Exogenous Sugar Effects on Fruit Quality in 'Petit Verdot' Grape Berry in Vitro
-
摘要: 本试验以酿酒葡萄品种‘小味儿多’(Vitis vinifera L. cv. Petit Verdot)为试验材料,选用蔗糖、葡萄糖、果糖和鼠李糖四种糖,设置质量分数分别为2%、5%和8%三个浓度,对葡萄果粒进行外源糖喷施处理,放置于人工气候培养箱中离体培养12 d后采样。统计离体培养过程中果实转色率,对葡萄果实可滴定酸、还原糖、花色苷、非花色苷酚类等主要品质指标进行测定与分析,并采用主成分分析方法对其进行综合评价。结果表明,在离体培养条件下,果糖、蔗糖和鼠李糖对酿酒葡萄果实品质均有较明显的改善作用,葡萄糖对提高葡萄果实品质作用不明显。在提高果实综合品质方面,处理效果最好为果糖,8% Fru综合得分排名第1,5% Fru综合排名第2,2% Fru第9;蔗糖的最适浓度为2%,综合排名为第3,8% Suc综合排名第5,5% Suc第8;鼠李糖的最适浓度为5%,综合排名在第4位,2% Rha排名第6,8% Rha排名在对照组后面,为第12名;葡萄糖对提高葡萄果实品质作用不明显,2% Glu排名在第7位,高于对照组两名,而5%和8% Glu排名均低于对照,分别为13和11名。从主成分1和主成分2的得分情况来看,果糖对花色苷和酚类物质(主成分1)积累有较明显的促进作用,其中5% Fru得分最高,8% Fru第2,2% Fru第3;蔗糖使可溶性固形物、还原糖和可滴定酸(主成分2)的含量明显增加,其中2% Suc得分最高,5% Suc第2,8% Suc第6。综上所述,不同种类糖进入果皮细胞后可能有不同的代谢途径和代谢产物,需要进一步探究不同种类糖在果皮细胞中的代谢机制。Abstract: The test material in this experiment was the wine grape variety 'Petit Verdot' (Vitis vinifera L.cv. Petit Verdot). Sucrose, glucose, fructose, and rhamnose were selected for sugars, with mass fractions of 2%, 5% and 8%, respectively. The grape was sprayed with exogenous sugars and cultured in vitro for 12 days in a plant growth incubator. The rate of fruit color change was monitored and analyzed, and the primary quality indicators such as titratable acids, reducing sugars, anthocyanins and non-anthocyanin phenolics were examined extensively using principal component analysis. According to the results, under in vitro culture conditions, fructose, sucrose and rhamnose improved grape fruit quality significantly, while glucose had no obvious effect on grape fruit quality. In terms of improving the comprehensive quality of fruit, the best treatment effect was fructose, with 8% Fru ranking the first, 5%Fru ranking the second and 2% Fru ranking the ninth. The optimum concentration of 2% Suc ranked third overall, 8% Suc ranked fifth overall, and 5% Suc ranked eighth. Rhamnose optimal concentration of 5%, ranked in the fourth, 2% Rha ranked sixth, 8% Rha ranking behind in the control group, as the 12th. Glucose function was not obvious to improve the quality of the grapes, 2% Glu ranking in the seventh, higher than that of control group two, while both 5% and 8% Glu ranked lower than the control, at 13 and 11, respectively. According to the scores of principal component 1 and principal component 2, fructose significantly promoted the accumulation of anthocyanins and phenols (principal component 1), in which 5% Fru scored the highest, 8% Fru the second and 2% Fru the third. Sucrose significantly increased the content of soluble solids, reducing sugars and titratable acids (principal component 2), with 2% Suc scoring highest, 5% Suc second, and 8% Suc sixth. To sum up, different kinds of sugar into the skin cells may have different metabolic pathways and metabolites, the mechanisms of metabolism of different types of sugars in grape skin cells need to be further explored.
-
Keywords:
- wine grape /
- exogenous sugar /
- in vitro culture /
- anthocyanins /
- phenols
-
葡萄是世界上最古老的水果之一,根据用途不同可将其分为酿酒葡萄、鲜食葡萄、制干葡萄和制汁、制罐葡萄四大类[1]。酿酒葡萄品种要求果粒小而紧凑,出汁率高,糖酸比适中,具有典型的风味和香气,红色品种还要求色泽亮丽[1]。葡萄品质的好坏是葡萄酒质量好坏的关键,通常用葡萄果实的可溶性固形物、糖酸比、pH、酚类物质的含量(包括单宁、花色苷、酚酸和黄酮类化合物)等指标来判定酿酒葡萄的品质[2]。糖类不仅具有重要的生理作用,且对酿酒葡萄的品质、口感以及深加工有很大影响,是色素及风味物质的基质[3−4]。酚类物质是衡量红色酿酒葡萄品质的重要指标,它们决定葡萄酒的色泽,影响葡萄酒的风味[5]。
葡萄的生长发育受到内部营养、激素以及外部环境等因素共同调节,受光照、温度、湿度等气候因子的影响,酿酒葡萄果实存在着色不良、酚类物质积累不足等现象,影响着葡萄与葡萄酒品质[6]。研究人员通过整形修剪、铺反光膜和补充施肥等方式调节葡萄果实生长区的微气候以及提供酿酒葡萄生长所必须的大量元素及微量元素,从而改善葡萄品质,或者通过外源施加植物生长调节剂提高花色苷合成途径相关酶和基因的表达,提高果实花色苷含量[7−10]。糖不仅可作为能源和结构物质,也参与调控植物生长发育及基因表达,具有和植物激素类似的作用[11]。Larronded等[12]对葡萄果肉细胞进行悬浮培养,发现外源添加糖有助于诱导葡萄多酚的积累,加速果实着色,这种影响是糖特异性的,独立于代谢和渗透效应[13−14],先前的研究发现糖通过上调葡萄花色苷合成基因F3H的表达,提高花色苷合成途径中F3H(黄烷酮3-羟化酶)的活性,进而促进果实花色苷的积累[15]。且许多研究表明,外源糖有促进草莓[16−17]、红皮梨[18]、血橙[19]、蓝莓[20]等果实花色苷积累,改善果实品质的作用,但关于外源糖对酿酒葡萄果实品质的改善效果、最适浓度和糖种类的相关研究较少。
目前,葡萄浆果的离体培养已被用于研究对碳源和蔗糖浓度的生长响应[21],在离体条件下,葡萄浆果可以从培养基中吸收碳源和氮源,有效地利用吸收的营养物质进行代谢[22],采用离体培养技术研究外部因素对葡萄果实花色苷合成的影响,不仅可以提高试验的可控性,还可更精确的调控养分和营养物质的输入[23−24],但在实际生产中应用植物激素改善葡萄果实品质时常采用外源喷施溶液的方法[25]。因此,本研究以酿酒葡萄品种‘小味儿多’为试验材料,分别喷施质量分数为2%、5%、8%的蔗糖、葡萄糖、果糖、鼠李糖溶液,在人工气候培养箱进行离体培养,期间统计各处理组葡萄转色率,分析外源喷施不同种类糖对果实基本理化指标、花色苷和酚类物质含量的影响,通过主成分分析,明确最佳外源糖种类和适宜浓度,为深入研究外源糖对酿酒葡萄果实品质的影响机制提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
试验所用材料为欧亚种(Vitis vinifera L.)酿酒葡萄 ‘小味儿多’(cv. Petit Verdot) 采自山东省烟台市蓬莱香格里拉玛桑酒庄葡萄园,于葡萄转色初期(转色初期:葡萄果粒颜色开始变化的阶段,整体转色率在5%左右)采集生长势基本一致的葡萄果穗,采收后立即运回实验室进行处理;葡萄糖(Glucose,Glu)、果糖(Fructose,Fru)、蔗糖(Sucrose,Suc) 分析纯(99.7%),光华科技股份有限公司;鼠李糖(Rhamnose,Rha) 纯度≥98%,源叶生物科技有限公司;甲醇 科密欧化学试剂有限公司;吐温80 赛默飞世尔科技有限公司。
LRX-1100D-LED人工气候培养箱 宁波普朗特仪器有限公司;YTLG-10A冷冻干燥机 上海叶拓科技有限公司;PAL-1手持糖度计 日本爱拓仪器公司;TGL20MW高速冷冻离心机 北京莱博瑞杰科技有限公司;UV-1800紫外可见分光光度计 日本岛津公司;超声提取器HAD-720 北京恒奥德仪器仪表有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品处理
样本处理参考Dai等[21]的方法并稍做改进:将葡萄果穗置于自来水下,使用流水冲洗15 min;再从整穗葡萄上剪下发育一致的未转色浆果簇放入70% 乙醇2 s然后转移到含2%有效氯的NaClO溶液中2 min,清洗过程模仿摇床;之后迅速转移到无菌去离子水中清洗2 min,重复3次;随后将葡萄转移到20 mmol/L EDTA溶液中,再次将果梗减切至约2 mm;而后将EDTA溶液中二次剪切的果粒随机摆放到72孔离心管盒中,盒中盛有3%蔗糖溶液(溶液于115 ℃灭菌15 min),使果梗浸到溶液中,按照试验设计对果粒进行喷施处理。
1.2.2 试验设计
试验共设13个处理,每个处理设置三个重复:a. 无菌水(CK);b. 2% Suc;c. 5% Suc;d. 8% Suc;e. 2% Fru;f. 5% Fru;g. 8% Fru;h. 2% Glu;i. 5% Glu;j. 8% Glu;k. 2% Rha;l. 5% Rha;m. 8% Rha;用无菌水将各处理的糖稀释至对应的浓度,以吐温80作为展开剂(吐温80体积分数为0.1%),对照组的无菌水里添加同等体积分数吐温80,以保证单一变量。按照上述试验设计对果粒进行均匀喷施糖溶液,直至有水滴形成为止,而后转移到恒温26±0.5 ℃,湿度70%,光照:黑暗=16 h:8 h,光照强度为80%的培养箱中。每天统计一次转色率,转色达率稳定在 90%左右时停止培养并采集样品,贮于−80 ℃冰箱中备用。
1.2.3 指标测定及方法
1.2.3.1 基本理化指标测定
转色率统计:转色率统计参照晁无疾等[26]的方法略有改动,观察离体培养过程的葡萄果皮着色情况,根据着色面积将每粒葡萄着色情况分别记为1,2/3,1/2、1/3和0,果实着色分级如表1所示:将每粒葡萄代表值相加再除以该处理总的葡萄粒数,结果用百分数表示。转色率计算公式:转色率(%)=(∑每粒葡萄着色代表值)/总葡萄粒数×100。
表 1 果实着色分级Table 1. Fruit coloring grading级别 着色状况 代表值 Ⅰ 红紫色,果面全部着色 1 Ⅱ 基本着色,红色占2/3 2/3 Ⅲ 中度着色,淡红色占1/2 1/2 Ⅳ 果面轻微着色,淡红色占1/3 1/3 Ⅴ 果实全部绿色 0 果实基本理化指标的测定方法参考《葡萄酒分析检验》[27]。
可溶性固形物:随机选取待用的葡萄果实 50粒,除去果皮表面水分,挤出汁液混匀,用手持糖量计测定每个处理的可溶性固形物含量,重复3次。
还原糖:取上述的葡萄汁液采用斐林试剂热滴定法测定还原糖含量(以葡萄糖计)。
可滴定酸:取上述的葡萄汁液采用氢氧化钠滴定法测定可滴定酸含量(以酒石酸计)。
1.2.3.2 果皮酚类物质含量的提取与测定
酚类物质的提取与测定参考苏鹏飞[28]的方法:避光状态下,在冰上剥取葡萄果皮,液氮冷冻粉碎成粉末装于培养皿中,在冷冻干燥机中冻干24 h,取出装于自封袋中,存放于−80 ℃冰箱中。提取时称取0.5 g干粉于50 mL离心管中,加入10 mL盐酸甲醇溶液(60%甲醇,0.1%盐酸)料液比1:20,于超声提取器中(水温30 ℃,功率40 W)下提取30 min,接着在4 ℃下10000 r/min下离心10 min,收集上清液于丝口瓶中。然后在沉淀物中加入10 mL盐酸甲醇重复以上提取步骤2次,合并3次所有上清液摇匀并储存于−80 ℃冰箱中备用。总花色苷含量采用pH示差法测定,总酚含量选用福林-肖卡比色法测定,类黄酮含量选用三氯化铝比色法测定,单宁含量选用甲基纤维素沉淀法测定,黄烷醇含量选用p-DMACA-盐酸法测定。
1.3 数据处理
采用Excel 2021对试验数据进行统计处理,然后采用SPSS 26.0进行方差分析和主成分分析,并进行Duncan's检验,用Excel 2021和Origin 2022b软件制作图表。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 离体培养过程中外源糖对酿酒葡萄‘小味儿多’果实转色率的影响
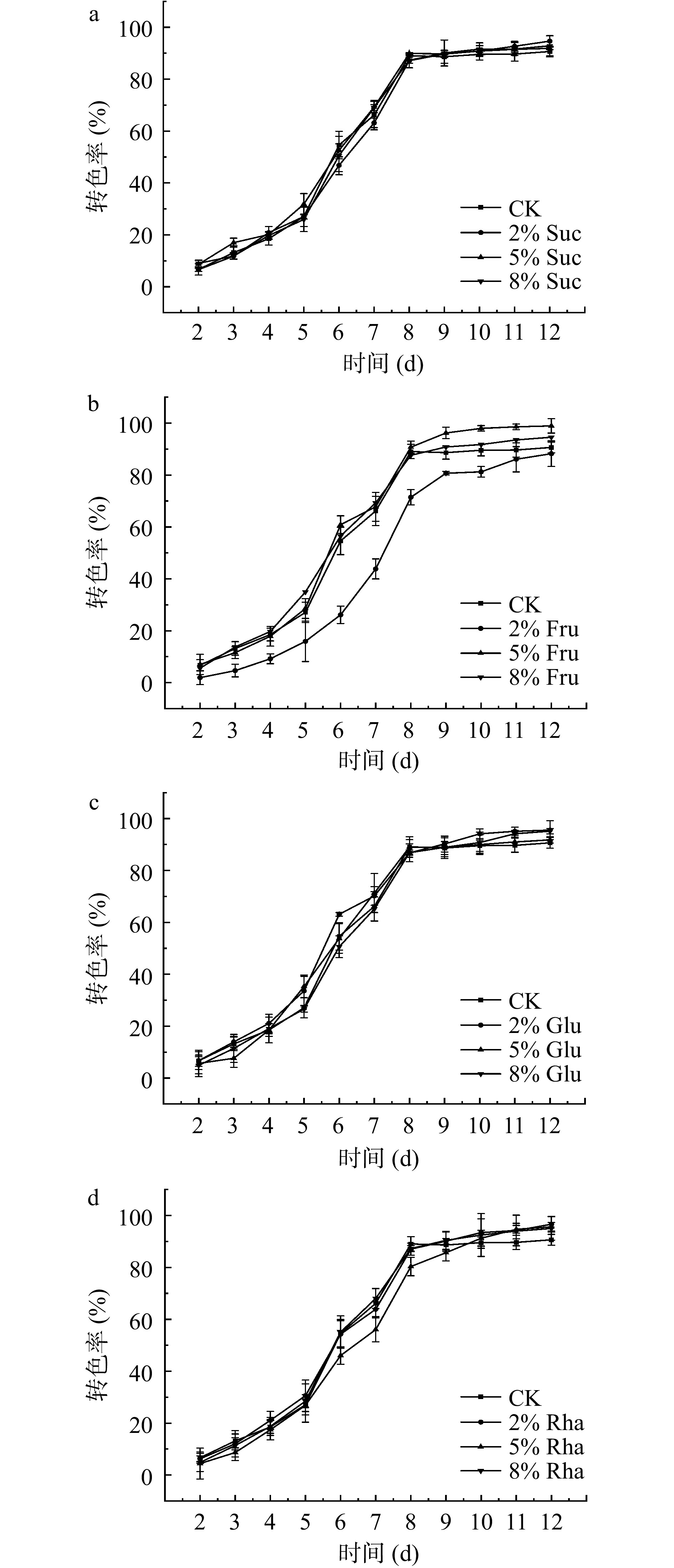
对于红色酿酒葡萄来说,葡萄果皮着色程度对红葡萄酒至关重要[28−29]。从葡萄颜色变化的总体趋势来看,第2~8 d时,葡萄转色率与培养时间成正比,这个时期葡萄吸收营养物质和糖分的速度较快[26]。在第8~12 d时,转色率缓慢增加后趋于稳定,这个阶段葡萄转色率基本达到80%以上。外源糖进入果皮细胞后无法直接转变为花色苷,需要进行一系列的生理生化反应,才能合成花色苷[30]。因此,外源糖可促进葡萄果皮花色苷的积累,但因糖的种类和浓度不同使其作用效果存在一定差异。
由图1a可知,在离体培养第3和第5 d时,5% Suc处理使葡萄转色率显著(P<0.05)高于对照和2% Suc和8% Suc处理组,而在第12 d时,2% Suc处理组转色率较高,为94.23%。如图1b所示,2% Fru处理使转色率始终低于对照组和其他处理组,在第2~8 d时,5% Fru和8% Fru处理使转色率与对照之间无显著(P>0.05)差异,但在第8~12 d时,5% Fru转色率较高,最高达98.9%,其次是8% Fru。葡萄糖对果实转色率影响如图1c所示,在离体培养期间,5% Glu和8% Glu处理对转色率影响变化不稳定,而2% Glu处理使转色率始终高于对照组。图1d反映了三个浓度的鼠李糖对果实转色率的影响,在第5~9 d时,5% Rha处理使转色率低于对照,在第10~12 d时,各处理转色率均高于对照,其中2% Rha处理转色率较高,为97.3%。
![]() 图 1 离体培养过程中四种外源糖对‘小味儿多’转色率的影响注:a. 蔗糖;b. 果糖;c. 葡萄糖;d. 鼠李糖;图2同。Figure 1. Effect of exogenous sugars on the color transfer rate of ‘Petit Verdot’ during in vitro culture
图 1 离体培养过程中四种外源糖对‘小味儿多’转色率的影响注:a. 蔗糖;b. 果糖;c. 葡萄糖;d. 鼠李糖;图2同。Figure 1. Effect of exogenous sugars on the color transfer rate of ‘Petit Verdot’ during in vitro culture综上所述,在本试验中,5% Fru促进果实转色效果较好,其次是2% Rha,2% Suc排第三,最后是2% Glu,这说明果皮着色程度会受到外源糖种类和浓度的影响[21−23]。
2.2 离体培养条件下外源糖对酿酒葡萄‘小味儿多’果实基本理化品质的影响
可溶性固形物和还原糖是酿酒葡萄内在品质的重要评价指标,在葡萄转色过程中,其含量间接影响果皮着色和酚类物质的积累[31−32]。如表2所示,三个浓度的蔗糖处理使可溶性固形物和还原糖含量均显著(P<0.05)高于对照,其中2% Suc处理使可溶性固形物和还原糖含量升高幅度较大;三个浓度的果糖处理显著(P<0.05)降低了果实可溶性固形物含量,其中5% Fru处理组含量最低,为4.13%,2% Fru处理组还原糖含量与对照组之间无显著(P>0.05)差异,5% Fru与8% Fru处理使果实的还原糖含量显著(P<0.05)增加;三个浓度的鼠李糖处理使可溶性固形物和还原糖均显著(P<0.05)高于对照,2% Rha处理含量最高,8% Rha最低;三个浓度的葡萄糖处理均可使葡萄果实中可溶性固形物和还原糖含量增加。
表 2 外源糖对‘小味儿多’果实可溶性固形物、还原糖和可滴定酸含量的影响Table 2. Effects of exogenous sugars on soluble solids, reducing sugars and titratable acids in ‘Petit Verdot’ grape berry处理 可溶性固形物
(%)还原糖
(g/L)可滴定酸
(g/L)CK 4.73±0.03f 25.13±0.98h 14.98±0.06g 2% Suc 6.40±0.00a 44.33±1.16a 16.68±0.09b 5% Suc 5.87±0.09b 34.93±0.37cd 16.49±0.05bc 8% Suc 5.50±0.06cd 32.33±0.77efg 16.54±0.16bc 2% Fru 4.17±0.09h 26.33±0.37h 14.85±0.05g 5% Fru 4.13±0.03h 30.07±0.77g 15.91±0.05e 8% Fru 4.40±0.06g 39.13±0.24b 16.57±0.03bc 2% Rha 5.60±0.00c 33.80±0.31de 17.01±0.08a 5% Rha 5.50±0.06cd 30.60±0.50fg 16.13±0.03d 8% Rha 5.37±0.03d 30.40±0.61g 16.38±0.01c 2% Glu 5.40±0.10d 32.87±0.48def 15.57±0.03f 5% Glu 5.17±0.07e 36.47±1.47c 14.94±0.05g 8% Glu 6.33±0.07a 39.87±0.71b 16.02±0.07de 注:表中数据为平均值±标准差,同列不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05);表3同。 可滴定酸也是果实内在品质的重要性状之一,其含量影响葡萄果实的风味和葡萄酒的口感[25]。本研究中,2% Fru处理使可滴定酸含量与对照之间无显著差异,5% Fru与8% Fru处理使果实可滴定酸含量显著(P<0.05)高于对照;三个浓度的蔗糖处理使可滴定酸含量均显著(P<0.05)高于对照,其中2% Suc处理使可滴定酸含量增幅较大,为11.3%,5% Suc和8% Suc处理之间无显著(P>0.05)差异。与对照相比, Rha处理使可滴定酸含量增加,2% Rha处理增幅最大,5% Rha处理组增幅最小。5%Glu处理组可滴定酸含量与对照相比无显著(P>0.05)差异,2%和8% Glu处理后,可滴定酸含量高于对照,8% Glu处理组增幅大于2% Glu处理组。总体来看,外源糖喷施处理使还原糖、可溶性固形物和可滴定酸含量增加,可能是因为外源糖作为基础原料,合成并转换成了内源糖、酸等物质[26]。
2.3 离体培养条件下外源糖对酿酒葡萄‘小味儿多’果皮总花色苷含量的影响
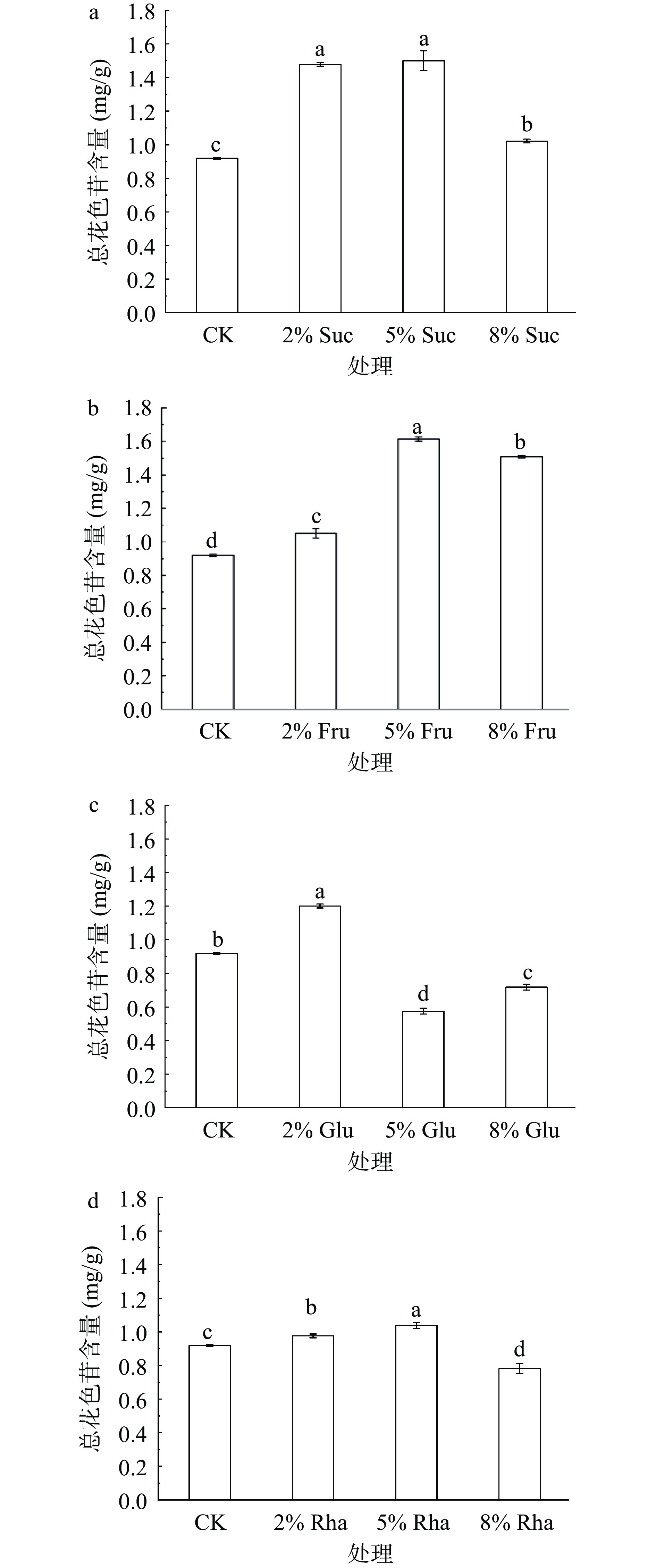
花色苷是红色酿酒葡萄的一个重要品质指标,其生物合成受到多方面因素的影响[6] ,糖不仅决定了果实的甜度与风味,也是果实和其他品质组成成分(如酚类物质、维生素和花色苷等)合成的基础原料[32]。如图2a所示,蔗糖可提高果皮花色苷含量,2% Suc和5% Suc处理之后花色苷含量显著(P<0.05)高于8% Suc处理,2% Suc和5% Suc处理组之间无显著(P>0.05)差异。果糖对花色苷的影响如图2b所示,5% Fru处理组含量最高,与对照组之间存在极显著差异(P<0.01),其次是8% Fru处理组,2% Fru处理组最低,但均高于对照组。从图2c可以看出,2% Glu能够促进果皮中花色苷的积累,而5% Glu和8% Glu会抑制‘小味儿多’果皮花色苷积累,这可能受到浓度的影响,较高浓度的葡萄糖可能通过提供一个高渗透压的环境,从而导致细胞皱缩死亡,进而抑制花色苷的积累[19]。从图2d可知,经2% Rha和5% Rha喷施处理后,‘小味儿多’果皮花色苷含量均高于对照,其中5% Rha处理后花色苷含量较高,显著(P<0.05)高于2% Rha处理,而8% Rha处理组花色苷含量显著(P<0.05)低于对照,这与前人研究不一致,可能与葡萄品种、糖浓度和培养条件有关[30]。总体来看,蔗糖和果糖对花色苷积累的促进效果优于葡萄糖和鼠李糖,果糖促进花色苷积累的最佳浓度为5%,蔗糖为2%和5%。
2.4 离体条件下外源糖对酿酒葡萄‘小味儿多’果皮花色苷酚类物质的影响
非花色苷酚类物质构成葡萄酒的骨架,赋予葡萄酒独特的口感,总酚、单宁、类黄酮和黄烷醇是葡萄果实的重要酚类物质,决定着葡萄酒的涩感、氧化性能等[31−35]。如表3所示,2% Fru处理使总酚含量显著(P<0.05)低于对照,5% Fru与8% Fru处理使果皮总酚含量显著(P<0.05)高于对照,其中8% Fru处理总酚含量最高,为45.87 mg/g;2% Suc处理果皮总酚的含量与对照之间无显著(P>0.05)性的差异,5% Suc和8% Suc处理组总酚含量均显著(P<0.05)低于对照;2% Rha和5% Rha处理使总酚含量均显著(P<0.05)高于对照,其中5% Rha处理总酚含量较高,为42.38 mg/g。2% Glu处理组果皮总酚含量与对照相比无显著(P>0.05)差异,5% Glu和8% Glu处理使总酚含量均显著(P<0.05)低于对照。
表 3 外源糖对‘小味儿多’果皮非花色苷酚类物质的影响Table 3. Effects of exogenous sugars on non-anthocyanin phenolics in ‘Petit Verdot’ grape skin处理 总酚
(mg/g)类黄酮
(mg/g)单宁
(mg/g)黄烷醇
(mg/g)CK 35.21±0.06e 19.72±0.25g 1.71±0.04bc 118.53±1.89g 2% Suc 34.70±0.23e 23.15±0.81cd 1.57±0.01d 151.85±3.22abc 5% Suc 28.05±0.22j 23.31±0.32c 1.21±0.10e 113.84±0.98g 8% Suc 33.18±0.22g 22.67±0.41de 1.73±0.04ab 146.33±3.13cd 2% Fru 33.99±0.24f 24.60±0.28a 1.55±0.07d 149.59±0.96bc 5% Fru 43.40±0.24b 23.32±0.21c 1.81±0.03a 155.49±1.48ab 8% Fru 45.87±0.14a 22.44±0.07e 1.64±0.12bcd 157.24±4.17a 2% Rha 39.26±0.10d 21.55±0.07f 1.62±0.04cd 128.23±5.29f 5% Rha 42.38±0.18c 23.36±0.18c 1.62±0.05cd 137.70±6.90e 8% Rha 28.70±0.09i 17.07±0.1hi 0.85±0.02g 100.60±1.28h 2% Glu 35.08±1.23e 23.99±0.09b 1.54±0.05d 142.27±4.90de 5% Glu 29.12±0.28i 17.33±0.21h 1.11±0.10ef 104.42±1.08h 8% Glu 30.25±0.12h 16.71±0.04i 1.11±0.04f 105.70±0.89h 单宁决定葡萄酒的涩感[33],从表3可知,与对照相比,5% Fru可显著(P<0.05)提高果皮单宁含量,增幅为5.8%,2% Fru和8% Fru均降低果皮单宁含量;8% Suc处理组单宁含量略高于对照组,2% Suc和5% Suc处理组单宁含量均显著(P<0.05)低于对照;三个浓度的葡萄糖处理组单宁含量均显著(P<0.05)低于对照,总体来看,外源糖抑制了酿酒葡萄单宁积累。
由表3可知,三个浓度的果糖处理均可显著(P<0.05)提高果皮类黄酮含量,其中2% Fru处理类黄酮含量较高,为24.60 mg/g,8% Fru处理类黄酮含量较低,类黄酮含量随果糖浓度增加而降低;蔗糖处理后果皮类黄酮含量均显著(P<0.05)高于对照,其中5% Suc处理组最高,为23.31 mg/g,8% Suc处理含量最低,为22.67 mg/g,处理组间变化幅度较小;2% Rha和5% Rha处理使类黄酮含量均显著(P<0.05)高于对照,其中,5%Rha处理使类黄酮含量高于2% Rha处理,为23.36 mg/g,8% Rha处理使类黄酮含量低于对照;2% Glu处理使类黄酮含量高于对照,为23.99 mg/g。5% Glu和8% Glu处理使类黄酮含量均显著(P<0.05)低于对照,综合来看,高浓度葡萄糖和鼠李糖抑制或减少葡萄类黄酮物质积累,低浓度葡萄糖和鼠李糖则促进类黄酮积累,而三个浓度的蔗糖和果糖均促进类黄酮物质积累,与先前研究结果存在一定差异[36]。
如表3所示,与对照相比,三个浓度的果糖均可提高果皮黄烷醇含量,与糖浓度呈正比,8% Fru处理组黄烷醇含量略高于5% Fru处理组;5% Suc处理组黄烷醇含量与对照组无显著(P>0.05)差异,质量浓度为2%的Suc和8% Suc均能提高果皮黄烷醇含量,其中2% Suc处理组黄烷醇增幅最大,增加了28.1%;2% Rha和5% Rha处理均能提高果皮黄烷醇含量,8% Rha处理使黄烷醇含量显著(P<0.05)低于对照;2% Glu能提高果皮黄烷醇含量,5% Glu和8% Glu则都降低了果皮黄烷醇含量。
2.5 主成分分析评价果实综合品质
主成分分析是利用降维的思想,将多个数据转化为少数综合数据,这个分析方法保留了原指标的大部分信息,比单一评价更方便准确[37]。本研究采用SPSS 26.0对外源喷施三个浓度的四种糖处理后的果实可溶性固形物(X1)、还原糖(X2)、可滴定酸(X3)、花色苷(X4)、总酚(X5)、类黄酮(X6)、单宁(X7)和黄烷醇(X8)含量进行主成分分析,结果如表4所示,共提取出两个特征值大于1的主成分,累计贡献率为76.416%,可以解释绝大部分变量信息[38]。
表 4 主成分特征值及累计贡献率Table 4. Principal component characteristic values and cumulative contribution rate主成分 特征值 贡献率(%) 累积贡献率 (%) 1 3.976 49.706 49.706 2 2.137 26.71 76.416 根据各指标主成分特征值(表4)与载荷表(表5) ,以载荷表中每一列的因子除以相对应的特征值的开方得到因子系数,再乘以标准化后的原始数据,计算得到各主成分得分,主成分得分方程式如下:
表 5 主成分载荷表Table 5. Principal component load table指标 成分 1 2 可溶性固形物(X1) −0.506 0.736 可滴定酸(X2) 0.148 0.839 还原糖(X3) −0.14 0.851 花色苷(X4) 0.775 0.374 总酚(X5) 0.821 0.004 类黄酮(X6) 0.858 0.08 单宁(X7) 0.886 −0.102 黄烷醇(X8) 0.94 0.102 Y1=−0.254X1−0.070X2+0.074X3+0.389X4+0.412X5+0.430X6+0.444X7+0.471X8
Y2=0.503X1+0.582X2+0.574X3+0.256X4+0.003X5+0.055X6−0.070X7+0.070X8
以各主成分所对应的贡献率为权重[39],建立综合得分方程式:Y=0.497Y1+0.267Y2,得出各处理主成分1得分(Y1)、主成分2得分(Y2)和综合得分(Y)及排名如表6所示。
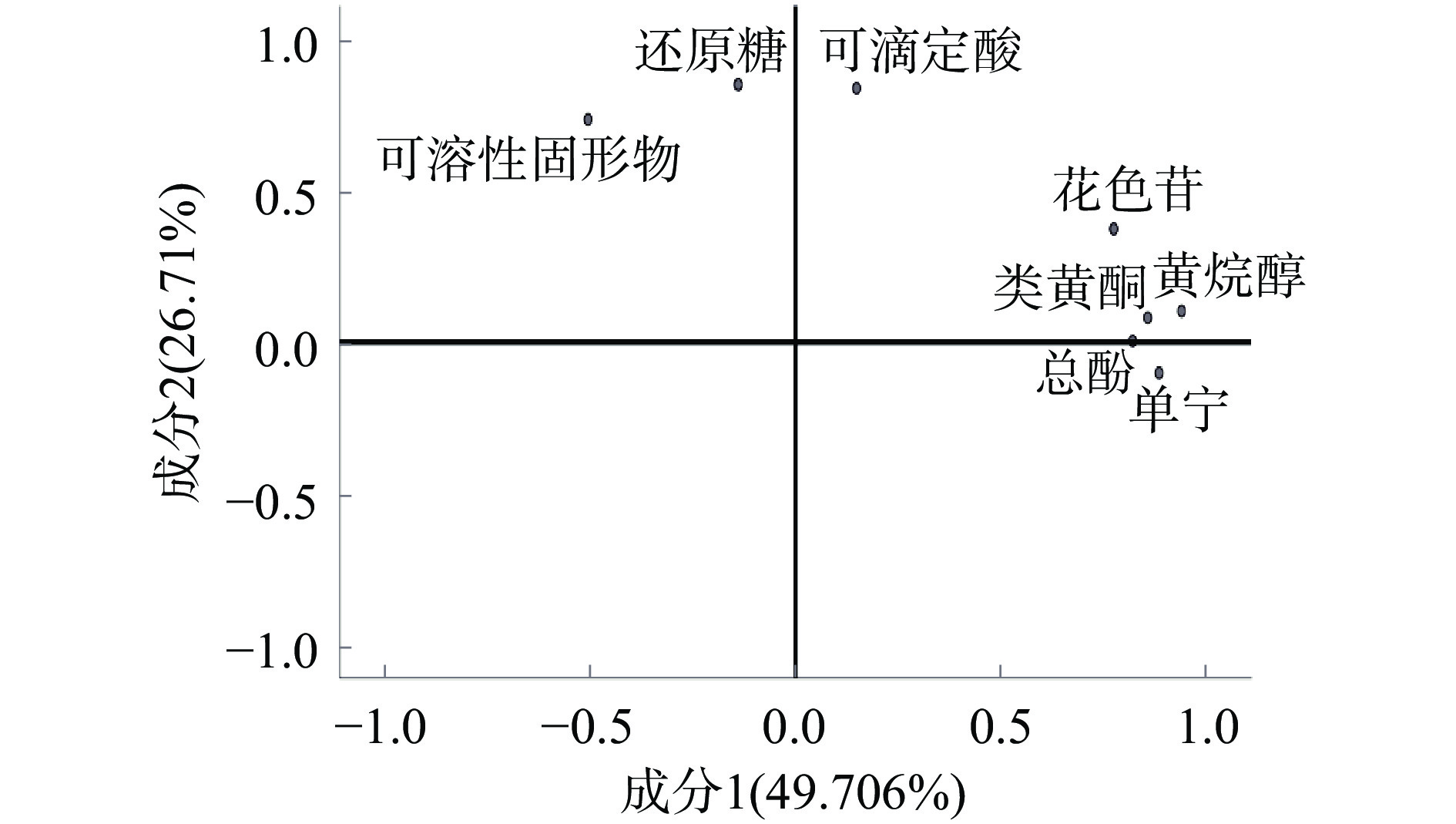
表 6 外源糖处理‘小味儿多’果实品质综合得分及排名Table 6. Comprehensive score and ranking of ‘Petit Verdot’ fruit quality under different exogenous sugars处理 Y1 Y2 Y 综合排名 CK −0.24 −2.38 −0.75 10 2% Suc 0.8 2.82 1.15 3 5% Suc −0.73 1.28 −0.02 8 8% Suc 0.65 0.39 0.43 5 2% Fru 1.2 −2.39 −0.04 9 5% Fru 2.93 −0.8 1.24 2 8% Fru 2.49 0.83 1.46 1 2% Rha 0.28 0.91 0.38 6 5% Rha 1.05 −0.09 0.5 4 8% Rha −3.1 −0.27 −1.61 12 2% Glu 0.75 −0.2 0.32 7 5% Glu −2.96 −1.11 −1.77 13 8% Glu −3.11 1.01 −1.28 11 由图3和表5可知,主成分1的贡献率最大,为49.706%,主要反映了花色苷、总酚、单宁、类黄酮和黄烷醇含量的信息,代表了葡萄果皮酚类物质的含量和品质,主成分2的贡献率为26.71%,主要反映了还原糖、可溶性固形物和可滴定酸含量的信息,代表了果实基本理化品质。
从表6可知,主成分1得分(Y1)最高的为5% Fru,其次是8% Fru,2% Fru第三,说明5% Fru对果皮酚类物质的积累更有效。主成分2的得分(Y2)最高的2% Suc,其次是5% Suc,8% Glu排第三,说明蔗糖能有效改善果实基本理化品质,其中2% Suc对果实基本理化品质改善效果较好。
从表6可知,8%Fru处理组果实综合品质得分最高,其次是5% Fru,排名第3、第4的分别是2% Suc和5% Rha,这也分别代表了不同种类糖处理的最佳浓度。但在葡萄糖中,得分最高的2% Glu,排名在第7位,且5%和8% Glu排名均在CK之后,分别为13和11名。三个浓度的果糖和蔗糖处理组排名均在对照之前,除5% Suc和2% Fru处理组外,其余组均在前6名。由此可见,在提高果实综合品质方面,处理效果最好为果糖,最适浓度为8%,综合排名第1,5% Fru综合排名第2,2% Fru综合排名为第9,仅高于对照组;其次为蔗糖,最适浓度为2%,综合排名为第3,8% Suc综合排名第5,5% Suc综合排名为第8;鼠李糖第3,最适浓度为5%,综合排名在第4位,2% Rha排名第6,8% Rha排名在对照组后面,为第12名;葡萄糖在提高葡萄果实品质方面作用不明显,2% Glu排名在第7位,高于对照组两名,而5%和8% Glu排名均低于对照,分别为13和11名。
3. 结论
在本试验中,果糖、蔗糖和鼠李糖对酿酒葡萄果实品质均有较明显的改善作用,主成分分析结果表明,在提高果实综合品质方面,处理效果最好为果糖,8% Fru综合排名第1,5% Fru综合排名第2,蔗糖的最适浓度为2%,综合排名为第3,鼠李糖的最适浓度为5%,综合排名在第4位,葡萄糖对提高葡萄果实品质作用不明显。从主成分1和主成分2的得分情况来看,果糖对花色苷和酚类物质(主成分1)积累有较明显的促进作用,其中5% Fru得分最高,8% Fru第2,2% Fru第3;蔗糖使可溶性固形物、还原糖和可滴定酸(主成分2)的含量明显增加,其中2% Suc得分最高,5% Suc第2,8% Suc第6。这表明不同种类糖进入果皮细胞后可能有不同的代谢途径和代谢产物,需要进一步深入研究不同种类糖在果皮细胞中的代谢机制。
-
图 1 离体培养过程中四种外源糖对‘小味儿多’转色率的影响
注:a. 蔗糖;b. 果糖;c. 葡萄糖;d. 鼠李糖;图2同。
Figure 1. Effect of exogenous sugars on the color transfer rate of ‘Petit Verdot’ during in vitro culture
表 1 果实着色分级
Table 1 Fruit coloring grading
级别 着色状况 代表值 Ⅰ 红紫色,果面全部着色 1 Ⅱ 基本着色,红色占2/3 2/3 Ⅲ 中度着色,淡红色占1/2 1/2 Ⅳ 果面轻微着色,淡红色占1/3 1/3 Ⅴ 果实全部绿色 0 表 2 外源糖对‘小味儿多’果实可溶性固形物、还原糖和可滴定酸含量的影响
Table 2 Effects of exogenous sugars on soluble solids, reducing sugars and titratable acids in ‘Petit Verdot’ grape berry
处理 可溶性固形物
(%)还原糖
(g/L)可滴定酸
(g/L)CK 4.73±0.03f 25.13±0.98h 14.98±0.06g 2% Suc 6.40±0.00a 44.33±1.16a 16.68±0.09b 5% Suc 5.87±0.09b 34.93±0.37cd 16.49±0.05bc 8% Suc 5.50±0.06cd 32.33±0.77efg 16.54±0.16bc 2% Fru 4.17±0.09h 26.33±0.37h 14.85±0.05g 5% Fru 4.13±0.03h 30.07±0.77g 15.91±0.05e 8% Fru 4.40±0.06g 39.13±0.24b 16.57±0.03bc 2% Rha 5.60±0.00c 33.80±0.31de 17.01±0.08a 5% Rha 5.50±0.06cd 30.60±0.50fg 16.13±0.03d 8% Rha 5.37±0.03d 30.40±0.61g 16.38±0.01c 2% Glu 5.40±0.10d 32.87±0.48def 15.57±0.03f 5% Glu 5.17±0.07e 36.47±1.47c 14.94±0.05g 8% Glu 6.33±0.07a 39.87±0.71b 16.02±0.07de 注:表中数据为平均值±标准差,同列不同小写字母表示不同处理间差异显著(P<0.05);表3同。 表 3 外源糖对‘小味儿多’果皮非花色苷酚类物质的影响
Table 3 Effects of exogenous sugars on non-anthocyanin phenolics in ‘Petit Verdot’ grape skin
处理 总酚
(mg/g)类黄酮
(mg/g)单宁
(mg/g)黄烷醇
(mg/g)CK 35.21±0.06e 19.72±0.25g 1.71±0.04bc 118.53±1.89g 2% Suc 34.70±0.23e 23.15±0.81cd 1.57±0.01d 151.85±3.22abc 5% Suc 28.05±0.22j 23.31±0.32c 1.21±0.10e 113.84±0.98g 8% Suc 33.18±0.22g 22.67±0.41de 1.73±0.04ab 146.33±3.13cd 2% Fru 33.99±0.24f 24.60±0.28a 1.55±0.07d 149.59±0.96bc 5% Fru 43.40±0.24b 23.32±0.21c 1.81±0.03a 155.49±1.48ab 8% Fru 45.87±0.14a 22.44±0.07e 1.64±0.12bcd 157.24±4.17a 2% Rha 39.26±0.10d 21.55±0.07f 1.62±0.04cd 128.23±5.29f 5% Rha 42.38±0.18c 23.36±0.18c 1.62±0.05cd 137.70±6.90e 8% Rha 28.70±0.09i 17.07±0.1hi 0.85±0.02g 100.60±1.28h 2% Glu 35.08±1.23e 23.99±0.09b 1.54±0.05d 142.27±4.90de 5% Glu 29.12±0.28i 17.33±0.21h 1.11±0.10ef 104.42±1.08h 8% Glu 30.25±0.12h 16.71±0.04i 1.11±0.04f 105.70±0.89h 表 4 主成分特征值及累计贡献率
Table 4 Principal component characteristic values and cumulative contribution rate
主成分 特征值 贡献率(%) 累积贡献率 (%) 1 3.976 49.706 49.706 2 2.137 26.71 76.416 表 5 主成分载荷表
Table 5 Principal component load table
指标 成分 1 2 可溶性固形物(X1) −0.506 0.736 可滴定酸(X2) 0.148 0.839 还原糖(X3) −0.14 0.851 花色苷(X4) 0.775 0.374 总酚(X5) 0.821 0.004 类黄酮(X6) 0.858 0.08 单宁(X7) 0.886 −0.102 黄烷醇(X8) 0.94 0.102 表 6 外源糖处理‘小味儿多’果实品质综合得分及排名
Table 6 Comprehensive score and ranking of ‘Petit Verdot’ fruit quality under different exogenous sugars
处理 Y1 Y2 Y 综合排名 CK −0.24 −2.38 −0.75 10 2% Suc 0.8 2.82 1.15 3 5% Suc −0.73 1.28 −0.02 8 8% Suc 0.65 0.39 0.43 5 2% Fru 1.2 −2.39 −0.04 9 5% Fru 2.93 −0.8 1.24 2 8% Fru 2.49 0.83 1.46 1 2% Rha 0.28 0.91 0.38 6 5% Rha 1.05 −0.09 0.5 4 8% Rha −3.1 −0.27 −1.61 12 2% Glu 0.75 −0.2 0.32 7 5% Glu −2.96 −1.11 −1.77 13 8% Glu −3.11 1.01 −1.28 11 -
[1] 张振文. 葡萄酒品种学[M]. 西安: 西安地图出版社, 2000:61−62 ZHANG Z W. Ampelography[M]. Xi'an:Xi'an Map Press, 2000: 61−62.
[2] 张晓煜, 亢艳莉, 袁海燕, 等. 酿酒葡萄品质评价及其对气象条件的响应[J]. 生态学报,2007,27(2):740−745 ZHANG X Y, KANG Y L, YUAN H Y, et al. The quality evaluation of wine grape and its respond to weather condition[J]. Acta Ecologica Sinica,2007,27(2):740−745.
[3] 谢兆森, 王世平, 许文平. 葡萄果实中的糖分积累和调控[J]. 植物生理学通讯,2008(4):178183 XIE Z S, WANG S P, XU W P. Accumulation of sugars and their regulation in grape berries[J]. Plant Physiology Journal,2008(4):178183.
[4] 牛生洋, 武凌峰, 赵瑞香, 等. 葡萄果实花色苷合成调控研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(9):219−223 doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201509041 NIU S Y, WU L F, ZHAO R X, et al. Progress in regulation of anthocyanin biosynthesis in grape berries[J]. Food Science,2015,36(9):219−223. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201509041
[5] GóMEZ GALLEGO M, GóMEZ GARCíA-CARPINTERO E, SáNCHEZ-PALOMO E, et al. Study of phenolic composition and sensory properties of red grape varieties in danger of extinction from the Spanish region of Castilla-La mancha[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2011,234(2):295−303.
[6] 赵新节, 韩爱芹, 杨亲正, 等. 葡萄花色苷合成的影响因素研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2015,36(18):391−394 ZHAO X J, HAN A Q, YANG Q Z, et al. Research on factors influencing the biosynthesis of anthocyanin in grape fruit[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2015,36(18):391−394.
[7] 姜润丽, 马起林, 赵洪康. 酿酒葡萄的整形修剪技术[J]. 落叶果树,2006(6):45−46 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2910.2006.06.021 JIANG R L, MA Q L, ZHAO H K. Shaping and pruning techniques of wine grapes[J]. Deciduous Fruits,2006(6):45−46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-2910.2006.06.021
[8] 王辉, 赵晨霞. 采前栽培技术措施对有机酿酒葡萄品质的影响[J]. 北京农业,2009(3):27−30 WANG H, ZHAO C L. Influence of the cultural technique measure before pick on the quality of organic wine grape[J]. Beijing Agriculture,2009(3):27−30.
[9] 王小龙, 张正文, 钟晓敏, 等. 不同施肥对酿酒葡萄果实产量和品质的影响[J]. 中国南方果树,2020,49(2):107−113 WANG X L, ZHANG Z W, ZHONG X M, et al. Effects of different fertilization on fruit yield and quality of wine grapes[J]. Southern Chinese fruit trees,2020,49(2):107−113.
[10] 张铁兵. 植物生长调节剂在葡萄生产中的应用[J]. 果树资源学报,2021,2(2):60−62 ZHANG T B. Application techniques of plant growth regulators in grape planting[J]. Journal of Fruit Tree Resources,2021,2(2):60−62.
[11] SOLFANELLI C, POGGI A, LORETI E, et al. Sucrose specific induction of the anthocyanin biosynthetic pathway in Arabidopsis[J]. Plant Physiology,2006,140:637−646. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.072579
[12] LARRONDE F, KRISA S, DECENDIT A, et al. Regulation of polyphenol production in Vitis vinifera cell suspension cultures by sugars[J]. Plant Cell Reports,1998,17(12):946. doi: 10.1007/s002990050515
[13] AZUMA A, KOSHITA Y, KOBAYASHI S. Flavonoid biosynthesis-related genes in grape skin are differentially regulated by temperature and light conditions[J]. Planta,2012,236(4):1067−1080. doi: 10.1007/s00425-012-1650-x
[14] PéREZ F, MEZA P, BERTI M, et al. Effect of carbon source and sucrose concentration on growth and hexose accumulation of grape berries cultured in vitro[J]. Plant Cell, Tissue and Organ Culture,2000,61, 37−40. doi: 10.1023/A:1006494918336
[15] ZHENG Y J, LI T, LIU H T, et al. Sugars induce anthocyanin accumulation and flavanone 3-hydroxylase expression in grape berries[J]. Plant Growth Regulation,2009,58(3):251−260. doi: 10.1007/s10725-009-9373-0
[16] 凌亚杰, 莫琴, 莫凡, 等. 外源糖处理对草莓果实品质和主要生物活性物质的影响[J]. 四川农业大学学报,2018,36(1):67−71 LING Y J, MO, MO F, et al. Effects of exogenous sugar treatment on fruit quality and main bioactive compounds in strawberry[J]. Journal of Sichuan Agricultural University,2018,36(1):67−71.
[17] LI D, ZHANG X, XU Y, et al. Effect of exogenous sucrose on anthocyanin synthesis in postharvest strawberry fruit[J]. Food Chemistry,2019(289):112−120.
[18] ZHANG X, LI B, DUAN R, et al. Transcriptome analysis reveals roles of sucrose in anthocyanin accumulation in 'Kuerle Xiangli' ( Pyrus sinkiangensis Yu)[J]. Genes (Basel),2022,13(6):1064. doi: 10.3390/genes13061064
[19] 刘雪峰, 向苹苇, 马晓丽, 等. 外源糖处理对塔罗科血橙果实品质的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学,2021,49(9):48−50,53 LIU X F, XIANG P W, MA X L, et al. Effects of exogenous sugar treatment on the quality of Taroko Blood orange fruit[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Science,2021,49(9):48−50,53.
[20] 彭舒, 张婷渟, 李丽, 等. 外源蔗糖处理对蓝莓果实发育过程关键品质的影响[J]. 绿色科技,2020(17):82−84 PENG S, ZHANG T T, LI L, et al. Effects of exogenous sucrose treatment on key qualities of blueberry fruit development[J]. Journal of Green Science and Technology,2020(17):82−84.
[21] DAI Z W, MEDDAR M, RENAUD C, et al. Long-term in vitro culture of grape berries and its application to assess the effects of sugar supply on anthocyanin accumulation[J]. Journal of Experimental Botany,2014(16):4665.
[22] DAI Z W, MEDDAR M, DELROT S, et al. Development and implementation of an in vitro culture system for intact detached grape berries[J]. Bio-Protocol,2015,5:1510.
[23] MAO J, LI W, MI B, et al. Different exogenous sugars affect the hormone signal pathway and sugar metabolism in “red globe” ( Vitis vinifera L.) plantlets grown in vitro as shown by transcriptomic analysis[J]. Planta,2017,246, 537−552. doi: 10.1007/s00425-017-2712-x
[24] HIRATSUKA S, ONODERA H, KAWAI Y, et al. ABA and sugar effects on anthocyanin formation in grape berry cultured in vitro[J]. Scientia Horticulturae,2001,90(1-2):121−130. doi: 10.1016/S0304-4238(00)00264-8
[25] 栾丽英. 油菜素内酯和脱落酸对酿酒葡萄花色苷调控及葡萄酒品质影响的研究[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2014 LUAN L Y. Study of the regulation of anthocyanin synthesis of grape and the quality of wine after brassinolide and abacisic acid treatments[D]. Yangling:Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, 2014.
[26] 晁无疾, 陆家云. 脱落酸对葡萄上色和果实品质的影响[J]. 中外葡萄与葡萄酒,2008(5):29−30, 34 CHAO W J, LU J Y. Effect of abscisic acid on grape coloring and fruit quality[J]. Sino-overseas Grapevine & Wine,2008(5):29−30, 34.
[27] 王华. 葡萄酒分析检验[M]. 北京:中国农业出版社, 2004:124−128 WANG H. Wine analysis and inspection[M]. Beijing:China Agriculture Press, 2004:124−128.
[28] 苏鹏飞. 宁夏青铜峡产区主栽红色酿酒葡萄成熟度控制指标的研究[D]. 杨凌:西北农林科技大学, 2016 SU P F. Study of maturity control indexes of major red wine grapes from Qingtongxia city in Ningxia[D]. Yangling:Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, 2016.
[29] 郝笑云, 王宏, 张军翔. 酚类物质对红葡萄酒颜色影响的研究进展[J]. 现代食品科技,2013,29(5):1192−1197 HAO X Y, WANG H, ZHANG J X. Research progress of influence of phenolic compounds on color of grape wine[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2013,29(5):1192−1197.
[30] 孙凌俊, 马丽, 王振家. 葡萄果实糖代谢的研究进展[J]. 中外葡萄与葡萄酒,2008,6:70−72 SUN L J, MA L, WANG Z J. Research progress on sugar metabolism in grape fruits[J]. Sino-overseas Grapevine & Wine,2008,6:70−72.
[31] 方芳, 王凤忠. UV-B照射对采后葡萄果实品质和黄酮醇积累的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(19):272−277,283 FANG F, WANG F Z. Effect of UV-B irradiation on fruit quality and flavonol accumulation of postharvest grape berry[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(19):272−277,283.
[32] 王贵元. 红肉脐橙(Citrus sinensis Osbeck cv. Cara Cara Navel orange)果实着色和糖积累规律的研究[D]. 武汉:华中农业大学, 2005 WANG G Y. Study on the rules of coloring and sugar accumulation in Cara Cara Navel orange (Citrus sinensis Osbeck cv. Cara Cara Navel orange)[D]. Wuhan:Central China Agricultural University, 2005.
[33] 回学宽, 王艳丽, 祝贺, 等. 葡萄酒中酚类物质的研究进展[J]. 中国果菜,2019,39(11):65−71,79 HIU X K, WANG Y L, ZHU H. Progress in polyphenol of wines[J]. China Fruit & Vegetable, 2019,39(11):65−71,79.
[34] 王秀芹, 张庆华, 战吉成, 等. 产地与品种对葡萄酒中酚类物质含量的影响[J]. 食品科学,2009,30(21):113−118 doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2009.21.027 WANG X Q, ZHANG Q H, ZHAN J C. Effects of grape varieties and geographical origins on contents of phenolic compounds in grape wine[J]. Food Science,2009,30(21):113−118. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2009.21.027
[35] 赵旭, 张欣珂, 陈新军, 等. 葡萄酒中的酚类物质Ⅱ:辅色效应与生物活性研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(17):284−294 ZHAO X, ZHANG X K, CHEN X J, et al. Phenolics in wines II:Progress in research on co-pigmentation and bioactivities[J]. Food Science,2019,40(17):284−294.
[36] 雷鸣. 植物生长调节剂、糖、光质对红地球葡萄果实品质的影响[D]. 合肥:安徽农业大学, 2008 LEI M. Influence of plant growth regulator, sugar and light quality on fruit quality of Red Globe grapes[D]. Hefei:Anhui Agricultural University, 2008.
[37] 王建芳, 高山, 牟德华. 基于主成分分析和聚类分析的不同品种燕麦品质评价[J]. 食品工业科技, 2020, 41(13):85−91 WANG J F, GAO S, MOU D H, Quality evaluation of different varieties of oat based on principal components analysis and cluster analysis [J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(13):85−91.
[38] 雷月, 宫彦龙, 唐会会, 等. 基于主成分和聚类分析的不同品种贵州禾酿酒适宜性品质评价[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(8):289−300 LEI Y, GONG Y L, TANG H H, et al. Evaluation of brewing suitability quality of Guizhou He varieties based on principal component analysis and cluster analysis[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(8):289−300.
[39] 颜孙安, 史梦竹, 林香信, 等. 基于主成分与聚类分析不同品种鲜食葡萄的氨基酸品质评价[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(6):372−379 YAN S A, SHI M H, LIN X X, et al. Principal component analysis and cluster analysis for evaluating amino acid of different table grapes ( Vitis vinifera L.) varieties[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(6):372−379.





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



