Optimization of Ultrasonic-Assisted Deep Eutectic Solvent Extraction Process, Biological Activities and Components of Burdock Polyphenols
-
摘要: 考察6种低共熔溶剂对牛蒡多酚的提取效果,运用响应面法优化超声波辅助低共熔溶剂提取牛蒡多酚的工艺条件,并通过分析其总还原力和清除DPPH自由基能力、对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制作用和对体外胆酸盐结合力,初步研究其生物活性,并分析其组成。结果显示,DES 5(氯化胆碱:乙二醇摩尔比为1:4)对牛蒡多酚的提取效果最优,料液比55:1 mg/mL,含水率为40%,提取温度49 ℃、时间41 min是其最佳提取工艺,在此条件下牛蒡多酚的得率为1.19%±0.11%。生物活性分析表明,牛蒡多酚的总还原力和清除DPPH自由基能力的IC50分别为0.93 mg/mL和7.03 μg/mL,表现出较好的抗氧化效果,但弱于VC;对α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制作用的IC50为0.13 mg/mL,高于阿卡波糖,表明其降血糖能力较强;另外,样品质量浓度为1.5 mg/mL时,其胆酸盐结合率为33.23%,提示其具有一定的降血脂能力。HPLC分析表明,牛蒡多酚中含有绿原酸、咖啡酸和阿魏酸。试验结果为牛蒡多酚的绿色制备和作为抗氧化和降血糖、血脂的功能性成分开发利用提供了一定的理论依据。Abstract: The extraction effects of six deep eutectic solvents on burdock polyphenols (BPs) were investigated, and the response surface methodology was used to optimize the process conditions of ultrasonic-assisted deep eutectic solvent extraction of BPs, moreover, the total reducing power, the DPPH• scavenging capacity, the inhibition of α-glucosidase and cholic acid binding capacity in vitro were studied, and its composition were analyzed by HPLC. The results showed that DES 5 (the molar ratio of choline chloride to ethylene glycol was 1:4) was the best solvent system for the extraction of BPs. The optimum technological conditions were as follows, the water content of deep eutectic solvent was 40%, the ratio of material to liquid was 55:1 mg/mL, the extraction temperature was 49 ℃, and the extraction time was 41 min, under the above conditions, the yield of BPs was 1.19%±0.11%. The biological activity analysis showed that the IC50 of the total reducing power and DPPH• scavenging capacity of burdock polyphenol were 0.93 mg/mL and 7.03 μg/mL, respectively, indicating that it had good antioxidant capacity, but weaker than VC. The IC50 of α-glucosidase inhibition was 0.13 mg/mL, which was higher than acarbose, indicating that it possessed excellent hypoglycemic activity. In addition, its cholic acid binding rate was 33.23% when the mass concentration was 1.5 mg/mL, implied that it had a certain hypolipidemic activity. HPLC analysis showed that BPs contained chlorogenic acid, caffeic acid and ferulic acid. The results would provide a theoretical basis for the green preparation of burdock polyphenol and its development and utilization as a functional component of antioxidation, hypoglycemia and blood lipids.
-
Keywords:
- deep eutectic solvent /
- burdock /
- polyphenols /
- biological activity /
- component analysis
-
牛蒡是药食两用的植物,具有很高的营养和保健价值,牛蒡根含有丰富的菊糖、多酚、蛋白质、膳食纤维、维生素和微量元素等营养成分[1],被开发成了牛蒡茶、牛蒡饮料、牛蒡酒等产品。多酚化合物,包括绿原酸、芦丁、咖啡酸、槲皮素等,是牛蒡中的主要活性成分之一,具有抗氧化、降血糖、保肝护肝、降血脂、抗过敏的等多种生物活性[2],引起了广泛关注,研究人员对其制备技术和生物活性进行了探讨[3−5],但多以有机溶剂为提取剂制备牛蒡多酚,存在易燃、易爆、易挥发和有毒有害等缺点,因此有必要探讨绿色、安全高效的牛蒡多酚制备工艺。
低共熔溶剂(Deep eutectic solvents,DESs)是由氢键受体和氢键供体在适当的摩尔比构成的,季铵盐类为最常用的氢键受体,而尿素、有机酸、多元醇、糖类等则常作为氢键供体,其熔点一般会远低于各组分的熔点,具有原料易得、合成方便、无需纯化、无毒性、不易燃、可回收、可降解等一系列优点,在绿色溶剂领域内应用广泛,有代替传统有机溶剂的巨大潜质[6]。Ali等[7]研究表明超声波辅助DES(氯化胆碱:对甲苯磺酸=1:2)较传统提取方法能明显提高枸杞果实中包括杨梅素、桑色素和芦丁在内的黄酮类化合物的得率;Cui等[8]研究表明DES提取沙棘叶中黄酮类化合物的效果明显优于70%乙醇溶剂;Tatjana等[9]提取薄荷中的总酚和Paula等[10]从橄榄叶中提取酚类化合物的研究中都得到了相似的结果,表明DES是一种新型和有效的从植物中提取活性成分的绿色溶剂,而采用绿色环保的DESs提取牛蒡多酚还未见报道。
本文研究筛选适合提取牛蒡多酚的DESs体系,并通过Box-Behnken设计优化超声波辅助DESs提取牛蒡多酚的最佳工艺,并通过测定DPPH•清除能力、总还原力、对α-葡萄糖苷酶的抑制作用和胆酸盐的结合能力,分析其体外生物活性。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
牛蒡 购于农副产品市场;氯化胆碱、丙二醇、丙三醇、乳酸、乙二醇、乙酰丙酸、没食子酸、儿茶素、绿原酸、咖啡酸、阿魏酸、芦丁、福林酚、抗坏血酸、1,1-二苯基-2-苦基肼(DPPH)、2,2'-联氮双(3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸)二铵盐(ABTS) AB-8大孔吸附树脂(比表面积 480~520 m2/g) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;葡萄糖、碳酸钠、柠檬酸 国药集团化学试剂有限公司公司;总胆汁酸测试盒 南京建成生物工程研究所;其余试剂均为分析纯。
SB-120D超声波清洗器 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司;TGL-16G 高速台式离心机 上海安亭科学仪器厂;HL-2S恒流泵 上海沪西分析仪器厂有限公司;真空冷冻干燥机 德国CHRIST公司;TU-1810紫外分光光度计 北京普析通用有限公司;L550离心机 湖南湘仪实验室仪器开发有限公司;1260Ⅱ高效液相色谱仪(配二极管阵列(DAD)检测器、自动进样器进样,Agilent C18色谱柱) 美国安捷伦科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 牛蒡的预处理
将新鲜牛蒡根清洗晾干后切片,置于1%的柠檬酸溶液中浸泡5 min,沥干水分后,于60 ℃恒温干燥箱中干燥,粉碎,过60目筛,于−20 ℃冰箱中保存,待用。
1.2.2 多酚含量的测定
参考文献[11]采用福林-酚比色法测定多酚含量,稍作修改,以没食子酸为标准品,分别取一定体积的没食子酸标准液于10 mL棕色容量瓶中,分别加入1 mL 10%的福林-酚试剂,摇匀,静置5 min后加入10 mL 7% Na2CO3,避光放置30 min,设置空白,测定765 nm的吸光度。所得回归方程为y=0.0095x+0.0547,R2=0.9959;样品测定时,将样品适当稀释,取1 mL稀释液按上述步骤进行测定,按公式(1)计算得率。
多酚得率(%)=c×n×Vm×100 (1) 式中:c为多酚的质量浓度(mg/mL);n为样品的稀释倍数;V为上清液液总体积(mL);m为样品质量(g)。
1.2.3 低共熔溶剂的制备与牛蒡多酚提取过程
DESs由氢受体(氯化胆碱)与氢供体(葡萄糖、乳酸、乙二醇等)按照不同摩尔比混匀、加热制得。分别取一定量的反应物于100 mL试剂瓶中,放置于80 ℃水浴锅中加热搅拌得到均一透明液体,冷却至室温,即得DESs,保存于干燥容器中,备用。
准确称取50 mg牛蒡粉末置于离心管中,加入1 mL DESs,摇匀,置于超声波清洗器中提取,然后于5000 r/min离心15 min,收集上清液测定多酚含量。
1.2.4 超声波辅助低共熔溶剂提取牛蒡多酚的工艺优化
1.2.4.1 最佳DESs体系的确定
以氯化胆碱作为氢供体,按表1所示配制不同体系的DESs,由于体系黏度较大,都加入30%的水,筛选最佳的DESs。
表 1 DESs组成Table 1. Composition of the DESs编号 组分 摩尔比 DES-1 氯化胆碱:葡萄糖 1:1 DES-2 氯化胆碱:乳酸 1:2 DES-3 氯化胆碱:丙三醇 1:2 DES-4 氯化胆碱:丙二醇 1:2 DES-5 氯化胆碱:乙二醇 1:4 DES-6 氯化胆碱:乙酰丙酸 1:2 1.2.4.2 单因素实验
在确定最佳DESs体系的基础上,以料液比55:1 mg/mL,提取温度50 ℃,提取时间为30 min,研究不同含水率(10%、20%、30%、40%和50%)对牛蒡多酚得率的影响;以含水率为40%,提取温度50 ℃,提取时间为30 min,研究不同料液比(25:1、35:1、45:1、55:1、65:1和75:1 mg/mL)对牛蒡多酚得率的影响;以含水率为40%,料液比55:1 mg/mL,提取时间为30 min,研究不同提取温度(30、40、50、60和70 ℃)对牛蒡多酚得率的影响;以含水率为40%,料液比55:1 mg/mL,提取温度50 ℃,研究不同提取时间(10、20、30、40和50 min)对牛蒡多酚得率的影响。
1.2.4.3 响应面优化试验设计
在单因素实验的基础上,采用响应面法(BBD-RSM)试验设计,考查含水率(A)、提取温度(B)和提取时间(C)3个对牛蒡多酚得率的影响,因素与水平见表2。
表 2 响应面分析因素与水平Table 2. Response surface analysis factors and levels因素 水平 −1 0 1 A 含水率(%) 35 40 45 B提取温度(℃) 45 50 55 C提取时间(min) 35 40 45 1.2.5 大孔吸附树脂富集回收牛蒡多酚
参考Cui等[8]报道的方法,将活化好的AB-8大孔吸附树脂填充在玻璃柱中(40 mm×600 mm)用于牛蒡多酚的富集。将在最佳提取条件获得到的50 mL提取液以3 BV/h的恒定流速流过柱,在样品吸附达到平衡后,首先用500 mL去离子水洗脱,然后用500 mL 70%乙醇洗脱,收集乙醇洗脱液,旋转蒸发后冷冻干燥,于−20 ℃下保存,备用。
1.2.6 牛蒡多酚的生物活性研究
1.2.6.1 清除 DPPH•能力测定
参照郎明紫等[12]报道的方法测定样品清除DPPH•的能力,并稍作修改,配置质量浓度3~45 μg/mL的牛蒡多酚溶液,各取2 mL于试管中,加入2 mL 0.05 mmol/L的DPPH-乙醇溶液,混合均匀,避光反应30 min后,使用0.5 cm光圈的比色皿测定517 nm处的吸光度值,记为A1;以样品和无水乙醇的为对照管,记为A2;以无水乙醇和DPPH溶液的为空白管,记为A0;并以抗坏血酸作为阳性对照,按公式(2)计算DPPH•清除率。
DPPH•清除率(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 (2) 1.2.6.2 总还原力的测定
参照刘文颖等[13]报道的方法测定样品总还原力,并稍作修改,配制质量浓度0.2~2.0 mg/mL的牛蒡多酚溶液,各取1 mL加入离心管中,加入0.2 mmol/L磷酸缓冲(pH为6.6)溶液2 mL和1%的铁氰化钾溶液1 mL,混匀后于50 ℃恒温水浴锅中反应20 min,冷却后加入10%的三氯乙酸溶液2 mL,涡旋混匀,3000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液2 mL于试管中,加入2 mL蒸馏水,最后加入0.4 mL 0.1%的FeCl3溶液,反应10 min后使用0.5 cm光圈的比色皿测定700 nm处的吸光值,吸光值越高,表示还原力越强。
1.2.6.3 抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶活性测定
参照於雨碟等[14]报道的方法测定样品抑制α-葡萄糖苷酶活性,并稍作修改,配制不同浓度的样品溶液,于试管中分别加入样品溶液、α-葡萄糖苷酶溶液(40 U/mL)和5 mmol/L PNPG试剂各100 μL,再加入700 μL磷酸缓冲液(pH6.0),混匀后在37 ℃水浴30 min,然后立即加入2 mL 0.1 mol/L的Na2CO3溶液终止反应。5 min后用0.5 cm光圈的比色皿测定405 nm的吸光值,记为A1;以磷酸缓冲液代替PNPG试剂的吸光值,记为A2;以磷酸缓冲液代替样品溶液的吸光值,记为A0;以阿卡波糖作为阳性对照,按照公式(3)计算抑制率。
α-葡萄糖苷酶活性抑制率(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 (3) 1.2.6.4 牛黄胆酸盐结合能力的测定
参照古丽米热•祖努纳等[15]报道的方法测定样品结合牛黄胆酸盐的能力,并稍作修改,取不同质量浓度的牛蒡多酚1 mL于试管中,加入0.01 mol/mL的HCl 1 mL,在37 ℃下模拟胃消化振荡消化1 h后,用0.1 mol/mL NaOH调pH至6.90,再分别加入1.5 mL 0.3 mmol/mL牛黄胆酸钠溶液和2 mL 10 mg/mL胰酶溶液,再于37 ℃下振荡消化1 h,于4500 r/min离心20 min后取上清液,按试剂盒的方法测定上清液中的总胆汁酸(TBA)含量。后按照公式(4)计算结合率。
牛黄胆酸盐结合率(%)=空白溶液中胆酸盐浓度(μmol/L)−样品溶液中胆酸盐浓度(μmol/L)空白溶液中胆酸盐浓度(μmol/L)×100 (4) 1.2.7 牛蒡多酚的组分分析
参考文献[16]的方法对牛蒡多酚进行分析。配置没食子酸、儿茶素、绿原酸、咖啡酸、阿魏酸和芦丁的单一标准液和混合标准品,样品用甲醇溶解,测定前用0.22 μm滤膜过滤。流动相 A 为 0.8%乙酸,B 为甲醇,柱温 28 ℃,进样量 10 μL,流速 0.9 mL/min,梯度洗脱程序见表3所示。用单一标准品绘制标准曲线后根据峰面积计算样品中组分的含量。
表 3 梯度洗脱程序Table 3. Gradient elution method时间 A:0.8%乙酸 B:甲醇 0 90 10 10 80 20 30 50 50 40 90 10 1.3 数据处理
所有试验均重复3次,采用Excel 2010软件进行数据处理和绘图,采用SPSS 18.0 软件对数据差异性进行分析;IC50值由曲线增长阶段拟合线性方程后计算获得(抑制率为50%或吸光值为0.5时的样品质量浓度)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 超声波辅助低共熔溶剂提取牛蒡多酚的工艺确定
2.1.1 最佳低共熔溶剂体系的选择
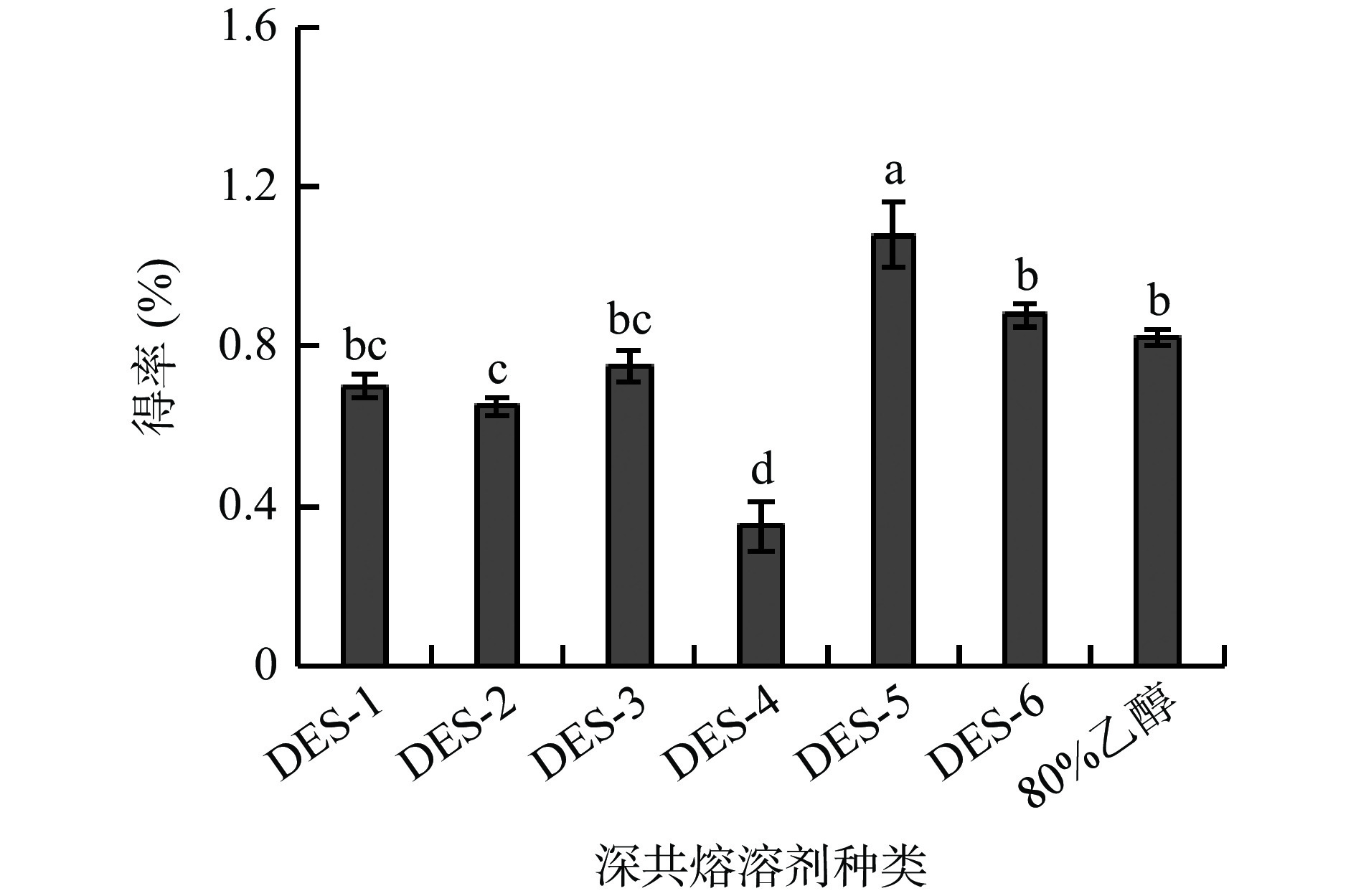
DESs的黏度、极性、溶解性和表面张力等理化特性会随着其氢供体和氢受体的组成和摩尔比的变化而改变,而这些特性是影响其对天然产物提取效率的重要原因[17]。试验依据氢键供体的不同设计了三类DESs,分别为多元醇类(丙二醇、丙三醇、乙二醇)、糖类(葡萄糖)和羧酸类(乳酸、乙酰丙酸),考查不同的DESs对多酚得率的影响,结果如图1所示,6种DESs中,DES-5对多酚的提取效果最佳,得率为1.08%,显著高于其他组分和80%乙醇组(P<0.05);Cui等[18]在考察DESs提取绿茶多酚时,也得到相似的结果,并认为可以用“相似相溶”的原理来解释。故选择DES-5(氯化胆碱/乙二醇,摩尔比1:4)进行后续试验。
2.1.2 含水率的选择
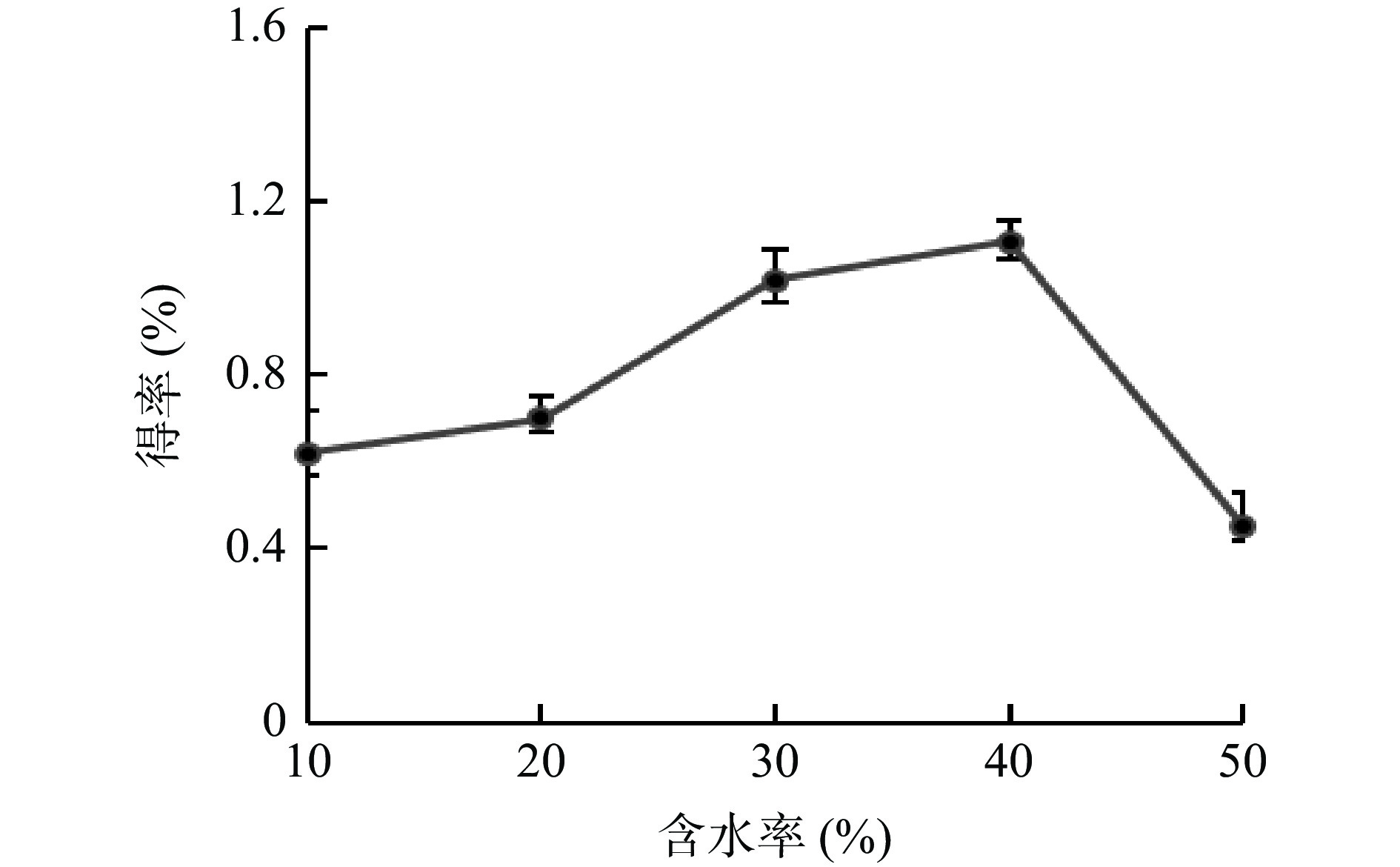
受氢键、范德华力等作用的影响,DESs一般具有较高的黏度,使其不易扩散到提取物的内部,影响目标活性物质的传质速率[19]。在DESs中加入适量的水能降低其黏度,改变体系的表面张力,使其更易进入细胞内部,改善提取效率[20]。不同含水率对多酚提取效率的影响结果见图2所示,随着含水率的增加,牛蒡多酚的得率先升高,在含水率为40%时达到最高,而当含水率超过40%时,多酚得率快速下降,这可能是由于过量的水会减弱DESs与多酚之间的相互作用[21]。因此选择40%左右的含水率进行后续试验。
2.1.3 料液比的选择
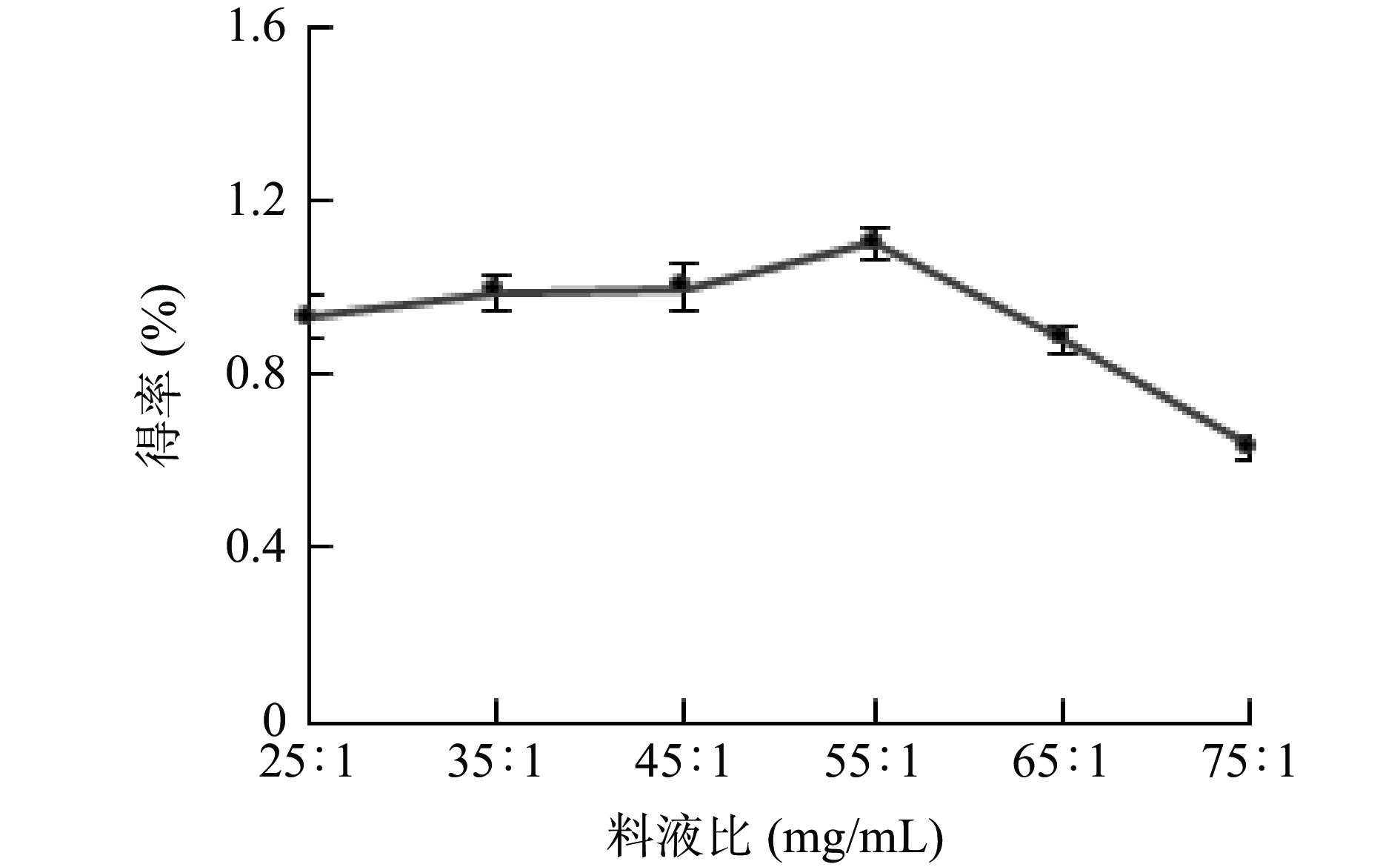
料液比对牛蒡多酚得率的影响如图3所示,料液比在25:1~55:1 mg/mL时,牛蒡多酚的得率呈略微上升趋势,且当料液比为55:1 mg/mL时得率达到最高值,而当料液比从55:1 mg/mL增大到75:1 mg/mL时,得率呈快速下降趋势。这是由于在提取过程中,适当的增大料液比,必然会导致传质推动力的提高,有利于多酚的提取[22]。然而,当溶质和溶液的比例扩大到一定程度后,萃取剂对多酚的提取已经达到饱和,再提高料液比可能会导致已被提取的多酚脱附重回到待提取物中[23],也会增加杂质的溶出,造成得率的下降。料液比从25:1增大到55:1过程中,对牛蒡多酚的得率影响较小,因此在后续工艺优化中选择料液比为55:1 mg/mL进行试验。
2.1.4 提取温度的选择
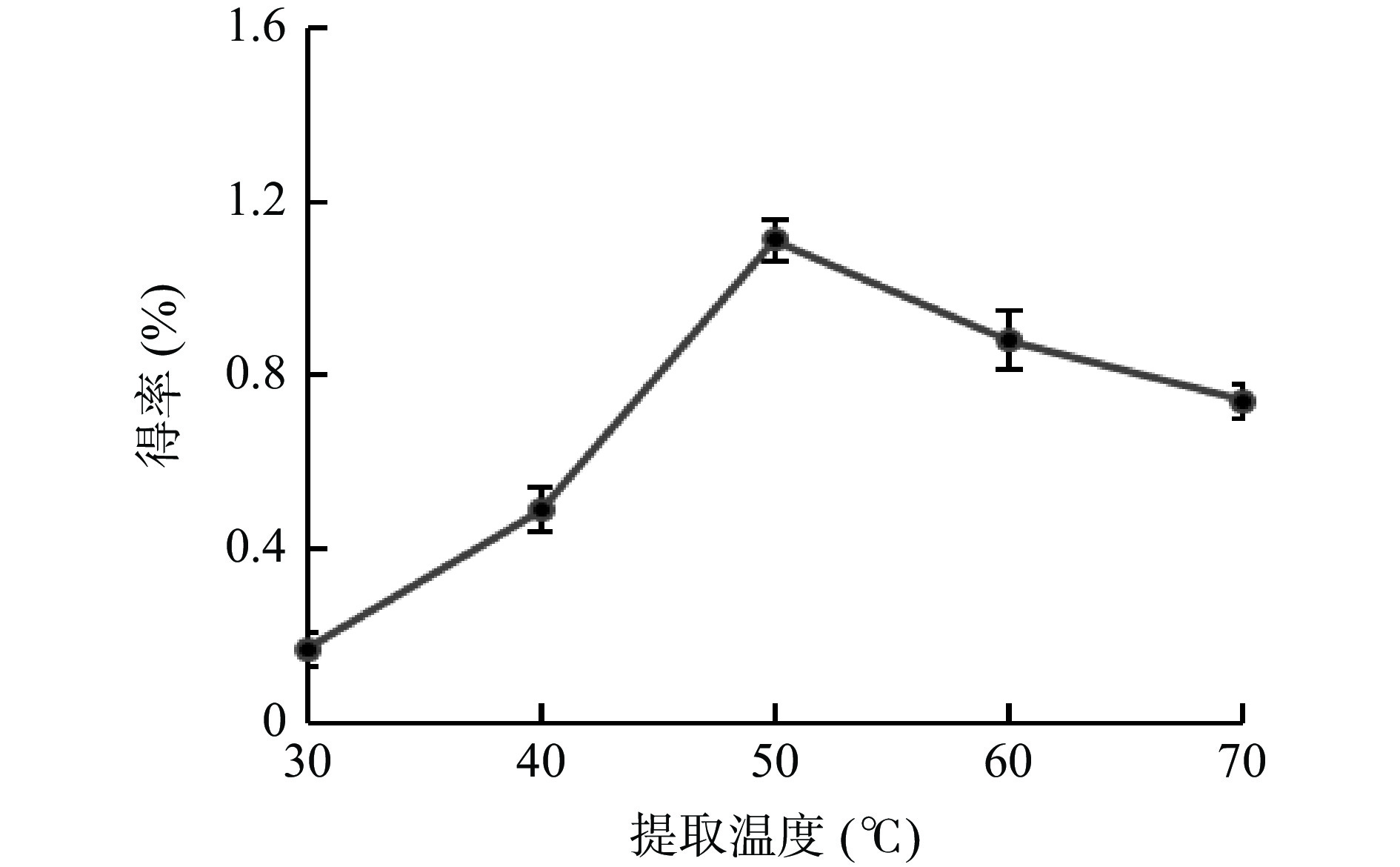
提取温度对牛蒡多酚得率的影响见图4所示,温度在30~50 ℃内,多酚得率随温度的增高而增大,并在50 ℃时达到顶峰,随后再升高温度时,多酚得率逐渐下降。结果与尚宪超[24]提取烟草绿原酸结果相似。可能是由于适当地提高温度可以降低 DESs的黏度,加速分子运动,使细胞内部的多酚类物质快速地扩散到溶剂中[25];但当温度过高时,多酚的结构会被破坏,从而得率就会下降。因此选择50 ℃左右的温度进行后续试验。
2.1.5 提取时间的选择
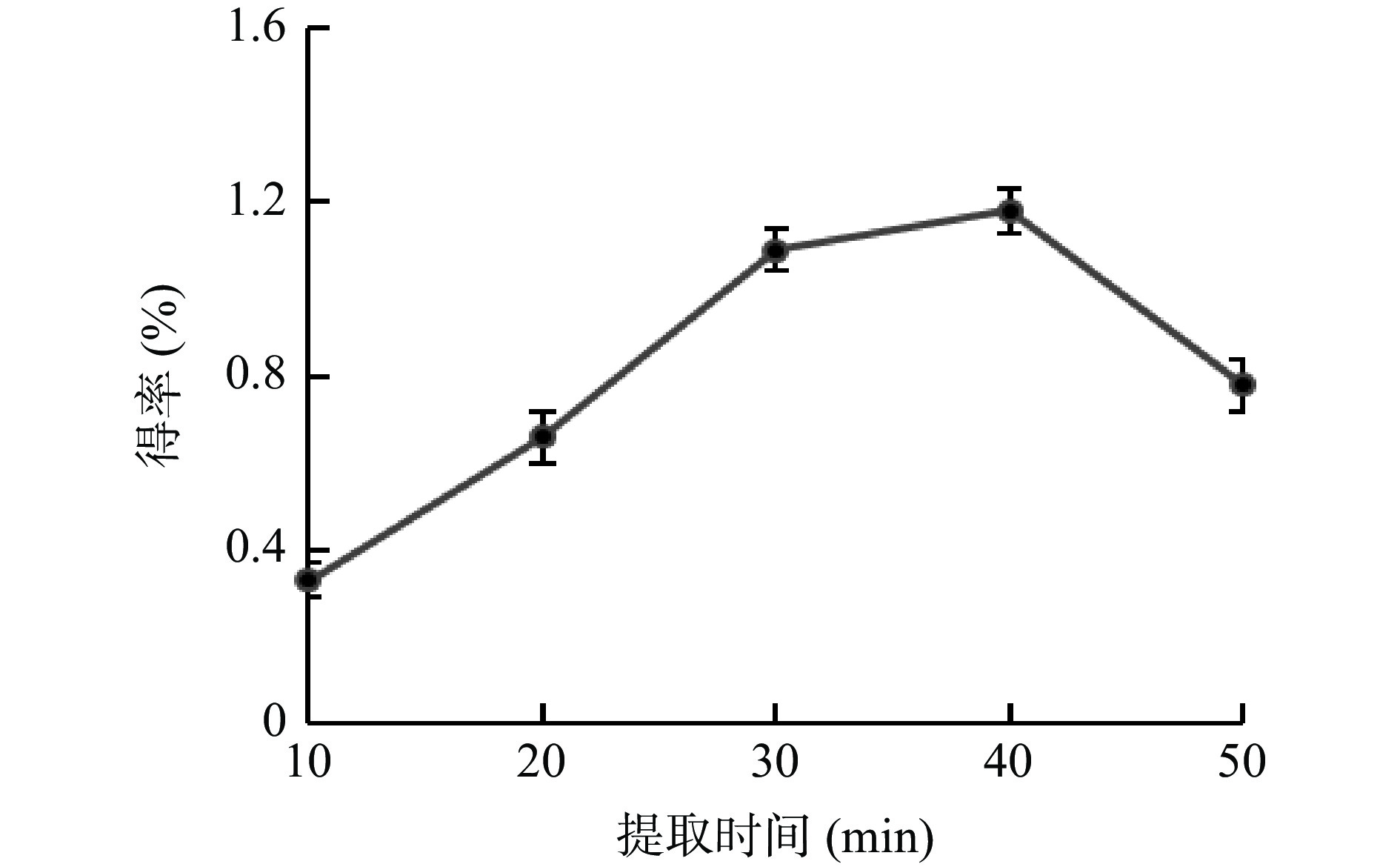
提取时间对牛蒡多酚得率的影响见图5所示,提取时间在10~40 min时,牛蒡多酚的得率逐渐上升,并在40 min时达到最高,之后多酚的得率开始下降。可能是由于过长的提取时间,会导致已溶出的多酚发生分解,从而使得率下降[26]。因此选择40 min左右的提取时间进行后续试验。
2.1.6 响应面优化试验结果
2.1.6.1 回归模型分析
单因素实验表明,料液比对结果的影响较小,而含水率(A)、提取温度(B)和提取时间(C)对结果影响较大,同时为了优化获得最佳的工艺条件,选择这三个因素最佳的单因素结果附近的值进行响应面设计试验,结果见表4,通过软件分析,得到牛蒡多酚得率(Y)的回归方程:Y=1.16−0.084A−0.062B+0.051C+0.047AB+0.001AC−0.078BC−0.26A2−0.17B2−0.18C2。
表 4 响应面试验设计及结果Table 4. Response surface test design and results实验号 A含水率(%) B提取温度(℃) C提取时间(min) 牛蒡多酚得率(%) 1 35 50 45 0.82 2 40 50 40 1.16 3 40 50 40 1.13 4 40 45 45 1.05 5 35 50 35 0.75 6 40 45 35 0.76 7 40 50 40 1.12 8 35 45 40 0.86 9 35 55 40 0.76 10 40 50 40 1.18 11 40 55 45 0.71 12 45 55 40 0.65 13 45 50 35 0.62 14 40 55 35 0.73 15 40 50 40 1.15 16 45 50 45 0.69 17 45 45 40 0.62 对结果进行响应面回归分析,结果见表5所示,由表5可知,模型P<0.0001(极显著);而表示模型与试验拟合程度的失拟项P>0.05(不显著),说明所得模型成立。模型的决定系数R2=0.9774,表明该模型的试验值与预测值拟合度良好的;校正决定系数R2Adj=0.9501,表明本模型可以解释95.01%响应值的变化。综上,试验所得的模型可以对低共熔溶剂提取牛蒡多酚工艺进行分析预测。此外,一次项A、B和二次项A2、B2、C2对牛蒡多酚得率影响极显著(P<0.01),一次项C及交互项BC对结果影响显著(P<0.05),由图6(c)中也可看出提取温度与提取时间相互作用的等高线呈椭圆形,进一步表明两者相互作用显著,3D响应面图可看出提高温度和延长提取时间时,牛蒡多酚得率先增大后减小;三个自变量对多酚得率的影响程度为含水率(A)>提取温度(B)>提取时间(C)。
表 5 二次响应面回归模型方差分析结果Table 5. Analysis of variance of quadratic response surface regression model方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 0.75 9 0.083 34.87 <0.0001 ** A 0.056 1 0.056 23.60 0.0018 ** B 0.031 1 0.031 13.14 0.0085 ** C 0.021 1 0.021 8.84 0.0207 * AB 9.025E-003 1 9.025E-003 3.80 0.0924 AC 0.000 1 0.000 0.000 1.0000 BC 0.024 1 0.024 10.10 0.0155 * A2 0.28 1 0.28 119.24 <0.0001 ** B2 0.12 1 0.12 49.38 0.0002 ** C2 0.14 1 0.14 60.28 0.0001 ** 残差 0.017 7 2.378E-003 失拟项 0.012 3 4.042E-003 3.58 0.1250 纯度差 4.520E-003 4 1.130E-003 总和 0.76 16 R2=0.9774 R2Adj=0.9501 Adeq Precision 15.481 注:**为差异极显著(P<0.01);*为差异显著(P<0.05)。 2.1.6.2 最佳工艺确定
通过响应面版软件分析得到最佳条件为:料液比55:1 mg/mL含水率为39.08%、温度48.71 ℃、时间40.97 min,在该条件下预测牛蒡多酚的得率为1.185%。为方便操作,修正条件为料液比为55:1 mg/mL,含水率为40%、提取温度49 ℃、时间为41 min,进行三次平行实验,得到牛蒡多酚的得率为1.19%±0.11%,结果与预测的理论值相近,表明模型拟合良好,优化条件可信,该模型可以用于预测牛蒡多酚的提取状况。
2.2 大孔吸附树脂对牛蒡多酚的纯化效果
由表6可知,采用试验优化的条件制备的牛蒡粗多酚的纯度为16.21%±1.32%,经AB-8大孔树脂纯化后其纯度提高到了67.86%±1.54%,显著提高了其纯度(P<0.05),提示AB-8大孔树脂能较好地去除牛蒡粗多酚中糖类和色素等杂质,有效实现了牛蒡多酚组分的富集、纯化。
表 6 AB-8大孔吸附树脂对牛蒡多酚的纯化效果Table 6. Purification effect of BPs by AB-8 macroporous adsorption resin样品 纯化前 纯化后 多酚纯度(%) 16.21±1.32a 67.86±1.54b 2.3 牛蒡多酚的生物活性分析
2.3.1 牛蒡多酚体外抗氧化活性试验结果
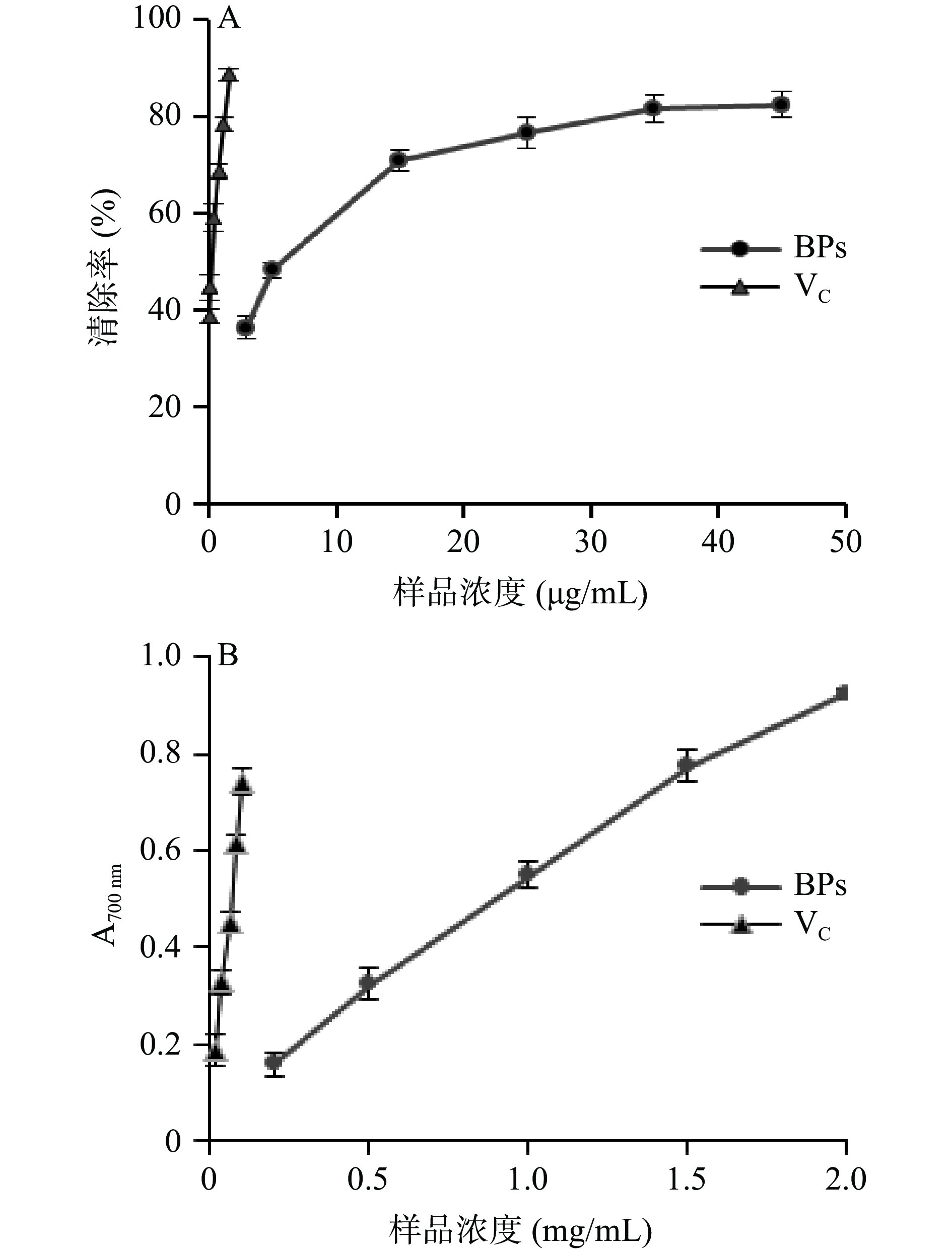
牛蒡多酚清除DPPH•和总还原力的结果见图7所示,牛蒡多酚和VC都具有较强的DPPH•清除能力和还原力,在实验浓度范围内,二者的清除率都随着浓度的增加而呈现着良好增加的趋势。由7A可知,当牛蒡多酚的浓度为35 μg/mL时,清除率为81.42%,再提高样品浓度时,清除率基本不变;对曲线回归后计算得出牛蒡多酚和VC清除DPPH•的IC50值分别为7.03 μg/mL和0.27 μg/mL,其总还原能力的IC50值分别为0.93 mg/mL和0.06 mg/mL,提示其具有较好的抗氧化活性,但牛蒡多酚对DPPH•自由基的清除能力和总还原力都低于对照品VC。范金波等[27]和蔡茜彤等[5]研究也发现牛蒡多酚具有较好的抗氧化活性,与本结果相似。
2.3.2 牛蒡多酚对α-葡萄糖苷酶活性抑制试验结果
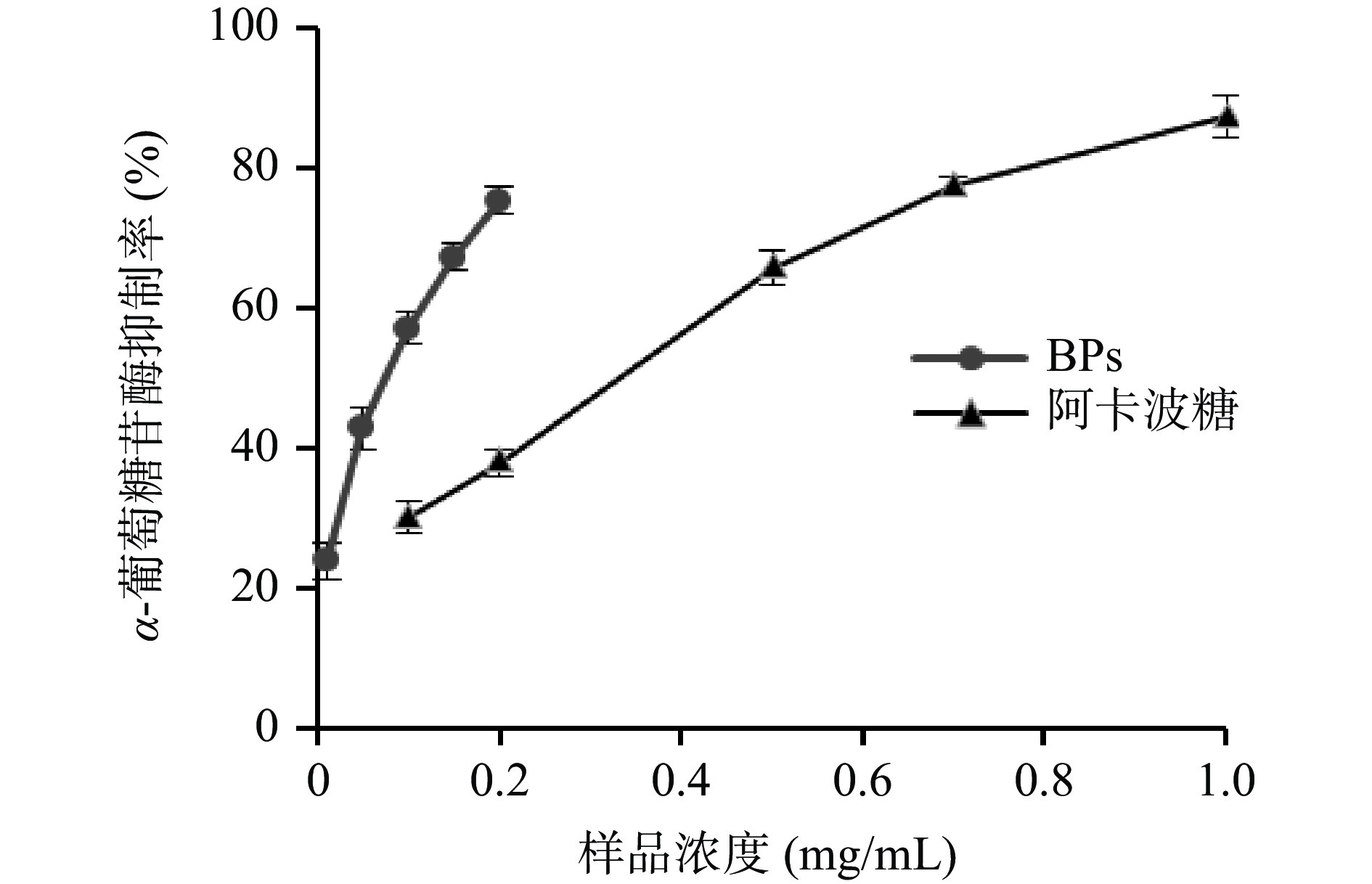
α-葡萄糖苷酶作为消化碳水化合物和葡萄糖释放的关键酶,通过抑制其活性,可以防止餐后血糖水平升高,对于治疗和预防糖尿病具有重要的意义[28]。由图8可知,牛蒡多酚对α-葡萄糖苷酶具有较强的抑制作用,随着牛蒡多酚浓度的增加抑制率也提高。牛蒡多酚和阿卡波糖对α-葡萄糖苷酶活性抑制率的IC50值分为0.13和0.37 mg/mL,牛蒡多酚的抑制率约为阿卡波糖的2.85倍,提示牛蒡多酚具有较强的降血糖能力。乔锦莉等[29]从野生蓝果忍冬果实中提取的多酚也表现出较强的α-葡萄糖苷酶抑制活性。
2.3.3 对胆酸盐结合能力
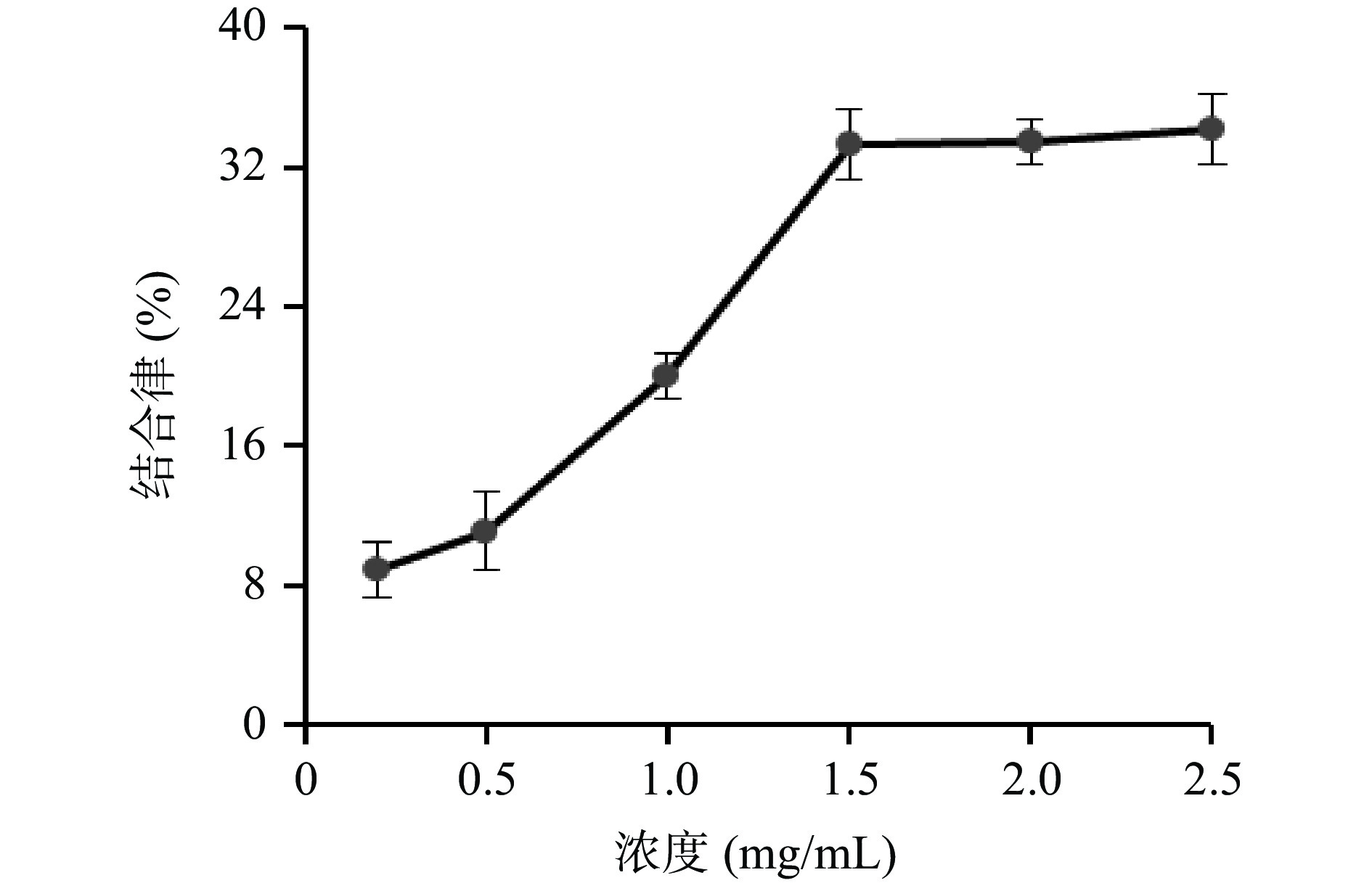
胆酸盐能通过“肝肠循环”而再利用,通过结合胆酸盐,肝脏会将胆固醇转化成胆汁酸,从而降低血液的胆固醇含量,达到降低血脂的效果[30]。样品对胆酸盐的吸附能力越强则降血脂效果越好。由图9可知,牛蒡多酚对胆酸盐的结合能力随着浓度的升高而逐渐增大,当质量浓度为1.5 mg/mL时,结合率为33.23%,继续增大浓度后,结合率基本不变,提示牛蒡多酚有一定的胆酸盐结合能力,具有一定的降血脂能力。徐一凡等[31]研究发现桑黄多酚具有一定的胆酸盐吸附能力,与本结果相似。
2.4 牛蒡多酚的组分分析结果
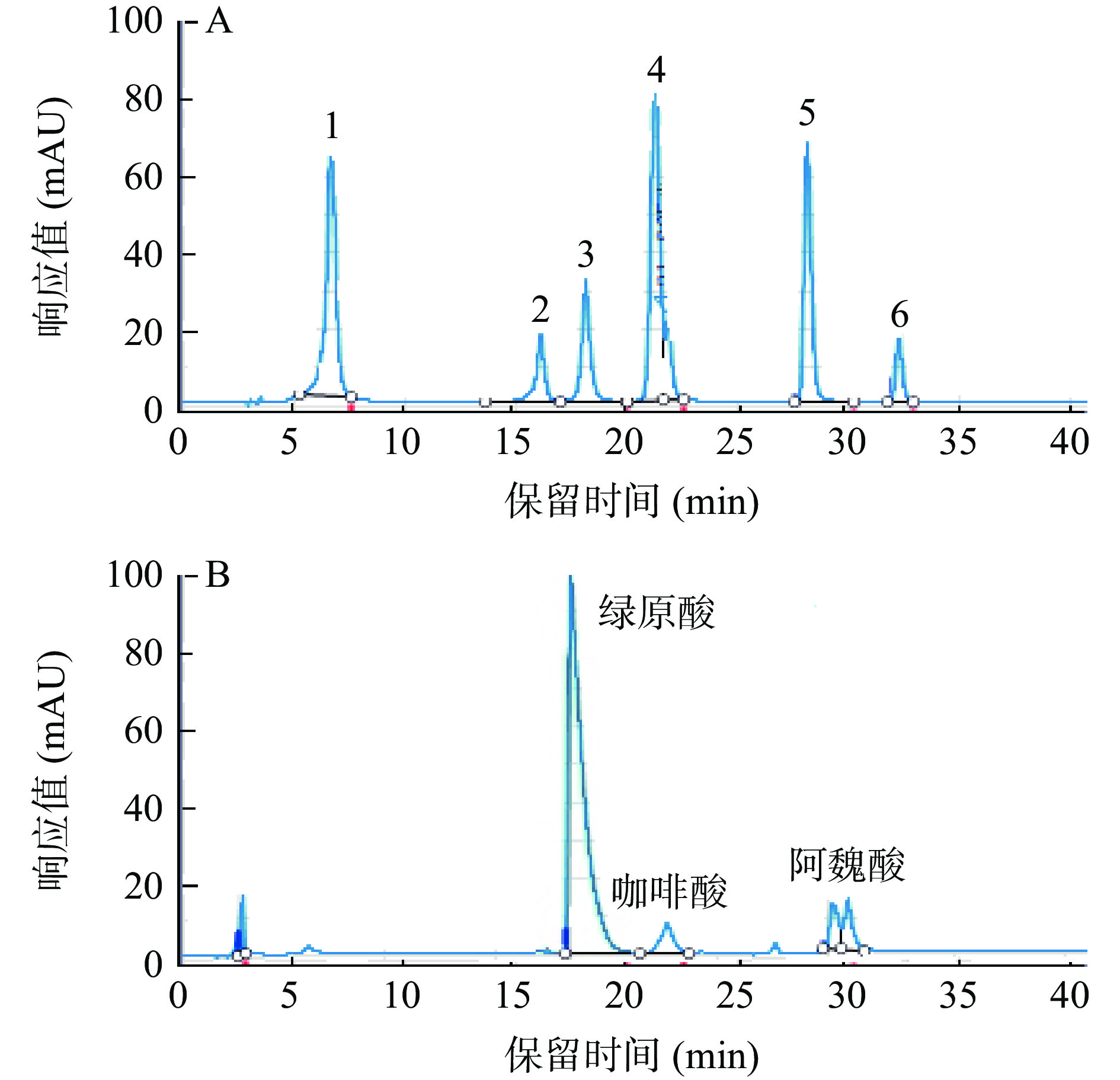
HPLC-DAD分析牛蒡多酚的组分结果见图10和表7,牛蒡多酚中主要峰的出峰时间与标准品中的3、4和5号峰的出峰时间基本一致,推测牛蒡多酚中主要含有绿原酸、咖啡酸和阿魏酸,其中绿原酸含量最高,为(63.25±1.12)µg/mL,蔡茜彤[32]也研究发现牛蒡中含有绿原酸、咖啡酸和阿魏酸,且绿原酸含量较高,结果与本试验结果一致。
表 7 牛蒡多酚组分及含量Table 7. Compositions and contents of BPs组分 绿原酸 咖啡酸 阿魏酸 保留时间(min) 18.09 21.81 28.08 含量(µg/mL) 63.25±1.12 10.57±1.23 18.23±0.96 3. 结论
本文筛选出对牛蒡多酚提取效果最佳的低共熔溶剂体系,采用响应面确定的超声波辅助低共熔溶剂提取牛蒡多酚的最佳工艺为,采用DES 5(氯化胆碱:乙二醇摩尔比为1:4)为提取剂,在含水率40%,料液比55:1 mg/mL,温度49 ℃和提取时间为41 min时,牛蒡多酚的得率最高,为1.19%±0.11%。牛蒡多酚提取物经AB-8大孔树脂富集、纯化后,纯度显著提高,且其具有较强的总还原力、清除DPPH自由基能力和对α-葡萄糖苷酶活性的抑制能力,并表现出一定的胆酸盐结合能力;结果提示牛蒡多酚较好的抗氧化效果和降血糖能力,并具有一定的降血脂能力。HPLC分析表明牛蒡多酚中绿原酸含量最高,另外还含有咖啡酸和阿魏酸。本研究为牛蒡多酚的绿色、安全制备提供了一定的基础,也为其作为天然抗氧化剂和降糖活性物质的研究提供了一定的理论依据。
-
表 1 DESs组成
Table 1 Composition of the DESs
编号 组分 摩尔比 DES-1 氯化胆碱:葡萄糖 1:1 DES-2 氯化胆碱:乳酸 1:2 DES-3 氯化胆碱:丙三醇 1:2 DES-4 氯化胆碱:丙二醇 1:2 DES-5 氯化胆碱:乙二醇 1:4 DES-6 氯化胆碱:乙酰丙酸 1:2 表 2 响应面分析因素与水平
Table 2 Response surface analysis factors and levels
因素 水平 −1 0 1 A 含水率(%) 35 40 45 B提取温度(℃) 45 50 55 C提取时间(min) 35 40 45 表 3 梯度洗脱程序
Table 3 Gradient elution method
时间 A:0.8%乙酸 B:甲醇 0 90 10 10 80 20 30 50 50 40 90 10 表 4 响应面试验设计及结果
Table 4 Response surface test design and results
实验号 A含水率(%) B提取温度(℃) C提取时间(min) 牛蒡多酚得率(%) 1 35 50 45 0.82 2 40 50 40 1.16 3 40 50 40 1.13 4 40 45 45 1.05 5 35 50 35 0.75 6 40 45 35 0.76 7 40 50 40 1.12 8 35 45 40 0.86 9 35 55 40 0.76 10 40 50 40 1.18 11 40 55 45 0.71 12 45 55 40 0.65 13 45 50 35 0.62 14 40 55 35 0.73 15 40 50 40 1.15 16 45 50 45 0.69 17 45 45 40 0.62 表 5 二次响应面回归模型方差分析结果
Table 5 Analysis of variance of quadratic response surface regression model
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 0.75 9 0.083 34.87 <0.0001 ** A 0.056 1 0.056 23.60 0.0018 ** B 0.031 1 0.031 13.14 0.0085 ** C 0.021 1 0.021 8.84 0.0207 * AB 9.025E-003 1 9.025E-003 3.80 0.0924 AC 0.000 1 0.000 0.000 1.0000 BC 0.024 1 0.024 10.10 0.0155 * A2 0.28 1 0.28 119.24 <0.0001 ** B2 0.12 1 0.12 49.38 0.0002 ** C2 0.14 1 0.14 60.28 0.0001 ** 残差 0.017 7 2.378E-003 失拟项 0.012 3 4.042E-003 3.58 0.1250 纯度差 4.520E-003 4 1.130E-003 总和 0.76 16 R2=0.9774 R2Adj=0.9501 Adeq Precision 15.481 注:**为差异极显著(P<0.01);*为差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 6 AB-8大孔吸附树脂对牛蒡多酚的纯化效果
Table 6 Purification effect of BPs by AB-8 macroporous adsorption resin
样品 纯化前 纯化后 多酚纯度(%) 16.21±1.32a 67.86±1.54b 表 7 牛蒡多酚组分及含量
Table 7 Compositions and contents of BPs
组分 绿原酸 咖啡酸 阿魏酸 保留时间(min) 18.09 21.81 28.08 含量(µg/mL) 63.25±1.12 10.57±1.23 18.23±0.96 -
[1] 徐艳平. 复合酶解法与固态发酵法研制新型牛蒡茶[D]. 泰安:山东农业大学, 2022 XU Y P. Preparation of new burdock tea by complex enzymatic hydrolysis and solid state fermentation[D]. Taian:Shandong Agricultural University, 2022.
[2] MORO T, CLERICI M. Burdock ( Arctium lappa L) roots as a source of inulin-type fructans and other bioactive compounds:Current knowledge and future perspectives for food and non-food applications[J]. Food Research International,2021,141:109889. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2020.109889
[3] 马艳弘, 孟勇, 崔晋, 等. 牛蒡多酚超声辅助酶法提取工艺及抗氧化活性[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2020,39(1):38−45 MA Y H, MENG Y, CUI J, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted enzyme extraction of polyphenols from burdock and its antioxidant activity evaluation[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2020,39(1):38−45.
[4] 王长凯, 江润生, 易香羽, 等. 牛蒡多酚的闪式提取工艺优化[J]. 农产品加工,2019,(9):28−30,33 WANG C K, JIANG R S, YI X Y, et al. Optimization of flash extraction for burdock polyphenols[J]. Farm Products Processing,2019,(9):28−30,33.
[5] 蔡茜彤, 范金波, 冯叙桥, 等. 微波辅助提取牛蒡多酚和黄酮工艺优化及抗氧化活性的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2015,36(3):275−280 CAI X T, FAN J B, FENG X Q, et al. Optimization of process for microwave-assisted extraction of polyphenols from burdock and its antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2015,36(3):275−280.
[6] 李吉超. 低共熔溶剂提取银杏叶中黄酮及纯化研究[D]. 北京:北京化工大学, 2020 LI J C. Extraction and purification of flavonoids from ginkgo biloba leaves by deep eutectic solvents[D]. Beijing:Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2020.
[7] ALI M C, CHEN J, ZHANG H J, et al. Effective extraction of flavonoids from Lycium barbarum L. fruits by deep eutectic solvents-based ultrasound-assisted extraction[J]. Talanta,2019,203:16−22. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2019.05.012
[8] CUI Q , LIU J Z , WANG L T , et al. Sustainable deep eutectic solvents preparation and their efficiency in extraction and enrichment of main bioactive flavonoids from sea buckthorn leaves[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2018,184:826−835.
[9] TATJANA J, NIKOLA M, ALEKSANDAR P, et al. The evaluation of phenolic content, in vitro antioxidant and antibacterial activity of Mentha piperita extracts obtained by natural deep eutectic solvents[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,362:130226. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130226
[10] PAULA V DE A P, SHIWAKU I A, MAXIMO G J, et al. Choline chloride-based deep eutectic solvents as potential solvent for extraction of phenolic compounds from olive leaves:Extraction optimization and solvent characterization[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,352:129346.
[11] REZA M, ZEINAB N, MARYAM R, et al. Determination and comparison of total polyphenol and vitamin C contents of natural fresh and commercial fruit juices[J]. Pakistan Journal of Nutrition,2010,9(10):968−972. doi: 10.3923/pjn.2010.968.972
[12] 郎明紫, 刘明明, 解鸿青, 等. 桑黄黄酮的超声波辅助醇提工艺优化及其体外抗氧化活性测定[J]. 蚕业科学,2019,45(2):262−268 LANG M Z, LIU M M, XIE H Q, et al. Optimizing ultrasonic-assisted ethanol extracting conditions of total flavonoids from Phellinus baumii and its antioxidant effect in vitro[J]. Acta Sericologica Sinica,2019,45(2):262−268.
[13] 刘文颖, 冯晓文, 李国明, 等. 牡蛎低聚肽的结构表征及体外抗氧化作用[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(12):261−269 LIU W Y, FENG X W, LI G M, et al. Structure characterization and antioxidant effects in vitro of oyster oligopeptides[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2021,21(12):261−269.
[14] 於雨碟, 张佳妍, 张酥, 等. 桦褐孔菌子实体多糖的提取及体外降血糖活性[J]. 菌物学报,2021,40(1):189−202 YU Y D, ZHANG J Y, ZHANG S, et al. Molecular screening of medicinal fungus Inonotus obliquus and anti-breast cancer activity of its submerged fermentation broth[J]. Mycosystema,2021,40(1):189−202.
[15] 古丽米热•祖努纳, 王伟雄, 吕泽, 等. 药桑葡萄酒发酵工艺优化及体外抗氧化与结合胆酸盐能力研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(5):199−208 GULIMIRE Z, WANG W X, LYU Z, et al. Optimization of fermentation process of grape medicine mulberry wine and its antioxidant and bile acid binding capacity in vitro[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(5):199−208.
[16] 巫永华, 张建萍, 赵节昌, 等. 大孔树脂纯化黄精多酚及其抗氧化性与组成分析[J]. 农业工程学报,2020,36(1):318−326 WU Y H, ZHANG J P, ZHAO J C, et al. Antioxidantion and composition analysis of purified Polygonatum sibiricum polyphenols using macroporous resin [J]. Transactions of the CSAE,2020,36(1):318−326.
[17] BI W T, TIAN M L, ROW K H. Evaluation of alcohol-based deep eutectic solvent in extraction and determination of flavonoids with response surface methodology optimization[J]. Journal of Chromatography A,2013,1285:22−30. doi: 10.1016/j.chroma.2013.02.041
[18] CUI Z F, DJOCKI A V E, YAO J H, et al. COSMO-SAC-supported evaluation of natural deep eutectic solvents for the extraction of tea polyphenols and process optimization[J]. Journal of Molecular Liquids,2021,328:115406. doi: 10.1016/j.molliq.2021.115406
[19] DAI Y T, WITKAMP G J, VERPOORTE R, et al. Tailoring properties of natural deep eutectic solvents with water to facilitate their applications[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,187:14−19. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.03.123
[20] 孔方, 李莉, 刘言娟. 超声辅助低共熔溶剂提取苹果叶中的总黄酮[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(14):134−139,147 doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.14.022 KONG F, LI L, LIU Y J. Ultrasonic-assisted deep eutectic solvents extraction of total flvonoids from apple leaves[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(14):134−139,147. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.14.022
[21] 倪玉娇, 赵春建, 李春英, 等. 超声辅助低共熔溶剂提取沙棘籽粕多酚的工艺优化[J]. 植物研究,2017,37(3):474−480 NI Y J, ZHAO C J, LI C Y, et al. Process optimization of ultrasonic assisted deep eutectic solvents (dess) extraction of polyphenols from Hippophae rhamnoides seed meal[J]. Bulletin of Botanical Research,2017,37(3):474−480.
[22] 李大婧, 宋江峰, 刘春泉, 等. 超声波辅助提取黑豆皮色素工艺优化[J]. 农业工程学报,2009,25(2):273−279 LI D J, SONG J F, LIU C Q, et al. Optimization of technology for ultrasonic-assisted extraction of pigments from black soybean hulls[J]. Transactions of the CSAE,2009,25(2):273−279.
[23] 崔萌, 胡乐根, 马停停, 等. 离子液体在番茄红素提取中的应用研究[J]. 化学研究与应用,2012,24(11):1771−1776 doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1656.2012.11.031 CUI M, HU L G, MA T T, et al. Ultrasonic wave-assisted extraction of lycopene from fresh tomato with ionic liquid[J]. Chemical Research and Application,2012,24(11):1771−1776. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1656.2012.11.031
[24] 尚宪超. 深共熔溶剂提取多酚类化合物的方法研究[D]. 北京:中国农业科学院, 2019 SHANG X C. Study on the extraction of polyphenolic compounds by deep eutectic solvent[D]. Beijing:Chinese Academy of Agricultural Sciences, 2019.
[25] 汪涛, 梁亮, 李旭锐, 等. 低共熔溶剂提取核桃青皮多酚工艺优化及抑菌活性[J]. 农业工程学报,2021,37(5):317−323 WANG T, LIANG L, LI X R, et al. Optimization of the technology for deep eutectic solvents extraction and antibacterial activity of walnut green husk polyphenols[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2021,37(5):317- 323.
[26] 黄皓, 王珍妮, 李莉, 等. 甘油水溶液提取米糠多酚绿色工艺优化及多酚种类鉴定[J]. 农业工程学报,2019,35(4):305−312 doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.04.038 HUANG H, WANG Z N, LI L, et al. Optimization of green extraction process and identification of polyphenols variety from rice bran using glycerol/water system [J]. Transactions of the CSAE,2019,35(4):305−312. doi: 10.11975/j.issn.1002-6819.2019.04.038
[27] 范金波, 蔡茜彤, 冯叙桥, 等. 牛蒡根多酚和黄酮超高压提取工艺优化及体外抗氧化活性[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(6):69−75 doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201506013 FAN J B, CAI X T, FENG X Q, et al. Optimization of process for ultra high pressure-assisted synchronous extraction of polyphenols and flavones from burdock roots and their antioxidant activity [J]. Food Science,2015,36(6):69−75. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201506013
[28] ZHANG L, ZHU M F, TU Z C, et al. α-Glucosidase inhibition, anti-glycation and antioxidant activities of liquidambar formosana hance leaf, and identification of phytochemical profile[J]. South African Journal of Botany,2017,113:239−247. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2017.08.010
[29] 乔锦莉, 张妍, 刘佩, 等. 野生蓝果忍冬多酚鉴定及其抗氧化、降血糖活性[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(11):47−55 doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200709-123 QIAO J L, ZHANG Y, LIU P, et al. Polyphenol composition and antioxidant and hypoglycemic activities in wild blue honeysuckle fruit[J]. Food Science,2021,42(11):47−55. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200709-123
[30] 姚旭, 郦萍, 顾青. 4种甜橙皮黄酮类化合物体外抗氧化活性及降糖降脂功能研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2022,22(1):49−57 YAO X, LI P, GU Q. Studies on antioxidant activity, hypoglycemic and lipid-lowering capacity of flavonoids in sweet orange peels in vitro[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2022,22(1):49−57.
[31] 徐一凡, 部建雯, 吴茂玉, 等. 蒸汽爆破对桑黄功能成分含量及活性的影响[J]. 食品科技,2022,47(7):52−59 XU Y F, BU J W, WU M Y, et al. Effect of steam explosion on content and activity of functional ingredients in Inonotus hispidus[J]. Food Science and Technology,2022,47(7):52−59.
[32] 蔡茜彤. 牛蒡根多酚类化合物提取工艺优化及抗氧化活性的研究[D]. 锦州:渤海大学, 2015 CAI X T. Technological optimization for extraction of polyphenols from burdock and assessment of their antioxidant activity[D]. Jinzhou:Bohai University, 2015.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 李琳,崔彦阁,赵娟娟,石晓丹,许军星,孙路. 调整膳食纤维和肠道菌群对延缓饮食诱导性肥胖的影响研究. 医学动物防制. 2025(02): 177-181 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王远利,王菲,张权,汤木果,陶亮,田洋. 海棠果果酱的研制及其品质分析. 食品工业科技. 2024(11): 175-186 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 毛欣欣,刘婧,梁文欧,蔡诗鸿,李彦勋. 果蔬加工副产物膳食纤维改性研究进展. 农产品加工. 2024(08): 94-98 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李国巍,石雨,张正海,姬妍茹,杨庆丽,董艳,高宝昌,李柏阳. 黑海棠果多酚提取工艺优化及抗氧化活性分析. 中国食品添加剂. 2024(12): 19-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李焱,林泳峰,刘文美,邹泽华,刘红,刘光明,刘庆梅. 食药同源植物多糖调控肠道稳态的研究进展. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2023(02): 25-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 雷延玲. 遮荫条件下栽培模式对草莓品质和产量的影响. 北方果树. 2022(05): 14-17 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



