Preparation and Characterization of Microcapsules by Heat Treated Myofibrillar Protein Coacervation
-
摘要: 探索罗非鱼(Oreochromis niloticus)中提取肌原纤维蛋白(MP)在热处理后(HMP)作为一种新型微胶囊的壳材料,在海藻酸钠(SA)和壳聚糖(CS)共存下,采用超声复凝聚法对玉米油进行微胶囊化,并对其性能进行表征。结果表明:当海藻酸钠含量2.5%,HMP含量3.0%,玉米油含量30%时,乳液粒径小而均匀,乳化稳定性高。壳聚糖含量为1.2%、海藻酸钠和壳聚糖质量比1:1、氯化钙浓度为5.0%时,通过超声复凝聚法得到的微胶囊平均粒径为88.74±2.60 μm,包封率为82.59%±1.44%;微胶囊具有不规则形状和起伏的表面;红外光谱和X射线衍射结果表明,海藻酸钠与壳聚糖因静电结合作用,与HMP共同构成了微胶囊致密的外壳;DSC结果显示HMP微胶囊具有一定的热稳定性;HMP微胶囊显著降低了贮存过程中油脂的POV值与TBA值,有效延缓了玉米油的氧化速度;HMP微胶囊在整个模拟消化阶段的游离脂肪酸(FFA)释放量为92.67%,且在肠消化阶段释放更多的FFA,表明微胶囊化对芯材的释放起到了缓释作用。这项研究显示,HMP与海藻酸钠和壳聚糖复合后,是可以用于微胶囊制备及保护生物活性物质,为HMP的乳化应用扩展途径。
-
关键词:
- 热处理肌原纤维蛋白(HMP) /
- 海藻酸钠 /
- 玉米油 /
- 微胶囊 /
- 性能表征
Abstract: Myogenic fibrin (MP) extracted from Tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) after heat treatment (HMP) was explored as a novel encapsulant for microencapsulation of corn oil together with sodium alginate (SA) and chitosan (CS), and its performance was characterized using ultrasonic coalescence. The results showed that at 2.5% sodium alginate, 3.0% HMP content and 30% corn oil, the emulsion had small and uniform particle size with high emulsification stability. The average particle size of microcapsules after ultrasonic recondensation was 88.74±2.60 μm while the encapsulation rate was 82.59%±1.44% under the following conditions: 1.2% CS, SA:CS mass ratio of 1:1, and 5.0% calcium chloride. The microcapsules had irregular shapes and undulating surfaces, and the results of infrared spectroscopy and X-ray diffraction indicated that CS and SA formed the dense shell of microcapsules together with HMP due to electrostatic binding. Results from DSC showed that HMP microcapsules had a degree of thermal stability, and the microencapsulation significantly reduced the POV and TBA values of oil during storage, which effectively slowed down the oxidation process. The release of free fatty acids (FFA) from HMP microcapsules was 92.67% during the whole simulated digestion phase with a greater amount released during the intestinal digestion phase, indicating that microencapsulation had a retarding effect on the release of core material. This study shows that HMP compounded with sodium alginate and chitosan is feasible for microencapsulation and protection of bioactive substances, and hence expanding the applications of HMP microgel particles. -
罗非鱼(Oreochromis niloticus)作为我国主要养殖的淡水鱼类之一,2020年产量达到165.54万吨。罗非鱼肉优质蛋白质含量丰富(20.5%)[1],必需氨基酸与非必需氨基酸的比值超过65%,是一种优质的蛋白质来源[2]。肌原纤维蛋白(myofibrillar protein, MP)是罗非鱼肉中含量最丰富的蛋白质,具有两亲性,有作为乳化剂的巨大潜力。而且相关研究表明MP具有良好的乳化性、发泡性、凝胶性等功能特性,具备作为良好乳化稳定剂的潜力[3]。
近年来,蛋白质类新微胶囊壁材的开发也备受关注。水产类蛋白已被证明是油脂微胶囊的潜在壳层材料。Intarasirisawat等[4]使用单宁酸通过喷雾干燥的方式,将鱼子蛋白水解物作为壳层材料对鱼油进行微胶囊化的过程,发现鱼油在储存期间(30 ℃,28 d)的氧化稳定性有所提高。Morales等[5]使用竹荚鱼和沙丁鱼的肌肉蛋白质水解物作为壁材,通过喷雾干燥技术将鱼油微胶囊化,获得了包封率超过97%和良好氧化稳定性的产品。Shi等[6]使用磷虾蛋白通过复合凝聚法将磷虾油微胶囊化。Bakry等[7]使用草鱼MP和卡拉胶混合壁材以复合凝聚法制得的金枪鱼油微胶囊粒径较小(6 μm),包封率高(98.65%),可见,水产类蛋白具有优越的应用前景。
目前,越来越多的学者开始关注热处理对肌原纤维蛋白特性的影响。肌原纤维蛋白在热处理中构象发生改变[8],从天然状态发生变性,氨基酸基团暴露,其分子间与分子内的相互作用力均发生改变[9-10]。王正雯等[11]研究表明,在70 ℃处理后,麻鸭肌原纤维蛋白形成了均匀致密的凝胶,且保水率优良。不同的热处理温度影响鲤鱼肌原纤维蛋白的热聚行为,对凝胶特性产生不同的影响[12]。郑云芳等[13]研究表明热处理增加了鲈鱼肌原纤维蛋白的乳化性能。张桂艳[14]研究同样发现热处理后牛肉肌原纤维蛋白乳化性能提升。综上可知,热处理后肌原纤维蛋白具有一定的应用价值,但目前对其应用方面的研究有限。利用热处理后的肌原纤维蛋白进行微胶囊的开发还鲜有报道。
本实验以海藻酸钠含量、HMP含量、油含量为变量,通过对乳液的微观结构、乳化稳定性和平均粒径的测定,确定SA-HMP稳定乳液的制备条件。将稳定乳液通过超声凝聚法制得冻干微胶囊产品,以壳聚糖含量、海藻酸钠/壳聚糖质量比和氯化钙含量为变量,根据微胶囊的平均粒径和包封率结果,优化微胶囊制备工艺。并利用超景深显微观察、红外光谱仪(FT-IR)、X射线衍射仪(XRD)、差示扫描热分析仪(DSC)、POV值和TBA值等对微胶囊的结晶度、热稳定性、抗氧化稳定性、体外消化特性等进行表征和分析。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
罗非鱼片 150±20 g,置于超低温冰箱−80 ℃条件保存,海南翔泰渔业股份有限公司;玉米油(食用级) 金龙鱼公司;海藻酸钠(粘度:15~60 mPa·s) 分析纯,Macklin公司;壳聚糖(脱乙酰度≥95%) 阿拉丁公司;胃蛋白酶(30000 U/g)、胰酶(4000 U/g)、猪胆盐(胆酸含量≥65%) 美国Sigma公司;其他试剂均为国产分析纯。
T6紫外可见分光光度计 北京普析通用公司;Q100差示扫描量热仪 美国TA公司;LS 13 320贝克曼库尔特激光粒度仪 贝克曼库尔特商贸公司;Frontier傅里叶变换红外光谱仪 美国Perkin-Elmer公司;LabMASTER-aw水分活度仪 瑞士Novasina公司;X1R高速冷冻离心机 美国Thermo Fisher公司;XHF-DY高速分散机 宁波Scientz公司;QSJ-B02R1绞肉机 小熊电器股份有限公司;B302光学显微镜 重庆奥特光学仪器有限责任公司;KQ2200DE超声仪 昆山市超声仪器公司; New Empyrean X射线衍射仪 荷兰Panalyticals公司;Smart Zoom5超景深三维显微系统 德国蔡司公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 肌原纤维蛋白(MP)的提取及热处理MP制备(HMP)
肌原纤维蛋白(MP)提取参考Bakry等[7]的研究并稍作修改。罗非鱼片取白肉部分70 g放入绞肉机中在冰浴条件下匀浆处理。绞碎后的鱼肉在4 ℃条件下离心三次(7000 g,10 min),每次均加入80 mL磷酸盐缓冲液A液(0.05 mol/L NaCl, 3.38 mmol/L NaH2PO4·2H2O, 15.5 mmol/L Na2HPO4·12H2O, pH7.5),弃去上清液。取沉淀加入80 mL磷酸盐缓冲液B液(0.6 mol/L NaCl, 3.38 mmol/L NaH2PO4·2H2O, 15.5 mmol/L Na2HPO4·12H2O, pH7.5),以同样条件离心三次后在4 ℃条件冷藏过夜。离心(16000 g,10 min)后,取上清液与5倍体积的蒸馏水混合后冷藏30 min,离心(16000 g,15 min)两次后得到的沉淀即为MP,4 ℃条件下,24 h内使用完毕。
将一定量的MP分散在去离子水中,在漩涡浴处理2 min,恒温振荡摇床中孵育100 ℃、30 min,高速分散器,8000 r/min、2 min中,得HMP蛋白。将得到的HMP蛋白颗粒4 ℃存储供下步使用。
1.2.2 HMP蛋白乳液(O/W)的制备单因素实验
1.2.2.1 HMP蛋白乳液的制备条件研究
取适量的HMP溶解于磷酸盐缓冲液中(0.6 mol/L NaCl, 3.38 mmol/L NaH2PO4·2H2O, 15.5 mmol/L Na2HPO4·12H2O,pH7.0),加入海藻酸钠并使其充分溶解。然后加入合适比例的玉米油,使用高速分散机在7000 r/min、2 min得到SA-HMP乳液。分别设置海藻酸钠、HMP和玉米油含量为变量,其中:设置体系中HMP含量为2%(w/w),海藻酸钠含量为1.5%、2.0%、2.5%、3.0%,玉米油含量30%,考察海藻酸钠(SA)含量对乳液的影响;设置体系中海藻酸钠含量为2.5%(w/w),HMP梯度为1%、2%、3%、4%(w/w),玉米油含量30%,考察HMP蛋白含量对乳液的影响;设置体系中HMP含量为3%(w/w),海藻酸钠含量为2.5%(w/w),油相含量10%、20%、30%、40%、50%,考察玉米油含量对乳液的影响。考察乳液平均粒径、微观结构和乳化稳定性的变化影响。每组样品设置三个平行。
1.2.2.2 乳液微观结构的测定
将乳液滴加于单凹面载玻片上,通过光学显微镜在10倍目镜下观察乳液的微观结构。
1.2.2.3 乳液平均粒径的测定
使用激光粒度仪对乳液的平均粒径进行测定。用滴管吸取1 mL乳液稀释后滴入加样水槽中,参数设置如下:介质为H2O,折射率(介质)1.333,折射率(物质)1.520。结果以表面平均粒径d3,2表示,每组样品测定三次取平均值。
1.2.2.4 乳液稳定性的测定
乳液稳定性测定依照刘成祥等[15]的方法并稍加修改。将制得的不同条件的乳液装入10 mL具塞刻度试管中,室温静置24 h后观察其分层情况,每组样品设置三个平行,乳液稳定性的计算按照以下公式进行:
乳液稳定性(%)=(未分层乳液高度/总乳液高度)×100 1.2.3 HMP微胶囊制备的单因素实验
1.2.3.1 HMP微胶囊制备条件研究
微胶囊的制备参考申莉莉[16]的方法并稍作修改。将装有200 mL蒸馏水的烧杯置于超声仪中,超声功率设置为120 W,向烧杯中同时滴加SA-HMP乳液和一定含量的壳聚糖乙酸(2 %)溶液,超声凝聚20 min,加入体系总体积10%的一定含量氯化钙溶液,超声条件(3000 W、25 ℃)下固化40 min后,调节溶液pH6.0,吸去下层水层,将上层微胶囊冻干处理,得到HMP微胶囊。分别考察壳聚糖含量、海藻酸钠和壳聚糖质量比、氯化钙浓度为变量,其中:设置海藻酸钠和壳聚糖质量比为1:1,氯化钙浓度3%(w/w),壳聚糖含量考察分别为0%、0.2%、0.4%、0.6%、0.8%、1.0%、1.2%、1.4%(w/w),考察壳聚糖含量对微胶囊影响;设置壳聚糖含量为1.0%(w/w),氯化钙浓度3%(w/w),海藻酸钠与壳聚糖质量比分别为1:4、3:7、1:1、7:3、4:1,考察海藻酸钠与壳聚糖质量比对微胶囊影响;设置壳聚糖含量为1.0%(w/w),海藻酸钠与壳聚糖质量比为1:1,氯化钙浓度分别为1.0%、3.0%、5.0%、7.0%、9.0%(w/w),考察氯化钙浓度对微胶囊影响。考察微胶囊平均粒径和包封率的变化,每组样品至少平行测定三次。
1.2.3.2 微胶囊平均粒径的测定
将待测的微胶囊样品稀释,滴加入激光粒度仪的水槽中,对样品进行粒度分析,以体积平均粒径d4,3表示微胶囊的平均粒径,每组样品至少做三个平行。
1.2.3.3 微胶囊包封率的测定
微胶囊包封率的测定采用紫外分光光度法,参考张珊珊[17]的方法并稍加修改。玉米油标准曲线为:y=0.2966x+0.0899,R2=0.9958。表面油含量的测定:称取50 mg微胶囊样品,使用5 mL乙酸乙酯迅速过滤,收集滤液用乙酸乙酯稀释至10 mL,测定滤液在268 nm处吸光度。总油含量的测定:取50 mg微胶囊样品,加入5 mL乙酸乙酯浸泡,置入超声仪以300 W功率超声破碎30 min,将溶液使用带过滤头(0.22 μm)的注射器过滤,收集滤液测定其268 nm吸光度。
微胶囊样品的包封率按照下式进行计算:
包封率(%)=(1−表面油含量/总油含量)×100 1.2.4 HMP微胶囊的性质分析与结构表征
1.2.4.1 微胶囊水分含量与水分活度的测定
准确称取2 g微胶囊样品,放入105 ℃烘箱中烘干至恒重,通过重量损失计算得微胶囊的水分含量[18-19]。每组样品平行测定三次。
微胶囊样品的水分活度使用水分活度仪测定。校准使用饱和NaCl溶液,室温下测定样品,平行测定三次取平均值。
1.2.4.2 微胶囊的溶解度测定
参考Rodríguez-Restrepo等[20]的方法并稍作修改。室温下称取1 g微胶囊粉末于100 mL蒸馏水中至完全分散,将溶液离心(3000 g,5 min),取25 mL上清液于培养皿中,置于105 ℃烘箱中烘干至重量恒定。微胶囊的溶解度即为培养皿中粉末质量与粉末总质量的比值。
1.2.4.3 微胶囊的润湿性测定
参考Fuchs等[21]的方法测定了微胶囊样品的润湿性。室温下称取0.1 g微胶囊样品,使其颗粒均匀散布于100 mL蒸馏水的表面,让样品自然润湿,记录每组样品完全被浸没所花费的时间。
1.2.4.4 微胶囊的微观结构观察
微胶囊的微观结构使用超景深三维显微系统进行测定。将少量微胶囊样品置于显微观察平台,在600倍放大倍数下,设置合适的步进距离和采集层数,对微胶囊的微观结构观察分析。
1.2.4.5 微胶囊的红外光谱分析
分别准确称取10 mg的海藻酸钠、HMP、壳聚糖、玉米油和微胶囊样品,与1 g烘干后的溴化钾混合均匀后研磨压片,压片置于红外光谱仪内进行400~4000 cm−1范围的红外扫描。
1.2.4.6 微胶囊的X射线衍射分析
X射线衍射分析根据罗文涛等[22]的方法进行测定。分别称取2 g海藻酸钠、HMP、壳聚糖和微胶囊样品,置于X射线衍射仪中进行分析,参数设置为:Cu-Kα射线作为激发源,扫描范围5°~50°(2θ),40 kV维持管电压,40 mA管电流,扫描速度设置为2 °/min。
1.2.4.7 微胶囊热稳定性分析
微胶囊的热稳定性测定参考Yang等[23]的方法并稍作修改,使用差式扫描量热仪(DSC)分析。
1.2.4.8 微胶囊的抗氧化稳定性分析
称取微胶囊样品装入50 mL离心管中,装满至顶部不留空隙,以锡箔纸包裹离心管遮光处理,以相同储存条件的玉米油作为对照组,置于60 ℃烘箱中,储存18 d,每隔3 d测定一次微胶囊样品与玉米油的过氧化值(POV)与硫代巴比妥酸(TBA)值。每组样品至少平行测定三次。
a.样品POV值的测定:根据Tatar等[24]的方法并稍作修改。准确称取2 g样品,放入250 mL碘量瓶中,加入30 mL的三氯甲烷-冰醋酸混合液(体积比2:3),摇晃碘量瓶至样品溶解完全。滴入1 mL饱和碘化钾溶液,振摇30 s使其混匀,室温避光反应放置3 min。加入100 mL蒸馏水,摇匀,以0.01 mol/L的硫代硫酸钠溶液滴定至溶液呈现淡黄色,加入1 mL 1%(w/w)淀粉指示剂,继续滴定直至蓝色消失。同时按相同方法做不加样品的空白实验,样品的POV值按照以下公式进行计算:
POV=(V−V0)×c×10002m 式中:POV为样品的过氧化值,mmol/kg;V为滴定样品消耗的硫代硫酸钠溶液体积,mL;V0为滴定空白消耗的硫代硫酸钠溶液体积,mL;c为硫代硫酸钠标准溶液的浓度,mol/L;m为样品中油的质量,g。
b.样品TBA值的测定:按照Rodríguez-Carpena等[25]的方法并稍作修改。精准称取2 g样品于离心管内,加入15 mL 10 g/L的三氯乙酸溶液,振荡摇匀2 min,过滤收集滤液,向5 mL滤液中加入5 mL TBA溶液,混合后于沸水浴中加热15 min,离心(4000 g,10 min)后取上清液测定其在532 nm处吸光值。按照以1,1,3,3-四乙氧基丙烷制备的标准曲线计算TBA值,结果单位为mg MDA/kg。
1.2.4.9 微胶囊的体外模拟释放
微胶囊样品的体外消化实验参考Kosaraju等[26]的方法并略加修改进行。至少做三次平行实验。模拟胃消化液和模拟肠消化液按照NaCl(20.00 g/L)、胃蛋白酶(3.20 g/L)、KH2PO4(17.00 g/L)、1 mol/L NaOH(调节pH至7.5)、1 mol/L HCl(调节pH至1.2)、胰酶(3.15 g/L)、胆汁盐(6.25 g/L)配制,现配现用。
称取2 g微胶囊样品放入装有50 mL模拟胃液的烧杯中,置于37 ℃条件的水浴摇床上,转速设置为100 r/min,模拟消化120 min,过程中使pH维持在1.2,每30 min记录一次消耗NaOH溶液的体积。胃液消化结束后,使用1 mol/L NaOH溶液迅速调节溶液pH至7.5以灭活胃蛋白酶,加入50 mL肠消化液,按照相同水浴搅拌条件继续消化180 min,过程中通过滴加0.1 mol/L NaOH溶液使pH维持在7.5,每隔30 min记录一次消耗NaOH溶液的体积。
游离脂肪酸释放率(FFA)的测定:
以FFA为纵坐标,以消化时间为横坐标,绘制曲线,样品的FFA值按照以下公式进行计算:
FFA(%)=V×M×cm×2×100 式中:V为消耗NaOH溶液的体积,mL;c为NaOH溶液的浓度mol/L;M为玉米油的平均分子质量,g/mol;m为所称样品中油的质量,g。
1.3 数据处理
本实验中每组实验均平行三次,数据取平均值分析,结果均以平均值±标准差形式表示。使用IBM SPSS Statistics 25软件采用单因素分析(ANOVA)检验数据的显著性差异,对数据进行分析,不同字母上标表示具有显著性差异(P<0.05),作图软件为OriginPro 8.0。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 HMP乳液的制备及单因素实验结果
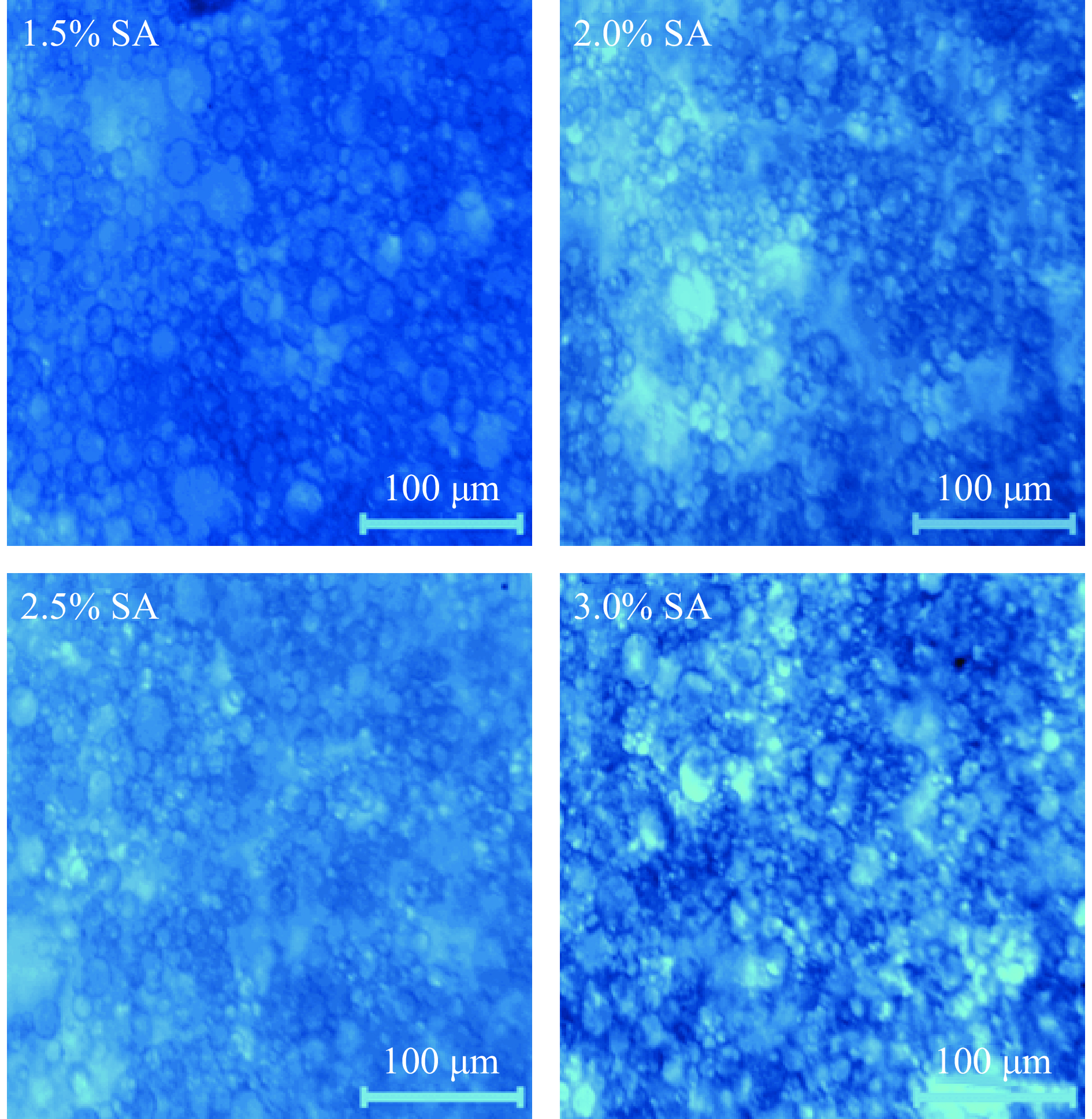
2.1.1 海藻酸钠含量对HMP乳液形成的影响
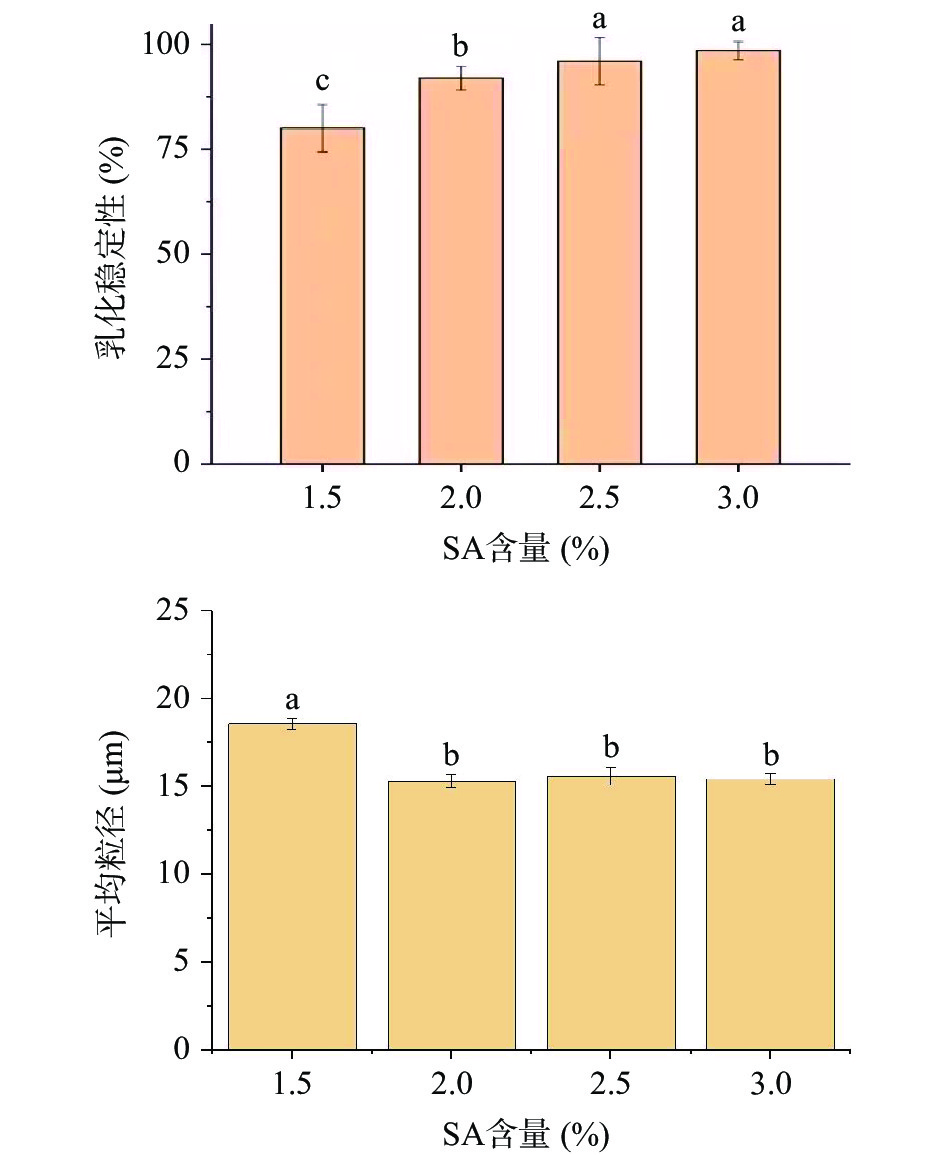
由图1可知,随着海藻酸钠含量的增加,光学显微结构表明乳液的液滴粒径变小,海藻酸钠含量低时,为了包裹尽可能多的乳液,粒径较大(图2),乳化稳定性低(图2)。当海藻酸钠含量增加时,乳液粒径显著变小(P<0.05),乳化稳定性显著提升(P<0.05)。海藻酸钠含量为2.5%时,光学显微结构显示乳液液滴粒径相对小而均匀,且乳液稳定性最佳,故选择海藻酸钠含量为2.5%的条件进行下步试验优化。
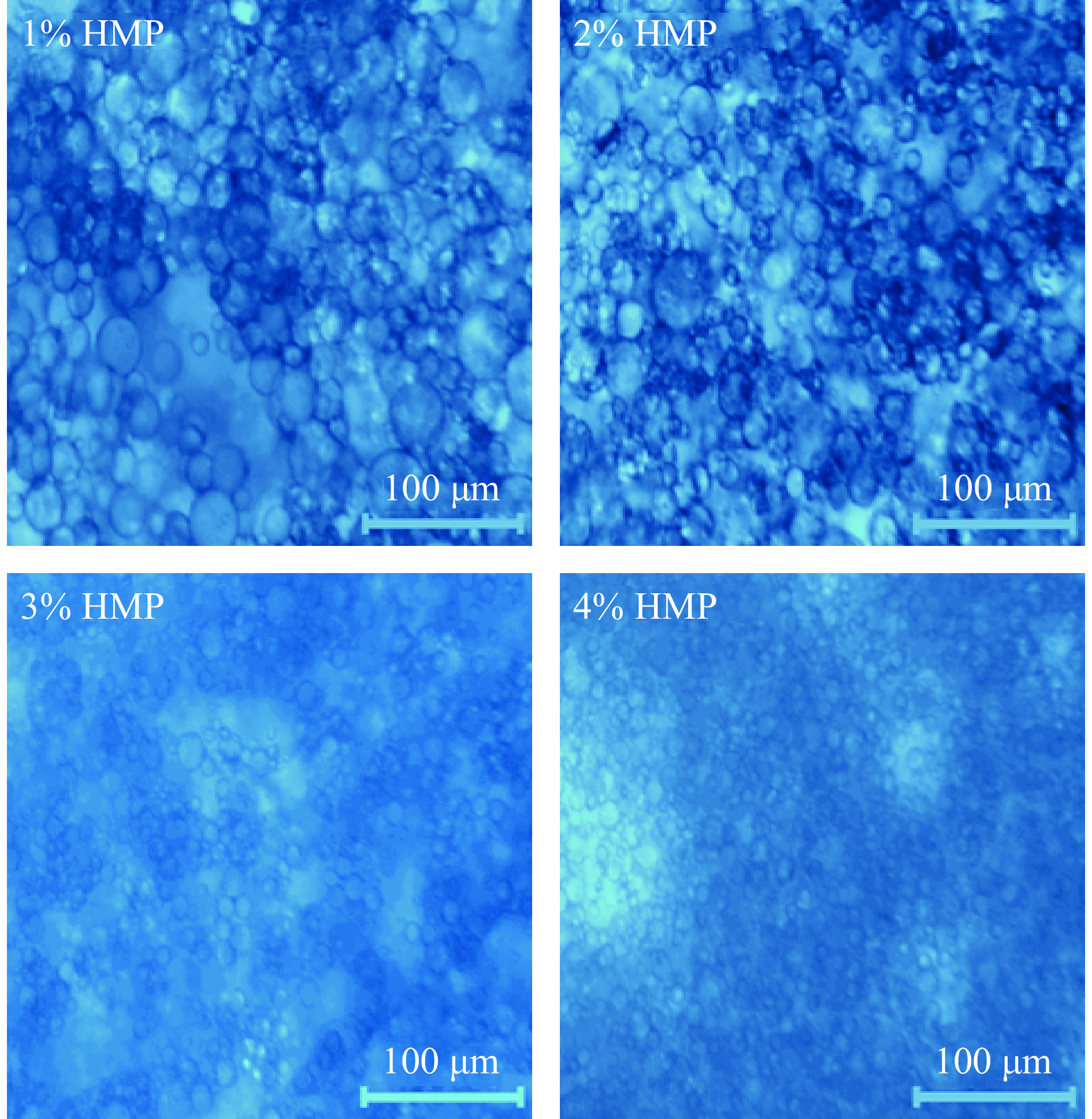
2.1.2 HMP含量对HMP乳液的影响
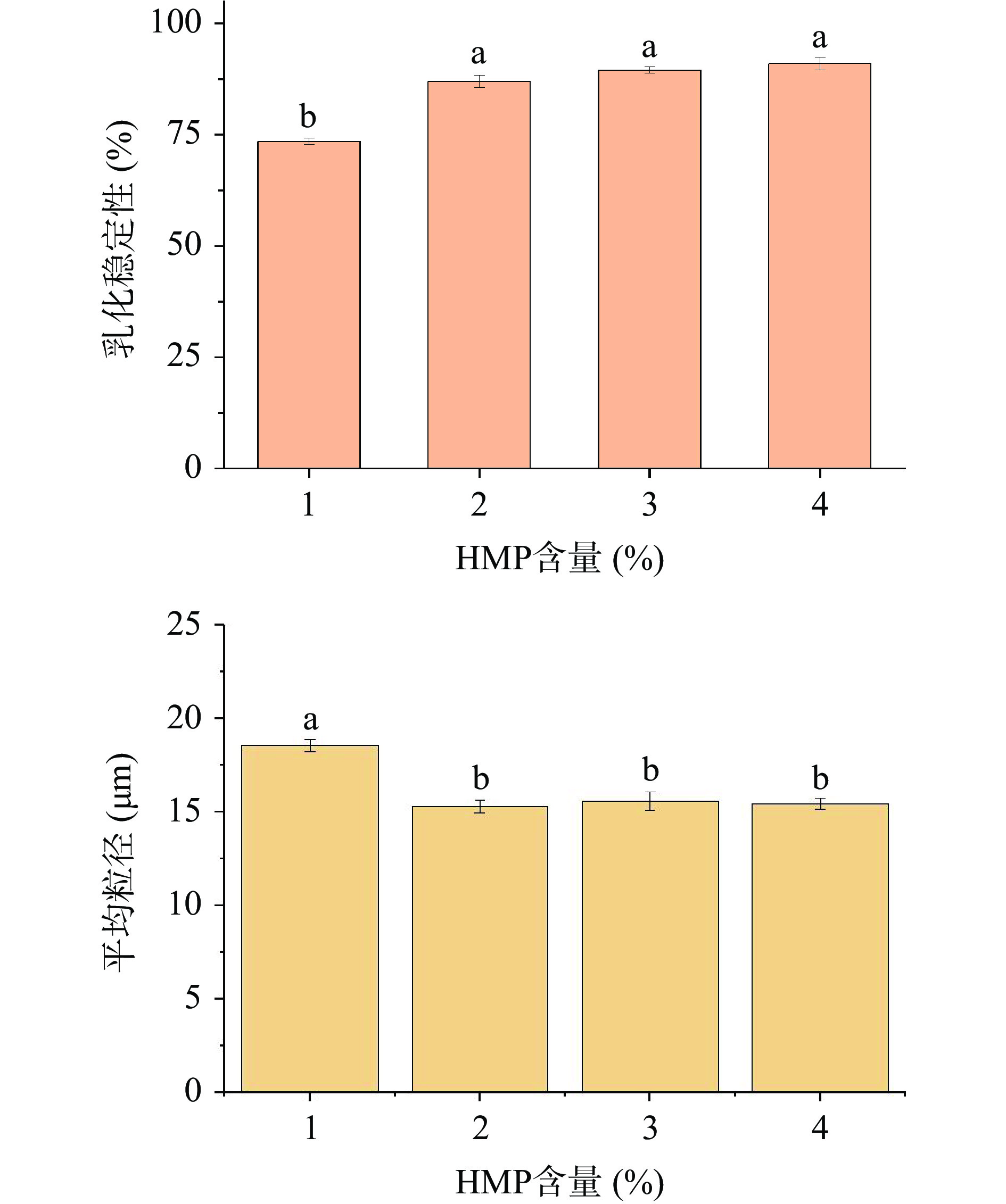
如图3所示,随着HMP含量的增加,光学显微结构表明乳液的液滴粒径显著变小(P<0.05),HMP含量高时,油滴被充分乳化,粒径变小(图4)。在HMP含量为3.0%和4.0%时,乳化稳定性较好且差异不显著(P>0.05),故选择HMP含量为3.0%进行下一步试验优化。
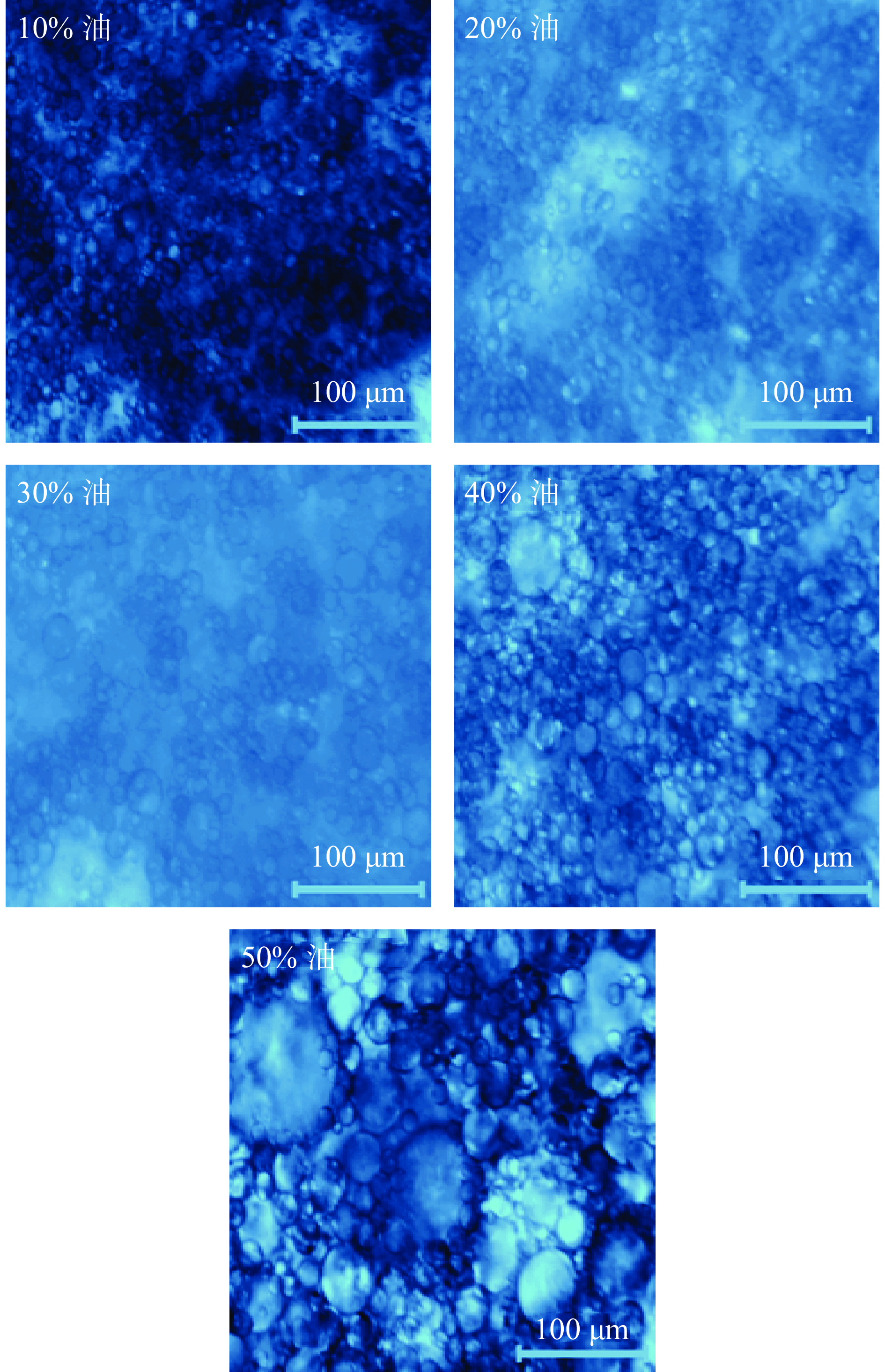
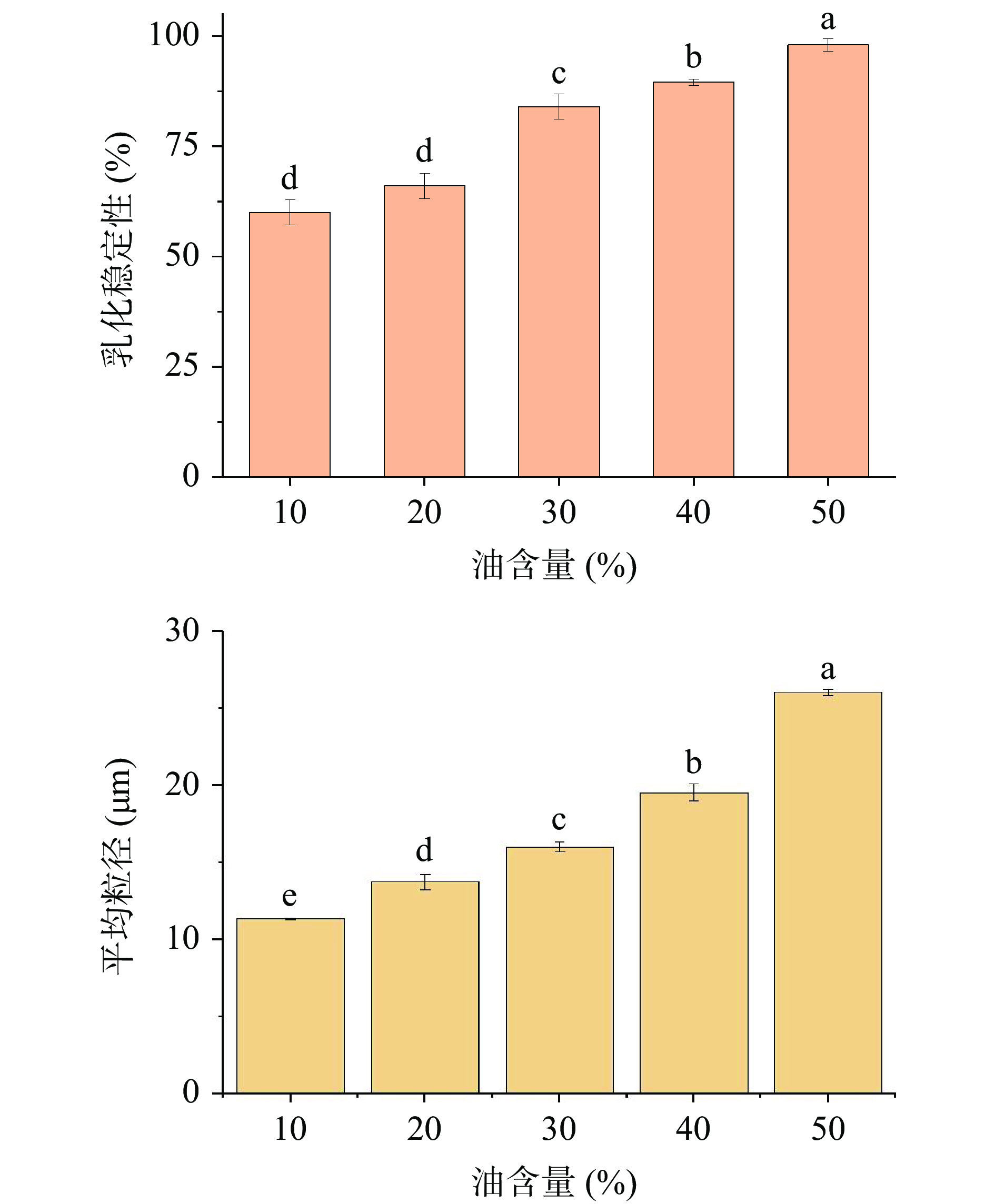
2.1.3 玉米油含量对HMP乳液的影响
由图5可知,随着玉米油含量的增加,光学显微结构表明乳液的液滴粒径逐渐变大,玉米油含量的增加,可用于乳化的海藻酸钠和HMP不足,粒径显著变大(P<0.05)(图6),乳化稳定性显示(图6),在玉米油含量40%和50%时乳化稳定性相对较高,但考虑到玉米油含量30%时的平均粒径(16.02±0.34 μm)要小于玉米油含量40%(18.31±0.44 μm)和50%(26.12±0.23 μm)的平均粒径,故选择玉米油含量为30%进行下一步试验优化。
综上结果,HMP乳液的最佳制备条件为:海藻酸钠含量2.5%,HMP含量3.0%,玉米油含量30%,以此乳化条件进行微胶囊的制备。
2.2 HMP微胶囊制备的单因素实验结果分析
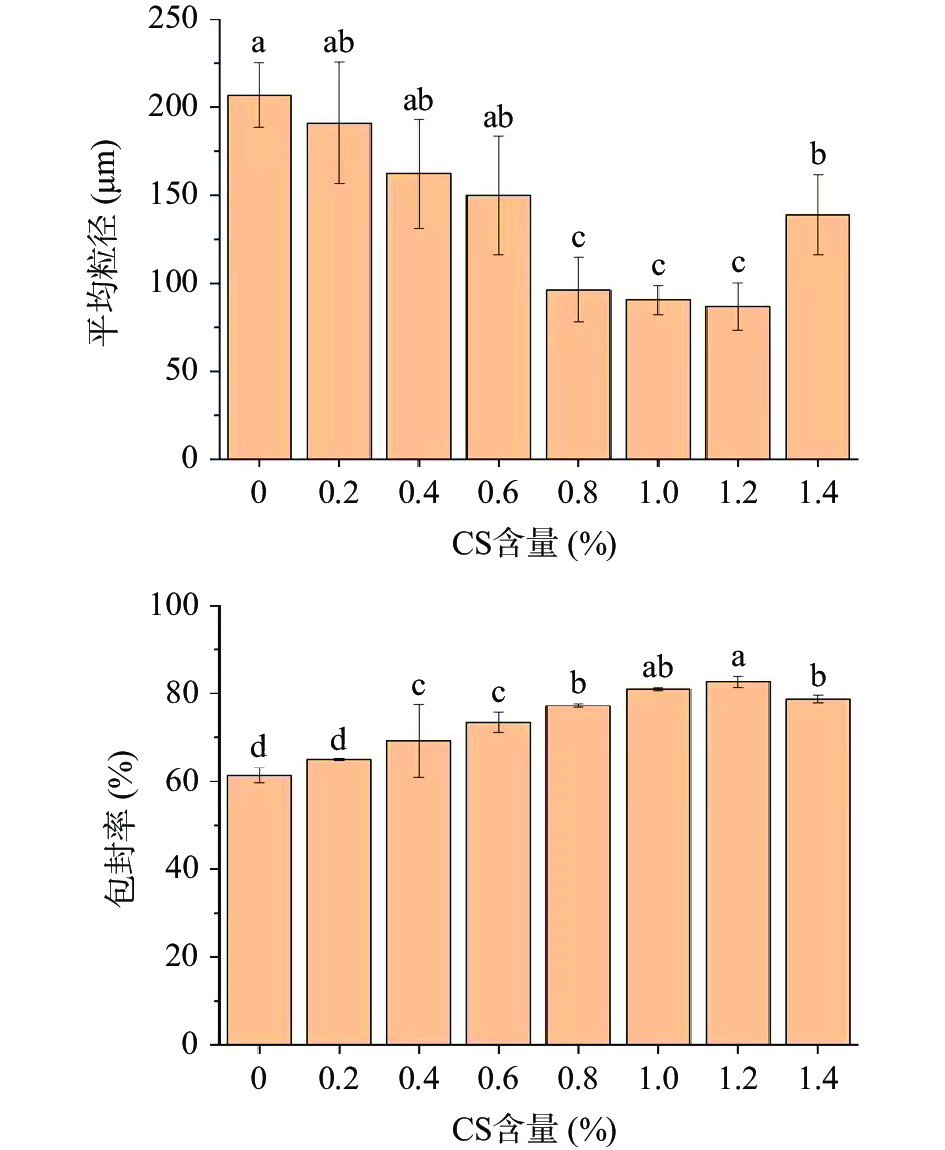
2.2.1 壳聚糖含量对微胶囊平均粒径及包封率的影响
如图7所示,随壳聚糖含量增大,HMP微胶囊的平均粒径先减后增,当壳聚糖含量为1.2%时,微胶囊粒径最小为(90.57±3.56)μm,表明此时壳聚糖与海藻酸钠结合最为充分。HMP微胶囊的包封率整体先增后减,与平均粒径变化趋势相反,在壳聚糖浓度1.2%时达到最大包封率82.59%±1.25%。
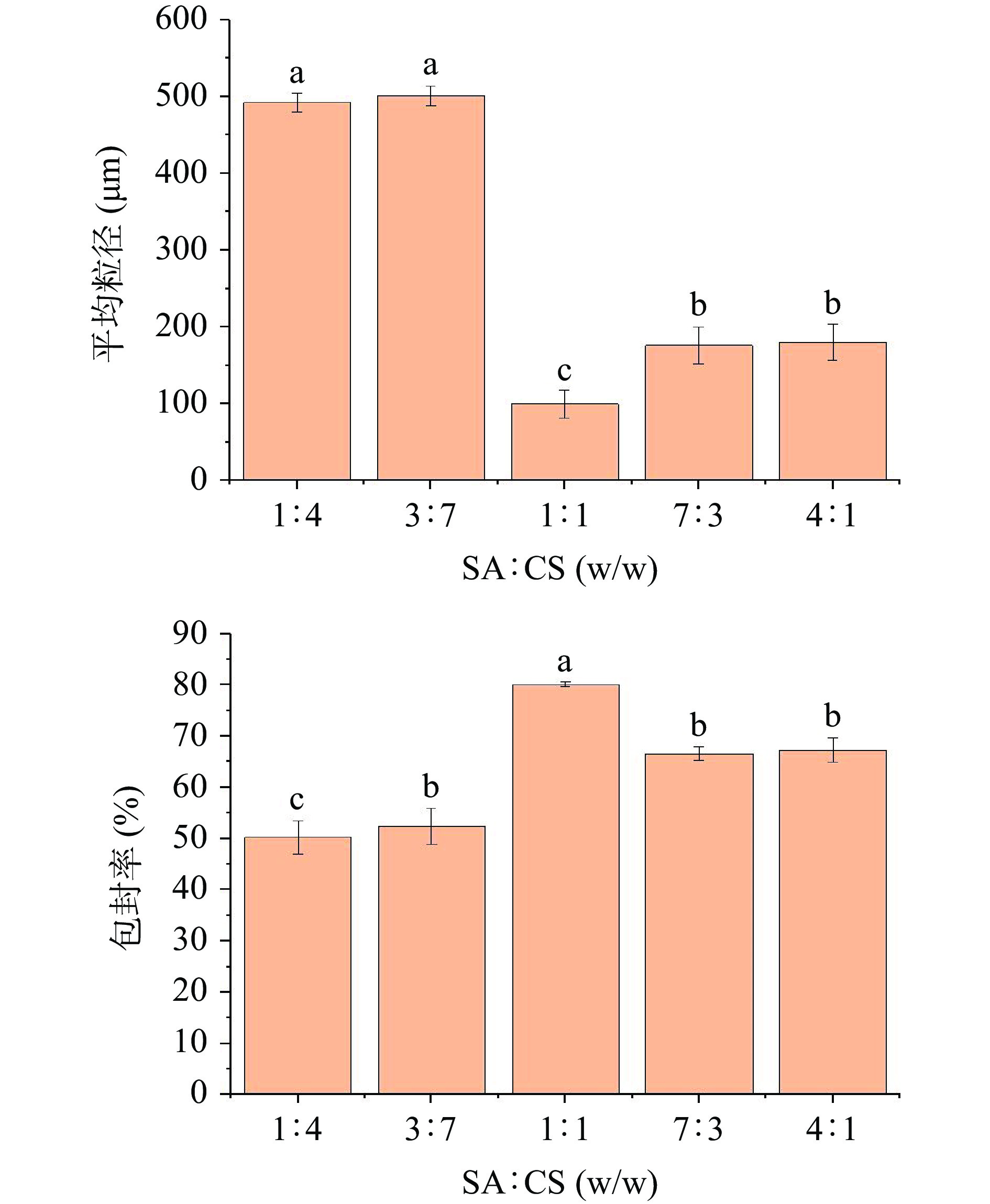
2.2.2 海藻酸钠/壳聚糖质量比对微胶囊平均粒径及包封率的影响
如图8所示,壳聚糖质量比低时,与海藻酸钠聚集电解质膜薄,形成了较大的HMP微胶囊,当壳聚糖质量比高时,HMP微胶囊快速形成并由于静电作用吸附聚集,造成HMP微胶囊平均粒径增大,当海藻酸钠/壳聚糖质量比为1:1时,海藻酸钠与壳聚糖混合均匀,微胶囊的粒径最小为(99.62±4.01)μm,此时HMP微胶囊的包封率也最佳80.10%±0.58%。
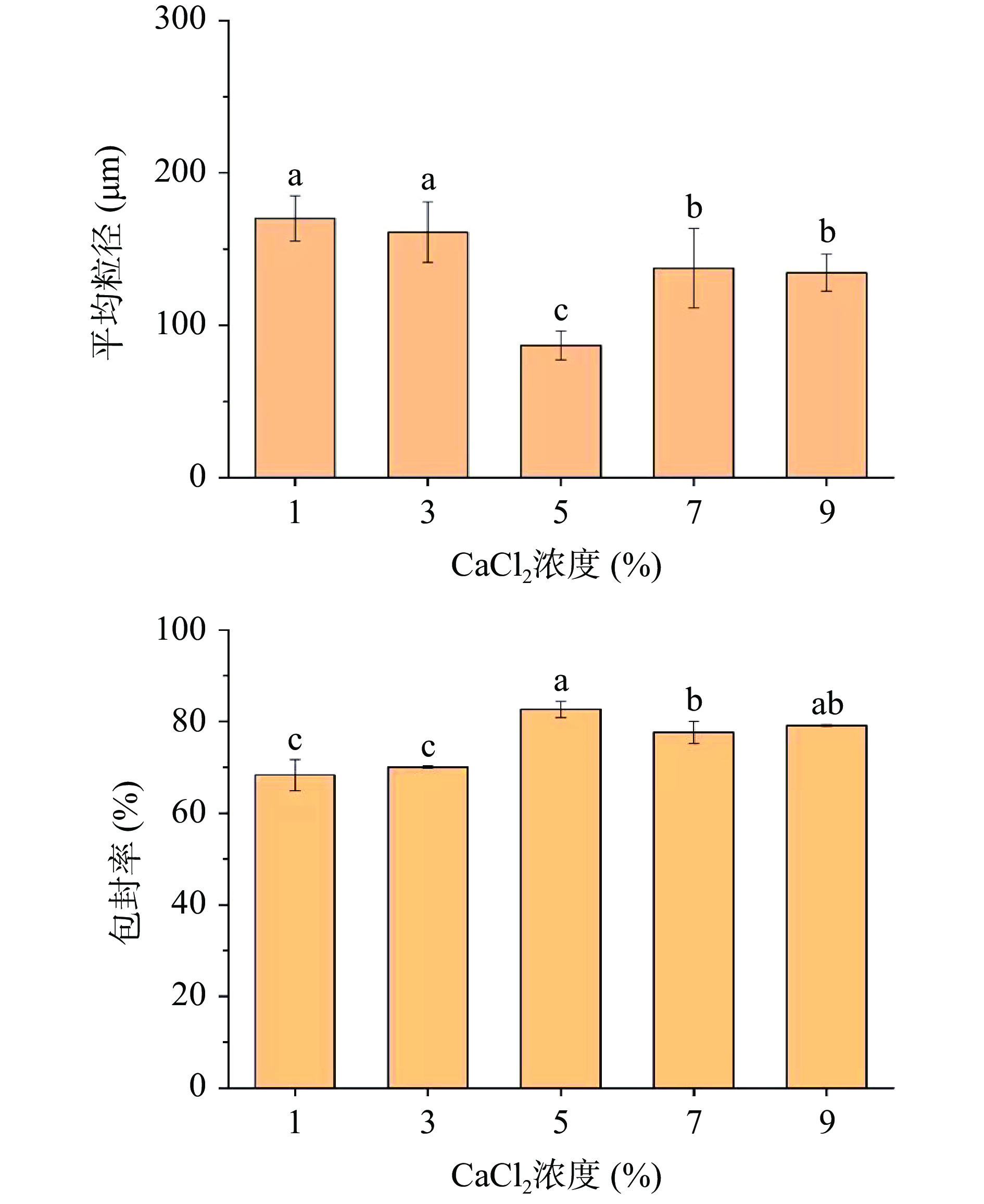
2.2.3 CaCl2浓度对微胶囊平均粒径及包封率影响
如图9所示,随着氯化钙浓度的增加,微胶囊的成型效果提高,包封率提升,在氯化钙浓度为5.0%时微胶囊的平均粒径最小为(88.74±2.60)μm,包封率最佳为82.59%±1.44%,随着氯化钙浓度的增加,微胶囊囊壁变厚,平均粒径增大。
综上,选择壳聚糖含量1.2%,海藻酸钠/壳聚糖质量比为1:1,氯化钙浓度5.0%,作为微胶囊的制备工艺参数,并对此工艺参数下制备的HMP微胶囊进行后续试验的性质研究与表征。
2.3 HMP微胶囊的性质与结构表征
2.3.1 微胶囊的理化性质
食品的水分含量对其理化性质和微生物稳定性具有重要影响,而水分活度可反映食品中酶促反应、脂质氧化和微生物生长程度[27]。如表1所示,HMP微胶囊的水分含量为2.82%±0.76%,HMP微胶囊产品的水分含量在2%~5%范围内,说明微胶囊产品水分含量合格[28]。另外,HMP微胶囊的水分活度为0.19±0.01。这也与Klaypradit等[29]使用壳聚糖和麦芽糊精混合壁材制备的鱼油微胶囊低于0.3的水分活度结果相似。较低的水分活度可以限制微生物的生长,减少结块现象,从而提高产品的理化性质和总体可接受度[30]。
表 1 微胶囊的理化性质Table 1. Physicochemical properties of microcapsules样品 水分含量
(%)水分活度 包封率
(%)粒径
(μm)润湿时间
(s)溶解度
(%)HMP
微胶囊2.82±0.76 0.19±0.01 82.59±1.44 88.74±2.60 37.00±4.00 6.17±1.76 HMP微胶囊的包封率为82.59%±1.44%。本研究的包封率与李一喆[31]使用冷冻干燥法制备的橘皮油微胶囊包封率相似(82.48%),但低于Bakry等[7]通过喷雾干燥制得的MP和卡拉胶复合壁材的金枪鱼油微胶囊包封率(97.96%)。这可能是预冻阶段生成的冰晶破坏了乳液的结构,降低了壁材的稳定性[32]。
润湿性通过微胶囊浸没在水中所需要的时间来测定,以评价微胶囊与水相互作用的能力[33]。HMP微胶囊的溶解度不高,可能与其壁材类型有关。壳聚糖较难溶解于中性条件的水中,而HMP是盐溶性蛋白,也难溶于蒸馏水中,这些都降低了微胶囊的溶解度。该结果与Santos等[34]制备的木糖醇微胶囊溶解度5.31%~13.90%相似。低溶解度对于微胶囊在水溶液中的稳定性以及活性物质释放的控制非常重要[35]。可知,本试验制备得的HMP微胶囊具有良好的性能特性。
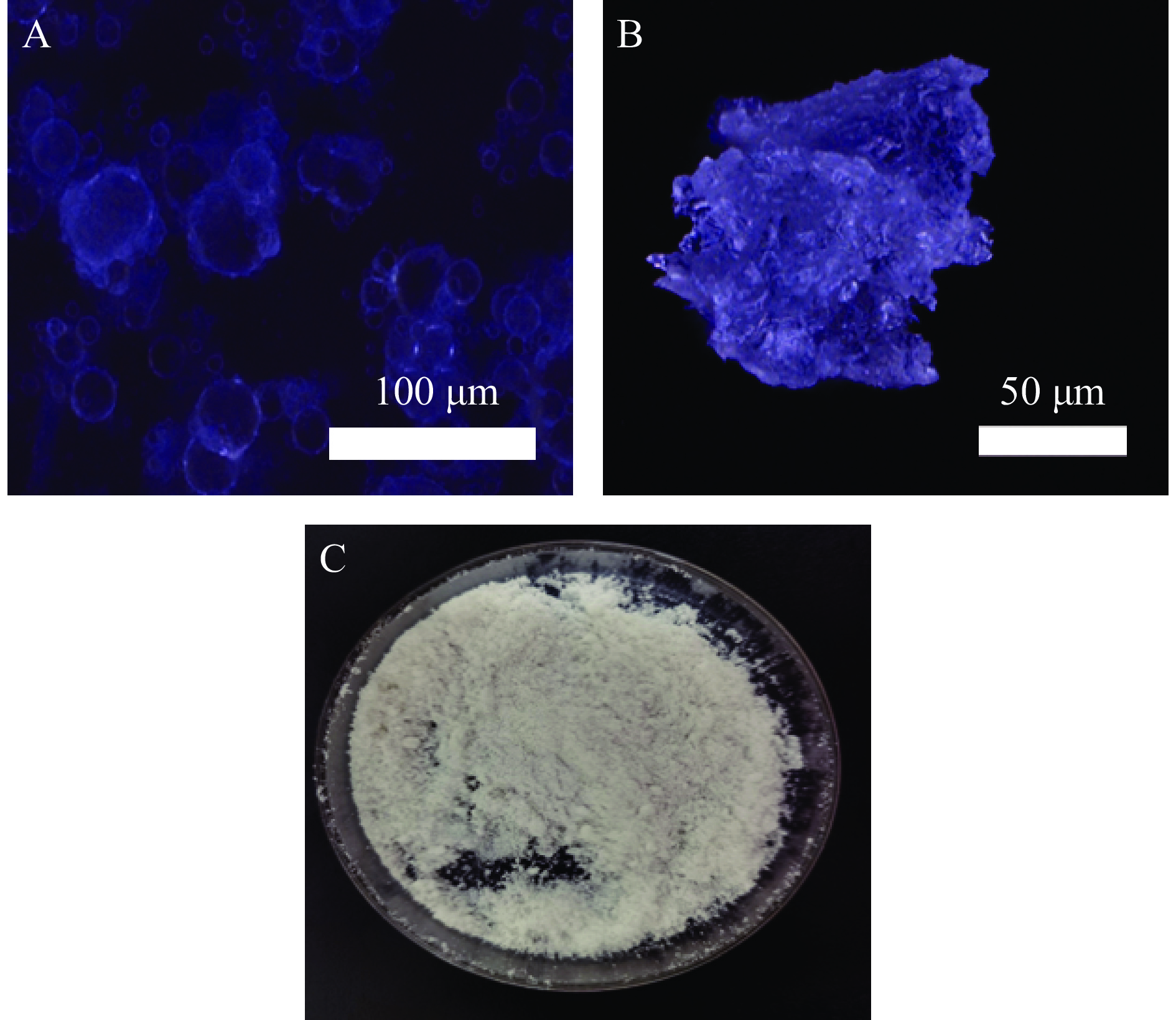
2.3.2 微胶囊的宏观与微观结构
如图10A所示,观察到HMP微胶囊在水溶液中以规则的球形结构聚集在一起,这与Saravanan等[36]使用果胶和海藻酸钠制备的微胶囊水溶液结构相似,且HMP微胶囊的单个球形结构更大。如图10B所示,与常见的使用喷雾干燥制备的微胶囊拥有的球形规则微观结构不同,使用冷冻干燥制备的HMP微胶囊产品呈现不规则的块状结构,且微胶囊表面并不平整,这种结构的产生可能是因为冷冻干燥过程中冰支撑着颗粒的冷冻结构,而在其升华后造成了微胶囊不规则的形态[37]。Rajam等[38]以乳清分离蛋白和海藻酸钠为壁材制得的冻干微胶囊微观结构也呈现相似的形态。图10C显示,HMP微胶囊的外观为白色粉末状颗粒,存在小部分聚集现象,但经振荡后块状聚集结构消失,因此本产品使用前需要进行适度振荡处理。
2.3.3 微胶囊的红外光谱分析
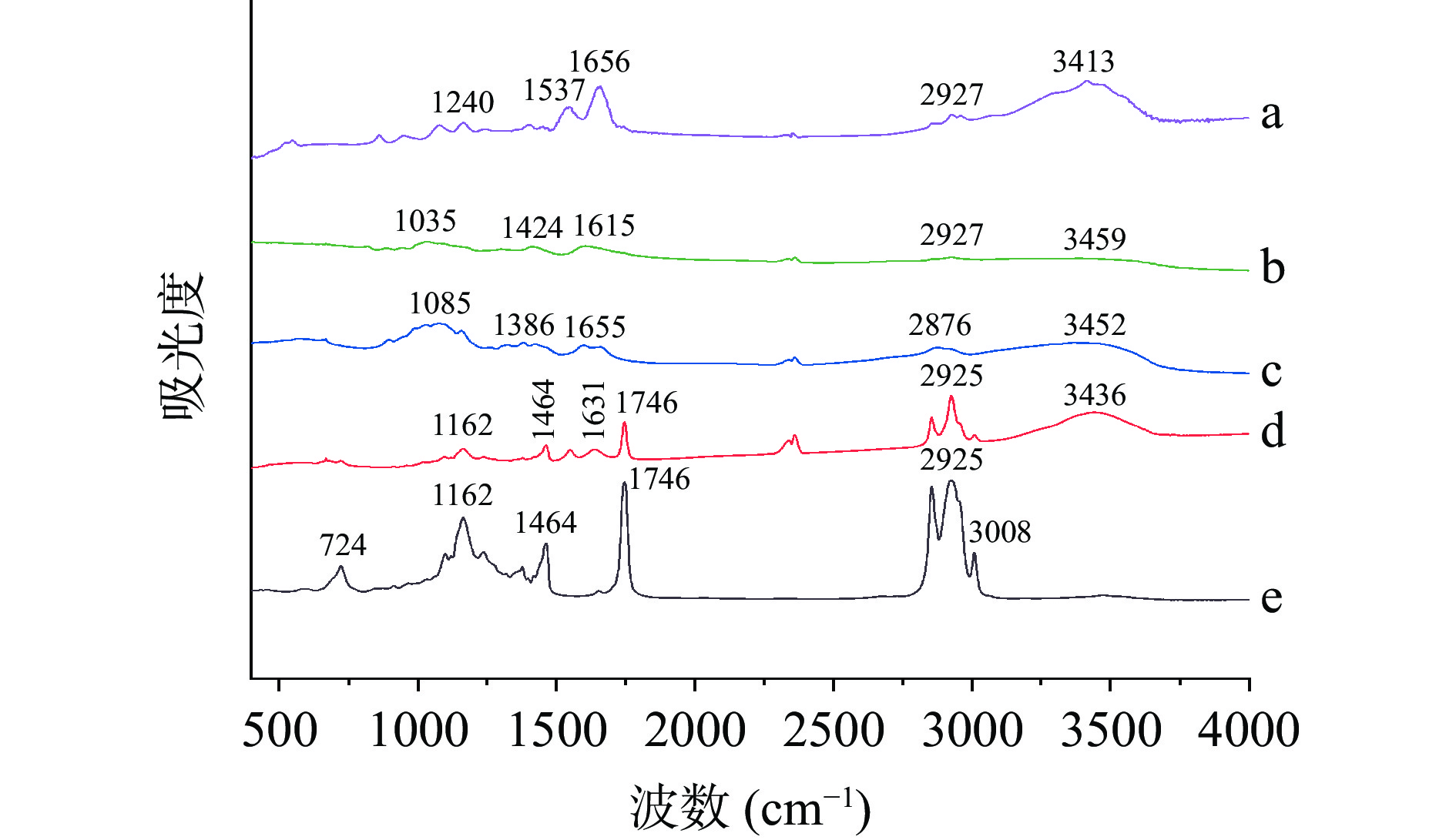
图11a所示HMP特征峰在3413 cm−1附近的酰胺A带,在2927 cm−1附近的酰胺B带,在1656 cm−1附近的酰胺Ⅰ带,在1537 cm−1附近的酰胺Ⅱ带,以及在1240 cm−1附近的酰胺Ⅲ带。由图11b可知,海藻酸钠在1035 cm−1附近存在吸收峰,这是由于多糖中C-O-C结构的拉伸振动引起的,2927 cm−1附近的吸收峰是由于-CH伸缩振动引起的,而对称和不对称羧酸基团分别在1615 cm−1和1424 cm−1处形成吸收峰[39]。图11c显示,壳聚糖在3452 cm−1附近的吸收峰是由羟基和氨基的拉伸振动导致的,2876 cm−1为烷烃C-H的吸收峰,1655 cm−1处为氨基Ⅰ吸收峰,1085 cm−1为C-O伸缩振动峰,1386 cm−1为C-N拉伸和N-H弯曲峰。由图11e可知,玉米油有多个特征吸收峰,3008 cm−1附近显示出的峰是由于玉米油中=C-H键的伸缩振动导致的,表明玉米油中含有较多的不饱和脂肪酸,2925 cm−1处的吸收峰是脂肪酸C-H伸缩振动导致的,1746 cm−1处为玉米油中C=O的特征吸收峰。除了玉米油样品外,所有样品均可以在3400~3500 cm−1处观察到-OH吸收峰。图11d显示氨基Ⅰ吸收峰移动至1631 cm−1处,且微胶囊产品中3436 cm−1处的羟基伸缩振动峰均变得更窄,表明壳聚糖的-NH3+和海藻酸钠的-COO−相互反应,产生了静电相互作用[40-41]。另外,图11d可观察玉米油的特征峰,但峰值强度遭到不同程度的削弱,表明玉米油被包埋入微胶囊腔体中,微胶囊包埋结构初步形成。
2.3.4 微胶囊的X射线衍射分析
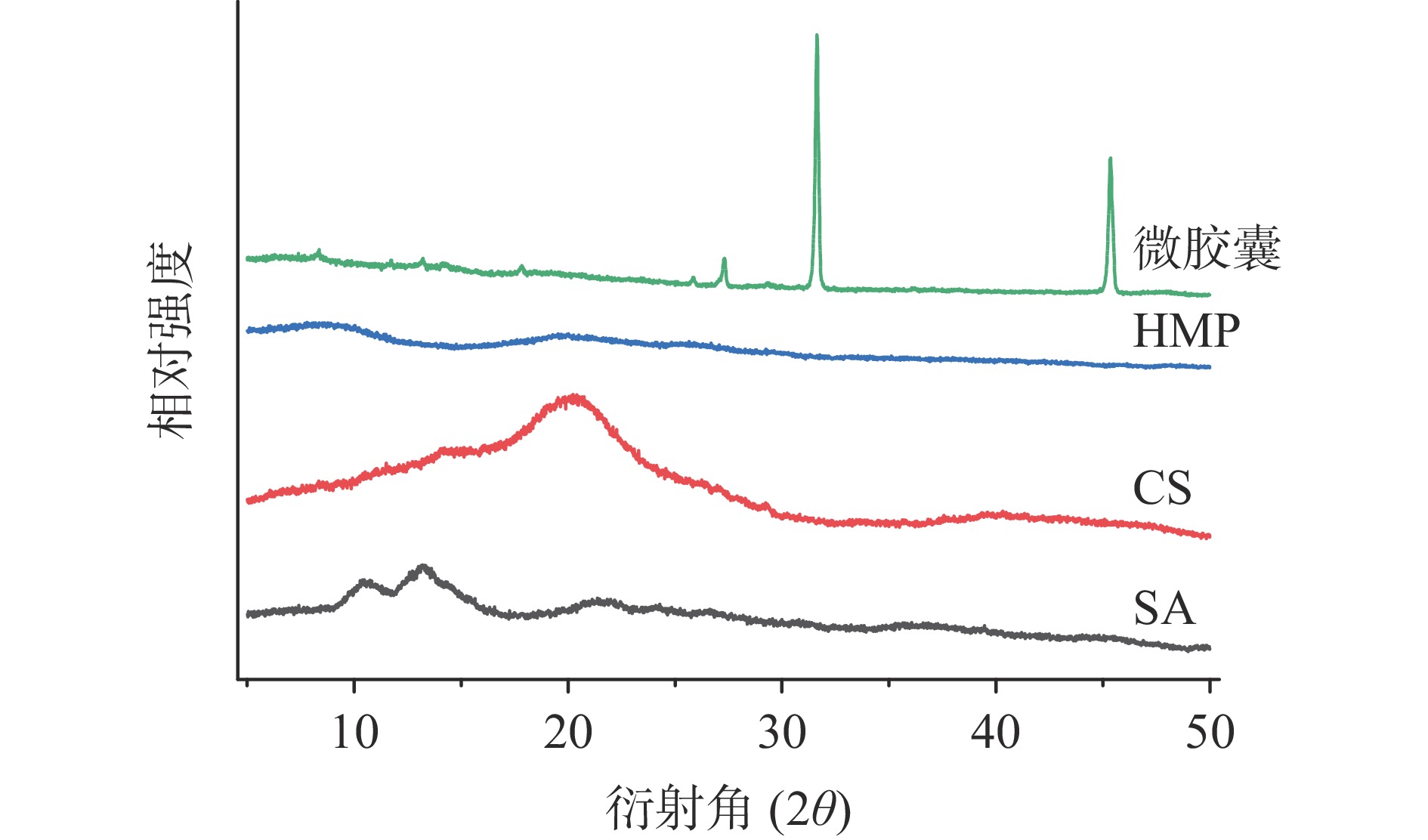
微胶囊的稳定性与其结晶度有关,因此通过X射线衍射图谱分析微胶囊是否具有结晶或无定形结构至关重要。通常情况下,图谱中弥散宽峰代表非晶型结构,因为非晶型材料是无序的,会产生弥散带,然而晶型结构因其良好的有序状态会产生的尖锐且明确的峰[42]。
由图12所示,壳聚糖在13.8°和20.7°附近存在衍射特征峰,在40°左右有一个弥散的宽峰,这些表明壳聚糖具有半结晶性质[43]。海藻酸钠在13°、21°附近存在两个弥散的衍射峰表明了海藻酸钠的非晶型结构,这也与先前的研究结果一致[44]。HMP均在10°和20°附近存在两个弥散的宽峰,这也与Song等[45]对鸡肉香肠的X射线衍射结果一致。由图12所示,HMP微胶囊的X射线衍射图谱中弥散的宽峰消失,海藻酸钠,壳聚糖,HMP的特征峰变得更窄强度更低,且在31°和45°附近新出现两个尖锐的衍射峰,可能原因是海藻酸钠和壳聚糖中的基团发生静电结合,这也与红外图谱的结果分析相吻合[46]。同时,尖锐强峰的出现表明微胶囊结晶度变高。
粉末的结晶度与其理化性质和贮存稳定性密切相关,微胶囊的溶解度受结晶度的影响,与无定形状态相比,结晶状态的微胶囊因其分子间键能水平更高,导致更难溶解[47]。因此, HMP微胶囊较高的结晶度也与其较低的溶解度相互验证。
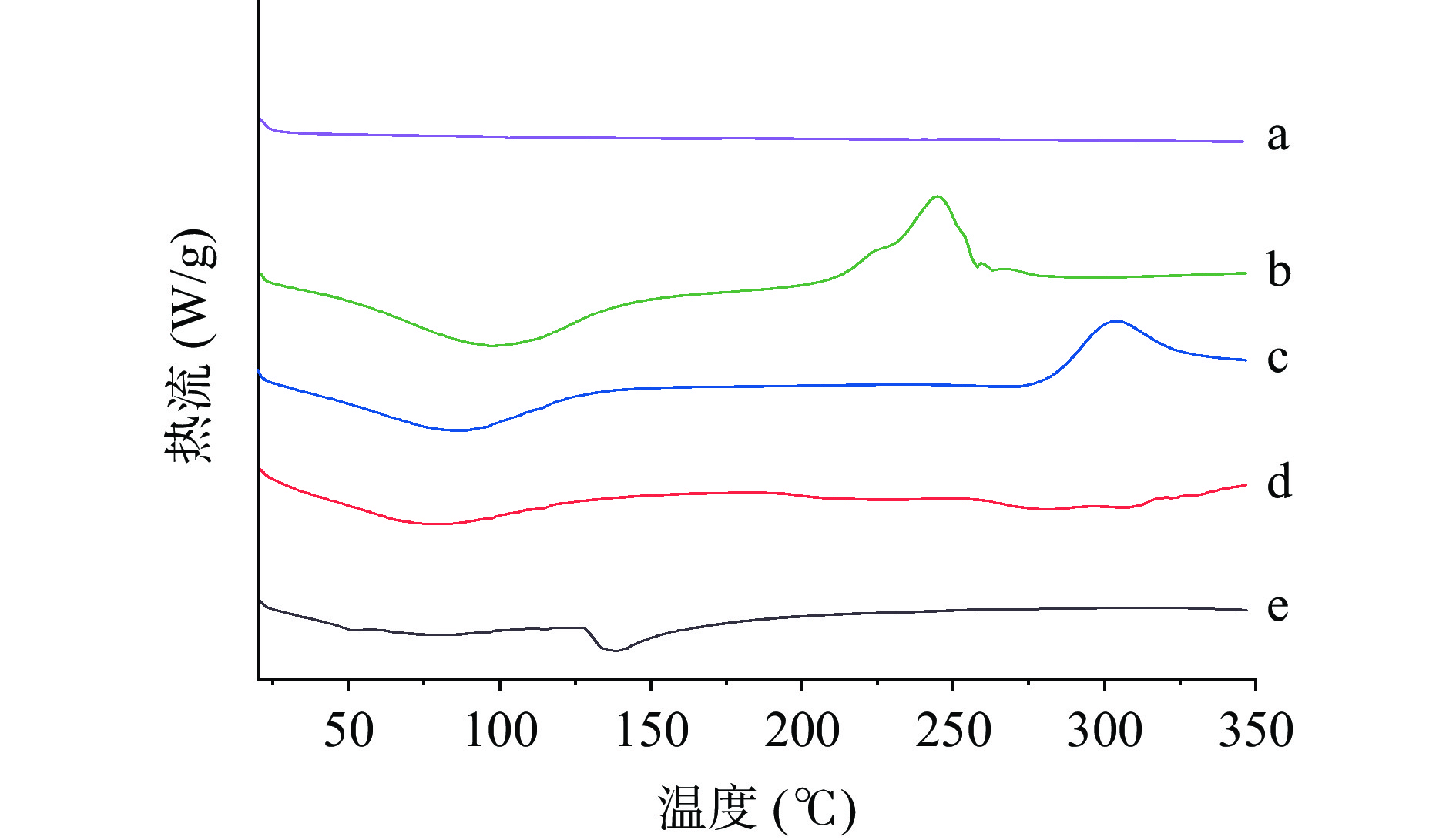
2.3.5 微胶囊的热稳定性分析
差示扫描量热法(DSC)用于确定固态复合物的形成[48]。如图13a所示,玉米油在整个温度范围内未出现吸热峰和放热峰,表明玉米油热稳定性良好。海藻酸钠和壳聚糖分别在95.7 ℃和85 ℃处出现吸热峰,主要由聚合物亲水基团失水导致[49]。HMP的吸热峰强度低,表明热处理使HMP的蛋白结构发生改变,热稳定性提高[50]。HMP微胶囊在50~60 ℃范围内出现第一个小吸热峰,这是由于微胶囊中结合水吸收热量蒸发引起的[51]。HMP微胶囊在139 ℃附近均出现新的吸热峰,这可能是海藻酸钠与壳聚糖静电相互作用结合后形成的新基团裂解引起的[50],相似的结果也在Pan等[52]对海藻酸钠与壳聚糖复合气凝胶的DSC结果中出现。微胶囊的DSC结果也与红外光谱与X射线衍射的分析相互验证。
2.3.6 微胶囊的抗氧化稳定性分析
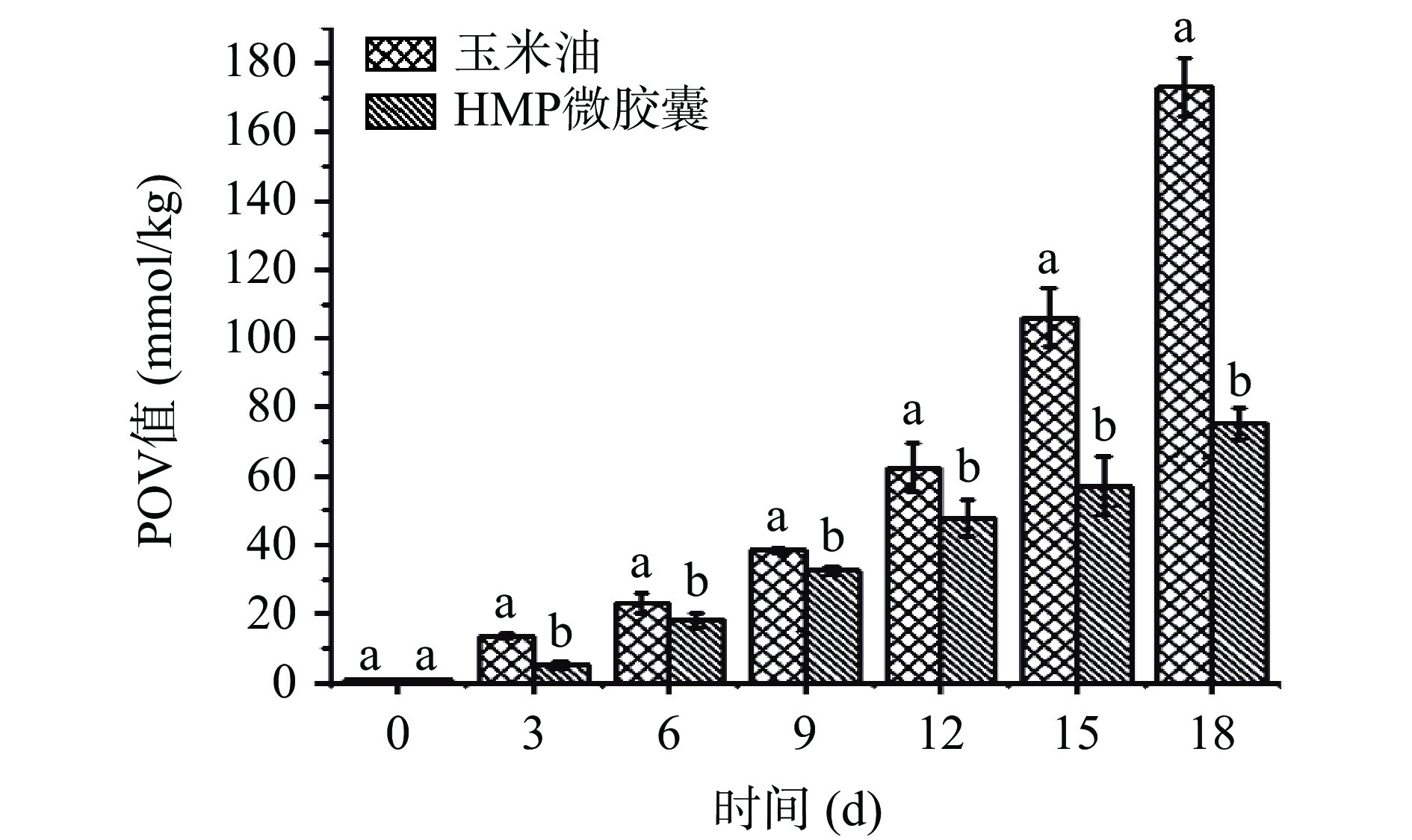
POV值是通过测定初级氧化产物的氢过氧化物产生量来反映样品的氧化程度(图14)。在第0 d时,玉米油的POV值为0.63 mmol/kg,而HMP微胶囊的POV值为0.83 mmol/kg,两者的初始POV值无显著性差异(P>0.05),表明乳液以及微胶囊的制备未对油脂氧化产生较大影响。随储存时间的延长,玉米油和HMP微胶囊的 POV 值逐渐增大,在 18 d 时达到173.00和75.30 mmol/kg。玉米油的POV值在0~6 d增长速率较慢,这是由于玉米油中含有的维生素E[53]起到了一定的抗氧化作用。而储存时间的增加,不饱和脂肪酸氧化,不稳定的氢过氧化物生成,玉米油氧化速率加快。HMP微胶囊POV值的增长速率较为平缓,表明制备的微胶囊对玉米油起到了很好的保护作用,其致密的壁材有利于隔绝玉米油与氧气的接触,减缓油脂的氧化速度。
![]() 图 14 储存期间玉米油和微胶囊POV值变化注:不同小写字母表示不同样品差异显著(P<0.05),图15同。Figure 14. POV trend of corn oil and microcapsules during storage
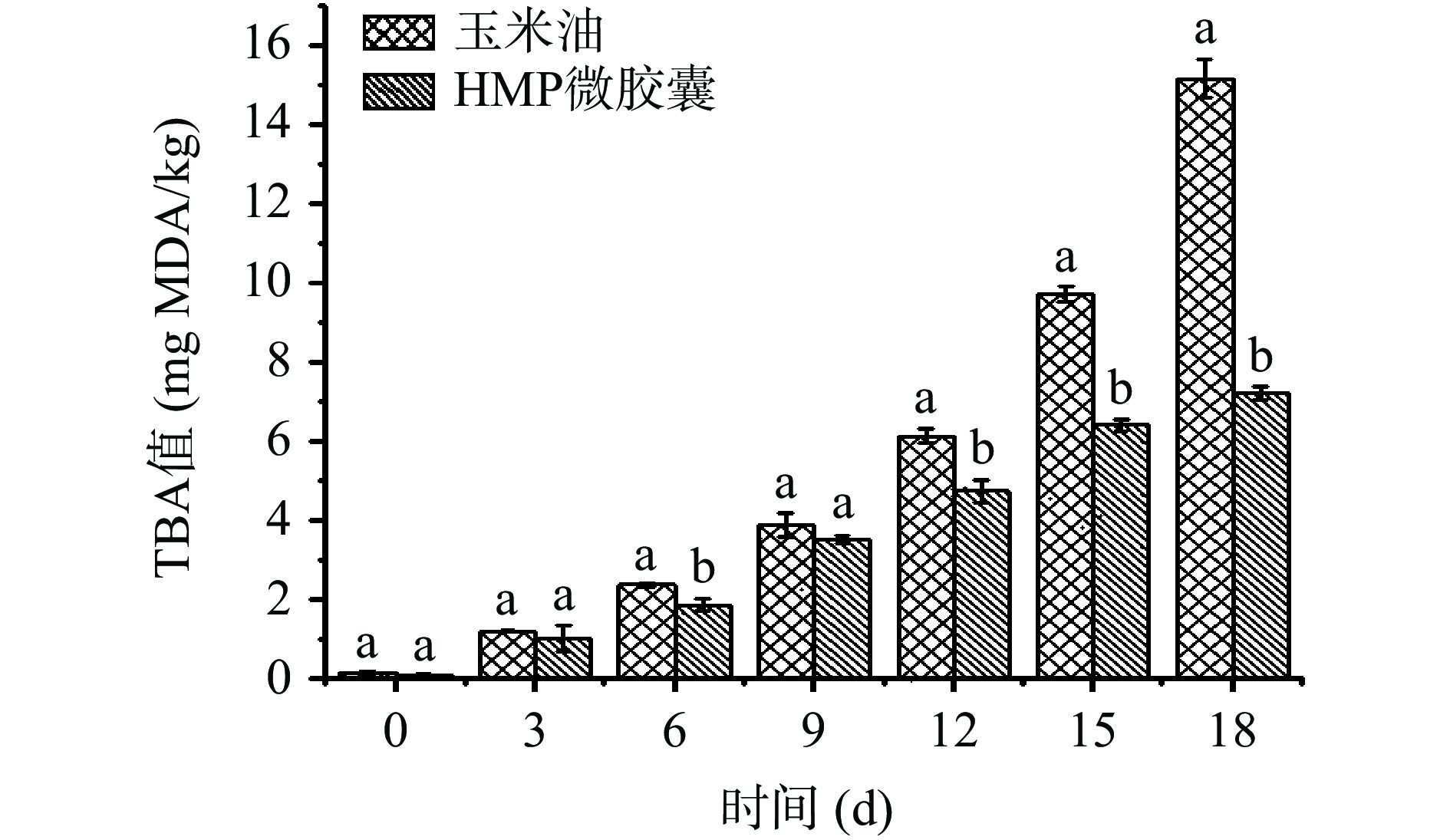
图 14 储存期间玉米油和微胶囊POV值变化注:不同小写字母表示不同样品差异显著(P<0.05),图15同。Figure 14. POV trend of corn oil and microcapsules during storage由于油脂在氧化过程中产生的初级氧化产物很不稳定,会进一步反应生成二级反应产物。作为主要的二级反应产物,丙二醛(MDA)能够与硫代巴比妥酸(TBA)反应。因此,测定TBA值可以进一步反映油脂的最终氧化程度[53]。
如图15所示,未包封玉米油的 TBA 值在 0~6 d增长速率较为平缓,随后加快,第18 d时达到最大值(15.19 mg MDA/kg)。与对照组相比,HMP微胶囊TBA值的增长速率更平缓,18 d后TBA值达到7.23 mg MDA/kg。该结果表明微胶囊化确保了玉米油较高的抗氧化稳定性,海藻酸钠与壳聚糖由于交联反应形成的致密壳结构限制了氧分子的流动性,因此降低了脂质氧化速率[54]。另外,具备良好乳化能力的HMP作为一道物理屏障吸附于油水界面上,一定程度上也起到了保护玉米油不被氧化的作用[53]。
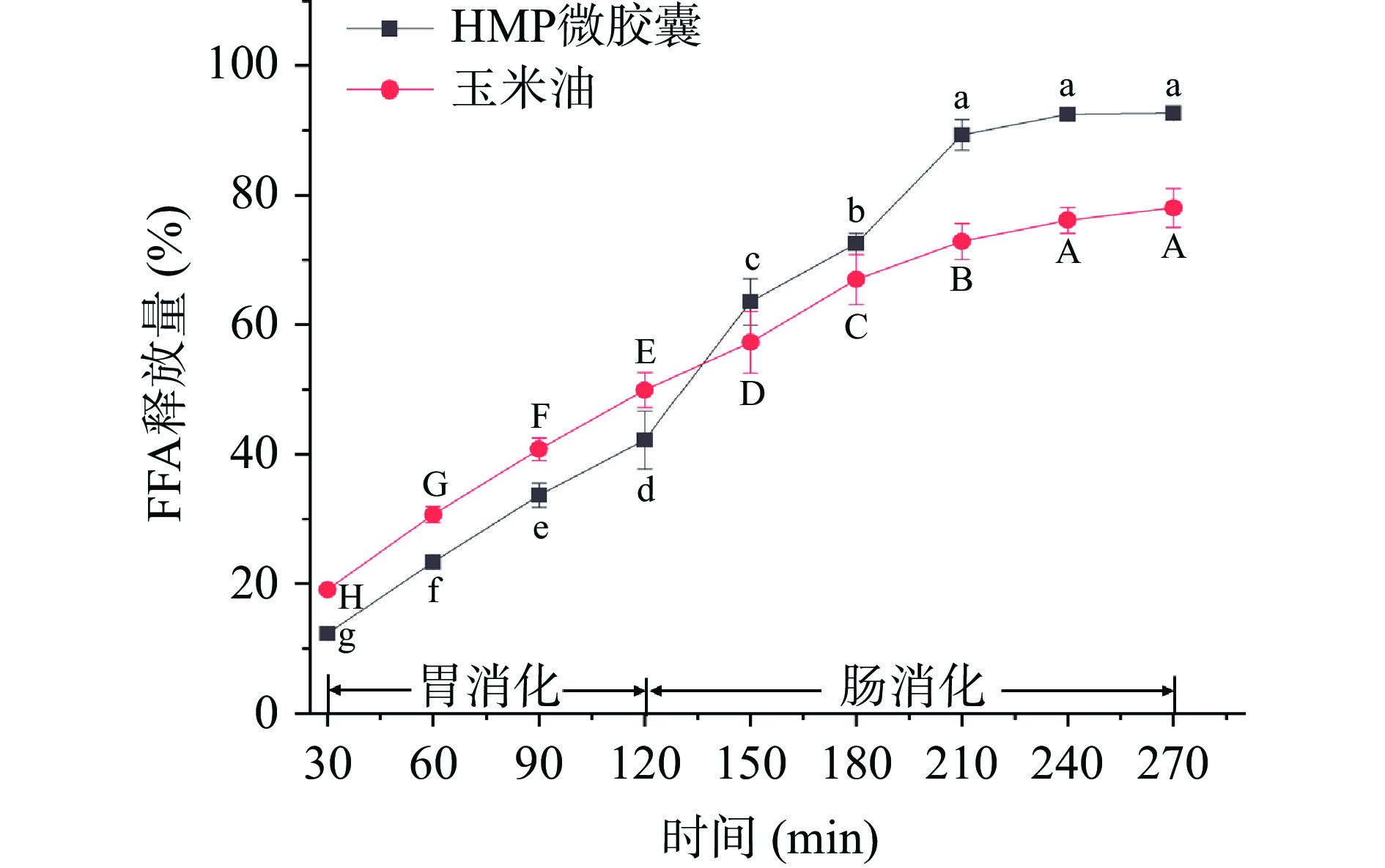
2.3.7 微胶囊的体外消化特性研究
在胃消化阶段,HMP微胶囊的FFA总释放量达到42.17%(图16),王帝等[55]制备南极磷虾油-海藻酸钠/壳聚糖微胶囊的FFA释放量在20.22%左右,HMP微胶囊在胃消化阶段存在较高的FFA释放量,这可能与壁材有关。研究表明MP经热处理后,HMP蛋白结构变得松散,使得更多与胃蛋白酶结合的特异位点暴露,从而提高HMP的消化性[56],因此,在胃消化阶段HMP微胶囊壁会因蛋白质被消化降解出现空隙,导致了FFA的释放量增加。在肠消化阶段中,胰酶和碱性条件的共同作用使蛋白质和多糖水解,导致HMP微胶囊的结构完整性遭到进一步破坏,最终使FFA释放量达到92.67%。
油脂在人体中的主要消化吸收部位是小肠,而HMP微胶囊在肠消化阶段均释放出更多的FFA,表明HMP微胶囊起到了较好的保护作用,延缓了油脂释放速度,使更多油脂进入小肠,从而提高了脂肪在体内的吸收和利用率。
3. 结论
SA-HMP乳液的最佳制备条件为:SA含量2.5%,HMP含量3.0%,玉米油含量30%。HMP微胶囊的最佳配方为:壳聚糖含量1.2%,SA/CS质量比1:1,氯化钙浓度5.0%,此条件下HMP微胶囊包封率和平均粒径分别为82.59%±1.44%和(88.74±2.60)μm。HMP微胶囊的水分含量和水分活度都处于较低水平。吸湿性结果显示,HMP微胶囊的抗潮性较差,则HMP微胶囊需要在干燥环境中储存。红外光谱、X射线衍射和DSC结果表明,微胶囊结晶度高;HMP微胶囊具有一定的热稳定性;微胶囊壁材间因静电相互作用结合,构成致密的微胶囊外壁,将玉米油成功包埋。贮存期间两种微胶囊的POV值与TBA值增长速度均慢于玉米油样品,说明微胶囊化延缓了玉米油的氧化速度。体外消化结果显示,HMP微胶囊的FFA释放量达到92.67%,且微胶囊在肠液中释放出更多的FFA,表明微胶囊对芯材有较好的缓解作用。
-
图 14 储存期间玉米油和微胶囊POV值变化
注:不同小写字母表示不同样品差异显著(P<0.05),图15同。
Figure 14. POV trend of corn oil and microcapsules during storage
表 1 微胶囊的理化性质
Table 1 Physicochemical properties of microcapsules
样品 水分含量
(%)水分活度 包封率
(%)粒径
(μm)润湿时间
(s)溶解度
(%)HMP
微胶囊2.82±0.76 0.19±0.01 82.59±1.44 88.74±2.60 37.00±4.00 6.17±1.76 -
[1] 农业部渔业渔政管理局. 中国渔业统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2021 Fishery and Fishery Administration of the Ministry of Agriculture. China fishery statistics yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Publishing House, 2021.
[2] 郝淑贤, 李来好, 杨贤庆, 等. 5种罗非鱼营养成分分析及评价[J]. 营养学报,2007(6):614−615. [HAO S X, LI L H, YANG X Q, et al. Analysis and evaluation of nutrient composition of tilapias[J]. Journal of Nutrition,2007(6):614−615. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0512-7955.2007.06.022 [3] XIONG Y, LI Q, MIAO S, et al. Effect of ultrasound on physicochemical properties of emulsion stabilized by fish myofibrillar protein and xanthan gum[J]. Innovative Food Science & Emerging Technologies,2019,54:225−234.
[4] INTARASIRISAWAT R, BENJAKUL S, VISSESSANGUAN W, et al. Skipjack roe protein hydrolysate combined with tannic acid increases the stability of fish oil upon microencapsulation[J]. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology,2015,117(5):646−656. doi: 10.1002/ejlt.201400247
[5] MORALES-MEDINA R, TAMM F, GUADIX A, et al. Functional and antioxidant properties of hydrolysates of sardine (S. pilchardus) and horse mackerel (T. mediterraneus) for the microencapsulation of fish oil by spray-drying[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,194:1208−1216. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.08.122
[6] SHI L, BEAMER S K, YANG H, et al. Micro-emulsification/encapsulation of krill oil by complex coacervation with krill protein isolated using isoelectric solubilization/precipitation[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,244:284−291. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.10.050
[7] BAKRY A, HUANG J, ZHAI Y, et al. Myofibrillar protein with κ-or λ-carrageenans as novel shell materials for microencapsulation of tuna oil through complex coacervation[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,96:43−53. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.04.070
[8] LIU R, ZHAO S M, LIU Y M, et al. Effect of pH on the gel properties and secondary structure of fish myosin[J]. Food Chemistry,2010,121(1):196−202. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.12.030
[9] 冯雪平. 热处理温度对鲢肌球蛋白结构和凝胶水分影响的研究[D]. 镇江: 江苏大学, 2016: 21−26 FENG X P. Effect of the heating temperature on changes of the bighead carp myosin structures and the gel water[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University, 2016: 21−26.
[10] LIU R, ZHAO S M, XIE B J, et al. Contribution of protein conformation and intermolecular bonds to fish and pork gelation properties[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2011,25(5):898−906. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2010.08.016
[11] 王正雯, 田宏伟, 周富裕, 等. 加热温度对麻鸭肌原纤维蛋白结构与凝胶特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(13):61−68. [WANG Z W, TIAN H W, ZHOU F Y, et al. Effect of heating temperature on the structure and gel properties of duck myofibrillar protein[J]. Food Science,2020,41(13):61−68. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191128-280 [12] 畅鹏, 谢艳英, 王浩, 等. 热处理温度及时间对镜鲤鱼肌原纤维蛋白热聚集行为的影响[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(1):101−107. [CHANG P, XIE Y Y, WANG H, et al. Effects of heat treatment temperature and time on thermal aggregation behavior of myofibrillar proteins from mirror carp (Cyprinus carpio)[J]. Food Science,2021,42(1):101−107. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191213-152 [13] 郑云芳, 李晨, 汪少芸, 等. 热处理对鲈鱼肌原纤维蛋白结构及功能特性的影响[J]. 福州大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(1):139−146. [ZHENG Y F, LI C, WANG S Y, et al. Study on the relationship between structure and function of myofibrillar protein in Lateolabrax japonicus based on thermal treatment[J]. Journal of Fuzhou University (Natural Science Edition),2022,50(1):139−146. [14] 张桂艳. 食盐和加热对肌原纤维蛋白与Ⅰ型胶原蛋白乳化特性的影响[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2022 ZHENG G Y. Effects of NaCl and heating on emulsifying properties of myofibrillar protein and type I collagen[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2022.
[15] 刘成祥, 王力, 苏建辉, 等. 牡丹籽油微胶囊的制备及特性研究[J]. 中国油脂,2016,41(11):12−16. [LIU C X, WANG L, SU J H, et al. Preparation and property of peony seed oil microcapsule[J]. China Oils and Fats,2016,41(11):12−16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7969.2016.11.003 [16] 申莉莉. 百里香微胶囊制备及抑菌效果和机理研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2015 SHEN L L. Preparation of thyme oil microencapsulation and its antibacterial activity and mechanism study[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2015.
[17] 张珊珊. 乳液模板—层层自组装百里香微胶囊制备、缓释和抑菌效果的研究[D]. 武汉: 华中农业大学, 2018 ZHANG S S. Preparation of thyme microcapsules by emulsion template layer by layer self assembly method and its controlled release and antibacterial effects research[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong Agricultural University, 2018.
[18] 卢艳慧. 牡丹籽油微胶囊化及理化和稳定特性的研究[D]. 济南: 齐鲁工业大学, 2021 LU Y H. Study on microencapsulation, physicochemical and stability properties of peony seed oil[D]. Jinan: Qilu University of Technology, 2021.
[19] ALCA B, AAAA B, YRS C, et al. Characterization of freeze-dried microencapsulation tuna fish oil with arrowroot starch and maltodextrin[J]. Food Hydrocolloids, 2020, 112.
[20] RODRÍGUEZ-RESTREPO Y, GIRALDO G, RODRÍGUEZ-BARONA S. Solubility as a fundamental variable in the characterization of wall material by spray drying of food components: Application to microencapsulation of Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis[J]. Journal of Food Process Engineering,2017,40(6):12557. doi: 10.1111/jfpe.12557
[21] FUCHS M, TURCHIULI C, BOHIN M, et al. Encapsulation of oil in powder using spray drying and fluidised bed agglomeration[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2006,75(1):27−35. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2005.03.047
[22] 罗文涛, 王姿颐, 彭彬倩, 等. 奇亚籽油微胶囊的制备[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(11):210−215. [LUO W T, WANG Z Y, PENG B Q, et al. Preparation of chia seed oil microcapsule[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(11):210−215. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.022577 [23] YANG X, GAO N, HU L, et al. Development and evaluation of novel microcapsules containing poppy-seed oil using complex coacervation[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2015,161(9):87−93.
[24] TATAR F, TUNÇ M T, DERVISOGLU M, et al. Evaluation of hemicellulose as a coating material with gum arabic for food microencapsulation[J]. Food Research International,2014,57:168−175. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2014.01.022
[25] RODRÍGUEZ-CARPENA J G, MORCUENDE D, ESTÉVEZ M. Avocado by-products as inhibitors of color deterioration and lipid and protein oxidation in raw porcine patties subjected to chilled storage[J]. Meat science,2011,89(2):166−173. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2011.04.013
[26] KOSARAJU S, WEERAKKODY R, AUGUSTIN M. In vitro evaluation of hydrocolloid-based encapsulated fish oil[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2009,23(5):1413−1419. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2008.10.009
[27] ĐORĐEVIĆ V, BALANČ B, BELŠČAK-CVITANOVIĆ A, et al. Trends in encapsulation technologies for delivery of food bioactive compounds[J]. Food Engineering Reviews,2015,7(4):452−490. doi: 10.1007/s12393-014-9106-7
[28] VELASCO J, DOBARGANES M, MÁRQUEZ-RUIZ G. Oxidation of free and encapsulated oil fractions in dried microencapsulated fish oils[J]. Grasasy Aceites,2000,51(6):439−446.
[29] KLAYPRADIT W, HUANG Y. Fish oil encapsulation with chitosan using ultrasonic atomizer[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2008,41(6):1133−1139. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2007.06.014
[30] CHEW S, TAN C, NYAM K. Microencapsulation of refined kenaf (Hibiscus cannabinus L.) seed oil by spray drying using β-cyclodextrin/gum arabic/sodium caseinate[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2018,237:78−85. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2018.05.016
[31] 李一喆. 橘皮油微胶囊制备及其理化性质研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2020 LI Y Z. Research on the microencapsulated mandarin oil preparation technology and the physicochemical property of the microcapsule[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2020.
[32] LIN D Q et al. Peptide/protein hydrolyses and their derivatives: Their role as emulsifying agents for enhancement of physical and oxidative stability of emulsions[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2022,129:11−24.
[33] DIMA C, PĂTRAŞCU L, CANTARAGIU A, et al. The kinetics of the swelling process and the release mechanisms of Coriandrum sativum L. essential oil from chitosan/alginate/inulin microcapsules[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,195:39−48. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.05.044
[34] SANTOS M, BOZZA F, THOMAZINI M, et al. Microencapsulation of xylitol by double emulsion followed by complex coacervation[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,171:32−39. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.08.093
[35] DA CRUZ M, DAGOSTIN J, PERUSSELLO C, et al. Assessment of physicochemical characteristics, thermal stability and release profile of ascorbic acid microcapsules obtained by complex coacervation[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,87:71−82. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.07.043
[36] SARAVANAN M, RAO K P. Pectin-gelatin and alginate-gelatin complex coacervation for controlled drug delivery: Influence of anionic polysaccharides and drugs being encapsulated on physicochemical properties of microcapsules[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2010,80(3):808−816. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2009.12.036
[37] EZHILARASI P, INDRANI D, JENA B S, et al. Freeze drying technique for microencapsulation of Garcinia fruit extract and its effect on bread quality[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2013,117(4):513−520. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2013.01.009
[38] RAJAM R, KARTHIK P, PARTHASARATHI S, et al. Effect of whey protein-alginate wall systems on survival of microencapsulated Lactobacillus plantarum in simulated gastrointestinal conditions[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2012,4(4):891−898. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2012.06.006
[39] LAWRIE G, KEEN I, DREW B, et al. Interactions between alginate and chitosan biopolymers characterized using FTIR and XPS[J]. Biomacromolecules,2007,8(8):2533−2541. doi: 10.1021/bm070014y
[40] HO Y, MI F, SUNG H, et al. Heparin-functionalized chitosan-alginate scaffolds for controlled release of growth factor[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics,2009,376(1-2):69−75. doi: 10.1016/j.ijpharm.2009.04.048
[41] LI Z, RAMAY H, HAUCH K, et al. Chitosan-alginate hybrid scaffolds for bone tissue engineering[J]. Biomaterials,2005,26(18):3919−3928. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.09.062
[42] KANG Y, LEE Y, KIM Y, et al. Characterization and storage stability of chlorophylls microencapsulated in different combination of gum Arabic and maltodextrin[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,272:337−346. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.08.063
[43] CAVALU S, PROKISCH J, LASLO V, et al. Preparation, structural characterisation and release study of novel hybrid microspheres entrapping nanoselenium, produced by green synthesis[J]. IET Nanobiotechnology,2017,11(4):426−432. doi: 10.1049/iet-nbt.2016.0107
[44] VENKATESAN J, LEE J, KANG D, et al. Antimicrobial and anticancer activities of porous chitosan-alginate biosynthesized silver nanoparticles[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2017,98:515−525. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.01.120
[45] SONG J, JIANG L, PENG H, et al. Microcapsule prepared by extruding starch and procyanidins inhibited protein oxidation and improved quality of chicken sausages[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2022,154:112617. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112617
[46] 廖腾飞. 用于乳液分离的壳聚糖/海藻酸钠复合海绵的制备与性能研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉工程大学, 2022 LIAO T F. Preparation and properties of chitosan/sodium alginate composite sponge for lotion separation[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Engineering, 2022.
[47] BAN Z, ZHANG J, LI L, et al. Ginger essential oil-based microencapsulation as an efficient delivery system for the improvement of jujube (Ziziphus jujuba Mill.) fruit quality[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,306:125628. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125628
[48] HASANI S, OJAGH S M, GHORBANI M. Nanoencapsulation of lemon essential oil in Chitosan-Hicap system. Part 1: Study on its physical and structural characteristics[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,115:143−151. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.04.038
[49] SARMENTO B, FERREIRA D, VEIGA F, et al. Characterization of insulin-loaded alginate nanoparticles produced by ionotropic pre-gelation through dsc and ftir studies[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2006,66(1):1−7. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2006.02.008
[50] MITRA B, RINNAN Å, RUIZ-CARRASCAL J. Tracking hydrophobicity state, aggregation behaviour and structural modifications of pork proteins under the influence of assorted heat treatments[J]. Food Research International,2017,101:266−273. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2017.09.027
[51] 薛艾莲. 不同干燥处理的板栗粉品质及老化改善研究[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2022 XUE A L. Study on the quality and aging improvement of chestnut powder under different drying treatments[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2022.
[52] PAN J, LI Y, CHEN K, et al. Enhanced physical and antimicrobial properties of alginate/chitosan composite aerogels based on electrostatic interactions and noncovalent crosslinking[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,266:118102. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118102
[53] 郝乾有, 侯利霞. 煎炸不同含水量食材对玉米油理化指标和维生素E含量变化影响的研究[J]. 粮食与食品工业,2016,23(4):5. [HAO Q Y, HOU L X. Study on the influence of frying food materials with different water content on the changes of physicochemical indexes and vitamin E content of corn oil[J]. Food and Food Industry,2016,23(4):5. [54] 王花花. 基于微胶囊化技术的精油-多酚生物活性膜的制备及其应用[D]. 长春: 吉林大学, 2022 WANG H H. Preparation and application of essential oil-polyphenol bioactive membrane based on microencapsulation technology[D]. Changchun: Jilin University, 2022.
[55] 王帝, 张海娇, 冯晓梅, 等. 南极磷虾油纳米复合微胶囊制备、表征及其性质研究[J]. 食品科技,2022,47(7):236−242. [WANG D, ZHANG H J, FENG X M, et al. Preparation, characterization and properties of Antarctic krill oil nanocomposite microcapsules[J]. Food Science and Technology,2022,47(7):236−242. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2022.7.spkj202207035 [56] 王军, 王忠合, 骆宝. 热处理对猪肉中蛋白质体外消化率及5-羟甲基糠醛形成的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(16):5. [WANG J, WANG Z H, LUO B. Effect of heating treatment on in vitro digestibility of protein and 5-hydroxymethylfurfural formation in pork meat[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(16):5. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2017.16.016 -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 孙怀竹,梁金玲,许天阳,于澎. 干燥对不同药用部位中草药化学成分影响的研究进展. 中华中医药学刊. 2025(02): 246-250 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王慧,杨馥源,王玉龙,邢普,闫艳,杜晨晖. 基于多指标综合分析酸枣仁最佳采收期的质量标志物研究. 中国野生植物资源. 2024(04): 1-9+21 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘天悦,滕晓祎,田永涛,么亚妹,王琰博,王文蜀. 灯笼果叶片、宿萼和果实化学成分分析及抗氧化活性评价. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(20): 243-251 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 谢玉蓉,邵大畏,贺建红. 扶正益气方对乳腺癌术后化疗患者不良反应的影响及改善生活质量的状况. 辽宁中医杂志. 2024(11): 138-141 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)









 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



