Effects of Oviductus Ranae on Follicular Developmental Dysfunction by Tripterygium in Rats
-
摘要: 目的:研究林蛙油对卵泡发育障碍模型大鼠卵巢中的卵泡和磷脂酰肌醇受体3-酪氨酸激酶(phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, PI3K)/卵蛋白激酶受体B(protein kinase B, Akt)的信号通路的影响。方法:筛选后的雌性WISTAR大鼠40只,随机分为对照组、模型组、阳性药组和林蛙油高、低剂量组;除对照组外其余各组大鼠每日灌胃雷公藤多苷溶液(40 mg/kg),阳性药组大鼠灌胃戊酸雌二醇溶液(0.1 mg/kg)和醋酸甲地孕酮溶液(0.8 mg/kg),林蛙油高、低剂量组大鼠分别灌胃林蛙油溶液(400、200 mg/kg)。第8周测定大鼠血清雌二醇(estradiol, E2)、孕酮(progesterone, P)、促黄体生成素(Luteinizing hormone, LH)、促卵泡生成素(Follicle-stimulating hormone, FSH)和睾酮(testosterone, T)含量;摘取卵巢和子宫称量记录,计算器官指数;一侧卵巢做HE染色和TUNEL染色计算各级卵泡数量。另外一侧卵巢测定其中PI3K、AKT、人第10号染色体缺失的磷酸酶(phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten, PTEN)和哺乳动物雷帕霉素靶蛋白(mammalian target of rapamycin, mTOR)的mRNA相对表达量以及PI3K、磷酸化蛋白激酶B(phosphorylated protein kinase B, p-Akt)的蛋白含量。结果:大鼠卵泡发育障碍模型成功建立。与模型组大鼠相比,林蛙油高剂量组大鼠子宫湿重和子宫指数显著升高(P<0.05);林蛙油高、低剂量组大鼠发情周期显著缩短(P<0.05),次级卵泡数量显著升高(P<0.05),卵泡闭锁率显著降低(P<0.05),血清FSH含量显著减少(P<0.05)、T和E2含量显著升高(P<0.05),PI3K蛋白含量显著增多(P<0.05),Akt蛋白磷酸化水平显著提高(P<0.05),PTEN mRNA相对表达量显著减少(P<0.05);林蛙油高剂量组大鼠卵巢中mTOR mRNA相对表达量显著低于模型组大鼠(P<0.05)。结论:林蛙油对雷公藤多苷所致大鼠卵泡发育障碍有明显的改善作用,林蛙油可以上调PI3K/Akt信号通路促进卵泡发育障碍的大鼠卵泡的生长和发育。
-
关键词:
- 林蛙油 /
- 卵泡发育障碍 /
- 卵巢 /
- 雷公藤多苷 /
- 磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(PI3K)/蛋白激酶B(Akt)信号通路
Abstract: Objective: To study the effect of oviductus ranae (OR) on follicle development and phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/protein kinase B (Akt) signaling pathway in the ovaries of follicular developmental dysfunction rats. Methods: Randomly divide the screened 40 female WISTAR rats into control group (CG), model group (MG), positive qroup (PG), OR high-dose (ORHG) and low-dose group (ORLG). Except the CG rats, the rats in other groups were treated with triptolide solution (40 mg/kg) once a day. The PG were treated with estradiol valerate solution (0.1 mg/kg) and megestrol acetate solution (0.8 mg/kg). The ORHG and ORLG were treated with OR solution (400、200 mg/kg). The rat serum was collected to determine the contents of estradiol (E2), progesterone (P), Luteinizing hormone (LH), Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and testosterone (T) at 8th week . The ovaries and uterus of rats were harvested and weighed, and the organ index was calculated. HE staining and TUNEL staining were performed on one ovary to calculate the number of follicles at all levels. The relative expression of PI3K, AKT, phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome ten (PTEN) mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) mRNA and the contents of PI3K, Akt, phosphorylated protein kinase B(p-Akt) protein in the other ovary was measured. Result: The results indicated that the follicular development dysfunction model was successfully established. Compared with the MG, the wet weight and index of uterus of the ORHG was increased significantly (P<0.05). The estrous cycle of rats in the ORHG and ORLG was significantly shortened (P<0.05), the number of secondary follicles was significantly increased (P<0.05), the follicular atresia rate was significantly reduced (P<0.05), the serum FSH and LH content was decreased significantly (P<0.05), the serum T and E2 content was increased significantly (P<0.05), PI3K protein content was increased significantly (P<0.05), Akt protein phosphorylation level was increased significantly (P<0.05), the relative expression of PTEN mRNA was decreased significantly (P<0.05). The relative expression of mTOR mRNA in ORHG was significantly lower than that of MG (P<0.05). Conclusion: OR can obviously improve the follicular development dysfunction of rats induced by triptolide, and it can up-regulate PI3K/Akt signal pathway to promote the growth and development of follicles in rats with follicular development dysfunction. -
林蛙油为中国林蛙(Rana temporaria chensinesis David)雌蛙输卵管干制品,属于名贵山珍,号称“绿色软黄金”,含有丰富的营养成分。林蛙油具有补肾益精、健脾益胃、滋阴补肾、润肺生津等功效,因此具有很好的食补作用,常被女性作为日常保健品服用。现代药理学研究也证实林蛙油具有抵抗环境应激、促进人体生长和发育、提高人体的免疫功能、镇咳和祛痰、耐疲劳性等多种生物活性功能[1-2]。
目前国内外有关林蛙油雌激素样作用机制的研究,大多数聚焦在林蛙油含有的外源雌激素及其主要成分[1-2],临床上常用其雌激素样作用治疗女性围绝经期症状,多数学者认为其能提升服用者体内雌激素含量。
实验室前期实验研究成果表明,林蛙油的雌激素样作用与外源雌激素作用不同[3-4],是通过影响卵巢内生长期卵泡发育程度从而使血清雌激素水平提升的结果。课题组提出假说“服用林蛙油刺激生长期卵泡发育,使得次级卵泡相应增多,这个过程中增多的卵泡和间质腺会导致服用者雌激素水平提高”。本次实验从“林蛙油刺激生长期卵泡发育”这一角度,通过建立卵泡发育障碍大鼠模型检验林蛙油对大鼠卵泡发育的影响,探讨林蛙油对大鼠卵巢中发育受抑制卵泡生长的促进作用和机制,进一步了解并阐明林蛙油雌激素样作用机制,分析林蛙油对服用者血清雌激素水平提升的作用机理,为林蛙油雌激素样作用机制提供理论依据。
1. 材料和方法
1.1 材料与仪器
雌性WISTAR大鼠 8周龄体质量180~200 g饲养于SPF级屏障系统,长春市亿斯实验动物技术有限责任公司[SCXK(吉)-2018-0007],由吉林省中医药科学院实验动物伦理委员会审核,符合实验动物伦理委员会规定;林蛙油 通化德正堂野生资源开发有限公司,经吉林省中医药科学院邸琳主任药师鉴定为正品;戊酸雌二醇片 DELPHARM Lille S.A.S.;醋酸甲地孕酮分散片 青岛国海生物制药有限公司;雷公藤多苷片 远大医药黄石飞云制药有限公司;革兰氏染液(快速法) 珠海贝索生物技术有限公司;雌二醇(Estradiol, E2)、孕酮(Progesterone, P)、促黄体生成素(Luteinizing hormone, LH)、促卵泡生成素(Follicle stimulating hormone, FSH)、睾酮(Testosterone, T)放射免疫法试剂盒(210420) 北京北方生物技术研究所有限公司;BCA蛋白浓度测定试剂盒(120720210408) 上海碧云天生物技术有限公司;β-肌动蛋白(β-actin)抗体、磷酸化蛋白激酶B(Protein kinase B, p-Akt)抗体、辣根过氧化物酶(Horseradish Peoxidase, HRP)标记二抗(活性>250 U/mg) 美国CST公司;磷酸化蛋白激酶(Akt)抗体、PI3K抗体 武汉爱博泰克生物科技有限公司;牛血清白蛋白(Bovine albumin, BSA) 美国VWR公司;SDS-PAGE凝胶配制试剂盒(B13300150) 北京鼎国昌盛生物技术有限责任公司;聚偏氟乙烯(PVDF)印记膜、ECL化学发光显色试剂盒(R9SA30527、2203001) 德国密理博公司;TRIzol、实时荧光定量聚合酶链式反应(Real-time PCR)反转录试剂盒(#AJ92014A)、TB Green™ Premix Ex Taq™ II荧光染料 大连宝生物工程有限公司;戊巴比妥钠 天津市光复精细化工研究所;甲醛 辽宁泉瑞试剂有限公司。
XH 6080型放免仪 西安核仪器厂;HC-3618R高速冷冻离心机 安徽中科中佳科学仪器有限公司;JA 2003 B型千分之一电子天平 上海越平科学仪器有限公司;Y-2000型电子天平 常熟双杰测试仪器厂;L18-Y928型搅拌机 九阳股份有限公司;CX 23型光学显微镜 日本Olympus公司;FLUOstar Omega型全自动酶标仪 德国BMG公司;SpectroArt 200S型超微量核酸测定仪 美国Wealtec公司;Agilent Stratagene Mx 3000P型Real-time PCR仪 美国安捷伦公司;Allegra X-30R高速离心机 美国Beckman公司;Mini-PROTEAN Tetra Cell型电泳槽、Trans-Blot SD型半干转印槽 美国Bio-Rad公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 实验动物分组、卵巢抑制模型建立及各组大鼠给药
实验动物分组:从60只雌性WISTAR大鼠中筛选40只发情周期正常的大鼠随机分为对照组、模型组、阳性药组、林蛙油高剂量组和林蛙油低剂量组,每组8只。实验大鼠均饲养在SPF级屏障系统内。
卵泡发育障碍模型的建立[5-8]:模型组、阳性药组、林蛙油高剂量组和林蛙油低剂量组大鼠,通过每日上午灌胃雷公藤多苷片溶液建立卵泡发育障碍模型,灌胃剂量为40 mg/kg,灌胃体积10 mL/kg,相当于人每日服用0.4 g雷公藤多苷片。连续灌胃8周,对照组大鼠每日等体积蒸馏水灌胃。
林蛙油溶液制备及给药:林蛙油于100倍蒸馏水中4 ℃下泡发16 h,灌胃前使用搅拌机充分搅拌至林蛙油溶液细腻均匀无明显大气泡及胶状物即可。林蛙油高、低剂量组灌胃剂量分别为400、200 mg/kg,单次灌胃体积为20 mL/kg[3-4]。剂量换算相当于人每日服用4、2 g林蛙油。林蛙油高剂量组每日灌胃两次林蛙油溶液,两次灌胃间隔至少4 h。自卵泡发育障碍模型造模第1 d开始灌胃,连续灌胃8周。
阳性药组给药[9]:使阳性药组大鼠摄入外源激素,以戊酸雌二醇溶液和醋酸甲地孕酮分散片溶液灌胃,灌胃体积均为20 mL/kg,戊酸雌二醇溶液灌胃剂量为0.1 mg/kg,剂量换算相当于人每日口服0.97 mg有效成分,醋酸甲地孕酮分散片溶液灌胃剂量为0.8 mg/kg,剂量换算相当于人每日口服7.78 mg有效成分,阳性药组大鼠以每5 d为一个周期灌胃,前3 d连续灌胃戊酸雌二醇溶液,第4 d戊酸雌二醇溶液与醋酸甲地孕酮分散片溶液共同灌胃,第5 d不给药,以此为周期连续灌胃8周。
1.2.2 大鼠发情期的测定及样本采集
大鼠阴道涂片制作[10]:处理大鼠前一周开始做大鼠阴道涂片,用胶头滴管吸取约0.1~0.2 mL生理盐水,反复冲洗大鼠阴道3~4次吸取足量大鼠阴道脱落细胞后,涂抹于载玻片上,自然风干后染色。染色采用革兰氏染色(快速法),根据试剂盒说明书内规范操作进行染色。
根据大鼠阴道涂片中脱落细胞判断大鼠所在发情时期[10],从而计算发情周期。确定大鼠发情周期后,各组大鼠按照发情周期推算发情期,将预计即将处于发情期的大鼠末次灌胃1 h后腹腔注射10%戊巴比妥钠溶液,3 mL/kg麻醉。腹主动脉采血后3000 r/min离心10 min分离大鼠血清,血清放入−20 ℃冰箱保存备用。取大鼠卵巢和子宫称重记录,计算大鼠器官指数。一侧卵巢放入4%甲醛保存、另外一侧卵巢液氮保存备用。
A(%)=BC×100 式中:A表示器官指数,%; B表示器官湿重,g;C表示大鼠体重,g。
1.2.3 血清性激素检测
取1.2.2中的大鼠血清,采用放射性免疫分析法,将血清样本及试剂平衡至室温后,按照说明书操作将125I-(E2、P、T、FSH、LH)与免抗-(E2、P、T、FSH、LH)抗体混匀,置37 ℃水浴相应时间后用γ-测量仪测定个管沉淀的放射性计数,根据标准曲线计算血清内E2、P、T、FSH和LH含量。
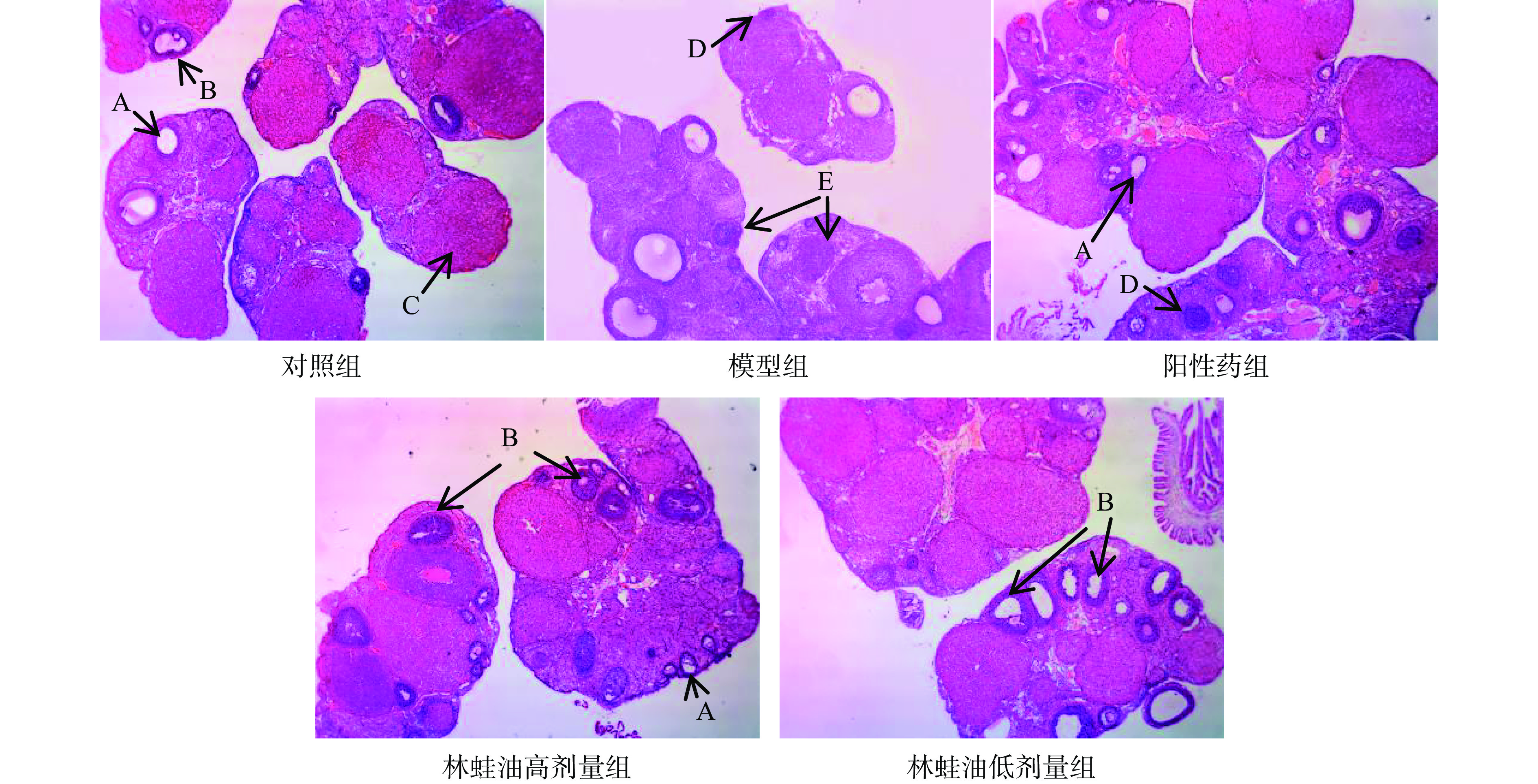
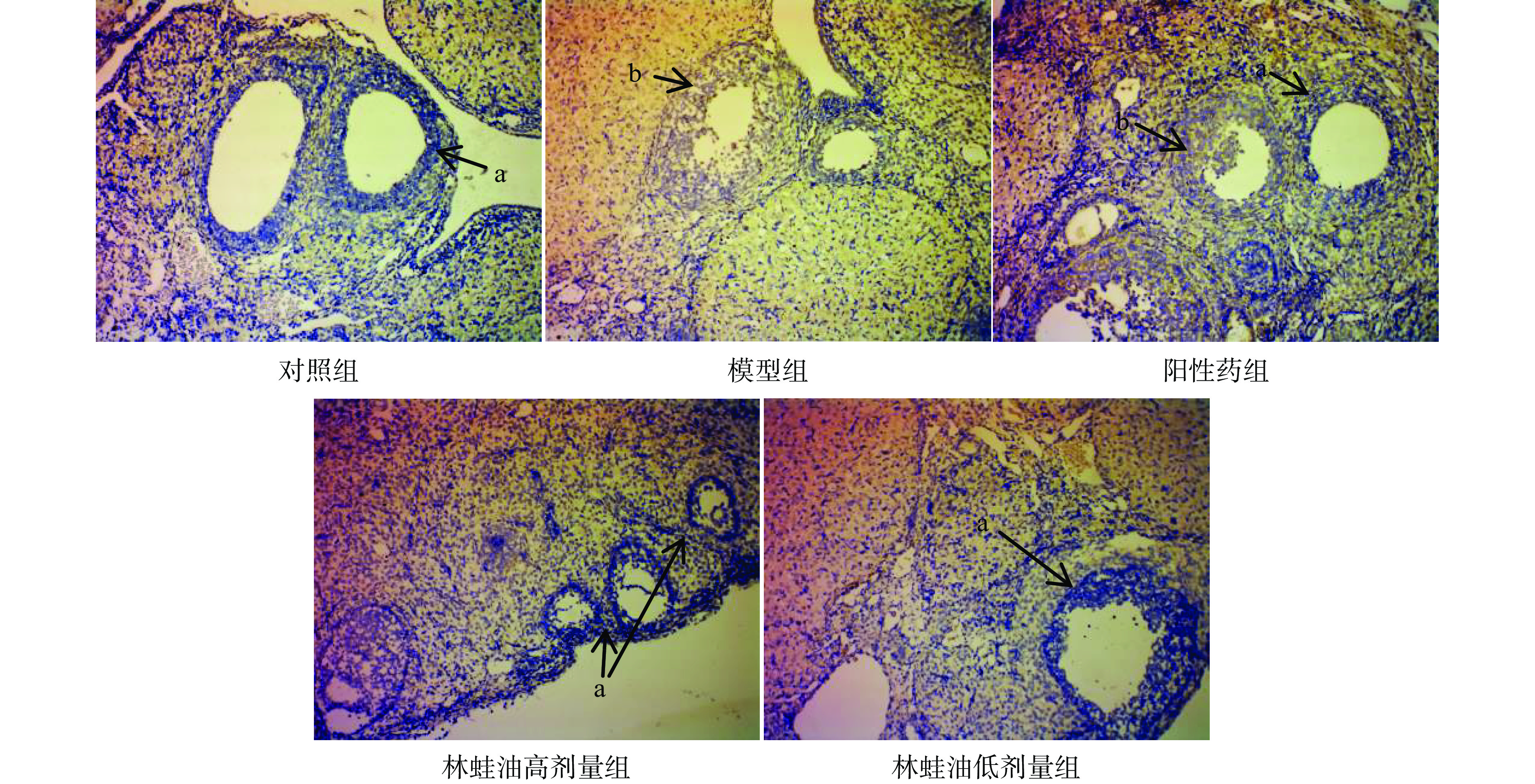
1.2.4 HE染色以及TUNEL染色
4%甲醛固定后的卵巢经石蜡包埋,进行连续切片,取连续位置的两个切片分别进行HE染色和TUNEL染色。
通过HE染色切片观察卵巢状态,并对各组大鼠不同发育阶段卵泡计数;TUNEL染色观察大鼠卵巢中细胞的凋亡情况,判断卵泡闭锁情况。
D(%)=EF×100 式中:D表示总闭锁率,%; E表示各级闭锁卵泡数;F表示各级卵泡总数。
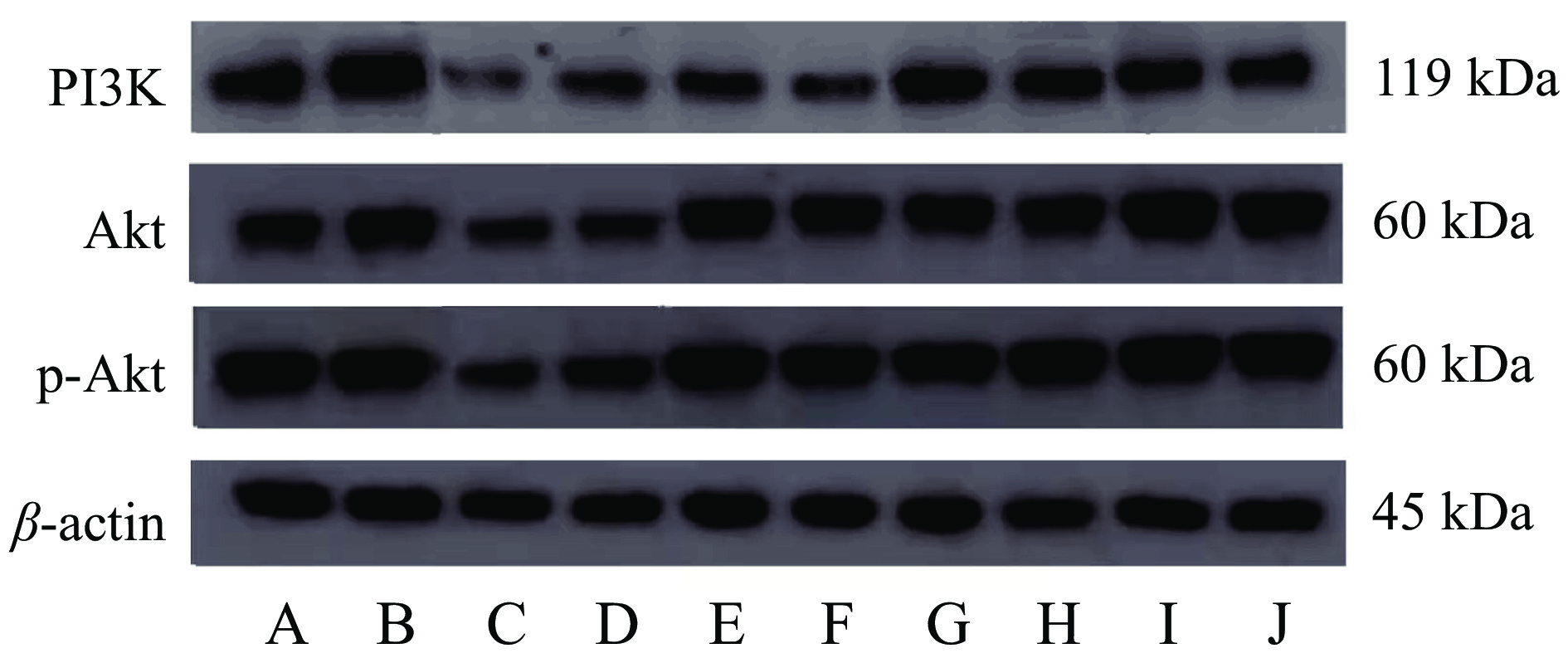
1.2.5 Western-blotting法检测PI3K、Akt、p-Akt蛋白含量及Akt蛋白磷酸化水平
低温条件下提取卵巢组织蛋白,用BCA试剂盒定量,经SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳分离后转印到PVDF膜上,用含5%BSA的TBST缓冲液封闭20 min。加入相应抗体胞内PI3K、Akt、p-Akt、β-actin(稀释倍数均为1:1000)室温孵育20 min。TBST洗膜,加入二抗(1:2000),室温孵育20 min。将PVDF膜浸泡到TBST溶液中,配制化学发光液,将其滴加到PVDF膜目的蛋白条带上,室温避光孵育2 min。使用化学发光系统采集条带图片,利用ImageJ软件对条带灰度值进行定量分析。
1.2.6 RT-PCR检测PI3K、Akt、PTEN、mTOR mRNA的相对表达量
取各组大鼠卵巢组织,在低温、灭酶条件下用TRIzol试剂从卵巢组织中提取总RNA,用反转录试剂盒将RNA反转录为cDNA,定量PCR反应程序:95 ℃预变性30 s;95 ℃变性10 s,57 ℃退火 30 s,72 ℃延伸30 s,共40个循环。结果以β-actin作为内参,采用2-ΔΔCt相对定量法分析各mRNA表达的影响。实验使用引物由吉林省库美生物科技有限公司合成,引物序列见表1。
表 1 引物序列Table 1. Primer sequences引物 序列(5’-3’) 长度(bp) PTEN 上游 TGTAAAGCTGGAAAGGGACG
下游 CCTCTGACTGGGAATTGTGAC20
21PI3K 上游 GGATGCTGAATGGTACTGGG
下游 TGTAAGAGTGTAATCGCCGTG20
21Akt 上游 GCCCTCAAGTACTCATTCCAG
下游 ACACAATCTCCGCACCATAG21
20mTOR* 上游 ATTCAATCCATAGCCCCGTC
下游 TGCATCACTCGTTCATCCTG20
20β-actin 上游 ACCTTCTACAATGAGCTGCG
下游 CTGGATGGCTACGTACATGG20
201.3 数据处理
使用SPSS20.0进行统计学分析,数据用
ˉx ±s 表示,多样本均数间比较采用Oneway ANOVA,卵泡闭锁率采用卡方检验,以P<0.05表示差异有统计学意义。2. 结果与分析
2.1 林蛙油对大鼠器官湿重、器官指数和大鼠发情周期的影响
由表2、表3知,与对照组大鼠相比,模型组大鼠卵巢湿重、卵巢指数及子宫指数显著降低(P<0.05);与模型组大鼠相比,阳性药组大鼠卵巢指数和子宫指数显著升高(P<0.05)。林蛙油高剂量组大鼠子宫湿重和子宫指数显著升高(P<0.05)。
表 2 各组大鼠器官指数以及器官湿重(ˉx ±s, n=8)Table 2. The organ index and organ wet weight of each group of rats (ˉx ±s, n=8)组别 卵巢湿重(mg) 卵巢指数
(mg·g−1)子宫湿重
(mg)子宫指数
(mg·g−1)对照组 100.00±16.84 0.41±0.08 426.00±41.04 1.72±0.17 模型组 84.00±12.58# 0.33±0.05# 400.62±29.45 1.56±0.13# 阳性药组 95.25±13.71 0.38±0.05* 423.00±31.22 1.71±0.15* 林蛙油高剂量 90.75±11.29 0.36±0.04 432.12±28.77* 1.72±0.11* 林蛙油低剂量 91.50±8.99 0.37±003 418.75±58.01 1.67±0.17 注:#表示与对照组相比差异显著P<0.05,*表示与模型组比差异显著P<0.05;表3~表5同。 表 3 各组大鼠发情周期(ˉx ±s, n=8)Table 3. Estrous cycle of rats by group (ˉx ±s, n=8)组别 发情周期(d) 对照组 4.39±0.67 模型组 5.50±1.31# 阳性药组 4.67±0.69 林蛙油高剂量组 4.00±0.00* 林蛙油低剂量组 4.25±0.45* 与对照组大鼠相比,模型组大鼠发情周期显著延长(P<0.05),与对照组大鼠相比,林蛙油高、低剂量组和阳性药组大鼠发情周期结果无显著性差异(P>0.05),与模型组大鼠相比林蛙油高、低剂量组大鼠发情周期显著缩短(P<0.05)。
2.2 林蛙油对大鼠血清激素水平的影响
由表4知,与对照组大鼠相比模型组大鼠血清中FSH、LH含量显著增多(P<0.05),P、T和E2含量显著减少(P<0.05);结合卵泡数量结果推测雷公藤多苷限制大鼠卵巢内卵泡发育,造成大鼠血清雌激素水平显著降低,导致发情期大鼠子宫指数显著降低。
表 4 各组大鼠血清激素水平(ˉx ±s, n=8)Table 4. Serum hormone levels in rat groups (ˉx ±s, n=8)FSH(mIU·mL−1) LH
(mIU·mL−1)P
(ng·mL−1)T
(ng·mL−1)E2
(pg·mL−1)对照组 2.92±0.82 4.29±0.87 11.08±3.31 0.050±0.03 7.16±2.47 模型组 4.08±0.71# 5.13±0.44# 7.95±1.64# 0.022±0.01# 4.38±1.48# 阳性药组 2.72±0.85* 3.41±1.10* 11.71±3.98* 0.046±0.02* 7.48±1.98* 林蛙油高剂量组 2.72±0.46* 4.37±1.22 8.85±2.62 0.045±0.02* 6.64±2.40* 林蛙油低剂量组 2.90±0.55* 4.65±1.04 9.20±2.57 0.048±0.02* 6.93±2.34* 与模型组相比,阳性药组大鼠血清中FSH、LH含量显著减少(P<0.05),血清中P、T及E2含量显著增多(P<0.05);林蛙油高、低剂量组大鼠血清中FSH含量显著减少(P<0.05),血清中T和E2含量显著增多(P<0.05)。阳性药组和林蛙油高剂量组大鼠改善了由雷公藤多苷引起的血清性激素变化,阳性药组大鼠通过补充外源性激素缓解了大鼠血清E2和P含量的下降,以外源性激素促进大鼠卵巢内卵泡发育,从而改善雷公藤多苷造成的低雌激素水平状态。
2.3 林蛙油对大鼠各级卵泡发育的影响
与对照组大鼠相比模型组大鼠卵巢中各级卵泡数量分布不均,凋亡卵泡数量增多,偶见大鼠卵巢萎缩空洞,脂肪填充,次级卵泡及黄体数量显著减少(P<0.05),卵泡总闭锁率显著升高(P<0.05)。表明雷公藤多苷限制卵巢内卵泡发育,本实验卵泡发育障碍模型成立,见表5、图1、图2。
表 5 各组大鼠各级卵泡数量(ˉx ±s, n=8)Table 5. Number of follicles at all levels in each group of rats (ˉx ±s, n=8)组别 初级卵泡(个) 闭锁初级卵泡(个) 次级卵泡(个) 闭锁次级卵泡(个) 黄体
(个)总闭锁率
(%)对照组 6.25±1.67 7.50±1.93 9.62±3.16 8.00±1.85 3.38±1.06 49.61±2.72 模型组 4.38±1.30 6.25±1.49 5.13±1.81# 8.25±1.85 1.63±0.52# 61.08±3.07# 阳性药组 4.00±1.07# 5.25±0.71# 8.50±1.69* 7.50±1.41 2.38±0.74*# 50.76±4.73* 林蛙油高剂量组 3.88±2.47# 4.75±1.98# 8.00±2.33* 7.75±3.20 2.38±1.60 52.51±3.94* 林蛙油低剂量组 3.88±1.64# 4.88±2.17# 7.50±2.33* 8.00±2.14 2.00±1.31# 53.13±6.29* 与模型组大鼠相比,阳性药组大鼠卵巢次级卵泡和黄体数量显著增多(P<0.05),卵泡总闭锁率显著下降(P<0.05);林蛙油高、低剂量组大鼠次级卵泡数量显著增多(P<0.05),卵泡总闭锁率显著下降(P<0.05)。表明阳性药及林蛙油均能改善雷公藤多苷引起的卵泡发育障碍,促进初级、次级卵泡的生长发育。
与对照组大鼠相比,林蛙油高、低剂量组和阳性药组大鼠卵巢初级卵泡数量和闭锁初级卵泡均显著减少(P<0.05),阳性药组和林蛙油低剂量组大鼠黄体数量显著减少(P<0.05)。表明林蛙油和阳性药能够改善由雷公藤造成的大鼠卵泡发育障碍,但并不能使大鼠完全恢复至原来水平,仅能在一定程度上改善大鼠卵泡发育障碍。
2.4 林蛙油对大鼠卵巢中PI3K、Akt、p-Akt蛋白及Akt蛋白磷酸化水平的影响
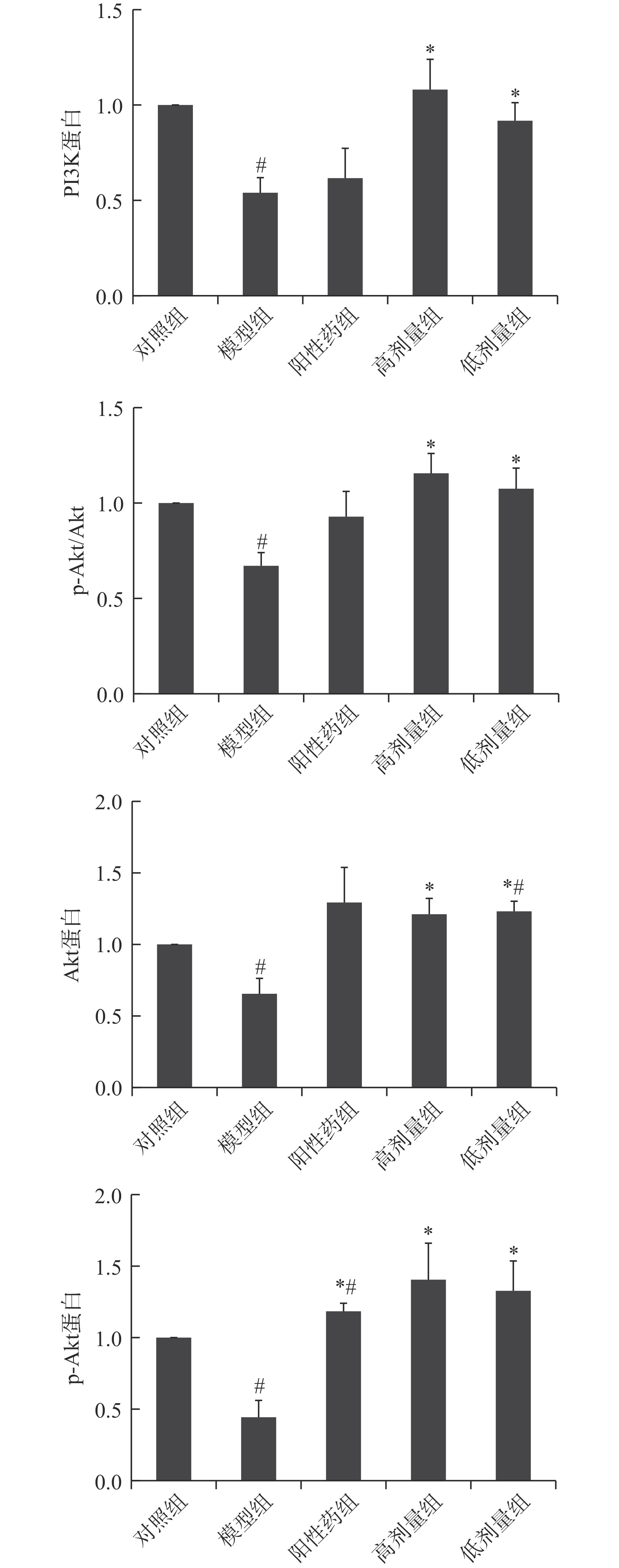
与对照组大鼠相比,模型组大鼠卵巢中PI3K蛋白含量显著减少(P<0.05),Akt蛋白水平显著减少(P<0.05),Akt蛋白磷酸化水平显著降低(P<0.05),表明雷公藤多苷阻碍大鼠PI3K/Akt信号通路转导,阻碍卵巢发育,见图3、图4。
![]() 图 4 大鼠卵巢PI3K、Akt及p-Akt蛋白含量和Akt蛋白磷酸化水平注:#表示与对照组相比差异显著P<0.05;*表示与模型组比差异显著P<0.05;图5同。Figure 4. The contents of PI3K, Akt and p-Akt protein and the phosphorylation level of Akt protein in rat ovary
图 4 大鼠卵巢PI3K、Akt及p-Akt蛋白含量和Akt蛋白磷酸化水平注:#表示与对照组相比差异显著P<0.05;*表示与模型组比差异显著P<0.05;图5同。Figure 4. The contents of PI3K, Akt and p-Akt protein and the phosphorylation level of Akt protein in rat ovary与模型组大鼠相比,阳性药组大鼠卵巢中PI3K蛋白含量无显著性差异(P>0.05);林蛙油高、低剂量组大鼠卵巢内PI3K蛋白水平及Akt蛋白磷酸化水平显著升高(P<0.05);推测林蛙油可能通过促进Akt蛋白磷酸化从而促进大鼠卵巢的发育。
与对照组大鼠相比,林蛙油低剂量组大鼠Akt蛋白表达显著增多(P<0.05),阳性药组p-Akt蛋白含量显著升高(P<0.05)。表明阳性药及林蛙油均能改善雷公藤多苷对PI3K/Akt信号通路的阻碍作用,使卵巢发育维持相对正常的状态。
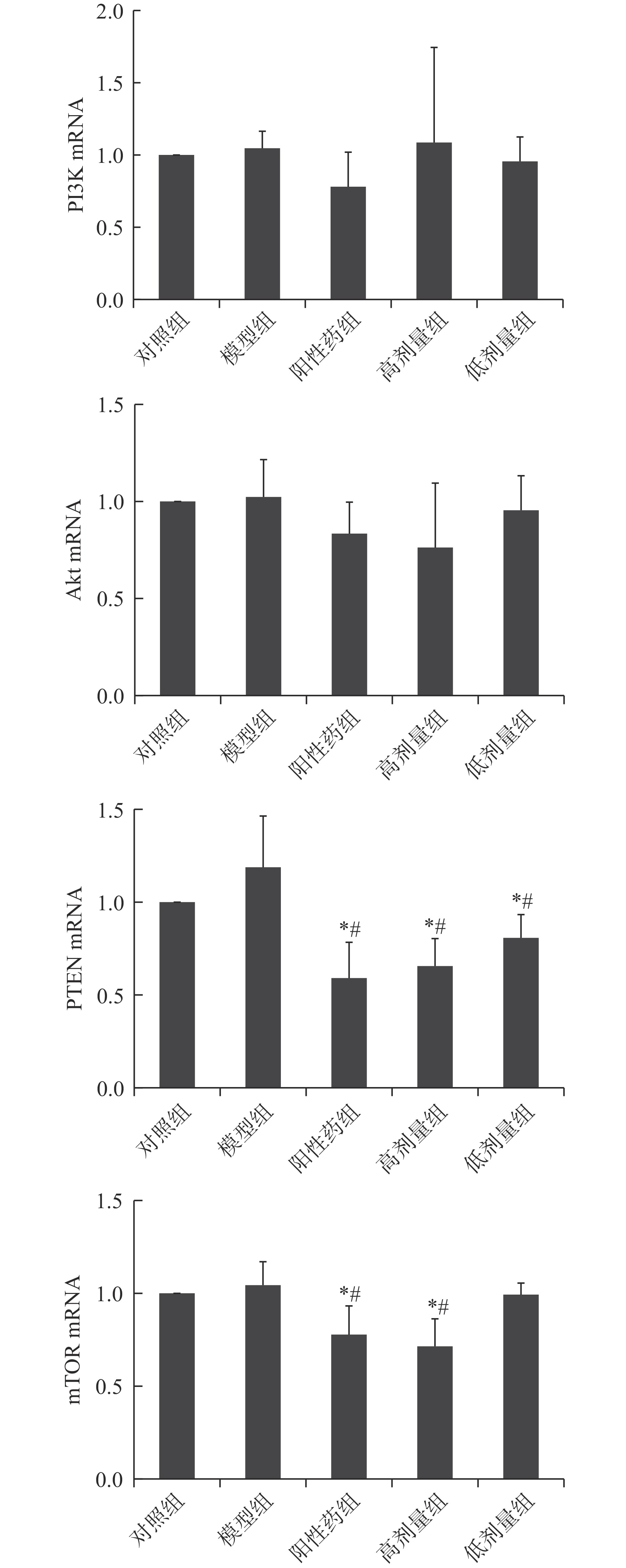
2.5 林蛙油对大鼠卵巢PI3K、Akt、PTEN、mTRO的mRNA 表达水平的影响
如图5所示,与对照组大鼠相比,模型组大鼠卵巢PI3K、Akt、PTEN及mTOR的mRNA表达水平无显著性变化(P>0.05);与模型组大鼠相比,阳性药组大鼠和林蛙油高剂量组大鼠的PTEN以及mTOR mRNA表达水平显著下降(P<0.05);林蛙油低剂量组大鼠PTEN mRNA表达水平与模型组大鼠相比显著下降(P<0.05)。
与对照组大鼠相比,阳性药组大鼠PTEN mRNA表达水平显著降低(P<0.05),mTOR mRNA表达水平显著降低(P<0.05);林蛙油高剂量组大鼠PTEN 和mTOR mRNA表达水平均显著降低(P<0.01),林蛙油低剂量组大鼠PTEN mRNA表达水平显著降低(P<0.05)。
基因表达结果提示林蛙油对大鼠卵泡发育的促进作用方式与阳性药不同,林蛙油不仅促进PI3K蛋白表达以及Akt蛋白磷酸化水平,同时减少PTEN mRNA表达,促进大鼠卵巢内卵泡生长发育。mTOR基因作为Akt基因的下游转导因子,其表达结果下降可能与卵泡被过度刺激有关,具体原因仍需进一步实验进行研究。
3. 讨论与结论
卵泡的发育和卵母细胞的成熟是哺乳动物生殖和发育的一个重要的环节[11-12],卵泡发育是指原始卵泡在性激素和各种细胞因子的共同作用下逐渐发育成为初级卵泡、次级卵泡、成熟卵泡、黄体的生理过程。大量的原始卵泡储存在卵巢的皮质层内,其中只有极少一部分的原始卵泡能发育成熟并成功排卵,其余的均在排卵前凋亡闭锁[13]。卵泡作为维持卵巢功能的基本单元,各级卵泡数量及闭锁卵泡比例反映卵巢发育状态。
雷公藤多苷具有一定的生殖毒性,雷公藤多苷能够引起大鼠卵巢血管生成障碍,造成卵泡发育障碍[14-16]。吴克明等[5-8]研究中发现,利用雷公藤多苷引起的大鼠卵泡发育障碍模型相对稳定,是研究卵巢功能低下类病症的一个比较可靠有效的病症结合的动物模型。本实验采用连续灌胃雷公藤多苷溶液八周、灌胃剂量为40 mg/kg[17],相当于人每日服用0.4 g雷公藤多苷片对模型组大鼠进行造模。实验结果显示与对照组大鼠相比,模型组大鼠卵巢的发情周期显著延长(P<0.05),偶见大鼠发情周期紊乱;大鼠血清激素水平有显著变化,FSH、LH显著上升,P、T及E2显著降低(P<0.05);大鼠卵巢内PI3K蛋白表达显著下降(P<0.05);卵泡闭锁率显著高于对照组(P<0.05)。以血清激素水平、发情周期及卵泡闭锁率为主要指标判断本实验大鼠卵泡发育障碍模型成功建立。
卵泡发育过程中分为非促性腺激素依赖性和促性腺素依赖性两个时期,当卵泡处于第二时期时卵泡和颗粒细胞的增殖和分化由FSH和LH协同作用[18-19],使卵泡内卵泡液增多促进卵泡发育。FSH还能够诱发晚期颗粒细胞中LH的受体表达,并促进新生细胞合成FSH受体增强FSH对卵泡生长发育的影响,为成熟卵泡的排卵及黄素化作准备;卵泡发育过程中主要分泌P、T和E2。P是孕激素中最强的激素,孕激素和雌激素在机体内通过联合作用保证月经和妊娠过程的正常进行。E2由卵巢颗粒细胞和膜细胞受FSH和LH协同作用下合成,颗粒细胞中的芳香化酶受FSH刺激后活化,芳香化酶将卵泡膜细胞内产生的雄激素转化为雌激素,LH促进黄体生成从而分泌雌激素和孕激素。在LH调控下细胞分泌T,但当T在机体内到达一定浓度时对LH/FSH的分泌有抑制作用,通过这些激素间的相互调控使卵泡发育维持稳定,卵巢内卵泡整体发育状态可以通过这些激素在大鼠血清内的含量作为判断依据。本实验中阳性药组通过直接补充外源性激素调整大鼠发情周期,改善了由雷公藤多苷造成的大鼠血清激素含量改变的现象,短期内外源性激素补充是目前常用的一种激素调节方法,但长期使用可能有服用者依赖外源激素的风险。大鼠血清激素和PI3K/Akt信号通路相关蛋白结果揭示林蛙油作用机理与直接补充外源性激素作用机理不同,林蛙油作用于卵巢细胞,通过促进其生长增殖间接使大鼠血清激素水平变化,增强卵巢功能,这与实验室前期结果相符合[3-4]。林蛙油通过促进大鼠自身卵巢功能,改善大鼠不良状态,不易产生依赖性。
国内外研究表明[20-21],PI3K/Akt信号通路是卵巢内重要的信号通路,包括原始卵泡的募集、颗粒细胞的增殖、黄体的形成以及卵母细胞的成熟。PI3K作为细胞内非常重要的信号转导分子,PI3K蛋白在卵巢内的表达含量能够反映卵巢的发育状态。PI3K能够将磷脂酰肌醇(4,5)-二磷酸(PIP2)磷酸化,磷酸化后的产物为磷脂酰肌醇(3,4,5)-三磷酸(PIP3),通过PIP3积累可以促进Akt及其下游蛋白激活[22],Akt的PH区能被PIP2及PIP3结合,导致Akt从胞质上转移,转移后的Akt在细胞膜上被完全的活化,活化的Akt引起信号转导通路的级联反应[23]。mTOR是Akt下游信号传导的重要传递者,在卵泡和颗粒细胞的增殖、凋亡和卵泡发育方面发挥极其重要的作用。PTEN能阻碍PI3K/Akt信号通路,其作用机理是由于PTEN的积累能够使PIP3脱磷酸导致PIP3含量减低[24-25];蛋白表达结果表明林蛙油能够促进大鼠卵巢PI3K蛋白表达及Akt蛋白磷酸化水平,能够下调由雷公藤多苷导致卵泡发育障碍的大鼠卵巢内PTEN mRNA表达,上调PI3K蛋白表达,促进Akt蛋白磷酸化水平升高。
综上所述,林蛙油可以有效上调PI3K/Akt信号通路,促进卵泡发育障碍的大鼠次级卵泡增殖发育,降低卵泡闭锁率,促进卵巢分泌E2和P,使血清激素水平维持正常水平。本实验研究结果为林蛙油的雌激素样作用机制提供了一定的科学依据,林蛙油对卵泡的作用机制仍需要进一步实验证明。
-
图 4 大鼠卵巢PI3K、Akt及p-Akt蛋白含量和Akt蛋白磷酸化水平
注:#表示与对照组相比差异显著P<0.05;*表示与模型组比差异显著P<0.05;图5同。
Figure 4. The contents of PI3K, Akt and p-Akt protein and the phosphorylation level of Akt protein in rat ovary
表 1 引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences
引物 序列(5’-3’) 长度(bp) PTEN 上游 TGTAAAGCTGGAAAGGGACG
下游 CCTCTGACTGGGAATTGTGAC20
21PI3K 上游 GGATGCTGAATGGTACTGGG
下游 TGTAAGAGTGTAATCGCCGTG20
21Akt 上游 GCCCTCAAGTACTCATTCCAG
下游 ACACAATCTCCGCACCATAG21
20mTOR* 上游 ATTCAATCCATAGCCCCGTC
下游 TGCATCACTCGTTCATCCTG20
20β-actin 上游 ACCTTCTACAATGAGCTGCG
下游 CTGGATGGCTACGTACATGG20
20表 2 各组大鼠器官指数以及器官湿重(
Table 2 The organ index and organ wet weight of each group of rats (
组别 卵巢湿重(mg) 卵巢指数
(mg·g−1)子宫湿重
(mg)子宫指数
(mg·g−1)对照组 100.00±16.84 0.41±0.08 426.00±41.04 1.72±0.17 模型组 84.00±12.58# 0.33±0.05# 400.62±29.45 1.56±0.13# 阳性药组 95.25±13.71 0.38±0.05* 423.00±31.22 1.71±0.15* 林蛙油高剂量 90.75±11.29 0.36±0.04 432.12±28.77* 1.72±0.11* 林蛙油低剂量 91.50±8.99 0.37±003 418.75±58.01 1.67±0.17 注:#表示与对照组相比差异显著P<0.05,*表示与模型组比差异显著P<0.05;表3~表5同。 表 3 各组大鼠发情周期(
Table 3 Estrous cycle of rats by group (
组别 发情周期(d) 对照组 4.39±0.67 模型组 5.50±1.31# 阳性药组 4.67±0.69 林蛙油高剂量组 4.00±0.00* 林蛙油低剂量组 4.25±0.45* 表 4 各组大鼠血清激素水平(
Table 4 Serum hormone levels in rat groups (
FSH(mIU·mL−1) LH
(mIU·mL−1)P
(ng·mL−1)T
(ng·mL−1)E2
(pg·mL−1)对照组 2.92±0.82 4.29±0.87 11.08±3.31 0.050±0.03 7.16±2.47 模型组 4.08±0.71# 5.13±0.44# 7.95±1.64# 0.022±0.01# 4.38±1.48# 阳性药组 2.72±0.85* 3.41±1.10* 11.71±3.98* 0.046±0.02* 7.48±1.98* 林蛙油高剂量组 2.72±0.46* 4.37±1.22 8.85±2.62 0.045±0.02* 6.64±2.40* 林蛙油低剂量组 2.90±0.55* 4.65±1.04 9.20±2.57 0.048±0.02* 6.93±2.34* 表 5 各组大鼠各级卵泡数量(
Table 5 Number of follicles at all levels in each group of rats (
组别 初级卵泡(个) 闭锁初级卵泡(个) 次级卵泡(个) 闭锁次级卵泡(个) 黄体
(个)总闭锁率
(%)对照组 6.25±1.67 7.50±1.93 9.62±3.16 8.00±1.85 3.38±1.06 49.61±2.72 模型组 4.38±1.30 6.25±1.49 5.13±1.81# 8.25±1.85 1.63±0.52# 61.08±3.07# 阳性药组 4.00±1.07# 5.25±0.71# 8.50±1.69* 7.50±1.41 2.38±0.74*# 50.76±4.73* 林蛙油高剂量组 3.88±2.47# 4.75±1.98# 8.00±2.33* 7.75±3.20 2.38±1.60 52.51±3.94* 林蛙油低剂量组 3.88±1.64# 4.88±2.17# 7.50±2.33* 8.00±2.14 2.00±1.31# 53.13±6.29* -
[1] 张熬, 张悦, 陈缘, 等. 东北林蛙油研究进展[J]. 养殖与饲料,2020(1):38−71. [ZHANG Ao, ZHANG Yue, CHEN Yuan, et al. Research progress of oviductus ranae in Northeast China[J]. Animals Breeding and Feed,2020(1):38−71. doi: 10.13300/j.cnki.cn42-1648/s.2020.01.025 ZHANG Ao, ZHANG Yue, CHEN Yuan, et al. Research progress of oviductus ranae in Northeast China[J]. Animals Breeding and Feed, 2020(1): 38-71. doi: 10.13300/j.cnki.cn42-1648/s.2020.01.025
[2] 郭宪一, 范红艳. 林蛙油的药理作用研究进展[J]. 吉林医药学院学报,2020,41(3):209−211. [GUO Xianyi, FAN Hongyan. Research progress on pharmacological effects of rana oil[J]. Journal of Jilin Medical University,2020,41(3):209−211. doi: 10.13845/j.cnki.issn1673-2995.2020.03.022 GUO Xianyi, FAN Hongyan. Research progress on pharmacological effects of rana oil[J]. Journal of Jilin Medical University, 2020, 41(3): 209-211. doi: 10.13845/j.cnki.issn1673-2995.2020.03.022
[3] 赵宏宇, 王玉, 孙雪缘, 等. 基于PI3K/Akt信号通路探讨哈蟆油对卵泡发育作用的影响[J]. 中国实验方剂学杂志,2021,27(21):121−130. [ZHAO Hongyu, WANG Yu, SUN Xueyuan, et al. Investigating the effect of oviductus ranae on follicle development based on PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae,2021,27(21):121−130. doi: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20212137 ZHAO Hongyu, WANG Yu, SUN Xueyuan, et al. Investigating the effect of oviductus ranae on follicle development based on PI3K/Akt signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Experimental Traditional Medical Formulae, 2021, 27(21): 121-130. doi: 10.13422/j.cnki.syfjx.20212137
[4] 赵宏宇, 王玉, 刘新宇, 等. 林蛙油提升雌激素的机制研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(19):296−300. [ZHAO Hongyu, WANG Yu, SUN Xueyuan, et al. Study on the mechanism of oviductus ranae to elevate estrogen[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(19):296−300. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2019.19.051 ZHAO Hongyu, WANG Yu, SUN Xueyuan, et al. Study on the mechanism of oviductus ranae to elevate estrogen[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2019, 40(19): 296-300. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2019.19.051
[5] 吴克明, 谌婕, 熊巍. 雷公藤多甙对雌性小鼠生殖功能影响的实验研究[J]. 中医研究,2007,20(4):28−33. [WU Keming, ZHAN Jie, XIONG Wei. Experimental study on the effects of Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides on reproductive function of female mice[J]. Traditional Chinese Medicinal Research,2007,20(4):28−33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6910.2007.04.012 WU Keming, ZHAN Jie, XIONG Wei. Experimental study on the effects of Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides on reproductive function of female mice[J]. Traditional Chinese Medicinal Research, 2007, 20(4): 28-33. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6910.2007.04.012
[6] 曹俊岩. 雷公藤多苷致大鼠卵泡发育障碍模型的中医症候属性研究[D]. 成都: 成都中医药大学, 2011 CAO Junyan. Study on TCM symptom attributes of rat follicular development disorder model induced by Tripterygium wilfordii[D]. Chengdu: Chengdu University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2011.
[7] 白俊, 吴也可, 吴克明, 等. 雷公藤甲素通过 PI3K /AKT / mTOR通路诱导卵巢颗粒细胞自噬的实验研究[J]. 中国中药杂志,2019,44(16):3429−3434. [BAI Jun, WU Yeke, WU Keming, et al. Experimental study on triptolide-induced autophagy in ovarian granulosa cells via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2019,44(16):3429−3434. BAI Jun, WU Yeke, WU Keming, et al. Experimental study on triptolide-induced autophagy in ovarian granulosa cells via PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2019, 44(16): 3429-3434.
[8] 谌婕, 吴克明, 王家葵, 等. 雷公藤多苷致雌性小鼠肾虚生殖功能低下动物模型的研究[J]. 中药新药与临床药理,2007,18(3):208−211. [ZHAN Jie, WU Keming, WANG Jiahui, et al. Study on the animal model of kidney deficiency and reproductive dysfunction in female mice induced by Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides[J]. Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology,2007,18(3):208−211. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-9783.2007.03.013 ZHAN Jie, WU Keming, WANG Jiahui, et al. Study on the animal model of kidney deficiency and reproductive dysfunction in female mice induced by Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides[J]. Traditional Chinese Drug Research and Clinical Pharmacology, 2007, 18(3): 208-211. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1003-9783.2007.03.013
[9] 张芳, 丁怡, 于潇, 等. 补肾养精颗粒调控早发性卵巢功能不全模型大鼠卵巢颗粒细胞凋亡机制研究[J]. 山东中医药大学学报,2022,46(3):365−372. [ZHANG Fang, DING Yi, YU Xiao, et al. Mechanism of Bushen Yangjing Granule in regulating apoptosis of ovarian granulosa cell in model rats with premature ovarian insufficiency[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2022,46(3):365−372. doi: 10.16294/j.cnki.1007-659x.2022.03.015 ZHANG Fang, DING Yi, YU Xiao, et al. Mechanism of Bushen Yangjing Granule in regulating apoptosis of ovarian granulosa cell in model rats with premature ovarian insufficiency[J]. Journal of Shandong University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2022, 46(3): 365-372. doi: 10.16294/j.cnki.1007-659x.2022.03.015
[10] 张婷, 王颖, 王莉. 大鼠阴道涂片两种染色方法比较[J]. 中国比较医学杂志,2018,28(12):98−101. [ZHANG Ting, WANG Ying, WANG Li. Comparison of two staining methods for rat vaginal smears[J]. Chinese Journal of Comparative Medicine,2018,28(12):98−101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2018.12.016 ZHANG Ting, WANG Ying, WANG Li. Comparison of two staining methods for rat vaginal smears[J]. Chinese Journal of Comparative Medicine, 2018, 28(12): 98-101. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2018.12.016
[11] 毛菁沁, 冒韵东. 原始卵泡激活与卵泡发育相关机制的研究进展[J]. 国际生殖健康/计划生育杂志,2020,39(3):225−228. [MAO Jingqin, MAO Yundong. Research progress on the mechanism of primordial follicle activation and follicle development[J]. Journal of International Reproductive Health/Family Planning,2020,39(3):225−228. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1889.2020.03.012 MAO Jingqin, MAO Yundong. Research progress on the mechanism of primordial follicle activation and follicle development[J]. Journal of International Reproductive Health/Family Planning, 2020, 39(3): 225-228. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-1889.2020.03.012
[12] 吕文漪, 董晓英. 卵泡发育与卵巢早衰相关性的研究进展[J]. 医学研究杂志,2016,45(12):160−162. [LÜ Wenyi, DONG Xiaoying. Research progress on the relationship between follicular development and premature ovarian failure[J]. Journal of Medical Research,2016,45(12):160−162. LV Wenyi, DONG Xiaoying. Research progress on the relationship between follicular development and premature ovarian failure[J]. Journal of Medical Research, 2016, 45(12): 160-162.
[13] ROLAKI A, DRAKAKIS P, MILLINGOS S, et al. Novel trends in follicular development, atresia and corpus luteum regression: A role for apoptosis[J]. Reprod Biomed Online,2005,11(1):93−103. doi: 10.1016/S1472-6483(10)61304-1
[14] 郝丽, 卢文, 林辉, 等. 雌孕激素替代治疗雷公藤所致卵巢早衰的疗效观察[J]. 中华肾脏病杂志,2005,21(3):143−145. [HAO Li, LU Wen, LIN Hui, et al. Efficacy of estrogen and progesterone replacement in the treatment of premature ovarian failure caused by Tripterygium wilfordii[J]. Chinese Journal of Nephrology,2005,21(3):143−145. doi: 10.3760/j.issn:1001-7097.2005.03.008 HAO Li, LU Wen, LIN Hui, et al. Efficacy of estrogen and progesterone replacement in the treatment of premature ovarian failure caused by Tripterygium wilfordii[J]. Chinese Journal of Nephrology, 2005, 21(3): 143-145. doi: 10.3760/j.issn:1001-7097.2005.03.008
[15] 付雨, 吴克. 雷公藤多苷对大鼠卵巢血管生成及血供的影响[J]. 四川中医,2011,29(6):50−52. [FU Yu, WU Ke. Effects of Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides on angiogenesis and blood supply in rat ovary[J]. Journal of Sichuan of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2011,29(6):50−52. FU Yu, WU Ke. Effects of Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides on angiogenesis and blood supply in rat ovary[J]. Journal of Sichuan of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2011, 29(6): 50-52.
[16] 王桂玲, 任春娥, 王丽. 雷公藤多甙对雌性大鼠不良反应的实验研究[J]. 河北医药,2009,31(4):416−418. [WANG Guiling, REN Chune, WANG Li. Experimental study on adverse reactions of Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides in female rats[J]. Hebei Medical Journal,2009,31(4):416−418. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2009.04.011 WANG Guiling, REN Chune, WANG Li. Experimental study on adverse reactions of Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides in female rats[J]. Hebei Medical Journal, 2009, 31(4): 416-418. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7386.2009.04.011
[17] 徐丽萍, 张蕾, 宋欣伟. 雷公藤多苷不同给药方式对雌性大鼠肝功能及生殖功能影响的比较研究[J]. 浙江中医药大学学报,2019,43(2):177−181. [XU Liping, ZHANG Lei, SONG Xinwei. Comparative study on the effects of different administration modes of Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides on liver function and reproductive function in female rats[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University,2019,43(2):177−181. doi: 10.16466/j.issn1005-5509.2019.02.013 XU Liping, ZHANG Lei, SONG Xinwei. Comparative study on the effects of different administration modes of Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosides on liver function and reproductive function in female rats[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University, 2019, 43(2): 177-181. doi: 10.16466/j.issn1005-5509.2019.02.013
[18] RICHARD S, BALTZ J M. Prophase I Arrest of mouse oocytes mediated by natriuretic peptide precursor c requires gja1 (connexin-43) andgja4 (connexin-37) gap Junctions in the antral follicle and cumulus-oocyte complex[J]. Biol Reprod,2014,90(6):137.
[19] CONTI M, HSIEH M, ZAMAH A M, et al. Novel signaling mechanisms in the ovary during oocyte maturation and ovulation[J]. Mol Cell Endocrinol,2012,356(1/2):65−73.
[20] ADHIKARI D, LIU K. Molecular mechanisms underlying the activation of mammalian primordial follicles[J]. Endocr Rev,2009(5):438−464.
[21] MAKKER A, GOEL M M, MAHDI A A. Pi3k/pten/akt and tsc/mtor signaling pathways, ovarian dysfunction, and infertility: An update[J]. J Mol Endocrinol,2014,53(3):103−118. doi: 10.1530/JME-14-0220
[22] 李娇娇, 焦亚飞, 石德顺. PI3K/Akt信号通路对卵泡发育和卵母细胞成熟作用的研究进展[J]. 中国畜牧杂志,2021,57(8):33−36. [LI Jiaojiao, JIAO Yafei, SHI Deshun. Research progress on the role of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway on follicle development and oocyte maturation[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science,2021,57(8):33−36. doi: 10.19556/j.0258-7033.20201010-02 LI Jiaojiao, JIAO Yafei, SHI Deshun. Research progress on the role of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway on follicle development and oocyte maturation[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Science, 2021, 57(8): 33-36. doi: 10.19556/j.0258-7033.20201010-02
[23] GROSBOIS J, DEMEESTERE I. Dynamics of pi3k and hippo signaling path ways during in vitro human follicle activation[J]. HumReprod,2018,33(9):1705−1714.
[24] MIRZA-AGHAZADEH-ATTARI M, EKRAMI E M, AGHDAS S A M, et al. Targeting pi3k/akt/mtor signaling pathway by polyphenols: Implication for cancer therapy[J]. Life Sciences,2020(255):117481.
[25] LEE H N, CHANG E M. Primordial follicle activation as new treatment for primary ovarian insufficiency[J]. Clin Exp Reprod Med,2019,46(2):43−49. doi: 10.5653/cerm.2019.46.2.43
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 李琳,崔彦阁,赵娟娟,石晓丹,许军星,孙路. 调整膳食纤维和肠道菌群对延缓饮食诱导性肥胖的影响研究. 医学动物防制. 2025(02): 177-181 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王远利,王菲,张权,汤木果,陶亮,田洋. 海棠果果酱的研制及其品质分析. 食品工业科技. 2024(11): 175-186 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 毛欣欣,刘婧,梁文欧,蔡诗鸿,李彦勋. 果蔬加工副产物膳食纤维改性研究进展. 农产品加工. 2024(08): 94-98 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李国巍,石雨,张正海,姬妍茹,杨庆丽,董艳,高宝昌,李柏阳. 黑海棠果多酚提取工艺优化及抗氧化活性分析. 中国食品添加剂. 2024(12): 19-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李焱,林泳峰,刘文美,邹泽华,刘红,刘光明,刘庆梅. 食药同源植物多糖调控肠道稳态的研究进展. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2023(02): 25-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 雷延玲. 遮荫条件下栽培模式对草莓品质和产量的影响. 北方果树. 2022(05): 14-17 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)







 下载:
下载:









 下载:
下载:



