Production of Cannabidiol Acid Synthase by Chassis Pichia pastoris and of Its Catalytic Activity Analysis
-
摘要: 为了实现大麻二酚酸合成酶(CBDAS)的微生物底盘高效表达,为体外合成大麻二酚(CBD)提供重组酶。首先从高CBD含量大麻叶片中克隆CBDAS基因,利用生物信息学方法分析其蛋白的基本理化性质,构建重组质粒pPIC9K-CBDAS后转化毕赤酵母菌,筛选重组蛋白CBDAS高表达的培养条件,并分析CBDAS的催化活性。结果表明,构建的pPIC9K-CBDAS融合蛋白表达系统能在毕赤酵母中表达;在甲醇添加量为1%、培养基pH6.0和培养48 h的诱导条件下表达量最大;重组酶CBDAS催化底物大麻萜酚酸(CBGA)反应4 h后大麻二酚酸(CBDA)含量显著增加(P<0.05),在8 h后CBD含量显著增加(P<0.05),在12 h时合成CBDA和CBD量达到最大值;CBDAS在大麻叶片大麻萜酚酸(CBGA)粗提液和CBGA标品中反应12 h后分别生成CBDA 60.64和20.12 ng/mL,CBD 128.01和207.87 ng/mL,具有较强的催化活性。通过酵母异源表达实现了大麻CBDAS的重组表达,为经济高效地合成CBDA和CBD提供活性酶。Abstract: In order to obtain the higher expression of cannabinoid acid synthase (CBDAS) through the microbial chassis, the recombinant enzyme for the in vitro synthesis of cannabinoid (CBD) was studied. The CBDAS gene was firstly cloned from cannabis leaves with higher content of CBD, its basic physicochemical properties of proteins were then analyzed by bioinformatics methods. After construction of the recombinant plasmid pPIC9K-CBDAS and transformation into Pichia pastoris, conditions of the recombinant protein CBDAS were optimized and its catalytic activities were finally analyzed. The results indicated that the constructed pPIC9K-CBDAS fusion protein expression system could be successfully expressed in P. pastoris. Under conditions of 1% of methanol addition, pH6.0 of medium, 48 h of induction, the maximum expression was obtained. At 4 h reaction, the product of cannabigerol acid (CBGA) was significantly increased, in which attributed to catalysis of substrate CBGA by the recombinant CBDAS. In the following, contents of CBD were significantly increased at 8 h (P<0.05) and those of CBDA and CBD were reached to the maximum at 12 h. After reactions at 12 h in the crude extract of cannabis leaf and the standardized CBGA, CBDAS could catalyze to product 60.64 and 20.12 ng/mL of CBDA, 128.01 and 207.87 ng/mL of CBD, respectively, in which CBDAS indicated a stronger catalytic activity. In conclusion, heterologous recombinant expression of cannabis CBDAS was achieved through yeast chassis, which provided active enzymes for the efficient synthesis of CBDA and CBD.
-
大麻是一年生麻科草本植物,被称为大麻或汉麻,在世界各地种植已有数千年,主要应用在医药、化工和食品领域[1-2]。天然产物大麻素是大麻植物产生的独特次级代谢物,主要存在于大麻的毛状体油室中,是由聚酮和单萜亚结构组成。目前为止,已分离出100多种大麻素[3]。其中,酸性大麻素四氢大麻酚酸(THCA)、大麻二酚酸(CBDA)和大麻环萜酚酸(CBCA)含量最丰富,且三者均以CBGA为底物经酶催化而成。其他类型大麻素大多是由这三种物质在热和光照下通过非酶转化、降解反应和自氧化等方式获得[4-5]。在这些代谢物中,具有精神活性的Δ9-四氢大麻酚(THC)[6],由于具有潜在的治疗价值,包括镇痛、抗惊厥、止吐和开胃性而备受关注[7-8]。大麻二酚(CBD)是一种与THC具有不同环状结构的同分异构体,近年来在治疗阿尔兹海默病、帕金森病、癫痫,以及抗肿瘤和神经保护等方面发挥着重要作用[9-11]。此外,CBD在食品和化妆品上的应用也比较广泛。CBD油可缓解焦虑,CBD糖浆可以安神和缓解疼痛,CBD苏打水可以舒缓痛症和调节亚健康问题;还有加入适量CBD的饼干、巧克力、啤酒、披萨等食品,具有独特香气,让人身心愉悦[12];含有CBD的化妆品具有舒缓皮肤敏感,抗炎及治疗粉刺等作用[13]。但目前CBD原料短缺、价格高昂、生物提取得率低等问题,限制了其产业发展和应用领域拓展。
酵母表达系统在上个世纪70年代被发现,在2006年经美国FDA批准,获得“最安全微生物”称号[14-15]。毕赤酵母(Pichia pastoris)是在甲醇培养基中生长的一种甲基营养菌,可利用AOX1启动子来驱动外源蛋白的高水平表达[16-17]。酵母异源表达系统有许多优点,发酵培养基取材稳定、成本低廉、繁殖快速;与细菌相比,具有翻译后修饰,易于遗传操作等优势[18]。外源目的基因线性化后,利用同源重组方式可将外源基因高效整合到酵母细胞的染色体中,产生稳定的细胞系[19-23]。
大麻二酚酸合成酶(CBDAS)可催化底物CBGA生成CBDA,而CBDA在高温下易脱羧形成CBD。以大麻花叶为材料生物提取大麻素的粗提液中含有很多组分,其中还有一定含量的CBGA未被完全转化。若能利用操作简便,经济高效的方法获得CBDAS,便可通过体外反应将粗提液中残存的CBGA进一步单一转化成CBD。本研究以高含量CBD品种为材料,采用PCR克隆技术获得CBDAS基因,并构建酵母表达载体,在毕赤酵母中重组表达,利用高效液相色谱分析CBDAS合成酶的催化活性。研究结果可为工业化定向提高CBD生物提取率奠定理论基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
大麻材料 由黑龙江省农业科学院经济作物所提供;毕赤酵母GS115和大肠杆菌DH5α感受态 购自昂羽生物技术(上海)有限公司;pPIC9K-His载体 购自淼灵生物技术(武汉)有限公司;GreenGate克隆载体C000 本实验室保存;植物DNA提取试剂盒 天根生化科技(北京)公司;质粒提取试剂盒 索莱宝科技(北京)有限公司;胶回收试剂盒 Omega(美国)公司;限制性内切酶EcoRI、NotI、SacI和PstI NEB(美国)公司;高保真酶Phanta Super-Fidenlity DNA Polymerase 诺唯赞生物科技(南京)有限公司;ThunderbirdTM SYBR® qPCR Mix TOYOBO(日本)公司。
5428高速冷冻离心机 德国艾本德公司;Veriti96梯度PCR扩增仪 美国赛默飞公司;HB-96D恒温槽 韩国WiseTherm公司;HV-50高压蒸汽灭菌器 日本Hirayama公司;V-1300可见光分光光度计 上海美析仪器公司;NS-100B恒温振荡摇床 杭州川恒实验仪器公司;CFX96实时荧光定量PCR仪 美国伯乐公司;1260高效液相色谱仪 美国安捷伦。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 大麻基因组提取
称取适量高CBD含量的大麻叶片经液氮研磨后,按照植物DNA提取试剂盒说明书提取总基因组。使用NanoDrop2000检测DNA浓度和质量。DNA保存在−20 ℃备用。
1.2.2 CBDAS基因的克隆
使用Primer3 plus(https://www.primer3plus.com/)在线网站设计特异引物。以大麻基因组DNA为模板进行PCR扩增。本实验选用高保真聚合酶进行目的片段的扩增,PCR扩增程序:95 ℃预变性2 min,95 ℃变性10 s,52 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸2 min,共32个循环,72 ℃延伸5 min,4 ℃保存。PCR产物经1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳后,切胶,按照胶回收试剂盒说明书进行纯化。将纯化产物与C000载体连接生成C000-CBDAS载体,转化DH5α感受态后选取阳性克隆进行测序。引物合成和测序均由北京擎科生物科技有限公司完成。
1.2.3 生物信息学分析
使用Snapgene软件将测序后的CBDAS基因序列翻译成氨基酸,利用在线软件Expasy(https://www.expasy.org/)中的ProtParam和ProtScale分析CBDAS蛋白的基本理化性质和亲/疏水性,利用Smart(http://smart.embl-heidelberg.de/)和NCBI的CD-search(https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/cdd/)在线软件分析CBDAS蛋白的保守结构域,利用NetNGlyc-1.0(https://services.healthtech.dtu.dk/service.php?NetNGlyc-1.0)在线软件分析CBDAS蛋白的糖基化位点。
1.2.4 酵母表达载体的构建
设计含有NotI和EcoRI酶切位点的特异性引物ppCBDAs-F和ppCBDAs-R,保护碱基和酶切位点用下划线表示(见表1)。以C000-CBDAS质粒为模板,用带接头引物进行PCR扩增,PCR产物经琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测后回收。使用NotI和EcoRI酶分别对回收产物和pPIC9K载体进行双酶切,纯化后连接成pPIC9K-CBDAS质粒,并转化大肠杆菌,通过测序和酶切鉴定筛选阳性克隆。
表 1 本研究使用的引物Table 1. Primers used in this study引物 引物序列(5'-3') 用途 CBDAS-F ATGAAGTACTCAACATTCTCCTTTTG 扩增CBDAS基因 CBDAS-R ATGACGATGCCGTGGAAGAG ppCBDAS-F CCGGAATTCATGAAGTACTCAACATTCTCCTTTTG 构建酵母表达载体 ppCBDAS-R AAGGAAAAAAGCGGCCGCATGACGATGCCGTGGAAGAG AOX-F GACTGGTTCCAATTGACAAGC 测序和鉴定 ACT-F TTTGGACTCTGGTGACGGTG qRT-PCR内参基因 ACT-R TCGGTCAAATCTCTACCGGC qCs11-F1 ACACAACCCCAAAACCACTT 基因表达量检测 qCs11-R1 CCCATGCAGTTTGGCTATGA 1.2.5 酵母转化和阳性重组菌的筛选
将重组质粒pPIC9K-CBDAS经SacI限制性内切酶进行线性化,再通过电转化方式导入毕赤酵母GS115感受态中;将细胞液均匀涂布于MD固体培养基上,于30 ℃倒置培养3~5 d。参考赵明明等[24]方法,用去离子水冲洗平板上的菌落并收集,吸取200 μL菌液涂布于不同G418浓度(1、2、4、6 mg/mL)的YPD平板上,于30 ℃倒置培养3~5 d。挑取YPD平板上的单克隆,采用高温-乙酸乙酯法提取酵母基因组[25];以AOX1-F和CBDAS-R为引物进行PCR鉴定。PCR反应程序:95 ℃预变性3 min;95 ℃变性20 s,54 ℃退火30 s,72 ℃延伸2 min 15 s,32个循环;72 ℃延伸5 min,4 ℃保存。PCR产物进行1%琼脂糖凝胶电泳鉴定。
1.2.6 重组蛋白的诱导表达
参考卢可心[26]方法,挑取鉴定为阳性的重组菌接种至YPD液体培养基,于30 ℃、190 r/min过夜培养;将活化的菌液按1%接种于20 mL BMGY培养基,于30 ℃、190 r/min培养至OD600为2~6时,利用血球计数板计算酵母菌数量,收集菌体后用BMMY培养基重悬至菌数约为8.0×109个/mL,再于30 ℃、190 r/min培养,每隔24 h补充1%体积比的甲醇,连续诱导96 h。每组3个重复,取菌体破碎后进行SDS-PAGE分析。
1.2.7 Western blot分析
将pPIC9K-CBDAS重组蛋白通过SDS-PAGE电泳分离后转移至PVDF膜上。5%脱脂奶粉封闭2 h后,用TBST冲洗表面。将PVDF膜转至含有His抗体(1:5000)的TBST中,4 ℃孵育过夜。TBST摇晃清洗6次(5 min/次)后移至含有HRP标记的二抗TBST中(1:4000),室温孵育2 h,TBST摇晃清洗6次(5 min/次)。最后用ECL超敏化学发光检测试剂盒和成像分析仪检测条带。
1.2.8 荧光定量PCR(qRT-PCR)检测基因表达情况
培养方法同1.2.6,在诱导48 h后收集酵母菌,用Trizol法提取总RNA,核酸蛋白测定仪检测RNA浓度及纯度,符合A260/A280=1.8~2.1后用于逆转录反应。使用逆转录试剂盒合成cDNA,反应体系10 μL,反应条件:37 ℃,15 min;50 ℃,5 min;98 ℃,5 min;4 ℃,保存。采用SYBR® Green Realtime PCR MasterMix进行qRT-PCR反应,反应体系20 μL,反应条件:95 ℃预变性10 min,95 ℃变性15 s,55 ℃退火30 s,共39个循环,引物序列见表1。反应完成后,确认扩增曲线及融解曲线,导出ct值,以毕赤酵母菌的Actin基因为内参,相对定量用2−∆Ct来分析基因的表达水平[27]。
1.2.9 重组蛋白诱导表达的条件筛选
选取可以成功表达的重组菌株进行后续筛选,诱导时间为0、12、24、48、72、96 h;诱导培养基BMMY的pH分别为3.0、4.5、6.0、6.5、7.0、7.5;甲醇添加量为0.5%、0.75%、1%、2%、4%,为保证甲醇浓度不变,每隔24 h再次添加;具体操作同1.2.6,每组三个重复。
1.2.10 CBDAS酶活性测定
1.2.10.1 大麻萜酚酸(CBGA)的提取
取高CBGA含量大麻品种的烘干叶片,每0.1 g中加入50 mL甲醇,超声破碎30 min后,4 ℃离心20 min收集上清液,再用0.22 μm滤膜去除杂质,−20 ℃保存备用。
1.2.10.2 反应液的制备
反应体系参照修改的Taura 等[28]方法,体系一中加入100 μL CBGA粗提液,0.5 μL TritionX-100,超滤浓缩后的重组蛋白液25 μg,用0.1 mol/L柠檬酸钠缓冲液(pH5.0)定容至500 μL。在37 ℃反应0、2、4、8、12 h后,加入600 μL甲醇终止反应,每组三次重复;将反应液离心3 min,取上清,过0.22 μm滤膜,用于HPLC检测;体系二中将CBGA粗提液换成终浓度为25 μmol/L CBGA标准品,在37 ℃反应12 h后,加入600 μL甲醇终止反应,其余成分和反应过程均和体系一相同。通过产生CBDA和CBD的含量来反映酶的生物活性。
1.2.10.3 液相色谱条件
色谱柱:Shimadzu sil-16 C18柱(150 mm×4.6 mm×3 µm),柱温:30 ℃;流动相:A为水溶液中含有0.1%甲酸,B为乙腈中含有0.1%甲酸;等度洗脱:25% A,75% B,保留时间30 min;紫外检测器:230 nm;流速:0.7 mL/min;进样量:10 μL。
1.3 数据处理
DNA序列和氨基酸序列数据用Snapgene软件处理。使用统计学软件SPSS 23.0和Prism 5.0进行分析作图,采用单因素方差分析比较各组间数据,t检验法进行组间差异显著性分析,P<0.05差异显著。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 CBDAS基因的克隆
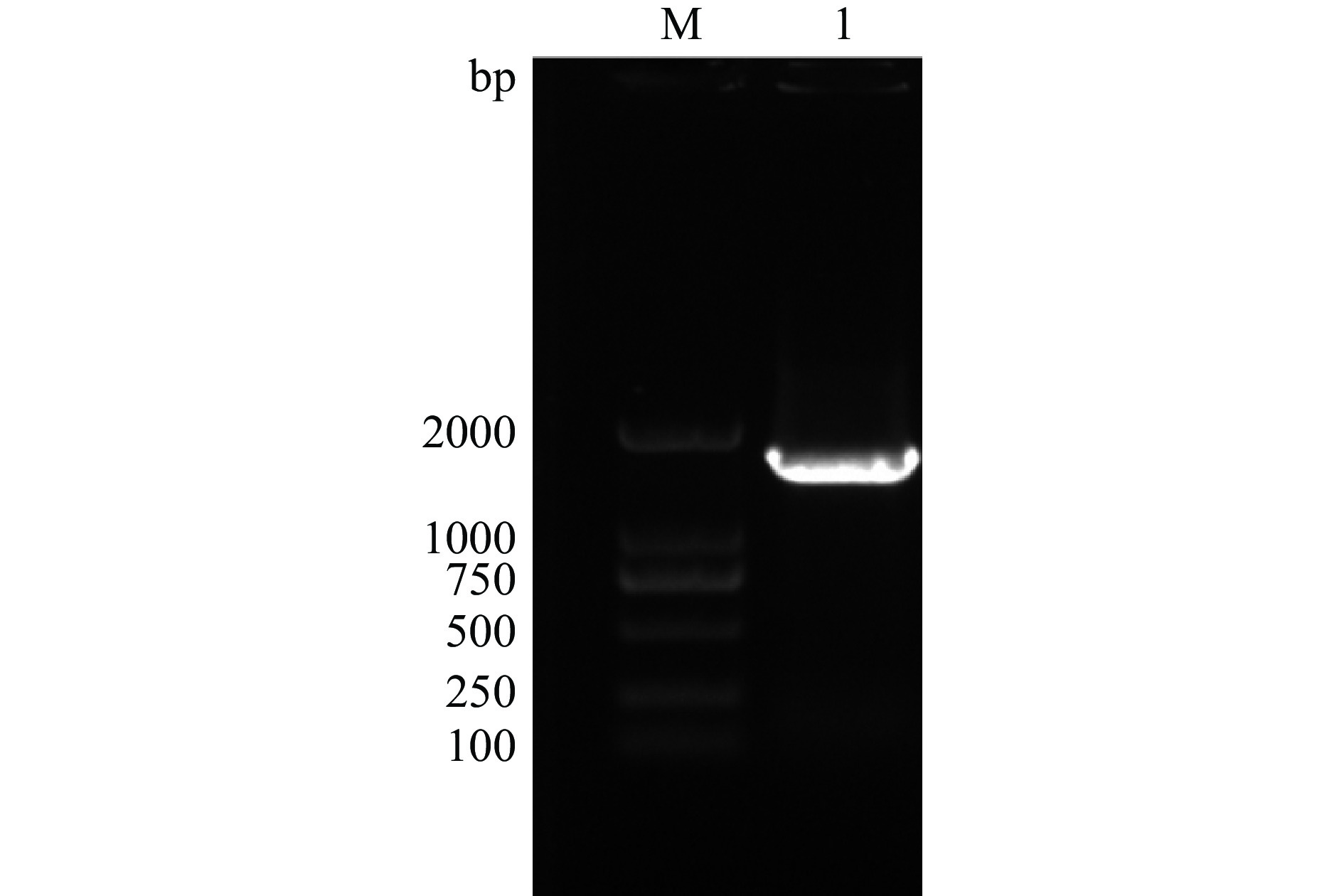
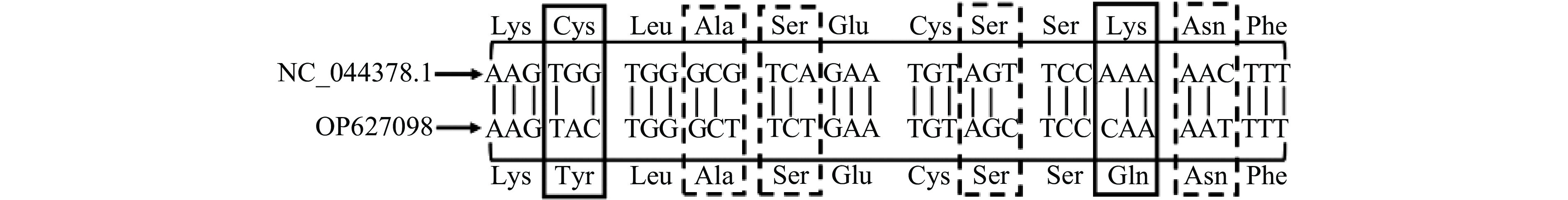
以大麻的基因组为模板,使用引物CBDAS-F和CBDAS-R进行PCR扩增,电泳图如图1。通过测序可知CBDAS基因全长1635 bp,编码544个氨基酸,Taura等[28]在克隆纤维型大麻CBDAS基因时,也得出该基因编码544个氨基酸的结论。将克隆的CBDAS基因序列信息提交到NCBI数据库(登录号OP627908),但与NCBI数据库已公布大麻CBDAS基因序列(登录号NC_044378.1)比较,有6处碱基不同,引起2个氨基酸发生改变(Cys-Tyr和Lys-Gln),其余4个为同义突变(图2)。可见,不同大麻品种间CBDAS基因存在差异。
2.2 CBDAS蛋白的生物信息学分析
利用在线分析软件ProtParam预测了大麻CBDAS蛋白的基本理化性质。结果表明,CBDAS蛋白分子量为62.3 kD,理论等电点pI为8.84;具有51个酸性氨基酸残基(Asp+Glu),59个碱性氨基酸残基(Arg+Lys);分子式为C2843H4351N745O793S20;在酵母中估算的半衰期大于20 h。此外,CBDAS蛋白的不稳定系数为29.28(小于40属于稳定蛋白),亲水性平均系数(Grand average of hydropathicity,GRAVY)为−0.219,因此,CBDAS是稳定的亲水性蛋白。常丽等[29]利用ProtPScale软件预测大麻品种Carmen的CBDAS蛋白时,得出其不稳定系数为30.57,GRAVY为−0.202,与本研究的结论相似。利用NetNGlyc-1.0在线软件分析发现CBDAS蛋白存在7个N-糖基化位点,分别是位于45、65、168、296、304、328、498位的天冬酰胺。利用Smart和NCBI的CD-search软件分析CBDAS蛋白的保守结构域,两者结果一致(图3),氨基酸479-537范围的结构域为BBE,存在于小檗碱桥和小檗碱桥样酶中,这些酶参与许多异喹啉生物碱的生物合成;而81-218结构域家族由多种利用FAD作为辅助因子的酶组成,大多数酶类似于氧化还原酶。
2.3 重组酵母表达载体构建与鉴定
以C000-CBDAS为模板,以ppCBDAS-F/R为引物,扩增获得的CBDAS基因片段大小约为1635 bp。CBDAS基因回收产物与酵母表达载体pPIC9K用EcoRI和NotI分别进行双酶切,经回收、连接、转化后进行鉴定。用AOX-F引物对载体进行测序,比对后表明序列正确。再用SacI限制性内切酶对测序正确的重组子进行线性化,再用PstI酶切,琼脂糖凝胶电泳结果显示,可见5297、2555、1827和1241 bp等不同片段(图4)。测序和酶切验证后表明,重组酵母表达载体pPIC9K-CBDAS构建成功。
2.4 毕赤酵母转化和阳性重组菌筛选
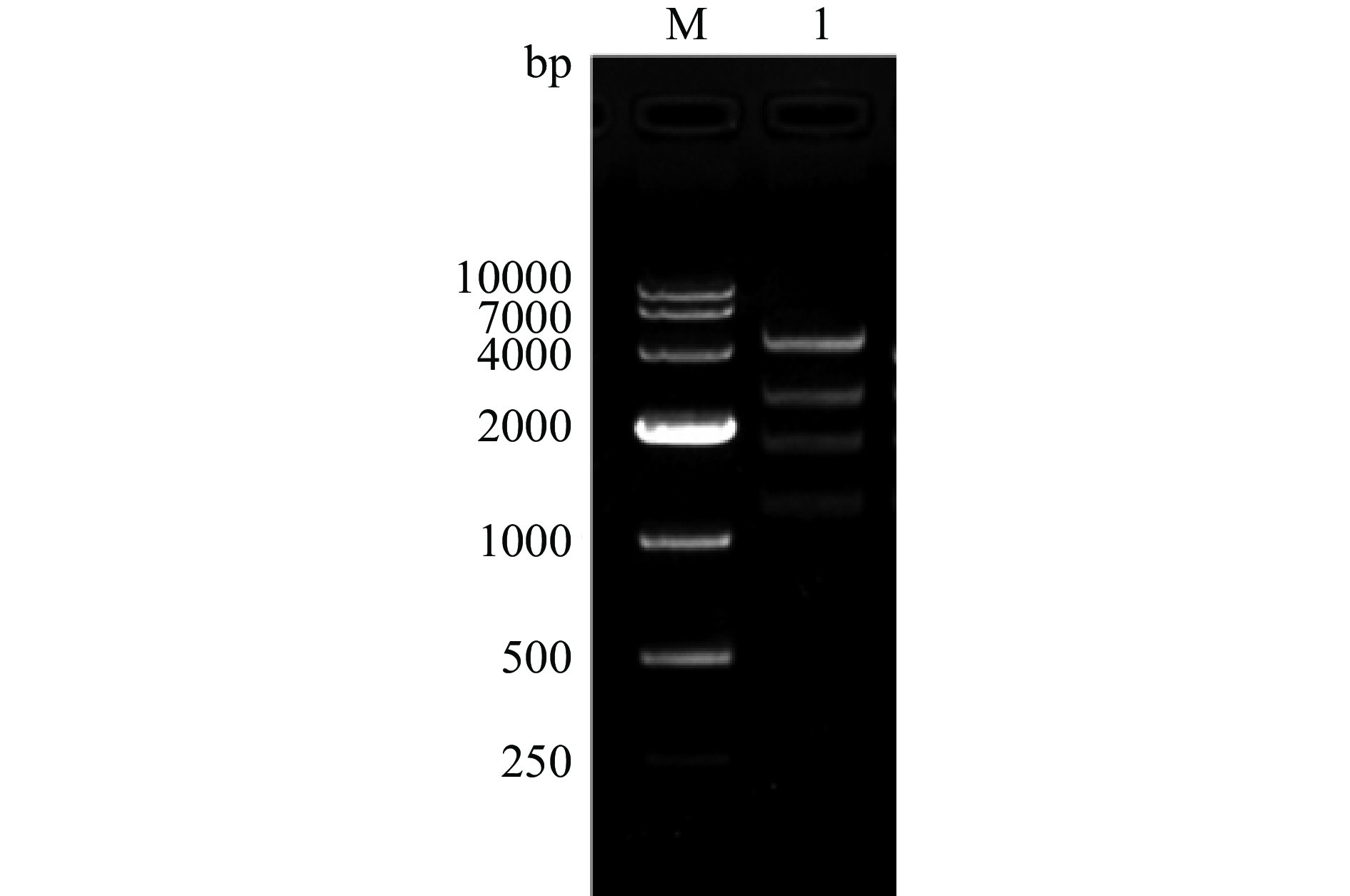
将线性化质粒电转入毕赤酵母GS115感受态中,30 ℃培养3~5 d,再利用不同浓度G418筛选高拷贝菌后,挑取单菌落提取基因组DNA,用pPIC9K载体中AOX1和CBDAS基因序列设计的引物进行PCR扩增,获得2002 bp的条带(图5),表明pPIC9K-CBDAS质粒已经整合到毕赤酵母GS115的染色体中。
2.5 Western blot和qRT-PCR验证重组蛋白表达
以酵母菌的Actin基因为内参,经qRT-PCR分析后发现,在以水为阴性对照(CK)和转入空载体pPIC9K的酵母菌中,均未检测到CBDAS基因的表达,而在重组菌中有该基因的表达(图6A)。Western blot分析显示,重组蛋白CBDAS在毕赤酵母中能正常表达,在75 kD处具有特异性条带,而在导入空载体酵母菌中无表达(图6B),比利用Protparam软件预测的蛋白分子质量(62.3 kD)略大,在前面糖基化位点分析时发现CBDAS蛋白存在多个N-糖基化位点,推测该酶在酵母表达中可能发生糖基化修饰而导致分子量变大。姚昌阳等[30]也在利用毕赤酵母诱导表达裂解多糖单加氧酶(LPMO)的研究中发现,重组的LPMO蛋白条带大小范围为46~50 kD,比预测的分子量34 kD大,认为该蛋白发生了糖基化修饰。
2.6 重组CBDAS蛋白诱导表达的条件筛选
pPIC9K为分泌型载体,理论上应会在胞外分泌出大量重组蛋白。但可能由于多肽链在内质网中聚集,导致加工以及囊泡运输等过程影响外源蛋白分泌表达,从而使一定量外源蛋白仍滞留在胞内[31]。由于上清中CBDAS蛋白较少所以收集菌体经超声破碎后的蛋白用于后续实验。为使重组CBDAS蛋白高效表达,对主要影响其表达的诱导时间、甲醇浓度和诱导培养基BMMY的pH等因素进行筛选,结果如图7。诱导时间、甲醇浓度和培养基的pH对重组蛋白表达确有较大影响,重组菌在培养48 h,诱导培养基pH6.0,1%甲醇添加量时表达量最大。
2.7 CBDAS酶活性分析
将转入空载体pPIC9K酵母菌株和导入目的基因的重组酵母菌株pPIC9K-CBDAS同时在诱导培养基BMMY(pH6.0),1%甲醇添加量下进行诱导培养,48 h后收集菌体经超声破碎收集上清液,用超滤管进行浓缩制备成待测酶液,利用BCA试剂盒检测总蛋白浓度,毕赤酵母重组酶活性测定如图8。反应体系的总体积保持不变,设置一组只加底物不加酶液的空白对照(CK),另两组分别加入pPIC9K和pPIC9K-CBDAS重组菌株提取的酶液。当使用大麻叶片粗提液中CBGA为底物发生反应时,由于粗提液中含有CBDA和CBD,因此,在0 h时三组均会检测到这两种物质。随着反应时间增加(0~12 h),CK组和pPIC9K组的CBDA和CBD的含量略微下降,但差异不显著。对于pPIC9K-CBDAS组来说,反应2 h后,CBDA和CBD的含量未发生显著变化;当反应4 h后,CBDA含量显著增加(P<0.05);在8h后CBD含量显著增加(P<0.05),12 h时生成的CBDA和CBD含量达到最大值;在重组酶CBDAS作用下,新合成CBDA 60.64 ng/mL,CBD 128.01 ng/mL,分别比pPIC9K组的高15.67倍和37.87倍(图8A~图8E)。为进一步确定重组CBDAS的生物活性,减少大麻叶片粗提液中其他物质对反应的干扰,以CBGA标准品为底物,反应12 h后分析重组酶催化底物CBGA产生CBDA和CBD的情况,结果如图8F。CK组和pPIC9K组中未检测到CBDA,但有CBD检出,这是因为CBGA标准品中含有少量的CBD而导致;pPIC9K-CBDAS组中新合成CBDA 20.12 ng/mL,CBD 207.87 ng/mL,CBD含量比pPIC9K组高9.34倍。CBDAS酶和底物发生反应直接生成CBDA,但当反应时间长于4 h后,CBDA就会发生脱羧反应生成CBD,所以在8和12 h时会产生大量的CBD。由上可知,通过毕赤酵母重组产生大麻的CBDAS无论在大麻叶片粗提液还是标准品中,都可以催化底物CBGA生成CBDA和CBD。经对比,以CBGA标准品为底物的转化效率明显低于大麻叶片粗提液,这可能由于在CBGA粗提液中含有的复杂物质成分所致,可促进CBDAS酶催化活性,并增强CBDA脱羧作用。
3. 结论
大麻品种间CBDAS基因存在差异,从而使蛋白的基本理化性质发生改变,本研究中克隆得到CBDAS经生信预测认为是一种稳定的亲水性蛋白。目前,人们多以大麻花叶为材料来提取大麻素,存在季节依赖、周期长、纯度低等问题,且在提取CBD过程中会浪费粗提液中尚存的CBGA。利用经济高效的方法获得CBDAS,便可通过体外反应将粗提液中残存的CBGA进一步转化成CBD。本文通过构建酵母表达载体,转化毕赤酵母获得重组菌,经qTR-PCR和Western blot验证后认为CBDAS基因可在酵母中得到表达。而重组菌在培养48 h、培养基pH6.0和1%甲醇添加量等诱导条件下CBDAS蛋白表达量最大。通过毕赤酵母重组产生大麻的CBDAS无论在大麻叶片粗提液还是标准品中,都可以催化底物CBGA生成CBDA和CBD,具有很强的生物活性。研究结果为今后CBD在医疗、食品和化妆品等领域的应用开发提供基础。重组CBDAS合成酶在大麻叶片粗提液中的催化活性高于CBGA标准品,其具体原因还有待于进一步研究。
-
表 1 本研究使用的引物
Table 1 Primers used in this study
引物 引物序列(5'-3') 用途 CBDAS-F ATGAAGTACTCAACATTCTCCTTTTG 扩增CBDAS基因 CBDAS-R ATGACGATGCCGTGGAAGAG ppCBDAS-F CCGGAATTCATGAAGTACTCAACATTCTCCTTTTG 构建酵母表达载体 ppCBDAS-R AAGGAAAAAAGCGGCCGCATGACGATGCCGTGGAAGAG AOX-F GACTGGTTCCAATTGACAAGC 测序和鉴定 ACT-F TTTGGACTCTGGTGACGGTG qRT-PCR内参基因 ACT-R TCGGTCAAATCTCTACCGGC qCs11-F1 ACACAACCCCAAAACCACTT 基因表达量检测 qCs11-R1 CCCATGCAGTTTGGCTATGA -
[1] ANDRE C M, HAUSMAN J F, GUERRIERO G. Cannabis sativa: The plant of the thousand and one molecules[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science,2016,7:19.
[2] BONINI S A, PREMOLI M, TAMBARO S, et al. Cannabis sativa: A comprehensive ethnopharmacological review of a medicinal plant with a long history[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2018,227:300−315. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.09.004
[3] ROSENBERG, E C, PATRA, P H, WHALLEY, B J. Therapeutic effects of cannabinoids in animal models of seizures, epilepsy, epileptogenesis, and epilepsy-related neuroprotection[J]. Epilepsy and Behavior, 2017, 70(Pt B): 319-327.
[4] CROMBIE L, PONSFORD R, SHANI A, et al. Photochemical production of cannabicyclol from cannabichromene[J]. Tetrahedron Letters,1968,55:5771−5772.
[5] MORIMOTO S, KOMATSU K, TAURA F, et al. Purification and characterization of cannabichromenic acid synthase from Cannabis sativa[J]. Phytochemistry,1998,49(6):1525−1529. doi: 10.1016/S0031-9422(98)00278-7
[6] AMIN M R, ALI D W. Pharmacology of medical cannabis[J]. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology,2019,1162:151−165.
[7] RUSSO E, GUY G W. A tale of two cannabinoids: The therapeutic rationale for combining tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabidiol[J]. Medical Hypotheses,2006,66(2):234−246. doi: 10.1016/j.mehy.2005.08.026
[8] LI H, LIU Y, TIAN D, et al. Overview of cannabidiol (CBD) and its analogues: Structures, biological activities, and neuroprotective mechanisms in epilepsy and Alzheimer's disease[J]. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry,2020,192:112−163.
[9] NACHNANI R, RAUP-KONSAVAGE W M, VRANA K E. The pharmacological case for cannabigerol[J]. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics,2021,376(2):204−212. doi: 10.1124/jpet.120.000340
[10] GASTON T E, FRIEDMAN D. Pharmacology of cannabinoids in the treatment of epilepsy[J]. Epilepsy and Behavior,2017,70:313−318. doi: 10.1016/j.yebeh.2016.11.016
[11] PISANTI S, MALFITANO A M, CIAGLIA E, et al. Cannabidiol: State of the art and new challenges for therapeutic applications[J]. Pharmacology and Therapeutics,2017,175:133−150. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2017.02.041
[12] 宁康, 董林林, 李孟芝, 等. 非精神活性药用大麻的应用及开发[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2020,26(8):228−240. [NING K, DONG L L, LI M Z, et al. Application and development of non-psychoactive medicinal cannabis[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Formulary,2020,26(8):228−240. [NING K, DONG L L, LI M Z, et al. Application and development of non-psychoactive medicinal cannabis[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Formulary, 2020, 26(8): 228-240.
[13] 常丽, 李建军, 黄思齐, 等. 植物大麻活性成分及其药用研究概况[J]. 生命的化学,2018,38(2):273−280. [CHANG L, LI J J, HUANG S Q, et al. Overview of research on the active ingredients of plant cannabis and their medicinal uses[J]. The Chemistry of Life,2018,38(2):273−280. [CHANG L, LI J J, HUANG S Q, et al. Overview of research on the active ingredients of plant cannabis and their medicinal uses[J]. The Chemistry of Life, 2018, 38(2): 273-280.
[14] MOHAMMADZADEH R, KARBALAEI M, SOLEIMANPOUR S, et al. Practical methods for expression of recombinant protein in the Pichia pastoris system[J]. Current Protocols,2021,1(6):155−161.
[15] RASCHMANOVÁ H, WENINGER A, KNEJZLÍK Z, et al. Engineering of the unfolded protein response pathway in Pichia pastoris: Enhancing production of secreted recombinant proteins[J]. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2021,5(11):4397−4414.
[16] TÜRKANOĞLU Ö A, YıLMAZ S, INAN M. Pichia pastoris promoters[J]. Methods in Molecular Biology,2019,1923:97−112.
[17] MASTROPIETRO G, AW R, POLIZZI K M. Expression of proteins in Pichia pastoris[J]. Methods in Enzymology,2021,660:53−80.
[18] DALY R, HEARN M T. Expression of heterologous proteins in Pichia pastoris: A useful experimental tool in protein engineering and production[J]. Journal of Molecular Recognition,2005,18(2):119−138. doi: 10.1002/jmr.687
[19] KARBALAEI M, REZAEE S A, FARSIANI H. Pichia pastoris: A highly successful expression system for optimal synthesis of heterologous proteins[J]. Journal of Cellular Physiology,2020,235(9):5867−5881. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29583
[20] ZHENG X, ZHANG Y, ZHANG X, et al. Fhl1p protein, a positive transcription factor in Pichia pastoris, enhances the expression of recombinant proteins[J]. Microbial Cell Factories,2019,18(207):1−12.
[21] THOMAS V, LEIGH G, ROBIN W, et al. Effect of plasmid design and type of integration event on recombinant protein expression in Pichia pastoris[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2018,84(6):2712−2717.
[22] LI J S, CHEN L, SUN L, et al. Optimization of the secretory expression of recombinant human C-reactive protein in Pichia pastoris[J]. 3 Biotech,2017,7(5):1−8.
[23] ELLIS S B, BRUST P F, KOUTZ P J, et al. Isolation of alcohol oxidase and two other methanol regulatable genes from the yeast Pichia pastoris[J]. Molecular and Cellular Biology,1985,5(5):1111−1121.
[24] 赵明明, 李星颖, 江文康, 等. 猫血清白蛋白在毕赤酵母中的分泌表达[J]. 中国畜牧兽医,2022,49(3):897−903. [ZHAO M M, LI X Y, JIANG W K, et al. Secretory expression of feline serum albumin in Pichia pastoris[J]. China Veterinary Animal Husbandry,2022,49(3):897−903. ZHAO M M, LI X Y, JIANG W K, et al. Secretory expression of feline serum albumin in Pichia pastoris[J]. China Veterinary Animal Husbandry, 2022, 49(3): 897-903.
[25] 刘微, 戴凌燕, 苗青, 等. 一种经济高效的酵母菌落PCR模板DNA制备方法的建立[J]. 中国生物制品学杂志,2022,35(7):848−852. [LIU W, DAI L Y, MIAO Q, et al. Establishment of an economical and efficient method for preparing yeast colony PCR template DNA[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Products,2022,35(7):848−852. LIU W, DAI L Y, MIAO Q, et al. Establishment of an economical and efficient method for preparing yeast colony PCR template DNA[J]. Chinese Journal of Biological Products, 2022, 35(7): 848-852.
[26] 卢可心. 产5-氨基乙酰丙酸重组毕赤酵母的构建及发酵研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2022 LU K X. Studies on construction and fermentation of a recombinant Pichia pastoris 5-aminolevulinic acid[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2022.
[27] 蔡欣月. 转录因子AtVIP1介导IAA与ABA信号途径调控高粱侧根发育的分子机制初探[D]. 大庆: 黑龙江八一农垦大学, 2020 CAI X Y. The molecular mechanism of AtVIP1 mediates IAA and ABA signaling pathways to regulate lateral root development in sorghum-preliminary study[D]. Daqing: Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University, 2020.
[28] TAURA F, SIRIKANTARAMAS S, SHOYAMA Y, et al. Cannabidiolic-acid synthase, the chemotype-determining enzyme in the fiber-type Cannabis sativa[J]. FEBS Letters,2007,581(16):2929−2934. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2007.05.043
[29] 常丽, 唐慧娟, 李建军, 等. 大麻CBDA1基因的生物信息学分析[J]. 安徽农业科学,2017,45(29):144−148. [CHANG L, TANG H J, LI J J, et al. Bioinformatics analysis of CBDA1 gene in Cannabis sativa[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science,2017,45(29):144−148. CHANG L, TANG H J, LI J J, et al. Bioinformatics analysis of CBDA1gene in Cannabis sativa[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science, 2017, 45(29): 144-148.
[30] 姚昌阳, 谢兴欢, 蒋思婧, 等. 裂解多糖单加氧酶在毕赤酵母中的异源表达[J]. 湖北大学学报(自然科学版),2019,41(6):561−566. [YAO C Y, XIE X H, JIANG S J, et al. Heterologous expression of lysolysaccharide monooxygenase in Pichia pastoris[J]. Journal of Hubei University (Natural Science Edition),2019,41(6):561−566. YAO C Y, XIE X H, JIANG S J, et al. Heterologous expression of lysolysaccharide monooxygenase in Pichia pastoris[J]. Journal of Hubei University (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 41(6): 561-566.
[31] 关波, 金坚, 李华钟. 改良毕赤酵母分泌表达外源蛋白能力的研究进展[J]. 微生物学报,2011,51(7):851−857. [GUAN B, JIN J, LI H Z. Research progress on the ability of improved Pichia pastoris to secrete and express foreign proteins[J]. Journal of Microbiology,2011,51(7):851−857. GUAN B, JIN J, LI H Z. Research progress on the ability of improved Pichia pastoris to secrete and express foreign proteins[J]. Journal of Microbiology, 2011, 51(7): 851-857.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 闫昱辛,何美军,李宇,袁晓曼,谭旭辉,程名,罗凯,廖璐婧. 铁皮石斛叶多糖美白和抗氧化活性. 植物研究. 2025(01): 111-118 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 代丽丽,王景,魏许瑞,马庆亚,王娜,都治香. 基于PI3K/Akt信号通路研究灯盏花乙素对子宫内膜癌Ishikawa细胞的影响. 中国临床药理学杂志. 2024(01): 27-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张琦,包小波,田冲冲. 灯盏花乙素增强4T1乳腺癌细胞对顺铂敏感性的体内外研究. 食品工业科技. 2024(05): 331-340 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 王佳恩,殷子喻,马莉,李双良,符德欢. 灯盏乙素抗肿瘤作用机制研究进展. 中草药. 2024(13): 4608-4621 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张琦,田冲冲,张洋,方晨曦,卜薇,李凤. 灯盏花乙素通过PPARγ-PGC1α-UCP1通路改善小鼠肥胖作用及机制. 药物评价研究. 2024(08): 1787-1796 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 田冲冲,张琦,陈延绅. 基于肠道微生态探讨灯盏花乙素对乳腺癌小鼠的化疗增敏作用及其机制. 中国微生态学杂志. 2024(12): 1374-1381+1387 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:



