Changes of Contents of Five Phenolic Acids Ingredients in Phyllanthus emblica L. during Different Harvesting Times by HPLC
-
摘要: 目的:建立同时测定不同采收期余甘子叶药材中5种酚酸类成分含量的方法,研究其变化规律,确定最佳采收期。方法:利用高效液相色谱法测定不同采收期余甘子叶药材中表没食子儿茶素、柯里拉京、诃子联苯酸、鞣花酸和诃子酸的含量并计算5种酚酸类成分的积累总量。色谱柱为Inertsil ODS-3 C18色谱柱,流动相为乙腈−0.1%磷酸水溶液,梯度洗脱,使用二极管阵列检测器全波长扫描,流速为1.0 mL·min−1,进样量为10 μL。并用SPSS 24.0软件进行主成分分析,选取了3个主成分,计算综合得分。结果:上述5种酚酸类成分线性关系良好,相关系数均大于0.998。平均加样回收率介于98.30%~101.22%,RSD为0.43%~2.66%。不同采收期余甘子叶中5种酚酸类成分含量存在一定差异。含量分别为0.2317~1.5074、1.9517~4.6593、2.5105~6.3325、2.2440~5.3386、13.5570~39.1897 mg·g−1。不同采收期5种酚酸类成分总含量变化为7月>5月>8月>6月>1月>9月>4月>2月>10月>12月>3月>11月,以7月份总含量最高,含量达到(55.158±0.83)mg/g,呈现先降后升的动态变化趋势。主成分分析结果表明综合得分最高的月份为7月。结论:建立的方法可用于同时测定不同采收期余甘子叶中5个酚酸类成分的含量。最适宜采收期为7月。Abstract: Objective: To establish the method for content determination of the five phenolic acids ingredients of Phyllanthus emblica L. in different harvest time, and to investigate its variation rules so as to determine the best harvest time. Methods: The contents of Epigallocatechin, Corilagin, Scorpion Biphenyl acid, Ellagic acid and Scorpion acid of Phyllanthus emblica L. in different harvest time were determined by HPLC, and the total amount of accumulation of the five active ingredients was calculated. The chromatographic column was Inertsil ODS-3 C18, acetonitrile−0.1% phosphoric acid aqueous solution as mobile phase for gradient elution. A diode array detector was used with full-wavelength scanning. Flow rate was 1.0 mL·min−1. Injection was 10 μL. Used SPSS 24.0 software for principal component analysis, three principal components were selected and the comprehensive score was calculated. Results: The above five ingredients had a good linear relationship, and the correlation coefficients was more than 0.998, while the average recovery rates were 98.30%~101.22% and RSD were 0.43%~2.66%. There were some differences in the contents of the five phenolic acids ingredients in the leaves of Phyllanthus emblica L. during different harvesting periods. The contents of above five ingredients were 0.2317~1.5074, 1.9517~4.6593, 2.5105~6.3325, 2.2440~5.3386, 13.5570~39.1897 mg·g−1, respectively. The change in content of the five phenolic acids ingredients in different harvest time was: July>May>August>June>January>September>April>February>October>December>March>November. The total content was the highest in July, which was (55.158±0.83) mg/g and showed a dynamic trend of decreasing first and then increasing. Principal component analysis results showed that the month with the highest comprehensive score was July. Conclusion: Established method can be used to determine the contents of the five phenolic acids ingredients of Phyllanthus emblica L. in different harvest time. July was the best harvest time for Phyllanthus emblica L.
-
余甘子是壮族习用药材,为大戟科植物余甘子Phyllanthus emblica L.的干燥成熟果实。其味甘、酸、涩、凉,归肺、胃经,具有清热凉血、消食健胃、生津止咳的功效,民间及临床上常将其用于治疗血热血瘀、消化不良、腹胀、咳嗽、喉痛、口干等[1]。据报道,余甘子果实具有多种药理特性,如抗氧化[2-3]、解热镇痛[4]、抗肿瘤[5-6]、抗炎[7]、调节脂质代谢[8]、肝保护作用[9-10]、胃保护作用[11-12]、保护缺血-再灌注诱导的氧化应激[13]、保护UVB诱导的光老化等[14]。余甘子作为重要的药食同源品种,其主要有效成分为酚类,包括酚酸类、鞣质类和黄酮类,包括没食子酸、柯里拉京、鞣花酸、诃子酸和诃子联苯酸等[15-17]。而余甘子叶作为余甘子重要的药用部位,具有免疫调节[18-19]、抗肿瘤[20]、抗炎[21]、抗氧化[22]、抗结直肠癌[23]等作用,被广泛应用于临床糖尿病、艾滋病与皮肤病等的治疗。有研究表明,余甘子叶主要含酚酸类、黄酮类、有机酸、多糖、三萜等活性成分[24-26]。
目前,有关余甘子叶的研究主要在化学成分的提取分离和生物活性研究等方面,对其最佳采收期的研究还未见报道,而酚酸类成分是余甘子叶的主要活性成分之一,活性成分的含量随着自然环境的改变而改变,比如气候、土壤和水分等。采收期不同,药材的成分含量也会有所差异。余甘子叶的质量控制方法目前主要有HPLC测定余甘子叶中槲皮素、山奈酚的含量[27-28],分光光度法测定总黄酮含量[29],但同时测定酚酸类成分如表没食子儿茶素、柯里拉京、诃子联苯酸、鞣花酸和诃子酸等的含量却未见报道。在本课题组前期的研究中,已通过HPLC建立余甘子叶指纹图谱,并指认了表没食子儿茶素、柯里拉京、诃子联苯酸、鞣花酸和诃子酸5种酚酸类成分。因此,在课题组前期研究基础上,本研究建立了HPLC同时测定余甘子叶5种酚酸类成分含量的方法,并结合主成分分析方法分析其含量变化,以确定余甘子叶的最佳采收期,为深入研究开发利用余甘子叶提供有效依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
余甘子叶 采集于广西贵港市平南种植基地,经广西医科大学中药教研室韦妍妍老师鉴定为大戟科叶下珠属植物余甘子Phyllanthus emblica L.的新鲜叶,样品采摘后经低温鼓风干燥,粉碎,过40目筛,避光密封保存,样品信息见表1。
表 1 样品信息Table 1. Information of samples批号 产地 采集时间 S1 广西贵港市平南县 2020年1月 S2 广西贵港市平南县 2020年2月 S3 广西贵港市平南县 2020年3月 S4 广西贵港市平南县 2020年4月 S5 广西贵港市平南县 2020年5月 S6 广西贵港市平南县 2020年6月 S7 广西贵港市平南县 2020年7月 S8 广西贵港市平南县 2020年8月 S9 广西贵港市平南县 2020年9月 S10 广西贵港市平南县 2020年10月 S11 广西贵港市平南县 2020年11月 S12 广西贵港市平南县 2020年12月 表没食子儿茶素(HPLC≥98%) 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;柯里拉京(HPLC>98%)、鞣花酸(HPLC≥98%) 成都瑞芬思生物科技有限公司;诃子联苯酸(HPLC 98%)、诃子酸(HPLC 98%) 成都普瑞法科技开发有限公司;甲醇、乙腈 色谱纯,赛默飞世尔科技有限公司。
LC-20A岛津高效液相色谱仪 日本岛津公司;KQ-500DB数控超声波清洗器 昆山市超声仪器有限公司;SHB-III循环水式多用真空泵 郑州长城科工贸有限公司;CD-UPH-II-20L超纯水器 成都优越科技有限公司;XT-YM-6001粉碎机 永康市共庆工贸有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 供试品溶液的制备
参照文献[30]优化得到供试品溶液的制备方法:将余甘子叶粉碎,过40目筛,于阴凉处密封保存备用。取余甘子叶粉末约0.5 g置于50 mL具塞锥形瓶内,精密称定,精密加入30%甲醇20 mL,称定重量,超声(500 W,60 kHz)30 min,静置冷却,称定重量,用30%甲醇补足减失重量,摇匀,0.22 μm微孔滤膜滤过至1.5 mL进样瓶,即得供试品溶液。
1.2.2 混合对照品溶液的制备
分别称取表没食子儿茶素、柯里拉京、诃子联苯酸、鞣花酸和诃子酸对照品适量,精密称定,甲醇溶解、定容,配制成浓度分别为551.0、622.5、715.0、520.0、508.0 μg·mL−1的混合对照品溶液。
1.2.3 色谱条件
参照冀静等[31]的方法。采用Inertsil ODS-3 C18色谱柱(5 μm,4.6×250 mm),流动相为乙腈(A)-0.1%磷酸水溶液(B),梯度洗脱,0~10 min,5%~10% A;10~20 min,10%~13% A;20~30 min,13%~17% A;30~40 min,17%~20% A;40~45 min,20%~25% A;45~65 min,25%~85% A;65~80 min,85%~5% A;80~95 min,5% A。二极管阵列全波长扫描,254 nm,流速:1.0 mL·min−1,进样量:10 μL。
1.2.4 系统适应性考察
取“1.2.1”和“1.2.2”项下供试品溶液、混合对照品溶液适量,按“1.2.3”项下色谱条件进样测定,记录色谱图。
1.2.5 线性关系考察
分别精密吸取混合对照品溶液0.4、0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0 mL置于10 mL容量瓶中,用甲醇定容稀释成系列浓度溶液,按“1.2.3”项下色谱条件进样分析,记录峰面积。
1.2.6 精密度试验
取编号为S4的余甘子叶1份,按“1.2.1”项下制备供试品溶液,按“1.2.3”项下色谱条件连续进样6次,记录峰面积。
1.2.7 稳定性试验
取编号为S4的余甘子叶1份,按“1.2.1”项下制备供试品溶液,按“1.2.3”项下色谱条件分别于0、2、4、8、12、24 h进样分析,记录峰面积。
1.2.8 重复性试验
取编号为S4的余甘子叶6份,按“1.2.1”项下制备供试品溶液,按“1.2.3”项下色谱条件进样分析,记录峰面积。
1.2.9 加样回收率试验
精密称取已知含量的编号为S4的余甘子叶6份,每份0.25 g,置具塞锥形瓶中,精密加入含量相当的混合对照品溶液,按“1.2.1”项下方法制备供试品溶液,按“1.2.3”项下色谱条件测定,记录色谱峰峰面积,计算回收率。
1.2.10 样品含量测定
定量方法采用外标法中的工作曲线法。分别取不同采集时间的余甘子叶按“1.2.1”项下制备供试品溶液,按“1.2.3”项下色谱条件进样分析,计算含量,每个样品取两份,每份平行测定两次,取平均值。
1.3 数据处理
本文采用SPSS 24.0、Microsoft Excel 2010、Origin2018软件处理数据及绘制图表,含量测定中每个样品取两份,每份平行测定两次,数据表现形式为“平均值±标准差”。
2. 结果与分析
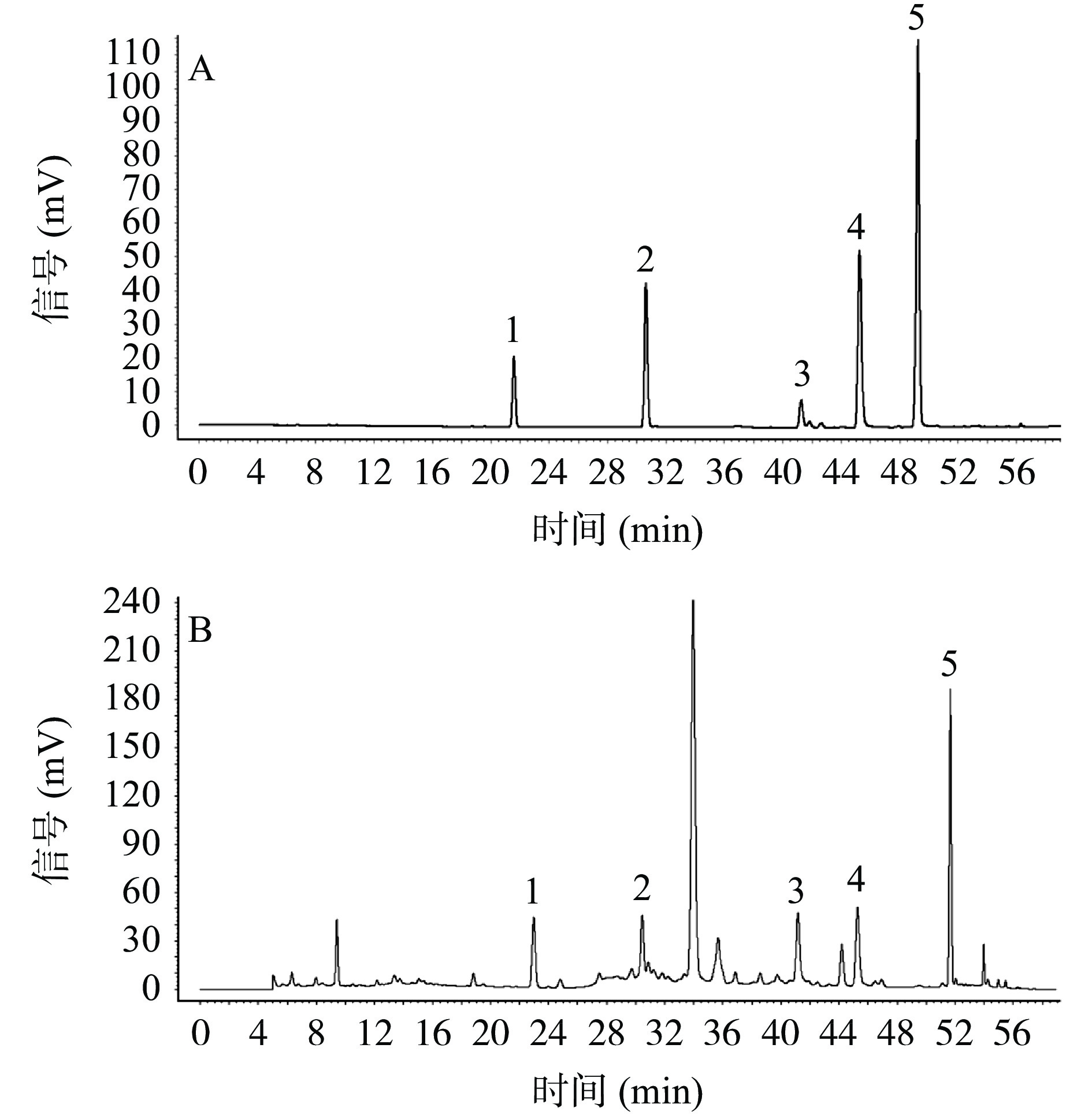
2.1 系统适应性考察结果
结果见图1。各成分理论板数不低于3000,分离度均大于1.5。
2.2 线性关系考察结果
以浓度(μg·mL−1)为横坐标(X),峰面积为纵坐标(Y),进行线性回归分析,得标准曲线方程,见表2。5个成分在相应的浓度范围内与峰面积的线性关系良好。
表 2 余甘子叶中5种成分标准曲线Table 2. Calibration curves of five constituents of Phyllanthus emblica L.成分 回归方程 线性范围(μg·mL−1) r 表没食子儿茶素 y=108x−511857 22.040~110.200 0.9992 柯里拉京 y=4×107x−530043 24.900~124.500 0.9989 诃子联苯酸 y=6×107x−2×106 28.600~143.000 0.9991 鞣花酸 y=2×107x−359549 20.800~104.000 0.9991 诃子酸 y=6×106x−92236 20.32~101.600 0.9993 2.3 精密度试验结果
计算得到表没食子儿茶素、柯里拉京、诃子联苯酸、鞣花酸、诃子酸峰面积的RSD分别为1.02%、1.09%、1.88%、0.83%、1.44%,表明仪器精密度良好。
2.4 稳定性试验结果
计算得到表没食子儿茶素、柯里拉京、诃子联苯酸、鞣花酸、诃子酸峰面积的RSD分别为1.91%、1.01%、2.27%、1.15%、1.49%,表明供试品溶液在24 h内稳定性良好。
2.5 重复性试验结果
计算得到表没食子儿茶素、柯里拉京、诃子联苯酸、鞣花酸、诃子酸的平均含量分别为1.51、1.93、2.49、2.54、49.80 mg·g−1,RSD分别为1.98%、2.05%、1.09%、0.63%、1.14%(n=6),表明该方法重复性良好。
2.6 加样回收率试验结果
通过计算得出表没食子儿茶素、柯里拉京、诃子联苯酸、鞣花酸、诃子酸的平均加样回收率分别为98.30%、101.22%、99.59%、98.73%、99.76%,RSD分别为2.66%、1.61%、0.43%、1.59%、0.60%,见表3。
表 3 余甘子叶加样回收率试验结果(n=6)Table 3. Results of recovery tests of Phyllanthus emblica L. (n=6)待测成分 取样量(g) 已知含量(mg) 加入量(mg) 测得量(mg) 加样回收率(%) 平均加样回收率(%) RSD(%) 表没食子儿茶素 0.2503 0.7537 0.7541 1.5074 99.95 98.30 2.66 0.2506 0.7534 0.7541 1.4981 98.75 0.2504 0.7530 0.7541 1.4572 93.38 0.2507 0.7531 0.7541 1.4884 97.51 0.2509 0.7533 0.7541 1.5093 100.25 0.2501 0.7534 0.7541 1.5072 99.96 柯里拉京 0.2503 0.9759 0.9763 1.9508 99.86 101.22 1.61 0.2506 0.9750 0.9763 1.9716 102.08 0.2504 0.9749 0.9763 1.9529 100.17 0.2507 0.9755 0.9763 1.9918 104.10 0.2509 0.9753 0.9763 1.9526 100.10 0.2501 0.9755 0.9763 1.9618 101.02 诃子联苯酸 0.2503 1.2553 1.2552 2.5103 99.98 99.59 0.43 0.2506 1.2551 1.2552 2.5004 99.21 0.2504 1.2553 1.2552 2.5102 99.98 0.2507 1.2554 1.2552 2.5003 99.18 0.2509 1.2556 1.2552 2.5104 99.97 0.2501 1.2550 1.2552 2.5003 99.21 鞣花酸 0.2503 1.2646 1.2644 2.5091 98.43 98.73 1.59 0.2506 1.2641 1.2644 2.5090 98.46 0.2504 1.2642 1.2644 2.4893 96.89 0.2507 1.2641 1.2644 2.5098 98.52 0.2509 1.2644 1.2644 2.5091 98.44 0.2501 1.2642 1.2644 2.5496 101.66 诃子酸 0.2503 25.0499 25.0498 50.0895 99.96 99.76 0.60 0.2506 25.0498 25.0498 50.0947 99.98 0.2504 25.0497 25.0498 50.1995 100.40 0.2507 25.0490 25.0498 50.0983 100.00 0.2509 25.0493 25.0498 49.7689 98.68 0.2501 25.0495 25.0498 49.9803 99.52 2.7 样品含量测定结果
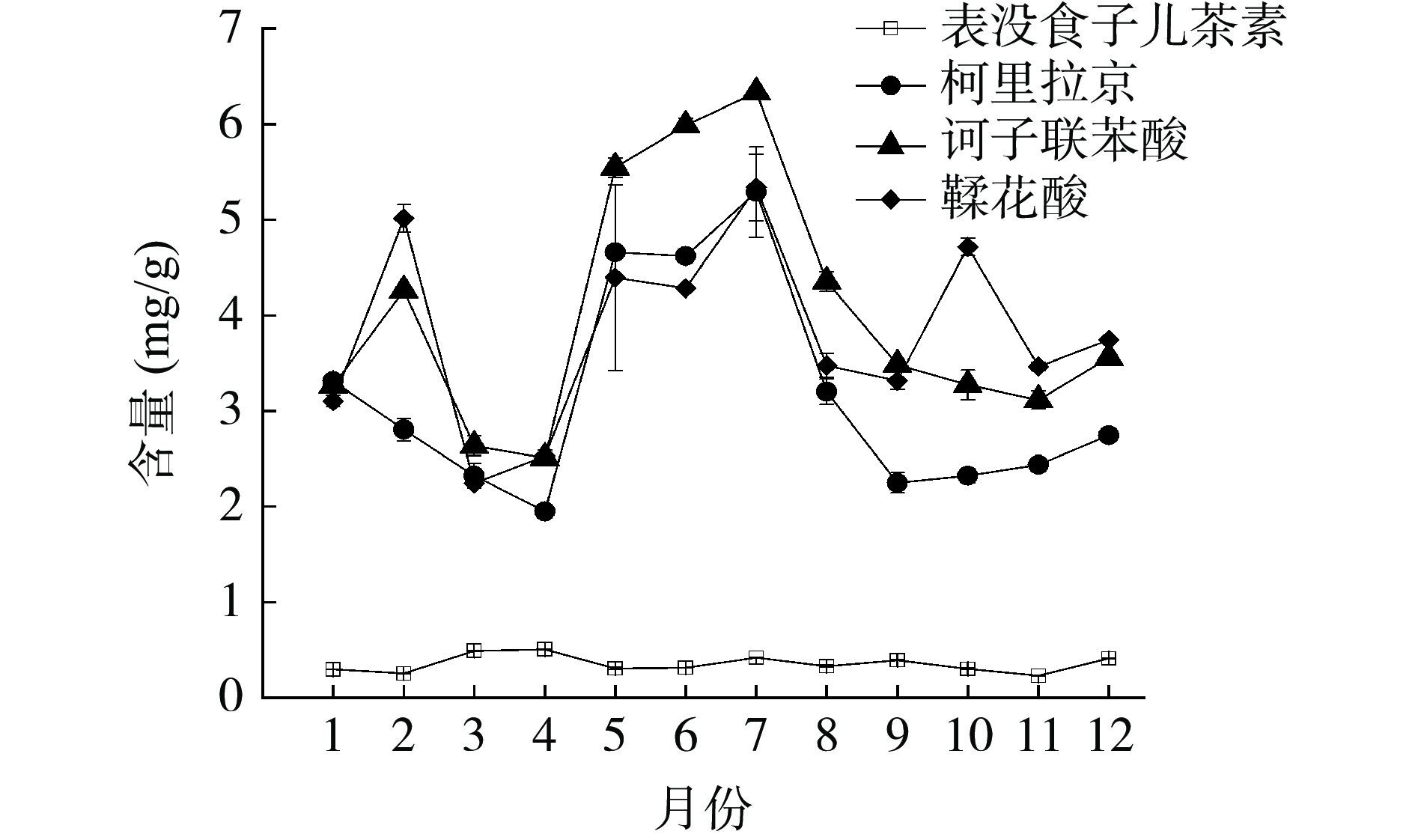
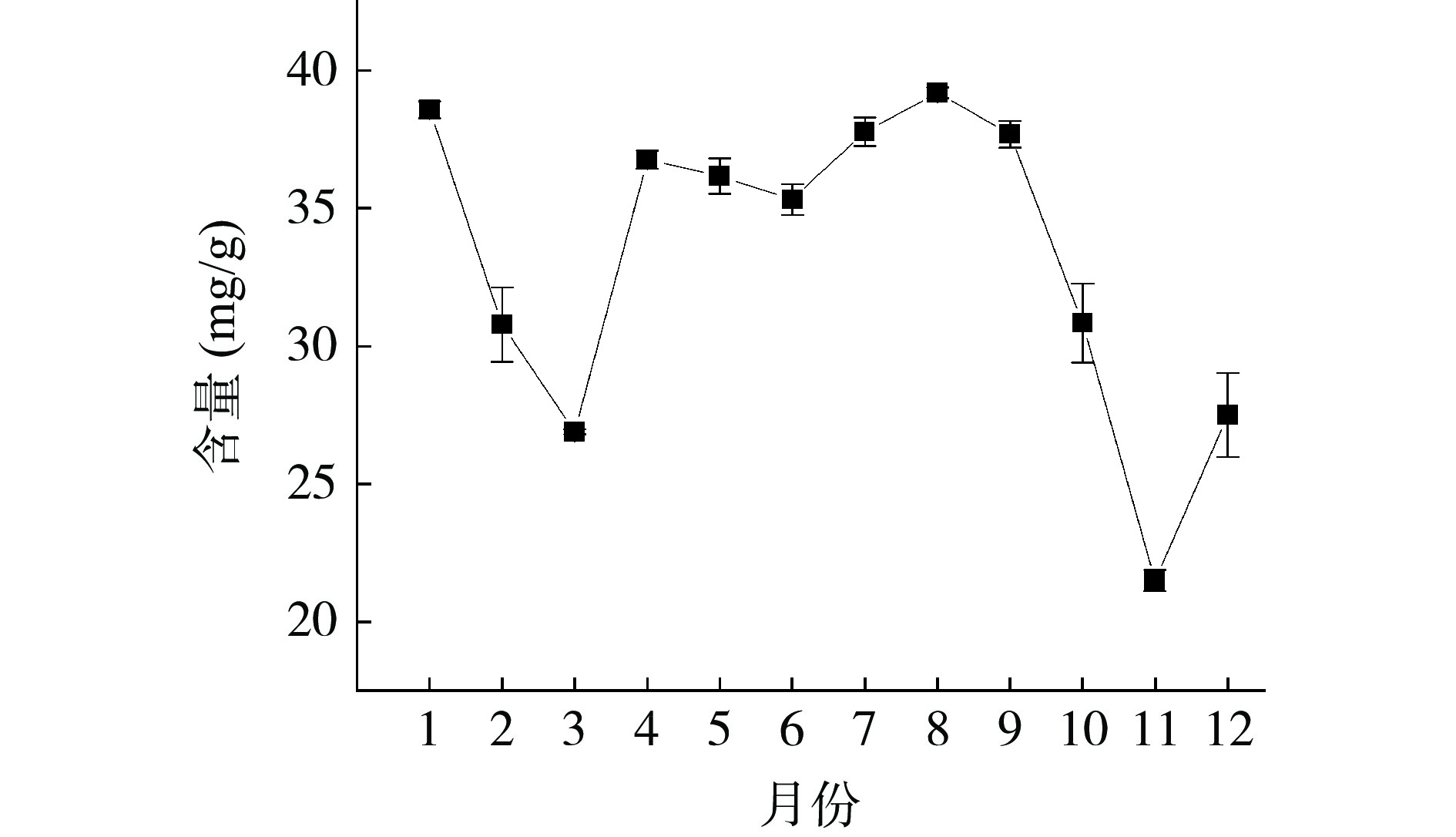
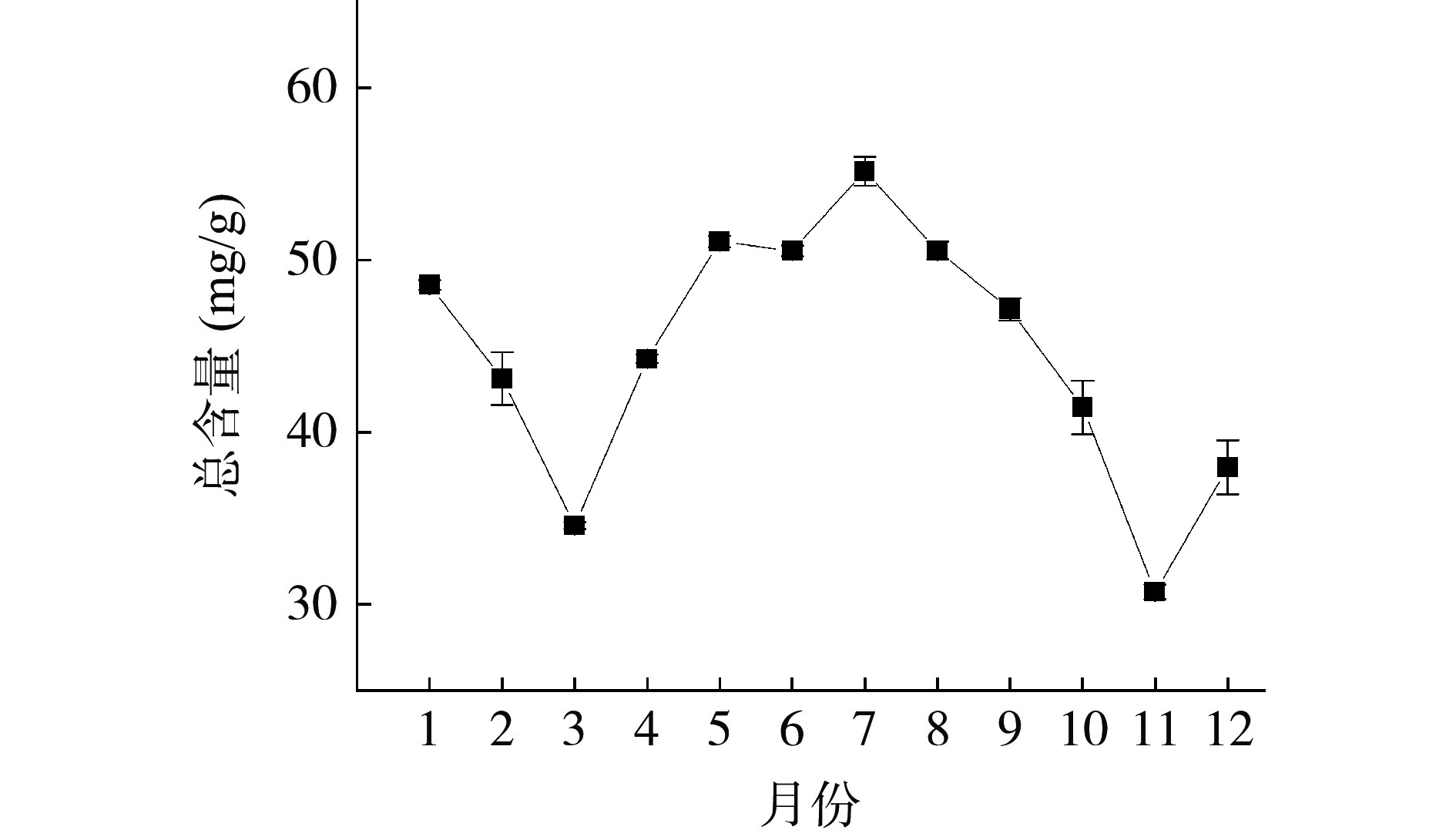
不同采收时期的余甘子叶中5种有效成分的含量动态变化见图2、图3与图4。对5种酚酸类成分各个月份的含量进行非参数检验中的Friedman检验,结果显示不同采收期的5种酚酸类成分含量均存在显著性差异(P<0.05),具有统计学意义,表明采收期不同,各成分含量存在差异。如图2和图3所示,不同采收期余甘子叶中5种酚酸类成分的含量呈动态变化。在整年中,表没食子儿茶素含量变化不大,基本趋于平稳,在4月、3月和7月含量达到高峰,11月最低。柯里拉京含量波动大,在7月达到最高,4月最低。诃子联苯酸含量也随采收期不同而有较大的起伏,在5月、6月和7月持续上升,并在7月到达顶峰。鞣花酸和诃子酸含量与柯里拉京、诃子联苯酸含量变化趋于一致,总体来说,随着采收期的延长,各成分含量基本呈现一个下降、上升、下降的变化,并且在夏季达到最大值。由图4所示,7月5种酚酸类成分总含量最高,为(55.158±0.83)mg/g,5月5种酚酸类成分总含量次之,为(51.077±0.33)mg/g,11月5种酚酸类成分总含量最低,为(30.740±0.43)mg/g。因此,余甘子叶可能受不同生长期的气候、水分和温度等因素的影响,其酚酸类成分含量的积累可能产生一定程度的差异。
2.8 主成分分析
由于不同采收期余甘子叶中5种酚酸类成分的含量差异较大,因此采用SPSS 24.0软件对各成分含量进行分析,将数据标准化处理后得到各原始变量的标准分:Z表没食子儿茶素、Z柯里拉京、Z诃子联苯酸、Z鞣花酸、Z诃子酸,然后进行降维因子分析,提取3个因子数,结果见表4,特征根λ1=2.939,特征根λ2=1.006,特征根λ3=0.704,前3个主成分的累积方差贡献率为92.976%,提示这3个主成分可以反映余甘子叶药材的全部信息,因此提取前3个主成分,分别记作F1、F2、F3。由表5成分得分系数矩阵可知,柯里拉京、诃子联苯酸和鞣花酸在第1主成分有较高载荷,表没食子儿茶素、柯里拉京和诃子酸在第2主成分有较高载荷,表没食子儿茶素、柯里拉京和诃子联苯酸在第3主成分有较高载荷。并且得到3个因子得分,分别记作FAC1_1、FAC2_1、FAC3_1。主成分的得分是相应的因子得分乘以相应的方差的算术平方根,即F1=FAC1_1×2.939的算术平方根,F2=FAC2_1×1.006的算术平方根,F3=FAC3_1×0.704的算术平方根,再以各主成分的贡献率对主成分得分进行加权平均,即综合得分=(58.779×F1+20.127×F2+14.071×F3)/92.976,求得主成分综合得分,结果见表6。由表6可知,综合得分最高的月份为7月,其次是6月。说明余甘子叶适合在7月采摘,此时酚酸类有效成分累积可能达到高峰。
表 4 不同采收期余甘子叶主成分分析结果Table 4. Analysis result of principal component of Phyllanthus emblica L. in different harvest periods成分 初始特征值 提取载荷平方和 总计 方差百分比 累积(%) 总计 方差百分比 累积(%) 1 2.939 58.779 58.779 2.939 58.779 58.779 2 1.006 20.127 78.906 1.006 20.127 78.906 3 0.704 14.071 92.976 0.704 14.071 92.976 4 0.314 6.289 99.265 5 0.037 0.735 100.000 表 5 不同采收期余甘子叶成分得分系数矩阵Table 5. Component score coefficient matrix of Phyllanthus emblica L. in different harvest periods成分 成分1 成分2 成分3 表没食子儿茶素 −0.151 0.831 0.330 柯里拉京 0.303 0.252 0.370 诃子联苯酸 0.322 0.171 0.305 鞣花酸 0.288 −0.275 0.149 诃子酸 0.198 0.368 −1.030 表 6 不同采收期余甘子叶药材主成分因子得分Table 6. Principal component factor scores of cotyledons of Phyllanthus emblica L. in different harvest periods采收期 FAC1_1 FAC2_1 FAC3_1 F1 F2 F3 综合得分 排序 1月 −0.0965 −0.1108 −1.2927 −0.1655 −0.1111 −1.0847 −0.2928 6 2月 0.4601 −1.4049 −0.0756 0.7888 −1.4091 −0.0634 0.1840 4 3月 −1.7355 0.4689 2.0786 −2.9752 0.4703 1.7440 −1.5152 12 4月 −1.2300 1.5178 −1.0001 −2.1086 1.5223 −0.8392 −1.1305 11 5月 1.1485 0.1173 0.2495 1.9689 0.1176 0.2093 1.3019 3 6月 1.1862 0.2021 0.4505 2.0336 0.2027 0.3780 1.3867 2 7月 1.6468 1.2298 1.0025 2.8231 1.2335 0.8412 2.1791 1 8月 0.2132 0.2473 −0.9695 0.3656 0.2480 −0.8135 0.1617 5 9月 −0.4574 0.4817 −1.0873 −0.7841 0.4831 −0.9123 −0.5292 9 10月 −0.0900 −1.0962 −0.3398 −0.1543 −1.0994 −0.2851 −0.3787 7 11月 −0.5825 −1.8420 0.4206 −0.9987 −1.8475 0.3529 −0.9779 10 12月 −0.4629 0.1890 0.5634 −0.7935 0.1895 0.4727 −0.3891 8 3. 讨论与结论
中药材成分复杂,往往是多种有效成分共同发挥作用,因此测定多种有效成分的含量来评价中药材的质量,而含量跟采收期有一定的联系[32]。余甘子树主要分布于我国的广西、广东、福建、贵州、云南等地,余甘子叶作为余甘子树新的研究部位,具有较高的食用和药用价值,酚酸类成分是余甘子叶中的主要活性成分,其中的表没食子儿茶素具有抗氧化、抗癌等作用[33-34];柯里拉京具有抗肿瘤、抗氧化、降血压、抗菌、抗炎等活性,具有很大的药用价值[35];诃子联苯酸具有较好的抗氧化、抗肿瘤、抗病毒、抗菌、抗脂质过氧化等药理作用,是许多常用中药的药效物质基础[36];鞣花酸具有天然抗氧化、清除体内自由基、保护低氧缺血所致的脑损伤等作用[37];诃子酸可显著缓解肾脏纤维化水平、改善肾脏功能[38]。因此,开展余甘子叶的研究对于开发利用新的药用资源具有重要的意义。
本研究对广西贵港市平南种植基地不同采收期的12批余甘子叶样品中的5种酚酸类有效成分进行含量测定,由图2、图3可看出,柯里拉京、诃子联苯酸和鞣花酸的含量随不同采收月份的变化趋势基本一致,在7月达到最高值,随后开始下降,含量最低值都在4月,这提示在余甘子叶中这3种酚酸类成分的代谢过程可能具有相关性,需要进一步深入研究;诃子酸全年各月份的含量均远远高于其他酚酸类成分,在11月达到最低值,在8月达到最高值;而表没食子儿茶素不同月份含量却远远低于其他成分,且含量在2月至4月呈上升趋势并在4月达到最高值,这时其他成分含量反而下降,这与其他成分含量变化趋势不同,其中的原因尚不明确,还需进一步探讨。由图4可知,不同采收期的余甘子叶中5种酚酸成分总含量变化为7月>5月>8月>6月>1月>9月>4月>2月>10月>12月>3月>11月,含量总和在7月达到最大值,在11月达到最小值。主成分分析的结果显示综合得分最高的月份为7月,说明此时酚酸类有效成分累积可能达到高峰,可能是因为7月正处于广西的夏季高温天气,伴随着强日照和强降水,酚酸类物质含量上升。范青等[39]研究表明红树莓叶片生长代谢过程中酚酸类物质在5~7月份含量最高。刘娟秀等[40]研究表明不同采收期苍耳草中总酚酸量在7月中旬较高,本研究结果与这二者的结果具有一致性。
综合考虑,7月份采摘余甘子叶其酚酸类成分含量最高,药用价值较高,因此以7月份为余甘子叶的最佳采收期。本研究建立了同时测定余甘子叶5种酚酸类成分含量的方法,为余甘子叶药材的最佳采收期及合理开发利用提供了实验依据,但在植物生长代谢过程中其酚酸类成分之间的相关性仍需进一步研究和完善。
-
表 1 样品信息
Table 1 Information of samples
批号 产地 采集时间 S1 广西贵港市平南县 2020年1月 S2 广西贵港市平南县 2020年2月 S3 广西贵港市平南县 2020年3月 S4 广西贵港市平南县 2020年4月 S5 广西贵港市平南县 2020年5月 S6 广西贵港市平南县 2020年6月 S7 广西贵港市平南县 2020年7月 S8 广西贵港市平南县 2020年8月 S9 广西贵港市平南县 2020年9月 S10 广西贵港市平南县 2020年10月 S11 广西贵港市平南县 2020年11月 S12 广西贵港市平南县 2020年12月 表 2 余甘子叶中5种成分标准曲线
Table 2 Calibration curves of five constituents of Phyllanthus emblica L.
成分 回归方程 线性范围(μg·mL−1) r 表没食子儿茶素 y=108x−511857 22.040~110.200 0.9992 柯里拉京 y=4×107x−530043 24.900~124.500 0.9989 诃子联苯酸 y=6×107x−2×106 28.600~143.000 0.9991 鞣花酸 y=2×107x−359549 20.800~104.000 0.9991 诃子酸 y=6×106x−92236 20.32~101.600 0.9993 表 3 余甘子叶加样回收率试验结果(n=6)
Table 3 Results of recovery tests of Phyllanthus emblica L. (n=6)
待测成分 取样量(g) 已知含量(mg) 加入量(mg) 测得量(mg) 加样回收率(%) 平均加样回收率(%) RSD(%) 表没食子儿茶素 0.2503 0.7537 0.7541 1.5074 99.95 98.30 2.66 0.2506 0.7534 0.7541 1.4981 98.75 0.2504 0.7530 0.7541 1.4572 93.38 0.2507 0.7531 0.7541 1.4884 97.51 0.2509 0.7533 0.7541 1.5093 100.25 0.2501 0.7534 0.7541 1.5072 99.96 柯里拉京 0.2503 0.9759 0.9763 1.9508 99.86 101.22 1.61 0.2506 0.9750 0.9763 1.9716 102.08 0.2504 0.9749 0.9763 1.9529 100.17 0.2507 0.9755 0.9763 1.9918 104.10 0.2509 0.9753 0.9763 1.9526 100.10 0.2501 0.9755 0.9763 1.9618 101.02 诃子联苯酸 0.2503 1.2553 1.2552 2.5103 99.98 99.59 0.43 0.2506 1.2551 1.2552 2.5004 99.21 0.2504 1.2553 1.2552 2.5102 99.98 0.2507 1.2554 1.2552 2.5003 99.18 0.2509 1.2556 1.2552 2.5104 99.97 0.2501 1.2550 1.2552 2.5003 99.21 鞣花酸 0.2503 1.2646 1.2644 2.5091 98.43 98.73 1.59 0.2506 1.2641 1.2644 2.5090 98.46 0.2504 1.2642 1.2644 2.4893 96.89 0.2507 1.2641 1.2644 2.5098 98.52 0.2509 1.2644 1.2644 2.5091 98.44 0.2501 1.2642 1.2644 2.5496 101.66 诃子酸 0.2503 25.0499 25.0498 50.0895 99.96 99.76 0.60 0.2506 25.0498 25.0498 50.0947 99.98 0.2504 25.0497 25.0498 50.1995 100.40 0.2507 25.0490 25.0498 50.0983 100.00 0.2509 25.0493 25.0498 49.7689 98.68 0.2501 25.0495 25.0498 49.9803 99.52 表 4 不同采收期余甘子叶主成分分析结果
Table 4 Analysis result of principal component of Phyllanthus emblica L. in different harvest periods
成分 初始特征值 提取载荷平方和 总计 方差百分比 累积(%) 总计 方差百分比 累积(%) 1 2.939 58.779 58.779 2.939 58.779 58.779 2 1.006 20.127 78.906 1.006 20.127 78.906 3 0.704 14.071 92.976 0.704 14.071 92.976 4 0.314 6.289 99.265 5 0.037 0.735 100.000 表 5 不同采收期余甘子叶成分得分系数矩阵
Table 5 Component score coefficient matrix of Phyllanthus emblica L. in different harvest periods
成分 成分1 成分2 成分3 表没食子儿茶素 −0.151 0.831 0.330 柯里拉京 0.303 0.252 0.370 诃子联苯酸 0.322 0.171 0.305 鞣花酸 0.288 −0.275 0.149 诃子酸 0.198 0.368 −1.030 表 6 不同采收期余甘子叶药材主成分因子得分
Table 6 Principal component factor scores of cotyledons of Phyllanthus emblica L. in different harvest periods
采收期 FAC1_1 FAC2_1 FAC3_1 F1 F2 F3 综合得分 排序 1月 −0.0965 −0.1108 −1.2927 −0.1655 −0.1111 −1.0847 −0.2928 6 2月 0.4601 −1.4049 −0.0756 0.7888 −1.4091 −0.0634 0.1840 4 3月 −1.7355 0.4689 2.0786 −2.9752 0.4703 1.7440 −1.5152 12 4月 −1.2300 1.5178 −1.0001 −2.1086 1.5223 −0.8392 −1.1305 11 5月 1.1485 0.1173 0.2495 1.9689 0.1176 0.2093 1.3019 3 6月 1.1862 0.2021 0.4505 2.0336 0.2027 0.3780 1.3867 2 7月 1.6468 1.2298 1.0025 2.8231 1.2335 0.8412 2.1791 1 8月 0.2132 0.2473 −0.9695 0.3656 0.2480 −0.8135 0.1617 5 9月 −0.4574 0.4817 −1.0873 −0.7841 0.4831 −0.9123 −0.5292 9 10月 −0.0900 −1.0962 −0.3398 −0.1543 −1.0994 −0.2851 −0.3787 7 11月 −0.5825 −1.8420 0.4206 −0.9987 −1.8475 0.3529 −0.9779 10 12月 −0.4629 0.1890 0.5634 −0.7935 0.1895 0.4727 −0.3891 8 -
[1] 国家药典委员会. 中国药典(一部)[M]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020: 186 National Pharmacopoeia Commission. Chinese Pharmacopoeia (Part 1)[M]. Beijing: China Medical Science Press, 2020: 186.
[2] CHAPHALKAR R, APTE K G, TALEKAR Y, et al. Antioxidants of Phyllanthus emblica L. bark extract provide hepatoprotection against ethanol-induced hepatic damage: A comparison with silymarin[J]. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity,2017,2017:3876040.
[3] LI Y, CHEN J, CAO L, et al. Characterization of a novel polysaccharide isolated from Phyllanthus emblica L. and analysis of its antioxidant activities[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2018,55(7):2758−2764. doi: 10.1007/s13197-018-3199-6
[4] PERIANAYAGAM J B, SHARMA S K, JOSEPH A, et al. Evaluation of anti-pyretic and analgesic activity of Emblica officinalis Gaertn[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2004,95(1):83−85. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2004.06.020
[5] RAJESHKUMAR N V, PILLAI M R, KUTTAN R. Induction of apoptosis in mouse and human carcinoma cell lines by Emblica officinalis polyphenols and its effect on chemical carcinogenesis[J]. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research: CR,2003,22(2):201−212.
[6] SULTANA S, AHMED S, JAHANGIR T. Emblica officinalis and hepatocarcinogenesis: A chemopreventive study in wistar rats[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2008,118(1):1−6. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2007.04.021
[7] MUTHURAMAN A, SOOD S, SINGLA S K. The antiinflammatory potential of phenolic compounds from Emblica officinalis L. in rat[J]. Inflammopharmacology,2011,19(6):327−334. doi: 10.1007/s10787-010-0041-9
[8] BALUSAMY S R, VEERAPPAN K, RANJAN A, et al. Phyllanthus emblica fruit extract attenuates lipid metabolism in 3T3-L1 adipocytes via activating apoptosis mediated cell death[J]. Phytomedicine:International Journal of Phytotherapy and Phytopharmacology,2020,66:153129. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2019.153129
[9] ACHLIYA G S, WADODKAR S G, DORLE A K. Evaluation of hepatoprotective effect of Amalkadi ghrita against carbon tetrachloride-induced hepatic damage in rats[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2004,90(2-3):229−232. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2003.09.037
[10] PRAMYOTHIN P, SAMOSORN P, POUNGSHOMPOO S, et al. The protective effects of Phyllanthus emblica Linn. extract on ethanol induced rat hepatic injury[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2006,107(3):361−364. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2006.03.035
[11] AL-REHAILY A J, AL-HOWIRINY T A, AL-SOHAIBANI M O, et al. Gastroprotective effects of 'Amla' Emblica officinalis on in vivo test models in rats[J]. Phytomedicine:International Journal of Phytotherapy and Phytopharmacology,2002,9(6):515−522. doi: 10.1078/09447110260573146
[12] CHATTERJEE A, CHATTERJEE S, BISWAS A, et al. Gallic acid enriched fraction of Phyllanthus emblica potentiates indomethacin-induced gastric ulcer healing via e-NOS-Dependent Pathway[J]. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine: eCAM,2012,2012:487380.
[13] BHATTACHARYA S K, BHATTACHARYA A, SAIRAM K, et al. Effect of bioactive tannoid principles of Emblica officinalis on ischemia-reperfusion-induced oxidative stress in rat heart[J]. Phytomedicine:International Journal of Phytotherapy and Phytopharmacology,2002,9(2):171−174. doi: 10.1078/0944-7113-00090
[14] ADILM D, KAISER P, SATTI N K, et al. Effect of Emblica officinalis (fruit) against UVB-induced photo-aging in human skin fibroblasts[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2010,132(1):109−114. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.07.047
[15] 孟达, 张雅琼, 秦定梅, 等. 余甘子的酚类成分及药理活性研究进展[J]. 中成药,2022,44(10):3269−3274. [MENG D, ZHANG Y Q, QIN D M, et al. Research progress on phenolic composition and pharmacological activity of Phyllanthus emblica L J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2022,44(10):3269−3274.
[16] 孟令志, 王佳慧, 王甄洁, 等. 余甘子多酚纯化工艺研究及组分分析[J]. 食品研究与开发,2022,43(21):147−153. [MENG L Z, WANG J H, WANG Z J, et al. Purification technology and component analysis of polyphenols from Phyllanthus emblica L doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2022.21.019 J]. Food Research and Development,2022,43(21):147−153. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2022.21.019
[17] 管芹, 冯丹萍, 段宝忠, 等. 余甘子化学成分、药理作用研究进展及质量标志物预测分析[J/OL]. 中草药: 1−14. http: //kns. cnki. net/kcms/detail/ 12.1108. R. 20220621.0902. 002. html. [GUAN Q, FENG D P, DUAN B Z, et al. Advances in research on chemical constituents and pharmacological effects of Phyllanthi fructus and prediction and analysis of quality markers[J/OL]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 1−14. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/ 12.1108.R. 20220621. 0902. 002.html. [18] 黄燕, 罗雪菲, 李舒, 等. 余甘子叶提取物对荷瘤小鼠抑瘤及免疫功能影响的研究[J]. 时珍国医国药,2011,22(9):2204−2206. [HUANG Y, LUO X F, LI S, et al. Study on the effect of Phyllanthus emblica cotyledon extract on tumor inhibition and immune function in tumor-bearing mice[J]. LIshizhen Medicine and Materia Medical Research,2011,22(9):2204−2206. HUANG Y, LUO X F, LI S, et al. Study on the effect of Phyllanthus emblica cotyledon extract on tumor inhibition and immune function in tumor-bearing mice[J]. LIshizhen Medicine and Materia Medical Research, 2011, 22(9): 2204-2206.
[19] 钟振国, 罗雪菲, 黄金兰, 等. 余甘子叶提取物对小鼠免疫功能的影响研究[J]. 中药材,2013,36(3):441−444. [ZHONG Z G, LUO X F, HUANG J L, et al. Study on the effect of extracts from the leaves of Phyllanthus emblica on immune function of mice[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2013,36(3):441−444. ZHONG Z G, LUO X F, HUANG J L, et al. Study on the effect of extracts from the leaves of Phyllanthus emblica on immune function of mice[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2013, 36(3): 441-444.
[20] ZHONG Z G, WU D P, HUANG J L, et al. Progallin a isolated from the acetic ether part of the leaves of Phyllanthus emblica L. induces apoptosis of human hepatocellular carcinoma BEL-7404 cells by up-regulation of bax expression and down-regulation of Bcl-2 expression[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2011,133(2):765−772. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.11.001
[21] IHANTOLA-VORMISTO A, SUMMANEN J, KANKAANRANTA H, et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of extracts from leaves of Phyllanthus emblica[J]. Planta Medica,1997,63(6):518−524. doi: 10.1055/s-2006-957754
[22] 杜丽娟, 苏秀芳, 黄成银. 余甘子叶总黄酮的超声波法提取工艺优化及其抗氧化能力研究[J]. 食品与机械,2020,36(3):185−189,193. [DU L J, SU X F, HUANG C Y. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of total flavonoids from leaves of Phyllanthus emblica and its antioxidant capacit[J]. Food & Machinery,2020,36(3):185−189,193. DU L J, SU X F, HUANG C Y. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of total flavonoids from leaves of Phyllanthus emblica and its antioxidant capacit[J]. Food&Machinery, 2020, 36(3): 185-189, 193.
[23] 黄燕, 邹天骏, 罗雪菲, 等. 基于网络药理学探讨余甘子叶总黄酮抗结直肠癌的分子机制及活性成分[J]. 中国中医药信息杂志,2020:1−5. [HUANG Y, ZHOU T J, LUO X F, et al. Molecular mechanism and active ingredients of total flavonoids from Phyllanthus emblica leaves against colorectal cancer based on network pharmacology[J]. Chinese Journal of Information on TCM,2020:1−5. HUANG Y, ZHOU T J, LUO X F, et al. Molecular mechanism and active ingredients of total flavonoids from Phyllanthus emblica leaves against colorectal cancer based on network pharmacology[J]. Chinese Journal of Information on TCM, 2020, 1-5.
[24] 杨鑫, 梁锐君, 洪爱华, 等. 野生余甘子树皮的化学成分研究[J]. 中草药,2014,45(2):170−174. [YANG X, LIANG R J, HONG A H, et al. Chemical constituents in barks of wild Phyllanthus emblica[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2014,45(2):170−174. YANG X, LIANG R J, HONG A H, et al. Chemical constituents in barks of wild Phyllanthus emblica[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2014, 45(2): 170-174.
[25] 程子贤, 郭思琪, 姜浩, 等. 余甘子种质资源及余甘子叶生物活性研究进展[J]. 农产品加工,2022(13):86−90,96. [CHENG Z X, GUO S Q, JIANG H, et al. Advances in studies on germplasm resources and biological activity of Phyllanthus emblica leaves[J]. Farm Products Processing,2022(13):86−90,96. CHENG Z X, GUO S Q, JIANG H, et al. Advances in studies on germplasm resources and biological activity ofPhyllanthus emblica Leaves[J]. Farm Products Processing, 2022(13): 86-90, 96.
[26] 李兵, 黄贵庆, 卢汝梅, 等. 余甘子化学成分研究[J]. 中药材,2015,38(2):290−293. [LI B, HUANG G Q, LU R M, et al. Study on chemical composition of Phyllanthus emblica[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2015,38(2):290−293. LI B, HUANG G Q, LU R M, et al. Study on chemical composition of Phyllanthus emblica[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials, 2015, 38(2): 290-293.
[27] 毛健, 刘振杰. HPLC同时测定余甘子叶中槲皮素和山奈酚的含量[J]. 中国当代医药,2014,21(19):50−52. [MAO J, LIU Z J. Simultaneous measurement of quercetin content and kaempferol content in Phyllanthus emblica leaf based on HPLC[J]. China Modern Medicine,2014,21(19):50−52. MAO J, LIU Z J. Simultaneous measurement of quercetin content and kaempferol content in Phyllanthus emblica leaf based on HPLC[J]. China Modern Medicine, 2014, 21(19): 50-52.
[28] 梁臣艳, 甄汉深, 马雯芳, 等. 高效液相色谱法测定广西余甘子叶中槲皮素和山奈酚的含量[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2010,16(8):41−43. [LIANG C Y, ZHEN H S, MA W F, et al. RP-HPLC determination of quercetin and kaempferol in the leaves of Phyllanthus emblica L doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9903.2010.08.013 J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2010,16(8):41−43. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9903.2010.08.013
[29] 李舒, 钟振国, 赖进科. 余甘子叶提取物总黄酮的含量测定[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报,2011,13(7):109−110. [LI S, ZHONG Z G, LAI J K. Determination of total flavonoids in the extracts from leaves of Phyllanthus emblica L J]. Journal Ournal of LiaoNing University of TCM,2011,13(7):109−110.
[30] 毛健, 刘振杰. 余甘子叶药材的HPLC指纹图谱研究[J]. 中国当代医药,2014,21(17):11−14. [MAO J, LIU Z J. Study on HPLC fingerprint analysis of Phyllanthus emblica L J]. China Modern Medicine,2014,21(17):11−14.
[31] 冀静, 杨继家, 廖琦, 等. 藏药余甘子中三种酚酸类成分的HPLC含量测定研究[J]. 中药与临床,2012,3(4):14−16,19. [JI J, YANG J J, LIAO Q, et al. Determination of gallic acid, corilagin and ellagic acid from tibetan traditional medicine Phyllanthus emblica L. by HPLC[J]. Pharmacy and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica,2012,3(4):14−16,19. JI J, YANG J J, LIAO Q, et al. Determination of gallic Acid, corilagin and ellagic Acid from tibetan traditional medicine Phyllanthus emblica L. by HPLC[J]. Pharmacy and Clinics of Chinese Materia Medica, 2012, 3(4): 14-16, 19.
[32] 王欣, 覃瑶, 王德江, 等. 一测多评法在中药质量控制中的应用进展[J]. 中成药,2016,38(2):395−402. [WANG X, QIN Y, WANG J D, et al. Application progress of one-test-multiple-evaluation method in quality control of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2016,38(2):395−402. WANG X, QIN Y, WANG J D, et al. Application progress of one-test-multiple-evaluation method in quality control of traditional Chinese medicine[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2016, 38(2): 395-402.
[33] AMBIGAIPALAN P, OH W Y, SHAHIDI F. Epigallocatechin (EGC) esters as potential sources of antioxidants[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,309:125609. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.125609
[34] SELVAKUMAR P, BADGELEY A, MURPHY P, et al. Flavonoids and other polyphenols act as epigenetic modifiers in breast cancer[J]. Nutrients,2020,12(3):761. doi: 10.3390/nu12030761
[35] 尹海波, 赵晓雨, 涂秀文, 等. 不同采收时期牻牛儿苗中4种酚酸类活性成分的动态分析[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2014,20(13):121−124. [YIN H B, ZHAO X Y, TU X W, et al. Dynamic analysis of four phenolic acid active components in geran seedlings at different harvesting periods[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Formulas,2014,20(13):121−124. YIN H B, ZHAO X Y, TU X W, et al. Dynamic analysis of four phenolic acid active components in geran seedlings at different harvesting periods[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Formulas, 2014, 20(13): 121-124.
[36] 黄宽, 付鹏, 林艾和, 等. HPLC法同时测定毛诃子中5种鞣质类成分的含量[J]. 中国药师,2021,24(3):607−609. [HUANG K, FU P, LIN A H, et al. Simultaneous determination of five tannins components in terminalia billirica by HPLC[J]. China Pharmacist,2021,24(3):607−609. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-049X.2021.03.043 HUANG K, FU P, LIN A H, et al. Simultaneous determination of five tannins components in terminalia billirica by HPLC[J]. China Pharmacist, 2021, 24(3): 607-609. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-049X.2021.03.043
[37] 杨洪亮, 张翼鷟, 王晓芳, 等. 鞣花酸对肿瘤细胞增殖抑制和诱导凋亡作用的初步研究[J]. 赤峰学院学报(自然科学版),2010,26(10):49−51. [YANG H L, ZHANG Y Z, WANG X F, et al. Preliminary study of ellagic acid on tumor cell proliferation inhibition and apoptosis induction[J]. Journal of Chifeng University (Natural Science Edition),2010,26(10):49−51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-260X.2010.10.020 YANG H L, ZHANG Y Z, WANG X F, et al. Preliminary study of Ellagic Acid on tumor cell proliferation inhibition and apoptosis induction[J]. Journal of Chifeng University (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 26(10): 49-51. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-260X.2010.10.020
[38] 柳敏娜, 王谨涵, 潘刚, 等. 诃子酸抗肾间质纤维化的作用及机制研究[J]. 解放军医药杂志,2020,32(6):1−5,13. [LIU M N, WANG J H, PAN G, et al. Study on the effect and mechanism of myrobic acid on renal interstitial fibrosis[J]. PLA Medical Journal,2020,32(6):1−5,13. LIU M N, WANG J H, PAN G, et al. Study on the effect and mechanism of Myrobic acid on renal interstitial fibrosis[J]. PLA Medical Journal, 2020, 32(6): 1-5, 13.
[39] 范青, 李程, 李明, 等. 红树莓叶片生长代谢过程中酚类物质含量及抗氧化酶活性分析[J]. 食品科学,2023,44(8):238−246. [FAN Q, LI C, LI M, et al. Analysis of phenolic compounds and antioxidant enzyme activities during the growth and metabolism of red raspberry leaves[J]. Food Science,2023,44(8):238−246. FAN Q, LI C, LI M, et al. Analysis of phenolic compounds and antioxidant enzyme activities during the growth and metabolism of red raspberry leaves[J]. Food Science, 2023, 44(8): 238-246.
[40] 刘娟秀, 罗益远, 刘训红, 等. 不同采收期苍耳草中酚酸类及蒽醌类成分的动态积累分析[J]. 中草药,2016,47(7):1204−1209. [LIU J X, LUO Y Y, LIU X H, et al. Dynamic changes of phenolic acids and anthraquinones in aerial parts of Xanthium sibiricum from different collection periods[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs,2016,47(7):1204−1209. LIU J X, LUO Y Y, LIU X H, et al. Dynamic changes of phenolic acids and anthraquinones in aerial parts of Xanthium sibiricum from different collection periods[J]. Chinese Traditional and Herbal Drugs, 2016, 47(7): 1204-1209.





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
