Electrochemical Aptasensor Based on Platinum @ Gold Nanowires as Signal Amplifier for Aflatoxin B1 Detection
-
摘要: 目的:为了满足食品质量安全并快速检测食品中黄曲霉毒素B1(AFB1)的含量,构建基于铂@金纳米线(Pt@AuNWs)作为信号放大物的电化学适配体传感器用于花生中AFB1的高灵敏、高选择性检测。方法:首先在玻碳电极(GC)表面修饰纳米金颗粒(AuNPs)构建AuNPs/GC电极,增强基底电极的电催化性能并通过Au﹣S键将互补链(cDNA)固定于AuNPs/GC,其次通过模板法合成Pt@AuNWs使其与适配体结合构建信号探针(记为Pt@AuNWs-apt),最后基于碱基互补配对作用构建电化学适配传感器。当AFB1存在时,其和cDNA竞争结合适配体,导致电极表面的Pt@AuNWs-apt信号探针部分脱落,使电化学适配体传感器催化H2O2产生的电流信号降低,从而间接定量检测AFB1。结果:该传感器在0.25 nmol/L cDNA、apt与cDNA孵育40 min、10 mmol/L H2O2、0.1 mol/L 磷酸盐浓度pH7.0的测试条件下具有最优的分析性能。该方法具有较宽的线性范围(1~100 ng/mL),检出限为0.41 ng/mL,具有良好的选择性、重现性和稳定性,将该传感器应用于花生样品中进行加标回收实验,结果表明回收率在85.1%~88.0%。结论:构建的电化学适配体传感器可应用于花生中AFB1的检测,在快速检测中具有较好的应用价值。Abstract: Objective: In this study, to meet food quality and safety and rapid determination of aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) content in food, an electrochemical aptamer-based sensor with plantium@gold nanowires (Pt@AuNWs) as the signal amplifier was developed for sensitive and selective detection of AFB1 in peanut. Method: Firstly, Au nanoparticles (AuNPs) were deposited on the surface of glassy carbon electrode (AuNPs/GC) for enhancing the electrocatalytic property of the sensor and linking complementary strand (cDNA) through Au-S bond. Then, the signal probes was constructed via template synthesis of Pt@AuNWs and combination with aptamer (Pt@AuNPs-apt), which could bind to the electrode based on base complementary pairing principle. In the presence of AFB1, it would compete with cDNA to bind aptamer and result in the detachment of some signal probes from the sensor surface, reducing the electrical signals generated by catalyzing H2O2, thereby the indirectly quantitative detection of AFB1 was achieved. Result: The sensor showed the best analytical performance with 0.25 nmol/L cDNA, incubating apt and cDNA for 40 min, 10 mmol/L H2O2, 0.1 mol/L pH7.0 PBS. Under optimization, this sensor showed good lineariy in the range of 1~100 ng/mL,with the calculated detection limit about 0.41 ng/mL. The present sensor delivered good sensitivity, selectivity and stability. The method was applied to the peanut samples for the recovery experiment and the recovery rate was 85.1%~88.0%. Conclusion: The constructed electrochemical adapter sensor can be applied to the detection of AFB1 in peanuts, and has great potential to be used in rapid detection.
-
Keywords:
- platinum @ gold nanowires /
- aptamer /
- electrochemical aptasensor /
- aflatoxin B1
-
作为黄曲霉毒素家族(B1、B2、G1、G2、M1、M2、GM、P1、Q1等)中的一员,黄曲霉毒素B1(AFB1)毒性最强[1−2]。农产品(花生、玉米)和许多其他食品均易受到AFB1污染,研究结果表明,AFB1有很强的致癌、致畸和致突变性,因此,为了保障人体健康,众多国家和组织对其残留量均有明确的限量标准[3−4]。准确检测AFB1含量对保障食品安全和经济健康发展具有重要意义[5−7]。目前,检测AFB1的方法主要是色谱以及色谱质谱联用法[8−11],但是该类方法普遍面临着需要昂贵的仪器设备和专业的技术人员的问题,主要在实验室中开展。随着经济的快速发展以及农产品的增产,对AFB1的检测尤其是对现场快速灵敏检测提出更高要求[12−13]。
电化学传感器因其所用仪器小型、灵敏度高,在现场检测中具有潜在的应用价值[14],因此开发灵敏度高、选择性高的电化学分析方法具有一定的研究意义。为了提高电化学分析方法的灵敏度,纳米材料常被应用于修饰电极以便提高其电催化性能从而获得更低的检测限,如碳基材料、金属有机框架材料、导电聚合物、金属及金属氧化物[15−17]。其中一维纳米线材料因其具有比表面积大,催化性能强等优点受到研究者的广泛关注,尤其是贵金属(金、铂、银等)纳米线[18−19]。研究表明,相对于单一金属组成的纳米线,双金属纳米线能够基于两种材料的协同作用提高催化效果,因此催化性能普遍高于单一金属材料[20−21]。使用双金属纳米线能提高电化学传感器的灵敏度,但其电催化能力却面临选择性仍需进一步提高的特点[22−23],为了解决纳米材料在应用过程中虽具有好的电催化性能,但选择性不高的问题,生物识别单元被引入到传感器中以提高方法的选择性。在传感器的制备过程中常使用酶、抗体等生物材料,但生物材料多存在着易失活、价格昂贵、稳定性有待提高的问题[24−26]。因此适配体的研究应运而生。近年来,基于指数富集配件系统(SELEX)技术筛选的适配体因其易于修饰、制备方法简单、易于批量生产,稳定性和特异性好,逐渐应用到传感器中以提高分析方法的选择性,改善传感器的分析性能[27−30]。
基于此,为了提高方法的选择性和材料的电催化性能,本实验采用黄曲霉毒素的适配体作为识别单元,将双金属Pt@AuNws作为信号放大物(以提高其电催化性能)引入电化学传感器的构建中,基于竞争作用,建立间接检测AFB1含量的分析方法,分别考察cDNA浓度、适配体孵育时间、H2O2浓度、缓冲液pH等因素对检测性能的影响,以期获得选择性好,灵敏度高的电化学适配体传感器,并在花生样品测定中验证构建的电化学适配体传感器的应用价值。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
亚碲酸钠(Na2TeO3) 武汉吉鑫益邦生物科技公司;聚乙烯吡咯烷酮(PVP)、水合肼(N2H4·H2O)、巯基乙醇(MCH)、乙二胺四乙酸钠盐(EDTA)、抗坏血酸(AA)、铁氰化钾(K3Fe(CN)6)、无水乙醇、氨水、乙二醇 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;氯金酸(HAuCl4 ·4H2O) 美国Sigma公司;氯铂酸(H2PtCl6) 阿拉丁生化科技公司;上述试剂均为分析纯,无需提纯直接应用后续实验;适配体、互补链 上海生工生物工程技术公司,互补链序列为5'-SH-(CH2)6- GCATCACTACAGTCATTACGCATCGGGTAAGCGGAACTGAGGAGTGGGAGGTAAATCGTGTGAAGTGCTGTCCC -3',下文简称cDNA;适配体序列为5'-NH2-(CH2)6-GTTGGGCACGTGTTGTCTCTCTGTTCGCCTTCGCTAGGCCCA CA-3',下文简称apt;无壳生花生米采集于学校超市。
CHI660E型电化学工作站 上海辰华仪器有限公司,电化学测试中使用三电极体系:玻碳电极以及修饰玻碳电极为工作电极,饱和甘汞电极为参比电极,铂丝为对电极;CD-D10型超声波清洗仪 亦为超声技术有限公司;TGL-16M型离心机 山东欧莱博医疗有限公司;DS-37型高温干燥箱 上海灯晟仪器有限公司;ZWYR-D2403型恒温培养振荡器 上海智城分析仪器制造有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 Pt@AuNWs的制备
参考文献[31−32]合成Pt@AuNWs,具体方法如下:取0.0406 g Na2TeO3和0.4524 g PVP溶解于13.5 mL蒸馏水中,剧烈搅拌下加入0.675 mL N2H4·H2O(w/w,50%)及1.35 mL NH3·H2O(w/w,25%)。充分搅拌混匀后,将混合溶液置于反应釜中于180 ℃反应4 h,冷却后制得产物,将所得产物进行离心洗涤,得到Te纳米线(TeNWs)。将其加入2 mL蒸馏水分散以备后续使用。
将2 mL TeNWs加入30 mL乙二醇中,持续搅拌下加入0.32 mL EDTA(0.2 mol/L)及0.32 mL HAuCl4(0.1 mol/L)。放置在室温反应1 h后,将所得产物离心洗涤数次,得到Au纳米线(AuNWs),分散于蒸馏水以备后续使用。之后将AuNWs与PVP一同加入蒸馏水中搅拌10 min。之后向混合溶液中依次迅速地加入1.6 mL H2PtCl6(w/w,50%)及2 mL AA(0.1 mol/L),放置在60 ℃水浴中反应2 h,可得到Pt@AuNWs,随后将所得材料离心洗涤数次,并分散于3 mL蒸馏水中,于4 ℃下保存备用。
1.2.2 Pt@AuNWs-apt复合物的制备
取11 μL 100 μmol/L的apt,将其加入到489 μL 0.1 mol/L PBS(pH7)中稀释apt。稀释后将其加入到1 mL Pt@AuNWs溶液中,于4 ℃下搅拌过夜。接着加入1 mL 10.2 mmol/L MCH继续搅拌30 min,用来封闭Pt@AuNWs上未被固载的活性位点,得到Pt@AuNWs-apt复合物,再将其离心洗涤重新分散于无菌水中,于4 ℃下保存备用。
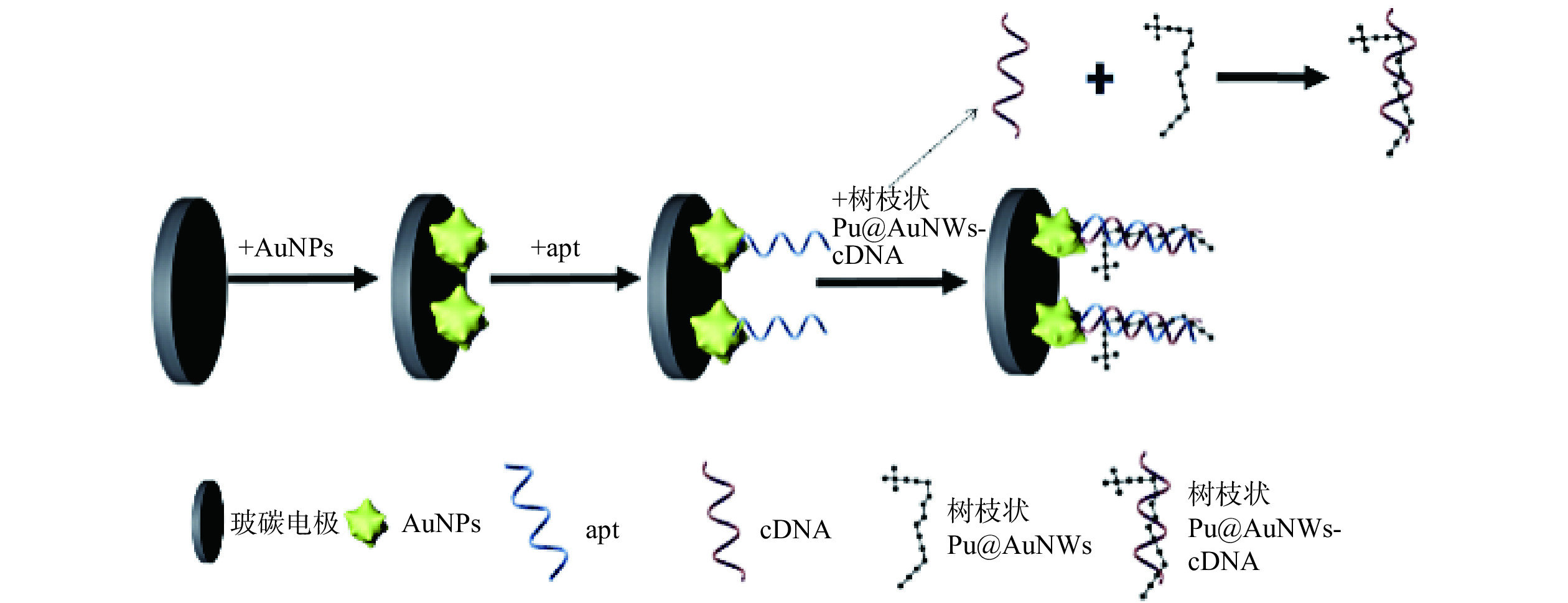
1.2.3 电化学适配体传感器制备
首先将玻碳电极(直径3 mm)依次用1、0.5、0.05 µm Al2O3粉抛光,用无水乙醇及蒸馏水超声洗涤30 s后干燥。将打磨好的工作电极、铂电极及饱和甘汞电极组成三电极系统,置于5 mmol/L K3Fe(CN)6 中,采用循环伏安法(CV)进行测定,若电位差≤80 V可进行后续操作。其次将电极置于0.4 g/L的HAuCl4的溶液中,使用恒电位沉积法(I-t)在−0.2 V将AuNPs修饰在电极表面(AuNPs/GC),随后,将10 µL 0.25 nmol/L cDNA滴涂在电极表面37℃孵育1 h,使含有巯基的cDNA通过Au-S自组装在电极表面(cDNA/AuNPs/GC),孵育后使用无菌水将表面洗净干燥,随后用10.2 mmol/L MCH封闭残余活性位点约1 h(MCH/cDNA/AuNPs/GC),最后将Pt@AuNWs-apt复合物滴加在电极表面(Pt@AuNWs-apt/cDNA/AuNPs/GC)。具体制作过程见图1。将所制得适体传感器储存于4 ℃备用。
1.2.4 电化学适配体传感器可行性探究
首先将制备好的传感器使用差分脉冲伏安法(DPV)在10 mmol/L H2O2中记录信号,然后在传感器上滴加10 μL 10 ng/mL的AFB1孵育并记录信号,比较两者的电流信号。
1.2.5 Pt@AuNWs的电催化性能探究
采用类似1.2.3中的方法制备两组传感器,实验组纳米材料为Pt@AuNWs,对照组为AuNWs,其他构建传感器过程均相同。将传感器置于10 mmol/L H2O2中进行DPV测试,记录两组电流信号。
1.2.6 电极修饰过程的表征
首先使用CV法在5 mmol/L的K3Fe(CN)6中对电极的逐步修饰过程进行测试,接下来采用交流阻抗扫描法(EIS)对电极的逐步修饰过程进行测试。
1.2.7 检测条件的优化
1.2.7.1 cDNA浓度的选择
将抛光后的电极置于0.4 g/L的HAuCl4中,在−0.2 V的恒电位下将AuNPs沉积在电极表面,其次将10 µL不同浓度(0.1、0.2、0.25、0.5、1.0 nmol/L)的cDNA溶液滴涂在电极表面,置于37 ℃孵育1 h,接下来清洗电极表面并干燥后,然后将10 μL Pt@AuNWs-apt复合物滴加在电极表面孵育,最后在传感器上滴加10 μL 10 ng/mL的AFB1孵育后,将传感器置于10 mmol/L H2O2溶液中进行DPV测试。
1.2.7.2 适配体和互补链孵育时间的选择
处理思路同1.2.7.1,在电极表面滴加10 μL Pt@AuNWs-apt复合物后,孵育不同的时间(10、20、30、40、50 min),最后在传感器上滴加10 μL 10 ng/mL AFB1孵育,将传感器置于10 mmol/L H2O2溶液中进行DPV测试。
1.2.7.3 测试底液pH的选择
处理思路同1.2.7.1,将制备好的电极在10 μL 10 ng/mL的AFB1孵育后,置于10 mmol/L H2O2溶液中(pH分别为5、6、7、8、9)进行DPV测试。
1.2.7.4 测试底液浓度的选择
处理思路同1.2.7.1,将制备好的电极在10 μL 10 ng/mL的AFB1孵育后,置于pH7的不同浓度的H2O2溶液中(浓度分别为5、8、10、15、20 mmol/L)进行DPV测试。
1.2.8 选择性、重现性、稳定性
选择性的探究:将制备好的电极依次在1 μg/mL单端孢霉烯(T-2毒素),1 μg/mL呕吐毒素(DON),1 μg/mL赭曲霉毒素(OTA)及100 ng/mL AFB1与上述三者混合液中,进行DPV测试。
重现性的探究:记录5支适配体传感器在10 mmol/L H2O2中的DPV信号。
稳定性的探究:将所构建的传感器储存于4℃条件下,分别记录1、3、5、7、14 d后在10 mmol/L H2O2中的DPV信号。
1.2.9 花生样品的制备及检测
准确称取5.0000 g花生,将花生用研钵和杵磨成细粉,使其尺寸不大于1 mm并通过2.0 mm圆孔筛碎粒。用14 mL甲醇和6 mL超纯水混合制备萃取液,将花生碎加入混合恒温培养振荡器上振摇60 min。然后以6000 r/min离心10 min,取其上清液2 mL,形成最终的待测溶液。
将所构建的适配体传感器用于花生样品的检测,首先在2 mL的待测液中检测,然后在待测液中依次加入5、25、50 ng/mL的AFB1,每组实验重复3次。
1.3 数据处理
将三次平行测得的数据先用Excel表格处理,再将实验数据图利用Origin 2019 绘图软件绘制图形。
2. 结果与分析
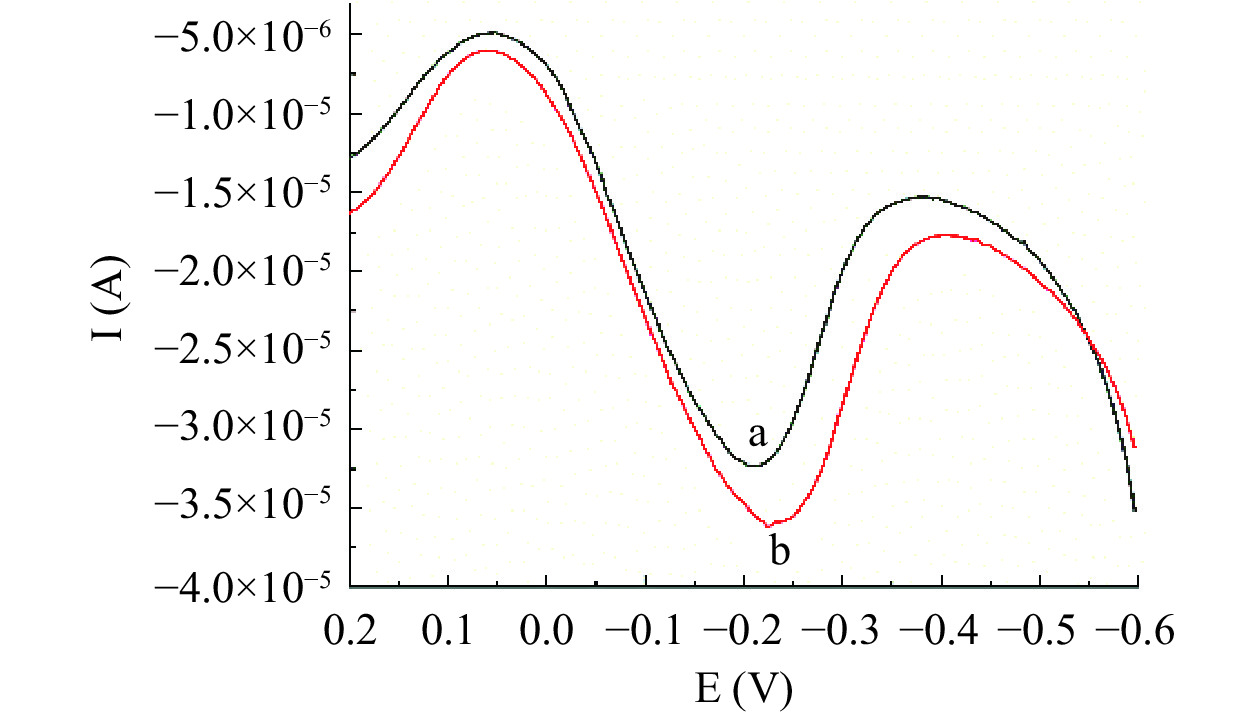
2.1 竞争型传感器可行性探究
首先考察该方法的可行性,结果见图2。结果表明,孵育AFB1后,峰电流有较明显的下降。由此可知该竞争型传感器检测AFB1具有可行性。
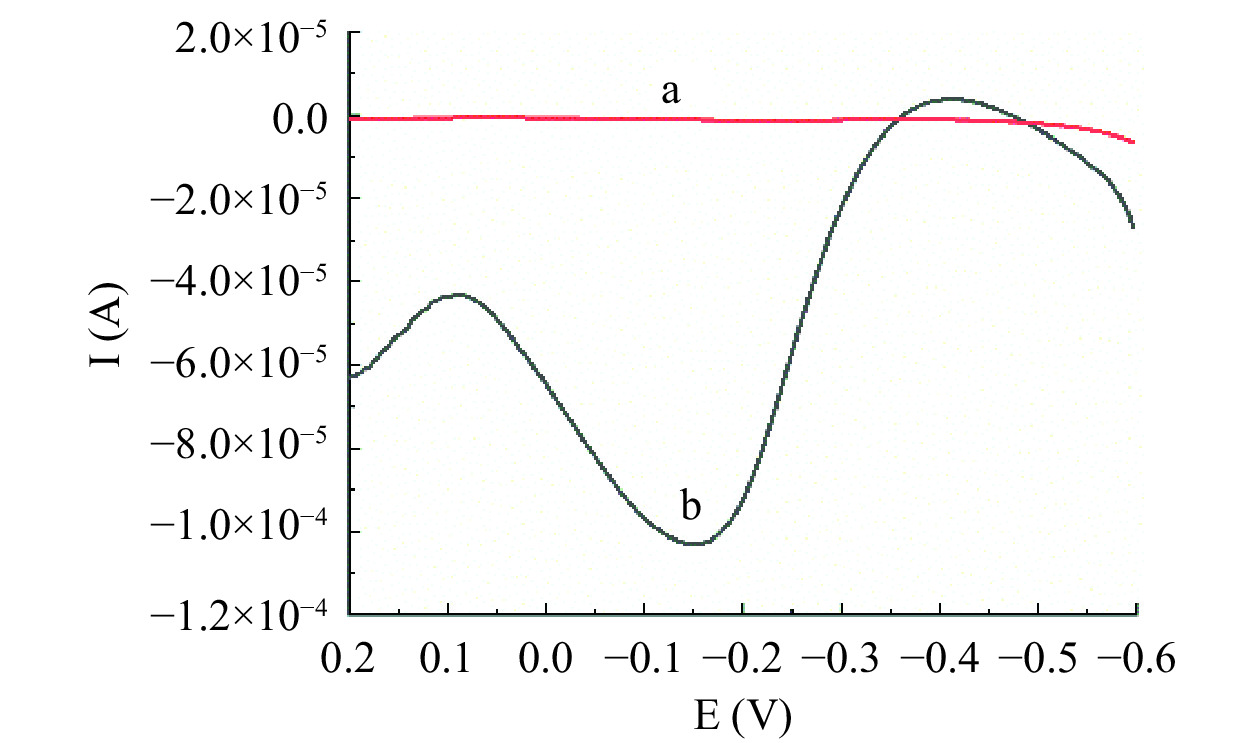
2.2 Pt@AuNWs的电催化性能
为了探究Pt@AuNWs的电催化性能,采用DPV法对其表征。Pt@AuNWs的电催化性能结果见图3。从图中可以发现,较之对照组(a线),修饰有Pt@AuNWs的传感器(b线)具有显著增大的电化学信号,这主要归因于Pt@AuNWs对H2O2的电化学行为有显著的电催化性能,从而使电化学信号明显增大,该结果表明采用Pt@AuNWs作为信号放大物构建的电化学适配体传感器能有效提高分析方法的灵敏度。
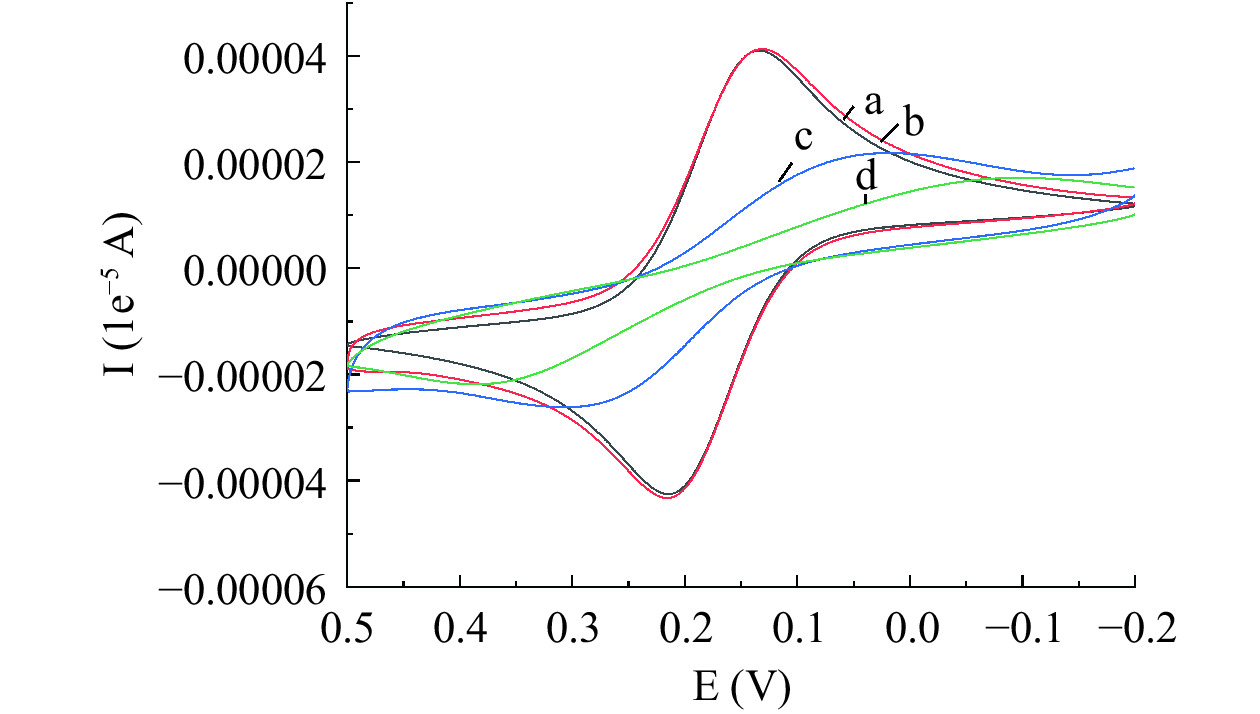
2.3 电极修饰过程的电化学表征
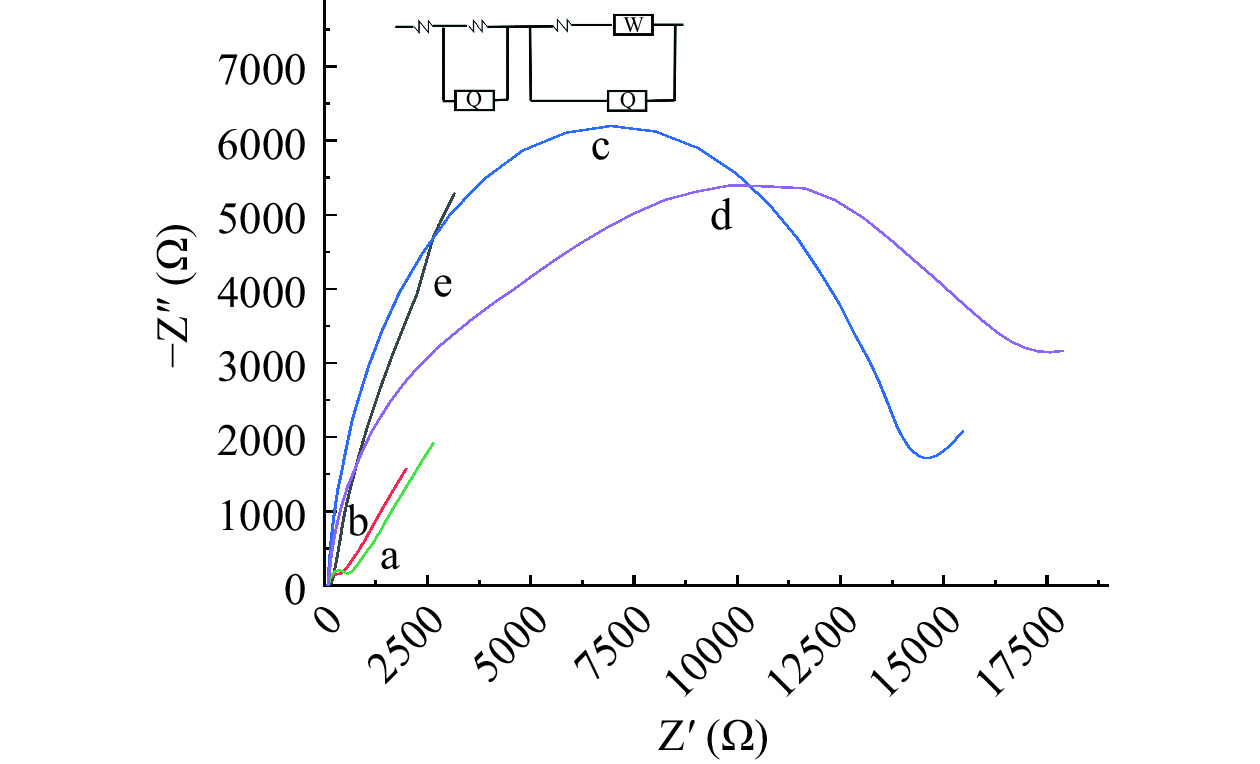
为了探究电化学传感器的成功构建,首先采用CV对其进行表征。CV表征结果见图4。从图中可以看出,裸GCE(a线)有一对明显的氧化还原峰。采用恒电位在玻碳电极表面沉积纳米金(b线)后,由于AuNPs具有优异的导电性,可加快电子传递,从而导致峰电流增大。当继续在电极表面修饰10 μL 0.25 nmol/L cDNA后(c线),由于cDNA不导电,对电子传递有阻碍作用,导致峰电流减小,当不导电的MCH固载在电极表面时(d线),峰电流继续减小。当孵育10 μL 0.25 nmol/L apt后,由于碱基互补配对作用形成的复合物不导电,峰电流进一步降低。由CV结果可知,电化学适配体传感器已经构建成功。
EIS表征结果见图5。裸GCE(a线)表面沉积AuNPs后,由于AuNPs具有良好的导电性,导致电极表面电子转移加快,电阻减小(b线)。当电极表面修饰cDNA后(简称cDNA/AuNPs/GCE),响应曲线的半径明显增大,这主要归因于cDNA阻碍电子传递,使得电阻明显增大(c线)。同理,由于MCH不导电,当MCH修饰于电极表面后(简称MCH/cDNA/AuNPs/GCE),响应曲线的半径继续增大,电阻进一步增大(d线)。最后,当电极表面修饰10 μL 0.25 nmol/L apt后,由于形成的碱基复合物不导电,进一步阻碍电子传递,使响应曲线的半径继续增大,即电阻也继续增大(e线)。CV和EIS两种表征方法结果一致,均证实电极逐步修饰过程的成功构建。
2.4 实验条件的优化
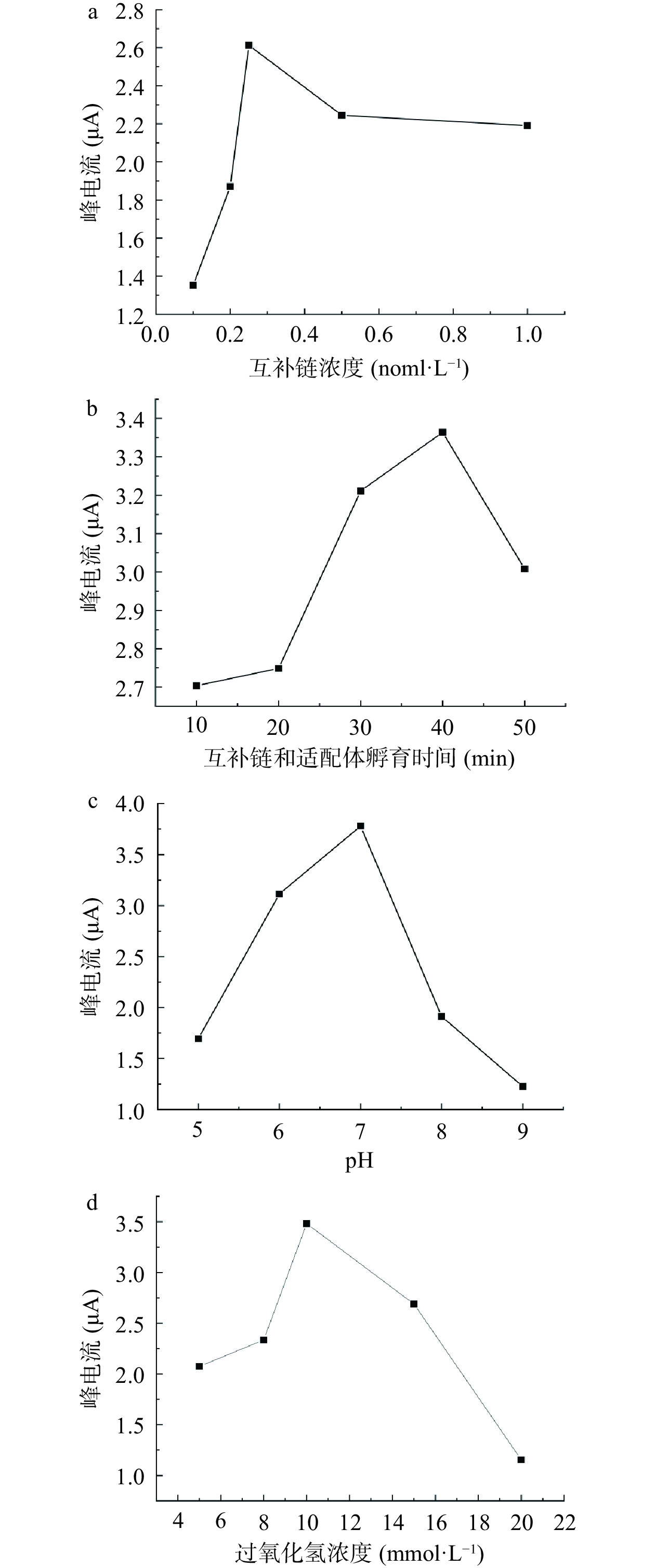
为使传感器具有更优的分析性能,对实验中的cDNA浓度、适配体孵育时间、H2O2浓度、缓冲液pH进行优化。在传感器构建过程中,cDNA浓度对传感器性能有重要影响。cDNA浓度低,将使电极表面固载的适配体的量减少,cDNA浓度过高,因其不导电,将造成电化学响应信号降低,因此,浓度过高或过低均会影响方法的灵敏度。实验中先对cDNA浓度进行优化,结果见图6a。从图中可知,随着cDNA浓度的增大,电流响应值逐渐增大并在0.25 nmol/L处达到最大值,之后峰电流开始下降。因此后续实验中选用0.25 nmol/L cDNA为最优浓度。适配体和互补链的孵育时间将影响最终电极上负载的Pt@AuNWs的量,会对其催化H2O2产生的电流响应显著影响。因此对两者的孵育时间进行考察。从图6b中可知,随着孵育时间的延长,电流响应值逐渐升高,在40 min时峰电流出现最大值,随着时间的进一步延长峰电流开始下降。因此,后续实验中最佳孵育时间选取为40 min。测试底液pH对适配体和互补链的相互作用也有明显的影响结果见图6c。由图中可以看出,随着pH的增大,电流信号也随之增大,在pH7处峰电流达到最大,随后开始下降。因此,后续实验中选用pH7为最佳测试条件。测试底液中H2O2的浓度对传感器的分析性能也有影响,结果见图6d。从图中可知,峰电流先随着H2O2浓度的增大而增大,在10 mmol/L处达到最大值,因此后续实验过程中使用10 mmol/L H2O2作为最佳测试条件。
2.5 适配体传感器的标准曲线
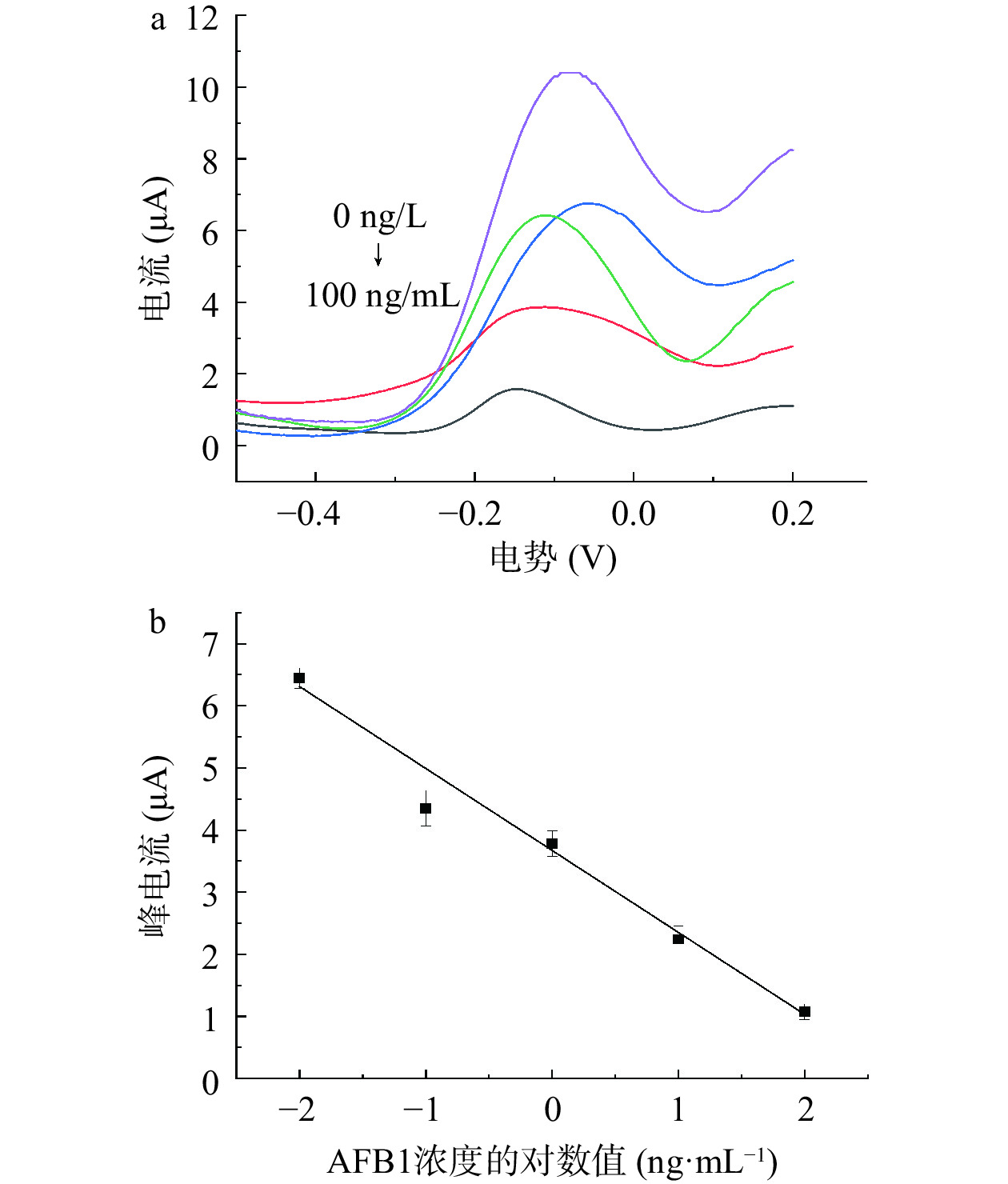
在最优条件下,对不同浓度的AFB1进行DPV检测(图7),结果表明,峰电流随着AFB1浓度的升高而降低,在0~100 ng/mL内有良好的线性反应。相应的线性方程为I (μA)=−1.2856lgc (ng/mL)+3.5782,线性相关系数R2为0.9764。经计算,该适体传感器的检出限0.41 ng/mL(S/N=3)。结果表明构建的传感器有较宽的线性范围,检出限较低。
2.6 适配体传感器的选择性、重现性、稳定性
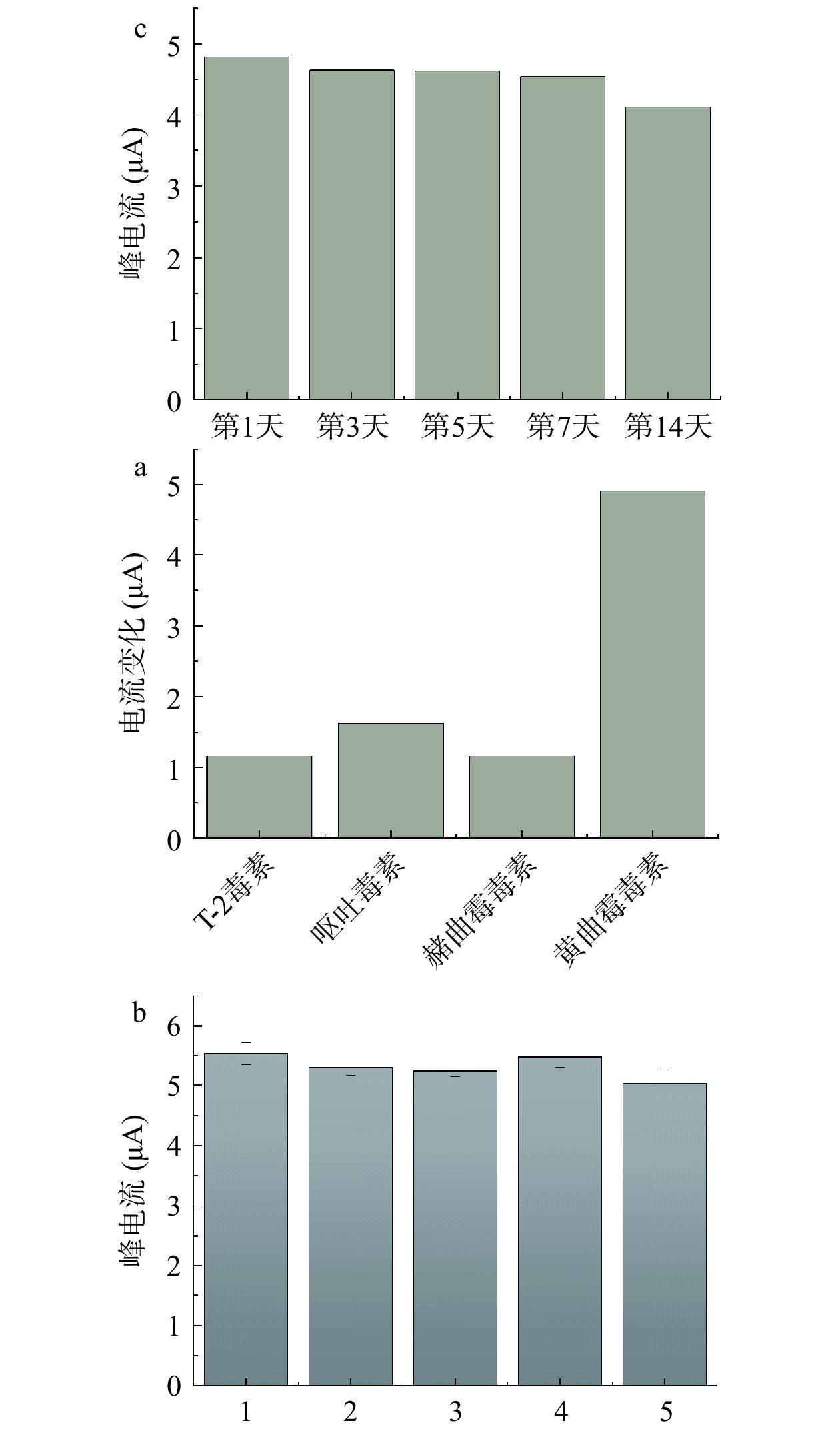
适配体传感器的选择性如图8a所示,当适体传感器用于检测浓度为1 μg/mL T-2毒素,呕吐毒素(DON),赭曲霉毒素(OTA)时,均没有产生明显的DPV信号变化,而当适体传感器检测10 ng/mL AFB1(仅为上述三种毒素浓度的1%)与上述物质的混合物时,DPV信号显著变化,这表明适配体传感器对AFB1具有很好的选择性。适配体传感器的重现性如图8b所示,RSD 为3.77%,该结果表明适配体传感器有良好的重现性。适配体传感器的稳定性见图8c,传感器在14 d后测得的电信号值下降约14.6%。表明该适体传感器具有良好的稳定性。
2.7 花生样品的检测
按1.3对实际样品进行前处理,采用标准加入法对样品中AFB1的加标回收率进行测定。结果见表1,实验结果表明,回收率在85.1%~88.0%,RSD≤6%,表明构建的传感器具有较好的回收率,可用于检测花生中AFB1。
表 1 花生待测液中AFB1的测定结果Table 1. Determination of AFB1 in peanut solution样品序号 加标量(μg/mL) 测定量(μg/mL) RSD(%) 回收率(%) 1 5 4.40 2.7 88.0 2 25 21.27 3.6 85.1 3 50 43.60 5.8 87.2 3. 结论
综上所述,构建的以Pt@AuNWs为信号放大物的电化学适配体传感器可用于无壳花生生中AFB1含量的准确、快速检测,在0.25 nmol/L cDNA、apt与cDNA孵育40 min、10 mmol/L H2O2、0.1 mol/L 磷酸盐浓度pH7的测试条件下具有最优的分析性能。Pt@AuNWs的信号放大物的使用以及适配体识别单元的引入,使得该传感器具有较宽的线性范围(1~100 ng/mL)和较低的检出限(0.41 ng/mL)。同时该传感器具有较好的选择性、重现性和稳定性,在花生样品的检测中具有较好的回收率(85.1%~88.0%)。虽然该方法存在着制备传感器略显复杂的局限,但其具有检测成本低、分析速度快的优势,便于后期的推广应用,可以作为检测花生中AFB1含量的一种有效手段,但目前传感器随着贮存时间的延长,检测性能面临下降的问题,如何提高传感器的长期稳定性是下一步研究的方向问题,以期更好的满足现场检测的需求。
-
表 1 花生待测液中AFB1的测定结果
Table 1 Determination of AFB1 in peanut solution
样品序号 加标量(μg/mL) 测定量(μg/mL) RSD(%) 回收率(%) 1 5 4.40 2.7 88.0 2 25 21.27 3.6 85.1 3 50 43.60 5.8 87.2 -
[1] WANG C, ZHAO Q. A reagentless electrochemical sensor for aflatoxin B1 with sensitive signal-on responses using aptamer with methylene blue label at specific internal thymine[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2020,167:112478−112483. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112478
[2] XU Z, LONG L L, CHEN Y Q, et al. A nanozyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on metal–organic frameworks (MOFs) for sensitive detection of aflatoxin B1[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,338:128039−128045. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128039
[3] QIAN J, REN C C, WANG C Q, et al. Gold nanoparticles mediated designing of versatile aptasensor for colorimetric/electrochemical dual-channel detection of aflatoxin B1[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2020,166:112443−112450. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2020.112443
[4] LI S Q, ZHONG X Y, XU Y N, et al. Smartphone-based reading system integrated with phycocyanin-enhanced latex nanospheres immunoassay for on-site determination of aflatoxin B1 in foodstuffs[J]. [J]. Food Chemistry,2021,360:130019. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130019
[5] SUN C N, LIAO X F, JIA B Y, et al. Development of a ZnCdS@ZnS quantum dots-based label-free electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for sensitive determination of aflatoxin B1 in lotus seed[J]. Microchimica Acta,2020,187(4):236−244. doi: 10.1007/s00604-020-4179-x
[6] JIANG S, ZHANG L X, LI J Z, et al. Pressure/colorimetric dual-readout immunochromatographic test strip for point-of-care testing of aflatoxin B1[J]. Talanta,2021,227:122207−122213. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122207
[7] BU T, BAI F E, SUN X Y, et al. An innovative prussian blue nanocubes decomposition-assisted signal amplification strategy suitable for competitive lateral flow immunoassay to sensitively detect aflatoxin B1[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,344:1287111−1287118.
[8] GELL R M, CARBONE I. HPLC quantitation of aflatoxin B1 from fungal mycelium culture[J]. Journal of Microbiological Methods,2019,158:14−17. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2019.01.008
[9] ALGAMMAL A M, ELSAYED M E, HASHEM H R, et al. Molecular and HPLC-based approaches for detection of aflatoxin B1 and ochratoxin A released from toxigenic Aspergillus species in processed meat[J]. BMC Microbiology,2021,21(1):82−91. doi: 10.1186/s12866-021-02144-y
[10] ZHANG B, YU L, LIU Z, et al. Rapid determination of aflatoxin B1 by an automated immunomagnetic bead purification sample pretreatment method combined with high-performance liquid chromatography[J]. Journal of Separation Science,2020,43(17):3509−3519. doi: 10.1002/jssc.202000293
[11] DENG Y J, WANG Y L, DENG Q, et al. Simultaneous quantification of aflatoxin B1, T-2 toxin, ochratoxin A and deoxynivalenol in dried seafood products by LC-MS/MS[J]. Toxins,2020,12(8):12,488−500.
[12] WANG C Q, ZHANG W H, QIAN J, et al. A FRET aptasensor for sensitive detection of aflatoxin B1 based on a novel donor-acceptor pair between ZnS quantum dots and Ag nanocubes[J]. Analytical Methods,2021,13(4):462−468. doi: 10.1039/D0AY02017F
[13] CHEN H F, HAN F, MAO B N, et al. Rapid and label free detection of aflatoxin B1 in alcoholic beverages with a microfluid fiber device[J]. Applied Optics,2021,60(7):1924−1929. doi: 10.1364/AO.414332
[14] WANG N, LIU Q Q, HU X F, et al. Electrochemical immunosensor based on AuNPs/Zn/Ni-ZIF-8-800@graphene for rapid detection of aflatoxin B1 in peanut oil[J]. Analytical Biochemistry,2022,650:114710. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2022.114710
[15] GUAN Y, SI P B, YANG T, et al. A novel method for detection of ochratoxin A in foods-Co-MOFs based dual signal ratiometric electrochemical aptamer sensor coupled with DNA walker[J] Food Chemistry, 2023, 403:134316.
[16] ZHANG K, WANG Y, WANG H Y, et al. Three-dimensional porous reduced graphene oxide modified electrode for highly sensitive detection of trace rifampicin in milk[J]. Analytical Methods,2022,14(23):2304−2310. doi: 10.1039/D2AY00517D
[17] ZHU C X, LIU X H, LI Y Y, et al. Dual-ratiometric electrochemical aptasensor based on carbon nanohorns/anthraquinone-2-carboxylic acid/Au nanoparticles for simultaneous detection of malathion and omethoate[J]. Talanta,2023,253:123966. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2022.123966
[18] PATIL J J, REESE M L, LEE E, et al. Oxynitride-encapsulated silver nanowire transparent electrode with enhanced thermal, electrical, and chemical stability[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2022,14(3):4423−4433.
[19] PARVIN S, KUMAR A, GHOSH A, et al. An earth-abundant bimetallic catalyst coated metallic nanowire grown electrode with platinum-like pH-universal hydrogen evolution activity at high current density[J]. Chemical Science,2020,11(15):3893−3902. doi: 10.1039/D0SC00754D
[20] LI W, DENG X, WU Z Y, et al. An electrochemical sensor for quantitation of the oral health care agent chlorogenic acid based on bimetallic nanowires with functionalized reduced graphene oxide nanohybrids[J]. ACS Omega,2022,7(5):4614−4623. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c06612
[21] SONG D D, LI Q, LU X, et al. Ultra-thin bimetallic alloy nanowires with porous architecture/monolayer MoS2 nanosheet as a highly sensitive platform for the electrochemical assay of hazardous omethoate pollutant[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2018,357:466−474. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.06.021
[22] SHETTY S, GAYEN M, AGARWAL S, et al. Tuning catalytic activity in ultrathin bimetallic nanowires via surface segregation:some insights[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry Letters,2022,13(3):770−776. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c03852
[23] WANG H, JIAO S, LIU S, et al. Mesoporous bimetallic au@rh core-shell nanowires as efficient electrocatalysts for ph-universal hydrogen evolution[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2021,13(26):30479−30485.
[24] SHARMA A S, ALI S, SABARINATHAN D, et al. Recent progress on graphene quantum dots-based fluorescence sensors for food safety and quality assessment applications[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2021,20(6):5765−5801. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12834
[25] SUN J, LI L, GE S, et al. Dual-mode aptasensor assembled by a Wo3/Fe2O3 heterojunction for paper-based colorimetric prediction/photoelectrochemical multicomponent analysis[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2021,13(3):3645−3652.
[26] WEI H, BU S, ZHANG W, et al. An electrochemical biosensor for the detection of pathogenic bacteria based on dual signal amplification of Cu3(PO4)2− mediated click chemistry and DNAzymes[J]. Analyst,2021,146(15):4841−4847. doi: 10.1039/D1AN00982F
[27] JIANG Z W, ZHAO T T, LI C M, et al. 2D mof-based photoelectrochemical aptasensor for sars-cov-2 spike glycoprotein detection[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2021,13(42):49754−49761.
[28] ZHANG B, LU Y, YANG C, et al. Simple "signal-on" photoelectrochemical aptasensor for ultrasensitive detecting AFB1 based on electrochemically reduced graphene oxide/poly(5-formylindole)/Au nanocomposites[J]. Biosensors & Bioelectronics,2019,134:42−48.
[29] ZHU L, ZHAO Y, YAO S L, et al. A colorimetric aptasensor for the simple and rapid detection of human papillomavirus type 16 L1 proteins[J]. Analyst,2021,146(8):2712−2717. doi: 10.1039/D1AN00251A
[30] PAN L M, ZHAO X, WEI X, et al. Ratiometric luminescence aptasensor based on dual-emissive persistent luminescent nanoparticles for autofluorescence- and exogenous interference-free determination of trace aflatoxin B1 in food samples[J]. Analytical Chemistry,2022,94(16):6387−6393. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.2c00861
[31] HONG W, WANG J, WANG E K. Dendritic Au/Pt and Au/PtCu nanowires with enhanced electrocatalytic ctivity for methanol electrooxidation[J]. Small,2014,10(16):3262−3265. doi: 10.1002/smll.201400059
[32] YANG Y, CHEN M, WU Y J, et al. Ultrasound assisted one-step synthesis of Au@Pt dendritic nanoparticles with enhanced NIR absorption for photothermal cancer therapy[J]. RSC Advances 2019, 9 (49):28541−28547.
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 杨敏,张密,叶贤胜,曾长立,马爱民,牛蒙亮,许丹云. 大球盖菇多肽的制备、抗氧化及抗肿瘤活性的研究. 山西农业大学学报(自然科学版). 2025(01): 123-132 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 魏磊,景炳年,李宁洁,金饶,谢晓阳,刘雨晴,马艳妮,梁雅辉,王韬,王伟. 赤松茸乙醇提取物不同萃取相生物活性对比. 食品研究与开发. 2025(04): 39-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王小平,刘忠莹,钟洋,张定秋,陆阳,朱敏敏,郑红毅,何叶馨,王鑫,黄韬睿,江祖彬. 基于离子色谱-电感耦合等离子体质谱法分析木耳、香菇、松茸和茶树菇中砷形态分布. 食品工业科技. 2024(07): 254-260 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 韦菡燕,蒋军文. 等离子体对松茸多糖抗疲劳作用的影响. 保鲜与加工. 2024(10): 128-133 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 黄磊,何春梅,司灿,石鸿宇,段俊. 大球盖菇栽培研究进展. 中国食用菌. 2023(03): 8-14 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 魏磊,王伟,谢晓阳,周雍,刘雨晴,马艳妮,宁二娟,王韬,李宁洁,景炳年. 响应面优化博爱赤松茸多糖提取工艺及其抑菌和抗氧化活性研究. 食品工业科技. 2023(15): 213-220 .  本站查看
本站查看
7. 曹燕妮,华蓉,邓雅元,王娟,游金坤. 食用菌中维生素测定方法研究. 中国食用菌. 2022(09): 44-47 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



