Evaluation of Medicinal Quality of Garlic Based on Principal Component Analysis
-
摘要: 通过比较分析大蒜的药用品质,建立大蒜药用质量评价体系。以水分、灰分、水溶性浸出物、大蒜素含量、蒜氨酸含量、大蒜辣素含量和蒜酶活力为指标,分析甘肃民乐、江苏邳州、山东金乡、河南郑州、重庆巫溪和新疆且末、拜城、种马场、虎头镇、大有镇、新地乡等11个产地大蒜的药用品质特征及差异,并通过相关性分析、主成分分析和聚类分析对大蒜质量进行综合评价。结果表明,不同产地大蒜的上述指标都具有显著性差异。相关性分析表明,蒜酶活力与水分呈极显著正相关性(P<0.01),蒜氨酸含量与灰分和大蒜辣素含量呈显著正相关性(P<0.05)。利用主成分分析可筛选出3个累计贡献率达到81.134%的主成分,在贡献率最大的第1主成分中,蒜氨酸对大蒜药用品质影响最大,其次为大蒜辣素和蒜酶活力。对11个产地大蒜进行综合评价,甘肃民乐大蒜的主成分综合评分得分最高为1.44,其余4个得分大于零的皆为新疆大蒜。系统聚类分析可将大蒜聚为四类,其中郑州大蒜单独为一类,金乡、巫溪和种马场大蒜聚为一类,新地、大有和民乐大蒜聚为一类,其余三地聚为一类。蒜氨酸、大蒜辣素和蒜酶活力可用于体现不同产地大蒜药用品质间的差距,利用综合评分可筛选出综合得分最高的大蒜,为优质大蒜的种质资源研究与药用大蒜规模化种植提供思路。Abstract: To compare and analyze the medicinal quality of garlic, a garlic medicinal quality evaluation system was established. Moisture, ash, water-soluble extract, diallyl trisulfide content, alliin content, allicin content and alliinase activity were screened out as indicators to analyze the medicinal quality of garlic from 11 regions, including Minle, Pizhou, Jinxiang, Zhengzhou, Wuxi, Qiemo, Baicheng, Zhongmachang, Hutou, Dayou and Xindi. The correlation analysis, principal component analysis and cluster analysis were performed to determine the quality of garlic in different regions. The results showed that all the above-mentioned indicators of garlic from different regions had significant differences. The correlation analysis showed that alliinase activity had an extremely significant and positive correlation with moisture (P<0.01), and alliin content showed a significant positive correlation with ash and alliin content (P<0.05). Three principal components with a cumulative contribution of 81.134% could be selected using the principal component analysis. Among the first principal component with the largest contribution, alliin had the greatest influence on the medicinal quality of garlic, followed by allicin and alliinase activity. In the comprehensive evaluation of garlic from 11 regions, the highest score of 1.44 was obtained from Minle, and the remaining four scores greater than zero were all from Xinjiang. The systematic clustering analysis revealed that the garlic from 11 regions could be clustered into four categories. Among them, Zhengzhou garlic was a separate category. Jinxiang, Wuxi and Zhongmachang garlic were clustered into one category. Xindi, Dayou and Minle garlic were clustered into one category, and the remaining three regions were clustered into one category. Alliin, allicin and alliinase activity could be used to reflect the disparity between the medicinal quality of garlic from different regions. The garlic with the highest overall score could be screened using the integrated score, which would provide ideas for the research of germplasm resources of high-quality garlic and the large-scale cultivation of medicinal garlic.
-
Keywords:
- garlic /
- alliin /
- alliinase activity /
- allicin /
- principal component analysis
-
大蒜是多年生广义百合科植物大蒜Allium sativum L.的鳞茎。中国是世界上重要的大蒜种植和出口国之一,2010~2021年,我国大蒜出口量稳居世界第一,占世界出口总量的40%以上[1]。我国疆域辽阔,海拔高度差异大,生态环境多样,形成了诸多具有地方特色的大蒜名优品种。大蒜不仅能食用,还有巨大的潜在药用价值。大量现代医学研究表明,大蒜在心血管疾病[2-5]、感染性疾病[6-7]、抗氧化[8-9]及肿瘤的预防与治疗[10-14]等方面具有活性作用。大蒜已被多国药典所收录,但其检测指标却不尽相同。《中国药典》[15]中,“大蒜”项下分别对总灰分、浸出物和大蒜素含量进行测定。而《美国药典》[16]和《欧盟药典》[17]中,大蒜及其相关制剂的检测指标却多为蒜氨酸、大蒜辣素和蒜酶活力。因此,为了更好地发掘中国大蒜的药用价值,增加其在国际市场的竞争力,亟需建立一套与国际接轨的大蒜药用品质评价体系。
国际公认的大蒜指标成分是蒜氨酸(S-烯丙基-L-半胱氨酸亚砜),它是大蒜的主要生物活性物质之一[18-19]。大蒜辣素(二烯丙基硫代亚磺酸酯)是大蒜最重要的生物活性成分之一,是其防治心脑血管疾病及感染性疾病的核心有效成分[20-22],已被《欧盟药典》及《美国药典》确定为大蒜及其制剂的指标成分。然而,完整大蒜本身并不含大蒜辣素,只有当其被切割或破碎时,分处细胞不同部位的蒜氨酸与蒜酶相遇,发生催化裂合反应才产生大蒜辣素[23]。大蒜辣素因其结构中包含不稳定的亚砜基和烯丙基,故极易分解。而《中国药典》“大蒜”项下的“大蒜素”(二烯丙基三硫醚),实为大蒜辣素的分解产物之一,它并非大蒜中的天然成分,自然也不能代表大蒜的药理作用。国内已有研究者对大蒜素和大蒜辣素的结构和命名进行了区分,并建议中国药典对大蒜的标准进行修订[24-26]。
研究者也对不同产地的大蒜开展了大量研究。赵东升[27]建立了以蒜氨酸为主的氨基酸类物质群和以大蒜辣素为主的含硫化合物类物质群的高效液相色谱指纹图谱方法,并进行了统计学分析。关明等[28-29]分别采用傅里叶红外光谱法和高效液相色谱法测定了25份大蒜样品,研究了不同地理居群对大蒜的理化性质和潜在大蒜辣素含量的影响。王薇薇等[30]对12份大蒜品种的23个性状进行遗传变异性分析,用于大蒜种质资源的综合评价。李攀龙等[31]研究了大蒜鳞茎品质与产地土壤养分的关系,利用主成分分析筛选出大蒜素、硒、锗和可溶性糖四个贡献率较大的主成分。目前,对于不同产地大蒜的药用品质研究与评价体系建立尚未见报道。因此,本研究通过收集国内11个产地的大蒜,参照《中国药典》、《美国药典》和《欧盟药典》中大蒜的检测指标,结合大蒜的功效研究成果,筛选了水分、总灰分、浸出物、大蒜素、蒜氨酸、大蒜辣素、蒜酶活力等7项指标,采用相关性分析、主成分分析和聚类分析,对大蒜质量进行综合评价,为药用大蒜的选材提供依据,也为优质大蒜种质资源的保护与利用提供科学指导。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
大蒜 夏季叶枯时采挖,去处须根和泥沙,通风晾晒至外皮干燥(自市场购入,详细产地信息见表1),为百合科植物大蒜Allium sativum L.的鳞茎,性状均符合《中国药典》大蒜的要求;蒜氨酸对照品 纯度≥99.0%,新疆埃乐欣药业有限公司;大蒜素对照品 纯度94.2%,中国食品药品检定研究院;甲醇 色谱纯,Sigma-Aldrich;实验用水 超纯水;其它分析试剂均为国产分析纯。
表 1 大蒜样品信息Table 1. Information of garlic samples from different regions编号 产地 备注 1# 江苏省邳州市 PZ 2# 山东省济宁市金乡县 JX 3# 河南省郑州市 ZZ 4# 新疆伊犁州昭苏县虎头镇75团 HTZ 5# 新疆伊犁州昭苏县种马场 ZMC 6# 新疆昌吉市吉木萨尔新地乡 XD 7# 新疆昌吉市吉木萨尔大有镇 DY 8# 新疆阿克苏地区拜城县 BC 9# 甘肃省张掖市民乐县 ML 10# 新疆巴州且末县 QM 11# 重庆市巫溪县 WX 注:大蒜购入时间2020年7~10月,购入后两个月内完成检测,期间于4 ℃冷藏保存。 AB135S分析天平 梅特勒-托利多;BPG-9070A精密鼓风干燥箱 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;SX-4-10中温箱式电阻炉 北京市永光明医疗仪器有限公司;UV2550紫外可见分光光度计、LC-2010A高效液相色谱仪 日本岛津公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 基本理化指标的测定
水分:参照《中国药典》2020版四部通则“0832水分测定法”第二法(烘干法);灰分:参照《中国药典》2020年版四部通则“2302灰分测定法”;浸出物:参照《中国药典》2020年版四部通则“2201水溶性浸出物测定法”项下“热浸法”;大蒜素含量:参照《中国药典》2020年版一部“大蒜”项下“含量测定”方法。
1.2.2 大蒜辣素含量的测定
参照《欧盟药典》。
1.2.3 蒜酶活力测定
大蒜蒜酶活力测定采用紫外-可见分光光度法[32]。
供试品溶液的制备:取各产地新鲜大蒜,脱皮后于4 ℃预冷12 h。称取100 g蒜瓣(平行测定三次)置匀浆机中,加入300 mL匀浆液(4 ℃),打浆20 s×5次,匀浆液经8层纱布过滤。收集滤液,于12000 r/min低温(4 ℃)离心5 min,合并上清,作为供试品溶液。
1.2.4 蒜氨酸含量的测定
蒜氨酸含量的测定采用高效液相色谱法[33]。
色谱条件:色谱柱:Innert Sustain C18(4.6 mm×250 mm,5 μm);柱温:35 ℃,流动相:0.04%三氟乙酸水溶液,流速:0.5 mL/min,检测波长:214 nm,进样量:10 µL。
对照品溶液的制备:称取蒜氨酸对照品适量,加水,制成每1 mL含150 µg的溶液,作为对照品溶液。
样品的前处理:取脱皮蒜瓣约100 g,精密称定,置500 mL烧杯中,加水200 mL,水煮灭酶10 min,匀浆1 min,浆液全部转移至500 mL量瓶中,加水稀释至刻度,摇匀,离心(8000 r/min)15 min,精密吸取上清液1.0 mL,置100 mL量瓶中,加水稀释至刻度,摇匀,即得。以保留时间定性,外标法定量,计算公式如下:
蒜氨酸含量(%)=Ax×Cs×D×VAs×W×1000×100 式中:Ax为供试品溶液峰面积,Cs为蒜氨酸对照品溶液浓度,As为蒜氨酸对照品溶液峰面积,V为匀浆液总体积,D为稀释倍数,W为蒜瓣称样量。
1.3 数据处理
每次实验均采取三次平行。数据处理和分析采用Excel 2007与SPSS 26.0相结合的方法,对所测大蒜的品质指标进行单因素方差分析、相关性分析、主成分分析和聚类分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同产地大蒜的指标测定结果
对不同产地大蒜的水分、总灰分、浸出物、大蒜素(按干品计)、蒜氨酸(按干品计)、大蒜辣素(按干品计)、蒜酶活力(按干品计)的测定结果见表2。其中,蒜氨酸含量最高的大蒜依次为新疆昭苏虎头镇(5.35%)、甘肃民乐(4.96%)和新疆昭苏种马场(4.51%),大蒜辣素含量的大蒜最高依次为甘肃民乐(2.46%)、新疆拜城(2.12%)和新疆昭苏虎头镇(1.94%),蒜酶活力最高的大蒜依次为河南郑州(3715.7 U/g)、山东金乡(3338.5 U/g)和重庆巫溪(3268.7 U/g)。利用单因素方差分析(ANOVA)法进行差异显著性分析,结果表明不同产地大蒜的水分、总灰分、浸出物、大蒜素、蒜氨酸、大蒜辣素和蒜酶活力都具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。
表 2 不同产地大蒜品质参数比较Table 2. Comparison of quality parameters of garlic from different regions产地 水分
(%)总灰分
(%)浸出物
(%)大蒜素
(%)蒜氨酸
(%)大蒜辣素
(%)蒜酶活力
(U/g)PZ 60.9±0.7a 1.20±0.02f 79.4±4.4abde 0.51±0.01a 2.99±0.04i 0.90±0.04h 2603.2±80.1c JX 64.1±1.3a 1.29±0.02ef 71.7±0.4cd 0.16±0.01g 3.24±0.10h 1.70±0.10d 3338.5±313.9abcde ZZ 63.0±0.7a 1.39±0.07cdf 80.3±0.1ab 0.36±0.02e 3.41±0.04g 1.31±0.02f 3715.7±84.9a HTZ 61.1±0.3a 1.98±0.02ac 73.1±0.8bc 0.43±0.01c 5.35±0.09a 1.94±0.20c 2319.7±276.2cd ZMC 61.5±0.4a 1.69±0.13adf 81.4±3.3abde 0.50±0.01a 4.51±0.15c 1.60±0.06e 2988.3±50.3b XD 61.3±1.4a 1.36±0.04ef 79.9±3.8abde 0.25±0.01f 4.49±0.14c 1.23±0.14f 1988.7±38.6d DY 61.0±0.7a 1.28±0.03ef 87.9±0.7a 0.38±0.02d 3.93±0.08e 1.61±0.06e 1753.7±35.3e BC 60.9±0.9a 1.46±0.01cbdf 91.3±1.6ad 0.51±0.03a 4.19±0.12d 2.12±0.10b 2591.4±104.5abcde ML 61.5±0.2a 1.84±0.04ad 63.9±0.8e 0.50±0.02a 4.96±0.11b 2.46±0.07a 2027.8±38.9d QM 60.4±0.5a 1.71±0.03ebd 78.2±2.6abde 0.25±0.01f 4.23±0.09d 1.76±0.04d 2269.6±49.6d WX 64.5±1.3a 1.94±0.05ab 87.1±1.1a 0.45±0.01b 3.53±0.08f 1.09±0.23g 3268.7±185.7abcde 注:同列不同字母表示不同产地间具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。 大蒜的生长发育,可分为萌发期、幼苗期、花芽鳞芽分化期、蒜薹伸长期、鳞茎膨大期和生理休眠期等6个时期。生理休眠期是指蒜头采收后到蒜瓣萌芽的阶段,大蒜采收时通常已进入休眠期,即使环境条件适宜也不会发芽。大蒜休眠期的长短与品种有关,一般为2~3个月[34],低温干燥是保持大蒜休眠的重要条件[35]。大蒜经过休眠期后,就要发芽,发芽时要消耗养分,使肉质变软,水分减少,蒜瓣干瘪,致使大蒜商品性下降。这时需要通过低温、干燥,强迫其继续休眠,才能继续贮藏。GB/T 24700-2010《大蒜 冷藏》规定:大蒜贮藏温度应在0±0.5 ℃,相对湿度应保持在65%~75%,且应保持空气在恒温条件下循环。因此,为了更加客观、真实地反映大蒜的药用品质,其相关研究应尽可能在大蒜生理休眠期内进行。
2.2 大蒜品质指标的相关性分析
利用SPSS 26.0软件对不同产地大蒜的7项指标进行了相关性分析。多样本两指标之间相关系数绝对值越大,表明两指标间的联系越紧密。由表3可知,蒜酶活力与水分呈极显著正相关性(P<0.01),蒜氨酸含量与灰分和大蒜辣素含量呈显著正相关性(P<0.05)。相关性分析结果表明,各指标之间都有一定的相关关系,说明所统计的原始数据反映的信息存在重叠,故适合使用主成分分析法对上述7项指标进行简化,以提高大蒜品质评价的分析效率。
表 3 不同产地大蒜各指标之间的相关性分析Table 3. Correlation analysis of garlic from different regions指标 水分 灰分 浸出物 大蒜素 蒜氨酸 大蒜辣素 蒜酶活力 水分 1 灰分 0.044 1 浸出物 −0.032 −0.258 1 大蒜素 −0.234 0.306 0.197 1 蒜氨酸 −0.532 0.639* −0.330 0.199 1 大蒜辣素 −0.344 0.389 −0.401 0.125 0.667* 1 蒜酶活力 0.759** −0.029 0.096 −0.071 −0.559 −0.351 1 注:**表示在0.01水平(双尾),极显著相关性,P<0.01;*表示在0.05水平(双尾),显著相关性,P<0.05。 2.3 大蒜品质指标的主成分分析及综合评价
大蒜品质的构成因子较多,不同的品质因子间存在密切相关性和相对独立性。为综合评价不同产地间大蒜的质量差异,对已测定7个指标进行主成分分析,将各指标因子进行无量纲标准处理化后,求得相关系数矩阵。通过选取特征值大于1的成分作为主成分,共提取了3个有效的主成分。第1个主成分(F1)贡献率为42.167%,第2个主成分(F2)贡献率为21.481%,第3个主成分(F3)贡献率为17.486%(表4)。前3个主成分的累计方差贡献率达81.134%,即代表了大蒜总信息的81.134%,说明这3个主成分已包含了原来7个指标的大部分信息。
表 4 各成分的特征值、方差贡献率和累积方差贡献率Table 4. Eigenvalue and variance cumulative contribution of garlic from different regions主成分 特征值 方差贡献率(%) 累积方差贡献率(%) F1 2.952 42.167 42.167 F2 1.504 21.481 63.648 F3 1.224 17.486 81.134 F4 0.542 7.741 88.876 F5 0.455 6.503 95.378 F6 0.215 3.078 98.457 F7 0.108 1.543 100.000 通过上述3个主成分的特征值和方差贡献率可以计算得到主成分因子荷载矩阵(表5)。结果表明,第1个主成分中,蒜氨酸、大蒜辣素和蒜酶活力的载荷系数较大,其值分别为0.926,0.771和-0.707,它们对第1个主成分的贡献最多。由此可知,蒜氨酸、大蒜辣素和蒜酶活力是判断不同产地大蒜药材质量的重要因素。
表 5 主成分因子载荷矩阵Table 5. Component load matrix after principal component analysis因子 主成分 F1 F2 F3 水分 −0.681 0.652 0.071 灰分 0.549 0.601 0.418 浸出物 −0.381 −0.578 0.516 大蒜素 0.299 −0.126 0.837 蒜氨酸 0.926 0.131 0.034 大蒜辣素 0.771 0.246 −0.122 蒜酶活力 −0.707 0.538 0.245 利用主成分载荷矩阵(表5)中各指标数据除以主成分相应的特征值开平方,便可得到3个主成分中各指标所对应的系数,即特征向量,根据特征向量可得3个主成分的得分表达式如下:
F1=−0.396X1+0.320X2−0.222X3+0.174X4+0.539X5+0.449X6−0.412X7,
F2=0.532X1+0.490X2−0.471X3−0.103X4+0.107X5+0.201X6+0.439X7,
F3=0.064X1+0.378X2+0.466X3+0.757X4+0.031X5−0.110X6+0.221X7。
根据上述3个主成分的方差贡献率,可得大蒜品质综合评价模型:F=42.167%F1+21.481%F2+17.486%F3。据该综合评价模型可计算各产地大蒜的主成分得分及综合得分,结果见表6。综合得分越高,表示该大蒜综合品质越好。测定结果表明,有5个产地大蒜的综合得分大于0,占比45.5%。其中,ML(甘肃民乐)大蒜综合得分最高为1.44,2~5名依次为HTZ(新疆昭苏虎头镇)、ZMC(新疆昭苏种马场)、BC(新疆拜城)、QM(新疆且末)大蒜。
表 6 不同产地大蒜的主成分得分及综合排序Table 6. Factor scores and comprehensive ranking of garlic from different regions产地 F1 F2 F3 综合得分 排序 PZ −1.54 −1.42 0.34 −0.90 10 JX −2.05 1.48 −1.94 −0.89 9 ZZ −2.08 0.65 0.12 −0.72 8 HTZ 2.39 0.90 0.26 1.24 2 ZMC 0.43 0.19 1.09 0.41 3 XD 0.08 −1.02 −1.25 −0.41 7 DY 0.15 −1.94 −0.29 −0.41 7 BC 0.61 −1.14 1.13 0.21 4 ML 2.88 1.27 −0.27 1.44 1 QM 0.93 −0.28 −0.96 0.16 5 WX −1.79 1.33 1.78 −0.16 6 我国幅员辽阔,大蒜的种植范围较广,产区主要集中在山东、江苏、甘肃、湖北、陕西、河南、新疆等地。李攀龙等[31]研究了全国16个省区的50个大蒜品种鳞茎品质与产地土壤养分的关系,结果表明土壤中硫元素与大蒜素和可溶性糖显著正相关,土壤pH与大蒜锗含量显著正相关,土壤N含量与大蒜可溶性糖极显著正相关。赵勇强[36]研究了大蒜品种、产地、海拔和生长期积温等因素对大蒜辣素、硒、锗、可溶性糖和可溶性蛋白的影响,发现可以通过筛选产地和品种来获得大蒜辣素、硒元素、锗元素较高的大蒜。从不同方面证明,产地的海拔、自然环境、气候特征、栽培品种和栽培方式的差异,都有可能影响大蒜的品质。
2.4 不同产地大蒜品质参数聚类分析
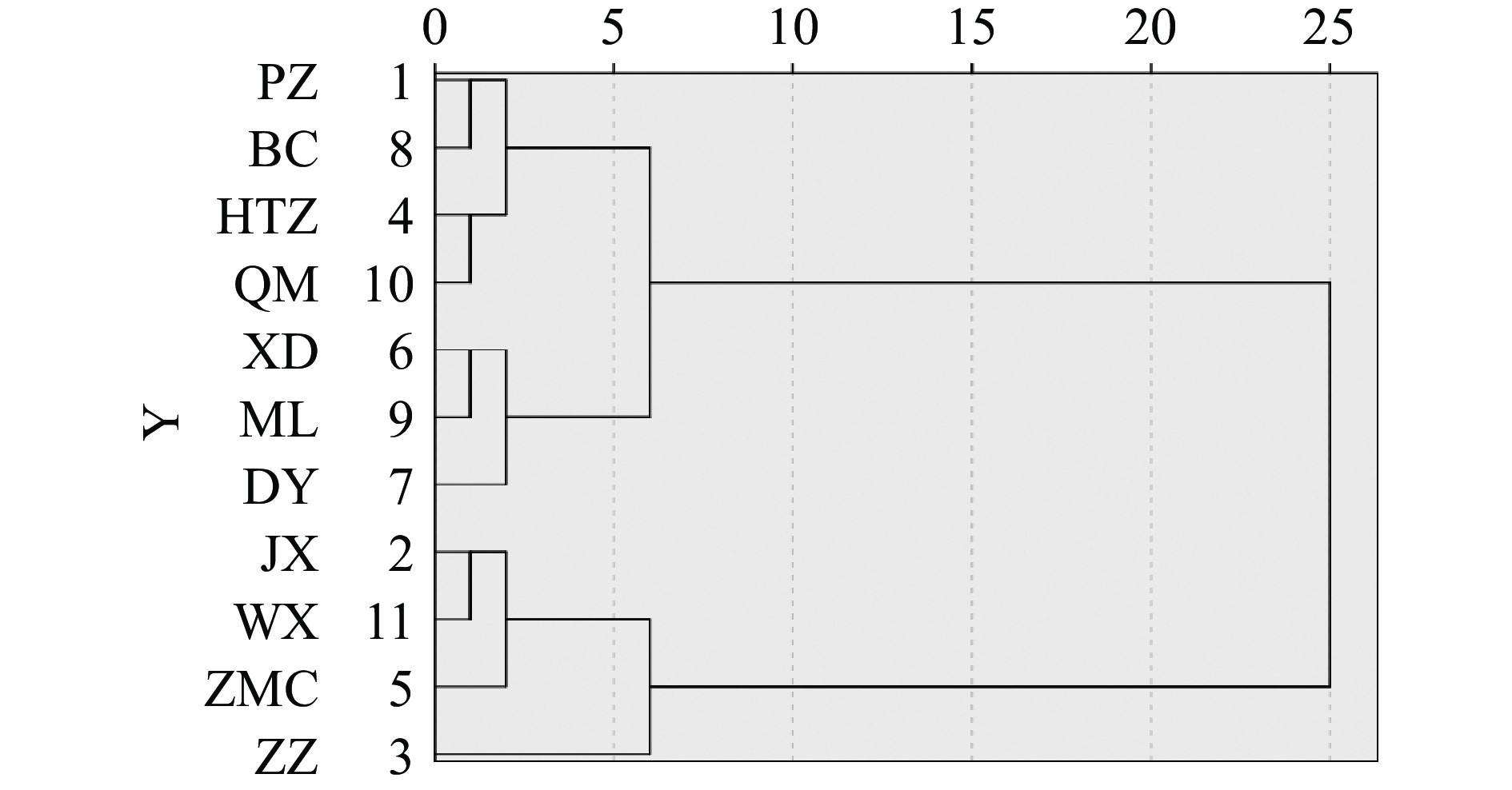
聚类分析是将相似度大的样品优先聚合,最终按照类别的综合性质完成多个品种聚合的过程。为考察大蒜中不同指标含量差异与产地之间的相互关系,以11批不同产地大蒜中7项指标为基准,采用系统聚类分析方法,通过组间连接方法,以平方欧氏距离作为样品相似性的判定,分析结果见图1。以欧式距离5为临界点时,11个产地的大蒜聚集为4类。其中ZZ单独为一类,其蒜酶活力最高;JX、WX和ZMC大蒜聚为一类,这些大蒜的蒜酶活力较高;XD、ML和DY大蒜聚为一类,这些大蒜的蒜酶活力较低;其余三地聚为一类。
3. 结论
本文以为水分、总灰分、浸出物、大蒜素、蒜氨酸、大蒜辣素和蒜酶活力为指标,研究了11个不同产地大蒜的药用品质差异。结果表明,不同产地大蒜的上述指标都具有显著性差异。相关性分析表明,蒜酶活力与水分呈极显著正相关性(P<0.01),蒜氨酸含量与灰分和大蒜辣素含量呈显著正相关性(P<0.05)。利用主成分分析,对大蒜的品质做出初步评价。根据主成分分析的降维思想,筛选出可代表大蒜81.134%总信息的3个主成分。其中,贡献率最大的第1主成分中,蒜氨酸、大蒜辣素和蒜酶活力的贡献最大,与《美国药典》和《欧盟药典》检测指标一致,也与大蒜的药效学研究结果一致[37-38]。利用主成分分析的综合评价,可完成对不同产地大蒜的品质评价工作。在综合得分大于0的五个大蒜产地中,除得分第一的甘肃民乐大蒜外,其余四个皆为新疆大蒜,表明新疆独特的气候环境及高海拔地理优势对于大蒜生长和优质蒜种的栽培具有重要意义。聚类分析可将上述大蒜分为四类,其中郑州大蒜单独为一类,金乡、巫溪和种马场大蒜聚为一类,新地、大有和民乐大蒜聚为一类,其余三地聚为一类。通过不同产地大蒜药用质量评价体系的建立,不仅可为药用大蒜选材提供科学依据,也为优势大蒜资源的选种,大蒜种质资源的保护与利用,规模化大蒜种植基地的建立提供数据支持。
大蒜药用质量不仅与其品种相关,还受到产地的自然环境、地理特征和栽培方式等多方面的影响。因此,通过统计分析对大蒜质量进行评分、评级与归类,尚需进行大量数据积累和产地调研工作。此外,大蒜种植过程中,由于长期的无性繁殖和不同地区间的引种,导致生产上用种混杂、品种更新慢及品种退化,使得大蒜栽培、育种工作难度增加,大大限制了大蒜产量和品质的提高。因此,新疆优质大蒜的种质资源研究与药用大蒜规模化种植已成为本课题组的后续研究重点之一。
-
表 1 大蒜样品信息
Table 1 Information of garlic samples from different regions
编号 产地 备注 1# 江苏省邳州市 PZ 2# 山东省济宁市金乡县 JX 3# 河南省郑州市 ZZ 4# 新疆伊犁州昭苏县虎头镇75团 HTZ 5# 新疆伊犁州昭苏县种马场 ZMC 6# 新疆昌吉市吉木萨尔新地乡 XD 7# 新疆昌吉市吉木萨尔大有镇 DY 8# 新疆阿克苏地区拜城县 BC 9# 甘肃省张掖市民乐县 ML 10# 新疆巴州且末县 QM 11# 重庆市巫溪县 WX 注:大蒜购入时间2020年7~10月,购入后两个月内完成检测,期间于4 ℃冷藏保存。 表 2 不同产地大蒜品质参数比较
Table 2 Comparison of quality parameters of garlic from different regions
产地 水分
(%)总灰分
(%)浸出物
(%)大蒜素
(%)蒜氨酸
(%)大蒜辣素
(%)蒜酶活力
(U/g)PZ 60.9±0.7a 1.20±0.02f 79.4±4.4abde 0.51±0.01a 2.99±0.04i 0.90±0.04h 2603.2±80.1c JX 64.1±1.3a 1.29±0.02ef 71.7±0.4cd 0.16±0.01g 3.24±0.10h 1.70±0.10d 3338.5±313.9abcde ZZ 63.0±0.7a 1.39±0.07cdf 80.3±0.1ab 0.36±0.02e 3.41±0.04g 1.31±0.02f 3715.7±84.9a HTZ 61.1±0.3a 1.98±0.02ac 73.1±0.8bc 0.43±0.01c 5.35±0.09a 1.94±0.20c 2319.7±276.2cd ZMC 61.5±0.4a 1.69±0.13adf 81.4±3.3abde 0.50±0.01a 4.51±0.15c 1.60±0.06e 2988.3±50.3b XD 61.3±1.4a 1.36±0.04ef 79.9±3.8abde 0.25±0.01f 4.49±0.14c 1.23±0.14f 1988.7±38.6d DY 61.0±0.7a 1.28±0.03ef 87.9±0.7a 0.38±0.02d 3.93±0.08e 1.61±0.06e 1753.7±35.3e BC 60.9±0.9a 1.46±0.01cbdf 91.3±1.6ad 0.51±0.03a 4.19±0.12d 2.12±0.10b 2591.4±104.5abcde ML 61.5±0.2a 1.84±0.04ad 63.9±0.8e 0.50±0.02a 4.96±0.11b 2.46±0.07a 2027.8±38.9d QM 60.4±0.5a 1.71±0.03ebd 78.2±2.6abde 0.25±0.01f 4.23±0.09d 1.76±0.04d 2269.6±49.6d WX 64.5±1.3a 1.94±0.05ab 87.1±1.1a 0.45±0.01b 3.53±0.08f 1.09±0.23g 3268.7±185.7abcde 注:同列不同字母表示不同产地间具有显著性差异(P<0.05)。 表 3 不同产地大蒜各指标之间的相关性分析
Table 3 Correlation analysis of garlic from different regions
指标 水分 灰分 浸出物 大蒜素 蒜氨酸 大蒜辣素 蒜酶活力 水分 1 灰分 0.044 1 浸出物 −0.032 −0.258 1 大蒜素 −0.234 0.306 0.197 1 蒜氨酸 −0.532 0.639* −0.330 0.199 1 大蒜辣素 −0.344 0.389 −0.401 0.125 0.667* 1 蒜酶活力 0.759** −0.029 0.096 −0.071 −0.559 −0.351 1 注:**表示在0.01水平(双尾),极显著相关性,P<0.01;*表示在0.05水平(双尾),显著相关性,P<0.05。 表 4 各成分的特征值、方差贡献率和累积方差贡献率
Table 4 Eigenvalue and variance cumulative contribution of garlic from different regions
主成分 特征值 方差贡献率(%) 累积方差贡献率(%) F1 2.952 42.167 42.167 F2 1.504 21.481 63.648 F3 1.224 17.486 81.134 F4 0.542 7.741 88.876 F5 0.455 6.503 95.378 F6 0.215 3.078 98.457 F7 0.108 1.543 100.000 表 5 主成分因子载荷矩阵
Table 5 Component load matrix after principal component analysis
因子 主成分 F1 F2 F3 水分 −0.681 0.652 0.071 灰分 0.549 0.601 0.418 浸出物 −0.381 −0.578 0.516 大蒜素 0.299 −0.126 0.837 蒜氨酸 0.926 0.131 0.034 大蒜辣素 0.771 0.246 −0.122 蒜酶活力 −0.707 0.538 0.245 表 6 不同产地大蒜的主成分得分及综合排序
Table 6 Factor scores and comprehensive ranking of garlic from different regions
产地 F1 F2 F3 综合得分 排序 PZ −1.54 −1.42 0.34 −0.90 10 JX −2.05 1.48 −1.94 −0.89 9 ZZ −2.08 0.65 0.12 −0.72 8 HTZ 2.39 0.90 0.26 1.24 2 ZMC 0.43 0.19 1.09 0.41 3 XD 0.08 −1.02 −1.25 −0.41 7 DY 0.15 −1.94 −0.29 −0.41 7 BC 0.61 −1.14 1.13 0.21 4 ML 2.88 1.27 −0.27 1.44 1 QM 0.93 −0.28 −0.96 0.16 5 WX −1.79 1.33 1.78 −0.16 6 -
[1] 李慧颖, 白丽. 中国大蒜出口价格波动特征分析[J]. 农村经济与科技,2021,32(17):124−126. [LI H Y, BAI L. Analysis on the characteristics of Chinese garlic export price fluctuation[J]. Rural Economy and Science of Technology,2021,32(17):124−126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7103.2021.17.044 LI H Y, BAI L. Analysis on the characteristics of Chinese garlic export price fluctuation [J]. Rural Economy and Science of Technology, 2021, 32 (17): 124-126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-7103.2021.17.044
[2] 张起毓, 严啸, 李汇华. 大蒜来源有机硫化物与心血管疾病的关系的研究进展[J]. 中国食物与营养,2020,26(1):54−58. [ZHANG Q Y, YAN X, LI H H. Research progress on the relationship between garlic-derived organic sulfides and cardiovascular diseases[J]. Food and Nutrition in China,2020,26(1):54−58. ZHANG Q Y, YAN X, LI H H. Research progress on the relationship between garlic-derived organic sulfides and cardiovascular diseases[J]. Food and Nutrition in China, 2020, 26 (1): 54-58.
[3] HUSSEIN J H, IMAD H H, MOHAMMED Y H. A review: Anti-microbial, anti-inflammatory effect and cardiovascular effects of garlic: Allium sativum[J]. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology,2017,10(11):4069−4078. doi: 10.5958/0974-360X.2017.00738.7
[4] ALARE K, ALARE T, LUCIANO N. Medicinal importance of garlic and onions on autonomic nervous system[J]. Clinical Pharmacology & Biopharmaceutics,2020,9(4):1−3.
[5] 崔天薇, 余丞浩, 刘伟宇, 等. 大蒜辣素的急性降压作用及其与硫化氢相关的作用机制[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2020,35(5):2618−2622. [CUI T W, YU C H, LIU W Y, et al. Acute anti-hypertensive effect of Allicin and its mechanisms relating with hydrogen sulfide[J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy,2020,35(5):2618−2622. CUI T W, YU C H, LIU W Y, et al. Acute anti-hypertensive effect of Allicin and its mechanisms relating with hydrogen sulfide[J]. Chinese Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Pharmacy, 2020, 35 (5): 2618-2622.
[6] 胡万超, 唐建国. 大蒜提取物抗白念珠菌作用机制研究进展[J]. 中国感染与化疗杂志,2020,20(2):221−225. [HU W C, TANG J G. Research updates on the mechanisms of garlic extract against Candida albicans[J]. Chinese Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy,2020,20(2):221−225. HU W C, TANG J G. Research updates on the mechanisms of garlic extract against Candida albicans[J]. Chinese Journal of Infection and Chemotherapy, 2020, 20 (2): 221-225.
[7] KAUR G, BANSAL A, PANDEY N. Antibacterial and pharmacological properties of garlic: A review [J]. Journal of Biology and Nature, 2020, 1-6.
[8] MOUSA A S, MOUSA S A. Anti-angiogenesis efficacy of the garlic ingredient alliin and antioxidants: role of nitric oxide and p53[J]. Nutrition and Cancer:An International Journal,2005,53(1):104−110. doi: 10.1207/s15327914nc5301_12
[9] 张云, 苗敬芝, 董玉玮, 等. 双酶法提取大蒜水溶性膳食纤维及其抗氧化活性分析[J]. 农产品加工(下半月),2021,9(9):15−17. [ZHANG Y, MIAO J Z, DONG Y W, et al. Extraction of water soluble dietary fiber from garlic by double enzyme method and analysis of its antioxidant activity[J]. AEM Products Processing,2021,9(9):15−17. ZHANG Y, MIAO J Z, DONG Y W, et al. Extraction of water soluble dietary fiber from garlic by double enzyme method and analysis of its antioxidant activity[J]. AEM Products Processing, 2021, 9 (9): 15-17.
[10] JIKIHARA, HIROSHI Q, GUANGYING N, KOICHIRO H, et al. Aged garlic extract inhibits 1, 2-dimethylhydrazine-induced colon tumor development by suppressing cell proliferation[J]. Oncology Reports,2015,33(3):1131−1140. doi: 10.3892/or.2014.3705
[11] FEDERICA B, PAOLA T, SILVIA G, et al. Ethanol-based garlic extract prevents malignant evolution of non-invasive breast tumor cells induced by moderate hypoxia[J]. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy,2021,142:112052.
[12] 陈雪艳, 熊婷, 刘晓旺, 等. 大蒜内烯丙基硫在恶性肿瘤中的作用[J]. 国际肿瘤学杂志,2017,44(2):122−124. [CHEN X Y, XIONG T, LIU X W, et al. The role of garlic allyl sulfide in malignant tumor[J]. Journal of International Oncology,2017,44(2):122−124. CHEN X Y, XIONG T, LIU X W, et al. The role of garlic allyl sulfide in malignant tumor[J]. Journal of International Oncology, 2017, 44 (2): 122-124.
[13] SUN D S, SUN C Q, QIU G C, et al. Allicin mitigates hepatic injury following cyclophosphamide administration via activation of Nrf2/ARE pathways and through inhibition of inflammatory and apoptotic machinery[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2021,28(29):39625−39636. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-13392-w
[14] JAN B, JANA F, ULRIKE K, et al. Allicin, the odor of freshly crushed garlic: a review of recent progress in understanding allicin’s effects on cells[J]. Molecules,2021,26(6):1505. doi: 10.3390/molecules26061505
[15] 国家药典委员会. 中华人民共和国药典(一部)[S]. 北京: 中国医药科技出版社, 2020: 25-26 National Pharmacopoeia Committee. Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of China, Volume I[S]. Beijing: China Medical Science and Technology Press, 2020: 25-26.
[16] The United States Pharmacopeial Convention. USP40-NF35 (U. S. Pharmacopeia 40-National Formulary 35)[S]. Rockville, Maryland: United Book Press, 2017: 6989-6991.
[17] European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines & Healthcare (EDQM). European Pharmacopeia 9thed[S]. Strasbourg: Council of Europe, 2017: 1364-1365.
[18] 蒋茂婷, 黄雪松. 蒜氨酸生物活性的研究现状[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(16):264−269. [JIANG M T, HUANG X S. Research progress on alliin bioactivity[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(16):264−269. JIANG M T, HUANG X S. Research progress on alliin bioactivity [J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2020, 46 (16): 264-269.
[19] BASTAKI S M A, OJHA S, KALASZ H, et al. Chemical constituents and medicinal properties of Allium species[J]. Molecular and Cellular Biochemistry,2021,476(12):4301−4321. doi: 10.1007/s11010-021-04213-2
[20] CAVALLITO C J, BAYLEY J H. Allicin, the antibacterial principle of Allium sativum: (i) Isolation, physical properties and anti-bacterial action[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,1944,66:1950−1951.
[21] MA L N, LI L D, LI S C, et al. Allicin improves cardiac function by protecting against apoptosis in rat model of myocardial infarction[J]. Chinese Journal of Integrative Medicine,2017,23(8):589−597. doi: 10.1007/s11655-016-2523-0
[22] CHOO S, CHIN V K, WONG E H, et al. Review: Antimicrobial properties of allicin used alone or in combination with other medications[J]. Folia Microbiologica,2020,65(3):451−465. doi: 10.1007/s12223-020-00786-5
[23] 李新霞, 史荣梅, 刘睿婷. 大蒜主要化学成分及检测标准[J]. 新疆医科大学学报,2020,43(6):697−700. [LI X X, SHI R M, LIU R T. The main chemical components and testing standards of garlic[J]. Journal of Xinjiang Medical University,2020,43(6):697−700. LI X X, SHI R M, LIU R T. The main chemical components and testing standards of garlic[J]. Journal of Xinjiang Medical University, 2020, 43 (6): 697-700.
[24] 魏宁漪, 吴建敏, 张启明. 关于大蒜和大蒜素质量标准的商榷[J]. 药物分析杂志,2011,31(1):180−185. [WEI N Y, WU J M, ZHANG Q M. Discussion on drug specification of garlic and alltride[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis,2011,31(1):180−185. WEI N Y, WU J M, ZHANG Q M. Discussion on drug specification of garlic and alltride[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 2011, 31 (1): 180-185.
[25] 李新霞, 赵东升, 关明, 等. 有关2010年版中国药典大蒜质量标准的几点建议[J]. 药物分析杂志,2012,32(4):682−688. [LI X X, ZHAO D S, GUAN M, et al. Suggestion about specification of garlic in Chinese Pharmacopeia[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis,2012,32(4):682−688. LI X X, ZHAO D S, GUAN M, et al. Suggestion about specification of garlic in Chinese Pharmacopeia[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 2012, 32 (4): 682-688.
[26] 赵东升, 史荣梅, 陈尚珂, 等. 《中华人民共和国药典》大蒜标准中含量测定的商榷[J]. 医学导报,2016,35(10):1117−1120. [ZHAO D S, SHI R M, CHEN S K, et al. Discussion of content determination on garlic standard in Chinese pharmacopeia[J]. Herald of Medicine,2016,35(10):1117−1120. ZHAO D S, SHI R M, CHEN S K, et al. Discussion of content determination on garlic standard in Chinese pharmacopeia [J]. Herald of Medicine, 2016, 35 (10): 1117-1120.
[27] 赵东升. 大蒜药材物质群特征成分分析及质量研究[D]. 乌鲁木齐: 新疆医科大学, 2012 ZHAO D S. Study on the characteristics active substances analysis and quality for garlic[D]. Urumqi: Xinjiang Medical University, 2012.
[28] 关明, 陈利新, 佟小强, 等. 不同地理居群大蒜中潜在大蒜辣素的含量测定及聚类分析[J]. 食品科学,2011,32(8):186−189. [GUAN M, CHEN L X, TONG X Q, et al. Determination and cluster analysis of potential allicin content in garlic from different geographic populations[J]. Food Science,2011,32(8):186−189. GUAN M, CHEN L X, TONG X Q, et al. Determination and cluster analysis of potential allicin content in garlic from different geographic populations [J]. Food Science, 2011, 32 (8): 186-189.
[29] 关明, 李晓静, 郭勇, 等. 不同地理居群大蒜FTIR图谱比较研究[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2011,31(6):1494−1497. [GUAN M, LI X J, GUO Y, et al. Comparative study on FTIR spectra of garlic from different geographical populations[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2011,31(6):1494−1497. GUAN M, LI X J, GUO Y, et al. Comparative study on FTIR spectra of garlic from different geographical populations[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2011, 31 (6): 1494-1497.
[30] 王薇薇, 郭军, 梅燚, 等. 大蒜种质资源的综合评价与聚类分析[J]. 江苏农业学报,2017,33(2):397−403. [WANG W W, GUO J, MEI Y, et al. Comprehensive evaluation and clustering analysis of garlic germplasm resources[J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agriculture Science,2017,33(2):397−403. WANG W W, GUO J, MEI Y, et al. Comprehensive evaluation and clustering analysis of garlic germplasm resources [J]. Jiangsu Journal of Agriculture Science, 2017, 33(2): 397-403.
[31] 李攀龙, 李夏夏, 杨帆, 等. 中国大蒜主产区主要品种鳞茎品质及其与产地土壤养分的关系[J]. 西北农业学报,2020,29(6):949−957. [LI P L, LI X X, YANG F, et al. Bulb quality of different collections from main producing areas in China and its relations with local soil nutrition[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica,2020,29(6):949−957. LI P L, LI X X, YANG F, et al. Bulb quality of different collections from main producing areas in China and its relations with local soil nutrition[J]. Acta Agriculturae Boreali-occidentalis Sinica, 2020, 29 (6): 949-957.
[32] 胡小霞, 肖文浚, 宋百灵, 等. 大蒜粉蒜酶活力的测定方法研究[J]. 化学与生物工程,2021,38(5):71−75. [HU X X, XIAO W J, SONG B L, et al. Determination of alliinase activity in garlic powder[J]. Chemistry & Bioengineering,2021,38(5):71−75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2021.05.015 HU X X, XIAO W J, SONG B L, et al. Determination of alliinase activity in garlic powder[J]. Chemistry & Bioengineering, 2021, 38 (5): 71-75. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-5425.2021.05.015
[33] 宋百灵, 张唯, 史荣梅, 等. 大蒜化学成分不同测定方法比较及相关性探讨[J]. 药物分析杂志,2016,36(4):727−732. [SONG B L, ZHANG W, SHI R M, et al. Study on the comparison and correlation of chemical constituents of garlic[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis,2016,36(4):727−732. SONG B L, ZHANG W, SHI R M, et al. Study on the comparison and correlation of chemical constituents of garlic[J]. Chinese Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis, 2016, 36 (4): 727-732.
[34] 刘国芬. 大蒜栽培与储藏[M]. 北京: 金盾出版社, 2000: 8−9 LIU G F. Garlic cultivation and storage[M]. Beijing: Jindun Publisher, 2000: 8−9.
[35] 翟广华. 大蒜贮藏原理及技法[J]. 农村实用技术与信息,2007,10:38−39. [ZHAI G H. Garlic storage principle and techniques[J]. Practical Rural Technology and Information,2007,10:38−39. ZHAI G H. Garlic storage principle and techniques[J]. Practical Rural Technology and Information, 2007, 10: 38-39.
[36] 赵勇强. 中国不同产区大蒜鳞茎品质评价及其与产地环境关系分析[D]. 陕西: 西北农林科技大学, 2018 ZHAO Y Q. Evaluation on the quality of garlic bulbs in different production areas in china and its relationship with the environment of producing areas[D]. Shanxi: Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, 2018.
[37] 李少春. 大蒜辣素对心肌缺血大鼠的心肌保护作用及机制研究[D]. 北京: 中国中医科学院, 2017 LI S C. Cardioprotective effect and mechanism of allicin on myocardial ischemia in rat[D]. Beijing: China Academy of Chinese Medical Science, 2017.
[38] 方奕巍, 朱文涛, 陈金明. 蒜氨酸微丸-蒜酶肠溶双层片制备工艺优选及体外抗肿瘤作用评价[J]. 中国药业,2022,31(3):59−64. [FANG Y W, ZHU W T, CHEN J M. Optimization of preparation process of enteric-coated alliin pellets-alliinase bilayer tablets and in vitro evaluation of their anti-tumor effect[J]. China Pharmaceuticals,2022,31(3):59−64. FANG Y W, ZHU W T, CHEN J M, Optimization of preparation process of enteric-coated alliin pellets - alliinase bilayer tablets and in vitro evaluation of their anti-tumor effect[J]. China Pharmaceuticals, 2022, 31 (3): 59-64.
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 黄潇漪,贾利蓉,孙玉鼎,曹月刚,冉旭. 天然香辛料对烘炒花生仁货架期品质的影响. 食品工业科技. 2024(12): 285-293 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 魏甜甜,魏勃,王承,李凯,谢彩锋,杭方学. 黄冰糖低温浸渍茉莉花制备风味糖浆工艺优化. 食品工业科技. 2022(12): 181-187 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 邹林武,姜福全,戚智胜. 白冰糖提取玫瑰花风味的工艺研究. 现代食品. 2022(15): 94-96+117 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 宣晓婷,陈思媛,乐耀元,尚海涛,曾昊溟,凌建刚,张文媛. 高水分南美白对虾虾干货架期预测模型的构建. 农产品加工. 2022(19): 78-82+90 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:
