Isolation, Identification, Optimization of Fermentation Conditions and Application of β-Phenylethanol-producing Yeast from Natural Soy Sauce Mash
-
摘要: 为了提升酱油品质,开展筛选产β-苯乙醇的酵母菌,并应用在高盐稀态发酵酱油酿造的研究。从天然酱醪中筛选出产β-苯乙醇的酵母菌株J13,对其进行形态学观察、生理生化实验及分子生物学鉴定,通过耐盐性、pH耐受性及温度耐受性分析研究Z. rouxii 13的生物学特性,并采用单因素和正交试验对培养基成分及发酵条件进行优化,在最优发酵条件下培养Z. rouxii 13,获得风味液并应用到高盐稀态发酵酱油的酿造工艺中。结果表明,J13鉴定为鲁氏接合酵母(Zygosaccharomyces rouxii),并命名为Z. rouxii 13,能在含盐量较高(18% NaCl)条件下生长,最适pH为4~8及最适温度为20~35 ℃,其产β-苯乙醇的最优发酵条件为:L-苯丙氨酸4 g/L、葡萄糖30 g/L、蛋白胨10 g/L、硫酸镁0.5 g/L、磷酸氢二钾5 g/L、NaCl 50 g/L、pH6.0,温度28 ℃,在此条件下β-苯乙醇含量达到1.40 g/L。该风味液用于酱油酿造获得成品的感官评定结果表明,相比不添加风味液的空白对照组,风味液组的酱香和醇厚感更突出,鲜味及整体评价更佳。Abstract: To improve the quality of soy sauce, this paper presented a study on the production of β-phenylethanol by Zygosaccharomyces rouxii and its application in the brewing of high-salt liquid-state fermented soy sauce. The β-phenylethanol-producing yeast strain J13, screened from natural sauce mash, was identified by morphological observation, physiological and biochemical results and molecular biological methods. The biological characteristics of Z. rouxii 13 through salt tolerance, pH tolerance and temperature tolerance analysis were studied. A series of single-factor and orthogonal tests were conducted to get the optimized medium composition and fermentation conditions for this strain. Z. rouxii 13 was then cultured under the optimal fermentation conditions to obtained flavor liquid and applied to the brewing process of high-salt liquid-state fermented soy sauce. The results showed that J13 was identified as Zygosaccharomyces rouxii, named Z. rouxii 13 accordingly. Z. rouxii 13 could successfully grow under high salinity (18% NaCl) conditions. The optimum pH was 4~8 and the optimum temperature was 25~35 ℃. Under the optimal fermentation conditions: L-phenylalanine concentration of 4 g/L, glucose concentration of 30 g/L, peptone concentration of 10 g/L, magnesium sulfate concentration of 0.5 g/L, dipotassium hydrogen phosphate concentration of 5 g/L, NaCl concentration of 50 g/L, pH6.0, and temperature of 28 ℃, the highest content with β-phenylethanol of 1.40 g/L was obtained. The flavor liquid was applied to soy sauce brewing and the finished products were obtained. The sensory evaluation showed that the flavor liquid group had more prominent soy sauce flavor and fullness, and better umami and overall evaluation compared with the control group that without flavor liquid.
-
Keywords:
- soy sauce /
- β-phenylethanol /
- Zygosaccharomyces rouxii /
- flavor liquid /
- brewing
-
酱油的生产工艺主要分为高盐稀态发酵和低盐固态发酵,前者发酵周期长,耐盐微生物能充分发挥作用[1-2],产生大量有机酸类、醇类、酯类等物质,使成品香气更加浓郁、色泽更加鲜艳[3-5]。这与醇类物质在其中发挥的作用密不可分[6],一方面,这类物质在酱油风味成分中占有很大的比重,能为酱油带来协调、柔和的口感;另一方面,又对酯类物质形成具有重要作用[7-8]。
在对高盐稀态发酵酱油香气成分的研究中发现,具有玫瑰型香气的β-苯乙醇常常作为其中一种特征风味物质被检出,且具有较高的香气活性值(odor activity value,OAV)[9-12],此外,Wang等[13]通过芳香萃取物稀释分析(Aroma extract dilution analysis,AEDA)验证了β-苯乙醇是高盐稀态发酵酱油11种关键香气化合物之一,说明β-苯乙醇对酱油的香气组成有重要贡献,可为酱油提供花香[14]。彭东等[15]将筛选出的耐盐生香酵母应用到酱油酿造中发现,β-苯乙醇为主要特征香气物质之一。Yao等[16]研究发现单独接种鲁氏接合酵母能提升β-苯乙醇等醇类物质的含量。此外,阮志强等[17]通过研究发酵过程优势真菌与风味物质相关性分析发现,接合酵母属与β-苯乙醇等多种醇类及酯类物质呈显著正相关。
尽管目前已有许多针对酱油酿造中的耐盐产香微生物进行分离筛选的研究[18-19],但少有以产β-苯乙醇菌株的筛选为目的,并找到与实际生产相适应的工艺,从而提升酱油风味的报道。本研究从高盐稀态发酵酱醪中筛选出一株产β-苯乙醇的耐盐酵母,在对其产β-苯乙醇发酵条件进行优化的基础上,将富含β-苯乙醇的风味液与盐水进行调配,并应用到高盐稀态发酵酱油的酿造中,旨在进一步提升酱油品质。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
发酵50 d酱醪样品 取自李锦记(新会)食品有限公司;面粉、黄豆、食盐 均为市售;酱油曲精(沪酿3.042米曲霉) 购于济宁祥园生物科技有限公司;β-苯乙醇 色谱纯,上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;二氯甲烷 色谱纯,天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司;果糖、D-半乳糖、L-苯丙氨酸、2,3,5-三苯基氯化四氮唑(TTC) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;葡萄糖、蔗糖、硫酸铵、氯化钠、氯化铵、麦芽糖及其他生化试剂 分析纯,广州化学试剂厂;尿素、硫酸镁、磷酸氢二钾 分析纯,广州市金华大化学试剂有限公司;三羟甲基氨基甲烷(Tris) 北京酷来搏科技有限公司;酵母浸膏、麦芽汁培养基 广东环凯微生物科技有限公司;DNA抽提试剂盒(真菌) Omega USA;PCR引物 擎科生物;TTC双层培养基:上层:葡萄糖5 g、琼脂粉15 g、TTC试剂0.5 g,蒸馏水1000 mL;下层:葡萄糖10 g、蛋白胨2 g、酵母膏1.5 g、MgSO4·7H2O 4 g、K2HPO4 1 g、琼脂粉20 g,蒸馏水1000 mL,调节pH5.6~5.8,121 ℃灭菌15 min;YPD 培养基:酵母膏 10 g,葡萄糖 20 g,蛋白胨20 g,琼脂粉 20 g,115 ℃ 灭菌 20 min;转化培养基:L-苯丙氨酸 4 g、葡萄糖 30 g、蛋白胨 6 g、硫酸镁 0.5 g、磷酸氢二钾 5 g、NaCl 100 g、蒸馏水 1000 mL,121 ℃ 灭菌 20 min。
TSQ 8000 Evo三重四级杆气质联用仪(色谱柱TG-WAXMS(60 m×0.25 mm,0.25 μm)) 美国赛默飞世尔科技公司;TGL-16gR台式高速冷冻离心机 上海安亭有限公司;UV-1240紫外-可见分光光度计 日本岛津公司;ABI GeneAmp® 9700 PCR仪 Applied Biosystems;FR-980A凝胶成像仪 上海复日科技仪器有限公司;DYCP-31DN DNA电泳仪 北京六一生物科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 产β-苯乙醇酵母菌株的筛选
取发酵50 d酱醪样品,富集培养48 h[20],稀释后涂布TTC下层平板,28 ℃培养72 h,倒入TTC上层培养基,28 ℃避光培养2~3 h后,挑选深色菌落作为初筛菌株,进一步分离纯化并接入麦芽汁培养基进行复筛,28 ℃、180 r/min培养72 h,用二氯甲烷提取发酵液中β-苯乙醇并通过气质联用仪定量检测其含量,最终得到高产β-苯乙醇的菌株,命名为J13。
1.2.2 菌株鉴定及生物学特性分析
1.2.2.1 细胞形态特征的显微镜观察
将J13接种于酵母膏胨葡萄糖培养基(YPD)上,28 ℃培养72 h,观察并记录菌落颜色、形状、质地情况等菌落特征。在干净载玻片上滴1滴蒸馏水,用接种环挑取少量菌体并涂布均匀中,盖上盖玻片,40倍镜下观察细胞形态特征。
1.2.2.2 生理生化实验
参考《酵母菌的特征与鉴定手册》[21],对J13进行生理生化试验。其中,糖发酵、碳源同化、氮源同化试验用培养基参照王靖雯等[18]的方法,接种量均为2×107个/mL,30 ℃条件下培养3~7 d,以不含碳源、氮源作为阴性对照。脲酶、产类淀粉化合物、重氮基蓝B(DBB)、高浓度葡萄糖生长试验用培养基均采用YPD培养基,具体实验方法参照《酵母菌的特征与鉴定手册》[21],尿素培养基、DBB染色剂的配制方法参照《现代食品微生物学实验技术》[22]。
1.2.2.3 分子生物学鉴定
以J13的全基因组为模板,以ITS1(5’-TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG-3’)和ITS4(5’-TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC-3’)为引物进行PCR扩增。PCR反应体系(20 μL):ddH2O 14.7 μL,10×Taq buffer 2.0 μL,Taq DNA聚合酶0.1 μL,dNTP Mix 1.6 μL,Primer1 0.8 μL,Primer2 0.8 μL,模板1 μL。PCR反应条件:95 ℃预变性10 min;95 ℃变性0.5 min,58 ℃退火0.5 min,72 ℃延伸35 s,30个循环;72 ℃延伸10 min。用2%琼脂糖凝胶对10 μL PCR扩增产物进行电泳检测并送至北京擎科生物科技有限公司进行测序。在NCBI数据库进行BLAST比对测序结果,用MEGA 11的邻位连接法(Neighbor-Joining method)[23]对选择的序列进行1000次步长计算,构建系统发育树。
1.2.2.4 生物学特性分析
将Z. rouxii 13接入麦芽汁培养基中,在NaCl质量分数为0、初始pH6、30 ℃、180 r/min条件下培养72 h。分别改变培养基NaCl质量分数(0、5%、10%、15%、20%、25%)、初始pH(3、4、5、6、7、8)、培养温度(20、25、30、35、40 ℃),以菌体干重为指标,考察Z. rouxii 13的耐盐性、pH耐受性、生长温度范围。
1.2.3 酵母菌株产β-苯乙醇发酵工艺的单因素实验
以碳源种类及浓度、氮源种类及浓度、接种量(v/v)、NaCl质量分数、初始pH、温度作为实验因素,按下述培养条件分别进行单因素实验[24-26]。挑取Z. rouxii 13斜面培养物接入麦芽汁培养基中,30 ℃,180 r/min培养48 h,得到种子液。发酵条件为培养基初始pH6、NaCl质量分数10%、L-苯丙氨酸4 g/L、葡萄糖30 g/L、蛋白胨6 g/L、30 ℃、180 r/min、5%接种量、培养96 h。
1.2.3.1 碳源种类及浓度对Z. rouxii 13生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响
分别以等量的麦芽糖、果糖、葡萄糖、D-半乳糖、蔗糖代替转化培养基中的碳源,其他成分不变,以菌体干重及β-苯乙醇产量为指标筛选最佳碳源种类。确定最佳碳氮源后,分别研究不同碳源浓度(10、30、50、70、90 g/L)对菌株生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响,筛选出最佳碳源浓度,用于后续实验。
1.2.3.2 氮源种类及浓度对Z. rouxii 13生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响
分别以等量的蛋白胨、酵母膏、硫酸铵、氯化铵、尿素代替转化培养基中的氮源,其他成分不变,以菌体干重及β-苯乙醇产量为指标筛选最佳氮源种类。确定最佳氮源后,研究不同氮源浓度(2、4、6、8、10 g/L)对菌株生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响,筛选出最佳氮源浓度,用于后续实验。
1.2.3.3 接种量对Z. rouxii 13生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响
改变接种量(3%、5%、7%、9%、11%(v/v)),其余条件不变,以菌体干重及 β-苯乙醇产量为指标,研究不同接种量对菌株生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响。
1.2.3.4 NaCl质量分数对Z. rouxii 13生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响
改变NaCl质量分数(0、5%、10%、15%、20%)其余条件不变,以菌体干重及β-苯乙醇产量为指标,研究不同NaCl质量分数对菌株生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响。
1.2.3.5 初始pH对Z. rouxii 13生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响
改变初始pH(4、5、6、7、8),其余条件不变,以菌体干重及β-苯乙醇产量为指标,研究不同初始pH对菌株生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响。
1.2.3.6 温度对Z. rouxii 13生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响
改变培养温度(18、23、28、33、38 ℃),其余条件不变,以菌体干重及β-苯乙醇产量为指标,研究不同温度对菌株生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响。
1.2.3.7 L-苯丙氨酸浓度对Z. rouxii 13生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响
改变L-苯丙氨酸浓度(0、4、8、10、12 g/L),其余条件不变,以菌体干重及β-苯乙醇产量为指标,研究不同L-苯丙氨酸浓度对菌株生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响。
1.2.4 酵母菌株产β-苯乙醇发酵工艺的正交试验
在单因素实验的基础上,选择蛋白胨(A)、NaCl质量分数(B)、温度(C)作为正交试验变量,设计L9(34)正交试验,以β-苯乙醇产量为考察指标,对发酵条件进行优化。正交试验因素与水平设计见表1。
表 1 正交试验设计因素与水平Table 1. Factors and levels of orthogonal test design水平 A蛋白胨(g/L) B NaCl质量分数(%) C温度(℃) 1 6 0 18 2 8 5 23 3 10 10 28 1.2.5 高盐稀态发酵酱油制作工艺
1.2.5.1 制曲工艺
参考高献礼[27]的酱油酿造工艺。黄豆浸泡3 h,在115 ℃下灭菌30 min,取出冷却。以黄豆:面粉质量比=3:1的比例混合,以万分之四的接种量接入曲精,31 ℃培养,在制曲的第10、18及26 h分别翻曲一次,第40 h时,曲料表面呈黄绿色,制曲完成。
1.2.5.2 发酵工艺
参考某企业生产参数并稍作修改,采用最优发酵条件培养Z. rouxii 13得到培养液,在6000 r/min,4 ℃,10 min条件下对培养液进行离心,去除菌体,得到风味液并加入2倍质量比的盐水,最终配成NaCl质量分数为18%的调配液,以成曲:调配液质量比=1:2.33的比例混合,置于3.2 L发酵罐中常温酿造20 d,每天搅拌一次。酿造结束后用纱布过滤酱醪,得到酱油用于感官评定。
1.2.6 指标测定
1.2.6.1 β-苯乙醇的提取及检测
参考荣绍丰等[28]的方法,提取并检测发酵液中的β-苯乙醇含量。发酵液于6000 r/min、4 ℃条件下离心10 min后取10 mL上清液,加入等体积二氯甲烷,萃取30 min后取有机相,根据浓度用二氯甲烷适当稀释,用0.22 μm有机相滤膜过滤并收集滤液。GC条件:载气为氦气,流速1.0 mL/min,进样量1.0 µL,分流比为10:1,色谱柱升温程序为:60 ℃,保留1 min;以8 ℃/min升温到180 ℃,保留2 min;再以5 ℃/min升温到220 ℃,保留10 min。MS条件:采用电子电离方式,电离能为70 eV,检测器电压为857 V,扫描范围为m/z 50~400,扫描速率为2.00 scans/s;进样口和离子源温度分别为250 ℃和230 ℃。采用SIM模式,以m/z 91.1和122.0两个离子为定量离子进行分析。采用外标法定量检测β-苯乙醇浓度。β-苯乙醇标准曲线绘制方法为:取β-苯乙醇标品梯度稀释到质量浓度5.1、10.2、20.4、30.6、40.8 mg/L,采用上述GC和MS条件检测不同质量浓度β-苯乙醇标准品,得到标准曲线方程为:y=3E+06x−7E+06(R2=0.9939)。以标准曲线方程计算β-苯乙醇含量。
1.2.6.2 生物量的测定
取9 mL发酵液,6000 r/min离心10 min,用蒸馏水洗涤三次,105 ℃烘干,称重。
1.2.7 酱油风味的感官评定
由17名具有感官评定经验的食品专业的人员组成评定小组,参照文献[29-30]中能代表酱油香气轮廓的描述词,对酱油的酱香、醇厚、鲜味、酸味、咸味、色泽、整体评价7个指标采用10分制进行评价(1表示无感觉,10表示感觉强烈)。评定时成员之间互不交流,样品评定之间用纯净水漱口。
1.3 数据处理
实验均重复3次,数据均采用平均值±标准差(mean±SD)表示,使用SPSS 24.0软件进行方差分析,并通过Duncan’s进行显著性差异分析(P<0.05),使用Origin 2021进行绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 产β-苯乙醇酵母菌株的筛选及鉴定
2.1.1 产β-苯乙醇酵母菌株的筛选
酵母活细胞中的脱氢酶能将无色的氧化态TTC还原为红色的三苯基甲瓒(TTF),从而将平板上的菌落染成红色[31]。因此可通过呈色的深浅来判断菌株产β-苯乙醇能力的高低。通过呈色反应,选出45株显色明显的菌株。进一步对比,选出4株颜色较深的菌株,分别为J5、J7、J13、J15,对这4株菌株进行复筛。通过GC-MS测定4株菌在麦芽汁培养基中的β-苯乙醇产量。结果表明,J13的β-苯乙醇产量最高,达到177.88 mg/L。因此,选择J13作为进一步研究对象。
2.1.2 酵母的形态特征
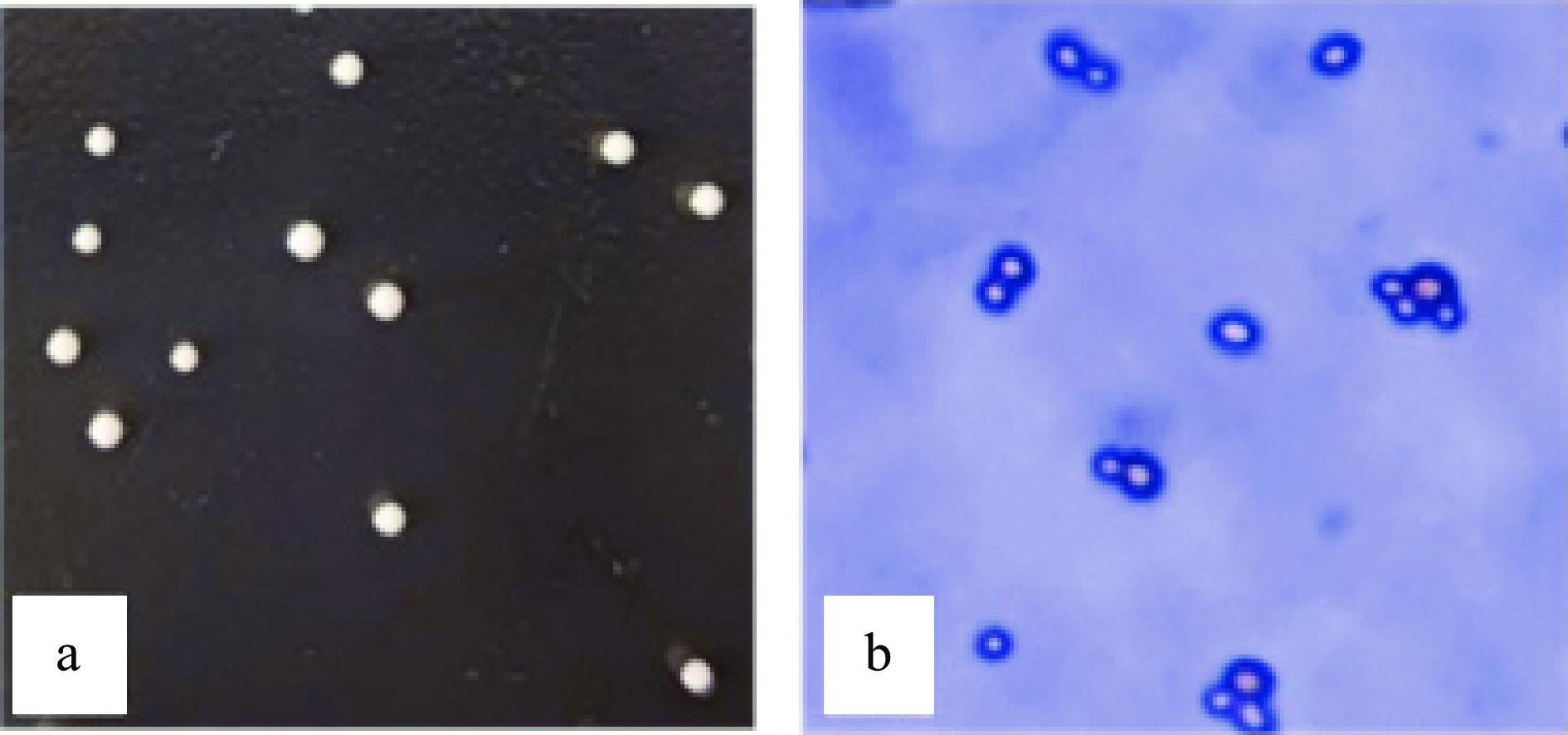
通过菌落形态观察(图1a),J13在YPD平板上培养的菌落形态呈圆形,乳白色,光滑,中间凸起。通过显微镜观察,J13细胞为椭圆形,出芽生殖(图1b)。
2.1.3 酵母的生理生化鉴定
如表2所示,J13能发酵葡萄糖、果糖,不能发酵木糖等其他糖类物质。能同化葡萄糖、麦芽糖和果糖,不能同化淀粉等其他碳源。能同化蛋白胨,不能同化尿素、硫酸铵和硝酸钠。其他试验结果表明,J13脲酶、DBB及产类淀粉化合物测试均为阴性,能在高葡萄糖浓度下生长。将这些结果与文献中的生理生化结果对比[32],发现J13与鲁氏接合酵母的描述基本一致。
表 2 J13生理生化鉴定结果Table 2. Physiological and biochemical identification of J13糖发酵 结果 碳源同化 结果 氮源同化 结果 其他试验 结果 葡萄糖 + 淀粉 − 尿素 − 脲酶试验 − 果糖 + 葡萄糖 + 硫酸铵 − DBB试验 − 木糖 − 麦芽糖 + 蛋白胨 + 高浓度葡萄糖生长 + 蔗糖 − 果糖 + 硝酸钠 − 产类淀粉化合物 − 乳糖 − 柠檬酸 − 37 ℃生长测试 + 麦芽糖 w 乳糖 − 海藻糖 − 木糖 − 半乳糖 − 蔗糖 w 注:“+”表示阳性,“−”表示阴性,“w”表示弱阳性反应。 2.1.4 酵母的ITS序列测定及系统发育分析
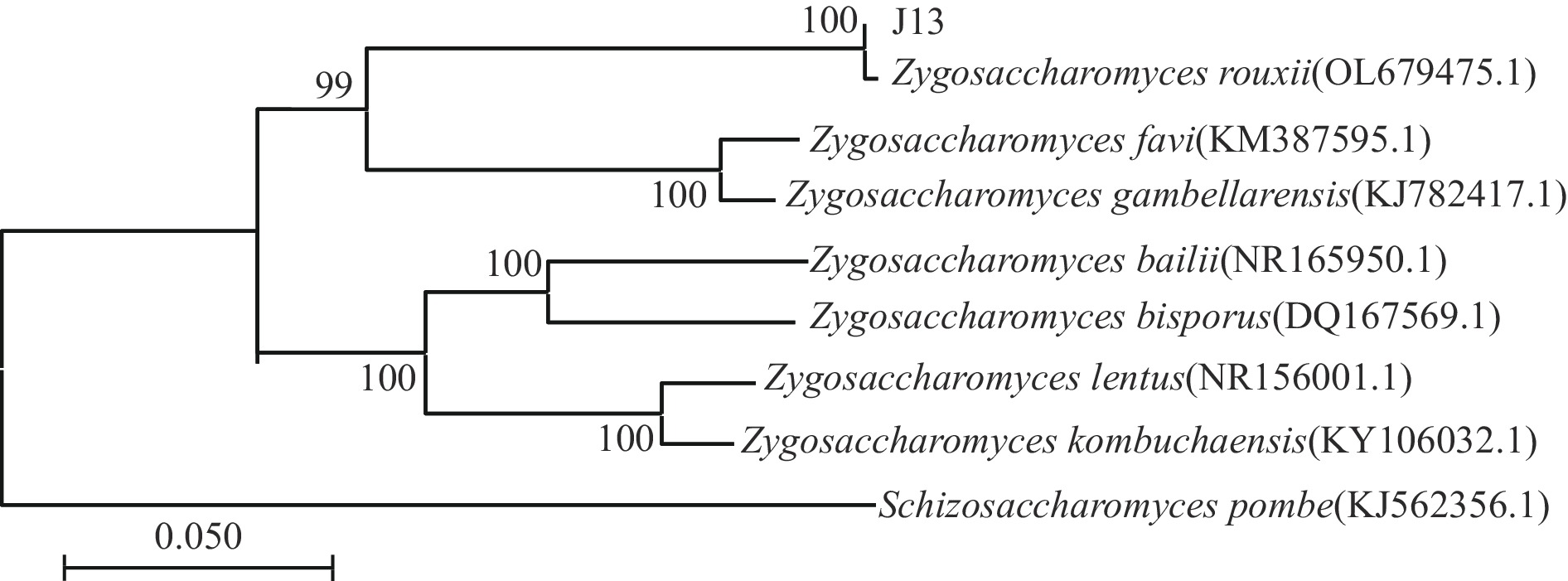
BLAST比对结果显示,J13与多株鲁氏接合酵母的ITS序列相似性高达100%,随机挑选几个菌种的ITS序列构建系统发育树,如图2所示。结果表明,J13与OL679475.1序列的亲缘关系最近,位于系统发育树的同一分支,可信度高达100%。初步确定分离菌株为鲁氏接合酵母。综合《酵母菌的特征与鉴定手册》中鲁氏结接合酵母的生理生化特征描述、ITS序列比对和系统发育进化树分析,最终鉴定J13为Z. rouxii。
2.1.5 酵母的生物学特性
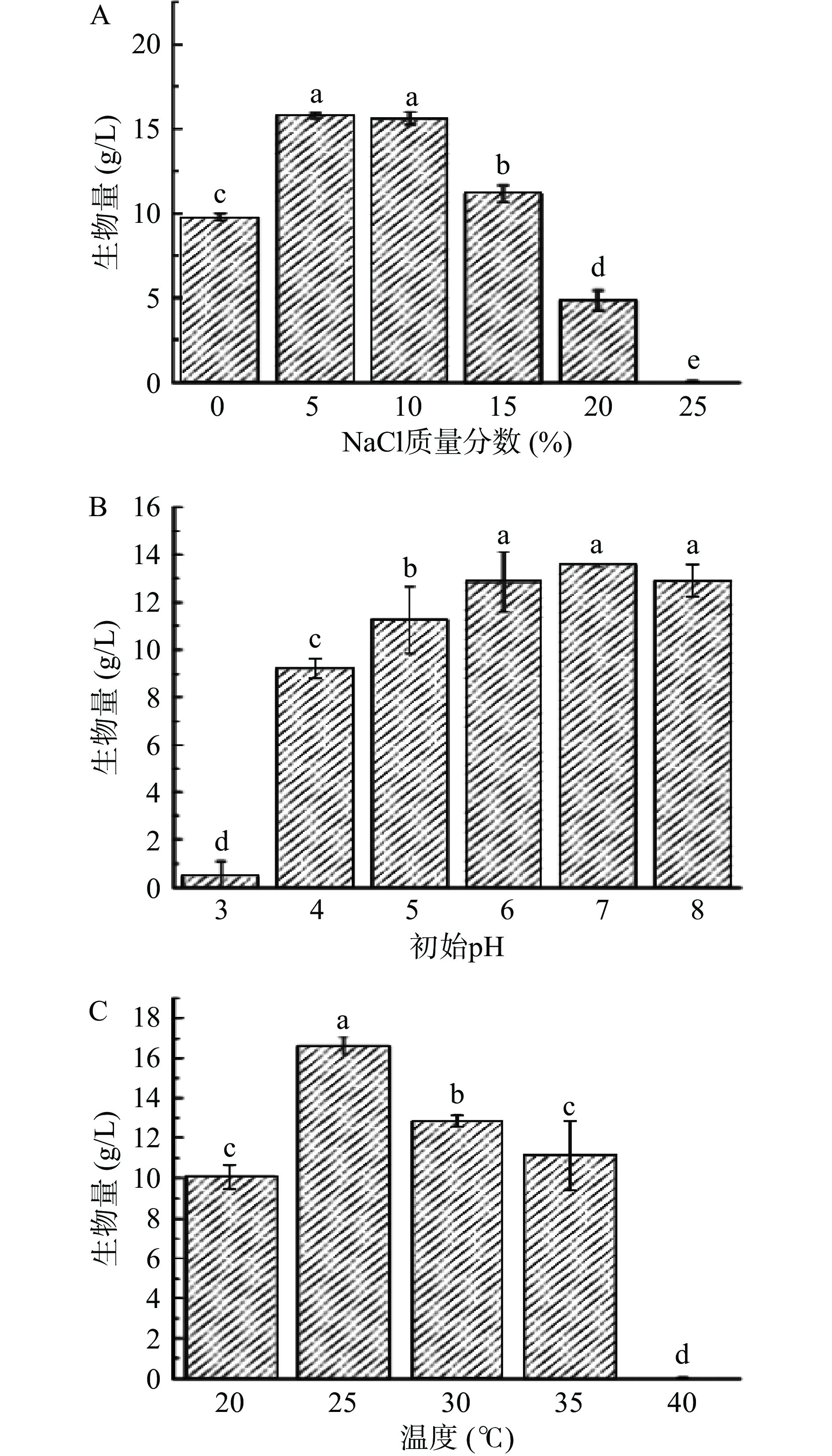
如图3A所示,NaCl质量分数对Z. rouxii 13的生物量影响显著。在NaCl质量分数为0~10%的范围内,Z. rouxii 13的生物量随着NaCl质量分数的升高而增加,当超过10%时,生物量随之下降,在NaCl质量分数为20%时,Z. rouxii 13仍然能生长,说明其具有一定的耐盐性,能在高盐稀态酱油中生长。
如图3B所示,培养基的初始pH对Z. rouxii 13的生物量影响显著。当培养基初始pH为3时,其生长明显受到抑制,当初始pH为4~7范围内,其生物量随着pH的增加而增加。这与酱油发酵过程中的pH范围相符[33],说明Z. rouxii 13能在高盐稀态酱油发酵过程中生长。
如图3C所示,在20~35 ℃温度范围内,Z. rouxii 13的生物量先增加后减少,25 ℃时生物量达到最高,当温度升高到40 ℃时,菌株生长明显受到抑制。
2.2 酵母菌株产β-苯乙醇的发酵条件优化
2.2.1 碳源种类及浓度对Z. rouxii 13生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响
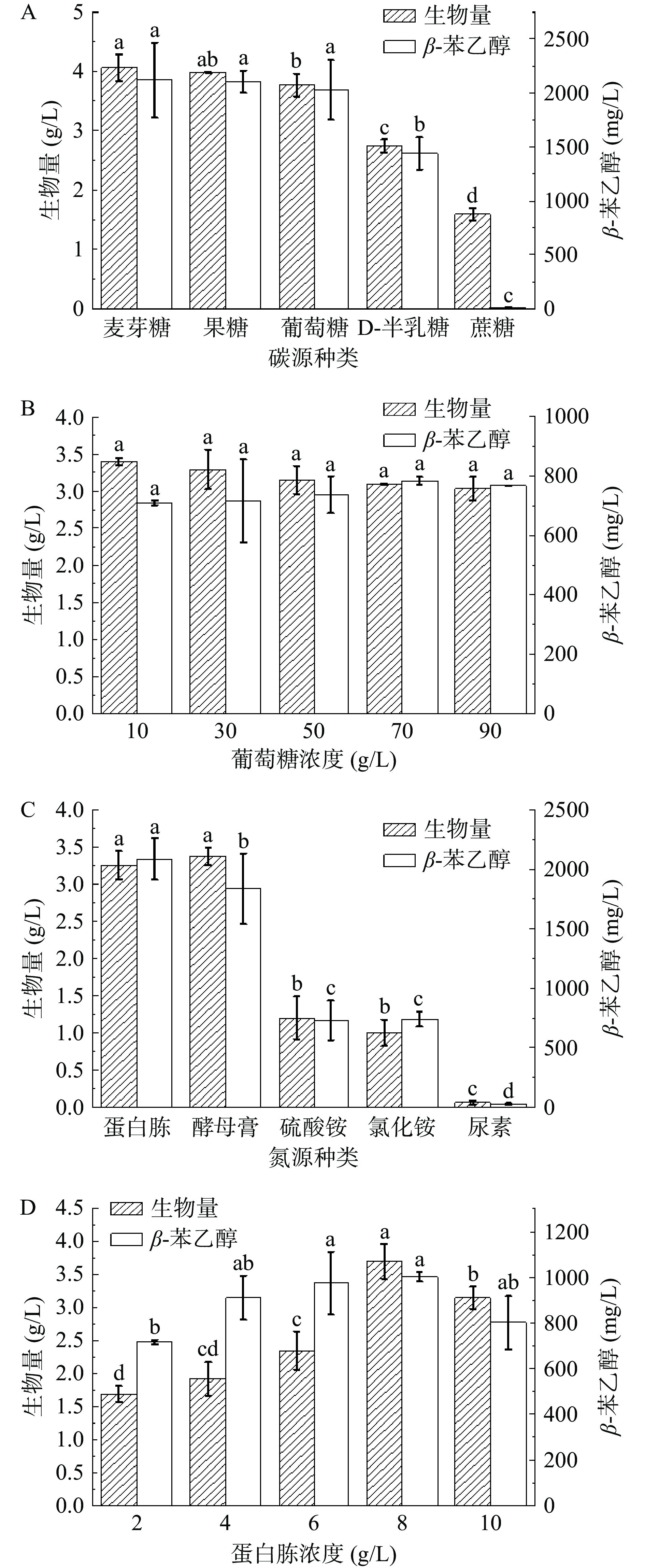
碳源种类对Z. rouxii 13的生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响如图4A所示,其影响从大到小排序依次为:麦芽糖>果糖>葡萄糖>D-半乳糖>蔗糖,而前三种碳源对β-苯乙醇产量无显著差异,考虑到葡萄糖廉价易得,因此以葡萄糖作为最优碳源。由图4B可得,在葡萄糖添加量为10~90 g/L范围内,Z. rouxii 13的生物量及β-苯乙醇产量均无显著性变化(P>0.05)。结合本研究L-苯丙氨酸浓度优化结果,分析可能是由于L-苯丙氨酸的存在使Z. rouxii 13的生长受到抑制[24],在这种条件下碳源浓度的改变对Z. rouxii 13的生物量影响不大。从经济成本的角度考虑,选择葡萄糖用量较少的浓度即30 g/L的水平进行正交试验优化。
2.2.2 氮源种类及浓度对Z. rouxii 13生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响
氮源种类对Z. rouxii 13的生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响如图4C所示,其影响从大到小排序依次为:蛋白胨>酵母膏>氯化铵>硫酸铵>尿素,因此以蛋白胨作为最优氮源。由图4D可得,在蛋白胨添加量为2~10 g/L范围内,随着蛋白胨浓度的增加,Z. rouxii 13的生物量及β-苯乙醇产量均先增加后减少,当蛋白胨浓度为8 g/L时,生物量达最大值3.7 g/L,β-苯乙醇产量为1002.8 mg/L。在蛋白胨浓度为4~10 g/L的范围内,β-苯乙醇产量无显著性差异(P>0.05),但在蛋白胨浓度分别为10 g/L和4 g/L时,生物量分别为3.15 g/L和1.92 g/L,前者的生物量显著高于后者(P<0.05),因此选择6~10 g/L水平进行正交试验。
2.2.3 接种量对Z. rouxii 13生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响
由图5A可得,在接种量为3%~11%范围内,随着接种量的增加,Z. rouxii 13的生物量先增加后不变,β-苯乙醇产量无显著差异(P>0.05),参考史荣超等[25]对发酵过程中接种量对β-苯乙醇产量影响的研究,接种量的改变对最终β-苯乙醇产量的影响并不显著(P>0.05),因此选择5%作为接种量。
2.2.4 NaCl质量分数对Z. rouxii 13生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响
由图5B可得,在NaCl质量分数为0~20%范围内,随着NaCl质量分数的升高,Z. rouxii 13的生物量及β-苯乙醇产量均显著性下降(P<0.05)。结合本研究L-苯丙氨酸浓度优化结果,分析可能是由于在L-苯丙氨酸的存在下,Z. rouxii 13的生长受到抑制[24],在这种条件下再去适当增加NaCl质量分数,反而会抑制其生长。当NaCl质量分数为20%时,Z. rouxii 13仍能生长,说明其具有一定的耐盐性,能在高盐稀态酱油中生长。在NaCl质量分数为0~10%的水平范围内,β-苯乙醇产量显著高于其他水平(P<0.05),因此选择这三个水平进行正交试验。
2.2.5 初始pH对Z. rouxii 13生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响
由图5C可得,在初始pH为4~8范围内,随着初始pH的增加,Z. rouxii 13的生物量及β-苯乙醇产量均先增加后不变。研究表明pH也会通过影响艾氏途径中的关键酶活性从而影响芳香醇的产量,而这种影响既有正相关的也有负相关的[34],因此需要采用折中的pH来平衡整个艾氏途径,故选择pH6水平进行正交试验。
2.2.6 温度对Z. rouxii 13生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响
由图5D可得,在发酵温度为18~38 ℃范围内,随着温度的升高,Z. rouxii 13的生物量及β-苯乙醇产量均先增加后减少,当温度为23 ℃时,生物量达最大值4.36 g/L,β-苯乙醇产量为878.38 mg/L。结果表明,在温度为18~28 ℃范围内,菌株生物量及β-苯乙醇产量均高于其他水平,因此选择这三个水平进行正交试验。
2.2.7 L-苯丙氨酸浓度对Z. rouxii 13生长及β-苯乙醇产量的影响
由图5E可得,随着L-苯丙氨酸浓度的增加,Z. rouxii 13的生物量逐渐减少,β-苯乙醇含量先增加后减少,当L-苯丙氨酸浓度为0 g/L时,有利于Z. rouxii 13生长,但由于缺少前体物质L-苯丙氨酸,Z. rouxii 13几乎不产β-苯乙醇,当L-苯丙氨酸浓度为4 g/L时,Z. rouxii 13的生长已明显受到抑制,但β-苯乙醇含量显著增加,说明L-苯丙氨酸的存在可以促进β-苯乙醇的合成,且抑制Z. rouxii 13生长。当继续增加L-苯丙氨酸浓度,Z. rouxii 13的生长受到严重抑制,因此选择L-苯丙氨酸浓度为4 g/L进行正交试验。
2.2.8 正交试验
正交试验结果与分析见表3及表4。由极差分析可知,影响Z.rouxii 13产β-苯乙醇含量的主次因素依次为温度、蛋白胨、NaCl质量分数。由方差分析可知,温度、蛋白胨达到了显著水平,分析可知理论最佳优化组合是A3B2C3。通过最佳组合验证性试验,结果表明最优组合为A3B2C3,即蛋白胨10 g/L、NaCl 5%、温度28 ℃,此条件下的β-苯乙醇含量为1.40 g/L。
表 3 正交试验设计与结果Table 3. Orthogonal experimental design and results实验号 A B C β-苯乙醇含量(g/L) 1 1 1 1 0.40±0.04 2 1 2 2 0.78±0.03 3 1 3 3 0.97±0.04 4 2 1 2 0.82±0.02 5 2 2 3 1.18±0.15 6 2 3 1 0.67±0.10 7 3 1 3 1.38±0.16 8 3 2 1 0.70±0.05 9 3 3 2 0.78±0.03 K1 2.15 2.60 1.77 K2 2.67 2.66 2.38 K3 2.86 2.42 3.53 ¯K1 0.72 0.87 0.59 ¯K2 0.89 0.89 0.79 ¯K3 0.95 0.81 1.18 R 0.23 0.08 0.59 表 4 试验结果方差分析Table 4. Analysis of variance of test results方差来源 自由度 均方 F值 蛋白胨 2 0.135 11.088** NaCl质量分数 2 0.016 1.298 温度 2 0.803 65.866** 误差 20 0.012 总计 27 注:**代表差异极显著(P<0.01)。 2.3 风味液对酱油感官品质的影响
对2个不同处理的样品进行感官评价,绘制雷达图,由图6可知,风味液组与对照组的整体评分分别为7.01分和6.22分,显示出风味液组具有更高的可接受度。在酱香、醇厚感和鲜味方面,风味液组得分分别为7.05分、7.02分、6.47分,对照组得分分别为5.62分、5.52分、5.77分。在色泽、酸味和咸味方面,两组差异不明显。综上分析,添加富含β-苯乙醇的风味液赋予酱油更加浓郁的酱香及醇厚的口感,且提升了酱油的鲜味。
3. 结论
本研究从天然酱醪中筛选出一株产β-苯乙醇的酵母,经形态学观察、生理生化实验及分子生物学方法鉴定并命名为Z. rouxii 13。其耐受20% NaCl,能适应宽广的pH环境及温度范围,具有优良的生物学特性。通过单因素和正交试验,对Z. rouxii 13产β-苯乙醇的培养基成分及发酵条件进行优化,最终得到的最优发酵条件为:L-苯丙氨酸4 g/L、葡萄糖30 g/L、蛋白胨10 g/L、硫酸镁0.5 g/L、磷酸氢二钾5 g/L、NaCl 50 g/L、pH6.0,温度28 ℃,β-苯乙醇含量达到1.40 g/L。通过发酵条件优化,得到富含β-苯乙醇的风味液,将其应用到高盐稀态发酵酱油的酿造工艺中发现,相比对照组,酱油的酱香及醇厚感明显提升。这一结果进一步说明β-苯乙醇对酱油香气组成有重要贡献,这与许多前期研究的结果一致[13,35],此外,本研究将富含β-苯乙醇的风味液应用于酱油酿造中以此提升酱油整体风味,这为企业改善酱油整体香气提供了一定的思路和方法。由于风味液在整体工艺中的添加时机及添加量对酱油的风味有至关重要的影响,本研究将进一步开展该方面的研究;同时,直接将高产β-苯乙醇的菌株选择合适的时机及接种量接种至酱醪中,同时优化发酵条件,使其适应并融入多菌种发酵体系,从而强化酱油酿造工艺也将是另一个可行的研究方向。
-
表 1 正交试验设计因素与水平
Table 1 Factors and levels of orthogonal test design
水平 A蛋白胨(g/L) B NaCl质量分数(%) C温度(℃) 1 6 0 18 2 8 5 23 3 10 10 28 表 2 J13生理生化鉴定结果
Table 2 Physiological and biochemical identification of J13
糖发酵 结果 碳源同化 结果 氮源同化 结果 其他试验 结果 葡萄糖 + 淀粉 − 尿素 − 脲酶试验 − 果糖 + 葡萄糖 + 硫酸铵 − DBB试验 − 木糖 − 麦芽糖 + 蛋白胨 + 高浓度葡萄糖生长 + 蔗糖 − 果糖 + 硝酸钠 − 产类淀粉化合物 − 乳糖 − 柠檬酸 − 37 ℃生长测试 + 麦芽糖 w 乳糖 − 海藻糖 − 木糖 − 半乳糖 − 蔗糖 w 注:“+”表示阳性,“−”表示阴性,“w”表示弱阳性反应。 表 3 正交试验设计与结果
Table 3 Orthogonal experimental design and results
实验号 A B C β-苯乙醇含量(g/L) 1 1 1 1 0.40±0.04 2 1 2 2 0.78±0.03 3 1 3 3 0.97±0.04 4 2 1 2 0.82±0.02 5 2 2 3 1.18±0.15 6 2 3 1 0.67±0.10 7 3 1 3 1.38±0.16 8 3 2 1 0.70±0.05 9 3 3 2 0.78±0.03 K1 2.15 2.60 1.77 K2 2.67 2.66 2.38 K3 2.86 2.42 3.53 ¯K1 0.72 0.87 0.59 ¯K2 0.89 0.89 0.79 ¯K3 0.95 0.81 1.18 R 0.23 0.08 0.59 表 4 试验结果方差分析
Table 4 Analysis of variance of test results
方差来源 自由度 均方 F值 蛋白胨 2 0.135 11.088** NaCl质量分数 2 0.016 1.298 温度 2 0.803 65.866** 误差 20 0.012 总计 27 注:**代表差异极显著(P<0.01)。 -
[1] DESMOND K. The role of microorganisms in soy sauce production[M]. London: Advances in Applied Microbiology, 2019: 45−113.
[2] QI Q, HUANG J, ZHOU R Q, et al. Characterizing microbial community and metabolites of Cantonese soy sauce[J]. Food Bioscience,2020,40:100872.
[3] 刘晓艳, 叶月华, 钱敏, 等. 大型发酵酱油酿造过程中风味物质的动态变化分析[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(12):242−247. [LIU X Y, YE Y H, QIAN M, et al. Analysis of dynamic changes of flavor components during Large-Scale brewing of soy sauce[J]. Food Science,2021,42(12):242−247. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200514-167 LIU X Y, YE Y H, QIAN M, et al. Analysis of dynamic changes of flavor components during Large-Scale brewing of soy sauce[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(12): 242-247. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200514-167
[4] DIEZ-SIMON C, EICHELSHEIM C, MUMM R, et al. Chemical and sensory characteristics of soy sauce: A review[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2020,68(42):11612−11630. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.0c04274
[5] DEVANTHI P V P, GKATZIONIS K. Soy sauce fermentation: Microorganisms, aroma formation, and process modification[J]. Food Research International,2019,120:364−374. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.03.010
[6] FENG Y Z, CUI C, ZHAO H F, et al. Effect of koji fermentation on generation of volatile compounds in soy sauce production[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2013,48(3):609−619.
[7] 葛金鑫, 李永凯, 曾斌. 酱油的风味物质[J]. 中国酿造,2019,38(10):16−20. [GE J X, LI Y K, ZENG B. Flavor substances in soy sauce[J]. China Brewing,2019,38(10):16−20. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2019.10.004 GE J X, LI Y K, ZENG B. Flavor substances in soy sauce[J]. China Brewing, 2019, 38(10): 16-20. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2019.10.004
[8] LEE S M, KIM S B, KIM Y S. Determination of key volatile compounds related to Long-Term fermentation of soy sauce[J]. Journal of Food Science,2019,84(10):2758−2776. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14771
[9] 陈杰, 赵莹, 韩舜羽, 等. 17种市售广式酱油中风味物质的检测分析[J]. 中国酿造,2021,40(12):165−170. [CHEN J, ZHAO Y, HAN S Y, et al. Detection and analysis of flavor substances in 17 kinds of commercially available Cantonese soy sauce[J]. China Brewing,2021,40(12):165−170. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2021.12.030 CHEN J, ZHAO Y, HAN S Y, et al. Detection and analysis of flavor substances in 17 kinds of commercially available Cantonese soy sauce[J]. China Brewing, 2021, 40(12): 165-170. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2021.12.030
[10] 白佳伟, 陈亮, 周尚庭, 等. 特级高盐稀态酿造酱油中关键香气物质的分析[J]. 中国酿造,2019,38(11):179−185. [BAI J W, CHEN L, ZHOU S T, et al. Analysis of key odor compounds in super grade soy sauce with high-salt and diluted-state fermentation[J]. China Brewing,2019,38(11):179−185. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2019.11.036 BAI J W, CHEN L, ZHOU S T, et al. Analysis of key odor compounds in super grade soy sauce with high-salt and diluted-state fermentation[J]. China Brewing, 2019, 38(11): 179-185. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2019.11.036
[11] 冯云子. 高盐稀态酱油关键香气物质的变化规律及形成机理的研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2015 FENG Y Z. The evolution and formation mechanism of keyaroma compounds during the process of high-salt liquid fermentation soy sauce[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2015.
[12] STEINHAUS P, SCHIEBERLE P. Characterization of the key aroma compounds in soy sauce using approaches of molecular sensory science[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2007,55(15):6262−6269. doi: 10.1021/jf0709092
[13] WANG X J, GUO M Y, SONG H L, et al. Characterization of key aroma compounds in traditional Chinese soy sauce through the molecular sensory science technique[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2020,128:1096−1127.
[14] 朱新贵, 李学伟, 曾小波. 典型广式酱油与日式酱油的风味物质差异研究[J]. 中国酿造,2016,35(7):30−35. [ZHU X G, LI X W, ZENG X B. Difference of flavor compounds in Cantonese-style soy sauce and Japanese-style soy sauce[J]. China Brewing,2016,35(7):30−35. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2016.07.007 ZHU X G, LI X W, ZENG X B. Difference of flavor compounds in Cantonese-style soy sauce and Japanese-style soy sauce[J]. China Brewing, 2016, 35(7): 30-35. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2016.07.007
[15] 彭东, 蒋雪薇, 陈幽, 等. 高盐稀态酱醪中耐盐生香酵母的筛选及生香特性研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(13):76−84. [PENG D, JIANG X W, CHEN Y, et al. Screening and aroma-producing characteristics of salt-tolerant aroma-producing yeasts from high-salt liquid-state Moromi[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(13):76−84. PENG D, JIANG X W, CHEN Y, et al. Screening and aroma-producing characteristics of salt-tolerant aroma-producing yeasts from high-salt liquid-state Moromi[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(13): 76-84.
[16] YAO S J, ZHOU R Q, JIN Y, et al. Effect of co-culture with Tetragenococcus halophilus on the physiological characterization and transcription profiling of Zygosaccharomyces rouxii[J]. Food Research International,2019,121:348−358. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.03.053
[17] 阮志强, 董玺梅, 蒋雪薇, 等. 高盐稀态酱油发酵优势真菌与风味物质相关性分析[J]. 食品科学,2021,43(10):1−11. [RUAN Z Q, DONG X M, JIANG X W, et al. Study on the correlation between dominant fungi and the variation of flavor compounds in high-salt liquid-state soy sauce fermentation[J]. Food Science,2021,43(10):1−11. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200514-165 RUAN Z Q, DONG X M, JIANG X W, et al. Study on the correlation between dominant fungi and the variation of flavor compounds in high-salt liquid-state soy sauce fermentation[J]. Food Science, 2021, 43(10): 1-11. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200514-165
[18] 王靖雯, 赵谋明, 陈涛, 等. 高盐稀态酱醪中功能性酵母菌的筛选、鉴定及发酵特性[J]. 食品科学, 2020: 1−11 WANG J W, ZHAO M M, CHEN T, et al. Screening, identification and fermentation characteristics of functional yeast from high-salt liquid-state moromi[J]. Food Science, 2020: 1−11.
[19] 马荣山, 王姗姗. 酱醪中耐高温耐盐酵母菌分离鉴定[J]. 食品工业科技,2013,34(14):191−196. [MA R S, WANG S S. Isolation, purification and identification of high temperature halophilic yeast from soy sauce Mash[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2013,34(14):191−196. MA R S, WANG S S. Isolation, purification and identification of high temperature halophilic yeast from soy sauce Mash[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2013, 34: 191-196.
[20] 刘滢, 朱新贵, 李学伟. 酱油增香用耐盐酵母的分离及生长特性分析[J]. 中国酿造,2012,31(10):109−112. [LIU Y, ZHU X G, LI X W. Isolation and growth characteristics of the salt-tolerant yeast for soy sauce flavor improvement[J]. China Brewing,2012,31(10):109−112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5071.2012.10.030 LIU Y, ZHU X G, LI X W. Isolation and growth characteristics of the salt-tolerant yeast for soy sauce flavor improvement[J]. China Brewing, 2012, 31: 109-112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5071.2012.10.030
[21] 巴尼特, 佩恩, 亚罗. 酵母菌的特征与鉴定手册[M]. 青岛: 青岛海洋大学出版社, 1991: 448 BARNETT, PENN, YARROW. Yeasts: characteristics and identification[M]. Qingdao: Qingdao Ocean University Press, 1991: 448.
[22] 刘慧. 现代食品微生物学实验技术[M]. 北京: 中国轻工业出版社, 2017 LIU H. Modern experiment technology of food microbiology[M]. 北京: China Light Industry Press, 2017.
[23] SAITOU N, NEI M. The neighbor-joining method: A new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees[J]. Molecular Biology and Evolution,1987,4(4):406−425.
[24] 许岱, 范光森, 富志磊, 等. 一株高产β-苯乙醇酵母菌的筛选、鉴定及其发酵条件优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(5):151−158. [XU D, FAN G S, FU Z L, et al. Screening of a high-yield β-phenylethanol yeast and optimization of its cultural conditions[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(5):151−158. XU D, FAN G S, FU Z L, et al. Screening of a high-yield β-phenylethanol yeast and optimization of its cultural conditions[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2017, 38(5): 151-158.
[25] 史荣超, 刘洒洒, 侯阳阳, 等. 梅奇酵母转化l-苯丙氨酸合成2-苯乙醇发酵条件优化[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(15):22−28. [SHI R C, LIU S S, HOU Y Y, et al. Optimized bio-conversion of L-phenylalanine to 2-phenylethanol in Metschnikowia sp J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(15):22−28.
[26] FAN G S, CHENG L J, FU Z L, et al. Screening of yeasts isolated from Baijiu environments for 2-phenylethanol production and optimization of production conditions[J]. 3 Biotech,2020,10(6):326−332.
[27] 高献礼. 高盐稀态酱油在发酵和巴氏杀菌过程中风味物质形成和变化的研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2010 GAO X L. Study on the formation and changes of flavor compounds in high-salt and diluted-state soy sauce during fermentation and pasteurization[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2010.
[28] 荣绍丰, 伍进, 管世敏, 等. 生物合成天然2-苯乙醇细菌的筛选及合成途径分析[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(16):69−75. [RONG S F, WU J, GUAN S M, et al. Isolation of 2-Phenylethanol-Synthesizing bacteria and synthetic pathway analysis[J]. Food Science,2021,42(16):69−75. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200515-174 RONG S F, WU J, GUAN S M, et al. Isolation of 2-Phenylethanol-Synthesizing bacteria and synthetic pathway analysis[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(16): 69-75. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200515-174
[29] IMAMURA M. Descriptive terminology for the sensory evaluation of soy sauce[J]. Journal of Sensory Studies,2016,31(5):393−407. doi: 10.1111/joss.12223
[30] CHERDCHU P, CHAMBERS E, SUWONSICHON T. Sensory lexicon development using trained panelists in thailand and the USA: Soy sauce[J]. Journal of Sensory Studies,2013,28(3):248−255. doi: 10.1111/joss.12041
[31] 陈卫平, 涂谨, 熊建华, 等. 红四氮唑在酒精酵母选育中的应用效果研究[J]. 酿酒科技,2003(6):35−37. [CHEN W P, TU J, XIONG J H, et al. Research on application effect of TTC in breeding of alcohol yeast[J]. Liquor-Making Science & Technology,2003(6):35−37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9286.2003.06.007 CHEN W P, TU J, XIONG J H, et al. Research on application effect of TTC in breeding of alcohol yeast[J]. Liquor-Making Science & Technology, 2003, (6): 35-37. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9286.2003.06.007
[32] 王虎玄, 岳田利, 胡仲秋, 等. 陕西浓缩苹果汁中高渗酵母的分离鉴定[J]. 农业机械学报,2015,46(4):246−251. [WANG H X, YUE T L, HU Z Q, et al. Identification of osmotolerant yeast in apple juice concentrate from shaanxi province[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2015,46(4):246−251. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2015.04.036 WANG H X, YUE T L, HU Z Q, et al. Identification of osmotolerant yeast in apple juice concentrate from shaanxi province[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery, 2015, 46(4): 246-251. doi: 10.6041/j.issn.1000-1298.2015.04.036
[33] SENG H T, 周斌, 侯莎, 等. 盐分对广式高盐稀态酱油发酵微生物菌群结构的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(1):45−54. [SENG T H, ZHOU B, HOU S, et al. Effect of salt on the microbial community structure of Cantonese-style high-salt dilute soy sauce fermentation[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(1):45−54. SENG T H, ZHOU B, HOU S, et al. Effect of salt on the microbial community structure of Cantonese-style high-salt dilute soy sauce fermentation[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2022, 48(1): 45-54.
[34] GHOSH S, KEBAARA B W, ATKIN A L, et al. Regulation of aromatic alcohol production in candida albicans[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2008,74(23):7211−7218. doi: 10.1128/AEM.01614-08
[35] 赵佳豪, 周韬, 刘爽, 等. 中日两国酱油香味与滋味差异[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(17):232−236. [ZHAO J H, ZHOU T, LIU S, et al. Differences in the flavor and taste between Chinese and Japanese soy sauce[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(17):232−236. ZHAO J H, ZHOU T, LIU S, et al. Differences in the flavor and taste between Chinese and Japanese soy sauce[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46(17): 232-236.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 王佳,丁方莉,安宇,曾雪莹,张智慧,李思楠,徐开媛,周芳,王颖,张璐,徐炳政,孙泽堃. 芸豆-蓝靛果复合发酵液制备工艺优化及其抗氧化活性. 食品工业科技. 2025(03): 222-231 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 王胜宇,杨梅,胡鹤宇,朱才庆,董欢欢,管咏梅,朱卫丰. 结合态酚类物质在植物生长、食品加工及人体消化过程中的释放规律研究进展. 食品工业科技. 2024(14): 408-417 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
