Antioxidant Components and Antioxidant Activity of Tibetan Propolis and Its Simulated Digestive Juices
-
摘要: 为研究西藏蜂胶抗氧化活性,评估开发潜力,分析了西藏蜂胶及其模拟消化液的抗氧化成分(总酚和总黄酮)和活性(还原力、羟自由基清除能力(·OH清除率)、1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼自由基清除率(DPPH·清除率)、金属离子螯合率和脂质过氧化抑制率)。结果表明,西藏蜂胶总酚和总黄酮含量分别为7.02%和10.05%。模拟消化液的总酚和总黄酮含量持续降低,模拟胃液(消化2 h)总酚和总黄酮含量分别为0.43%和6.43%,模拟肠液(消化2 h)则为0.32%和5.11%。西藏蜂胶在1 mg/mL时,还原力、·OH清除率、DPPH·清除率、金属离子螯合率和脂质过氧化抑制率达到最高值,分别为0.35、96.60%、92.53%、19.96%和97.01%。模拟胃液还原力和DPPH·清除率的最高值比未消化时升高,分别为0.39和95.69%。·OH清除率、金属离子螯合率和脂质过氧化抑制率较未消化时降低。模拟肠液·OH清除率、金属离子螯合率和脂质过氧化抑制率较模拟胃液提高,最高值分别为99.72%、69.26% 和80.69%;还原力和DPPH·清除率则降低,但DPPH·最高清除率仍有74.74%。综上所述,西藏蜂胶具有较好的体外抗氧化活性,胃肠模拟消化对抗氧化各指标均有显著影响,各指标的变化趋势不一致,但多个指标仍有较好表现。西藏蜂胶可作为一种天然抗氧化剂进行后续研发。Abstract: To evaluate the antioxidant activity and potential of propolis, Tibetan propolis and its simulated digestive juice were analyzed for its chemical composition (contents of total phenolics (TPC) and total flavonoids (TFC)), reducing power and antioxidant activity (hydroxyl radical scavenging activity, 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH) assays, metal iron chelating activity and lipid peroxidation inhibition ability). The results showed that the contents of TPC and TFC in Tibetan propolis were 7.02% and 10.05%, respectively. The contents of TPC and TFC in simulated digestive juices were diminished. The contents of TPC and TFC in simulated gastric digestive juices (2 h) were 0.43% and 6.43%, respectively. The contents of TPC and TFC in simulated intestinal digestive juices (2 h) were 0.32% and 5.11%, respectively. The highest values of antioxidant activity was achieved at a concentration of 1 mg/mL, and the values of reducing power, hydroxyl radical scavenging activity, DPPH radical scavenging activity, metal iron chelating activity and lipid peroxidation inhibition ability in Tibetan propolis were 0.35, 96.60%, 92.53%, 19.96% and 97.01%, respectively. Reducing power and DPPH radical scavenging activity of simulated gastric digestive juices exhibited an increasing trend, with respect to the undigested sample. The highest values of reducing power and DPPH radical scavenging activity were 0.39 and 95.69%, respectively. Hydroxyl radical scavenging activity, metal iron chelating activity and lipid peroxidation inhibition ability of simulated gastric digestive juices exhibited a decreasing trend, with respect to the undigested sample. Simulated intestinal digestive had higher hydroxyl radical scavenging rates, metal ion chelation rates and lipid peroxidation inhibition rates than simulated gastric digestive, with highest values of 99.72%, 69.26% and 80.69%, respectively, the reducing power and DPPH radical scavenging rate experienced a decreasing tendency, but the highest DPPH radical scavenging rate remained at 74.74%. All of these suggested that Tibetan propolis had high antioxidant activity. During in vitro digestion, antioxidant indicators significantly changed, but the changing trend of each indicator was inconsistent. Several indicators still performed well. Tibetan propolis can be used as a premium natural antioxidant.
-
蜂胶是一种传统的天然药物,是由蜜蜂科昆虫的工蜂采集植物树脂与其上颚腺、蜡腺等分泌物混合形成的具有粘性的固体胶状物[1]。蜂胶中含有约500多种化合物,其中黄酮和多酚具有很强的抗氧化活性[2-3]。研究显示,蜂胶在自由基清除、还原力等方面显示出优异的抗氧化能力[4–6]。河南蜂胶的乙醇提取物浓度为800 μg/mL时,DPPH·、ABTS+·清除能力和铁还原力分别为62.43%、89.50%和0.52[7]。广东蜂胶在浓度为8 mg/mL时,DPPH·和ABTS+·清除能力分别为66.91%和55.91%[8]。西藏被称为“世界屋脊”和“地球第三极”,具有独特的地理位置和季节特征。西藏蜂场平均海拔4000米以上,高度罕见,并有大量特色蜜源植物,所得蜂胶产品可能有其独到的抗氧化功效。目前,这方面的报道甚是有限,充分理解西藏蜂胶的抗氧化活性是开发该资源的关键。
开发西藏蜂胶资源,还需考虑其在体内的消化情况。蜂胶摄入后在人体胃肠道中进行消化,其活性成分的化学组成和构像在胃肠特殊环境,如pH、热、氧、酶等因素影响下,可能发生改变并进一步影响抗氧化能力[9-10]。胃肠模拟消化模型可用于预测酚类物质的生物可及性和抗氧化能力,具有简便、快速和标准化等特点[11]。该模型已广泛用于蜂胶[12]、红酒[13]和水果[14]等食物多酚的模拟消化研究。然而,未见西藏蜂胶的胃肠模拟消化相关报道。明确消化过程中西藏蜂胶抗氧化成分和活性变化,对开发相关产品意义重大。
本研究以西藏蜂胶为研究对象,测定其体外抗氧化活性、总酚和总黄酮含量;利用体外胃肠消化模型,明确西藏蜂胶在模拟胃肠消化过程中抗氧化成分及活性的变化。以期为开发西藏蜂胶资源提供依据,有助于发现新型的强效抗氧化剂,促进西藏蜂胶的开发和商业化应用。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
西藏蜂胶(原料蜂胶) 由成都四十一度蜂业有限公司提供,2019年5月至7月期间蜂胶收集者从西藏乃东区各地(海拔3560 m,北纬28°44′~29°36′,东经91°32′~92°02′)的蜂箱中采收,贮藏于−20 ℃冰箱冷冻;没食子酸、芦丁 HPLC≥98%,上海源叶生物科技有限公司;1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl,DPPH) 分析纯,成都格利普生物科技有限公司;水杨酸 分析纯,成都叮当时代医药科技有限公司;硫酸亚铁 分析纯,成都市科龙化工试剂厂;硫代巴比妥酸 分析纯,上海科丰实业有限公司;氯化亚铁、胃蛋白酶(≥3000 U/g)、胰蛋白酶(≥4000 U/g)、Ferrozine、卵磷脂 百灵威科技有限公司;磷酸氢二钠(Na2HPO4)、磷酸二氢钠(NaH2PO4)、铁氰化钾(K3[Fe(CN)6])、三氯化铁(FeCl3)、邻苯三酚、盐酸、过氧化氢、三氯乙酸、无水乙醇 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
UV754紫外分光光度计 上海仪电科学仪器股份有限公司;JA303P分析天平 郑州安晟科学仪器有限公司;pHSJ-4F酸度计 上海仪电科学仪器股份有限公司;C-3610低速离心机 安徽中科中佳科学仪器有限公司;HWS12恒温水浴锅 上海一恒科技有限公司;DF-101S磁力搅拌器 上海五相仪器有限公司;RE-52CS旋转蒸发仪 上海旦鼎国际贸易有限公司;DW-YL270抽屉型低温保存箱 上海旦鼎国际贸易有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 蜂胶提取液的制备
西藏蜂胶提取液(记为TP):选出西藏蜂胶中的蜜蜂尸体,将蜂胶置于−20 ℃低温冰箱冷藏24 h,破壁机打碎过60目筛。称取1.00 g蜂胶于小烧杯中,用80%乙醇溶解,磁力搅拌器在20 ℃持续搅拌48 h,置于4 ℃冰箱过夜,滤膜过滤,40 ℃旋转蒸发后定容至100 mL。
1.2.2 体外消化模型
模拟胃液(记为GS)[15]:将0.8 g胃蛋白酶、4.375 g NaCl溶于250 mL去离子水中,用3 mol/L盐酸溶液调节pH至2.0得到人工胃液。取10 mL 1.0 mg/mL西藏蜂胶,分别加入40 mL人工胃液,在37 ℃ 100 r/min摇床中避光消化(0.5、1、2、3 h),70 ℃水浴灭酶,冷却,迅速终止反应,离心10 min,取上清液待测。
模拟肠液(记为IS)[15]:0.143 g胰蛋白酶和0.857 g胆汁溶于100 mL 0.1 mol/L的NaHCO3溶液得到人工肠液。取消化2 h的胃消化液10 mL加入40 mL人工肠液,用0.4 mol/L NaOH溶液将pH调至6.8,在37 ℃ 100 r/min摇床中避光消化(0.5、1、2、3 h),70 ℃水浴灭酶,冷却,迅速终止反应,离心,取上清液待测。
1.2.3 总酚和总黄酮含量测定
测定西藏蜂胶未消化前、胃消化2 h和肠消化2 h后消化液的总酚和总黄酮含量。采用福林酚法测定总酚含量[16-17]。以没食子酸为标准品,得标准曲线回归方程为y=0.9469x+0.0101,R2=0.9992。总酚含量以每克蜂胶中所含没食子酸质量百分比表示。
参考GB/T 20574-2006采用硝酸铝显色法测定总黄酮含量。以芦丁为标准品,得标准曲线回归方程y=0.7334x−0.0287,R2=0.9994。总黄酮含量以每克蜂胶中所含芦丁质量百分比表示。
1.2.4 抗氧化活性测定
将TP稀释为不同浓度梯度(0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8、1.0 mg/mL),各浓度下以VC作为对照,测定各抗氧化指标。
1.2.4.1 还原力的测定
还原力的测定参照Gulcin[18]的方法。将1 mL样品与磷酸盐缓冲液(2.5 mL,0.2 mol/L,pH6.6)和铁氰化钾[K3Fe(CN)6](2.5 mL,1%)混合。将混合物在50 ℃下孵育20 min。2.5 mL三氯乙酸(10%)加入混合物中。取上清液(2.5 mL)与蒸馏水(2.5 mL)和FeCl3(0.5 mL,0.1%)混合,用分光光度计在700 nm处测量吸光度。反应混合物吸光度的增加表明还原能力的增加。
1.2.4.2 ·OH清除率的测定
水杨酸法测定·OH清除率[19]。将1 mL样品溶液与1 mL 9 mmol/L 的FeSO4和1 mL 8.8 mmol/L的H2O2在37 ℃混合10 min,然后加入1 mL 9 mmol/L的水杨酸的乙醇溶液10 min,5000 r/min离心5 min,取上清液在550 nm处测吸光值。每份样品平行操作三次,·OH清除率计算见公式(1):
⋅OH清除率(%)=[1−(AHX−AH0)/AX0]×100 (1) 式中,AHx:1 mL FeSO4+1 mL样品+1 mL H2O2+1 mL水杨酸-乙醇;AH0:1 mL FeSO4+1 mL样品+1 mL蒸馏水+1 mL水杨酸-乙醇;AX0:1 mL FeSO4+1 mL蒸馏水+1 mL H2O2+1 mL水杨酸-乙醇。
1.2.4.3 DPPH·清除率的测定
参照Yang等[20]的方法测定DPPH·清除率。将样品(100 μL)与DPPH自由基(100 μL,0.2 mmol)搅拌混匀,在黑暗中静置15 min。于517 nm处测定吸光度。所有的测定都重复进行3次。DPPH·清除率计算见公式(2):
DPPH⋅清除率(%)=[1−(A1−A2)/A0]×100 (2) 式中,A0为对照(不含样品)的吸光度,A1为样品存在时的吸光度,A2为不含DPPH自由基的样品的吸光度。
1.2.4.4 金属离子螯合率的测定
参照Cai等[21]的方法测定金属离子螯合率。取0.8 mL样品溶液与50 µL 2 mmol/L的氯化亚铁溶液和2.75 mL蒸馏水。通过添加200 μL 5 mmol/L的菲洛嗪引发反应,剧烈摇动混合物,并在室温下培养10 min。检测562 nm处的吸光度。以EDTA-2Na为阳性对照。每份样品平行操作3次,金属离子螯合率计算见公式(3):
金属离子螯合率(%)=[1−(A1−A2)/A0]×100 (3) 式中,A0为对照品的吸光度(蒸馏水代替样品溶液);A1为反应混合物中样品的吸光度;A2仅为样品的吸光度(蒸馏水代替氯化亚铁溶液)。
1.2.4.5 脂质过氧化抑制率的测定
参照赵博等[22]的方法测定脂质过氧化抑制率。300 mg卵磷脂溶于300 mL 10 mmol/L pH7.4的磷酸缓冲液中,水浴振荡,制成脂质体PBS分散系(LLS)。15 g TCA,0.375 g TBA,2.1 mL浓盐酸加入100 mL水中,制成TCA-TBA-HCl混合液。1.0 mL LLS依次加入1.0 mL 400 μmol/L FeCl3溶液、1.0 mL样品,于37 ℃恒温避光60 min,再加入2.0 mL TCA-TBA-HCl混合液,沸水浴15 min,迅速冷却,2000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液在535 nm下测吸光度。空白管吸光度以1.0 mL蒸馏水代替1.0 mL样品测定。脂质过氧化抑制率的计算见公式(4):
脂质过氧化抑制率(%)=(Ac−As)/Ac×100 (4) 式中,Ac为空白管吸光度;As为水解产物的吸光度。
1.3 数据处理
各处理重复3次,采用IBM SPSS Statistics 24.0软件进行数据分析,采用GraphPad Prism 7.00对结果制图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 西藏蜂胶总酚和总黄酮含量
西藏蜂胶总酚含量为7.02%,总黄酮含量为10.05%。与已有文献对比可知,西藏蜂胶总黄酮含量高于辽宁绥中蜂胶(5.35%)、吉林吉安蜂胶(6.38%)、吉林长白山蜂胶(8.41%)、南昌蜂胶(3.91%)、安徽舒城蜂胶(4.44%)[23-25]。虽然黄酮类化合物属于酚类物质的亚组,但在本研究中总酚含量低于总黄酮含量,与Yesiltas等[26]的研究结果一致。这可能是因为分光光度法没有检测出所有种类的酚类化合物[27]。
由表1可知,西藏蜂胶总酚和总黄酮含量从消化前的7.02%和10.05%降到模拟胃液的0.43%和6.43%,而模拟肠液会进一步降低到0.32%和5.11%。这可能是由于消化酶的存在降低了胃或肠消化产物中总酚和总黄酮的含量[12]。
表 1 西藏蜂胶及其模拟消化液的总酚和总黄酮含量(%)Table 1. Contents of total phenolics and flavonoids in Tibetan propolis and its simulated digestive juices (%)样品 未消化 模拟胃液(2 h) 模拟肠液(2 h) 总酚 7.02±0.02a 0.43±0.04b 0.32±0.01b 总黄酮 10.05±0.02a 6.43±0.54b 5.11±1.09b 注:不同的小写字母表示差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),试验数据以平均值±标准差表示。 2.2 西藏蜂胶及其模拟消化液的的抗氧化活性
2.2.1 西藏蜂胶及其模拟消化液的还原力
西藏蜂胶和VC的还原力随质量浓度的增加而增加(如图1A所示)。各质量浓度下西藏蜂胶还原力远低于VC的还原力(P<0.05)。
如图1B所示,模拟胃液还原力随着消化时间的延长而增加,消化3 h时吸光度达到0.39,显著高于0~2 h时。说明胃消化能提高西藏蜂胶的还原力。模拟肠液还原力随消化时间的推移先增加后降低,消化1 h时还原能力达到最大值0.13,之后再增加消化时间,还原力逐渐降低。纵观模拟胃肠消化过程,模拟肠液还原力远低于模拟胃液。模拟肠消化阶段还原力降低可能是因为小肠中性或微碱性环境下酚类形成不稳定的醌中间体和其他氧化物[28],进而改变其抗氧化活性[29]。
2.2.2 西藏蜂胶及其模拟消化液的·OH清除率
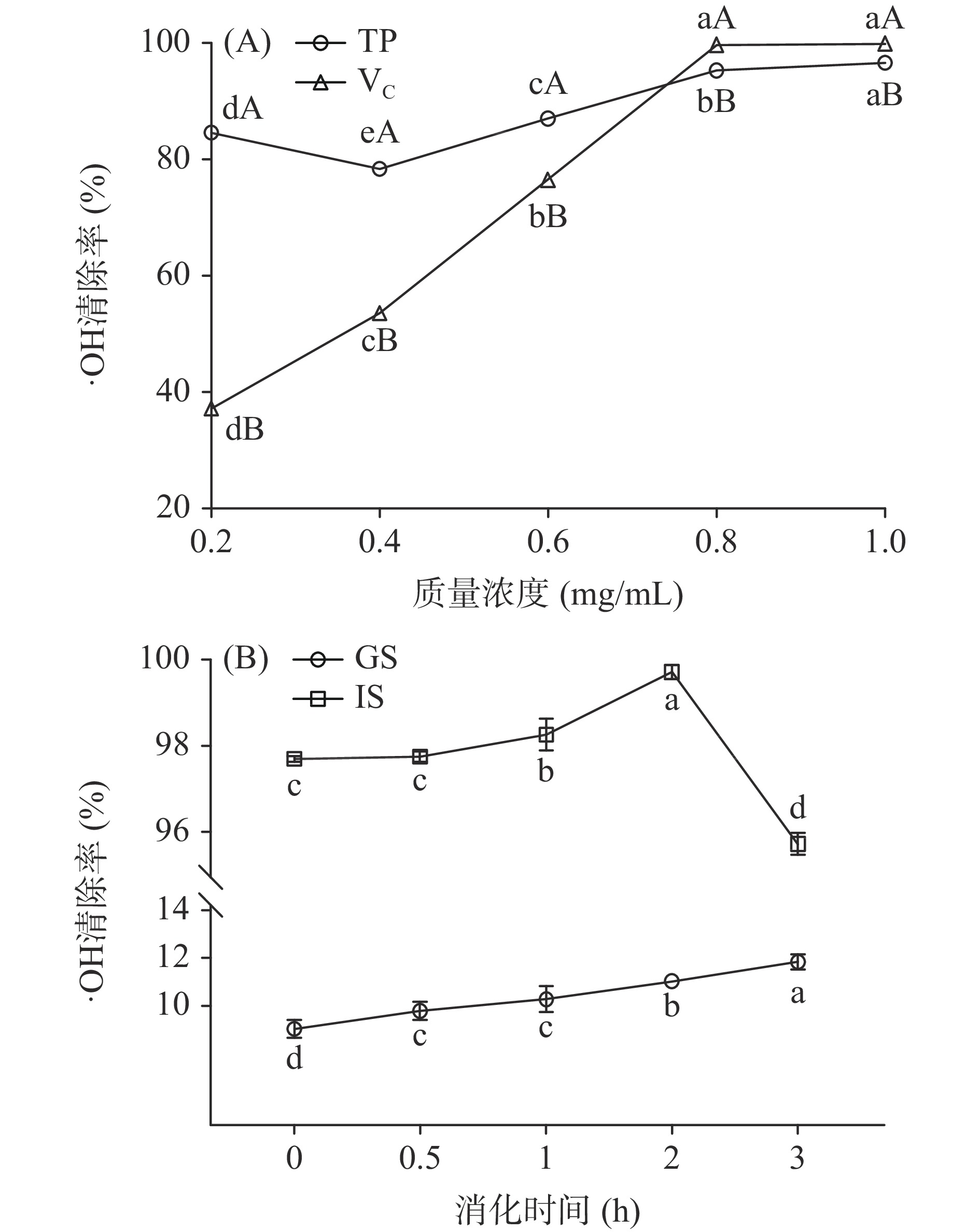
西藏蜂胶·OH清除率随着质量浓度的增加先略降低后增加(如图2A所示),清除率在78.41%~96.60%。在0.2~0.6 mg/mL质量浓度范围内,西藏蜂胶·OH清除率显著高于VC,0.8~1.0 mg/mL范围略低于VC(P<0.05)。已有文献显示,陕西蜂胶的·OH清除率在67.50%~84.70%之间,低于西藏蜂胶的清除率[30]。由此可见,西藏蜂胶在·OH清除上具有优势。
由图2B可知,随着消化时间的延长,模拟胃液的·OH清除率逐渐提升,消化3 h达到最高值11.84%。此时清除能力显著高于0~2 h的清除能力(P<0.05)。模拟肠液对·OH的清除率先增加后降低,在2 h时达到最大值99.72%。模拟肠液·OH的最高清除率高于模拟胃液。说明肠消化能提高西藏蜂胶的·OH清除率,这可能与胃肠不同的pH环境有关。酚类化合物的自由基清除率活性依赖于反应体系的pH,其能力会随pH的增加而增加[31-32]。
2.2.3 西藏蜂胶及其模拟消化液的DPPH·清除率
随着质量浓度的增大,西藏蜂胶DPPH·清除率逐渐增大(如图3A所示)。在0.2~1.0 mg/mL质量浓度范围内,西藏蜂胶DPPH·清除率在76.04~92.53%之间,显著低于VC(P<0.05)。已有研究显示,立陶宛蜂胶DPPH·清除率在23.00%~80.00%之间[33],土耳其蜂胶则在26.49%~65.64%之间[34],均低于西藏蜂胶。由此可见,西藏蜂胶具有较强的DPPH·清除能力。
如图3B所示,模拟胃液的DPPH·清除率在1 h时达到最大值95.69%,说明西藏蜂胶在模拟胃阶段能有效清除DPPH·。模拟肠液DPPH·的清除率先缓慢增加,在1 h时迅速增加,2 h时达到最大值74.74%,后略有降低。说明模拟肠消化阶段,西藏蜂胶仍有较强的DPPH·清除能力。Tu等[11]指出,胃肠消化后的DPPH·清除率与其消化过程的总酚含量有关。西藏蜂胶模拟胃液DPPH·清除率高于模拟肠液,可能与总酚含量的变化相关。
2.2.4 西藏蜂胶及其模拟消化液的金属离子螯合率
西藏蜂胶和VC的金属离子螯合率随着质量浓度的增加而增大(如图4A所示)。在0.2~1.0 mg/mL浓度范围内,质量浓度相同时,西藏蜂胶金属离子螯合率显著低于VC(P<0.05)。
如图4B所示,模拟胃液的金属离子螯合率随着消化时间的延长,先增加后略减少,消化时间为2 h时达到最大值(10.49%),显著高于0、0.5、1和3 h时(P<0.05)。模拟肠液的金属离子螯合率随消化时间的延长持续上涨,且在3 h时达到最大值69.26%,均高于模拟胃液。说明模拟肠消化过程有利于提高西藏蜂胶的金属离子螯合率。这是因为大多数黄酮类化合物在pH为6.8和7.5下具有高螯合活性,而在酸性条件(pH≤4.5)下活性低,甚至无活性[35]。
2.2.5 西藏蜂胶及其模拟消化液的脂质过氧化抑制率
西藏蜂胶的脂质过氧化抑制率随着质量浓度的增大变化不大,略有增加(如图5A所示)。VC则在0.2~0.6 mg/mL范围内保持平稳,0.6~1.0 mg/mL范围内迅速降低。在0.2~1.0 mg/mL浓度范围内,西藏蜂胶的脂质过氧化抑制率保持在80%以上,显著高于VC(P<0.05)。说明蜂胶具有较好的脂质过氧化抑制力。这与曹炜和卢珂等[36]的研究结果类似。其机制是酚类作为氢供体,将氢供给脂类化合物自由基,形成稳定的酚基自由基,降低了自动氧化链式反应的传递速度[36]。
如图5B所示,模拟胃液脂质过氧化抑制率先增加后略降低,2 h时达到最大值26.69%,显著高于0、0.5和3 h时(P<0.05)。肠消化对西藏蜂胶脂质过氧化抑制率的提升较大,该阶段最高值为80.69%,高于模拟胃液的最高值。说明经过肠消化,西藏蜂胶具有较好的脂质过氧化抑制力。模拟胃肠消化下,蜂胶的脂质过氧化抑制率的研究较少,肠消化引起脂质过氧化抑制率提高的原因还有待进一步研究。
2.3 西藏蜂胶总酚、总黄酮含量和体外抗氧化活性间的相关性
西藏蜂胶总酚和总黄酮含量和体外抗氧化活性间的相关性结果见表2。西藏蜂胶的总酚含量和总黄酮含量之间呈极显著正相关,总酚与DPPH·、·OH的清除率和金属离子螯合率具有极显著正相关(P<0.01),相关系数r分别为0.981、0.922、0.935;总酚与还原力具有显著负相关(P<0.05),相关系数r为−0.817。总黄酮与DPPH·、·OH清除率和金属离子螯合率具有极显著正相关(P<0.01),相关系数r分别为0.990、0.993、0.966;总黄酮与还原力具有显著负相关(P<0.05),相关系数r为−0.815。表明西藏蜂胶抗氧化活性主要与总酚和总黄酮的存在有关,与之前的研究结果一致[37]。
表 2 西藏蜂胶总酚、总黄酮与抗氧化活性的相关性Table 2. Correlation between total phenolics and flavonoids and the antioxidant capacity of Tibetan propolis指标名称 总酚 总黄酮 还原力 DPPH·
清除率·OH
清除率脂质过氧化
抑制率金属离子
螯合率总酚 1.000 总黄酮 0.984** 1.000 还原力 −0.817* −0.815* 1.000 DPPH·
清除率0.981** 0.990** −0.818* 1.000 ·OH
清除率0.992** 0.993** −0.814* 0.988** 1.000 脂质过氧
化抑制率0.723 0.744 −0.395 0.788 0.772 1.000 金属离子
螯合率0.935** 0.966** −0.895* 0.937** 0.953** 0.612 1.000 注:**在0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关;*在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关。 3. 结论
综上,西藏蜂胶总酚和总黄酮含量分别为7.02%和10.05%。在体外抗氧化活性多个指标上表现优异,其中·OH、DPPH·清除率和脂质过氧化抑制率分别高达96.60%、92.53%和97.01%。在模拟胃肠消化过程中,模拟消化液总酚和总黄酮含量持续降低。模拟胃液DPPH·清除率高达95.69%;模拟肠液仍具有很高的·OH清除率(99.72%)、DPPH·清除率(74.74%)、金属离子螯合率(69.26%)和脂质过氧化抑制率(80.69%)。因此,西藏蜂胶可作为优质天然抗氧化剂进行后续研发。
-
表 1 西藏蜂胶及其模拟消化液的总酚和总黄酮含量(%)
Table 1 Contents of total phenolics and flavonoids in Tibetan propolis and its simulated digestive juices (%)
样品 未消化 模拟胃液(2 h) 模拟肠液(2 h) 总酚 7.02±0.02a 0.43±0.04b 0.32±0.01b 总黄酮 10.05±0.02a 6.43±0.54b 5.11±1.09b 注:不同的小写字母表示差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),试验数据以平均值±标准差表示。 表 2 西藏蜂胶总酚、总黄酮与抗氧化活性的相关性
Table 2 Correlation between total phenolics and flavonoids and the antioxidant capacity of Tibetan propolis
指标名称 总酚 总黄酮 还原力 DPPH·
清除率·OH
清除率脂质过氧化
抑制率金属离子
螯合率总酚 1.000 总黄酮 0.984** 1.000 还原力 −0.817* −0.815* 1.000 DPPH·
清除率0.981** 0.990** −0.818* 1.000 ·OH
清除率0.992** 0.993** −0.814* 0.988** 1.000 脂质过氧
化抑制率0.723 0.744 −0.395 0.788 0.772 1.000 金属离子
螯合率0.935** 0.966** −0.895* 0.937** 0.953** 0.612 1.000 注:**在0.01水平(双侧)上显著相关;*在0.05水平(双侧)上显著相关。 -
[1] 管蕊. 蜂胶乙醇提取物对MIN6细胞及2型糖尿病小鼠血糖调节的研究[D]. 济南: 山东师范大学, 2022 GUAN R. Study on the effect of ethanol extract of propolis on MIN6 cells and blood glucose regulation of type 2 diabetic mice[D]. Jinan: Shandong Normal University, 2022.
[2] WIECZOREK P P, HUDZ N, YEZERSKA O, et al. Chemical variability and pharmacological potential of propolis as a source for the development of new pharmaceutical products[J]. Molecules,2022,27(5):1600−1628. doi: 10.3390/molecules27051600
[3] ZHANG C, SHEN X, CHEN J, et al. Identification of free radical scavengers from Brazilian green propolis using off-line HPLC-DPPH assay and LC-MS[J]. Journal of Food Science,2017,82(7):1602−1607. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.13730
[4] KEKECOGLU M, SONMEZ E, YALCIN N E, et al. Analysis of detailed chemical and bioactive components of Yigilca honeybee propolis and determination of antioxidant potential[J]. Biology Bulletin,2022,49(5):381−391. doi: 10.1134/S1062359022050144
[5] CUESTA-RUBIO O, MARQUEZ HERNANDEZ I, FERNANDEZ M C, et al. Chemical characterization and antioxidant potential of Ecuadorian propolis[J]. Phytochemistry, 2022: 113415.
[6] ELSWABY S, SADIK M, AZOUZ A, et al. In vitro evaluation of antimicrobial and antioxidant activities of honeybee venom and propolis collected from various regions in Egypt[J]. Egyptian Pharmaceutical Journal,2022,21(2):207−213. doi: 10.4103/epj.epj_18_22
[7] 邱潍. 蜂胶有效成分提取及抗氧化活性研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉轻工大学, 2019 QIU W. Study on extraction and antioxidant activity of effective components of propolis[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan Polytechnic University, 2019.
[8] 王启海, 左坚, 戴胜, 等. 蜂胶中总酚提取纯化工艺及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 湘南学院学报(医学版),2019,21(4):1−6. [WANG Q H, ZUO J, DAI S, et al. Extraction, purification and antioxidant activity of total phenolic from propolis[J]. Journal of Xiangnan University (Medical Sciences),2019,21(4):1−6. WANG Q H, ZUO J, DAI S, et al. Extraction, purification and antioxidant activity of total phenolic from propolis[J]. Journal of Xiangnan University (Medical Sciences), 2019, 21(4): 1-6.
[9] REGINIO F C, QIN W, KETNAWA S, et al. Bio-properties of Saba banana (Musa ‘saba’, ABB Group): Influence of maturity and changes during simulated in vitro gastrointestinal digestion[J]. Scientific Reports,2020,10(1):6701. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-63501-x
[10] ZHANG Q, XING B, SUN M, et al. Changes in bio-accessibility, polyphenol profile and antioxidants of quinoa and djulis sprouts during in vitro simulated gastrointestinal digestion[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2020,8(8):4232−4241.
[11] TU F, XIE C, LI H, et al. Effect of in vitro digestion on chestnut outer-skin and inner-skin bioaccessibility: The relationship between biotransformation and antioxidant activity of polyphenols by metabolomics[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,363:130277. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130277
[12] YEN C H, CHIU H F, WU C H, et al. Beneficial efficacy of various propolis extracts and their digestive products by in vitro simulated gastrointestinal digestion[J]. LWT,2017,84:281−289. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2017.05.074
[13] SUN X, CHENG X, ZHANG J, et al. Letting wine polyphenols functional: Estimation of wine polyphenols bioaccessibility under different drinking amount and drinking patterns[J]. Food Research International,2020,127:108704. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108704
[14] BOUAYED J, HOFFMANN L, BOHN T. Total phenolics, flavonoids, anthocyanins and antioxidant activity following simulated gastro-intestinal digestion and dialysis of apple varieties: Bioaccessibility and potential uptake[J]. Food Chemistry,2011,128(1):14−21. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.02.052
[15] 封易成, 牟德华. 体外模拟胃肠消化过程中山楂的活性成分及抗氧化性规律[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(7):139−145. [FENG Y C, MOU D H. Changes in active components and antioxidant activity of hawthorn during simulated gastrointestinal digestion in vitro[J]. Food Science,2018,39(7):139−145. FENG Y C, MOU D H. Changes in active components and antioxidant activity of hawthorn during simulated gastrointestinal digestion in vitro[J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(7): 139-145.
[16] 程启斌, 李石飞, 张立伟. 连翘不同部位总酚含量测定及抗氧化活性比较研究[J]. 化学研究与应用, 2016, 28(5): 610−616 CHENG Q B, LI S F, ZHANG L W. Study on comparison of antioxidant activity and determination of total phenol content in different parts of Forsythia suspensa[J]. Chemical Research and Application, 2016, 28(5): 610−616.
[17] 周利平, 何志敏, 潘小红. 不同仪器检测方法及标准品对保健食品中茶多酚含量测定的影响[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2017,8(5):1616−1621. [ZHOU L P, HE Z M, PAN X H. Effects of different instrument testing methods and standard substances on determination of tea polyphenols in health food[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2017,8(5):1616−1621. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2017.05.016 ZHOU L P, HE Z M, PAN X H. Effects of different instrument testing methods and standard substances on determination of tea polyphenols in health food[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality, 2017, 8(5): 1616-1621. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2017.05.016
[18] GULCIN I. Antioxidant activity of caffeic acid (3, 4-dihydroxycinnamic acid)[J]. Toxicology,2006,217(2-3):213−220. doi: 10.1016/j.tox.2005.09.011
[19] SHUAI L, MENGYUN J, JIAJUN C, et al. Removal of bound polyphenols and its effect on antioxidant and prebiotics properties of carrot dietary fiber[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,93(2):284−292.
[20] HAISHA Y, YUQIONG D, HUIJING D, et al. Antioxidant compounds from propolis collected in Anhui, China[J]. Molecules,2011,16:3444−3455. doi: 10.3390/molecules16043444
[21] CAI L, ZOU S, LIANG D, et al. Structural characterization, antioxidant and hepatoprotective activities of polysaccharides from Sophorae tonkinensis Radix[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,184(12):354−365.
[22] 赵博, 乔长晟, 汪建明, 等. 出芽短梗霉黑色素的抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2013,34(6):108−112. [ZHAO B, QIAO C S, WANG J M, et al. Study on antioxidant activities of melanin of Aureobasidium pullulans[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2013,34(6):108−112. ZHAO B, QIAO C S, WANG J M, et al. Study on antioxidant activities of melanin of Aureobasidium pullulans[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2013, 34(6): 108-112.
[23] 刘学医, 王晓卉, 刘丽敏. 不同产地蜂胶抗氧化活性评价与抗氧化活性成分研究[J]. 河南农业,2020(20):13−15. [LIU X Y, WANG X H, LIU L M. Evaluation and antioxidant activity of propolis from different producing areas sexual composition research[J]. Henan Agriculture,2020(20):13−15. doi: 10.15904/j.cnki.hnny.2020.20.006 LIU X Y, WANG X H, LIU L M. Evaluation and antioxidant activity of propolis from different producing areas sexual composition research[J]. Henan Agriculture, 2020(20): 13-15. doi: 10.15904/j.cnki.hnny.2020.20.006
[24] 曾林晖. 不同提取方法蜂胶提取物的化学成分、代谢及抗氧化能力的研究[D]. 江西: 南昌大学, 2016 ZENG L H. Study on the chemical components, metabolism and antioxidant activities of propolis extracted by different methods[D]. Jiangxi: Nanchang University, 2016.
[25] 蒋侠森. 蜂胶的化学成分、抗氧化谱效分析及长白山蜂胶的特性研究[D]. 浙江: 浙江大学, 2020 JIANG X S. Analysis of the chemical composition and anti-oxidation spectrum effect of propolis and the characteristics of Changbai mountains propolis[D]. Zhejiang: Zhejiang University, 2020.
[26] YESILTAS B, CAPANOGLU E, FIRATLIGIL-DURMUS E, et al. Investigating the in-vitro bioaccessibility of propolis and pollen using a simulated gastrointestinal digestion system[J]. Journal of Apicultural Research,2014,53(1):101−108. doi: 10.3896/IBRA.1.53.1.10
[27] CHANG C C, YANG M H, WEN H M, et al. Estimation of total flavonoid content in propolis by two complementary colorimetric methods[J]. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis,2002,10(3):178−182.
[28] FRIEDMAN M, JÜRGENS H S. Effect of pH on the stability of plant phenolic compounds[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2000,48(6):2101−2110. doi: 10.1021/jf990489j
[29] BERMUDEZSOTO M, TOMASBARBERAN F, GARCIACONESA M. Stability of polyphenols in chokeberry (Aronia melanocarpa) subjected to in vitro gastric and pancreatic digestion[J]. Food Chemistry,2007,102(3):865−874. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2006.06.025
[30] 曹炜, 尉亚辉, 雒西萍, 等. 蜂胶的抗氧化作用研究-Ⅰ. 蜂胶对超氧阴离子和羟基自由基的抑制作用[J]. 西北大学学报(自然科学版),2001(2):146−148. [CAO W, WEI Y H, LUO X P, et al. A study on peroxy radical and hydroxy radical scavenging acitivity of propolis[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition),2001(2):146−148. CAO W, WEI Y H, LUO X P, et al. A study on peroxy radical and hydroxy radical scavenging acitivity of propolis[J]. Journal of Northwest University (Natural Science Edition), 2001(2): 146-148.
[31] TAGLIAZUCCHI D, VERZELLONI E, BERTOLINI D, et al. In vitro bio-accessibility and antioxidant activity of grape polyphenols[J]. Food Chemistry,2010,120(2):599−606. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.10.030
[32] TYRAKOWSKA B, SOFFERS A E M F, SZYMUSIAK H, et al. TEAC antioxidant activity of 4-hydroxybenzoates[J]. Free Radical Biology and Medicine,1999,27(11−12):1427−1436. doi: 10.1016/S0891-5849(99)00192-6
[33] BARTKIENE E, LELE V, SAKIENE V, et al. Variations of the antimicrobial, antioxidant, sensory attributes and biogenic amines content in Lithuania-derived bee products[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2020,118:108793. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108793
[34] OZDAL T, CEYLAN F D, EROGLU N, et al. Investigation of antioxidant capacity, bioaccessibility and LC-MS/MS phenolic profile of Turkish propolis[J]. Food Research International,2019,122:528−536. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.05.028
[35] SFORCIN J M. Biological properties and therapeutic applications of propolis: properties and applications of propolis[J]. Phytotherapy Research,2016,30(6):894−905. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5605
[36] 曹炜, 卢珂, 陈卫军, 等. 不同种类蜂蜜抗氧化活性的研究[J]. 食品科学,2005(8):352−356. [CAO W, LU K, CHEN W J, et al. Study on antioxidation effects of different honeys[J]. Food Science,2005(8):352−356. CAO W, LU K, CHEN W J, et al. Study on antioxidation effects of different honeys[J]. Food Science, 2005(8): 352-356.
[37] BANKOVA V. Recent trends and important developments in propolis research[J]. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine,2005,2(1):29−32. doi: 10.1093/ecam/neh059
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 李杨,李想,曾凤玲,戢得蓉,段丽丽. 三种天然甜味剂在红烧肉中的应用研究. 农产品加工. 2025(03): 17-22 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 刘丽莉,陈卉,郭净芳,张潇丹,苏克楠,于影. 儿茶素-糖基化猪血红蛋白对肉糜品质的影响及抑菌作用. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(21): 224-231 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 林婷,张永敏,许巧霞. 罗汉果甜苷研究进展综述. 食品安全导刊. 2023(10): 147-149 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:



