Separation and Purification of Ginseng Polysaccharide and Its Protective Effect on Skin Damage by UVB
-
摘要: 以药食同源中药材人参为原材料,通过超声辅助热水法提取人参多糖(Ginseng polysaccharides,GPS),经酶解法去除淀粉和蛋白质,再经DEAE-52纤维素柱层析分离纯化得到精制人参多糖(GPS-1)。通过高效凝胶渗透色谱、红外光谱和核磁共振波谱测定了GPS-1的相对分子质量、单糖构成和结构特征,另外研究了GPS-1对人皮肤成纤维细胞(Human skin fibroblasts,HFF-1)存活率和HFF-1中活性氧(Reactive oxygen,ROS)、丙二醛(Malondialdehyde,MDA)、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(Glutathion peroxidase,GSH-Px)、超氧化物歧化酶(Superoxide dismutase,SOD)、金属蛋白酶1(Metalloproteinase 1,MMP-1)和金属蛋白酶9(Metalloproteinase 9,MMP-9)的影响。结果表明,GPS-1为均一性多糖,多糖纯度为95.13%,重均分子量为2.104 kDa,由α-D-葡萄糖、α-D-半乳糖醛酸、α-D-阿拉伯糖、α-D-岩藻糖、α-D-核糖、β-D-甘露糖和β-D-阿拉伯糖构成。GPS-1可保护UVB照射下的HFF-1细胞活性,质量浓度为200 μg/mL的GPS-1溶液即可显著抑制MMP-1和MMP-9的表达(P<0.01),显著提升SOD和GSH-Px的含量(P<0.01),显著降低ROS和MDA的含量(P<0.01),为人参多糖的分离纯化以及在开发抗衰老产品的应用提供了科学依据。
-
关键词:
- 人参多糖 /
- 分离纯化 /
- 中波紫外线(UVB) /
- 抗衰老 /
- 人皮肤成纤维细胞(HFF-1)
Abstract: Ginseng polysaccharide (GPS) was obtained from ginseng, a traditional Chinese medicinal material, through an efficient extraction method in this work. Namely, the extracts of ginseng were first collected by ultrasonic assisted extraction of hot water, then purified through enzymolysis to remove the starch and protein, and finally refined by DEAE-52 cellulose column chromatography to get the desired ginseng polysaccharide (GPS-1). The molecular weight, monosaccharide composition and structure of GPS-1 were determined by high performance gel permeation chromatography, infrared spectroscopy and nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy. In addition, the role of GPS-1 in human skin fibroblasts (HFF-1) survival rate and the effect on reactive oxygen species (ROS), malondialdehyde (MDA), glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px), superoxide dismutase (SOD), metalloproteinase 1 (MMP-1) and metalloproteinase 9 (MMP-9) were studied. The results showed that GPS-1 was a homogeneous polysaccharide with a purity of 95.13% and an average molecular weight of 2.104 kDa, which was composed of α-D-glucose, α-D-galacturonic acid, α-D-arabinose, α-D-fucose, α-D-ribose, β-D-mannose and β-D-arabinose. Moreover, the cell experiments confirmed that GPS-1 could protect HFF-1 cells from UVB irradiation, and the expression of MMP-1 and MMP-9 could be significantly inhibited by GPS-1 solution at the concentration of 200 μg/mL (P<0.01). Further study revealed that GPS-1 could also significantly increase SOD and GSH-Px content (P<0.01) and decrease the contents of ROS and MDA (P<0.01). These results would provide a scientific basis for the isolation and purification of ginseng polysaccharide and its application in the development of anti-aging products. -
皮肤是人体的最外层器官,很容易暴露在紫外线下造成刺激。根据波长的不同,紫外线可以分为UVA(320~400 nm)、UVB(280~320 nm)、UVC(100~280 nm)。大气中的臭氧层对UVC有较强的吸收能力,到达地球表面的紫外线主要是UVA和UVB[1]。UVB的波长处于DNA和蛋白质的吸收峰附近,其辐射是皮肤光化学反应中最活跃部分,诱发的炎症在皮肤光老化中起核心作用[2-3]。过量的UVB辐射导致皮肤组织中的ROS被大量激活,超过了机体的清除能力,导致细胞膜受损,脂质过氧化产生过量MDA,致使细胞凋亡从而引起光老化[4-5]。因此,开发含有天然成分或配方的药物、食物抑制UVB对皮肤的损伤实现抗衰老受到越来越多人的关注。
人参作为一种被广泛使用了几千年的著名中药材,其有效成分包括皂苷、多糖、挥发油和氨基酸等[6]。主要有效成分人参皂苷的研究比较完整,其生理功能已经有了大量的实验依据和证明[7-9]。然而,人参成分中最丰富的多糖(约占总含量的40%)还没有得到充分的研究,此前对人参多糖的研究主要集中在其具有抗氧化作用[10],通过降低组织过氧化程度,保护组织器官免受氧化损伤[11-13]。目前还缺乏人参多糖在皮肤抗衰老方面的研究。抗衰老活性研究中,细胞模型和动物模型都已有报道。董坤等[14]建立了UVB致HFF-1损伤模型,考察草莓叶水提物对UVB致皮肤损伤的保护作用,结果表明草莓叶水提物有助于缓解氧化应激造成的细胞损伤,达到延缓衰老的功效。王慧云[15]通过建立过氧化氢刺激人脐静脉血管内皮细胞诱导的衰老细胞模型发现,党参多糖干预后细胞血清中内皮素-1(Endothelin-1,ET-1)、诱导型一氧化氮合酶(Inducible nitric oxide synthase,iNOS)、ROS含量降低,内皮型一氧化氮合酶(Endothelial nitric oxide synthase,eNOS)含量升高,DNMT1、EZH2、Bmi-1蛋白与基因表达量、细胞DNA甲基化水平也得到了调节,表明党参多糖可以延缓内皮细胞衰老。赵苑伶等[16]分离纯化得到铁皮石斛多糖,以秀丽隐杆线虫为模式生物,研究了铁石斛多糖的抗衰老作用,结果表明铁皮石斛多糖可以显著延长秀丽隐杆线虫的寿命,对高温损伤和氧化应激损伤有一定的抵御作用。朱秋轶等[17]利用秀丽隐杆线虫模型研究羊乳酪蛋白酶解物的抗衰老作用,实验表明羊乳酪蛋白酶解物能延长线虫寿命,降低线虫体内脂褐素积累,提高线虫在应激条件下的抵抗能力和体内抗氧化酶活力,具有较好的抗衰老活性。
由于对分离纯化后的人参多糖在皮肤抗衰老方面的研究较为少见,因此,本文制备了人参精多糖,对其进行均一性测定、波谱表征及延缓皮肤衰老功效评价,为人参多糖的分离纯化及在延缓皮肤衰老方面的应用提供科学依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
人参的干燥根及根茎 河北省安国市药材市场;α-淀粉酶(酶活力4000 U/g)、木瓜蛋白酶(酶活力3000 U/g) 分析纯,麦克林试剂生化科技有限公司;无水乙醇 市售,分析纯;窄分部普鲁兰多糖标准品 日本Shodex公司;Cell Counting Kit-8(CCK-8)试剂盒、人基质活性氧(ROS)ELISA试剂盒、人基质丙二醛(MDA)ELISA试剂盒、人基质谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(GSH-Px)试剂盒、人基质超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)ELISA试剂盒 深圳子科生物科技有限公司;人基质金属蛋白酶1(MMP-1)ELISA试剂盒、人基质金属蛋白酶9(MMP-9)ELISA试剂盒 杭州联科生物技术股份有限公司。
TDZ4-WS离心机 上海卢湘仪离心机仪器有限公司;DNM-9602酶标分析仪 北京普朗新技术有限公司;BHC-1300IIB2生物安全柜 苏州金净净化设备公司;Thermo Forma 3111 CO2恒温培养箱 美国Thermo公司;XDS-500C显微镜 上海蔡康光学仪器有限公司;UV-1750紫外-可见分光光度计、GPC-20A凝胶渗透色谱仪、RID-20A示差折光检测器 日本岛津公司;iS10红外(FT-IR)光谱仪 美国尼高力公司;AVANCE III 400M核磁共振波谱仪 德国BRUKER;TSKgel GMPWXL水相凝胶色谱柱 东曹(上海)生物科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 人参粗多糖(GPS)的制备
参考文献[18]制备人参粗多糖。称取干燥过筛后的人参样品,置于玻璃烧杯内,按料液比1:30(g/mL)加入去离子水,在70 ℃温度、60 Hz超声功率下提取30 min。待溶液冷却后离心(6000 r/min),取上清液。在上清液中加入约4倍体积的无水乙醇溶液,放置在−20 ℃环境中醇沉24 h。过滤收集沉淀,将其放入真空干燥箱(70 ℃)中干燥至恒重,即得人参粗多糖(GPS),备用。
1.2.2 GPS纯化
参考文献[19]对GPS进行纯化。利用α-淀粉酶去除上述提取的GPS的淀粉。精密称取10.0 g GPS,用少量去离子水溶解后转移至1000 mL容量瓶中,用去离子水定容,得到10 mg/mL的GPS溶液。向配制好的GPS溶液中加入800 U α-淀粉酶,50~60 ℃酶解30 min,然后转移至沸水浴中加热5 min终止酶解反应。溶液降至室温后离心(4000 r/min,10 min),收集上清液。
利用木瓜蛋白酶去除上述提取的GPS中的蛋白质。将200 U木瓜蛋白酶加入上述溶液中,30~40 ℃酶解2 h,然后转移至沸水浴中加热5 min终止酶解反应。溶液降至室温后离心(4000 r/min,10 min),收集上清液。
将上清液加热至70 ℃以蒸发除去过多的水分,浓缩至50 mL,向浓缩液加入200 mL无水乙醇,摇匀,−20 ℃冰箱冻存静置24 h,过滤得到白色固体,放置真空干燥箱中烘干(60 ℃)至恒重,得到4.8 g酶解后的GPS。
取酶解后的GPS 4.0 g,配制成10 mg/mL的溶液。溶液用DEAE-52纤维素填料进行柱层析洗脱,以去离子水为洗脱液,使用试管收集,每管收集10 mL。采用苯酚-硫酸法对每管溶液在490 nm处吸光度进行检测,对出现吸收峰的溶液进行收集,将收集的溶液冷冻干燥(−40 ℃),得到2.5 g人参精多糖(GPS-1)。
1.2.3 GPS-1的均一性鉴定及相对分子质量测定
采用高效凝胶渗透色谱法测定GPS-1的相对分子质量和纯度。采用TSKgel GMPWXL水相凝胶色谱柱,以0.1 mol/L NaNO3+0.06% NaN3(质量分数)水溶液为流动相,流速0.6 mL/min,检测温度35 ℃,进样体积20 μL。采用示差折光检测器,窄分部普鲁兰多糖标准品进行对照,对GPS-1的分子量分布进行测试。
1.2.4 GPS-1的初级结构表征
采用溴化钾压片法对GPS-1样品进行FT-IR测试,波数范围:400~4000 cm−1,光谱仪分辨率4 cm−1,信躁比50000:1,扫描64次。采用核磁共振氢谱(1H NMR)和核磁共振碳谱(13C NMR)对GPS-1的初级结构进行表征:称取GPS-1样品5 mg,放入核磁管,加入1 mL氘代试剂(重水)充分溶解样品,检测其1H NMR和13C NMR谱图。
1.2.5 细胞培养、细胞活力测试
采用含10%胎牛血清和1%双抗(青霉素(10000 U/mL)与链霉素(10 mg/L)混合液)的DMEM培养基培养HFF-1细胞,将其置于37 ℃,5% CO2的培养箱中。显微镜下观察HFF-1细胞为贴壁细胞。
将处于对数生长期的细胞经胰蛋白酶消化,显微镜下计数后制成3×104个细胞/L的细胞悬液。分别取100 µL至96孔培养板,每种细胞每块板设置3个复孔,3×103个细胞/孔,然后添加100 µL不同质量浓度的GPS-1溶液,同时以100 µL培养液做空白对照,将培养板放置37 ℃、5% CO2的培养箱中培养过夜。分别处理细胞在0、48 h后,按1:10体积比混合CCK-8和无血清必需基本培养基,每孔100 µL加入待测孔中,在37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱中孵育1 h。用酶标仪测定450 nm波长下培养板每孔吸光度,记录数值。
1.2.6 急性光损伤模型的建立及分组
参照文献[14]建立急性光损伤细胞模型。选择生长状态良好、对数生长期的HFF-1,接种密度3×104个/孔,建立实验分组,每组设置3个复孔。空白对照组:不照射UVB,不加GPS-1溶液,细胞正常培养72 h;UVB照射组:细胞正常培养48 h后,在功率密度68 µW/cm2、照射距离10 cm条件下,UVB辐照100 s后细胞培养24 h;GPS-1高中低剂量组(200、500和800 μg/mL):细胞正常培养24 h后,添加GPS-1溶液和培养基条件下培养24 h,然后在功率密度68 µW/cm2,照射距离10 cm条件下,UVB辐照100 s后,再进行细胞培养24 h。
1.2.7 GPS-1对SOD、MDA、MMP-1、MMP-9、ROS、GSH-Px的影响
培养后,收集细胞上清,按照ELISA试剂盒说明书对SOD、MDA、MMP-1、MMP-9、ROS、GSH-Px含量进行测定。
1.3 数据处理
采用SPSS statistics软件对数据进行One-way ANOVA检验,数据结果以±s表示,以*P<0.05为差异有统计学意义,**P<0.01为差异极其显著。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 GPS-1的纯度及相对分子质量分析
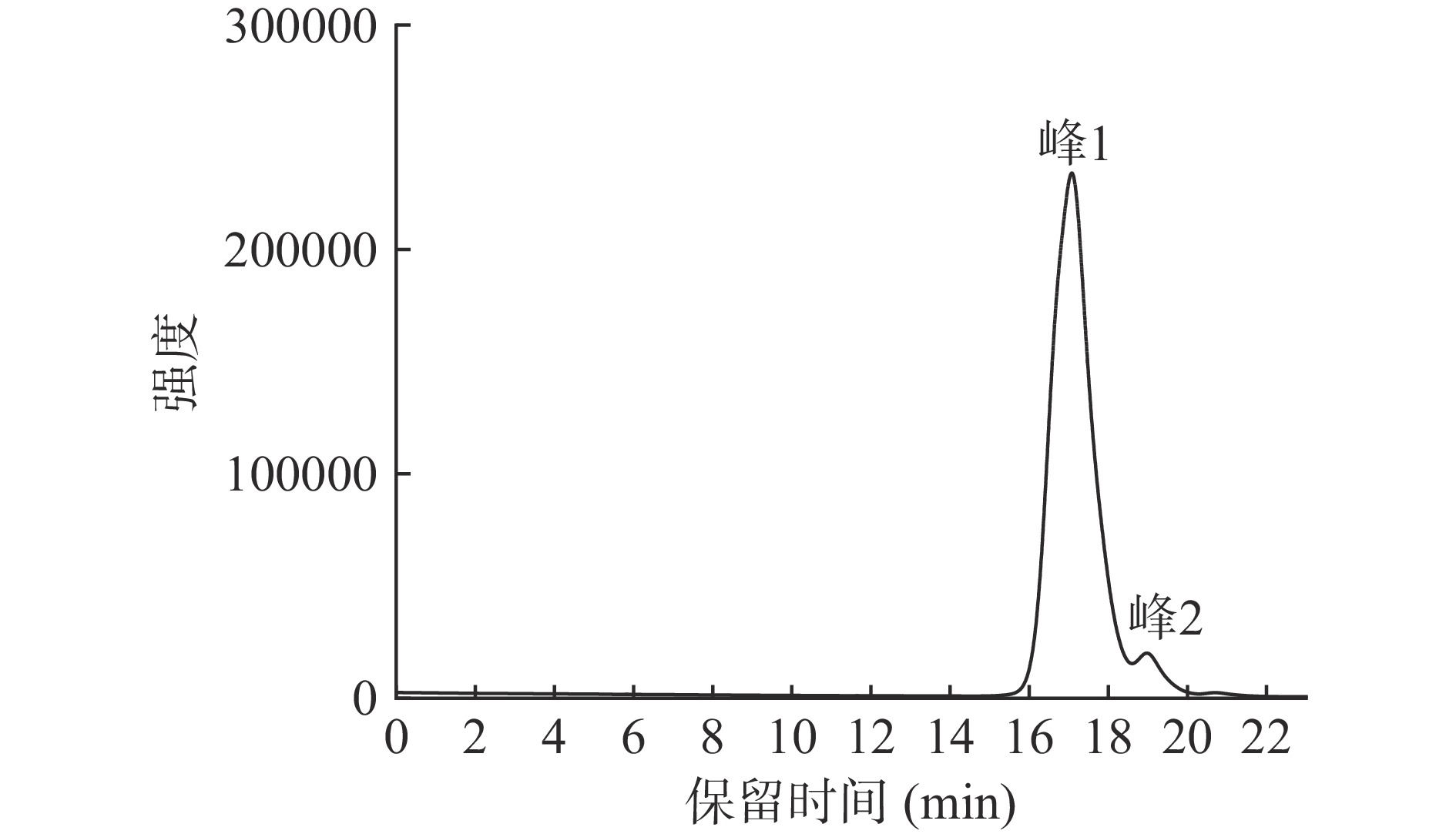
纯化后的人参多糖GPS-1的HPGPC结果显示,分子量分布图(图1)有两个峰,其中峰1峰面积占95.13%,此峰数均分子量(Mn)为1.079 kDa,重均分子量(Mw)为2.104 kDa,分布宽度指数PD(Mw/Mn)为1.95。峰2峰面积占比4.87%,数均分子量(Mn)为0.055 kDa,重均分子量(Mw)为0.072 kDa,分布宽度指数PD(Mw/Mn)为1.29。结果表明GPS-1分子量分布相对均一,多糖纯度为95.13%,相对分子质量较低。
2.2 GPS-1的初级结构表征
2.2.1 GPS-1的红外光谱表征
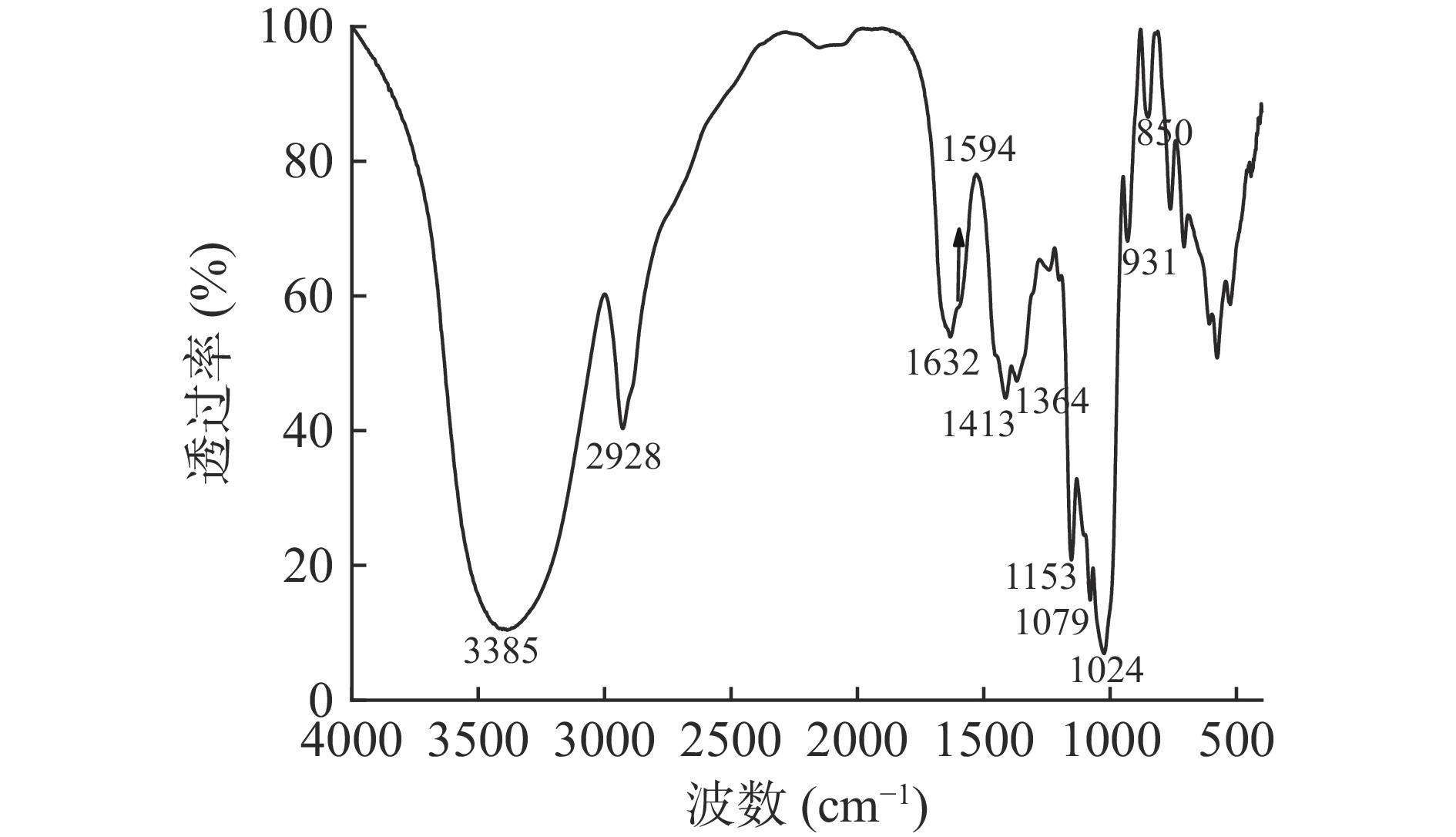
图2为GPS-1的FT-IR谱图,该谱图表现出多糖的特征吸收峰,分别在3385、2928、1632、1594、1413、1364、1153、1079、1024、931和850 cm−1处出现特征吸收峰。在3385 cm−1附近出现相对较宽的强吸收峰,是由分子间或分子内的O-H伸缩振动引起的,表明样品含多糖羟基。2928 cm−1附近的肩峰,是由C-H或O-H的伸缩振动引起的特征吸收峰[20]。1632 cm−1是C=O非对称伸缩振动峰,是未酯化的糖醛酸羧基特征峰[21];1413 cm−1处为C-H的变形吸收峰。在1200~1000 cm−1区间的多糖特征吸收峰是由C-O-C和C-O-H的伸缩振动引起的[20]。在1024、1079和1153 cm−1处分别有三个吡喃糖特征吸收峰,表明该样品多糖结构为吡喃糖环状结构。α-型或β-型吡喃葡萄糖通常在960~730 cm−1内有特征吸收峰,其中,在844±8 cm−1处有吸收峰为α-型异构体,在891±7 cm−1处有吸收峰为β-型异构体[22]。该样品的红外谱图在891 cm−1处无吸收峰,在850 cm−1处出现明显的吸收峰,表明存在α-D-吡喃葡萄糖[23]。红外光谱分析结果表明GPS-1存在α-D-吡喃葡萄糖构型。
2.2.2 GPS-1的核磁表征
糖苷异头氢的1H NMR信号一般处于δ 4.2~5.8 ppm范围,其中,α-型糖苷的异头质子处于δ 4.8~5.8 ppm范围内,β-型糖苷的异头质子处于δ 4.2~4.8 ppm范围[24]。图3显示,δ 4.7 ppm为重水溶剂峰,δ 3.2~4.0 ppm为人参多糖糖环上的质子信号。人参多糖糖苷键的质子化学位移在δ 4.5~5.4 ppm范围内,表明含有α-型和β-型两类糖苷键。在糖苷键质子共振区δ 4.2~5.8 ppm范围内出现7个信号峰,表明样品由7种单糖组成。根据文献[25]报道推断氢谱上7个信号δ 5.31 ppm、δ 5.27 ppm、δ 5.14 ppm、δ 5.13 ppm、δ 4.88 ppm、δ 4.57 ppm、δ 4.56 ppm分别归属为α-D-葡萄糖、α-D-半乳糖醛酸、α-D-阿拉伯糖、α-D-岩藻糖、α-D-核糖、β-D-甘露糖、β-D-阿拉伯糖糖苷键质子信号。
13C NMR谱图中,糖苷碳的信号共振区通常在δ 95~110 ppm范围内。根据图4可知,δ 100.33 ppm、δ 99.94 ppm、δ 99.69 ppm、δ 99.58 ppm、δ 98.57 ppm、δ 98.25 ppm、δ 95.75 ppm分别对应七种单糖的糖苷碳,表明GPS-1含有七种单糖成分,与其1H NMR结果一致。糖环上化学位移一般在δ 50~85 ppm范围内,其中,未发生取代的C6在δ 60~63 ppm附近,连接到另一个糖残基的C6特征峰出现在δ 65~70 ppm附近;糖环上C2、C3、C4位置未发生取代时特征信号峰在δ 70~77 ppm范围内,糖环上C2、C3、C4位置发生取代时特征信号峰在δ 77 ppm以上[26]。图4中GPS-1信号在δ 68~69.5 ppm范围内有特征峰,说明C6位发生取代;在δ 70~77 ppm范围内出现明显的特征峰,可以判断GPS-1在C2、C3、C4位置未发生取代。
2.3 GPS-1对正常生长HFF-1细胞增殖的影响
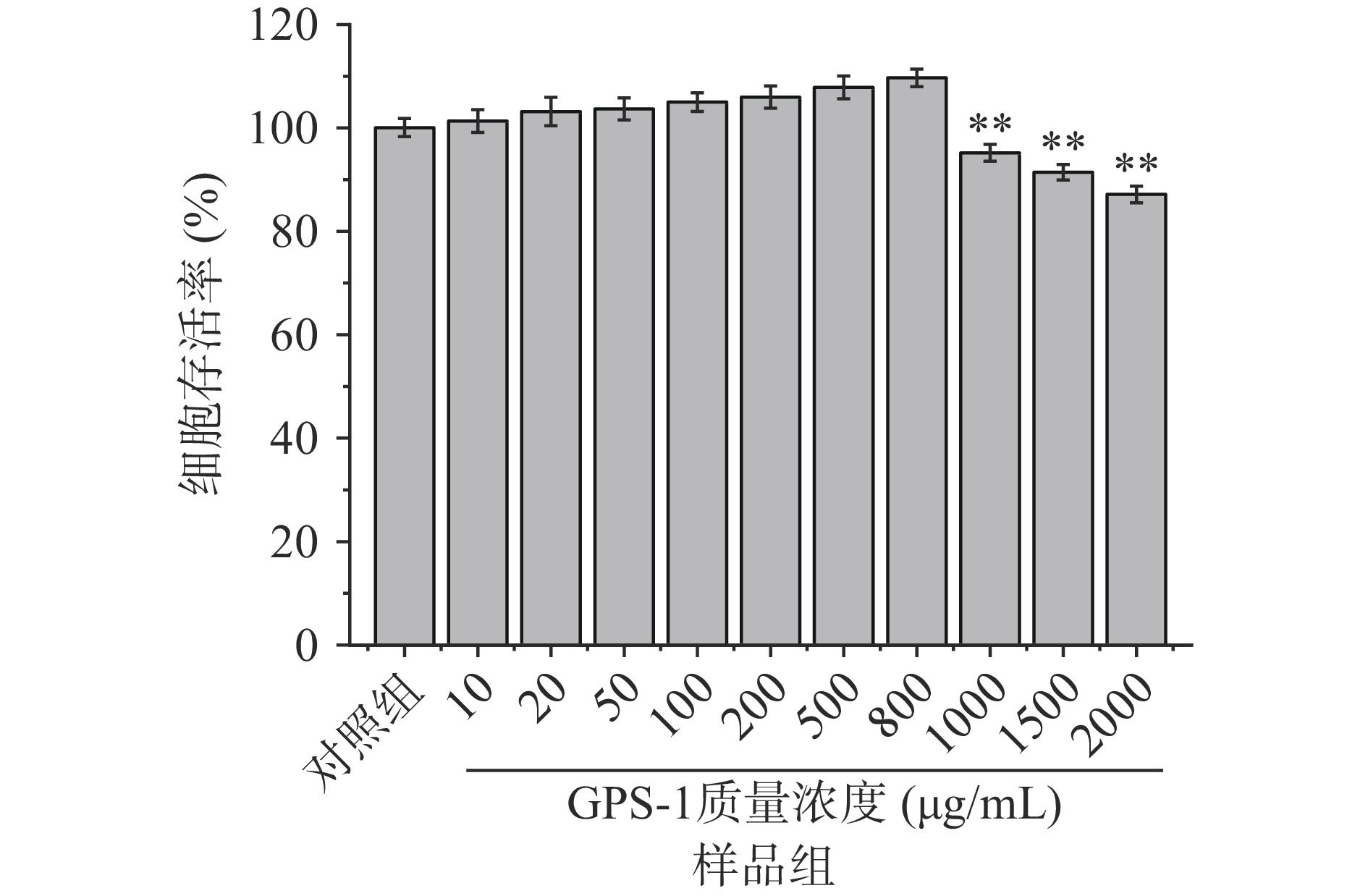
本实验使用可快速高灵敏度检测细胞增殖和细胞毒性的CCK-8试剂盒,考察GPS-1对正常生长HFF-1细胞增殖情况的影响。细胞存活率是可直接表达各组细胞状态的指标,反映细胞增殖情况,细胞存活率越高说明细胞状态越好[27]。由图5可知,与对照组相比,当GPS-1的质量浓度小于等于800 μg/mL时,对HFF-1细胞存活率无显著影响(P>0.05)。当GPS-1的质量浓度大于800 μg/mL时,HFF-1细胞存活率降低,GPS-1质量浓度增至2000 μg/mL时,细胞活率降至87.1%(P<0.01)。最终选取200、500和800 μg/mL三个质量浓度用于后续实验。
2.4 GPS-1对UVB致HFF-1细胞损伤的保护作用
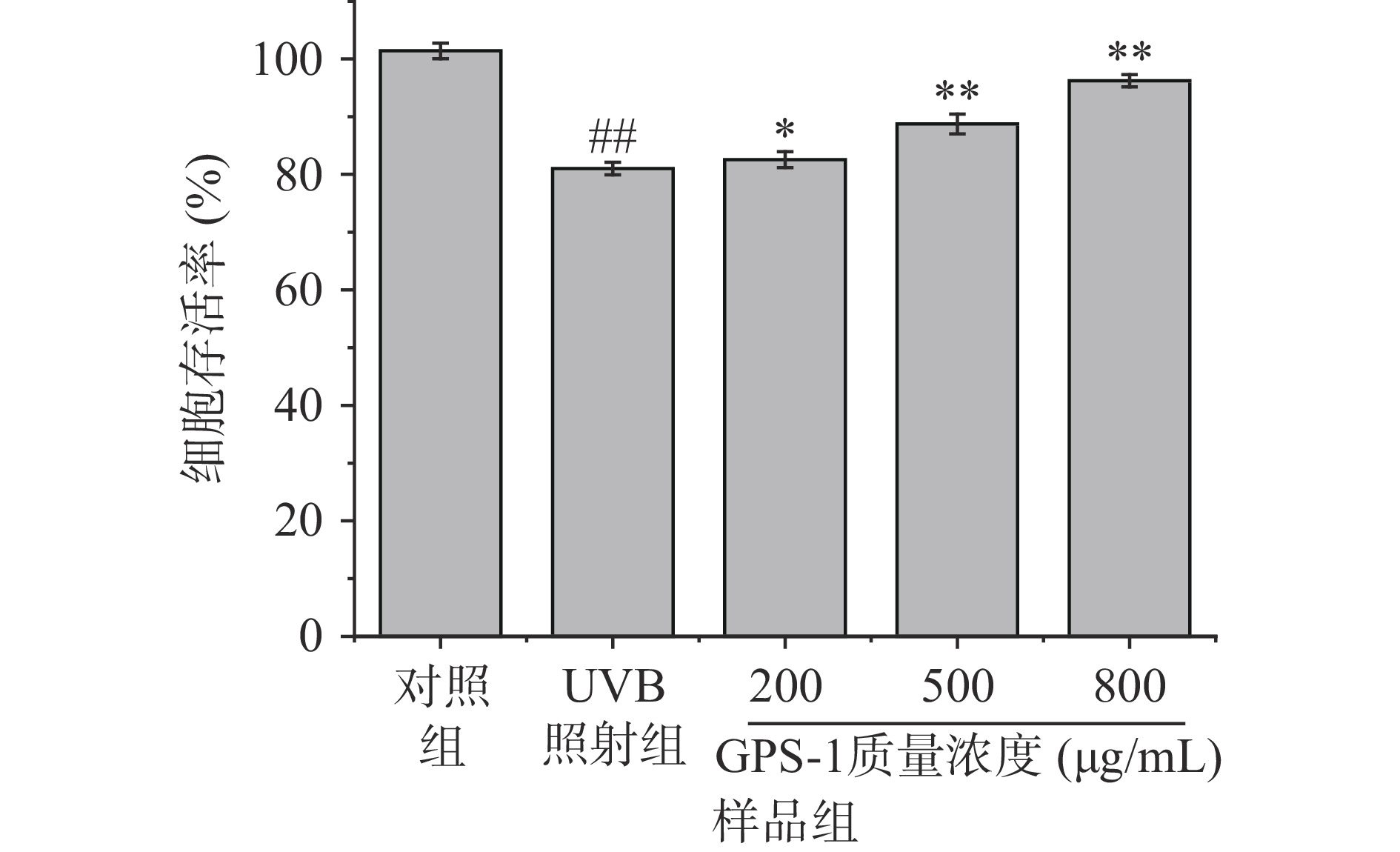
由图6可知,经UVB辐射后,与对照组相比,UVB照射组细胞存活率下降了20.1%,细胞存活率显著降低(P<0.01),说明UVB致HFF-1细胞损伤模型建立成功。而经GPS-1保护干预后,与UVB照射组相比,GPS-1质量浓度分别为200、500和800 µg/mL时,细胞存活率分别增加了1.9%(P<0.05)、9.5%(P<0.01)和18.8%(P<0.01),均具有显著性差异,说明GPS-1对UVB损伤HFF-1细胞具有明显的保护作用,在GPS-1质量浓度为200~800 µg/mL范围内,随着质量浓度增高,对损伤细胞的保护作用随之增强。
2.5 GPS-1对UVB照射组细胞内SOD、MDA、ROS、GSH-Px、MMP-1、MMP-9的影响
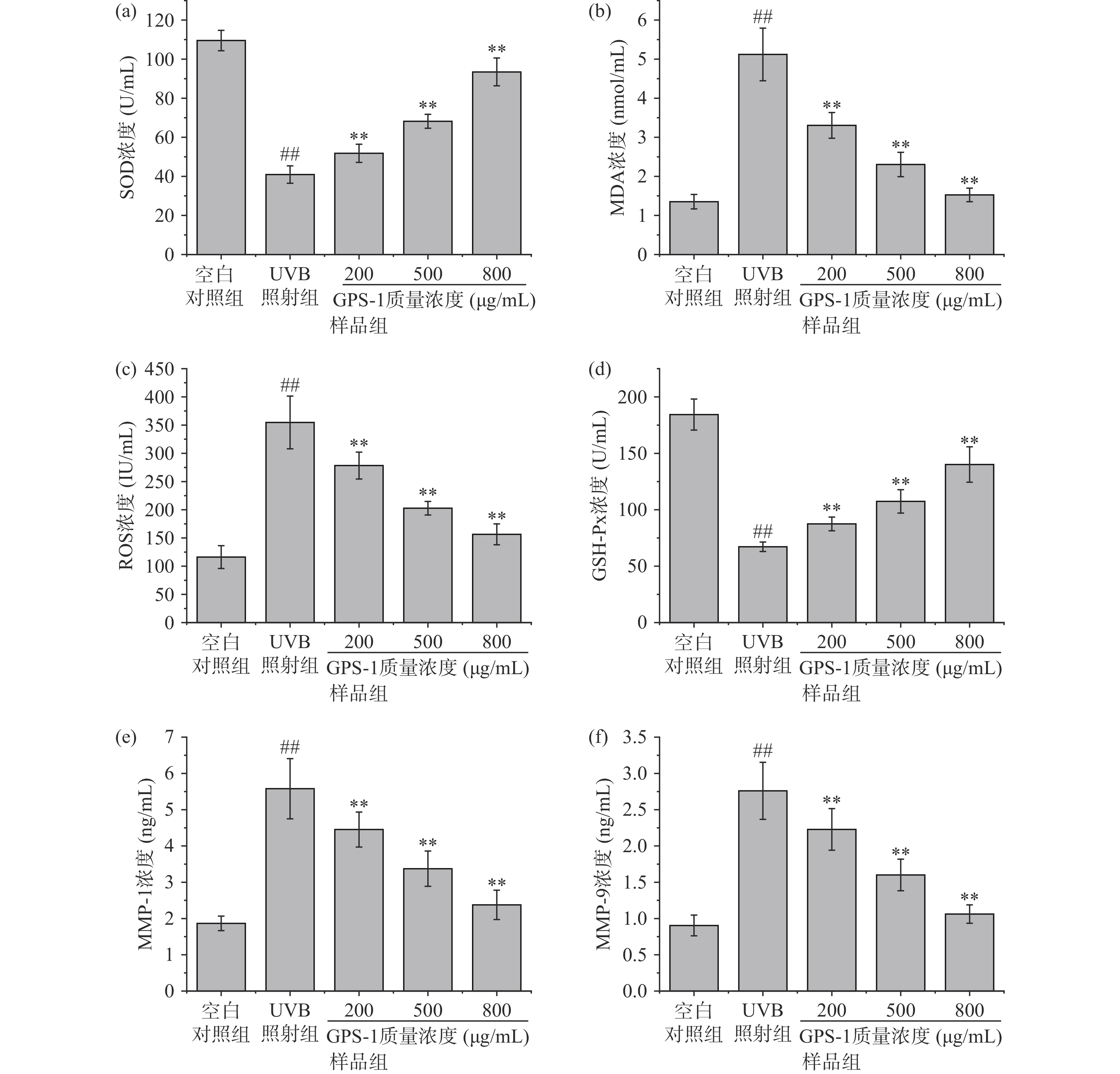
皮肤成纤维细胞是合成胶原及弹性纤维的主要场所,虽然此种细胞位于真皮层,但更易发生氧化损伤[28]。当UVB照射成纤维细胞时,细胞内SOD和GSH-Px抗氧化酶的活性受到抑制,当大量的ROS未能得到及时清除出现氧化应激反应,将破坏细胞内脂质、蛋白质、核酸等大分子物质,激活基质金属蛋白酶表达,导致脂质分解,引发脂质过氧化反应,形成过氧化脂质产物(MDA)[14]。因此,测定MDA含量,可间接反映细胞损伤程度,而SOD作为衡量机体抗氧化能力大小的重要因素,可反映细胞消除ROS的能力[29]。
如图7所示,与空白对照组相比,UVB照射组HFF-1细胞中ROS和MDA含量显著增高(P<0.01),SOD和GSH-Px酶活力显著降低(P<0.01),说明UVB照射对HFF-1有明显损伤作用,大量的ROS未能被细胞清除,同时导致生成过量的MDA,造成细胞氧化损伤,引起机体衰老。与UVB照射组相比,经GPS-1保护干预后,HFF-1中ROS含量降低,GPS-1低、中、高剂量组分别下降了21.5%、42.8%、56.5%,且具有显著性差异(P<0.01),说明GPS-1可有效降低因UVB刺激产生的ROS。同样地,当GPS-1质量浓度分别为200、500和800 μg/mL时,HFF-1中MDA含量降低,分别为4.9、3.4、2.9 nmol/mL(P<0.01),呈剂量依赖性。与UVB照射组相比,当GPS-1质量浓度分别为200、500和800 μg/mL时,SOD含量分别提高了32.5%、75.0%、128.9%(P<0.01),说明GPS-1显著提升HFF-1细胞SOD活力。与UVB照射组相比,当GPS-1质量浓度分别为200、500和800 μg/mL时,GSH-Px含量分别提高了29.7%、59.9%、108.3%(P<0.01),说明GPS-1可以调节HFF-1细胞GSH-Px含量。在衰老细胞中,ROS和MDA含量显著增加,SOD和GSH-Px酶活力显著降低,在该模型下,GPS-1能有效减少细胞中ROS和MDA含量,有效提高SOD和GSH-Px酶活力,说明GPS-1能够通过减少ROS含量,防止细胞产生氧化应激,对MDA的产生具有抑制作用,降低细胞氧化损伤,同时促进细胞内SOD和GSH-Px活力提升,提高细胞抗氧化能力,从而帮助细胞对抗由UVB诱导引起的细胞衰老。
基质金属蛋白酶(MMPs)是一种具有广泛特异性的而且几乎可以分解所有细胞外基质成分的水解酶。MMP-1特异性降解I型胶原蛋白,使得I、III型胶原比例下降,MMP-9作为一种明胶酶,可以继续降解MMP-1降解产物,导致皮肤胶原蛋白流失,继而发生衰老发生[30]。如图7e、图7f所示,与UVB线照射组相比,低剂量的人参多糖即可极显著降低HFF-1细胞内MMP-1和MMP-9的含量(P<0.01),而当添加高剂量的人参多糖时,MMP-1和MMP-9含量接近正常未经UVB照射组细胞内水平,说明人参多糖可以抑制MMP-1和MMP-9的表达,达到减少胶原分解的功效,改善细胞结构,从而具有延缓皮肤衰老的效果。
3. 结论
本实验以人参为原料,通过提取分离纯化得到人参精多糖。采用高效凝胶渗透色谱法对人参精多糖进行分析,结果表明该人参多糖为均一性多糖,相对分子质量为2.104 kDa,多糖纯度为95.13%,另外通过红外光谱、核磁谱图对人参结构进行了初步分析。进一步利用UVB照射HFF-1细胞模型,通过ROS、MDA、SOD、GSH-Px、MMP-1和MMP-9等指标的测定,对人参精多糖进行抗皮肤衰老的探究。实验结果表明人参精多糖可有效去除细胞中的ROS,抑制MDA的含量,缓解由外源条件(UVB)造成的细胞受损,同时,促进SOD和GSH-Px抗氧化酶活提升,提高细胞抗氧化能力,通过维持氧化还原平衡来达到抗衰老的作用,为皮肤提供有利的组织环境;此外,人参精多糖还可抑制MMP-1和MMP-9的表达,达到减少胶原分解的功效,维持皮肤弹性,延缓皮肤衰老。因此,人参多糖具有一定的抗皮肤衰老作用,可作为一种延缓衰老功效原料,应用于化妆品、保健品等领域,可以有力提升人参的市场竞争能力,进一步提高经济效益。
-
-
[1] BAI F, FAN C, LIN X, et al. Hemin protects UVB-induced skin damage through inhibiting keratinocytes apoptosis and reducing neutrophil infiltration[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology,2023,238:112604. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotobiol.2022.112604
[2] 邓映, 钟建桥. 皮肤光损伤与氧化应激研究进展[J]. 临床皮肤科杂志,2017,46(9):671−673. [DENG Y, ZHONG J Q. Advances in skin photodamage and oxidative stress[J]. Journal of Clinical Dermatology,2017,46(9):671−673. DENG Y, ZHONG J Q. Advances in skin photodamage and oxidative stress[J]. Journal of Clinical Dermatology, 2017, 46(9): 671-673.
[3] 殷花, 林忠宁, 朱伟. 皮肤光老化发生机制及预防[J]. 环境与职业医学,2014,31(7):565−569. [YIN H, LIN Z N, ZHU W. Mechanisms and prevention of skin photoaging[J]. Journal of Environmental and Occupational Medicine,2014,31(7):565−569. YIN H, LIN Z N, ZHU W. Mechanisms and prevention of skin photoaging[J]. Journal of Environmental and Occupational Medicine, 2014, 31(7): 565-569.
[4] DENG L, LI Y, WU Q, et al. Investigating potential ferroptosis-related differentially expressed genes of UVB-induced skin photodamage[J]. International Journal of Dermatology,2023,62:79−87. doi: 10.1111/ijd.16472
[5] LEE H, KIM S Y, LEE S W, et al. Amentoflavone-enriched Selaginella rossii protects against ultraviolet- and oxidative stress-induced aging in skin cells[J]. Life,2022,12(12):2106−2106. doi: 10.3390/life12122106
[6] TAO R Z, LU K Q, ZONG G F, et al. Ginseng polysaccharides: Potential antitumor agents[J]. Journal of Ginseng Research, 2022, in press.
[7] 董微, 郜玉钢, 何忠梅, 等. 人参中人参皂苷提取分离研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2014(17):366−369. [DONG W, GAO Y G, HE Z M, et al. Research progress in extraction and separation technology of ginsenosides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2014(17):366−369. DONG W, GAO Y G, HE Z M, et al. Research progress in extraction and separation technology of ginsenosides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2014(17): 366-369.
[8] 赵信平, 徐龙权, 宋建国, 等. 人参皂苷Rb3木糖苷酶的纯化及其酶学性质[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(17):112−117. [ZHAO X P, XU L Q, SONG J G, et al. Purification and characterization of ginsenoside Rb3 xylosidase[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(17):112−117. ZHAO X P, XU L Q, SONG J G, et al. Purification and characterization of ginsenoside Rb3 xylosidase[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2018, 39(17): 112-117.
[9] 赵钰, 刘春莹, 赵妍, 等. 人参果浆中人参皂苷Re的提取和生物转化[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(4):25−30. [ZHAO Y, LIU C Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Extraction and biotransformation of ginsenoside Re from ginseng fruit pulp[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(4):25−30. ZHAO Y, LIU C Y, ZHAO Y, et al. Extraction and biotransformation of ginsenoside Re from ginseng fruit pulp[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(4): 25-30.
[10] 李珊珊, 祝贺, 祁玉丽, 等. 人参果多糖的分离纯化及体外抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(4):73−76, 99. [LI S S, ZHU H, QI Y L, et al. Research on extraction, purification and antioxidant activity in vitro of polysaccharide from ginseng berry[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(4):73−76, 99. LI S S, ZHU H, QI Y L, et al. Research on extraction, purification and antioxidant activity in vitro of polysaccharide from ginseng berry[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2018, 39(4): 73-76, 99.
[11] 杨松, 王隶书, 刘美辰, 等. 人参多糖对氧化应激损伤肝细胞的保护作用机制研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(5):280−285,292. [YANG S, WANG L S, LIU M C, et al. Mechanism of protective effect of ginseng polysaccharide on hepatocytes induced by oxidative stress[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(5):280−285,292. YANG S, WANG L S, LIU M C, et al. Mechanism of protective effect of ginseng polysaccharide on hepatocytes induced by oxidative stress[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(5): 280-285, 292.
[12] 王顺鹏, 韩翰. 人参多糖抗氧化延缓衰老作用研究进展[J]. 沈阳医学院学报,2020,22(1):87−89. [WANG S P, HAN H. Research progress on anti-aging effects of ginseng polysaccharide through anti-oxidation[J]. Journal of Shenyang Medical College,2020,22(1):87−89. WANG S P, HAN H. Research progress on anti-aging effects of ginseng polysaccharide through anti-oxidation[J]. Journal of Shenyang Medical College, 2020, 22(1): 87-89.
[13] GUO M K, SHAO S, WANG D, et al. Recent progress in polysaccharides from Panax ginseng CA Meyer[J]. Food & Function,2021,12(2):494−518.
[14] 董坤, 翟文丽, 王兰青, 等. 草莓叶水提物对UVB致皮肤损伤的保护作用[J]. 精细化工,2021,38(4):806−814. [DONG K, ZHAI W L, WANG L Q, et al. Protective effect of strawberry (Fragaria×Ananassa) leaves water extract on skin damage by UVB[J]. Fine Chemicals,2021,38(4):806−814. DONG K, ZHAI W L, WANG L Q, et al. Protective effect of strawberry (Fragaria×Ananassa) leaves water extract on skin damage by UVB[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2021, 38(4): 806-814.
[15] 王慧云. 党参多糖对活性氧诱导的血管内皮细胞衰老的影响及机制研究[D]. 兰州: 甘肃中医药大学, 2018 WANG H Y. Study on the effect and mechanism of Codonopsis pilosula polysaccharide on the senescent vascular endothelial cells induced by active oxygen[D]. Lanzhou: Gansu University of Chinese Medicine, 2018.
[16] 赵苑伶, 张雪, 陈林珍, 等. 铁皮石斛多糖的分离纯化及抗衰老活性研究[J]. 世界中医药,2022,17(17):2410−2415. [ZHAO Y L, ZHANG X, CHEN L Z, et al. Separation, purification, and anti-aging activity of Caulis Cendrobii Officinalis polysaccharides[J]. World Chinese Medicine,2022,17(17):2410−2415. ZHAO Y L, ZHANG X, CHEN L Z, et al. Separation, purification, and anti-aging activity of Caulis Cendrobii Officinalis polysaccharides[J]. World Chinese Medicine, 2022, 17(17): 2410-2415.
[17] 朱秋轶, 宋玉, 刘星雨, 等. 羊乳酪蛋白酶解物对秀丽线虫衰老的改善作用[J/OL]. 现代食品科技, 2022: 1−9. doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2023.4.0466. SONG Q Y, SONG Y, LIU X Y, et al. Effect of goat milk casein hydrolysates on senescence of Caenorhabditis elegans[J/OL]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2022: 1−9. doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2023.4.0466.9078.2023.4.0466.
[18] 赵立春, 张亚玉, 李小沛, 等. 人参多糖3种提取工艺的优化比较[J]. 江苏农业科学,2019,47(21):254−260. [ZHAO L C, ZHANG Y Y, LI X P, et al. Optimization and comparison of three extraction processes of ginseng polysaccharide[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences,2019,47(21):254−260. ZHAO L C, ZHANG Y Y, LI X P, et al. Optimization and comparison of three extraction processes of ginseng polysaccharide[J]. Jiangsu Agricultural Sciences, 2019, 47(21): 254-260.
[19] 黄冬婷, 黄俊生, 汤静洁, 等. 超声辅助离子液体提取人参多糖工艺及其抗氧化活性[J]. 精细化工,2022,39(9):1851−1857,1871. [HUANG D T, HUANG J S, TANG J J, et al. Ultrasonic-assisted ionic liquid extraction of ginseng polysaccharide and its antioxidant activity[J]. Fine Chemicals,2022,39(9):1851−1857,1871. HUANG D T, HUANG J S, TANG J J, et al. Ultrasonic-assisted ionic liquid extraction of ginseng polysaccharide and its antioxidant activity[J]. Fine Chemicals, 2022, 39(9): 1851-1857, 1871.
[20] YU X H, LIU Y, WU X L, et al. Isolation, purification, characterization and immunostimulatory activity of polysaccharides derived from American ginseng[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2017,156:9−18. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.08.092
[21] 郑艳. 西洋参多糖的分离纯化及结构研究[D]. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2015 ZHENG Y. Purification and structural analysis of the polysaccharides from Panax quinguefolius[D]. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2015.
[22] 盈盈. 一种低分子量中性人参多糖的提纯与表征[D]. 北京: 北京林业大学, 2018 CHEN Y Y. Purification and characterization of a low molecular weight polysaccharide from Panax ginseng by enzymatic hydrolysis[D]. Beijing: Beijing Forestry University, 2018.
[23] NI W, ZHANG X, BI H T, et al. Preparation of a glucan from the roots of Rubus crataegifolius Bge. and its immunological activity[J]. Carbohydrate Research,2009,344(18):2512−2518. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2009.08.042
[24] WANG F X, WANG W, HUANG Y L, et al. Characterization of a novel polysaccharide purified from a herb of Cynomorium songaricum Rupr[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2015,47:79−86. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.01.006
[25] HE P F, HE L, ZHANG A Q, et al. Structure and chain conformation of a neutral polysaccharide from sclerotia of Polyporus umbellatus[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2017,155:61−67. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.08.041
[26] 李先华. 人参多糖的分离、纯化及结构研究[D]. 长春: 东北师范大学, 2007 LI X H. Isolation, purification and structural analysis of the polysaccharides from Panax ginseng[D]. Changchun: Northeast Normal University, 2007.
[27] 王振. 不同茶类抗UVB致表皮细胞衰老作用研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2018 WANG Z. Study on anti-aging effect of different tea against UVB induced epidermal cells[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2018.
[28] 李振洁, 彭丽倩, 高爱莉, 等. 枸杞多糖对紫外线致人皮肤成纤维细胞脂质损伤的防御作用[J]. 中国激光医学杂志,2017,26(3):127−132. [LI Z J, PENG L Q, GAO A L, et al. Effect of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on UV-mediated lipid peroxide damage of HSF cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Laser Medicine & Surgery,2017,26(3):127−132. LI Z J, PENG L Q, GAO A L, et al. Effect of Lycium barbarum polysaccharide on UV-mediated lipid peroxide damage of HSF cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Laser Medicine & Surgery, 2017, 26(3): 127-132.
[29] 李强, 李宏彬, 布海霞, 等. 二氧化硫对小鼠肺组织超氧化物歧化酶活性及丙二醛含量的影响[J]. 新乡医学院学报,2009,26(3):251−253. [LI Q, LI H B, BU H X, et al. Effect of sulfur dioxide on the activity of superoxide dismutase and the concentration of malondialdehyde in the lung tissue of mice[J]. Journal of Xinxiang Medical College,2009,26(3):251−253. LI Q, LI H B, BU H X, et al. Effect of sulfur dioxide on the activity of superoxide dismutase and the concentration of malondialdehyde in the lung tissue of mice[J]. Journal of Xinxiang Medical College, 2009, 26(3): 251-253.
[30] MONDAL S, ADHIKARI N, BANERJEE S, et al. Matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and its inhibitors in cancer: A minireview[J]. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry,2020,194:112260. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2020.112260
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 代莹,刘双能,刘晋琦,邢莉那,朱童,周素梅,芦晶. 多重酶解协同制备绿豆基植物乳及其品质分析. 食品科技. 2024(09): 175-183 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
