Effects of Sacha Inchi Leaf Alcohol Extract on Delaying Aging of Caenorhabditis elegans
-
摘要: 本文以美藤果叶醇提物(Sacha inchi leaf alcohol extract,SILAE)为研究对象,通过构建秀丽隐杆线虫(以下简称线虫)衰老模型,探究了不同质量浓度(5、10、15 mg/mL)SILAE对线虫寿命、运动能力、生殖能力、抗氧化应激能力与体内ROS、脂褐质和丙二醛(MDA)水平的作用效果,以及SILAE对线虫体内酶和非酶抗氧化剂的影响,旨为美藤果叶的进一步研究和应用提供一定的理论参考。结果表明:与空白组相比,5、10 mg/mL的SILAE能显著延长线虫寿命(P<0.05),分别提高了59.3%、30.2%,15 mg/mL SILAE也能延长其寿命但无显著性差异。与此同时,SILAE还能有效提高其生殖能力和运动能力。在氧化应激环境中,SILAE使线虫的H2O2应激寿命分别延长了约2、4、5倍,5、10 mg/mL的SILAE也显著提高了线虫的胡桃醌应激寿命(P<0.05)。SILAE能不同程度地降低线虫体内的ROS和脂褐质(P<0.001),以及MDA(P<0.05)的积累量。此外,15 mg/mL SILAE极显著提高了线虫体内超氧化物歧化酶和过氧化氢酶的活性(P<0.001),谷胱甘肽过氧化酶活性和谷胱甘肽含量分别在5 mg/mL(P<0.05)和10 mg/mL(P<0.01)SILAE组中得到显著提高。综上,SILAE具有抗衰老功效,是具有缓解氧化、延缓衰老的功能食品或替代药物的一种新的可能来源。Abstract: In this study, the effects of different mass concentrations (5, 10 and 15 mg/mL) of Sacha inchi leaf alcohol extract (SILAE) on Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans) longevity, mobility, reproductive capacity, resistance to oxidative stress and levels of ROS, lipofuscin and malondialdehyde (MDA) in vivo, as well as the effects of SILAE on enzymatic and non-enzymatic antioxidants in C. elegans were investigated by constructing a senescence model of C. elegans, with the aim of providing certain theoretical references to the further research and application of Sacha inchi leaf. The results showed that SILAE at 5 and 10 mg/mL significantly prolonged the life span of C. elegans compared with the blank group (P<0.05) by 59.3% and 30.2%, respectively, and 15 mg/mL SILAE also prolonged their life span but without significant differences. Meanwhile, their reproductive and motility abilities were also effectively improved by SILAE. In oxidative stress environments, SILAE prolonged the life span of C. elegans under H2O2 stress by approximately 2, 4, and 5-fold, respectively, and 5 and 10 mg/mL of SILAE also significantly prolonged the life span of C. elegans under juglone stress (P<0.05). The accumulation of ROS, lipofuscin (P<0.001), and MDA (P<0.05) in C. elegans was reduced to varying degrees by SILAE. In addition, both superoxide dismutase and catalase activities in C. elegans were highly significantly increased by SILAE (P<0.001), while glutathione peroxidase activity and glutathione content were significantly increased by SILAE at 5 mg/mL (P<0.05) and 10 mg/mL (P<0.01), respectively. In conclusion, SILAE has anti-aging property and is a new possible source of functional foods or alternative drugs with oxidative mitigation and aging retardation effects.
-
Keywords:
- Sacha inchi leaf /
- alcohol extract /
- Caenorhabditis elegans /
- oxidative aging
-
衰老是一个保守的、复杂且不可逆转的退行性生理过程,其特征是身体生理功能的下降和综合表现的退化,甚至可能危及生命[1]。已发表的与衰老有关的理论大多可分为程序化衰老和损伤衰老两种,其中最普遍的观点是氧化应激损伤,其强调的是生物体在代谢过程中由一些相互关联的反应产生的过量ROS对核酸、脂质和蛋白质等细胞生物大分子造成渐进和累积性损伤,进而加速衰老[2−3]。随着衰老模型和衰老表型指标的建立,具有功能多样性的天然植物提取物已被证明能预防和/或缓解生理功能的自然下降,有望成为健康寿命和长寿的促进剂[4−6]。
美藤果(Sacha inchi,又名Plukenetia volubilis Linneo),亦称南美油藤、印奇花生、星油藤等,属大戟科多年生常绿木质含油攀援植物,原产于南美洲亚马逊地区的热带雨林,包括秘鲁和巴西西北部的部分地区,其叶子和种子被一些土著部落群体以煮熟和烘烤形式作为传统食物食用[7]。研究表明[8],美藤果叶乙醇提取物在7000 mg/kg的质量浓度范围内对瑞士白化小鼠没有产生任何不利影响,即没有毒副作用,可以安全食用。Lin等[9]发现,美藤果叶水提取物可改善小鼠的高血糖症状和肠道微生物群的结构紊乱,有成为功能性饮料的潜力。Nascimento等[10]对从水、甲醇、乙醇、氯仿和己烷这5种不同溶剂中提取的新鲜美藤果叶提取物进行相关分析,发现它们含有酚类化合物、蛋白质、糖以及萜类化合物和/或类固醇,活性试验结果表明这些提取物具有抗氧化活性,可刺激成纤维细胞3T3的增殖,还能通过诱导细胞凋亡,不同程度地抑制肿瘤细胞HeLa和A549的增殖活性。Kittibunchakul等[11]对经烘箱干燥和冷冻干燥后美藤果嫩叶和成熟叶中的酚类成分含量和抗氧化潜力进行研究,发现冻干叶的总酚含量高于烘干叶,烘干后幼叶的抗氧化活性高于成熟叶,而冷冻干燥的结果则与之相反。综上所述,美藤果叶提取物有成为功能食品或药物补充剂的潜力。
从目前来看,大多数具有抗衰老作用的生物活性成分都是首先以秀丽隐杆线虫为模式生物的活性试验发现的。这可归因于线虫所具有的优势:微小透明、解剖结构简单,这为在体式显微镜下观察线虫的行动轨迹提供了便利;基因组特征明确,有与人类同源的肠道、神经元和肌肉细胞,这对神经系统和代谢功能至关重要[12−14];生命周期较短、繁衍能力强与人类高度保守的衰老信号网络等[15],这些优势满足了实验的灵活性、稳定性和可靠性等要求,使其成为衰老生物学研究的理想模型生物。另外,以哺乳动物为模型进行实验虽然很有说服力,但它耗时长且有伦理问题的限制。
因此,本文以秀丽隐杆线虫为模型生物,探究了美藤果叶醇提物(SILAE)的抗衰老活性,丰富了对美藤果叶功效作用的认识,为综合开发美藤果叶提供借鉴和参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
N2野生型线虫(Caenorhabditis elegans) 美国秀丽隐杆线虫遗传中心;美藤果叶(干燥) 普洱联众生物资源开发有限公司;大肠杆菌OP50(以下简称OP50) 上海南方模式生物科技股份有限公司;超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)试剂盒、MDA试剂盒、过氧化氢酶(catalase,CAT)试剂盒、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(glutathione peroxidase,GSH-Px)、谷胱甘肽(glutathione,GSH)试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所;其他试剂 广州齐湘生物科技有限公司。
SN-HWS250B型恒温生化培养箱 甘易仪器设备(上海)有限公司;FA2204型万分之一天平 上海舍岩仪器有限公司;LD-SY96S型多功能酶标仪 美谷分子仪器(上海)有限公司;MF53-N型荧光显微镜 上海蔡康光学仪器有限公司;LC-LX-HR185C型冷冻离心机 日本久保田公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品溶液的制备
干燥的美藤果叶经粉碎机粉碎后,过80目筛后,参考文献[16]进行超声辅助乙醇提取。提取液4000 r/min离心10 min,合并上清液并旋转蒸发浓缩,冷冻干燥。用体积分数为70%的乙醇溶液复溶,过0.22 μm滤膜,采用D101大孔树脂进行柱层析[17],先后分别用去离子水、体积分数10%和70%的乙醇梯度洗脱,收集70%乙醇的洗脱液,旋转蒸发浓缩,冷冻干燥得SILAE,用于基本活性成分的含量测定和线虫的抗衰老实验。
1.2.2 培养基及相关溶液配制
1.2.2.1 线虫生长培养基(nematode growth medium,NGM)
0.08 g链霉素硫酸盐,1.0 g胰蛋白胨,1.2 g NaCl,8.0 g琼脂粉,加入一级水390 mL,121 ℃灭菌30 min。然后转入无菌超净台中,降至适宜温度后,加入1 mol/L CaCl2、1 mol/L MgSO4和5 mg/mL溶解于乙醇中的胆固醇(已过滤除菌)各400 μL,以及10 mL 1 mol/L pH为6.0的磷酸盐缓冲液(除胆固醇外,其余三种溶液高温灭菌后再加入),混匀后在无菌超净台中趁热将其倒进培养皿中,待平板水汽干燥后方可用于实验。
1.2.2.2 M9缓冲液
取3 g Na2HPO4或7.56 g Na2HPO4·12H2O,1.5 g KH2PO4,2.5 g NaCl,0.125 g MgSO4·7H2O,加水至500 mL,121 ℃灭菌15 min。
1.2.2.3 OP50的制备
在超净台内,挑取OP50单菌落接入晾凉至约60 ℃的20 mg/mL的LB培养基中,而后置于恒温摇床内,在37 ℃,150 r/min条件下,培养20 h,至OD595=1.0左右即可。
1.2.3 线虫的培养和同期化
线虫的培养:用NGM于20 ℃的恒温培养箱中进行培养,NGM中涂有0.2 mL OP50作为线虫的食物。
线虫的同期化:将处于产卵期的线虫用1 mL M9缓冲溶液从NGM洗至无菌离心管中,3000 r/min离心1 min,弃去上清液,重复上述步骤2~3次后。再向其中加入1 mL裂解液(5 mol/L NaOH:质量分数0.5%的NaClO:超纯水=1:1:1),上下轻缓颠倒,裂解约4 min后3000 r/min离心1 min,吸除上清液,再向管中加1 mL M9缓冲液冲洗线虫,3000 r/min离心1 min,重复两次,弃去上清液后用移液枪吸取离心管中的线虫悬液50~100 μL滴在NGM的无菌区,在20 ℃培养箱中恒温培养约48 h(不超过60 h)后,此时的线虫即为同一生长发育水平L4期的幼虫,可用于相关实验。
1.2.4 实验分组与给药途径
实验分组:以H2O2氧化应激实验结果为依据,设置含有质量浓度为5、10、15 mg/mL SILAE的低、中、高剂量样品组,以及用超纯水和维生素C(10 mg/mL)代替样品的空白组和阳性对照组。
给药途径:样品、VC、超纯水分别与OP50按3:2的比例配制成给药样液,向新鲜NGM中央滴入0.1 mL样液,放置24 h后用于线虫实验。
1.2.5 SILAE中基本活性成分的测定
将1.2.1中获得的SILAE配制成0.1 mg/mL的样品溶液,进行含量测定。
1.2.5.1 总酚含量的测定
参考杨云等[18]方法并调整。用没食子酸标准品配制0.1 mg/mL的没食子酸标准溶液。以没食子酸浓度(mg/mL)为X轴,吸光值为Y轴,绘制标准曲线。
取12.5 μL 0.1 mg/mL的SILAE,定容至250 μL作为样品待测液。向待测样品和蒸馏水中加入福林酚试剂0.25 mL,混匀,避光反应2 min,依次加入1 mL的7.5% Na2CO3和0.5 mL水,混匀。40 ℃避光水浴30 min。在760 nm处测定吸光值。
1.2.5.2 多糖含量的测定
参考海力茜·陶尔大洪等[19]的方法,略有改动。准确称取葡萄糖标准品10.0 mg,用一级水配制成0.1 mg/mL的葡萄糖标准溶液,绘制标准曲线。
取1 mL 0.1 mg/mL的SILAE于试管中,而后依次加入1 mL 5%苯酚和5 mL浓硫酸,混匀,30 ℃水浴20 min,490 nm处检测吸光值,计算总糖含量。
1.2.5.3 蛋白质含量的测定
参考黄婉玉等[20]方法。以2 mg/mL牛血清蛋白溶液为母液,配制浓度分别为0、5、25、50、125和500 μg/mL的标准溶液。分别取不同浓度的标准品20 μL于96孔板中,再加入200 μL考马斯亮蓝G250,混合均匀,在595 nm出检测吸光值。以牛血清蛋白浓度为横坐标,吸光值为纵坐标,制作标准曲线。用待测SILAE替换牛血清蛋白溶液,重复上述步骤,测定其蛋白质含量。
1.2.5.4 总黄酮含量的测定
参考王冰芳[16]的方法,略有修改。用60%乙醇配制0.20 mg/mL的芦丁标准品溶液,准确移取0.0、1.0、2.0、3.0、4.0、5.0 mL的芦丁标准品溶液于6个10 mL的刻度比色管中。先加入0.3 mL 5%的NaNO2溶液于各管中,充分摇匀后静置6 min;再向各管中加入0.3 mL 10%的Al(NO3)3溶液,摇匀,静置6 min;最后加入4.0 mL 4%的NaOH溶液于各管中,并用60%的乙醇定容至刻度,摇匀后静置15 min。以60%乙醇作为空白对照,分别在510 nm处测定吸光值值,绘制标准曲线。
用待测SILAE替换芦丁溶液,重复上述步骤,测定其总黄酮含量。
1.2.6 线虫寿命的测定
挑取同步化的L4期幼虫到新的各组平板上(每个平板30条,每组3个平板),于20 ℃恒温箱中继续培养,定为第0 d。为保证处理化合物的浓度,随后每天将线虫转移到相应的新鲜NGM板中,直到生殖后期(第6 d),此后每2 d将线虫转到新的各组平板中,记录线虫存活、死亡以及剔除条数,直至所有组线虫死亡,实验结束[21]。
线虫死亡判断标准:无吞咽或移动动作,铂丝轻触虫体仍无任何反应。剔除标准:钻入琼脂中;逃离至平皿壁或盖上而干死;虫卵在体内孵化而成袋样虫。剔除意外死亡、逃逸和袋样虫。
1.2.7 线虫运动能力的测定
在同步的寿命实验中进行评估,每4 d观察并记录线虫的运动情况[22]。记录标准:虫体20 s内有自发连续协调的正弦运动,不需要触碰刺激,记为“A”;虫体必须受到触碰刺激才运动,记为“B”;线虫受到触碰刺激后只摆头或尾,记为“C”。
1.2.8 线虫产卵量的测定
挑取同期化的L4期幼虫到各组NGM中,每组5个板,每个平板1条线虫。每隔24 h将线虫转移至相应的新NGM中(大约转移4~5次),直到线虫不再产卵。将有虫卵的NGM再放回恒温培养箱中20 ℃孵育24 h,待虫卵孵化长大后(在其进入产卵期之前)进行计数,即为每条线虫的产卵量。
1.2.9 线虫应激能力实验
氧化应激NGM的配制:将0.1% H2O2和用无水乙醇配制好的240 μmol/L胡桃醌溶液,在无菌超净台中倒入冷却至60 ℃左右的NGM中(按400 mL计),混匀后倒入培养皿中,避光放置。
H2O2急性氧化应激[23]:挑取同期化的L4期幼虫到各组NGM中(每个平板20条,每组3个板),干预5 d后,将各组线虫转移至含有0.1% H2O2的NGM中,每隔1 h统计一次线虫的生存情况,直到线虫全部死亡。
胡桃醌氧化应激[24]:挑取同期化后处于L4期的幼虫到各组NGM中(每个平板30条,每组3个平板)继续干预5 d,随后将各组线虫转移至含有240 μmol/L胡桃醌的NGM中,每隔1 h统计一次线虫的生存情况,直到线虫全部死亡。
1.2.10 线虫体内ROS及脂褐质水平测定
ROS水平的测定:将同期化的L4期幼虫挑到新的各组NGM上(每个平板30条,每组3个平板)继续干预5 d后,用M9缓冲溶液冲洗培养基3次并转移至无菌离心管中,离心取上清液。从上清液中吸取50 μL和50 μL H2DCF-DA避光混匀加入黑色96孔板中,在荧光显微镜下每20 min进行1次荧光强度测定(激发波长:485 nm,发射波长:530 nm),连续测定2 h,并以上清液蛋白质浓度进行相对荧光强度标准化。
脂褐质水平的测定[25]:将同期化的L4期幼虫挑到相应的NGM上(每个平板30条,每组3个平板)继续干预7 d后,以1%叠氮化钠溶液作麻醉剂麻醉各组线虫,随即转移到2%琼脂糖凝胶垫片上,并在激发波长365 nm、发射波长420 nm下用荧光倒置显微镜、单色数码相机以及Image J获取荧光图像。
1.2.11 线虫体内抗氧化酶活性和MDA水平的测定
将同期化后生长到L4期的线虫转移到各组NGM上,分别继续干预5 d后,用M9缓冲溶液冲洗2次培养皿并将各板上的成虫收集到无菌离心管中。冷冻研磨后离心,收集上清液后制成5%的线虫匀浆,分别按照试剂盒测定CAT、SOD、GSH-Px活力及MDA与GSH含量,并以上清液蛋白质浓度进行标准化[26]。
1.3 数据处理
每组实验均重复进行3次,数据采用平均值±标准差(ˉx±SD)表示。数据处理采用Excel 2016、GrapPad Primsm 8以及Image J等软件作图,采用SPSS 26进行单因素方差分析并用最小显著性差异法进行多重比较。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 SILAE基本活性成分的含量
表1是SILAE中总糖、总酚、蛋白质和总黄酮含量的比重。由表1可知,在所测定的四个指标中,总糖的含量最高,占34.70%±2.30%,依次分别是总酚、蛋白质和总黄酮。
表 1 SILAE中活性成分含量Table 1. Content of active ingredients in SILAE成分 线性回归方程 回归系数(R2) 含量(%) 总糖 y=0.0721x−0.0137 0.9949 34.70±2.30 总酚 y=10.258x+0.0918 0.9980 13.57±0.26 蛋白质 y=0.001x+0.2883 0.9950 12.70±1.00 总黄酮 y=12.182x+0.0037 0.9998 7.63±0.82 2.2 SILAE对线虫寿命的影响
衰老是一种与时间依赖性损伤、细胞稳态衰退和功能能力下降的生理过程,其特征主要是线粒体功能障碍、细胞衰老、蛋白质平衡丧失和营养传感失调等,最终会导致死亡易感性的增加[27]。因此,抗衰老研究中的寿命长度可作为老化的评价指标。
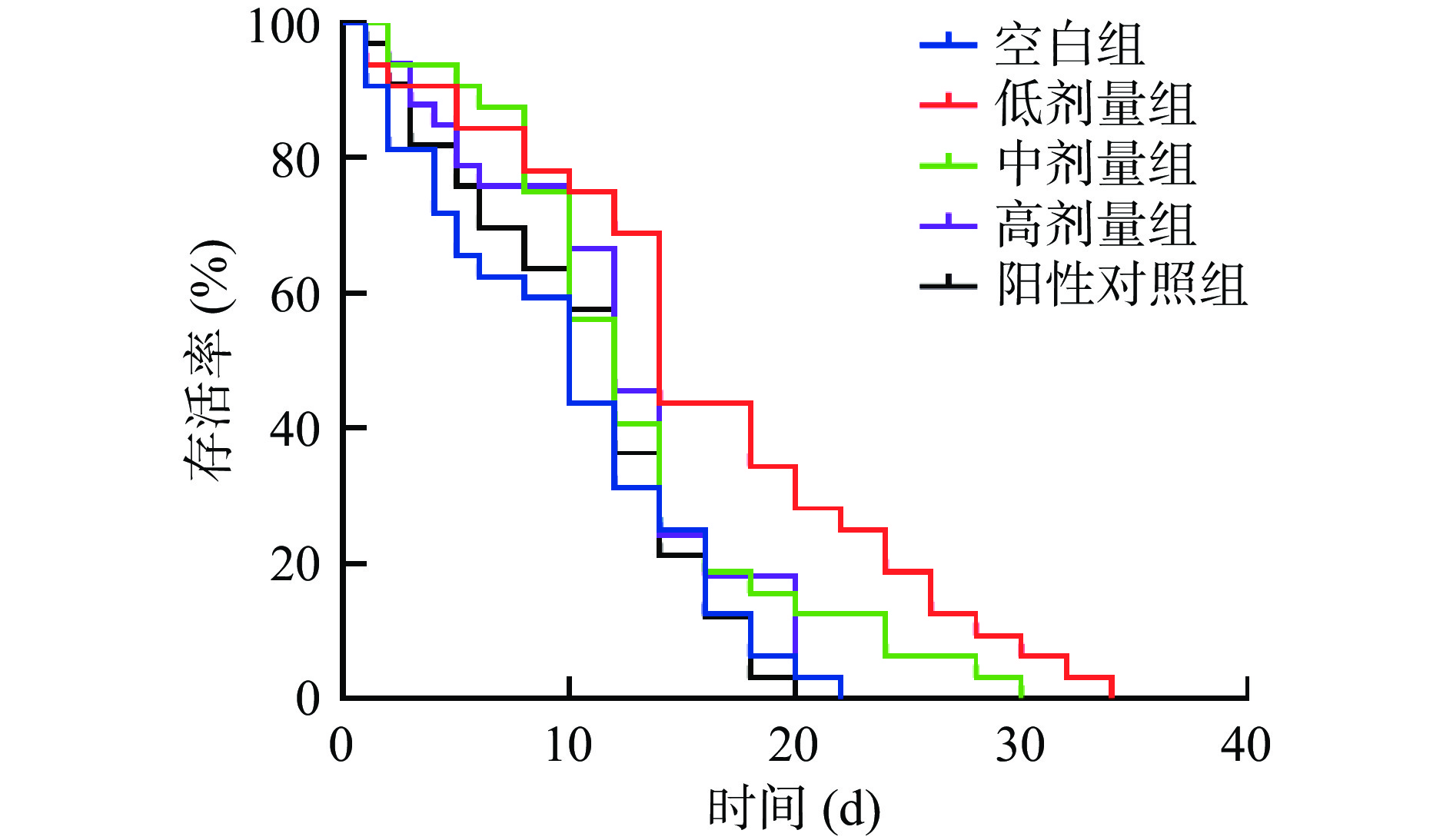
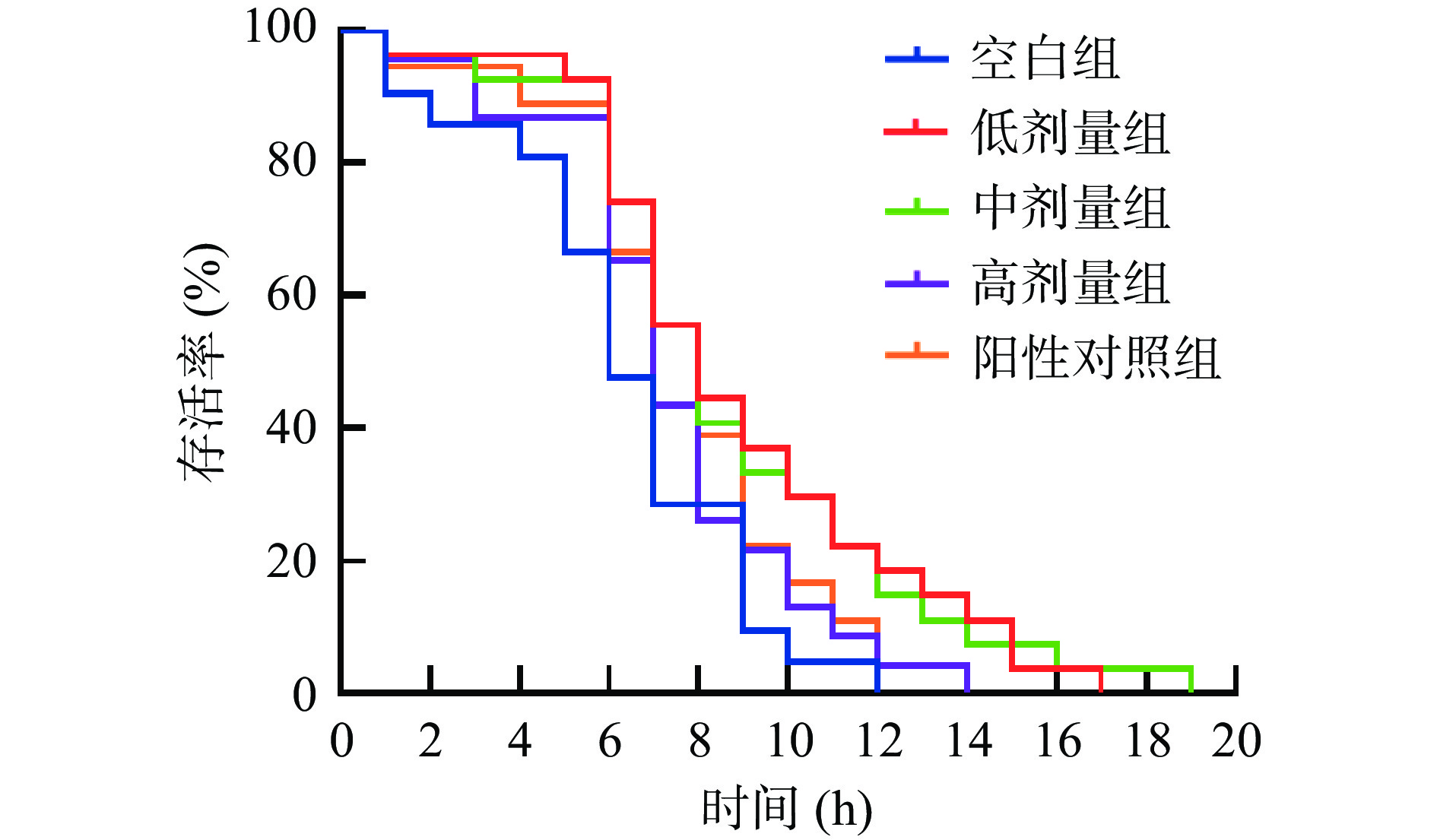
本研究以VC为阳性对照,探究了低、中、高(5、10、15 mg/mL)剂量的SILAE对线虫寿命的影响,结果如图1和表2所示。由图1可知,与空白组相比,不同剂量的SILAE使线虫的生存曲线明显右移,延长了寿命,尤其是低、中剂量组。由表2可知,空白组线虫的平均寿命为9.86±0.93 d,阳性对照组线虫的平均寿命为10.60±0.23 d,低剂量组线虫的平均寿命较二者分别延长了59.3%和48.2%,中剂量组则分别提高了30.2%和21.1%,高剂量组也提高了21.4%和12.9%。由此可见,SILAE延长线虫健康寿命的效果优于阳性对照VC。
表 2 SILAE对线虫平均寿命和最长寿命的影响Table 2. Effects of SILAE on average and maximum life span of C.elegans组别 中位寿命(d) 平均寿命(d) 最长寿命(d) 空白组 10.00±1.00 9.86±0.93 20.00±2.00 低剂量组 13.33±0.58**## 15.71±0.75***### 31.33±1.15***### 中剂量组 11.00±1.00 12.84±1.49* 26.00±4.00**## 高剂量组 11.33±0.58 11.97±1.96 20.00±2.00 阳性对照组 10.33±1.15 10.60±0.23 18.00±0.00 注:与空白组比,“*”代表差异显著(P<0.05),“**”代表差异极显著(P<0.01),“***”代表差异高度显著(P<0.001);与阳性对照组比,“#”代表差异显著(P<0.05),“##”代表差异极显著(P<0.01),“###”代表差异高度显著(P<0.001);表3同。 综上,不同浓度的SILAE虽然不同程度地延长了线虫的寿命,但却呈现剂量依赖地缩短了寿命的延长。这种剂量反应效应与甾体皂甙Shatavarin IV[28]、柚皮苷[29]和番茄碱[30]一致,即延长寿命的作用在较高浓度下被降低了。这可能是因为高浓度的SILAE作为一种压力刺激引发了一种类似于毒物兴奋效应的现象,进而降低SILAE的正向保护作用[31]。另外,较高浓度的SILAE可能还抑制了线虫体内的线粒体分裂融合蛋白导致线粒体功能障碍,使线粒体中的超氧阴离子自由基等ROS累积增多,进而引发氧化应激并损伤细胞,细胞增殖受到抑制而降低了寿命的延长[32−33]。
2.3 SILAE对线虫运动能力的影响
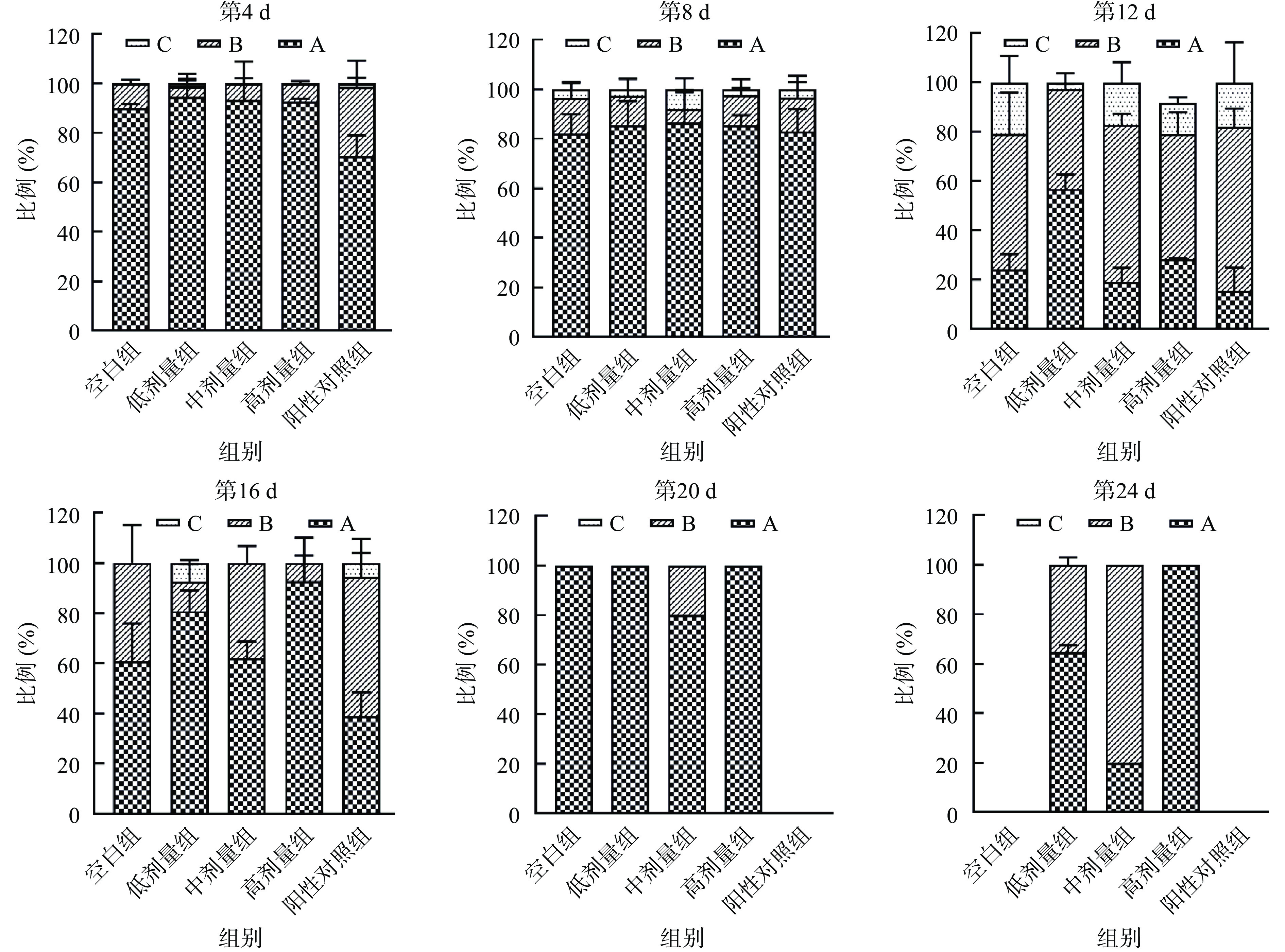
机体衰老通常伴随着各项生理机能的衰退,包括引起机体肌肉的退化而导致其运动能力随着寿命的延长而降低[34]。图2表明了SILAE对第4、8、12、16、20、24 d线虫运动能力的影响:在线虫寿命的早期阶段(第4 d和第8 d),各组均有70.0%以上的线虫处于A状态,较为活跃,其中保持在A状态的SILAE各组线虫高于空白组和阳性对照组;与早期线虫相比,第12 d时,除了低剂量组(5 mg/mL)仍有接近50.0%的线虫保持在A状态,其余各组线虫大都处于B状态,其中中、高剂量组和阳性对照组分别有66.7%、56.2%、61.5%的线虫处于B状态,与空白组比分别提高了33.3%、50%、33.3%。黄少杰等[35]的研究发现,铁皮石斛多糖对处于生命早期的线虫的运动能力影响并不显著,这与本实验结果类似。而在第16、20 d时,处于A状态的线虫比例出现上升(与第12 d比),推测出现这种情况的原因可能是从第12 d存活下来的线虫生存能力较强。直到寿命的末期(第24 d),仅有SILAE组线虫存活。可见,SILAE在延长线虫寿命的同时,还能有效延缓肌肉的退化,提高其运动能力。
2.4 SILAE对线虫产卵量的影响
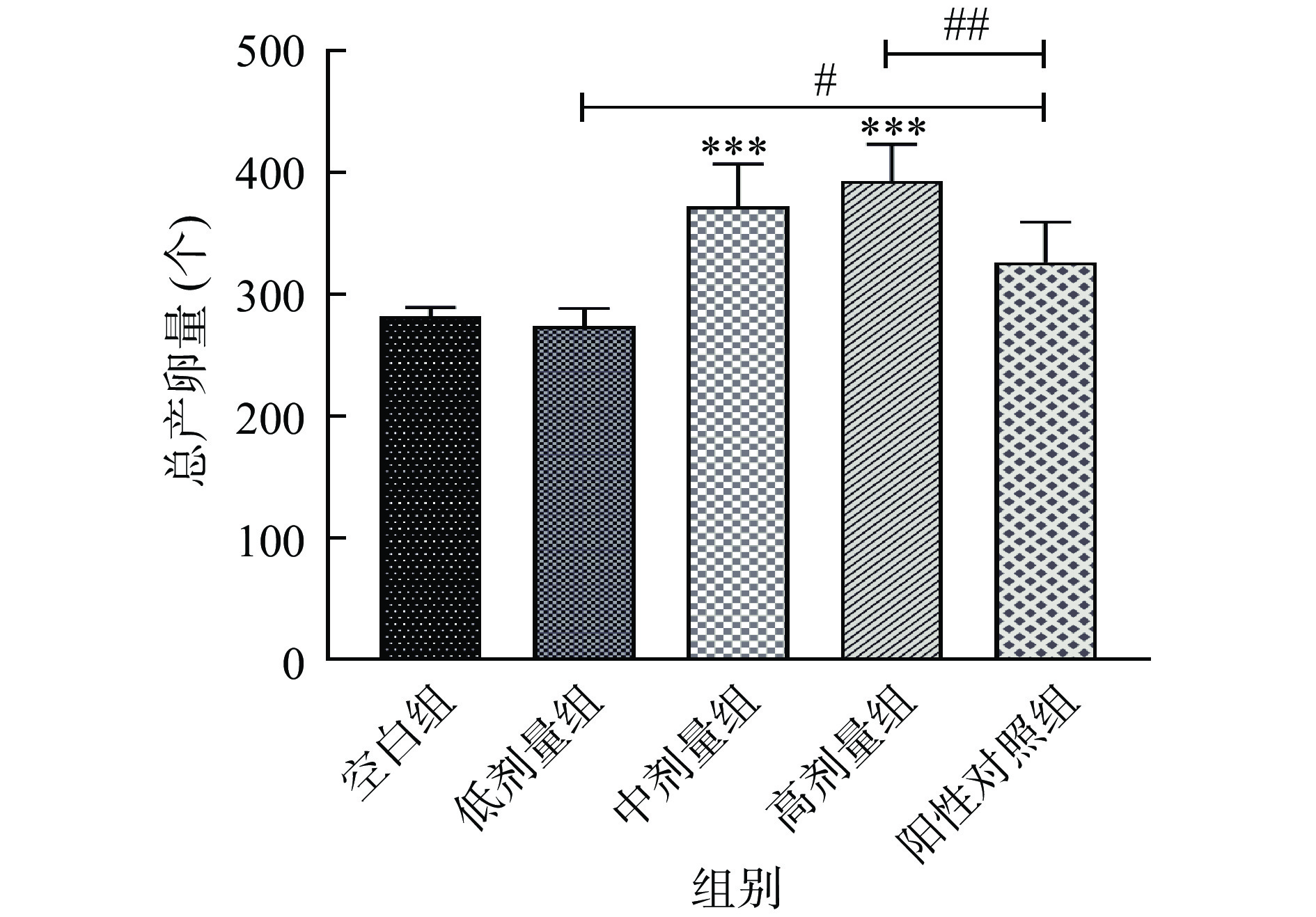
衰老研究发现,寿命延长的代价通常是生殖能力的降低或丧失[36−37],但也有研究报道表明寿命的延长并不影响线虫的生殖能力[38−39]。因此,本研究通过测定产卵量来评价SILAE在延长线虫寿命的同时是否会损害其生殖能力,结果如图3所示。由2.2可知,低剂量(5 mg/mL)的SILAE能显著延长线虫寿命,但由图3可知该组线虫的产卵量与空白组无显著性差异(P>0.05),即寿命的延长,没有影响低剂量组线虫的生殖能力。而中、高剂量组线虫的总产卵量均高于空白组产卵量,存在高度显著的差异性(P<0.001)。另外,高剂量组线虫的生殖能力亦极显著高于阳性对照组(P<0.01)。由此可见,SILAE在延长线虫寿命的同时,不会损伤线虫的生殖能力,且在一定浓度范围内能提高线虫的生殖能力,符合对抗衰老物质的需求。
2.5 SILAE对线虫应激能力的影响
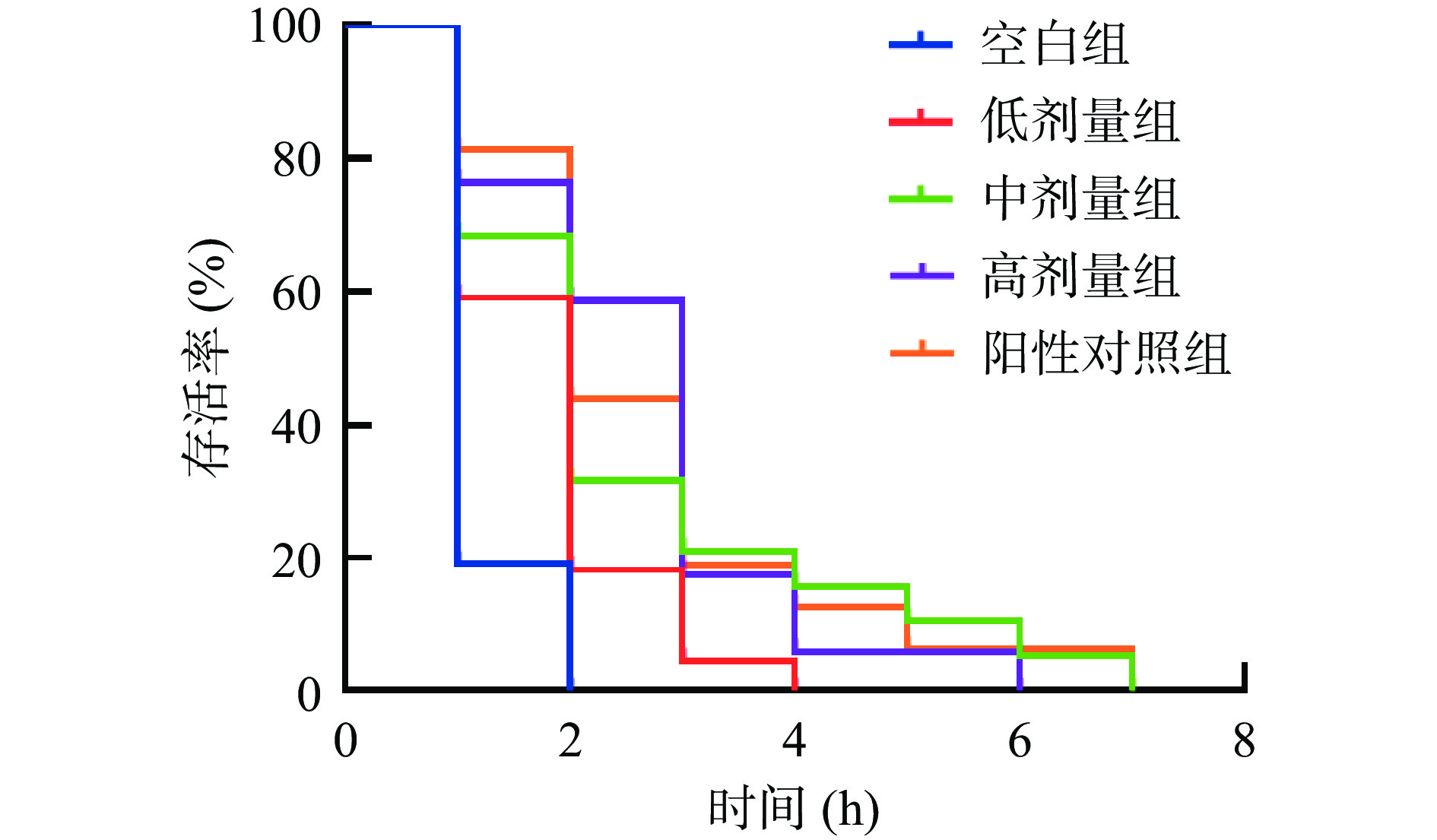
H2O2是胞内最常见的一种活性氧,会触发细胞脂质过氧化反应而产生自由基,进而引起急性氧化损伤[40]。图4表明,在H2O2急性应激实验中,空白组线虫的最长存活时间为2 h,低、中、高剂量和阳性对照组线虫的存活时间分别被延长至4、7、6和7 h,且生存曲线较空白组均有明显右移。有报道发现[41],中、高剂量的玫瑰类黄酮能显著提高线虫在H2O2应激环境中的存活率。因此,本实验结果表明,SILAE不同程度地缓解了H2O2引起的氧化应激对线虫造成的损伤,延长其存活率,且与阳性对照无显著性差异。
本研究还用细胞内活性氧发生器—胡桃醌[42],评估了SILAE对线虫氧化应激耐受性的影响,结果如图5所示。由表3可知,低、中、高剂量组线虫的寿命较空白组分别延长了41.7%、58.3%、16.7%,但与阳性对照组无显著性差异。其中,低、中剂量组线虫的生存能力显著高于空白组线虫(P<0.05)。
以上结果说明,一定浓度范围内的SILAE在过氧化氢应激、胡桃醌等急性氧化应激环境下对线虫有一定的保护作用,能延长线虫寿命。
表 3 SILAE对线虫应激能力的影响Table 3. Effect of SILAE on stress ability of C. elegans组别 H2O2应激平均寿命(h) 胡桃醌应激平均寿命(h) 空白组 2.00±0.00 10.33±1.53 低剂量组 4.50±0.71 15.00±3.61* 中剂量组 7.50±2.12* 15.33±3.51* 高剂量组 9.50±2.12** 12.67±1.15 阳性对照组 8.40±1.41* 12.33±0.58 2.6 SILAE对线虫体内ROS及脂褐质水平的影响
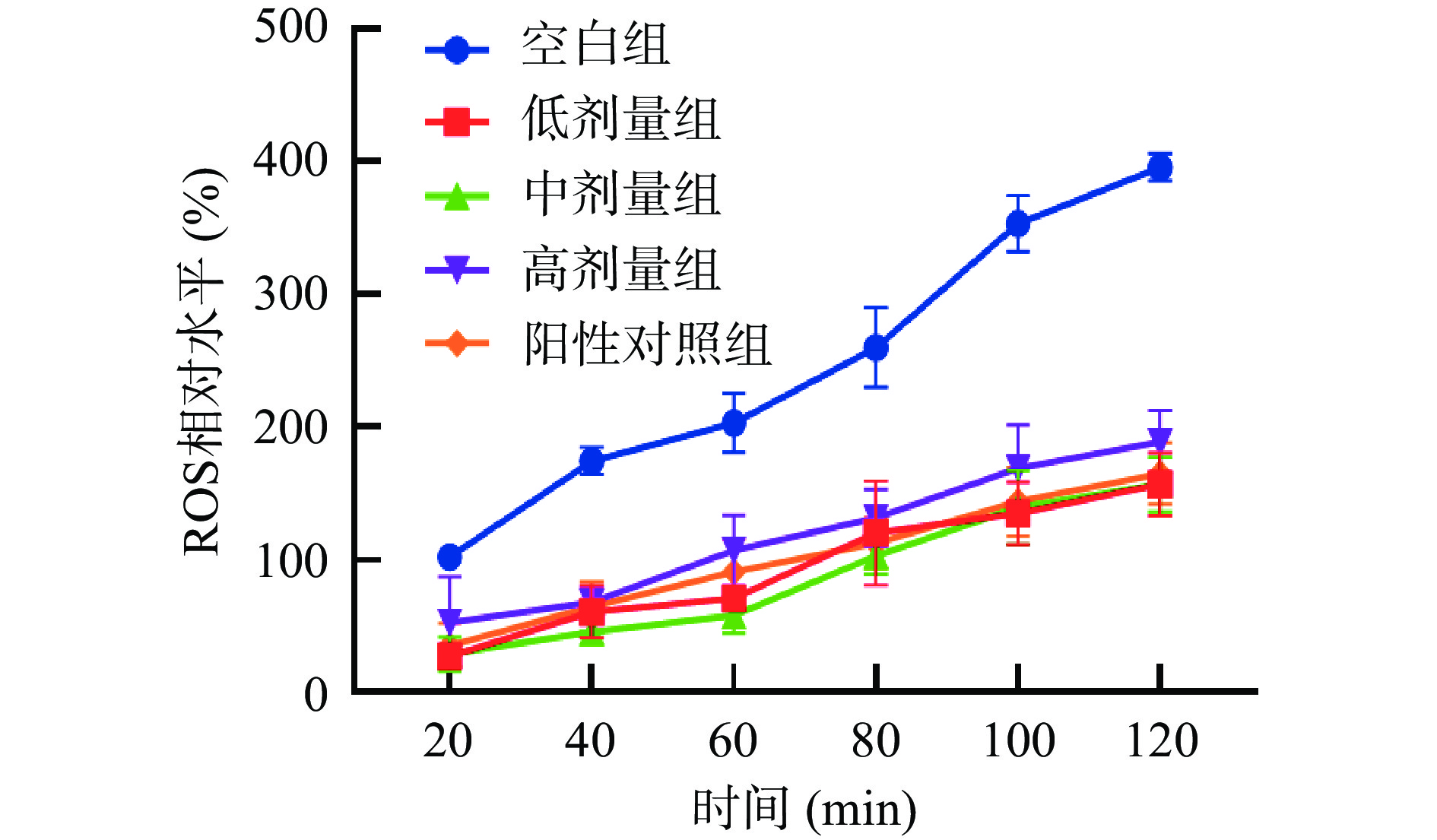
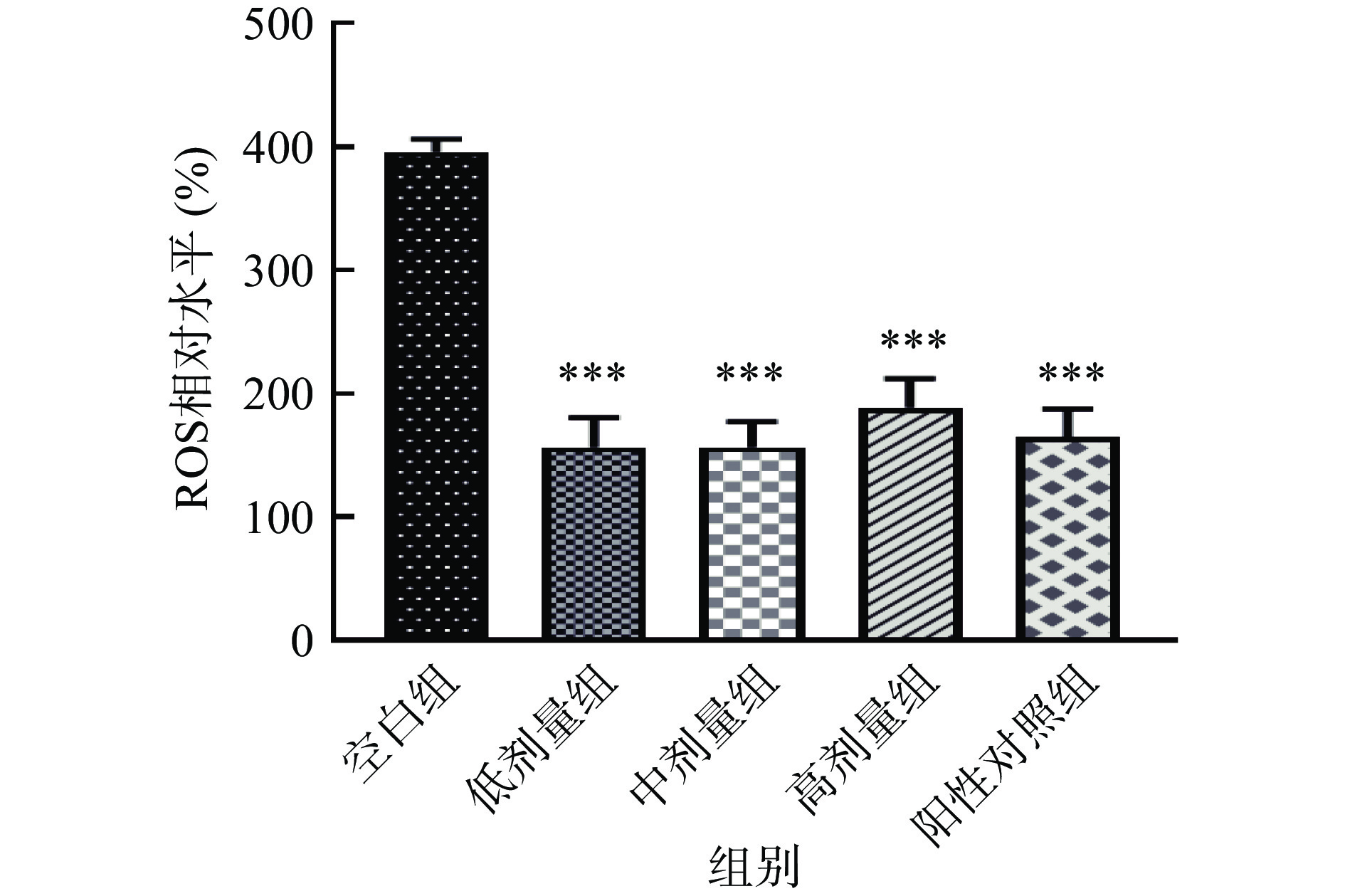
过量的ROS会诱导氧化应激并损害脂质、蛋白质和核酸等生物大分子,导致许多疾病的发生,如炎症、衰老和癌症等[43−44]。由图6和图7可知,线虫体内ROS水平随时间的延长而增加,在120 min时,SILAE各剂量组线虫体内的ROS相对水平较空白组有极显著降低(P<0.001),但与阳性对照无显著性差异。这表明,SILAE能有效清除线虫体内的ROS,降低ROS对线虫的氧化损伤,提高其生存能力。
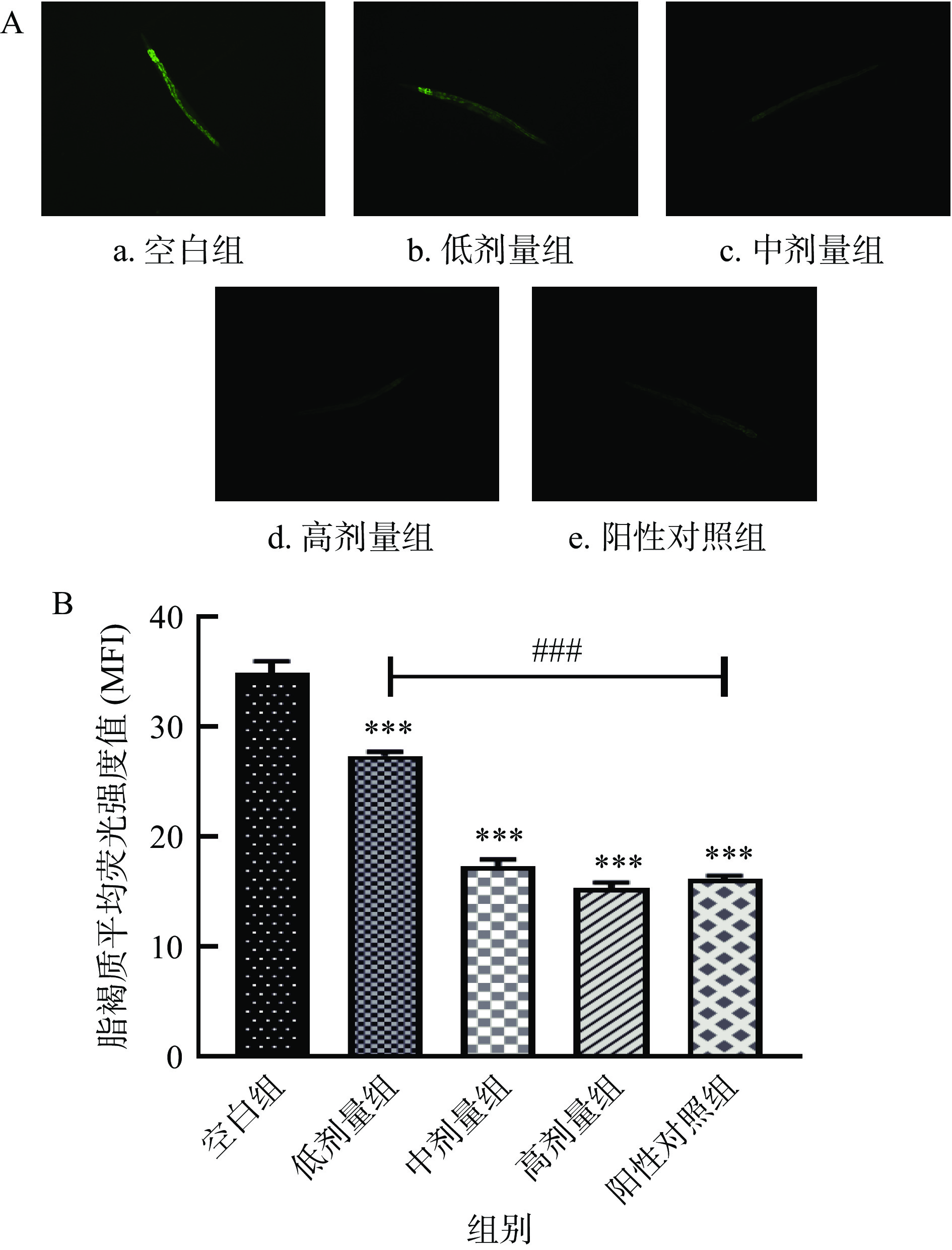
脂褐质是一种能自发荧光的黄褐色物质,其沉积量与荧光强度成正比,细胞成分的氧化降解和自噬会促进脂褐质的形成[45]。而随着寿命的延长,脂褐质会在线虫体内沉淀并损伤组织细胞,加速衰老[45−46]。因此,脂褐质可作为衰老的生物标志物。如图8所示,与空白组相比,SILAE各剂量组以剂量依赖的方式极显著地降低了线虫体内的脂褐质水平(P<0.001),其中高剂量组(15 mg/mL)线虫体内的脂褐质水平较空白组降低了56.1%。此外,经中、高剂量SILAE喂养的线虫,其体内的脂褐质水平与阳性对照组VC无显著性差异。由此可见,SILAE能有效减少脂褐质在线虫体内的积累,降低脂褐质堆积造成的细胞成分的氧化降解,延缓氧化损伤并延长线虫寿命。
2.7 SILAE对线虫体内抗氧化系统和MDA含量的影响
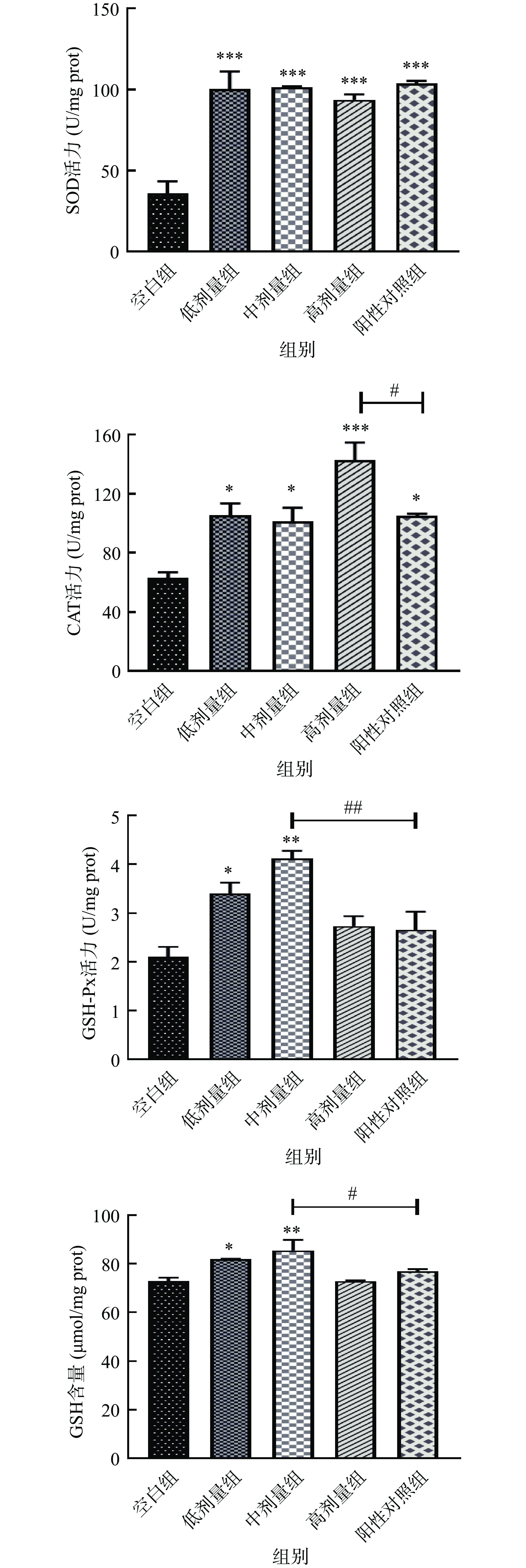
抗氧化防御系统作为机体具有抗氧化能力的重要组成部分,其复杂的酶和非酶抗氧化剂可通过抵消总ROS水平来维持生理稳态[47]。该系统涉及了包括SOD、CAT和GSH-Px在内的多种酶系统,以及由谷胱甘肽、维生素E等组成的非酶抗氧化剂,它们通过直接淬灭自由基、清除过氧化物质或螯合金属离子参与抗氧化[48]。MDA是氧化应激的重要生物标志物,也是ROS引发的主要脂质过氧化物[49]。因此,为了评价SILAE对线虫内源性抗氧化防御系统的影响,本研究测定了抗氧化酶(SOD、CAT和GSH-Px)的活性以及非酶抗氧化剂(GSH)的含量,并对线虫体内的MDA含量进行了测定。
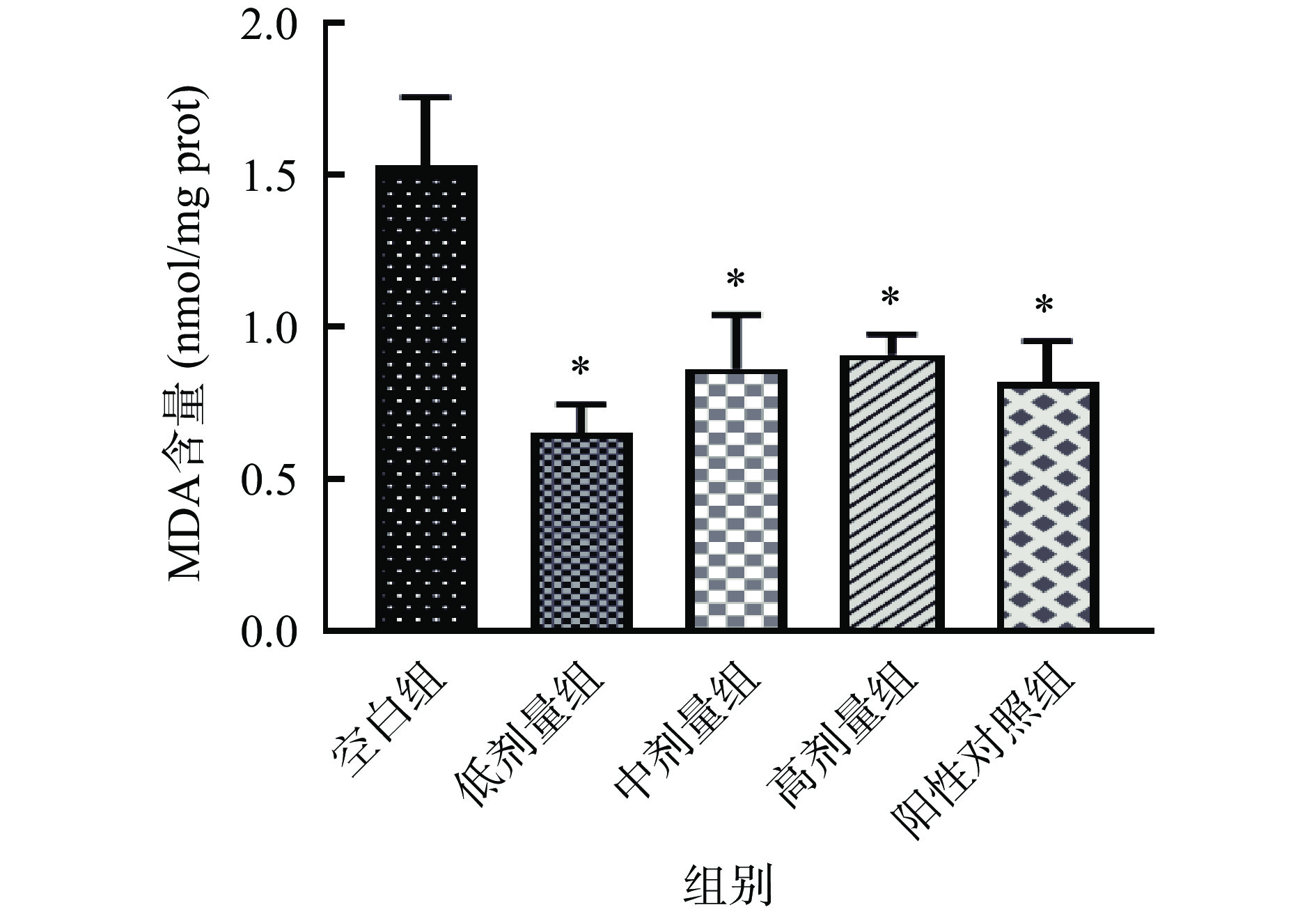
提高SOD活力有助于将超氧阴离子转化为H2O2,而H2O2又是CAT和GSH-Px的底物,CAT能将H2O2代谢分解成水和氧气,GSH-Px则是在与非酶抗氧化剂GSH反应时减少H2O2和有机氢过氧化物[50]。由图9可知,经SILAE干预的线虫,其体内的SOD活力较空白组有高度显著差异(P<0.001),都提高了约2倍,但与阳性对照无显著性差异;CAT活力较空白组分别提高了66.8%、60.3%、125.6%,其中高剂量组线虫体内的CAT活力与VC组具有显著性差异(P<0.05);中剂量组(10 mg/mL)线虫中的GSH-Px活力极显著提高了95.5%,且与VC组也存在极显著差异(P<0.01)。而非酶抗氧化剂GSH在中剂量组线虫体内的含量也极显著高于空白组(P<0.01),且显著高于VC组。此外,如图10所示,SILAE各剂量组线虫中的MDA含量较空白组均有显著下降(P<0.05),但与阳性对照无显著性差异。
这些数据表明,SILAE能有效提高线虫体内酶和非酶物质的抗氧化活性,增强其对氧化应激的响应和防御能力,降低体内MDA等氧化产物的含量,进而减缓衰老过程中过氧化反应对线虫造成氧化损伤,提高其生存能力,延长线虫寿命。
3. 结论
基于衰老的自由基理论,本文以秀丽隐杆线虫为模型生物,相对完整地评价了SILAE对线虫寿命及与年龄相关的生理机能、抗氧化应激能力、抗氧化防御系统的影响。结果表明,SILAE以不损伤线虫生殖能力的方式延长了其寿命,并在一定剂量范围内还能有效提高其生殖能力和运动能力。SILAE也提高了线虫体内的抗氧化酶SOD、CAT和GSH-Px的活力和非酶抗氧化剂GSH的含量。此外,SILAE还能有效降低线虫体内的ROS水平及其引发的氧化应激产物—脂褐质和MDA的水平,提高线虫的氧化应激抵抗力,降低由此引发的氧化损伤。
综上,SILAE可能通过捕获并猝灭线虫体内的活性氧和降低不利于健康长寿的物质含量,增强线虫的氧化应激抵抗能力和抗氧化能力并提高生活质量,延长了健康寿命。因而,SILAE有可能成为一种潜在的膳食补充剂和具有抗氧化衰老特性的替代药物。本实验也为天然植物抗氧化剂在功能食品中的进一步研究和应用提供了新的来源和理论参考。
-
表 1 SILAE中活性成分含量
Table 1 Content of active ingredients in SILAE
成分 线性回归方程 回归系数(R2) 含量(%) 总糖 y=0.0721x−0.0137 0.9949 34.70±2.30 总酚 y=10.258x+0.0918 0.9980 13.57±0.26 蛋白质 y=0.001x+0.2883 0.9950 12.70±1.00 总黄酮 y=12.182x+0.0037 0.9998 7.63±0.82 表 2 SILAE对线虫平均寿命和最长寿命的影响
Table 2 Effects of SILAE on average and maximum life span of C.elegans
组别 中位寿命(d) 平均寿命(d) 最长寿命(d) 空白组 10.00±1.00 9.86±0.93 20.00±2.00 低剂量组 13.33±0.58**## 15.71±0.75***### 31.33±1.15***### 中剂量组 11.00±1.00 12.84±1.49* 26.00±4.00**## 高剂量组 11.33±0.58 11.97±1.96 20.00±2.00 阳性对照组 10.33±1.15 10.60±0.23 18.00±0.00 注:与空白组比,“*”代表差异显著(P<0.05),“**”代表差异极显著(P<0.01),“***”代表差异高度显著(P<0.001);与阳性对照组比,“#”代表差异显著(P<0.05),“##”代表差异极显著(P<0.01),“###”代表差异高度显著(P<0.001);表3同。 表 3 SILAE对线虫应激能力的影响
Table 3 Effect of SILAE on stress ability of C. elegans
组别 H2O2应激平均寿命(h) 胡桃醌应激平均寿命(h) 空白组 2.00±0.00 10.33±1.53 低剂量组 4.50±0.71 15.00±3.61* 中剂量组 7.50±2.12* 15.33±3.51* 高剂量组 9.50±2.12** 12.67±1.15 阳性对照组 8.40±1.41* 12.33±0.58 -
[1] OKORO N O, ODIBA A S, OSADEBE P O, et al. Bioactive phytochemicals with anti-aging and lifespan extending potentials in caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland),2021,26(23):7323. doi: 10.3390/molecules26237323
[2] DA COSTA J P, VITORINO R, SILVA G M, et al. A synopsis on aging-theories, mechanisms and future prospects[J]. Ageing Research Reviews,2016,29:90−112. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2016.06.005
[3] BACK P, BRAECKMAN B P, MATTHIJSSENS F. ROS in aging Caenorhabditis elegans: Damage or signaling?[J]. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity,2012,2012:608478.
[4] FONTANA L, PARTRIDGE L. Promoting health and longevity through diet: From model organisms to humans[J]. Cell,2015,161(1):106−118. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.02.020
[5] 庄燕苹, 杨帆, 肖曼, 等. 忧遁草乙醇提取物对秀丽隐杆线虫的抗衰老作用及机制[J]. 食品工业科技, 2023, 44(11):411−417 ZHUANG Y P, YANG F, XIAO M, et al. Anti-aging effect and mechanism of ethanolic extract of Clinacanthus nutans on Caenorhabditis elegans[J] Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(11):411−417.
[6] LIANG T, ZHOU J, JING P, et al. Anti-senescence effects of Rhodiola crenulate extracts on LO(2) cells and bioactive compounds [J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2023,306:116179. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116179
[7] GOYAL A, TANWAR B, KUMAR S M, et al. Sacha inchi (Plukenetia volubilis L.): An emerging source of nutrients, omega-3 fatty acid and phytochemicals[J]. Food Chemistry, 2022, 373(Pt B):131459.
[8] TRAN P T, TRAN T T N. Evaluation of acute and subchronic toxicity induced by the crude ethanol extract of Plukenetia volubilis Linneo leaves in Swiss albino mice[J]. BioMed Research International,2021,2021:6524658.
[9] LIN J, WEN J, XIAO N, et al. Anti-diabetic and gut microbiota modulation effects of sacha inchi ( Plukenetia volubilis L.) leaf extract in streptozotocin-induced type 1 diabetic mice[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2022,102(10):4304−4312. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.11782
[10] NASCIMENTO A K L, MELO-SILVEIRA R F, DANTAS-SANTOS N, et al. Antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of leaf extracts from Plukenetia volubilis Linneo (Euphorbiaceae)[J]. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine:eCAM, 2013, 2013:950272.
[11] KITTIBUNCHAKUL S, HUDTHAGOSOL C, SANPORKHA P, et al. Effects of maturity and thermal treatment on phenolic profiles and in vitro health-related properties of Sacha inchi leaves[J]. Plants (Basel, Switzerland),2022,11(11):1515.
[12] PALLAUF K, DUCKSTEIN N, RIMBACH G. A literature review of flavonoids and lifespan in model organisms[J]. The Proceedings of the Nutrition Society,2017,76(2):145−162. doi: 10.1017/S0029665116000720
[13] SCERBAK C, VAYNDORF E M, HERNANDEZ A, et al. Mechanosensory neuron aging: Differential trajectories with lifespan-extending alaskan berry and fungal treatments in caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience,2016,8:173.
[14] YE Y, GU Q, SUN X. Potential of Caenorhabditis elegans as an antiaging evaluation model for dietary phytochemicals: A review[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2020,19(6):3084−3105. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12654
[15] 王凤, 肖楚翔, 刘淑珍, 等. 榴莲核黄酮的提取及其对秀丽隐杆线虫氧化和衰老的影响[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(9):123−129 doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200409-127 WANG F, XIAO Z X, LIU S Z, et al. Extraction of flavonoids from durian seeds and its antioxidant and anti-aging effects on Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Food Science,2021,42(9):123−129. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200409-127
[16] 王冰芳. 西兰苔叶黄酮的提取、分离、鉴定及体外抗癌活性研究[D]. 广州:华南理工大学, 2010 WANG B F. Extraction, isolation, characterization and in vitro anticancer activity of leaf flavonoids from the Broccolini[D]. Guangzhou:South China University of Technology, 2010.
[17] 杨永涛. 罗布麻总黄酮的提取、分离纯化及其抗氧化性能研究[D]. 广州:华南理工大学, 2018 YANG Y T. Extraction, purification and antioxidant properties of total flavonoids from Rhubarb[D]. Guangzhou:South China University of Technology, 2018.
[18] 杨云, 蔡朝霞. 天麻总酚闪式提取工艺研究及含量测定[J]. 食品工业,2021,42(9):43−46 YANG Y, CAI Z X. Flash extraction process of total phenol and determination of content from Gastrodia elata [J]. The Food Industry,2021,42(9):43−46.
[19] 海力茜·陶尔大洪, 祖丽皮艳·阿布力米特, 李亚童, 等. 新疆芜菁多糖含量测定及提取工艺优化[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(5):1960−1965 doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2021.05.054 HAILIQIAN T E D H, ZUPILIYAN A B L M T, LI Y T, et al. Determination of polysaccharide content from Brassica rapa L. in Xinjiang and optimization of extraction technology[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2021,12(5):1960−1965. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2021.05.054
[20] 黄婉玉, 曹炜, 李菁, 等. 考马斯亮蓝法测定果汁中蛋白质的含量[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2009,35(5):160−162 doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.2009.05.015 HUANG W Y, CAO W, LI, J, et al. Determination of protein content in juice by coomassie brilliant blue[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2009,35(5):160−162. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.2009.05.015
[21] SUN J, ZHONG X, SUN D, et al. Anti-aging effects of polysaccharides from ginseng extract residues in Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2022,225:1072−1084.
[22] YANG J, WAN Q, MU Q, et al. The lifespan-promoting effect of otophylloside B in Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Natural Products and Bioprospecting,2015,5(4):177−183. doi: 10.1007/s13659-015-0064-4
[23] 王猛, 马浩天, 关思宇, 等. 螺旋藻多糖对秀丽隐杆线虫氧化应激及寿命的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2022,22(5):137−146 WANG M, MA H T, GUANG S Y, et al. Effects of spirulina polysaccharides on oxidative stress and life span of Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2022,22(5):137−146.
[24] 李振旺. 马鹿角水提物对秀丽隐杆线虫抗衰老作用研究[D]. 长春:长春工业大学, 2022 LI Z W. Study on the anti-aging effect of aqueous extract of horse antler on Caenorhabditis elegans[D]. Changchun:Changchun University of Technology, 2022.
[25] 陈宇. 银杏叶黄酮延长秀丽隐杆线虫寿命及作用机制研究[D]. 重庆:重庆三峡学院, 2021 CHEN Y. Prolongation of life span and mechanism of action of ginkgo biloba flavonoids in Caenorhabditis elegans[D]. Chongqin:Chongqing Three Gorges University, 2021.
[26] HUI H, XIN A, CUI H, et al. Anti-aging effects on Caen orhabditis elegans of a polysaccharide, O-acetyl glucomannan, from roots of Lilium davidii var. unicolor cotton[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,155:846−852. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.206
[27] LOPEZ-OTIN C, BLASCO M A, PARTRIDGE L, et al. The hallmarks of aging[J]. Cell,2013,153(6):1194−1217. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.05.039
[28] SMITA S S, TRIVEDI S, PANDEY T, et al. A bioactive compound shatavarin IV-mediated longevity as revealed by dietary restriction-induced autophagy in Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Biogerontology,2020,21(6):827−844. doi: 10.1007/s10522-020-09897-5
[29] GUO P, WANG P, LIU L, et al. Naringin alleviates glucose-induced aging by reducing fat accumulation and promoting autophagy in Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Nutrients,2023,15(4):907. doi: 10.3390/nu15040907
[30] FANG E F, WALTZ T B, KASSAHUN H, et al. Tomatidine enhances lifespan and healthspan in C. elegans through mitophagy induction via the SKN-1/Nrf2 pathway[J]. Scientific Reports,2017,7:46208. doi: 10.1038/srep46208
[31] 郭佑铭. 以秀丽隐杆线虫为模型的铃兰毒甙抗衰老研究[D]. 长春:吉林大学, 2014 GUO Y M. Anti-aging study of Suzuki glucoside using Caenorhabditis elegans as a model[D]. Changchun:Jilin University, 2014.
[32] 鹿颜. EGCG调控线粒体和氧化还原动态平衡影响秀丽线虫幼虫发育作用研究[D]. 长沙:湖南农业大学, 2021 LU Y. EGCG regulates the dynamic balance of mitochondria and redox to influence the development of Caenorhabditis elegans[D]. Changsha:Hunan Agricultural University, 2021.
[33] SCHLOTTERER A, KUKUDOV G, BOZORGMEHR F, et al. C. elegans as model for the study of high glucose-mediated life span reduction[J]. Diabetes,2009,58(11):2450−2456. doi: 10.2337/db09-0567
[34] 刘静. 金钗石斛总生物碱抗秀丽隐杆线虫衰老作用及其机制研究[D]. 遵义:遵义医科大学, 2019 LIU J. Study on the anti-aging effect and mechanism of total alkaloids from Dendrobium nobile on Caenorhabditis elegans[D]. Zunyi:Zunyi Medical University, 2019.
[35] 黄少杰, 陈宏著, 钟淳菲, 等. 铁皮石斛叶多糖对秀丽隐杆线虫体内抗衰老作用[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(21):203−208 doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20211202-031 HUANG S J, CHEN H Z, ZHONG C F, et al. Anti-aging effect of polysaccharide from dendrobium officinale leaves in Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Food Science,2022,43(21):203−208. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20211202-031
[36] 杨文旭, 王昌禄, 崔桂友, 等. 香椿叶总黄酮对延缓秀丽线虫衰老影响的初步研究[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2010(6):143−146 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2010.06.021 YANG W X, WANG C L, CUI G Y, et al. Study on the effect of toona sinensis leaf flavonoids on anti-aging of Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. China Food Additives,2010(6):143−146. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2010.06.021
[37] 王怀玲. 蓝莓多酚化合物抗衰老活性及作用机制研究[D]. 广州:华南理工大学, 2018 WANG H L. Study on the anti-aging activity and mechanism of action of blueberry polyphenolic compounds[D]. Guangzhou:South China University of Technology, 2018.
[38] 袁梦, 阙斐, 肖楚翔, 等. 基于秀丽隐杆线虫模型的樱桃乙醇提取物抗衰老作用研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(13):375−382 YUAN M, QUE F, XIAO C X, et al. Study on the anti-aging effect of cherry ethanol extract based on Caenorhabditis elegans mode[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(13):375−382.
[39] 王晶. 江西蜜柑酚类化合物抗氧化、抗癌、抗衰老活性及作用机理研究[D]. 广州:华南理工大学, 2020 WANG J. Antioxidant, anticancer and anti-aging activities and mechanism of action of phenolic compounds in Jiangxi mandarin[D]. Guangzhou:South China University of Technology, 2020.
[40] 张慧康, 马佳波, 司奇, 等. 基于线虫模型的木姜叶柯抗氧化应激及抗衰老作用[J]. 食品工业科技, 2023, 44(12):363−370 ZHANG H K, MA J B, SI Q, et al. Anti-oxidative stress and anti-aging effects of Mucuna pruriens based on Caenorhabditis elegans model[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(12):363−370.
[41] 王梅霖. 玫瑰类黄酮的生物活性及其应用研究[D]. 济南:齐鲁工业大学, 2021 WANG M L. Study on the biological activities of rose flavonoids and their applications[D]. Jinan:Qilu University of Technology, 2021.
[42] PANDEY T, SAMMI S R, NOOREEN Z, et al. Anti-ageing and anti-parkinsonian effects of natural flavonol, tambulin from Zanthoxyllum aramatum promotes longevity in Caenorhabditis elegans [J]. Experimental Gerontology,2019,120:50−61. doi: 10.1016/j.exger.2019.02.016
[43] LI Q, LIU Y, DAI X, et al. Nanozymes regulate redox homeostasis in ROS-related inflammation[J]. Frontiers in Chemistry,2021,9:740607. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2021.740607
[44] 刘嘉榆. 内源代谢小分子甘油磷酰胆碱抗衰老活性及作用机制研究[D]. 北京:军事科学院, 2022 LIU J Y. Study on the anti-aging activity and mechanism of action of endogenously metabolized small molecule glycerophosphorylcholine[D]. Beijing:Academy of Military Science, 2022.
[45] GERSTBREIN B, STAMATAS G, KOLLIAS N, et al. In vivo spectrofluorimetry reveals endogenous biomarkers that report healthspan and dietary restriction in Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Aging Cell,2005,4(3):127−137. doi: 10.1111/j.1474-9726.2005.00153.x
[46] HU Q, LIU Z, GUO Y, et al. Antioxidant capacity of flavonoids from folium artemisiae argyi and the molecular mechanism in Caenorhabditis elegans[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2021,279:114398. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2021.114398
[47] LIN C, CHEN Y, LIN Y, et al. Antistress and anti-aging activities of Caenorhabditis elegans were enhanced by Momordica saponin extract[J]. European Journal of Nutrition,2021,60(4):1819−1832. doi: 10.1007/s00394-020-02338-6
[48] VILLALPANDO-RODRIGUEZ G E, GIBSON S B. Reactive oxygen species (ROS) regulates different types of cell death by acting as a rheostat[J]. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity,2021,2021:9912436.
[49] LIN C, SU Z, LUO J, et al. Polysaccharide extracted from the leaves of Cyclocarya paliurus (Batal.) Iljinskaja enhanced stress resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans via skn-1 and hsf-1[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,143:243−254. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.12.023
[50] MUNTEANU I G, APETREI C. Analytical methods used in determining antioxidant activity: A Review[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2021,22(7):3380. doi: 10.3390/ijms22073380





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



