Isolation, Identification and Biological Activity of Fermented Chinese Yam Polysaccharides by Saccharomyces boulardii
-
摘要: 目的:探究通过布拉氏酵母发酵怀山药,来提高发酵怀山药多糖(Fermented Chinese yam polysaccharides,FCYP)的多糖含量以及生物活性。方法:采用苯酚-硫酸法、考马斯亮蓝法及福林酚法分别检测FCYP和未发酵怀山药多糖(Unfermented Chinese yam polysaccharides,UCYP)中多糖、总蛋白和多酚的含量;用高效液相色谱、紫外和红外光谱分析发酵怀山药多糖的单糖组成以及理化性质;对比分析布拉氏酵母发酵前后怀山药多糖的体外抗氧化活性和免疫调节活性。结果:相较于UCYP(383.03±12.57 mg/g),FCYP中的多糖含量得到显著提高(480.71±5.93 mg/g,P<0.001);红外光谱分析发现FCYP在3279和1636 cm−1处具有多糖典型官能团(O-H和C-O);FCYP的单糖组成以半乳糖和甘露糖为主,二者质量百分比分别为48.70%和16.19%;此外,体外抗氧化实验结果显示,FCYP在1.0~5.0 mg/mL浓度范围内具有良好的DPPH自由基清除能力,并且FCYP在5.0 mg/mL浓度下的还原力显著高于UCYP(P<0.05);免疫调节结果显示,FCYP的促RAW264.7细胞增殖活性和促NO产生能力优于UCYP。结论:布拉氏酵母发酵处理怀山药是一种有效的提高多糖含量与生物活性的方法。本研究可为发酵怀山药多糖天然抗氧化产品的开发提供依据。Abstract: Objective: To improve the polysaccharide content and biological activities of the fermented Chinese yam polysaccharides (FCYP) by fermentation with Saccharomyces boulardii. Methods: The contents of polysaccharides, total protein and polyphenols of FCYP and unfermented Chinese yam polysaccharides (UCYP) were determined by phenol-sulfuric acid method, coomassie bright blue method and folin-ciocalteu method, respectively. The monosaccharide composition and physicochemical properties of FCYP and UCYP were determined by ultraviolet spectrum analysis, high performance liquid chromatography and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. Then the antioxidant activity and immunomodulatory activity were compared and analyzed. Results: Compared with UCYP (383.03±12.57 mg/g), the polysaccharide content in FCYP was significantly increased (480.71±5.93 mg/g, P<0.001). The Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy analysis showed that FCYP had typical polysaccharide functional groups (O-H and C-O) at 3279 and 1636 cm−1, respectively. The monosaccharide composition of FCYP was mainly galactose and mannose, with the mass percentage of 48.70% and 16.19%, respectively. In addition, the results of antioxidant activity in vitro showed that FCYP had the best DPPH free radical scavenging activity in the concentration range of 1.0~5.0 mg/mL. And the reducing power of FCYP at 5.0 mg/mL was significantly higher than that of UCYP (P<0.05). Finally, the results of immunomodulatory activity showed that FCYP showed good enhanced cell proliferation activity and promoted NO production in RAW264.7 cells. Conclusion: It was an effective method to improve the polysaccharide content and biological activity of Chinese yam by fermentation with Saccharomyces boulardii. This study would provide a basis for the development of natural antioxidant products of fermented polysaccharides of Chinese yam.
-
怀山药是一种典型的药食同源的天然绿色食品,含有丰富的蛋白质和黏性多糖等活性成分,具有抗氧化、降血脂、提高肠道免疫力等功能[1]。目前对怀山药的开发利用以及相关研究逐渐增多。
多糖是怀山药中主要的活性物质,具有降血糖、抑制肿瘤细胞增长、抗氧化、调节免疫等多种保健作用[2-3]。用传统的超声等方法从怀山药实体中提取多糖,提取效率低并且还存在损失率大、成本高昂等缺点。为了提高怀山药多糖得率和活性,利用微生物发酵技术制备多糖成为一种新兴技术应运而生[4-5]。前人研究表明经过微生物发酵后可以有效提高多种活性物质释放,如酚类、多糖等,可提高机体抗氧化能力。例如,联合植物乳杆菌C88发酵后的人参多糖具有更明显的免疫调节活性以及体外抗氧化活性[6];采用灰树花菌发酵米糠粕提取液后,其中多糖总含量降低但对DPPH自由基和·OH的清除率显著提高,同时在抗炎和提高免疫力方面均具有良好效果[7];另外,Tseng等[8]通过红曲霉发酵山药及大米所得的发酵多糖均具有较强的清除自由基等体外抗氧化能力和对RAW264.7细胞的良好的免疫调节能力(包括细胞增殖、一氧化氮产生、吞噬和TNF-α等细胞因子的产生)。
布拉氏酵母是一种很好的发酵益生菌,生长过程中产生的代谢物不仅可发挥本身的药用价值,又能调节并改善发酵液中的液态环境,充分释放中草药中的有效成分[9]。目前常用的发酵菌种主要有酵母菌、益生芽孢菌、乳杆菌、双歧杆菌等,鲜有利用布拉氏酵母菌发酵提取多糖的研究。因此,本研究用布拉氏酵母菌对怀山药进行发酵处理,充分释放其中的有效成分,通过水提醇沉法提取发酵怀山药中的多糖组分,并对其单糖组成、分子量以及结构进行鉴定,初步探讨布拉氏酵母发酵怀山药多糖的体外抗氧化和免疫调节活性,为发酵怀山药多糖作为功能食品的开发利用提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
怀山药 购买于河南省焦作市温县;布拉氏酵母 由天津科技大学食品营养与安全国家重点实验室提供;RAW264.7巨噬细胞系 购买自中国科学院细胞库;胎牛血清 杭州四季青生物有限公司;一氧化氮检测试剂盒、脂多糖(lipopolysaccharide,LPS) 上海碧云天生物技术有限公司;DMEM高糖培养基、中性红、耐高温α-淀粉酶(酶活力为40000 U/g)、淀粉葡萄糖苷酶(酶活力为104 U/g) 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl,DPPH)、2,2'-联氨-双(3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸)二胺盐(2,2'-azino-bis-(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid),ABTS) 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;三氟乙酸 分析纯,上海阿拉丁生化科技有限公司;葡萄糖、铁氰化钾 分析纯,天津致远化学试剂有限公司;苯酚 分析纯,天津市凯通化学试剂有限公司。
PerkinElmer傅里叶红外光谱仪 上海珀金埃尔默仪器有限公司;Agilent1260高效液相色谱仪 美国Agilent公司;Model 680酶标仪 美国Bio-Rad公司;YXQ-SG46-280S高压灭菌锅 上海博讯实业有限公司;SHZ-3水循环真空泵 河南省予华仪器有限公司;3111恒温培养箱 美国Thermo公司;JW 1016低速离心机 安徽嘉文仪器装备有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 怀山药的发酵
将新鲜怀山药洗净去皮、切片晒干,40目粉碎过筛,得到样品粉末之后密封保存。取布拉氏酵母菌(甘油冷冻菌种)接种于已灭菌的沙氏培养基中(121 ℃,20 min),于180 r/min的摇床中30 ℃培养12 h。随后按照相同的方法进行二次活化,即得种子液。取活化后酵母菌按照2%接种量接种到灭菌后山药培养基(山药块茎粉末4%,蛋白胨1%,pH5.5)于180 r/min的摇床中30 ℃发酵24 h,未发酵对照组按照0%接种量接种,其他步骤保持一致。将不同条件制备的发酵液冷冻干燥,即得发酵怀山药(Fermented Chinese yam,FCY)和未发酵怀山药(Unfermented Chinese yam,UCY)。
1.2.2 UCYP和FCYP的提取制备
UCYP和FCYP的提取制备以及发酵方法基于已有文献稍作修改[10-11]。分别称取冻干后的UCY和FCY粉末,按照料液比1:25 g/mL加入蒸馏水,置于90 ℃水浴锅中浸提150 min,随后4000 r/min离心10 min,分离上清和沉淀,沉淀继续按照原比例再次热水浸提和离心,而后合并两次上清液。在60 ℃下旋转蒸发浓缩2/3提取液,随后向其中加入耐高温α-淀粉酶液(20 U/mL),混合均匀后,90 ℃水浴反应90 min,流水冷却至60 ℃,将溶液pH调为4.0~4.5,而后向溶液中加入淀粉葡萄糖苷酶(11 U/mL),继续混合均匀,于60 ℃水浴反应30 min,通过碘-碘化钾试剂确定淀粉完全去除后,于100 ℃水浴反应20 min,将酶灭活。灭活后溶液4000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液加入4倍95%乙醇,4 ℃放置12 h进行醇沉。对醇沉后溶液4000 r/min离心10 min,获得不溶于醇的沉淀即怀山药发酵粗多糖,复溶、透析并冻干,即得发酵怀山药多糖(Fermented Chinese yam polysaccharides,FCYP)和未发酵怀山药多糖(Unfermented Chinese yam polysaccharides,UCYP)。
1.2.3 发酵前后粗多糖的组成分析
1.2.3.1 多糖含量测定
采用苯酚-硫酸法测定样品中多糖含量[12]。以标品葡萄糖的质量浓度为横坐标,使用紫外分光光度计于490 nm处检测的溶液吸光值为纵坐标,绘制标准曲线并计算出相应线性方程为y=12.763x−0.0541(R2=0.9993)。多糖含量以每克多糖组分所含有的葡萄糖毫克数表示,实验平行重复三次。
1.2.3.2 多酚含量测定
采用福林酚法测定样品中的多酚含量[13]。以标品没食子酸的质量浓度为横坐标,使用紫外分光光度计于760 nm处检测的溶液吸光值为纵坐标,绘制标准曲线并计算出线性回归方程:y=29.671x−0.0364(R2=0.9967)。多酚含量以每克多糖组分所含有的没食子酸毫克数表示,实验平行重复三次。
1.2.3.3 蛋白质含量测定
采用考马斯亮蓝法测定样品中的蛋白含量[14]。以牛血清标准蛋白浓度为横坐标,于595 nm处检测的溶液吸光值为纵坐标,绘制标准曲线并计算出线性回归方程:y=4.9573x+0.0132(R2=0.9974)。蛋白质含量以每克多糖组分所含有的蛋白质毫克数表示,实验平行重复三次。
1.2.4 多糖理化性质分析
1.2.4.1 紫外光谱
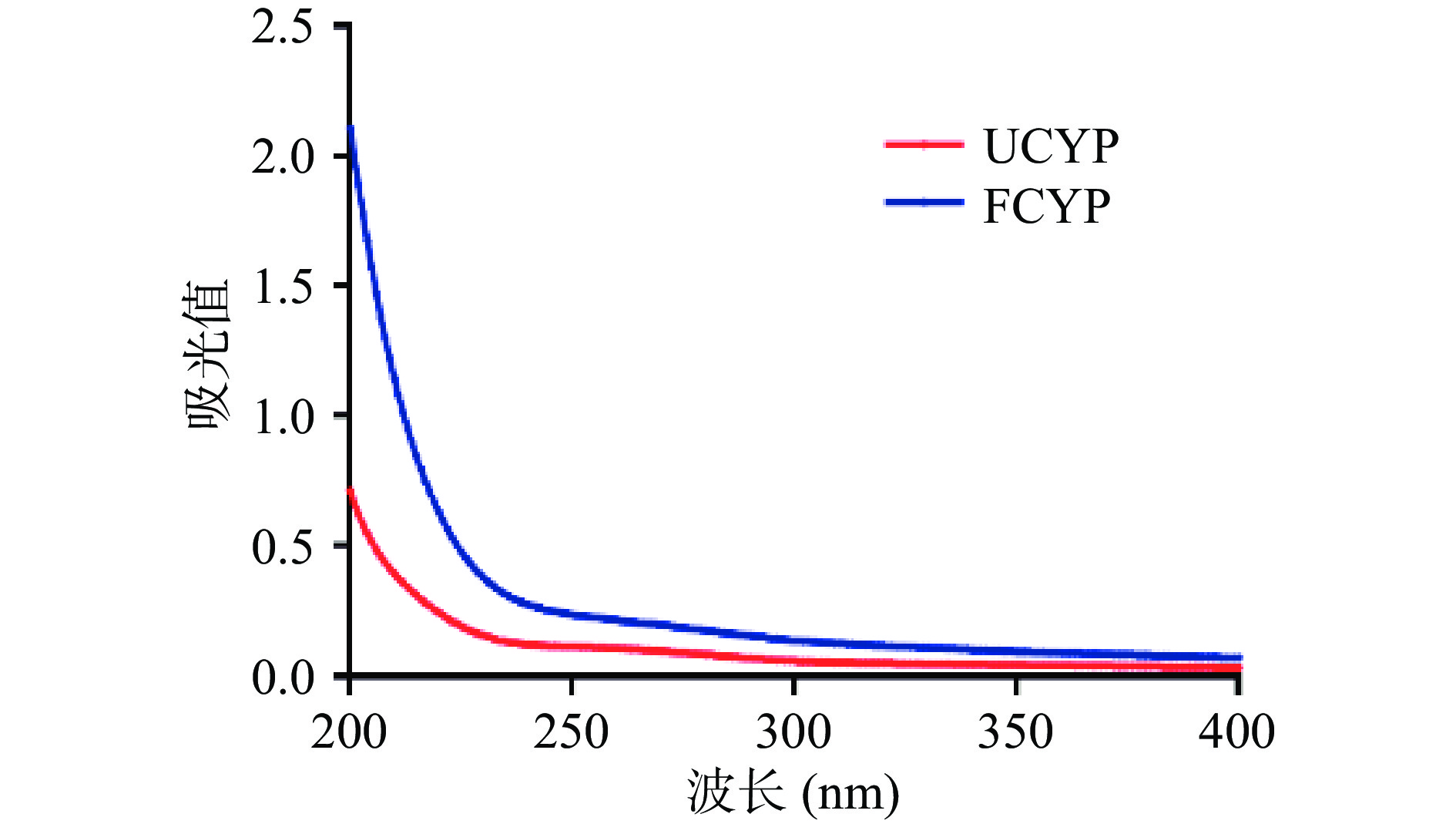
称取冻干的FCYP和UCYP多糖样品,配制为0.5 mg/mL溶液,于200~400 nm光谱范围内进行紫外扫描,观察多糖溶液的特征吸收峰[15]。
1.2.4.2 红外光谱
称取0.1 g冻干的FCYP和UCYP多糖样品,使用PerkinElmer傅里叶红外光谱仪进行红外波长扫描[16],扫描范围为450~4000 cm−1。
1.2.4.3 单糖组成
采用高效液相色谱法(High performance liquid chromatography,HPLC)测定多糖样品中的单糖含量[17]。分别称取鼠李糖(Rha)、葡萄糖(Glc)、葡萄糖醛酸(GlcA)、半乳糖醛酸(GalA)、核糖(Rib)、甘露糖(Man)、N-乙酰-氨基半乳糖(N-acetyl-Gal)、N-乙酰-氨基葡萄糖(N-acetyl-Glc)、半乳糖(Gal)、阿拉伯糖(Ara)、木糖(Xyl)及岩藻糖(Fuc)标准品溶于超纯水,精确配制混合标品溶液(各标品浓度均为50 μg/mL)。准确吸取250 μL混合标品溶液于5 mL EP管中,依次加入NaOH溶液(0.6 mol/L,250 μL)和PMP-甲醇溶液(0.4 mol/L,500 μL),70 ℃反应60 min。冷水冷却10 min后,继续加入HCl溶液(0.3 mol/L,500 μL)进行中和,与氯仿(1 mL)混合后涡旋1 min,离心(3000 r/min,10 min)取上清,萃取操作重复3次。所得上清即可用于HPLC。
同样称取待测多糖样品适量至5 mL安瓿瓶中,加入2 mol/L三氟乙酸(Trifluoroacetic acid,TFA)3.0 mL并封管,于110 ℃酸解反应8 h。反应结束后取出,将TFA挥干,接着加入3.0 mL超纯水进行复溶,精确测定复溶样品溶液中的多糖浓度。后续准确吸取250 μL样品溶液于5 mL EP管中,衍生操作方法同上。最终所得上清用于HPLC检测分析。
色谱条件:仪器为赛默飞U3000,色谱柱为Xtimate C18 4.6×200 mm 5 μm,柱温为30 ℃,流速为1.0 mL/min,检测波长为:250 nm,进样量为20 μL,流动相为0.05 mol/L磷酸二氢钾溶液(用NaOH溶液调pH为6.70):乙腈=83:17。
1.2.4.4 相对分子量
采用高效凝胶渗透色谱法(High performance gel permeation chromatography,HPGPC)测定多糖样品中的相对分子质量[18]。将样品溶于水配制为1.0 mg/mL的溶液,若有浑浊需离心后再过0.22 μm滤膜,样品处理好后取10 μL溶液进行上样。HPGPC条件:分析柱为PL aquagel-OH 30(8 μm,300 mm×7.5 mm)不锈钢色谱柱;上样量20 μL;流速1.0 mL/min;柱温28 ℃;流动相为超纯水;示差检测器检测。标准品为不同分子量的葡聚糖(3.62、12.6、70.8和126.0 kDa),分别溶于超纯水制备标准品溶液(1.0 mg/mL),采用GPC软件绘制标准曲线,以标准品相对分子质量的对数值为纵坐标、相应色谱峰的保留时间为横坐标进行线性回归,得到回归方程,根据样品的保留时间,代入标准方程计算其相对分子质量。
1.2.5 抗氧化活性
1.2.5.1 总还原力测定
参照Xiao等[19]方法略有修改。分别将不同浓度的样品溶液(2 mL)、磷酸缓冲液(pH6.6,0.2 mol/L,2 mL)和1% K3[Fe(CN)6]溶液(2 mL)混合均匀,于50 ℃下水浴反应20 min,随后加入等量的10%三氟乙酸(2 mL)终止反应。将反应液于3000 r/min离心10 min后,分别取上清液(2 mL)与超纯水(2 mL)、0.1% FeCl3溶液(0.4 mL)充分混合,继续于50 ℃下水浴反应10 min。以0.001~0.005 mg/mL的维生素C溶液作为阳性对照组。以加入超纯水的反应液为空白对照组,检测OD700 nm处混合溶液的吸光值。每份样品平行重复3次。
1.2.5.2 DPPH自由基清除能力测定
参照Luan等[20]方法略有修改。分别取等体积样品溶液(2 mL)与0.1 mmol/L DPPH无水乙醇溶液(2 mL)混合均匀,室温静置20 min后,以0.001~0.005 mg/mL的维生素C溶液作为阳性对照组,以等体积超纯水与无水乙醇的混合液作为空白对照组,检测OD517 nm处混合溶液的吸光值。每份样品平行重复3次。DPPH自由基清除率可按照以下公式计算:
(1) 式中:A0代表超纯水与DPPH溶液混合后的吸光值;A1代表样品溶液与DPPH溶液混合后的吸光值;A2则代表样品溶液与无水乙醇混合后的吸光值。
1.2.6 免疫调节活性
1.2.6.1 对巨噬细胞增殖活性的影响(CCK8法)
参照杜娟[21]方法略有修改。使用含有10%胎牛血清的DMEM高糖培养基在细胞培养箱(37 ℃,5% CO2)中培养RAW264.7巨噬细胞,对生长状态良好的细胞进行离心收集(1000 r/min,5 min),使用血球计数板进行细胞计数后,按照1×104个/孔的浓度将细胞接种于96孔板中,培养12 h使之充分贴壁。配制不同浓度梯度的样品溶液(溶于PBS)并加入到细胞培养基中,PBS组和LPS组(10 μg/mL)分别作为空白对照和阳性对照,继续培养24 h。每份样品5个平行重复。24 h后,避光配置CCK-8反应溶液(含10% CCK-8和10%胎牛血清的培养基),与96孔板中原有的培养基上清进行替换,随后继续孵育1~2 h。使用酶标仪对450 nm处吸光值进行测定,计算细胞增殖率。
1.2.6.2 对巨噬细胞吞噬活性的影响(中性红法)
参照Li等[22]方法略有修改。按照1.2.6.1中步骤进行细胞培养。24 h后,弃去96孔板中原有培养基,按照200 µL/孔加入0.1%的中性红染液,孵育1 h后,弃去中性红染液,用PBS缓冲液清洗残液后,将96孔板甩干,而后按照200 µL/孔加入细胞裂解液(醋酸:乙醇=1:1)。4 ℃裂解细胞12 h,使用酶标仪对570 nm下的吸光值进行检测。
1.2.6.3 对巨噬细胞一氧化氮(NO)产生的影响
参照Liu等[23]方法略有修改。首先对标准品原液进行梯度稀释,按照50 μL/孔依次加入不同浓度标准品、Griess Reagent I以及Griess Reagent Ⅱ,振荡混匀。使用酶标仪对540 nm处吸光值进行测定,以标准品浓度为横坐标,相应浓度吸光值为纵坐标,绘制标准曲线并计算出线性回归方程:y=0.0066x+0.0943(R2=0.9995)。以加入不同浓度样品的细胞培养上清液替换标准品溶液,其余步骤同上,根据所得OD540 nm代入标准曲线方程即可计算NO含量。
1.3 数据处理
每组实验均重复3次,结果以均数±标准差(SD)表示。采用GraphPad Prism 8.0软件绘图并进行数据分析,统计分析采用单因素方差分析(ANOVA),然后采用Tukey检验,判断两组间差异是否显著。差异有统计学意义分别为*P<0.05,**P<0.01,***P<0.001。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 多糖的组成
为了探究发酵前后怀山药多糖的组成,对其多酚、多糖以及总蛋白进行了检测和分析,结果如表1所示。结果表明:怀山药粗多糖中多糖占主要成分,FCYP的多酚、多糖以及总蛋白含量分别为0.92±0.01、480.71±5.93和35.30±4.74 mg/g。相较于UCYP(383.03±12.57 mg/g),FCYP中的多糖含量得到显著提高,(P<0.001),与郭欣等[24]通过安琪酵母发酵黑木耳,能够显著促进黑木耳多糖的溶出与释放的研究结果一致。二者的多酚含量没有显著变化,而与UCYP相比,FCYP的蛋白含量显著降低(P<0.01),这一结果与Shao等[25]含淀粉的发酵山药多糖中蛋白含量变化一致。以上结果说明布拉氏酵母发酵过程有助于怀山药中多糖的释放和提取,可提高怀山药多糖含量,这对于FCYP的工业生产应用具备一定参考意义。
表 1 发酵前后怀山药粗多糖的组成Table 1. Composition analysis of Chinese yam crude polysaccharide before and after fermentation活性成分(mg/g) UCYP FCYP 多糖 383.03±12.57 480.71±5.93*** 多酚 0.92±0.04 0.92±0.01 总蛋白 50.40±1.40 35.30±4.74** 注:数据表示为平均值±标准差(n=3);与UCYP相比存在统计学差异即表示为**P<0.01,***P<0.001。 2.2 多糖理化性质
2.2.1 紫外光谱分析
如图1所示,FCYP和UCYP整体呈现为两条光滑平整的曲线,在260、280 nm处均无明显吸收峰。鉴于核酸和蛋白质分别在260和280 nm附近存在明显的特征吸收峰[26-27],这一结果表明FCYP和UCYP中蛋白质和核酸杂质含量均较低,可基本忽略不计。
2.2.2 红外光谱分析
红外光谱法是一种常见的鉴定多糖主要官能团的方法,特别是O-H、C-H和C=O官能团,它们是多糖的重要组成部分。由图2可以看出,在波数3279和1636 cm−1处的特征峰分别是糖类物质的O-H伸缩振动峰和C=O伸缩振动峰[28],FCYP和UCYP均表现出典型的多糖吸收峰。此外,1240 cm−1处推测为C-C骨架伸缩振动吸收峰,在1000~1200 cm−1范围内的吸收峰属于吡喃环拉伸振动[29],在1148和1023 cm−1处两个相关吸收峰则可能为吡喃环上C-O-C和C-O-H的伸缩振动。结果表明,在4000~400 cm−1范围内FCYP和UCYP均具有多糖特征吸收峰,有多糖的典型官能团,主要基团无明显差异,二者可能均为吡喃糖环结构。
2.3 单糖组成
单糖组成和纯度是决定多糖理化特性和生物活性的重要因素[30],对FCYP和UCYP的单糖组成测定结果如图3所示,UCYP主要由葡萄糖、半乳糖、甘露糖、核糖、鼠李糖、半乳糖醛酸、葡萄糖醛酸、木糖、阿拉伯糖和岩藻糖组成,其质量百分比分别为55.26%、21.67%、6.83%、3.80%、3.48%、1.48%、1.06%、1.22%、1.51%、3.68%;而FCYP主要由半乳糖、甘露糖、鼠李糖、葡萄糖、半乳糖醛酸、葡萄糖醛酸、岩藻糖、核糖、阿拉伯糖和木糖组成,其质量百分比分别为48.70%、16.19%、8.27%、6.02%、5.10%、4.27%、4.32%、3.58%、2.75%、0.79%。对比分析可发现UCYP主要由葡萄糖和半乳糖组成,几乎不含糖醛酸,这与已有研究中的怀山药水溶性多糖CYP-1相似,其主要由葡萄糖(79.72%)和半乳糖(3.03%)组成[31];而FCYP的单糖组成中葡萄糖含量显著降低,半乳糖、甘露糖、鼠李糖和糖醛酸含量显著增加,这与刘玉辉等[32]研究结果类似,与发酵前相比,发酵后玉米芯多糖含量提高了77.34%,阿拉伯糖、半乳糖和甘露糖的含量提高,而葡萄糖含量降低了57.29%。艾雨晴[33]通过纳豆芽孢杆菌发酵提取的刺参多糖也有类似的结果,发酵后刺身多糖葡萄糖含量降低而岩藻糖含量增高,这一变化推测是由于纳豆芽孢杆菌发酵产生。多糖组成的不同一般也会引起功能活性的变化[34],关于FCYP与UCYP之间的功能差异后续也进行了初步研究与验证。
2.4 粗多糖的相对分子量
FCYP与UCYP的HPGPC图能够直观地体现多糖分子量的分布。多糖的出峰时间与分子量的对数具有一定的相关性,可用于未知样品多糖分子量的检测[35]。如图4所示,发酵后的FCYP相较于发酵前UCYP相对分子量基本无明显变化。发酵前后的粗多糖均主要呈现三个峰,表2中FCYP三个峰的分子量依次为2419、599和2.76 kDa,其中峰2在色谱图中占比最高,峰1的分子量最大,高于刘艺珠等[36]研究中黄花菜多糖峰1分子量(1310.32 kDa),分子量高的多糖,具有更为复杂的结构,往往会有较高的生物活性,具体的生物活性还需要后续实验验证。
表 2 UCYP和FCYP的相对分子量Table 2. Relative molecular weight of UCYP and FCYP样品 组成 峰面积(%) 重均分子量(kDa) UCYP 1
2
314.42
46.46
28.662485
649
2.8FCYP 1
2
320.3
42.64
35.172419
599
2.762.5 多糖的体外抗氧化活性
DPPH自由基是一种较稳定的自由基,广泛应用于抗氧化剂清除自由基活性测定。还原能力也是衡量物质潜在抗氧化能力的重要指标[37]。对FCYP和UCYP的体外抗氧化活性评估如图5所示。从图5A中可见,在1.0~5.0 mg/mL浓度范围内,FCYP相较于UCYP总还原力有显著的提高(P<0.05),且VC的还原力随其浓度的增加而增加。当浓度达到5.0 mg/mL时,UCYP的OD700 nm为0.512±0.010,FCYP的OD700 nm则达到0.632±0.003。这说明FCYP在还原力方面具有较高的活性。在图5B中,FCYP的DPPH自由基清除活性与UCYP无显著差异(P>0.05),经计算FCYP清除DPPH自由基的IC50值为1.712 mg/mL,与陈丽叶等[38]的研究结果类似,其对山药多糖提取除杂后得山药多糖对DPPH自由基的IC50值为1.06 mg/mL。阳性对照VC具有强抗氧化性,其清除DPPH自由基的能力呈剂量依赖性,VC的IC50值为0.00364 mg/mL,IC50值越低,清除能力越强,表明VC清除DPPH自由基的能力强于FCYP。总之,在1.0~5.0 mg/mL浓度范围内,FCYP和UCYP的总还原力与DPPH自由基清除活性均随着浓度的增加而逐渐提高,二者的DPPH自由基清除活性无明显差异,但是相较于UCYP,FCYP的抗氧化活性在总还原力方面表现出一定优势。这与酿酒酵母发酵人参的研究结果相似,发酵人参粗多糖具有更高的得率,且含有更高比例的中性糖及糖醛酸,但总抗氧化能力无明显变化[39]。
2.6 多糖对巨噬细胞的免疫调节活性
巨噬细胞是先天免疫系统中的重要组成之一,在炎症反应和宿主防御中起不可或缺的关键作用[40]。根据细胞因子以及微环境和趋化因子的不同,巨噬细胞能够从一种表型转换为另一种表型,即经历两种不同的极化状态:经典激活(M1)和交替激活(M2)巨噬细胞,通过极化巨噬细胞能够调节机体受到刺激后的后续免疫反应,使其产生促炎(M1)或抗炎(M2)表型[41]。
对RAW264.7细胞的免疫调节实验结果表明,通过CCK-8法测定细胞活力是评估巨噬细胞活化状态的最直接有效的方法之一。如图6A所示,在1~50 μg/mL浓度范围内,FCYP与UCYP二者均对RAW264.7具有显著的免疫调节作用(P<0.001),二者的最高促细胞增殖率分别可达81.65%±8.85%和109.11%±9.11%。此外,巨噬细胞对中性红的胞饮作用能够体现出其吞噬能力的强弱,间接地反映了其细胞活力的高低。图6B中,FCYP与UCYP在1~50 μg/mL范围内表现出相似的促进RAW264.7细胞吞噬的功能。而NO在活化巨噬细胞中的产生主要用来抑制外来病原体的侵入,从而发挥免疫调节的作用。如图6C所示,随着浓度由1 μg/mL升至50 μg/mL,FCYP和UCYP促进巨噬细胞产生NO的活性具有明显的浓度梯度依赖性,并且FCYP的效果显著优于UCYP(P<0.05)。可以看出,在提高细胞活力和促进NO的产生两方面,FCYP表现优于UCYP(P<0.05),但二者对巨噬细胞吞噬功能的增强效果基本无显著差异(P>0.05)。说明整体上FCYP具有更强的免疫调节活性,布拉氏酵母发酵对怀山药中非淀粉多糖的免疫功能是具有一定改善作用的。已有研究表明,酿酒酵母发酵甘薯多糖能够显著促进RAW264.7细胞产生NO[42];另外,相较于未发酵山药多糖,红曲霉发酵的山药多糖表现出更好的免疫调节活性[8],这与本研究中的结果相类似。
3. 结论
本研究采用布拉氏酵母发酵怀山药,通过水提醇沉法提取发酵怀山药粗多糖,并分别测定了发酵前后的多糖含量,发现FCYP的多糖含量明显提高;高效液相色谱测得FCYP主要是由半乳糖、甘露糖、核糖、葡萄糖、半乳糖醛酸、岩藻糖等单糖组成。红外光谱表明FCYP和UCYP均具有典型多糖官能团。其次,与UCYP相比,FCYP的体外抗氧化和免疫调节活性有很大程度的提高。研究结果表明布拉氏酵母发酵有益于怀山药的开发利用与高值化,FCYP也有望作为一种天然抗氧化剂应用在功能食品等领域。
-
表 1 发酵前后怀山药粗多糖的组成
Table 1 Composition analysis of Chinese yam crude polysaccharide before and after fermentation
活性成分(mg/g) UCYP FCYP 多糖 383.03±12.57 480.71±5.93*** 多酚 0.92±0.04 0.92±0.01 总蛋白 50.40±1.40 35.30±4.74** 注:数据表示为平均值±标准差(n=3);与UCYP相比存在统计学差异即表示为**P<0.01,***P<0.001。 表 2 UCYP和FCYP的相对分子量
Table 2 Relative molecular weight of UCYP and FCYP
样品 组成 峰面积(%) 重均分子量(kDa) UCYP 1
2
314.42
46.46
28.662485
649
2.8FCYP 1
2
320.3
42.64
35.172419
599
2.76 -
[1] 郝丽鑫. 水溶性山药多糖免疫和抗结肠癌活性的初步研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2016 HAO L X. A brief study on immunomodulatory and anti-cancer activities of water soluble yam polysaccharides[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2016.
[2] 李美东. 壶瓶碎米荠多糖分离纯化、结构鉴定及生物活性研究[D]. 恩施: 湖北民族大学, 2021 LI M D. Study on the isolation, purification, structure identification and biological activity of Cardamine hupingshanensis polysaccharides[D]. Enshi: Hubei Minzu University, 2021.
[3] 关倩, 张文龙, 杜方岭, 等. 山药多糖生物活性及作用机理研究进展[J]. 中国食物与营养,2018,24(3):11−14. [GUAN Q, ZHANG W L, DU F L, et al. Research advancement in bioactivity of polysaccharide from Chinese yam and its mechanism[J]. Food and Nutrition in China,2018,24(3):11−14. GUAN Q, ZHANG W L, DU F L, et al. Research advancement in bioactivity of polysaccharide from Chinese yam and its mechanism[J]. Food and Nutrition in China, 2018, 24(3): 11-14.
[4] 张朋展. 怀山药附属资源多糖的结构、理化性质及抗氧化活性研究[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2020 ZHANG P Z. Physicochemical, structural, antioxidant activities of bulbil starch and polysaccharides from Dioscorea opposita Thunb. by-products[D]. Zhengzhou: Hebei Agricultural University, 2020.
[5] 李保珍, 刘琪, 樊金华, 等. 沼泽红假单胞菌发酵提高黄芪多糖含量的条件优化[J]. 中国兽药杂志,2022,56(7):68−74. [LI B Z, LIU Q, FAN J H, et al. Optimization of conditions for increasing the contents of Astragalus polysaccharide by microbial fermentation[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Drug,2022,56(7):68−74. LI B Z, LIU Q, FAN J H, et al. Optimization of conditions for increasing the contents of Astragalus polysaccharide by microbial fermentation[J]. Chinese Journal of Veterinary Drug, 2022, 56(7): 68-74.
[6] 王晓慧. 人参多糖联合植物乳杆菌抗氧化及免疫调节活性研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2015 WANG X H. Antioxidant activities and immunomodulatory effects of ginseng polysaccharides combined with Lactobacillus plantarum strains[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2015.
[7] 曹秀娟. 发酵米糠多糖的制取及其生物活性研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2015 CAO X J. Extracting rice bran polysaccharides by fermentation and bioactivity[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2015.
[8] TSENG K C, FANG T J, CHIANG S S, et al. Immunomodulatory activities and antioxidant properties of polysaccharides from Monascus-fermented products in vitro[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2012,92(7):1483−1489. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.4731
[9] 索梦莹. 灵芝与布拉氏酵母菌共发酵及其对多糖产量和活性影响的研究[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2020 SUO M Y. Study on the co-fermentation of Ganoderma lucidum and Saccharomyces boulardii and its effect on polysaccharide yield and activity[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2020.
[10] 胡爱军, 李杨, 郑捷, 等. 鹰嘴豆非淀粉多糖的分离纯化及结构表征[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(8):22−26. [HU A J, LI Y, ZHENG J, et al. Separation, purification and structural analysis of non-starch polysaccharides from chickpea seeds[J]. Food Science,2019,40(8):22−26. HU A J, LI Y, ZHENG J, et al. Separation, purification and structural analysis of non-starch polysaccharides from chickpea seeds[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(8): 22-26.
[11] XU S Y, CHEN X Q, LIU Y, et al. Ultrasonic/microwave-assisted extraction, simulated digestion, and fermentation in vitro by human intestinal flora of polysaccharides from Porphyra haitanensis[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,152:748−756. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.305
[12] 李哲明, 谢集照, 罗迪, 等. 青天葵多糖的分离纯化、结构表征及其抗氧化活性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(22):61−67. [LI Z M, XIE J Z, LUO D, et al. Separation, purification, structural characterization and antioxidation effects of a polysaccharide from Nervilia fordii[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(22):61−67. LI Z M, XIE J Z, LUO D, et al. Separation, purification, structural characterization and antioxidation effects of a polysaccharide from Nervilia fordii[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(22): 61-67.
[13] 黄莹偲, 储大可, 邓晓婷, 等. 8种市售茶类饮料抗氧化活性及总酚含量的研究[J]. 广东农业科学,2013,40(18):101−104. [HUANG Y S, CHU D K, DENG X T, et al. Antioxidant activities and total phenolic contents of eight kinds of commercial tea drinks[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences,2013,40(18):101−104. HUANG Y S, CHU D K, DENG X T, et al. Antioxidant activities and total phenolic contents of eight kinds of commercial tea drinks[J]. Guangdong Agricultural Sciences, 2013, 40(18): 101-104.
[14] BRADFORD M M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding[J]. Analytical Biochemistry,1976,72:248−254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
[15] 刘晓庆. 沙枣多糖纯化、结构表征及其生物活性研究[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2015 LIU X Q. Purification, strucutral characterization and biological activities of a polysaccharide from Elaeagnusangustifolia L[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2015.
[16] 赵建成, 刘慧燕, 方海田. 骏枣多糖的分离纯化、结构表征及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(23):1−8. [ZHAO J C, LIU H Y, FANG H T. Study on isolation, purification, structure characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Zizyphus jujuba cv. Junzao[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(23):1−8. ZHAO J C, LIU H Y, FANG H T. Study on isolation, purification, structure characterization and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Zizyphus jujuba cv. Junzao[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(23): 1−8.
[17] 冯荦荦, 王锐, 董兆斌, 等. 欧李多糖的制备、结构表征及免疫调节活性研究[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2022,34(5):739−749. [FENG L L, WANG R, DONG Z B, et al. Preparation, structure characterization and immunoregulatory activity of Cerasus humilis polysaccharide[J]. Natural Product Research and Development,2022,34(5):739−749. FENG L L, WANG R, DONG Z B, et al. Preparation, structure characterization and immunoregulatory activity of Cerasus humilis polysaccharide[J]. Natural Product Research and Development, 2022, 34(5): 739-749.
[18] 江琦, 娄在祥, 王正齐, 等. 蛹虫草虫草多糖的分离纯化、分子构象分析及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(1):22−28. [JIANG Q, LOU Z X, WANG Z Q, et al. Isolation and purification, structure and molecular conformation and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from Cordyceps militaris[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(1):22−28. JIANG Q, LOU Z X, WANG Z Q, et al. Isolation and purification, structure and molecular conformation and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from Cordyceps militaris[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2019, 45(1): 22-28.
[19] XIAO H W, CAI X R, FAN Y J, et al. Antioxidant activity of water-soluble polysaccharides from Brasenia schreberi[J]. Pharmacognosy Magazine,2016,12(47):193−197. doi: 10.4103/0973-1296.186343
[20] LUAN X X, FENG M Q, SUN J. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum on antioxidant activity in fermented sausage[J]. Food Research International,2021,144:110351. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110351
[21] 杜娟. rHP-NAP对巨噬细胞极化与代谢的影响及初步机制研究[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2019 DU J. The regulatory effects and preliminary mechanism of rHP-NAP on the polarization and metabolism of macrophages[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2019.
[22] LI X, WANG P, ZHU J Q, et al. Comparative study on the bioactive components and in vitro biological activities of three green seedlings[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,321:126716. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126716
[23] LIU W, WANG H, YU J P, et al. Structure, chain conformation, and immunomodulatory activity of the polysaccharide purified from Bacillus Calmette Guerin formulation[J]. Carbohydr Polymers,2016,150:149−158. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.05.011
[24] 郭欣, 郭萌. 酵母发酵法提高黑木耳多糖溶出率的工艺优化[J]. 盐城工学院学报(自然 科学版),2020,33(1):67−73. [GUO X, GUO M. Process optimization for improving the dissolution rate of Auricularia auricula polysaccharide by yeast fermentation method[J]. Journal of Yancheng Institute of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2020,33(1):67−73. GUO X, GUO M. Process optimization for improving the dissolution rate of Auricularia auricula polysaccharide by yeast fermentation method[J]. Journal of Yancheng Institute of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 33(1): 67-73.
[25] SHAO Y W, KANG Q Z, ZHU J Q, et al. Antioxidant properties and digestion behaviors of polysaccharides from Chinese yam fermented by Saccharomyces boulardii[J]. LWT,2022,154:112752. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112752
[26] 李松昂. 红薯叶多糖的提取纯化、结构表征及其应用的研究[D]. 长春: 吉林农业大学, 2021 LI S A. Extraction, purification, structure characterization and application of polysaccharide from sweet potato leaves[D]. Changchun: Jilin Agricultural University, 2021.
[27] 吴丹, 徐桂英. 光谱法研究蛋白质与表面活性剂的相互作用[J]. 物理化学学报,2006(2):254−260. [WU D, XU G Y. Study on protein-surfactant inter action by spectroscopic methods[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica,2006(2):254−260. WU D, XU G Y. Study on protein-surfactant inter action by spectroscopic methods[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica, 2006(2): 254-260.
[28] 刘思美, 赵鹏, 张婷婷, 等. 地黄硒多糖的合成、表征及免疫活性分析[J]. 中国中药杂志,2022,7(11):2938−2946. [LIU S M, ZHAO P, ZHANG T T, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and immunological activity of Rehmannia glutinosa seleno-polysaccharides[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2022,7(11):2938−2946. LIU S M, ZHAO P, ZHANG T T, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and immunological activity of Rehmannia glutinosa seleno-polysaccharides[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2022, 7(11): 2938-2946.
[29] 刘娜, 范明君, 安晓萍, 等. 灵芝发酵麸皮粗多糖的组成及抗氧化活性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(20):45−50. [LIU N, FAN M J, AN X P, et al. Composition and antioxidant activity analysis of crude polysaccharide from Ganoderma lucidum fermented wheat bran[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(20):45−50. LIU N, FAN M J, AN X P, et al. Composition and antioxidant activity analysis of crude polysaccharide from Ganoderma lucidum fermented wheat bran[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(20): 45−50.
[30] 殷红, 赵时荆, 韩姗姗, 等. 木耳多糖提取分离纯化、结构表征及生物活性研究进展[J]. 食品工业,2022,43(8):269−273. [YIN H, ZHAO S J, HAN S S, et al. Research progress on extraction, purification, structure characterization and biological activity of Auricularia auricula polysaccharide[J]. The Food Industry,2022,43(8):269−273. YIN H, ZHAO S J, HAN S S, et al. Research progress on extraction, purification, structure characterization and biological activity of Auricularia auricula polysaccharide[J]. The Food Industry, 2022, 43(8): 269-273.
[31] LI P, XIAO N, ZENG L P, et al. Structural characteristics of a mannoglucan isolated from Chinese yam and its treatment effects against gut microbiota dysbiosis and DSS-induced colitis in mice[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,250:116958. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116958
[32] 刘玉辉, 王瑞芳, 安晓萍, 等. 玉米芯多糖的微生物发酵工艺及其单糖组成和体外益生活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(5):107−112. [LIU Y H, WANG R F, AN X P, et al. Study on microbial fermentation technology of corn cob polysaccharide and its monosaccharide composition and prebiotic activity in vitro[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(5):107−112. LIU Y H, WANG R F, AN X P, et al. Study on microbial fermentation technology of corn cob polysaccharide and its monosaccharide composition and prebiotic activity in vitro[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(5): 107-112.
[33] 艾雨晴. 纳豆芽孢杆菌发酵刺参中多糖的结构表征及消化特性研究[D]. 大连: 大连海洋大学, 2022 AI Y Q. Structural characterization and digestive characteristics of polysaccharides from Apostichopus jsponicus fermented by Bacillus Natto[D]. Dalian: Dalian Ocean University, 2022.
[34] REN L, PERERA C, HEMAR Y. Antitumor activity of mushroom polysaccharides: A review[J]. Food & Function,2012,3(11):1118−1130.
[35] 陈淑芳. 篱栏网多糖的提取分离及抗氧化活性的研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2022 CHEN S F. Extraction, isolation and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Merremia hederacea[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2022.
[36] 刘艺珠, 刘佩冶, 赵玉梅, 等. 黄花菜多糖的表征与抗氧化活性分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(12):54−61. [LIU Y Z, LIU P Z, ZHAO Y M, et al. Characterization and antioxidant activity analysis of daylily polysaccharides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(12):54−61. LIU Y Z, LIU P Z, ZHAO Y M, et al. Characterization and antioxidant activity analysis of daylily polysaccharides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(12): 54-61.
[37] KANG W Y, LI C F, LIU Y X. Antioxidant phenolic compounds and flavonoids of Mitragyna rotundifolia (Roxb.) Kuntze in vitro[J]. Medicinal Chemistry Research,2010,19(9):1222−1232. doi: 10.1007/s00044-009-9265-x
[38] 陈丽叶, 常希光, 冯晓光, 等. 山药多糖的体外抗氧化活性[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(19):122−128. [CHEN L Y, CHANG X G, FENG X G, et al. In vitro antioxidant activity of Chinese yam polysaccharides[J]. Food Science,2021,42(19):122−128. CHEN L Y, CHANG X G, FENG X G, et al. In vitro antioxidant activity of Chinese yam polysaccharides[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(19): 122-128.
[39] 李万丛, 艾芷伊, 游颖, 等. 酿酒酵母CCTCC M 2016373发酵对人参多糖组分及抗氧化能力的影响[J]. 食品科技,2019,44(8):1−5. [LI W C, AI Z Y, YOU Y, et al. Effects of Saccharomyces cerevisiae CCTCC M 2016373 fermentation on the composition and antioxidant capacity of ginseng polysaccharides[J]. Food Science and Technology,2019,44(8):1−5. LI W C, AI Z Y, YOU Y, et al. Effects of Saccharomyces cerevisiae CCTCC M 2016373 fermentation on the composition and antioxidant capacity of ginseng polysaccharides[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2019, 44(8): 1-5.
[40] MANTOVANI A, BISWASI S K, GALDIERO M R, et al. Macrophage plasticity and polarization in tissue repair and remodelling[J]. Journal of Pathology,2013,229(2):176−185. doi: 10.1002/path.4133
[41] SRIDHARAN R, CAMERON A R, KELLY D J, et al. Biomaterial based modulation of macrophage polarization: A review and suggested design principles[J]. Materials Today,2015,18(6):313−325. doi: 10.1016/j.mattod.2015.01.019
[42] EOM S J, KIM T W, KIM S, et al. Immune-enhancing effects of polysaccharide extract of byproducts of Korean liquor fermented by Saccharomyces cerevisiae[J]. Int J Biol Macromol,2021,188:245−252. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.08.044





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:
