Optimization of Extraction Process of Polysaccharides from Stropharia rugosoannulata in Bo'ai County by Response Surface Method and Evalation of Their Antibacterial and Antioxidant Activity
-
摘要: 优化博爱赤松茸多糖超声辅助提取工艺,并研究其抑菌和抗氧化活性。以多糖得率为评价指标,在单因素实验基础上,采用3 因素3 水平的Box-Benhnken设计优化赤松茸多糖超声辅助提取工艺;分别采用二倍稀释法和平板涂布法测定博爱赤松茸多糖提取物的最小抑菌浓度(Minium inhibitionconcentration,MIC)和最小杀菌浓度(Minimum bactericidal concentration,MBC);分别采用ABTS法和 FRAP 法测定博爱赤松茸多糖的抗氧化能力。结果表明:博爱赤松茸多糖超声辅助最佳提取工艺为超声温度62 ℃、料液比1:30(g/mL)、超声时间62 min,在此条件下,博爱赤松茸多糖的平均得率为13.25%,与理论预测值(13.35%)相对误差为0.75%。在供试的5种常见致病菌中,博爱赤松茸多糖提取物仅对鼠伤寒沙门氏菌具有较强的抑制作用,其MIC和MBC分别为6.25 mg/mL和12.5 mg/mL。博爱赤松茸多糖提取物具有较强的清除ABTS+自由基的能力和还原 Fe3+的能力,且在一定质量浓度范围内呈量效关系,但均弱于相同质量浓度下的阳性对照VC。优化后的博爱赤松茸多糖超声辅助提取工艺稳定可行,且其提取物具有较强抗氧化活性和抑菌活性,但其抑菌作用具有选择性。Abstract: The ultrasonic-assisted extraction process of polysaccharides from Stropharia rugosoannulata in Bo'ai County and the antibacterial and antioxidant activities were analyzed. On the basis of single factor experiments, with the polysaccharide yield as response value, the ultrasonic-assisted extraction process of polysaccharides from Stropharia rugosoannulata in Bo'ai County was optimized using Box-Behnken experimental design with three factors and three levels. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and minimum bactericidal concentration (MBC) of the polysaccharides extracted from Stropharia rugosoannulata in Bo'ai County were determined using the double dilution method and the plate coating method, respectively. The antioxidant activity was determined using ABTS method and FRAP methods. The results showed that the optimal ultrasonic-assisted extraction conditions were 62 ℃ (ultrasonic temperature), 1:30 g/mL (solid-liquid ratio) and 62 min (ultrasonic time). Under these conditions, the average yield of polysaccharide was 13.25%, which agreed well with the predicted value of 13.35%, the relative error was 0.75%. Among the five common pathogenic bacteria tested, the polysaccharide extract showed the strongest inhibitory effect on Salmonella typhimurium with the minimum inhibitory concentration of 6.25 mg/mL and the minimum bactericidal concentration of 12.5 mg/mL. Meanwhile, the polysaccharide extract showed strong ability to scavenge ABTS+ free radicals and reduce Fe3+, and showed dose-effect relationship within a certain concentration range, although weaker than the positive control (VC) at the same concentration. The results suggested that the regression models were stable and feasible for polysaccharide extraction from Stropharia rugosoannulata in Bo'ai County and the extract had strong antioxidant and antibacterial activities, but its antibacterial effect was selective.
-
Keywords:
- Stropharia rugosoannulata /
- polysaccharide /
- Bo'ai County /
- bacteriostasis /
- antioxidant activity
-
赤松茸(Stropharia rugosoannulata)作为食用菌新秀[1],因其食味清香,肉质滑嫩柄爽脆,且富含18种氨基酸(包括8种人体必需氨基酸)、多种矿物质与微量元素,以及多糖、甾醇、黄酮等生物活性成分[2-3],而被冠之“素中之荤”的美称[4]。现代药理学研究显示,赤松茸提取物,特别是赤松茸多糖具有抗氧化[5]、抑菌[6]、抑制肿瘤[7]、降血糖[8]及增强小鼠免疫力[9]等诸多药理作用成为研究的热点。目前对赤松茸多糖的研究主要集中在赤松茸胞外多糖的培养条件优化[10-11]、赤松茸多糖或发酵菌丝体多糖提取工艺优化[12-14]、赤松茸多糖(硒多糖)的分离纯化、结构表征及生物活性评价等方面[15-17]。这些研究进一步表明赤松茸多糖具有极大研究价值和开发应用前景。
本研究室在前期研究中发现,博爱县赤松茸因其特殊的竹下栽培模式和种植环境,导致博爱赤松茸在营养成分和生物活性物质含量方面与其它栽培模式下的赤松茸存在很大的差异[18]。博爱赤松茸多糖的含量为(13.18%±0.05%)[2],要高于现有文献报道的多糖含量(6.3%)[19],且博爱赤松茸富含硒(2.57±0.47) mg/kg[2]。目前对赤松茸的富硒方式主要是通过液体发酵培养,但关于天然富硒赤松茸的研究较少。硒多糖是硒在食用菌中的主要赋存形式之一,兼具硒和多糖的双重生物活性,具有比未富硒多糖更高的抗氧化、增强免疫,抗肿瘤等生物活性[20-21]。苗元振的研究也表明赤松茸硒多糖抗氧化能力更优于多糖[22]。博爱赤松茸中的硒是否以硒多糖的形式存在及生物活性是否增强也尚未可知。而研究上述问题的前提就是如何高效获得博爱赤松茸多糖。
为此,本研究以获得高效提取博爱赤松茸多糖工艺为目标,采用响应曲面方法(response surface methodoloy,RSM)进行提取工艺优化,并研究其抑菌和抗氧化活性,旨在为博爱天然富硒赤松茸和赤松茸多糖的高值化利用提供依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
赤松茸 购自博爱县祥竹种植专业合作社赤松茸种植基地,采收于2021年6月;葡萄糖标准品(纯度≥98%) 天津市博迪化工有限公司;苯酚 天津市恒兴化学试剂制造有限公司;大肠杆菌(Escherichiacoli)、金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus)、化脓性链球菌(Streptococcus pyogenes)、鼠伤寒沙门氏菌(Salmonella typhimurium)、肺炎链球菌(Streptococcus pneumoniae) 均由河南省科学院天然产物重点试验室提供;Oxoid 胰蛋白胨 上海艾研生物科技有限公司;牛肉浸膏 广东环凯微生物科技有限公司;微量MIC测定板 美国Corning公司;总抗氧化能力检测试剂盒、ABTS自由基清除能力检测试剂盒 均购置索莱宝生化试剂盒事业部。
ME-204型电子天平 美国Mettler公司;KQ-500E型超声波清洗仪(功率500 W,频率40 kHz) 昆山市超声仪器有限公司;RE100-S-数显旋转蒸发仪 大龙兴创实验仪器(北京)股份公司;TU-1810型紫外分光光度计 北京普析通用仪器有限责任公司;YJ-VS-2型超净工作台 无锡一净净化设备有限公司;LDZF-75L-II立式高压蒸汽灭菌器 上海申安医疗器械厂。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 博爱赤松茸多糖提取工艺
采用超声辅助法提取博爱赤松茸多糖,具体工艺如下:将干燥至恒重的博爱赤松茸粉碎过40目筛,精密称取博爱赤松茸粉末1 g置于100 mL锥形瓶中,按不同液料比加入蒸馏水浸泡12 h,在不同温度和不同时间下超声提取3次,滤液合并后浓缩,定容至50 mL,摇匀备用。
1.2.2 单因素实验
按照1.2.1中的方法,在料液比1:25(g/mL)、超声时间60 min的条件下,考察20、30、40、50、60、70 ℃超声温度对博爱赤松茸多糖得率的影响;在最佳超声温度、超声60 min条件下,考察1:10、1:15、1:20、1:25、1:30、1:35(g/mL)料液比对博爱赤松茸多糖得率的影响;在最佳提取料液比、最佳提取超声温度的条件下,分别考察20、30、40、50、60、70 min超声时间对博爱赤松茸多糖得率的影响。
1.2.3 响应面试验
以多糖得率作为响应值,根据单因素实验结果,设计3因素3水平的Box-Behnken的中心组合试验,对博爱赤松茸多糖提取工艺进行优化,响应面因素水平设计见表1。
表 1 响应曲面试验因素水平表Table 1. Response surface test factor level table水平 因素 A
超声温度(℃)B
料液比(g/mL)C
超声时间(min)−1 50 1:25 50 0 60 1:30 60 1 70 1:35 70 1.2.4 博爱赤松茸多糖含量及得率的测定
参考NY/T 1676-2008的方法进行[23]。以葡萄糖(0.1 g/mL) 作为标准品,以葡萄糖浓度为横坐标,吸光度为纵坐标,求得葡萄糖标准曲线的回归线方程为:A=0.01027C+0.25195,R2=0.9981。精密吸取1.2.1中的待测多糖提取液0.2 mL于20 mL具塞试管中,同法操作进行测定,根据标准曲线计算出被测液中多糖质量浓度,并按下式计算各处理的多糖得率:
多糖得率(%)=c×v×nm×1000×100 式中:c为根据标准曲线求得的样品质量浓度,mg/mL;v为提取液体积,mL;n为稀释倍数;m为原料重量,g。
1.2.5 博爱赤松茸多糖提取物抑菌活性测定
参照文献[24]的方法测定博爱赤松茸多糖提取物的MIC和MBC。利用二倍稀释法将博爱赤松茸多糖稀释成质量浓度分别为400、200、100、50、25、12.5、6.25和3.125 mg/mL,在96孔细胞培养板中加入0.1 mL稀释好的博爱赤松茸多糖和0.1 mL浓度为 1×106~1×108 CFU/mL的菌悬液,37 ℃恒温箱中培养24 h观察结果,完全没有细菌生长时即为 MIC。在MIC实验基础上,采用平板涂布法测定MBC。
1.2.6 博爱赤松茸多糖提取物的抗氧化活性测定
参照ABTS试剂盒说明书中的方法测定博爱赤松茸多糖提取物对自由基的清除效果,反应体系中博爱赤松茸多糖的质量浓度分别为 0.3125、0.625、1.25、2.5、5.0 mg/mL,以VC作为对照组;参照T-OAC试剂盒说明书中的方法测定博爱赤松茸多糖提取物总抗氧化能力,反应体系中博爱赤松茸多糖的质量浓度分别为0.008、0.04、0.2、1、5 mg/mL,以VC作为对照组。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验均重复3次,数据结果用均值±标准差表示。使用Origin 7.5软件绘制趋势曲线图;使用SPSS 22.0软件进行方差分析及显著性检验;Design-Expert 8.0.6对响应面试验结果进行分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验
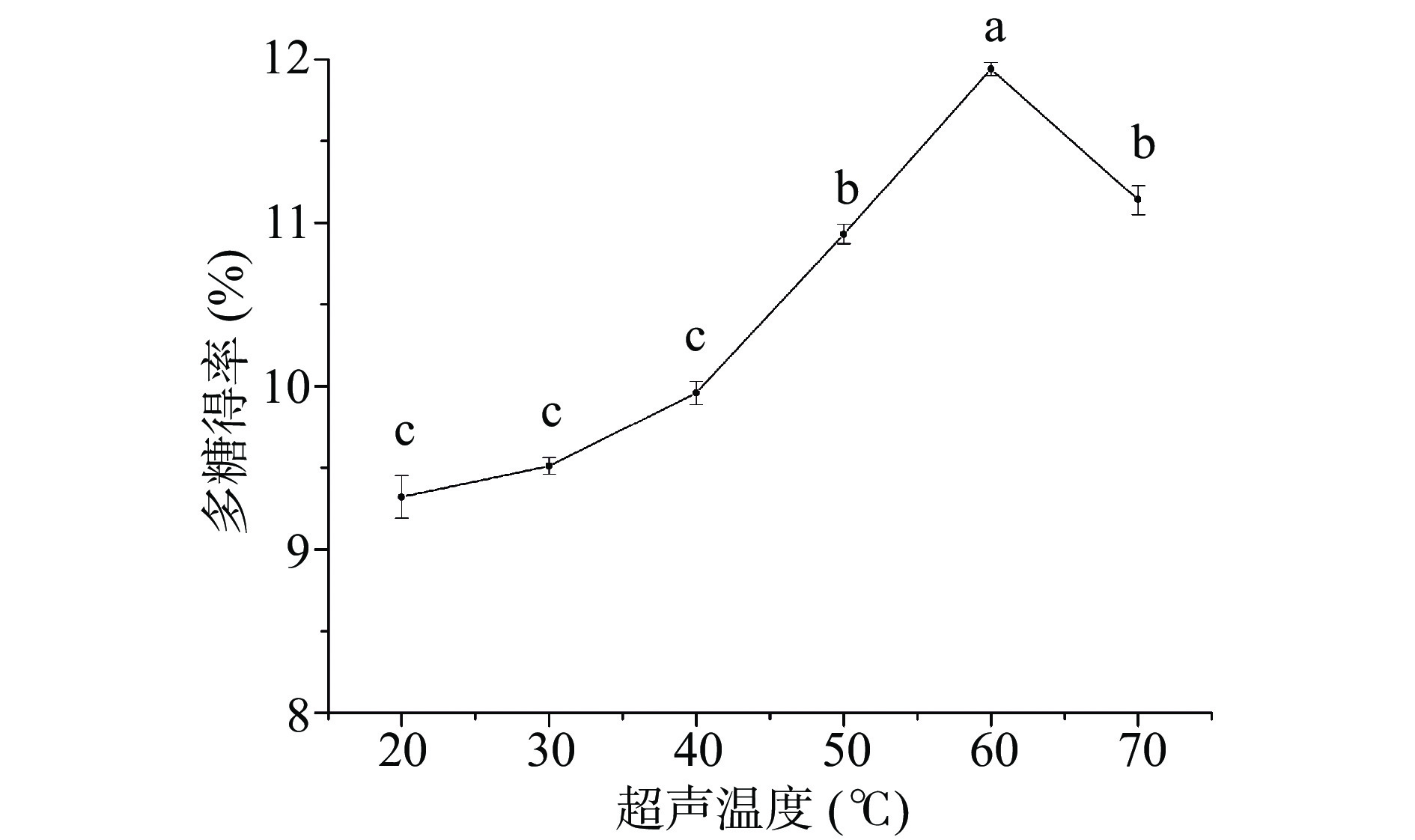
2.1.1 超声温度对博爱赤松茸多糖得率的影响
由图1可知,在料液比1:25(g/mL)、超声时间60 min固定条件下,博爱赤松茸多糖得率随超声温度的升高呈先升后降趋势,在60 ℃时,多糖得率达到最高,为11.94%,说明在60 ℃时,赤松茸多糖的溶出效果最佳,温度再升高时,伴着超声波的空化作用,可能引起多糖的裂解,导致多糖得率下降[25]。因此,超声温度选60 ℃为宜。
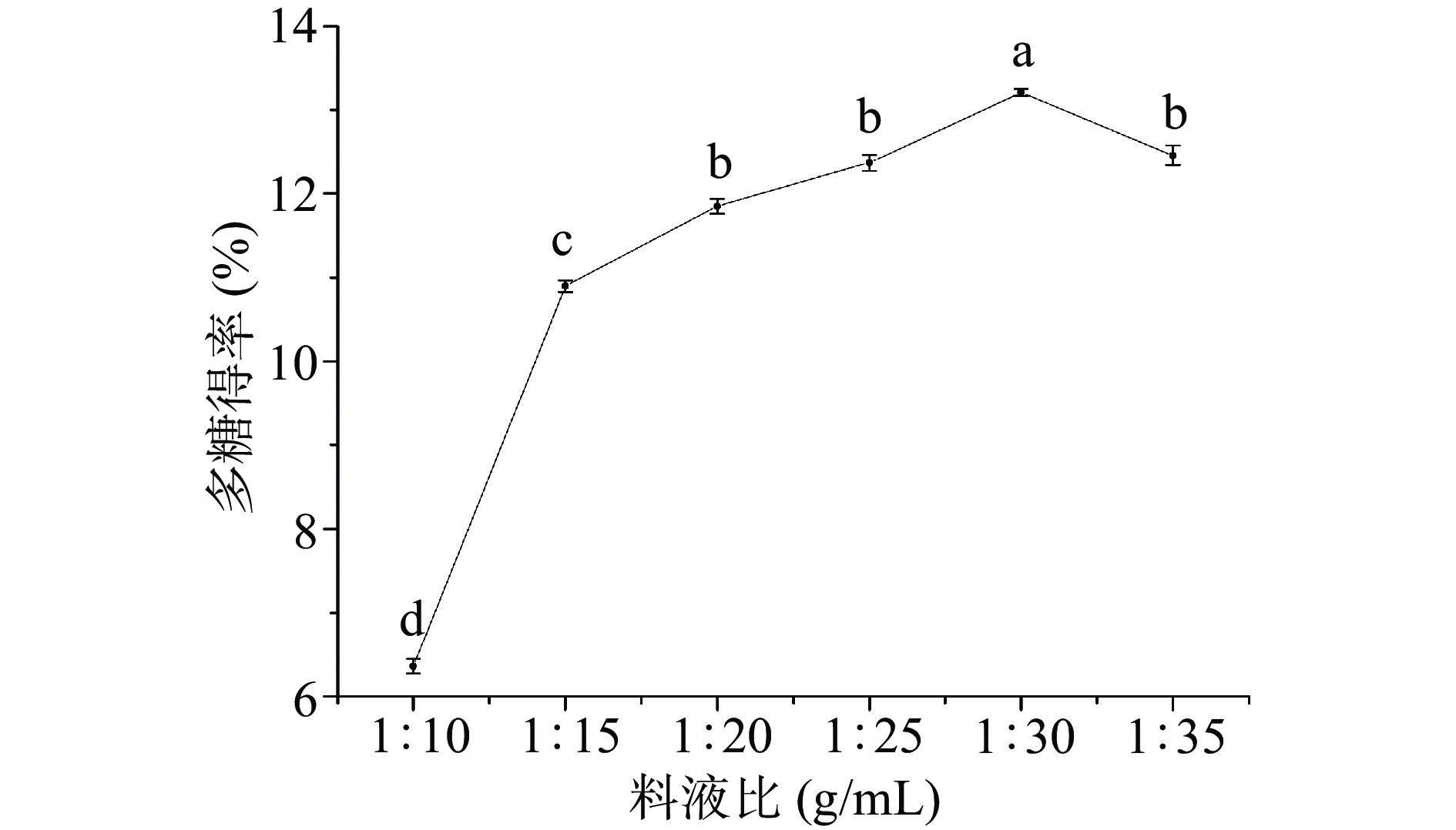
2.1.2 料液比对博爱赤松茸多糖得率的影响
由图2可知,在设定的料液比水平范围内,博爱赤松茸多糖得率随料液比增加呈先升后降趋势,在料液比1:10~1:25 g/mL时,多糖得率增幅比较大;在1:25~1:30 g/mL区间时,多糖得率趋于平稳,表明液料比在此区间时,绝大部分多糖已溶出并达到了平衡,溶剂的增多对多糖溶出度的影响较小,但再继续增加料液比,多糖得率呈明显下降趋势,这可能是由于溶剂用量增大,导致超声波对赤松茸粗粉作用力减弱。因此,料液比以1:30 g/mL为宜。
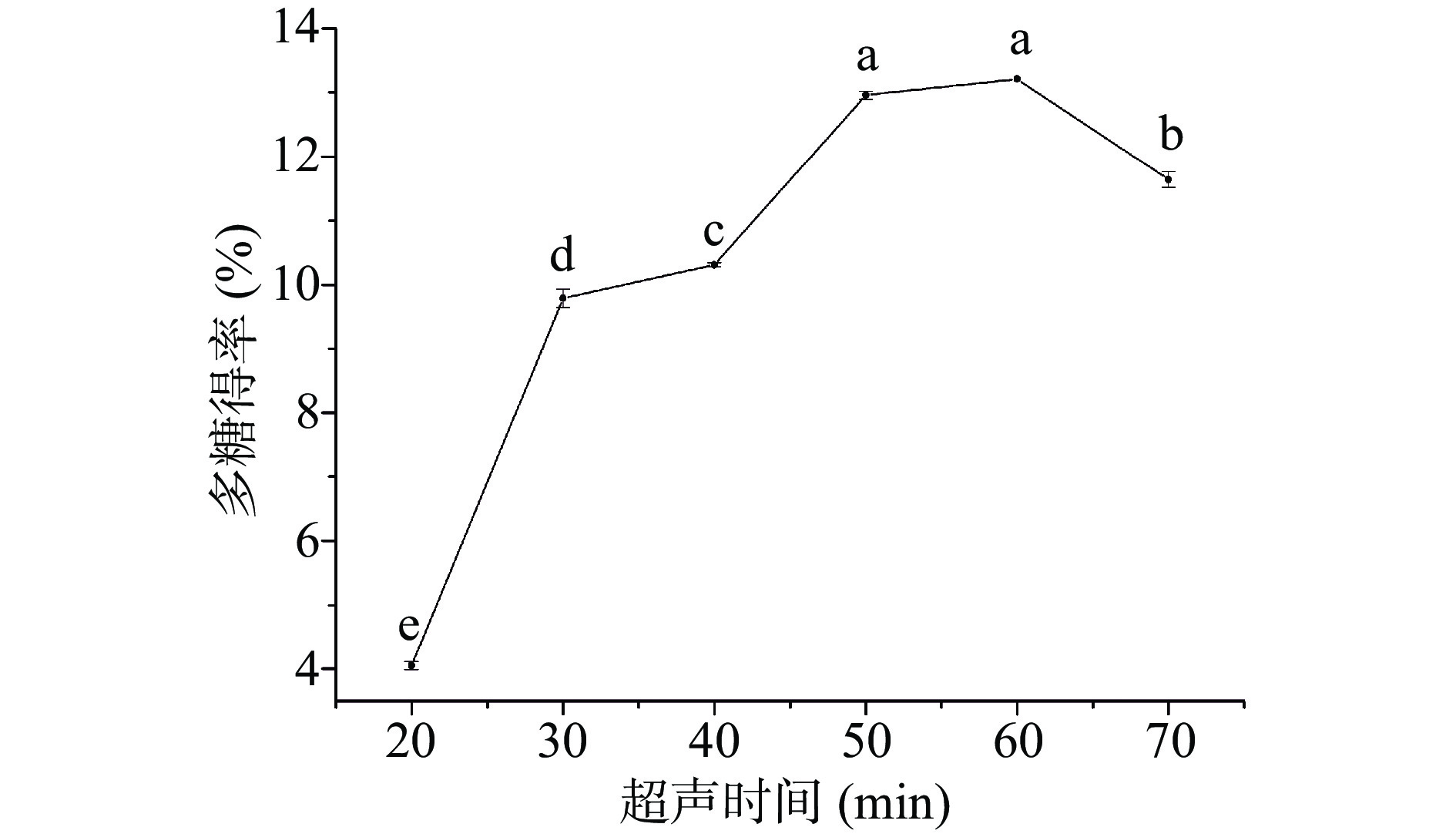
2.1.3 超声时间对博爱赤松茸多糖得率的影响
从图3中可以看出,在20~50 min这一区间内,超声时间的增加显著提高了赤松茸多糖的溶出效果(P<0.05);在50~60 min这一区间内,赤松茸多糖溶出效率趋于平缓,在超声时间60 min,赤松茸多糖已基本溶出,得率最大值为13.55%;之后再增加超声时间,多糖得率下降较为显著(P<0.05),可能是因长时间超声使赤松茸中部分多糖类化合物发生降解[26-27],同时杂质溶出也会增加,导致赤松茸多糖得率不升反降,所以超声时间以60 min为宜。
2.2 响应曲面法优化博爱赤松茸多糖得率的提取工艺
2.2.1 响应面试验设计与结果
根据单因素实验结果,采用三因素三水平响应面试验对博爱赤松茸多糖提取工艺进行优化,试验设计和结果见表2。
表 2 响应面试验设计方案和试验结果Table 2. Design and experiments results of response surface methodology试验号 A
超声温度B
料液比C
超声时间Y 多糖得率
(%)1 0 −1 1 11.34 2 0 0 0 13.28 3 0 1 1 11.71 4 0 0 0 13.31 5 −1 0 1 10.93 6 −1 −1 0 9.47 7 1 0 −1 11.56 8 0 1 −1 11.49 9 1 −1 0 11.34 10 1 1 0 11.30 11 0 −1 −1 10.97 12 0 0 0 13.22 13 −1 1 0 10.15 14 −1 0 −1 10.59 15 1 0 1 12.12 16 0 0 0 13.32 17 0 0 0 13.14 2.2.2 模型的建立及显著性检验
采用Design-Expert 12.0软件进行回归拟合,得到二次多项回归方程为:Y=13.25+0.6475A+0.19135B+0.1862C−0.1800AB+0.0550AC−0.0375BC−1.38A2−1.30B2−0.5687C2
由表3可知,该模型P<0.0001,表明该模型高度显著,实验设计合理可信;失拟项P=0.0546,不显著,表明其它未知因素对本实验结果影响较小;模型的决定系数R2=0.9939,校正决定系数RAdj2=0.9861,两者较为接近,表明该模型拟合性良好,可用于分析和预测博爱赤松茸多糖提取工艺;变异系数 CV为1.19%,远小于10%,说明本实验准确度和可信度较高,模型拟合度好,模型具有统计学意义,可以用来优化博爱赤松茸多糖超声提取工艺;该模型的信噪比为34.6104,大于4,表明该模型具有良好的分辨能力,可以用来预测。另外,从F值可以看出,本实验中3个因素对赤松茸多糖得率的影响程度次序为:A(超声温度)>B(料液比)>C(超声时间)。
表 3 二次回归模型的方差分析结果Table 3. Analysis of variance of quadratic regression model方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方和 F值 P值 显著水平 模型 22.29 9 2.48 127.20 <0.0001 ** A 3.35 1 3.35 172.29 <0.0001 ** B 0.2926 1 0.2926 15.03 0.0061 ** C 0.2775 1 0.2775 14.25 0.0069 ** AB 0.1296 1 0.1296 6.66 0.0365 * AC 0.0121 1 0.0121 0.6215 0.4563 BC 0.0056 1 0.0056 0.2889 0.6076 A2 8.03 1 8.03 412.63 <0.0001 ** B2 7.16 1 7.16 367.63 <0.0001 ** C2 1.36 1 1.36 69.96 <0.0001 ** 残差 0.1363 7 0.0195 失拟项 0.1123 3 0.0374 6.24 0.0546 净误差 0.0240 4 0.0060 校正项 22.42 16 注:*表示显著影响(P<0.05),**表示极显著影响(P<0.01);R2=0.9939;RAdj2=0.9861;PredR2=0.9182;Adeq Precision=34.6104;变异系数(CV)= 1.19%。 2.2.3 响应面交互作用分析
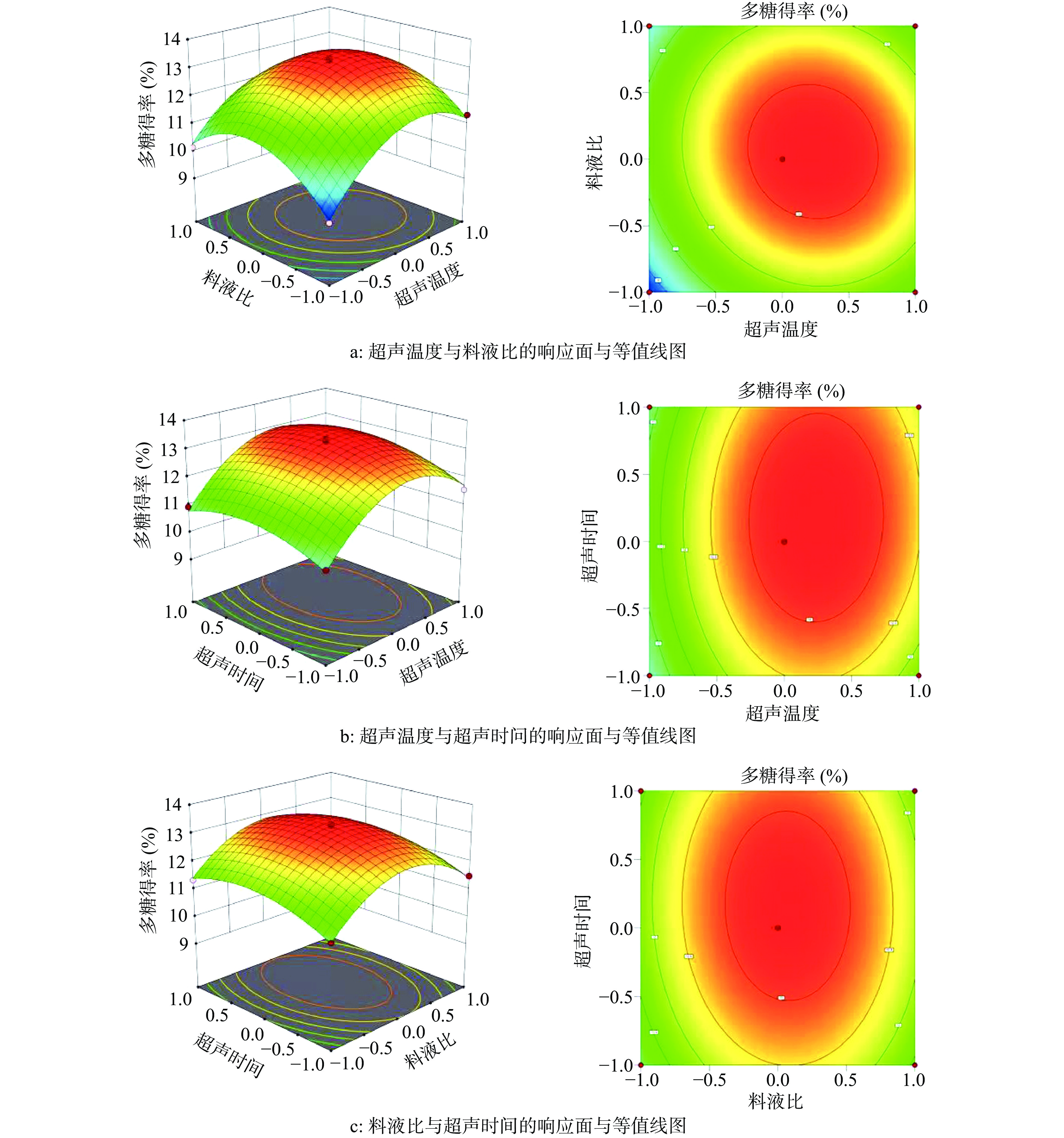
图4为各两因素交互作用对赤松茸多糖得率影响的响应面与等值线图,从图可以看出,3D响应面图均为开口朝下的凸形曲面,表明在实验范围内存在最高点;等高线为椭圆形,表明在实验范围内存在中心点,综合响应面和等高线图,可知在本实验所设计的因素水平范围之内可以获得赤松茸多糖超声提取最优工艺。实验因素对响应值的影响力大小可以从响应曲面的陡峭程度来推断,曲面越陡,影响力越大,反之则越小,因此,本实验中3个实验因素对博爱赤松茸多糖得率的影响依次为,超声温度>料液比>超声时间,这与方差分析结果相一致。总的来看,3 个实验因素对多糖得率响应值的影响均不是简单的线性关系,交互项对响应值也有很大的影响,其中超声温度和料液比交互项对多糖得率的影响达到了显著水平(P<0.05)。
通过分析软件,求得博爱赤松茸多糖最优提取工艺参数为超声温度62.34 ℃、料液比1:30.275 (g/mL)、超声时间61.73 min,在此条件下赤松茸多糖的理论预测含量为13.35%。
结合实际操作,将博爱赤松茸多糖最优提取工艺参数修正为:超声温度62 ℃、料液比1:30 (g/mL)、超声时间62 min,在此条件下重复实验 3 次,测得博爱赤松茸多糖的平均得率为13.25%,与理论预测值相对误差为0.75%,表明由该理论模型得到博爱赤松茸多糖最优提取工艺是可行的,具有一定的实际应用价值。
2.3 抑菌实验结果
表4为博爱赤松茸多糖提取物对5种供试菌的抑制活性结果,由表可知博爱赤松茸多糖提取物仅对鼠伤寒沙门氏菌有较强的抑制作用,其MIC和MBC分别为6.25 mg/mL和12.5 mg/mL;对金黄色葡萄球菌和肺炎链球菌具有一定的抑制作用,其MIC和MBC均在25 mg/mL以上;对大肠杆菌和化脓性链球菌在供试浓度范围无明显抑制作用。
表 4 博爱赤松茸多糖对5种常见致病菌的抑菌实验结果Table 4. Results of antimicrobial tests for the effects of polysaccharides from Stropharia rugosoannulata in Bo'ai County on 5 kinds of common pathogens菌种名称 革兰氏染色 MIC
(mg/mL)MBC
(mg/mL)大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli) − >200 >200 金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus) + 25 50 化脓性链球菌(Streptococcus pyogenes) + >200 >200 肺炎链球菌(Streptococcus pneumoniae) + 100 100 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌(Salmonella typhimurium) − 6.25 12.5 注:“+”表示革兰氏染色阳性,“−”表示革兰氏染色阴性;“>200”表示在此浓度下无法观察MIC、MBC值。 2.4 抗氧化实验结果
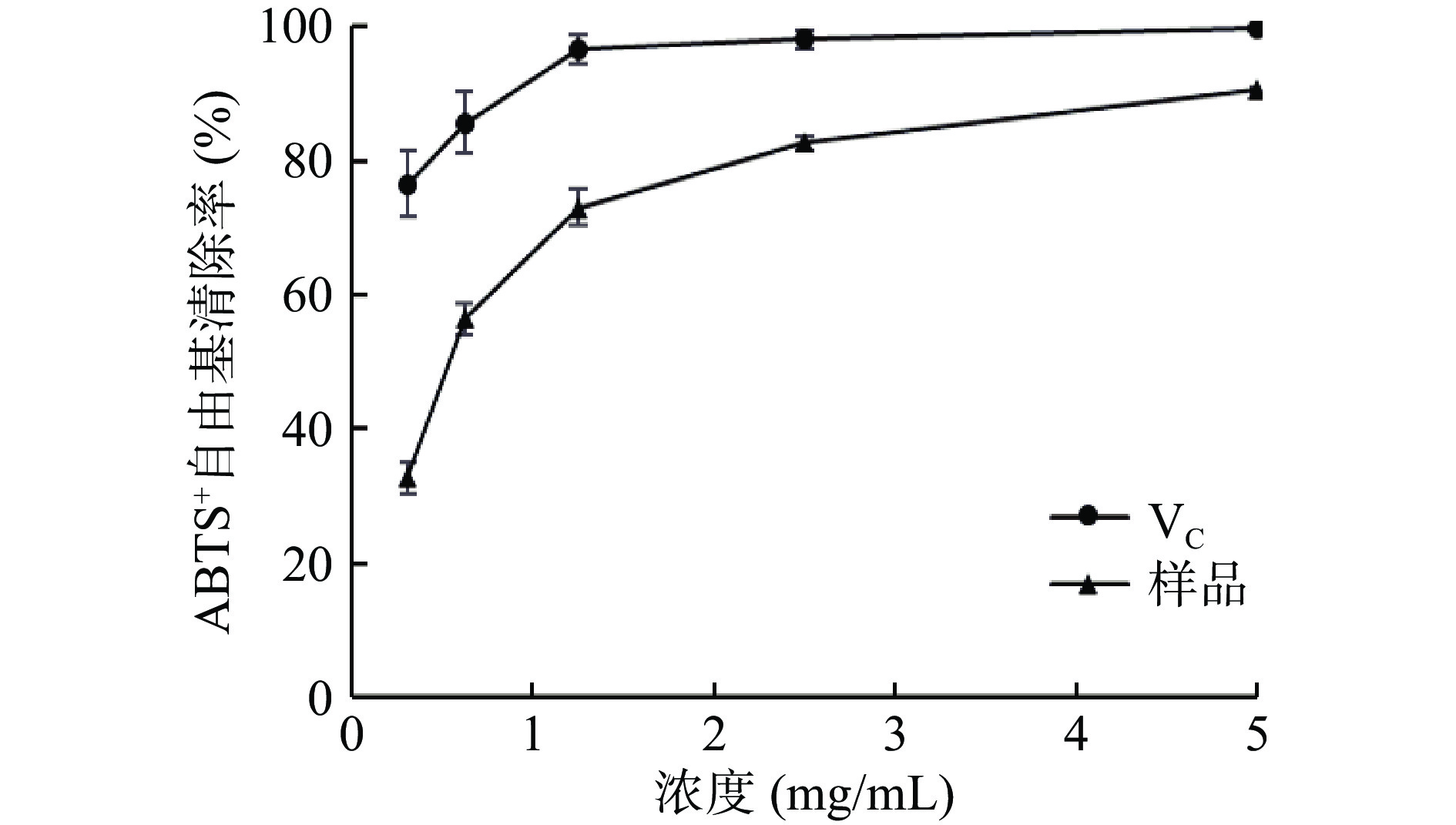
由图5可知,博爱赤松茸多糖提取物对ABTS+自由基清除效果随浓度升高而增加,呈明显量效关系,在5 mg/mL时,对ABTS+自由基的清除率达90.60%,但在检测范围内,博爱赤松茸多糖对ABTS+自由基清除能力整体低于VC。采用 SPSS22.0 软件进行回归拟合,计算得博爱赤松茸多糖提取物对ABTS+自由基清除率的IC50为0.54 mg/mL,远小于10 mg/mL,一般认为,某物质的 IC50 在10 mg/mL以下时,表明其具有较好的抗氧化活性[28],因此博爱赤松茸多糖提取物的抗氧化性有潜在的研究价值。
在593 nm下,以FeSO4为标准物质绘制标准曲线,求得回归方程为:Y=19.569X−0.0344,相关系数R2=0.9911。由图6可知,在0.008~5 mg/mL供试浓度范围内,博爱赤松茸多糖提取物对Fe3+的还原能力随浓度的升高而增加,但在相同供试浓度下,博爱赤松茸多糖的总抗氧化能力要弱于VC。
3. 讨论与结论
多糖是赤松茸的主要活性成分,具有广泛的应用价值和前景,因而对其活性成分的提取分离就显得尤为重要。杜敏华等[12]采用正交试验也得到了赤松茸多糖的最优提取工艺,提取温度65 ℃、提取时间1.0 h、超声波功率600 W、料液比1:35(g/mL),此条件多糖得率为8.16%。该正交试验所得赤松茸多糖最优提取工艺条件和本研究所得最优提取工艺条件除超声波功率外,其它条件较为接近,但多糖得率比本研究低38.42%,导致二者多糖得率差异较大的主要原因可能是实验所用赤松茸样品不同。此外,赤松茸采摘时间、超声功率及工艺优化所采用的方法等也会对赤松茸多糖得率造成一定的影响。
本研究抑菌实验表明,博爱赤松茸多糖提取物的杀菌谱比较窄,其仅对鼠伤寒沙门氏菌具有较强的抑制作用,对金黄色葡萄球菌和肺炎链球菌具有一定的抑制活性,但对大肠杆菌和化脓性链球菌在供试浓度范围无明显抑制作用,这与翁敏劼[29]的抑菌实验结果较为一致,但与王瑞瑞[30]的结果差异较大。王瑞瑞[30]的研究表明,25 mg/mL的赤松茸胞外多糖对大肠杆菌、枯草杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的抑菌率均在90%以上,导致本研究与王瑞瑞赤松茸多糖抑菌效果差异较大的原因可能是因赤松茸子实体多糖和菌丝体胞外多糖在结构方面存在较大差异。
本研究结果表明,博爱赤松茸多糖具有很强的体外抗氧化活性,且其含量与ABTS+自由基清除率、Fe3+还原能力呈正相关性。赤松茸多糖的抗氧化活性及免疫活性是其最主要的活性,也是目前多糖研究领域的热点。目前的研究显示,赤松茸多糖具有比香菇、姬松茸等食用菌多糖更强的清除·OH和·O2−的能力[31],且能通过对自由基的清除、血液和组织抗氧化酶和非酶体系的抗氧化能力的提升,显著改善对D-半乳糖致衰小鼠氧化损伤作用[32]。赤松茸多糖还具有预防急性肝损伤小鼠肝脏和主要脏器的氧化损伤作用、增强小鼠免疫力、恢复运动疲劳等活性[17, 33]。因此,赤松茸多糖具有很大的开发潜力。
综上可知,博爱赤松茸多糖超声最优提取工艺条件为:超声温度62 ℃、料液比1:30 (g/mL)、超声时间62 min,此条件下,多糖的平均得率为13.25%。且博爱赤松茸多糖提取物具有较强的清除ABTS+自由基能力、还原 Fe3+的能力和抑菌活性,但其抑菌作用具有选择性。本研究也仅局限于确定了博爱赤松茸多糖超声最优提取工艺和初步评价了博爱赤松茸多糖的抑菌、抗氧化活性,但对博爱赤松茸中硒是否强化多糖的生物活性及是否以硒多糖形式存在尚未研究,这将是本研究室下一步重点研究内容。
-
表 1 响应曲面试验因素水平表
Table 1 Response surface test factor level table
水平 因素 A
超声温度(℃)B
料液比(g/mL)C
超声时间(min)−1 50 1:25 50 0 60 1:30 60 1 70 1:35 70 表 2 响应面试验设计方案和试验结果
Table 2 Design and experiments results of response surface methodology
试验号 A
超声温度B
料液比C
超声时间Y 多糖得率
(%)1 0 −1 1 11.34 2 0 0 0 13.28 3 0 1 1 11.71 4 0 0 0 13.31 5 −1 0 1 10.93 6 −1 −1 0 9.47 7 1 0 −1 11.56 8 0 1 −1 11.49 9 1 −1 0 11.34 10 1 1 0 11.30 11 0 −1 −1 10.97 12 0 0 0 13.22 13 −1 1 0 10.15 14 −1 0 −1 10.59 15 1 0 1 12.12 16 0 0 0 13.32 17 0 0 0 13.14 表 3 二次回归模型的方差分析结果
Table 3 Analysis of variance of quadratic regression model
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方和 F值 P值 显著水平 模型 22.29 9 2.48 127.20 <0.0001 ** A 3.35 1 3.35 172.29 <0.0001 ** B 0.2926 1 0.2926 15.03 0.0061 ** C 0.2775 1 0.2775 14.25 0.0069 ** AB 0.1296 1 0.1296 6.66 0.0365 * AC 0.0121 1 0.0121 0.6215 0.4563 BC 0.0056 1 0.0056 0.2889 0.6076 A2 8.03 1 8.03 412.63 <0.0001 ** B2 7.16 1 7.16 367.63 <0.0001 ** C2 1.36 1 1.36 69.96 <0.0001 ** 残差 0.1363 7 0.0195 失拟项 0.1123 3 0.0374 6.24 0.0546 净误差 0.0240 4 0.0060 校正项 22.42 16 注:*表示显著影响(P<0.05),**表示极显著影响(P<0.01);R2=0.9939;RAdj2=0.9861;PredR2=0.9182;Adeq Precision=34.6104;变异系数(CV)= 1.19%。 表 4 博爱赤松茸多糖对5种常见致病菌的抑菌实验结果
Table 4 Results of antimicrobial tests for the effects of polysaccharides from Stropharia rugosoannulata in Bo'ai County on 5 kinds of common pathogens
菌种名称 革兰氏染色 MIC
(mg/mL)MBC
(mg/mL)大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli) − >200 >200 金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus) + 25 50 化脓性链球菌(Streptococcus pyogenes) + >200 >200 肺炎链球菌(Streptococcus pneumoniae) + 100 100 鼠伤寒沙门氏菌(Salmonella typhimurium) − 6.25 12.5 注:“+”表示革兰氏染色阳性,“−”表示革兰氏染色阴性;“>200”表示在此浓度下无法观察MIC、MBC值。 -
[1] 李正鹏, 李玉, 周峰, 等. 大球盖菇工厂化栽培技术[J]. 食用菌,2018,40(5):49−50. [LI Z P, LI Y, ZHOU F, et al. Industrial culture technology of Stropharia rugosoannulata[J]. Edible Fungi,2018,40(5):49−50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8357.2018.05.019 LI Z P, LI Y, ZHOU F, et al. Industrial culture technology of Stropharia rugosoannulata[J]. Edible Fungi, 2018, 40(5): 49-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8357.2018.05.019
[2] 景炳年, 常霞, 魏磊, 等. 博爱县赤松茸营养成分、生物活性物质及重金属含量分析与评价[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(4):278−285. [JING B N, CHANG X, WEI L, et al. Analysis and evaluation of nutrient components, bioactive substances and heavy metal content of Stropharia rugosoannulata in Bo'ai County[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(4):278−285. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021050090 JING B N, CHANG X, WEI L, et al. Analysis and evaluation of nutrient components, bioactive substances and heavy metal content of Stropharia rugosoannulata in Bo'ai County[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(4): 278-285. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021050090
[3] 王丽, 倪淑君, 李淑荣, 等. 大球盖菇菇盖和菇柄营养成分分析[J]. 黑龙江农业科学,2016(11):143−145. [WANG L, NI S J, LI S R, et al. Analysis of the different parts of base nutrition of Stropharia rugosoannulata[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences,2016(11):143−145. WANG L, NI S J, LI S R, et al. Analysis of the different parts of base nutrition of Stropharia rugoso-annulata[J]. Heilongjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2016(11): 143-145.
[4] 叶岚. 秦巴山区大球盖菇优质高产栽培技术[J]. 食用菌, 2018, 40(1): 51−52. YE L. High quality and high yield cultivation technology of Stropharia rugosoannulata in Qinba mountain area[J] Edible Fungi, 2018, 40(1): 51−52.
[5] 贾娇, 解修超, 宋玉, 等. 大球盖菇液体发酵培养基优化及其胞外多糖抗氧化活性[J]. 北方园艺,2021(24):105−115. [JIA J, XIE X C, SONG Y, et al. Optimizing culture medium and antioxidant activity of extracellular polysaccharides in liquid fermentation of Stropharia rugosoannulata[J]. Northern Horticulture,2021(24):105−115. JIA J, XIE X C, SONG Y, et al. Optimizing culture medium and antioxidant activity of extracellular polysaccharides in liquid fermentation of Stropharia rugosoannulata[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2021(24): 105-115.
[6] 汪虹, 陈辉, 张津京, 等. 大球盖菇生物活性成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 食用菌学报,2018,25(4):115−120. [WANG H, CHEN H, ZHANG J, et al. Research progresses on bioactive components in Stropharia rugosoannulata and their pharmacological effects[J]. Acta Edulis Fungi,2018,25(4):115−120. doi: 10.16488/j.cnki.1005-9873.2018.04.017 WANG H, CHEN H, ZHANG J, et al. Research progresses on bioactive components in Stropharia rugosoannulata and their pharmacological effects[J]. Acta Edulis Fungi, 2018, 25(4): 115-120. doi: 10.16488/j.cnki.1005-9873.2018.04.017
[7] SINGH R S, KAUR H P, KANWAR J R. Mushroom lectins as promising anticancer substance[J]. Current Protein & Peptide Science,2016,17(999):797−807.
[8] ZHAI X H, ZHAO A J, GENG L J, et al. Fermentation characteristics and hypoglycemic activity of an exopolysaccharide produced by submerged culture of Stropharia rugosoannulata #2[J]. Annals of Microbiology,2013,63:1013−1020. doi: 10.1007/s13213-012-0555-z
[9] 伍玉兰, 冯婉滢, 张玲雨, 等. 赤松茸多糖的提取及对小鼠免疫力的影响[J]. 中国食物与营养,2020,26(10):50−53. [WU Y L, FENG W Y, ZHANG L Y, et al. Extraction of polysaccharide from Stropharia rugosoannulata and its effect on immunity of mice[J]. China Food and Nutrition,2020,26(10):50−53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9577.2020.10.010 WU Y L, FENG W Y, ZHANG L Y, et al. Extraction of polysaccharide from Stropharia rugoso-annulata and its effect on immunity of mice[J]. China Food and Nutrition, 2020, 26 (10): 50-53. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9577.2020.10.010
[10] ZHOU B, JIA L, MENG F Y, et al. Statistical optimization of cultivation conditions for exopolysacchride production and mycelia growth by Stropharia rugosoannulata[J]. Annals of Microbiology,2010,60:89−96. doi: 10.1007/s13213-009-0006-7
[11] HE P X, GENG L J, WANG J Z, et al. Production, purfication, molecular characterization and bioactivities of exopolysaccharides produced by the wine cap culinary-medicinal mushroom, Stropharia rugosoannulata 2# (higher Basidiomycetes)[J]. Int J Med Mushrooms,2012,14(4):365−76. doi: 10.1615/IntJMedMushr.v14.i4.40
[12] 杜敏华, 王小立, 苏海飞, 等. 大球盖菇多糖超声波提取及抗氧化活性[J]. 食品研究与开发,2013,34(16):18−22. [DU M H, WANG X L, SU H F, et a. Optimization of extraction process by using ultrasound-assisted methodology and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Stropharia rugosoannulata[J]. Food Research and Development,2013,34(16):18−22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2013.16.006 DU M H, WANG X L, SU H F, et a. Optimization of extraction process by using ultrasound-assisted methodology and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Stropharia rugosoannulata[J]. Food Research and Development, 2013, 34 (16): 18-22. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2013.16.006
[13] 钱春强, 林文飞, 吴德平, 等. 碱提法提取大球盖菇多糖工艺及其清除氧自由基研究[J]. 现代食品,2021,27(3):99−102. [QIAN C Q, LIN W F, WU D P, et al. Study on the extraction of polysaccharides from Stropharia rugosoannulata by alkaline extraction and its scavenging oxygen free radical[J]. Modern Food,2021,27(3):99−102. doi: 10.16736/j.cnki.cn41-1434/ts.2021.03.031 QIAN C Q, LIN W F, WU D P, et al. Study on the extraction of polysaccharides from Stropharia rugoso-annulata by alkaline extraction and its scavenging oxygen free radical[J]. Modern Food, 2021, 27 (3): 99-102. doi: 10.16736/j.cnki.cn41-1434/ts.2021.03.031
[14] 王米雪, 圣志存, 陈晓兰. 大球盖菇发酵菌丝体多糖提取条件优化与结构分析[J]. 北方园艺,2020(1):111−116. [WANG M X, SHENG Z C, CHEN X L. Optimization of extraction and characterization of polysaccharide from Stropharia rugosoannulata fermentation mycelium[J]. Northern Horticulture,2020(1):111−116. doi: 10.11937/bfyy.20191112 WANG M X, SHENG Z C, CHEN X L. Optimization of extraction and characterization of polysaccharide from Stropharia rugosoannulata fermentation mycelium[J]. Northern Horticulture, 2020 (1): 111-116. doi: 10.11937/bfyy.20191112
[15] LIU Y, HU C F, FENG X, et al. Isolation, characterization and antioxidant of polysaccharides from Stropharia rugosoannulata[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,155(15):883−889.
[16] JIANG L, HOU Y L, DING X. Structure identification and biological activities of a new polysaccharides from Stropharia rugosoannulata[J]. Latin American Journal of Pharmacy,2020,39(8):1594−1604.
[17] 邵华. 大球盖菇多糖对大鼠运动疲劳恢复的影响[J]. 中国食用菌,2020,39(7):68−71. [SHAO H. Extraction of polysaccharide from Stropharia rugosoannulata and its effect on sportsfatigue recovery[J]. Chinese Edible Fungi,2020,39(7):68−71. doi: 10.13629/j.cnki.53-1054.2020.07.017 SHAO H. Extraction of polysaccharide from Stropharia rugoso-annulata and its effect on sportsfatigue recovery[J]. Chinese Edible Fungi, 2020, 39 (7): 68-71. doi: 10.13629/j.cnki.53-1054.2020.07.017
[18] WEI L, JING B N, LI X, et al. Evaluation of nutritional ingredients, biologically active materials, and pharmacological activities of Stropharia rugosoannulata grown under the bamboo forest and in the greenhouse[J]. Journal of Food Quality,2021,2021:5478227.
[19] 李淑荣, 王丽, 倪淑君, 等. 大球盖菇不同部位氨基酸含量测定及营养评价[J]. 食品研究与开发,2017,38(8):95−99. [LI S R, WANG L, NI S J, et al. The amino acids content of different part of Stropharia rugosoannulata and their nutrition evaluation[J]. Food Research and Development,2017,38(8):95−99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2017.08.021 LI S R, WANG L, NI S J, et al. The amino acids content of different part of Stropharia rugoso-annulata and their nutrition evaluation[J]. Food Research and Development, 2017, 38(8): 95−99. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2017.08.021
[20] WANG Y F, LI Y F, LIU Y Y, et al. Extraction, characterization and antioxidant activities of Se-enriched tea polysaccharides[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2015,77:76−84. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.02.052
[21] LI Q, WANG W, ZHU Y, et al. Structural elucidation and antioxidant activity a novel Se-polysaccharide from Se enriched Grifola frondosa[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2017,161:42−45. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.12.041
[22] 苗元振. 大球盖菇硒多糖分离纯化及其抗氧化活性分析[D]. 泰安: 山东农业大学, 2009. MIAO Y Z. Separation and purification of Se-olysaccharide from Stropharia rugosoannulata and its antioxidant activities[D]. Tai'an: Shandong Agricultural University, 2009.
[23] 中国人民共和国农业部. NY/T 1676—2008食用菌中粗多糖含量的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. Ministry of Agriculture of the People's Republic of China. NY/T 1676-2008 Determination of crude polysaccharides in edible fungi[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2008.
[24] 景炳年, 魏磊, 周雍, 等. 山银花总三萜超声辅助提取工艺优化及其抗菌抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021(1):174−181. [JING B N, WEI L, ZHOU Y, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction process for total triterpenoids from Lonicera confuse and its antibacterial and antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021(1):174−181. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020030330 JING B N, WEI L, ZHOU Y, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction process for total triterpenoids from Lonicera confuse and its antibacterial and antioxidant activity[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2021 (1): 174-181. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020030330
[25] WANG Y P, LIU Y, HU Y H. Optimization of polysaccharides extraction from Trametes robiniophila and its antioxidant activities[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2014(111):324−332.
[26] 洪胜, 潘利华, 罗建平. 生物多糖超声波辅助提取研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2011,32(8):481−484. [HONG S, PAN L H, LUO J P. Progress of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of biological polysaccharides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2011,32(8):481−484. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2011.08.128 HONG S, PAN L H, LUO J P. Progress of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of biological polysaccharides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2011, 32 (8): 481-484. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2011.08.128
[27] 杨文雅, 李长征, 张海晖, 等. 蛹虫草多糖的亚临界水萃取及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2016,37(5):252−257. [YANG W Y, LI C Z, ZHANG H H, et al. Study on the optimization for the extraction and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Cordyceps militaris by subcritical water[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2016,37(5):252−257. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2016.05.041 YANG W Y, LI C Z, ZHANG H H, et al. Study on the optimization for the extraction and antioxidant activity of polysaccharide from Cordyceps militaris by subcritical water[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2016, 37 (5): 252-257. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2016.05.041
[28] 郑义, 邵颖, 陈安徽, 等. 益智仁总黄酮超声辅助提取工艺优化及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(6):44−49. [ZHENG Y, SHAO Y, CHEN A H, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction and antioxidant activities of total flavonoids from Alpinia oxyphylla fruits[J]. Food Science,2014,35(6):44−49. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201406009 ZHENG Y, SHAO Y, CHEN A H, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction and antioxidant activities of total flavonoids from Alpinia oxyphylla fruits[J]. Food Science, 2014, 35 (6): 44-49. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201406009
[29] 翁敏劼. 大球盖菇多糖的提取、结构及生物活性研究[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2010. WENG M J. Extraction, structure and bioactivity of polysaccharides from Stropharia rugosoannulata[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2010.
[30] 王瑞瑞. 真菌发酵胞外多糖的硫酸化及生物活性研究[D]. 郑州: 河南农业大学, 2014. WANG R R. Study on sulfated modification of exopolysaccharides from fungi fermentation and its biological activity[D]. Zhenzhou: Henan Agricultural University, 2014.
[31] 林桂兰, 许学书, 连文思. 食用菇多糖提取物体外抗氧化性能研究[J]. 华东理工大学学报(自然科学版),2006(3):278−281, 317. [LIN G L, XU X H, LIAN W S. Antioxidant activity of edible mushroom polysaccharide extracts in vitro[J]. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition),2006(3):278−281, 317. LIN G L, XU X H, LIAN W S. Antioxidant activity of edible mushroom polysaccharide extracts in vitro[J]. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2006 (3): 278-281, 317.
[32] 王峰, 王晓炜, 陶明煊, 等. 大球盖菇提取物对CCl_4所致急性肝损伤小鼠的抗氧化酶活性及同工酶的影响[J]. 食品科学,2010,31(7):263−268. [WANG F, WANG X W, TAO M G, et al. Effect of Stropharia rugosoannulata extract (SRE) on activities and isozyme profiles of antioxidant enzymes in mice with carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury[J]. Food Science,2010,31(7):263−268. WANG F, WANG X W, TAO M G, et al. Effect of Stropharia rugoso-annulata extract (SRE) on activities and isozyme profiles of antioxidant enzymes in mice with carbon tetrachloride-induced acute liver injury[J]. Food Science, 2010, 31 (7): 263-268.
[33] 陶明煊, 王峰, 王晓炜, 等. 大球盖菇多糖对小鼠心脏抗氧化作用研究[J]. 食品科学,2007(9):529−532. [TAO M X, WANG F, WANG X W, et al. Study on antioxidant of Stropharia rugosoannulata polysaccharide on mouse heart[J]. Food Science,2007(9):529−532. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2007.09.130 TAO M X, WANG F, WANG X W, et al. Study on antioxidant of Stropharia rugosoannulata polysaccharide on mouse heart[J]. Food Science, 2007(9): 529-532. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6630.2007.09.130
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 郭玉龙,邵高耸,史轻舟,许焯,胡定煜,符式瑜. 纳米材料在食品检验鉴定中的应用研究进展. 山东化工. 2024(01): 91-94 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 左海根,黄芷诺,李毛英,袁小珍,杜永琴,刘小玉,陈雨. 核酸适配体在雌二醇分析中的研究进展. 理化检验-化学分册. 2023(07): 862-868 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 唐春花,杨洁,卢晓玲,陈美仑,魏铮,余鹏,赵佳. 甾体激素核酸适配体的筛选与应用. 生物化学与生物物理进展. 2023(09): 2146-2161 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 于开宁,王润忠,刘丹丹. 水环境中新污染物快速检测技术研究进展. 岩矿测试. 2023(06): 1063-1077 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 常嵘,叶巧燕,刘慧敏,郝欣雨,郭洪侠,郑楠. 牛奶中激素检测方法的研究进展. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2022(16): 5235-5243 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 史学丽,高辉,周永红,赵伟. 一种基于适配体传感器的17β-雌二醇定量分析方法. 河北工业科技. 2021(05): 431-437 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



