Investigation on the Transport Mechanism of Penicillium expansum MFS Protein Based on Molecular Dynamics Simulation
-
摘要: 扩展青霉可产生具有毒性的次生代谢产物—棒曲霉素。PatC基因编码MFS转运蛋白将棒曲霉素的前体物质转运至胞外,在棒曲霉素防治中具有较高的参考价值。为研究PatC蛋白的转运机制,利用生物信息学方法预测PatC的空间结构,采用分子对接和分子动力学模拟解析棒曲霉素前体分子(E-ascladiol)与PatC的作用位点及可能的作用机制。结果表明,该蛋白含有546个氨基酸,含有14个跨膜螺旋且具有MFS功能结构域;分子对接结果显示,该蛋白与E-ascladiol存在4个结合位点,分别为SER353、TYR336、PRO339、PRO188。针对Wild蛋白复合体系及P188A突变体系进行200 ns的分子动力学模拟,结果显示小分子底物与PatC结合紧密,且位于氨基酸序列Pro188~Ser197aa和Gly231~Val241aa区域内形成复合体后,蛋白的柔性发生强烈变化,由此可推测这两个区域可能存在作用位点。通过对P188A突变体系的各参数数据的分析,可以预测PRO188作为PatC的重要靶点,为后续的分子实验提供基础理论。该研究结果为探索棒曲霉素的转运机制奠定基础,为防治苹果腐烂提供了新策略。Abstract: The Penicillium expansum produces a toxic secondary metabolite, patulin. The PatC gene encodes the MFS transport protein, and transports the patulin precursor substance to the extracellular space, ultimately forming PAT. This has high reference value in the prevention of patulin. In order to study the transport mechanism of the PatC, the spatial structure of the PatC was predicted by using bioinformatics methods, and the interaction site and possible mechanism of E-ascladiol and the PatC were analyzed by molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation. The results showed that the gene encoded 546 amino acids, containing 14 transmembrane helix and MFS functional domains. The molecular docking results showed that the protein had 4 binding sites with the E-ascladiol, namely SER353, TYR336, PRO339, and PRO188. Molecular dynamics simulations of 200 ns were performed for the Wild protein complex system and the P188A mutant system. The results showed that the small molecule substrate and the PatC were tightly bound, and that the protein's flexibility changed strongly after forming a complex in the Pro188~Ser197aa and Gly231~Val241aa regions. It could be inferred that these two regions might have functional sites. By analyzing the parameter data of the P188A mutant system, it could be predicted that PRO188 was an important target of the PatC protein, which could provide a basis for subsequent molecular experiments. The results of the research could lay the foundation for exploring the transport mechanism of patulin, and provide new strategies for the prevention of apple rot.
-
Keywords:
- Penicillium expansum /
- patulin(PAT) /
- MFS transporter /
- molecular docking /
- molecular dynamics
-
青霉病是全球最常见且经济上最重要的采后水果腐烂病之一[1],其中扩展青霉(Penicillium expansum,P.expansum) 是引起果实青霉病或软腐病的主要病原菌[2]。P. expansum可在水果作物(苹果、梨、柑橘和樱桃等)及其衍生品、加工产品的采后、贮藏、运输和加工期间侵袭[3-7]。同时,P. expansum还可产生具有危害的次级代谢产物——棒曲霉素(Patulin,PAT)[8-10],通过诱导DNA链断裂、氧化损伤以及DNA链之间相互交联、产生核质桥等机制影响微核形成,从而引起DNA结构性损伤[11],产生遗传毒性、细胞毒性和免疫毒性作用等[12]。
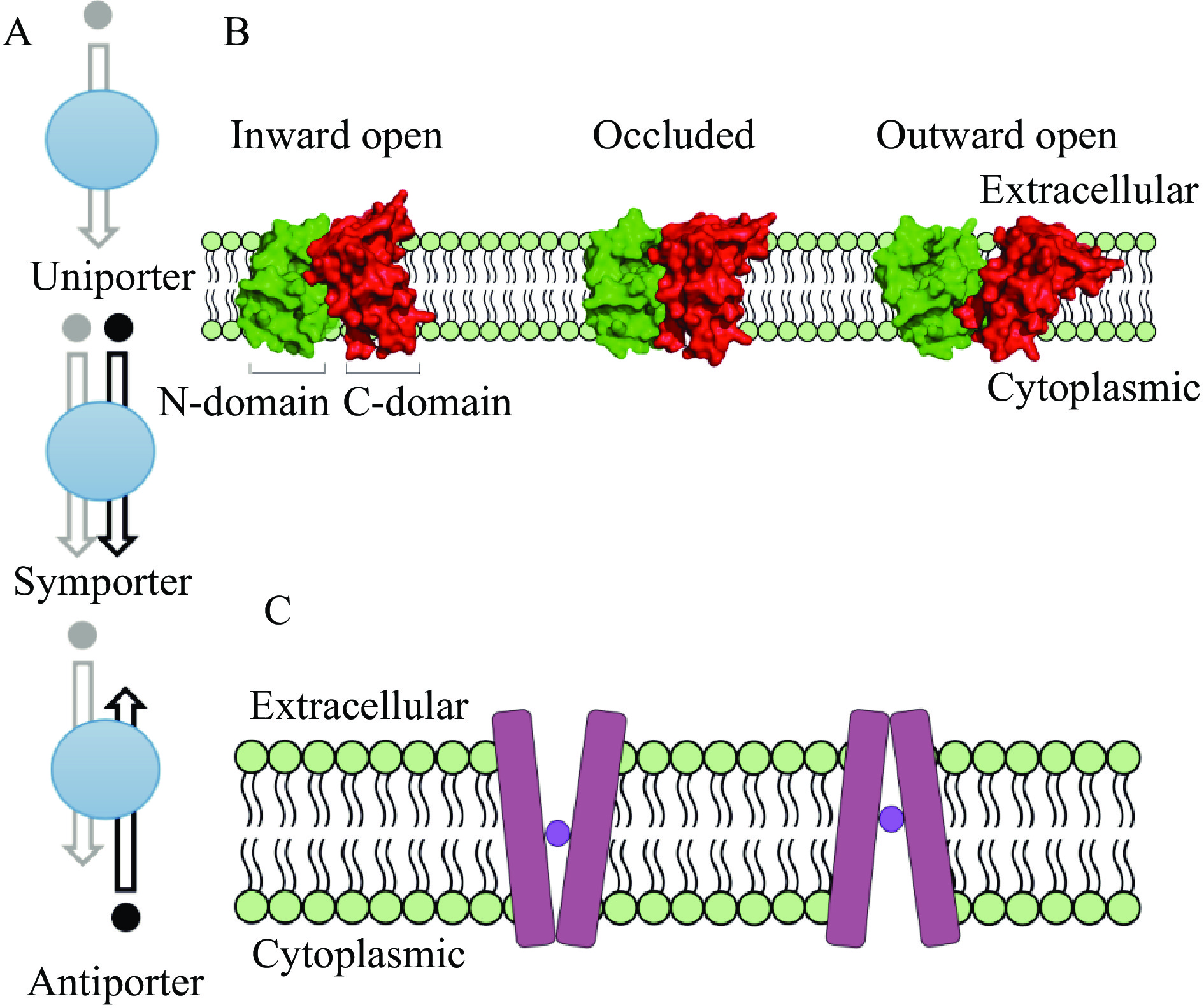
20世纪80年代,Puel等提出PAT的生物合成途径是一个酶级联反应[13-14]。近几年,Li等[15]鉴定得到参与PAT生物合成的基因簇,包括15个基因(PatA~PatO),具体合成途径见图1。其中PatC基因编码MFS超家族转运蛋白(Major Facilitator Superfamily,MFS)。MFS的主要功能是将PAT的前体E-ascladiol转运至胞外,最终合成PAT[16],但具体的转运机制尚不清楚。研究表明,E-ascladiol对来自人类肝、肾、肠和免疫系统的细胞无毒性,因此,增加E-ascladiol累积以减少棒曲霉素含量是控制棒曲霉素风险的有效手段[17]。目前,MFS转运蛋白包括105个家族,是最大的次级跨膜转运蛋白超家族[18]。MFS转运蛋白大多数都含有400~600个氨基酸残基[19],具有12、14或24个不规则跨膜α-螺旋(TMSs)包围形成深中央亲水腔[20-21],催化底物在两个方向上进行跨膜运输,可以是运输单个底物的单转运子,可以是将底物和偶联离子运输在一起的同转运子,也可以是按相反方向依次运输两个不同分子的反转运子(图2a)。根据交替开放模型,MFS能够在向胞内开放,闭塞和向外开放构象之间变化(图2b),转运蛋白上的底物结合位点暴露在细胞膜的不同侧,底物从细胞膜的一侧结合到蛋白上,而从另一侧被释放(图2c)。此外,MFS转运蛋白还可以间接调节真菌的内部pH和应激反应机制[22],参与多种真菌毒素的输出。如拟枝孢镰刀菌(Fusarium sporotrichioides)的TRI12和大豆紫斑菌(Cercospora kikuchii)的CFP[23-24],两者均编码MFS转运蛋白,分别参与真菌毒素-单端孢霉烯(Trichothecenes)和尾孢菌素(Cercosporin)的分泌。植物病原体,玉米圆斑真菌(Cochliobolus carbonum)的TOXA也与HC毒素的宿主特异性毒素的分泌有关[25-26]。TOXA、Tri12及CFP缺失突变体都显示出毒素产生的急剧减少,Tri12缺失突变体也观察到生长迟缓,但CFP缺失突变体与野生型菌株一样正常生长,只是对大豆的毒力降低[26-28]。此外,在携带毒素合成基因的基因簇中也发现了一些编码MFS的基因[29]。然而,它们在运输特定代谢产物中的作用仍待阐明。可惜的是,对MFS转运机制的研究甚少,目前只解析得到几个细菌蛋白的完整拓扑结构。相关PAT毒素输出的研究更是没有。因此致力于探索PatC的转运机制,有利于苹果青霉病病原菌的防治的研究。
随着计算生物学的发展,越来越多的研究者采用分子动力学模拟生物大分子在三维空间的运动状态,从而分析其发挥生物功能的作用机制。本研究采用生物信息学及分子动力学模拟方法探索扩展青霉棒曲霉素PatC的转运机制,研究其与底物分子E-ascladiol的结合位点,并针对PRO188定点突变,分析复合体及突变体的RMSD、Rg、RMSF等变化,以期为研究该蛋白的结构和转运机制奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 生物信息学分析
通过美国国家生物技术信息中心(National Center for Biotechnology Information,NCBI)搜索Penicillium expansum T01(登录号:AYHP00000000.1),下载Penicillium expansum T01 中全部527段鸟枪法测序结果。利用DNAMAN生物信息软件BLAST其他亚种Penicillium expansum strain NRRL 35695(登录号:KF899892.1)中PatC基因及其编码的氨基酸信息,结果与Penicillium expansum T01中PatC基因序列完全一致。采用Mega 5.0邻近法(Neighbor Joining,NJ)进行氨基酸序列同源性分析及构建系统进化树;通过在线网站分析PatC的理化性质、跨膜结构域、蛋白质功能结构域、二级结构及三级结构等,具体所用网站见表1。
表 1 生物信息学相关分析工具Table 1. Bioinformatics correlation analysis tools网站名称 网址 功能 SMART http://smart.embl.de/ 蛋白的功能结构域 NCBI NCBI Conserved Domain Search (nih.gov) 蛋白的功能结构域 ExPASy-ProtParam https://web.expasy.org/protparam/ 蛋白的理化性质 TMHMM-2.0 http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM 蛋白的跨膜结构 SOPMA https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=npsa%20_sopma.html 蛋白的二级结构 AlphaFold https://www.alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/ 蛋白的三级结构 Uniprot https://www.uniprot.org/ 蛋白质数据库 1.2 分子对接
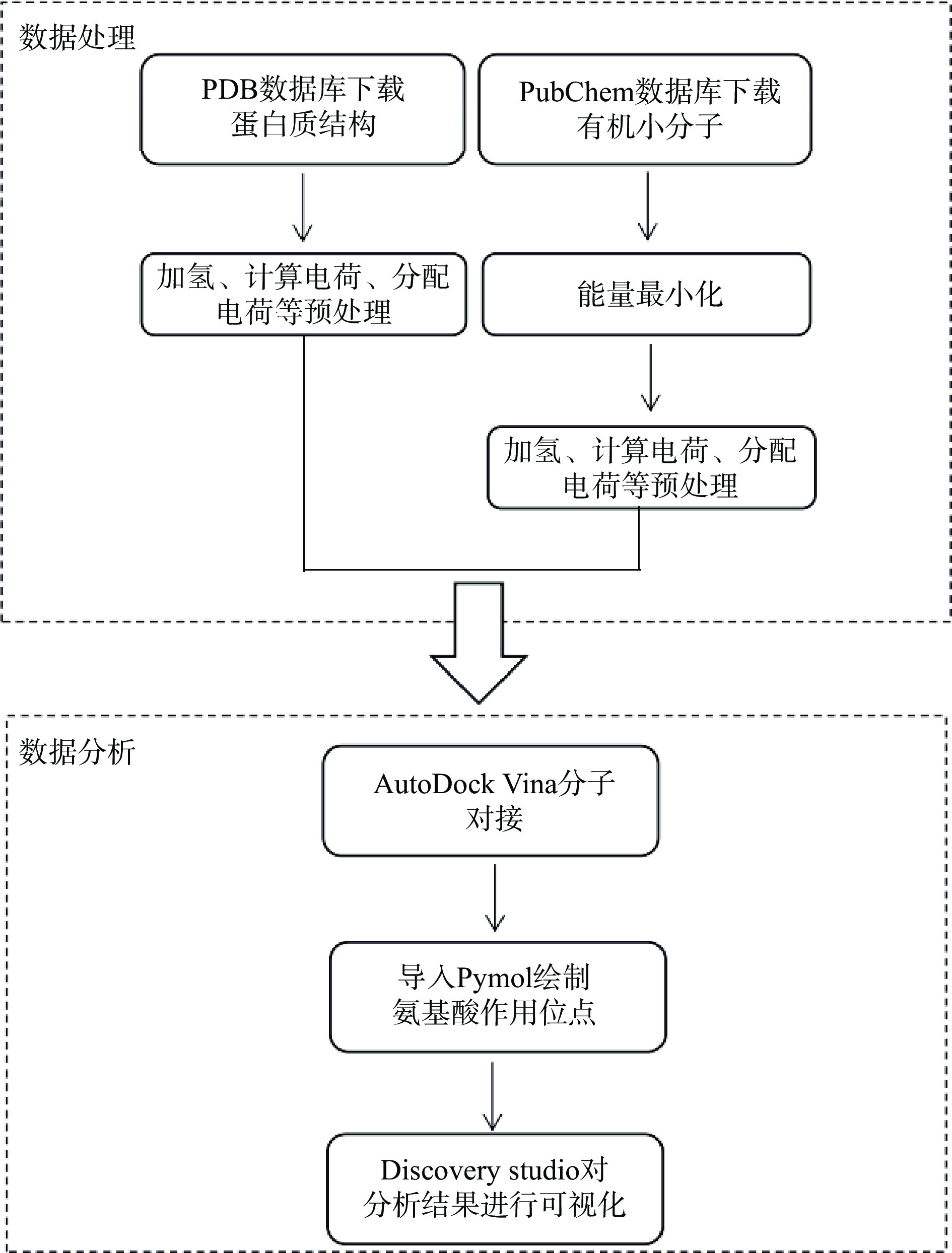
配体分子和蛋白三维结构的优化:分子对接用于验证活性成分与关键靶点之间的结合活性。通过AlphaFold蛋白质三维结构数据库在线搜索PatC的三维结构,再对其三维模型导入AutoDocktools(v1.5.6)进行加氢、计算电荷、分配电荷、指定原子类型等优化处理;从Pubchem数据库下载小分子或蛋白的3D结构,导入ChemBio3D Ultra 14.0 进行能量最小化。将优化好的小分子导入AutodockTools-1.5.6进行加氢、计算电荷、分配电荷等处理。
分子对接:AutoDock Vina1.1.2是一个采用半柔性对接方法运行的程序,对接精度高达78%,被用来作为本研究的分子对接程序[32],分子对接流程如图3。
1.3 分子动力学模拟
先将Wild PatC和E-ascladiol对接的最佳结合构象,作为初始复合物结构进行MD模拟。随后使用蛋白定点突变软件,构建新型PatC突变体结构(P188A)观察突变后的蛋白与底物对接后复合物的活性。
具体操作如下:使用分子动力学软件Gromacs 2020.6进行模拟。复合物小分子在GAFF力场下生成拓扑文件,蛋白在AMBER99SB-ILDN力场生成相应参数化文件。以复合物为中心,添加SPC/E水模型分子,生成立方体水盒子,向复合物水盒子里添加4个CL-离子保持模拟体系的电中性。在体系完成后,使用最陡能量下降法进行50000步能量最小化,使体系充分稳定。采用正则系综(NVT),Berendsen热浴法控制温度为298.15 K,模拟50000步,步长2 fs。采用等温等压系综(NPT),Parrinello-Rahman控压,1个大气压,模拟50000步,步长2 fs。进行mdrun,步长2 fs,模拟10000000,总计20 ns的模拟,对模拟后的数据计算MMPBSA。
1.4 数据处理
利用Discovery studio 2016对分子对接结果进行可视化,且利用PyMOL(4.3.0版)软件绘制蛋白与分子之间相互作用的氨基酸残基。分子动力学模拟使用软件gromacs分析各组参数变化,最终通过程序统计结果文件计算出体系各种宏观性质和微观性质,并使用xmgrace绘制相应的数据图,如RMSD、RMSF、SASA及氢键变化等。PAT生物合成图(图1)使用在线网站FigDraw(https://www.figdraw.com)绘制,图2使用Adobe Illustrator软件绘制。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 构建系统进化树
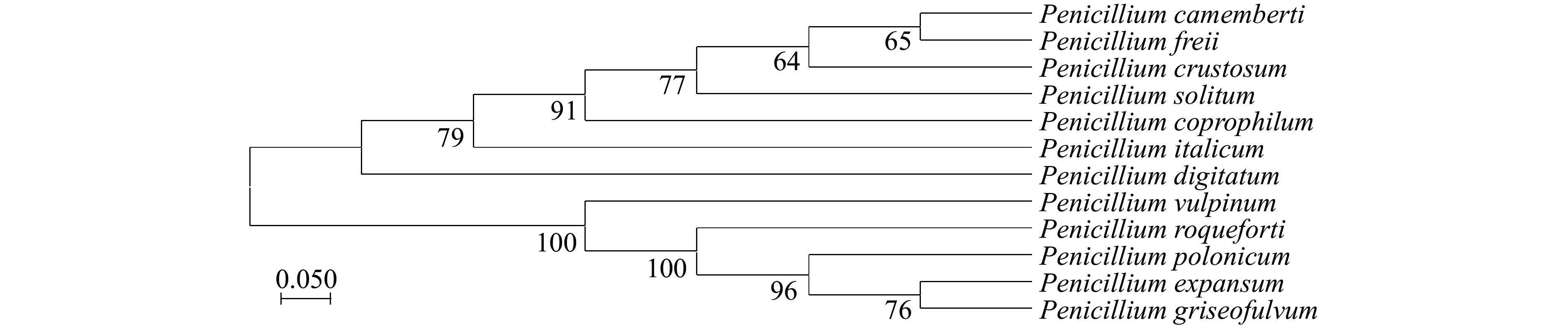
选取与PatC同源性较高的多条已知菌株的氨基酸序列(表2),利用MEGA5.0软件构建NJ系统进化树(图4)。所选的11个物种序列与PatC的氨基酸序列一致性较高。系统进化树结果表明,Penicillium expansum(扩展青霉)与Penicillium griseofulvum(灰黄青霉)处于同一分支,亲缘关系较近。此现象可能是因为两者的PAT合成基因簇均包含相同的15个基因,且基因排布顺序相同。此外,与Penicillium digitatum(指状青霉)和Penicillium italicum(意大利青霉)关系较远,推测是因为两者均只含有棒曲霉素生物合成基因簇的部分基因且不产生PAT[33]。
表 2 11个MFS转运蛋白登录号Table 2. 11 MFS transporters accession numbers种名 蛋白登录号 序列一致性 Penicillium polonicum OQD65553.1 95.60% Penicillium crustosum KAF7524359.1 95.06% Penicillium freii KUM63383.1 95.06% Penicillium camemberti CRL29157.1 95.06% Penicillium solitum XP_040815823.1 94.88% Penicillium coprophilum OQE43159.1 92.32% Penicillium italicum KGO71590.1 92.21% Penicillium griseofulvum XP_040649532.1 91.94% Penicillium roqueforti KAI3112831.1 91.41% Penicillium digitatum KAG0160219.1 88.67% Penicillium vulpinum OQE09870.1 88.27% 2.2 蛋白结构功能域预测
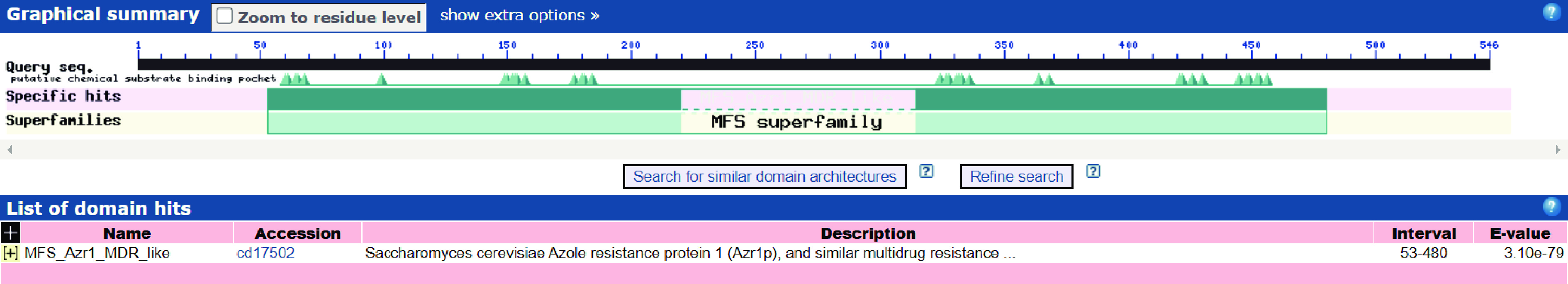
利用NCBI Domains & Structures对PatC进行功能结构域预测分析。如图5结果表明,该蛋白氨基酸序列53aa~480aa为MFS结构域,验证PatC属于MFS转运蛋白超家族。Paulsen等[34]研究MFS家族时发现,大多数MFS蛋白的保守特征序列是基序A(GrLaDrfGrRRv)、基序B(LvaaRvlQGxGA)和基序C(gxxxGPxxxGGxl),其中位于TMS4内的基序B参与大多数MFS成员的质子转移。Jiang等[35]提出基序A是MFS成员中高度保守的基序,位于TMS 2和TMS 3之间的环中,在构象调节中起着至关重要的作用,特别是对外构象的稳定性。此外,Motif C被称为反转运基序,在TMS5内形成纽扣,可能与底物结合位点的取向有关[36]。
2.3 理化性质分析
利用在线软件ProtParam对PatC的理化性质进行预测,结果显示(表3),PatC的氨基酸数量是546个,分子量为58733.15;理论等电点PI:5.57,为酸性蛋白;该蛋白氨基酸序列中亮氨酸(Leu)、甘氨酸(Gly)及丙氨酸(Ala)三种氨基酸含量较高,所占比值分别为12.1%、10.1%和9.7%;蛋白不稳定指数:40.3,为不稳定蛋白;从脂肪系数数据分析表明该蛋白脂肪系数:113.77,为脂溶性蛋白。亲水性平均系数(GRAVY)值为0.712,表明该蛋白为疏水性蛋白。
表 3 PatC的理化性质分析Table 3. Physicochemical property analysis of PatC蛋白名称 氨基酸残基 分子量 理论等电点 蛋白不稳定指数 脂肪系数 亲水性平均系数 主要氨基酸 PatC 546 58733.15 5.57 40.3 113.77 0.712 Leu、Gly、Ala 2.4 跨膜结构预测
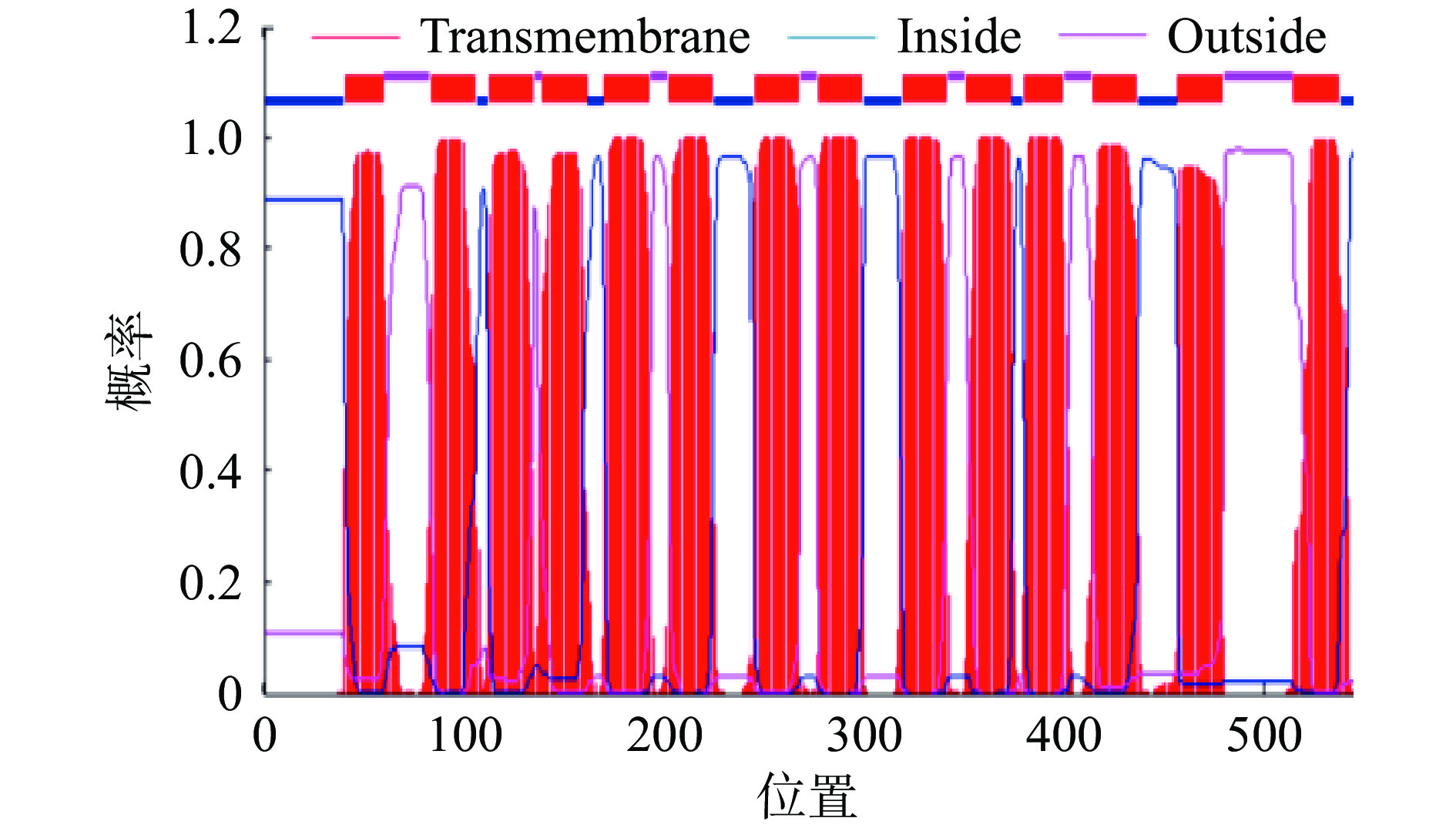
采用在线软件TMHMM对PatC的跨膜结构进行预测,由图6和上述理化性质结果表明该蛋白具有强疏水性氨基酸,具有能够行使跨膜转运的功能,符合转运蛋白的特点。
2.5 蛋白质二级结构预测
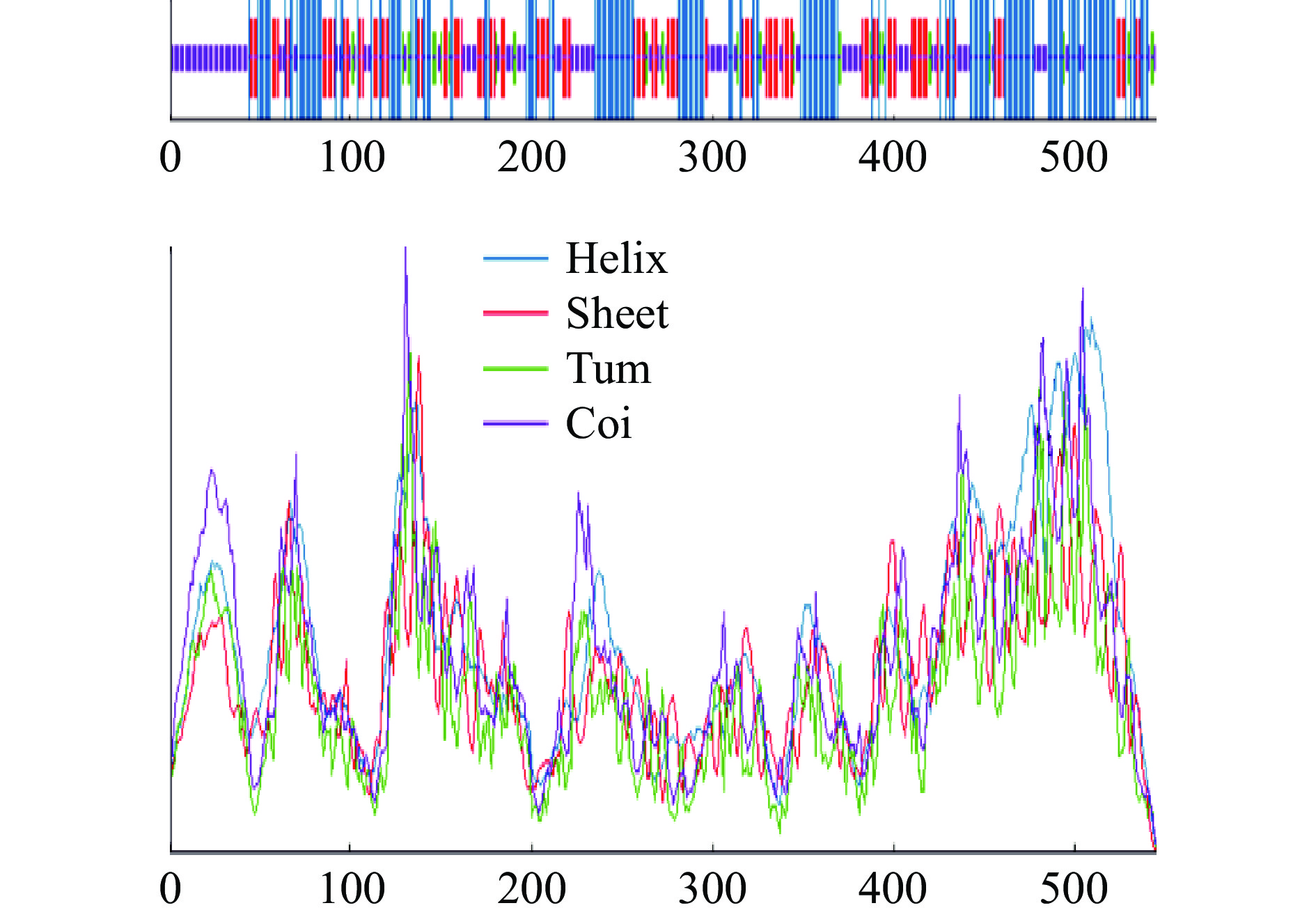
利用在线SOPMA软件对PatC二级结构进行预测和分析(图7),PatC中二级结构主要存在4种:α-螺旋、β-转角、β-折叠和无规则卷曲。二级结构元件中α-螺旋所占比例最高,此外无规则卷曲、β-折叠和β-转角所占比例依次减少分别为30.95%、24.73%和6.23%。
2.6 蛋白质三级结构预测
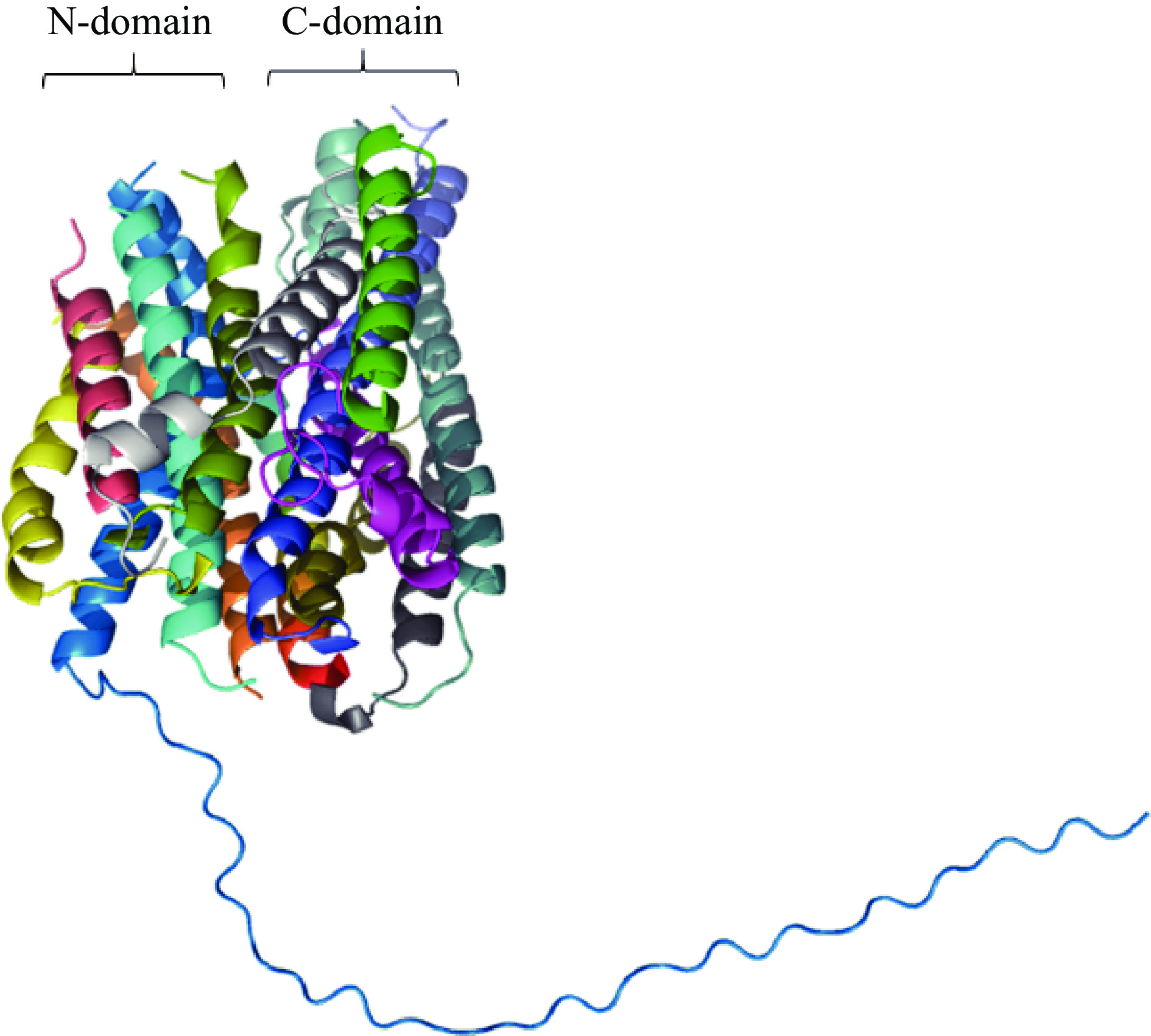
PatC同源性蛋白较少,无法利用SWISS MODEL同源建模方法得到其三级结构。因此通过AlphaFold预测PatC的三级结构。由图8说明该蛋白是14次α-螺旋结构(与跨膜结构预测相吻合),可能是进化过程中以12次跨膜α-螺旋为基础产生的[37],分为2个结构域:N端结构域和C端结构域。每个结构域都由6个α-螺旋组成,2个结构域呈现二次赝对称(two-fold psudosymmetry)[20]。与大肠杆菌中的二肽转运蛋白(Escherichia coli YbgH,EcYbgH)结构类似,为经典的12次跨膜α-螺旋构象加两个TM螺旋的插入(HA和HB)[38]。
2.7 分子对接
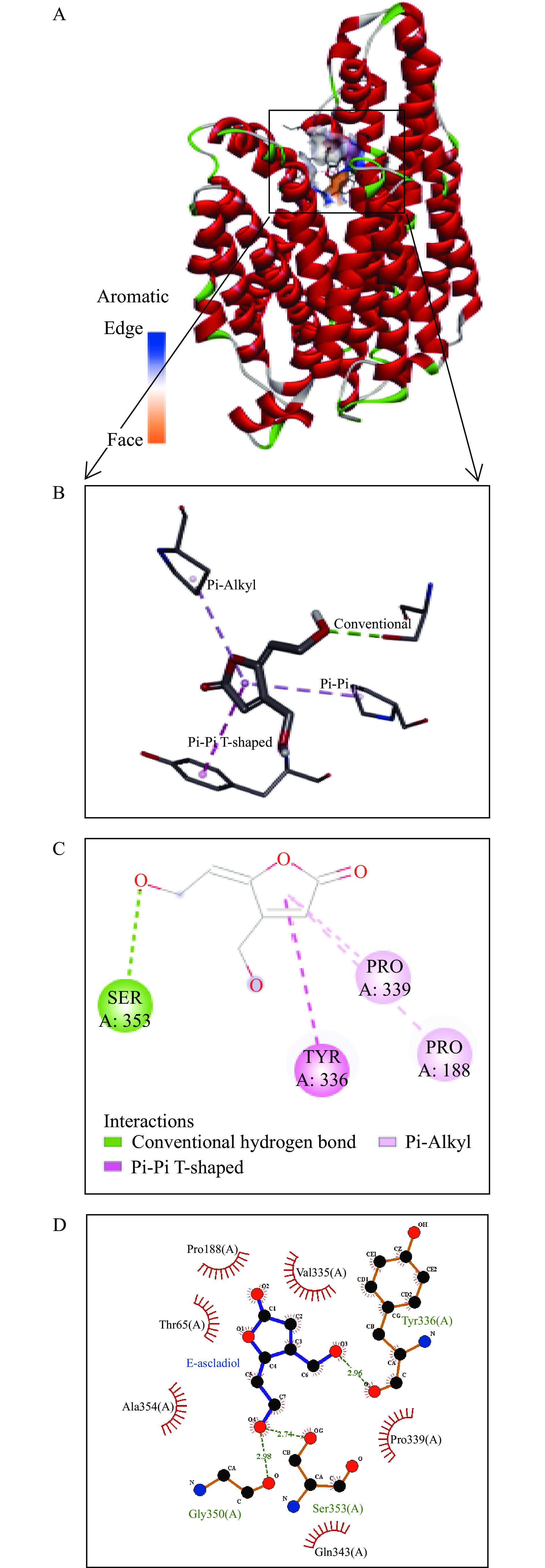
采用AutoDock Vina1.1.2将PatC与E-ascladiol进行半柔性对接,分子对接结果如图9,其之间的平均结合能为−5.0 kcal/mol(<0),说明配体和受体蛋白可以自发结合。PatC与E-ascladiol之间主要以传统氢键(Conventional hydrogen bond)、堆积键(Pi-Pi T-shaped)及疏水作用力(Pi-Alkyl)相互作用。具体相互结合模式:E-ascladiol与PatC结合至蛋白空腔,且与该蛋白受体的氨基酸残基SER353、TYR336、PRO339、及PRO188分别形成2.74Å氢键,2.96ÅPi-Pi堆积作用力,5.21Å和529Å疏水作用力,这些相互作用使得蛋白质与小分子紧密结合。
2.8 分子动力学模拟
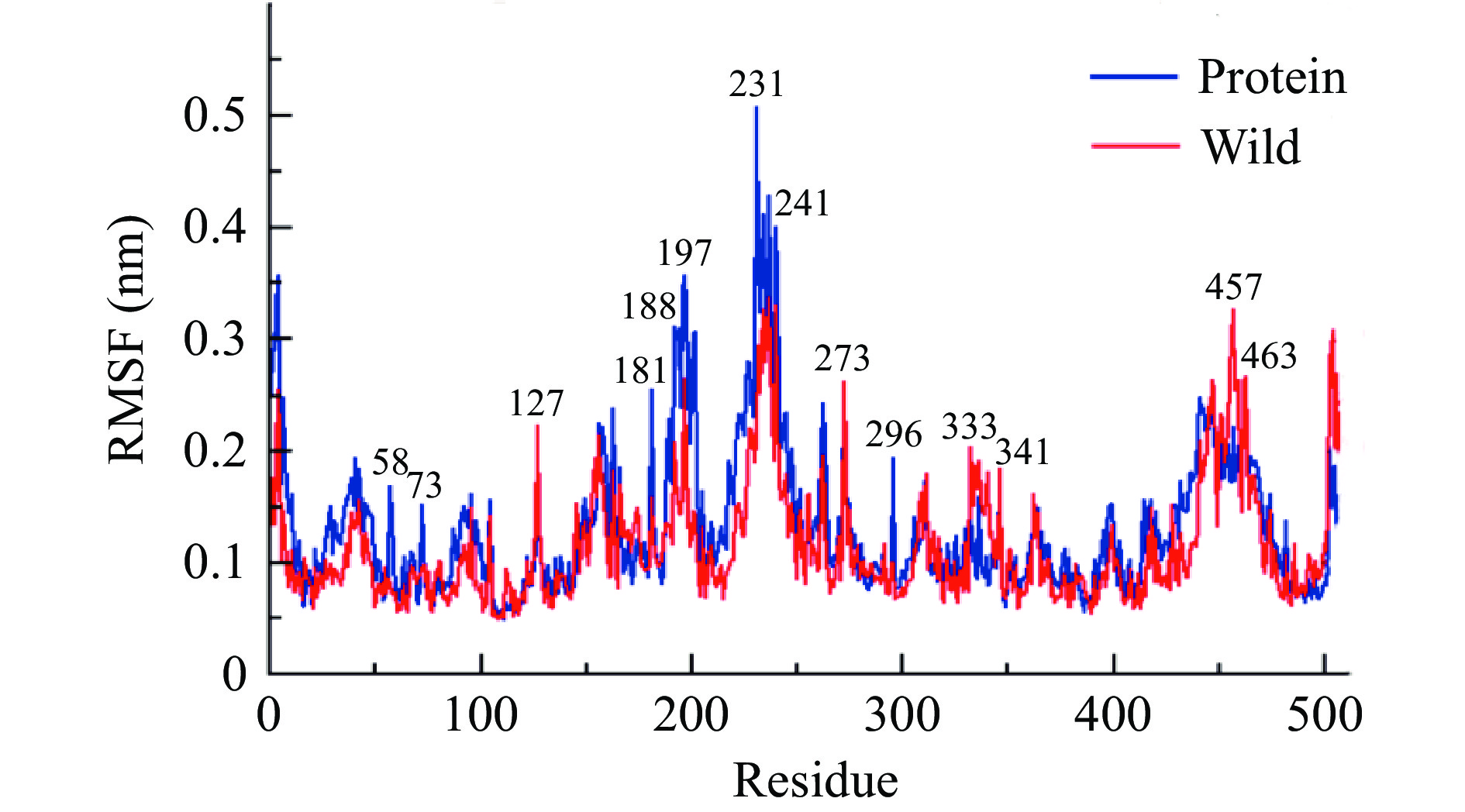
2.8.1 RMSF分析
RMSF(Root Mean Square Fluctuation,RMSF)是用来衡量一段时间内分子结构中原子位置的平均移动,是目的结构特定原子相对于参照结构在整个时间范围内的距离均方根,是判断蛋白质结构结构变化的重要参数之一[39]。
通过Protein(纯蛋白)与Wild(野生型复合体)的RMSF数据分析,如图10所示,PatC在多个氨基酸位点发生柔性变化。与野生型复合物对比,纯PatC分别在第127、181、188~197、231~241、273、296、333~341、457~463位残基区域即(Ala127、Gly181、Pro188~Ser197、Gly231~Val241、Asp273、Phe296、Val333~Try341、Gln457~Ala463)发生了形变拉伸或缩短。其中位于Pro188~Ser197aa、Gly231~Val241aa氨基酸区域内,结合底物分子后的PatC发生柔性变化,在一定程度上增加其灵活度,改变其空间构象。因此可推测出上述氨基酸区域内可能存在PatC与E-ascladiol之间的结合位点。
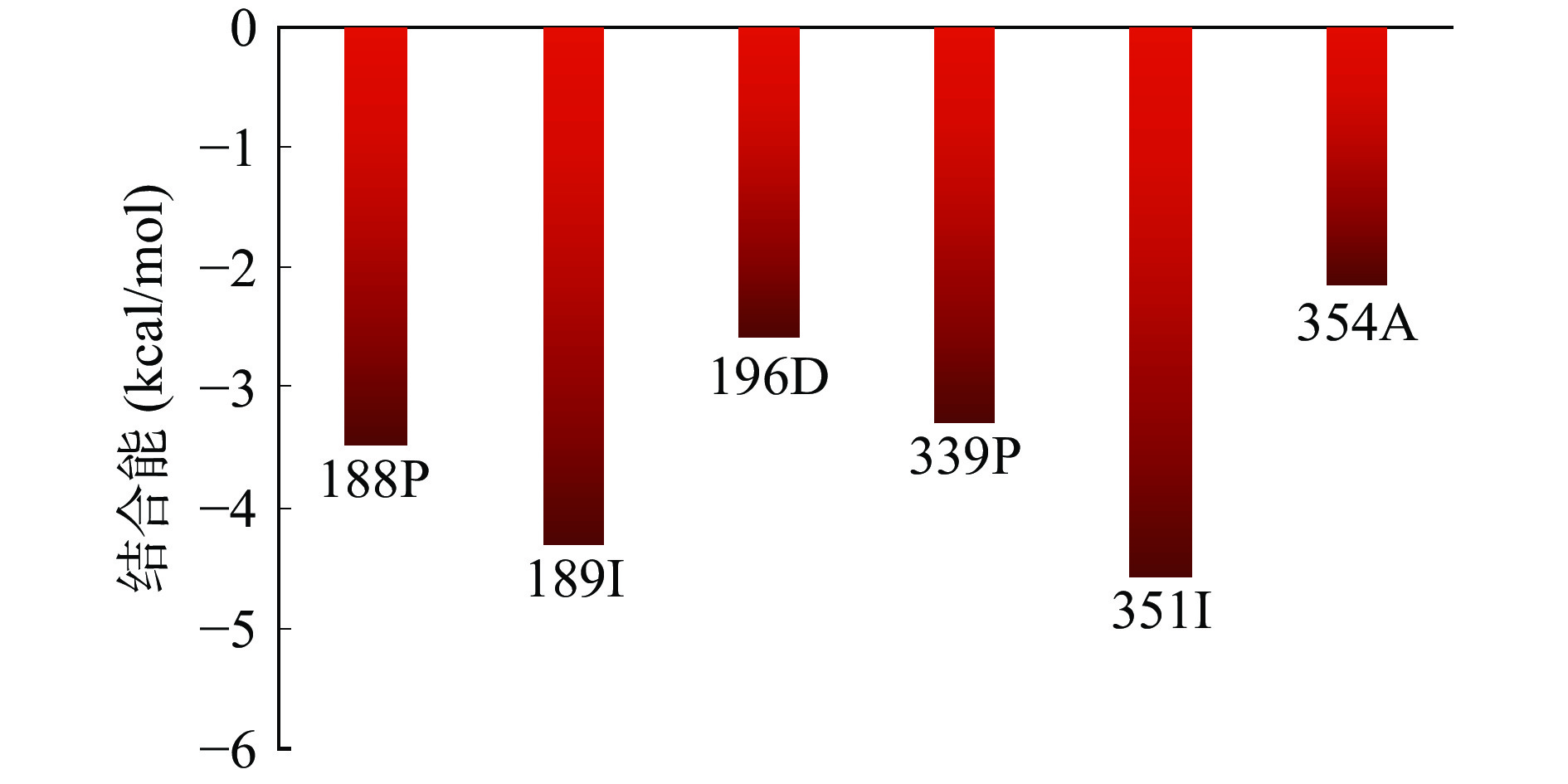
2.8.2 点突变分析
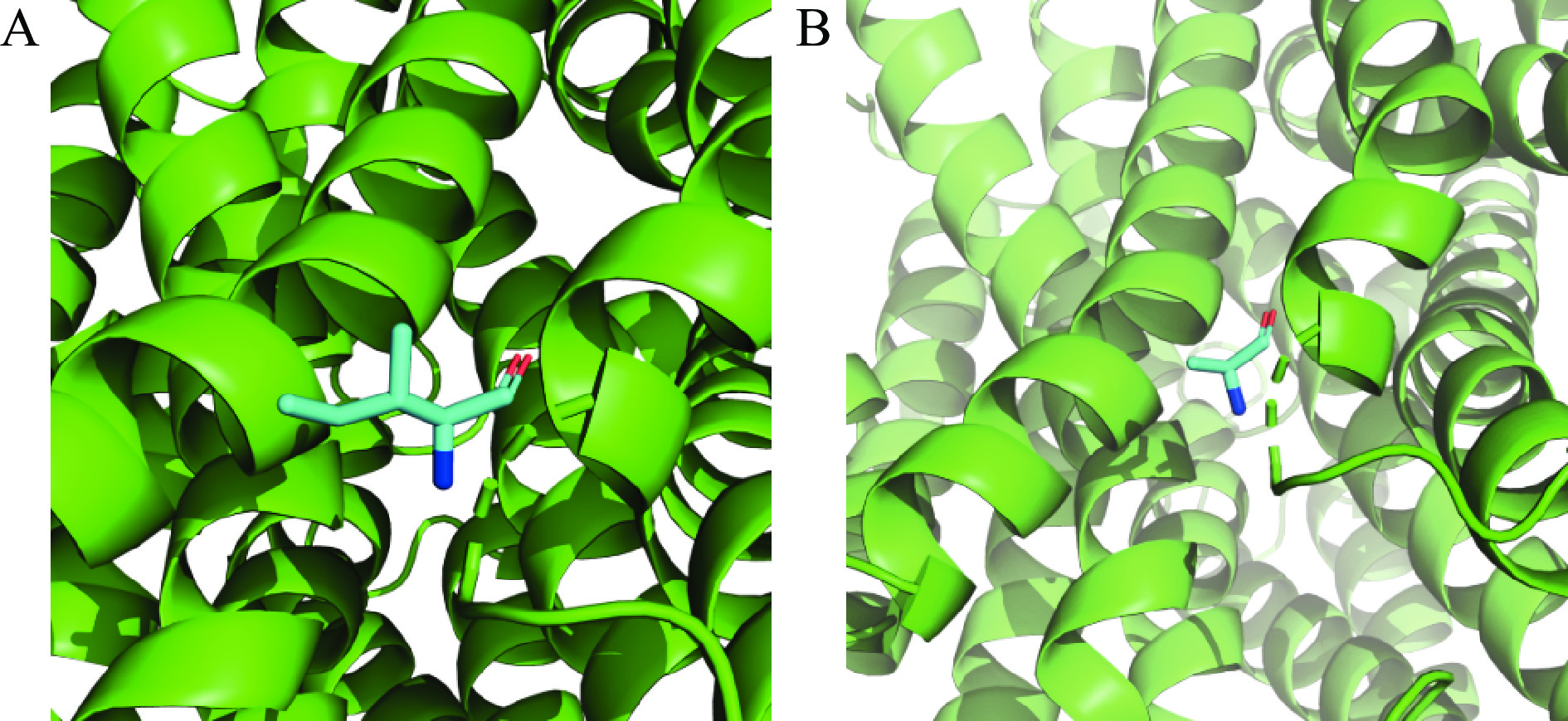
通过上述分子对接和复合物分子动力学模拟两种方法得出不同的结合位点。由图11可知,MD计算得到6个结合位点,其中第188位氨基酸与分子对接结果重叠,且与RMSF数据相吻合,因此使用Pymol软件对PatC中第188位氨基酸残基位点突变,将原有的脯氨酸(P)突变为丙氨酸(A),即产生新的P188A的PatC突变体。通过将PatC与P188A的突变位点进行构象对比,如图12,发现在第188位氨基酸位置上的点突变并未使该位点的二级结构出现明显差别,且不影响整体蛋白质构型,因此继续使用此结果进行后续实验研究。
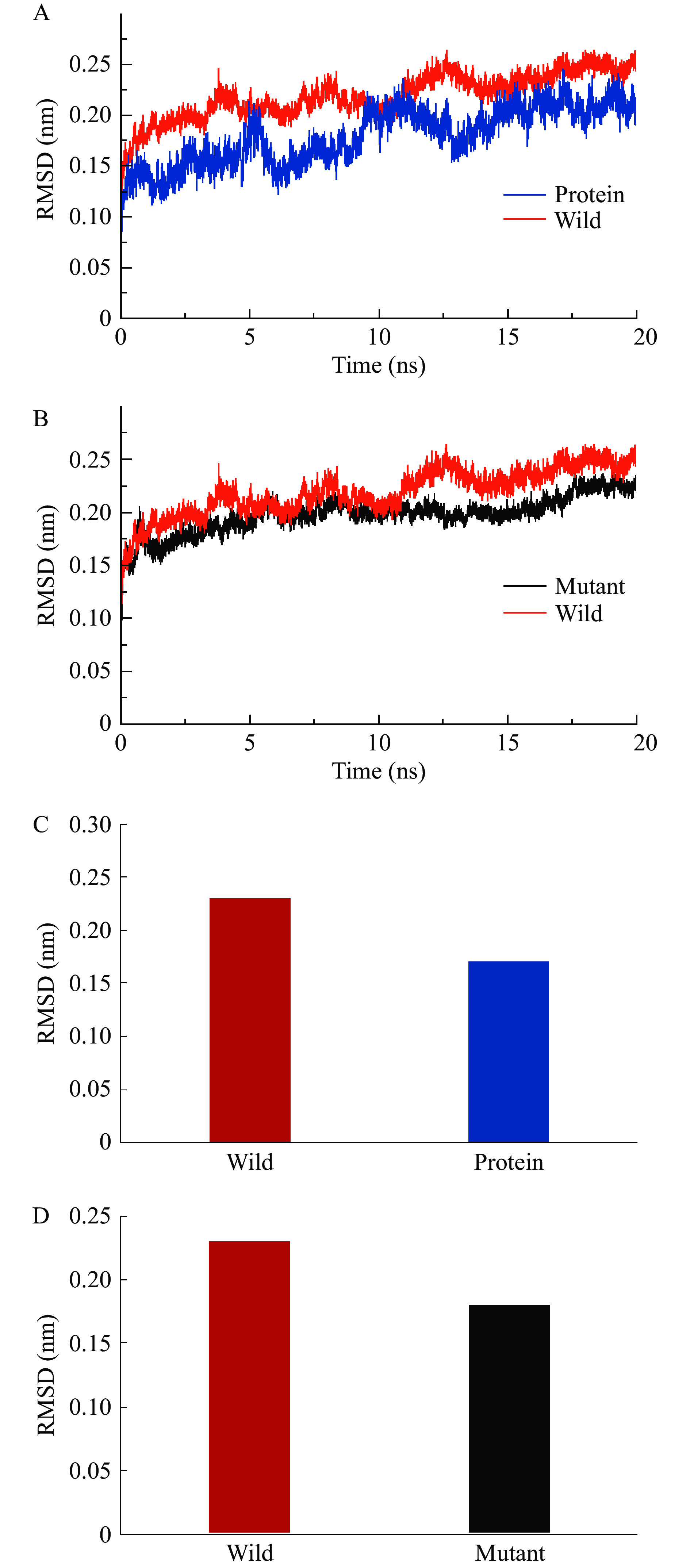
2.8.3 RMSD分析
RMSD(Root Mean Square Distance/Deviation,RMSD)是用来衡量同一分子结构不同构象之间的差异,常用来分析体系分子整体结构的稳定性,RMSD变小表明结构趋于稳定,反之趋于不稳定[39]。
将纯Protein(纯蛋白)、Wild(野生型复合体)、P188A(突变体复合体)三个复合体系体系分别进行了20 ns的分子动力学模拟实验。在对其数据进行采集和分析中,三个模拟体系结构中的原子骨架的根均方偏差RMSD值如图13所示。当反应进行至15 ns时,三个反应体系曲线趋于平稳,虽有一定的波动,但范围在0.05 nm之内。说明三个体系均达到了平衡状态,且三个反应体系的RMSD终值都停留在0.3 nm以下,其中Protein、Wild复合体系和Mutant复合体系的RMSD平均值分别为0.17、0.23和0.18 nm左右,可看出三者在模拟过程中结构均保持稳定。且相较于Wild,Mutant稳定性更佳。
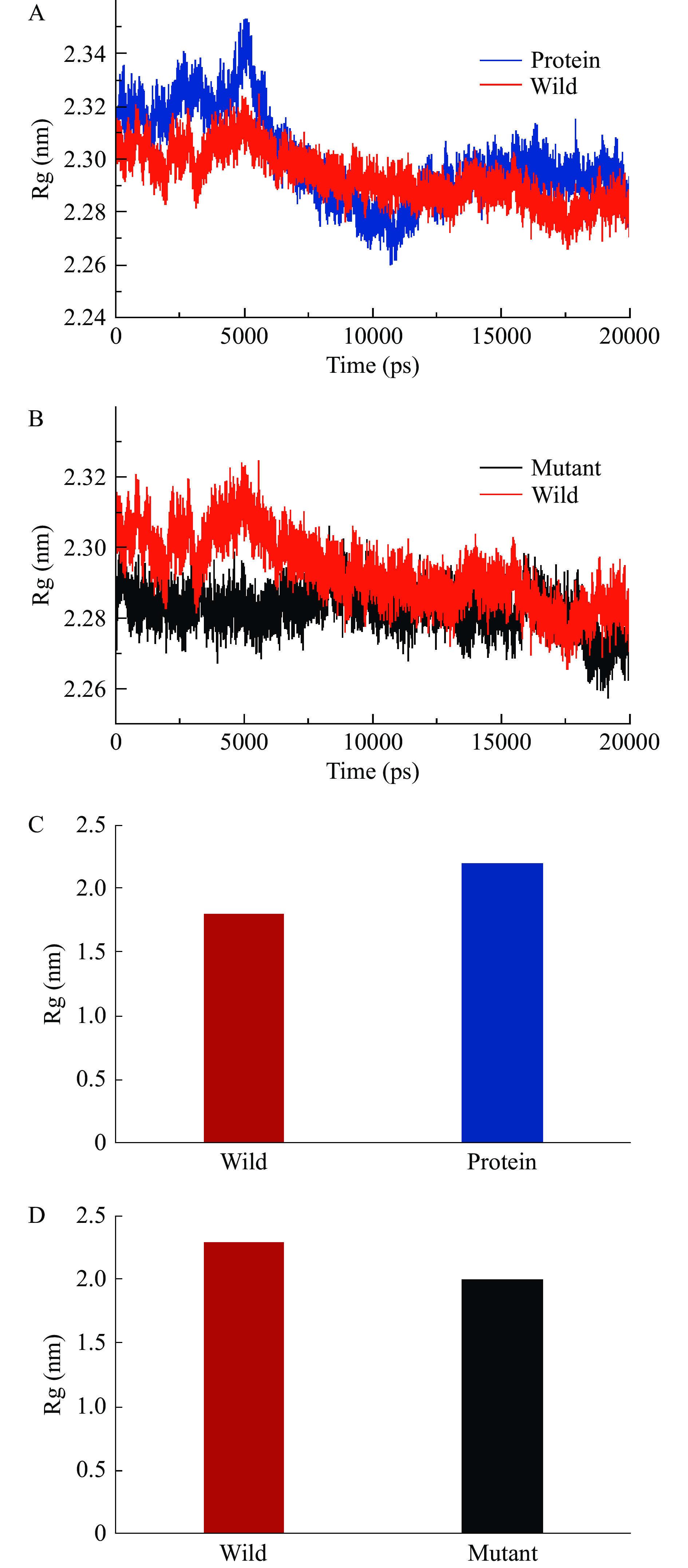
2.8.4 Rg分析
Rg(Radius of Gyratio,Rg)回旋半径用来衡量分子结构的紧密度或折叠程度,Rg考察主要选择平衡时状态进行[39],因此主要选择后10 ns进行分析,由图14可得,后10 ns两个反应体系中Rg变化均很小,表明这三个反应体系稳定且在反应过程中均为平衡状态且复合物结构致密,且三个反应体系的平均值均在2.5 nm以下,并且空白蛋白的Rg值最高,两种结合底物分子的复合物体系中Rg值均有明显减少,由此可见在PatC结合了底物分子后,整体构象进行了收缩。
3. 结论
本研究基于PatC与E-ascladiol结合的前提下,运用生物信息学、分子对接和分子动力学模拟方法预测蛋白与分子之间的重要作用位点,以研究PatC转运机制。生物信息学结果表明,该蛋白的二级结构以为α-螺旋和无规则卷曲为主,三级空间构象含有14个跨膜螺旋,含有2个结构域:N端结构域和C端结构域,形成独特的MFS折叠。根据以上结果说明PatC作为毒素输出泵转运PAT,但其理化性质也需进一步的验证。分子对接结果表明PatC与E-ascladiol之间存在多个结合位点与多种相互作用力,与RMSF数据结合分析得出P188作为重要结合位点并对其进行模拟突变。此外,本研究通过分子动力学方法对两种复合体系(野生型Wild和突变体P188A)进行各参数分析,结果说明P188氨基酸位点可能是PatC的关键作用位点,可为后续的微生物分子实验提供基础论证。综上所述,本文为棒曲霉素合成途径中的MFS蛋白的转运机制(毒素外排作用)提供一定的基础,并进一步为毒素输出泵的生物学功能与转运机制研究提供参考。
-
表 1 生物信息学相关分析工具
Table 1 Bioinformatics correlation analysis tools
网站名称 网址 功能 SMART http://smart.embl.de/ 蛋白的功能结构域 NCBI NCBI Conserved Domain Search (nih.gov) 蛋白的功能结构域 ExPASy-ProtParam https://web.expasy.org/protparam/ 蛋白的理化性质 TMHMM-2.0 http://www.cbs.dtu.dk/services/TMHMM 蛋白的跨膜结构 SOPMA https://npsa-prabi.ibcp.fr/cgi-bin/npsa_automat.pl?page=npsa%20_sopma.html 蛋白的二级结构 AlphaFold https://www.alphafold.ebi.ac.uk/ 蛋白的三级结构 Uniprot https://www.uniprot.org/ 蛋白质数据库 表 2 11个MFS转运蛋白登录号
Table 2 11 MFS transporters accession numbers
种名 蛋白登录号 序列一致性 Penicillium polonicum OQD65553.1 95.60% Penicillium crustosum KAF7524359.1 95.06% Penicillium freii KUM63383.1 95.06% Penicillium camemberti CRL29157.1 95.06% Penicillium solitum XP_040815823.1 94.88% Penicillium coprophilum OQE43159.1 92.32% Penicillium italicum KGO71590.1 92.21% Penicillium griseofulvum XP_040649532.1 91.94% Penicillium roqueforti KAI3112831.1 91.41% Penicillium digitatum KAG0160219.1 88.67% Penicillium vulpinum OQE09870.1 88.27% 表 3 PatC的理化性质分析
Table 3 Physicochemical property analysis of PatC
蛋白名称 氨基酸残基 分子量 理论等电点 蛋白不稳定指数 脂肪系数 亲水性平均系数 主要氨基酸 PatC 546 58733.15 5.57 40.3 113.77 0.712 Leu、Gly、Ala -
[1] ZHONG L, CARERE J, LU Z, et al. Patulin in apples and apple-based food products: The burdens and the mitigation strategies[J]. Toxins,2018,10(11):475. doi: 10.3390/toxins10110475
[2] LUCIANO-ROSARIO D, KELLER N P, JURICK W M. Penicillium expansum: Biology, omics, and management tools for a global postharvest pathogen causing blue mould of pome fruit[J]. Mol Plant Pathol,2020,21(11):1391−1404. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12990
[3] TANNOUS J, KELLER N P, ATOUI A, et al. Secondary metabolism in Penicillium expansum: Emphasis on recent advances in patulin research[J]. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr,2018,58:2082−2098. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2017.1305945
[4] ZHENG X, WEI W, ZHOU W, et al. Prevention and detoxification of patulin in apple and its products: A review[J]. Food Res Int,2021,140:110034. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.110034
[5] GAO L, ZHANG Q, SUN X, et al. Etiology of moldy core, core browning, and core rot of Fuji apple in China[J]. Plant Disease,2013,97(4):510−516. doi: 10.1094/PDIS-01-12-0024-RE
[6] WANG Z, WANG L, MING Q, et al. Reduction the contamination of patulin during the brewing of apple cider and its characteristics[J]. Food Addit Contam Part A Chem Anal Control Expo Risk Assess,2022,39(6):1149−1162. doi: 10.1080/19440049.2022.2055155
[7] ZHOU T, WANG X, LUO J, et al. Identification of differentially expressed genes involved in spore germination of Penicillium expansum by comparative transcriptome and proteome approaches[J]. Microbiology Open,2018,7(3):e562.
[8] SAJID M, MEHMOOD S, YUAN Y, et al. Mycotoxin patulin in food matrices: Occurrence and its biological degradation strategies[J]. Drug Metab Rev,2019,51(1):105−120. doi: 10.1080/03602532.2019.1589493
[9] PLEADIN J, FRECE J, MARKOV K. Mycotoxins in food and feed[J]. Adv Food Nutr Res,2019,89:297−345.
[10] CHENG M, ZHAO S, LIU H, et al. Functional analysis of a chaetoglobosin A biosynthetic regulator in Chaetomium globosum[J]. Fungal Biol,2021,125(3):201−210. doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2020.10.010
[11] GUERRA-MORENO A, HANNA J. Induction of proteotoxic stress by the mycotoxin patulin[J]. Toxicol Lett,2017,276:85−91. doi: 10.1016/j.toxlet.2017.05.015
[12] GLASER N, STOPPER H. Patulin: Mechanism of genotoxicity[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology,2012,50(5):1796−1801. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2012.02.096
[13] WEI C, YU L, QIAO N, et al. Progress in the distribution, toxicity, control, and detoxification of patulin: A review[J]. Toxicon,2020,184:83−93. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2020.05.006
[14] LI B, CHEN Y, ZHANG Z, et al. Molecular basis and regulation of pathogenicity and patulin biosynthesis in Penicillium expansum[J]. Compr Rev Food Sci Food Saf,2020,19(6):3416−3438. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12612
[15] LI B, CHEN Y, ZONG Y, et al. Dissection of patulin biosynthesis, spatial control and regulation mechanism in Penicillium expansum[J]. Environmental Microbiology,2019,21(3):1124−1139. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.14542
[16] LI B, ZONG Y, DU Z, et al. Genomic characterization reveals insights into patulin biosynthesis and pathogenicity in Penicillium Species[J]. Mol Plant Microbe Interact,2015,28(6):635−647. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-12-14-0398-FI
[17] TANNOUS J, ELKHOURY R, SNINI S P, et al. Physical organization and kinetic expression of the patulin biosynthetic gene cluster from Penicillium expansum[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2014,189:51−60. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2014.07.028
[18] WANG S C, DAVEJAN P, HENDARGO K J, et al. Expansion of the Major Facilitator Superfamily (MFS) to include novel transporters as well as transmembrane-acting enzymes[J]. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr,2020,1862(9):183277. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2020.183277
[19] DE RAMÓN-CARBONELL M, SÁNCHEZ-TORRES P. Penicillium digitatum MFS transporters can display different roles during pathogen-fruit interaction[J]. Int J Food Microbiol,2021,337:108918. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2020.108918
[20] DREW D, NORTH R, NAGARATHINAM K, et al. Structures and general transport mechanisms by the major facilitator superfamily (MFS)[J]. Chem Rev,2021,121(9):5289−5335. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.0c00983
[21] KUMAR S, LEKSHMI M, PARVATHI A, et al. Functional and structural roles of the major facilitator superfamily bacterial multidrug efflux pumps[J]. Microorganisms,2020,8(2):e266. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms8020266
[22] MADEJ M G, DANG S, YAN N, et al. Evolutionary mix-and-match with MFS transporters[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2013,110(15):5870−5874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1303538110
[23] ALEXANDER N J, MCCORMICK S P, HOHN T M. TRI12, atrichothecene efflux pump from Fusarium sporotrichioides: Geneisolation and expression in yeast[J]. Mol Gen Genet,1999,261(6):977−984. doi: 10.1007/s004380051046
[24] CALLAHAN T M, ROSE M S, MEADE M J, et al. CFP, the putative cercosporin transporter of Cercospora kikuchii, is required for wild type cercosporin production, resistance, and virulence on soybean[J]. Mol Plant Microbe Interact,1999,12(10):901−910. doi: 10.1094/MPMI.1999.12.10.901
[25] LIESCH J M, SWEELEY C C, STAFFELD G D, et al. Structure of HC-toxin, a cyclic tetrapeptide from helminthosporium carbonum[J]. Tetrahedron,1982,38(1):45−48. doi: 10.1016/0040-4020(82)85043-6
[26] PITKIN J W, PANACCIONE D G, WALTON J D. A putative cyclic peptide efflux pump encoded by the TOXA gene of the plant-pathogenic fungus Cochliobolus carbonum[J]. Microbiology (Reading),1996,142(6):1557−1565. doi: 10.1099/13500872-142-6-1557
[27] MOFFAT C S, SEE P T, OLIVER R P. Generation of a ToxA knockout strain of the wheat tan spot pathogen Pyrenophora tritici-repentis[J]. Mol Plant Pathol,2014,15(9):918−926. doi: 10.1111/mpp.12154
[28] MENKE J, DONG Y, KISTLER H C. Fusarium graminearum Tri12p influences virulence to wheat and trichothecene accumulation[J]. Mol Plant Microbe Interact,2012,25(11):1408−1418. doi: 10.1094/MPMI-04-12-0081-R
[29] BRADSHAW R E, BHATNAGAR D, GANLEY R J, et al. Dothistroma pini, a forest pathogen, contains homologs of aflatoxin biosynthetic pathway genes[J]. Appl Environ Microbiol,2002,68:2885−2892. doi: 10.1128/AEM.68.6.2885-2892.2002
[30] 王艳玲, 郭小洁, 张紊玮, 等. 棒曲霉素生物合成及分子调控研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(17):267−274. [WANG Y L, GUO X J, ZHANG W W, et al. Recent advances in patulin biosynthesis and its molecular regulation[J]. Food Science,2020,41(17):267−274. WANG Y L, GUO X J, ZHANG W W, et al. Recent Advances in Patulin Biosynthesis and Its Molecular Regulation[J]. Food Science, 2020, 41(17): 267−274.
[31] QUISTGAARD E M, LÖW C, GUETTOU F, et al. Understanding transport by the major facilitator superfamily (MFS): Structures pave the way[J]. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol,2016,17(2):123−132. doi: 10.1038/nrm.2015.25
[32] 钟红梅, 蔡开聪. AutoDock软件在生物化学教学中的应用-半柔性对接[J]. 化学教育(中英文),2020,41(6):86−89. [ZHONG C M, CAI K C. Application of AutoDock software in teaching of biochemistry: Semi-flexible docking[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Education,2020,41(6):86−89. ZHONG C M, CAI K C. Application of AutoDock software in teaching of biochemistry: Semi-flexible docking[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Education, 2020, 41(6): 86−89.
[33] MARCET-HOUBEN M, BALLESTER A R, FUENTE B, et al. Genome sequence of the necrotrophic fungus Penicillium digitatum, the main postharvest pathogen of citrus[J]. BMC Genomics,2012,13:646. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-13-646
[34] PAULSEN I T, BROWN M H, SKURRAY R A. Proton-dependent multidrug efflux systems[J]. Microbiol Rev,1996,60(4):575−608. doi: 10.1128/mr.60.4.575-608.1996
[35] JIANG D, ZHAO Y, WANG X, et al. Structure of the YajR transporter suggests a transport mechanism based on the conserved motif A[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA,2013,110(36):14664−14669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1308127110
[36] LAMBERT E, MEHIPOUR A R, SCHMIDT A, et al. Evidence for a trap-and-flip mechanism in a proton-dependent lipid transporter[J]. Nat Commun,2022,13(1):1022. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-28361-1
[37] SAIER M H. Genome archeology leading to the characterization and classification of transport proteins[J]. Curr Opin Microbiol,1999,2(5):555−561. doi: 10.1016/S1369-5274(99)00016-8
[38] ZHAO Y, MAO G, LIU M, et al. Crystal structure of the E. coli peptide transporter YbgH[J]. Structure,2014,22(8):1152−1160. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2014.06.008
[39] 杨萍, 孙益民. 分子动力学模拟方法及其应用[J]. 安徽师范大学学报(自然科学版),2009,32(1):51−54. [YANG P, SUN Y M. Method of molecular dynamics simulation and its application[J]. Journal of Anhui Normal University (Natural Science),2009,32(1):51−54. YANG P, SUN Y M. Method of molecular dynamics simulation and its application[J]. Journal of Anhui Normal University, 2009, 32(1): 51−54.






 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
