Phenolic Ketone Contents and Antioxidant, Antibacterial Properties and Inhibitory Tyrosinase Activity of the Ethyl Acetate Extracted from Calendula officinalis L.
-
摘要: 本文研究了金盏菊乙酸乙酯萃取相(Ethyl acetate extraction,EA相)及其相关萃取相的总酚、总黄酮含量、体外抗氧化及抑菌活性,采用高效液相色谱(High performance liquid chromatography,HPLC)分析其中没食子酸、绿原酸、咖啡酸、芦丁和阿魏酸5种酚酮类物质的含量。结果表明,EA相的总酚酮含量、抗氧化和抑菌活性均高于其他萃取相,EA相总酚酮含量为330.760±4.640 mg/g,芦丁和没食子酸在EA相中含量最高,分别为0.978±0.203和0.230±0.301 mg/g;EA相抗氧化活性与阳性对照VC接近,对金黄色葡萄球菌属于中度敏感;EA相对酪氨酸酶活性有较好地抑制作用,其IC50为0.965±0.001 mg/mL,优于阳性对照熊果苷,其抑制作用表现为可逆的混合型抑制,抑制常数KI和KIS分别为0.254和5.577 mg/mL。EA相抗氧化、抑菌、抑制酪氨酸酶活性作用最好,与其总酚、总黄酮含量较高且富含功能成分有较大的相关性,这些酚酮类活性物质更易被乙酸乙酯溶剂所萃取。Abstract: In this paper, the total phenolic and total flavonoid content, in vitro antioxidant and antibacterial activities of ethyl acetate extraction (EA phase) and its related extracted phases of Calendula officinalis L were studied. The content of five phenolic ketones, namely gallic acid, chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid, rutin and ferulic acid was analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The results showed that the total phenolic ketone content, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of EA phase were higher than other extracted phases, the total phenolic ketone content of EA phase was 330.760±4.640 mg/g, rutin and gallic acid were the highest in EA phase, which were 0.978±0.203 and 0.230±0.301 mg/g, respectively. The antioxidant activity of EA phase was close to that of the positive control VC, and moderately sensitive to Staphylococcus aureus. The enzyme kinetic experiment showed that EA phase had a good inhibiting effect on tyrosinase activity with an IC50 of 0.965±0.001 mg/mL, which was better than that of the positive control arbutin. The results demonstrated that EA phase suppressed the activity of tyrosinase in a reversible mixed-inhibition, and the inhibition constants KI and KIS were 0.254 and 5.577 mg/mL, respectively. The best antioxidant, antibacterial and tyrosinase inhibiting effects of EA phase were correlated with the high content of total phenols and total flavonoids and their richness in functional components, which were more easily extracted by ethyl acetate solvent.
-
Keywords:
- Calendula officinalis L /
- total flavonoids /
- total phenol /
- tyrosinase /
- antioxidant activity
-
酪氨酸酶是一种含金属铜离子的多功能氧化酶,是黑色素生物合成过程的关键限速酶,其可以将L-酪氨酸经两步催化氧化成多巴醌[1],这是人体皮肤变黑及果蔬产生褐变的主要原因。因此,寻找安全高效的集酪氨酸酶活性抑制、防腐抑菌、抗氧化等多功效于一体的天然产物在防止黑色素过量表达、果蔬褐变、食品保鲜等方面具有重要的意义。研究表明,中草药等天然植物提取物中的黄酮、多酚类物质具有潜在的消炎、抗菌、抗氧化、降低血脂、抑制酪氨酸酶活性等功能[2-3]。傅佳瑜等[4]研究了不同溶剂提取茶花粉中黄酮多酚类物质,发现茶花粉中多酚、黄酮含量与抑制酪氨酸酶活性呈现中度正相关。潘振东等[5]研究发现太白韭醇提物对金黄色葡萄球菌具有较好的抑制作用,并指出抑菌活性可能与其含有的黄酮类等化合物有关。霍锦双等[6]通过对咖啡酸、芦丁等酚酮类物质的抑菌活性检测,发现咖啡酸的抑菌活性强于芦丁。许恩婷等[7]对金线莲不同器官的不同萃取部位的抗氧化活性进行了研究,发现抗氧化活性与其多酚含量正相关。马嘉洁等[8]发现,紫苏叶中黄酮、多酚类化合物与抗氧化活性为显著的正相关。酚酮类化合物具有较好的抗氧化、抑菌、美白等功效,因此通过适宜的提取工艺富集天然植物中酚酮类物质,具有良好的应用前景。
金盏菊(Calendula officinalis L.)属于药食两用植物,来源丰富且价格低廉。近年来,国内对金盏菊的研究多集中在提取工艺、药理作用、成分分析等方面。研究发现,金盏菊中富含类胡萝卜素、黄酮、多酚类、挥发油等成分[9-10],具有清除自由基、抑菌、抗炎等作用[9-13]。Fatima等[14]用乙醇和索氏提取装置提取金盏菊干粉,发现金盏菊提取物具有明显的自由基清除活性和铁还原能力。Monica等[9]发现金盏菊80%甲醇提取物中总酚酮含量约为2.50 mg/mL,且具有较好的抗氧化作用,并指出抗氧化活性与多酚含量为正相关性。Olennikov等[15]发现金盏花中酚类物质对酪氨酸酶活性有较好的抑制作用,但未对其机理进一步深入研究。郑佳等[16]发现金盏菊醇提物对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的MIC值均为100 mg/mL。Rigane等[17]检测金盏菊花提取物中芦丁、没食子酸含量分别为 34.33±0.02 和 10.15±0.02 mg/g。Frum[18]检测金盏菊水提物中芦丁含量最高为0.031 mg/g,阿魏酸含量最低为0.0024 mg/g。
金盏菊酚酮类物质同时具有抗氧化性、抑菌、抑制酪氨酸酶活性等功效[9-13],且所用萃取溶剂不同,可富集酚酮类活性物质的种类和含量也不同。本课题组前期通过研究发现金盏菊醇提物及其萃取物均具有一定的抑制酪氨酸酶活性作用,但未进行深入研究;现有文献关于金盏菊提取物在酚酮类物质的富集、抗氧化、抑菌、抑制酪氨酸酶活性方面的研究也很少。因此,本研究通过溶剂萃取富集金盏菊中酚酮类活性物质,同时研究其抗氧化性、抑菌、抑制酪氨酸酶活性,并探寻相应的构效关系,可为深入研发金盏菊等天然植物中酚酮类活性物质,及其在食品和日化领域的应用提供一定理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
金盏菊干花 上海仁和堂国家医药中心;抗坏血酸、3,4-二羟基苯胺酸(L-多巴)、酪氨酸酶、熊果苷、石油醚、乙酸乙酯、正丁醇等 分析纯,上海泰坦科技股份有限公司;1,1-苯基-2苦基肼自由基(DPPH·)、福林试剂、2,2-双(3-乙基-苯并噻唑-6-磺酸)二铵盐(ABTS+·)、没食子酸、芦丁 分析纯,上海宝曼生物科技有限公司;绿原酸、咖啡酸、阿魏酸 分析纯,美利尔生物科技有限公司(中国上海);硫酸链霉素 上海摩楷生物科技有限公司;营养肉汤培养基、营养琼脂培养基 青岛海博生物技术有限公司;大肠杆菌(ATCC25922)、金黄色葡萄球菌(ATCC25923) 上海应用技术大学香料香精化妆品学部。
Shimadzu Excellence DGU-20A5高效液相色谱仪 日本岛津公司;TECAN-M200PRO多功能酶标仪 奥地利Tecan有限公司;722S型可见分光光度计 上海菁华科技仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品制备
参照文献[13]制备金盏菊乙醇提取物(EE)和不同萃取相。精确称取一定量的金盏菊干花粉末(精确至0.0001 g),以料液比1:10(g/mL)与体积分数为75%乙醇在105 ℃下回流提取2 h,抽滤、浓缩至浸膏状,得到乙醇提取物(EE)。将浸膏与蒸馏水混悬,依次用等体积的石油醚、乙酸乙酯、正丁醇萃取,挥去有机溶剂并浓缩至浸膏状,即得到石油醚萃取相(PEE相)、乙酸乙酯萃取相(EA相)、正丁醇萃取相(N-BE相)。
1.2.2 总酚和总黄酮含量的测定
使用DMSO溶解金盏菊醇提物和各萃取相的浸膏。采用福林酚法测定总酚含量[19]。以没食子酸为标准品,在760 nm处检测吸光度值,没食子酸质量浓度为横坐标(C1),吸光度值为纵坐标(A1),绘制标准曲线:A1=0.0155C1+0.0338,R2=0.9988。按照上述绘制标准曲线的方法测定样品中总酚含量。
采用硝酸铝-亚硝酸钠比色法测定总黄酮含量[20]。以芦丁为标准品,在505 nm处检测吸光度,芦丁质量浓度为横坐标(C2),吸光度为纵坐标(A2),绘制标准曲线:A2=1.0806C2−0.0124,R2=0.9993。按照上述绘制标准曲线的方法检测样品中总黄酮含量。
1.2.3 高效液相色谱(HPLC)分析
色谱柱:Syncronis-C18柱(100 mm×2.1 mm,5 μm,Phenomenex)。流动相A为0.1%甲酸,B为乙腈。梯度洗脱程序如下:0~5 min,25% B;5~11 min,30% B;11~17 min,35% B;17~20 min,100% B;20~25 min,10% B;流速0.3mL/min,进样量1 µL,检测波长280 nm[21]。
分别配制质量浓度为1、1.5、1.5、1、1mg/mL的没食子酸、绿原酸、咖啡酸、芦丁、阿魏酸的对照品储备液,冷藏备用[21]。分别取一定量的5种对照品储备液,混合定容至10 mL容量瓶中,配制成标准混合工作液进行测定,平行测定3次。以样品浓度为横坐标,响应值为纵坐标进行线性回归分析。
使用甲醇溶解金盏菊醇提物和各萃取相的浸膏,配制成质量浓度为10 mg/mL的溶液,静置,0.45 μm水系滤膜过滤后,按上述条件进行高效液相色谱分析。
1.2.4 体外抗氧化研究
先使用DMSO溶解金盏菊醇提物和各萃取相的浸膏,再用蒸馏水定容至所需浓度。参照文献[22-23]进行体外抗氧化实验。EE和PEE相质量浓度均为0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8、1 mg/mL,EA相和N-BE相质量浓度均为0.02、0.04、0.06、0.08、0.1 mg/mL。测定不同质量浓度的金盏菊提取物对DPPH·和ABTS+·的清除能力,试验中均以VC作为阳性对照。根据以下公式计算提取物和VC对自由基的清除率。平行3次实验,取平均值。
清除率 (%)=Ac−(Ai−Aj)Ac×100 (1) 式中,Ai:样品溶液+ABTS+·(或DPPH·)溶液的吸光度;Aj:样品溶液+样品溶剂的吸光度;Ac:样品溶剂+ABTS+·(或DPPH·)溶液的吸光度。
1.2.5 抑菌活性研究
使用DMSO溶解金盏菊醇提物和各萃取相的浸膏,并定容至所需浓度。采用滤纸片法测定金盏菊提取物对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌活性[24]。滤纸片直径为6 mm。以DMSO(样品溶剂)作为空白对照,硫酸链霉素作为阳性对照,用游标卡尺测量抑菌圈直径(Φ)。平行3次实验,取平均值。抑菌圈试验结果的判定标准:Φ>15 mm为高度敏感,10<Φ≤15 mm为中度敏感,6<Φ≤10 mm为低度敏感,Φ≤6 mm为不敏感。质量浓度均为15 mg/mL。
1.2.6 抑制酪氨酸酶活性研究
先使用DMSO溶解金盏菊醇提物和各萃取相的浸膏,再用蒸馏水定容至所需浓度。参照文献[25],测定不同质量浓度(EE质量浓度为0.5、1、1.5、2、2.5 mg/mL,EA相质量浓度为0.25、0.5、1、1.5、2 mg/mL)的金盏菊提取物对酪氨酸酶活性抑制实验。准确吸取50 µL不同质量浓度的提取物,50 µL酪氨酸酶溶液(50 U/mL),50 µL pH为6.8的磷酸缓冲溶液,室温静置10 min;加入100 µL 0.015 mol/L的L-多巴溶液,混合均匀室温反应10 min后,用酶标仪在475 nm处测量吸光度,以熊果苷为阳性对照。平行3次实验,取平均值。酪氨酸酶抑制率计算公式(2)如下:
抑制率 (%)=(ODA−ODB)−(ODC−ODD)(ODA−ODB)×100 (2) 式中,ODA:含有酪氨酸酶但不含样品组吸光度;ODB:不含酪氨酸酶和样品组吸光度;ODC:含有酪氨酸酶和样品组吸光度;ODD:含有样品但不含酪氨酸酶组吸光度。
1.2.7 酪氨酸酶抑制机理及动力学研究
1.2.7.1 酪氨酸酶活性抑制的可逆性判断
参照文献[25]方法,固定一定浓度的底物L-多巴的添加量不变,改变酪氨酸酶的添加量,测定不同质量浓度的EA相溶液对酪氨酸酶催化速率的影响。以酶活力对酪氨酸酶的添加量作图,判断EA相对酪氨酸酶活性的抑制是否可逆。
1.2.7.2 金盏菊乙酸乙酯相对酪氨酸酶的抑制类型分析
固定酪氨酸酶溶液的添加量不变,改变底物L-多巴的浓度,测定不同质量浓度EA相对酪氨酸酶活力的影响。以Lineweaver-Burk双倒数曲线作图,判断EA相对酪氨酸酶的抑制作用类型[26],双倒数方程如公式4所示;根据直线方程的斜率(Km/Vm)和截距(1/Vm),可以计算得出米氏常数Km和最大反应速度Vm。通过双倒数直线的斜率和纵轴截距对不同质量浓度的抑制剂二次作图,求出抑制剂对游离酶(E)的抑制常数(KI)和对酶-底物络合物(ES)的抑制常数(KIS)。双倒数方程如下:
1 V0=KmVm1[C]+1 Vm (3) 式中,V0:酶促反应的初速度,ΔOD/min;C:L-多巴浓度,mol/L;Vm:最大反应速率,ΔOD/min;Km:米氏常数,mol/L。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验重复3次,结果均为平均值±标准偏差。采用Microsoft Excel 2010和Origin 8.6进行数据分析和作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 总酚和总黄酮含量
本文按照1.2.2中的方法测定金盏菊乙醇提取物及其各萃取相的总酚和总黄酮含量,结果如表1所示。
表 1 金盏菊不同萃取相总酚和总黄酮含量Table 1. Total phenolic and flavonoid contents in the different extraction from C. officinalis样品名称 总酚(mg/g) 总黄酮(mg/g) 总和(mg/g) EE 15.930±1.700 67.850±0.900 83.780±2.600 PEE相 2.500±0.040 15.700±0.190 18.200±0.230 EA相 66.860±1.340 263.900±3.300 330.760±4.640 N-BE相 74.610±0.560 171.570±0.560 246.180±1.120 研究表明,酚酮类物质具有较好的抗氧化、抑菌、抑制酪氨酸酶等活性。金盏菊提取物中的主要化学成分包含黄酮类、多酚类和类胡萝卜素等[9,21]。由表1可知,EE的总酚和总黄酮含量分别为15.930±1.700和67.850±0.9000 mg/g,与文献[2,13,27]报道的金盏菊提取物中总酚和总黄酮含量约为10~35和20~115 mg/g相吻合,而明显富集酚酮物质的EA相中的酚酮含量分别为66.860±1.340和263.900±3.300 mg/g。在金盏菊不同萃取相中,总酚含量顺序为N-BE相>EA相>EE>PEE相,总黄酮含量顺序为EA相>N-BE相>EE>PEE相,酚酮含量的总和顺序为EA相>N-BE相>EE>PEE相,且各萃取相的总黄酮含量均高于总酚含量。表明金盏菊中黄酮、多酚类物质的溶出与萃取溶剂类型有关,在EA相和N-BE相中酚酮含量最高,约为25%~33%。Imane等[28]等同时分别以甲醇、乙醇、乙酸乙酯为溶剂提取金盏菊花中酚酮类物质,发现3种溶剂的提取物中多酚类物质含量基本相同,约为58 mg/g,但黄酮含量以甲醇提取物中最高,约为22 mg/g;采用乙酸乙酯溶剂一步提取金盏菊中的总酚酮含量约为80 mg/g,明显低于本文采用乙酸乙酯多步萃取所得总酚酮含量。研究还表明,酚酮类物质的提取除受溶剂影响外还与提取方法有关,在多步的萃取条件下,金盏菊提取物中具有功效性的酚酮类物质更容易被极性中等和极性偏大的溶剂萃取[7]。
2.2 HPLC分析
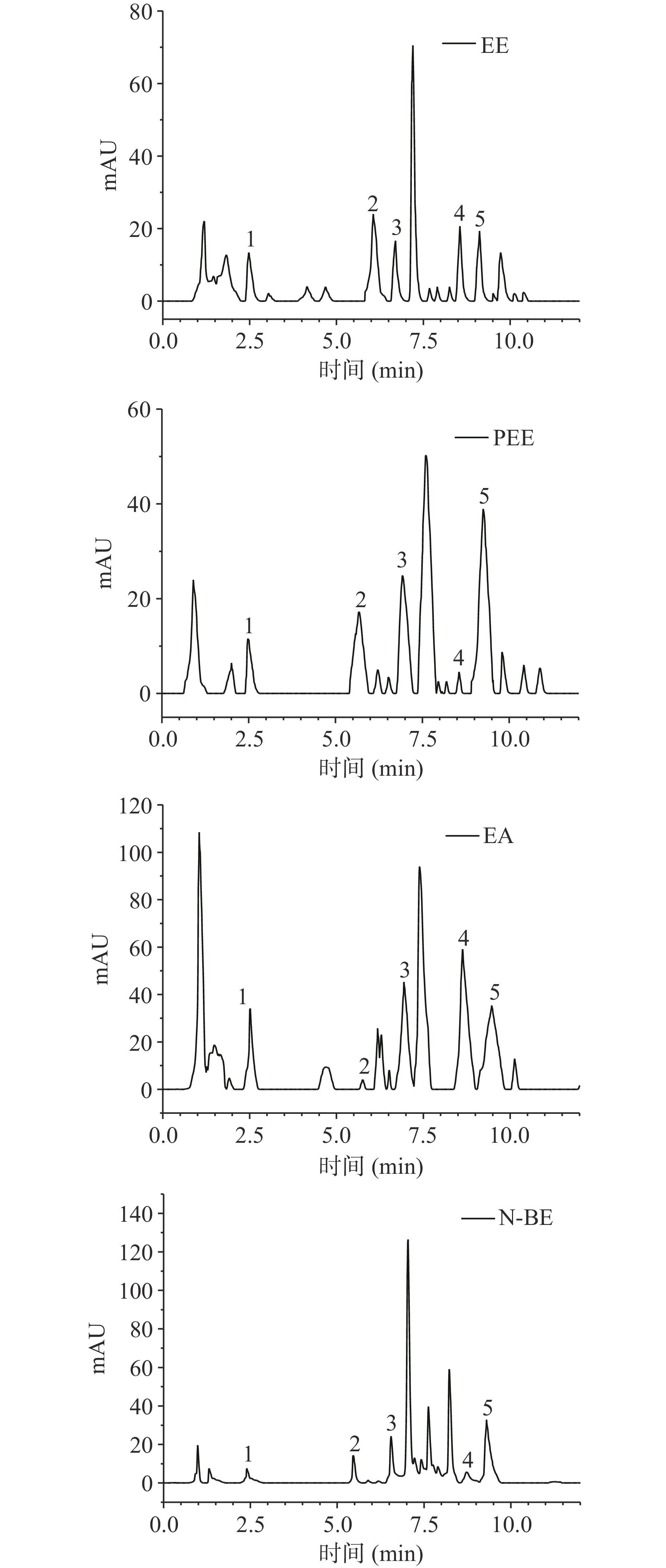
由文献知,金盏菊酚酮类物质主要包括咖啡酸、3-咖啡酰奎宁酸、绿原酸、阿魏酸、没食子酸、芦丁和1,5-二异咖啡酰奎宁酸等[9,17,29],其中没食子酸、咖啡酸、芦丁、绿原酸和阿魏酸这5种成分具有较好的抗氧化、抑菌活性,对酪氨酸酶也有一定的抑制作用,故本文以这5种成分为代表进行HPLC分析。本文按照1.2.3中的方法分析金盏菊乙醇提取物及其各萃取相中这5种成分,结果如图1~图2和表2所示。
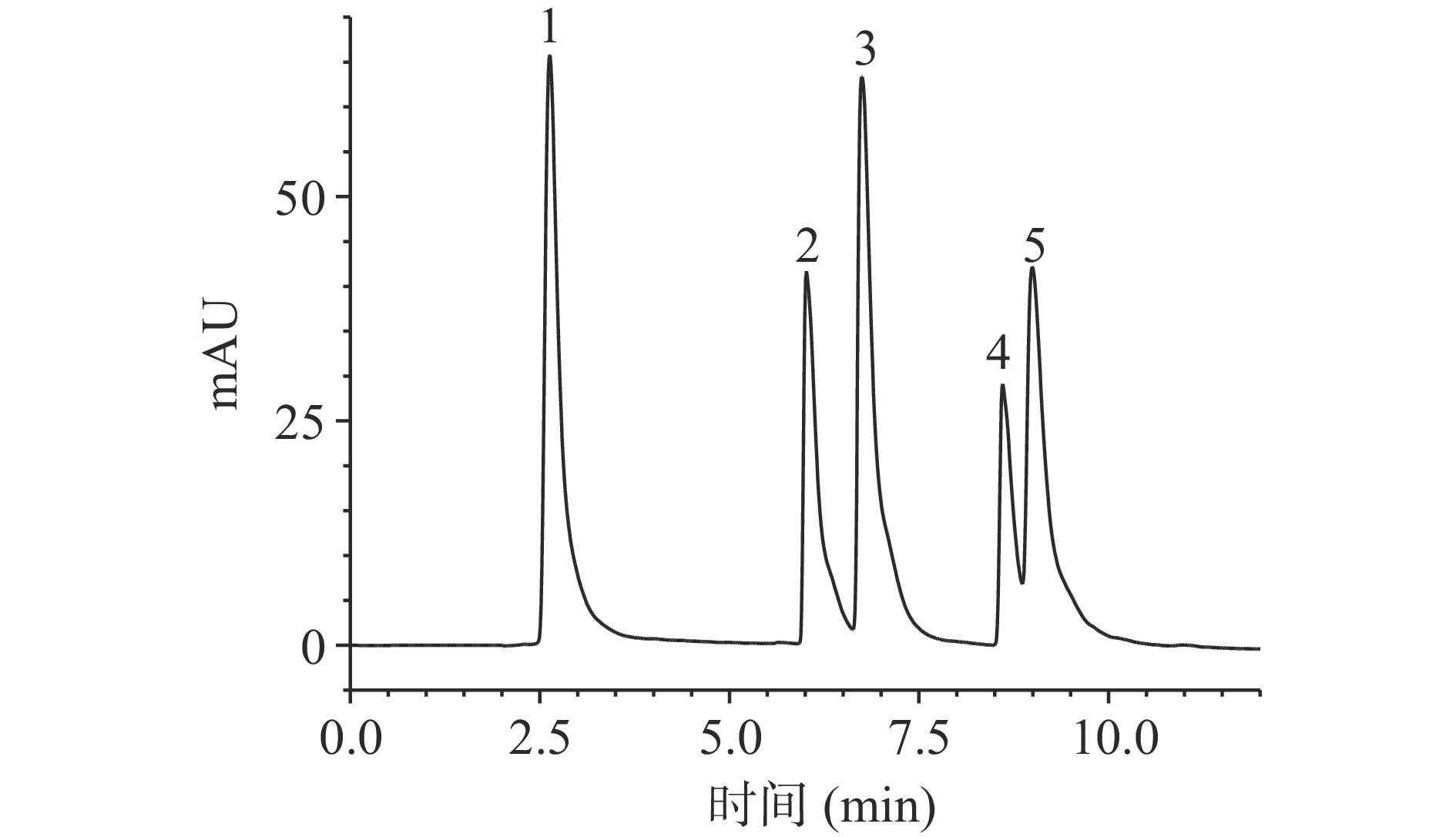
![]() 图 1 5种混合标准品(280 nm)的HPLC图谱注:1:没食子酸;2:绿原酸;3:咖啡酸;4:芦丁;5:阿魏酸;图2同。Figure 1. HPLC chromatogram of five mixed standards (280 nm)表 2 金盏菊不同萃取相酚酮类物质含量的测定结果Table 2. Content of phenolic and flavonoid compounds of different extraction from C. officinalis
图 1 5种混合标准品(280 nm)的HPLC图谱注:1:没食子酸;2:绿原酸;3:咖啡酸;4:芦丁;5:阿魏酸;图2同。Figure 1. HPLC chromatogram of five mixed standards (280 nm)表 2 金盏菊不同萃取相酚酮类物质含量的测定结果Table 2. Content of phenolic and flavonoid compounds of different extraction from C. officinalis化学成分 含量(mg/g) EE PEE相 EA相 N-BE相 没食子酸 0.198±0.001 0.128±0.016 0.230±0.031 0.135±0.017 绿原酸 0.417±0.006 0.141±0.013 0.021±0.006 0.279±0.032 咖啡酸 0.203±0.009 0.237±0.023 0.344±0.138 0.644±0.016 芦丁 0.232±0.008 0.037±0.007 0.978±0.203 0.039±0.017 阿魏酸 0.204±0.102 0.690±0.026 0.502±0.104 0.814±0.029 从表2中可以得出,5种成分在金盏菊乙醇提取物和不同萃取相中的含量不同。其中,芦丁和没食子酸在EA相中含量最高,分别为0.978±0.203和0.230±0.031 mg/g,在PEE相中含量最低;阿魏酸和咖啡酸在N-BE相中含量最高,分别为0.814±0.029和0.644±0.016 mg/g;绿原酸在EE中含量最高为0.417±0.006 mg/g,在EA相中含量最低为0.021±0.006 mg/g。
天然多酚类化合物具有抗氧化、抗炎、抑菌、抗衰老等多种功效[30],如范金波等[31]研究发现芦丁清除DPPH·和ABTS+·的IC50值为0.057和0.13 mg/mL,与阳性对照VC相当。研究表明在极性溶剂中不同酚酸的抗氧化活性强弱顺序为:没食子酸>咖啡酸>绿原酸>阿魏酸[32]。此外,霍锦双等[6]研究发现,咖啡酸对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制作用较强,MIC值均为47 μg/mL,芦丁对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制作用略低于咖啡酸,MIC值均为188 μg/mL。
结合文献[31-32]可知,咖啡酸、没食子酸、芦丁的抗氧化、抑菌等生物活性较好。由表2知,5种成分在各萃取相中的含量差异较大。EA相中没食子酸和芦丁含量最高,咖啡酸含量仅次于N-BE相;N-BE相咖啡酸含量最高,但没食子酸和芦丁含量都较低;故各萃取相之间的生物活性差异可能受这些物质含量影响。由表2中5种成分萃取前后含量差异可知,EA相是乙醇提取物(EE)萃取后功效物富集最多的萃取相,除绿原酸外,EA相中其他4种成分的含量均高于EE。故本文也重点研究EA相酚酮类物质的功效,及EE与EA相对抗氧化、抑菌、抑制酪氨酸酶活性的功效差异,进而考察酚酮类物质与功效之间的关系。
2.3 体外抗氧化活性
本文按照1.2.4中的方法检测金盏菊乙醇提取物及其各萃取相清除DPPH·和ABTS+·的能力。结果表明,所有物质均具有清除DPPH·和ABTS+·的能力,如表3所示,IC50为各物质对自由基清除率为50%时所需浓度。
表 3 金盏菊不同萃取相抗氧化能力比较Table 3. Antioxidant capacities of the different extraction from C. officinalis萃取相 IC50(mg/mL) DPPH· ABTS+· EE 0.470±0.001 0.430±0.001 PEE相 0.710±0.003 0.770±0.002 EA相 0.080±0.001 0.062±0.001 N-BE相 0.094±0.001 0.084±0.004 VC 0.030±0.001 0.051±0.005 从表3中得出,EA相对DPPH·的清除效果最好,IC50为0.080±0.001mg/mL,PEE相对DPPH·清除效果最差,IC50为0.710±0.003 mg/mL;对ABTS+·清除能力也是EA相最高,IC50为0.062±0.001 mg/mL,与阳性对照VC接近。Imane等[28]研究发现金盏菊的甲醇提取物对ABTS+·和DPPH·的清除率IC50值分别为168.44和172.51 μg/mL;只德贤等[33]研究发现,金盏菊皂苷对ABTS+·和DPPH·的清除率IC50值分别为0.337和0.282 mg/mL。本文中EA相的抗氧化能力优于文献值。由表3知,各萃取相的抗氧化能力依次为:EA相>N-BE相>EE>PEE相,结合表1中总酚酮含量顺序为:EA相>N-BE相>EE>PEE相,金盏菊不同萃取相的抗氧化活性与其总酚酮含量之间为正相关性,EA相总酚酮含量最高,抗氧化活性最好。
由文献[31-32]可知,咖啡酸和芦丁对DPPH·和ABTS+·的清除率均不低于阳性对照VC,且没食子酸、咖啡酸的抗氧化能力均高于绿原酸、阿魏酸,故咖啡酸、芦丁和没食子酸具有较强的抗氧化活性。由表2知,咖啡酸、没食子酸、芦丁在不同萃取相中的总含量顺序为EA相>N-BE相>EE>PEE相,与其抗氧化能力呈正相关性。大量研究表明,抗氧化活性与酚酮类物质的含量之间存在正相关性,金盏菊乙醇提取物及其各萃取相抗氧化能力存在差异可能是因为总酚、总黄酮及其单一活性成分在各萃取相中的含量不同所造成。以上结果也说明金盏菊EA相可能富含多种具有抗氧化活性的酚酮类成分,其抗氧化能力也最强。
2.4 抑菌活性
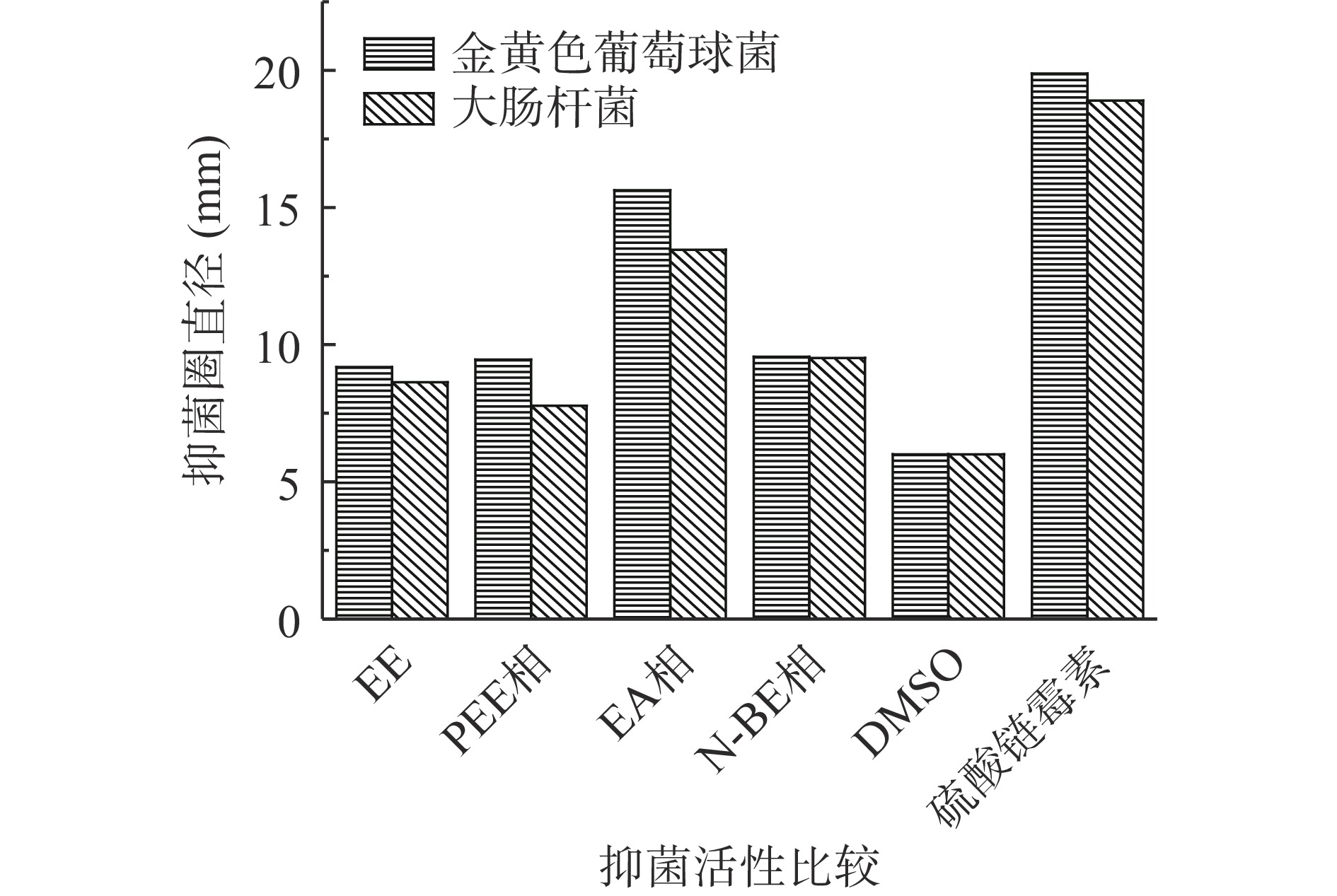
研究发现,多酚类物质因具有较好的抑菌等活性,在食品运输、储藏中可被用作天然食品防腐剂[34]。本文按照1.2.5中的方法检测金盏菊乙醇提取物及其各萃取相在质量浓度为15 mg/mL时,对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌效果,结果如图3所示。
从图3可看出,金盏菊乙醇提取物和各萃取相对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌均有一定的抑制能力。此外,EA相抑菌效果均强于其他萃取相,对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的Φ分别为14.60和12.56 mm,达到了中敏的效果。在表2的5种分析成分中,EA相中芦丁含量最多,咖啡酸的含量仅次于N-BE相,但咖啡酸和芦丁含量总和明显高于其它萃取相,且芦丁和咖啡酸具有较强的抑菌作用[6,35-38],这可能是EA相抑菌效果强于其他萃取相的主要原因。在EE、PEE相、N-BE相中咖啡酸和芦丁含量差异不显著,且多酚类物质抑菌作用较为复杂,抑菌机理也不完全明确,可能是导致EE、PEE相、N-BE相之间抑菌效果差异不大的原因。以上结果表明,使用不同有机溶剂萃取金盏菊乙醇提取物,乙酸乙酯溶剂可进一步富集其酚酮类抑菌功效成分,使EA相总酚酮含量增加,进而提高其抑菌活性,但对其抑菌机理还需进一步的研究。
2.5 对酪氨酸酶抑制作用
金盏菊乙醇提取物(EE)经乙酸乙酯萃取后,可得到抗氧化、抑菌效果均优于其它萃取相的乙酸乙酯萃取相(EA相),按照1.2.6中的方法进一步比较EE和EA相对酪氨酸酶活性抑制作用,结果如表4所示。
表 4 金盏菊EE和EA相对酪氨酸酶的抑制效果Table 4. Effect of EE and EA on tyrosinase activity抑制酪氨酸酶活性 EE相 EA相 熊果苷 IC50(mg/mL) 1.905±0.001 0.965±0.001 2.049±0.001 由表4知,EA相IC50值为0.965±0.001 mg/mL,明显低于阳性对照熊果苷IC50值2.049±0.001 mg/mL和EE的IC50值1.905±0.001 mg/mL。EA相对酪氨酸酶抑制作用高于EE和阳性对照熊果苷的原因可能与其富含酚酮类物质及表2中5种化合物的含量和活性有关。从HPLC分析结果可以发现,除绿原酸外,EA相中其他4种化合物的含量明显高于EE,EA相中芦丁含量最高,达到0.978±0.203 mg/g。结合文献[39-43]可知,没食子酸、芦丁和咖啡酸对酪氨酸酶的活性抑制较强,且三者在EA相中含量均高于EE。推测金盏菊中对酪氨酸酶活性抑制发挥主要作用的物质可能与没食子酸、芦丁、咖啡酸等酚酮活性物有关。
2.6 金盏菊乙酸乙酯萃取相对酪氨酸酶抑制机理
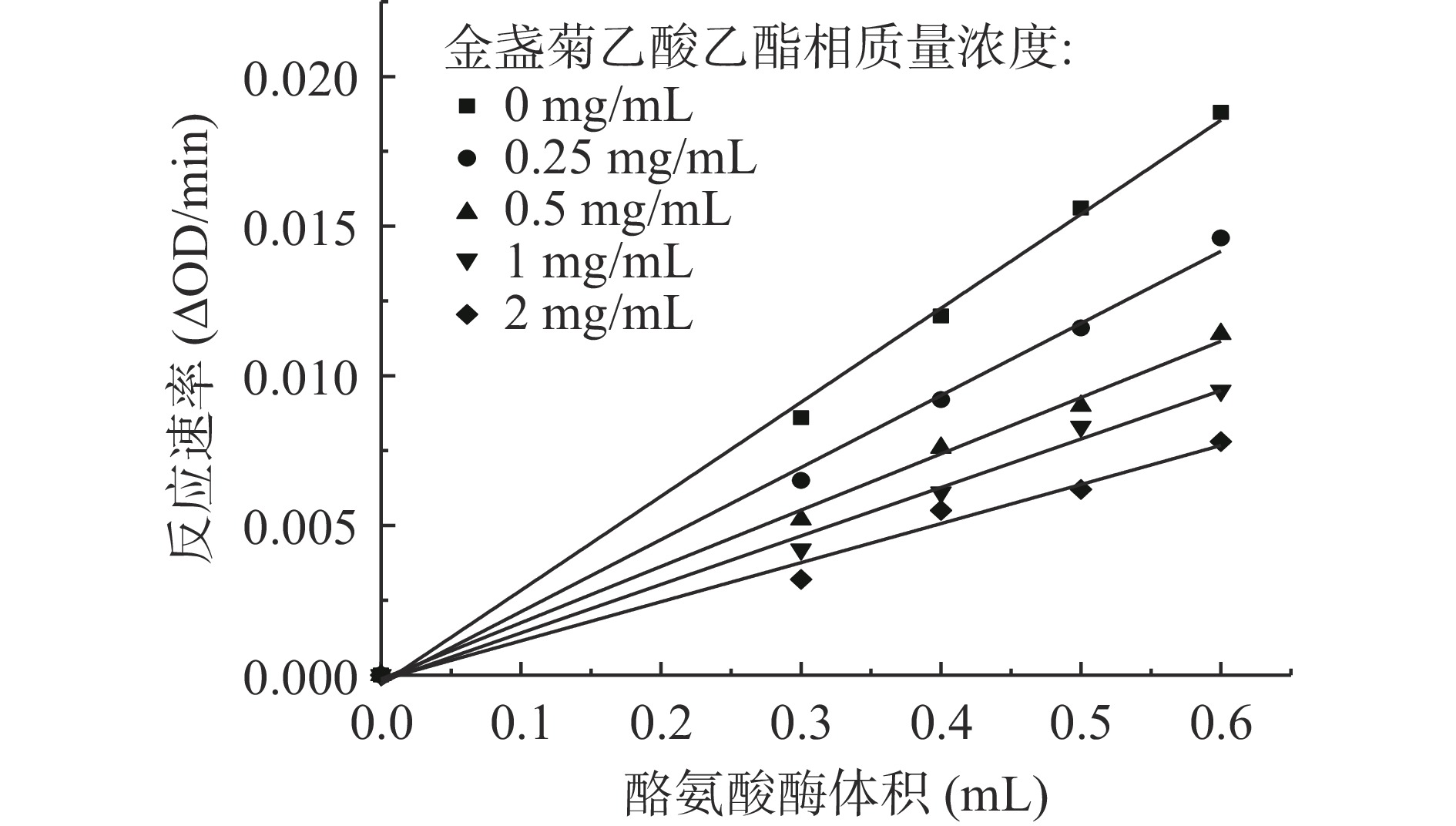
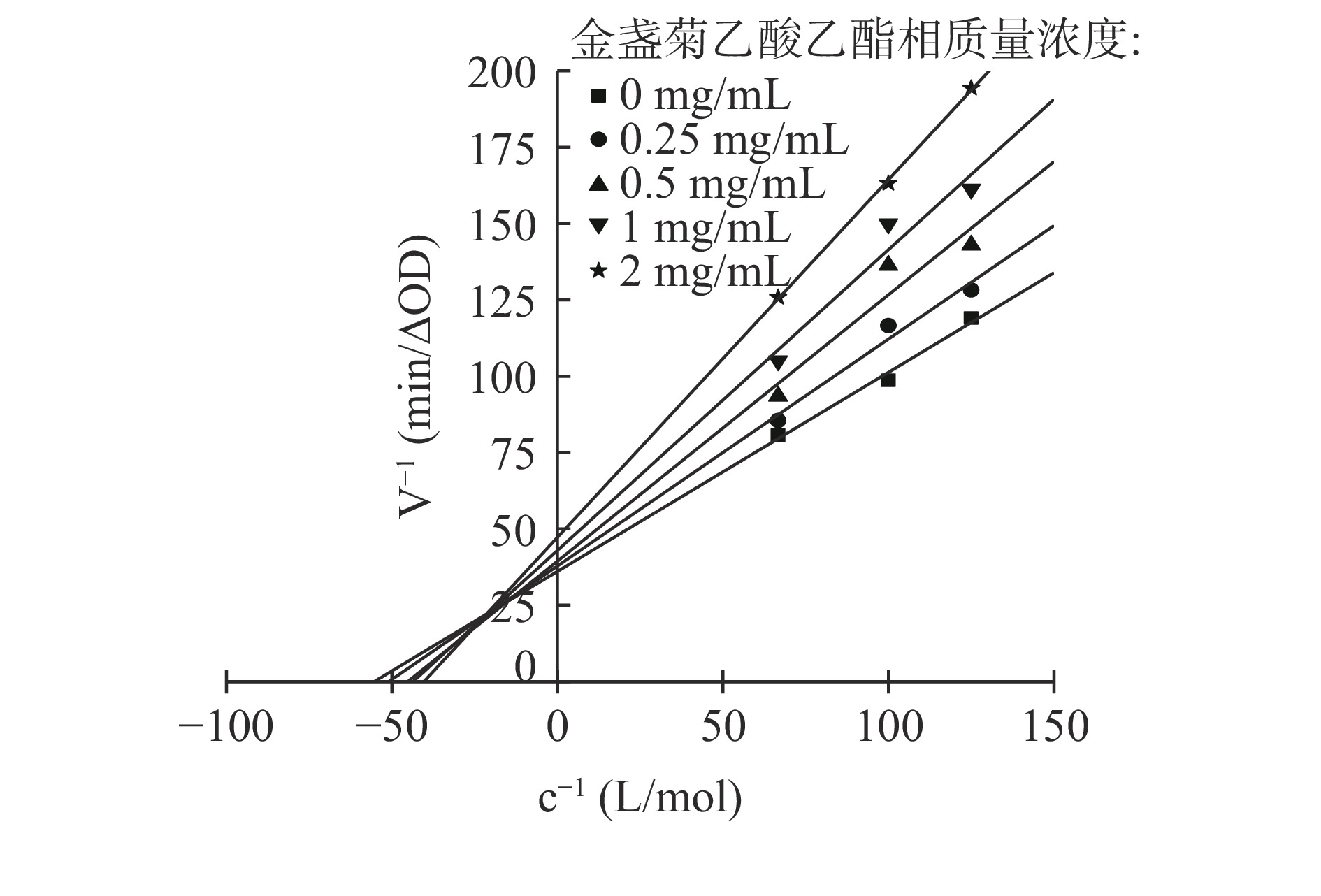
按照1.2.7中的测试方法进一步研究EA相对酪氨酸酶的抑制机理,如图4所示。由图4知,以酶活反应速率为Y轴,酪氨酸酶溶液的体积为X轴作图,得到5条相交于原点的直线,且直线的斜率与EA相质量浓度呈反比,说明EA相对酪氨酸酶活性的抑制作用是可逆的,只是抑制酶活力降低酪氨酸酶生成多巴醌的速率,而并未对有效酶量产生影响。
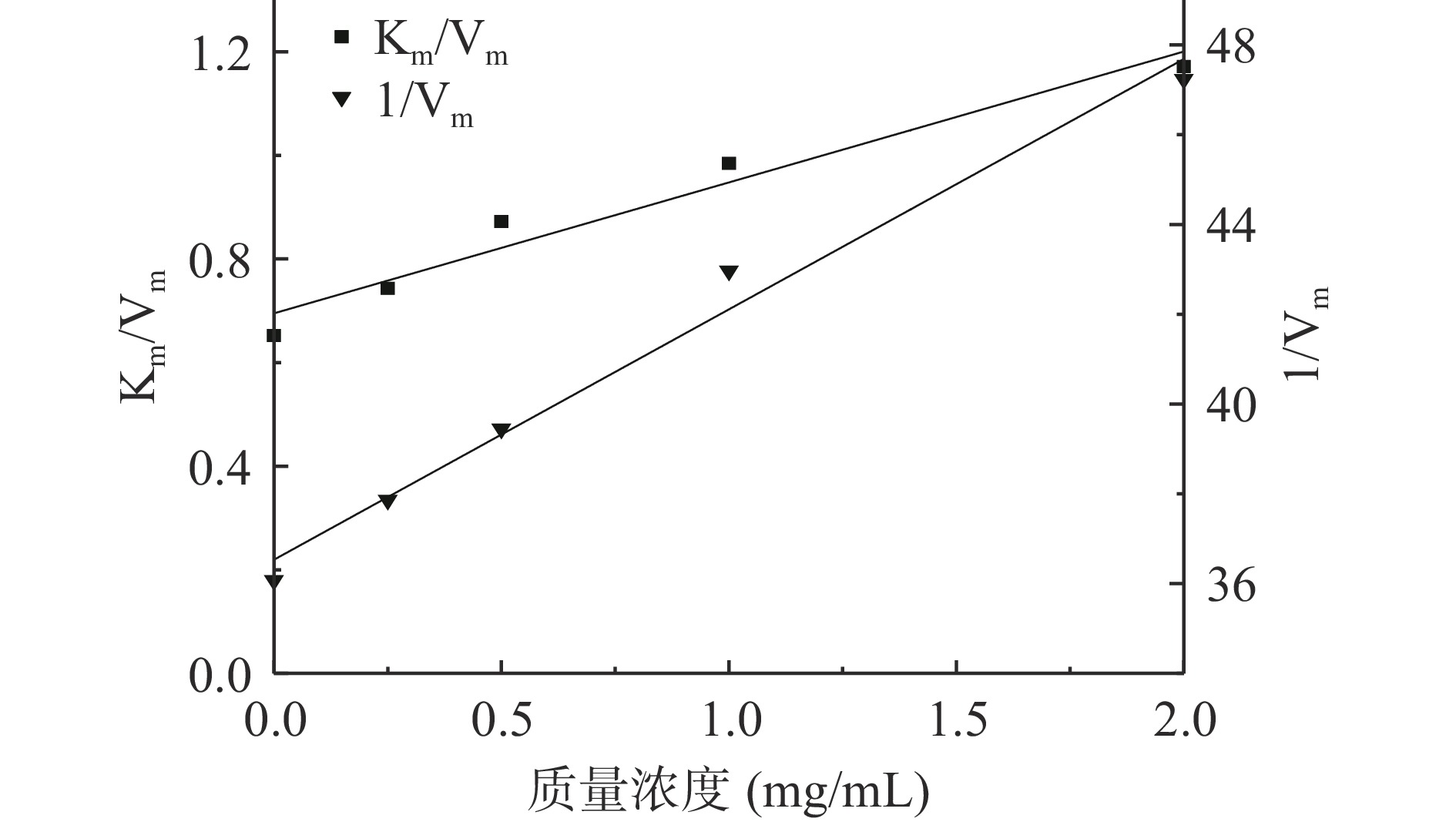
通过酶动力学实验进一步研究EA相对酪氨酸酶的抑制机理。图5为酪氨酸酶与不同质量浓度EA相的Lineweaver-Burk双倒数直线图。从图5可以看出,EA相的Line weaver-Burk双倒数直线图相交于第二象限,且直线截距(1/Vm)和斜率(Km/Vm)随着EA相质量浓度增加而逐渐增大;通过对动力学参数计算,结果如表5所示,当EA相质量浓度增大时,Vm值减小,米氏常数Km值逐渐增大。结合文献[26,44],并根据图4、图5及表5的结果可得,EA相对酪氨酸酶的抑制类型为混合I型,即竞争与非竞争混合型抑制,表明EA相能同时与游离酶(E)和酶-底物的络合物(ES)结合。以米氏方程的斜率和截距对不同质量浓度的EA相进行二次作图(如图6所示),得到EA相对游离酶的抑制常数KI为0.254 mg/mL,对酶与底物络合物的抑制常数KIS为5.577 mg/mL,KI<KIS说明EA相对酪氨酸酶的抑制作用强于对酶和底物复合物的抑制作用。研究发现酚酮类物质能抑制酪氨酸酶活性,也能与酶-底物络合物相结合,从而阻止结合物分解成产物并抑制黑色素的形成[43]。推测EA相对酪氨酸酶二酚酶表现为可逆的混合型抑制,可能与其含有较多酚酮类活性物有关。
表 5 酪氨酸酶抑制动力学参数Table 5. Inhibitory kinetic parameters of tyrosine diphenolaseρ(mg/mL) 回归方程 Vmax
(ΔOD/min)Km
(mol/L)KI
(mg/mL)KIS
(mg/mL)0 y=0.652x+36.07 0.028 0.018 0.254 5.577 0.25 y=0.743x+37.858 0.026 0.020 0.5 y=0.8721x+39.444 0.025 0.022 1 y=0.9848x+42.964 0.023 0.023 2 y=1.1713x+47.235 0.021 0.025 芦丁和阿魏酸对酪氨酸酶的抑制类型为竞争型[40,42];绿原酸、咖啡酸、没食子酸对酪氨酸酶的抑制类型为非竞争型[39,41,43],含有这些酚酮类物质的EA相对酪氨酸酶的抑制作用也表现为包含竞争型和非竞争型的混合型抑制;EA相抑制酪氨酸酶活性较强可能与这些活性组分间发挥协同作用有关,如咖啡酸和阿魏酸分别为非竞争型和竞争型抑制,两种物质对酪氨酸酶的作用位点不同,有可能产生协同作用,增强对酪氨酸酶的抑制作用[45]。
由于酪氨酸酶催化氧化L-多巴的过程需要氧的参与[46],EA相具有较好的抗氧化能力、以可逆的混合型方式抑制酪氨酸酶活性。推测EA相对酪氨酸酶的抑制机理可能是[39,46-47]:a. 活性氧作为引发剂及反应物,具有促进酪氨酸酶催化氧化的作用;而酚酮类物质具有较好清除活性氧的作用,EA相中酚酮含量较高,抗氧化活性较强,很大程度上清除了活性氧,可阻断反应的引发,也削弱了对酪氨酸酶的供氧作用;此外,酚酮类物质具有很强的还原能力,可使被酪氨酸酶催化氧化的产物还原,减缓了酪氨酸酶催化氧化速率。因而EA相中的酚酮类物质可以使其具有较好地降低酪氨酸酶催化氧化的能力;b. 酚酮类化合物具有较强的吸电子能力,如咖啡酸、绿原酸等,EA相中含有的这些酚酸类物质,可与酪氨酸酶发生键合反应,阻碍氧化态酪氨酸酶的氧原子发生取代反应,使氧化态的酶与这些酚酸类物质形成终端产物,从而减缓或抑制氧化反应;c. EA相中含有的多酚类物质具有与L-多巴相似的化学结构,其能够与底物多巴竞争性地与酪氨酸酶结合,从而削弱酪氨酸酶催化氧化作用。
EA相中酚酮等活性物质可能从抗氧化、竞争和非竞争等多途径地抑制酪氨酸酶催化氧化活性,这也与文献[46,48]报道的对酪氨酸酶活性有抑制作用的化合物一般都会具有较好的抗氧化活性的现象相吻合。
3. 结论
本文通过比较金盏菊乙酸乙酯萃取相(EA相)及其相关萃取相的抗氧化、抑菌及对酪氨酸酶抑制作用,发现其功效性能与各萃取相的酚酮含量呈正向相关性。其中,金盏菊乙酸乙酯萃取相(EA相)总酚酮含量最高,为330.760±4.640 mg/g;乙酸乙酯溶剂可富集更多的酚酮功效物质,如咖啡酸、芦丁、没食子酸等。因此,EA相具有很好的生物活性:对ABTS+·和DPPH·的IC50值分别为0.062±0.001、0.080±0.001 mg/mL,与阳性对照VC接近;对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制作用最好,达到了中敏的效果;能有效抑制酪氨酸酶活性,半数抑制浓度IC50为0.965±0.001 mg/mL,优于阳性对照熊果苷,对酪氨酸酶抑制作用表现为可逆的混合型抑制。本研究通过采用多步的乙酸乙酯溶剂萃取富集金盏菊中酚酮类活性物,获得了具有较好的抗氧化、抑菌、抑制酪氨酸酶活性的天然功效提取物,可为金盏菊在食品保鲜、防腐抑菌及日化产品等领域的应用提供一定理论依据。
-
图 1 5种混合标准品(280 nm)的HPLC图谱
注:1:没食子酸;2:绿原酸;3:咖啡酸;4:芦丁;5:阿魏酸;图2同。
Figure 1. HPLC chromatogram of five mixed standards (280 nm)
表 1 金盏菊不同萃取相总酚和总黄酮含量
Table 1 Total phenolic and flavonoid contents in the different extraction from C. officinalis
样品名称 总酚(mg/g) 总黄酮(mg/g) 总和(mg/g) EE 15.930±1.700 67.850±0.900 83.780±2.600 PEE相 2.500±0.040 15.700±0.190 18.200±0.230 EA相 66.860±1.340 263.900±3.300 330.760±4.640 N-BE相 74.610±0.560 171.570±0.560 246.180±1.120 表 2 金盏菊不同萃取相酚酮类物质含量的测定结果
Table 2 Content of phenolic and flavonoid compounds of different extraction from C. officinalis
化学成分 含量(mg/g) EE PEE相 EA相 N-BE相 没食子酸 0.198±0.001 0.128±0.016 0.230±0.031 0.135±0.017 绿原酸 0.417±0.006 0.141±0.013 0.021±0.006 0.279±0.032 咖啡酸 0.203±0.009 0.237±0.023 0.344±0.138 0.644±0.016 芦丁 0.232±0.008 0.037±0.007 0.978±0.203 0.039±0.017 阿魏酸 0.204±0.102 0.690±0.026 0.502±0.104 0.814±0.029 表 3 金盏菊不同萃取相抗氧化能力比较
Table 3 Antioxidant capacities of the different extraction from C. officinalis
萃取相 IC50(mg/mL) DPPH· ABTS+· EE 0.470±0.001 0.430±0.001 PEE相 0.710±0.003 0.770±0.002 EA相 0.080±0.001 0.062±0.001 N-BE相 0.094±0.001 0.084±0.004 VC 0.030±0.001 0.051±0.005 表 4 金盏菊EE和EA相对酪氨酸酶的抑制效果
Table 4 Effect of EE and EA on tyrosinase activity
抑制酪氨酸酶活性 EE相 EA相 熊果苷 IC50(mg/mL) 1.905±0.001 0.965±0.001 2.049±0.001 表 5 酪氨酸酶抑制动力学参数
Table 5 Inhibitory kinetic parameters of tyrosine diphenolase
ρ(mg/mL) 回归方程 Vmax
(ΔOD/min)Km
(mol/L)KI
(mg/mL)KIS
(mg/mL)0 y=0.652x+36.07 0.028 0.018 0.254 5.577 0.25 y=0.743x+37.858 0.026 0.020 0.5 y=0.8721x+39.444 0.025 0.022 1 y=0.9848x+42.964 0.023 0.023 2 y=1.1713x+47.235 0.021 0.025 -
[1] CHEN Y S, LEE S M, LIN Y J, et al. Effects of Danshensu and Salvianolic Acid B from Salvia miltiorrhiza Bunge (Lamiaceae) on cell proliferation and collagen and melanin production[J]. Molecules,2014,19(2):2029−2041. doi: 10.3390/molecules19022029
[2] PASCA C, MARGHITAS L A, BOBIS O, et al. Total content of polyphenols and antioxidant activity of different melliferous plants[J]. Animal Science and Biotechnologies,2016,73(1):2−9.
[3] ILKAY E O, SEZER S F, SINEM A E, et al. Tyrosinase and cholinesterase inhibitory potential and flavonoid characterization of Viola odorata L. (Sweet Violet)[J]. Phytotherapy Research,2015,29(9):1304−1310. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5378
[4] 傅佳愈, 杨远帆, 倪辉, 等. 茶花粉提取物对酪氨酸酶的抑制作用[J]. 中国食品学报,2015,15(7):66−72. [FU J Y, YANG Y F, NI H, et al. The anti-tyrosinase effect of extract from Camellia pollen[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2015,15(7):66−72. FU J Y, YANG Y F, NI H, et al. The anti-tyrosinase effect of extract from Camellia pollen[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2015, 15(7): 66-72.
[5] 潘振东, 李璐, 薛梦莹, 等. 太白韭对金黄色葡萄球菌的抑制作用[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(1):318−326. [PAN Z D, LI L, XUE M Y, et al. Antibacterial activity of allium prattii against Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2021,21(1):318−326. PAN Z D, LI L, XUE M Y, et al. Antibacterial activity of allium prattii against Staphylococcus aureus[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2021, 21(1): 318-326.
[6] 霍锦双, 隋伟策, 孙红男, 等. 甘薯茎叶多酚类物质的组分构成及抑菌活性[J]. 新疆农业科学,2021,58(3):556−564. [HUO J S, SUI W C, SUN H N, et al. Individual phenolic composition and antimicrobial activity of sweet potato leaf polyphenols[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences,2021,58(3):556−564. HUO J S, SUI W C, SUN H N, et al. Individual phenolic composition and antimicrobial activity of sweet potato leaf polyphenols[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2021, 58(3): 556-564.
[7] 许恩婷, 许梦洁, 邵清松, 等. 金线莲不同器官及萃取部位的抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2019,19(1):28−33. [XU E T, XU M J, SHAO Q S, et al. Studies on the active ingredients and antioxidant capacity from different organs and extraction parts of Anoectochilus roxburghii[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2019,19(1):28−33. XU E T, XU M J, SHAO Q S, et al. Studies on the active ingredients and antioxidant capacity from different organs and extraction parts of Anoectochilus roxburghii[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2019, 19(1): 28-33.
[8] 马嘉洁, 赵端端, 全世航, 等. 紫苏叶黄酮、多酚提取工艺优化及不同品种抗氧化活性比较[J/OL]. 食品工业科技: 344−352. [2022-11-23]. DOI: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2022080165. MA J J, ZHAO D D, QUAN S H, et al. Optimization of extraction process of flavonoids and polyphenols from Perilla frutescens (L.) Britt leaves and comparison of antioxidant activities of different varieties[J/OL]. Scienceand Technology of FoodIndustry: 344−352. [2022-11-23]. doi:10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2022080165.
[9] BUTNARIU M, CORADINI C Z. Evaluation of biologically active compounds from Calendula officinalis flowers using spectrophotometry[J]. Chemistry Central Journal,2012,6(1):1−7. doi: 10.1186/1752-153X-6-1
[10] SAHINGIL D. GC/MS-Olfactometric characterization of the volatile compounds, determination antimicrobial and antioxidant activity of essential oil from flowers of Calendula (Calendula officinalis L.)[J]. Journal of Essential Oil Bearing Plants,2019,22(6):1571−1580. doi: 10.1080/0972060X.2019.1703829
[11] ZAKI A, ASHOUR A, MIRA A, et al. Biological activities of oleanolic acid derivatives from Calendula officinalis seeds[J]. Phytotherapy Research: PTR,2016,30(5):835−841. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5589
[12] MULEY B P, KHADABADI S S, BANARASE N B. Phytochemical constituents and pharmacological activities of Calendula officinalis Linn (Asteraceae): A review[J]. Tropical Journal of Pharmaceutical Research,2009,8(5):455−465.
[13] 崔彬淯. 天然美白原料的筛选及金盏菊美白作用研究[D]. 上海: 上海应用技术大学, 2019 CUI B Y. Screening of natural whitening raw materials and study on the whitening effect of Calendula[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Institute of Technology, 2019.
[14] FATIMA S S, GOVEKAR S U, SATARDEKAR K V, et al. In vitro analysis of ethanolic extract of flowers of Calendula officinalis for antioxidant, antimicrobial and UV-H2O2 induced DNA damage protection activity[J]. Journal of Pharmacognosy and Phytochemistry,2018,7(5):2378−2383.
[15] OLENNIKOV D N, KASHCHENKO N I. 1, 5-Di-O-isoferuloylquinic acid and other phenolic compounds from pollen of Calendula officinalis[J]. Chemistry of Natural Compounds,2014,50(4):589−593. doi: 10.1007/s10600-014-1030-9
[16] 郑佳, 卢先明, 邓晶晶. 金盏菊不同提取液体外抑菌作用初步研究[J]. 中药与临床,2016,7(3):45−46. [ZHENG J, LU X M, DENG J J. Study on the bacteriostatic effects of Jinzhanju extract in vitro[J]. Pharmacy and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica,2016,7(3):45−46. ZHENG J, LU X M, DENG J J. Study on the bacteriostatic effects of Jinzhanju extract in vitro[J]. Pharmacy and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica, 2016, 7(3): 45-46.
[17] RIGANE G, YOUNES S B, GHAZGHAZI H, et al. Investigation into the biological activities and chemical composition of Calendula officinalis L. growing in Tunisia[J]. International Food Research Journal,2013,20(6):3001−3007.
[18] ADINA F. HPLC determination of polyphenols from Calendula officinalis L. flowers[J]. Acta Universitatis Cinbinesis, Series E: Food Technology,2017,21(2):97−101.
[19] SINGLETON V L, ROSSI J A. Colorimetry of total phenolics with phosphomolybdic-phosphotungstic acid reagents[J]. American Journal of Enology and Viticulture,1965,16(3):144−158. doi: 10.5344/ajev.1965.16.3.144
[20] HAMEED A, AKHTAR N. Comparative chemical investigation and evaluation of antioxidant and tyrosinase inhibitory effects of Withania somnifera (L. ) dunal and Solanum nigrum (L.) berries[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica,2018,68(1):47−60. doi: 10.2478/acph-2018-0007
[21] LOESCHER C M, MORTON D W, RAZIC S, et al. High performance thin layer chromatography (HPTLC) and high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) for the qualitative and quantitative analysis of Calendula officinalis-Advantages and limitations[J]. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis,2014,98:52−59. doi: 10.1016/j.jpba.2014.04.023
[22] ABDULLAH F O, HAMAHAMEEN B, DASTAN D. Chemical constituents of the volatile and nonvolatile, cytotoxic and free radical scavenging activities of medicinal plant: Ranunculus millefoliatus and Acanthus dioscoridis[J]. Polish Journal of Environmental Studies,2021,30(3):1981−1989. doi: 10.15244/pjoes/128265
[23] CHATATIKUN M, CHIABCHALARD A. Thai plants with high antioxidant levels, free radical scavenging activity, anti-tyrosinase and anti-collagenase activity[J]. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine,2017,17(1):487. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1505-2
[24] SU X D, Gao Y, XIANG Y X, et al. Chemical composition and biological activities of the essential oil from Aristolochia fordiana hemsl[J]. Records of Natural Products,2019,13(4):346−354. doi: 10.25135/rnp.111.18.09.897
[25] 吴颖, 刘晴, 唐文, 等. 丹参挥发油与蒲公英提取物复配物在化妆品中的应用[J]. 精细化工,2022,39(3):562−568. [WU Y, LIU Q, TANG W, et al. Application of complexes of Salvia miltiorrhiza volatile oil and dandelion extract in cosmetics[J]. Fine Chemicals,2022,39(3):562−568. WU Y, LIU Q, TANG W, et al. Application of complexes of Salvia miltiorrhiza volatile oil and dandelion extract in cosmetics[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2022, 39(3): 562-568.
[26] LEE G Y, CHO B O, SHIN J Y, et al. Tyrosinase inhibitory components from the seeds of Cassia tora[J]. Archives of Pharmacal Research,2018,41(5):490−496. doi: 10.1007/s12272-018-1032-4
[27] XUAN S H, KIM G Y, YU J Y, et al. Antioxidant and cellular protective effects against oxidative stress of Calendula officinalis flowers extracts in human skin cells[J]. Applied Chemistry for Engineering,2016,27(6):620−626. doi: 10.14478/ace.2016.1093
[28] OURABIA I, DJEBBAR R, SAMIRA T, et al. Determination of essential oil composition, phenolic content, and antioxidant, antibacterial and antifungal activities of Marigold (Calendula officinalis L.) cultivated in Algeria[J]. Carpathian Journal of Food Science & Technology,2019,11(2):93−110.
[29] LI H R, HABASI M, XIE L Z, et al. Effect of chlorogenic acid on melanogenesis of B16 melanoma cells[J]. Molecules,2014,19(9):12940−12948. doi: 10.3390/molecules190912940
[30] 何雅静, 张群琳, 谷利伟, 等. 柑橘中酚酸类化合物及其生物活性与机理的研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(15):301−306. [HE Y J, ZHANG Q L, GU L W, et al. Research progress on phenolic acids in citrus and their biological activities and mechanisms[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(15):301−306. HE Y J, ZHANG Q L, GU L W, et al. Research progress on phenolic acids in citrus and their biological activities and mechanisms[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(15): 301-306.
[31] 范金波, 蔡茜彤, 冯叙桥, 等. 5种天然多酚类化合物抗氧化活性的比较[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2014,40(7):77−83. [FAN J B, CAI Q T, FENG X Q, et al. The comparison of five natural phenolic compounds on antioxidant activity in vitro[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2014,40(7):77−83. FAN J B, CAI Q T, FENG X Q, et al. The comparison of five natural phenolic compounds on antioxidant activity in vitro[J]. Food and fermentation industries, 2014, 40(7): 77-83.
[32] 陈莹. 桑葚酒的发酵工艺及酚酸抗氧化研究[D]. 西安: 西北大学, 2011 CHEN Y. Studies on the fermentation process of mulberry wine and the antioxidant activity of phenolics[D]. Xi’an: Northwest University, 2011.
[33] 只德贤, 覃海波, 李建颖. 微波超声协同提取金盏菊皂苷工艺及其抗氧化性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(19):118−125. [ZHI D X, QIN H B, LI J Y, et al. Microwave-ultrasonic extraction of Calendula officinalis saponins and their antioxidant analysis[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(19):118−125. ZHI D X, QIN H B, LI J Y, et al. Microwave-Ultrasonic extraction of Calendula officinalis saponins and their antioxidant analysis[J]. Food Research and Development, 2021, 42(19): 118-125.
[34] 王婧, 宋莲军, 马燕, 等. 豌豆多酚的组成、提取和生理活性的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(23):418−428. [WANG J, SONG L J, MA Y, et al. Research progress on composition, extraction and physiological activity of Pea Polyphenols[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(23):418−428. WANG J, SONG L J, MA Y, et al. Research progress on composition, extraction and physiological activity of Pea Polyphenols[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(23): 418-428.
[35] 杨阳, 李祥松, 郭倩. 刺梨中芦丁的提取及其抑菌效果的研究[J]. 生物化工,2019,5(6):28−30. [YANG Y, LI X S, GUO Q. Study on extraction and antibactereial effect of rutin form Rosa roxburghii[J]. Biological Chemical Engineering,2019,5(6):28−30. LI Y, LI X S, GUO Q. Study on extraction and antibactereial effect of rutin form Rosa roxburghii[J]. Biological Chemical Engineering, 2019, 5(6): 28-30.
[36] 张康逸, 杨徐宁, 许国震, 等. 青麦仁麸皮中阿魏酸的抗氧化性和抑菌活性研究[J]. 包装与食品机械,2021,39(5):27−34. [ZHANG K Y, YANG X N, XU G Z, et al. Study on antioxidant and antibacterial activity of ferulic acid in green wheat bran[J]. Packaging and Food Machinery,2021,39(5):27−34. ZHANG K Y, YANG X N, XU G Z, et al. Study on antioxidant and antibacterial activity of ferulic acid in green wheat bran[J]. Packaging and Food Machinery, 2021, 39(5): 27-34.
[37] 张易, 顾瑜. 绿原酸的抑菌作用及其在口腔中的应用进展[J]. 医药论坛杂志,2022,43(7):104−107. [ZHANG Y, GU Y. Bacteriostasis of chlorogenic acid and its application in oral cavity[J]. Journal of Medical Forum,2022,43(7):104−107. ZHANG Y, GU Y. Bacteriostasis of chlorogenic acid and its application in oral cavity[J]. Journal of Medical Forum, 2022, 43(7): 104-107.
[38] 梁桂星, 张文婷, 汪最, 等. 没食子酸抑制生物被膜机制的初步研究[J/OL]. 中国动物传染病学报, 2022: 1−9. [2022-05-05]. doi: 10.19958/j.cnki.cn31-2031/s.20220505.001. LIANG G X, ZHANG W T, WANG Z, et al. Preliminary study on the mechanism of gallic acid inhibiting biofilm[J/OL]. Chinese Journal of Animal Infectious Diseases, 2022: 1−9. [2022-05-05]. doi: 10.19958/j.cnki.cn31-2031/s.20220505.001.
[39] 石嘉怿. 青梅花提取物的酪氨酸酶抑制作用及机理研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2011,32(10):205−207,211. [SHI J Y. Inhibitory effect and mechanism of prunus mume flowers extracts on tyrosinase[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2011,32(10):205−207,211. SHI J Y, Inhibitory effect and mechanism of prunus mume flowers extracts on tyrosinase[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2011, 32(10): 205-207,211.
[40] SI Y X, YIN S J, OH S, et al. An integrated study of tyrosinase inhibition by rutin: Progress using a computational simulation[J]. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics,2012,29(5):999−1012. doi: 10.1080/073911012010525028
[41] MARUYAMA H, KAWAKAMI F, LWIN T T, et al. Biochemical characterization of ferulic acid and caffeic acid which effectively inhibit melanin synthesis via different mechanisms in B16 melanoma cells[J]. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin,2018,41(5):806−810. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b17-00892
[42] KIM Y J. Antimelanogenic and antioxidant properties of gallic acid[J]. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin,2007,30(6):1052−1055. doi: 10.1248/bpb.30.1052
[43] NIRMAL N P, BENJAKUL S. Inhibition kinetics of catechin and ferulic acid on polyphenoloxidase from cephalothorax of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei)[J]. Food Chemistry,2012,131(2):569−573. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.09.025
[44] WIJAYA C, ELYA B, YANUAR A. Study of tyrosinase inhibitory activity and phytochemical screening of Cassia fistula L. leaves[J]. International Journal of Applied Pharmaceutics,2018,10(1):384−387. doi: 10.22159/ijap.2018.v10s1.85
[45] 袁博, 曹健, 秦朗, 等. 四种酚类化合物体外抗氧化活性的比较研究[J]. 食品工业,2018,39(9):200−204. [YUAN B, CAO J, QIN L, et al. Study on the comparison of antioxidant activity in vitro of four phenolic compounds[J]. The Food Industry,2018,39(9):200−204. YUAN B, CAO J, QIN L, et al. Study on the comparison of antioxidant activity in vitro of four phenolic compounds[J]. The Food Industry, 2018, 39(9): 200-204.
[46] XIE P J, HUANG L X, ZHANG C H, et al. Skin-care effects of dandelion leaf extract and stem extract: Antioxidant properties, tyrosinase inhibitory and molecular docking simulations[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2018,111:238−246. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.10.017
[47] 羿月同, 李莎莎, 樊梓鸾, 等. 红豆越橘花青素与金银花多酚协同抗氧化活性[J]. 精细化工,2021,38(5):967−972,1029. [YI Y T, LI S S, FAN Z L, et al. Synergism antioxidation of lingonberry anthocyanin and lonicera japonica polyphenols[J]. Fine Chemicals,2021,38(5):967−972,1029. YI Y T, LI S S, FAN Z L, et al. Synergism antioxidation of lingonberry anthocyanin and lonicera japonica polyphenols[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2021, 38(5): 967-972, 1029.
[48] AGRAWAL S, BARROW C J, ADHOLEYA A, et al. Unveiling the dermatological potential of marine fungal species components: antioxidant and inhibitory capacities over tyrosinase[J]. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry,2022,69(3):1252−1266. doi: 10.1002/bab.2201
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 岳丹,陆颖,李梦飞,黄代涛,张锦标,种玉晴. 基于斑马鱼SLC17A8基因的表达特征验证其对黑色素转运的影响. 饲料研究. 2024(18): 81-87 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



