Comparison of Functional Components and Antioxidant Activities of Soy Sauces Brewed with Different Raw Materials
-
摘要: 分别以黑豆、黄豆和豆粕为原料,以高盐稀态法制备酿造酱油,采用常规方法及液相色谱-质谱(LC-MS/MS)法检测3种酱油的品质指标、功能成分及抗氧化活性,分析其抗氧化活性与功能成分的相关性,并基于酱油的功能成分进行偏最小二乘判别分析(PLS-DA)。结果表明,3种酱油的感官和理化指标均达到国标GB 18186—2000《酿造酱油》中一级酱油要求。三种酱油的功能成分(总酚、总黄酮、类黑精、总游离多酚、总游离黄酮、总游离氨基酸)分别为4.78~7.14 mgGAE/mL、2.75~4.34 mgRE/mL、1.25%~1.70%、25.54~35.08 μg/mL、11.37~20.20 μg/mL、42.36~48.61 mg/mL;抗氧化指标(总抗氧化能力、ABTS+及DPPH自由基清除率)分别为24.27~605.57 U/mL、6.43~8.57 mgVCE/mL、3.53~5.30 mgVCE/mL。除游离氨基酸外,各功能成分含量及抗氧化活性均为黑豆酱油>豆粕酱油>黄豆酱油,且三种酱油间的抗氧化指标差异显著(P<0.05)。相关性结果表明,酱油抗氧化活性与总多酚、总黄酮及类黑精含量均呈显著正相关(P<0.05);PLS-DA结果表明,可以通过功能成分区分不同原料酿造的酱油。综上,以功能成分组成和含量不同的原料制备酱油的抗氧化活性会有所差异,可以通过原料选择及某些活性成分强化提高酱油功能保健作用。Abstract: Using black bean, soybean and soybean meal as raw materials, soy sauce was prepared by high-salt dilution method. The quality indexes, functional components and antioxidant activities of the three soy sauce were detected by conventional methods and liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS), and the correlation between antioxidant activities and functional components was analyzed. Partial least squares discriminant analysis (PLS-DA) was performed based on the functional components of soy sauce. The results showed that the sensory and physicochemical indexes of the three kinds of soy sauce all met the requirements of the first grade soy sauce in national standard GB 18186-2000 "Brewing Soy Sauce". The functional components of the three kinds of soy sauce (total phenols, total flavonoids, melanoid, total free polyphenols, total free flavonoids, total free amino acids) were 4.78~7.14 mgGAE/mL, 2.75~4.34 mgRE/mL, 1.25%~1.70%, 25.54~35.08 μg/mL, 11.37~20.20 μg/mL, 42.36~48.61 mg/mL, respectively. The antioxidant indexes (total antioxidant capacity, ABTS+ and DPPH free radical scavenging rate) were 24.27~605.57 U/mL, 6.43~8.57 mgVCE/mL and 3.53~5.30 mgVCE/mL, respectively. Except for free amino acids, the functional components contents and antioxidant activities of the three kinds of soy sauce were black soy sauce>soybean meal soy sauce>soybean soy sauce, and there were significant differences in antioxidant indexes among the three soy sauce (P<0.05). The correlation results showed that the antioxidant activity of soy sauce was significantly positively correlated with the contents of total polyphenols, total flavonoids and melanoid (P<0.05). PLS-DA results showed that the soy sauce brewed with different raw materials could be distinguished by functional components. In conclusion, the antioxidant activities of soy sauce brewed with different raw materials of different composition and contents of functional components were different, and the functional health effects of soy sauce could be improved by the selection of raw material and enhancement of certain active ingredients.
-
Keywords:
- soy sauce /
- black bean /
- soybean /
- polyphenol /
- flavone /
- melanoid /
- antioxidant activity /
- correlation
-
酱油是我国传统的发酵调味品,主要是以豆粕或大豆、面粉为原料,经制曲和后酵等工艺,在复杂的微生物和酶系共同作用下发酵制成[1-2]。酱油作为调味品,不仅有着色泽鲜艳、香气浓郁和滋味鲜美等特点[3-4],同时大豆的营养功能成分在微生物酶的作用下发生系列生物化学反应,使得酱油在发酵过程中还代谢产生多种成分,产品具有一定的功能活性[5]。酱油的制备通常采用低盐固态和高盐稀态发酵工艺,前者发酵周期短,但出品率高,成本低,口感欠佳;后者发酵时间充足、香气物质丰富,成品口感好[6]。
大豆含多种具有生理功效的物质,如大豆异黄酮、大豆多肽、儿茶酚、大豆苷元等,这些活性物质具有抗氧化、抗癌、预防心血管疾病、抗癌等多种生理功能[7-9];黑豆种皮含原花青素和花色苷类物质,具有抗氧化及保护视力等作用[10]。酱油中的异黄酮、大豆多肽等生理活性物质使得酱油在起到调味作用的同时也具有较好的功能特性[11],具有功能活性的酱油已经逐渐成为酱油市场的新宠[12]。大量研究表明,不同发酵原料对酱油的抗氧化活性有着显著的影响。钟小廷等[5]分析了黄豆、豆粕和黑豆酱油的体内抗氧化活性,发现黑豆酱油的抗氧化活性显著高于前两种酱油;冯拓等[13]比较了不同原料酱油的抗氧化活性与功能成分的关系,结果表明总酚、总黄酮和色深物质是造成不同酱油抗氧化活性存在差异的原因。有研究表明,酱油具有的抗氧化性主要来源于蛋白质降解产生的小分子活性肽、类黑精、酚类物质等[14],随着人们的需求从温饱型趋向于保健型,在满足食品口感和营养的前提下,具有抗氧化、降血脂、降血压等功能活性的产品更容易被消费者选择,因此有必要深入了解不同原料酱油中多酚、黄酮、类黑精等功能成分与抗氧化活性的关系,以期为酱油的功能保健作用提供理论基础,进一步提高酱油品质满足消费者的需求。
本研究分别以黑豆、黄豆和豆粕为原料,采用高盐稀态发酵工艺酿造酱油,测定其总酚、总黄酮、原花青素、类黑精含量及游离氨基酸含量,采用液相色谱串联质谱仪(liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry,LC-MS/MS)测定并分析3种酱油中游离黄酮和游离多酚含量,比较不同原料酿造酱油的功能成分和抗氧化活性,对二者进行相关性分析,并基于酱油功能成分进行偏最小二乘判别分析(partial least squares discriminant analysis,PLS-DA),旨在探讨不同原料酿造酱油的功能组分及其抗氧化活性的差异,对功能性酱油的研制及产业化生产提供科学依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
黑豆、黄豆(东北大豆)、面粉、无碘食盐 北京某市场;豆粕 同一批次黄豆实验室破碎后有机溶剂浸提去油脂得到;米曲霉(Aspergillus oryzae)(沪酿3.042) 北京市食品酿造研究所;福林酚试剂、碳酸钠、维生素C(vitamin C,VC)、2,2'-联氮-二(3-乙基-苯并噻唑-6-磺酸)二铵盐(2,2'-azinobis-(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulphonate),ABTS)、2,2-联苯基-1-苦基肼基(2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl,DPPH) 美国Sigma公司;大豆苷(daidzin)、大豆苷元(daidzein)、染料木苷(genistein)、染料木素(genistin)、黄豆黄苷(glycitin)、黄豆黄素(glycitein)、鸢尾黄素(tectorigenin)、和鸢尾黄酮甙(tectoridin)、鹰嘴豆芽素(biochanin A)、(+)-儿茶素((+)-catechin)、表没食子儿茶素(epigallocatechin)、原儿茶素(protocatechuic acid)、表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯(epigallocatechin gallate)、表儿茶素(epicatechin)、咖啡酸(cafeic acid)、香草酸(vanillic acid)、4-羟基苯甲酸(p-hydroxybenzoic acid)、阿魏酸(ferulic acid)、丁香酸(syringic acid)、表儿茶素没食子酸酯(epicatechin gallate)、没食子酸(gallic acid)、原花青素(proanthocyanidins)(纯度≥98%) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;甲醇(色谱纯) 德国默克有限公司;总抗氧化能力(total antioxidant capacity,T-AOC)检测试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所;其他试剂 均为国产分析纯。
Synergy HTX多功能微孔板酶标仪 美国Biotek科技有限公司;1290超高效液相色谱仪-6470串联四级杆质谱、5975-7890A气相色谱-质谱仪 美国Agilent科技有限公司;5910 R高速冷冻离心机 德国Eppendorf科技有限公司;BT25S电子天平 Sartorius科学仪器(北京)有限公司;L-8900氨基酸自动分析仪 日本日立公司;Mill-Q纯水仪 美国Millipore公司;DHG-9030电热恒温干燥箱 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;HI208酸度计(附磁力搅拌棒) 上海持互电子有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 酱油的制备工艺与操作要点
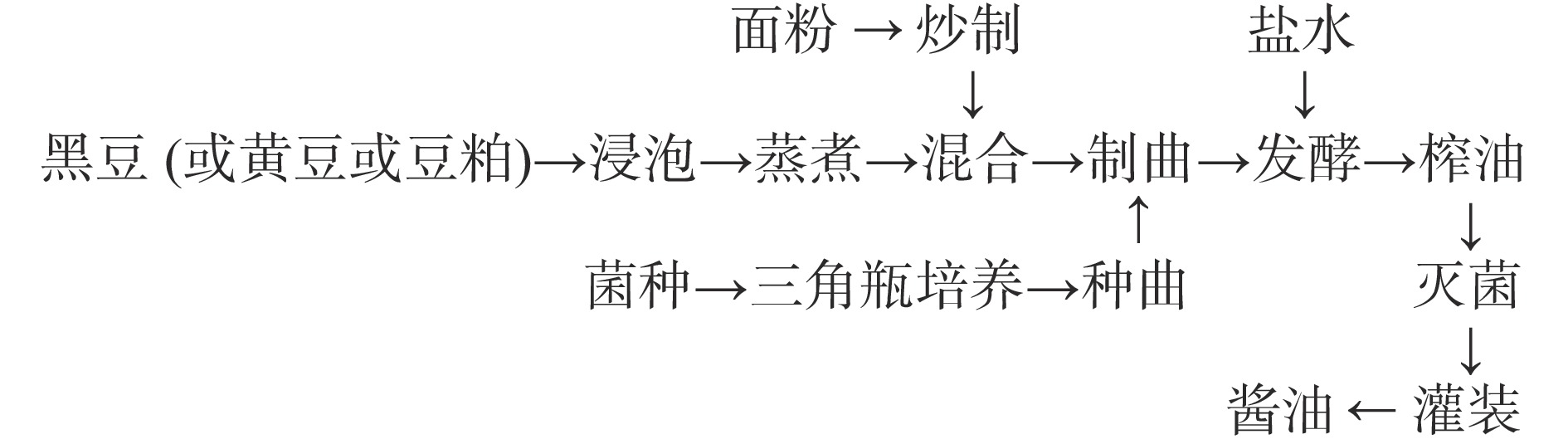
酱油的制备采用高盐稀态发酵工艺[15],工艺流程如下:
操作要点:将6 kg原料(黑豆或黄豆或豆粕)在25 ℃下浸泡8 h,之后蒸豆30 min,使大豆蛋白变性。将蒸好的原料与4 kg面粉混匀并平铺至培养板中,冷却至35 ℃。接种0.5‰的米曲霉,在32~35 ℃下培养48 h,得到成曲。将成曲和20%盐水以料液比1.0:2.5(g:mL)混合入缸发酵6个月,前一个月每天翻浆1次,之后静置发酵。发酵结束后,采用压榨机进行压榨。压榨后的酱油用板式加热器在80 ℃条件下灭菌,存放于−80 ℃冰箱保存,备用。
1.2.2 感官及理化指标测定
参考国标GB 18186-2000《酿造酱油》中的方法进行测定。
1.2.3 总酚、总黄酮、原花青素及类黑精含量测定
总酚含量测定参考Xu等[16]的方法,结果以没食子酸当量(gallic acid equivalent,GAE)表示;总黄酮含量测定参考Gao等[17]的方法,结果以芦丁当量(rutin equivalent,RE)表示;原花青素含量测定参考容晨曦等[18]的方法;类黑精含量测定参考秦礼康等[19]的方法。
1.2.4 游离黄酮及游离多酚化合物含量测定
游离黄酮及游离多酚含量测定采用LC-MS/MS法。取酱油2 mL,按照文献[20]的方法进行样品前处理及标准溶液制备。高效液相色谱条件:Eclipse plus C18色谱柱(50 mm×2.1 mm,1.8 µm),柱温40 ℃,流速0.4 mL/min。流动相:A为0.01%甲酸溶液,B为甲醇,流动相梯度洗脱程序:0~1 min,90% A;1~6 min,90%~40% A;6~10 min,40%~10% A;10~12 min,10% A;12~14 min,90% A。进样量1.0 µL。质谱条件:电喷雾离子(electron spray ionization,ESI)源,负离子模式,喷雾电压3000 V,辅助气气化温度200 ℃,鞘气流速11 mL/min,鞘气温度325 ℃。多反应监测(multiple reaction monitoring,MRM)模式下质谱参数见表1。
表 1 目标化合物多反应监测质谱参数Table 1. Mass spectrum parameters of multiple reaction monitoring of target compounds化合物 母离子(m/z) 子离子(m/z) 毛细管电压(V) 碰撞能量(eV) 鸢尾黄酮甙 461.2 299.6 185 20 283.5* 185 38 黄豆黄苷 445.1 267.2 200 50 239.2* 200 45 染料木素 431.1 269.6* 185 15 239.5 185 55 大豆苷 415.2 252.4* 200 30 223.2 200 55 鸢尾黄苷 299.1 284.1* 160 20 217.0 160 30 黄豆黄素 283.1 268.1* 175 20 240.0 175 28 鹰嘴豆芽素 283.1 267.1* 160 35 239.1 160 38 染料木苷 269.1 132.1* 180 55 65.1 180 60 大豆苷元 253.1 223.0* 180 40 208.1 180 35 (+)-儿茶素 289.1 245.2* 150 15 203.2 150 20 表没食子儿茶素 305.1 125.0* 90 23 178.9 90 13 原儿茶素 152.9 108.8* 110 15 107.9 110 30 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯 457.2 169.2* 143 15 125.2 143 48 表儿茶素 289.0 244.9* 160 15 202.9 160 20 咖啡酸 179.0 135.0* 120 15 香草酸 166.9 152.2* 100 13 107.8 100 18 4-羟基苯甲酸 137.2 92.9* 100 18 65.1 100 35 阿魏酸 193.1 178.0 120 13 134.0* 120 18 丁香酸 197.0 182.2* 110 13 123.1 110 25 表儿茶素没食子酸酯 441.0 289.2 130 18 169.0* 130 20 没食子酸 169.0 125.1* 110 15 79.0 110 25 注:“*”表示定量离子。 1.2.5 游离氨基酸含量的测定
按照GB 5009.124-2016《食品安全国家标准 食品中氨基酸的测定》方法进行测定[21]。
1.2.6 不同原料酿造酱油抗氧化能力测定
1.2.6.1 总抗氧化能力的测定
参考康子悦等[22]的方法,采用总抗氧化能力试剂盒测定。
1.2.6.2 DPPH自由基清除能力测定
参考张欢欢等[23]的方法。取2.0 mL样品稀释液(OD517 nm在0.5~1.0范围内),加入2 mL 0.2 mmol/L的DPPH-乙醇溶液,在室温下避光反应30 min后在517 nm波长处测定吸光度值,记为A样品;将2 mL 0.2 mmol/L的DPPH-乙醇溶液与2 mL体积分数80%乙醇溶液混合避光30 min,测定吸光度值并记为A空白;将2 mL样品稀释液与2 mL无水乙醇混合避光30 min,测定吸光度值并记为A对照。样品的DPPH自由基清除率计算公式如下:
1.2.6.3 ABTS+自由基清除能力测定
参考李莹等[24]的方法。配制吸光度值为0.700±0.020(734 nm波长)的ABTS测试液,取4.0 mL ABTS测试液,加入40 μL样品稀释液并振荡30 s,静置反应30 min后测定在波长734 nm处的吸光度值,记为A样品;将40 μL蒸馏水与4.0 mL ABTS测试液混合振荡,静置反应30 min后测定在波长734 nm处的吸光度值,记为A空白;将40 μL样品稀释液与4.0 mL体积分数60%乙醇溶液混合振荡,静置反应30 min后测定在波长734 nm处的吸光度值,记为A对照。样品的ABTS+自由基清除率计算公式如下:
以VC作为自由基清除能力阳性对照,配制不同浓度VC溶液,分别以其浓度和自由基清除率为横纵坐标,绘制VC标准曲线,计算DPPH和ABTS+自由基清除能力的抗坏血酸当量(vitamin C equivalent,VCE)。
1.3 数据处理
所有测定包含3个平行样品,结果均以“平均值±标准差”的形式表示。采用SPSS 20.0软件对数据进行相关性分析及差异显著性检验分析,以P<0.05为差异显著。采用SIMCA 14.1软件对数据进行偏最小二乘判别分析(partial least squares-discriminant analysis,PLS-DA)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同原料酿造酱油感官及理化指标分析
对不同原料酿造3种酱油的感官及理化指标进行测定,结果分别见表2和表3。
表 2 不同原料酿造3种酱油感官评价结果Table 2. Sensory evaluation results of three kinds of soy sauce brewed with different raw materials项目 黑豆酱油 黄豆酱油 豆粕酱油 色泽 红褐色,色泽鲜艳 浅红褐色,色泽鲜艳 红褐色,色泽鲜艳 香气 浓郁的酱香气 浓郁的酱香气 浓郁的酱香气 滋味 味鲜美醇厚,
鲜咸适口味鲜美醇厚,
鲜咸适口味鲜美醇厚,
鲜咸适口体态 澄清无杂质 澄清无杂质 澄清无杂质 表 3 不同原料酿造3种酱油理化指标测定结果Table 3. Determination results of physicochemical indexes of three kinds of soy sauce brewed with different raw materials项目 黑豆酱油 黄豆酱油 豆粕酱油 GB 18186-2000
(一级酱油)可溶性无盐固形物
(g·100 mL−1)17.22 16.84 17.32 ≥13.00 全氮(以氮计)
(g·100 mL−1)1.56 1.48 1.58 ≥1.30 氨基酸态氮(以氮计)
(g·100 mL−1)0.74 0.72 0.78 ≥0.70 由表1和表2可知,三种不同原料通过高盐稀态法酿造酱油的感官和理化指标均达到国家标准GB 18186-2000《酿造酱油》中一级酱油的要求。
2.2 不同原料酿造酱油的总酚、总黄酮、原花青素、类黑精含量比较
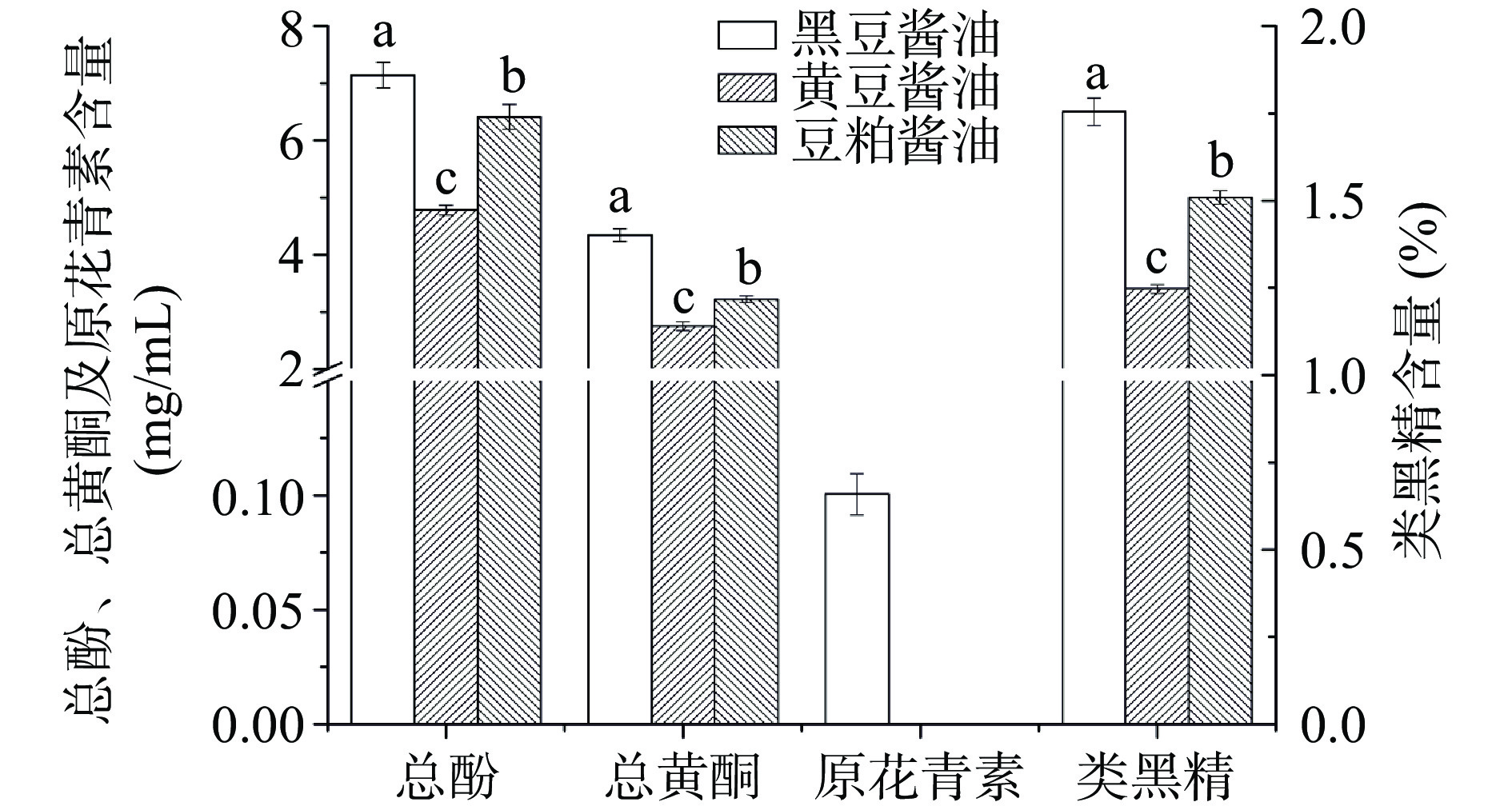
多酚类化合物分子结构中一般含有酚羟基,具有抗氧化作用[25],黄酮可作为天然抗氧化剂应用于食品行业[26];原花青素存在于植物中,具有抗炎、抗肿瘤、抗氧化应激等功效[27];此外,美拉德反应过程中产生的类黑精是糖类与氨基酸、多肽等含氮化合物发生美拉德反应后期形成的一类结构复杂的大分子化合物,具有很强的抗氧化和自由基清除能力,还具有抗癌、抑制血糖上升等作用[9]。对不同原料酿造3种酱油的总酚、总黄酮、原花青素、类黑精含量进行测定,结果见图1。
由图1可知,3种酱油中总酚、总黄酮和类黑精含量次序均为黑豆酱油>豆粕酱油>黄豆酱油,其中总酚、总黄酮和类黑精含量分别为4.78~7.14 mgGAE/mL、2.75~4.34 mgRE/mL、1.25%~1.70%,黑豆酱油的总酚、总黄酮和类黑精含量显著高于其他两种酱油(P<0.05)。此外,仅在黑豆酱油中检出原花青素,含量为0.10 mg/mL。已有研究表明,黑豆含有丰富的总黄酮和总多酚,黑豆中的黄酮类化合物含量与普通大豆相比高出5~7倍,而且相比于黄豆,黑豆种皮中含有丰富的原花青素及花色苷等特有的多酚类物质,这可能是导致黑豆酱油中总酚、总黄酮含量显著高于其他两种酱油的原因[28]。由于原花青素多存在于深色植物中,黑豆种皮富含原花青素[29],黄豆种皮的原花青素类物质含量很低,所以黄豆酱油和豆粕酱油均未检出原花青素。张欢欢等[30-31]研究发现,黑豆酱油中含有较高的淀粉酶活性,有利于酱油原料中多酚类化合物的释放。黑豆中大豆蛋白含量比黄豆高出25%左右,在发酵过程中大豆蛋白可以降解为大量的含氮化合物,更容易形成具有抗氧化活性的类黑精[32]。豆粕是大豆提取豆油后得到的一种副产品,大豆中的油脂被提出,使豆粕中的酚类及黄酮类物质等成分含量相应升高,所以豆粕酱油中的总酚、总黄酮含量显著高于黄豆酱油(P<0.05)。结果表明,黑豆酱油的总酚、总黄酮、原花青素、类黑精含量最高。
2.3 不同原料酿造酱油的游离多酚化合物含量比较
不同原料酿造3种酱油的游离多酚含量测定结果见图2。由图2可知,3种酱油中共检出10种游离多酚化合物,黑豆、黄豆以及豆粕酱油中总游离多酚含量分别为35.08、25.54和34.57 μg/mL。其中,香草酸和丁香酸是酱油中主要的游离多酚化合物,其含量分别为7.85~15.48和6.43~13.04 μg/mL。酱油中的游离多酚化合物主要来源于酱油发酵过程中酶促及非酶促反应间大分子降解和生物转化,能通过与氧化反应产生的脂类自由基等结合,最终减少或阻断组织中氧化反应的进行[12,30]。不同发酵原料酱油中的游离多酚组成成分存在一定的差异,黑豆酱油中原儿茶素和丁香酸含量均显著高于其他两种酱油(P<0.05),其原儿茶素可能是由黑豆中丰富的花色苷类物质—矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖苷降解产生的[33];除此之外,黑豆酱油中的香草酸(7.85 μg/mL)和阿魏酸(0.48 μg/mL)含量显著低于其他两种酱油(P<0.05),而豆粕酱油中的香草酸和阿魏酸含量显著高于黄豆酱油和黑豆酱油(P<0.05),这可能是由于大豆中香草酸和阿魏酸含量高于黑豆。综上结果表明,黑豆酱油的总游离多酚含量最高。
2.4 不同原料酿造酱油的游离黄酮含量比较
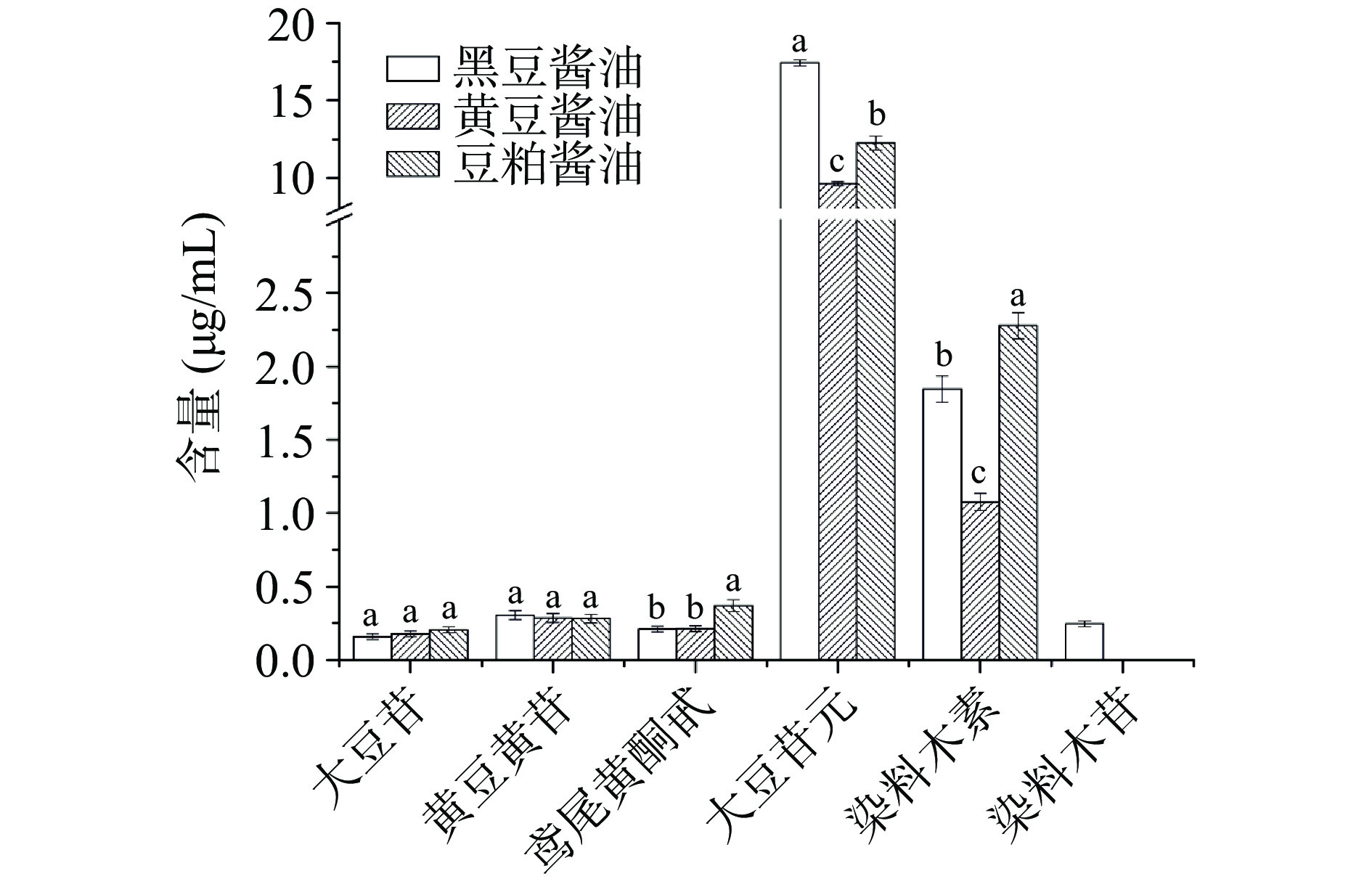
不同原料酿造3种酱油的游离黄酮含量测定结果见图3。由图3可知,3种酱油中共检出6种大豆异黄酮,包括大豆苷、大豆苷元、黄豆黄苷、染料木素、鸢尾黄酮甙和染料木苷。其中,大豆苷、黄豆黄苷、染料木苷属于结合型的糖苷,而大豆苷元、染料木素、鸢尾黄酮甙属于游离型的苷元,具有更强的生理活性[34-35]。黑豆、黄豆以及豆粕酱油中总游离黄酮含量分别为20.20、11.37和15.38 μg/mL,黑豆酱油中的总游离黄酮含量显著高于黄豆和豆粕酱油(P<0.05),这与其总黄酮含量趋势较为一致。大豆苷元和染料木素等苷元类异黄酮是酱油中的主要异黄酮,而糖苷类异黄酮(大豆苷和染料木苷)含量最低,这可能是因为微生物在发酵过程中产生的β-葡萄糖苷酶或酸水解的作用,将糖苷型异黄酮转化为苷元类异黄酮[36-37]。不同原料酿造酱油中的游离黄酮组成成分存在一定的差异,黑豆酱油中大豆苷元含量显著高于其他两种酱油(P<0.05);豆粕酱油与黄豆酱油中的大豆异黄酮组成较为相似,均检出5种大豆异黄酮,除黄豆黄苷外,豆粕酱油中其他4种大豆异黄酮含量均高于黄豆酱油,这可能与豆粕的脱脂处理有关。结果表明,黑豆酱油的总游离黄酮含量最高。
2.5 不同原料酿造酱油的游离氨基酸含量比较
不同原料酿造3种酱油的游离氨基酸组成及含量测定结果见表4。由表4可知,三种酱油中均检出18种游离氨基酸(含8种必需氨基酸),黑豆酱油、黄豆酱油、豆粕酱油中总游离氨基酸分别为48.61、45.51及42.36 mg/mL;总必需氨基酸含量分别为22.71、20.83、20.19 mg/mL。酱油中氨基酸主要来源于蛋白质分解、微生物合成以及微生物菌体自溶[38]。结果表明,豆粕酱油中的氨基酸含量低于黑豆酱油和黄豆酱油,榨取油之后豆粕原料营养不够完善,大豆和黑豆原料各种营养成分更全面,多酶系、低温发酵充分发挥酶解作用,使酱油氨基酸含量更高[15]。黑豆酱油中的总游离氨基酸、总必需氨基酸含量最高,可能是由于黑豆原料可以比黄豆原料提供更多的蛋白质与淀粉[39],在制曲过程中可提供的营养物质多,米曲霉生长旺盛,从而黑豆大曲具有更高的酶活[12],使得黑豆蛋白质被降解成更多的氨基酸。
表 4 不同原料酿造3种酱油的游离氨基酸含量测定结果Table 4. Determination results of free amino acids contents in three kinds of soy sauce brewed with different raw materials序号 氨基酸 英文缩写 含量(mg·mL−1) 黑豆酱油 黄豆酱油 豆粕酱油 1 谷氨酸 Glu 5.50 5.56 5.29 2 天冬氨酸 Asp 4.86 5.29 4.51 3 丙氨酸 Ala 2.53 2.28 2.33 4 甘氨酸 Gly 2.59 2.26 1.99 5 赖氨酸* Lys 6.53 6.02 5.43 6 脯氨酸 Pro 1.75 1.27 0.95 7 丝氨酸 Ser 3.01 2.72 2.55 8 苏氨酸* Thr 2.33 1.82 1.99 9 苯丙氨酸* Phe 2.81 2.89 2.73 10 蛋氨酸* Met 0.88 0.77 0.57 11 精氨酸 Arg 2.18 2.15 1.78 12 酪氨酸 Tyr 1.94 1.83 1.63 13 亮氨酸* Leu 4.87 4.26 4.28 14 缬氨酸* Val 2.75 2.69 2.73 15 异亮氨酸* Ile 2.30 2.18 2.32 16 组氨酸 His 1.46 1.26 1.09 17 色氨酸* Trp 0.24 0.20 0.14 18 半胱氨酸 Cys 0.08 0.06 0.05 总含量 48.61 45.51 42.36 注:“*”表示必需氨基酸。 2.6 不同原料酿造酱油的抗氧化活性比较
采用总抗氧化能力、ABTS+自由基清除能力和DPPH自由基清除能力评价不同原料酿造3种酱油的抗氧化活性,结果见表5。
表 5 不同原料酿造3种酱油的抗氧化活性Table 5. Antioxidant activities of three kinds of soy sauce brewed with different raw materials黑豆酱油 黄豆酱油 豆粕酱油 总抗氧化能力(U·mL−1) 605.57±10.22a 424.27±5.06c 538.97±7.69b ABTS+自由基清除能力
(mgVCE·mL−1)8.57±0.15a 6.43±0.12c 8.04±0.17b DPPH自由基清除能力
(mgVCE·mL−1)5.30±0.07a 3.53±0.03c 4.64±0.04b 注:同行不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 由表3可知,3种酱油的总抗氧化能力及ABTS+和DPPH自由基清除能力分别为424.27~605.57 U/mL、6.43~8.57 mgVCE/mL及3.53~5.30 mgVCE/mL。不同原料酿造的酱油总抗氧化能力、ABTS+自由基清除能力和DPPH自由基清除能力均有显著差异(P<0.05)。不同原料酿造酱油抗氧化活性顺序由大到小均为黑豆酱油>豆粕酱油>黄豆酱油,黑豆酱油的总抗氧化能力、ABTS+自由基和DPPH自由基清除能力显著高于其他两种酱油(P<0.05),由于豆粕酱油中总酚、总黄酮等抗氧化活性成分含量高于黄豆酱油,故抗氧化能力也高于黄豆酱油。陈彩云等[40]研究表明,不同豆类的总黄酮含量和抗氧化活性均为黑豆大于黄豆;张欢欢等[30]研究结果表明,由于黑豆中含有更多的花青素等花色苷类物质,所以抗氧化活性高于另外两种酱油;还有研究表明,酱油的色深物质如类黑精是酱油中抗氧化活性的重要组成部分[41]。这些研究结果均与本研究结果一致。
2.7 酱油的功能成分与抗氧化活性的相关性分析
植物多酚、黄酮是以游离和结合两种形态存在的,总多酚(总黄酮)的抗氧化活性是游离态多酚(游离态黄酮)和结合态多酚(结合态黄酮)二者抗氧化活性的总和[42],研究表明,大豆中总酚和总黄酮是抗氧化作用的重要物质基础,因此有必要基于总酚与总黄酮分析二者与抗氧化活性的关系[35];类黑精是美拉德反应产生的具有抗氧化活性的物质;氨基酸是酱油中重要的营养、风味成分。对酱油的总酚、总黄酮、类黑精、总游离氨基酸等功能成分与抗氧化活性进行相关性分析,结果见表6。
表 6 酱油中功能成分与抗氧化活性的相关性分析结果Table 6. Correlation analysis results between the functional components in soy sauce and antioxidant activities项目 相关系数r 总酚 总黄酮 类黑精 总游离氨基酸 总抗氧化能力 0.998* 0.927* 0.999* 0.725 ABTS自由基清除力 0.998* 0.907* 0.986* 0.798 DPPH自由基清除力 0.997* 0.930* 0.999* 0.542 注:“*”表示在0.05水平(双侧)显著相关。 由表4可知,不同原料酿造酱油的总抗氧化能力、ABTS+和DPPH自由基清除能力与总酚、总黄酮及类黑精含量的相关系数r均>0.900,与总游离氨基酸含量的相关系数r为0.542~0.798。酱油的抗氧化活性与其总酚、总黄酮及类黑精含量均呈显著正相关(P<0.05),但与总游离氨基酸含量无显著相关性(P>0.05)。可推断总酚、总黄酮及类黑精可能是影响酱油抗氧化能力的重要因子[16],且影响大小的顺序为总酚>类黑精>总黄酮。结果表明,酱油的抗氧化活性与其功能成分显著相关。
2.8 多元统计分析
采用PLS-DA对不同原料酿造3种酱油功能组分进行相似性和差异性分析,结果见图4。由图4可知,PC1和PC2的方差贡献率分别为70.0%和16.4%,累计方差贡献率为86.4%,说明这两个主成分可以代表样品的主要信息。黑豆酱油分布在主成分PC1轴的正象限,豆粕酱油和黄豆酱油分布在PC1的负象限,可以较好区分3种酱油。在PC1主成分正象限上特征值向量较大的组分有原花青素、染料木苷、原儿茶素、没食子酸和大豆苷元,负象限上主要有香草酸、阿魏酸和大豆苷等化合物,这些化合物可能是导致3种酱油抗氧化活性差异的主要物质,且黑豆酱油的化合物相对集中,豆粕酱油和黄豆酱油的特征化合物相对分散。此外,黄豆酱油与豆粕酱油间的差异化合物主要包括表儿茶素、4-羟基苯甲酸、鸢尾黄酮甙和染料木素。结果表明,不同原料酱油中主要功能成分组成和含量不同,可以通过功能成分的差异来判别不同原料酿造酱油。
3. 结论
本研究以黑豆、黄豆和豆粕为原料,采用高盐稀态发酵工艺酿造酱油,并对不同原料酿造酱油的功能成分及其抗氧化功能进行分析比较。结果表明,黑豆酱油的总酚、总黄酮、总游离多酚、总游离黄酮、类黑精及总游离氨基酸含量以及抗氧化能力均高于豆粕酱油和黄豆酱油。酱油的抗氧化活性与其总酚、总黄酮及类黑精含量呈显著正相关(P<0.05),与总游离氨基酸含量无显著相关性(P>0.05)。结果表明,原料中功能成分组成及含量不同会导致酱油的抗氧化活性会有所差异,可以通过酱油原料中功能物质的差异区分不同原料酱油,后续研究可以通过原料复配及某种功能成分强化提高酱油的抗氧化活性,从而进一步提高酱油的功能保健作用。
-
表 1 目标化合物多反应监测质谱参数
Table 1 Mass spectrum parameters of multiple reaction monitoring of target compounds
化合物 母离子(m/z) 子离子(m/z) 毛细管电压(V) 碰撞能量(eV) 鸢尾黄酮甙 461.2 299.6 185 20 283.5* 185 38 黄豆黄苷 445.1 267.2 200 50 239.2* 200 45 染料木素 431.1 269.6* 185 15 239.5 185 55 大豆苷 415.2 252.4* 200 30 223.2 200 55 鸢尾黄苷 299.1 284.1* 160 20 217.0 160 30 黄豆黄素 283.1 268.1* 175 20 240.0 175 28 鹰嘴豆芽素 283.1 267.1* 160 35 239.1 160 38 染料木苷 269.1 132.1* 180 55 65.1 180 60 大豆苷元 253.1 223.0* 180 40 208.1 180 35 (+)-儿茶素 289.1 245.2* 150 15 203.2 150 20 表没食子儿茶素 305.1 125.0* 90 23 178.9 90 13 原儿茶素 152.9 108.8* 110 15 107.9 110 30 表没食子儿茶素没食子酸酯 457.2 169.2* 143 15 125.2 143 48 表儿茶素 289.0 244.9* 160 15 202.9 160 20 咖啡酸 179.0 135.0* 120 15 香草酸 166.9 152.2* 100 13 107.8 100 18 4-羟基苯甲酸 137.2 92.9* 100 18 65.1 100 35 阿魏酸 193.1 178.0 120 13 134.0* 120 18 丁香酸 197.0 182.2* 110 13 123.1 110 25 表儿茶素没食子酸酯 441.0 289.2 130 18 169.0* 130 20 没食子酸 169.0 125.1* 110 15 79.0 110 25 注:“*”表示定量离子。 表 2 不同原料酿造3种酱油感官评价结果
Table 2 Sensory evaluation results of three kinds of soy sauce brewed with different raw materials
项目 黑豆酱油 黄豆酱油 豆粕酱油 色泽 红褐色,色泽鲜艳 浅红褐色,色泽鲜艳 红褐色,色泽鲜艳 香气 浓郁的酱香气 浓郁的酱香气 浓郁的酱香气 滋味 味鲜美醇厚,
鲜咸适口味鲜美醇厚,
鲜咸适口味鲜美醇厚,
鲜咸适口体态 澄清无杂质 澄清无杂质 澄清无杂质 表 3 不同原料酿造3种酱油理化指标测定结果
Table 3 Determination results of physicochemical indexes of three kinds of soy sauce brewed with different raw materials
项目 黑豆酱油 黄豆酱油 豆粕酱油 GB 18186-2000
(一级酱油)可溶性无盐固形物
(g·100 mL−1)17.22 16.84 17.32 ≥13.00 全氮(以氮计)
(g·100 mL−1)1.56 1.48 1.58 ≥1.30 氨基酸态氮(以氮计)
(g·100 mL−1)0.74 0.72 0.78 ≥0.70 表 4 不同原料酿造3种酱油的游离氨基酸含量测定结果
Table 4 Determination results of free amino acids contents in three kinds of soy sauce brewed with different raw materials
序号 氨基酸 英文缩写 含量(mg·mL−1) 黑豆酱油 黄豆酱油 豆粕酱油 1 谷氨酸 Glu 5.50 5.56 5.29 2 天冬氨酸 Asp 4.86 5.29 4.51 3 丙氨酸 Ala 2.53 2.28 2.33 4 甘氨酸 Gly 2.59 2.26 1.99 5 赖氨酸* Lys 6.53 6.02 5.43 6 脯氨酸 Pro 1.75 1.27 0.95 7 丝氨酸 Ser 3.01 2.72 2.55 8 苏氨酸* Thr 2.33 1.82 1.99 9 苯丙氨酸* Phe 2.81 2.89 2.73 10 蛋氨酸* Met 0.88 0.77 0.57 11 精氨酸 Arg 2.18 2.15 1.78 12 酪氨酸 Tyr 1.94 1.83 1.63 13 亮氨酸* Leu 4.87 4.26 4.28 14 缬氨酸* Val 2.75 2.69 2.73 15 异亮氨酸* Ile 2.30 2.18 2.32 16 组氨酸 His 1.46 1.26 1.09 17 色氨酸* Trp 0.24 0.20 0.14 18 半胱氨酸 Cys 0.08 0.06 0.05 总含量 48.61 45.51 42.36 注:“*”表示必需氨基酸。 表 5 不同原料酿造3种酱油的抗氧化活性
Table 5 Antioxidant activities of three kinds of soy sauce brewed with different raw materials
黑豆酱油 黄豆酱油 豆粕酱油 总抗氧化能力(U·mL−1) 605.57±10.22a 424.27±5.06c 538.97±7.69b ABTS+自由基清除能力
(mgVCE·mL−1)8.57±0.15a 6.43±0.12c 8.04±0.17b DPPH自由基清除能力
(mgVCE·mL−1)5.30±0.07a 3.53±0.03c 4.64±0.04b 注:同行不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 6 酱油中功能成分与抗氧化活性的相关性分析结果
Table 6 Correlation analysis results between the functional components in soy sauce and antioxidant activities
项目 相关系数r 总酚 总黄酮 类黑精 总游离氨基酸 总抗氧化能力 0.998* 0.927* 0.999* 0.725 ABTS自由基清除力 0.998* 0.907* 0.986* 0.798 DPPH自由基清除力 0.997* 0.930* 0.999* 0.542 注:“*”表示在0.05水平(双侧)显著相关。 -
[1] 王夫杰, 鲁绯. 我国酱油研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 中国酿造,2010,29(12):3−7. [WANG F J, LU F. Research and development of soy sauce in China[J]. China Brewing,2010,29(12):3−7. WANG F J, LU F. Research and development of soy sauce in China[J]. China Brewing, 2010, 29(12): 3-7.
[2] DEVANTHI P V P, GKATZIONIS K. Soy sauce fermentation: Microorganisms, aroma formation, and process modification[J]. Food Research International,2019,120:364−374. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.03.010
[3] 袁圆, 鲁绯, 黄持都, 等. 酱油功能性研究最新进展[J]. 中国酿造,2010,29(1):1−4. [YUAN Y, LU F, HUANG C D, et al. Recent progress on functionality of soy sauce[J]. China Brewing,2010,29(1):1−4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5071.2010.01.002 YUAN Y, LU F, HUANG C D, et al. Recent progress on functionality of soy sauce[J]. China Brewing, 2010, 29(1): 1-4. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5071.2010.01.002
[4] 黄持都, 鲁绯, 纪凤娣, 等. 酱油研究进展[J]. 中国酿造,2009,28(10):7−10. [HUANG C D, LU F, JI F D, et al. Research progress of soy sauce[J]. China Brewing,2009,28(10):7−10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5071.2009.10.003 HUANG C D, LU F, JI F D, et al. Research progress of soy sauce[J]. China Brewing, 2009, 28(10): 7-10. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-5071.2009.10.003
[5] 钟小廷, 吕杰, 易谦武, 等. 不同原料酱油抗氧化活性生物测试及风味分析[J]. 中国酿造,2020,39(9):69−74. [ZHONG X T, LÜ J, YI Q W, et al. Analysis of antioxidant activity and flavor substances in soy sauce with different materials[J]. China Brewing,2020,39(9):69−74. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2020.09.013 ZHONG X T, LÜ J, YI Q W, et al. Analysis of antioxidant activity and flavor substances in soy sauce with different materials[J]. China Brewing, 2020, 39(9): 69-74. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2020.09.013
[6] 张振斌. 新型减盐酱油及固态发酵工艺的开发与研究[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2021 ZHANG Z B. Development and research of new salt-reducing soy sauce and solid-state fermentation process[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2021.
[7] 王丹, 邹雨婷, 王悦, 等. 2种豆类制备大豆黄卷过程中多种营养成分及活性成分含量变化的研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2022,37(2):62−67. [WANG D, ZOU Y T, WANG Y, et al. Changes of contents of various nutrients and active components during preparation of sojae semen germinatum with two kinds of beans[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2022,37(2):62−67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2022.02.011 WANG D, ZOU Y T, WANG Y, et al. Changes of contents of various nutrients and active components during preparation of sojae semen germinatum with two kinds of beans[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association, 2022, 37(2): 62-67. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2022.02.011
[8] 赵晓佳, 李易聪, 王秀伶. 大豆异黄酮微生物转化研究进展[J]. 微生物学报,2020,60(2):211−226. [ZHAO X J, LI Y C, WANG X L. Progress in microbial conversion of soy isoflavones[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica,2020,60(2):211−226. ZHAO X J, LI Y C, WANG X L. Progress in microbial conversion of soy isoflavones[J]. Acta Microbiologica Sinica, 2020, 60(2): 211-226.
[9] 周文红, 郭咪咪, 李秀娟, 等. 大豆异黄酮提取及其生物转化的研究进展[J]. 粮油食品科技,2019,27(5):37−42. [ZHOU W H, GUO M M, LI X J, et al. Research progress of extraction and biotransformation of soybean isoflavones[J]. Science and Technology of Cereal, Oils and Foods,2019,27(5):37−42. ZHOU W H, GUO M M, LI X J, et al. Research progress of extraction and biotransformation of soybean isoflavones[J]. Science and Technology of Cereal, Oils and Foods, 2019, 27(5): 37-42.
[10] 冯云子, 周婷, 吴伟宇, 等. 酱油风味与功能性成分研究进展[J]. 食品科学技术学报,2021,39(4):14−28. [FENG Y Z, ZHOU T, WU W Y, et al. Research progress on flavor and functional components of soy sauce[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2021,39(4):14−28. doi: 10.12301/j.issn.2095-6002.2021.04.002 FENG Y Z, ZHOU T, WU W Y, et al. Research progress on flavor and functional components of soy sauce[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2021, 39(4): 14-28. doi: 10.12301/j.issn.2095-6002.2021.04.002
[11] 何婷. 大豆粕酶解物对酱油风味品质的影响及呈味肽的分离鉴定[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2019 HE T. Effect of deffacted soybean hydrolysate on soy sauce flavor and identification of taste peptides[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2019.
[12] YANG C S, HO C T, ZHANG J, et al. Antioxidants: Differing meanings in food science and health science[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2018,66(12):3063−3068. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.7b05830
[13] 冯拓, 单培, 盛明健, 等. 5种不同酱油抗氧化活性的对比分析[J]. 现代食品科技,2022,38(3):159−167,313. [FENG T, SHAN P, SHENG M J, et al. Comparative analysis of antioxidant activity of five kinds of soy sauces[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2022,38(3):159−167,313. FENG T, SHAN P, SHENG M J, et al. Comparative analysis of antioxidant activity of five kinds of soy sauces[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology, 2022, 38(3): 159-167, 313.
[14] 李莹. 传统发酵酱油生理活性成分的分离鉴定及作用机制研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2011 LI Y. Isolation and identification of physical active ingredients in traditional say sauce and its mechanism study[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2011.
[15] 包启安. 酱油科学与酿造技术[M]. 北京: 中国轻工业出版社, 2011 BAO Q A. Science and brewing technology of soy sauce[M]. Beijing: China Light Industry Press, 2011.
[16] XU B J, CHANG S K C. A comparative study on phenolic profiles and antioxidant activities of legumes as affected by extraction solvents[J]. Journal of Food Science,2010,72(2):S159−S166.
[17] GAO X L, LIU E M, ZHANG J K, et al. Effects of sonication during moromi fermentation on antioxidant activities of compounds in raw soy sauce[J]. LWT,2019,116:108605. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108605
[18] 容晨曦, 张秀玲, 李铁柱, 等. 响应面试验优化微波法提取刺玫籽原花青素的工艺[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(18):41−46. [RONG C X, ZHANG X L, LI T Z, et al. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of proanthocyanidins from Rosa davurica Pall. seeds by response surface methodology[J]. Food Science,2016,37(18):41−46. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201618007 RONG C X, ZHANG X L, LI T Z, et al. Optimization of microwave-assisted extraction of proanthocyanidins from Rosa davurica Pall. seeds by response surface methodology[J]. Food Science, 2016, 37(18): 41-46. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201618007
[19] 秦礼康, 丁霄霖. 陈窖豆豉粑类黑精组分体外抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2006,32(1):88−92. [QIN L K, DING X L. Studies on in vitro antioxidant activities of the melanoidin fractions separated from long-ripened douchiba (DCB)[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2006,32(1):88−92. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-990X.2006.01.021 QIN L K, DING X L. Studies on in vitro antioxidant activities of the melanoidin fractions separated from long-ripened douchiba (DCB)[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2006, 32(1): 88-92. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-990X.2006.01.021
[20] 张露, 梁寒峭, 刘伟, 等. 酿造酱油中10种单体酚酸成分的检测分析[J]. 安徽农业科学,2018,46(25):172−175. [ZHANG L, LIANG H Q, LIU W, et al. Detection and analysis of ten monomeric phenolic acids in fermented soy sauce[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Science,2018,46(25):172−175. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2018.25.052 ZHANG L, LIANG H Q, LIU W, et al. Detection and analysis of ten monomeric phenolic acids in fermented soy sauce[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Science, 2018, 46(25): 172-175. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2018.25.052
[21] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.124—2016食品安全国家标准 食品中氨基酸的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016 China's National Health and Family Planning Commission. GB 5009.124—2016 National food safety standard, determination of amino acid in foods[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2016.
[22] 康子悦, 沈蒙, 葛云飞, 等. 基于植物广泛靶向代谢组学技术探究小米粥中酚类化合物组成及其抗氧化性[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(4):206−214. [KANG Z Y, SHEN M, GE Y F, et al. Analysis of phenolic composition in millet porridge using widely-targeted metabolomics and evaluation of antioxidant activity[J]. Food Science,2021,42(4):206−214. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190813-145 KANG Z Y, SHEN M, GE Y F, et al. Analysis of phenolic composition in millet porridge using widely-targeted metabolomics and evaluation of antioxidant activity[J]. Food Science, 2021, 42(4): 206-214. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190813-145
[23] 张欢欢, 耿予欢, 李国基, 等. 麦胚对高盐稀态酱油理化特性及抗氧化活性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(4):108−115. [ZHANG H H, GENG Y H, LI G J, et al. Effects of wheat germ on physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of chinese traditional high-salt diluted soy sauce[J]. Food Science,2019,40(4):108−115. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20170926-366 ZHANG H H, GENG Y H, LI G J, et al. Effects of wheat germ on physicochemical properties and antioxidant activities of chinese traditional high-salt diluted soy sauce[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(4): 108-115. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20170926-366
[24] 李莹, 刘敏, 崔春, 等. 酱油抗氧化能力评价及聚类分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2008,34(1):14−19. [LI Y, LIU M, CUI C, et al. Antioxidant activity assessment and cluster analysis of retail soy sauce products[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2008,34(1):14−19. LI Y, LIU M, CUI C, et al. Antioxidant activity assessment and cluster analysis of retail soy sauce products[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2008, 34(1): 14-19.
[25] 胡栋宝, 黄淑佩, 祝晓慧, 等. 响应面优化鸡油菌多酚的超声辅助提取工艺及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(18):177−184. [HU D B, HUANG S P, ZHU X H, et al. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of polyphenols from the mushroom of Cantharelles cibarius and its antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(18):177−184. HU D B, HUANG S P, ZHU X H, et al. Ultrasound-assisted extraction of polyphenols from the mushroom of Cantharelles cibarius and its antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(18): 177−184.
[26] 雷秋琪, 叶诗洁, 黄永康, 等. 菱角壳黄酮提取工艺优化及抑肿瘤细胞增殖活性作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(14):224−232. [LEI Q Q, YE S J, HUANG Y K, et al. Optimization of extraction process of flavonoids from water chestnut shell and effect on anti-tumor cell proliferation activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(14):224−232. LEI Q Q, YE S J, HUANG Y K, et al. Optimization of extraction process of flavonoids from water chestnut shell and effect on anti-tumor cell proliferation activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(14): 224−232.
[27] 张丽明, 马雅鸽, 牛若楠, 等. 宾川葡萄籽原花青素纯化及对HepG2细胞增殖的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(5):230−236. [ZHANG L M, MA Y G, NIU R N, et al. Purification of proanthocyanidins from Binchuan grape seed and its effects on proliferation of HepG2 cells[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(5):230−236. ZHANG L M, MA Y G, NIU R N, et al. Purification of proanthocyanidins from Binchuan grape seed and its effects on proliferation of HepG2 cells[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(5): 230−236.
[28] ITO C, OKI T, YOSHIDA T, et al. Characterisation of proanthocyanidins from black soybeans: Isolation and characterisation of proanthocyanidin oligomers from black soybean seed coats[J]. Food Chemistry,2013,141(3):2507−2512. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.05.039
[29] 王鹏, 王文平, 续丹丹, 等. 黑豆酱油的开发及其品质分析[J]. 中国酿造,2018,37(10):25−30. [WANG P, WANG W P, XU D D, et al. Development and quality analysis of black soybean sauce[J]. China Brewing,2018,37(10):25−30. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2018.10.006 WANG P, WANG W P, XU D D, et al. Development and quality analysis of black soybean sauce[J]. China Brewing, 2018, 37(10): 25-30. doi: 10.11882/j.issn.0254-5071.2018.10.006
[30] 张欢欢, 耿予欢, 李国基. 黄豆酱油与黑豆酱油抗氧化活性及风味物质的比较[J]. 现代食品科技,2018,34(6):97−106. [ZHANG H H, GENG Y H, LI G J. Comparison of antioxidant activities and flavor compounds of soy sauces prepared with yellow soybean and black soybean[J]. Morden Food Technology,2018,34(6):97−106. ZHANG H H, GENG Y H, LI G J. Comparison of antioxidant activities and flavor compounds of soy sauces prepared with yellow soybean and black soybean[J]. Morden Food Technology, 2018, 34(6): 97-106.
[31] LERTSIRI S, MAUNGMA R, ASSAVANIG A, et al. Roles of the Maillard reaction in browning during moromi process of Thai soy sauce[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2001,25(2):149−162. doi: 10.1111/j.1745-4549.2001.tb00450.x
[32] 朱怡霖. 不同大豆品种蛋白质、脂肪、多酚组成成分及抗氧化活性研究[D]. 西安: 陕西师范大学, 2017 ZHU Y L. Study on the composition of protein, fat, polyphenol and antioxidant activity of different soybean varieties[D]. Xi'an: Shannxi Normal University, 2017.
[33] SHIN H Y, KIM S M, LEE J H, et al. Solid-state fermentation of black rice bran with Aspergillus awamori and Aspergillus oryzae: Effects on phenolic acid composition and antioxidant activity of bran extracts[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,272:235−241. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.07.174
[34] 李笑梅, 王如梦. 酸-超声水解法对大豆苷元转化的影响[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2018,177(11):114−123. [LI X M, WANG R M. Effect of combined acid-ultrasonic processing on the conversion of soybean isoflavones to aglycones[J]. China Food Additives,2018,177(11):114−123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2018.11.017 LI X M, WANG R M. Effect of combined acid-ultrasonic processing on the conversion of soybean isoflavones to aglycones[J]. China Food Additives, 2018, 177(11): 114-123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2513.2018.11.017
[35] 朱怡霖, 张海生, 杨淑芳, 等. 18种大豆多酚含量组成及抗氧化活性分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2017,43(1):241−245. [ZHU Y L, ZHANG H S, YANG S F, et al. Comparisons of phenolic composition and antioxidant activity in 18 different varieties of soybean[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2017,43(1):241−245. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.201701040 ZHU Y L, ZHANG H S, YANG S F, et al. Comparisons of phenolic composition and antioxidant activity in 18 different varieties of soybean[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2017, 43(1): 241-245. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.201701040
[36] SANTOS V A Q, NASCIMENTO C G, SCHMIDT C A P, et al. Solid-state fermentation of soybean okara: Isoflavones biotransformation, antioxidant activity and enhancement of nutritional quality[J]. LWT,2018,92:509−515. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.02.067
[37] CHUA J Y, LU Y, LIU S Q. Biotransformation of soy whey into soy alcoholic beverage by four commercial strains of Saccharomyces cerevisiae[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2017,262:14−22. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2017.09.007
[38] 王猛. 黑豆酱油的初步研发[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2013 WANG M. Preliminary research and development of black bean sauce[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2013.
[39] 徐飞, 葛阳阳, 刘新春, 等. 黑豆营养成分及生物活性的研究进展[J]. 中国食物与营养,2019,25(9):55−61. [XU F, GE Y Y, LIU X C, et al. Research advancement of nutritional composition and biological activiey of black soybean[J]. Food and Nutrition in China,2019,25(9):55−61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9577.2019.09.013 XU F, GE Y Y, LIU X C, et al. Research advancement of nutritional composition and biological activiey of black soybean[J]. Food and Nutrition in China, 2019, 25(9): 55-61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9577.2019.09.013
[40] 陈彩云, 尹淑英, 林莺, 等. 黄豆中总黄酮提取及不同豆类抗氧化活性研究[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报,2019,21(4):70−73. [CHEN C Y, YIN S Y, LIN Y, et al. Study on the extraction of total flavonoids in soybeans and the antioxidant activity of different beans[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2019,21(4):70−73. doi: 10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2019.04.019 CHEN C Y, YIN S Y, LIN Y, et al. Study on the extraction of total flavonoids in soybeans and the antioxidant activity of different beans[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2019, 21(4): 70-73. doi: 10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2019.04.019
[41] 张怡洁. 酱油的风味及其生理活性的研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工商大学, 2012 ZHANG Y J. Study on flavor and physiological activity of soy sauce[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Gongshang University, 2012.
[42] 程安玮, 吴剑夫, 秦宏伟, 等. 4种豆类中多酚、类黄酮含量及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2017,32(10):28−32. [CHENG A W, WU J F, QIN H W, et al. Content and antioxidant activity of polyphenols and flavonoids from four food beans[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oil Association,2017,32(10):28−32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2017.10.005 CHENG A W, WU J F, QIN H W, et al. Content and antioxidant activity of polyphenols and flavonoids from four food beans[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oil Association, 2017, 32(10): 28-32. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2017.10.005
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 薛淑贞,梁婷,赵祥民,张家玮,汝应俊,唐德富. 葡萄籽提取物和有机铁对蛋鸡生产性能和蛋品质的影响. 饲料工业. 2025(04): 59-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 常安其,毛帅翔,柳广斌. 葡萄残渣的饲料化利用及其在羊生产中的应用研究进展. 中国畜牧兽医. 2024(11): 4842-4850 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨辉,胡雅婕. 活性包装薄膜对冷藏圣女果的保鲜效果研究. 农业科技与装备. 2024(05): 61-64 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王建康,郭诗琼,王静,魏丽娜,冯莉,黄峻榕,Fereidoon SHAHIDI. 浆果籽油的生物活性与应用研究进展. 食品与生物技术学报. 2024(10): 32-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 赵明洪,卢天明,刘莉,王启新,杨通,林娜,邱崇,钟田雨,郭秋岩,王继刚. 甘草减轻雷公藤多苷片所致肝损伤的作用机制. 中国实验方剂学杂志. 2023(05): 24-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 尚嘉毅,初柏君,赵文君,翟孟婷,王翔宇,马欲明,孙晴,孟祥永,陈吉江,张宇. 市售牛油果油和葡萄籽油品质研究. 中国油脂. 2023(06): 119-125+152 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 盖永强,蓝天婵,李金生,朴美子,李岩. 葡萄籽果冻的工艺. 食品工业. 2022(06): 107-110 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



