Interaction Mechanism of Lactic Acid Bacteria in Fermented Milk and Its Effect on Product Characteristics
-
摘要: 乳酸菌作为食品、农业和医药领域重要的微生物资源,具有良好的发展前景。但经过长期的生产实践发现,某些重要的生化反应过程仅靠单种微生物很难实现,需两种或两种以上微生物共同培养来完成,即混合培养。本文简述了发酵乳中不同乳酸菌菌株间的相互作用机制以及乳酸菌混合培养对发酵乳制品感官特性、营养特性等产品特性的影响。了解发酵乳中乳酸菌菌群间的相互作用方式及机制有利于提高产品底物转化率、改善工艺性能等,为乳酸菌共培养在产量调控、产品功能化和资源利用等方面提供一定理论参考。Abstract: As an important microbial resource in the fields of food, agriculture and medicine, lactic acid bacteria have good development prospects. A long period of production experience has found that some important biochemical reaction process is difficult to complete by one bacterial starter during fermentation, and two or more microbial co-culture, namely mixed culture, are needed. This paper briefly describes the interaction mechanism between different lactic acid bacteria strains in fermented milk and the effect of mixed culture of lactic acid bacteria on the sensory and nutritional characteristics of fermented dairy products. Uncover the interaction mode and mechanism among lactic acid bacteria flora in fermented milk is conducive to improving substrate conversion rate and process performance of product, which provides a theoretical reference for lactic acid bacteria co-culture in yield regulation, product functionalization and resource utilization.
-
Keywords:
- lactic acid bacteria /
- interaction /
- mechanism /
- fermented milk /
- mixed culture
-
发酵乳是以生牛(羊)乳或乳粉为原料,经杀菌、发酵后制成的pH降低的产品[1]。由于发酵乳具有更高的消化率,更高的营养价值,兼具抗高血压、降低胆固醇、抗氧化或免疫调节等健康功效,使消费者对发酵乳的兴趣与日俱增[2]。在过去的几十年里,人们对酸奶、奶酪、开菲尔等发酵乳制品进行了大量的研究,发现乳制品在发酵过程中发生的主要生化反应是乳酸菌作用于乳糖,将乳糖转化为乳酸,引起发酵乳的质构改变,以获得理想的质地和粘度。同时,研究发现乳酸菌可以产生代谢物和生物活性化合物(如胞外多糖、细菌素等),赋予了发酵乳一定的功能特性[3]。
乳酸菌指可以发酵乳糖产生乳酸的一类无芽孢、革兰氏阳性细菌的总称,主要包括双歧杆菌属、乳杆菌属、链球菌属和片球菌属等约41个属[4-5],常被用作发酵剂以开发发酵食品,加速和控制发酵食品的发酵过程。乳酸菌产生的有机酸可以促进原料乳快速酸化,产生醋酸、乙醇、胞外多糖等风味化合物,赋予发酵乳制品各种理想的功能属性,同时还可以延长食品货架期。此外,乳酸菌因具有改善肠道菌群平衡[6]、降低胆固醇[7]、提高机体免疫力[8]等多种潜在的生物功能,已被广泛用于乳品加工、健康食品、动物养殖以及活菌药物开发,成为食品、农业和医药领域重要的微生物资源。
尽管乳酸菌具有诸多潜在的益生特性,但存在其在原料乳发酵过程中存在生长速度缓慢、菌体密度低、营养物质需求复杂等局限性,因此可以通过不同乳酸菌菌株混合培养的方式,使物种间相互刺激生长,以达到提高菌体生长速率、增加菌体密度、获得目标产物等目的。本文主要介绍了发酵乳中不同乳酸菌菌株间的相互作用方式和作用机制以及不同菌株共培养对发酵乳制品感官特性、营养特性等产品特性的影响,为将乳酸菌更好地应用于实际提供一定理论基础。
1. 发酵乳中乳酸菌菌株间的相互作用
传统发酵乳生产中,乳酸菌不仅同发酵过程中的环境有着密切联系,乳酸菌间的生态学关系也十分复杂,不同种类的乳酸菌产生的各类代谢物,使各菌株间存在着多样的互作形式,影响彼此的生长。将乳酸菌菌株共培养时,营养缺陷型菌株可以利用其他菌株产生的代谢产物达到加快自身生长的目的,但同时,共培养也会改变发酵微环境、刺激菌株沉默基因的表达,改变菌株的生存状态,使某些菌株的生长繁殖受到抑制。乳酸菌间的互生作用、拮抗作用等对发酵乳最终风味的形成和新物质的产生有着深刻影响。
1.1 互生作用
1.1.1 保加利亚乳杆菌和嗜热链球菌间的互生作用
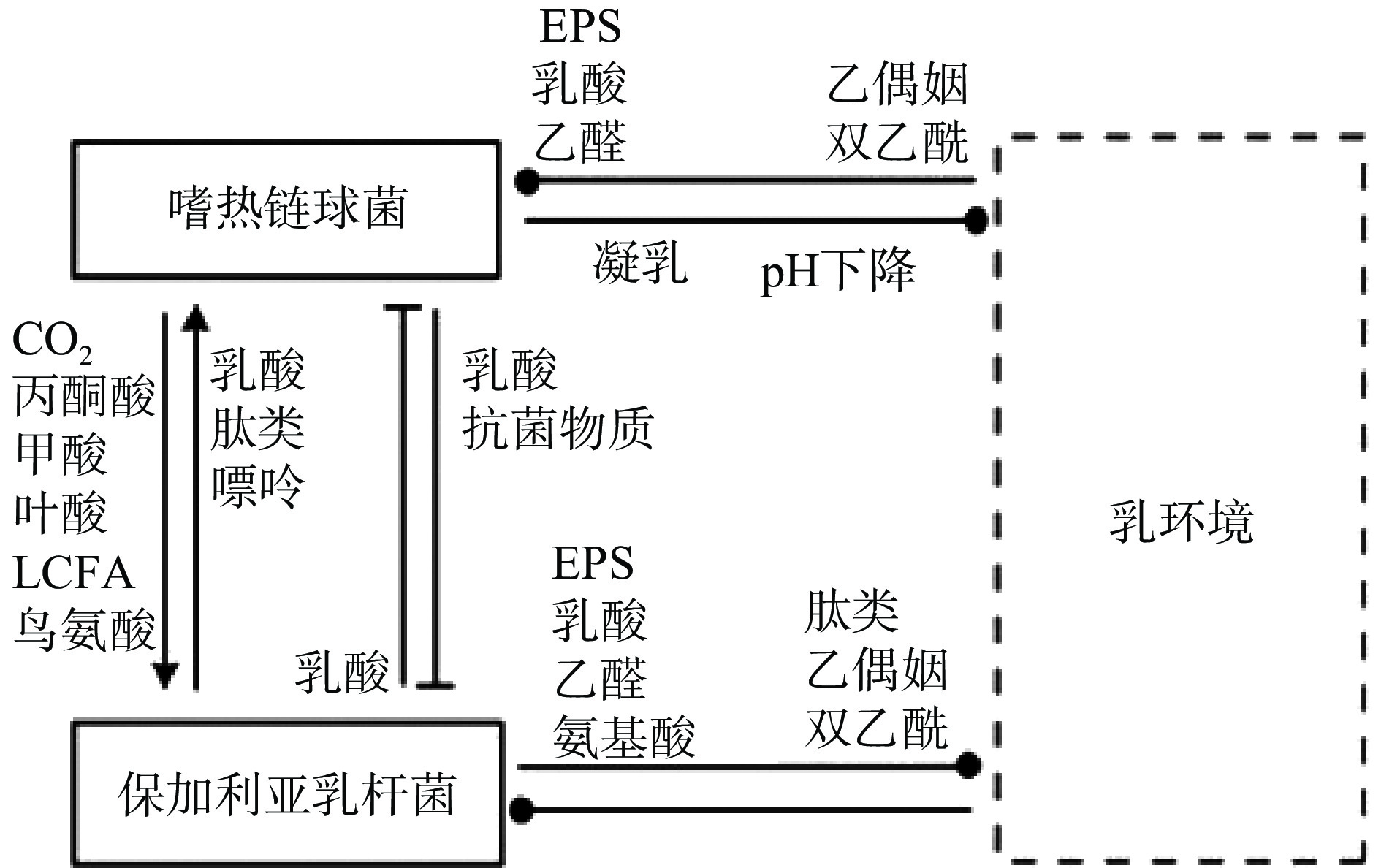
保加利亚乳杆菌和嗜热链球菌作为传统的酸奶发酵剂被广泛研究。二者间的互生作用主要体现在氨基酸和氮源利用方面(如图1)。YONEZAWA等[9]研究发嗜热链球菌可以通过上调amiABCDE(负责转运寡肽的操纵子)等方式获取保加利亚乳杆菌降解蛋白后产生的组氨酸、脯氨酸、甲硫氨酸等氨基酸,从而促进自身的生长[10-11]。同时,嗜热链球菌还可以通过脲酶调控二氧化物浓度从而影响保加利亚乳杆菌的酸化[12],并促进后者对天冬氨酸、谷氨酸、精氨酸以及核苷酸的合成速率[13]。
其次,在氮源利用方面,由于保加利亚乳杆菌和嗜热链球菌在共培养过程中,对不同的肽利用程度不同,从而提高了氮源的利用率。在二者共培养期间主要增加了C末端含有焦谷氨酸的肽的相对浓度,这种肽主要被保加利亚乳杆菌转运并被其多肽酶进一步降解以产生更多谷氨酸[14]。进入对数阶段后,保加利亚乳杆菌更有效地运输在N末端含有半胱氨酸的肽,而嗜热链球菌对这种肽的利用率较低。在环境肽利用方面,两种菌株主要在同一时间点使用不同类型的肽,从而提高了每种菌株对必需肽的转运效率[13]。最后,在核苷酸代谢方面,嗜热链球菌可以为保加利亚乳杆菌提供甲酸以及嘌呤和氨基酸生物合成的辅助因子叶酸促进其生长[15-16]。
1.1.2 双歧杆菌和干酪乳杆菌间的互生作用
双歧杆菌能够定殖于人体肠道中,通过代谢产生乙酸、乳酸等,降低肠道pH,进而抑制致病菌的生长,被广泛应用于发酵乳制品的生产中[18]。干酪乳杆菌是乳酸菌中研究和应用最广泛的益生菌,由于干酪乳杆菌能产生许多生物活性代谢物,因具有预防或治疗与肠道微生物区系紊乱等疾病的健康功效而被广泛研究。将其应用于发酵乳的制备时,可以赋予产品更好的感官特性和益生特性[19]。在干酪乳杆菌Zhang与乳双歧杆菌V9生长与代谢机制的试验中发现,乳双歧杆菌V9通过上调乳糖降解,丙酮酸代谢和维生素代谢来促进其快速生长,干酪乳杆菌Zhang可能通过上调丙酮酸代谢与脂肪酸合成,下调糖酵解保持快速生长[20]。与单独培养相比,在42 ℃条件下两株菌共培养后乳双歧杆菌V9的活菌数增加了1.04倍。
1.1.3 乳酸乳球菌和其他菌株间的互生作用
乳酸乳球菌可作为多种发酵乳制品的发酵剂,具有发酵乳糖、水解蛋白及产生胞外多糖的能力,是发酵乳制品最终香气、质地和酸度形成的关键因素。发酵乳中乳酸乳球菌可以产生蛋白水解酶,并降解乳蛋白,为双歧杆菌在脱脂乳中的生长提供寡肽、氨基酸等氮源,与双歧杆菌共培养时通过氮需求的刺激性相互作用促进彼此的生长[21]。一项关于乳酸乳球菌MCC857与双歧杆菌共培养的研究也发现乳酸乳球菌通过向后者提供氮源的方式刺激其生长[9]。但在CANON等[22]的研究中发现乳酸乳球菌NCDO2111不能水解蛋白,将其与能进行蛋白水解的粪肠球菌CIRM-BIA2412共同培养时,乳酸乳球菌NCDO2111生长速率提高,活菌数高达109 CFU/mL,两菌株之间显示出强烈的相互作用。这是由于粪肠球菌为乳酸乳球菌NCDO2111提供了较高浓度的色氨酸、缬氨酸、苯丙氨酸、亮氨酸、异亮氨酸和多肽,这些氨基酸和多肽可以加快乳酸乳球菌NCDO2111的产酸速率,提高棉子糖利用率,增加挥发性化合物的浓度。
1.2 拮抗作用
发酵乳中不同乳酸菌菌株在共培养过程中也存在着拮抗作用。如将保加利亚乳杆菌与干酪乳杆菌混合培养后得到的实际菌体浓度为理论浓度的0.3倍[23]。刘学云等[24]通过研究九种益生菌之间的相互作用发现,三分之一的益生菌之间存在拮抗作用,其中嗜酸乳杆菌的代谢产物对植物乳杆菌、乳双歧杆菌、副干酪乳杆菌有抑制作用;副干酪乳杆菌的代谢产物对嗜酸乳杆菌也有抑制作用;嗜热链球菌的代谢产物产物对两歧双歧杆菌有抑制作用。
乳酸菌间的拮抗作用通常认为是由于不同菌株之间资源竞争或某些菌株产生了有害毒素而引起的[25]。尽管保加利亚乳杆菌和嗜热链球菌共生现象普遍存在,但在LIU等[13]的研究中发现嗜热链球菌对肽的吸收能力强于保加利亚乳杆菌2038,在氮源利用方面二者也存在一定的竞争关系;另一方面,保加利亚乳杆菌2038失去了优先利用环境中游离支链氨基酸(BCAA)的能力,在与嗜热链球菌共培养时被诱导停止将天冬氨酸转化为碳骨架中间体,使得共培养期间保加利亚乳杆菌的生长速度低于单菌株培养时的速度。因此并不是所有的保加利亚乳杆菌和嗜热链球菌菌株之间都存在共生关系,还有一部分菌株之间可能存在拮抗作用[16]。
乳酸菌在发酵过程中会产生细菌素、胞外多糖、生物活性肽等抑菌化合物,具有抗炎、抗氧化等益生作用,但与其他微生物共培养时这些代谢产物也会抑制其它菌种的生长繁殖[23]。VAN等[26]的研究表明,保加利亚乳杆菌产生的过氧化氢和细菌素等抑菌物质,破坏了其与嗜热链球菌之间的平衡。由于产生细菌素而导致中间关系受到影响的还有保加利亚乳杆菌和嗜酸乳杆菌,在VINDEROLA等[27]的研究中发现保加利亚乳杆菌的生长完全受到嗜酸乳杆菌CNRZ1881的抑制,这是由于后者产生类细菌素导致的。了解这些拮抗作用为进一步探究乳酸菌间的作用机制以及开发有益生特性的产品奠定基础。
2. 互作机制
乳制品发酵过程中,不同乳酸菌菌株间的相互作用可以通过多种机制进行,如通过鞭毛等直接接触的方式,或通过信号分子等相互作用,此外,乳酸菌在共培养时还会在介质中释放一些可以共享的分子,如酶、生物表面活性剂等,这些可以被共用的分子称为公共产品[28]。近几十年来,这些互作背后的机制逐渐成为研究的焦点。
2.1 营养机制
发酵乳中的许多乳酸菌可以共同利用环境中的某些营养物质,如共享转化酶、脂肪酶和蛋白水解酶等胞外水解酶,乳酸菌通过这些酶将“公共分子池”中直接可用的底物分解并利用。此外,乳酸菌也可以通过不同菌株之间的交叉喂养发生互生作用。交叉喂养,即一种微生物(称为供体)吸收初级底物并将其转化为作为“公共物品”排出,随后由接受者使用的现象[28-30]。如双歧杆菌通过为乳杆菌提供胞外多糖作为发酵底物和生长基质来提高乳杆菌的生物量[31]。保加利亚乳杆菌水解蛋白产生多肽后与嗜热链球菌共享也被证明是两种菌株发生相互作用的关键[32]。乳酸菌之间也存在营养物质的非特异性竞争,这些营养物质是发酵体系中微生物生长所必需的,其中优势菌群会消耗其他菌种用于生长的基质,从而抑制它们的生长。
2.2 代谢产物作用机制
乳酸菌在发酵乳的生产过程中会产生代谢分泌物,对周围环境中的其他微生物产生协同作用或拮抗作用。刘学云等[33]将嗜酸乳杆菌、嗜热链球菌及干酪乳杆菌的无细胞上清液分别经高压灭菌法和过滤法处理后与另一菌株共培养,结果显示,三者之间存在协同共生作用,值得注意的是,与过滤除菌法相比,无细胞上清液经高压灭菌法处理后再与其他菌株混合培养时活菌数明显降低,这是由于上清液经高温处理后菌株的部分代谢产物被热破坏,菌株间的协同作用减弱,导致活菌数下降,说明乳酸菌的协同作用与其代谢产物有关。
乳酸菌产生的主要抗菌化合物是糖发酵过程中形成的有机酸,这会导致环境快速酸化,氧化还原位点降低,从而抑制其他微生物的生长。此外,乳酸菌也会产生细菌素、过氧化氢等抗菌化合物。乳酸菌产生的细菌素是核糖体合成的抗菌肽,具有绿色、安全的优点,是天然抗菌剂的重要来源[34]。细菌素主要作用于靶细胞的细胞膜,增加细胞通透性,使胞内物质被释放,菌体细胞裂解死亡,如肠球菌产生的细菌素使单增李斯特菌胞内蛋白质类和核酸类释放到细胞外环境中从而导致其死亡[35]。过氧化氢的抗菌活性与其强烈的氧化作用有关。在有氧存在条件下,益生菌通过辅酶Q的作用进行电子转移而产生过氧化氢,导致超氧化阴离子形成,破坏性氢氧游离基。这类超氧游离基对细菌细胞壁有强氧化作用,可破坏核酸及细胞内蛋白质从而影响细胞活性[36]。
2.3 信号分子形成机制
在乳制品发酵过程中,乳酸菌会形成一种群体水平上的相互作用,即群体感应。乳酸菌群体感应系统可以通过感知细胞浓度来调控特定的基因表达[37],并进一步调节乳酸菌的生物膜形成[38]、酸胁迫应答[39]、抗菌肽和胞外酶的合成[40-41]等重要的生理过程。乳酸菌自身会分泌被称为信号分子的胞外小分子,信号分子能出入细胞并在环境中积累,随着乳酸菌菌体密度的增加,信号分子在环境中的浓度也增加,当这些信号分子在乳酸菌的生长环境及细胞内的积累都达到一定的阈值时,就会被特异受体识别,启动某些特定基因的表达,相关的蛋白合成上升,因此形成了种内或种间的相互作用,达到对自身或其他微生物的协同或抑制作用[42]。目前报道中,乳酸菌的信号分子有AIPII、LamD、PltA、IP-TX、PlnA和IP-673等[43]。
3. 发酵乳中乳酸菌菌株相互作用对发酵乳制品的影响
乳酸菌有助于发酵乳最终感官、营养和健康特性的形成。随着乳酸菌理论研究的不断突破,其技术成果被加速转化。发酵乳制品是乳酸菌的优良载体,以乳酸菌为发酵剂制备发酵乳制品已有上百年的历史。对于传统发酵过程,除发酵条件影响乳酸菌群落结构变化外,其群落结构内部的相互作用贯穿了整个发酵过程。乳酸菌菌群间的相互作用可以赋予发酵食品特殊的风味,也对发酵食品质量的稳定性有着很大的影响。
3.1 感官特性
乳酸菌产生的乳酸、醋酸等有机酸,氨基酸、双乙酰、多肽、胞外多糖等芳香化合物,以及水解酶、细菌素和过氧化氢等物质为发酵食品提供了各种理想的感官特性。发酵乳中具有不同功能特性的乳酸菌菌株通过优势互补,可以产生单菌株无法获得的发酵产物,改善发酵乳的风味、质地、口感等感官特性。张筠等[44]将鼠李糖乳杆菌和嗜热链球菌混合发酵,发现菌种产酸产黏性能良好,产品中乳酸菌活菌数增加,在短时间内即得到风味俱佳的酸花生乳。将瑞士乳杆菌LH-3和嗜热链球菌427混合发酵后凝乳时间比瑞士乳杆菌LH-3单独发酵缩短了3.5 h,粘度增加1.8倍,改善了发酵乳乳清析出和质构,此外,两者混合发酵可以降低发酵乳中谷氨酸脱羧酶的活性,抑制乳糖的消耗及乳酸的产出,从而延缓了发酵乳的后酸化[45]。
发酵剂培养物与益生菌共发酵有助于产生乙醛和双乙酰等理想的挥发性代谢物,改善酸奶的风味。当发酵乳中添加干酪乳杆菌Zhang与发酵剂共培养可以增加己酸和3-羟基-2-丁酮等挥发性风味物质的产生[19]。通过比对不同菌株组合在贮藏过程中主要风味物质组分与含量的变化情况,发现多菌株发酵的发酵乳挥发性风味物质含量显著高于单一菌株的平均水平[46]。在传统乳制品的发酵过程中,微生物不仅与发酵环境有着密切联系,不同菌株间的生态学关系也十分复杂,彼此间的协同作用或拮抗作用对发酵食品最终的感官特性有着深刻影响。
3.2 营养特性
尽管感官指标仍然是决定发酵乳制品质量的主要指标,但消费者对发酵乳的营养需求也是决定其未来发展、新产品开发和产品规模的重要因素。
发酵过程提高了乳制品的营养价值,增加了营养物质的生物利用率。传统发酵剂嗜热链球菌和保加利亚乳杆菌通常代谢乳糖的葡萄糖部分,并将半乳糖释放到胞外介质中,导致酸奶中残留的半乳糖和未发酵的乳糖水平较高,不利于乳糖不耐症患者的消化吸收,而植物乳杆菌能够有效地代谢乳糖和半乳糖,以乳糖为基础将植物乳杆菌WCFS1与基础酸奶发酵剂共培养,结果表明,乳糖消耗完全,半乳糖代谢效率高,与传统发酵工艺相比,添加植物乳杆菌WCFS1和酸奶发酵剂结合降低了乳制品的总糖含量,产品在外观、质地和风味上也都得到了消费者的认可,具有发酵低糖酸奶的潜力[47]。KIMOTO-NIRA等[48]将乳酸乳球菌和棉子乳球菌共培养用于发酵牛奶和植物基质混合物,非蛋白水解型棉子乳球菌能够降解引起肠道不适的棉子糖、蜜二糖和水苏糖,且当这两种菌株一起生长时可以更好地酸化牛奶。
3.3 功能特性
发酵乳制品既保留了发酵乳本身的营养特性,又赋予了产品一定的益生特性。NISHIYAMA等[49]通过双盲对照实验,发现含动物双歧杆菌Bb12和乳酸乳球菌11/19-B1的酸奶能降低血清低密度脂蛋白的含量,并加强细胞免疫刺激功能。由青春双歧杆菌B8589和副干酪乳酪杆菌PC-01复合发酵的益生菌发酵乳饮料通过调控三羧酸循环和谷氨酸代谢途径,显著提升益生菌发酵乳饮料中γ-氨基丁酸和L-苹果酸等生物活性物质的含量,且整个贮藏期(30 d)内,该复合益生菌发酵乳饮料的活菌数高于5×108 CFU/g ,足量的益生菌及发酵乳饮料中大量的生物活性代谢物可共同赋予复合益生菌发酵乳饮料双重的益生功效[50]。连续四周食用含有干酪乳杆菌Zhang和动物双歧杆菌乳酸菌亚种V9的发酵乳后可以改善便秘患者排便频次、排便时间和粪便黏稠度等症状[51]。人群随机对照实验表明,乳双歧杆菌CNCMI-2494发酵牛乳可以在2周内快速改善腹胀、腹痛、肠胃胀气等轻微消化不良症状,且症状改善与膳食纤维补充及运动无关[52]。
在长期的生产实践中发现,对于成分或生化过程过于复杂的发酵来说,单一菌种发酵的局限性日益突出,而混合培养因菌种之间可以优势互补,从而提高活菌数、缩短发酵周期,并有效改善产品特性,为发酵乳生产开启了新的途径。
4. 总结与展望
近年来,乳酸菌越来越多的益生特性被揭示出来,发酵乳中乳酸菌菌株共培养在产量调控、产品功能化和资源利用等方面为发酵食品提供了新的机遇。但从目前的研究报道发现,由于菌株的多样性和发酵底物的复杂性,发酵产物的确切组成和分子结构尚不完全清楚,大多数混合菌体系中菌株间相互关系和作用机制的研究也不够深入,微生物混合培养研究更多地局限于工艺的优化。因此,在未来实际应用中,全面深入的了解发酵乳制品中乳酸菌菌株之间的相互作用方式及作用机制,探究微生物组的特定功能及其与风味、香气和其他特性的关系,合理地利用乳酸菌资源,开发出更加高效、安全、且健康的乳酸菌产品对乳酸菌后续的开发与应用具有显著的意义。
-
[1] 中华人民共和国卫生部. GB 19302-2010食品安全国家标准发酵乳[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2010. Ministry of Health of the People's Republic of China. GB 19302-2010 Food safety national standard fermented milk[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2010.
[2] GARCÍA-BURGOS M, MORENO-FERNÁNDEZ J, ALFÉREZ M J M, et al. New perspectives in fermented dairy products and their health relevance[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2020,72:104059. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2020.104059
[3] SHARMA H, OZOGUL F, BARKIENE E, et al. Impact of lactic acid bacteria and their metabolites on the techno-functional properties and health benefits of fermented dairy products[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2021,30:1−23.
[4] TARRAH A, VINÍCIUS, DE CASTILHOS J, et al. Probiotic potential and biofilm inhibitory activity of Lactobacillus casei group strains isolated from infant feces[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2019,54:489−497. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.02.004
[5] 左梦楠, 刘伟, 全琦, 等. 乳酸菌高密度培养技术的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(19):436, 445−445. [ZUO M N, LIU W, QUAN Q, et al. Research progress of high density culture of lactic acid bacteria[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2022,43(19):436, 445−445. ZUO M N, LIU W, QUAN Q, et al. Research progress of high density culture of lactic acid bacteria[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2022, 43(19): 436, 445.
[6] CUCICK A, GIANNI K, TODOROV S D, et al. Evaluation of the bioavailability and intestinal effects of milk fermented by folate producing lactic acid bacteria in a depletion/repletion mice model[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2020,66:103−785.
[7] 李权威, 张开屏, 赵艳红, 等. 乳酸菌调控胆固醇代谢关键因子的研究进展[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(1):341−350. [LI Q W, ZHANG K P, ZHAO Y H, et al. Research progress on key factors of cholesterol metabolism regulated by lactic acid bacteria[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2021,21(1):341−350. LI Q W, ZHANG K Z, ZHAO Y H, et al. Research progress on key factors of cholesterol metabolism regulated by lactic acid bacteria[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2021, 21(1): 341-350.
[8] 王淑梅, 邸维, 妥彦峰, 等. 益生菌的免疫调控作用研究进展[J]. 粮食与油脂,2021,34(5):23−26. [WANG S M, DI W, TUO Y F, et al. Research progress on immune regulation of probiotics[J]. Cereals & Oils,2021,34(5):23−26. WANG S M, DI W, TUO Y F, et al. Research progress on immune regulation of probiotics[J]. Cereals & Oils, 2021, 34(5): 23-26.
[9] YONEZAWA S, XIAO J Z, ODAMAKI T, et al. Improved growth of Bifidobacteria by cocultivation with Lactococcuslactis subspecies lactis[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2010,93(5):1815−1823. doi: 10.3168/jds.2009-2708
[10] 赵春雨, 曲晓军, 崔艳华, 等. 德氏乳杆菌保加利亚亚种和嗜热链球菌的共生机制研究进展[J]. 乳业科学与技术,2015,38(4):21−24. [ZHAO C Y, QU X J, CUI Y H, et al. Research progress on symbiotic mechanism of Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophiles[J]. Journal of Dairy Science and Technology,2015,38(4):21−24. ZHAO C Y, QU X J, CUI Y H, et al. Research progress on symbiotic mechanism of Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophiles[J]. Journal of Dairy Science and Technology, 2015, 38(4): 21-24.
[11] KURT S, JOAKIM M A, RODOLPHE B. Short communication: Transcriptional response to a large genomic island deletion in the dairy starter culture Streptococcus thermophilus[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2019,102(9):7800−7806. doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-16397
[12] YAMAUCHI R, MAGUIN E, HORIUCHI H et al. The critical role of urease in yogurt fermentation with various combinations of Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus delbrueckii ssp. bulgaricus[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2019,102(2):1033−1043. doi: 10.3168/jds.2018-15192
[13] LIU E, ZHENG H J, SHI T, et al. Relationship between Lactobacillus bulgaricus and Streptococcus thermophilus under whey conditions: Focus on amino acid formation[J]. International Dairy Journal,2016,56:141−150. doi: 10.1016/j.idairyj.2016.01.019
[14] MUCCHETTI G, LOCCI F, MASSARA P, et al. Production of pyroglutamic acid by thermophilic lactic acid bacteria in hard-cooked mini-cheeses[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2002,85(10):2489−2496. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(02)74331-2
[15] GARAULT P, LETORT C, JUILLARD V, et a1. Branched-chain amino acid biosynthesis is essential for optimal growth of Streptococcus thermophilus in milk[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2000,66(12):5128−5133. doi: 10.1128/AEM.66.12.5128-5133.2000
[16] SERRAZANETTI D I, GUERZONI M E, CORSETTI A, et a1. Metabolic impact and potential exploitation of the stress reaction in Lactobacilli[J]. Food Microbiology,2009,26(7):700−711. doi: 10.1016/j.fm.2009.07.007
[17] 刘文俊. 嗜热链球菌和保加利亚乳杆菌产酸、风味特性及其功能基因分型和表达研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2014. LIU W J. Characteristics of acid and flavor-producing Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus, as well as their functional gene typing and expression[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2014.
[18] 柴茂. 双歧杆菌对便秘的缓解作用及其机制分析[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2021. CHAI M. Analysis of relieving effect of Bifidobacterium on constipation and its mechanism[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2021.
[19] HILL D, SUGRUE I, TOBIN C, et al. The Lactobacillus casei group: History and health related applications[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2018,19:2107.
[20] 孙浩天. 发酵乳中干酪Zhang与乳双歧V9生长和代谢互作机制研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2020. SUN H T. Growth and metabolic interaction of Lactobacillus casei Zhang and Bifidobacterium animalis subsp. lactis V9 in yoghurt fermentation[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2020.
[21] JUILLARD V, LE BARS D, KUNJI E R, et al. Oligopeptides are the main source of nitrogen for Lactococcus lactis during growth in milk[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,1995,61(8):3024−3030. doi: 10.1128/aem.61.8.3024-3030.1995
[22] CANON F, MAILLARD M B, HENRY G, et al. Positive interactions between lactic acid bacteria promoted by nitrogen-based nutritional dependencies[J]. Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2021,87(20):e01055−21.
[23] 鲁笛, 缪元浩, 张邑恒, 等. 4种乳酸菌之间的相互作用比较[J]. 现代农业科技,2019(20):226−232. [LU D, MIAO Y H, ZHANG Y H, et al. Comparison of interactions among four kinds of lactic acid bacteria[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2019(20):226−232. LU D, MIAO Y H, ZHANG Y H, et al. Comparison of interactions among four kinds of lactic acid bacteria[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology, 2019(20): 226-232.
[24] 刘学云, 于新, 何嘉敏, 等. 九种益生菌之间的相互作用及协同共生机理[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(13):65−70. [LIU X Y, YU X, HE J M, et al. Interaction and synergistic symbiosis mechanism among nine probiotics[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(13):65−70. LIU X Y, YU X, HE J M, et al. Interaction and synergistic symbiosis mechanism among nine probiotics[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2019, 45(13): 65-70.
[25] CLARE A, ANTHONY O L, JEFF G. Pairing off: A bottom-up approach to the human gut microbiome[J]. Molecular Systems Biology,2018,14(6):e8425. doi: 10.15252/msb.20188425
[26] VAN DE GUCHTE M, EHRLICH S D, MAGUIN E. Production of growth-inhibiting factors by Lactobacillus delbrueckii[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology,2001,9l:147−153.
[27] VINDEROLA C G, MOCCHIUTTI P, REINHEIMER J A. Interactions among lactic acid starter and probiotic bacteria used for fermented dairy products[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2002,85(4):721−729. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(02)74129-5
[28] CAVALIERE M, FENG S, SOYER O S, et al. Cooperation in microbial communities and their biotechnological applications[J]. Environmental Microbiology,2017,19(8):2949−2963. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13767
[29] CANON F, NIDELET T, GUÉDON E, et al. Understanding the mechanisms of positive microbial interactions that benefit lactic acid bacteria co-cultures[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2020,11:2088. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.02088
[30] D'SOUZA G, SHITUT S, PREUSSGER D, et al. Ecology and evolution of metabolic cross-feeding interactions in bacteria[J]. Natural Product Reports,2018,35(5):455−488. doi: 10.1039/C8NP00009C
[31] 白少峰, 陈华海, 王欣, 等. 双歧杆菌胞外多糖研究进展[J]. 中国微生态学杂志,2017,29(10):1207−1211, 1218. [BAI S F, CHEN H H, WANG X, et al. Research progress of Bifidobacterium extracellular polysaccharides[J]. Chinese Journal of Microecology,2017,29(10):1207−1211, 1218. BAI S F, CHEN H H, WANG X, et al. Research progress of Bifidobacterium extracellular polysaccharides[J]. Chinese Journal of Microecology, 2017, 29(10): 1207-1211, 1218.
[32] SETTACHAIMONGKON S, NOUT M J R, FERNANDES E C A, et al. Influence of different proteolytic strains of Streptococcus thermophilus in co-culture with Lactobacillus delbrueckii subsp. bulgaricus on the metabolite profile of set-yoghurt[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2014,177:29−36. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2014.02.008
[33] 刘学云, 于新, 何嘉敏, 等. 三种乳酸菌相互作用及混合发酵条件优化研究[C]. 健康中国2030·健康食品的安全与创新“学术研讨会暨2018年广东省食品学会年会论文集”, 2018: 41−47 LIU X Y, YU X, HE J M, et al. Study on the interaction of three lactic acid bacteria and optimization of mixed fermentation conditions[C]. Healthy China 2030·Safety and Innovation of Healthy Food "Academic Seminar and Proceedings of the 2018 Guangdong Food Society Annual Meeting", 2018: 41−47.
[34] PANG X, SONG X, CHEN M, et al. Combating biofilms of foodborne pathogens with bacteriocins by lactic acid bacteria in the food industry[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2022,21(2):1657−1676. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12922
[35] 吴学友, 朱悦, 陈正行, 等. 乳酸菌细菌素Durancin GL对单增李斯特菌的抗菌活性及机制[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(23):731. [WU X Y, ZHU Y, CHEN Z X, et al. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of lactic acid bacteriocin Durancin GL against Listeria monocytogenes[J]. Food Science and Technology,2019,40(23):731. WU X Y, ZHU Y , CHEN Z X, et al. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of lactic acid bacteriocin Durancin GL against Listeria monocytogenes[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2019, 40(23): 731.
[36] 郭本恒. 益生菌[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2004: 441 GUO B H. Probiotics[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2004: 441.
[37] PARK H, SHIN H, LEE K, et al. Autoinducer-2 properties of kimchi are associated with lactic acid bacteria involved in its fermentation[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2016,225:38−42. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2016.03.007
[38] LIU L, WU R Y, ZHANG J L, et al. Overexpression of luxS promotes stress resistance and biofilm formation of Lactobacillus paraplantarum L-ZS9 by regulating the expression of multiple genes[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2018,9:2628. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02628
[39] JOHANSEN P, JESPERSEN L. Impact of quorum sensing on the quality of fermented foods[J]. Current Opinion in Food Science,2017,13:16−25. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2017.01.001
[40] WASFI R, EL-RAHMAN O A A, ZAFER M M, et al. Probiotic Lactobacillus sp. inhibit growth, biofilm formation and gene expression of caries-inducing Streptococcus mutans[J]. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine,2018,22(3):1972−1983. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13496
[41] PEZZULO A A, HOMICK E E, RECTOR M V, et al. Expression of human paraoxonase 1 decreases superoxide levels and alters bacterial colonization in the gut of Drosophila melanogaster[J]. PLoS One,2012,7(8):e43777. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0043777
[42] YAO Q F, QI S H. Advance in quorum sensing autoinducers among microbes[J]. Journal of Microbiology,2015,35(4):63−71.
[43] PANG X Y, ZHU Q, LU J, et al. Progress in quorum sensing system of lactic acid bacteria[J]. Chinese Journal of Bioprocess Engineering,2020,18(2):141−149.
[44] 张筠, 赵晶, 陈喜君, 等. 鼠李糖乳杆菌与嗜热链球菌协同发酵制备酸花生乳研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(24):143−149, 156. [ZHANG Y, ZHAO J, CHEN X J, et al. Study on preparation of sour peanut milk by cooperative fermentation of Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Streptococcus thermophiles[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(24):143−149, 156. ZHANG Y, ZHAO J, CHEN X J, et al. Study on preparation of sour peanut milk by cooperative fermentation of Lactobacillus rhamnosus and Streptococcus thermophiles[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2020, 41(24): 143-149, 156.
[45] 张臣臣, 於和飞, 张兆俊, 等. 嗜热链球菌对瑞士乳杆菌发酵乳后酸化的影响[J]. 乳业科学与技术,2018,41(5):1−5. [ZHANG C C, YU H F, ZHANG Z J, et al. Effect of Streptococcus thermophilus on acidification of fermented milk by Lactobacillus helveticus[J]. Journal of Dairy Science and Technology,2018,41(5):1−5. ZHANG C C, YU H F, ZHANG Z J, et al. Effect of Streptococcus thermophilus on acidification of fermented milk by Lactobacillus helveticus[J]. Journal of Dairy Science and Technology, 2018, 41(5): 1-5.
[46] 姜滢滢, 朱双双, 章苗, 等. 微生物共培养研究进展[J]. 中国微生态学杂志,2017,29(2):239−244. [JIANG Y Y, ZHU S S, ZHANG M, et al. Research progress of microbial co-culture[J]. Chinese Journal of Microecology,2017,29(2):239−244. JIANG Y Y, ZHU S S, ZHANG M, et al. Research progress of microbial co-culture[J]. Chinese Journal of Microecology, 2017, 29(2): 239-244.
[47] ZHANG S S, XU Z S, QIN L H, et al. Low-sugar yogurt making by the co-cultivation of Lactobacillus plantarum WCFS1 with yogurt starter cultures[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2020,103(4):3045−3054. doi: 10.3168/jds.2019-17347
[48] KIMTOT-NIRA H, AOKI R, MIZUMACHI K, et al. Interaction between Lactococcus lactis and Lactococcus raffinolactis during growth in milk: Development of a new starter culture[J]. Journal of Dairy Science,2012,95(4):2176−2185. doi: 10.3168/jds.2011-4824
[49] NISHIYAMA K, KOBAYASHI T, SATO Y, et al. A double-blind controlled study to evaluate the effects of yogurt enriched with Lactococcus lactis 11/19-b1 and Bifidobacterium lactis on serum low-density lipoprotein level and antigen-specific interferon-γ releasing ability[J]. Nutrients,2018,10(11):1778. doi: 10.3390/nu10111778
[50] 李培培, 武婷, 杨阳, 等. 副干酪乳酪杆菌PC-01和青春双歧杆菌B8589在复合益生菌发酵乳饮料中的应用研究[C]. 第十七届益生菌与健康国际研讨会摘要集, 2022: 31−32. LI P P, WU T, YANG Y, et al. Study on application of Lactobacillus paracasei PC-01 and Bifidobacterium adolescentis B8589 in compound probiotic fermented milk beverage[C]. Summary of the 17th International Symposium on Probiotics and Health, 2022: 31−32.
[51] 白晓晔. 干酪乳杆菌Zhang和动物双歧杆菌乳亚种V9发酵乳缓解便秘机制研究[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古农业大学, 2020. BAI X Y. Study on the mechanism of Lactobacillus casei Zhang and Bifidobacterium lactis V9 fermented milk to relieve constipation[D]. Hohhot: Inner Mongolia Agricultural University, 2020.
[52] MARTEAU P, LE NEVE B, QUINQUIS L, et al. Consumption of a fermented milk product containing Bifidobacterium lactis CNCM1-2494 in women complaining of minor digestive symptoms: Rapic response which is independent of dietary fibre intake or physical activity[J]. Nutrients,2019,11(1):1−8.





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



