Identification of Malus toringoides (Rehd.) Hughes Teas with Different Processes Based on E-nose and GC-MS
-
摘要: 为探究3种不同工艺加工的俄色茶气味差异,采用电子鼻、捕集阱顶空-气质联用仪(trap head space-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry,HS-Trap-GC-MS)结合正交偏最小二乘法判别分析(orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis,OPLS-DA)、相对气味活度值(relative odor activity value,ROAV)和差异性热图分析俄色红茶、绿茶和康砖茶挥发性物质的差异。结果表明,电子鼻能有效区分3种俄色茶,电子鼻结合OPLS-DA建立预测模型其预测能力达95.70%。GC-MS分析表明醛类、酯类、烃类是主要挥发性物质,醇类是红茶、绿茶主要共有挥发性物质;醛类、酯类、烃类和醇类的含量差异是导致不同工艺俄色茶香气异同的主要原因。ROAV值结合香气类型分析表明果香类挥发性物质对俄色茶气味形成的贡献相对较大;异戊醛可能是俄色茶的关键香气物质。差异性热图分析表明,三甲氧基酯、异戊醛、2-乙基呋喃是俄色茶主要共有挥发性物质。
-
关键词:
- 俄色茶 /
- 不同工艺 /
- 气相色谱-质谱联用法 /
- 电子鼻 /
- 正交偏最小二乘判别分析 /
- 相对气味活度值 /
- 差异性热图
Abstract: The volatile substances among Malus toringoides (Rehd.) Hughes black tea, green tea and Kang brick tea were detected by electronic nose (E-nose), trap head space-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (HS Trap GC-MS) and the differences of the volatile substances were analyzed by orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis (OPLS-DA), relative odor activity value (ROAV) and differential thermography in order to explore the odor differences of Malus toringoides (Rehd.) Hughes teas with three different processes. Result showed that E-nose could effectively distinguish three kinds of Malus toringoides (Rehd.) Hughes teas, and the prediction ability of the model established by E-nose combined with OPLS-DA was 95.70%. GC-MS analysis showed that aldehydes, esters and hydrocarbons were the main volatile substances, while alcohols were the main common volatile substances of black tea and green tea. The differences in the contents of aldehydes, esters, hydrocarbons and alcohols account for the variations in the aroma of Malus toringoides (Rehd.) Hughes teas produced by different processes. ROAV value combined with aroma type analysis showed that the volatile components of fruit aroma had a relatively large contribution to the formation of the odor of Malus toringoides (Rehd.). Isovaleraldehyde might be the key aroma substance to Malus toringoides (Rehd.) Hughes teas. Differential thermogram analysis showed that trimethoxyester, isovaleraldehyde and 2-ethylfuran were the main common volatile substances in Malus toringoides (Rehd.) Hughes teas. -
变叶海棠(Malus toringoides (Rehd.) Hughes)为蔷薇科苹果属落叶灌木,大多分布在海拔3000~3500 m的高海拔地区,是中国特有植物资源,在四川、西藏等高海拔地区有分布。以变叶海棠叶为原料,按制茶工艺制成的饮品,当地人称为俄色茶。藏医和现代医学均认为俄色茶具有治疗消化不良,降血压、血脂[1-3]等功效。近年来通过质谱、核磁、液相、气相和IRIS Intrepid II XSP等分析发现俄色茶主要成分为二氢查耳酮、黄酮、氨基酸、多糖、脂肪酸等[4-6]。由此可见,俄色茶保健价值极高。
茶叶香气的形成既与所含香气物质(占茶叶质量的0.01%~0.05%)有关[7],又与后序加工工艺存在极大联系[8]。茶叶香气形成的4条途径[9]是影响茶叶香气差异的重要因素。有研究表明,茶叶香气对茶叶品质的贡献率在25%~40%[9-10]之间。郭洪伟等[11]分析红茶和绿茶的主要香气成分表明:醇类和醛类物质是红茶的主要挥发性物质;醇类和酯类是绿茶的主要挥发性物质。乔小燕等[12]的研究表明康砖茶主要挥发性物质为酮类、醛类和醇类。以变叶海棠叶为原料,通过不同加工工艺形成了俄色红茶、绿茶和康砖茶,其整体香味轮廓是否存在差异以及具体香气物质的差异未见相关报道。
茶叶中的香气物质分子量小、沸点低、挥发性强。选择有效香气检测方法至关重要。电子鼻是一种快速识别样品整体气味轮廓的仪器,其检测结果具有客观性、重复性、可视性等优点,但无法判断样品之间气味差异的具体物质。捕集阱自动顶空(trap head space)具有样品处理简单,气味物质自动萃取、富集和进样,方便快捷等特点。气相色谱质谱联用仪(gas chromatography-mass spectrometry,GC-MS)是分离、鉴定物质的有效工具。电子鼻和GC-MS在茶叶整体气味轮廓及具体物质的鉴定领域有广泛应用。陆晨浩等[13]发现发芽3天的黑麦茶香气与未发芽的差异明显。邵淑贤等[14]研究表明利用黄观音乌龙茶的5种主要香气成分所构建SVM判别模型,其识别不同产地的黄观音乌龙茶的识别率为100%。WANG等[15]研究表明,不同工艺制备的茶叶其香气和含量差异大,挥发性物质含量结合聚类分析能够准确分类。另外,正交偏最小二乘判别分析(orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis,OPLS-DA)是一种有监督的分析方法,其通过去除变量的数据变异,将分离信息集中在一个主成分中,使模型变得简单且易于解释。
本研究以不同工艺的俄色茶为研究对象,采用电子鼻、HS- Trap- GC-MS技术结合OPLS-DA、ROAV、差异性热图,识别不同工艺的俄色茶整体气味轮廓,鉴定俄色茶挥发性物质,分析俄色茶主要香气物质及差异,旨在比较不同工艺条件下俄色茶气味异同,探明不同工艺条件下俄色茶气味特点,为俄色茶风味研究提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
俄色茶样品 由四川炉霍雪域俄色有限公司提供,样品信息见表1,样品加工方法参见文献[16]。取四个不同年份(2019、2020、2021和2022年)的俄色红茶、绿茶和康砖茶各3份,将样品分别混匀,研磨成粉,过40目筛,备用。
表 1 样品信息表Table 1. Sample information样品编号 样品名称 配料 A 俄色红茶 高山变叶海叶棠嫩芽 B 俄色绿茶 高山变叶海叶棠嫩芽 C 俄色康砖茶 高山变叶海棠叶碎嫩芽 FOX 4000电子鼻 Alpha MOS公司;Clarus 680气相色谱仪、Elite-5MS(30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm)色谱柱、Clarus SQ8T质谱仪、HST40捕集阱顶空进样器 美国珀金埃尔默公司;DFY-400C高速粉碎机 温岭市林大机械有限公司;ME203E电子天平 梅特勒-托利多仪器(上海)有限责任公司;6CR-40型揉捻机、6CFJ-1发酵机、6CH-12烘干机 信阳一鼎茶业科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品工艺及参数
俄色红茶制备工艺及参数:采摘(高山变叶海棠嫩芽)、萎凋(加温50 ℃萎凋,至含水量60%左右)、揉捻(40型揉捻机按轻、重、轻进行冷揉,至成条率90%)、发酵(发酵机温度35 ℃,相对湿度80%,发酵时间6 h)、干燥(烘焙100 ℃,时间45 min)、筛选、检验、包装。
俄色绿茶制备工艺及参数:采摘(高山变叶海棠嫩芽)、摊青(摊青床,厚度2~5 cm,通微风,15 min翻动一次,至鲜叶含水量70%)、杀青(温度为270 ℃,至含水量为60%)、揉捻(40型揉捻机按轻、重、轻进行冷揉,至成条率90%)、烘干(温度100 ℃,至含量水为6%)、筛选 、检验、包装。
俄色康砖茶制备工艺参数:采摘(高山变叶海棠嫩芽或碎嫩芽)、杀青(温度为270 ℃,至含水量为55%)、揉捻(40型揉捻机按轻、重、轻进行冷揉,揉捻叶细胞破坏率为80%)、渥堆(堆高80 cm,室温25 ℃,茶坯含水量35%,渥堆时间为15 d)、干燥(烘焙200 ℃,时间15 min)、筛拼(蒸压成型)、干燥(压饼成型后的俄色茶置于干燥环境,自然干燥)、检验、包装。
1.2.2 电子鼻检测
样品前处理:取2.0 g俄色茶粉装入洁净的10 mL顶空瓶,用顶空盖、垫密封,备用。
电子鼻检测条件:样品在孵化器(70 ℃)内孵化5 min,进样量500 μL,进样速度500 μL/s,手动进样。每个样品检测120 s,检测器清洁180 s。每个样品检测20次,取10次稳定(依据其在主成分二维图中的集中程度)数据进行分析。
1.2.3 GC-MS检测
样品前处理:取俄色茶粉4.0 g装入20 mL顶空瓶,用GC-MS专用瓶盖密封,装入自动进样器。备用。
萃取及进样条件:萃取温度70 ℃,进样针温度75 ℃,传输线温度80 ℃,萃取时间1800 s,干吹120 s,解析10 s,顶空瓶加压/释压120 s,捕集阱保持240 s,捕集阱循环4次。
气相条件[17]:载气(99.999% He),流速1.0 mL/min。起始温度30 ℃,保持3 min,然后以2 ℃/min升至160 ℃,再以10 ℃/min升至230 ℃,保留3 min。
质谱条件:EI离子源,电子轰击能量为70 eV,离子源温度230 ℃,电子倍增电压1650 V;质量扫描范围:45~450 m/z;标准调谐文件。
定性、定量:首先去除柱流失的含硅类物质,然后选取正反匹配度均大于700(最大999), 参考NIST 2011谱库,同时结合质谱图进行定性。以相对峰面积计算相对含量。
检测结果有效性选择:每个样品检测5次,仅取3次都能检测到的物质作为有效结果。
1.2.4 相对气味活度值(relative odor activity value,ROAV)的计算
相对气味活度值(ROAV)是一种结合阈值判定化合物重要性的方法,其原理及计算方法见参考文献[18-19]。
式中:C表示某物质的相对百分含量;T表示该物质的呈香阈值。
1.3 数据处理
OPLS-DA分析、绘图、预测变量重要性投影(variable importance in projection,VIP):SIMCA14.1软件。平均值及标准偏差():SPSS 25。电子鼻雷达图、差异性热图:数据归一化处理及制图采用origin 2021。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 电子鼻分析俄色茶整体气味轮廓
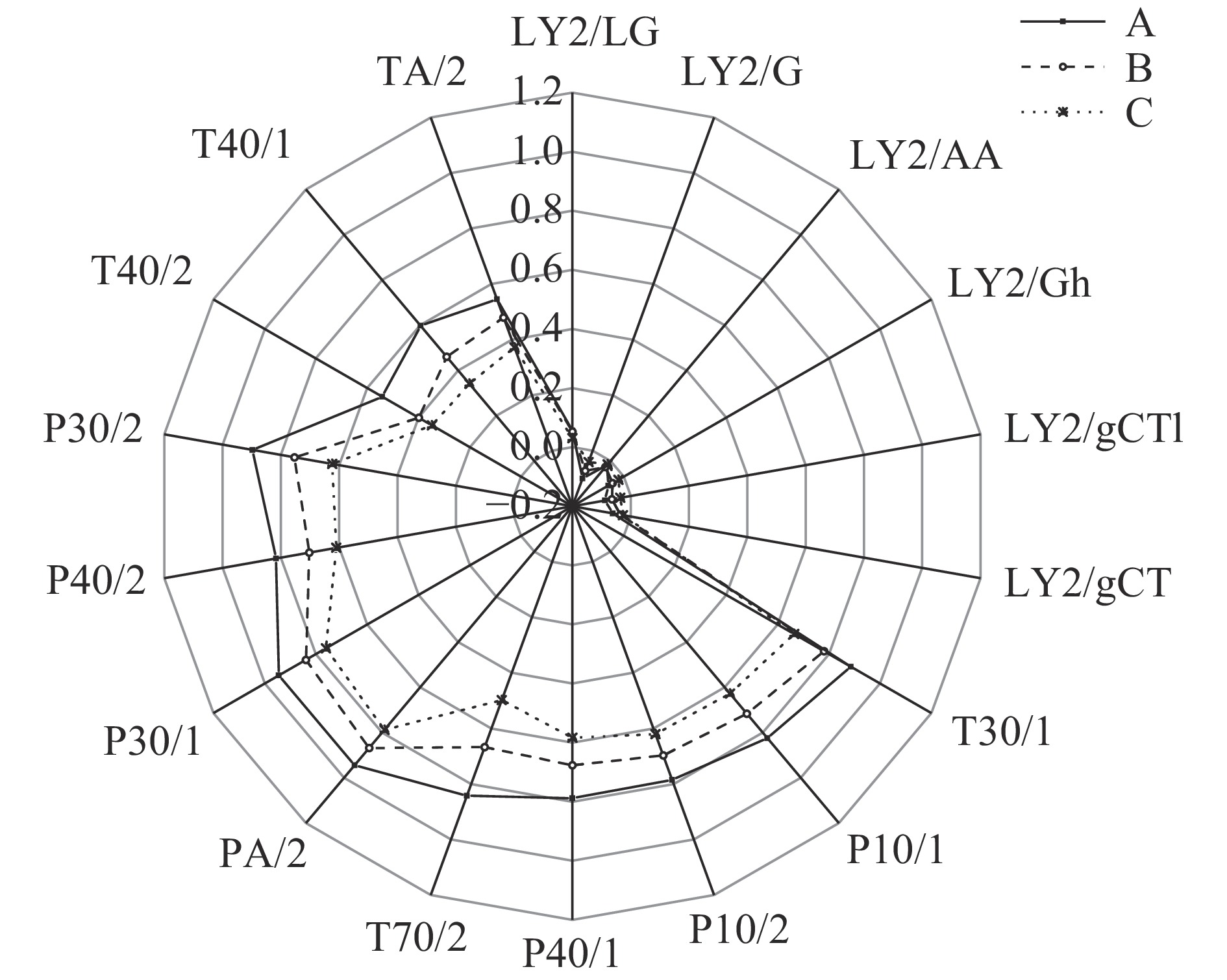
表2是电子鼻检测3种工艺的俄色茶传感器响应数据,经OPLS-DA分析的结果。表中可以看出,传感器(LY2/LG、LY2/G 、LY2/AA、LY2/Gh、LY2/gCT、P30/2、TA/2)的响应值差异不显著(P>0.05),其他传感器差异则显著(P<0.05)。从VIP值可知,LY2/LG、LY2/AA、T40/2这3根传感器的值大于1,说明其在识别样品中贡献比其他传感器大;3个样品在T40/2传感器上,差异显著且VIP值大于1,说明传感器T40/2在识别俄色茶中有重要作用。
表 2 不同工艺俄色茶电子鼻传感器响应值Table 2. Response value of Malus toringoides (Rehd.) Hughes tea electronic nose sensor in different processes传感器 性能 红茶(A) 绿茶(B) 康砖茶(C) P-value VIP LY2/LG 对氧化能力较强的气体敏感 0.056±0.004 0.052±0.004 0.031±0.005 0.309 1.018 LY2/G 对有毒气体敏感 −0.100±0.004 −0.073±0.004 −0.041±0.003 0.064 0.899 LY2/AA 对有机化合物敏感 −0.018±0.003 −0.027±0.003 −0.015±0.002 0.356 1.929 LY2/Gh 对有毒气体敏感 −0.060±0.003 −0.043±0.003 −0.020±0.005 0.122 0.915 LY2/gCTl 对有毒气体敏感 −0.088±0.004 −0.064±0.004 −0.036±0.002 0.04 0.899 LY2/gCT 对易燃气体敏感 −0.061±0.004 −0.035±0.002 −0.026±0.004 0.224 0.941 T30/1 对极性化合物敏感 0.886±0.005 0.781±0.015 0.665±0.009 0.021 0.896 P10/1 对非极性化合物敏感 0.824±0.013 0.717±0.017 0.628±0.009 0.026 0.903 P10/2 对非极性易燃气体敏感 0.785±0.013 0.698±0.014 0.621±0.011 0.038 0.898 P40/1 对氧化能力较强的气体敏感 0.788±0.017 0.677±0.020 0.583±0.008 0.034 0.901 T70/2 对芳香族化合物敏感 0.843±0.006 0.668±0.021 0.498±0.012 0.03 0.896 PA/2 对有机化合物、有毒气体敏感 0.945±0.006 0.868±0.013 0.788±0.01 0.021 0.893 P30/1 对可燃气体、有机化合物敏感 0.946±0.004 0.840±0.01 0.761±0.007 0.039 0.910 P40/2 对氧化能力较强的气体敏感 0.817±0.006 0.703±0.012 0.610±0.009 0.038 0.902 P30/2 对有机化合物敏感 0.898±0.012 0.753±0.014 0.624±0.006 0.054 0.896 T40/2 对氧化能力较强的气体敏感 0.542±0.009 0.399±0.013 0.348±0.005 0.049 1.010 T40/1 对氧化能力较强的气体敏感 0.598±0.020 0.461±0.027 0.342±0.009 0.039 0.897 TA/2 对有机化合物敏感 0.546±0.024 0.480±0.026 0.373±0.015 0.102 0.894 图1是电子鼻检测结果的传感器数据绘制的雷达图。图中可以看出红茶样品在所有传感器(除LY2型)上的响应值均高于其他样品。有研究表明,电子鼻能快速识别不同香气的茶叶,茶叶香气越浓郁,其电子鼻传感器的响应值越高[20]。说明红茶样品香气浓郁,其次是绿茶,康砖茶香气最次。
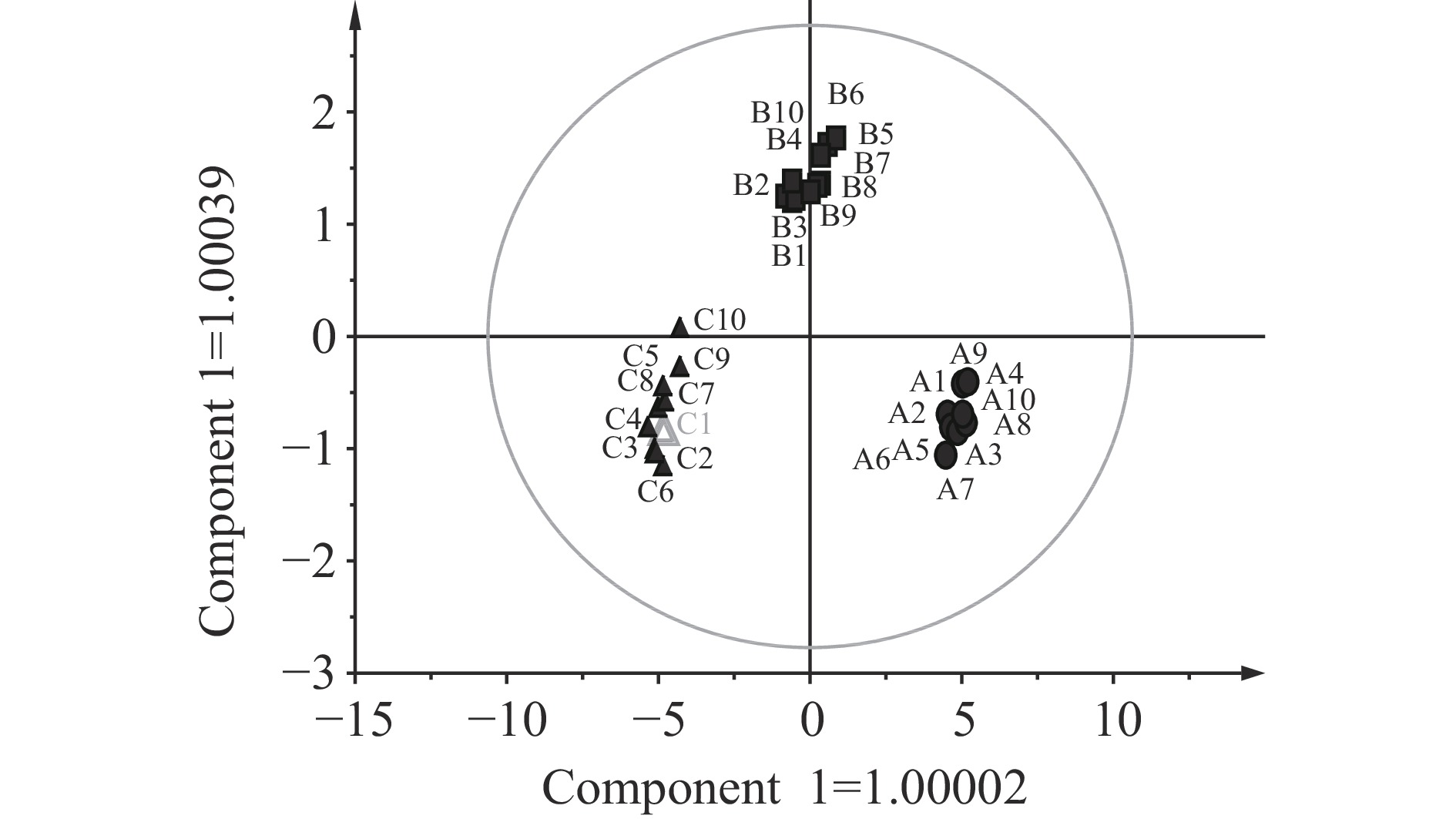
图2是样品经OPLS-DA分析的散点图。3个样品分布在不同区域,均无交叉,这既能说明工艺对俄色茶香气形成的影响大,又能说明电子鼻能够有效区分样品且重复性良好。3个样品自变量拟合指数R2X= 0.991,因变量指数R2Y=0.964;模型预测指数Q2=0.957,其预测能力为95.70%。一般认为自变量和因变量拟合指数大于0.5即可接受[21]。
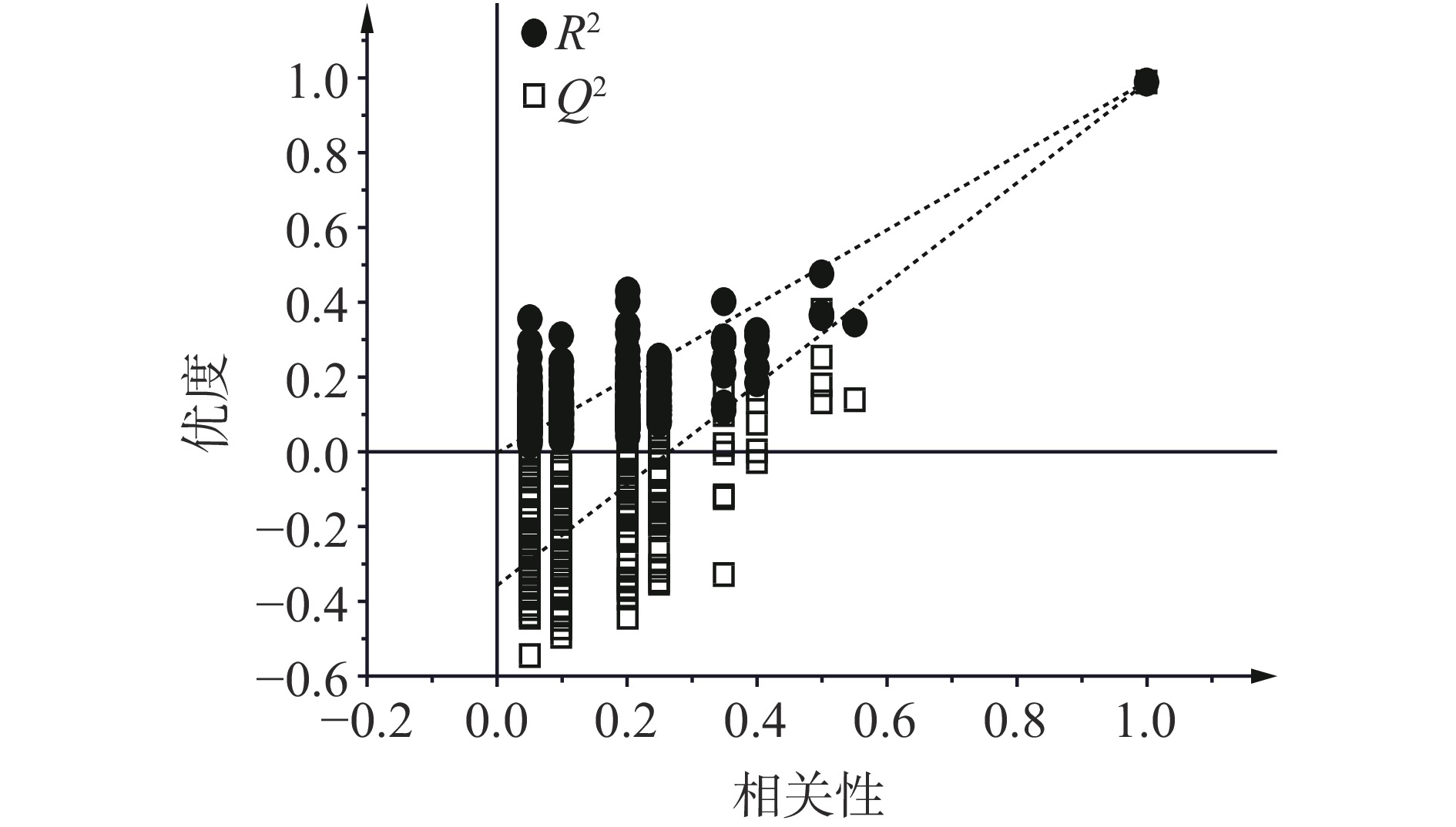
图3是判别模型经过300次(最大999)置换检验的结果。图中,所有方形和圆形点横坐标均在大于0的位置,Q2回归线与Y轴的交点小于0。这说明模型拟合效果好,模型验证有效。由此可见,通过电子鼻结合OPLS-DA数据模型来区分不同工艺的俄色茶效果良好。
2.2 不同工艺的俄色茶挥发性物质差异分析
GC-MS对俄色茶挥发物质的定性及定量检测结果见表3,分类见表4。3种工艺的俄色茶共鉴定出98种挥发性物质,红茶、绿茶和康砖茶分别鉴定出52、52和52种;相对含量分别为94.01%、90.20%和92.98%。其中包括醛类24种、酯类5种、醇类16种、烃类21种、酮类13种、呋喃4种、其他物质15种。醛类、酯类、醇类(康砖茶除外)、烃类(康砖茶)是样品主要挥发性物质。共有物质10种:异戊醛、辛醛、2-甲基庚醛、庚醛、三甲氧基酯、癸烷、2,2-二甲基癸烷、2,2,4,4-四甲基辛烷、4-甲基-3-丁烯-2-酮、2-乙基呋喃。这些被检测到的物质、种类、共有物质及含量的差异,初步反映了3种工艺条件下俄色茶气味的差异。
表 3 俄色茶挥发性物质差异分析Table 3. Difference analysis of volatile substances in Malus toringoides (Rehd.) Hughes tea序号 保留时间(min) CAS 中文名称 红茶(A,%) 绿茶(B,%) 康砖茶(C,%) 分类 1 2.121 78-84-2 异丁醛 13.48±1.00 醛类 2 2.919 16630-91-4 2-甲基庚醛 4.54±0.44 1.98±0.15 0.89±0.17 3 2.927 123-15-9 2-甲基戊醛 0.21±0.10 4 3.022 96-17-3 异戊醛 10.87±1.13 4.75±1.47 10.94±0.81 5 4.518 497-03-0 顺-2-甲基-2-丁醛 0.56±0.02 6 4.65 107-86-8 3-甲基-2-丁烯醛 0.30±0.04 11.32±1.15 7 4.743 5435-64-3 3,5,5-三甲基己醛 0.25±0.05 8 4.758 110-62-3 戊醛 0.63±0.54 9 4.833 4009-55-6 五-3,4-二烯醛 0.38±0.09 2.15±0.50 10 4.908 1576-87-0 反式-2-戊烯醛 0.70±0.16 0.34±0.05 11 6.372 66-25-1 己醛 12.69±2.40 7.51±1.04 12 7.548 63883-69-2 (E) -2-乙基-2-烯醛 0.85±0.46 13 7.628 1998-01-1 糠醛 0.77±0.04 14 8.106 872-53-7 环戊甲醛 0.10±0.02 0.17±0.05 15 8.659 505-57-7 2-己烯醛 0.78±0.09 0.25±0.06 16 8.716 6789-80-6 3-己烯醛 0.37±0.11 17 11.159 6728-31-0 (Z)-4-庚烯醛 0.15±0.01 18 11.301 111-71-7 庚醛 0.46±0.03 0.65±0.04 0.54±0.11 19 14.769 100-52-7 苯甲醛 0.81±0.17 0.69±0.24 20 17.934 124-13-0 辛醛 0.30±0.06 0.75±0.02 1.76±0.39 21 20.516 122-78-1 苯乙醛 0.27±0.03 0.27±0.04 22 25.162 42452-48-2 2,4-二甲基庚-2,4-二烯醛 0.23±0.10 23 25.257 124-19-6 壬醛 2.17±0.39 2.04±0.32 24 32.585 112-31-2 癸醛 0.12±0.00 1 1.793 687-47-8 L-乳酸乙酯 0.12±0.06 1.69±0.71 酯类 2 1.871 503-30-0 三甲氧基酯 16.70±0.61 32.29±4.17 17.73±0.54 3 3.887 109-60-4 乙酸丙酯 0.38±0.04 0.55±0.02 4 6.499 107-31-3 甲酸甲酯 3.42±1.25 5 7.010 123-86-4 乙酸丁酯 0.21±0.10 0.27±0.04 1 2.349 2026-48-4 L-缬氨醇 0.26±0.04 醇类 2 2.454 1569-50-2 3-戊烯-2-醇 1.63±0.89 2.64±0.08 3 2.899 765-42-4 环丙基甲基甲醇 2.25±0.98 4 3.322 4415-82-1 环丁基甲醇 7.20±0.56 5.78±0.78 5 3.334 1576-95-0 顺-2-戊烯-1-醇 0.07±0.03 6 4.535 123-51-3 异戊醇 0.26±0.03 0.42±0.04 7 4.563 137-32-6 活性戊醇 0.51±0.04 8 5.349 71-41-0 戊醇 0.74±0.11 0.58±0.02 9 5.416 1576-96-1 反-2-戊醇 0.44±0.04 10 8.834 928-96-1 青叶醇 3.99±0.23 1.17±0.22 11 16.485 26001-58-1 (2Z)-2-辛烯-1-醇 0.13±0.11 12 20.066 100-51-6 苯甲醇 0.20±0.04 0.78±0.22 13 23.043 111-87-5 辛醇 0.24±0.05 14 25.955 19780-39-3 3-乙基-2-庚醇 0.17±0.06 0.22±0.01 15 70.813 29783-26-4 顺-4-环戊烯-1,3-二醇 2.08±0.36 0.80±0.22 16 74.221 3391-86-4 1-辛烯-3-醇(蘑菇醇) 0.89±0.09 1 2.101 558-30-5 甲基环氧丙烷 6.33±0.33 3.46±0.25 烃类 2 2.476 18631-84-0 1-甲基-2-亚甲基环丙烷 0.38±0.09 3 5.183 2422-86-8 双环[3.2.0]庚-2,6-二烯 0.66±0.17 4 5.424 591-93-5 1,4-戊二烯 1.16±0.32 0.28±0.05 5 5.456 18631-83-9 亚乙基环丙烷 0.18±0.06 6 6.032 7423-69-0 3,5-二甲基-1-己烯 0.11±0.04 0.39±0.09 7 8.866 65378-76-9 1,2,4,4-四甲基环戊烯 0.89±0.11 8 9.437 926-54-5 trans-2-甲基戊二烯 0.36±0.09 2.13±0.09 9 9.667 2415-72-7 丙基环丙烷 0.20±0.03 1.54±0.04 10 15.737 5911-04-6 3-甲基壬烷 0.09±0.03 7.68±1.04 11 16.836 17302-37-3 2,2-二甲基癸烷 4.99±0.60 1.03±0.42 0.22±0.05 12 17.776 124-18-5 癸烷 0.29±0.06 0.29±0.02 0.33±0.08 13 18.439 13643-08-8 2,4-辛二烯 0.18±0.06 0.13±0.05 14 19.410 62183-79-3 2,2,4,4-四甲基辛烷 0.69±0.22 0.24±0.05 0.10±0.03 15 19.490 5989-27-5 D-柠檬烯 0.18±0.02 0.39±0.02 16 19.918 62108-25-2 2,6,7-三甲基癸烷 0.32±0.09 17 22.735 34825-93-9 3-(溴甲基)环己烯 0.14±0.07 18 25.020 629-50-5 正十三烷 0.25±0.04 19 30.139 1002-43-3 3-甲基十一烷 0.22±0.08 20 32.330 62108-22-9 2,5,9-三甲基癸烷 0.28±0.07 21 58.419 62108-26-3 2,6,8-三甲基癸烷 0.34±0.09 1 2.311 78-93-3 2-丁酮 2.86±0.18 酮类 2 4.475 3102-33-8 4-甲基-3-丁烯-2-酮 0.21±0.04 0.17±0.03 0.71±0.19 3 4.773 565-69-5 2-甲基-3-戊酮 0.69±0.12 4 6.284 4359-77-7 3-亚甲基-2-酮 0.14±0.01 0.59±0.03 5 8.261 110-93-0 甲基庚烯酮 0.36±0.04 0.30±0.03 6 10.653 110-43-0 2-庚酮 0.12±0.02 7 10.743 10493-98-8 2-羟基-2-环戊烯-1-酮 2.21±0.48 8 16.703 10408-15-8 6-甲基-6-庚-2-酮 0.18±0.03 9 19.913 2408-37-9 2,2,6-三甲基环己酮 0.39±0.03 10 22.094 98-86-2 苯乙酮 0.11±0.02 11 22.652 30086-02-3 3.5 -辛二烯-2-酮 0.15±0.00 12 24.421 38284-27-4 3,5-辛二烯酮 0.14±0.07 0.10±0.03 13 26.225 78-59-1 异佛尔酮 1.60±0.30 1 3.570 3208-16-0 2-乙基呋喃 1.88±0.62 2.25±1.36 8.38±0.58 呋喃 2 4.803 930-27-8 3-甲基呋喃 0.62±0.07 3 16.953 3777-69-3 2-正戊基呋喃 0.29±0.01 4 17.553 70424-14-5 (E)-2-(2-戊烯基)呋喃 0.28±0.02 1 1.768 64-18-6 甲酸 0.27±0.04 0.77±0.18 其他 2 2.789 115-10-6 二甲醚 0.11±0.08 0.79±0.05 3 5.559 13218-13-8 硝基乙腈 0.37±0.03 4 7.225 646-07-1 4-甲基戊酸 0.17±0.05 5 7.308 5390-28-3 2-硝基乙醇丙酸盐 0.32±0.04 0.23±0.14 6 9.350 108-38-3 间二甲苯 0.11±0.02 0.15±0.05 7 10.488 7714-32-1 苯乙基甲基亚砜 3.08±0.59 8 10.506 106-42-3 对二甲苯 0.22±0.13 0.08±0.03 9 13.097 95-65-8 3,4-二甲基苯酚 0.48±0.15 10 18.187 71487-16-6 3-甲基-4-戊醇醋酸盐 0.17±0.07 11 22.987 4810-09-7 3-甲基-1-庚烯 0.10±0.03 0.19±0.02 12 25.91 527-53-7 1,2,3,5-四甲基苯 0.14±0.04 13 30.226 91-20-3 萘 0.13±0.02 14 38.132 91-57-6 2-甲基萘 0.48±0.09 15 70.703 2443-40-5 3-甲基环氧乙烷-2-羧酸 0.71±0.27 1.15±0.18 表 4 俄色茶挥发性物质种类及相对含量Table 4. Types and relative content of volatile substances in Malus toringoides (Rehd.) Hughes tea类别 红茶(A) 绿茶(B) 康砖茶(C) 种类 含量(%) 种类 含量(%) 种类 含量(%) 醛类 15 48.62 16 21.33 10 29.04 酯类 4 17.41 4 36.53 2 19.42 醇类 9 14.09 7 13.93 8 5.43 烃类 12 8.89 7 8.55 16 19.30 酮类 5 1.54 7 4.29 6 5.20 呋喃 1 1.88 3 3.16 2 8.66 其他 6 1.59 8 2.41 8 5.93 合计 52 94.01 52 90.20 52 92.98 醛类物质生成途径比较复杂,一般认为醛类物质是微生物发酵时,不同氨基酸在对应酶作用下生成不同的醛类物质[22];醛类物质也可通过脂肪酸过氧化及降解产生或者是某些不稳定醇被氧化而成为醛类物质[23]。醛类物质是俄色茶主要挥发性物质,其含量在21.33%~48.62%之间。异戊醛(沸点92~93 ℃)是三个样品主要共有物质,且含量较高(10.87%、4.75%、10.94%),在发酵茶中,特别是红茶[19]和黑茶[24]中比较常见。异丁醛(沸点94 ℃)是俄色红茶独有的主要挥发性物质,含量为13.48%。李慧等[19]认为异戊醛、异丁醛是构成红茶果香、甜香、焦糖香的主体香气物质。因此可认为异丁醛是红茶区别于绿茶和康砖茶的关键物质。已醛是红茶和绿茶检测到的共有物质,含量均大于7.50%,在康砖茶中未检出。已醛在大多数茶叶中均有检出,其含量在红茶中相对较高[19]。3-甲基-2-丁烯醛(异戊烯醛)是康砖茶中检出的含量很高的物质(11.32%),是一种具有脂肪香味的物质[25];其在六大茶类[26-27]以及一些六大茶类以外的茶(如各种保健茶)中含量均不高[25,28],而俄色康砖茶含量高,但无阈值相关数据,需要进一步研究。
酯类香气形成[29]可能是氨基酸在脱氨、脱羧而氧化形成酸和醇,最后经过酯合成酶作用,从而形成酯香。酯类物质在三个样品中种类较少,但含量高(17.41%~36.53%)。三甲氧基酯在三个样品中的含量均高于16%,是含量最高物质,但无其气味和阈值相关数据。三甲氧基酯在金牡丹[30]及铁观音[31]中有检出。甲酸甲酯是一种具有甜香、青果香气的物质,仅在俄色绿茶中有检出,且含量较高(3.42%)。
茶叶中醇类物质的形成:蛋白质水解成氨基酸以及氨基酸与酶、邻醌等作用生成醇类物质[32]。醇类物质含量在5.43%~14.09%之间,通常具有花、果气息。红茶和绿茶共有物质3种,环丁基甲醇、青叶醇是含量较高的物质(>1%)。红茶与康砖茶共有物质2种,为苯甲醇,3-戊烯-2-醇(>1.50%)。绿茶与康砖茶共有物质1种:顺-4-环戊烯-1,3-二醇。
三个样品均检测到烃类物质,其含量均大于8%。康砖茶烃类物质含量最高(19.30%)。烃类物质中以烷烃为主,一般认为烷烃类物质阈值较高[33],其可能对康砖茶香气形成贡献较小。
2.3 俄色茶ROAV分析及差异比较
为探明3种工艺的俄色茶中各挥发性组分对样品整体香气贡献,实验结合挥发性物质的气味阈值、香气描述以及香气类型,对52种(能检索到阈值)挥发性物质进行分析,结果见表5。红茶、绿茶、康砖茶分别检测到28、35、19种有阈值的香气物质。根据香气描述和香气类型:果香(17个)、腥香(8个)、焙烤香(6个)、异香(4个)、花香(3个)、焦香(2个)、迷香(1个)、奶香(1个)、肉香(1个)、焦糖香(1个)、烟香(1个);果香、腥香和焙烤香是样品主要香气。依据香气类型和ROAV值,果香(12160768)、甜香焦糖香(8986444)、腥香(596098)对红茶气味的形成相对贡献较大;对红茶香气贡献最大的10种物质是异戊醛、异丁醛、壬醛、1-辛烯-3-醇、辛醛、己醛、庚醛、异戊醇、苯乙醛、活性戊醇;果香(6297561)、花香(1317535)、焙烤香(285808)对绿茶气味的形成相对贡献较大;对绿茶贡献最大的10种物质是异戊醛、壬醛、辛醛、庚醛、己醛、2-正戊基呋喃、苯乙醛、癸醛、萘、2-己烯醛;果香(10129749)、花香(3001136)、腥香(1918858)对康砖茶气味的形成贡献相对较大;对康砖茶香气贡献最大的10种香气物质是异戊醛、辛醛、3-己烯醛、庚醛、2-甲基萘、异戊醇、2-甲基戊醛、戊醛、D-柠檬烯、3-戊烯-2-醇。果香类物质对俄色茶气味的形成贡献大,醛、醇是俄色茶香气的主要来源。异戊醛、辛醛、庚醛是3种俄色茶共有主要香气物质,且异戊醛是含量最高(有气味)的物质。可以推测异戊醛可能是俄色茶关键香气物质。
表 5 俄色茶香气成分的ROAV分析Table 5. ROAV analysis of aroma components of Malus toringoides (Rehd.) Hughes tea序号 中文名称 阈值(g·kg−1) 红茶(A) 绿茶(B) 康砖茶(C) 香气描述 香气类型 1 异丁醛 0.0000015 8986444.44 0.00 0.00 焦糖、可可 甜香、焦糖香 2 甲酸 2.44 0.11 0.32 0.00 − − 3 反-2-戊醇 0.0000892 0.00 4970.10 0.00 − − 4 二甲醚 0.303967 0.35 2.59 0.00 轻微醚香味 迷香 5 癸醛 0.000003 0.00 40555.56 0.00 青草味 腥香 6 2-丁酮 0.0354 0.00 80.80 0.00 奶油味 奶香 7 3-戊烯-2-醇 0.0004 0.00 4078.33 6594.17 草青味 腥香 8 2-甲基戊醛 0.0000032 0.00 0.00 65312.50 果香 果香 9 异戊醛 0.0000011 9881515.15 4318484.85 9945757.58 果香 果香 10 顺-2-戊烯-1-醇 0.00072 0.00 0.00 90.28 脂香味 焙烤香 11 2-乙基呋喃 0.008 235.21 281.54 1046.88 烧焦味 焦香 12 乙酸丙酯 0.002 187.50 274.33 0.00 水果味 果香 13 异戊醇 0.000004 63750.00 0.00 105333.33 水果香 果香 14 活性戊醇 0.0000159 31823.90 0.00 0.00 水果香 果香 15 2-甲基-3-戊酮 0.00008 8645.83 0.00 0.00 − − 16 顺-2-甲基-2-丁醛 0.00046 0.00 1227.54 0.00 苹果香 果香 17 戊醛 0.000012 0.00 0.00 52472.22 杏仁、麦芽、脂香 焙烤香 18 反式-2-戊烯醛 0.00098 712.93 344.22 0.00 胶臭味 异香 19 戊醇 0.0001502 4906.79 3854.86 0.00 果香 果香 20 己醛 0.000073 173803.65 102899.54 0.00 苹果、鲜香 果香 21 甲酸甲酯 0.49 0.00 6.99 0.00 芳香 花香 22 乙酸丁酯 0.000058 3534.48 4609.20 0.00 杏仁、青草 焙烤香 23 糠醛 0.009562 80.70 0.00 0.00 水果香 果香 24 4-甲基戊酸 0.00081 0.00 209.88 0.00 似红糖香 焦香 25 2,2,6-三甲基环己酮 0.0001 0.00 0.00 3923.33 − − 26 苯乙酮 0.000065 0.00 0.00 1692.31 蘑菇味 腥香 27 2-己烯醛 0.00003 26000.00 8300.00 0.00 苹果 果香 28 青叶醇 0.0019 2097.54 614.39 0.00 青草 腥香 29 间二甲苯 0.001 112.67 146.00 0.00 塑料味 异香 30 3-己烯醛 0.00000021 0.00 0.00 1750793.65 青草味 腥香 31 对二甲苯 0.001 216.00 81.33 0.00 坚果味 果香 32 2-庚酮 0.00014 0.00 854.76 0.00 坚果味 果香 33 (Z)-4-庚烯醛 0.00004 0.00 3800.00 0.00 油脂味 肉香 34 庚醛 0.0000028 165833.33 231428.57 193095.24 脂香、坚果香 焙烤香 35 3,4-二甲基苯酚 0.0012 0.00 0.00 399.72 − − 36 苯甲醛 0.00075089 1079.16 915.36 0.00 樱桃 果香 37 甲基庚烯酮 0.000068 5284.31 4338.24 0.00 柑橘香、青草 果香 38 2-正戊基呋喃 0.0000058 0.00 49770.11 0.00 可可、烧烤味 焙烤香 39 癸烷 0.01 29.00 29.10 33.40 汽油味 异香 40 辛醛 0.000000587 508233.96 1275411.70 3001135.72 芳香 花香 41 2,4-辛二烯 0.012 14.64 11.00 0.00 − − 42 苯甲醇 0.00254621 78.81 0.00 306.60 果香、焙烤味 焙烤香 43 D-柠檬烯 0.000034 0.00 5421.57 11421.57 柑橘、水果味 果香 44 苯乙醛 0.0000063 43333.33 42116.40 0.00 风信子、水仙花 花香 45 3.5 -辛二烯-2-酮 0.00015 0.00 995.56 0.00 − − 46 辛醇 0.0001258 0.00 0.00 1923.69 柑橘味 果香 47 异佛尔酮 0.011 0.00 0.00 145.21 刺激性气味 异香 48 萘 0.000006 0.00 21444.44 0.00 香辛味、烟味 烟香 49 正十三烷 0.042 0.00 5.92 0.00 青草味 腥香 50 壬醛 0.0000011 1972121.21 1850909.09 0.00 青香、柠檬 果香 51 2-甲基萘 0.000003 0.00 0.00 159777.78 青草味、霉味 腥香 52 1-辛烯-3-醇 0.0000015 594000.00 0.00 0.00 蘑菇、泥土 腥香 注:所有阈值数据均来自文献[34],“−”表示没有查阅到其香气类型。 2.4 挥发性物质差异性分析
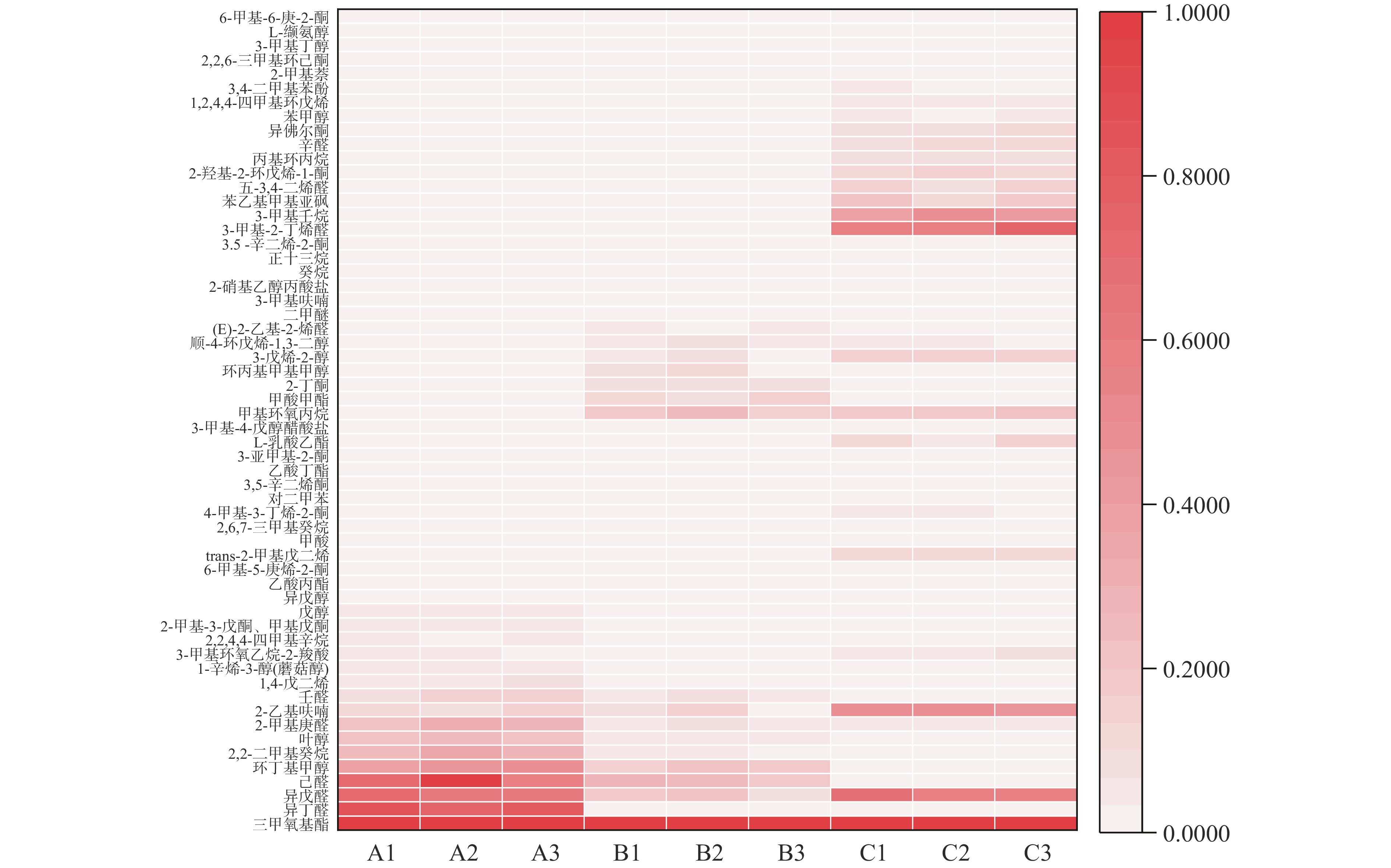
根据表4的分类,选取每个样品中每类含量前5的物质[35]进行差异性热图分析,其结果见图4。由图4各种物质丰度可知,三甲氧基酯、异戊醛、2-乙基呋喃是3个样品的主要共有挥发性物质。除共有物之外,红茶主要挥发性物质是异丁醛、己醛、环丁基甲醇、2,2-二甲基癸烷、叶醇、2-甲基庚醛、2-乙基呋喃;绿茶主要挥发性物质是己醛、环丁基甲醇、2-乙基呋喃、甲基环氧丙烷、甲酸甲酯、环丙基甲基甲醇;康砖茶主要挥发性物质为2-乙基呋喃、trans-2-甲基戊二烯、L-乳酸乙酯、甲基环氧丙烷、3-戊烯-2-醇、3-甲基-2-丁烯醛、3-甲基壬烷、苯乙基甲基亚砜、五-3,4-二烯醛、2-羟基-2-环戊烯-1-酮、辛醛、异佛尔酮。
2,2-二甲基癸烷、叶醇、2-甲基庚醛、甲基环氧丙烷、甲酸甲酯、环丙基甲基甲醇的丰度反应了红茶、绿茶的差异。己醛、环丁基甲醇、trans-2-甲基戊二烯、L-乳酸乙酯、3-戊烯-2-醇、3-甲基-2-丁烯醛、3-甲基壬烷、苯乙基甲基亚砜、五-3,4-二烯醛、2-羟基-2-环戊烯-1-酮、辛醛、异佛尔酮的丰度反应了绿茶、康砖茶的差异。红茶、康砖茶的差异与绿茶、康砖茶类似,仅在绿茶、康砖茶差异的基础上增加了叶醇、甲基环氧丙烷。纵观整个热图, 3个样品差异明显。
3. 结论
实验以俄色茶为研究对象,通过电子鼻和GC-MS分析,结合OPLS-DA、ROAV、差异性热图等方法对俄色茶整体气味轮廓进行识别和鉴定具体挥发性物质。电子鼻雷达图及OPLS-DA分析表明不同工艺的俄色茶差异明显。GC-MS检测表明三种处理方式分别鉴定出52、52和52种,共计98种挥发性物质;醛类、酯类、烃类是俄色茶主要挥发性物质,醇类是红茶、绿茶主要挥发性物质;醛类、酯类、烃类和醇类的含量差异是导致不同工艺俄色茶香气异同的主要原因。ROAV值结合香气类型分析表明:果香、甜香和腥香对红茶香气的形成贡献较大,果香、花香、焙烤香对绿茶香气的形成贡献较大,果香、花香和腥香对康砖茶香气的形成贡献较大;果香对俄色茶香气的形成相对贡献较大,异戊醛可能是俄色茶的关键香气物质。差异性热图分析表明三甲氧基酯、异戊醛、2-乙基呋喃是3个样品主要共有挥发性物质。
三甲氧基酯是俄色茶含量最高的共有物质,3-甲基-2-丁烯醛(有气味的相关报道)是康砖茶中含量较高的物质(11.32%),但目前没有其气味及阈值相关报道,故无法判断其在俄色茶中具体作用。下一步课题组将结合GC-O对其进行进一步研究。
-
表 1 样品信息表
Table 1 Sample information
样品编号 样品名称 配料 A 俄色红茶 高山变叶海叶棠嫩芽 B 俄色绿茶 高山变叶海叶棠嫩芽 C 俄色康砖茶 高山变叶海棠叶碎嫩芽 表 2 不同工艺俄色茶电子鼻传感器响应值
Table 2 Response value of Malus toringoides (Rehd.) Hughes tea electronic nose sensor in different processes
传感器 性能 红茶(A) 绿茶(B) 康砖茶(C) P-value VIP LY2/LG 对氧化能力较强的气体敏感 0.056±0.004 0.052±0.004 0.031±0.005 0.309 1.018 LY2/G 对有毒气体敏感 −0.100±0.004 −0.073±0.004 −0.041±0.003 0.064 0.899 LY2/AA 对有机化合物敏感 −0.018±0.003 −0.027±0.003 −0.015±0.002 0.356 1.929 LY2/Gh 对有毒气体敏感 −0.060±0.003 −0.043±0.003 −0.020±0.005 0.122 0.915 LY2/gCTl 对有毒气体敏感 −0.088±0.004 −0.064±0.004 −0.036±0.002 0.04 0.899 LY2/gCT 对易燃气体敏感 −0.061±0.004 −0.035±0.002 −0.026±0.004 0.224 0.941 T30/1 对极性化合物敏感 0.886±0.005 0.781±0.015 0.665±0.009 0.021 0.896 P10/1 对非极性化合物敏感 0.824±0.013 0.717±0.017 0.628±0.009 0.026 0.903 P10/2 对非极性易燃气体敏感 0.785±0.013 0.698±0.014 0.621±0.011 0.038 0.898 P40/1 对氧化能力较强的气体敏感 0.788±0.017 0.677±0.020 0.583±0.008 0.034 0.901 T70/2 对芳香族化合物敏感 0.843±0.006 0.668±0.021 0.498±0.012 0.03 0.896 PA/2 对有机化合物、有毒气体敏感 0.945±0.006 0.868±0.013 0.788±0.01 0.021 0.893 P30/1 对可燃气体、有机化合物敏感 0.946±0.004 0.840±0.01 0.761±0.007 0.039 0.910 P40/2 对氧化能力较强的气体敏感 0.817±0.006 0.703±0.012 0.610±0.009 0.038 0.902 P30/2 对有机化合物敏感 0.898±0.012 0.753±0.014 0.624±0.006 0.054 0.896 T40/2 对氧化能力较强的气体敏感 0.542±0.009 0.399±0.013 0.348±0.005 0.049 1.010 T40/1 对氧化能力较强的气体敏感 0.598±0.020 0.461±0.027 0.342±0.009 0.039 0.897 TA/2 对有机化合物敏感 0.546±0.024 0.480±0.026 0.373±0.015 0.102 0.894 表 3 俄色茶挥发性物质差异分析
Table 3 Difference analysis of volatile substances in Malus toringoides (Rehd.) Hughes tea
序号 保留时间(min) CAS 中文名称 红茶(A,%) 绿茶(B,%) 康砖茶(C,%) 分类 1 2.121 78-84-2 异丁醛 13.48±1.00 醛类 2 2.919 16630-91-4 2-甲基庚醛 4.54±0.44 1.98±0.15 0.89±0.17 3 2.927 123-15-9 2-甲基戊醛 0.21±0.10 4 3.022 96-17-3 异戊醛 10.87±1.13 4.75±1.47 10.94±0.81 5 4.518 497-03-0 顺-2-甲基-2-丁醛 0.56±0.02 6 4.65 107-86-8 3-甲基-2-丁烯醛 0.30±0.04 11.32±1.15 7 4.743 5435-64-3 3,5,5-三甲基己醛 0.25±0.05 8 4.758 110-62-3 戊醛 0.63±0.54 9 4.833 4009-55-6 五-3,4-二烯醛 0.38±0.09 2.15±0.50 10 4.908 1576-87-0 反式-2-戊烯醛 0.70±0.16 0.34±0.05 11 6.372 66-25-1 己醛 12.69±2.40 7.51±1.04 12 7.548 63883-69-2 (E) -2-乙基-2-烯醛 0.85±0.46 13 7.628 1998-01-1 糠醛 0.77±0.04 14 8.106 872-53-7 环戊甲醛 0.10±0.02 0.17±0.05 15 8.659 505-57-7 2-己烯醛 0.78±0.09 0.25±0.06 16 8.716 6789-80-6 3-己烯醛 0.37±0.11 17 11.159 6728-31-0 (Z)-4-庚烯醛 0.15±0.01 18 11.301 111-71-7 庚醛 0.46±0.03 0.65±0.04 0.54±0.11 19 14.769 100-52-7 苯甲醛 0.81±0.17 0.69±0.24 20 17.934 124-13-0 辛醛 0.30±0.06 0.75±0.02 1.76±0.39 21 20.516 122-78-1 苯乙醛 0.27±0.03 0.27±0.04 22 25.162 42452-48-2 2,4-二甲基庚-2,4-二烯醛 0.23±0.10 23 25.257 124-19-6 壬醛 2.17±0.39 2.04±0.32 24 32.585 112-31-2 癸醛 0.12±0.00 1 1.793 687-47-8 L-乳酸乙酯 0.12±0.06 1.69±0.71 酯类 2 1.871 503-30-0 三甲氧基酯 16.70±0.61 32.29±4.17 17.73±0.54 3 3.887 109-60-4 乙酸丙酯 0.38±0.04 0.55±0.02 4 6.499 107-31-3 甲酸甲酯 3.42±1.25 5 7.010 123-86-4 乙酸丁酯 0.21±0.10 0.27±0.04 1 2.349 2026-48-4 L-缬氨醇 0.26±0.04 醇类 2 2.454 1569-50-2 3-戊烯-2-醇 1.63±0.89 2.64±0.08 3 2.899 765-42-4 环丙基甲基甲醇 2.25±0.98 4 3.322 4415-82-1 环丁基甲醇 7.20±0.56 5.78±0.78 5 3.334 1576-95-0 顺-2-戊烯-1-醇 0.07±0.03 6 4.535 123-51-3 异戊醇 0.26±0.03 0.42±0.04 7 4.563 137-32-6 活性戊醇 0.51±0.04 8 5.349 71-41-0 戊醇 0.74±0.11 0.58±0.02 9 5.416 1576-96-1 反-2-戊醇 0.44±0.04 10 8.834 928-96-1 青叶醇 3.99±0.23 1.17±0.22 11 16.485 26001-58-1 (2Z)-2-辛烯-1-醇 0.13±0.11 12 20.066 100-51-6 苯甲醇 0.20±0.04 0.78±0.22 13 23.043 111-87-5 辛醇 0.24±0.05 14 25.955 19780-39-3 3-乙基-2-庚醇 0.17±0.06 0.22±0.01 15 70.813 29783-26-4 顺-4-环戊烯-1,3-二醇 2.08±0.36 0.80±0.22 16 74.221 3391-86-4 1-辛烯-3-醇(蘑菇醇) 0.89±0.09 1 2.101 558-30-5 甲基环氧丙烷 6.33±0.33 3.46±0.25 烃类 2 2.476 18631-84-0 1-甲基-2-亚甲基环丙烷 0.38±0.09 3 5.183 2422-86-8 双环[3.2.0]庚-2,6-二烯 0.66±0.17 4 5.424 591-93-5 1,4-戊二烯 1.16±0.32 0.28±0.05 5 5.456 18631-83-9 亚乙基环丙烷 0.18±0.06 6 6.032 7423-69-0 3,5-二甲基-1-己烯 0.11±0.04 0.39±0.09 7 8.866 65378-76-9 1,2,4,4-四甲基环戊烯 0.89±0.11 8 9.437 926-54-5 trans-2-甲基戊二烯 0.36±0.09 2.13±0.09 9 9.667 2415-72-7 丙基环丙烷 0.20±0.03 1.54±0.04 10 15.737 5911-04-6 3-甲基壬烷 0.09±0.03 7.68±1.04 11 16.836 17302-37-3 2,2-二甲基癸烷 4.99±0.60 1.03±0.42 0.22±0.05 12 17.776 124-18-5 癸烷 0.29±0.06 0.29±0.02 0.33±0.08 13 18.439 13643-08-8 2,4-辛二烯 0.18±0.06 0.13±0.05 14 19.410 62183-79-3 2,2,4,4-四甲基辛烷 0.69±0.22 0.24±0.05 0.10±0.03 15 19.490 5989-27-5 D-柠檬烯 0.18±0.02 0.39±0.02 16 19.918 62108-25-2 2,6,7-三甲基癸烷 0.32±0.09 17 22.735 34825-93-9 3-(溴甲基)环己烯 0.14±0.07 18 25.020 629-50-5 正十三烷 0.25±0.04 19 30.139 1002-43-3 3-甲基十一烷 0.22±0.08 20 32.330 62108-22-9 2,5,9-三甲基癸烷 0.28±0.07 21 58.419 62108-26-3 2,6,8-三甲基癸烷 0.34±0.09 1 2.311 78-93-3 2-丁酮 2.86±0.18 酮类 2 4.475 3102-33-8 4-甲基-3-丁烯-2-酮 0.21±0.04 0.17±0.03 0.71±0.19 3 4.773 565-69-5 2-甲基-3-戊酮 0.69±0.12 4 6.284 4359-77-7 3-亚甲基-2-酮 0.14±0.01 0.59±0.03 5 8.261 110-93-0 甲基庚烯酮 0.36±0.04 0.30±0.03 6 10.653 110-43-0 2-庚酮 0.12±0.02 7 10.743 10493-98-8 2-羟基-2-环戊烯-1-酮 2.21±0.48 8 16.703 10408-15-8 6-甲基-6-庚-2-酮 0.18±0.03 9 19.913 2408-37-9 2,2,6-三甲基环己酮 0.39±0.03 10 22.094 98-86-2 苯乙酮 0.11±0.02 11 22.652 30086-02-3 3.5 -辛二烯-2-酮 0.15±0.00 12 24.421 38284-27-4 3,5-辛二烯酮 0.14±0.07 0.10±0.03 13 26.225 78-59-1 异佛尔酮 1.60±0.30 1 3.570 3208-16-0 2-乙基呋喃 1.88±0.62 2.25±1.36 8.38±0.58 呋喃 2 4.803 930-27-8 3-甲基呋喃 0.62±0.07 3 16.953 3777-69-3 2-正戊基呋喃 0.29±0.01 4 17.553 70424-14-5 (E)-2-(2-戊烯基)呋喃 0.28±0.02 1 1.768 64-18-6 甲酸 0.27±0.04 0.77±0.18 其他 2 2.789 115-10-6 二甲醚 0.11±0.08 0.79±0.05 3 5.559 13218-13-8 硝基乙腈 0.37±0.03 4 7.225 646-07-1 4-甲基戊酸 0.17±0.05 5 7.308 5390-28-3 2-硝基乙醇丙酸盐 0.32±0.04 0.23±0.14 6 9.350 108-38-3 间二甲苯 0.11±0.02 0.15±0.05 7 10.488 7714-32-1 苯乙基甲基亚砜 3.08±0.59 8 10.506 106-42-3 对二甲苯 0.22±0.13 0.08±0.03 9 13.097 95-65-8 3,4-二甲基苯酚 0.48±0.15 10 18.187 71487-16-6 3-甲基-4-戊醇醋酸盐 0.17±0.07 11 22.987 4810-09-7 3-甲基-1-庚烯 0.10±0.03 0.19±0.02 12 25.91 527-53-7 1,2,3,5-四甲基苯 0.14±0.04 13 30.226 91-20-3 萘 0.13±0.02 14 38.132 91-57-6 2-甲基萘 0.48±0.09 15 70.703 2443-40-5 3-甲基环氧乙烷-2-羧酸 0.71±0.27 1.15±0.18 表 4 俄色茶挥发性物质种类及相对含量
Table 4 Types and relative content of volatile substances in Malus toringoides (Rehd.) Hughes tea
类别 红茶(A) 绿茶(B) 康砖茶(C) 种类 含量(%) 种类 含量(%) 种类 含量(%) 醛类 15 48.62 16 21.33 10 29.04 酯类 4 17.41 4 36.53 2 19.42 醇类 9 14.09 7 13.93 8 5.43 烃类 12 8.89 7 8.55 16 19.30 酮类 5 1.54 7 4.29 6 5.20 呋喃 1 1.88 3 3.16 2 8.66 其他 6 1.59 8 2.41 8 5.93 合计 52 94.01 52 90.20 52 92.98 表 5 俄色茶香气成分的ROAV分析
Table 5 ROAV analysis of aroma components of Malus toringoides (Rehd.) Hughes tea
序号 中文名称 阈值(g·kg−1) 红茶(A) 绿茶(B) 康砖茶(C) 香气描述 香气类型 1 异丁醛 0.0000015 8986444.44 0.00 0.00 焦糖、可可 甜香、焦糖香 2 甲酸 2.44 0.11 0.32 0.00 − − 3 反-2-戊醇 0.0000892 0.00 4970.10 0.00 − − 4 二甲醚 0.303967 0.35 2.59 0.00 轻微醚香味 迷香 5 癸醛 0.000003 0.00 40555.56 0.00 青草味 腥香 6 2-丁酮 0.0354 0.00 80.80 0.00 奶油味 奶香 7 3-戊烯-2-醇 0.0004 0.00 4078.33 6594.17 草青味 腥香 8 2-甲基戊醛 0.0000032 0.00 0.00 65312.50 果香 果香 9 异戊醛 0.0000011 9881515.15 4318484.85 9945757.58 果香 果香 10 顺-2-戊烯-1-醇 0.00072 0.00 0.00 90.28 脂香味 焙烤香 11 2-乙基呋喃 0.008 235.21 281.54 1046.88 烧焦味 焦香 12 乙酸丙酯 0.002 187.50 274.33 0.00 水果味 果香 13 异戊醇 0.000004 63750.00 0.00 105333.33 水果香 果香 14 活性戊醇 0.0000159 31823.90 0.00 0.00 水果香 果香 15 2-甲基-3-戊酮 0.00008 8645.83 0.00 0.00 − − 16 顺-2-甲基-2-丁醛 0.00046 0.00 1227.54 0.00 苹果香 果香 17 戊醛 0.000012 0.00 0.00 52472.22 杏仁、麦芽、脂香 焙烤香 18 反式-2-戊烯醛 0.00098 712.93 344.22 0.00 胶臭味 异香 19 戊醇 0.0001502 4906.79 3854.86 0.00 果香 果香 20 己醛 0.000073 173803.65 102899.54 0.00 苹果、鲜香 果香 21 甲酸甲酯 0.49 0.00 6.99 0.00 芳香 花香 22 乙酸丁酯 0.000058 3534.48 4609.20 0.00 杏仁、青草 焙烤香 23 糠醛 0.009562 80.70 0.00 0.00 水果香 果香 24 4-甲基戊酸 0.00081 0.00 209.88 0.00 似红糖香 焦香 25 2,2,6-三甲基环己酮 0.0001 0.00 0.00 3923.33 − − 26 苯乙酮 0.000065 0.00 0.00 1692.31 蘑菇味 腥香 27 2-己烯醛 0.00003 26000.00 8300.00 0.00 苹果 果香 28 青叶醇 0.0019 2097.54 614.39 0.00 青草 腥香 29 间二甲苯 0.001 112.67 146.00 0.00 塑料味 异香 30 3-己烯醛 0.00000021 0.00 0.00 1750793.65 青草味 腥香 31 对二甲苯 0.001 216.00 81.33 0.00 坚果味 果香 32 2-庚酮 0.00014 0.00 854.76 0.00 坚果味 果香 33 (Z)-4-庚烯醛 0.00004 0.00 3800.00 0.00 油脂味 肉香 34 庚醛 0.0000028 165833.33 231428.57 193095.24 脂香、坚果香 焙烤香 35 3,4-二甲基苯酚 0.0012 0.00 0.00 399.72 − − 36 苯甲醛 0.00075089 1079.16 915.36 0.00 樱桃 果香 37 甲基庚烯酮 0.000068 5284.31 4338.24 0.00 柑橘香、青草 果香 38 2-正戊基呋喃 0.0000058 0.00 49770.11 0.00 可可、烧烤味 焙烤香 39 癸烷 0.01 29.00 29.10 33.40 汽油味 异香 40 辛醛 0.000000587 508233.96 1275411.70 3001135.72 芳香 花香 41 2,4-辛二烯 0.012 14.64 11.00 0.00 − − 42 苯甲醇 0.00254621 78.81 0.00 306.60 果香、焙烤味 焙烤香 43 D-柠檬烯 0.000034 0.00 5421.57 11421.57 柑橘、水果味 果香 44 苯乙醛 0.0000063 43333.33 42116.40 0.00 风信子、水仙花 花香 45 3.5 -辛二烯-2-酮 0.00015 0.00 995.56 0.00 − − 46 辛醇 0.0001258 0.00 0.00 1923.69 柑橘味 果香 47 异佛尔酮 0.011 0.00 0.00 145.21 刺激性气味 异香 48 萘 0.000006 0.00 21444.44 0.00 香辛味、烟味 烟香 49 正十三烷 0.042 0.00 5.92 0.00 青草味 腥香 50 壬醛 0.0000011 1972121.21 1850909.09 0.00 青香、柠檬 果香 51 2-甲基萘 0.000003 0.00 0.00 159777.78 青草味、霉味 腥香 52 1-辛烯-3-醇 0.0000015 594000.00 0.00 0.00 蘑菇、泥土 腥香 注:所有阈值数据均来自文献[34],“−”表示没有查阅到其香气类型。 -
[1] 嘎务. 藏药晶镜本草: 藏文[M]. 北京: 民族出版社, 1995 GA W . Tibetan medicine crystal mirror herb: Tibetan[M]. Beijing: Ethnic Publishing House, 1995.
[2] 周海玉, 李敏, 蔡晓洋, 等. 藏药俄色果对急性酒精性肝损伤小鼠的保护作用及其机制初探[J]. 中药材,2016(1):193−196. [ZHOU H Y, LI M, CAI X Y, et al. Preliminary study on the protective effect and mechanism of Tibetan medicine Oseko on mice with acute alcoholic liver injury[J]. Traditional Chinese Medicine,2016(1):193−196. ZHOU H Y, LI M, CAI X Y, et al. Preliminary study on the protective effect and mechanism of Tibetan medicine Oseko on mice with acute alcoholic liver injury [J] Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2016 (1): 4.
[3] LI D, PENG C, XIE X, et al. Antidiabetic effect of flavonoids from Malus toringoides (Rehd.) Hughes leaves in diabetic mice and rats[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2014,153(3):561−567. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.02.026
[4] WANG H, XU Q, CHAI C, et al. Nutritional components of fruits and leaves of Malus toringoides and Malus transitoria in western Sichuan[J]. Scientia Silvae Sinicae,2010,46(8):157−161.
[5] 夏冬梅, 李敏, 王道清, 等. 藏药俄色叶中根皮苷, 根皮素含量分析[J]. 中国现代中药,2014(8):618−622. [XIA D M, LI M, WANG D Q, et al. Analysis of phloridzin and phloridzin contents in the leaves of Tibetan medicine Ruse[J]. Modern Chinese Medicine,2014(8):618−622. XIA D M, LI M, WANG D Q, et al. Analysis of phloridzin and phloridzin contents in the leaves of Tibetan medicine Ruse [J] Modern Chinese Medicine, 2014 (8): 5.
[6] 温馨, 田甜, 沈悦, 等. 超声波辅助提取变叶海棠中总黄酮工艺优化及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2016,28(3):452−456, 461. [WEN X, TIAN T, SHEN Y, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic assisted extraction process and antioxidant activity of total flavonoids from Begonia variabilis[J]. Research and Development of Natural Products,2016,28(3):452−456, 461. WEN X, TIAN T, SHEN Y, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic assisted extraction process and antioxidant activity of total flavonoids from Begonia variabilis [J] Research and Development of Natural Products, 2016, 28 (3): 6.
[7] 宛晓春. 茶叶生物化学[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2003. WAN X C. Tea biochemistry[M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2003.
[8] 郭雯飞. 茶叶香气生成机理的研究[J]. 中国茶叶加工,1996(4):34−37. [GUO W F. Study on the mechanism of tea aroma generation[J]. China Tea Processing,1996(4):34−37. GUO W F. Study on the mechanism of tea aroma generation [J]. China Tea Processing, 1996 (4): 34-37.
[9] 王力, 林智, 吕海鹏, 等. 茶叶香气影响因子的研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2010(15):293−298. [WANG L, LIN Z, LÜ H P, et al. Research progress in influencing factors of tea aroma[J]. Food Science,2010(15):293−298. WANG L, LIN Z, LÜ H P, et al. Research progress in influencing factors of tea aroma [J] Food Science, 2010 (15): 6.
[10] 施梦南, 龚淑英. 茶叶香气研究进展[J]. 茶叶,2012,38(1):19−23. [SHI M N, GONG S Y. Research progress in tea aroma[J]. Tea,2012,38(1):19−23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0577-8921.2012.01.004 SHI M N, GONG S Y. Research progress in tea aroma [J]. Tea, 2012, 38 (1): 19-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0577-8921.2012.01.004
[11] 郭洪伟, 田云刚, 王建霞, 等. 不同工艺古丈毛尖红茶与绿茶的香气成分分析[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2020,11(1):19−28. [GUO H W, TIAN Y G, WANG J X, et al. Analysis of aroma components of Guzhang Maojian black tea and green tea with different processes[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection,2020,11(1):19−28. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2020.01.004 GUO H W, TIAN Y G, WANG J X, et al. Analysis of aroma components of Guzhang Maojian black tea and green tea with different processes [J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection, 2020, 11 (1): 19-28. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2020.01.004
[12] 乔小燕, 操君喜, 车劲, 等. 基于滋味和香气成分结合化学计量法鉴别不同贮藏年份的康砖茶[J]. 现代食品科技,2020,36(9):260−269, 299. [QIAO X Y, CAO J X, CHE J, et al. Identification of Kangzhuan tea in different storage years based on taste and aroma components combined with chemometric method[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2020,36(9):260−269, 299. doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2020.9.0178 QIAO X Y, CAO J X, CHE J, et al. Identification of Kangzhuan tea in different storage years based on taste and aroma components combined with chemometric method [J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2020, 36 (9): 260-269, 299. doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2020.9.0178
[13] 陆晨浩, 王曦如, 仲梦涵, 等. 基于GC-MS和电子感官技术分析发芽对黑麦茶风味的影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(10):192−197. [LU CH H, WANG X R, ZHONG M H, et al. Analysis of the effect of germination on the flavor of rye tea based on GC-MS and electronic sensory technology[J]. Food Science,2020,41(10):192−197. LU CH H, WANG X R, ZHONG M H, et al. Analysis of the effect of germination on the flavor of rye tea based on GC-MS and electronic sensory technology [J] Food Science, 2020, 41 (10): 6.
[14] 邵淑贤, 徐梦婷, 林燕萍, 等. 基于电子鼻与HS-SPME-GC-MS技术对不同产地黄观音乌龙茶香气差异分析[J/OL]. 食品科学: 1−12[2022-10-03]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2206.ts.20220621.1725.047.html. SHAO S X, XU M T, LIN Y P, et al. Analysis of aroma difference of Huangguanyin Oolong tea from different places based on electronic nose and HS-SPME-GC-MS technology[J/OL]. Food Science: 1−12 [2022-10-03] http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2206.ts.20220621.1725.047.html.
[15] WANG K, LIU F, LIU Z, et al. Comparison of catechins and volatile compounds among different types of tea using high performance liquid chromatograph and gas chromatograph mass spectrometer[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2011,46(7):1406−1410.
[16] DB 5133/T 50-2021, 地理标志产品—炉霍雪域俄色茶生产技术规程[S]. DB 5133/T 50-2021, Technical procedures for the production of luhuo snow region russian tea as a product of geographical indications[S].
[17] 王小会, 张丽霞, 孙庆娜. 干燥温度对景天三七茶香气的影响[J]. 食品研究与开发,2013,34(8):28−32. [WANG X H, ZHANG L X, SUN Q N. Effect of drying temperature on the aroma of Jingtian Sanqi tea[J]. Food Research and Development,2013,34(8):28−32. WANG X H, ZHANG L X, SUN Q N. Effect of drying temperature on the aroma of Jingtian Sanqi tea [J]. Food Research and Development, 2013, 34 (8): 28-32.
[18] WANG W, QIAO W U, DONG Q, et al. Effect of processing conditions on the key flavor compounds of baked quail eggs as analyzed by "ROAV" method[J]. Food Science,2013,34(22):234−238.
[19] 李慧, 聂枞宁, 熊丙全, 等. 摇青工艺对“崇庆枇杷茶”加工红茶的香气品质的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(2):188−195. [LI H, NIE Z N, XIONG B Q, et al. Effect of shaking green process on the aroma quality of "Chongqing Loquat Tea" processed black tea[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2021,47(2):188−195. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.024660 LI H, NIE Z N, XIONG B Q, et al. Effect of shaking green process on the aroma quality of "Chongqing Loquat Tea" processed black tea [J]. Food and Fermentation Industry, 2021, 47 (2): 188-195. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.024660
[20] WANG S Y, ZHAO F, WU W X, et al. Comparison of volatiles in different jasmine tea grade samples using electronic nose and automatic thermal desorption-gas chromatography-mass spectrometry followed by multivariate statistical analysis[J]. Molecules,2020,25(2):380. doi: 10.3390/molecules25020380
[21] YUN J, CUI C J, ZHANG S H, et al. Use of headspace GC/MS combined with chemometric analysis to identify the geographic origins of black tea[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,360:130033. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130033
[22] 范文来, 徐岩. 酒类风味化学[M]. 北京: 中国轻工业出版社, 2014. FAN W L, XU Y. Flavor chemistry of alcohol[M] . Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 2014.
[23] 徐春晖, 王远兴. 基于GC-MS结合化学计量学方法鉴别3种江西名茶[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(20):141−150. [XU C H, WANG Y X. Identification of three kinds of famous tea in Jiangxi based on GC-MS and chemometrics[J]. Food Science,2020,41(20):141−150. XU C H, WANG Y X. Identification of three kinds of famous tea in Jiangxi based on GC-MS and chemometrics [J] Food Science, 2020, 41 (20): 10.
[24] 舒娜. 六堡茶关键风味物质研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2021. SHU N. Research on key flavor substances of Liubao tea[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2021.
[25] 梁贵秋, 李全, 陆飞, 等. 桑叶茶挥发性成分的GC-MS分析[J]. 现代食品科技,2013,29(5):1157−1159, 1177. [LIANG G Q, LI Q, LU F, et al. GC-MS analysis of volatile components of mulberry leaf tea[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2013,29(5):1157−1159, 1177. doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2013.05.006 LIANG G Q, LI Q, LU F, et al. GC-MS analysis of volatile components of mulberry leaf tea [J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2013, 29 (5): 1157-1159, 1177. doi: 10.13982/j.mfst.1673-9078.2013.05.006
[26] 孟雪莉. 雅安藏茶色香味品质研究[D]. 雅安: 四川农业大学, 2019. MENG X L. Study on the quality of Ya'an Tibetan tea[D]. Ya'an: Sichuan Agricultural University, 2019.
[27] 刘珍珍. 汉中绿茶加工过程中风味物质的形成与变化分析[D]. 汉中: 陕西理工大学, 2020. LIU Z Z. Analysis on the formation and change of flavor substances during the processing of Hanzhong green tea[D]. Hanzhong: Shanxi University of Science and Technology, 2020.
[28] 邓媛元, 张雁, 汤琴, 等. 干燥方式对苦瓜茶感官品质及挥发性物质的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2019,19(2):173−184. [DENG Y Y, ZHANG Y, TANG Q, et al. Effects of drying methods on the sensory quality and volatile substances of balsam pear tea[J]. Chinese Journal of Food,2019,19(2):173−184. DENG Y Y, ZHANG Y, TANG Q, et al. Effects of drying methods on the sensory quality and volatile substances of balsam pear tea [J]. Chinese Journal of Food, 2019, 19 (2): 173-184.
[29] 高丽萍, 夏涛. 茉莉花香气形成机理及其影响因素初探[J]. 茶业通报,2000(3):13−16. [GAO L P, XIA T. Preliminary study on the formation mechanism of jasmine fragrance and its influencing factors[J]. Tea Industry Bulletin,2000(3):13−16. doi: 10.16015/j.cnki.jteabusiness.2000.03.006 GAO L P, XIA T. Preliminary study on the formation mechanism of jasmine fragrance and its influencing factors [J]. Tea Industry Bulletin, 2000 (3): 13-16. doi: 10.16015/j.cnki.jteabusiness.2000.03.006
[30] 林家正, 涂政, 陈琳, 等. 红光萎凋对茶叶挥发性成分及其成品红茶品质的影响[J]. 茶叶科学,2021,41(3):393−405. [LIN J Z, TU Z, CHEN L, et al. The effect of red light withering on the volatile components of tea and the quality of finished black tea[J]. Tea Science,2021,41(3):393−405. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2021.03.010 LIN J Z, TU Z, CHEN L, et al. The effect of red light withering on the volatile components of tea and the quality of finished black tea [J]. Tea Science, 2021, 41 (3): 393-405. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-369X.2021.03.010
[31] 王蔚, 黄旭建, 林允志, 等. 铁观音茶梗中挥发性物质分析[J]. 热带作物学报,2019,40(5):965−972. [WANG W, HUANG X J, LIN Y Z, et al. Analysis of volatile substances in Tieguanyin tea stem[J]. Journal of Tropical Crops,2019,40(5):965−972. WANG W, HUANG XJ, LIN YZH, ET AL. Analysis of volatile substances in Tieguanyin tea stem [J] Journal of Tropical Crops, 2019, 40 (5): 8 .
[32] 李丹, 陈岗, 练学燕, 等. 自动化生产线加工过程中“川红芽茶”主要品质成分变化及回归分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2015,36(23):79−83, 88. [LI D, CHEN G, LIAN X Y, et al. Change and regression analysis of main quality components of "Sichuan red bud tea" in the process of automatic production line processing[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2015,36(23):79−83, 88. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2015.23.008 LI D, CHEN G, LIAN XY, et al. Change and regression analysis of main quality components of "Sichuan red bud tea" in the process of automatic production line processing [J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2015, 36 (23): 79-83, 88. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2015.23.008
[33] 王丽丽, 张应根, 杨军国, 等. 顶空固相微萃取/气相色谱——质谱联用法分析绿茶和白茶香气物质[J]. 茶叶学报,2017,58(1):1−7. [WANG L L, ZHANG Y G, YANG J G, et al. Analysis of aroma substances in green tea and white tea by headspace solid phase microextraction/gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Journal of Tea Science,2017,58(1):1−7. WANG L L, ZHANG Y G, YANG J G, et al. Analysis of aroma substances in green tea and white tea by headspace solid phase microextraction/gas chromatography-mass spectrometry [J]. Journal of Tea Science, 2017, 58 (1): 1-7.
[34] 里奥·范海默特. 化合物嗅觉阈值汇编[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2018: 1−659. LEO V H. Compilation of olfactory threshold of compounds[M]. Bejing: Science Press, 2018: 1−659.
[35] ZHANG X, WEI J P, ZHAO S Y, et al. Flavor differences between commercial and traditional soybean paste[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2021,142:111052. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.111052
-
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 胡烘陶,王晶,字成庭,孙培元. 天然化合物基于Notch通路抑制肿瘤的研究进展. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2024(05): 138-146 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘馨颐,梁晓杰,马静阁,魏峰. 香菇多糖的生物活性及在鸡、猪养殖中的应用研究进展. 中国畜牧杂志. 2024(04): 64-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李俊生,管丽,李嘉慧,夏至,谭冲,左金龙. 香菇多糖提取、结构特征及生物活性研究进展. 中国调味品. 2024(09): 208-214 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王大军,徐红伟,王亮,彭亚南. 增强CT对胰腺癌的周围血管侵犯的评估价值分析. 中国CT和MRI杂志. 2024(11): 106-108 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 刘俊杰,梁家,庞天舒,薛佳龙,刘德纯. 香菇多糖通过IL-6/STAT3通路对AOM/DSS诱导结肠炎相关结直肠癌的抑制作用及机制. 肿瘤防治研究. 2024(11): 908-912 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
