Antimicrobial Activity of Three Flavonoids of Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. yunnanensis Berries
-
摘要: 研究云南沙棘果实中3种主要黄酮类化合物对4种病原菌的抑制作用。首先采用滤纸片法检测沙棘果实总黄酮对金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌、枯草芽孢杆菌、白色念珠菌的抑制效果;其次通过超高效液相色谱-串联质谱(Ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry,UPLC-MS/MS)对总黄酮进行成分鉴定并利用高效液相色谱(High performance liquid chromatography,HPLC)定量检测其主要成分,最后采用二倍稀释法和考马斯亮蓝法评价3种主要黄酮类成分的抑菌效果。结果表明,云南沙棘果实黄酮提取物中主要黄酮类成分为异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖-7-O-鼠李糖苷(Isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside-7-O-rhamnoside,Is-3-G-7-Rh)、芦丁(Quercetin-3-O-rutinoside,Qu-3-R)、异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖苷(Isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside,Is-3-G),含量分别为38.43±0.85、29.44±0.42、21.11±0.55 mg/g;总黄酮及3种主要黄酮类成分对4种供试菌均有一定的抑制作用,Is-3-G-7-Rh和Is-3-G对4种菌的抑制效果均优于Qu-3-R和总黄酮,蛋白检测结果表明沙棘黄酮使细胞内蛋白流出导致菌体死亡。本研究可为沙棘属植物果实中黄酮类化合物在抑菌方面的应用提供科学依据。Abstract: This study aimed to investigate the inhibitory effects of three major flavonoids from the Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. yunnanensis berries on four pathogenic microorganisms. The antimicrobial activity of total flavonoids from Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. yunnanensis berries on Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Bacillus subtilis and Candida albicans was firstly measured by filter paper method. Then, the total flavonoids compositions were identified by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS) and the main components were quantified by high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). Finally, the Bradford method and the double dilution method were used to assess the antimicrobial effect of the three flavonoids. The results showed that the major flavonoid components of the Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. yunnanensis berries were isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside-7-O-rhamnoside (Is-3-G-7-Rh), quercetin-3-O-rutinoside (Qu-3-R) and isorhamnetin-3-O-glucoside (Is-3-G), which with the contents of 38.43±0.85, 29.44±0.42 and 21.11±0.55 mg/g, respectively. The extract and its three main flavonoids had inhibitory effect on the four microorganisms. The inhibitory effects of Is-3-G-7-Rh and Is-3-G on the microorganisms were better than Qu-3-R and extract, and the results of protein detection showed that flavonoids induced antimicrobial death through intracellular protein efflux. This study can provide a scientific basis for the application of flavonoids in the berries of Hippophae rhamnoides for antimicrobial purposes.
-
沙棘属(Hippophae Linn.)植物广泛分布于亚欧大陆,具有防风固沙的作用[1]。沙棘作为一种药食同源植物富含多种活性物质与营养成分,被广泛应用于保健和医疗领域[2]。黄酮类化合物是沙棘中的重要活性成分,具有抗肿瘤、抗氧化和抑菌等多种药理功效[3-4],沙棘也因含有丰富的黄酮类化合物受到了广泛的关注。
金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌、枯草芽孢杆菌是生活中常见的食源性细菌,易造成食物腐败等食品安全问题[5-6];白色念珠菌作为一种真菌,可在人体口腔、皮肤等多处引发炎症[7]。目前使用抗生素是解决由细菌和真菌引起的疾病有效方式,但会对生物体产生副作用,且随着抗生素大量使用,一些病原菌已经对整类抗生素产生耐药性[8-9]。因此,寻求更健康有效的方法来对抗由病原菌引发的疾病日益成为人们的共识[10]。天然植物源抑菌剂以其天然、安全、高效等特性受到越来越多关注[11]。有研究表明,黄酮类化合物对多种细菌具有良好抑制效果,对人体产生的副作用小且不会使细菌产生耐药性[12]。因此,将沙棘属植物中黄酮类化合物制作为天然抑菌剂具有广泛的前景。目前,对沙棘果实黄酮类化合物的研究多涉及沙棘果实黄酮提取工艺的优化及总黄酮的抑菌效果,但关于黄酮单体抑菌活性的研究较少。
为探究沙棘果实黄酮类化合物对常见病原菌的抑菌活性,本研究选取金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌、枯草芽孢杆菌、白色念珠菌等4株病原菌作为供试菌,采用滤纸片法测定沙棘果实黄酮提取物的抗菌性能,通过UPLC-MS/MS和HPLC技术检测黄酮类化合物的主要成分及含量,并测定3种主要黄酮类成分的最低抑菌浓度(Minimum inhibitory concentration,MIC)以及细菌的蛋白流出含量,讨论3种黄酮类成分的抑菌效果,以期提高沙棘果实资源的利用效率,为云南沙棘果实黄酮类物质的深入研究提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
云南沙棘果实 2020年11月采自西藏林芝市巴宜区,经东北林业大学森林植物生态学教育部重点实验室张莹副研究员鉴定为胡颓子科植物云南沙棘(Hippophae rhamnoides subsp. yunnanensis)的果实,样品经室温干燥(25±5 ℃)至恒重,研磨后过0.425 mm筛,−20 ℃冷藏备用;金黄色葡萄球菌(Staphylococcus aureus,ATCC 6538)、枯草芽孢杆菌(Bacillus subtilis,ATCC 6633)、大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli,ATCC 8739)、白色念珠菌(Candida albicans,ATCC 10231) 黑龙江省科学院应用微生物研究所;Qu-3-R、Is-3-G 纯度≥98%,上海源叶生物科技有限公司;Is-3-G-7-Rh 纯度≥98%,四川维克奇生物科技有限公司;营养肉汤(Nutrient broth,NB)、营养琼脂(Nutrient agar,NA) 北京奥博星生物技术有限责任公司;甲醇(色谱级)、考马斯亮蓝G-250 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;甲酸、磷酸 均为国产分析纯。
JP-100ST超声波清洗机 深圳洁盟超声科技有限公司;NEO 15离心机 上海力申科学仪器有限公司;Q-focus高分辨液质联用仪(配有电喷雾离子源(ESI)及Xcalibur4.1数据处理系统) 美国Thermo Scientific公司;1260高效液相色谱仪 美国Agilent公司;Synergy2多功能酶标仪 美国BioTek公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 云南沙棘总黄酮的制备
采用超声辅助提取法[13],取干燥沙棘果实粉末1 g,加入体积分数为60%的乙醇溶液30 mL,振荡混匀后静置30 min,在50 ℃环境下以400 W的功率超声提取30 min,离心(10000 r/min,10 min)后取上清液。参考康莹[14]的方法将上清液利用AB-8大孔树脂进行纯化,旋转蒸干(80 r/min,60 ℃),得到纯度为56.11%的黄酮提取物。
1.2.2 菌悬液的制备
用消毒的接种环蘸取少量供试菌种,加入到30 mL无菌NB培养基中,置于37 ℃恒温培养箱中培养18 h。取活化好的供试菌种,用NB培养基将菌液浓度稀释至1×108 CFU/mL备用[15]。
1.2.3 总黄酮抑菌圈的测定
采用滤纸片法测定云南沙棘总黄酮对4种供试菌的抑菌活性。称取纯化后的黄酮提取物溶于生理盐水中配成1 mg/mL的黄酮待测液。将灭菌后的NA培养基(20 mL)倒入培养皿(90 mm×15 mm)中,培养基凝固后,将直径为6 mm,提前浸泡在待测液中取出风干后的滤纸片置于已涂布200 μL菌液的琼脂板上,生理盐水为阴性对照,甲硝唑为阳性对照。将培养皿置于37 ℃培养箱培养24 h后,用游标卡尺测量抑菌圈直径[16]。
1.2.4 UPLC-MS/MS法鉴定云南沙棘黄酮提取物
1.2.4.1 色谱条件
色谱柱:Hyperil Gold(100 mm×2.1 mm,1.9 μm);柱温25 ℃;流动相:流动相A为0.1%甲酸水溶液(v/v),流动相B为甲醇;梯度洗脱程序:0~1 min,2% B;1~9 min,2%~98% B;9~12 min,98% B;12~12.1 min,98%~2% B;12.1~15 min,2% B。流速0.3 mL/min;进样量10 μL。
1.2.4.2 质谱条件
电喷雾离子源(ESI),负离子模式扫描;毛细管电压为3800 V;气体温度为350 ℃;毛细管温度为320 ℃;辅助气为10 arb;碰撞能量为20、40和60 V;一级扫描分辨率为70000,二级扫描分辨率为17500;质谱扫描范围为m/z 70~1000。
1.2.5 黄酮类成分的含量测定
1.2.5.1 HPLC条件
色谱柱:Curosil-PFP(250 mm×4.6 mm,5 µm)反向色谱柱;柱温:30 ℃;流动相A和B分别为0.03%(v/v)甲酸的水溶液和甲醇;梯度洗脱条件:0 min,30% B;10 min,50% B;20 min,70% B;25 min,75% B;28 min,30% B;紫外检测波长:370 nm;流速:1 mL/min;进样量:20 μL[17]。
1.2.5.2 样品含量测定
精确称取Is-3-G-7-Rh、Qu-3-R、Is-3-G,用甲醇溶解,配成适量浓度范围内的混合标准品溶液,精密吸取不同浓度梯度对照品溶液20 μL,根据色谱条件进样测定峰面积,计算含量。以质量浓度(X,μg/mL)为横坐标、峰面积(Y)为纵坐标,根据如下公式建立标准校准曲线。
式中:a为标准曲线斜率,b为标准曲线截距。
准确称取纯化后的黄酮提取物10 mg,加入10 mL甲醇溶解配制成1 mg/mL样品溶液,将溶液用0.22 μm微孔滤膜过滤,作为待测液。精密吸取20 μL待测液进样测定,根据标准曲线计算含量[18]。
1.2.6 MIC的测定
用二倍稀释法[19]测定云南沙棘总黄酮及单一黄酮样品对4种供试菌的最低抑制浓度。将纯化后的沙棘总黄酮样品溶解在DMSO中,0.22 μm微孔滤膜过滤除菌,用无菌生理盐水将母液依次稀释成质量浓度为1000、500、250、125、62.5、31.25、15.63 μg/mL的总黄酮样品溶液。将4种供试菌悬浮液(1×108 CFU/mL,100 µL)分别添加到96孔细胞培养板中。然后依次添加不同浓度的总黄酮样品溶液100 μL。将培养板放置于37 ℃培养箱中培养24 h。使用酶标仪测量每个孔在600 nm处的吸光度,MIC定义为最后一个孔中未发现细菌生长的样品浓度[20]。使用相同的方法测定3种单一黄酮成分的MIC,3种成分的浓度梯度为500、250、125、62.5、31.25、15.63、7.81 μg/mL。
1.2.7 细胞外蛋白含量的测定
采用考马斯亮蓝法[21]将浓度为MIC的总黄酮和单一黄酮溶液分别作用到大肠杆菌悬浮液(1×108 CFU/mL)中,培养4 h后离心(5000 r/min,6 min)取上清液,测量上清液在595 nm处吸光度,以此来检测上清液中的蛋白含量,每隔4 h检测一次,记录处理后的24 h内菌液中的蛋白含量变化。
1.3 数据处理
上述实验均重复3次,实验数据采用SPSS Statistics 26软件进行分析处理,实验结果以平均值±标准差表示;采用origin 2019 b软件进行绘图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 抑菌圈测定结果
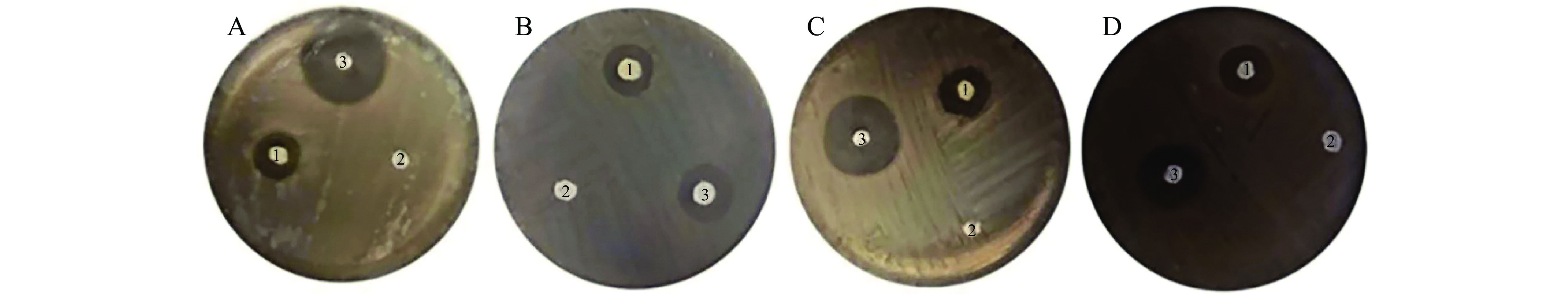
纸片法测定云南沙棘果实总黄酮对供试菌种的抑制效果见表1和图1。由表1可知,沙棘果实黄酮提取物对4种供试菌的抑菌圈直径均在8 mm以上。总黄酮对枯草芽孢杆菌的抑菌圈直径达到10.56±0.42 mm,显著大于其他3个菌种的抑菌圈直径(P<0.05),对白色念珠菌的抑制效果次之(9.02±0.96 mm),对金黄色葡萄球菌和大肠杆菌的抑制效果较弱,抑菌圈直径分别为8.36±0.36 mm和8.43±0.53 mm。结果表明,云南沙棘果实黄酮提取物对4种供试菌均有一定抑菌活性,且对不同供试菌的抑制效果不同。由提取物中总黄酮为大量成分,参考相关文献的研究结果[22-23],推测黄酮类成分可能是其抑菌作用的主要活性成分。
表 1 总黄酮对4种供试菌的抑菌圈直径(n=3)Table 1. Diameter of inhibition zone of total flavonoids against four tested microorganisms (n=3)菌种 抑菌圈直径(mm) 沙棘总黄酮 甲硝唑 生理盐水 大肠杆菌 8.43±0.53c 22.2±0.26a − 金黄色葡萄球菌 8.36±0.36c 9.33±0.22d − 白色念珠菌 9.02±0.96b 19.23±1.65b − 枯草芽孢杆菌 10.56±0.42a 14.75±0.56c − 注:“−”代表无抑菌圈;甲硝唑溶液浓度为16 μg/mL;同一列中不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 2.2 UPLC-MS/MS分析结果
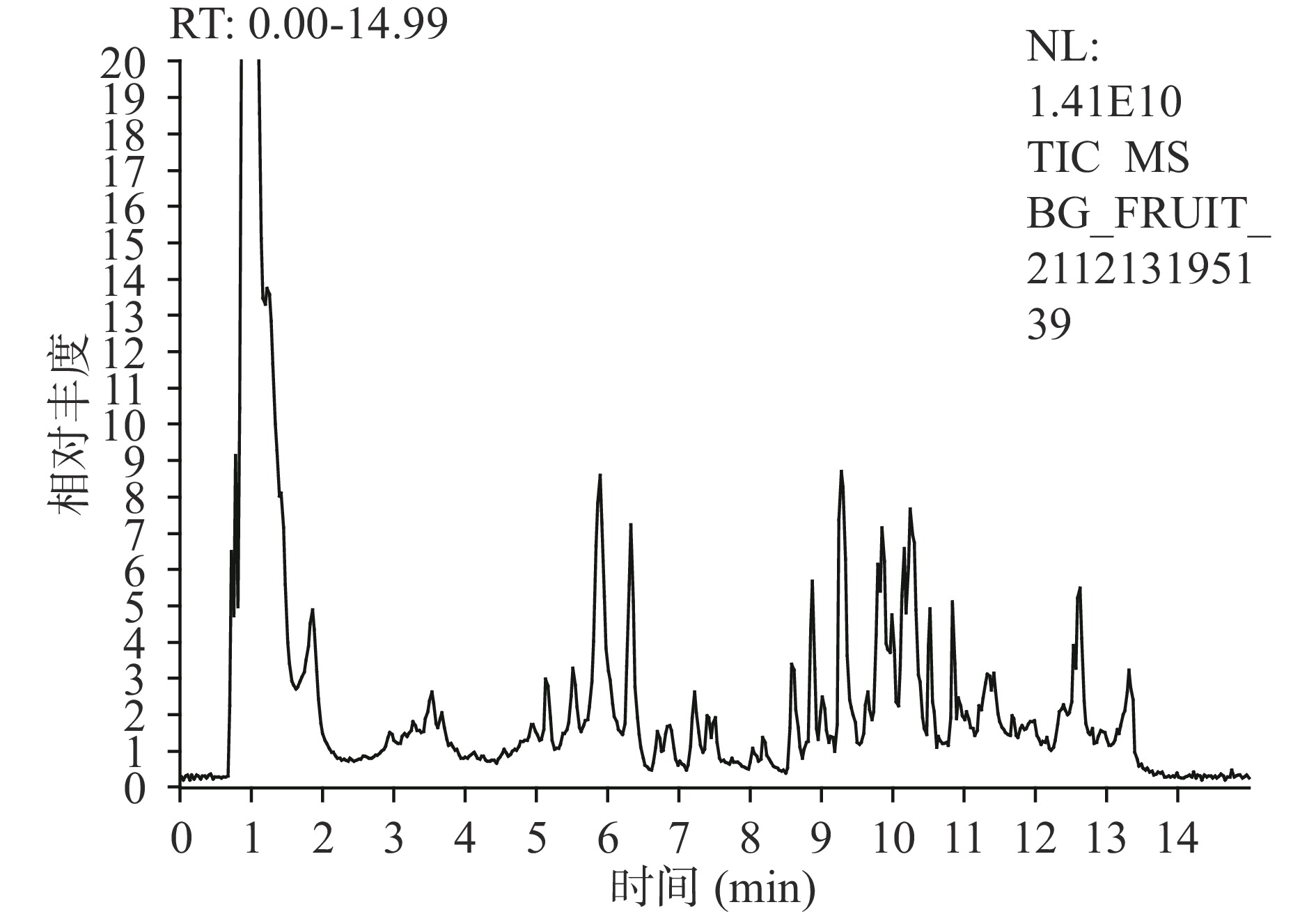
使用UPLC-MS/MS对云南沙棘果实黄酮提取物进行了分析,负离子流图如图2,根据保留时间、相对分子质量、分子离子峰、二级质谱图碎片离子峰,利用mzCloud数据库并参考文献[24-26]鉴定出12种黄酮类成分,时间分布范围为5.14~7.39 min,结果见表2。云南沙棘中的黄酮类化合物主要是以异鼠李素、山奈酚和槲皮素为苷元和糖结合形成的黄酮醇苷类物质,这与王婉宁[27]所得结论一致。
表 2 沙棘果实中黄酮类化合物的UPLC-MS/MS鉴定结果Table 2. Identified flavonoid compounds in sea buckthorn berries by UPLC-MS/MS序号 tR(min) [M–H]−(m/z) 碎片离子 分子式 化合物 1 5.14 755.19 609.13*,284.03*,
431.09C33H40O20 山奈酚-3-O-槐糖-7-O-鼠李糖苷 2 5.52 609.13 463.08*,447.08*,
299.01C27H30O16 槲皮素-3-O-葡萄糖-7-O-鼠李糖苷 3 5.87 623.15 477.09*,315.04*,
313.03C28H32O16 异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖-7-O-鼠李糖苷 4 5.92 609.13 300.02*,271.02*,
255.02C27H30O16 芦丁 5 5.95 463.08 301.03,300.02*,
271.02C21H20O12 异槲皮苷 6 6.27 593.14 285.03*,255.02,
227.03C27H30O15 山奈酚-3-O-芸香糖苷 7 6.31 623.15 315.04*,300.01*,
271.02*,243.02*C28H32O16 异鼠李素-3-O-芸香糖苷 8 6.33 477.09 314.04,315.04*,
243.02*,271.02*C22H22O12 异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖苷 9 6.73 447.08 301.03*,151.00*,
107.01C21H20O11 槲皮素-7-O-鼠李糖苷 10 6.81 301.03 151.00*,121.03,
107.01C15H10O7 槲皮素 11 7.22 461.10 315.04*,299.01,
271.02C22H22O11 异鼠李素-7-O-鼠李糖苷 12 7.39 315.04 300.02*,107.01*,
243.03C16H12O7 异鼠李素 注:“*”标注为主要定性离子。 参考樊轻亚等[28]的方法根据峰强度选取3种含量最高的黄酮类成分:Is-3-G-7-Rh(5.87 min)、Qu-3-R(5.92 min)、Is-3-G(6.33 min),利用高效液相色谱对其进行定量检测。
2.3 黄酮含量测定结果
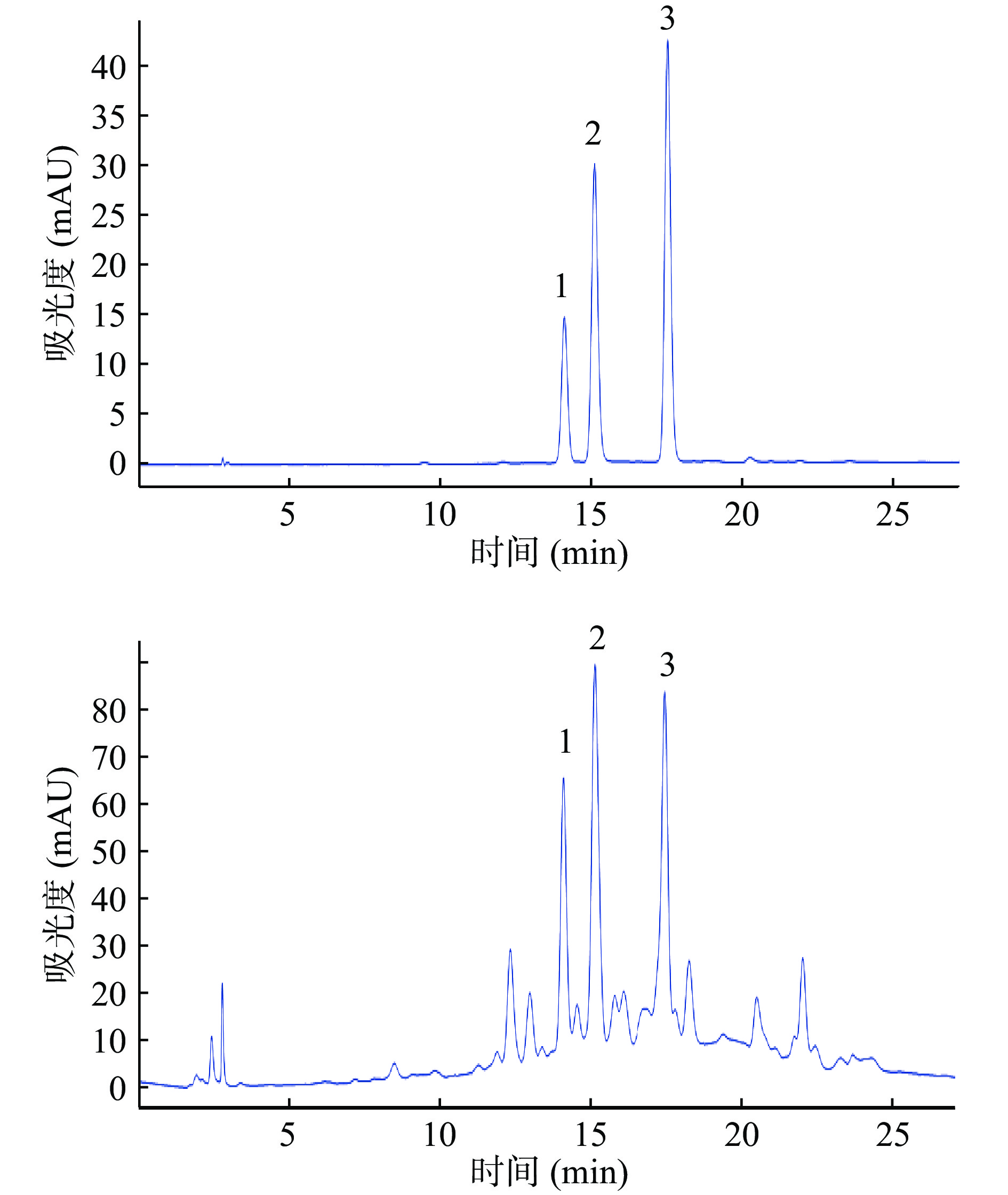
利用HPLC对云南沙棘果实总黄酮中3种主要黄酮类成分进行了定量分析,液相色谱图如图3所示,峰1~峰3分别为Is-3-G-7-Rh、Qu-3-R、Is-3-G。Is-3-G-7-Rh质量浓度在10~50 mg/L范围内与峰面积线性关系良好,回归方程Y=5.3226X−4.9282(R2=0.9992),Qu-3-R质量浓度在3~36 mg/L范围内与峰面积线性关系良好,回归方程Y=10.98X+2.8071(R2=0.9996),Is-3-G质量浓度在6~27 mg/L范围内与峰面积线性关系良好,回归方程Y=16.769X−9.2253(R2=0.9991)。
沙棘果实总黄酮中,Is-3-G-7-Rh的含量为38.43±0.85 mg/g,Qu-3-R含量为29.44±0.42 mg/g,Is-3-G含量为21.11±0.55 mg/g。Ma等[29]的研究发现,‘Pertsik’沙棘(Finland)中含量最高的黄酮类化合物为Is-3-G-7-Rh,这与本文的检测结果是一致的。而‘Vitaminaya’沙棘(Canada)中Is-3-G-7-Rh(3.9±0.6 mg/100 g鲜果)的含量要低于Is-3-G(5.8±0.7 mg/100 g鲜果),不同的研究结果表明不同产地沙棘中的黄酮类成分含量是不同的,造成这种现象的原因可能是气候、地理等因素[30]。
2.4 MIC的测定结果
沙棘总黄酮和3种主要黄酮类成分进行了4种供试菌的MIC测定,结果见表3。结果表明单一黄酮类成分对4种供试菌的抑制效果普遍高于沙棘总黄酮。Is-3-G和Is-3-G-7-Rh对金黄色葡萄球菌、枯草芽孢杆菌和大肠杆菌表现出比Qu-3-R更优秀的抑制效果,对金黄色葡萄球菌的MIC值均为62.5 μg/mL,对大肠杆菌的MIC值更是达到了31.25 μg/mL,推测二者是沙棘果实总黄酮中发挥抗菌作用的主要物质。
表 3 黄酮类化合物对4种供试菌的MIC(n=3)Table 3. MIC of flavonoids against four tested microorganisms (n=3)样品 MIC(μg/mL) 大肠杆菌 金黄色葡萄球菌 白色念珠菌 枯草芽孢杆菌 沙棘总黄酮 250 250 500 250 Qu-3-R 125 250 125 250 Is-3-G 31.25 62.5 125 62.5 Is-3-G-7-Rh 31.25 62.5 125 125 20% DMSO − − − − 注:“−”表示在所有浓度下均有菌类生长。 Qu-3-R对大肠杆菌和白色念珠菌的MIC均为125 μg/mL。Gutierrez-Venegas等[31]研究发现一定浓度的Qu-3-R溶液对大肠杆菌和金黄色葡萄球菌的生长都起到了抑制作用,并且对于这两种细菌的抑制效果要明显优于柚皮苷等其他黄酮类化合物,这为Qu-3-R作为替代抗生素的天然抑菌剂来对抗这些细菌提供了重要支持。对于白色念珠菌,总黄酮和Is-3-G和Is-3-G-7-Rh的MIC值普遍高于其他几种细菌,总黄酮的MIC值更是达到500 μg/mL,说明白色念珠菌对黄酮类化合物不敏感,所以将沙棘果实中提取的黄酮类化合物用作白色念珠菌抑菌剂还需考究。此外,Janeczko等[32]发现有些黄酮类化合物可以通过相互作用来达到更佳的抑菌效果。本研究中总黄酮和Qu-3-R对于金黄色葡萄球菌和枯草芽孢杆菌的MIC值相同,Is-3-G和Is-3-G-7-Rh对两种菌的MIC值要低于总黄酮,总黄酮并未表现出更佳的抑制效果,所以Qu-3-R、Is-3-G和Is-3-G-7-Rh是否具有协同抑菌作用有待考究。
2.5 细胞外蛋白含量测定结果
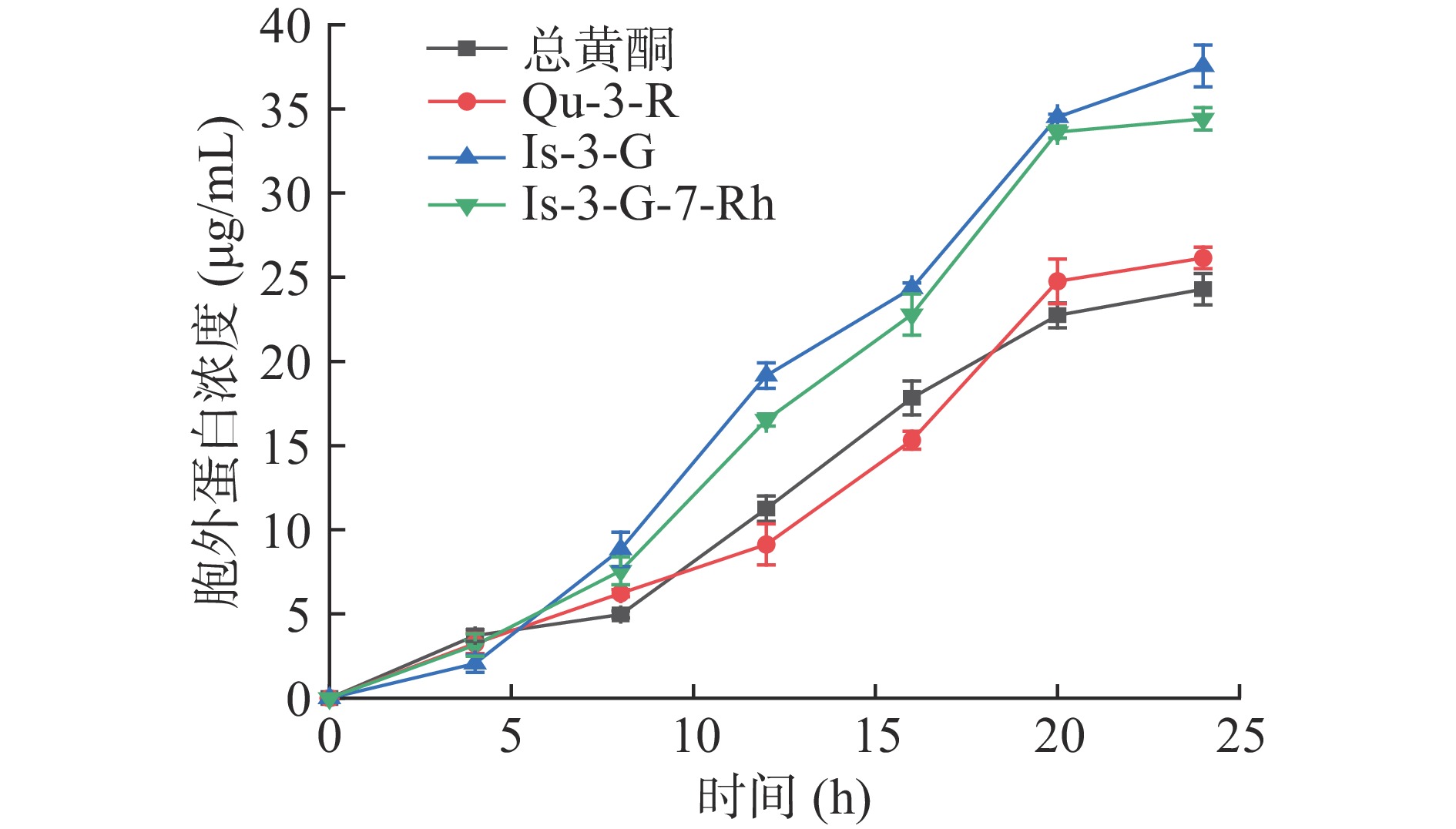
将浓度为MIC的总黄酮和单一黄酮样品作用于大肠杆菌,测量24 h内大肠杆菌的蛋白释放量,结果见图4。随着时间延长,Is-3-G和Is-3-G-7-Rh作用的菌液中蛋白含量要明显高于总黄酮和Qu-3-R作用的菌液。当时间达到24 h,Is-3-G和Is-3-G-7-Rh作用的菌液中蛋白含量分别达到了37.55±1.24 μg/mL和34.41±0.76 μg/mL,而总黄酮和Qu-3-R作用的菌液中蛋白质含量分别为24.29±0.93 μg/mL和26.15±0.64 μg/mL,并且增加趋势变缓,这与MIC的测定结果一致。推测沙棘黄酮类化合物可能是通过破坏细菌的细胞膜结构,使细菌内的物质流出导致的细菌死亡[33],而黄酮类成分如何破坏细胞结构导致蛋白流出,有待更深层次的研究。
3. 结论
通过UPLC-MS/MS技术对云南沙棘果实总黄酮进行了成分分析,共鉴定出了12种黄酮类化合物,并利用HPLC法测定3种主要黄酮类化合物含量分别为Is-3-G-7-Rh:38.43±0.85 mg/g、Qu-3-R:29.44±0.42 mg/g、Is-3-G:21.11±0.55 mg/g。沙棘果实总黄酮及3种主要黄酮类成分对金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌、枯草芽孢杆菌、白色念珠菌4种常见致病菌均有一定抑制作用,单一黄酮类成分的抑制效果均优于总黄酮,尤其是Is-3-G-7-Rh和Is-3-G对4种细菌的抑制作用最强,Qu-3-R对金黄色葡萄球菌和枯草芽孢杆菌的抑制效果和沙棘总黄酮相同,由体外蛋白流出曲线推测黄酮类成分可能通过破坏细胞结构使胞内蛋白流出导致菌体死亡。
-
表 1 总黄酮对4种供试菌的抑菌圈直径(n=3)
Table 1 Diameter of inhibition zone of total flavonoids against four tested microorganisms (n=3)
菌种 抑菌圈直径(mm) 沙棘总黄酮 甲硝唑 生理盐水 大肠杆菌 8.43±0.53c 22.2±0.26a − 金黄色葡萄球菌 8.36±0.36c 9.33±0.22d − 白色念珠菌 9.02±0.96b 19.23±1.65b − 枯草芽孢杆菌 10.56±0.42a 14.75±0.56c − 注:“−”代表无抑菌圈;甲硝唑溶液浓度为16 μg/mL;同一列中不同小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 2 沙棘果实中黄酮类化合物的UPLC-MS/MS鉴定结果
Table 2 Identified flavonoid compounds in sea buckthorn berries by UPLC-MS/MS
序号 tR(min) [M–H]−(m/z) 碎片离子 分子式 化合物 1 5.14 755.19 609.13*,284.03*,
431.09C33H40O20 山奈酚-3-O-槐糖-7-O-鼠李糖苷 2 5.52 609.13 463.08*,447.08*,
299.01C27H30O16 槲皮素-3-O-葡萄糖-7-O-鼠李糖苷 3 5.87 623.15 477.09*,315.04*,
313.03C28H32O16 异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖-7-O-鼠李糖苷 4 5.92 609.13 300.02*,271.02*,
255.02C27H30O16 芦丁 5 5.95 463.08 301.03,300.02*,
271.02C21H20O12 异槲皮苷 6 6.27 593.14 285.03*,255.02,
227.03C27H30O15 山奈酚-3-O-芸香糖苷 7 6.31 623.15 315.04*,300.01*,
271.02*,243.02*C28H32O16 异鼠李素-3-O-芸香糖苷 8 6.33 477.09 314.04,315.04*,
243.02*,271.02*C22H22O12 异鼠李素-3-O-葡萄糖苷 9 6.73 447.08 301.03*,151.00*,
107.01C21H20O11 槲皮素-7-O-鼠李糖苷 10 6.81 301.03 151.00*,121.03,
107.01C15H10O7 槲皮素 11 7.22 461.10 315.04*,299.01,
271.02C22H22O11 异鼠李素-7-O-鼠李糖苷 12 7.39 315.04 300.02*,107.01*,
243.03C16H12O7 异鼠李素 注:“*”标注为主要定性离子。 表 3 黄酮类化合物对4种供试菌的MIC(n=3)
Table 3 MIC of flavonoids against four tested microorganisms (n=3)
样品 MIC(μg/mL) 大肠杆菌 金黄色葡萄球菌 白色念珠菌 枯草芽孢杆菌 沙棘总黄酮 250 250 500 250 Qu-3-R 125 250 125 250 Is-3-G 31.25 62.5 125 62.5 Is-3-G-7-Rh 31.25 62.5 125 125 20% DMSO − − − − 注:“−”表示在所有浓度下均有菌类生长。 -
[1] 牟春堂, 郝小燕, 刁小高, 等. 沙棘果渣在动物饲粮中应用的研究进展[J]. 动物营养学报,2019,31(7):2965−2970. [MOU Chuntang, HAO Xiaoyan, DIAO Xiaogao, et al. Research progress of application of sea buckthorn pomace in animal diets[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2019,31(7):2965−2970. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2019.07.004 MOU Chuntang, HAO Xiaoyan, DIAO Xiaogao, et al. Research progress of application of sea buckthorn pomace in animal diets[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2019, 31(7): 2965-2970. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2019.07.004
[2] 张程慧, 祁玉霞, 程康蓉, 等. 沙棘的综合价值研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(22):331−335. [ZHANG Chenghui, QI Yuxia, CHENG Kangrong, et al. Advances on research and applications of Hippophea rhamnoides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(22):331−335. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2017.22.064 ZHANG Chenghui, QI Yuxia, CHENG Kangrong, et al. Advances on research and applications of Hippophea rhamnoides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2017, 38(22): 331-335. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2017.22.064
[3] GU Y J, WANG X X, LIU F, et al. Total flavonoids of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) improve MC903-induced atopic dermatitis-like lesions[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2022,292:115195. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115195
[4] CAO J G, ZHENG Y X, XIA X, et al. Total flavonoid contents, antioxidant potential and acetylcholinesterase inhibition activity of the extracts from 15 ferns in China[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2015,75:135−140. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.04.064
[5] 王雪薇, 李德海. 红松不同部位精油的成分分析及抑菌活性[J]. 中南林业科技大学学报,2021,41(2):154−161. [WANG Xuewei, LI Dehai. Phytochemical composition and antibacterial activity of the essential oils from different parts of Korean pine[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology,2021,41(2):154−161. doi: 10.14067/j.cnki.1673-923x.2021.02.018 WANG Xuewei, LI Dehai. Phytochemical composition and antibacterial activity of the essential oils from different parts of Korean pine[J]. Journal of Central South University of Forestry & Technology, 2021, 41(2): 154-161. doi: 10.14067/j.cnki.1673-923x.2021.02.018
[6] CHEN Z F, HE B, ZHOU J, et al. Chemical compositions and antibacterial activities of essential oils extracted from Alpinia guilinensis against selected foodborne pathogens[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2016,83:607−613. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2015.12.063
[7] YIN S, LI L, SU L Q, et al. Synthesis andin vitro synergistic antifungal activity of analogues of Panax stipulcanatus saponin against fluconazole-resistant Candida albicans[J]. Carbohydrate Research,2022,517:108575. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2022.108575
[8] ASLAM B, WANG W, ARSHAD M I, et al. Antibiotic resistance: A rundown of a global crisis[J]. Infection and Drug Resistance,2018,11:1645−1658. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S173867
[9] 孙悦, 刘佳伊, 陈璐, 等. 抗耐药性大肠杆菌乳酸菌的筛选及抑菌机制[J]. 食品科学,2022,42(2):122−125. [SUN Yue, LIU Jiayi, CHEN Lu, et al. Screening of lactic acid bacteria for antagonistic activity against drug-resistant Escherichia coli and underlying mechanism[J]. Food Science,2022,42(2):122−125. SUN Yue, LIU Jiayi, CHEN Lu, et al. Screening of lactic acid bacteria for antagonistic activity against drug-resistant Escherichia coli and underlying mechanism[J]. Food Science, 2022, 42(2): 122-125.
[10] BARRETO H M, TINTINO S R, REGO J V, et al. Chemical composition and possible use as adjuvant of the antibiotic therapy of the essential oil of Rosmarinus officinalis L.[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2014,59:290−294. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.05.026
[11] DRA L A, BOUALY B, AGHRAZ A, et al. Chemical composition, antioxidant and evidence antimicrobial synergistic effects of Periploca laevigata essential oil with conventional antibiotics[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2017,109:746−752. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.09.028
[12] TIAN C L, WANG H, GUO Y R, et al. Abutilon theophrasti medic. Episperms as a total flavonoids fraction for pharmaceutical applications: In vitro antioxidant, antibacterial, anti-inflammatory activities, extraction technology and HPLC-MS profiles[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2017,109:100−106.
[13] 刘馨雨, 张海生, 许铭芯, 等. 超声波微波协同提取沙棘叶黄酮及其组成和活性研究[J]. 核农学报,2022,36(7):1382−1384. [LIU Xinyu, ZHANG Haisheng, XU Mingxin, et al. Ultrasonic-microwave assisted extraction, composition and activity of flavonoids from Hippophae rhamnoides L. leaves[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2022,36(7):1382−1384. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2022.07.1381 LIU Xinyu, ZHANG Haisheng, XU Mingxin, et al. Ultrasonic-microwave assisted extraction, composition and activity of flavonoids from Hippophae rhamnoides L. leaves[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 36(7): 1382-1384. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2022.07.1381
[14] 康莹. 中国沙棘叶黄酮提取精制工艺优化及其活性的初步评价[D]. 北京: 北京中医药大学, 2019 KANG Ying. Extraction and purfication of flavonoids from sea buckthorn leaves in China and preliminary evaluation of their activity[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chinese Medicine, 2019.
[15] WANG L J, YANG X S, QIN P Y, et al. Flavonoid composition, antibacterial and antioxidant properties of tartary buckwheat bran extract[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2013,49:312−317. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.04.039
[16] JAIN S, BHANJANA B, HEYDARIFARD S, et al. Enhanced antibacterial profile of nanoparticle impregnated cellulose foam filter paper for drinking water filtration[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,202:219−226. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.08.130
[17] MANSUR A R, KIM K J, JANG H W, et al. Matrix solid-phase dispersion extraction method for HPLC determination of flavonoids from buckwheat sprouts[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2020,133:110121. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110121
[18] 施丽娟, 陈宁, 王丹, 等. 超高效液相色谱-三重四极杆串联质谱法定量分析云南大叶种茶酚类成分[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(8):271−280. [SHI Lijuan, CHEN Ning, WANG Dan, et al. Quantitative and comparative studies on phenolic constituents in different types of Yunnan large leaf tea based on validated ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Food Science,2022,43(8):271−280. SHI Lijuan, CHEN Ning, WANG Dan, et al. Quantitative and comparative studies on phenolic constituents in different types of Yunnan large leaf tea based on validated ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole-tandem mass spectrometry[J]. Food Science, 2022, 43(8): 271-280.
[19] 吴萌萌, 刘怡, 严馨, 等. 苦荞麸皮黄酮提取物及有效成分的抑菌活性[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2021,40(11):77−83. [WU Mengmeng, LIU Yi, YAN Xin, et al. Antibacterial activities of flavonoid extracts of tartary buckwheat bran and its effective components[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2021,40(11):77−83. WU Mengmeng, LIU Yi, YAN Xin, et al. Antibacterial activities of flavonoid extracts of Tartary buckwheat bran and its effective components[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology, 2021, 40(11): 77-83.
[20] MIAO N, HAN S L, SHI Y T, et al. Postharvest UV-A radiation affects flavonoid content, composition, and bioactivity of Scutellaria baicalensis root[J]. Postharvest Biology and Technology,2022,189:111933. doi: 10.1016/j.postharvbio.2022.111933
[21] BAO Y, GAO L, WANG F T, et al. Heterocyclic cationic Gemini surfactants for efficient antibacterial, dispersion and fixation[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection,2021,159:168−177.
[22] 王慧芳, 苏淑云, 邵圣娟, 等. 大孔树脂分离纯化陈皮黄酮工艺及其抑菌活性[J]. 中成药,2018,40(12):2667−2672. [WANG Huifang, SU Shuyun, SHAO Shengjuan, et al. Flavonoids from Citri reticulatae pericarpium, their isolation, purification with macroporous resin and antibacterial activity[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2018,40(12):2667−2672. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2018.12.011 WANG Huifang, SU Shuyun, SHAO Shengjuan, et al. Flavonoids from Citri reticulatae pericarpium, their isolation, purification with macroporous resin and antibacterial activity[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2018, 40(12): 2667-2672. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2018.12.011
[23] 邵金华, 何福林, 陈霞, 等. 梓树根皮总黄酮分离纯化及其抑菌活性研究[J]. 食品与机械,2017,33(2):140−144. [SHAO Jinhua, HE Fulin, CHEN Xia, et al. Separation, purification and antibacterial activity of total flavonoids from Catalpa root bark[J]. Food & Machinery,2017,33(2):140−144. doi: 10.13652/j.issn.1003-5788.2017.02.030 SHAO Jinhua, HE Fulin, CHEN Xia, et al. Separation, purification and antibacterial activity of total flavonoids from Catalpa root bark[J]. Food & Machinery, 2017, 33(2): 140-144. doi: 10.13652/j.issn.1003-5788.2017.02.030
[24] 秦振娴, 张瑜, 齐梦蝶, 等. 中国沙棘和西藏沙棘叶中化学成分的UPLC/Q-TOF-MS快速分析[J]. 中国中药杂志2016, 41(8): 1461-1468 QIN Zhenxian, ZHANG Yu, QI Mengdie, et al. Rapid analysis of compounds in leaves of Chinese seabuckthorn and Tibetan seabuckthorn by UPLC/Q-TOF-MS[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 2016, 41(8): 1461-1468.
[25] 郑文惠, 白海英, 王丽瑶, 等. UPLC-QTOF-MS法分析沙棘果实、叶和枝的成分[J]. 中成药,2020,42(11):2944−2946. [ZHENG Wenhui, BAI Haiying, WANG Liyao, et al. Analysis of constituents in the fruit, leaf and twig of Hippophae rhamnoides by UHPL-QTOF-MS[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2020,42(11):2944−2946. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2020.11.022 ZHENG Wenhui, BAI Haiying, WANG Liyao, et al. Analysis of constituents in the fruit, leaf and twig of Hippophae rhamnoides by UHPL-QTOF-MS[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine, 2020, 42(11): 2944-2946. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2020.11.022
[26] DONG R F, SU J, NIAN H, et al. Chemical fingerprint and quantitative analysis of flavonoids for quality control of sea buckthorn leaves by HPLC and UHPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2017,37:513−522. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2017.08.019
[27] 王婉宁. 沙棘果实中黄酮类物质的分析[D]. 哈尔滨: 东北农业大学, 2020 WANG Wanning. Analysis of flavonoids in sea buckthorn fruits[D]. Harbin: Northeast Agricultural University, 2020.
[28] 樊轻亚, 白泽方, 汪学猛, 等. 分散固相萃取/超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定药用狗牙花中6种生物碱[J]. 分析测试学报,2022,41(8):1235−1241. [FAN Qingya, BAI Zefang, WANG Xuemeng, et al. Determination of six alkaloids in Ervatamia officinalis Tsiang by ultra high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry with dispersive solid phase extraction[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis,2022,41(8):1235−1241. doi: 10.19969/j.fxcsxb.22041303 FAN Qingya, BAI Zefang, WANG Xuemeng, et al. Determination of six alkaloids in Ervatamia officinalis Tsiang by ultra high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry with dispersive solid phase extraction[J]. Journal of Instrumental Analysis, 2022, 41(8): 1235-1241. doi: 10.19969/j.fxcsxb.22041303
[29] MA X Y, LAAKSONEN O, ZHENG J, et al. Flavonol glycosides in berries of two major subspecies of sea buckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) and influence of growth sites[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,200:189−198. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.01.036
[30] 汪成, 王怀友, 汪蔓青, 等. 不同产地沙棘果化学成分含量及抗氧化活性的研究[J]. 华西药学杂志,2020,35(5):513−517. [WANG Cheng, WANG Huaiyou, WANG Manqing, et al. Study on content of major chemical constituents and anti-oxidation activities of sea buckthorn fruit[J]. West China Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences,2020,35(5):513−517. doi: 10.13375/j.cnki.wcjps.2020.05.010 WANG Cheng, WANG Huaiyou, WANG Manqing, et al. Study on content of major chemical constituents and anti-oxidation activities of sea buckthorn fruit[J]. West China Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences, 2020, 35(5): 513-517. doi: 10.13375/j.cnki.wcjps.2020.05.010
[31] GUTIÉRREZ-VENEGAS G, GÓMEZ-MORA J A, MERAZ-RODRÍGUEZ M A, et al. Effect of flavonoids on antimicrobial activity of microorganisms present in dental plaque[J]. Heliyon,2019,5(12):e03013. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2019.e03013
[32] JANECZKO M, GMUR D, KOCHANOWICZ E, et al. Inhibitory effect of a combination of baicalein and quercetin flavonoids against Candida albicans strains isolated from the female reproductive system[J]. Fungal Biology,2022,126(6-7):407−420. doi: 10.1016/j.funbio.2022.05.002
[33] DONG S X, YANG X S, ZHAO L, et al. Antibacterial activity and mechanism of action saponins from Chenopodium quinoa Willd. husks against foodborne pathogenic bacteria[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2020,149:112350. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2020.112350





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



