Structural Characterization and Stability Study of Iron-Chelating Peptides from Chicken Blood
-
摘要: 为了评估鸡血用于膳食铁补充剂的潜力,本文以鸡血和氯化亚铁为原料制备了鸡血球肽螯合铁,采用扫描电镜及差示扫描量热对其结构进行表征,分析了其在不同温度(30~80 ℃)及pH(2~9)下的稳定性,并对其体外稳定性进行了探讨。结果表明鸡血球肽和铁结合生成一种新的肽铁螯合物。该螯合物具有良好的热稳定性(铁保留率73.76%以上)并耐酸碱。经体外模拟消化发现,鸡血球肽螯合铁的消化稳定性(铁保留率为86.01%)优于硫酸亚铁和葡萄糖酸亚铁。此外,在1%植酸、1%草酸和8%膳食纤维这三种膳食因素的影响下,鸡血球肽螯合铁显示出比硫酸亚铁和葡萄糖酸亚铁更好的生物可及性。Abstract: To evaluate the potential of chicken blood for dietary iron supplementation, chicken blood and ferrous chloride were used as raw materials to prepare iron-chelating peptides from chicken blood in this paper. The structure of iron-chelating peptides from chicken blood was characterized by scanning electron microscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. The stability of iron-chelating peptides from chicken blood was analyzed at different temperatures (30~80 ℃) and pH (2~9), and its in vitro stability was also discussed. The study confirmed that it had good thermal stability (iron retention rate above 73.76%) and acid and alkali resistance. The digestive stability of iron-chelating peptides from chicken blood (iron retention of 86.01%) was found to be better than that of ferrous sulfate and ferrous gluconate by simulated digestion in vitro. In addition, under the influence of three dietary factors, namely 1% phytic acid, 1% oxalic acid, and 8% dietary fiber, iron-chelating peptides from chicken blood showed better bioaccessibility than ferrous sulfate and ferrous gluconate.
-
我国是世界上畜禽资源最丰富的国家之一。近年来,我国鸡肉生产保持持续增长,鸡肉产量仅次于美国,位居世界第二位[1]。鸡肉消费大大促进了鸡肉生产的增长。但与此同时,鸡屠宰的过程中也会产生大量的副产品,如皮、骨、血等。鸡血通常用于动物饲料[2],其附加值很低。但是其血球中富含蛋白质和血红蛋白铁[3],具有很高的营养价值,也是生产多肽的良好来源[4],可以应用于食品、医药等行业。
铁是一种重要的微量营养元素,在许多生理过程中发挥作用,如红细胞生成,循环系统的氧气输送和转移以及各种器官的抗氧化能力[5]。膳食铁的吸收受到多种因素的限制,如膳食纤维,谷物和豆类中的植酸,以及茶叶和红酒中的多酚类物质(如单宁酸)[6],这些饮食成分会与铁离子形成沉淀物,从而影响铁的吸收[7]。强化食品中的铁,是解决长期缺铁问题的一个富有成本效益的方法[8],目前首选的治疗方法是口服铁。硫酸亚铁、葡萄糖酸亚铁及其他铁盐作为营养强化剂[9],已广泛用于治疗铁缺乏。但是它们易对胃肠造成刺激,生物利用率较低[10]。肽铁螯合物以多肽中的共价键、氢键等作为铁结合配体,与亚铁离子契合形成。它因其稳定性高、能弥补铁盐普遍生物利用度较低的缺点等而引起广泛关注[11]。
目前已有研究利用桃仁[12]、羊骨[13]、鳕鱼皮[14]等作为肽源制备并表征了许多食源性肽铁螯合物,发现其可以提高铁的生物利用度。多肽铁螯合物作为营养补充剂,亟需研究其在胃肠消化及饮食成分共存情况下的生物利用率。因此本文旨在利用鸡血水解产物,制备鸡血球肽螯合铁,并对其稳定性和生物可及性进行研究。该研究对于鸡血资源利用及鸡血肽螯合铁营养强化剂的开发提供理论支持。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
鸡血球肽 本实验室自制;胃蛋白酶(100 U/mg)、胰蛋白酶(250 U/mg) 上海源叶生物技术有限公司;无水乙醇 国药集团化学试剂有限公司;DMEM高糖培养基 美国Hyclone公司;胎牛血清 美国Gibco公司;MTT 美国Sigma公司;Caco-2细胞 南京凯基生物科技有限公司;其他所用试剂均为分析纯。
PTX-FA210S型电子天平 福州华志科学仪器有限公司;DF-101S型数显集热式磁力搅拌器 上海易友仪器有限公司;TG16-WS型台式高速离心机 湖南湘仪实验室仪器开发有限公司;PILot2-4LD真空冷冻干燥机 北京博医康实验仪器有限公司;EVO-LS 10扫描电子显微镜 德国蔡司公司;NexIon2000电感耦合等离子体质谱仪 美国珀金埃尔默股份有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 鸡血球肽螯合铁的制备
将新鲜抗凝鸡血除杂后,于3000 r/min离心15 min,收集沉淀并加入5倍体积的去离子水,均质化处理40 min后,3000 r/min离心10 min,获得沉淀血细胞。参照Yang等[15]的方法并稍作修改,对沉淀血细胞进行酶解,酶解反应结束后于3000 r/min离心10 min,收集上清液,获得鸡血球多肽,冷冻干燥后收集鸡血球肽(CBP)粉末。根据杨静等[16]的方法,将鸡血球肽粉末溶解在去离子水中(终浓度为20 mg/mL),置于30 ℃的水浴中并调节pH至5.1,按质量比(5:1)加入FeCl2·4H2O水浴搅拌反应33 min。反应结束立即加入9倍体积的无水乙醇中静置4 h。随后,4 ℃下以10000 r/min离心10 min,收集沉淀冻干得到鸡血球肽螯合铁(CBP-Fe),其螯合率为72.17%。
1.2.2 表征分析
1.2.2.1 扫描电镜
取适量的CBP和CBP-Fe样品,经真空喷金处理后,在扫描电镜下观察样品的微观结构。具体条件参数为放大倍率1000,电压15 kV,工作距离6.5 mm。
1.2.2.2 差示扫描量热分析
用差示扫描量热仪对CBP和CBP-Fe进行差示扫描量热分析。将3 mg的冻干样品放在铝锅中。然后用压片机将铝制锅密封。在干燥氮气环境(N2流速50 mL/min)下,按10 ℃/min从25 ℃升温到300 ℃对样品进行加热扫描[17]。
1.2.3 稳定性分析
1.2.3.1 热稳定性试验
将CBP-Fe溶解于超纯水中至浓度为2 mg/mL,在不同温度(30、40、50、60、70、80 ℃)下分别加热1 h后加入乙醇静置4 h,随后反应液在8000 r/min下离心10 min,取上清液[18]。CBP-Fe的热稳定性以铁保留率表示,计算方法如下:
铁保留率(%)=A−A0A×100 式中:A代表样品中的总铁含量(mg);A0代表上清液中的铁含量(mg)。
1.2.3.2 酸碱稳定性试验
将CBP-Fe溶解在超纯水中至浓度为2 mg/mL,在37 ℃下不同pH(2、3、4、5、6、7、8、9)中反应1 h,接着加入乙醇静置4 h并将反应液在8000 r/min下离心10 min,取上清液[18]测铁离子含量。CBP-Fe的酸碱稳定性以铁保留率表示,计算方法同1.2.3.1中的公式。
1.2.4 Caco-2细胞活力试验
将Caco-2细胞置于DMEM培养基(含有10%胎牛血、1%非必需氨基酸及1%双抗),在37 ℃、5%CO2恒温培养箱中培养。在细胞覆盖率达80%时,用胰蛋白酶-EDTA消化液分散细胞,进行传代。参考Cai等[19]的方法,选取第23代对数生长期细胞,将其以每孔5×104个细胞的密度接种在96孔板中,并在37 ℃、5% CO2恒温培养箱中继续培养。24 h后,分别加入不同浓度的CBP-Fe溶液继续培养24 h。接着向每个孔注入20 μL MTT培养2 h,随后加入150 μL的二甲基亚砜立即振荡10 min后,使用酶标仪检测其在490 nm波长下的吸光值,按照如下公式计算细胞的相对活力(%):
细胞的相对活力(%)=As−AbAc−Ab×100 式中:As代表样品处理的吸光度值,Ab代表无细胞的吸光度值,Ac代表无样品处理的吸光度值。
1.2.5 体外模拟消化
参考Wu等[20]的方法,模拟CBP-Fe分别在胃、肠及胃肠的消化,并计算其在消化过程中的稳定性,计算公式同1.2.3.1。同时该试验以硫酸亚铁和葡萄糖酸亚铁作为对照。
1.2.5.1 体外模拟胃消化
将样品溶液(2.5 mg/mL)的pH调至2,加入2%(w/w)胃蛋白酶,在37 ℃下水浴反应2 h后,立即于100 ℃加热10 min。接着加入乙醇静置2 h后离心,测定上清液中的铁含量。
1.2.5.2 体外模拟肠消化
样品溶液(2.5 mg/mL)的pH调至7.6,并加入2%(w/w)胰蛋白酶。37 ℃下水浴反应2 h后,反应液在100 ℃加热10 min。然后加入乙醇静置2 h并将其离心,测定上清液中的铁含量。
1.2.5.3 体外模拟肠道消化
将样品溶液(2.5 mg/mL)的pH调至2,并加入2%(w/w)胃蛋白酶,然后在37 ℃下水浴反应2 h。随后将反应液pH调至7.6,加入2%(w/w)的胰蛋白酶继续水浴反应2 h。100 ℃下加热10 min,终止反应[21]。加入乙醇静置2 h后将反应液离心,测定其上清液中的铁含量。
1.2.6 模拟消化过程中不同膳食成分对鸡血球肽螯合铁的影响
分别称取一定量CBP-Fe、葡萄糖酸亚铁和硫酸亚铁溶解在超纯水中(Fe2+含量为1.2 mg/mL)。溶液在37 ℃水浴中预热后,pH调至2,加入1%草酸溶液。接着加入3%的胃蛋白酶(w/w)反应2 h,用1.0 mol/L NaOH将溶液的pH调整到7.6,加入3%的胰蛋白酶(w/w)继续反应2 h。然后于100 ℃下加热10 min,在4500 r/min下离心10 min,测定上清液中的铁含量[22]。此外,各加入1%植酸溶液和8%膳食纤维,重复上述操作进行。可溶性铁含量用以下公式计算:
可溶性铁含量(%)=SC×100 式中:S是上清液中的铁含量(mg);C是样品中的总铁含量(mg)。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验均重复三次。采用SPSS 25.0版的方差分析(Analysis of Variance)对数据进行分析,并进行独立样本T检验和Duncan’s多重范围检验以确定统计学意义(P<0.05)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 鸡血球肽及其铁螯合物的微观结构
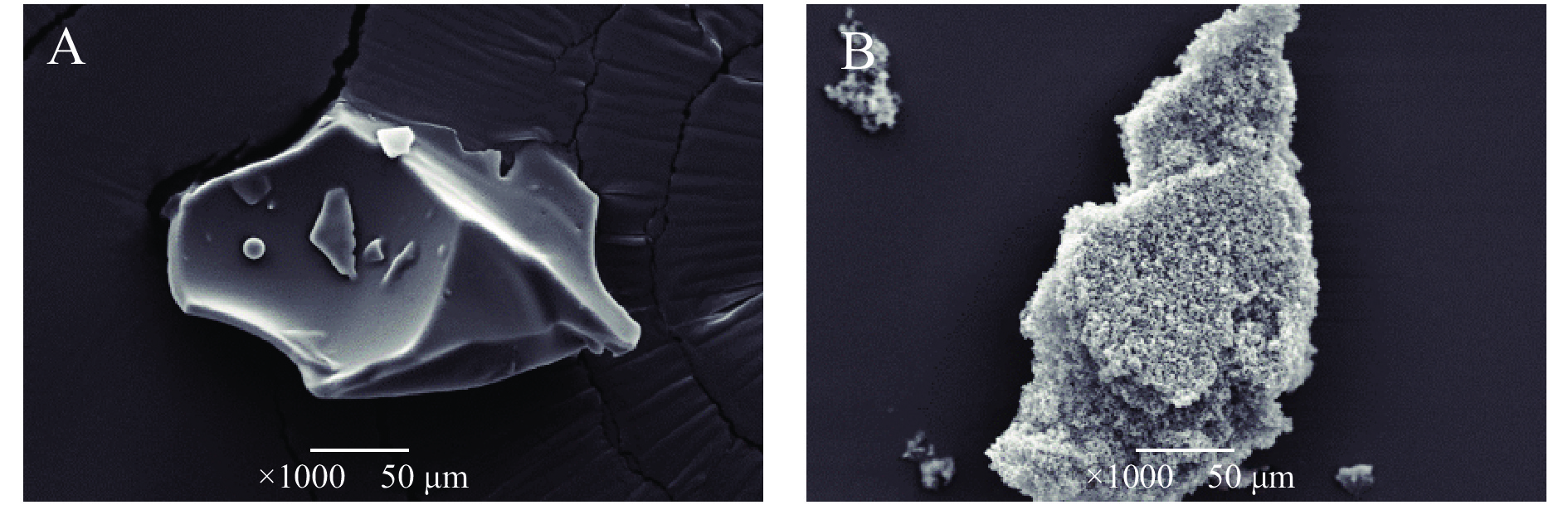
利用SEM对鸡血球肽及其铁螯合物的微观结构进行了研究。从图1可以看到,图1A中鸡血球肽呈现出表面较为平滑、疏松的板状结构。图1B中鸡血球肽螯合铁的表面则呈现出较为绵密的状态,并聚集了一些突起的颗粒。陈嘉琪等[13]也发现了类似的结果,其制备的羊骨多肽亚铁螯合物在微观结构下,表面松散粗糙,同时附有大密度颗粒。
SEM结果表明多肽与亚铁在螯合反应后结构发生了变化。它们之间存在差异的主要原因可能是多肽与亚铁离子通过离子键和配位键发生了相互作用[18]。此外,鸡血球肽螯合铁表面附着的小颗粒聚集体,可能是吸附在上面的亚铁晶体[23]。因此,多肽与亚铁离子之间可能还存在着一定的吸附作用。
2.2 差示扫描量热分析
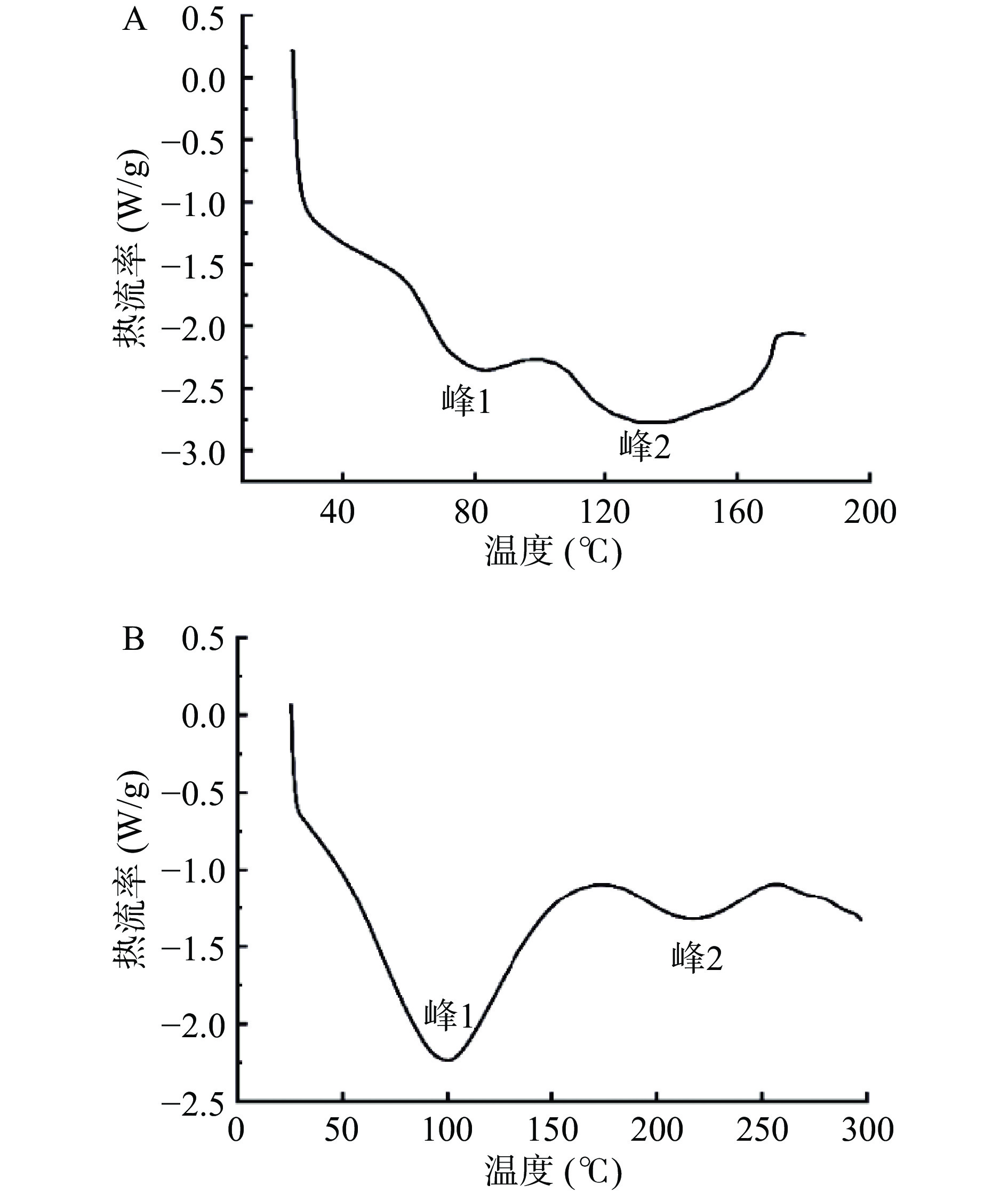
差示扫描量热法是一种热分析技术,可以测量物质在受热过程中其能量差与温度的关系,已广泛应用于分析蛋白质的热稳定性和构象上。图2为鸡血球肽(CBP)和鸡血球肽螯合铁(CBP-Fe)的差示扫描量热分析图谱,表1总结了CBP和CBP-Fe的峰值变性温度及熔融焓(△H)。图中结果所示CBP和CBP-Fe都为吸热转变。CBP的吸热峰出现在81.97 ℃和135.34 ℃,键能为15.13 J/g和45.37 J/g,CBP-Fe的吸热峰右移,依次出现在100.16 ℃和217.49 ℃,键能则为224.69 J/g和29.58 J/g。两者之间的明显差异可能是源于鸡血球肽与铁离子之间发生了螯合[24],螯合物具有更加紧密的的结构,比鸡血球肽更加稳定。因此化学键断裂所需的能量更大,断裂温度也升高。
表 1 鸡血球肽和鸡血球肽螯合铁的熔融焓和变性温度Table 1. Enthalpy of fusion and denaturation temperature and of chicken blood peptide and iron chelated chicken blood peptide样品 峰1 峰2 变性温度(℃) △H(J/g) 变性温度(℃) △H(J/g) CBP 81.97±5.674a 15.13±9.016a 135.34±1.802a 45.37±5.011b CBP-Fe 100.16±7.342b 224.69±8.823b 217.49±6.184b 29.58±5.945b 注:表中数据表示为平均值±标准差,同一列中上标不同字母表示差异显著性(P<0.05)。 2.3 CBP-Fe的热稳定性分析
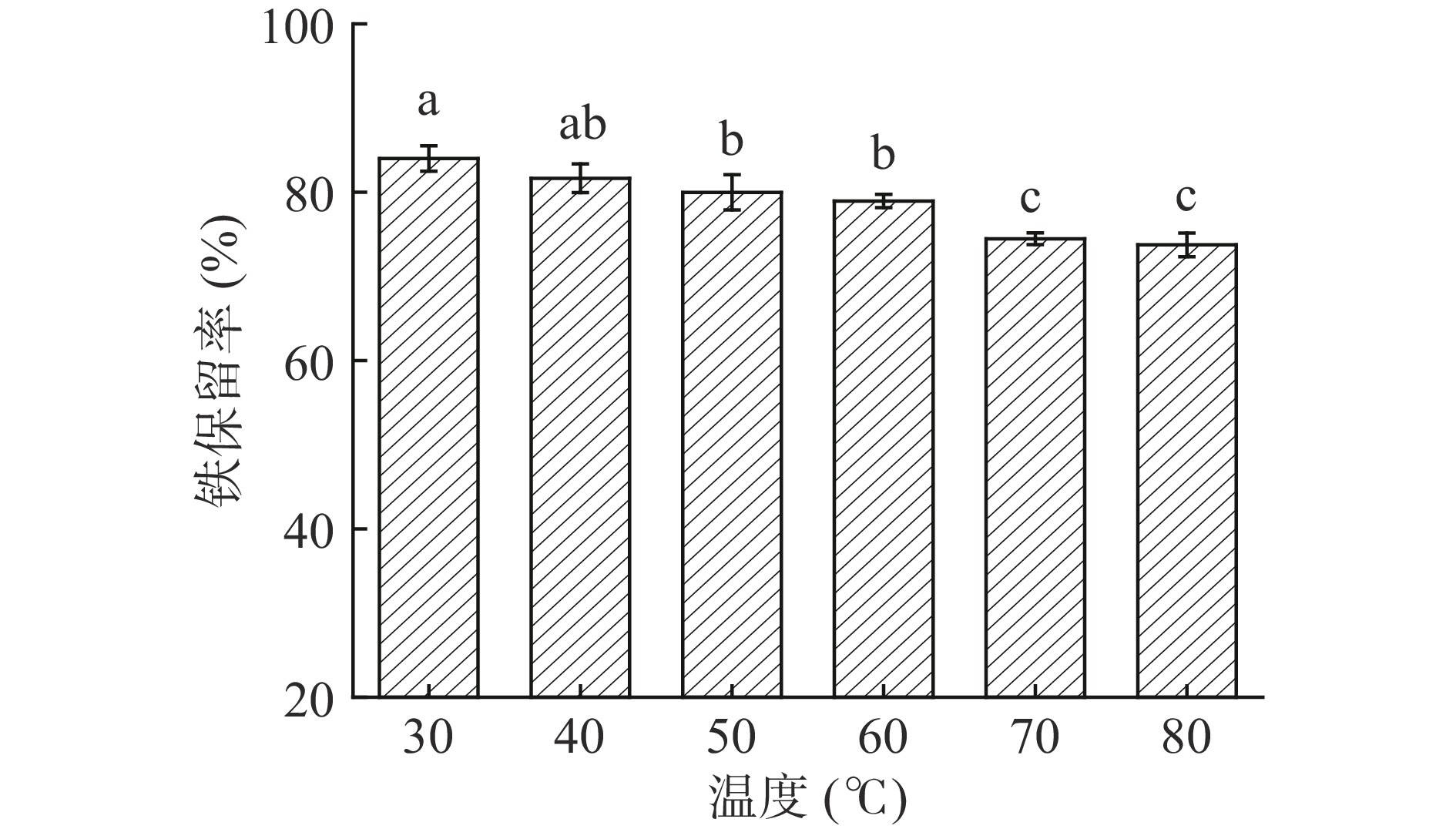
由图3可知,鸡血球肽螯合铁在30 ℃时具有最高的铁保留率(84.01%)。随着温度的升高,铁的保留率逐渐下降。这可能是由于铁离子和肽之间的配位键在高温下断裂导致CBP-Fe分解。当温度升高至80 ℃时,铁保留率为73.76%。温度从30 ℃升至80 ℃,CBP-Fe稳定性变化相对稳定。这一趋势与之前Shilpashree等[25]制备铁结合的浓缩乳清蛋白复合物中得到的结果一致。总的来说,铁的保留率可以保持在70%到85%之间,表明当鸡血球肽螯合铁在30~80 ℃温度范围内热加工处理时,具有良好的热稳定性。
2.4 CBP-Fe的酸碱稳定性分析
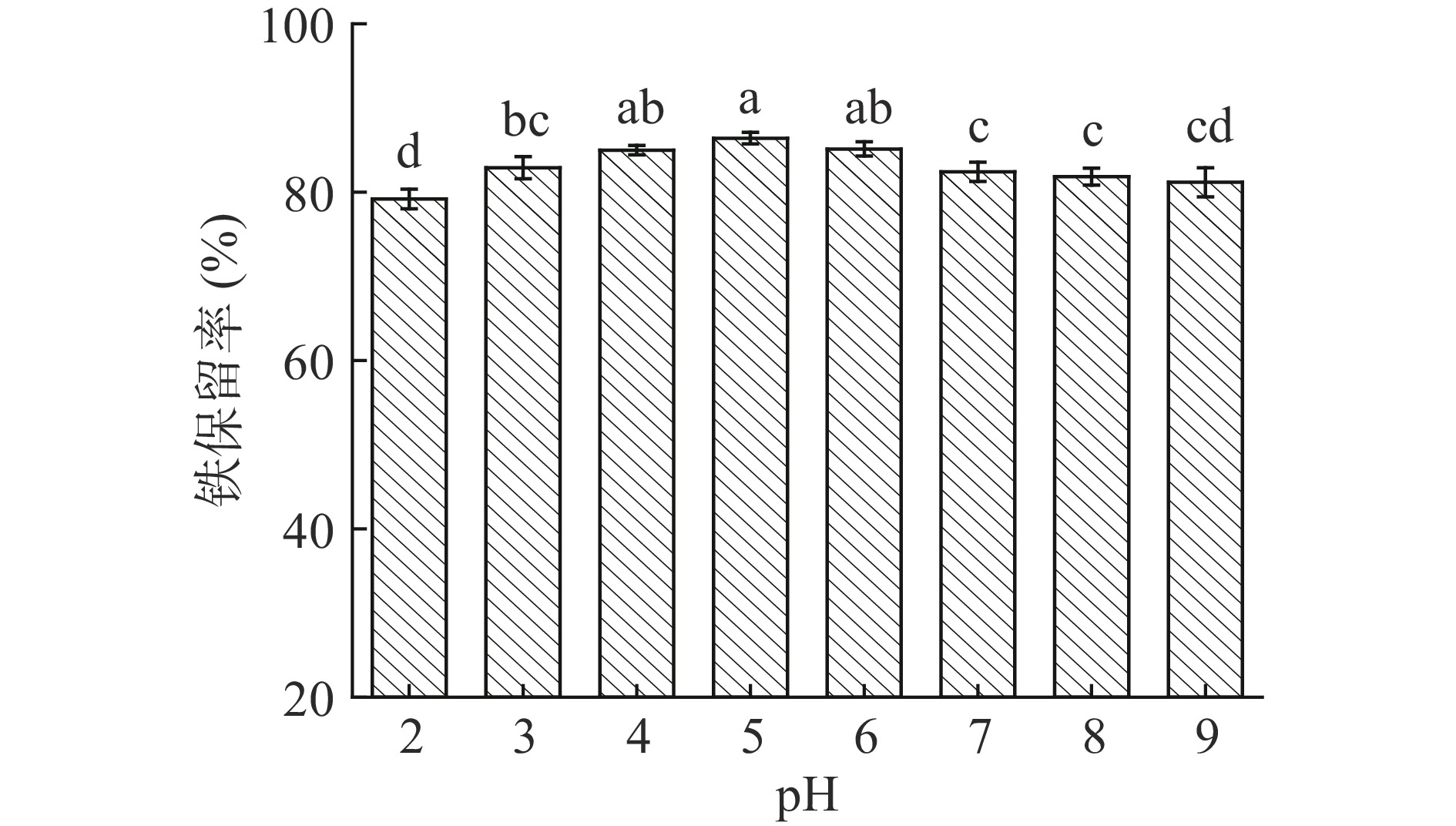
图4所示为鸡血球肽螯合铁在不同pH下的铁保留率。由图4可以看出,CBP-Fe在pH为2时铁保留率最低,为79.18%。当pH从3到5时,铁的保留率从82.89%增加到86.41%。在pH为5时,铁保留率最高。随着pH的继续增加,保留率开始下降,但下降不明显。当pH为9时,铁保留率为81.17%。从总体变化上看,CBP-Fe的铁保留率在碱性环境中更高。这一研究结果与汪卓[26]提出的蛋黄蛋白亚铁螯合肽酸碱稳定性结论一致。这可能是因为当环境pH为酸性时,H+会与Fe2+竞争与肽的螯合位点,导致部分Fe2+无法与肽结合[23]。因此CBP-Fe在碱性环境中要比在酸性环境中更加稳定。
2.5 Caco-2细胞毒性试验分析
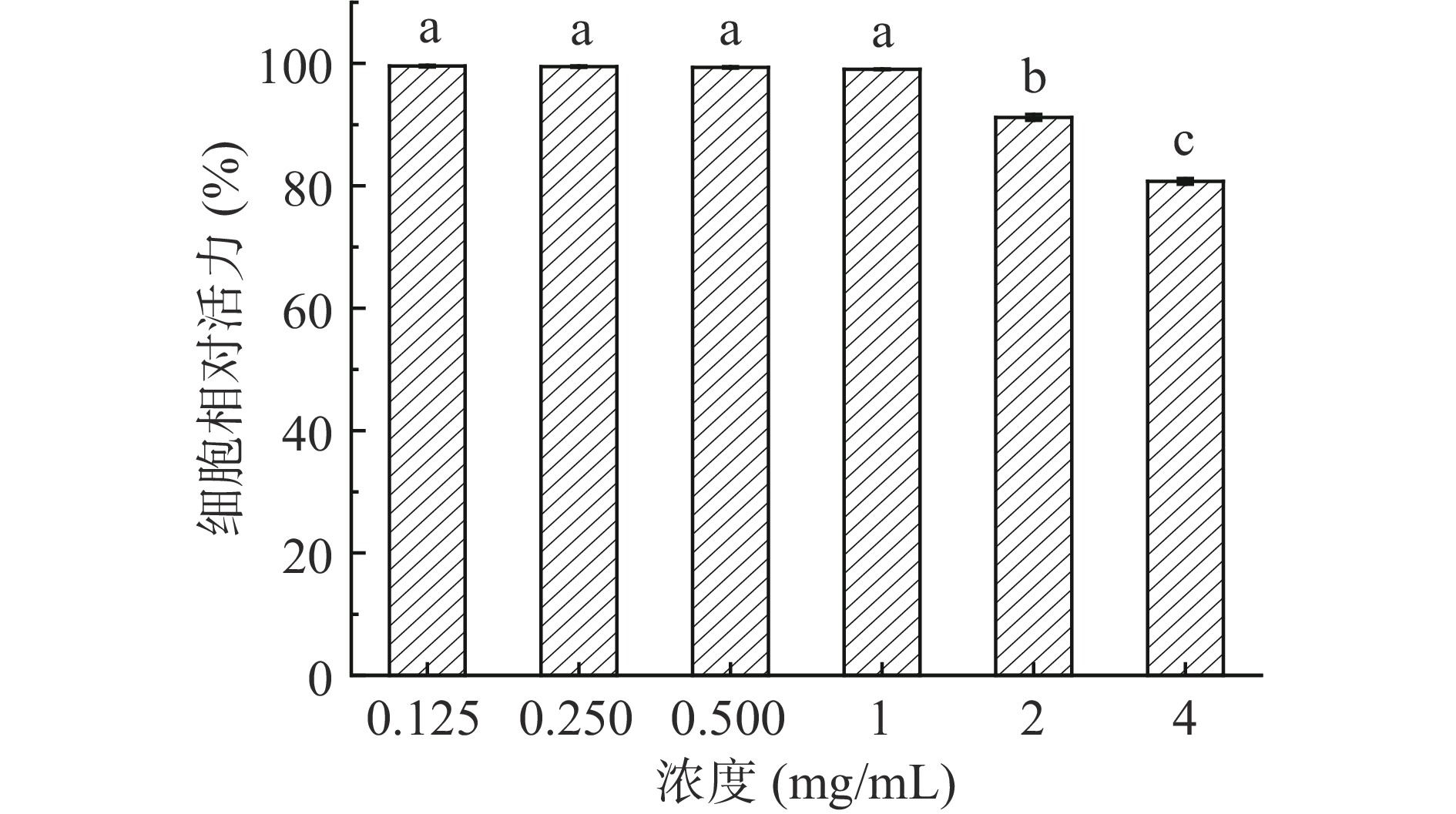
选用不同浓度(0.125、0.25、0.5、1、2、4 mg/mL)的CBP-Fe通过MTT法来测定其对于Caco-2细胞活力的影响,结果如图5所示。结果表明,当浓度在0.125~0.1 mg/mL时,细胞活力降低不显著(P>0.05)。而浓度升至2 mg/mL时,细胞活力显著下降(P<0.05)。当CBP-Fe溶液浓度升至4 mg/mL时,作用后的细胞活力仍高于80%。Caetano-silva等[27]提出经乳清肽铁复合物处理后的Caco-2细胞活力大于87%,表明复合物不会损害细胞生长。这为后续试验提供了一定的参考。
2.6 CBP-Fe体外模拟消化
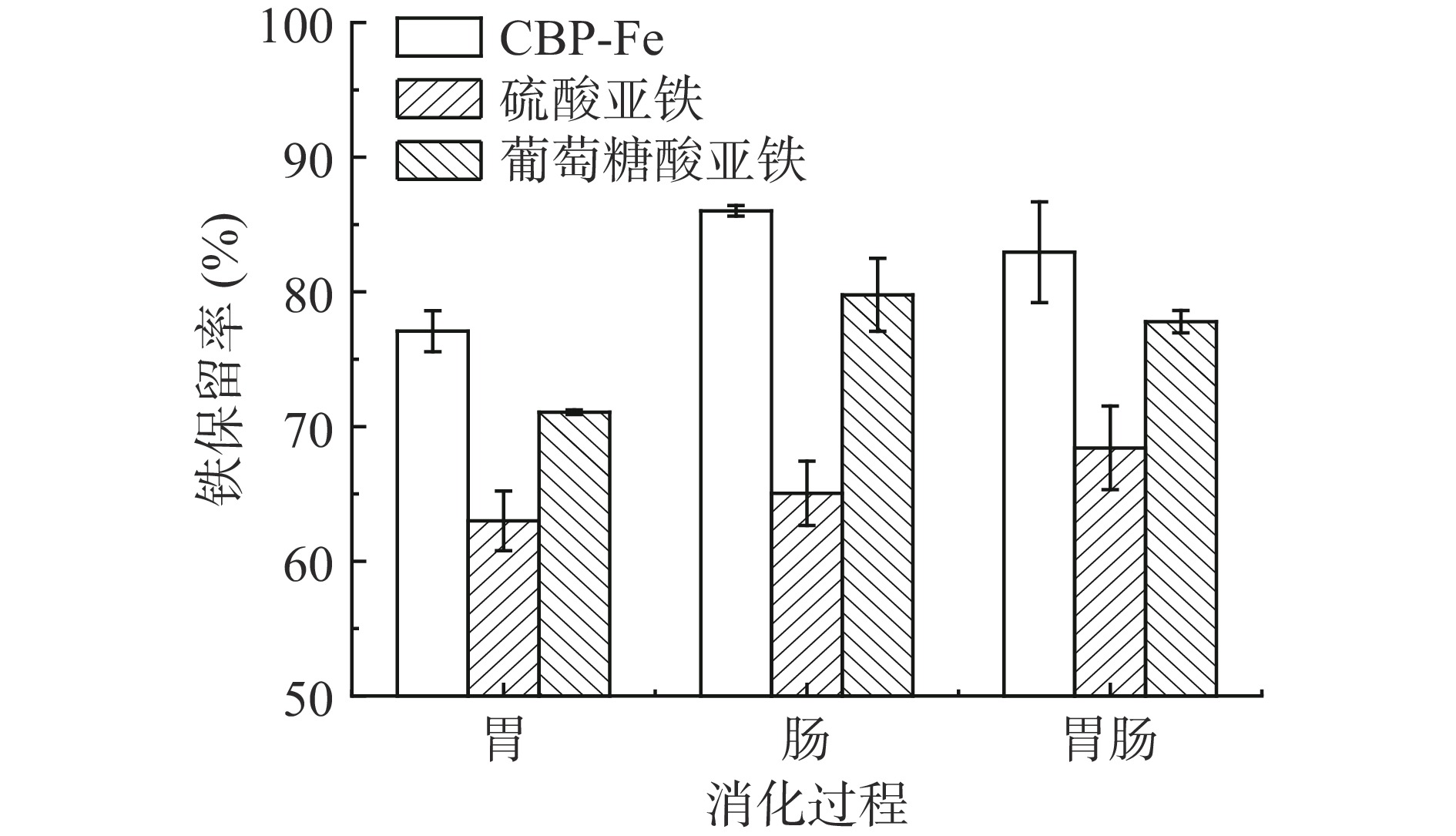
铁补充剂进入胃肠道后,受周围环境中pH的变化和胃胰腺分泌蛋白酶等因素影响,会形成不溶性化合物,从而导致铁的生物利用度降低[28]。因此,铁补充剂在胃肠道环境中的稳定性是其被充分利用,提高铁生物利用度的关键因素。CBP-Fe、硫酸亚铁和葡萄糖酸亚铁在胃肠道中的稳定性结果见图6。
CBP-Fe经胃消化后的铁保留率为77.08%,肠消化后为82.94%,肠消化的铁保留率要高于胃消化部分,这可能是因为模拟胃消化时,H+浓度高,与铁离子竞争给电子基团,不利于肽和铁离子的结合[29]。而肠道为碱性环境,CBP-Fe本身在碱性环境中要比在酸性环境中更加稳定,并且铁离子可能会在肠道中与肽重新螯合生成新的肽螯合铁[26]。CBP-Fe经完整的胃肠消化后,铁保留率为82.94%。这表明CBP-Fe在体外模拟胃肠消化时,可以保持良好的稳定性。
此外,CBP-Fe的铁保留率仍然要优于硫酸亚铁和葡萄糖酸亚铁。这说明CBP-Fe相比于其他膳食铁补充剂,具有更好的生物利用度。Hu等[29]也提出了南极磷虾衍生的七肽铁络合物铁螯合肽对铁吸收的促进作用要比FeSO4更好。这些结果表明CBP-Fe具有一定的抗消化性,有望作为功能性食品缓解铁缺乏。
2.7 不同膳食成分对CBP-Fe的影响分析
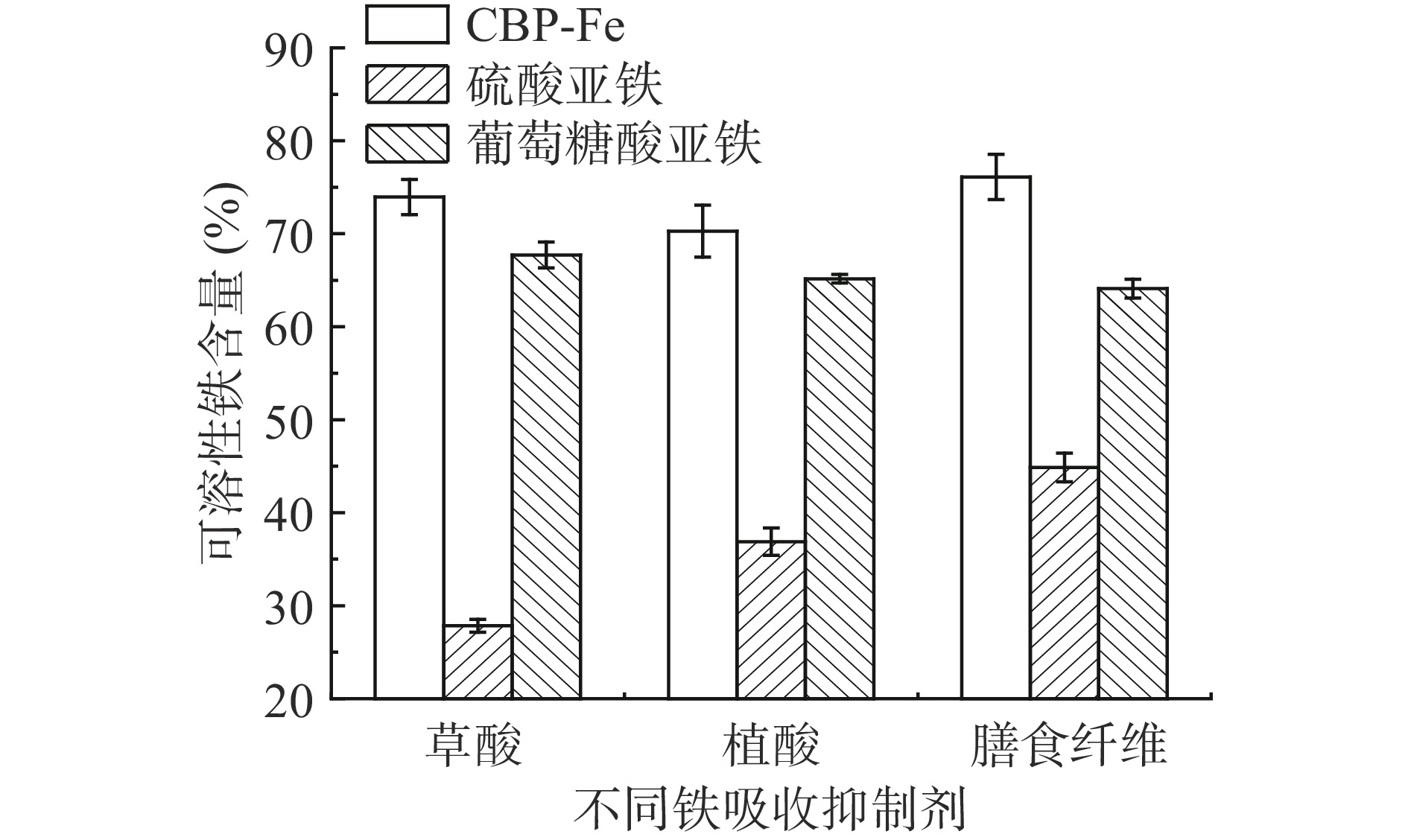
在日常饮食中如谷物、茶叶等通常含有植酸、草酸、多酚、膳食纤维等成分,这些膳食成分具有金属螯合能力,会与铁离子结合形成沉淀,从而影响人体对铁的吸收,降低铁的生物利用度[30]。因此研究膳食成分对不同铁补充剂的影响,对分析其生物利用度具有重要意义。
从图7可以看出,植酸、草酸、膳食纤维分别存在的条件下,三种铁补充剂的可溶性铁含量大小依次为:CBP-Fe最高,葡萄糖酸亚铁次之,硫酸亚铁最低。表明CBP-Fe在膳食成分中比葡萄糖酸亚铁和硫酸亚铁稳定性更好。膳食成分的添加降低了金属离子的吸收,而CBP-Fe由于CBP对铁离子有更强的螯合能力,阻止了铁离子的沉淀。其他研究也表明铁肽复合物可以保护铁离子免受膳食成分的影响[31]。此外,图7也显示三种膳食成分中,植酸对CBP-Fe的影响最大(可溶性铁含量为70.28%),其次是草酸(可溶性铁含量为73.96%),膳食纤维的影响最小(可溶性铁含量为76.11%)。这可能是因为植酸的磷酸基团与铁离子的结合能力更强[32]。总体来说,CBP-Fe能更好地抵抗植酸等膳食成分对铁吸收的抑制作用,提高铁在人体内的生物利用度。
3. 结论
本文利用鸡血球肽制备了鸡血球肽螯合铁,并通过试验表明它能够经受热处理和酸碱处理。在体外模拟胃肠消化试验中,鸡血球肽螯合铁的稳定性优于葡萄糖酸亚铁和硫酸亚铁。此外,鸡血球肽螯合铁相比于葡萄糖酸亚铁和硫酸亚铁,能有效抵抗植酸、草酸和膳食纤维对铁吸收的抑制作用。本研究结果表明鸡血球肽螯合铁可以用作膳食补铁剂。此外,未来还需对鸡血球肽与铁的具体结合方式以及吸收机制进行更多研究,以便更好地提高铁在人体中的生物利用度。
-
表 1 鸡血球肽和鸡血球肽螯合铁的熔融焓和变性温度
Table 1 Enthalpy of fusion and denaturation temperature and of chicken blood peptide and iron chelated chicken blood peptide
样品 峰1 峰2 变性温度(℃) △H(J/g) 变性温度(℃) △H(J/g) CBP 81.97±5.674a 15.13±9.016a 135.34±1.802a 45.37±5.011b CBP-Fe 100.16±7.342b 224.69±8.823b 217.49±6.184b 29.58±5.945b 注:表中数据表示为平均值±标准差,同一列中上标不同字母表示差异显著性(P<0.05)。 -
[1] 2021年肉鸡产业发展形势及2022年展望[J]. 中国畜牧业, 2022(3): 43−46 Development situation of broiler industry in 2021 and prospect in 2022[J]. China Animal Husbandry, 2022(3): 43−46.
[2] HAMZEH A, WONGNGAM W, KIATSONGCHAI R, et al. Cellular and chemical antioxidant activities of chicken blood hydrolysates as affected byin vitro gastrointestinal digestion[J]. Poultry Science,2019,98(11):6138−6148. doi: 10.3382/ps/pez283
[3] 宁芯, 黎梓玉, 班薇薇, 等. 酶法制备鸡血抗氧化肽及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品工业,2020,41(12):129−133. [NING X, LI Z Y, BAN W W, et al. Optimization of preparation process for antioxidant peptides from chicken plasma and its antioxidant activities[J]. Food Industry,2020,41(12):129−133. NING X, LI Z Y, BAN W W, et al. Optimization of preparation process for antioxidant peptides from chicken plasma and its antioxidant activities[J]. Food Industry, 2020, 41(12): 129-133.
[4] ZHENG Z, SI D, AHMAD B, et al. A novel antioxidative peptide derived from chicken blood corpuscle hydrolysate[J]. Food Research International,2018,106:410−419. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2017.12.078
[5] 郑敏, 王钏. 螯合铁工艺的研究进展[J]. 现代食品,2019(22):32−34, 37. [ZHENG M, WANG C. Research processing of iron-chelation technology[J]. Modern Food,2019(22):32−34, 37. ZHENG M, Wang C. Research processing of Iron-chelation Technology[J]. Modern Food, 2019(22): 32-34, 37.
[6] KALGAONKAR S, LÖNNERDAL B. Effects of dietary factors on iron uptake from ferritin by Caco-2 cells[J]. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry,2008,19(1):33−39. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2007.02.001
[7] CAETANO-SILVA M E, NETTO F M, BERTOLDO-PACHECO M T, et al. Peptide-metal complexes: Obtention and role in increasing bioavailability and decreasing the pro-oxidant effect of minerals[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2021,61(9):1470−1489. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1761770
[8] SHUBHAM K, ANUKIRUTHIKA T, DUTTA S, et al. Iron deficiency anemia: A comprehensive review on iron absorption, bioavailability and emerging food fortification approaches[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2020,99:58−75.
[9] 管玲娟, 曹丛丛, 屠飘涵, 等. 缺铁对肠道免疫功能的影响及新型补铁剂的研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(19):264−270. [GUAN L J, CAO C C, TU P H, et al. Research progress of the effect of iron deficiency on intestinal immune function and new iron supplements[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2020,46(19):264−270. GUAN L J, CAO C C, TU P H, et al. Research progress of the effect of iron deficiency on intestinal immune function and new iron supplements[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry, 2020, 46(19): 264-270.
[10] 林海燕, 王珊, 孙珊, 等. 响应面法优化南极磷虾亚铁螯合肽制备工艺及其理化性质[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(21):166−173. [LIN H Y, WANG S, SUN S, et al. Optimization of preparation of iron-chelating peptides from Antarctic krill by response surface methodology and its physicochemical properties[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(21):166−173. LIN H Y, WANG S S, SUN S, et al. Optimization of preparation of iron-chelating peptides from Antarctic krill by response surface methodology and its physicochemical properties[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2019, 40(21): 166-173.
[11] TIAN Q, FAN Y, HAO L, et al. A comprehensive review of calcium and ferrous ions chelating peptides: Preparation, structure and transport pathways[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2021:1−13.
[12] 杨玉蓉, 李安平, 钟政昌, 等. 桃仁多肽螯合亚铁的抑菌活性及结构表征[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(5):57−62. [YANG Y R, LI A P, ZHONG Z C, et al. Antibacterial activity and structural characterization of peach kernel peptide-ferrous chelate[J]. Food Science,2019,40(5):57−62. YANG Y R, LI A P, ZHONG Z C, et al. Antibacterial activity and structural characterization of peach kernel peptide-ferrous chelate[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(5): 57-62.
[13] 陈嘉琪, 张珍, 费莹莹, 等. 羊骨多肽亚铁螯合物的制备工艺优化及结构表征[J]. 食品与发酵科技,2021,57(5):1−7, 21. [CHEN J Q, ZHANG Z, FEI Y Y, et al. Preparation process optimization and structural characterization of sheep bone polypeptide chelate with ferrous iron[J]. Food and Fermentation Science and Technology,2021,57(5):1−7, 21. CHEN J Q, ZHANG Z, FEI Y Y, et al. Preparation process optimization and structural characterization of sheep bone polypeptide chelate with ferrous iron[J]. Food and Fermentation Science and Technology, 2021, 57(5): 1-7, 21.
[14] CHEN Q, GUO L, DU F, et al. The chelating peptide (GPAGPHGPPG) derived from Alaska pollock skin enhances calcium, zinc and iron transport in Caco-2 cells[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2017,52(5):1283−1290.
[15] YANG J, HUANG J, DONG X, et al. Purification and identification of antioxidant peptides from duck plasma proteins[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,319:126534. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126534
[16] 杨静, 石景, 邹烨, 等. 鸡血多肽亚铁螯合物的制备工艺优化及结构表征[J]. 江苏农业学报,2022,38(6):1678−1685. [YANG J, SHI J, ZOU Y, et al. Preparation process optimization and structural characterization of chicken blood peptides-iron chelate[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agriculture Science,2022,38(6):1678−1685. YANG J, SHI J, ZOU Y, et al. Preparation process optimization and structural characterization of chicken blood peptides-iron chelate[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agriculture Science, 2022, 38(6): 1678-1685.
[17] 冯思敏, 王晶, 王羽莹, 等. 珍珠肽螯合钙的制备与性质表征[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(1):119−126. [FENG S M, WANG J, WANG Y Y, et al. Preparation and properties of pearl peptide chelated calcium[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(1):119−126. FENG S M, WANG J, WANG Y Y, et al. Preparation and properties of pearl peptide chelated calcium[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2022, 43(1): 119-126.
[18] 庞忠莉. 牡蛎肽亚铁螯合物的制备及性质研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2020 PANG Z L. Study on preparation and properties of oyster peptide ferrous chelate[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2020.
[19] CAI X X, ZHAO L N, WANG S Y, et al. Fabrication and characterization of the nano-composite of whey protein hydrolysate chelated with calcium[J]. Food & Function,2015,6(3):816−823.
[20] WU W, HE L, LIANG Y, et al. Preparation process optimization of pig bone collagen peptide-calcium chelate using response surface methodology and its structural characterization and stability analysis[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,284:80−89. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.103
[21] 张玲. 罗非鱼皮胶原降解反应行为及肽钙螯合物制备研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2020 ZHANG L. Studies on tilapia skin collagen degradation behavior and preparation of peptide calcium chelate[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2020.
[22] JIANG Y, LI J, ZHAO H, et al. Preparation of grape seed polypeptide and its calcium chelate with determination of calcium bioaccessibility and structural characterisation[J]. International Journal of Food Science and Technology,2021,56(1):166−177. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.14616
[23] ZHANG Y, DING X, LI M. Preparation, characterization and in vitro stability of iron-chelating peptides from mung beans[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,349:129101. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129101
[24] LI B, HE H, SHI W, et al. Effect of duck egg white peptide-ferrous chelate on iron bioavailability in vivo and structure characterization[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2019,99(4):1834−1841. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.9377
[25] SHILPASHREE B G, ARORA S, SHARMA V. Preparation of iron/zinc bound whey protein concentrate complexes and their stability[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2016,66:514−522. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2015.11.005
[26] 汪卓. 蛋黄蛋白亚铁螯合肽的制备及螯合特性研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2021 WANG Z. Preparation and chelating properties of egg yolk protein ferrous chelating peptide[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2021.
[27] CAETANO-SILVA M E, CILLA A, BERTOLDO-PACHECO M T, et al. Evaluation of in vitro iron bioavailability in free form and as whey peptide-iron complexes[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2018,68:95−100. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2017.03.010
[28] SUN X, SARTESHNIZI R A, BOACHIE R T, et al. Peptide-mineral complexes: Understanding their chemical interactions, bioavailability, and potential application in mitigating micronutrient deficiency[J]. Foods,2020,9(10):1−17.
[29] HU S, LIN S, LIU Y, et al. Exploration of iron-binding mode, digestion kinetics, and iron absorption behavior of Antarctic krill-derived heptapeptide-iron complex[J]. Food Research International, 2022: 154.
[30] MATTAR G, HADDARAH A, HADDAD J, et al. New approaches, bioavailability and the use of chelates as a promising method for food fortification[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,373:131394. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.131394
[31] LI Y, JIANG H, HUANG G. Protein hydrolysates as promoters of non-haem iron absorption[J]. Nutrients,2017,9(6):609. doi: 10.3390/nu9060609
[32] LI J P, GONG C G, WANG Z Y, et al. Oyster-derived zinc-binding peptide modified by plastein reaction via zinc chelation promotes the intestinal absorption of zinc[J]. Marine Drugs,2019,17(6):341. doi: 10.3390/md17060341
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 祝超智,温耀涵,许龙,张秋会,王兴辉,赵改名,韩广星. 牛血红蛋白肽的酶解工艺优化及其亚铁螯合物结构、稳定性研究. 食品工业科技. 2024(08): 75-87 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 吴晗硕,任杰,张新雪,付少委,李书国,刘文颖. 玉米肽亚铁螯合物的结构特性及稳定性. 现代食品科技. 2024(07): 137-144 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



