Inhibition of Myristic Acid on Suilysin and the Molecular Mechanism
-
摘要: 为研究肉豆蔻酸对猪链球菌细胞溶素生物活性抑制作用及相互作用机制,本文开展了成孔活性试验、寡聚化试验、分子对接、分子动力学模拟、抗菌活性试验和乳酸脱氢酶活性试验。结果表明,肉豆蔻酸浓度为16 μg/mL时显著降低了细胞溶素寡聚体的形成量,进而抑制了细胞溶素的成孔活性,血红素释放量是对照组的8.88%,抑制率达到91.12%。分子对接和分子动力学模拟结果表明肉豆蔻酸结合到细胞溶素的第一、二和三级结构域的交界处,且82Asn、83Asn、84Ser、87Ile、88Ala、90Ile、193Phe、194Gly、275Phe、372Ile、373Leu、374Ser贡献了较大结合能,在细胞溶素和肉豆蔻酸的结合过程中发挥了关键作用。无抗猪链球菌活性的肉豆蔻酸(最低抑菌浓度128 μg/mL)浓度为16 μg/mL时细胞溶素处理组和猪链球菌处理组乳酸脱氢酶释放量是对照组的67.84%和45.72%,表明肉豆蔻酸可显著缓解细胞溶素和猪链球菌介导的细胞毒性作用。以上研究结果表明:肉豆蔻酸通过与细胞溶素结合,影响了其寡聚体的形成,抑制了其成孔活性,在无抗菌活性的前提下显著缓解了细胞溶素和猪链球菌引发的细胞毒性作用,未来有望开发为抗猪链球菌感染药物。Abstract: To explore the inhibitory effect of myristic acid against suilysin biological activity and the interactive mechanism, pore-forming assay, oligomerization assay, molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulation, minimal inhibitory concentration assay and lactate dehydrogenase activity assays were performed. The results showed that the formation of suilysin oligomer significant decreased when the concentration of myristic acid was 16 μg/mL, thereby inhibiting the pore-forming activity of suilysin, the release of hemoglobin was 8.88% of the control group, and the inhibition rate reached 91.12%. The results of molecular docking and molecular dynamics simulation showed that myristic bound to the junction of domain one, two and three, and 82Asn, 83Asn, 84Ser, 87Ile, 88Ala, 90Ile, 193Phe, 194Gly, 275Phe, 372Ile, 373Leu, 374Ser contributed higher energy which were the critical residues during the binding. Myristic did not showed anti-Streptococcus suis character (MIC values was 128 μg/mL), and the release of lactic dehydrogenase in suilysin or Streptococcus suis treatment group was 67.84% and 45.72% of the control group when the cells received 16 μg/mL myristic treatment. Taken together, myristic inhibited the pore-forming of suilysin by affecting the formation of its oligomer based on a direct binding and protected cells from suilysin or Streptococcus suis cytotoxicity which promised it a candidate for developing anti-Streptococcus suis infection drug.
-
Keywords:
- suilysin /
- molecular simulation /
- myristic acid /
- cytotoxicity
-
猪链球菌(Streptococcus suis,S. suis)是一种具有荚膜的革兰氏阳性条件病原菌,也是一种重要的人兽共患病原菌[1-2]。根据荚膜抗原不同,猪链球菌被分为35个血清型,其中2型血清型被认为是毒力最强的猪链球菌,可引发人和动物产生多种疾病,如引发人产生细菌性脑膜炎、链球菌中毒样休克综合征等疾病,也可引发猪的急性败血症、肺炎、脑膜炎、心内膜炎、关节炎等疾病[3-5]。我国在2005年爆发了较大规模猪链球菌感染人案例,上百人发病并有数十人死亡[6]。近年来,由于抗生素的大量使用甚至滥用,导致猪链球菌产生耐药性并呈现逐渐严重的趋势[7],使得针对该菌的感染防治变得非常困难。猪链球菌感染每年给畜禽养殖业造成巨大经济损失,严重影响畜禽养殖业的健康发展[8]。“限抗”、“减抗”政策的实施使畜禽养殖业面临猪链球菌感染“复燃”,无药可用等困境,因此临床上迫切需要新的抗菌药物应对猪链球菌尤其是耐药性猪链球菌感染。
猪链球菌的感染和致病过程依赖于其产生和分泌的多种毒力因子,包括分选酶、荚膜多糖等[9]。细胞溶素是猪链球菌感染及致病过程中非常重要的毒力因子,被誉为猪链球菌的“毒力标志物”[10]。猪链球菌细胞溶素相对分子量54 kD,隶属于胆固醇依赖型细胞溶素毒素家族,是典型的成孔毒素,具有裂解细胞、穿过血脑屏障和致死性等功能[11-12]。此外,猪链球菌细胞溶素可通过作用于TLR4和p38-MAPK信号通路相关蛋白引发炎症反应,促进炎症因子TNF-α和IL-1β的释放[13-14]。猪链球菌细胞溶素对猪和人肠上皮细胞、脑微血管细胞等多种细胞有细胞毒性作用[15]。研究者分别用野生株和敲除细胞溶素的猪链球菌感染小鼠,在相同感染时间内敲除株不能引发小鼠死亡[16]。细胞溶素在感染过程中的重要作用使其成为筛选抗猪链球菌感染药物的理想靶标。
肉豆蔻酸又名十四烷酸,属于饱和脂肪酸的一种,在食品行业用于各种香料的制备,同时也被用做增香剂添加到食品中。研究表明13-甲基肉豆蔻酸有多种药理作用,如降低血糖[17],保护神经系统[18],抗肿瘤[19]等。但是肉豆蔻酸药理作用研究相对较少,本研究基于成孔活性试验和寡聚化试验分析了肉豆蔻酸对猪链球菌细胞溶素生物活性及寡聚体形成的影响;通过分子对接和分子模拟试验阐述了肉豆蔻酸与细胞溶素的作用机制,并在细胞水平上证实了肉豆蔻酸对猪链球菌及细胞溶素介导的细胞毒性的缓解作用,为猪链球菌感染防治提供了潜在先导化合物。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
肉豆蔻酸 纯度≥98%,购于成都瑞芬思生物科技有限公司;猪链球菌细胞溶素蛋白 纯度≥80%,来自本实验室;无菌脱纤维羊血 购自郑州九龙生物制品公司;细胞培养基、胎牛血清 购买于Thermo Fisher Scientific;小鼠巨噬细胞J774(BFN60807356) 购买于美国模式培养物集存库;乳酸脱氢酶试剂盒 购买于Roche;2型猪链球菌(ZY05719) 来自本实验室保存。
Multiskan Spectrum全波长酶标仪 赛默飞世尔科技实验室产品;CLX双色红外激光成像系统 基因有限公司;DK-8D电热恒温水槽 上海一恒科技有限公司;H2050R离心机 湖南湘仪离心机仪器有限公司;ZWY-211C恒温培养振荡器 上海智城分析仪器制造有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 血红素释放率及寡聚化试验
根据作者前期研究经验及本次预实验确定肉豆蔻酸浓度为4、8、16 μg/mL。0.25 μg细胞溶素蛋白与不同浓度肉豆蔻酸于485 μL磷酸盐缓冲液(pH7.0)中在37 ℃共孵育20 min。随后加入无菌脱纤维羊血(终浓度25%,500 μL反应体系),继续在37 ℃孵育10 min,离心处理(10000 r/min,1 min),取上清置于酶标仪中检测543 nm处吸光值。经无菌水或无菌磷酸盐缓冲液处理的羊血作为阳性或阴性对照。血红素释放率(%)=(A1−A0)/(A2−A0)×100,式中A0为阴性对照吸光值,A1为加肉豆蔻酸组吸光值,A2为不加肉豆蔻酸组吸光值。寡聚试验:细胞溶素蛋白与不同浓度肉豆蔻酸(0、4、16 μg/mL)共孵育(37 ℃,20 min)后加入羊血红细胞诱导寡聚体形成,随后加入无β-巯基乙醇的蛋白质上样缓冲液在55 ℃恒温水浴锅中处理10 min。蛋白样品用6%分离胶进行分离后经转膜实验转移至聚偏二氟乙烯膜(PVDF, 60 V,1.5 h)。转膜结束后将PVDF膜置于5%脱脂奶粉中封闭2 h,PBST洗三次(80 r,5 min/次)后用鼠源细胞溶素一抗孵育2 h,PBST洗三次后用荧光标记二抗室温孵育1 h,洗膜后于成像系统采集图像,分析肉豆蔻对细胞溶素寡聚体形成的影响。
1.2.2 分子对接
细胞溶素作为受体蛋白,其结构文件从Protein Data Bank(PDB)网站获得(编号:3hvn),分子对接前受体(蛋白质)和能量最小化后的配体小分子(肉豆蔻酸)用Autodock Tools软件进行预处理。应用Autodock Vina[20]软件进行对接试验,对接试验参数如下:size_x=120.0,size_y=74.0,size_z=72.0,center_x=33.558,center_y=20.947,center_z=34.705,间距1.0 Å。对接过程中蛋白质保持刚性,小分子柔性键可旋转,获得稳定的对接结构,供后续分析。
1.2.3 分子模拟
经对接分析确定最佳结合模式并获得蛋白配体复合物后,从复合物中提取配体坐标文件,并应用Amber GAFF立场获得其拓扑文件,蛋白拓扑文件应用Amber99SB立场获得。应用Gromacs 2020.6[21]软件进行分子动力学模拟试验,水模型采用TIP3P,模拟时长130 ns。通过分析均方根偏差(RMSD)评价细胞溶素和肉豆蔻酸在模拟过程中的构型,通过均方根波动(RMSF)分析残基结合肉豆蔻酸前后的柔性变化,基于残基与配体的距离、氢键、结合能等指标阐述肉豆蔻酸和细胞溶素作用的机制。
1.2.4 抗菌活性试验
采用微量肉汤稀释法测定肉豆蔻酸对猪链球菌的抗菌活性。96孔微量培养板中通过倍比稀释法获得含有不同浓度肉豆蔻酸(1~128 μg/mL)的猪链球菌生长培养基,随后向每孔加入培养至对数生长期的猪链球菌并使其终浓度为5×105 CFUs/mL。将培养板置于37 ℃恒温培养静置培养24 h,肉眼观察没有细菌生长的最小浓度定义为肉豆蔻酸的最低抑菌浓度(Minimal Inhibitory Concentration,MIC)[22]。
1.2.5 乳酸脱氢酶活性实验
小鼠巨噬细胞J774于含10%胎牛血清,100 U青霉素和100 μg/mL链霉素细胞培养基中生长,培养条件37 ℃、5% CO2。细胞接种到96孔板中(5×104 细胞/孔)过夜培养。将培养至OD600=0.8的猪链球菌离心(4000 r/min,5 min),无菌磷酸盐缓冲液洗三次后用细胞培养基重悬并调整浓度至5×107 CFUs/mL备用;细胞溶素(1.5 μg/mL)加入细胞培养基混匀备用。用上述制备的菌液或细胞溶素溶液置换细胞培养液(100 μL/孔)并加入不同浓度肉豆蔻酸(0、4、16 μg/mL)继续培养5 h后离心(1000 r/min,10 min)处理,取100 μL上清加入等体积乳酸脱氢酶活性检测试剂体积细胞毒性试剂,室温避光反应30 min,于酶标仪中检测OD490。乳酸脱氢酶活性(%)=A1/A2×100[22],式中A1为加肉豆蔻酸组吸光值,A2为不加肉豆蔻酸组吸光值。
1.3 数据处理
试验独立重复3次,试验数据以平均值±标准差表示;应用GraphPad Prism6.0软件进行统计分析,P≤0.05 为差异显著,P≤0.01为差异极显著。
2. 结果与分析
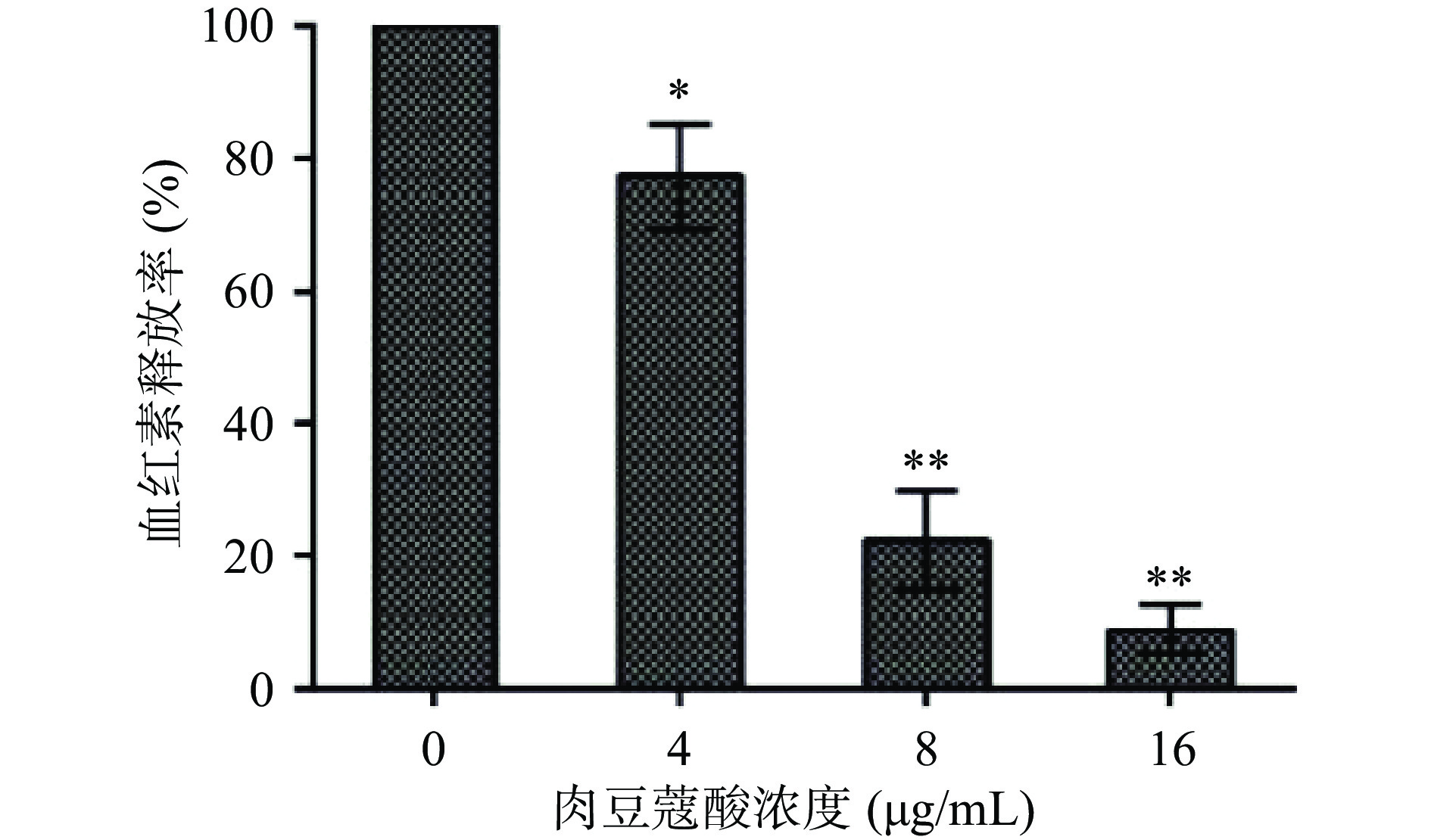
2.1 肉豆蔻酸抑制猪链球菌细胞溶素成孔活性
血细胞被裂解后,其中的血红素会释放到体系中,血红素在543 nm处有最大吸光值,通过检测其相对含量可定量评价细胞被裂解程度[23-25]。肉豆蔻酸对猪链球菌细胞溶素成孔活性抑制作用见图1,当反应体系中肉豆蔻酸浓度为0 μg/mL时,血红素释放率为100%,表明血细胞被细胞溶素裂解了,但是随着肉豆蔻酸浓度的升高,体系中血红素的比例呈现逐渐降低的趋势,当肉豆蔻酸浓度为4、8和16 μg/mL时,血红素释放量分别是对照组的77.21%、22.2%和8.88%,即对细胞溶素生物活性抑制率分别为22.79%、77.8%和91.12%,表明肉豆蔻酸可剂量依赖性抑制猪链球菌细胞溶素的成孔活性。
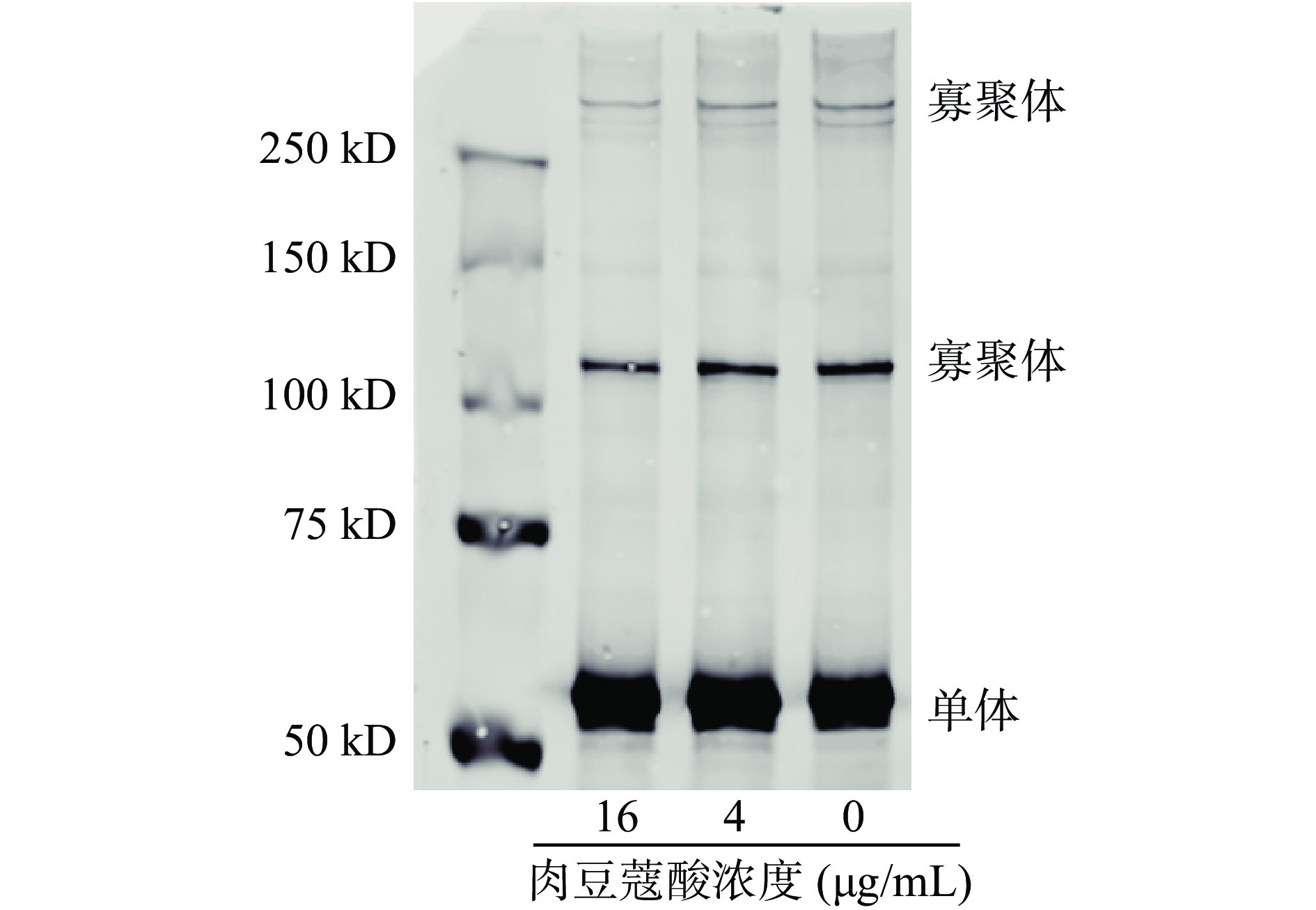
2.2 肉豆蔻酸抑制细胞溶素寡聚体形成
作为胆固醇依赖型细胞溶素,形成寡聚体刺入细胞膜是其发挥成孔活性的重要前提[26-27]。本研究通过体外诱导寡聚体形成试验分析了肉豆蔻酸对猪链球菌细胞溶素寡聚体形成的影响,结果见图2,当反应体系中没有肉豆蔻酸时,形成了不同分子量大小的寡聚体,而当体系中加入肉豆蔻酸且随着其浓度的增加,寡聚体的形成表现出逐渐减少的趋势,表明肉豆蔻酸通过影响细胞溶素寡聚体的形成抑制其生物活性。
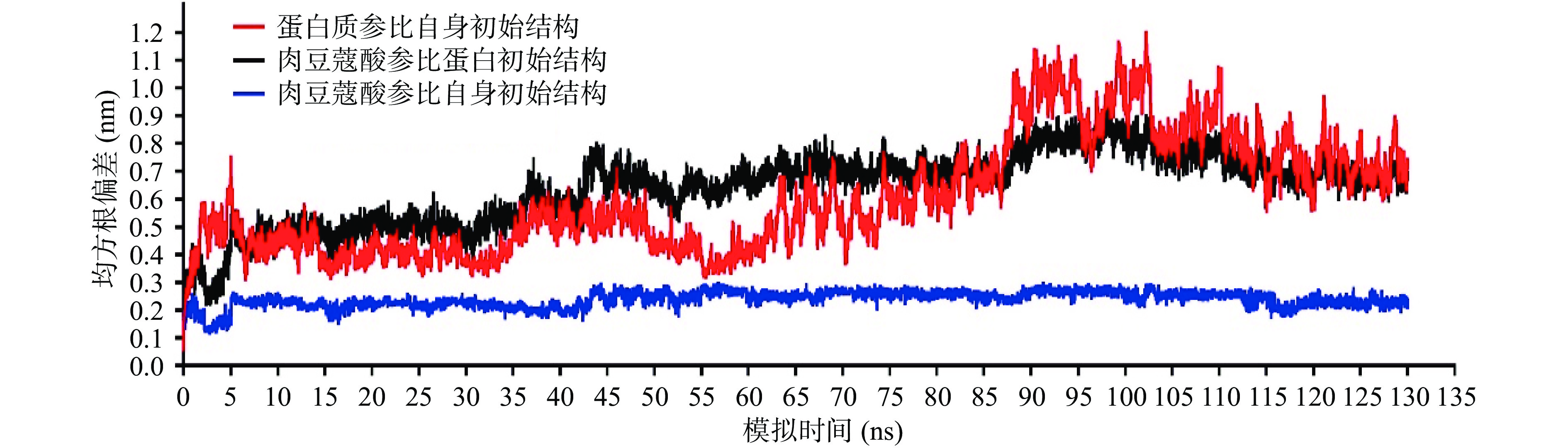
2.3 肉豆蔻酸与细胞溶素在模拟过程中的稳定性
以蛋白质初始结构为参照,模拟过程中蛋白主链相对初始结构的RMSD均值为0.60 nm(红色线),表明蛋白在模拟过程中保持了相对稳定的空间结构,肉豆蔻酸相对蛋白初始结构的RMSD均值为0.64 nm(黑色线),表明在整个模拟过程中蛋白与配体保持了相对稳定的结合模式。以肉豆蔻酸初始结构为参照,其重原子(非氢原子)相对于初始结构的RMSD均值为0.24 nm(蓝色线),表明肉豆蔻酸在模拟过程中保持了稳定的结构(图3)。综上所述模拟过程中蛋白和配体均保持了相对稳定的构型和结合模式,可用于后续分析。
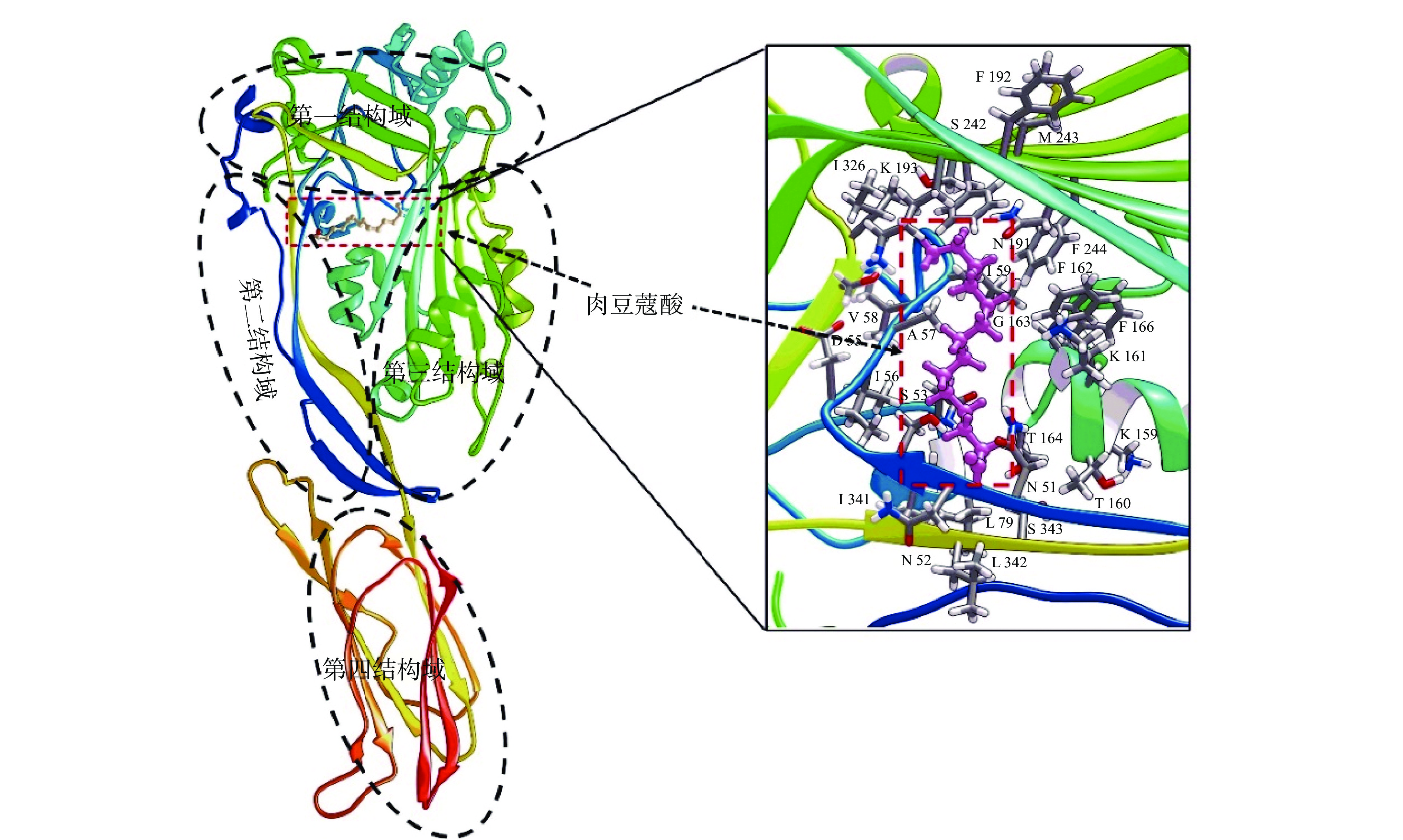
2.4 肉豆蔻酸与细胞溶素的结合模式
细胞溶素和肉豆蔻酸对接结果如图4所示,肉豆蔻酸结合到细胞溶素第1、2和3结构域的交界处,分布在肉豆蔻酸周围的氨基酸残基与其有潜在的相互作用。
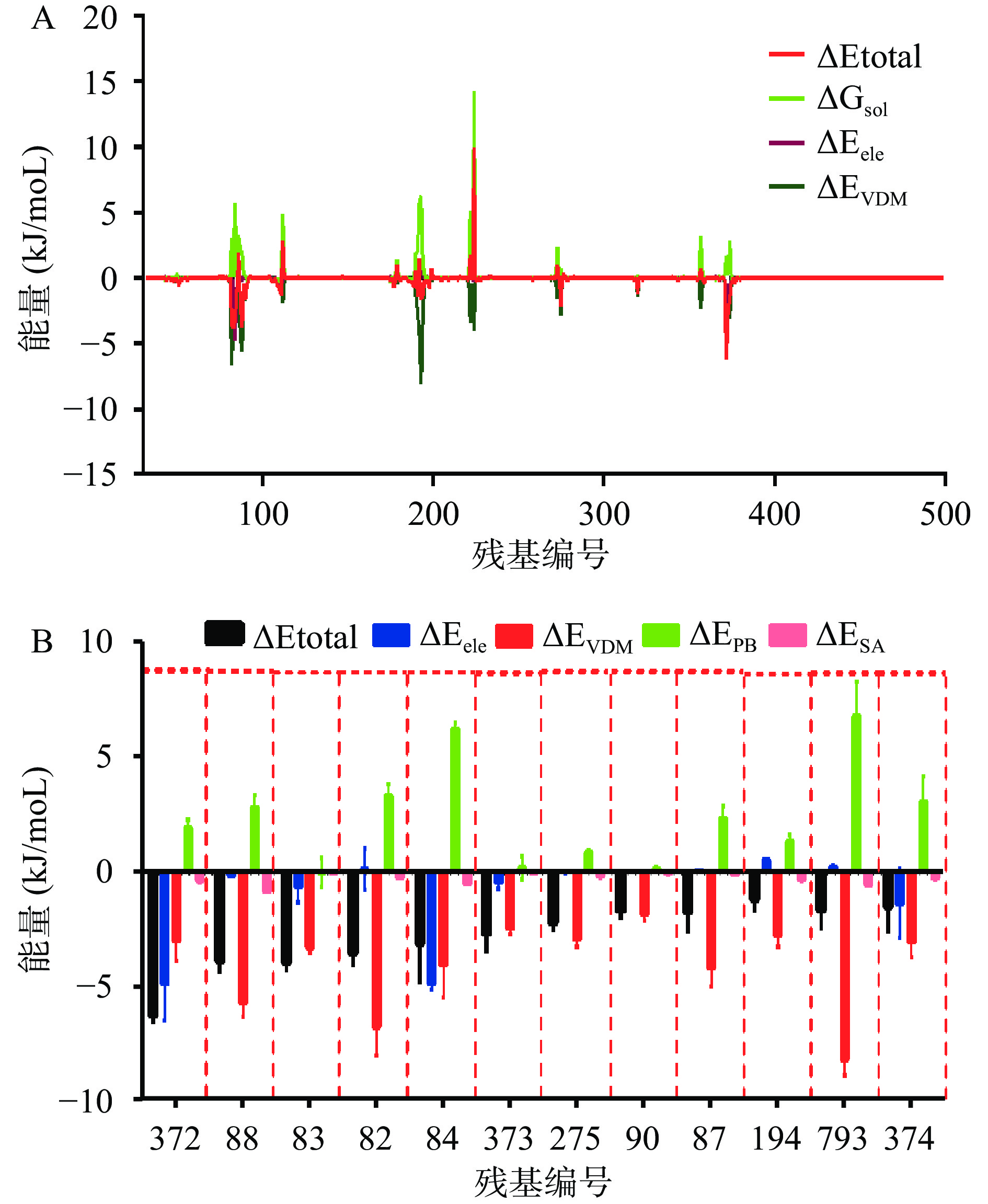
为了进一步确认与肉豆蔻酸相互作用的残基,通过分子力学/泊松-波尔兹曼表面积(Molecular Mechanics Poisson Boltzmann Surface Area,MMPBSA)方法分析了结合过程中的总结合能,结果如表1所示,肉豆蔻酸和细胞溶素的总结合能平均值为−112.39 kJ/mol,表明二者之间有较强的相互作用力,其中范德华作用力−167.68 kJ/mol,静电相互作用−27.32 kJ/mol,非极性溶剂化能量−20.93 kJ/mol,表明范德华在肉豆蔻酸和细胞溶素的结合过程中发挥了非常关键的作用,此外静电相互作用和非极性溶剂能也促进了二者的结合。极性溶剂化能为103.53 kJ/mol。
表 1 肉豆蔻酸和细胞溶素结合过程能量值(kJ/mol)Table 1. The energy between myristic acid and suilysin (kJ/mol)能量类别 能量值 总结合能 −112.39±10.65 范德华作用力 −167.68±5.92 静电作用 −27.32±6.05 极性溶剂化能 103.53±6.04 非极性溶剂化能 −20.93±0.26 氢键是蛋白配体结合过程中常见的相互作用力,本研究基于GROMACS软件分析,发现4个氢键存在于细胞溶素和肉豆蔻酸的相互作用中,形成氢键的残基分别是84位和374位的丝氨酸、372位的异亮氨酸和82位的天冬酰胺(表2)。84位和372位氨基酸残基和肉豆蔻酸形成氢键在模拟过程中存在率均为90%,表明这两个氢键是稳定存在的,而另外两个氢键的存在率分别为10%和30%,表明这两个氢键并非稳定存在于整个模拟过程中。因此84位和372位残基与配体形成氢键对稳定复合物体系有较大贡献。
表 2 肉豆蔻酸与细胞溶素结合过程氢键详情Table 2. The details of H-bond between myristic acid and suilysin残基编号 供体 氢 受体 存在率(%) 84 Ser O Ser H Myr O 90 372 Myr O Myr H Ile O 90 374 Ser O Ser H Myr O 30 82 Myr O Myr H Asn O 10 2.5 细胞溶素与肉豆蔻酸的结合能分析
分子力学/泊松-波尔兹曼表面积方法(MMPBSA)广泛应用于蛋白配体相互作用能分析[28-30],本研究为了进一步明确细胞溶素和肉豆蔻酸的结合位点,基于MMPBSA结合能分析程序包,分析了结合过程中每个氨基酸残基的能量贡献,各个氨基酸残基分解能量见图5A,其中82Asn、83Asn、84Ser、87Ile、88Ala、90Ile、193Phe、194Gly、275Phe、372Ile、373Leu、374Ser有相对较大的总能量贡献值,表明这些残基是结合过程中的关键残基。进一步分析了残基各个能量分项的贡献值,结果如图5B所示,上述12个残基与肉豆蔻酸都有较强的范德华作用力,再次证实范德华是二者结合的重要作用方式,此外84Ser、372Ile和374Ser与肉豆蔻酸有较大的静电相互作用,说明静电作用是细胞溶素和肉豆蔻酸另一种重要的相互作用力。
2.6 结合位点的确证
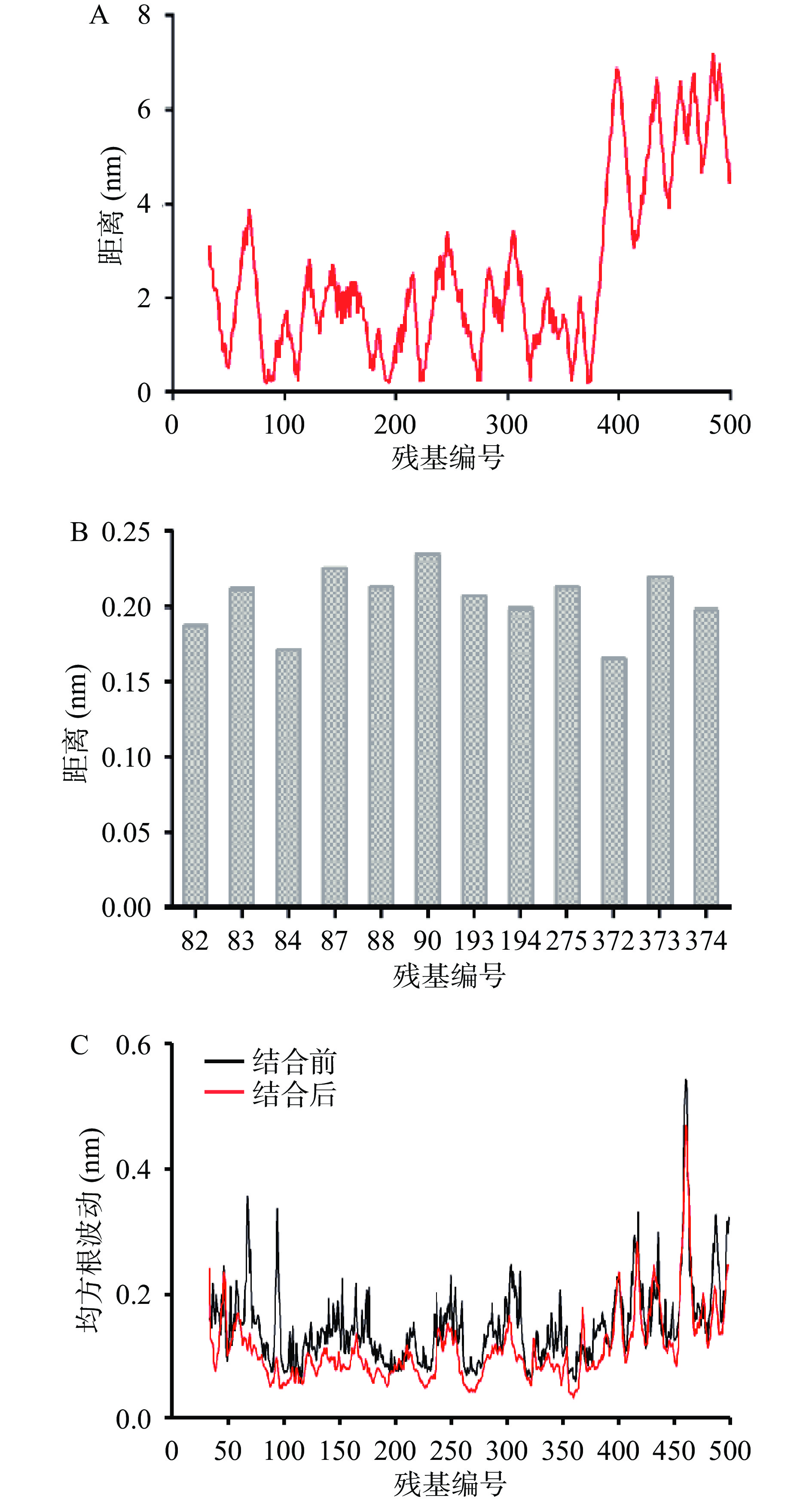
为了进一步确认,分析了结合过程中各残基与肉豆蔻酸的距离,从结合过程中细胞溶素各个残基与肉豆蔻酸的距离(图6A)中发现上述能量贡献较大的残基与肉豆蔻酸有更近的距离(图6B)。均方根波动数值(RMSF)可反映原子或残基的柔性,本研究分别分析了蛋白质在结合配体前后的RMSF值,发现蛋白结合小分子后各残基的RMSF值(尤其是上述能量贡献较大的残基)较结合小分子前小(图6C),表明结合小分子后,这些残基受到了束缚,变得刚性。
2.7 肉豆蔻酸的抗猪链球菌活性
细菌在长期生存压力下会进化出耐药性,本研究根据MIC试验结果判定标准(肉眼观察没有细菌生长的最小浓度定义为肉豆蔻酸的最低抑菌浓度)确定肉豆蔻酸对猪链球菌的最低抑菌浓度为128 μg/mL,表明肉豆蔻酸无抗猪链球菌活性,不会对该菌造成生长压力。
2.8 肉豆蔻酸缓解猪链球菌及细胞溶素介导的细胞毒性
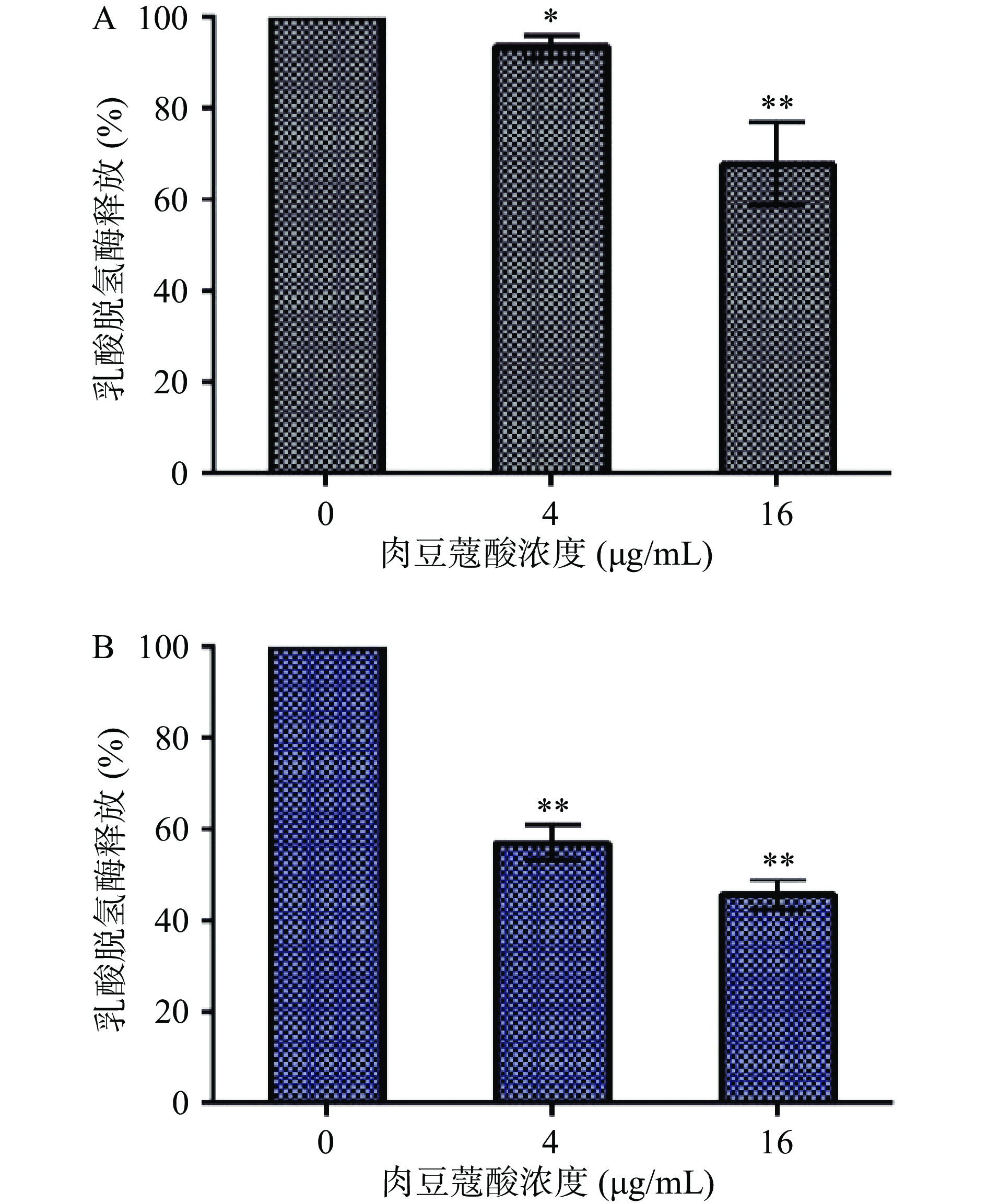
细胞溶素与细胞膜上的胆固醇结合后形成寡聚体刺入细胞膜会引发细胞毒性作用,研究表明猪链球菌细胞溶素的细胞毒性作用在其致病性中发挥重要作用[31-32],因此药物缓解细胞溶素介导的细胞毒性有望延迟猪链球菌感染病程的发展。细胞受外界刺激死亡后,其中的乳酸脱氢酶(LDH)会释放到外环境,该酶在490 nm处有最大吸光值;本研究通过检测乳酸脱氢酶活性分别评价了肉豆蔻酸对细胞溶素和猪链球菌介导的细胞毒性的缓解效果。以细胞溶素或猪链球菌处理组释放的乳酸脱氢酶作为参比,当加入肉豆蔻酸处理后,LDH释放量显著减少(P<0.05),且呈现剂量依赖关系(图7A、7B),表明肉豆蔻酸可在细胞水平显著缓解细胞溶素或猪链球菌引发的细胞毒性作用。
3. 讨论
细胞溶素可从多个方面促进猪链球菌的致病性,是抗猪链球菌感染抑制剂开发重要靶标[27, 33]。成孔活性是细胞溶素发挥生物学功能的基础,本研究基于成孔活性试验发现食源性成分肉豆蔻酸浓度在16 μg/mL时对细胞溶素成抗活性抑制率达到90%以上。作为胆固醇依赖型细胞溶素家族成员,形成寡聚体对其发挥成孔活性至关重要,于是推测肉豆蔻酸可能直接与细胞溶素结合并影响了其寡聚体的形成,体外诱导寡聚试验证实在16 μg/mL时肉豆蔻酸显著抑制了细胞溶素寡聚体的形成。
细胞溶素蛋白由四个结构域构成,每一个结构域在寡聚体的形成过程中都发挥着至关重要的作用,任何一个结构域构象变化都会影响寡聚体的形成[34]。本研究为了深入分析肉豆蔻酸与细胞溶素的作用机制,开展了分子对接和对子动力学模拟试验,发现肉豆蔻酸可直接结合到猪链球菌细胞溶素的第一、第二和第三结构域的交界处,并通过能量分解,残基柔性变化及距离分析等确定87Ile、193Phe、194Gly、275Phe、372Ile和373Leu等氨基酸残基是二者结合过程中的关键残基。
作为猪链球菌的关键毒力因子,细胞溶素的成孔活性能导致细胞裂解,内容物释放,引发细胞毒性[11, 15],因此缓解其细胞毒性作用可在一定程度上延迟猪链球菌感染疾病的进程。本研究发现肉豆蔻酸浓度在16 μg/mL时对细胞溶素和猪链球菌引发的细胞毒性分别降低了32.16%和54.28%。
4. 结论
本文首次发现食源性生物活性成分肉豆蔻酸可直接结合到猪链球菌细胞溶素的第一、第二和第三结构域的交界处,并在浓度为16 μg/mL通过抑制细胞溶素寡聚体形成,对其成孔活性抑制率达91.12%。无抗菌活性的肉豆蔻酸(MIC=128 μg/mL)在浓度为16 μg/mL时对细胞溶素和猪链球菌引发的细胞毒性分别降低了32.16%和54.28%。以上结果表明肉豆蔻酸有望作为先导化合物被开发为抗猪链球菌感染的临床药物,作用机制的阐明为该化合物更好更快地应用于实际提供了重要理论基础。
-
表 1 肉豆蔻酸和细胞溶素结合过程能量值(kJ/mol)
Table 1 The energy between myristic acid and suilysin (kJ/mol)
能量类别 能量值 总结合能 −112.39±10.65 范德华作用力 −167.68±5.92 静电作用 −27.32±6.05 极性溶剂化能 103.53±6.04 非极性溶剂化能 −20.93±0.26 表 2 肉豆蔻酸与细胞溶素结合过程氢键详情
Table 2 The details of H-bond between myristic acid and suilysin
残基编号 供体 氢 受体 存在率(%) 84 Ser O Ser H Myr O 90 372 Myr O Myr H Ile O 90 374 Ser O Ser H Myr O 30 82 Myr O Myr H Asn O 10 -
[1] GOTTSCHALK M, XU J, CALZAS C, et al. Streptococcus suis: A new emerging or an old neglected zoonotic pathogen?[J]. Future Microbiology,2010,5(3):371−391. doi: 10.2217/fmb.10.2
[2] WANG J, LIANG P, SUN H, et al. Comparative transcriptomic analysis reveal genes involved in the pathogenicity increase of Streptococcus suis epidemic strains[J]. Virulence,2022,13(1):1455−1470. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2022.2116160
[3] GOYETTE-DESJARDINS G, AUGER J P, XU J, et al. Streptococcus suis, an important pig pathogen and emerging zoonotic agent| [mdash]| an update on the worldwide distribution based on serotyping and sequence typing[J]. Emerging Microbes & Infections,2014,3(6):e45.
[4] GOTTSCHALK M, XU J, LECOURS M P, et al. Streptococcus suis infections in humans: What is the prognosis for Western countries? (Part II)[J]. Clinical Microbiology Newsletter,2010,32(13):97−102. doi: 10.1016/j.clinmicnews.2010.06.001
[5] ZHONG X, MA J, BAI Q, et al. Identification of the RNA-binding domain-containing protein RbpA that acts as a global regulator of the pathogenicity of Streptococcus suis serotype 2[J]. Virulence,2022,13(1):1304−1314. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2022.2103233
[6] YU H, JING H, CHEN Z, et al. Human Streptococcus suis outbreak, Sichuan, China[J]. Emerging Infectious Diseases,2006,12(6):914. doi: 10.3201/eid1206.051194
[7] MAREN S, PETER V, JORG W. Use of antibiotics and antimicrobial resistance in veterinary medicine as exemplified by the swine pathogen Streptococcus suis[M]. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol, 2016.
[8] TAN C, ZHANG A, CHEN H, et al. Recent proceedings on prevalence and pathogenesis of Streptococcus suis[J]. Current Issues in Molecular Biology,2019,32:473−520.
[9] HAAS B, GRENIER D. Understanding the virulence of Streptococcus suis: A veterinary, medical, and economic challenge[J]. Medecine Et Maladies Infectieuses,2017,48(3):159−166.
[10] LEUNG C, DUDKINA N V, LUKOYANOVA N, et al. Stepwise visualization of membrane pore formation by suilysin, a bacterial cholesterol-dependent cytolysin[J]. ELife,2014,3:e04247. doi: 10.7554/eLife.04247
[11] TENENBAUM T, SEITZ M, SCHROTEN H, et al. Biological activities of suilysin: Role in Streptococcus suis pathogenesis[J]. Future Microbiology,2016,11:194.
[12] LUN S, PEREZ-CASAL J, CONNOR W, et al. Role of suilysin in pathogenesis of Streptococcus suis capsular serotype 2[J]. Microbial Pathogenesis,2003,34(1):27−37. doi: 10.1016/S0882-4010(02)00192-4
[13] VADEBONCOEUR N, SEGURA M, ALNUMANI D, et al. Pro-inflammatory cytokine and chemokine release by human brain microvascular endothelial cells stimulated by Streptococcus suis serotype 2[J]. Pathogens & Disease,2003,35(1):49−58.
[14] BI L L, PIAN Y Y, CHEN S L, et al. Toll-like receptor 4 confers inflammatory response to suilysin[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2015,6:644.
[15] SEITZ M, BAUMS C G, NEIS C, et al. Subcytolytic effects of suilysin on interaction of Streptococcus suis with epithelial cells[J]. Veterinary Microbiology,2013,167(3−4):584−591. doi: 10.1016/j.vetmic.2013.09.010
[16] DAN T , YUKIHIRO A , TATSUYA N, et al. The contribution of suilysin to the pathogenesis of Streptococcus suis meningitis[J]. Journal of Infectious Diseases,2014,209(10):1509−1519. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jit661
[17] 翁绳美. 13-甲基肉豆蔻酸对小鼠的调节血糖作用[J]. 海峡药学,2005(6):46−48. [WENG S M. Effects of 13-methyltetradecanoic acid on the regulation of blood glucose[J]. Straits Pharmacy,2005(6):46−48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3765.2005.06.022 WENG S M. Effects of 13-methyltetradecanoic acid on the regulation of blood glucose[J]. Straits Pharmacy, 2005(6): 46-48. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-3765.2005.06.022
[18] 何宏星, 翁绳美, 胡潇, 等. 13-甲基十四烷酸对大鼠局灶性缺血脑组织的保护作用[J]. 福建医科大学学报,2018,52(2):80−84. [HE H X, WENG S M, HU X, et al. Protective effects of 13-methyltetradecanoic acid on focal cerebral ischemia in rats[J]. Journal of Fujian Medical University,2018,52(2):80−84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4194.2018.02.003 HE H X, WENG S M, HU X, et al. Protective effects of 13-methyltetradecanoic acid on focal cerebral ischemia in rats [J]. Journal of Fujian Medical University, 2018, 52(2): 80-84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4194.2018.02.003
[19] 权美平. 13-甲基肉豆蔻酸抗肿瘤机制研究进展[J]. 动物医学进展,2013,34(9):103−106. [QUAN M P. Progress on anti-tumor mechanism of 13-methyltetradecanoic acid[J]. Progress in Veterinary Medicine,2013,34(9):103−106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5038.2013.09.025 QUAN M P. Progress on anti-tumor mechanism of 13-methyltetradecanoic acid [J]. Progress in Veterinary Medicine, 2013, 34(9): 103-106. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-5038.2013.09.025
[20] TROTT O, OLSON A J. Autodock vina: Improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading[J]. Journal of Computational Chemistry,2010,31(2):455−461.
[21] KUTZNER C, KNIEP C, CHERIAN A, et al. GROMACS in the cloud: A global supercomputer to speed up alchemical drug design[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling,2022,62(7):1691−711. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.2c00044
[22] WANG T, ZHANG P, LÜ H, et al. A natural dietary flavone myricetin as an α-hemolysin inhibitor for controlling Staphylococcus aureus infection[J]. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology,2020,10:330. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2020.00330
[23] DONG J, ZHANG L, LIU Y, et al. Luteolin decreases the pathogenicity of Aeromonas hydrophila via inhibiting the activity of aerolysin[J]. Virulence,2021,12(1):165−76. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2020.1867455
[24] XU L, LU G, ZHAN B, et al. Uncovering the efficacy and mechanisms of genkwa flos and bioactive ingredient genkwanin against L. monocytogenes infection[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2022,297:115571. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2022.115571
[25] WANG T, LIU B, ZHANG C, et al. Kaempferol-driven inhibition of listeriolysin O pore formation and inflammation suppresses Listeria monocytogenes infection[J]. Microbiology Spectrum,2022,10(4):e0181022. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.01810-22
[26] TINGTING W, TIANQI F, XINYU W, et al. Amentoflavone attenuates Listeria monocytogenes pathogenicity through an LLO-dependent mechanism[J]. British Journal of Pharmacology,2022,179(14):3839−3858. doi: 10.1111/bph.15827
[27] ZHANG J, LIU S, XIA L, et al. Verbascoside protects mice from Clostridial gas gangrene by inhibiting the activity of alpha toxin and perfringolysin O[J]. Front Microbiol,2020,11:1504. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01504
[28] KUMARI R, KUMAR R, LYNN A. g_mmpbsa-a GROMACS tool for high-throughput MM-PBSA calculations[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling,2014,54(7):1951−1962. doi: 10.1021/ci500020m
[29] VALDÉS-TRESANCO M S, VALDÉS-TRESANCO M E, VALIENTE P A, et al. gmx_MMPBSA: A new tool to perform end-state free energy calculations with GROMACS[J]. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation,2021,17(10):6281−6291. doi: 10.1021/acs.jctc.1c00645
[30] GREENE D, QI R, NGUYEN R, et al. Heterogeneous dielectric implicit membrane model for the calculation of MMPBSA binding free energies[J]. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling,2019,59(6):3041−3056. doi: 10.1021/acs.jcim.9b00363
[31] LI G, SHEN X, WEI Y, et al. Quercetin reduces Streptococcus suis virulence by inhibiting suilysin activity and inflammation[J]. International Immunopharmacology,2019,69:71−78.
[32] MENG F, TONG J, VÖTSCH D, et al. Viral coinfection replaces effects of suilysin on Streptococcus suis adherence to and invasion of respiratory epithelial cells grown under air-liquid interface conditions[J]. Infection and Immunity,2019,87(8):e00350.
[33] BERCIER P, GOTTSCHALK M, GRENIER D. Streptococcus suis suilysin compromises the function of a porcine tracheal epithelial barrier model[J]. Microb Pathog,2020,139:103913.
[34] VERHERSTRAETEN S, GOOSSENS E, VALGAEREN B, et al. Perfringolysin O: The underrated clostridium perfringens toxin?[J]. Toxins,2015,7(5):1702−1721. doi: 10.3390/toxins7051702
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 李文廷,叶沛,刘玲,陶蓉蓉,张瑞雨,师真,蒋孟圆. 超高效液相色谱-串联质谱法测定发酵乳制品中米酵菌酸和异米酵菌酸. 分析测试学报. 2025(02): 326-333 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 郑圣乐,李卓颖,王家浩,刘峻铭,方桂娇,韩鹿. 益生菌清除食品毒素的研究进展. 农产品加工. 2024(21): 129-134+139 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 宋娓娜,薛笛笛,路飞,李国德,肖志刚,史梦娜,张一凡. 食品中米酵菌酸的相关研究. 现代食品. 2023(11): 23-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 宋娓娜,张嘉慧,赵秀红,路飞,肖志刚,张一凡. 植物乳杆菌对食品中常见毒素的抑制作用研究进展. 食品安全导刊. 2023(24): 174-177 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
