Study on the Dynamics of Differential Metabolites of Pu-erh Tea Fermented by Exogenous Added Bacteria
-
摘要: 为探究外源添加菌在普洱茶发酵过程中的作用,以及对普洱茶品质的影响,以添加不同菌种发酵的普洱茶为研究对象,采用非靶向代谢组学技术结合多元统计分析、差异性热图进行数据分析,探究不同菌种处理的普洱茶在发酵过程中的差异代谢物变化。结果表明,通过对黄酮类、生物碱类、萜类代谢物的种类和相对含量进行分析,发现H组香气花果香带甜香,汤色红亮,滋味浓厚较甜醇;A组香气花香浓郁带蜜香,汤色红亮,浓厚回甘;R组香气果香带乳香,汤色黄亮,滋味浓厚、但涩且透苦,这些品质的不同与锦葵色素、芫花素、儿茶素、咖啡碱、莴苣苦素等代谢物的含量的高低有关。本研究初步探明不同菌种发酵普洱茶的差异代谢物含量变化,其变化对茶叶的滋味、香气、汤色会产生不同的影响,对后续普洱茶发酵提供一定的理论依据。
-
关键词:
- 普洱茶 /
- 外源添加菌 /
- 液相色谱-质谱联用(LC-MS) /
- 差异代谢物 /
- 茶叶品质
Abstract: In order to explore the role of exogenous bacteria in the fermentation process of Pu-erh tea and its impact on tea quality, the present study aimed to explore the differences in metabolite changes during fermentation of Pu-erh tea treated with different bacterial strains. To achieve this, non-targeted metabolomics technology was employed, which was combined with multivariate statistical analysis and differential heat maps. The study analyzed the flavonoids, alkaloids, and terpenoids present in the tea samples. The H group was found to have a fruity and sweet aroma, a bright red soup color, and a strong and sweet taste. The A group had a strong floral and honey aroma, a bright red soup color, and a strong and sweet aftertaste. The R group had a fruity and milky aroma, a bright yellow soup color, and a strong but astringent and bitter taste. These differences in quality were found to be related to the levels of metabolites such as malvidin, genkwanin, catechins, caffeine, and lactucin. The study provided preliminary insights into the differences in metabolite content during the fermentation of Pu-erh tea with different bacterial strains, which can have varying effects on the taste, aroma, and soup color of the tea. The findings of this study could provide theoretical assistance for future Pu-erh tea fermentation. -
普洱茶(熟茶)是以地理标志保护范围内的云南大叶种晒青毛茶为原料,经适度潮水渥堆以及一定时间发酵而成的具有独特品质的茶叶[1]。普洱茶(熟茶)品质形成的关键工序为渥堆发酵,微生物及其代谢产物在普洱茶发酵过程中有着至关重要的作用。近年来,有益微生物接种发酵普洱茶的研究层出不穷,大量研究证明,将有益微生物应用于普洱茶的固态发酵中,可以增加普洱茶的代谢产物含量,大大缩短发酵时间,提升普洱茶的滋味、香气,改变微生物群落结构,进而提高普洱茶的感官风味品质[2−4] 。
红曲霉(M. purpureus)的利用在我国历史悠久,其代谢产物十分丰富,主要次生代谢产物有洛伐他汀、GABA、红曲色素、多不饱和脂肪酸、多酚、麦角固醇、红曲多糖等活性物质[5−6],红曲霉多应用于发酵食品、酿造酒、酱油增色等方面[7−8],李亚莉等[9]人工添加红曲霉发酵普洱茶发现,茶叶的香气和滋味在传统风味的基础上增加了明显的酯香;宋诗颖等[10]将夏秋茶与红曲菌结合,发现红曲菌可将茶叶作为基质进行很好的生物转化。植物乳杆菌是我国卫生部颁布的可用于食品的益生菌之一,被广泛应用于食品发酵中,以提高食品品质及香气的丰富度[11],且植物乳杆菌具有多种益生作用,如降低胆固醇、调节肠道菌群、免疫调节等[12]。王子浩等[13]添加外源乳酸菌发酵普洱茶发现,乳酸菌在一定程度上抑制了茶红素向茶褐素的转化,对普洱茶汤色、品质具有积极作用。茶叶品质与茶叶次级代谢及代谢产物关系密切,在茶叶加工过程中,茶叶中的多酚类、生物碱类、萜类等次级代谢物产物发生了变化,这些次级代谢产物变化对提高茶叶品质,改善茶叶风味有重要作用[14],有研究表明红曲霉和植物乳杆菌有协同作用,植物乳杆菌能够促进红曲霉代谢产物的提高[15],以往研究多为单菌发酵普洱茶,混菌发酵普洱茶的研究较少,本文首次以红曲霉和植物乳杆菌混合接种发酵普洱茶,期望通过两者混合发酵生成新的物质,增加代谢物,提高普洱茶的风味品质。
本文以红曲霉、植物乳杆菌的单菌和混菌发酵普洱茶,对发酵过程中主要的差异代谢物进行研究,以探明外源微生物发酵普洱茶过程中差异代谢物的动态变化,为外源添加菌发酵普洱茶的研究提供一定的参考依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
茶样 购于云南临沧大叶种晒青毛茶;红曲霉(M. purpureus)(专利菌种MPT13,专利号为201010182965) 实验室保存;植物乳杆菌菌种L34(编号为BMZ144978) 宁波明舟生物科技有限公司;甲醇、乙腈、甲酸、水、丙醇 色谱纯,Fisher公司。
DY04-13-38-00 BL-75G灭菌锅 上海博迅实业有限公司;SW-CJ-ZD超净工作台 苏州净化设备有限公司;HPX-250B恒温恒湿培养箱 天津市宏诺仪器有限公司;SKY-210Z摇床 上海苏坤实业有限公司;TripleTOF5600三重四级杆质谱、ExionLC AD液相色谱系统 AB SCIEX公司;BEH C18色谱柱(100 mm×2.1 mm i.d.,1.8 μm) 美国Waters公司;JXDC-20型氮气吹扫仪 上海净信实业发展有限公司;LNG-T88型台式快速离心浓缩干燥器 太仓市华美生化仪器厂;SBL-10TD型超声波清洗机(300 W-10 L) 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 菌液制备
红曲霉菌液:将红曲霉接种于PDA培养基(马铃薯100 g加水煮烂,过滤后加葡萄糖10 g,琼脂9 g,加水融化后补水至500 mL),于温度28 ℃,湿度为70%条件下培养6~8 d后,菌丝用无菌水洗脱,计数后调整浓度为106个/mL,后加入50 mL的无菌水中,制备成菌液。
植物乳杆菌菌液:将植物乳杆菌接种于MRS培养基(蛋白胨5.0 g,牛肉膏粉2.5 g,酵母膏粉2.0 g,葡萄糖10.0 g,吐温80 0.5 mL,磷酸氢二钾1.0 g,乙酸钠2.5 g,、柠檬酸三铵1.0 g、硫酸镁0.1 g、硫酸锰0.025 g、琼脂粉7.5 g、蒸馏水500 mL),于温度28 ℃,湿度为70%条件下培养2~3 d后,用无菌水洗脱菌丝,计数后调整浓度为106个/mL,后加入50 mL的无菌水中,制备成菌液。
1.2.2 茶样制备
根据以往发酵经验及预试验结果,得出以下方案,将50 g晒青毛茶置于玻璃罐中,向晒青毛茶中洒35%清水,在121 ℃、20 min条件下高温高压灭菌,灭菌结束冷却至室温后添加10 mL提前制备好的菌液,后将茶叶与菌液混合均匀进行渥堆发酵,每隔1周(7 d)添加一次菌液,控制温度35±5 ℃、湿度70%~80%、恒温恒湿箱发酵6周,于第2周、第4周、第6周取适量茶样用于后续检测。茶样编号分别为:原料(CK0);每周添加等量的无菌水发酵(CK2、CK4、CK6);每周添加10 mL的植物乳杆菌菌液发酵(R2、R4、R6);每周添加10 mL的红曲霉菌液发酵(H2、H4、H6);第一周添加10 mL的红曲霉,第二周添加10 mL的植物乳杆菌菌液,第三、四、五、六周添加10 mL的红曲霉菌液发酵(A2、A4、A6)。
1.2.3 样品处理
取50 mg样品于1.5 mL离心管中,加入400 μL提取液(乙腈:甲醇=1:1),涡旋混匀30 s后,低温超声提取30 min (5 ℃,40 kHz),将样品静置于-20 ℃,30 min;然后以13000 r/min、4 ℃离心15 min,移取上清液,氮气吹干,120 μL复溶液(乙腈:水=1:1)复溶,低温超声萃取5 min(5 ℃,40 kHz),4 ℃、13000 r/min离心5 min,移取上清液至带内插管的进样小瓶中上机分析。
1.2.4 非挥发性物质色谱质谱采集条件
色谱条件:10 μL样本经BEH C18 色谱柱(100 mm×2.1 mm,1.8 μm)分离后进入质谱检测。流动相A:水(含0.1%甲酸),流动相B:乙腈/异丙醇(1/1)(含0.1%甲酸)。分离梯度见表1,流速为0.40 mL/min,柱温为40 ℃。
表 1 流动相分离梯度Table 1. Flow phase separation gradient时间(min) 流动相A(%) 流动相B(%) 0 95 5 3 80 20 9 5 95 13 5 95 13.1 95 5 16 95 5 质谱条件:采用正负离子扫描模式,质量扫描范围m/z:50~1000。离子喷雾电压,正离子电压5000 V,负离子电压4000 V,去簇电压 80 V,喷雾气50 psi,辅助加热气50 psi,气帘气30 psi,离子源加热温度500 ℃,20~60 V循环碰撞能。
1.3 数据处理
原始数据采用软件Progenesis QI (Waters Corporation,Milford,USA)进行分析。将测出的非挥发性代谢物的保留时间、质荷比、峰强度与代谢公共数据库HMDB和Metlin数据库进行匹配,得到代谢物信息,随后对其进行峰面积积分,并进行积分校正,每个色谱峰的峰面积代表对应物质的相对含量,后续采用美吉生物云平台进行数据分析,相对含量标准化(计算出数据的均值、标准差,然后原始数据减去均值,再除以标准差)处理后作图。
2. 结果分析
2.1 不同菌种发酵阶段的PLS-DA分析
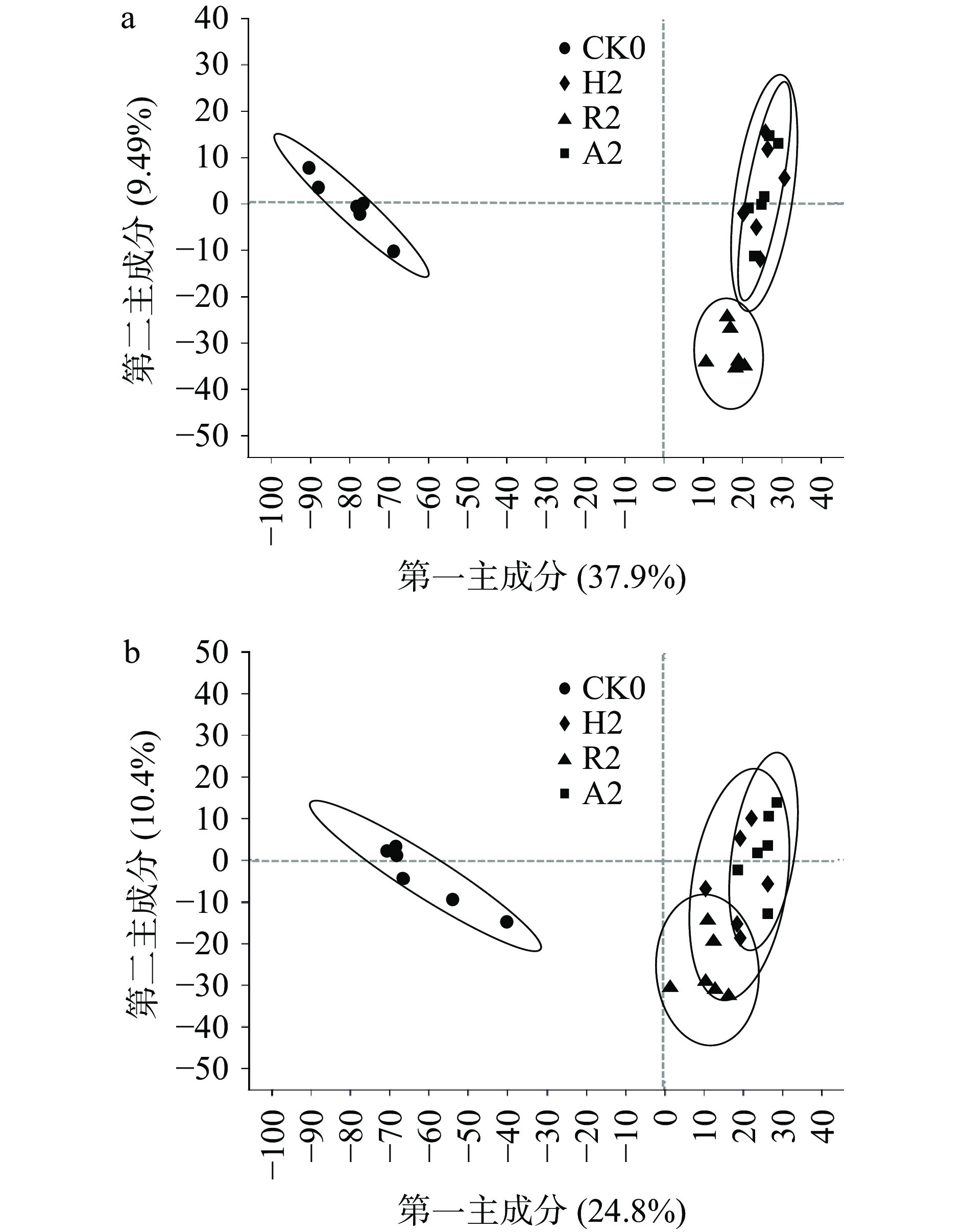
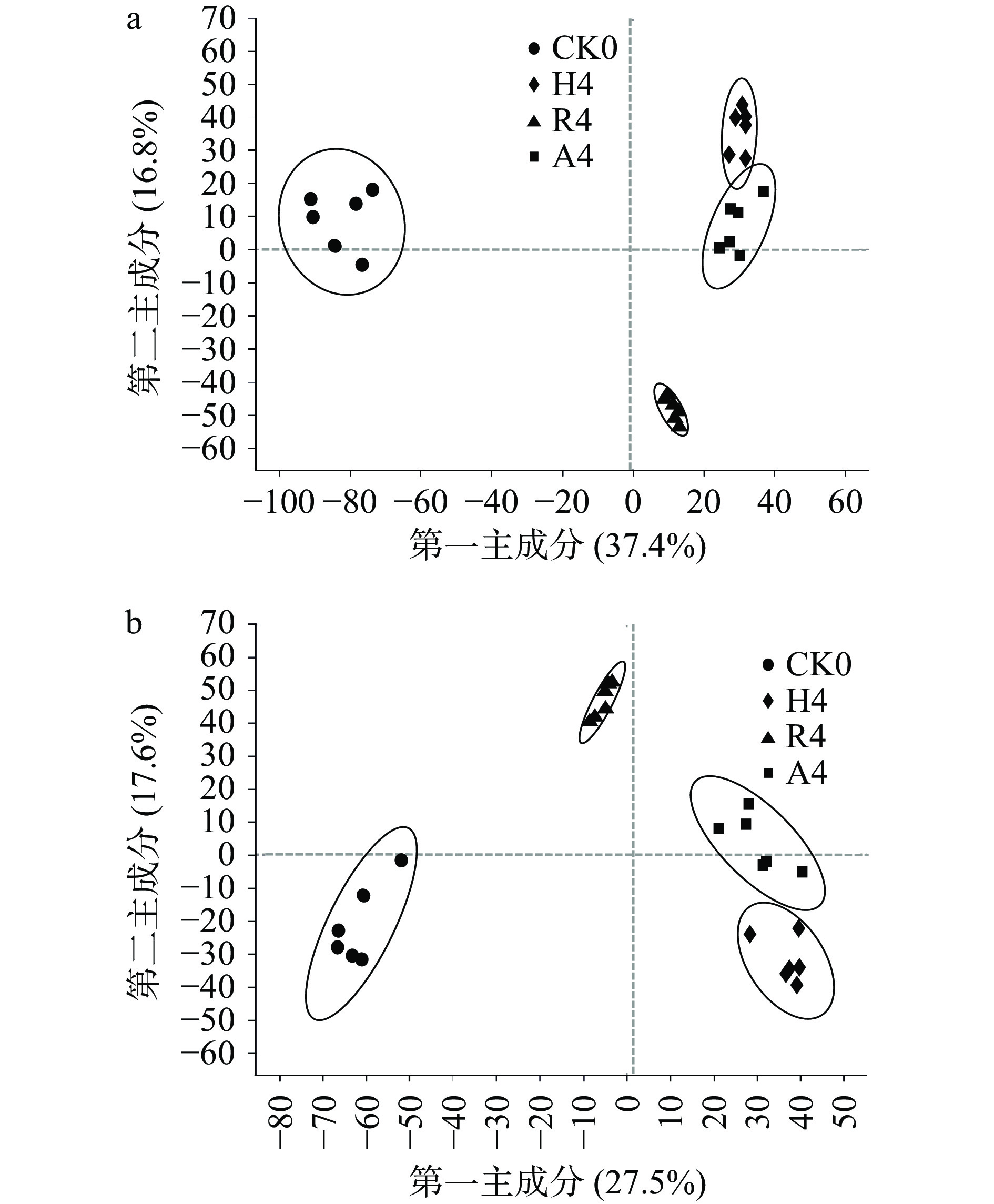
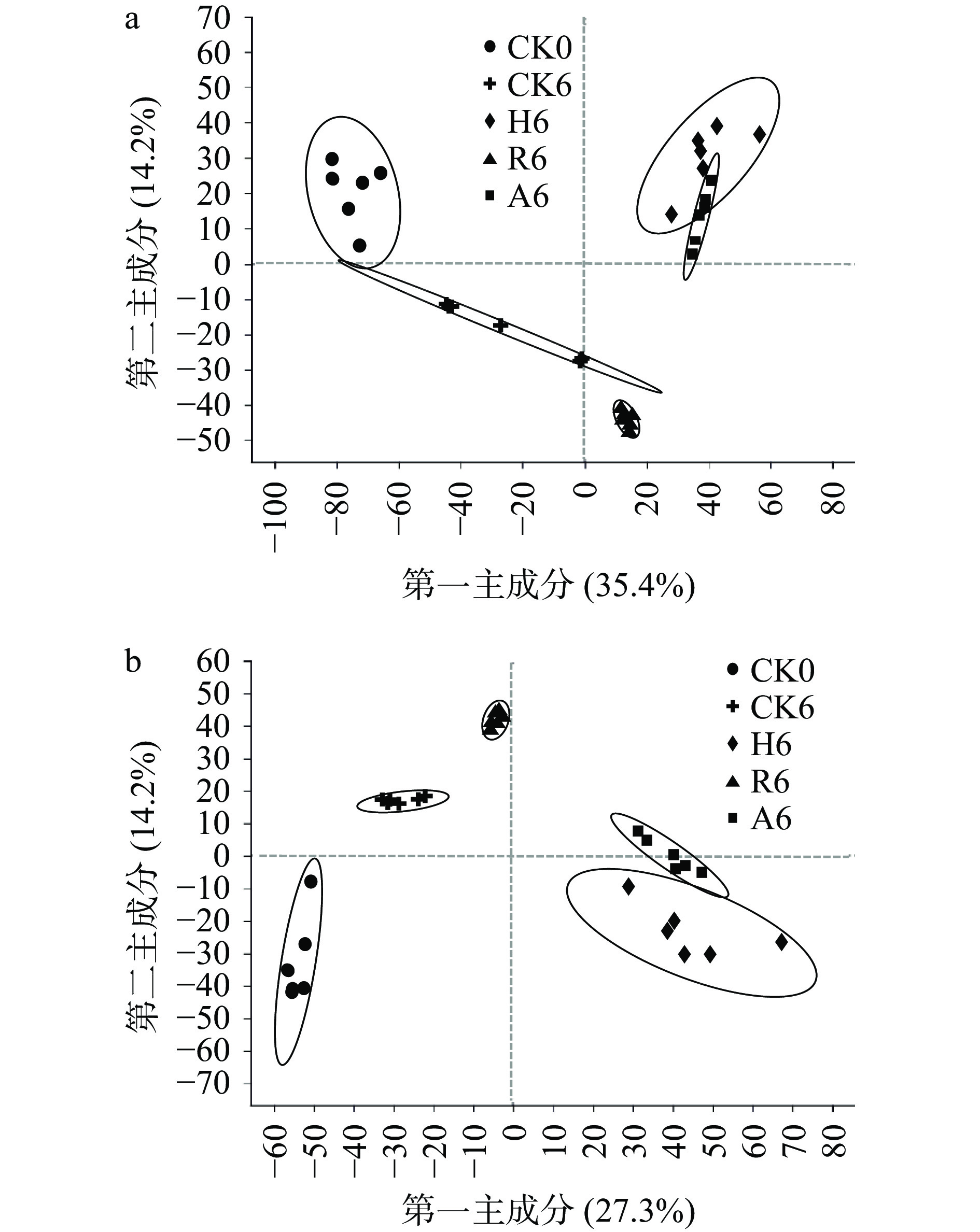
不同菌种不同发酵阶段茶样共检测出1378种代谢物,对于不同发酵阶段的代谢物进行阴阳离子偏最小二乘法判别分析(PLS-DA)。本研究主要比较添加单独菌种和添加混合菌种发酵过程的差异,因此全文主要针对CK0、CK6、R2、R4、R6、H2、H4、H6、A2、A4、A6展开分析。 如图1可看出,在阳离子模式下,A2和H2有重合,在阴离子模式下,R2、H2、A2之间有部分重合,说明发酵两周的普洱茶,其代谢物的变化虽存在一定差异,但也有部分相似;如图2所示,不同菌种发酵的四周阶段样,在阳离子模式下,除H4和A4之间稍有重合外,其他茶样之间都能很好的区分开,在阴离子模式下,所有样品之间都能完全区分开;如图3所示,不同菌种发酵的六周阶段样,阳离子模式下,样品CK0、CK6、R6之间都能够区分开,但H6和A6之间有重合,在阴离子模式下,所有样品之间都能完全区分开;随着发酵时间的延长,代谢物的变化逐渐明显,茶样之间的差异逐渐显著。
2.2 差异代谢物筛选及分析
以VIP>1且P<0.05为筛选条件,对1378种代谢物进行差异代谢物筛选,共筛选出1061种差异代谢物,在KEGG数据库中注释到的总共有217种,植物次级代谢物有64种,其中黄酮类化合物有20种、生物碱类有11种、萜类化合物18种以及其他化合物15种,其他化合物对茶叶品质影响较小,本文不对其进行分析,接下来对黄酮类化合物、生物碱类化合物、萜类化合物的代谢物不同阶段表达量进行分析。
2.2.1 黄酮类代谢物不同发酵阶段表达量变化
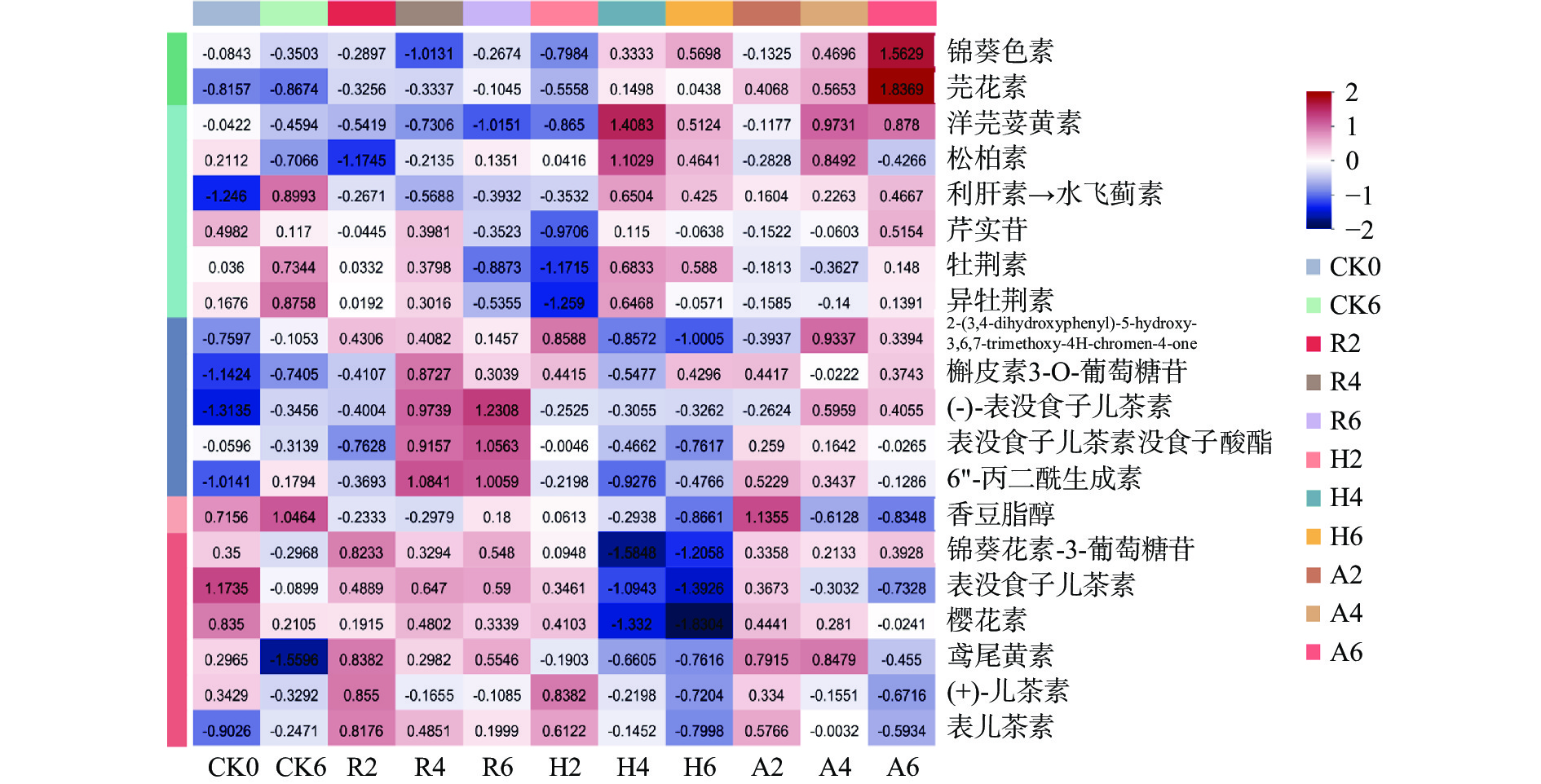
图4为差异代谢物相对含量变化热图,红色越深、数值越大代表该代谢物相对含量越高,蓝色越深、数值越小代表该代谢物相对含量越低。黄酮类化合物在本研究中是差异代谢物数量最多的一类化合物,共有20种,黄酮类化合物是影响茶汤滋味、色泽的物质之一,在发酵的过程中,不同处理的茶叶中代谢物变化趋势如图4所示。
CK组的利肝素→水飞蓟素(利肝素的主要有效成分是水飞蓟素)、牡荆素、异牡荆素、香豆脂醇等的相对含量与原料样相比,发酵后这些物质的相对含量上升;发酵结束后,表没食子儿茶素相对含量与原料样相比下降了很多;在普洱茶渥堆发酵过程中,儿茶素会发生氧化、聚合、降解等反应,使得儿茶素的含量会有不同程度的减少,在高温高湿的环境下,微生物会分泌一些胞外酶,儿茶素会被这些胞外酶不断地氧化降解[16];相对含量明显降低的还有鸢尾黄素,发酵后相对含量明显降低的原因可能是在高温高湿发酵过程中,鸢尾黄素发生了转化[17]。发酵结束后,CK组槲皮素3-O-葡萄糖苷的相对含量比其他组低,可能是外源添加菌发酵普洱茶会促进槲皮素糖苷化的形成,黄酮糖苷类物质的形成对茶汤滋味和色泽具有促进作用[18]。
R组的芫花素、利肝素→水飞蓟素、2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxy-3,6,7-trimethoxy-4H-chromen-4-one、槲皮素3-O-葡萄糖苷、(-)-表没食子儿茶素、表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯、6"-丙二酰生成素、锦葵花素-3-葡萄糖苷、鸢尾黄素、表儿茶素的相对含量在发酵过程中是呈波式增加,其中(-)-表没食子儿茶素、表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯、6"-丙二酰生成素在第六周时相对含量达到最大,R组的儿茶素类代谢物相对含量整体上较其他组高,可能是因为添加植物乳杆菌发酵茶叶会降低儿茶素类物质降解、促进其生物转化,具体机制还有待研究[19]。其他代谢物的相对含量在发酵过程中整体上都呈波动式下降。其中洋芫荽黄素、牡荆素、异牡荆素的相对含量在经过小范围的增减(波动)后,在第六周相对含量达到最小。
H组的锦葵色素、芫花素、洋芫荽黄素、松柏素、利肝素→水飞蓟素、牡荆素、槲皮素3-O-葡萄糖苷、(-)-表没食子儿茶素、6"-丙二酰生成素、表儿茶素的相对含量在发酵过程中呈波动式增加,其中,洋芫荽黄素、松柏素和牡荆素的相对含量从原料开始先是减少,在第四周时增加至最大,后又减少,但整体上相对含量是增加的;除香豆脂醇、鸢尾黄素、表没食子儿茶素和樱花素的相对含量是持续降低趋势外,剩余其他代谢物的相对含量在发酵过程中是波动式下降的趋势,H组的儿茶素类物质相对含量整体上都较低,(-)-表没食子儿茶素、表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯、(+)-儿茶素、表儿茶素相对含量都是先升后降,表没食子儿茶素的相对含量是呈持续性下降趋势,儿茶素是茶汤苦涩味的主要来源[20],红曲霉单菌发酵普洱茶的后期,儿茶素类物质的相对含量降低,从而降低了茶汤的苦涩味,使茶汤更加甜醇。锦葵花素-3-葡萄糖苷是一种花色苷,是花青素与糖形成的一种更为稳定的形式,其相对含量在第四周开始迅速下降,与其他组相比,H组发酵后期的锦葵花素-3-葡萄糖苷相对含量明显较低;樱花素的相对含量在第四周也开始迅速下降,到第六周降到最低。H组在第四周、第六周大部分黄酮类代谢物的变化不是很大。
A组的芫花素、利肝素→水飞蓟素的相对含量在发酵过程中呈持续性增加趋势,锦葵色素、洋芫荽黄素、芹实苷、牡荆素、2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-5-hydroxy-3,6,7-trimethoxy-4H-chromen-4-one、槲皮素3-O-葡萄糖苷、(-)-表没食子儿茶素、表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯、6"-丙二酰生成素、锦葵花素-3-葡萄糖苷、表儿茶素的相对含量在发酵过程中呈波动式增加趋势。值得注意的是,A组的锦葵色素和芫花素的相对含量在第六周时较其他组高的多,锦葵色素是茶树最主要的花青素之一,它具有抗炎、抗氧化等药理活性[21−22],它在第六周时相对含量增加到最大,可能是因为红曲霉和植物乳杆菌共同发酵使得锦葵色素合成酶基因的表达量升高,进而促进了锦葵色素的合成[23];芫花素是一种甲氧基化黄酮,在芫花的干燥花蕾中首次被分离得到,有抗炎、调节免疫、缓解疼痛、抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶等作用[24]。
如表2所示,发酵结束后H组和A组的汤色为红亮,CK组和R组的汤色为黄亮,可能是锦葵色素、芫花素、锦葵花素-3-葡萄糖苷等代谢物的含量造成了不同茶样的汤色差异;发酵结束后R组的滋味为浓厚、涩且透苦,而A组为浓厚回甘、H组为浓厚较甜醇,可能是儿茶素类代谢物的含量高造成了R组茶样滋味的苦涩。
表 2 不同菌种发酵阶段的普洱茶感官品质变化Table 2. Sensory quality changes of Pu-erh tea in different fermentation stages样品 外形 香气 汤色 滋味 CK0 墨绿带毫 馥郁带花香 浅黄亮 浓厚回甘 CK6 乌黑泛棕 浓郁带花果香 黄亮 浓厚回甘 R2 乌黑紧实 酒曲香馥郁 黄亮 甜醇带果酸 R4 乌黑紧结 馥郁带花果香 黄亮 浓厚显涩 R6 乌黑带棕红 浓郁果香带乳香 黄(+)亮 浓厚涩透苦 H2 乌黑带毫 米曲香、甜香、花香 橙黄亮 甜醇回甘 H4 乌黑润、紧结 馥郁带花果香 橙红亮 浓厚回甘 H6 乌黑显红 浓郁花果香带甜香 红亮 浓厚较甜醇 A2 乌黑紧结 浓郁复合香 黄尚亮 浓厚微涩 A4 乌黑紧实 馥郁复合香 橙红亮 浓厚回甘 A6 乌黑显红 花香浓郁带蜜香 红亮 浓厚回甘 2.2.2 生物碱类代谢物不同发酵阶段表达量变化
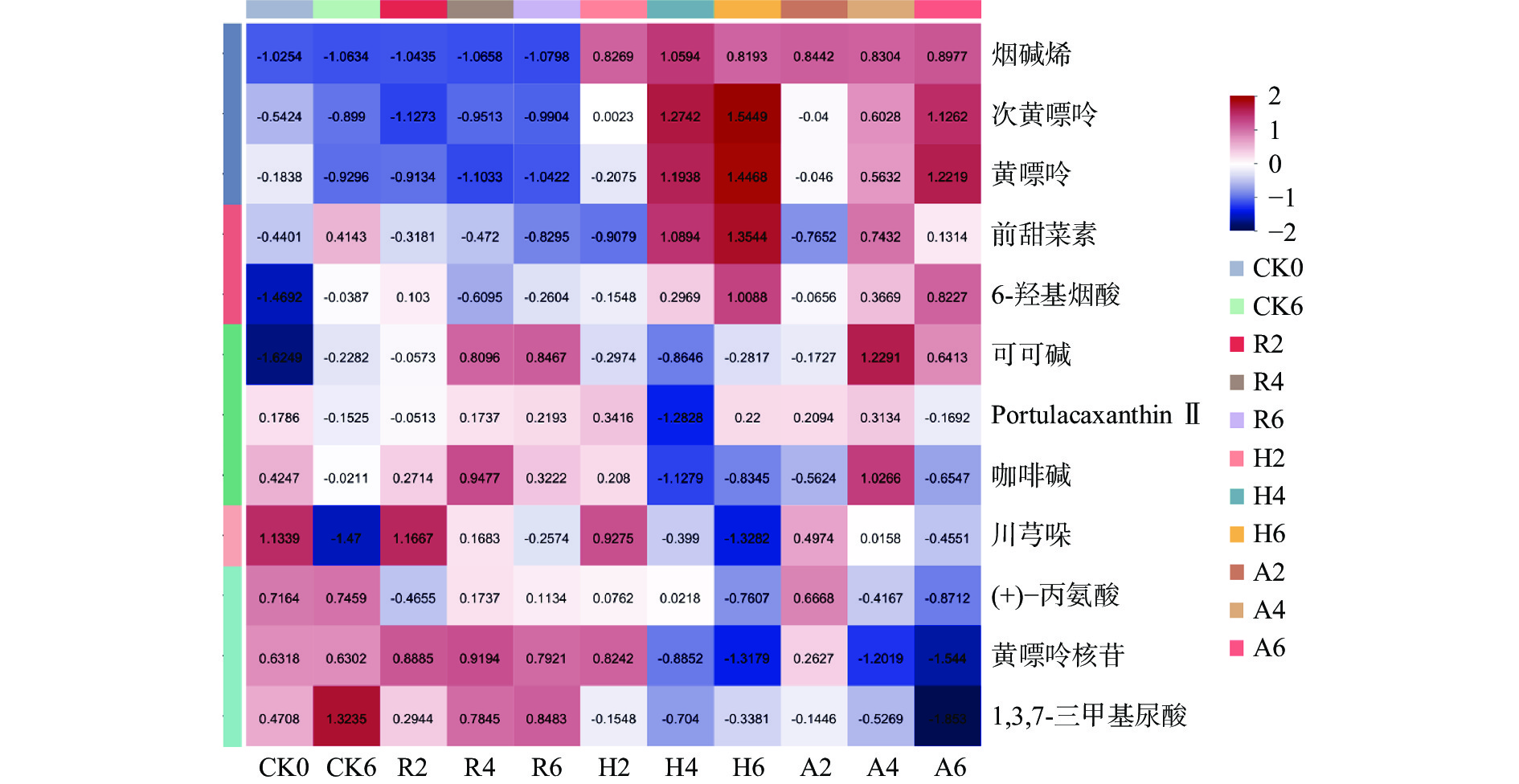
茶叶生物碱是指茶叶富含的一类含氮杂环结构的有机化合物,是茶叶中重要的化学成分之一,是形成茶叶滋味的重要物质,同时也是对人体有益的功能成分。随着发酵的进行,不同发酵处理的茶叶中代谢物变化趋势如图5所示。
CK组发酵后前甜菜素、6-羟基烟酸、可可碱、1,3,7-三甲基尿酸的相对含量增加,黄嘌呤核苷、烟碱烯的相对含量变化不大,川芎哚的相对含量明显减少。有研究发现,1,3,7-三甲基尿酸是咖啡碱生成苦茶碱的中间体[25],1,3,7-三甲基尿酸先是由咖啡碱氧化、异构化转化而成,再由1,3,7-三甲基尿酸形成苦茶碱[26],CK组发酵后1,3,7-三甲基尿酸的相对含量增加,咖啡碱的相对含量减少,可能是在发酵的过程中,咖啡碱部分氧化产生1,3,7-三甲基尿酸[27]。
R组的可可碱相对含量在发酵过程中呈持续性增加趋势,6-羟基烟酸、portulacaxanthinⅡ、黄嘌呤核苷、1,3,7-三甲基尿酸的相对含量在发酵过程中呈波动式增加,烟碱烯的相对含量增减变化不大,次黄嘌呤、黄嘌呤、可可碱、portulacaxanthinⅡ、1,3,7-三甲基尿酸的相对含量在第四周到第六周变化不大,咖啡碱也是影响茶叶品质的因素之一,与茶汤苦味及鲜爽味有关。R组在发酵过程中,咖啡碱的相对含量先减少后增加再减少,第四周增加至最大。烟碱烯、次黄嘌呤、黄嘌呤、前甜菜素的相对含量在发酵过程中都较低。
H组的次黄嘌呤、6-羟基烟酸相对含量在发酵过程中不断增加,烟碱烯、黄嘌呤、前甜菜素、可可碱、portulacaxanthinⅡ的相对含量在发酵过程中呈波动式增加,川芎哚的相对含量持续减少,咖啡碱、黄嘌呤核苷、1,3,7-三甲基尿酸的相对含量呈波动式减少趋势。发酵过程中,咖啡碱、可可碱、黄嘌呤核苷的相对含量较低,次黄嘌呤、黄嘌呤的相对含量较高,次黄嘌呤的增加,可能与咖啡碱、可可碱的降解代谢有关,在嘌呤代谢过程中,黄嘌呤核苷也可生成黄嘌呤[28],猜测这是使黄嘌呤核苷相对含量减少,而黄嘌呤相对含量增加的原因。烟碱烯的相对含量与原料相比明显增加,第二周至第六周的变化不大,次黄嘌呤、黄嘌呤、前甜菜素、咖啡碱、黄嘌呤核苷的相对含量在第四周到第六周变化不大。
A组的次黄嘌呤、黄嘌呤、6-羟基烟酸的相对含量在发酵过程中持续增加,烟碱烯、前甜菜素、可可碱的相对含量呈波动式增加趋势,川芎哚、黄嘌呤核苷、1,3,7-三甲基尿酸的相对含量持续减少,咖啡碱的相对含量在发酵过程中先减少再到第四周增加到最大后又减少。在发酵的过程中,R组和A组的咖啡碱相对含量在第四周最高,而H组的咖啡碱相对含量在第四周最低,可能是添加植物乳杆菌后可以增加咖啡碱的合成,也有可能是添加红曲霉可以加快咖啡碱的降解,具体原因有待研究[29]。R组和A组的可可碱相对含量在第四周到第六周明显高于其他两组。
如表2,R组从第二周开始出现苦、涩滋味,而H组和A组整体滋味为浓厚回甘,造成这种差异的原因可能是烟碱烯、次黄嘌呤、黄嘌呤、6-羟基烟酸、咖啡碱含量的高低;发酵结束A组为浓厚回甘而H组为浓厚较甜醇,可能是可可碱和前甜菜素的含量使得H组茶汤滋味较甜醇。
2.2.3 萜类代谢物不同发酵阶段表达量变化
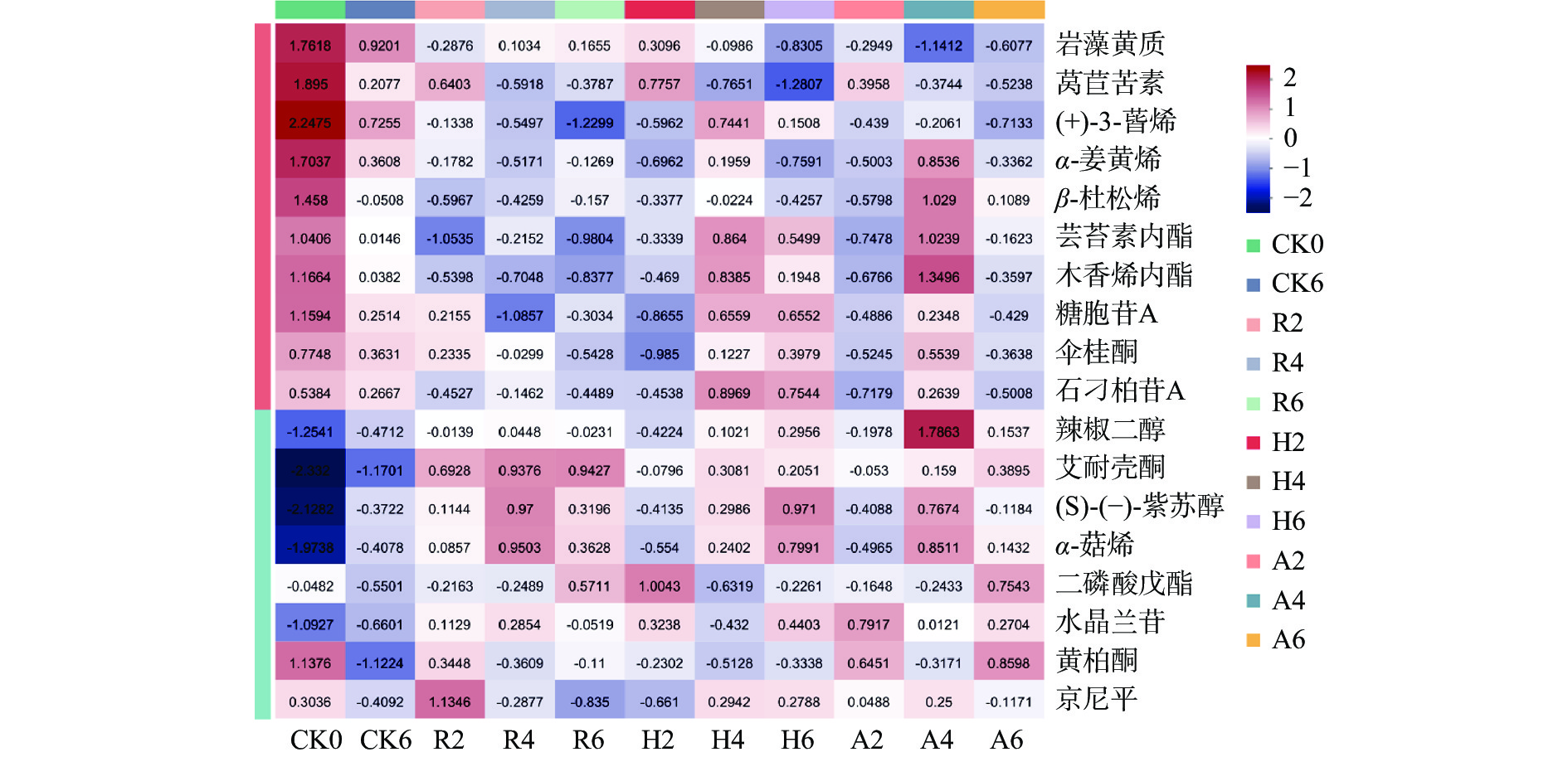
萜类化合物广泛存在于自然界,是一类由异戊二烯为基本结构单元构建的化合物,按异戊二烯单位的数目可分为单萜、倍半萜、二萜、二倍半萜、三萜、四萜、多萜[30],一般单萜和倍半萜较多。萜类化合物是构成某些植物的香精、树脂、营养制品等的主要成分,是茶叶香气的主要来源,也是评价茶叶品质的重要指标。随着发酵的进行,不同发酵处理的茶叶中代谢物变化趋势如图6所示。
整体来看,岩藻黄质、莴苣苦素、(+)-3-蒈烯、α-姜黄烯、β-杜松烯的相对含量在发酵结束后均明显下降,CK组下降的比其他组少,其中的莴苣苦素在R组、H组、A组的第二周含量较高,随着发酵的进行,其相对含量开始不同程度地降低;芸苔素内酯、木香烯内酯、糖胞苷A、伞桂酮、石刁柏苷A的相对含量在R组整个发酵过程中都相对较低,而在H组的第四周、第六周、A组的第四周其含量相对较高,可以看出,添加植物乳杆菌发酵会使这些物质的相对含量降低,而添加红曲霉发酵后,这些物质的相对含量在前期减少,而在后期开始增加,有研究表明,有些微生物可以增加萜类物质的含量,可能是添加红曲霉发酵后,促进了某些萜类物质的合成[31]。辣椒二醇、艾耐壳酮、(S)-(-)-紫苏醇、α-萜烯的相对含量在发酵的过程中呈不同程度的增加,其中辣椒二醇的相对含量在A组的第四周时达到最大,相对含量明显高于其他,辣椒二醇属于倍半萜类化合物,而倍半萜类物质对生物转化具有高度敏感性,某些微生物会对倍半萜类化合物的生物转化更加高效,辣椒二醇在第四周含量最大,猜测可能是红曲霉和植物乳杆菌混合发酵,使得辣椒二醇的生物转化更加高效,具体机制有待研究[32]。艾耐壳酮的相对含量在R组整个发酵过程都较高,可能是植物乳杆菌对它的合成具有促进作用。H组的第四周、第六周以及A组的第四周的萜类代谢物大部分含量都较高。
如表2所示,发酵结束后,R组香气为浓郁果香带乳香,H组香气为浓郁花果香带甜香,A组香气为花香浓郁带蜜香,发现植物乳杆菌发酵会产生乳香,红曲霉发酵会产生甜香,混合发酵的香气更加丰富。
3. 结论
本研究基于LC-MS技术研究外源添加菌发酵普洱茶过程中的差异代谢物动态变化, 发酵过程中,茶样之间的代谢物差异逐渐明显,锦葵色素、芫花素、锦葵花素-3-葡萄糖苷等代谢物的含量造成了不同茶样汤色的差异;儿茶素、咖啡碱、可可碱等代谢物的含量变化影响了茶汤滋味;芸苔素内酯、木香烯内酯、α-萜烯等代谢物含量的不同对茶样风味品质有不同的影响。除此之外,还发现添加红曲霉发酵普洱茶时,部分黄酮类、生物碱类、萜类物质在第四周到第六周的变化不大,这为缩短普洱茶发酵时间提供了一个新思路。本研究通过对发酵过程中普洱茶代谢产物的变化进行分析,初步探明了添加不同菌种发酵普洱茶中的差异代谢物,明确发酵过程中各代谢物的变化,为开发新型风味的普洱茶产品提供一定的参考依据。本研究仅为实验室小型试验,若应用于产品,则还需根据实际情况进一步改进。
-
表 1 流动相分离梯度
Table 1 Flow phase separation gradient
时间(min) 流动相A(%) 流动相B(%) 0 95 5 3 80 20 9 5 95 13 5 95 13.1 95 5 16 95 5 表 2 不同菌种发酵阶段的普洱茶感官品质变化
Table 2 Sensory quality changes of Pu-erh tea in different fermentation stages
样品 外形 香气 汤色 滋味 CK0 墨绿带毫 馥郁带花香 浅黄亮 浓厚回甘 CK6 乌黑泛棕 浓郁带花果香 黄亮 浓厚回甘 R2 乌黑紧实 酒曲香馥郁 黄亮 甜醇带果酸 R4 乌黑紧结 馥郁带花果香 黄亮 浓厚显涩 R6 乌黑带棕红 浓郁果香带乳香 黄(+)亮 浓厚涩透苦 H2 乌黑带毫 米曲香、甜香、花香 橙黄亮 甜醇回甘 H4 乌黑润、紧结 馥郁带花果香 橙红亮 浓厚回甘 H6 乌黑显红 浓郁花果香带甜香 红亮 浓厚较甜醇 A2 乌黑紧结 浓郁复合香 黄尚亮 浓厚微涩 A4 乌黑紧实 馥郁复合香 橙红亮 浓厚回甘 A6 乌黑显红 花香浓郁带蜜香 红亮 浓厚回甘 -
[1] 段凤敏, 孙力元, 魏用林. GB/T 22111-2008《地理标志产品 普洱茶》标准的分析探讨[J]. 安徽农业科学,2018,46(3):173−177,182. [DUAN F M, SUN L Y, WEI Y L. GB/T 22111-2008《Standard of Pu-erh tea》of geographical indication products analysis discussion[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Science,2018,46(3):173−177,182. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2018.03.054 DUAN F M, SUN L Y, WEI Y L . GB/T 22111-2008《Standard of Pu-erh tea》of geographical indication products analysis discussion[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Science,2018 ,46 (3 ):173 −177,182 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2018.03.054[2] JENG K C, CHEN C S, FANG Y P, et al. Effect of microbial fermentation on content of statin, GABA, and polyphenols in Pu-erh tea[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2007,55(21):8787−8792.
[3] 彭翠珍, 刘川, 李晚谊. 云南普洱茶人工接种发酵研究[J]. 云南大学学报(自然科学版),2008(S1):351−355. [PENG C Z, LIU C, LI W Y. Research on artificial inoculation fermentation of Yunnan Pu-erh tea[J]. Journal of Yunnan University (Natural Science Edition),2008(S1):351−355. PENG C Z, LIU C, LI W Y . Research on artificial inoculation fermentation of Yunnan Pu-erh tea[J]. Journal of Yunnan University (Natural Science Edition),2008 (S1 ):351 −355 .[4] 刘琨毅, 王利妍, 安江珊, 等. 接种地衣芽孢杆菌发酵的普洱茶品质与微生物群落分析[J]. 食品科学技术学报,2022,40(2):108−118. [LIU K Y, WANG L Y, AN J S, et al. Analysis of quality and microbial communities of Pu-erh tea through inoculation fermentation with Bacillus licheniformis[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2022,40(2):108−118. doi: 10.12301/spxb202100420 LIU K Y, WANG L Y, AN J S, et al . Analysis of quality and microbial communities of Pu-erh tea through inoculation fermentation with Bacillus licheniformis[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2022 ,40 (2 ):108 −118 . doi: 10.12301/spxb202100420[5] 颜丽, 刘秀河, 李钰涵. 红曲霉代谢产物的研究进展与应用[J]. 中国调味品,2020,45(7):191−193. [YAN L, LIU X H, LI Y H. Research progress and application of metabolites from Monascus[J]. China Seasoning,2020,45(7):191−193. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2020.07.043 YAN L, LIU X H, LI Y H . Research progress and application of metabolites from Monascus[J]. China Seasoning,2020 ,45 (7 ):191 −193 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2020.07.043[6] PATAKOVA P. Monascus secondary metabolites:Production and biological activity[J]. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology,2013,40(2):169−181. doi: 10.1007/s10295-012-1216-8
[7] SRIANTA I, RISTIARINI S, NUGERAHANI I, et al. Recent research and development of Monascus fermentation products[J]. International Food Research Journal,2014,21(1):1−12.
[8] REN X Y, HE Z G, LIN X J, et al. Screening and evaluation of Monascus purpureus FJMR24 for enhancing the raw material utilization rate in rice wine brewing[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2021,101(1):185−193.
[9] 李亚莉, 黑利生, 秘鸣, 等. 产洛伐他汀紫色红曲霉发酵普洱茶初探[J]. 食品与发酵科技,2013,49(2):34−39. [LI Y L, HEI L S, MI M, et al. Application of Monascus purpureus MPT13 producing lovastatin for Pu-erh tea fermentation[J]. Food and Fermentation Science and Technology,2013,49(2):34−39. LI Y L, HEI L S, MI M, et al . Application of Monascus purpureus MPT13 producing lovastatin for Pu-erh tea fermentation[J]. Food and Fermentation Science and Technology,2013 ,49 (2 ):34 −39 .[10] 宋诗颖, 林雨蝶, 周罗娜, 等. 红曲发酵夏秋茶菌种筛选及基质适生性研究[J]. 食品科技,2022,47(10):62−69. [SONG S Y, LIN Y D, ZHOU L N, et al. Screening of Monascus fermented summer and autumn tea and study on substrate adaptability[J]. Food Technology,2022,47(10):62−69. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2022.10.045 SONG S Y, LIN Y D, ZHOU L N, et al . Screening of Monascus fermented summer and autumn tea and study on substrate adaptability[J]. Food Technology,2022 ,47 (10 ):62 −69 . doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2022.10.045[11] 陈瑞鑫, 牛诗源, 赵雨欣, 等. 益生菌发酵模拟芒果汁特性及产香能力分析[J]. 中国酿造,2022,41(7):87−93. [CHEN R X, NIU S Y, ZHAO Y X, et al. Characteristics of probiotic in the fermentation of simulated mango juice and its aroma production ability analysis[J]. China Brewing,2022,41(7):87−93. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2022.07.016 CHEN R X, NIU S Y, ZHAO Y X, et al . Characteristics of probiotic in the fermentation of simulated mango juice and its aroma production ability analysis[J]. China Brewing,2022 ,41 (7 ):87 −93 . doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2022.07.016[12] KHARE A, GAUR S. Cholesterol-lowering effects of Lactobacillus species[J]. Current Microbiology,2020,77(4):638−644.
[13] 王子浩, 秦廷发, 张可, 等. 外源添加乳酸菌发酵对云南普洱茶特征成分的影响[J]. 云南农业大学学报,2014,29(6):867−872. [WANG Z H, QIN T F, ZHANG K, et al. Effect of lactic acid bacteria inoculation fermentation on the characteristic chemical composition of Yunnan Pu-erh tea[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University,2014,29(6):867−872. WANG Z H, QIN T F, ZHANG K, et al . Effect of lactic acid bacteria inoculation fermentation on the characteristic chemical composition of Yunnan Pu-erh tea[J]. Journal of Yunnan Agricultural University,2014 ,29 (6 ):867 −872 .[14] 虞昕磊, 艾于杰, 曲凤凤, 等. 代谢组学在研究茶叶品质形成中的应用[J]. 茶叶科学,2018,38(1):20−32. [YU X L, AI Y J, QU F F, et al. Metabolomics application in the study of tea quality formation[J]. Tea Science,2018,38(1):20−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2018.01.003 YU X L, AI Y J, QU F F, et al . Metabolomics application in the study of tea quality formation[J]. Tea Science,2018 ,38 (1 ):20 −32 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2018.01.003[15] 陈璐, 祁勇刚, 王常苏, 等. 多菌混合发酵红曲生产Monacolin K与GABA的研究[J]. 中国酿造,2012,31(11):124−128. [CHEN L, QI Y G, WANG C S, et al. Study on the production of Monacolin K and GABA by multibacterial mixed fermentation of red yeast[J]. China Brewing,2012,31(11):124−128. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5071.2012.11.033 CHEN L, QI Y G, WANG C S, et al . Study on the production of Monacolin K and GABA by multibacterial mixed fermentation of red yeast[J]. China Brewing,2012 ,31 (11 ):124 −128 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5071.2012.11.033[16] 罗燕, 唐玉雪, 文敏, 等. 青砖茶渥堆过程中理化特性及细菌多样性分析[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(16):5128−5136. [LUO Y, TANG Y X, WEN M, et al. Analysis of physicochemical property and bacterial diversity during the pile-fermentation of Qingzhuan tea[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2022,13(16):5128−5136. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.16.spaqzljcjs202216005 LUO Y, TANG Y X, WEN M, et al . Analysis of physicochemical property and bacterial diversity during the pile-fermentation of Qingzhuan tea[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2022 ,13 (16 ):5128 −5136 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.16.spaqzljcjs202216005[17] 杨雅雯, 刘勇, 刘雨, 等. 不同干燥方法对射干药材干燥特性、外观性状和有效成分的影响[J]. 中国中药杂志,2021,46(2):366−373. [YANG Y W, LIU Y, LIU Y, et al. Effects of different drying methods on drying characteristics, appearance and active ingredients of Belamcanda chinensis[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2021,46(2):366−373. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20201022.305 YANG Y W, LIU Y, LIU Y, et al . Effects of different drying methods on drying characteristics, appearance and active ingredients of Belamcanda chinensis[J]. China Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2021 ,46 (2 ):366 −373 . doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20201022.305[18] 曾议霆, 吴雪莉, 杨春梅, 等. 基于非靶向代谢组学比较不同发酵方式红茶滋味物质差异[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(16):5288−5296. [ZENG Y T, WU X L, YANG C M, et al. Comparison of taste substances of black tea with different fermentation methods based on non-targeted metabolomics[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Testing,2022,13(16):5288−5296. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.16.spaqzljcjs202216024 ZENG Y T, WU X L, YANG C M, et al . Comparison of taste substances of black tea with different fermentation methods based on non-targeted metabolomics[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Testing,2022 ,13 (16 ):5288 −5296 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2022.16.spaqzljcjs202216024[19] 李海燕, 罗程, 李瑶, 等. 酸茶加工工艺、成分、微生物多样性及生物学功效研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技, 2023, 44(14):430−437. [LI H Y, LUO C, LI Y, et al. Research progress on processing technology, composition, microbial diversity and biological efficacy of sour tea[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(14):430−437. LI H Y, LUO C, LI Y, et al. Research progress on processing technology, composition, microbial diversity and biological efficacy of sour tea[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2023, 44(14): 430−437.
[20] 张英娜, 嵇伟彬, 许勇泉, 等. 儿茶素呈味特性及其感官分析方法研究进展[J]. 茶叶科学,2017,37(1):1−9. [ZHANG Y N, JI W B, XU Y Q, et al. Rewiew on taste characteristic of catechins and its sensory analysis method[J]. Tea Science,2017,37(1):1−9. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2017.01.001 ZHANG Y N, JI W B, XU Y Q, et al . Rewiew on taste characteristic of catechins and its sensory analysis method[J]. Tea Science,2017 ,37 (1 ):1 −9 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2017.01.001[21] LIU X Y, ZHENG F, LI S, et al. Malvidin and its derivatives exhibit antioxidant properties by inhibiting MAPK signaling pathways to reduce endoplasmic reticulum stress in ARPE-19 cells[J]. Food & Function,2021,12(16):7198−7213.
[22] BASTIN A R, SADEGHI A, ABOLHASSANI M, et al. Malvidin prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells[J]. Iubmb Life,2020,72(7):1504−1514. doi: 10.1002/iub.2286
[23] 许倩, 张晨, 吴嘉维, 等. 花青素的生物合成研究进展[J]. 林产化学与工业,2020,40(3):1−11. [[XU Q, ZHANG C, WU J W, et al. Advances in the biosynthesis of anthocyanins[J]. Chemistry and Industry of Forest Products,2020,40(3):1−11. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2417.2020.03.001 [XU Q, ZHANG C, WU J W, et al . Advances in the biosynthesis of anthocyanins[J]. Chemistry and Industry of Forest Products,2020 ,40 (3 ):1 −11 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-2417.2020.03.001[24] 江友娅, 陈琦, 张露, 等. 芫花素对 α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(15):43−47. [JIANG Y Y, CHEN Q, ZHANG L, et al. Inhibitory effect of genkwanin on α-glucosidase[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(15):43−47. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020110126 JIANG Y Y, CHEN Q, ZHANG L, et al . Inhibitory effect of genkwanin on α-glucosidase[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021 ,42 (15 ):43 −47 . doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020110126[25] ZHANG Y H, LI Y F, WANG Y J, et al. Identification and characterization of N9-methyltransferase involved in converting caffeine into non-stimulatory theacrine in tea[J]. Nature Communications,2020,11(1):1−8. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-13993-7
[26] 刘玉飞, 庞丹丹, 李友勇, 等. 苦茶碱代谢关键转录因子基因的筛选鉴定[J]. 茶叶科学,2022,42(1):41−50. [LIU Y F, PANG D D, LI Y Y, et al. The screening and identification of key transcription factor genes for theacrine metabolism[J]. Tea Science,2022,42(1):41−50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2022.01.005 LIU Y F, PANG D D, LI Y Y, et al . The screening and identification of key transcription factor genes for theacrine metabolism[J]. Tea Science,2022 ,42 (1 ):41 −50 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2022.01.005[27] 秦丹丹, 王秋霜, 李红建, 等. 苦茶及其特异性成分苦茶碱研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(13):353−359. [QIN D D, WANG Q S, LI H J, et al. Research progress on bitter tea and its specific component, bitter theophylline[J]. Food Science,2021,42(13):353−359. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200617-231 QIN D D, WANG Q S, LI H J, et al . Research progress on bitter tea and its specific component, bitter theophylline[J]. Food Science,2021 ,42 (13 ):353 −359 . doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200617-231[28] 张广辉, 梁月荣, 吴颖. 咖啡因生物合成研究进展及在茶树育种中的应用[J]. 茶叶,2005(1):18−23. [ZHANG G H, LIANG Y R, WU Y. Research progress on caffeine biosynthesis and its application in tea breeding[J]. Tea,2005(1):18−23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0577-8921.2005.01.012 ZHANG G H, LIANG Y R, WU Y . Research progress on caffeine biosynthesis and its application in tea breeding[J]. Tea,2005 (1 ):18 −23 . doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0577-8921.2005.01.012[29] 陈玲, 熊智, 孙浩, 等. 四种不同年份普洱茶中茶多酚与咖啡碱成分的分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2011,32(10):132−134,138. [CHEN L, XIONG Z, SUN H, et al. Analysis of tea polyphenols and caffeine in four different years of Pu-erh tea[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry ,2011,32(10):132−134,138. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2011.10.059 CHEN L, XIONG Z, SUN H, et al . Analysis of tea polyphenols and caffeine in four different years of Pu-erh tea[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry ,2011 ,32 (10 ):132 −134,138 . doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2011.10.059[30] 梁宗锁, 方誉民, 杨东风. 植物萜类化合物生物合成与调控及其代谢工程研究进展[J]. 浙江理工大学学报(自然科学版),2017,37(2):255−264. [LIANG Z S, FANG Y M, YANG D F. Biosynthesis, regulation and metabolic engineering of terpenoids in plants[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2017,37(2):255−264. LIANG Z S, FANG Y M, YANG D F . Biosynthesis, regulation and metabolic engineering of terpenoids in plants[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2017 ,37 (2 ):255 −264 .[31] 薛海洁, 王颖, 李春. 植物天然产物的微生物合成与转化[J]. 化工学报,2019,70(10):3825−3835. [XUE H J, WANG Y, LI C. Microbial synthesis and transformation of plant-derived natural products[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering,2019,70(10):3825−3835. XUE H J, WANG Y, LI C . Microbial synthesis and transformation of plant-derived natural products[J]. Journal of Chemical Engineering,2019 ,70 (10 ):3825 −3835 .[32] 王佳, 游松, 周丽娜. 倍半萜生物转化的研究进展[J]. 沈阳药科大学学报,2012,29(2):156−164. [WANG J, YOU S, ZHOU L N. Progress in research of sesquiterpenoids biotransformation[J]. Journal of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,2012,29(2):156−164. doi: 10.14066/j.cnki.cn21-1349/r.2012.02.006 WANG J, YOU S, ZHOU L N . Progress in research of sesquiterpenoids biotransformation[J]. Journal of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University,2012 ,29 (2 ):156 −164 . doi: 10.14066/j.cnki.cn21-1349/r.2012.02.006 -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 马红艺,李圣胜,陆华瑜,罗鎏欣,李凯,毛瑞丰. 武宣红曲米发酵夏茶工艺研究. 轻工科技. 2024(04): 50-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



