺五加叶黄酮类成分生物合成的影响. 中国农学通报. 2024(03): 145-151 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陆少君,蔡肇栩,郭瑞雪,谢群巧,罗力,唐春萍,陈文健,江涛. 基于TLR-4/NF-κB信号通路探究金花茶提取物对非酒精性脂肪肝的作用. 食品工业科技. 2024(20): 349-360 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 周月,王一珈,臧健,高英旭,潘丰,郭志富,李胤之. 刺五加活性成分及药用价值研究进展. 辽宁林业科技. 2024(06): 48-50+71 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 何嘉伟,江汉美,黄振阳,曾格格,戴全武,刘天琪,韩蔓. HS-SPME-GC-MS结合化学计量法分析刺五加不同部位的挥发性成分. 南京中医药大学学报. 2023(02): 146-156 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李强,袁勇,李玉,于建海. 刺五加多糖对奶牛生产性能、抗氧化指标及免疫功能的影响. 中国饲料. 2023(12): 28-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 丁思宇,张道涵,韩丽琴. 星点-响应面法优化刺五加根黄酮闪式提取工艺研究. 吉林医药学院学报. 2023(04): 269-271 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 孙琳,井长欣,邹睿,辛宇,张晓旭,邱智东,王伟楠. 刺五加-灵芝双向固体发酵工艺优化及抗氧化活性评价. 科学技术与工程. 2023(21): 9004-9014 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 李强,张若冰,杨玉赫,田冰,李文兰,李陈雪. 刺五加叶化学成分及药理作用研究进展. 药学研究. 2023(07): 495-501 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 石玉璞,牛思思,韩璐瑶,李莞颖,余君伟,武冰辉,徐波,张艳萍,曹艳,乔长晟. 枸杞刺梨复合饮料的工艺优化及其降血糖性能. 食品研究与开发. 2023(18): 149-157 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 茆鑫,郑剑斌,李广耀,曲敏,郑心琪. 响应曲面法优化刺五加-五味子混菌发酵工艺的研究. 食品科技. 2023(09): 57-64 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 戴丛书,柴晶美,林长青. 金银花黄酮提取物的降血糖作用. 食品工业科技. 2022(24): 386-393 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(5)
-
其他相关附件
-
其他文件格式
EI收录证明
-





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



