Proteomic Analysis of Difference in Toxin Production of Pseudomonas cocovenenans subsp. farinofermentans
-
摘要: 为了从蛋白质水平探索椰毒假单胞菌米酵菌酸毒素产生机制,采用数据依赖型采集(data dependent acquisition,DDA)非标记定量蛋白质组学技术对该菌产毒培养前后蛋白质变化进行了分析。结果显示:产毒培养后,产毒株中显著性上调表达蛋白25个,显著性下调表达蛋白31个,其中显著性上调表达的蛋白中有与细菌趋化性信号转导相关的ABC转运蛋白、反应调节受体蛋白、甲基受体趋化性蛋白II,以及与细菌运动相关的鞭毛蛋白如鞭毛P环蛋白、鞭毛M环蛋白、鞭毛钩蛋白FlgE等,推测趋化性运动可能在椰毒假单胞菌米酵菌酸毒素产生过程中发挥重要作用。椰毒假单胞菌米酵菌酸毒素产生机制研究,可为人们更好地降低食源性疾病的发生提供理论支撑。
-
关键词:
- DDA非标记定量蛋白质组学 /
- 椰毒假单胞菌 /
- 米酵菌酸 /
- 产毒机制 /
- 食物中毒
Abstract: To study the mechanism of bongkrekic acid production by Pseudomonas cocovenenans subsp. farinofermentans at proteome level, data-dependent acquisition (DDA) unlabeled quantitative proteomics technique was used to analyze the protein changes of P. cocovenenans before and after toxin production. The results showed that 25 proteins were up-regulated and 31 proteins were down-regulated in toxin-producing strains. Among them, ABC transporters, response regulatory receptor protein, methyl-accepting chemotaxis protein II were related to bacterial chemotactic signal transduction. And flagellins such as P-cyclin, M-cyclin and FlgE were all related to chemotaxis. It is supposed that chemotactic movement plays an important role in the production of bongkrekic acid. The study on the production mechanism of bongkrekic acid can provide theoretical evidence to decrease the incidence of foodborne diseases. -
椰毒假单胞菌酵米面亚种(Pseudomonas cocovenenans subsp. farinofermentans,简称椰毒假单胞菌),属于唐菖蒲伯克霍尔德菌(Burkholderia gladioli)致病变种,它容易在酵米面制品、淀粉制品及变质的木耳或银耳等食物中生长,在适宜的温湿度条件下短时间内即可产生大量的米酵菌酸毒素,误食后会引发严重食物中毒甚至死亡[1−2]。椰毒假单胞菌是一种高致死性的食源性致病菌,米酵菌酸毒素是主要致死因子,探讨该菌米酵菌酸毒素产生机制,对于有效防控由该菌引起食物中毒事件的发生具有重要指导意义[3−8]。
国内外针对椰毒假单胞菌米酵菌酸毒素产生机制及致病机理等方面的研究均有报道[8−11],尤其是近年来随着分子生物学技术的发展,利用基因测序技术从基因组水平揭示米酵菌酸毒素产生机制,发现米酵菌酸毒素产生与bon基因簇有关[12−13]。产毒株中存在较完整的bon基因簇,而非产毒株中存在该基因簇的缺失,推测是同源重组导致[13]。利用蛋白质组学技术从蛋白质组水平探讨米酵菌酸毒素产生机制的研究还未见报道。
目前基于多组学包括基因组、转录组、蛋白质组、代谢组等技术开展致病菌产毒机制及致病机理的研究报道较多[13−16],采用多组学技术可以从基因、蛋白和通路等多个分子水平进行综合分析,更深入地探讨相关分子机制。本研究对3株椰毒假单胞菌完成了基因测序基础上[13],利用DDA非标记定量蛋白质组学技术对菌株产毒培养前后差异表达蛋白进行分析,试图找到产毒相关蛋白,从蛋白质水平探讨米酵菌酸毒素产生机制。利用多组学技术探讨米酵菌酸毒素产生机制,可为酵米面制品、淀粉制品等食品生产企业、餐饮企业有效防控由椰毒假单胞菌导致的食品安全风险,进而更好地控制其危害提供理论支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
菌株YD、YF、YM分别从泰国碎白米、东北云耳以及缅甸碎白米中分离且鉴定为产米酵菌酸毒素的椰毒假单胞菌(P. cocovenenans subsp. farinofermentans),即产毒株;唐菖蒲伯克霍尔德氏菌CICC 10574(B. gladioli,自命名为菌株BL)为不产生米酵菌酸毒素的对照菌株,即非产毒株 购于中国工业微生物菌种保藏中心;马铃薯葡萄糖琼脂(PDA)培养基(批号11110101)、马铃薯葡糖糖半固体琼脂培养基(批号1101651) 广东环凯微生物科技有限公司;米酵菌酸对照品 上海安谱公司,纯度≥95%;QuEChERS dSPE EMR-Lipid增强型脂质去除净化管 广州安捷伦科技公司;ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18色谱柱(2.1 mm×100 mm,1.7 μm) 美国沃特世;Bradford 蛋白定量试剂盒(批号P0006) 碧云天。
B80-1600‖A2生物安全柜 苏州安泰空气技术有限公司;BSP-400型生化培养箱 上海博讯医疗生物仪器股份有限公司;GT-2227QTS型智能超声波清洗仪 广东固特超声股份有限公司;Fotector Plus型高通量全自动固相萃取仪 厦门睿科集团股份有限公司;LCMS-8040三重四级杆液质联用仪 日本岛津公司;EASY-nLC1200 纳升液相色谱仪、Orbitrap exploris 480高分辨质谱仪 赛默飞世尔科技中国。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 产毒培养
参照GB 4789.29-2020进行产毒试验[17]。将试验用菌株YD、YF、YM以及BL分别接种于PDA培养基上,(36±1)℃培养24~36 h活化。用灭菌接种环刮取适量菌苔,加到3 mL无菌生理盐水的试管中,配成1麦氏浓度(MCF)的菌悬液(约108 CFU/mL),用无菌吸管吸取0.5 mL,滴在铺好无菌玻璃纸的直径150 mm马铃薯葡萄糖半固体平板上,用无菌L棒涂布均匀,于(26±1)℃培养5 d。无菌吸管吸取0.5 mL无菌生理盐水作为空白对照。
1.2.2 毒素含量测定
毒素制备参考文献[18]。将产毒培养后的马铃薯葡萄糖半固体琼脂转移至三角瓶,100 ℃流动蒸汽灭菌30 min,室温冷却后置于-20 ℃冰箱冷冻过夜,第2 d取出三角瓶置室温融化,用无菌吸管吸出冻融液,经滤纸过滤至无菌试管或锥形瓶中即为毒素粗提液。取5 mL毒素粗提液于50 mL离心管中,加入2倍体积的80%甲醇水溶液,超声提取10 min,离心后吸取上清液进行净化处理。取5 mL上清液于装有dSPE EMR-Lipid吸附剂的净化柱中,涡旋2 min后离心,取2 mL上清液于40 ℃水浴中氮吹至近干,用甲醇定容至1 mL,0.22 μm有机滤膜过滤后测定。
毒素测定参考文献[18]。标准溶液配制:准确称取米酵菌酸标准品10 mg(精确至0.01 mg),用甲醇溶解后转移至100 mL容量瓶中,用甲醇定容,终浓度为0.1 mg/mL。色谱条件:ACQUITY UPLC BEH C18色谱柱(2.1 mm×100 mm,1.7 μm);流动相:A:0.1%甲酸水溶液,B:乙腈;流速:0.3 mL/min;柱温:30 ℃;进样量:2 µL;梯度洗脱程序为:0~1.5 min,B:20%;1.5~2.5 min,B:20%~95%;2.5~5.0 min,B:95%;5.0~6.0 min,B:95%~20%;6.0~7.0 min,B:20%。质谱条件:电喷雾离子源(electrospray ionization,ESI);多反应监测(multiple reaction monitoring,MRM);负离子扫描模式;DL管温度为250 ℃;加热器温度为400 ℃;雾化气流量为3 L/min;干燥气流量为15 L/min;其他质谱参数见表1。
表 1 米酵菌酸的质谱参数Table 1. Chromatogram parameters of bongkrekic acid化合物 母离子(m/z) 子离子(m/z) Q1Pre偏差(V) 碰撞电压CE(V) Q3Pre偏差(V) 米酵菌酸 485.05 397.25* 24 18 23 441.30 25 10 15 注:“*”为定量离子。 1.2.3 蛋白质组学分析
菌体收集:产毒培养结束后将带菌的玻璃纸放入灭菌的50 mL离心管中,加入30 mL无菌生理盐水,振荡5 min,用灭菌后的镊子取出玻璃纸,离心管10000 g离心10 min,弃去上清液,再加入30 mL无菌生理盐水,振荡后离心,重复2~3次,沉淀即为收集的菌体。试验重复3次,每次3个平行,每3个平行样混合为1个样本,用于蛋白质样本制备。
样品前处理为课题组自建方法,具体操作如下:称取100 mg样本,加入500 µL 尿素裂解液(尿素8 mol/L,tris 50 mmol/L,含1×蛋白酶抑制剂,pH8.0),样本在冰水浴中用探头式超声仪超声10 min(超3 s,停2 s,功率30%)至溶液变澄清;超声处理后的样品于4 ℃下20000×g离心15 min,取上清480 µL至新的离心管,使用Bradford蛋白定量试剂盒定量,加50 mmol/L 碳酸氢铵稀释样本,使蛋白浓度约5 µg/µL左右;加1 mol/L二硫苏糖醇(DTT)到样本中,终浓度为10 mmol/L,37 ℃孵育1 h;样本冷却至室温,加1 mol/L碘乙酰胺(IAA)至终浓度为20 mmol/L,室温避光孵育1 h;样本全部转移至FASP超滤管中14000×g离心15 min,加入200 µL 50 mmol/L 碳酸氢铵,14000×g离心15 min,除去收集管中废液,重复2 次;超滤管放到新EP管上(封口膜密封接口处),加入100 µL 50 mmol/L碳酸氢铵和2 µL trypsin,37 ℃孵育12~16 h;14000×g离心15 min收集肽段,加100 µL H2O,14000×g离心15 min,以彻底收集肽段;加入20%甲酸至终浓度0.5%,冰上静置15 min终止酶解;在含有抽干肽段的离心管中加40 μL 0.1%甲酸水溶液,剧烈涡旋5 min充分溶解肽段,4 ℃下20000×g离心30 min,取上清35 µL于新的离心管;使用nanodrop测定肽段浓度,用0.1%甲酸水溶液调节其浓度到500 ng/µL。
液相色谱条件:色谱柱:C18自制柱(内径:100 µm,长度30 cm);流动相:A:0.1%甲酸水;B:20%乙腈水+0.1%甲酸;梯度洗脱程序:0~95 min,B:5%~40%;95~113 min,B:40%~50%;113~115 min,B:50%~90%;115~120 min,B:90%;流速:300 nL/min;上样量:500 ng。质谱条件:一级质谱参数为分辨率:60000;扫描范围(m/z):350~1500;射频透镜(%):50;自动增益控制目标(%):300;最大累积时间(ms):20;电荷价态范围:2~7;动态排除模式:排除前1次扫描,排除时间持续60 s,强度阈值:5e4;二级质谱参数为隔离窗口(m/z):1.6;碰撞能(%):30;分辨率:15000;自动增益控制目标(%):标准模式;最大累积时间(ms):22。
1.3 数据处理
采用MaxQuant软件(version 2.0.3.1)对DDA质谱数据进行搜索鉴定,数据库为Uniprot(Burkholderia gladioli),蛋白FDR(假阳性率)<0.01的为鉴定成功。数据的统计分析主要由R软件(Version 4.0)完成,显著差异蛋白分析由R包metaX完成。产毒前后显著性差异蛋白的筛选主要通过单变量分析来计算。菌株产毒培养前的2次重复蛋白表达量平均值作为一个变量(D(菌株YD)/F(菌株YF)/M(菌株YM)/L(菌株BL)),产毒培养后3次重复蛋白表达量平均值作为一个变量(CD(菌株YD)/CF(菌株YF)/CM(菌株YM)/CL(菌株BL)),差异倍数FC(Fold change)则为CD:D、CF:F、CM:M和CL:L的比值。当FC≥1.5且T检验统计显著性P-value≤0.05则为上调(up-regulated),FC≤0.67且P-value≤0.05的则为下调(down-regulated)[19−20]。采用BLAST软件与KEGG数据库比对,设置E-value<1e-5,从而注释到每个鉴定蛋白的通路。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 显著性差异蛋白的统计
利用DDA非标记定量蛋白质组学技术对4个菌株产毒培养前后菌体蛋白质进行分析。共鉴定到38161条序列,4420个蛋白。产毒培养后菌株米酵菌酸毒素产生情况(结果表示为平均数±标准差)及鉴定蛋白统计见表2。
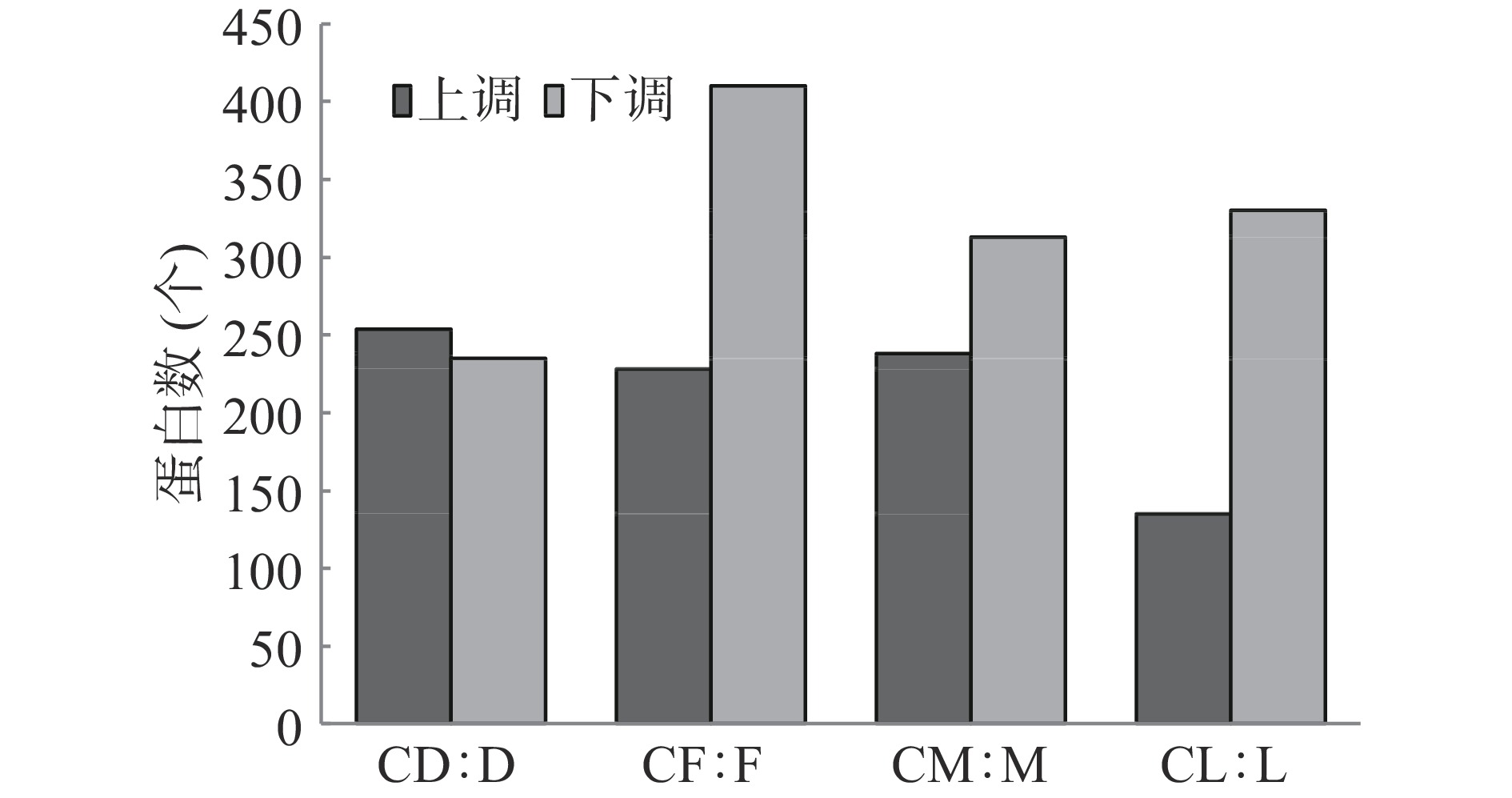
表 2 菌株产毒及鉴定蛋白统计Table 2. Statistics of toxin production and identification proteins of strains编号 米酵菌酸含量(mg·kg−1) 鉴定蛋白数(个) 产毒培养前 产毒培养后 产毒培养前 产毒培养后 菌株YD 0 26.17±1.89 3102±3 3068±91 菌株YF 0 31.58±1.11 3224±10 3007±53 菌株YM 0 25.32±1.16 3126±21 3072±7 菌株BL 0 0 3096±35 3025±16 产毒培养5 d后,菌株YD、YF、YM及BL中较接种前显著性差异表达蛋白统计见图1。产毒菌株YD上调表达蛋白为254个,下调表达为235个;产毒菌株YF上调表达蛋白为228个,下调表达为410个;产毒菌株YM上调表达蛋白为238个,下调表达为313个;标准菌株BL上调表达蛋白为135个,下调表达为330个。产毒培养后,产毒菌株YD、YF及YM中上调表达的蛋白在228~254个之间,均明显多于标准菌株BL,下调表达的蛋白则菌株YD低于菌株BL,而菌株YF高于菌株BL,菌株YM与菌株BL较接近。
2.2 显著性差异蛋白的功能注释
本研究利用多个功能数据库(GO、Pathway、Reactome等)对鉴定到的蛋白进行功能注释,以期揭示显著性差异蛋白功能分类。其中KEGG PATHWAY 数据库中将生物代谢路径划分为6类。产毒培养后菌株YD、YF、YM及BL中显著性差异表达蛋白参与代谢路径统计见表3。差异表达的蛋白中,参与新陈代谢路径蛋白占比最多,占71.86%,如碳水化合物代谢、氨基酸代谢、辅助因子和维生素代谢、脂质代谢等;其次为参与遗传信息传递蛋白,占9.70%,如翻译、折叠、分类和降解以及复制、修复等;参与人类疾病蛋白也较多,占9.51%,如耐药性等;再其次为参与生物体系统蛋白,占5.61%,如衰老、免疫系统等;参与细胞过程蛋白,占2.00%,如运输和分解代谢等;参与环境信息处理蛋白最少,占1.33%,如信号转导等。
表 3 显著性差异蛋白参与代谢路径统计Table 3. Significant difference in protein participation in metabolic pathway statistics编号 路径 新陈代谢
(个)遗传信息
传递(个)环境信息
处理(个)细胞过程
(个)人类疾病
(个)生物体
系统(个)菌株YD 182 22 3 5 24 16 菌株YF 246 23 7 8 41 19 菌株YM 182 19 3 5 19 13 菌株BL 146 38 1 3 16 11 2.3 产毒株与非产毒株间显著性差异蛋白分析
为了从蛋白质水平探索米酵菌酸毒素产生机制,对产毒株与非产毒株产毒培养前后差异表达蛋白进行了分析。产毒培养后,在3株产毒株中均显著性上调表达蛋白为30个,其中有5个蛋白在非产毒株BL中也上调表达,故选取仅在产毒株产毒过程中显著性上调表达的25个蛋白进行分析(见表4)。产毒培养后,在3株产毒株中均显著性下调表达蛋白为65个,其中34个蛋白在非产毒株BL中也下调表达,故选取仅在产毒株产毒过程中显著性下调表达的31个蛋白进行分析(见表5)。产毒培养后,未找到在产毒株中显著性上调表达而在非产毒株中显著性下调表达或者在产毒株中显著性下调表达而在非产毒株中显著性上调表达的蛋白。
表 4 产毒培养后在产毒株中显著性上调表达的蛋白Table 4. Proteins significantly up-regulated in toxin-producing strains after toxin-producing culture序号 蛋白 ID 蛋白名称 路径 1 F2LER0 推断的二氢吡啶二羧酸合成酶 氨基酸的生物合成;赖氨酸生物合成;单内酰胺生物合成 2 F2LGB2 二羟基酸脱水酶 抗生素、氨基酸合成;2-氧代羧酸代谢;泛酸和辅酶a合成 3 F2LQ90 α淀粉酶家族蛋白 淀粉和蔗糖代谢 4 F2LME2 含铁硫簇的氢化酶组分1 碳代谢;乙醛酸和二羧酸代谢;甲烷代谢 5 F2L8E3 Io1C蛋白 磷酸肌醇代谢 6 A0A2S4NNW6 NADH:黄素氧化还原酶/NADH氧化酶 氨基苯甲酸酯降解 7 A0A833Q1X9 过氧化氢酶 抗生素的生物合成;碳代谢;乙醛酸和二羧酸代谢;色氨酸代谢 8 A0A808W7Z3 碳酸酐酶 氮素代谢 9 A0A838C8H7 酰胺水解酶 苯丙氨酸代谢 10 A0A833Q4M2 O-乙酰基-ADP-核糖脱乙酰酶 胁迫响应 11 A0A838BZ61 MFS转运子 转运蛋白 12 F2LHM9 脂蛋白,推定的 与细胞外脂质包装,运输,储存,代谢有关 13 F2LH04 转录调节因子,LysR家族蛋白 群体感应,毒力,毒素产生 14 F2LPZ3 核糖ABC转运蛋白,周质核糖结合蛋白 ABC转运子;细菌趋化性 15 F2LGT7 反应调节受体蛋白 双组分系统;细菌趋化性 16 A0A833QAY0 甲基受体趋化性蛋白II 双组分系统;细菌趋化性 17 A0A808W715
流出RND转运蛋白周质适配器亚单位双组分系统 18 F2LFX9 鞭毛P环蛋白 鞭毛组件 19 F2LGE3 鞭毛M环蛋白 鞭毛组件 20 F2LFY3 鞭毛钩蛋白FlgE 鞭毛组件 21 F2LLT3 未知蛋白 未知 22 A0A838C8T4 未知蛋白 未知 23 A0A833Q8X0 未知蛋白 未知 24 A0A833QAT8 未知蛋白 未知 25 A0A833Q2I7 未知蛋白 未知 表 5 产毒培养后在产毒株中显著性下调表达的蛋白Table 5. Proteins significantly down-regulated in toxin-producing strains after toxin-producing culture序号 蛋白ID 蛋白名称 路径 1 A0A808VXY1 角鲨烯-蒎烯环化酶 倍半萜和三萜生物合成 2 A0A838C237 4-羟基苯丙酮酸双加氧酶 苯丙氨酸、酪氨酸代谢;泛醌和其他萜类醌生物合成 3 F2LGR6 4-羟基-3-甲基丁-2-烯基二磷酸还原酶 抗生素的生物合成;萜类骨架生物合成 4 A0A3G3KZ4 CDP-6-脱氧-δ-3,4-葡萄糖还原酶 氨基糖和核苷酸糖代谢 5 A0A3G3L016 UDP-N-乙酰烯醇丙酮酰葡糖胺还原酶 氨基糖和核苷酸糖代谢;肽聚糖合成 6 F2LME9 UTP -葡萄糖-1-磷酸尿苷酰转移酶 抗生素的生物合成;氨基糖和核苷酸糖代谢;淀粉和蔗糖代谢;半乳糖代谢;
戊糖和葡糖醛酸的相互转化7 A0A808WG5 GTP 3’,8-环化酶 叶酸生物合成;硫磺中继系统 8 F2LNT4 GTP环化水解酶FolE2 叶酸生物合成 9 A0A833Q9I1 多胺氨丙基转移酶 精氨酸和脯氨酸、半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸、谷胱甘肽、β-丙氨酸代谢 10 A0A2A7S5N4 氨甲酰磷酸合酶大链 嘧啶代谢;丙氨酸、天冬氨酸和谷氨酸代谢 11 A0A2A7SA03 磷酸组氨醇转氨酶 新生霉素、氨基酸的生物合成;苯丙氨酸、酪氨酸、组氨酸代谢;苯丙氨酸、
酪氨酸和色氨酸的生物合成12 F2LDK0 前卡林-2c(20)-甲基转移酶 卟啉和叶绿素代谢 13 A0A833V588 4-磺基粘内酯水解酶 不同环境中的微生物代谢;苯甲酸盐、氨基苯甲酸酯降解 14 F2LGJ6 染色体复制起始蛋白DnaA 双组分系统 15 A0A2A7S4A4 组氨酸- tRNA连接酶 氨酰tRNA生物合成 16 F2LCQ6 50S核糖体蛋白L31型B 核糖体 17 F2LG14 30S核糖体蛋白S2 核糖体 18 F2LMT2 ABC甘氨酸甜菜碱/L-脯氨酸转运蛋白,内膜亚单位 ABC转运 19 A0A3G3L9W9 位点特异性DNA甲基转移酶 胁迫响应 20 F2LAQ5 LysR家族转录调节因子 群体感应,毒力,毒素产生 21 F2LJV4 GntR类似蛋白 转录调控因子,参与病原菌致病过程;调控氨基酸、碳水化物、脂肪代谢 22 F2LG61 ADP-核糖基化/晶体蛋白J1 细胞内物质运输、跨膜运输、信号转导 23 A0A833Q3M3 金属蛋白酶TldD 生物膜形成、毒力因子、致病性相关 24 F2LFZ7 5-氧代脯氨酸酶亚单位A 氨基酸代谢、转运 25 F2LG09 铁氧还蛋白- NADP(+)还原酶 能量代谢 26 A0A104JY06 锌依赖性蛋白酶 细胞凋亡、免疫应答 27 A0A808W6E1 LysR家族转录调节因子 群体感应,毒力,毒素产生 28 F2LP64 未知蛋白 未知 29 F2LFD9 未知蛋白 未知 30 F2LE86 未知蛋白 未知 31 F2LJP9 未知蛋白 未知 产毒培养后,仅在产毒株中显著性上调表达蛋白有25个,包括参与抗生素、氨基酸合成的二氢吡啶二羧酸合成酶、二羟基酸脱水酶,参与氨基酸代谢的过氧化氢酶、酰胺水解酶,参与淀粉和蔗糖代谢的α淀粉酶家族蛋白,参与氮素代谢的碳酸酐酶,参与磷酸肌醇代谢的Io1C蛋白等。与细菌趋化性相关蛋白有核糖ABC转运蛋白、反应调节受体蛋白、甲基受体趋化性蛋白II等,鞭毛组件包括鞭毛P环蛋白、鞭毛M环蛋白、鞭毛钩蛋白FlgE,鞭毛是细菌移动和趋化性的运动器官,同时与细菌致病性也密切相关[21]。此外,与群体感应、毒素产生相关的转录调节因子LysR家族蛋白(F2LH04)也在产毒培养后显著性上调表达。除上述蛋白外,还有5个未知蛋白也在产毒培养后显著性上调表达。
产毒培养后,仅在产毒株中显著性下调表达蛋白有31个,包括参与萜类骨架及萜类生物合成的角鲨烯-蒎烯环化酶、4-羟基苯丙酮酸双加氧酶、4-羟基-3-甲基丁-2-烯基二磷酸还原酶,参与淀粉和糖类代谢的CDP-6-脱氧-δ-3,4-葡萄糖还原酶、UDP-N-乙酰烯醇丙酮酰葡糖胺还原酶、UTP -葡萄糖-1-磷酸尿苷酰转移酶,参与氨基酸代谢的多胺氨丙基转移酶、氨甲酰磷酸合酶、磷酸组氨醇转氨酶,还有参与叶酸生物合成的GTP 3’,8-环化酶、GTP环化水解酶FolE2,与核糖体相关的50S核糖体蛋白L31型B、30S核糖体蛋白S2。转录调节因子LysR家族蛋白(F2LAQ5)在产毒培养后其表达量降低。除上述蛋白外,还有4个未知蛋白也在产毒培养后显著性下调表达。
3. 讨论
本研究应用DDA非标记定量蛋白质组学技术对椰毒假单胞菌(产毒株)与非产毒株产毒培养前后差异表达的蛋白进行分析,旨在从蛋白质水平探索米酵菌酸毒素产毒机制。通过对产毒株与非产毒株产毒培养前后差异蛋白分析,筛选到56个显著性差异蛋白,其中包括上调蛋白25个,下调蛋白31个。这些蛋白中有参与抗生素合成、氨基酸合成与代谢、淀粉和糖代谢、能量代谢等相关蛋白,也有与生物膜形成、群体感应、毒素产生、胁迫响应等相关蛋白,还有一些功能未知蛋白。产毒培养后,产毒株中显著性上调表达的25个蛋白中,有6个蛋白与细菌趋化性相关,占比较高,基于趋化性与病原菌致病性等相关研究的报道[21−24],推测趋化性可能在椰毒假单胞菌米酵菌酸毒素产生过程中发挥重要作用。
趋化现象在运动性细菌中普遍存在,细菌通过受体蛋白感知环境信号,随后调整鞭毛运动方向来趋利避害进而得以存活下来[22]。有研究发现趋化性与病原菌致病性相关,在病原菌定殖和侵染过程中发挥重要作用,趋化性和运动性增强了病原菌的侵染力,运动和趋化突变体导致致病性明显减弱[23−24]。了解趋化性在细菌致病机理中的作用,可为通过趋化性控制细菌侵染、减少病害发生提供理论依据。此外,有些细菌对环境污染物如芳香族化合物、硫化物等具有趋化性,越来越多的研究结果显示趋化性与降解性紧密相关,细菌趋化性在环境污染治理、生物修复中也发挥重要作用[25−26]。
趋化运动在伯克霍尔德菌(Burkholderia)中也普遍存在。伯克霍尔德菌利用趋化性寻找盘基网柄菌宿主以维持共生关系[27]。洋葱伯克霍尔德氏菌G4对甲苯、三氯乙烯、和维生素C等具有趋化性[28]。伯克霍尔德氏菌SJ98对氯代芳香族化合物具有趋化性等[29]。椰毒假单胞菌是唐菖蒲伯克霍尔德菌中的致病变种,趋化性与该菌致病性等相关研究还未见报道。基于趋化性与细菌致病性相关研究的报道,以及本研究发现产毒培养后产毒株中趋化性及鞭毛运动性相关蛋白表达量显著增加现象,推测趋化性可能在椰毒假单胞菌米酵菌酸毒素产生过程中发挥重要作用,后续可开展趋化性与该菌米酵菌酸毒素产生及致病相关机理研究。
此外,椰毒假单胞菌产毒培养后,基质中可检测到高含量的米酵菌酸毒素,该毒素为一种脂肪酸类物质,有研究报道磷脂类和不饱和长链脂肪酸类可引起假单胞菌(Pseudomonas)负趋化运动[30],米酵菌酸毒素是否作为负趋化物,介导了椰毒假单胞菌的趋化性运动以躲避有害环境进而攫取营养产生更多的米酵菌酸毒素,后续还需进一步实验确证,比如通过电镜观察毒素产生过程是否发生鞭毛着生方式的变化,通过游动平板法等方式观察产毒培养过程中是否会发生运动方式的改变以及群集趋化性反应等。通过了解趋化性在椰毒假单胞菌米酵菌酸毒素产生及致病过程中的作用,后续可以通过趋化性控制细菌感染及毒素产生,进而为减少由该菌引起的食品安全事故的发生提供理论依据。
4. 结论
通过对椰毒假单胞菌产毒培养前后差异蛋白质组学分析,筛选出了56个仅在产毒株中显著性差异表达蛋白,这些蛋白参与抗生素合成、氨基酸代谢、群体感应、趋化性以及毒素产生等活动。趋化性在运动细菌中普遍存在,产毒培养后产毒株中趋化性信号受体蛋白以及鞭毛组件蛋白表达量显著增加,推测趋化性运动可能在米酵菌酸毒素产生过程中发挥重要作用,米酵菌酸毒素是否作为趋化物介导了椰毒假单胞菌趋化性运动以趋利避害进而更有利于米酵菌酸毒素的产生,还需进一步确证。
-
表 1 米酵菌酸的质谱参数
Table 1 Chromatogram parameters of bongkrekic acid
化合物 母离子(m/z) 子离子(m/z) Q1Pre偏差(V) 碰撞电压CE(V) Q3Pre偏差(V) 米酵菌酸 485.05 397.25* 24 18 23 441.30 25 10 15 注:“*”为定量离子。 表 2 菌株产毒及鉴定蛋白统计
Table 2 Statistics of toxin production and identification proteins of strains
编号 米酵菌酸含量(mg·kg−1) 鉴定蛋白数(个) 产毒培养前 产毒培养后 产毒培养前 产毒培养后 菌株YD 0 26.17±1.89 3102±3 3068±91 菌株YF 0 31.58±1.11 3224±10 3007±53 菌株YM 0 25.32±1.16 3126±21 3072±7 菌株BL 0 0 3096±35 3025±16 表 3 显著性差异蛋白参与代谢路径统计
Table 3 Significant difference in protein participation in metabolic pathway statistics
编号 路径 新陈代谢
(个)遗传信息
传递(个)环境信息
处理(个)细胞过程
(个)人类疾病
(个)生物体
系统(个)菌株YD 182 22 3 5 24 16 菌株YF 246 23 7 8 41 19 菌株YM 182 19 3 5 19 13 菌株BL 146 38 1 3 16 11 表 4 产毒培养后在产毒株中显著性上调表达的蛋白
Table 4 Proteins significantly up-regulated in toxin-producing strains after toxin-producing culture
序号 蛋白 ID 蛋白名称 路径 1 F2LER0 推断的二氢吡啶二羧酸合成酶 氨基酸的生物合成;赖氨酸生物合成;单内酰胺生物合成 2 F2LGB2 二羟基酸脱水酶 抗生素、氨基酸合成;2-氧代羧酸代谢;泛酸和辅酶a合成 3 F2LQ90 α淀粉酶家族蛋白 淀粉和蔗糖代谢 4 F2LME2 含铁硫簇的氢化酶组分1 碳代谢;乙醛酸和二羧酸代谢;甲烷代谢 5 F2L8E3 Io1C蛋白 磷酸肌醇代谢 6 A0A2S4NNW6 NADH:黄素氧化还原酶/NADH氧化酶 氨基苯甲酸酯降解 7 A0A833Q1X9 过氧化氢酶 抗生素的生物合成;碳代谢;乙醛酸和二羧酸代谢;色氨酸代谢 8 A0A808W7Z3 碳酸酐酶 氮素代谢 9 A0A838C8H7 酰胺水解酶 苯丙氨酸代谢 10 A0A833Q4M2 O-乙酰基-ADP-核糖脱乙酰酶 胁迫响应 11 A0A838BZ61 MFS转运子 转运蛋白 12 F2LHM9 脂蛋白,推定的 与细胞外脂质包装,运输,储存,代谢有关 13 F2LH04 转录调节因子,LysR家族蛋白 群体感应,毒力,毒素产生 14 F2LPZ3 核糖ABC转运蛋白,周质核糖结合蛋白 ABC转运子;细菌趋化性 15 F2LGT7 反应调节受体蛋白 双组分系统;细菌趋化性 16 A0A833QAY0 甲基受体趋化性蛋白II 双组分系统;细菌趋化性 17 A0A808W715
流出RND转运蛋白周质适配器亚单位双组分系统 18 F2LFX9 鞭毛P环蛋白 鞭毛组件 19 F2LGE3 鞭毛M环蛋白 鞭毛组件 20 F2LFY3 鞭毛钩蛋白FlgE 鞭毛组件 21 F2LLT3 未知蛋白 未知 22 A0A838C8T4 未知蛋白 未知 23 A0A833Q8X0 未知蛋白 未知 24 A0A833QAT8 未知蛋白 未知 25 A0A833Q2I7 未知蛋白 未知 表 5 产毒培养后在产毒株中显著性下调表达的蛋白
Table 5 Proteins significantly down-regulated in toxin-producing strains after toxin-producing culture
序号 蛋白ID 蛋白名称 路径 1 A0A808VXY1 角鲨烯-蒎烯环化酶 倍半萜和三萜生物合成 2 A0A838C237 4-羟基苯丙酮酸双加氧酶 苯丙氨酸、酪氨酸代谢;泛醌和其他萜类醌生物合成 3 F2LGR6 4-羟基-3-甲基丁-2-烯基二磷酸还原酶 抗生素的生物合成;萜类骨架生物合成 4 A0A3G3KZ4 CDP-6-脱氧-δ-3,4-葡萄糖还原酶 氨基糖和核苷酸糖代谢 5 A0A3G3L016 UDP-N-乙酰烯醇丙酮酰葡糖胺还原酶 氨基糖和核苷酸糖代谢;肽聚糖合成 6 F2LME9 UTP -葡萄糖-1-磷酸尿苷酰转移酶 抗生素的生物合成;氨基糖和核苷酸糖代谢;淀粉和蔗糖代谢;半乳糖代谢;
戊糖和葡糖醛酸的相互转化7 A0A808WG5 GTP 3’,8-环化酶 叶酸生物合成;硫磺中继系统 8 F2LNT4 GTP环化水解酶FolE2 叶酸生物合成 9 A0A833Q9I1 多胺氨丙基转移酶 精氨酸和脯氨酸、半胱氨酸和蛋氨酸、谷胱甘肽、β-丙氨酸代谢 10 A0A2A7S5N4 氨甲酰磷酸合酶大链 嘧啶代谢;丙氨酸、天冬氨酸和谷氨酸代谢 11 A0A2A7SA03 磷酸组氨醇转氨酶 新生霉素、氨基酸的生物合成;苯丙氨酸、酪氨酸、组氨酸代谢;苯丙氨酸、
酪氨酸和色氨酸的生物合成12 F2LDK0 前卡林-2c(20)-甲基转移酶 卟啉和叶绿素代谢 13 A0A833V588 4-磺基粘内酯水解酶 不同环境中的微生物代谢;苯甲酸盐、氨基苯甲酸酯降解 14 F2LGJ6 染色体复制起始蛋白DnaA 双组分系统 15 A0A2A7S4A4 组氨酸- tRNA连接酶 氨酰tRNA生物合成 16 F2LCQ6 50S核糖体蛋白L31型B 核糖体 17 F2LG14 30S核糖体蛋白S2 核糖体 18 F2LMT2 ABC甘氨酸甜菜碱/L-脯氨酸转运蛋白,内膜亚单位 ABC转运 19 A0A3G3L9W9 位点特异性DNA甲基转移酶 胁迫响应 20 F2LAQ5 LysR家族转录调节因子 群体感应,毒力,毒素产生 21 F2LJV4 GntR类似蛋白 转录调控因子,参与病原菌致病过程;调控氨基酸、碳水化物、脂肪代谢 22 F2LG61 ADP-核糖基化/晶体蛋白J1 细胞内物质运输、跨膜运输、信号转导 23 A0A833Q3M3 金属蛋白酶TldD 生物膜形成、毒力因子、致病性相关 24 F2LFZ7 5-氧代脯氨酸酶亚单位A 氨基酸代谢、转运 25 F2LG09 铁氧还蛋白- NADP(+)还原酶 能量代谢 26 A0A104JY06 锌依赖性蛋白酶 细胞凋亡、免疫应答 27 A0A808W6E1 LysR家族转录调节因子 群体感应,毒力,毒素产生 28 F2LP64 未知蛋白 未知 29 F2LFD9 未知蛋白 未知 30 F2LE86 未知蛋白 未知 31 F2LJP9 未知蛋白 未知 -
[1] 汪廷彩, 雷毅, 周露, 等. 唐菖蒲伯克霍尔德氏菌(椰毒假单胞菌酵米面亚种)的研究进展[J]. 食品与机械,2021,37(5):194−202. [WANG Tingcai, LEI Yi, ZHOU Lu, et al. Recent advance on Burkholderia galdioli ( Pseudomonas cocovenenans subsp. farinofermentans)[J]. Food & Machinery,2021,37(5):194−202. doi: 10.13652/j.issn.1003-5788.2021.05.035 WANG Tingcai, LEI Yi, ZHOU Lu, et al . Recent advance on Burkholderia galdioli (Pseudomonas cocovenenans subsp. farinofermentans)[J]. Food & Machinery,2021 ,37 (5 ):194 −202 . doi: 10.13652/j.issn.1003-5788.2021.05.035[2] 陈荣桥, 陈汉金, 胡均鹏, 等. 米和食用淀粉中椰毒假单胞菌米面亚种污染调查与风险分析[J]. 现代食品科技,2021,37(1):1−7. [CHEN Rongqiao, CHEN Hanjin, HU Junpeng, et al. Investigation and risk analysis of Pseudomonas cocovenenans subsp. farinofermentans from rice and edible starch[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2021,37(1):1−7. CHEN Rongqiao, CHEN Hanjin, HU Junpeng, et al . Investigation and risk analysis of Pseudomonas cocovenenans subsp. farinofermentans from rice and edible starch[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2021 ,37 (1 ):1 −7 .[3] FALCONER T M, KERN S E, BRZEZINSKI J L, et al. Identification of the potent toxin bongkrekic acid in a traditional African beverage linked to a fatal outbreak[J]. Forensic Science International,2017,270:e5−e11. doi: 10.1016/j.forsciint.2016.10.015
[4] LI J H, ZHOU L, LONG C Y, et al. An investigation of bongkrekic acid poisoning caused by consumption of a nonfermented rice noodle product without noticeable signs of spoilage[J]. Journal of Food Protection,2019,82(10):1650−1654. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-19-121
[5] JIAO Z Q, KAWAMURA Y, MISHIMA N, et al. Need to differentiate lethal toxin-producing strains of Burkholderia gladioli, which cause severe food poisoning:Description of B. gladioli pathovar cocovenenans and an emended description of B. gladioli[J]. Mriobiology and Immunology,2013,47(12):915−925.
[6] ANWAR M, KASPER A, STECK A R, et al. Bongkrekic acid-a review of a lesser-known mitochondrial toxin[J]. Journal of Medical Toxicology,2017,13(2):173−179. doi: 10.1007/s13181-016-0577-1
[7] RAFAE A G, JOSEPH H H, KEITH H S. The effect of lipids on bongkrekic (Bongkrek) acid toxin production by Burkholderia co-covenenans in coconut media[J]. Food Additives and Contaminants,1999,16(2):63−69. doi: 10.1080/026520399284217
[8] BUCKLE K A, KARTADARMA E. Inhibition of bongkrek acid and toxoflavin production in tempe bongkrek containing Pseudomonas cocovenenans[J]. Journal of Applied Bacteriology,1990,68:571−576. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1990.tb05222.x
[9] 陈卫真, 周方, 孟昭赫, 等. 椰酵假单胞菌毒素 - 米酵菌酸形成机理的探 讨[J]. 中华微生物学和免疫学杂志,1991,11(3):151−154. [CHEN Weizhen, ZHOU Fang, MENG Zhaohe, et al. Studies on the mechanism of formation of Pseudomonas cocovenenans toxin-bongkrekic acid[J]. Chinese Journal of Microbiology and Immunology,1991,11(3):151−154. CHEN Weizhen, ZHOU Fang, MENG Zhaohe, et al . Studies on the mechanism of formation of Pseudomonas cocovenenans toxin-bongkrekic acid[J]. Chinese Journal of Microbiology and Immunology,1991 ,11 (3 ):151 −154 .[10] 王静, 刘秀梅. 糖对椰酵假单胞菌产毒性能的影响研究[J]. 卫生研究,1996,25(4):46−48. [WANG Jing, LIU Xiumei. Effect of sugar on the toxigenicity of Pseudomonas cocovenenans subsp. farinofermentans[J]. Journal of Hygiene Research,1996,25(4):46−48. doi: 10.19813/j.cnki.weishengyanjiu.1996.04.015 WANG Jing, LIU Xiumei . Effect of sugar on the toxigenicity of Pseudomonas cocovenenans subsp. farinofermentans[J]. Journal of Hygiene Research,1996 ,25 (4 ):46 −48 . doi: 10.19813/j.cnki.weishengyanjiu.1996.04.015[11] MOEBIUS N, ROSS C, SCHERLACH K, et al. Biosynthesis of the respiratory toxin bongkrekic acid in the pathogenic bacterium Burkholderia gladioli[J]. Chemistry & biology,2012,19(9):1164−1174.
[12] 彭子欣, 陈雪, 李孟寒, 等. 唐菖蒲伯克霍尔德菌椰毒致病型菌株Co14毒力相关基因解析[J]. 中国食品卫生杂志,2018,30(6):558−562. [PENG Zixin, CHEN Xue, LI Menghan, et al. Analyzing the virulence factor biosynthesis genes of a food pathogen Burkholderia gladioli pv. cocovenenans strain Co14[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene,2018,30(6):558−562. doi: 10.13590/j.cjfh.2018.06.002 PENG Zixin, CHEN Xue, LI Menghan, et al . Analyzing the virulence factor biosynthesis genes of a food pathogen Burkholderia gladioli pv. cocovenenans strain Co14[J]. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene,2018 ,30 (6 ):558 −562 . doi: 10.13590/j.cjfh.2018.06.002[13] GONG H, HUANG X L, ZHU W J, et al. Pan-genome analysis of the Burkholderia gladioli PV. Cocovenenans reveal the extent of variation in the toxigenic gene cluster[J]. Food Microbiology,2023,113:104249−104259. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2023.104249
[14] TENG T, XI B W, CHEN K, et al. Comparative transcriptomic and proteomic analyses reveal upregulated expression of virulence and iron transport factors of Aeromonas hydrophila under iron limitation[J]. BMC Microbiology,2018,18:52−68. doi: 10.1186/s12866-018-1178-8
[15] CACACE G, MAZZEO M F, SORRENTINO A, et al. Proteomics for the elucidation of cold adaptation mechanisms in Listeria monocytogenes[J]. Journal of Proteomics,2010,73(10):2021−2030. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2010.06.011
[16] TIAN X J, LIU Y, YU Q Q, et al. Label free-based proteomic analysis of Escherichia coli O157:H7 subjected to ohmic heating[J]. Food Research International,2020,128:108815−108824. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108815
[17] 国家市场监督管理总局, 国家卫生健康委员会. GB 4789.29-2020 食品微生物学检验 唐菖蒲伯克霍尔德氏菌(椰毒假单胞菌酵米面亚种)检验[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社,2020. [State Administration for Market Regulation, National Health Commission. GB 4789.29-2020 Microbiological examination of food hygiene. Examination of Burkholderia gladioli (Pseudomonas cocovenenans subsp. farinofermentans)[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2020. State Administration for Market Regulation, National Health Commission. GB 4789.29-2020 Microbiological examination of food hygiene. Examination of Burkholderia gladioli (Pseudomonas cocovenenans subsp. farinofermentans)[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2020.
[18] 朱文娟, 黄永德, 黄秀丽, 等. 椰毒假单胞菌酵米面亚种及毒素的污染调查与湿米粉生产风险控制[J]. 中国粮油学报,2022,37(12):203−211. [ZHU Wenjuan, HUANG Yongde, HUANG Xiuli, et al. Investigation contamination of Pseudomonas cocovenenas subsp. farinofermentants and risk control of wet rice noodle production[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2022,37(12):203−211. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2022.12.030 ZHU Wenjuan, HUANG Yongde, HUANG Xiuli, et al . Investigation contamination of Pseudomonas cocovenenas subsp. farinofermentants and risk control of wet rice noodle production[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2022 ,37 (12 ):203 −211 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2022.12.030[19] 窦 玥, 熊为亮, 梁如冰, 等. 基于非数据依赖的鞘脂菌蛋白质组学分析方法的建立[J]. 微生物学通报,2020,47(8):2630−2651. [DOU Yue, XIONG Weiliang, LIANG Rubing, et al. Establishment of a data-independent acquisition proteomic analysis method for Sphingobium yanoikuyae[J]. Microbiology China,2020,47(8):2630−2651. doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.190868 DOU Yue, XIONG Weiliang, LIANG Rubing, et al . Establishment of a data-independent acquisition proteomic analysis method for Sphingobium yanoikuyae[J]. Microbiology China,2020 ,47 (8 ):2630 −2651 . doi: 10.13344/j.microbiol.china.190868[20] CHAWADE A, SANDIN M, TELEMAN J, et al. Data processing has major impact on the outcome of quantitative label-free LC-MS analysis[J]. Journal of Proteome Research,2015,14(2):676−687. doi: 10.1021/pr500665j
[21] SANDRAD W, VERMEIREN H, MUIDERS I H M, et al. Flagella- driven chemotaxis towards exudate components is an important trait for tomato root colonization by Pseudomonas fluorescens[J]. Molecular Plant-Microbe Interactions,2002,15(11):1173−1180. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.2002.15.11.1173
[22] BAKER M D, WOLANIN P M, STOCK J B. Signal transduction in bacterial chemotaxis[J]. Bioessays,2006,28(1):9−22. doi: 10.1002/bies.20343
[23] FRETER R, O'BRIEN P C. Role of chemotaxis in the association of motile bacteria with intestinal mucosa:chemotactic responses of Vibrio cholerae and description of motile nonchemotactic mutants[J]. Infection and Immunity,1981(34):215−221.
[24] PORTER S L, WADHAMS G H, ARMITAGE J P. Signal processing in complex chemotaxis pathways[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology,2011,9(3):153−165. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2505
[25] 蒋建东, 张瑞福, 何健, 等. 细菌对环境污染物的趋化性及其在生物修复中的作用[J]. 生态学报,2005,25(7):1764−1771. [JIANG Jiandong, ZHANG Ruifu, HE Jian, et al. Bacterial chemotaxis to environmental pollutants and its significance in bioremediation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2005,25(7):1764−1771. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2005.07.033 JIANG Jiandong, ZHANG Ruifu, HE Jian, et al . Bacterial chemotaxis to environmental pollutants and its significance in bioremediation[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2005 ,25 (7 ):1764 −1771 . doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-0933.2005.07.033[26] PARALES R E, DITTY J L, HARWOOD C S. Toluene-degrading bacteria are chemotactic towords the environmental pollutants benzene, toluene, and trichoroethylene[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2000,66(9):4098−4104. doi: 10.1128/AEM.66.9.4098-4104.2000
[27] SHU L, ZHANG B, QUELLER D C, et al. Burkholderia bacteria use chemotaxis to find social amoeba Dictyostelium discoideum hosts[J]. Multidisciplinary Journal of Microbial Ecology,2018,12(8):1977−1993.
[28] VARDAR G, BARBIERI P, WOOD T K. Chemotaxis of Pseudomonas stutzeri OX1 and Burkholderia cepacia G4 toward chlorinated ethenes[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2005,66(6):696−701. doi: 10.1007/s00253-004-1685-4
[29] KUMAR S, VIKRAM S, RAGHAVA G P S. Genome annotation of Burkholderia sp. SJ98 with special focus on chemotaxis genes[J]. PLoS One,2013,8(8):e70624−70632. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0070624
[30] SAMPEDRO I, PARALES R E, KRELL T, et al. Pseudomonas chemotaxis[J]. FEMS Microbiology Reviews,2015,39:17−46.





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



