Risk Assessment and Ranking of Pesticide Residues in Xinjiang Apricot
-
摘要: 为明确新疆杏中残留农药的种类、残留风险水平,本研究以2021年和2022年新疆6个杏主产区的77份样品为研究对象,使用液相色谱-质谱法和气相色谱-质谱法对杏中的99种农药进行定量分析,计算杏中农药残留的急性、慢性膳食摄入风险,并进行排序,针对杏中检出的无最大残留限量的农药,提出了最大残留限量建议值。研究结果显示,新疆杏样品农药残留检出率较高,达到96.1%,样品残留农药共计23种,其中多菌灵、啶虫脒、氯氟氰菊酯的检出率较高。残留农药的急慢性膳食摄入风险在可接受水平。根据农药风险评估排序,克百威、甲拌磷、甲氨基阿维菌素苯甲酸盐、三唑磷4种农药被确定为高风险农药,风险得分分别为25.3、25.1、20.2、20.1。抽查的77份样品不存在高风险的样品,主要以低风险和极低风险样品为主。检出的农药中有10种尚未制定最大残留限量,综合分析,建议优先制定虫酰肼、甲氨基阿维菌素苯甲酸盐、三唑磷3种残留农药的最大限量值,建议值分别为:6、0.1、0.3 mg/kg。可见,新疆杏质量安全状况整体良好,建议完善杏中常用而无农药残留最大限量值规定农药的限量值。Abstract: In order to clarify the types and risk levels of residual pesticides in Xinjiang apricots, in this study, 77 samples from six major apricot producing areas of Xinjiang in 2021 and 2022 were selected as the research objects. The liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry were used to quantitatively analyze 99 kinds of pesticides in apricot, and acute and chronic dietary intake risks of pesticide residues in apricot were calculated and sorted. For the maximum residual limited pesticides detected in apricot, the recommended value of maximum residual limit was put forward. The results of the study showed that the detection rate of pesticide residues in Xinjiang apricot sample was 96.1%, and there were 23 pesticide residues in total, of which carbendazim, acetamiprid, and cyhalothrin had relatively high detection rates. The risk of acute and chronic dietary intake of residual pesticides was at acceptable levels. According to the order of pesticide risk assessment, four pesticides were identified as high risk pesticides, namely, carbofuran, phorate, emamectin benzoate, and triazophos, with risk scores of 25.3, 25.1, 20.2, and 20.1 respectively. There were no high risk samples in 77 samples, mainly low risk and very low risk samples. Of the pesticides detected, 10 had not yet been established maximum residue limits. Based on the comprehensive analysis, it iwas recommended to prioritize the maximum limit values of three residual pesticides, namely, tebufenozide, emamectin benzoate, and triazophos, and the recommended values were 6, 0.1, and 0.3 mg/kg, respectively. It can be seen that the quality and safety of Xinjiang apricot is generally good, and it is suggested to improve the maximum limit value of pesticides which is commonly used in apricot without pesticide residue.
-
Keywords:
- Xinjiang apricot /
- pesticide residues /
- risk assessment /
- maximum residue limit
-
杏(Prunus armeniaca L.)属于蔷薇科杏属落叶乔木,新疆是世界杏属植物起源中心之一,具有悠久的栽培历史[1],2020年新疆杏种植面积11.6万公顷,产量93.8万吨[2],新疆杏品种资源丰富,果实品质优异。但是,在杏果实的生长成熟阶段易患果实斑点病、裂果病、细菌性穿孔病[3],且会受到黄斑长翅卷叶蛾和桃粉大尾蚜等虫害[4−5],而多菌灵、甲胺磷、哒螨灵、氟菌唑、氯氰菊酯、嘧菌环胺、噻螨酮、吡虫啉等农药作为一种快速、有效的手段被广泛应用于杏生产中病虫害的防治[6−8]。这给杏的质量安全带来潜在风险,所以对杏果实进行农药残留风险评估是非常有必要的。
近年来,果蔬农药残留风险问题已广泛引起人们的重视[9−10],风险评估是食品质量安全监管的重要手段之一[11],对农药残留进行风险评估可以评判出果蔬中风险程度较高的农药,并在生产中对其进行监控,保障消费者的饮食健康[12−13]。风险评估包括采用%ADI进行慢性膳食摄入风险评估,采用%ARfD进行急性膳食摄入风险评估[14−15],采用食品安全指数(IFS)进行蔬菜农药残留风险评估[16]等。常薇等[17]采用急性(%ARfD)、慢性(%ADI)膳食风险评估方法对成都市售9类果蔬中的农药残留进行了风险评估,慢性膳食暴露评估结果显示所有检出农药的食品安全指数值均小于1,表明风险可以接受。黄惠玲等[18]检测海南省2015~2020年水果中有机磷农药的残留情况,发现其农药残留检出率为9.79%,超标率为9.22%,超标的农药包括毒死蜱、氧化乐果、甲胺磷等高毒农药,计算接触风险发现,对人体健康危害的农残主要来自氧化乐果农药残留,但对人体危害的风险较小。Yang等[19]采集了山东、北京、新疆等7个地区共计210批次的杏,检测了11种农药残留,41批次样品检出农药残留,检出率为19.5%,检出农药主要为甲氰菊酯、吡虫啉、啶虫脒、联苯菊酯,其中新疆杏中检测到吡虫啉,残留量低于最大残留限量,对中国不同年龄、性别人群膳食摄入风险进行评估,结果显示,我国不同性别、不同年龄组人群的膳食风险商数在0.003%~1.184%之间,对一般人群没有不可接受的公共卫生风险。可见,我国果蔬的质量安全状况整体良好,但是偶尔也见果蔬中农药残留超标的现象。新疆杏果肉橙黄,柔软多汁,味甜可口,不论是鲜食还是干制,都深受市场喜欢。随着交通的发展,新疆杏也广泛销售于全国各地,但是目前关于新疆杏农药残留系统风险评估尚未见报道,其风险水平不明,存在潜在的安全风险。
本研究通过对新疆杏中农药的残留水平与膳食暴露风险进行评估,明确新疆杏中常用农药残留状况及风险水平,确定杏中主要的农药残留种类以及关键的农药风险因子,同时针对杏中部分尚未制定农药最大残留限量的农药,计算出最大残留限量估计值,给出建议值,为新疆杏的安全生产、消费及质量安全监管提供借鉴和依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
杏果实样品 在2021和2022年杏上市期,实地抽样采集新疆6个杏主产区的即将上市销售的杏果实样品,共采集了77批次样品。采集地区包括库车县、轮台县、皮山县、疏附县、托克逊县、英吉沙县等6个县,每次采样后将样品去除果核后匀浆处理,并贮存于−18 ℃低温冰箱待测;甲醇、乙腈、乙酸乙酯 色谱纯,赛默飞世尔科技(中国);乙酸铵、氯化钠、无水硫酸镁 分析纯,北京北化精细化学品有限责任公司;环氧七氯B、99种单一农药标准品(浓度均为:1000 mg/L,规格:1 mL) 国家标准物质中心。
N-EVAP 112型氮吹仪 美国Organomation公司;Biofugerstratos全能型高性能台式冷冻离心机 德国贺利氏公司;旋涡混合仪 上海汗诺仪器有限公司;TRACE 1310气相色谱仪、TSQ 8000 Evo 三重四极杆GC-MS/MS 赛默飞世尔科技公司;R-210型旋转蒸发仪 瑞士步琦公司;氨基固相萃取小柱(1 g/6 mL)、弗罗里硅土柱(1 g/6 mL) 迪马科技有限公司;ACQUITY UPLC H-Class超高效液相色谱、三重四极杆质谱仪Xevo TQ-S micro 沃特世科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 检测农药的种类与方法
1.2.1.1 气相色谱-质谱联用法检测的农药种类
采用GB 23200.113-2018食品安全国家标准植物源性食品中208种农药及其代谢物残留量的测定气相色谱-质谱联用法[20]检测样品中的50种农药,检测农药名称如下所示:丙溴磷、敌百虫、敌敌畏、毒死蜱、对硫磷、二嗪磷、伏杀硫磷、甲胺磷、甲拌磷、甲拌磷砜、甲拌磷亚砜、甲基硫菌磷、甲基异柳磷、甲基对硫磷、乐果、马拉硫磷、三唑磷、杀螟硫磷、水胺硫磷、辛硫磷、亚胺硫磷、氧乐果、乙酰甲胺磷、α-666、β-666、δ-666、百菌清、氟胺氰菊酯、氟氰戊菊酯、腐霉利、甲氰菊酯、联苯菊酯、氯氟氰菊酯、氯菊酯、氯氰菊酯、氰戊菊酯、三氯杀螨醇、三唑酮、五氯硝基苯、溴氰菊酯、乙烯菌核利、异菌脲、3-羟基克百威、甲萘威、克百威、灭多威、涕灭威、涕灭威砜、涕灭威亚砜、异丙威。
1.2.1.2 液相色谱-质谱联用法检测的农药种类
采用GB 23200.121-2021食品安全国家标准植物源性食品中331种农药及其代谢物残留量的测定液相色谱-质谱联用法[21]检测样品中的49种农药,检测农药名称如下所示:2,4,6-三氯苯酚、2-奈氧乙酸、3,5-二氯苯胺、3-吲哚乙酸、阿维菌素、矮壮素、苯醚甲环唑、吡虫啉、吡唑醚菌酯、丙环唑、虫螨腈、虫酰肼、除虫脲、哒螨灵、啶虫脒、多菌灵、多效唑、二甲戊灵、伏杀硫磷、氟虫腈、氟虫腈砜、氟虫腈硫醚、氟虫腈亚砜、氟啶脲、氟甲腈、甲氨基阿维菌素苯甲酸盐、甲霜灵、腈苯唑、抗蚜威、氯苯嘧啶醇、氯吡脲、氯虫苯甲酰胺、咪鲜胺、醚菌酯、嘧霉胺、灭蝇胺、灭幼脲、噻虫嗪、噻嗪酮、三唑醇、霜霉威、缩结胺、脱落酸、戊唑醇、烯酰吗啉、烯效唑、异丙甲草胺、异菌尿、芸苔素内酯。
1.2.1.3 农药的提取与净化
称取10.0 g试样于50 mL离心管中,加入10 mL乙腈和一颗均质子,涡旋1 min,室温摇床振荡30 min后,再向离心管中加入2 g NaCl和2 g无水硫酸镁,涡旋1 min,10000×g常温离心3 min,取上清液10 mL加入到PSA管中,充分振荡1 min,10000×g常温离心1 min,取2 mL上清液用一次性针管过0.22 μm滤膜加入到进样小瓶中,放入−20 ℃保存,待进行液相色谱-质谱联用测定[22];另取2 mL上清液于10 mL试管中,40 ℃水浴氮气吹至近干,加入20 μL环氧七氯B内标溶液,加入2.5 mL乙酸乙酯复溶,0.22 μm滤膜过滤至进样瓶,−20 ℃保存待进行气相色谱-质谱联用测定[20]。
1.2.1.4 气相色谱-质谱联用法检测农残
检测方法依据:GB 23200.113-2018[20];使用Thermo TSQ 8000气质联用仪,色谱柱:HP-5MS (30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm);载气:He(纯度>99.99%),载气流量:1.0 mL/min,进样口温度:250 ℃,扫描模式:SRM,离子源:EI,离子源温度:300 ℃,传输线温度:280 ℃;升温程序:80 ℃保持1 min,以20 ℃ /min,升温至280 ℃,保持9 min。定量分析:根据GB 23200.113-2018采用内标法进行定量分析,定量限范围为0.002~0.01 mg/kg;定性分析:根据保留时间进行匹配,被测试样中目标农药色谱峰的保留时间与相应标准色谱峰的保留时间相比较。
1.2.1.5 液相色谱-质谱联用法检测农残
检测方法依据:GB 23200.121-2021[21]。使用Waters Xevo TQ-S micro超高效液相色谱串联质谱仪,色谱柱:C18(2.1 mm×100 mm×1.8 μm);流动相:A:甲醇,B:1 mol/L甲酸铵水溶液;流量:0.2 mL/min;离子化模式:ESI(+);扫描模式:MRM;柱温:40 ℃;离子源温度:350 ℃;气体流量:N2:1.0 L/hr;Ar:0 mL/min;毛细血管电压:3.00 kV;脱溶剂温度:650 ℃;锥孔气流量:0 L/hr;六级杆透镜电压:0 V。定量分析:根据GB 23200.121-2021采用外标法进行定量分析,定量限范围为0.002~0.01 mg/kg;定性分析:根据保留时间进行匹配,被测试样中目标农药色谱峰的保留时间与相应标准色谱峰的保留时间相比较。
1.2.1.6 判定方法
检测结果根据GB 2763-2021标准[23]中杏或者核果类水果最大残留限量判定是否超标,检出的23种农药的超标范围为0.01~3 mg/kg,尚未制定杏或核果类水果的农药残留最大限量的结果暂不判定。
1.2.2 农药残留安全性评估方法
参照聂继云等[24]报道的方法残留农药慢性、急性膳食摄入风险、风险排序及农药最大残留限量估计值的计算。
1.2.2.1 慢性膳食摄入风险的计算
用公式(1)计算各农药的慢性膳食摄入风险(%ADI)。%ADI越大,风险越大,当%ADI>100%时,表示有不可接受的风险;反之,当%ADI≤100%时,表示风险可以接受。
%ADI=STMR×0.000172bw×ADI×100 (1) 式中,STMR:规范试验残留中值,取平均残留值,单位mg·kg−1;0.000172:居民日均杏消费量,单位kg;ADI:每日允许摄入量,单位mg·kg−1;bw:体重,单位kg,按60 kg计[25]。
1.2.2.2 急性膳食摄入风险的计算
急性膳食摄入风险(%ARfD)使用公式(2)、(3)计算,当%ARfD≤100%时,表示风险可以接受;反之,%ARfD>100%时,表示有不可接受的风险。
ESTI=U×HR×v+(LP−U)×HRbw (2) %ARfD=ESTIARfD×100 (3) 式中,ESTI:估计短期摄入量,单位kg;U:单果重量,单位kg,杏为0.0372 kg;HR:最高残留量,取99.9百分位点值,单位mg/kg;v:变异因子,对于个体超过25 g的产品,采用默认值3[25],杏为3;LP:大份餐,单位kg,杏为0.2128 kg[26];ARfD:急性参考剂量[27],单位mg/kg。
1.2.2.3 风险排序
借鉴英国兽药残留委员会兽药残留风险排序矩阵,综合考虑各种农药残留风险因子的毒性、毒效、使用频率、高暴露人群和残留水平等5项指标[24],利用公式(5)计算出各农药残留风险得分(S),并进行风险排序,各指标的赋值标准见表1。利用公式(6)计算风险指数(risk index,RI),该指数越大,风险越大。
表 1 农药残留风险排序指标得分赋值标准Table 1. Evaluation standard of pesticide residue risk ranking index score序号 指标 指标值 得分 指标值 得分 指标值 得分 指标值 得分 A 毒性 低毒 2 中毒 3 高毒 4 剧毒 5 B 毒效(mg·kg−1) >1×10−2 0 1×10−4~1×10−2 1 1×10−6~1×10−4 2 <1×10−6 3 C 膳食比例(%) <2.5 0 2.5~20 1 20~50 2 50~100 3 D 使用频率(%) <2.5 0 2.5~20 1 20~50 2 50~100 3 E 高暴露人群 无 0 不太可能 1 很可能 2 有或无相关数据 3 F 残留水平
(mg·kg−1)未检出 1 <1 MRL 2 ≥1 MRL 3 ≥10 MRL 4 注:各农药的毒性从中国农药信息网[28]查得;ADI值从国家标准查得;杏的膳食比例为2.5%~20%,其膳食比例赋值为1;农药使用频率(FOD)按公式(4)计算;残留水平中最大残留限量(MRL)参考GB 2763-2021。 FOD=TP×100 (4) S=(A+B)×(C+D+E+F) (5) RI=∑ni=1S−TS0 (6) 式中,FOD:种植过程中农药的使用频率;P:新疆杏果实发育日数,100 d;T:新疆杏果实发育过程中使用该农药的次数;n:检出的农药,单位为种;TS0:n种农药均未检出的样品的残留风险得分,用公式(5)算出n种农药各自的残留风险得分后求和得到。
1.2.2.4 最大残留量估计值的计算
为保护消费者健康,理论最大摄入量不应大于每日允许摄入量,公式(7)为最大残留限值估计值。
eMRL=ADI×bwF (7) 式中,eMRL:最大残留限量估计值,单位mg/kg;F:杏消费量,按照最大风险原则,取大份餐(LP),单位kg。
1.3 数据处理
实验数据使用Excel进行统计处理,使用origin 2018对实验数据进行图表处理。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 农药残留水平分析
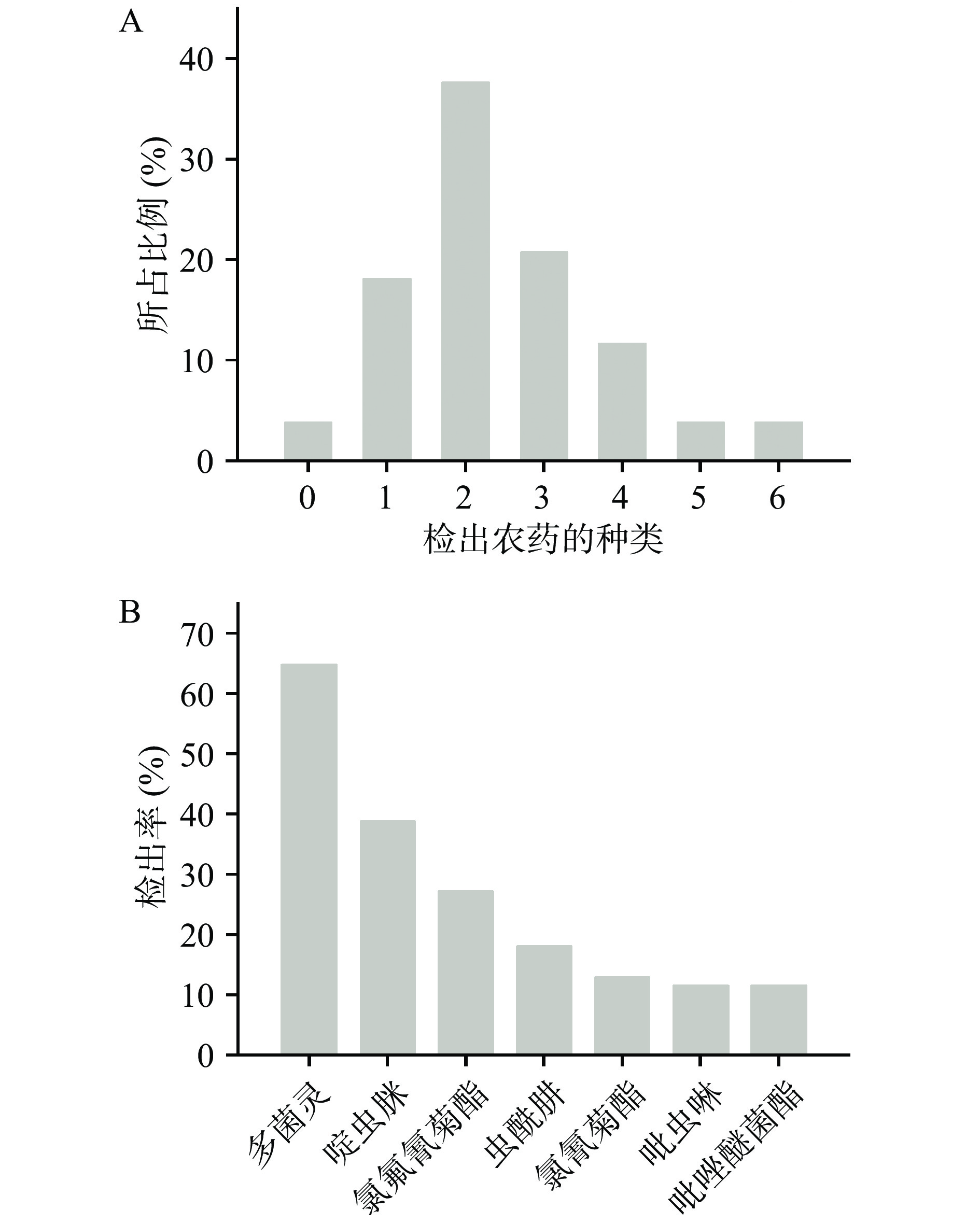
如表2所示,检测的77个杏样品中,96.1%的样品检出了农药残留,平均每个样品检出农药2.45种,同一样品最多检出6种农药,如图1A所示,农药多残留样品指同一样品中检出3种及以上的农药残留,农药多残留样品占比40.27%,农药残留无超标样品。
表 2 新疆杏质量安全状况Table 2. Quality and safety status of Xinjiang apricot序号 名称 农药残留情况 1 样品数量(批次) 77 2 检出农药数量(种) 23 3 检出个数/检出率 74/96.1% 4 超标个数/超标率 0/0% 共检出农药23种,残留样品比例处于1.3%~64.94%之间,7种农药检出率在10%以上,包括3种中等毒农药(氯氟氰菊酯、氯氰菊酯、吡唑醚菌酯),和4种低毒农药(多菌灵、啶虫脒、虫酰肼、吡虫啉)。如图1B所示,多菌灵所占比例最高为64.94%,其次为啶虫脒、氯氟氰菊酯、虫酰肼、氯氰菊酯、吡虫啉、吡唑醚菌酯,所占比例分别为38.96%、27.27%、18.18%、12.99%、11.69%、11.69%,其它农药的残留样品所占比例均低于10%。
根据中国农药信息网查询,杏作物已登记农药仅有石硫合剂,此次检出的农药均未在杏树上进行登记,为超登记范围使用。从检测结果来看,多菌灵在杏生产中使用最为普遍,为低毒杀菌剂,是一种广谱性杀菌剂,可以有效防治由真菌引起的多种作物病害。但是,多菌灵未登记在杏生产中使用,使用后产生的一些风险未经审核认可。因此,杏生产中农药的登记及其使用管理方面还有待加快推进。
Cámara等[29]在未经加工的杏中检测到磺嘧菌灵、多杀菌素A+D、氟硅唑、氟菌唑、哒螨灵等农药,并发现通过清洗可以减少20%~40%的农药残留。Bakirci等[30]对土耳其市售的45批次杏样品进行农药残留检测,其中9批次样品检出农药残留,共计11种,包括:啶虫脒、多菌灵、氯吡硫磷、氯氰菊酯、嘧菌环胺、噻螨酮、吡虫啉、伏杀硫磷、吡丙醚、肟菌酯,残留量均低于土耳其法规对每种商品的最大残留限量。以上学者的研究结果表明杏果实检出率相对较低,质量相对安全。而此次检出的新疆杏样品中农药残留现象较为普遍,可能是由于杏作物中登记的农药较少,生产者没有用药参考,仅以习惯为主,大量、高频的使用各种农药对杏生长过程中可能发生的多种病虫害进行预防,导致农药残留样品比例较高,残留农药种类较多。因此,加强杏生产中农药的登记及使用管理是非常有必要的。
2.2 新疆杏农药残留安全性评估
2.2.1 慢性膳食摄入风险
根据公式(1)可计算出残留农药的慢性膳食摄入风险。如表3所示,残留农药的%ADI处于0.0000%~0.0001%之间不等,均远低于100%,23种农药中,啶虫脒的%ADI相对较高,为0.0001%,其余22种农药的%ADI均小于0.0001%,表明新疆杏农药残留慢性膳食摄入风险很低。
表 3 新疆杏农药残留安全性评估Table 3. Safety assessment of pesticide residues in Xinjiang apricot序号 农药名称 毒性 残留平均值
(mg/kg)最大残留值
(mg/kg)ADI
(mg/kg)%ADI ARfD
(mg/kg)%ARfD 1 氯氟氰菊酯 中 0.0017126 0.02860 0.02 0.000024548 0.02 0.684483892 2 氯氰菊酯 中 0.0005177 0.00984 0.02 0.000007420 0.04 0.117782152 3 咪鲜胺 低 0.0000191 0.00147 0.01 0.000000547 0.1 0.007036400 4 吡虫啉 低 0.0041018 0.21706 0.06 0.000019598 0.4 0.259748467 5 啶虫脒 低 0.0256929 0.44287 0.07 0.000105218 0.1 2.119871067 6 多菌灵 低 0.0026325 0.04692 0.03 0.000025155 0.1 0.224590400 7 噻虫嗪 低 0.0013994 0.05202 0.08 0.000005015 1 0.024900240 8 虫酰肼 低 0.0037301 0.03893 0.02 0.000053465 0.9 0.020704993 9 丙环唑 低 0.0002356 0.01378 0.07 0.000000965 0.3 0.021986756 10 戊唑醇 低 0.0007639 0.03093 0.03 0.000007299 0.3 0.049350533 11 噻嗪酮 低 0.0000426 0.00218 0.009 0.000001357 0.5 0.002086987 12 腈菌唑 低 0.0006257 0.02503 0.03 0.000005979 0.3 0.039936756 13 异丙甲草胺 低 0.0041265 0.05322 0.1 0.000011829 / / 14 霜霉威 低 0.0000004 0.00003 0.4 0.000000000 2 0.000007019 15 克百威 高 0.0001435 0.00798 0.001 0.000041136 0.001 3.819400527 16 甲拌磷 高 0.0000036 0.00017 0.0007 0.000001470 0.003 0.027722008 17 三唑磷 中 0.0000020 0.00015 0.001 0.000000576 0.001 0.073996779 18 哒螨灵 低 0.0000032 0.00025 0.01 0.000000093 / / 19 吡唑醚菌酯 中 0.0000022 0.00003 0.03 0.000000021 0.7 0.000023791 20 苯醚甲环唑 低 0.0000019 0.00014 0.01 0.000000053 0.3 0.000228161 21 氯虫苯甲酰胺 低 0.0000337 0.00259 2 0.000000005 / / 22 甲氨基阿维菌素苯甲酸盐 中 0.0000058 0.00024 0.0005 0.000003338 0.02 0.005851963 23 毒死蜱 中 0.0004232 0.01502 0.01 0.000012132 0.1 0.071896408 合计 —— — —— —— —— 0.00033 —— 7.5716 2.2.2 急性膳食摄入风险
根据IESTI calculation for FAO/WHO acute dietary intake assessment数据[26],中国居民杏消费的大份餐(LP)为0.2128 kg,23种农药中有20种具有急性毒性值(ARfD),根据公式(3)计算出残留农药的急性膳食摄入风险如表3所示,检出的20种农药的急性膳食摄入风险(%ARfD)处于0.0000%~3.8194%,其中农药急性膳食摄入风险低于1%的农药有18种,1%~5%的有2种,远低于100%,风险在可接受范围内,若将农药毒性视为协同效应,其急性膳食摄入风险总和为7.5716%,也在可接受范围内。
本研究采用急性慢性膳食风险评估,能够直接反映新疆杏膳食摄入风险水平,是一种应用广泛、简单易行的评估方法。刘霞丽等[31]通过检测河南省韭菜中的农药残留情况,发现克百威和甲拌磷存在超标情况,超标率分别为0.44%、1.55%,且急性风险超过可接受水平。Soydan等[32]检测了土耳其爱琴海地区果蔬农药残留,发现33.3%的新鲜杏样品中检出农残,38.2%的杏干检出农残,农药检出量均未超出土耳其当局批准的最高残留限量,杏干的长期慢性饮食风险或危害商数(HQ)<0.01,表示不太可能发生不良反应,因此可以认为是可忽略的危害。总体而言,新疆杏中的急性、慢性膳食风险均在可接受范围内。为了及时对可能存在的风险进行管理,更好地了解急性慢性膳食摄入风险,未来仍需定期监管,展开急性慢性膳食风险评估。
2.3 残留农药风险排序
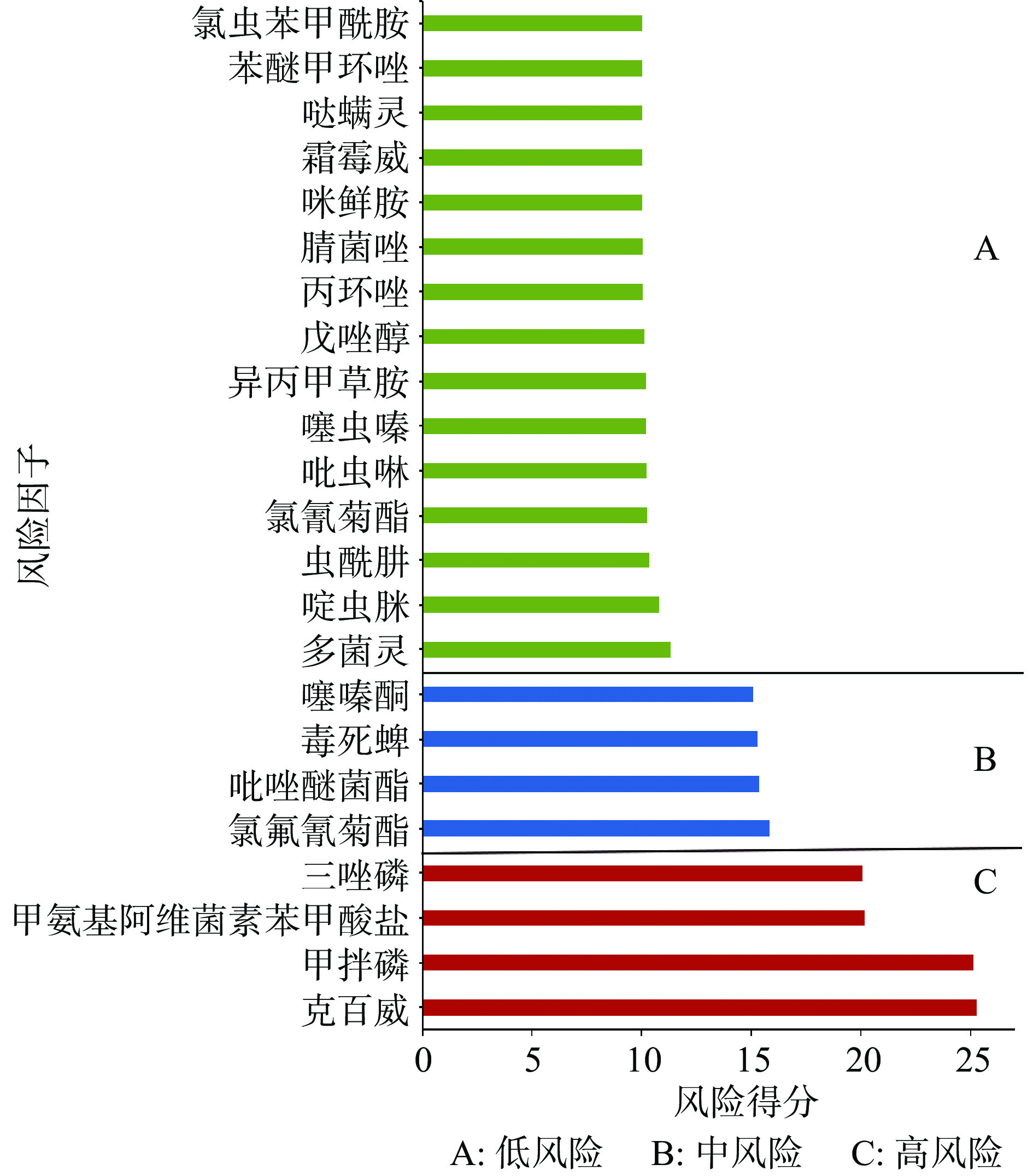
按照表1的赋分方法,计算出各农药残留风险得分,并对残留农药进行风险排序,按照风险得分将其分为3类:风险得分≥20为高风险农药、风险得分<20且≥15为中风险农药、风险得分<15为低风险农药,结果如图2所示。杏中存在4个高风险因子,包括克百威、甲拌磷、甲氨基阿维菌素苯甲酸盐、三唑磷,占全部农药的17.39%;中风险的关键危害因子有4个,其余为低风险因子,占全部农药的65.22%。
目前,关于果蔬中的农药残留关键危害因子(高风险农药)已有很多研究。张嘉坤等[33]对河北产区的桃农药残留开展风险评估,结果显示甲氨基阿维菌素苯甲酸盐检出率为18.6%,且存在超标情况,将甲氨基阿维菌素苯甲酸盐列为高风险农药,为重点关注的风险因子。段夏菲等[34]的评估结果显示,广州市海珠区果品中甲拌磷的危害物风险系数>2.5,为高度风险农药。张惠珠等[35]的研究表明,三唑磷的急性膳食摄入风险比较高,尤其针对低年龄组2~13岁儿童,其%ARfD高达140%以上,高于100%,为不可接受的风险。田耿智[9]在对西北地区的蔬菜水果和食用菌的质量安全情况研究中,将甲氨基阿维菌素苯甲酸盐、克百威列为高风险农药,其风险得分分别为20.006、20.0225。综上,克百威、甲拌磷、甲氨基阿维菌素苯甲酸盐、三唑磷4个高风险农药是果蔬中重点关注的高风险因子。对于杏中的高风险农药必须长期持续开展监管行为,加强农业行业管控,加强对生产者的农药安全用药培训,积极推广使用安全低毒的农药。
2.4 新疆杏样品风险指数分析
根据杏中各样品的风险指数大小,可将杏样品分为四类,分别是高风险样品(RI≥15)、中风险样品(10≤RI<15)、低风险样品(5≤RI<10)、极低风险样品(RI<5)。
77批次杏样品的农药残留风险指数(RI)如表4所示,从杏样品风险等级来看,新疆杏样品中不存在高风险样品,其中,中等风险样品有3个,占全部样品的3.9%;低风险样品有42个,占全部样品数的54.55%;极低风险样品有32个,占全部样品的42.56%。分析中等风险样品中的农药残留发现,这3个中等风险样品均为农药多残留样品,其检出的农药均为6种。
表 4 新疆杏样品农药残留风险等级及指数划分Table 4. Classification of risk levels and indices of pesticide residues in Xinjiang apricot samples风险等级及风险指数划分 77批次样品 风险指数
(RI)最小值 0 最大值 17 平均值 5.753 极低风险 RI<5 32/41.56% 低风险 15>RI≥5 42/54.55% 中等风险 20>RI≥15 3/3.9% 高风险 RI≥20 0/0% 聂继云等[24]对苹果中的农药残留评估发现,高毒农药残留超标的样品为高风险样品,中等风险样品大多为农药多残留样品。一方面,样品中高毒农药残留超标会直接导致样品的风险指数(RI)≥15,所以在果蔬种植中应当尽量避免使用高毒农药,如非必须使用,也应农药使用规范,按照规定周期和频率使用,且采摘前需预留足够的农药安全间隔期;另一方面,样品中农药残留数量过多,可能会引起不同农药毒性的累积效应,所以应当提倡使用低毒安全的农药,混用农药时,要注意用药的质量浓度,合理调配,避免因使用农药种类过多而造成水果质量安全问题。
2.5 现有农药最大残留限量的适用性
杏样品残留的23种农药中,我国尚未制定杏最大残留限量的农药有10种,包括咪鲜胺、虫酰肼、丙环唑、噻嗪酮、异丙甲草胺、霜霉威、三唑磷、哒螨灵、苯醚甲环唑、甲氨基阿维菌素苯甲酸盐。及时修订杏中的MRL可以提高产品合格率判定的准确性,能够全面、正确的衡量杏的质量安全现状。
23种残留农药的最大残留限量估计值(eMRL)和最大残留限量建议值(RMRL)如表5所示,氯虫苯甲酰胺的ADI高达2 mg/kg,在杏中的eMRL为564 mg/kg,且氯虫苯甲酰胺为低毒农药,所以没有必要制定该农药在杏中的最大残留量。
表 5 残留农药的最大残留限量估计值和最大残留限量建议值Table 5. eMRLs and RMRLs for residual pesticides种类 ADI
(mg/kg)eMRL
(mg/kg)MRL
(mg/kg)RMRL
(mg/kg)p99.5
(mg/kg)氯氟氰菊酯 0.02 6 0.5 6 0.0122 氯氰菊酯 0.02 6 2 6 0.0075 咪鲜胺 0.01 3 − 3 0.0000 吡虫啉 0.06 17 0.5 17 0.0641 啶虫脒 0.07 20 2 20 0.4204 多菌灵 0.03 8.5 2 8 0.0192 噻虫嗪 0.08 23 1 23 0.0240 虫酰肼 0.02 6 − 6 0.0348 丙环唑 0.07 20 − 20 0.0044 戊唑醇 0.03 8 2 8 0.0134 噻嗪酮 0.009 3 − 3 0.0011 腈菌唑 0.03 8 3 8 0.0232 异丙甲草胺 0.1 28 − 28 0.0499 霜霉威 0.4 113 − 113 0.0000 克百威 0.001 0.3 0.02 0.3 0.0018 甲拌磷 0.0007 0.2 0.01 0.2 0.0001 三唑磷 0.001 0.3 − 0.3 0.0000 哒螨灵 0.01 3 − 3 0.0000 吡唑醚菌酯 0.03 8 3 8 0.0000 苯醚甲环唑 0.01 3 − 3 0.0000 氯虫苯甲酰胺 2 564 1 564 0.0000 甲氨基阿维菌
素苯甲酸盐0.0005 0.1 − 0.1 0.0002 毒死蜱 0.01 3 3 3 0.0074 注:ADI:每日允许摄入量;eMRL:最大残留限量估计值;MRL:最大残留限量;RMRL:最大残留限量建议值;p99.5:99.5百分位点残留量。 综合23种农药检出率、急性、慢性膳食风险评估及风险排序结果,按照最大残留限量可比eMRL略低或者略高的原则,建议优先制定虫酰肼、甲氨基阿维菌素苯甲酸盐、三唑磷3种残留农药的最大限量值,建议值分别为:6、0.1、0.3 mg/kg。如表5所示,残留农药的p99.5均低于MRL或RMRL表明最大残留限量建议值(RMRL)符合制定要求。
3. 结论
新疆杏样品农药残留风险总体良好。样品中农药残留检出率较高为96.1%,样品残留农药共计23种,其中多菌灵、啶虫脒、氯氟氰菊酯,残留样品所占比例较高。杏样品残留农药的急慢性膳食风险在可接受水平,且样品以低风险和极低风险样品为主,不存在高风险的样品。根据农药风险排序,确定杏农药的关键危害因子为:克百威、甲拌磷、甲氨基阿维菌素苯甲酸盐、三唑磷。杏中检出的农药有10种尚未制定最大残留限量,综合分析,建议优先制定虫酰肼、甲氨基阿维菌素苯甲酸盐、三唑磷3种残留农药的最大限量值。
-
表 1 农药残留风险排序指标得分赋值标准
Table 1 Evaluation standard of pesticide residue risk ranking index score
序号 指标 指标值 得分 指标值 得分 指标值 得分 指标值 得分 A 毒性 低毒 2 中毒 3 高毒 4 剧毒 5 B 毒效(mg·kg−1) >1×10−2 0 1×10−4~1×10−2 1 1×10−6~1×10−4 2 <1×10−6 3 C 膳食比例(%) <2.5 0 2.5~20 1 20~50 2 50~100 3 D 使用频率(%) <2.5 0 2.5~20 1 20~50 2 50~100 3 E 高暴露人群 无 0 不太可能 1 很可能 2 有或无相关数据 3 F 残留水平
(mg·kg−1)未检出 1 <1 MRL 2 ≥1 MRL 3 ≥10 MRL 4 注:各农药的毒性从中国农药信息网[28]查得;ADI值从国家标准查得;杏的膳食比例为2.5%~20%,其膳食比例赋值为1;农药使用频率(FOD)按公式(4)计算;残留水平中最大残留限量(MRL)参考GB 2763-2021。 表 2 新疆杏质量安全状况
Table 2 Quality and safety status of Xinjiang apricot
序号 名称 农药残留情况 1 样品数量(批次) 77 2 检出农药数量(种) 23 3 检出个数/检出率 74/96.1% 4 超标个数/超标率 0/0% 表 3 新疆杏农药残留安全性评估
Table 3 Safety assessment of pesticide residues in Xinjiang apricot
序号 农药名称 毒性 残留平均值
(mg/kg)最大残留值
(mg/kg)ADI
(mg/kg)%ADI ARfD
(mg/kg)%ARfD 1 氯氟氰菊酯 中 0.0017126 0.02860 0.02 0.000024548 0.02 0.684483892 2 氯氰菊酯 中 0.0005177 0.00984 0.02 0.000007420 0.04 0.117782152 3 咪鲜胺 低 0.0000191 0.00147 0.01 0.000000547 0.1 0.007036400 4 吡虫啉 低 0.0041018 0.21706 0.06 0.000019598 0.4 0.259748467 5 啶虫脒 低 0.0256929 0.44287 0.07 0.000105218 0.1 2.119871067 6 多菌灵 低 0.0026325 0.04692 0.03 0.000025155 0.1 0.224590400 7 噻虫嗪 低 0.0013994 0.05202 0.08 0.000005015 1 0.024900240 8 虫酰肼 低 0.0037301 0.03893 0.02 0.000053465 0.9 0.020704993 9 丙环唑 低 0.0002356 0.01378 0.07 0.000000965 0.3 0.021986756 10 戊唑醇 低 0.0007639 0.03093 0.03 0.000007299 0.3 0.049350533 11 噻嗪酮 低 0.0000426 0.00218 0.009 0.000001357 0.5 0.002086987 12 腈菌唑 低 0.0006257 0.02503 0.03 0.000005979 0.3 0.039936756 13 异丙甲草胺 低 0.0041265 0.05322 0.1 0.000011829 / / 14 霜霉威 低 0.0000004 0.00003 0.4 0.000000000 2 0.000007019 15 克百威 高 0.0001435 0.00798 0.001 0.000041136 0.001 3.819400527 16 甲拌磷 高 0.0000036 0.00017 0.0007 0.000001470 0.003 0.027722008 17 三唑磷 中 0.0000020 0.00015 0.001 0.000000576 0.001 0.073996779 18 哒螨灵 低 0.0000032 0.00025 0.01 0.000000093 / / 19 吡唑醚菌酯 中 0.0000022 0.00003 0.03 0.000000021 0.7 0.000023791 20 苯醚甲环唑 低 0.0000019 0.00014 0.01 0.000000053 0.3 0.000228161 21 氯虫苯甲酰胺 低 0.0000337 0.00259 2 0.000000005 / / 22 甲氨基阿维菌素苯甲酸盐 中 0.0000058 0.00024 0.0005 0.000003338 0.02 0.005851963 23 毒死蜱 中 0.0004232 0.01502 0.01 0.000012132 0.1 0.071896408 合计 —— — —— —— —— 0.00033 —— 7.5716 表 4 新疆杏样品农药残留风险等级及指数划分
Table 4 Classification of risk levels and indices of pesticide residues in Xinjiang apricot samples
风险等级及风险指数划分 77批次样品 风险指数
(RI)最小值 0 最大值 17 平均值 5.753 极低风险 RI<5 32/41.56% 低风险 15>RI≥5 42/54.55% 中等风险 20>RI≥15 3/3.9% 高风险 RI≥20 0/0% 表 5 残留农药的最大残留限量估计值和最大残留限量建议值
Table 5 eMRLs and RMRLs for residual pesticides
种类 ADI
(mg/kg)eMRL
(mg/kg)MRL
(mg/kg)RMRL
(mg/kg)p99.5
(mg/kg)氯氟氰菊酯 0.02 6 0.5 6 0.0122 氯氰菊酯 0.02 6 2 6 0.0075 咪鲜胺 0.01 3 − 3 0.0000 吡虫啉 0.06 17 0.5 17 0.0641 啶虫脒 0.07 20 2 20 0.4204 多菌灵 0.03 8.5 2 8 0.0192 噻虫嗪 0.08 23 1 23 0.0240 虫酰肼 0.02 6 − 6 0.0348 丙环唑 0.07 20 − 20 0.0044 戊唑醇 0.03 8 2 8 0.0134 噻嗪酮 0.009 3 − 3 0.0011 腈菌唑 0.03 8 3 8 0.0232 异丙甲草胺 0.1 28 − 28 0.0499 霜霉威 0.4 113 − 113 0.0000 克百威 0.001 0.3 0.02 0.3 0.0018 甲拌磷 0.0007 0.2 0.01 0.2 0.0001 三唑磷 0.001 0.3 − 0.3 0.0000 哒螨灵 0.01 3 − 3 0.0000 吡唑醚菌酯 0.03 8 3 8 0.0000 苯醚甲环唑 0.01 3 − 3 0.0000 氯虫苯甲酰胺 2 564 1 564 0.0000 甲氨基阿维菌
素苯甲酸盐0.0005 0.1 − 0.1 0.0002 毒死蜱 0.01 3 3 3 0.0074 注:ADI:每日允许摄入量;eMRL:最大残留限量估计值;MRL:最大残留限量;RMRL:最大残留限量建议值;p99.5:99.5百分位点残留量。 -
[1] 李俊芳, 景伟文, 加列西·马那甫. 串联质谱法测定小白杏中农药残留[J]. 食品研究与开发,2018,39(8):99−106 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2018.08.018 LI Junfang, JING Weiwen, JIALIEXI·Manafu. Determination of pesticide residues in Xinjiang apricot by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Food Research and Development,2018,39(8):99−106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2018.08.018
[2] 刘均勇, 胡乐鸣. 中国农业年鉴[M]. 北京:中国农业出版社, 2020:211 LIU Junyong, HU Yueming. China agriculture yearbook[M]. Beijing:China Agricultural Press, 2020:211.
[3] 杨爱军, 王娜, 黄红梅. 杏树病虫害发生及防治[J]. 农村科技,2007,(11):20−21 YANG Aijun, WANG Na, HUANG Hongmei. Occurrence and control of almond diseases and insect pests[J]. Rural Science & Technology,2007,(11):20−21.
[4] 张仁福, 于江南, 古丽加马丽·吐尔汗, 等. 有机农药防治杏园害虫试验[J]. 农药,2010,49(10):762−764 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0413.2010.10.020 ZHANG Renfu, YU Jiangnan, GULIJIAMALI·Tuerhan, et al. Experiment of using organic pesticide control pest in apricot orchard[J]. Agrochemicals,2010,49(10):762−764. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0413.2010.10.020
[5] 刘佳, 李靖, 李菊. 四川地区杏病虫害绿色防控技术[J]. 四川农业科技,2017(4):32−33 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1028.2017.04.011 LIU Jia, LI Jing, LI Ju. Green prevention and control technology of apricot diseases and insect pests in Sichuan[J]. Sichuan Agricultural Science and Technology,2017(4):32−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1028.2017.04.011
[6] 樊振利, 沈植国, 丁鑫. 无公害大杏生产常见病虫害防治及农药使用原则[J]. 河南林业科技,2005,25(2):50−52 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2630.2005.02.025 FAN Zhenli, SHEN Zhiguo, DING Xin. The principle of pest control and pesticide use in the production of non-pollution apricot[J]. Journal of Henan Forestry Science and Technology,2005,25(2):50−52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-2630.2005.02.025
[7] 李燕. 杏园虫害无公害防治技术研究[J]. 现代农业科技,2011(21):173−174 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2011.21.107 LI Yan. Research on Effect of apricot orchard diseases and pests non-pollution control[J]. Modern Agricultural Science and Technology,2011(21):173−174. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5739.2011.21.107
[8] BRANCATO A, BROCCA D, De LENTDECKER C, et al. Setting of import tolerances for flubendiamide in apricots, peaches, nectarines, plums and soya beans[J]. Efsa Journal,2018,16(1):5128.
[9] 田耿智. 基地蔬菜水果中农药残留暴露风险和预警风险评估[J]. 中国农学通报,2021,37(27):112−116 doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0046 TIAN Gengzhi. Vegetables and fruits at the production base: Assessment of pesticide residue exposure and early warning of risk[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2021,37(27):112−116. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb2021-0046
[10] MEDINA-PASTOR P, TRIACCHINI G. The 2018 European Union report on pesticide residues in food, EFSA journal[J]. European Food Safety Authority,2020,18:e06057.
[11] 陈君石. 风险评估在食品安全监管中的作用[J]. 农业质量标准,2009 (3):4−8 CHEN Junshi. The role of risk assessment in food safety regulation[J]. Agricultural Quality & Standards,2009 (3):4−8.
[12] 梁靖凯, 蒲云霞. 蔬菜与水果中农药残留现状及风险评估工作进展[J]. 公共卫生与预防医学,2022,33(3):123−126 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2483.2022.03.028 LIANG Jingkai, PU Yunxia. Current status of pesticide residues in vegetables and fruits and progress in risk assessment[J]. Journal of Public Health and Preventive Medicine,2022,33(3):123−126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2483.2022.03.028
[13] KAUSHAL J , KHATRI M, ARYA S K. Atreatise on organophosphate pesticide pollution: Current strategies and advancements in their environmental degradation and elimination[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2021,207:111483. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111483
[14] SUNGUR S, TUNUR C. Investigation of pesticide residues in vegetables and fruits grown in various regions of Hatay, Turkey[J]. Food Addit Contam Part B Surveill,2012,5(4):265−267. doi: 10.1080/19393210.2012.704597
[15] 何伟忠, 陶永霞, 闫巧俐, 等. 新疆红枣农药残留风险评估与排序[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(21):202−206 doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2018.21.036 HE Weizhong, TAO Yongxia, YAN Qiaoli, et al. Risk assessment and ranking of pesticide residues in Xinjiang jujube[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2018,39(21):202−206. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2018.21.036
[16] 江景勇, 王会福, 何玲玲, 等. 台州草莓农药残留风险评估[J]. 江苏农业学报,2017,33(6):1408−1414 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2017.06.030 JIANG Jingyong, WANG Huifu, HE Lingling, et al. Risk assessment of pesticide residues in strawberry from Taizhou City[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agricultural Sciences,2017,33(6):1408−1414. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-4440.2017.06.030
[17] 常薇, 李慧, 李春梅, 等. 成都市售果蔬中农药残留水平分析及慢性膳食风险评估[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(6):258−268 CHANG Wei, LI Hui, LI Chunmei, et al. Residue levels and chronic dietary intake risk of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables in Chengdu[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(6):258−268.
[18] 黄惠玲, 王朝政, 庄鹏, 等. 海南省蔬菜、水果中有机磷农药残留情况的调查和风险评估[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志,2021,31(13):1637−1640 HUANG Huiling, WANG Zhaozheng, ZHUANG Peng, et al. Survey and risk assessment of organophosphorus pesticide residues in vegetables and fruits in Hainan Province[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Technology,2021,31(13):1637−1640.
[19] YANG S, XING Y, LIU Q, et al. Residual levels and dietary intake risk assessment of 11 pesticides in apricots from different ecological planting regions in China[J]. Scientific Reports,2022,12:18818. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-23564-4
[20] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会, 国家市场监督管理总局. GB 23200.113-2018 食品安全国家标准植物源性食品中208种农药及其代谢物残留量的测定气相色谱-质谱联用法[S]. 北京:中国农业出版社, 2021 National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration of Market Supervision. GB 23200.113-2018 National standard for food safety, determination of 208 pesticides and their metabolites residues in plant derived foods, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[S]. Beijing:China Agricultural Press, 2021.
[21] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会, 国家市场监督管理总局. GB 23200.121-2021 食品安全国家标准植物源性食品中331种农药及其代谢物残留量的测定液相色谱-质谱联用法[S]. 北京:中国农业出版社, 2021 National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration of Market Supervision. GB 23200.121-2021 National food safety standard, determination of 331 pesticides and their metabolites residues in plant derived foods, liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry[S]. Beijing:China Agricultural Press, 2021.
[22] 张微微, 古丽斯坦·阿不都拉, 贾秦岚, 等. 新疆不同品种红枣农药残留风险评估与排序[J]. 食品工业科技,2023,44(9):262−270 ZHANG Weiwei, ABUDULA·Gulisitan, JIA Qinlan, et al. Risk assessment and ranking of pesticide residues in different varieties of Xinjiang red jujube[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2023,44(9):262−270.
[23] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会, 国家市场监督管理总局. GB2763-2021 食品安全国家标准 食品中农药最大残留限量[S]. 北京:中国农业出版社, 2021 National Health Commission of the People's Republic of China, State Administration of Market Supervision. GB2763-2021 National food safety standard, maximum residue limit of pesticides in food[S]. Beijing:China Agricultural Press, 2021.
[24] 聂继云, 李志霞, 刘传德, 等. 苹果农药残留风险评估[J]. 中国农业科学,2014,47(18):3655−3667 NIE Jiyun, LI Zhixia, LIU Chuande, et al. Risk assessment of pesticide residues in apples[J]. Scientia Agricultura Sinica,2014,47(18):3655−3667.
[25] FORKUOH F, BOADI N O, BORQUAYE L S, et al. Risk of human dietary exposure to organochlorine pesticide residues in fruits from Ghana[J]. Scientific Reports,2018,8:16686. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-35205-w
[26] WHO (World Health Organization). A template for the automatic calculation of the IESTI[EB/OL]. http://www.who.int/foodsafety/chem/IESTI_calculation_13c.xlt. 2021-1-16.
[27] WHO (World Health Organization). Inventory of evaluations performed by the Joint Meeting on Pesticide Residues (JMPR)[EB/OL]. https://apps.who.int/pesticide-residues-jmpr-database/2022-10-27.
[28] 中华人民共和国农业部农药检定所. 中国农药信息网[DB/OL]. http://www.chinapesticide.gov.cn/service/zhcx/yxcfxx.html. 2022-1-16[Institute for the Control of Agrochemicals, Ministry of Agriculture, People’s Republic of China. China Pesticide Information Network[DB/OL]. http://www.chinapesticide.gov.cn/service/zhcx/yxcfxx.html. 2022-1-16 Institute for the Control of Agrochemicals, Ministry of Agriculture, People’s Republic of China. China Pesticide Information Network[DB/OL]. http://www.chinapesticide.gov.cn/service/zhcx/yxcfxx.html. 2022-1-16
[29] CÁMARA M A, CERMEÑO S, MARTÍNEZ G, et al. Removal residues of pesticides in apricot, peach and orange processed and dietary exposure assessment[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,325:126936.
[30] BAKIRCI G T, ACAY D B Y, BAKIRCI F, et al. Pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables from the Aegean region, Turkey[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,160(10):379−392.
[31] 刘霞丽, 姚晓洁, 宁亚萍, 等. 河南省韭菜中农药残留情况分析及膳食暴露评估[J/OL]. 中国食品卫生杂志. https://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.3156.r.20220902.1536.002.html[LIU Xiali, YAO Xiaojie, NING Yaping, et al. Detection and exposure assessment of pesticide residues in leek in Henan Province[J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene. LIU Xiali, YAO Xiaojie, NING Yaping, et al. Detection and exposure assessment of pesticide residues in leek in Henan Province[J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Food Hygiene.
[32] SOYDAN D K, TURGUT N, YALN M, et al. Evaluation of pesticide residues in fruits and vegetables from the Aegean region of Turkey and assessment of risk to consumers[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2021,28(22):27511−27519. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-12580-y
[33] 张嘉坤, 及增发, 郑振山, 等. 河北产区桃农药残留风险评估[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(7):2662−2669 doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2021.07.024 ZHANG Jiakun, JI Zengfa, ZHENG Zhenshan, et al. Risk assessment of pesticide residues in peaches from Heibei Province[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection,2021,12(7):2662−2669. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2021.07.024
[34] 段夏菲, 曾雅, 李映霞, 等. 食品安全指数法评估广州市海珠区果品中有机磷类农药残留的风险[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志,2020,30(1):87−90 DUAN Xiafei, ZENG Ya, LI Yingxia, et al. Risk assessment of organophosphorus pesticide residues in fruits in Haizhu District of Guangzhou based on food safety indexes[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Technology,2020,30(1):87−90.
[35] 张惠珠, 张翠霞. 2016年-2019年市售苹果中农药残留状况及膳食摄入风险评估[J]. 中国卫生检验杂志,2021,21(19):2410−2413 ZHANG Huizhu, ZHANG Cuixia. Current situation and dietary intake assessment of pesticide residues in apples from markets, 2016-2019[J]. Chinese Journal of Health Laboratory Technology,2021,21(19):2410−2413.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 李琳,崔彦阁,赵娟娟,石晓丹,许军星,孙路. 调整膳食纤维和肠道菌群对延缓饮食诱导性肥胖的影响研究. 医学动物防制. 2025(02): 177-181 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王远利,王菲,张权,汤木果,陶亮,田洋. 海棠果果酱的研制及其品质分析. 食品工业科技. 2024(11): 175-186 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 毛欣欣,刘婧,梁文欧,蔡诗鸿,李彦勋. 果蔬加工副产物膳食纤维改性研究进展. 农产品加工. 2024(08): 94-98 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李国巍,石雨,张正海,姬妍茹,杨庆丽,董艳,高宝昌,李柏阳. 黑海棠果多酚提取工艺优化及抗氧化活性分析. 中国食品添加剂. 2024(12): 19-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李焱,林泳峰,刘文美,邹泽华,刘红,刘光明,刘庆梅. 食药同源植物多糖调控肠道稳态的研究进展. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2023(02): 25-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 雷延玲. 遮荫条件下栽培模式对草莓品质和产量的影响. 北方果树. 2022(05): 14-17 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



