Research Progress on Preparation of Nanocellulose
-
摘要: 纳米纤维素因具有可再生、易改性以及优异的机械性能,在众多领域具有广阔的应用前景。植物来源的纳米纤维素主要包括纤维素纳米晶体和纤维素纳米纤维,本文主要介绍了以农副产品为原料的纤维素纳米化处理技术及其分类,包括制备纤维素纳米晶体的经典无机酸水解法以及有机酸水解法、低共熔溶剂法和离子液体法等新型制备方法。此外,还介绍了制备纤维素纳米纤维常用的预处理手段和制备方法,预处理方法包括以2,2,6,6-四甲基哌啶-1-氧自由基氧化为代表的氧化法预处理以及酶法预处理;制备方法包括高压均质、精细研磨、高强度超声和高压微射流等技术。最后,对现行纤维素纳米化处理技术中存在的问题进行综合分析,并探讨了其未来研究需求,以期为纳米纤维素的绿色高效生产提供理论参考。Abstract: Nanocellulose is a sustainable resource that combines a modifiable surface with excellent mechanical strength. It has been increasingly applied to applications in different fields. Plant-based nanocellulose primarily contains cellulose nanocrystal and cellulose nanofibrils. This review summarizes the preparation methods for cellulose nanocrystal and cellulose nanofibrils that emerged from agricultural by-products. The different sorts of cellulose nanocrystal preparation methods that have been discussed include the inorganic acid hydrolysis method, organic acid hydrolysis method, ionic liquid method, deep eutectic solvent method, and so forth. Also, several methods of pretreatment and preparation of cellulose nanofibrils are characterized, encompassing the oxidation pretreatment represented by 2,2,6,6-tetramethylpiperidine-1-oxy radical oxidation and enzymatic pretreatment. The high pressure homogenization, fine grinding, high-strength ultrasound and high pressure microfluidization techniques are used to prepare cellulose nanofibrils. This review's objective is to offer a theoretical framework for the economical and environmentally responsible manufacturing of nanocellulose.
-
Keywords:
- cellulose nanocrystal /
- cellulose nanofibrils /
- pretreatment /
- preparation
-
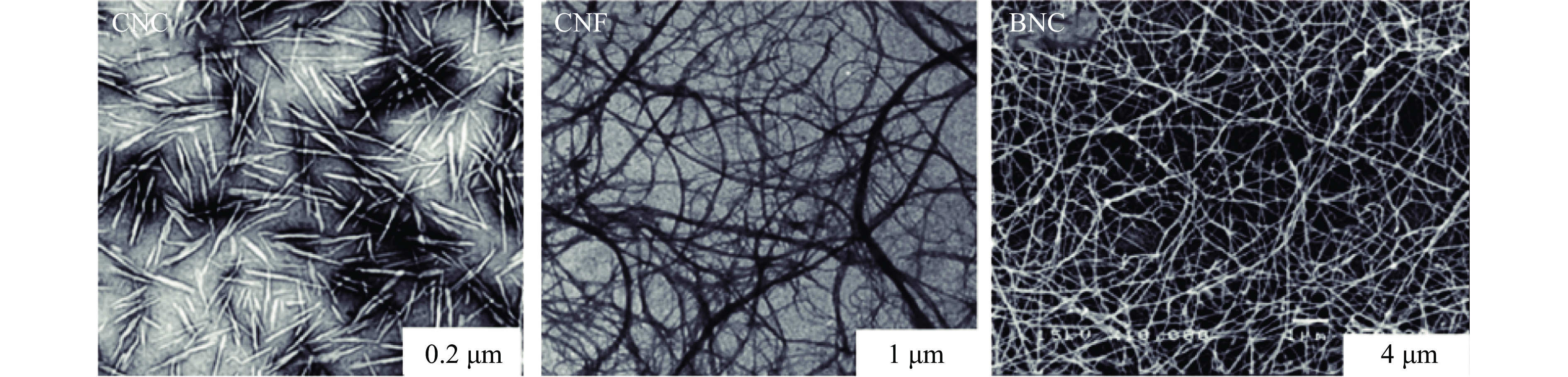
纳米纤维素因具有来源广、成本低、可再生以及理化特性优良等特点,近年来已成为食品、医学、化工、材料学等领域的研究热点[1]。作为纤维素材料和纳米化技术结合的产物,纳米纤维素是指从植物纤维原料中分离或由细菌生物合成的直径小于100 nm、长度在纳米或微米级的一类工程纳米材料[2]。它不仅具有天然纤维素无毒、可再生等固有特性,还具有纳米材料特有的属性,如比表面积大、表面易改性、高强度等[3]。其应用市场前景广阔,预计到2023年,全球纳米纤维素市场将增长到7.3亿美元[4]。在食品领域,纳米纤维素因其独特的力学性能、阻隔性能和界面活性,在开发新型食品包装和乳化稳定剂方面具有较大的应用潜力[5]。根据微观结构和形貌的差异,一般可以将纳米纤维素分为3种类型,分别是:因纤维素无定形区解离而形成的具有高机械强度的纳米级棒状或晶须状颗粒,称为纤维素纳米晶体(cellulose nanocrystal,CNC);通常由高压均质、研磨等机械处理得到的,直径在10到几百纳米、长度可达微米级的柔软纤维素长链,称为纤维素纳米纤维(cellulose nanofibrils,CNF),以及由微生物进行生物合成所制得的纳米级网状结构,称为细菌纳米纤维素(bacterial nanocellulose,BNC)。三种纳米纤维素的微观结构如图1所示。
通常,CNC和CNF采用自上而下法进行制备,即以富含纤维素的物质为原料,经纳米化技术处理得到纳米级结构。因此,二者相较于BNC,具有更为广泛的生物质来源。农业副产品以其资源丰富、易获得、成本低等优点,已成为制备CNC和CNF的常用原料。另外,从农副产品中提取纤维素相较于传统的填埋、焚烧等处理方法,不仅可以减少大量的资源浪费和环境污染,还能够带动就业、增加农民收入,具有良好的环境和社会经济效益[8]。
本文以CNC和CNF的制备为切入点,对近年来国内外文献报道的纤维素纳米化技术及相关方法特点进行梳理总结,以期为以纳米纤维素的绿色高效生产提供参考。
1. CNC的制备
纤维素纳米晶体(CNC)是一种天然的结晶高分子化合物,典型直径为3~50 nm,长度为100~400 nm[9]。其具有无毒、可降解、高强度、轻质量等特点,目前已在纳米复合材料、食品、化妆品、电子等领域得到广泛应用[1]。在制备CNC前,首先需要对纤维原料进行初步粉碎以确保后续化学反应速度的均一性,随后通过预处理除去非纤维素组分、获得高纯度的纤维素,如常见的漂白处理和碱处理[10]。无机酸水解法是制备CNC最常用的方法;近年来,为实现绿色环保生产的目标,已陆续开发出新型制备方法,如有机酸水解法、离子液体法、低共熔溶剂法等。制备CNC的原料、方法及特性如表1所示。
表 1 不同方法制备CNC特性对比Table 1. Comparison of characteristics of CNC from different methods方法 主要试剂 纤维素原料 反应条件 CNC特性 方法特点 尺寸 结晶度(%) 产率(%) 无机酸水解法 硫酸 柠檬籽[11] 64 wt%,90 min,45 ℃ 长130~170 nm,
宽12~25 nm69.7 27.6 能有效制备分散性良好、颗粒细小
均匀的CNC但产率低、污染大盐酸 棉花[12] 60 mL/g,180 min,
110 ℃直径20 nm左右,
长径比13.9− 85.2 制备的CNC热稳定性良好但易团聚 有机酸水解法 甲酸 玉米芯[13] 88%,30 min,95 ℃ 直径6.5 nm左右,
长径比6763.8 66.3 产率可观、溶剂可回收,但需与
其他试剂(如氯化铁)联合使用草酸 油棕[14] 结合水热处理,
13 wt%,60 min,121 ℃长256 nm,
宽24.56 nm70 − 方法绿色高产,所得CNC热稳定性
良好,但分散性仍逊于硫酸法离子液体法 氯化1-丁基-3-甲基咪唑 蔗渣[15] 120 min,130 ℃ 直径10~20 nm 52 − 试剂可回收并重复利用,但回收
过程复杂且试剂成本高低共熔溶剂法 氯化胆碱-二水草酸 棉花[16] 60 min,80 ℃ 长162 nm,
长径比25.2370.8 − 溶剂成本较低,绿色环保,但多需
采用机械或酸水解进一步处理氧化法 TEMPO/NaBr/NaClO体系 柠檬籽[11] 240~300 min,室温 长340~380 nm,
宽26~42 nm66.1 52.0 CNC分散性良好,但热稳定性低,
且TEMPO氧化剂成本相对昂贵1.1 酸水解法
酸水解是从纤维素中分离CNC最经典的方法。该方法通常采用无机酸、有机酸或混合酸来水解纤维素分子非结晶区域的糖苷键,进而引起原纤维束的层次结构断裂,从而获得高结晶度的CNC[17]。在酸水解法中,产物的结构、形态等特性受诸多因素的影响,包括原料性质、酸的种类和浓度、水解温度及时间、辅助手段等,其中酸的性质对成品CNC的影响尤为重要[18]。
1.1.1 无机酸水解法
1.1.1.1 硫酸水解法
自上世纪五十年代,Ranby[19]最先使用硫酸对木材纤维素水解并成功制备悬浮液后,硫酸水解已成为目前分离、制备CNC最普遍的一种方法。与其它酸相比,在制备中使用硫酸的突出优点是生产出的CNC悬浮液稳定、抗絮凝性好。这是因为经硫酸水解制备的CNC表面上具有带负电荷的硫酸酯基团,其通过提高粒子的分散性使CNC在水溶液中具有良好的静电稳定性[20]。同时,硫酸水解法还能有效地消除非晶态部分,从而产生更短且均匀、结晶度达90%以上的CNC。Kusmono等[21]从苎麻中成功分离出了高结晶度的CNC,其结晶度达90.77%,在替代增强材料方面具有较高应用潜力。除结晶度外,形貌、尺寸等基本特性对于纳米纤维素的研究也具有重要意义。Guo等[22]成功从茶杆中分离出宽度集中在4~8 nm的棒状CNC颗粒,表征结果显示该茶杆CNC与普通木材CNC具有相似的物理化学性质,且具有更好的稳定性。
然而,残留在反应体系内的硫酸盐基团会导致产物脱水,甚至引起分解反应,导致成品CNC的热稳定性降低,限制了其在高温生产加工行业中的应用[23]。Huang等[24]以甘蔗渣为原料通过酸水解方式制备CNC,发现硫酸水解法所得CNC在600 ℃下残余质量相对减少17.7%。此外,长时间与强酸作用以及温度的变化会导致纳米纤维素分解成小的有机分子,加之硫酸水解纤维素是一个突变的过程,进程难以控制,所以硫酸法制备CNC的得率通常较低[24]。吴巧妹等[25]以丝瓜络废弃物为原料,利用梯度质量分数(58wt%~66wt%)的硫酸制备CNC。当硫酸质量分数过高(66wt%)时,会引起丝瓜络纤维素炭化,生成细小的黑色炭颗粒,降低产品得率;而水解时间过短会导致纤维素非晶态区域水解不完全从而影响CNC的结晶度。因此,一般需要根据不同纤维素原料的性质、预处理条件等选用合适的水解方案。在实际实验中,通常采用64wt%左右的硫酸进行水解,反应温度控制在40~70 ℃之间,反应时间则根据温度的不同从半小时到十几个小时不等[26]。
1.1.1.2 其它无机酸水解法
为克服硫酸水解法低得率、热稳定性差的问题,研究人员还使用其他无机酸进行了大量尝试,如盐酸、磷酸、溴酸、磷钨酸等。但因所得的CNC悬浮液稳定性差、水解程度有限等问题,上述无机酸单独应用的比较有限,多与其它处理联合进行CNC的制备[27]。Yu等利用盐酸水解结合氨中和的方法,成功从棉花中分离、制备了CNC。结果表明,该方法不仅产率高(93.7%),而且所得CNC的热稳定性和分散性俱佳[12]。
1.1.2 有机酸水解法
近年来,由于常规的无机酸水解法存在腐蚀性强、废酸处理困难、污染环境等问题,除采用回收硫酸进行循环水解等方法外,越来越多的研究人员开始利用易回收、无毒或低毒、环境压力更小的有机酸制备CNC[28]。
1.1.2.1 甲酸水解法
Liu等[13]以玉米芯为原料,采用甲酸水解法制备了热稳定性良好、产率高达66.3%的CNC。但因其zeta电势值较低、易凝聚,需进一步进行表面改性,否则难以直接应用。因此,甲酸水解法通常还需要联合其它处理以改善产品性质,如氯化铁催化、2,2,6,6-四甲基哌啶-1-1氧自由基(TEMPO)氧化等。杜海顺[29]采用氯化铁催化甲酸水解法制备出了高得率、高热稳定性的CNC,再将其分散在二甲亚砜中,得到了可稳定分散在溶液中的CNC。在该方法中,氯化铁可转化为高附加值的氢氧化铁并回收,甲酸水解液经回收后可利用1~3次,这表明氯化铁催化甲酸水解法是一种可持续、经济可行的方法。
1.1.2.2 草酸水解法
与甲酸水解不同,草酸水解制备的CNC悬浮液具有良好的分散稳定性。这是因为草酸作为一种高酸度的二元羧酸,可通过与纤维素原料的表面羟基发生酯化反应,将游离的羧基引入CNC表面,使其带有大量的负电荷,提高粒子的分散性,从而改善悬浮液的稳定性。Jiang等[30]采用草酸水解法高效制备出了含木质素的CNC,并显示其具有良好的热稳定性以及较高的结晶度。此外,在常温下,草酸水溶性较差,可采用低成本的重结晶法进行回收,提高利用率并降低对环境的影响[31]。
除上述两种有机酸外,已被报道用于制备CNC的有机酸还包括马来酸、柠檬酸和对甲苯磺酸等。相较于传统的无机酸水解法,有机酸水解法具有对设备腐蚀性小、酸易回收、对环境污染较小等优点。但该方法也存在分散性有限、酸性较弱导致得率低和反应活性较低等问题,需进行催化优化或进一步改性。
1.1.3 混合酸水解法
除单独使用一种酸进行水解外,还可以采用多种酸按比例混合,配制成混合酸体系来水解制备CNC。已有多项研究表明,纤维素原料在混合酸体系中的水解效果会更好。彭大钊[32]以葛根提取淀粉后剩余的葛渣为原料,经磷酸-草酸混合处理成功制备了葛渣CNC。结果显示,当混合酸的比例为30:45时,CNC产率高达67%,直径为5.7~23.9 nm、结晶度为82.5%,并且该CNC还具有较好的热稳定性和分散稳定性。此外混合酸水解还可大幅度降低无机酸用量,相较于传统无机酸水解,更加绿色环保。Wang等[33]报道称,与典型的硫酸水解制备CNC相比,硫酸-甲酸混合水解法中硫酸用量减少了约20倍;实验所用甲酸也可通过真空蒸发进行回收,回收率高达90%。
1.2 离子液体法
离子液体是一类完全由离子组成的体系,在室温或近室温下呈液体状态,也称低温熔融盐[34]。与传统溶剂相比,其具有挥发性低、热稳定性好、溶解性好、可设计性、易分离回收和可循环使用等特点,被称为“新型绿色溶剂”[35]。在纤维素纳米化领域中,离子液体的应用历史相对较短,Swatloski等[36]于2002年首次发现离子液体能有效溶解纤维素,自此,离子液体已吸引国内外许多研究人员的关注,目前多用于木质纤维素材料的处理。上述研究中的结论也成为了现有研究的普遍共识,即离子液体中的阴离子在溶解纤维素过程中起主导作用,其可与纤维素链上羟基氢原子形成强氢键。侯其东等[37]总结了在阳离子相同前提下,不同阴离子对纤维素的溶解能力:[(CH3CH2)2PO4]−≈[OAc]−>[SHCH2COO]−>[HCOO]−>Cl−>Br−≈[SCN]−。上述阴离子的溶解纤维素能力与各自氢键形成能力一致。这表明增强氢键形成力有助于纤维素的溶解。基于此,研究人员已开发出多种离子液体用以溶解纤维素,其结构如图2所示。
1.3 低共熔溶剂法
低共熔溶剂(deep eutectic solvent,DES)是由一定比例的氢键受体和氢键供体,经简单的加热方式制备而成的共熔混合物,具有优良的热稳定性、化学稳定性、低熔点、易回收等特征,是一种绿色环保的新型溶剂[39]。常见的氢键受体有季铵盐、两性离子;氢键供体包括羧酸、多元醇和酰胺等。由于和离子液体具有许多共同特性,DES也被认为是一类“新型离子液体”。其能够选择性地溶解纤维原料中的木质素和半纤维素,同时通过破坏纤维间的氢键引起纤维的润胀,有利于纤维素在后续外力作用下的分离和制备。Hong等[40]以丝瓜络为原料,经氯化胆碱-草酸二水合物组成的酸性DES处理,再结合超声处理成功制备了含木质素的CNC。结果表明,经DES处理后,可以得到更小、更均匀的粒径分布。但纤维素原料中存在的木质素过多,限制了DES溶解纤维素结构,大大降低了产品得率,因此未来的研究中需开发更多、更高效的低共熔溶剂体系。
1.4 氧化法
除上述几种方法外,已有大量研究采用氧化法来制备CNC,其原理是氧化剂能够与纤维素原料颗粒的表面羟基发生反应,并使其转化为醛基、羧基等功能性基团[1]。常见的氧化方法有TEMPO氧化法、过硫酸铵氧化法和高碘酸盐氧化法[17]。众多研究结果表明,氧化方法不会改变CNC的构型,但通常采用TEMPO氧化法制备的CNC具有更高的产量和较大尺寸;采用过硫酸铵氧化法制备的CNC具有更好的热稳定性和较高的结晶度,更适合应用于热加工;而采用高碘酸盐氧化法制备的CNC溶液稳定性好、不易凝聚,在形状和尺寸上表现出优良的均匀性[11]。在实际应用中,该方法通常需要机械法来辅助氧化,尽管其可以显著降低能耗,但仍存在处理效率低、使用危险试剂、化学品回收困难等缺点。而且,相对于无机酸水解法,在氧化过程中,通常伴随着纤维素主链降解、酸性水解等副反应,因此成品CNC的结晶度相对更低。
2. CNF的制备
纤维素纳米纤维(CNF)由无定形区和结晶区组成,直径为5~60 nm,长度可达数微米,具有高亲水性、易降解、凝胶性、易降解等特点,在食品、医学、造纸等领域有着广泛的应用[41]。与CNC的制备流程相似的是,制备CNF前通常也需要进行原料的机械粉碎和预处理。常见的预处理包括化学预处理和酶预处理。当前已有许多研究报道过CNF的制备方法,其中应用最广泛的是以高压均质为代表的机械处理法[6]。不同的预处理和机械处理方式有各自的特点,其具体内容如下文所示。
2.1 原料预处理
CNF通常采用预处理辅助机械处理的方式[23]。其中,预处理主要通过打断氢键、引入电荷使纤维膨胀和减少无定形区的粘结,进而达到降低能耗的目的[42]。当下研究中常用的两种预处理手段为化学预处理和酶预处理。
2.1.1 化学预处理
纤维素预处理过程中的化学改性可以有目的地赋予纤维素更多的功能特性,便于其后续在特定领域的应用。在预处理过程中,具有特定功能的化学官能团一般作用于纤维素表面的羟基和吡喃葡萄糖环。羟基的取代和带电基团的引入可以削弱纤维素链之间的内聚力,有利于纳米纤维素在悬浮液中的分散[9]。TEMPO氧化是最常用的一种化学预处理方法。该方法通过在纤维素表面生成带负电荷的羧酸盐基团,进而再由羧酸盐基团产生的排斥力来提高纤维素的静电稳定性[17]。此外,该方法在降低后续机械处理能耗方面具有巨大潜力。
有研究通过实验对比发现,在高压均质制备纳米纤维素的过程中,采用TEMPO氧化预处理后的节能效果可提高100~200倍[43]。当前关于TEMPO氧化预处理制备CNF的研究一般集中在纤维素原料、氧化参数等条件对成品CNF特性的影响方面。Ferran等[44]的研究结果表明,同样是采用TEMPO氧化联合高压均质处理,黄麻CNF与一些木材CNF具有相似的纤维网状结构,而剑麻和大麻原料制成的CNF中则有明显的棒状结构。陈欢等[45]研究了次氯酸钠浓度对柑橘皮渣CNF特性的影响。研究发现,随次氯酸钠浓度的升高,柑橘CNF的平均粒径、直径和长度等尺寸指标都显著降低,且在较高浓度下,CNF的结晶度和热稳定性会有轻微降低。因此,在具体实验中,需根据纤维素原料性质对氧化参数进行设置,以期获得更理想的CNF制备条件。
2.1.2 酶法预处理
除使用化学试剂进行预处理外,生物酶降解也是常见预处理方法之一。因单一生物酶难以完全水解纤维素,所以在实际应用中往往采用复合酶来进行预处理。常见的纤维素酶包括内切葡聚糖酶、外切葡聚糖酶和β-葡萄糖苷酶。它们的作用分别是随机切断β-1,4糖苷键,切下位于分子链末端的一个纤维二糖,以及通过切断纤维二糖来产生葡萄糖单体[46]。王思[47]以甘草渣为原料,采用复合酶预处理结合高压均质处理的方式制备出了甘草渣CNF。结果表明,与采用TEMPO氧化预处理制备的CNF相比,酶预处理制备的CNF具有较高的结晶度和热稳定性。Mariño等[48]从柑橘溃疡病得到启发,利用地毯草黄单胞菌柑橘致病变种Xanthomonas axonopodis pv. Citri中的天然酶对柑橘组织进行酶解,再通过超声处理,得到了高纵横比的CNF,结果表明,与仅经过超声制备的CNF相比,酶解处理使成品CNF产率增加7%。
2.2 机械处理
已报道过的CNF制备方法有很多,其中以机械处理最为常见,包括高压均质、精细研磨、高强度超声和高压微射流等。制备CNF的不同方法对比如表2所示。
表 2 制备CNF的不同方法对比Table 2. Comparison of different methods for preparing CNF原料 主要机械处理 CNF基本特性 方法特点 优点 局限 玉米秸秆[49] 高压均质 直径5~50 nm,长度达微米级 CNF分散性良好 能耗高、均质机易堵塞 漂白桉木浆[50] 精细研磨 直径4~30 nm 不易堵塞,可一次加工大量原料,
成本较低生产效率低、磨盘摩擦引入大量杂质
碎屑影响CNF纯度葎草茎[51] 高强度超声 平均直径12.54 nm,
热分解温度达262.7 ℃CNF热稳定性良好 得率低且尺寸不均一 棕榈空果串[52] 高压微射流 横向尺寸10~30 nm 处理效率较高 结晶度降低、蠕变性能等发生改变 小麦秸秆[53] 静电纺丝 直径为270±97 nm 可调控CNF结构 溶液体系的甄选 谷壳[54] 蒸汽爆破 直径10~12 nm,
结晶度为58.5%有效破坏非纤维素部分,
制备过程绿色环保难以对纤维素原料中的度多组分
进行有效分离2.2.1 高压均质法
作为制备CNF最常用的一种机械方法,高压均质法的原理是,纤维素原料悬浮液反复、高速通过均质阀阀门,在高压剪切力的作用下发生原纤化,从而将纤维尺寸逐步减小至纳米级。采用高压均质法制备CNF时,影响成品性能的因素有很多。Davoudpour等[55]的研究结果证明,均质压力和循环次数对CNF的产率、结晶度和直径有显著影响。除工艺参数外,如表3所示,纤维素原料种类的不同也对成品CNF的特性和应用有影响。
表 3 不同来源高压均质CNF特性对比Table 3. Comparison of characteristics of high pressure homogeneous CNF from different sources原料 预处理 工艺参数 CNF特性 潜在应用市场 尺寸 结晶度(%) 玉米秸秆[49] NaOH碱处理,漂白 500 bar下均质20~30次 直径5~50 nm,长度达数微米 − 复合材料
增强剂去果胶
甜菜渣[56]NaOH碱处理,漂白 800 bar下均质10次 直径10~70 nm 77.89 生物相容性材料 花生壳[57] 索氏提取,漂白,NaOH碱处理,
二次漂白研磨后1000 bar下均质5次 平均直径15 nm 60.90 功能性纳米材料基材 漂白甘蔗渣[58] KOH碱处理,酶解 研磨后先400 bar均质5次再
2500 bar下均质10次宽度20 nm − 复合材料
增强剂木薯渣[59] 酶解,漂白 1034 bar下均质30次 直径10 nm左右 57.51 复合材料
增强剂龙须草[60] 甲酸水解,离心,二甲基乙酰胺溶剂置换 900 bar均质10次以上 直径5~15 nm − 纳米纸和水处理膜 香蕉皮[55] KOH碱处理,漂白,硫酸水解 两级高压均质:500和50 bar,
均质次数为5次直径3.5 nm,
长径比143.563.1~66.4 食品包装 高压均质虽是制备CNF的有效方法,但也存在着明显的局限性,如能耗高和均质机易堵塞。因此,在实际应用中,研究人员往往预先采用化学法、生物法和其他机械处理等方式对纤维素原料进行精制。
2.2.2 精细研磨法
制备CNF常采用的研磨方法有纳米研磨法和球磨法。前者通过磨盘相互作用产生的机械力对纤维素原料进行剪切摩擦以减小纤维的尺寸,后者则通过研磨体与样品间的碰撞、研磨达到粉碎原料的目的[1]。在农副产品综合利用领域中,已不乏有采用研磨法制备CNF的报道。如Yang等[61]以漂白甘蔗渣为原料,经多次纳米研磨制备了直径小于100 nm、长度分布在10~100 μm之间的CNF。图3为甘蔗渣纤维经不同研磨次数后的扫描电镜图像。由此可见,在纳米研磨法中研磨程度是影响成品CNF性能的重要因素之一。这种影响同样存在于球磨法中,Gallego等[62]的研究结果表明,黄麻纳米纤维素的形态与球磨的时间和转速有关;并且该研究还发现,在减小纤维素分子尺寸的同时,球磨法还可以对CNF进行活化,便于后续进行功能化改性。
![]() 图 3 不同研磨程度的蔗渣纤维素纳米纤维扫描电镜图像[61]注:(a)制备蔗渣CNF的研磨机;(b~h)蔗渣纤维经过不同磨机次数后的扫描电镜图像:(b)原始蔗渣纤维;(c)研磨1次;(d)研磨3次;(e)研磨5次;(f)研磨7次;(g)研磨9次;(h)研磨11次。Figure 3. Scanning electron microscopic images of bagasse cellulose nanofibrils with different grinding degrees
图 3 不同研磨程度的蔗渣纤维素纳米纤维扫描电镜图像[61]注:(a)制备蔗渣CNF的研磨机;(b~h)蔗渣纤维经过不同磨机次数后的扫描电镜图像:(b)原始蔗渣纤维;(c)研磨1次;(d)研磨3次;(e)研磨5次;(f)研磨7次;(g)研磨9次;(h)研磨11次。Figure 3. Scanning electron microscopic images of bagasse cellulose nanofibrils with different grinding degrees2.2.3 高强度超声处理
该方法主要依靠声波空化作用产生的强大机械力来分离纤维素纳米纤维;并且声流在传导过程中还可导致溶液的强烈混合,进一步促进纳米纤维的纤颤[63]。研究表明,超声处理后的成品纳米纤维的特性与原料性质、超声时间以及超声功率等相关[1]。Monika等[64]利用超声处理成功制备了在形态、尺寸、结晶度等方面具有明显差异的苹果CNF和胡萝卜CNF,这些差异可能源自植物组织本身在生长过程中的形态差异。Khawas等[65]以香蕉皮为原料,经超声处理制备CNF,结果显示,在0~1000 W的输出功率范围内,随着超声输出功率的增大,香蕉皮CNF的尺寸减小,热稳定性增加。
2.2.4 高压微射流处理
高压微射流与高压均质具有类似的处理效果,均通过强烈剪切、冲击、膨爆、空化等综合作用,实现原料的纳米化,因此也有学者将其归类为高压均质的一种。研究发现,高压微射流处理具有均匀分散纤维颗粒、改善纤维水化性能等作用,所以也被广泛地应用于CNF的制备中。Kassab等[66]以灯芯草茎为原料,通过TEMPO氧化结合高压微射流生产出了直径仅为2.5 nm、且分散性良好的羧基化CNF。Ferrer等[52]采用磨浆精炼预处理结合高压微射流方式制备的棕榈空果串CNF同样具有尺寸分布均匀的优点。
2.2.5 静电纺丝
采用静电纺丝制备CNF通常需要先将纤维素制成溶液,再经注射泵推动,聚合物溶液被挤出形成液滴,随着电场力不断增大,带电纺丝液克服自身表面张力、形成泰勒锥。当施加的电压达到一定程度时,泰勒锥中的静电斥力大于其表面张力,纺丝液即从泰勒锥尖端喷射而出,随着溶剂的快速挥发,纺丝液固化形成纳米纤维,最终沉积在接收器上形成纳米纤维网[67]。该方法通常需要直接溶解纤维素再静电纺丝制备CNF,常用的溶剂有很多种,如DMSO/三乙胺/SO2溶剂体系、N-甲基吗啉-N-氧化物(NMMO)溶剂体系、氯化锂(LiCl)/N,N-二甲基乙酰胺(DMAC)溶剂体系等。该方法最大的优点是结构可调控,即可通过改变溶液浓度、电场强度等参数来调节CNF的结构、形貌,且成品CNF具有直径小、比表面积大等优点[68]。但由于纤维素具有溶解性差、易团聚的特点,所以选择合适溶液体系仍是限制该方法应用的主要因素。
2.2.6 蒸汽爆破法
蒸汽爆破法是通过快速释放高压蒸汽进入纤维原料内部,实现由内而外破坏纤维内部结构。具体过程为:在高温下的高压釜中,首先由蒸汽携带的大量热量通过扩散作用渗透纤维原料,部分水分子与原料中纤维素的羟基形成氢键,取缔原有氢键;随后在突然的减压作用下,水分子发生爆裂,出现空化作用,以裂解纤维原料内部的糖苷键和氢键,导致原料崩解成纤维状分散固体,进而有效去除原纤维中的非纤维素成分,减小纤维直径。在减压过程中还伴随着水分子与纤维素间氢键的断裂,进一步促进了空化效应发挥作用[69]。目前,该方法多结合酸处理等技术开展研究,已应用在谷壳CNF[54]、黄麻CNF[70]等的制备中。
3. 总结与展望
当前,纤维素纳米化技术主要集中在酸水解和机械处理,此类工艺存在能耗高、污染严重、效率低等问题。随着可持续发展理念不断深化,尽管研究人员已探索出离子液体法、低共熔溶剂法等新型环保制备方法,但由于单一处理方法往往存在更大的局限性,因此多种方法协同制备纳米纤维素已成为现行主流研究方法。不同方法对成品纳米纤维素特性的影响也已成为研究热点,但具体制备条件对纳米纤维素形态结构、理化特性的影响仍缺乏系统研究,且部分制备方法的原理、机制仍未有定论。因此,未来需要进一步探索更加高效便捷的分离技术或提高纳米纤维素分散性的可行方法,明确不同条件对成品纳米纤维素的具体影响,解析各类方法的作用机制,实现调控纳米纤维素尺寸、结晶度等特性指标的目的,以期开发出高效率、低能耗、低污染的绿色纤维素纳米化技术。另一方面,农副产物资源除少部分用于工业生产外,大部分作为废弃物自然降解或燃烧,造成资源浪费与环境污染。在这种现状下,以农副产物中丰富的天然纤维素为原料,制备纳米纤维素能够带来不可估量的经济和生态效益,符合社会可持续发展的要求。
-
图 3 不同研磨程度的蔗渣纤维素纳米纤维扫描电镜图像[61]
注:(a)制备蔗渣CNF的研磨机;(b~h)蔗渣纤维经过不同磨机次数后的扫描电镜图像:(b)原始蔗渣纤维;(c)研磨1次;(d)研磨3次;(e)研磨5次;(f)研磨7次;(g)研磨9次;(h)研磨11次。
Figure 3. Scanning electron microscopic images of bagasse cellulose nanofibrils with different grinding degrees
表 1 不同方法制备CNC特性对比
Table 1 Comparison of characteristics of CNC from different methods
方法 主要试剂 纤维素原料 反应条件 CNC特性 方法特点 尺寸 结晶度(%) 产率(%) 无机酸水解法 硫酸 柠檬籽[11] 64 wt%,90 min,45 ℃ 长130~170 nm,
宽12~25 nm69.7 27.6 能有效制备分散性良好、颗粒细小
均匀的CNC但产率低、污染大盐酸 棉花[12] 60 mL/g,180 min,
110 ℃直径20 nm左右,
长径比13.9− 85.2 制备的CNC热稳定性良好但易团聚 有机酸水解法 甲酸 玉米芯[13] 88%,30 min,95 ℃ 直径6.5 nm左右,
长径比6763.8 66.3 产率可观、溶剂可回收,但需与
其他试剂(如氯化铁)联合使用草酸 油棕[14] 结合水热处理,
13 wt%,60 min,121 ℃长256 nm,
宽24.56 nm70 − 方法绿色高产,所得CNC热稳定性
良好,但分散性仍逊于硫酸法离子液体法 氯化1-丁基-3-甲基咪唑 蔗渣[15] 120 min,130 ℃ 直径10~20 nm 52 − 试剂可回收并重复利用,但回收
过程复杂且试剂成本高低共熔溶剂法 氯化胆碱-二水草酸 棉花[16] 60 min,80 ℃ 长162 nm,
长径比25.2370.8 − 溶剂成本较低,绿色环保,但多需
采用机械或酸水解进一步处理氧化法 TEMPO/NaBr/NaClO体系 柠檬籽[11] 240~300 min,室温 长340~380 nm,
宽26~42 nm66.1 52.0 CNC分散性良好,但热稳定性低,
且TEMPO氧化剂成本相对昂贵表 2 制备CNF的不同方法对比
Table 2 Comparison of different methods for preparing CNF
原料 主要机械处理 CNF基本特性 方法特点 优点 局限 玉米秸秆[49] 高压均质 直径5~50 nm,长度达微米级 CNF分散性良好 能耗高、均质机易堵塞 漂白桉木浆[50] 精细研磨 直径4~30 nm 不易堵塞,可一次加工大量原料,
成本较低生产效率低、磨盘摩擦引入大量杂质
碎屑影响CNF纯度葎草茎[51] 高强度超声 平均直径12.54 nm,
热分解温度达262.7 ℃CNF热稳定性良好 得率低且尺寸不均一 棕榈空果串[52] 高压微射流 横向尺寸10~30 nm 处理效率较高 结晶度降低、蠕变性能等发生改变 小麦秸秆[53] 静电纺丝 直径为270±97 nm 可调控CNF结构 溶液体系的甄选 谷壳[54] 蒸汽爆破 直径10~12 nm,
结晶度为58.5%有效破坏非纤维素部分,
制备过程绿色环保难以对纤维素原料中的度多组分
进行有效分离表 3 不同来源高压均质CNF特性对比
Table 3 Comparison of characteristics of high pressure homogeneous CNF from different sources
原料 预处理 工艺参数 CNF特性 潜在应用市场 尺寸 结晶度(%) 玉米秸秆[49] NaOH碱处理,漂白 500 bar下均质20~30次 直径5~50 nm,长度达数微米 − 复合材料
增强剂去果胶
甜菜渣[56]NaOH碱处理,漂白 800 bar下均质10次 直径10~70 nm 77.89 生物相容性材料 花生壳[57] 索氏提取,漂白,NaOH碱处理,
二次漂白研磨后1000 bar下均质5次 平均直径15 nm 60.90 功能性纳米材料基材 漂白甘蔗渣[58] KOH碱处理,酶解 研磨后先400 bar均质5次再
2500 bar下均质10次宽度20 nm − 复合材料
增强剂木薯渣[59] 酶解,漂白 1034 bar下均质30次 直径10 nm左右 57.51 复合材料
增强剂龙须草[60] 甲酸水解,离心,二甲基乙酰胺溶剂置换 900 bar均质10次以上 直径5~15 nm − 纳米纸和水处理膜 香蕉皮[55] KOH碱处理,漂白,硫酸水解 两级高压均质:500和50 bar,
均质次数为5次直径3.5 nm,
长径比143.563.1~66.4 食品包装 -
[1] YADAV C, SAINI A, ZHANG W, et al. Plant-based nanocellulose: A review of routine and recent preparation methods with current progress in its applications as rheology modifier and 3D bioprinting[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,166:1586−1616. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.11.038
[2] 隋文杰, 贾洪玉, 敬佩, 等. 中国果品加工固体废弃物资源化利用现状与分类管理研究[J]. 农业工程学报,2018,34(S1):172−180. [SUI W J, JIA H Y, JING P, et al. Research on utilization status and classification management of solid waste in fruit processing in China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering,2018,34(S1):172−180. SUI W J, JIA H Y, JING P, et al. Research on utilization status and classification management of solid waste in fruit processing in China[J]. Transactions of the Chinese Society of Agricultural Engineering, 2018, 34(S1): 172-180.
[3] FAROOQ A, PATOARY M K, ZHANG M, et al. Cellulose from sources to nanocellulose and an overview of synthesis and properties of nanocellulose/zinc oxide nanocomposite materials[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,154:1050−1073. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.163
[4] VENTURA C, PINTO F, LOURENO A F, et al. On the toxicity of cellulose nanocrystals and nanofibrils in animal and cellular models[J]. Cellulose,2020,27:5509. doi: 10.1007/s10570-020-03176-9
[5] 董秀瑜, 唐世英, 杨贺棋, 等. 纳米纤维素的制备及其在食品领域中的应用研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(24):434−444. [DONG X Y, TANG S Y, YANG H Q, et al. Preparation of nano-cellulose and its application in food field[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(24):434−444. DONG X Y, TANG S Y, YANG H Q, et al. Preparation of nano-cellulose and its application in food field[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021, 42(24): 434-444.
[6] TAYEB A, AMINI E, GHASEMI S, et al. Cellulose nanomaterials—Binding properties and applications: A review[J]. Molecules,2018,23(10):2684. doi: 10.3390/molecules23102684
[7] MUENDUEN P, NIRUN J. Biosynthesis and characterization of bacteria cellulose-chitosan film[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2008,74(3):482−488. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2008.04.004
[8] 朱亚崇, 吴朝军, 于冬梅, 等. 纳米纤维素制备方法的研究现状[J]. 中国造纸,2020,39(9):74−83. [ZHU Y C, WU C J, YU D M, et al. Research status of nanocellulose preparation methods[J]. China Pulp and Paper,2020,39(9):74−83. ZHU Y C, WU C J, YU D M, et al. Research status of nanocellulose preparation methods[J]. China Pulp and Paper, 2020, 39(9): 74-83.
[9] HABIBI Y. Key advances in the chemical modification of nanocelluloses[J]. Chemical Society Reviews,2014,43(5):1519−1542. doi: 10.1039/C3CS60204D
[10] VENTURA-CRUZ S, TECANTE A. Nanocellulose and microcrystalline cellulose from agricultural waste: Review on isolation and application as reinforcement in polymeric matrices[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,118:106771. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2021.106771
[11] ZHANG H, CHEN Y, WANG S, et al. Extraction and comparison of cellulose nanocrystals from lemon (Citrus limon) seeds using sulfuric acid hydrolysis and oxidation methods[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,238:116180. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116180
[12] YU H, QIN Z, LIANG B, et al. Facile extraction of thermally stable cellulose nanocrystals with a high yield of 93% through hydrochloric acid hydrolysis under hydrothermal conditions[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2013,1(12):3938. doi: 10.1039/c3ta01150j
[13] LIU C, LI B, DU H, et al. Properties of nanocellulose isolated from corncob residue using sulfuric acid, formic acid, oxidative and mechanical methods[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,151:716−724. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.06.025
[14] ABU BAKAR N F, ABD RAHMAN N, MAHADI M B, et al. Nanocellulose from oil palm mesocarp fiber using hydrothermal treatment with low concentration of oxalic acid[J]. Materials Today:Proceedings,2022,48:1899−1904. doi: 10.1016/j.matpr.2021.09.357
[15] LI J, WEI X, WANG Q, et al. Homogeneous isolation of nanocellulose from sugarcane bagasse by high pressure homogenization[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2012,90(4):1609−1613. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2012.07.038
[16] LING Z, EDWARDS J V, GUO Z, et al. Structural variations of cotton cellulose nanocrystals from deep eutectic solvent treatment: Micro and nano scale[J]. Cellulose,2018,26(2):861.
[17] MA T, HU X N, LU S Y, et al. Nanocellulose: A promising green treasure from food wastes to available food materials[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2022,62(4):989−1002. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2020.1832440
[18] 吕天艺, 张书敏, 陈媛, 等. 不同形态纳米纤维素的制备方法研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(8):281−288. [LÜ T Y, ZHANG S M, CHEN Y, et al. Research progress on preparation methods of different morphologies of nanocellulose[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022,48(8):281−288. LYV T Y, ZHANG S M, CHEN Y, et al. Research progress on preparation methods of different morphologies of nanocellulose[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2022, 48(8): 281-288.
[19] RANBY B G. The cellulose micelles[J]. Tappi,1952,35(2):53.
[20] LE GARS M, DOUARD L, BELGACEM N, et al. Cellulose nanocrystals: From classical hydrolysis to the use of deep eutectic solvents[M]. Smart Nanosystems for Biomedicine, Optoelectronics and Catalysis. Intech Open, 2020.
[21] KUSMONO, LISTYANDA R F, WILDAN M W, et al. Preparation and characterization of cellulose nanocrystal extracted from ramie fibers by sulfuric acid hydrolysis[J]. Heliyon,2020,6(11):e05486. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2020.e05486
[22] GUO Y, ZHANG Y, ZHENG D, et al. Isolation and characterization of nanocellulose crystals via acid hydrolysis from agricultural waste-tea stalk[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,163:927−933. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.009
[23] NOREMYLIA M B, HASSAN M Z, ISMAIL Z. Recent advancement in isolation, processing, characterization and applications of emerging nanocellulose: A review[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2022: 954-976.
[24] HUANG B, HE H, LIU H, et al. Multi-type cellulose nanocrystals from sugarcane bagasse and their nanohybrids constructed with polyhedral oligomeric silsesquioxane[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,227:115368. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115368
[25] 吴巧妹, 王嘉伦, 刘晓泽, 等. 丝瓜络纳米纤维素晶体制备工艺的优化[J]. 西北农林科技大学学报(自然科学版),2015,43(4):179−184. [WU Q M, WANG J L, LIU X Z, et al. Optimizing preparation process for Luffa sponge nanocellulose crystals[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition),2015,43(4):179−184. WU Q M, WANG J L, LIU X Z, et al. Optimizing preparation process for Luffa sponge nanocellulose crystals[J]. Journal of Northwest A&F University (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(4): 179-184.
[26] 刘鹤. 纤维素纳米晶体及其复合物的制备与应用研究[D]. 北京: 中国林业科学研究院, 2011. LIU H. Synthesis and applications of cellulose nanocrystals and its nanocomposites[D]. Beijing: Chinese Academy of Forestry, 2011.
[27] KONTTURI E, MERILUOTO A, PENTTILÄ P A, et al. Degradation and crystallization of cellulose in hydrogen chloride vapor for high-yield isolation of cellulose nanocrystals[J]. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition,2016,55(46):14455−14458. doi: 10.1002/anie.201606626
[28] MA T, HU X N, LU S Y, et al. Cellulose nanocrystals produced using recyclable sulfuric acid as hydrolysis media and their wetting molecular dynamics simulation[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,184:405−414. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.06.094
[29] 杜海顺. 甲酸水解法制备纳米纤维素及其自组装膜的表征[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2017. DU H S. Preparation and characterization of nanocellulose and self-assembly nanocellulose films based on formic acid hydrolysis[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2017.
[30] JIANG J, ZHU Y, ZARGAR S, et al. Rapid, high-yield production of lignin-containing cellulose nanocrystals using recyclable oxalic acid dihydrate[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2021,173:114148. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.114148
[31] 王旺霞, 孙楠勋, 董继红, 等. 酸法制备纤维素纳米晶体的研究进展[J]. 生物化工,2020,6(2):133−138. [WANG W X, SUN N X, DONG J H, et al. Advances in cellulose nanocrystal preparation by acid hydrolysis[J]. Biological Chemical Engineering,2020,6(2):133−138. WANG W X, SUN N X, DONG J H, et al. Advances in cellulose nanocrystal preparation by acid hydrolysis[J]. Biological Chemical Engineering, 2020, 6(2): 133-138.
[32] 彭大钊. 葛渣中纤维素的分离及功能化研究[D]. 吉首: 吉首大学, 2021. PENG D Z. Study on separation and functionalization of cellulose from Pueraria lobata residue[D]. Jishou: Jishou University, 2021.
[33] WANG H, DU H S, LIU K, et al. Sustainable preparation of bifunctional cellulose nanocrystals via mixed H2SO4/formic acid hydrolysis[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2021,266:118107. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2021.118107
[34] 刘思洁, 陆燕玲, 黄家荣, 等. 离子液体催化生物质选择性转化[J]. 中国科学:化学,2021,51(10):1382−1390. [LIU S J, LU Y L, HUANG J R, et al. Selective conversion of biomass catalyzed by ionic liquids[J]. Scientia Sinica (Chimica),2021,51(10):1382−1390. doi: 10.1360/SSC-2021-0090 LIU S J, LU Y L, HUANG J R, et al. Selective conversion of biomass catalyzed by ionic liquids[J]. Scientia Sinica (Chimica), 2021, 51(10): 1382-1390. doi: 10.1360/SSC-2021-0090
[35] 曹雨, 桑燊, 邓海波, 等. 离子液体中阳离子纤维素的制备及对酸性蓝40的吸附性能[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程,2021,37(6):8−16. [CAO Y, SANG S, DENG H B, et al. Preparation of cationic cellulose in lonic liquid and its adsorption for Anionic blue 40[J]. Polymer Materials Science and Engineering,2021,37(6):8−16. CAO Y, SANG S, DENG H B, et al. Preparation of cationic cellulose in lonic liquid and its adsorption for Anionic blue 40[J]. Polymer Materials Science and Engineering, 2021, 37(6): 8-16.
[36] SWATLOSKI R P, SPEAR S K, HOLBREY J D, et al. Dissolution of cellulose with ionic liquids[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,2002,124(18):4974−4975. doi: 10.1021/ja025790m
[37] 候其东, 鞠美庭, 李维尊, 等. 基于离子液体的生物质组分分离研究进展[J]. 化工进展,2016,35(10):3022−3031. [HOU Q D, JU M T, LI W Z, et al. Research progress on biomass fractionation using ionic liquids[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2016,35(10):3022−3031. HOU Q D, JU M T, LI W Z, et al. Research progress on biomass fractionation using ionic liquids[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2016, 35(10): 3022-3031.
[38] 李俊峰, 张景顺, 李宁宁, 等. 离子液体在纤维素资源化利用中的应用研究进展[J]. 河南大学学报(自然科学版),2017,47(4):418−433. [LI J F, ZHANG J S, LI N N, et al. Progress of the application of lonic liquids in cellulose resource utilization[J]. Journal of Henan University (Natural Science),2017,47(4):418−433. LI J F, ZHANG J S, LI N N, et al. Progress of the application of lonic liquids in cellulose resource utilization[J]. Journal of Henan University (Natural Science), 2017, 47(4): 418-433.
[39] 张宁, 辛向东, 张月月, 等. 桑枝纤维素的低共熔溶剂法提取及其结构表征[J]. 蚕业科学,2021,47(5):451−458. [ZHANG N, XIN X D, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Extraction of cellulose from mulberry branch by deep eutecitic solvent and its structure characterization[J]. Acta Sericologica Sinica,2021,47(5):451−458. ZHANG N, XIN X D, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Extraction of cellulose from mulberry branch by deep eutecitic solvent and its structure characterization[J]. Acta Sericologica Sinica, 2021, 47(5): 451-458.
[40] HONG S, SONG Y, YUAN Y, et al. Production and characterization of lignin containing nanocellulose from luffa through an acidic deep eutectic solvent treatment and systematic fractionation[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2020,143:111913. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111913
[41] TIBOLLA H, PELISSARI F M, MARTINS J T, et al. Cellulose nanofibers produced from banana peel by chemical and mechanical treatments: Characterization and cytotoxicity assessment[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,75:192−201. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.08.027
[42] 冯彦洪, 周玉娇, 程天宇, 等. 纤维素纳米微纤机械制备方法进展[J]. 塑料,2015,44(4):28−31. [FENG Y H, ZHOU Y J, CHEN T Y, et al. Progress on mechanical production methods of microfibrillated cellulose[J]. Plastics,2015,44(4):28−31. FENG Y H, ZHOU Y J, CHEN T Y, et al. Progress on mechanical production methods of microfibrillated cellulose[J]. Plastics, 2015, 44(4): 28-31.
[43] KAMEL R, EL-WAKIL N A, DUFRESNE A, et al. Nanocellulose: From an agricultural waste to a valuable pharmaceutical ingredient[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,163:1579−1590. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.242
[44] SERRA-PARAREDA F, TARRÉS Q, SANCHEZ-SALVADOR J L, et al. Tuning morphology and structure of non-woody nanocellulose: Ranging between nanofibers and nanocrystals[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2021,171:113877. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2021.113877
[45] 陈欢, 钟洪浩, 王鲁峰. TEMPO氧化-高压均质联用制备柑橘纳米纤维素及其性质表征[J]. 食品科学技术学报,2022,40(4):35−44. [CHEN H, ZHONG H H, WANG L F. Preparation of citrus nanofibers by tempo oxidation-hiah pressure homogenization and its characterization[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2022,40(4):35−44. CHEN H, ZHONG H H, WANG L F. Preparation of citrus nanofibers by tempo oxidation-hiah pressure homogenization and its characterization[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 2022, 40(4): 35-44.
[46] 林凤采, 卢麒麟, 卢贝丽, 等. 纳米纤维素及其聚合物纳米复合材料的研究进展[J]. 化工进展,2018,37(9):3454−3470. [LIN F C, LU Q L, LU B L, et al. Research progress of nanocellulose and its polymer nanocomposites[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress,2018,37(9):3454−3470. LIN F C, LU Q L, LU B L, et al. Research progress of nanocellulose and its polymer nanocomposites[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2018, 37(9): 3454-3470.
[47] 王思. 甘草渣纤维素基抗菌材料的制备及其性能研究[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2019. WANG S. Research on preparation and properties of antibacterial composites based on licorice residues cellulose[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2019.
[48] MARIÑO M, LOPES DA SILVA L, DURÁN N, et al. Enhanced materials from nature: Nanocellulose from citrus waste[J]. Molecules,2015,20(4):5908−5923. doi: 10.3390/molecules20045908
[49] XU J, KRIETEMEYER E F, BODDU V M, et al. Production and characterization of cellulose nanofibril (CNF) from agricultural waste corn stover[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,192:202−207. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.03.017
[50] WANG Q Q, ZHU J Y, GLEISNER R, et al. Morphological development of cellulose fibrils of a bleached eucalyptus pulp by mechanical fibrillation[J]. Cellulose,2012,19(5):1631−1643. doi: 10.1007/s10570-012-9745-x
[51] 姜亚妮, 周骥平, 张琦, 等. 4种方法从葎草中制备的纳米纤维素性能[J]. 草业科学,2017,34(8):1748−1754. [JIANG Y N, ZHOU J P, ZHANG Q, et al. Comparative analysis of nanocellulose from Humulus scandens stems using four isolation methods[J]. Pratacultural Science,2017,34(8):1748−1754. JIANG Y N, ZHOU J P, ZHANG Q, et al. Comparative analysis of nanocellulose from Humulus scandens stems using four isolation methods[J]. Pratacultural Science, 2017, 34(8): 1748-1754.
[52] FERRER A, FILPPONEN I, RODRÍGUEZ A, et al. Valorization of residual Empty Palm Fruit Bunch Fibers (EPFBF) by microfluidization: production of nanofibrillated cellulose and EPFBF nanopaper[J]. Bioresource Technology,2012,125:249−255. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.08.108
[53] MONTAÑO-LEYVA B, RODRIGUEZ-FELIX F, TORRES-CHÁVEZ P, et al. Preparation and characterization of durum wheat (Triticum durum) straw cellulose nanofibers by electrospinning[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2011,59(3):870−875. doi: 10.1021/jf103364a
[54] MIDHUN DOMINIC C D, RAJ V, NEENU K V, et al. Chlorine-free extraction and structural characterization of cellulose nanofibers from waste husk of millet (Pennisetum glaucum)[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2022,206:92−104. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.02.078
[55] DAVOUDPOUR Y, HOSSAIN S, KHALIL H P S A, et al. Optimization of high pressure homogenization parameters for the isolation of cellulosic nanofibers using response surface methodology[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2015,74:381−387. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.05.029
[56] LI M, WANG L J, LI D, et al. Preparation and characterization of cellulose nanofibers from de-pectinated sugar beet pulp[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2014,102:136−143. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.11.021
[57] 王宝霞. 花生壳纤维素纳米纤维及其复合材料的制备与性能研究[D]. 南京: 南京林业大学, 2017. WANG B X. Preparation and properties of peanut shell cellulose nanofibers and its composites[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Forestry University, 2017.
[58] 陶鹏. 蔗渣纳米纤维素的制备及其热稳定性影响机制研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2019. TAO P. Preparation of bagasse nanocellulose and its influence mechanism of thermal stability[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2019.
[59] 张晓晓. 木薯渣纳米纤维素/木薯淀粉复合薄膜的制备与性能研究[D]. 南宁: 广西大学, 2019. ZHANG X X. Preparation and properties of cassava residue nanocellulose/cassava starch composite films[D]. Nanning: Guangxi University, 2019.
[60] 吴国栋. 基于生物质精炼的龙须草制浆过程及纳米纤维素制备的研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛科技大学, 2019. WU G D. Pulpand nanocellulose from Eulaliopsis binata based on biorefinefy[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University of Science and Technology, 2019.
[61] YANG Y, LIU H, WU M, et al. Bio-based antimicrobial packaging from sugarcane bagasse nanocellulose/nisin hybrid films[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,161:627−635. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.081
[62] GALLEGO R, PIRAS C C, RUTGEERTS L A J, et al. Green approach for the activation and functionalization of jute fibers through ball milling[J]. Cellulose,2020,27(2):643−656. doi: 10.1007/s10570-019-02831-0
[63] YI T, ZHAO H Y, MO Q, et al. From cellulose to cellulose nanofibrils-a comprehensive review of the preparation and modification of cellulose nanofibrils[J]. Materials (Basel),2020,13(22):5062. doi: 10.3390/ma13225062
[64] SZYMAŃSKA-CHARGOT M, CHYLIŃSKA M, PIECZYWEK P M, et al. Tailored nanocellulose structure depending on the origi. Example of apple parenchyma and carrot root celluloses[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2019,210:186−195. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.01.070
[65] KHAWAS P, DEKA S C. Isolation and characterization of cellulose nanofibers from culinary banana peel using high-intensity ultrasonication combined with chemical treatment[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,137:608−616. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2015.11.020
[66] KASSAB Z, MANSOURI S, TAMRAOUI Y, et al. Identifying Juncus plant as viable source for the production of micro-and nano-cellulose fibers: Application for PVA composite materials development[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2020,144:112035. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.112035
[67] 王增义. 稻草纤维素纳米纤维及其复合材料薄膜的制备与性能研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2019. WANG Z Y. Preparation and properties of rice straw cellulose nanofibrils and their composite films[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2019.
[68] 史杏娟, 蔡志江. 静电纺丝法制备纤维素纳米纤维的研究进展[J]. 高分子通报,2013(8):45−50. [SHI X J, CAI Z J. Advances in preparation of cellulose nanofibers by electrospinning method[J]. Polymer Bulletin,2013(8):45−50. SHI X J, CAI Z J. Advances in preparation of cellulose nanofibers by electrospinning method[J]. Polymer Bulletin, 2013(8): 45-50.
[69] DEEPA B, ABRAHAM E, CHERIAN B M, et al. Structure, morphology and thermal characteristics of banana nano fibers obtained by steam explosion[J]. Bioresource Technology,2011,102(2):1988−1997. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2010.09.030
[70] THOMAS M G, ABRAHAM E, JYOTISHKUMAR P, et al. Nanocelluloses from jute fibers and their nanocomposites with natural rubber: Preparation and characterization[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2015,81:768−777. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.08.053
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 周柯鑫,张晨曦,吴柔芬,王文俊,杨轩. 植物纳米纤维素材料制备的研究进展. 中国科学:化学. 2025(01): 242-257 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 席越阳,余秋雨,蒙志明,刘莹,朱迎春. 金针菇纳米纤维素复合凝胶的制备及结构表征. 肉类研究. 2024(02): 1-8 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 吴奇,户昕娜,卢舒瑜,崔然然,马涛,宋弋. 纤维素纳米纤维复合膜的制备及其作为食品包装材料的优异性能研究进展. 食品工业科技. 2024(17): 436-444 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 肖梦兰,彭钟海,谢冰和,黎惠红. 聚乳酸材料的阻气性能研究进展. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2024(24): 153-160 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(6)





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



