Structure Analysis and Anti-inflammatory Activity Evaluation of Neutral Polysaccharides from Arctium lappa L.
-
摘要: 对水提醇沉法获得的牛蒡粗多糖进行分离纯化并对中性多糖组分进行结构表征和抗炎活性评价。通过DEAE-52纤维素柱制备牛蒡中性多糖,通过单糖组成、分子量、紫外、红外、XRD、粒径和核磁等方法对其进行结构表征,利用硫酸铜诱导的斑马鱼急性炎症模型,评价不同剂量牛蒡粗多糖和牛蒡中性多糖对斑马鱼巨噬细胞移动的影响。通过实时荧光定量PCR分析测定核转录因子激活蛋白-1(AP-1)、环氧化酶-2(COX-2)、IKBα、白细胞介素-1β(IL-1β)、白细胞介素-12(IL-12)和髓样分化因子(MyD88)等不同炎性因子mRNA的表达量。结果表明,牛蒡中性多糖重均分子量为2682 Da,数均分子量为2079 Da,主要由果糖和葡萄糖组成,摩尔比为11.32:1,粒径主要分布在80~110 nm。牛蒡中性多糖主要由β构型的呋喃糖组成,有明显的尖而窄的晶体衍射峰,结晶度较高,核磁结果显示其结构为α-D-吡喃葡萄糖基-(1→2)-[β-D-呋喃果糖基-(1→2)]10-β-D-呋喃果糖基。牛蒡中性多糖可以显著(P<0.05)减少斑马鱼巨噬细胞的迁移数目,且当浓度为100 µg/mL时,巨噬细胞数量较模型组下降了41.11%,抗炎效果最佳;牛蒡中性多糖可能通过沉默炎性细胞因子信号传导,抑制TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路的过度激活,从而抑制炎症反应。本研究可为牛蒡中性多糖的抗炎活性和开发功能性食品提供理论依据。Abstract: A neutral polysaccharide was purified by DEAE-52 cellulose column chromatography from the crude polysaccharide of Arctium lappa L. obtained by hot water extraction and ethanol precipitation, and the structure and anti-inflammatory activity of the neutral polysaccharide were characterized. The structure of Arctium lappa L. neutral polysaccharide were investigated through monosaccharide composition, molecular weight, ultraviolet spectra, infrared spectroscopy analysis, X-ray diffraction spectroscopy, particle size analysis and NMR analysis. The effect of different doses of crude polysaccharide and neutral polysaccharide from Arctium lappa L. on macrophage movement was evaluated in zebrafish acute inflammation model induced by copper sulfate. The mRNA expressions of different inflammatory factors such as nuclear transcription factor activator protein-1 (AP-1), cycloxygenase-2 (COX-2), IKBα, interleukin-1β (IL-1β), interleukin-12 (IL-12) and myeloid differentiation factor (MyD88) were determined by real-time PCR analysis. Results showed that the weight-average molecular weight and number-average molecular weight of Arctium lappa L. neutral polysaccharide were 2682 and 2079 Da, which were mainly composed of fructose and glucose with a molar ratio of 11.32:1. The particle size mainly ranged from 80 nm to 110 nm. The neutral polysaccharide of Arctium lappa L. was mainly composed of furanose with β configuration, with obvious sharp and narrow crystal diffraction peaks and high crystallinity. The NMR analysis showed that its structure was α-D-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-[β-D-fructofuranosyl-(1→2)]10-β-D-fructofuranosyl. Arctium lappa L. neutral polysaccharide could significantly (P<0.05) reduce the migration number of zebrafish macrophages, and the anti-inflammatory effect was the best at the concentration of 100 µg/mL, as well as the number of macrophages decreased by 41.11% compared with the model group. The Arctium lappa L. neutral polysaccharide may be inhibited the overactivation of TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway by silting the signal transduction of inflammatory cytokines. This study could provide a theoretical basis for the anti-inflammatory activity of neutral polysaccharide from Arctium lappa L. and the development of functional foods.
-
牛蒡(Arctium lappa L.)为药食同源的两年生菊科植物,作为食用蔬菜被广泛种植,目前种植的主要品种有:东京理想、东京白肌、柳川理想、白肌大长以及地皇早生等[1-2]。牛蒡根提取物具有广泛的生物活性和药理作用[3]。多糖是牛蒡重要的活性成分,含量占鲜重的13.8%,是菊糖的良好来源[4]。Li等[5]从白肌牛蒡中提取了一种中性多糖,分子量约为2676 Da,主要由果糖和葡萄糖组成,甲基化分析和核磁共振分析表明结构为α-D-吡喃葡萄糖基-(1→2)-[β-D-呋喃果糖基-(1→2)]13-β-D-呋喃果糖基,对氧化损伤具有优异的缓解作用。植物的代谢产物多糖是一种有效的抗炎活性物质,在炎症反应过程中可以在多个靶点发生反应[6]。Wang等[7]和Zhang等[8]从新林牛蒡中提取了一种水溶性多糖,主要由果糖和葡萄糖组成,核磁共振结果证实了牛蒡水溶性多糖具有与菊粉类果聚糖相似的构型,由(2→1)-β-D-呋喃果糖骨架与端基(2→1)-α-D-吡喃葡萄糖相连,同时具有(2→6)-β-D-呋喃果糖支链,分子量为5.12×103 Da,可以干预调节结肠炎小鼠的促炎和抗炎细胞因子,显著减轻结肠炎引起的病理损伤及脂多糖刺激的炎症。柳川理想为目前牛蒡的主要栽培品种,且牛蒡中性多糖在牛蒡粗多糖中含量最高。多糖的提取率、结构和生物活性会因原材料的不同产生较大的差别。
炎症是病原体入侵或感染过程中免疫系统反应的一种防御反应,并伴有各种病理损害[9]。炎症发生时,免疫细胞常通过释放免疫细胞因子抵抗病原体,其中巨噬细胞是免疫细胞的重要组成部分,可以释放NO、IL-1β和TNF-α等多种免疫调节因子[10-11]。Zhang等[12]从牛蒡中提取和纯化了一种碱溶性多糖,发现其可以显著抑制脂多糖诱导的巨噬细胞和小鼠炎症模型中NO和促炎细胞因子的产生,并促进抗炎细胞因子的产生,表明牛蒡多糖可以通过改善促炎和抗炎细胞因子的失调来有效缓解炎症。Zhu等[13]制备了牛蒡多糖及牛蒡多糖-齐墩果酸/熊果酸纳米颗粒,通过CuSO4诱导的斑马鱼炎症模型研究发现牛蒡粗多糖及纳米颗粒通过NF-κB途径在体内发挥较好的抗炎活性,但并未对粗多糖进行分离纯化和进一步结构解析。
本文从柳川理想牛蒡中提取中性多糖,对其进行结构解析,并通过构建硫酸铜诱导的斑马鱼急性炎症模型评价牛蒡中性多糖对炎症细胞因子mRNA的表达量的影响,探究牛蒡中性多糖的抗炎特性。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
牛蒡干片 品种为柳川理想,沛县轶伟食品有限公司;斑马鱼(Tg:zlyz-EGFP) 山东省科学院,养殖条件和饲喂方法按照国家斑马鱼资源中心指导意见进行,本研究中的动物实验在山东省科学院生物研究所完成,项目全过程受到山东省科学院生物研究所实验动物伦理委员会的监督,并通过伦理审查;无水乙醇、氯仿、正丁醇、浓硫酸、苯酚 分析纯,天津市凯通化学试剂有限公司;透析袋(500 Da) 怡康科贸生物试剂耗材试验有限公司;单糖标准品(鼠李糖、阿拉伯糖、半乳糖、葡萄糖、甘露糖和果糖)、葡聚糖(100000 Da)、DEAE-52纤维素 上海源叶生物技术有限公司;五水合硫酸铜、布洛芬、三氟乙酸 西格玛奥德里奇贸易有限公司;RNA提取试剂盒、HiScript® Ⅲ RT SurperMix for qPCR(+gDNA wiper)试剂盒、SYBR(Ace QqPCR) 南京维诺赞生物科技股份有限公司;Supelclean™ ENVI-18 SPE管 德国默克试剂公司;Dionex™ AminoPac™ PA10 IC色谱柱 赛默飞公司。
SPECTRO star Nano全波长酶标仪 广州伯齐生物科技有限公司;UV2450分光光度计 日本岛津公司;Nicolet iS 10傅里叶变换红外光谱 美国赛默飞世尔科技公司;EMPYREAN锐影X射线衍射仪 荷兰帕纳科公司;激光纳米粒度分析仪 英国马尔文公司;AVANCE IIIHD400高分辨率核磁共振光谱仪 德国布鲁克公司;ESEN-AW-S1斑马鱼养殖饲养设备 北京爱生科技公司;BIO-RAD C100梯度PCR仪 赛默飞公司;LightCycler 96荧光定量PCR仪 罗氏公司;SZX16型荧光显微镜及DP2-BSW图像采集系统 日本奥林巴斯公司;AXIO Zoom.V16蔡司体式显微镜 德国蔡司公司;SPX-280B-G型博讯光照培养箱 上海基星生物科技公司;CBM-20A高效液相色谱仪(配备RID-10A检测器) 日本岛津公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 牛蒡中性多糖的制备
采用水提醇沉法提取牛蒡多糖[14]。称取牛蒡粉末于圆底烧瓶中,以料液比1:10稀释,热水回流提取1.5 h,重复提取3次。合并滤液,浓缩,加入4倍体积无水乙醇醇沉,沉淀用水复溶,二次醇沉后,经Sevag法脱蛋白,冷冻干燥得牛蒡粗多糖。准确称量5 g牛蒡粗多糖用100 mL去离子水溶解,离心(8000 r/min,15 min)过0.45 μm水系滤膜,用含有500 g DEAE-52纤维素的玻璃层析柱(6.0×100.0 cm)进行分离[15]。样品以去离子水洗脱,流速为5 mL/min。每管收集洗脱液50 mL,在490 nm处用苯酚-硫酸法跟踪检测,计算得率及总糖含量,葡萄糖标准曲线回归方程为Y=5.7496X−0.0299,R2=0.9992。经过分离后得牛蒡中性多糖,使用截流量500 Da的透析袋进行透析,冷冻干燥后进行后续分析。
式中:W代表牛蒡多糖得率(%);m1为冻干后粗多糖的质量(g);m2为牛蒡粉末总重(g)。
式中:ω代表牛蒡多糖得率(%);C是根据标准曲线计算的多糖浓度(mg/mL);n为稀释倍数;V为多糖溶液的体积(mL);M为多糖样品质量(mg)。
1.2.2 牛蒡中性多糖结构表征
1.2.2.1 单糖组成
使用高效阴离子交换色谱法结合脉冲安培检测器(HPAEC-PAD)分析样品的单糖组成[16]。用2 mL的2.0 mol/L三氟乙酸将10 mg的牛蒡粗多糖和中性多糖在80 ℃下水解5 h。水解后加入去离子水并多次旋蒸除去残留的三氟乙酸,使溶液呈中性,用超纯水将溶液定容至10 mL,用Supelclean™ ENVI-18 SPE管(500 mg/6 mL)和0.22 μm水系微孔过滤器进行澄清净化。色谱柱为AminoPac™ PA10 IC(Dionex™,3×250 mm),流动相为0.20 mol/L氢氧化钠溶液,流速为0.25 mL/min,柱温30 ℃。
1.2.2.2 分子量测定
采用高效液相色谱仪(配备RID-10A示差检测器)测定牛蒡中性多糖的分子量[17]。配制10 mg/mL的牛蒡中性多糖溶液,用0.22 μm的水系滤头过滤。色谱条件:色谱柱为Shodex OHpak SB-803 HQ(300×8 mm,6 μm)及保护柱串联,流动相为0.3 mol/L硝酸钠溶液(含0.02%叠氮化钠),流速为0.3 mL/min,柱温为25 ℃,进样量为20 μL。
1.2.2.3 紫外光谱分析
将牛蒡中性多糖配制成1 mg/mL水溶液,使用全波长紫外-可见光分光光度计对样品进行全波长扫描,波长范围为200~800 nm[18]。重复3次。
1.2.2.4 傅里叶变换红外光谱分析
采用傅里叶变换红外光谱-衰减全反射光谱技术对样品进行分析[19]。将牛蒡多糖粉末约5 mg放置在锥形附件板上并压实,在4000~500 cm−1波数范围内进行扫描分析,仪器扫描次数为64次,分辨率4 cm−1。
1.2.2.5 X-射线衍射分析
X-射线衍射仪配备Cu靶陶瓷X光管,加速电压40 kV,电流40 mA,在2θ=5°~80°范围内测定样品的X射线衍射强度[20]。
1.2.2.6 粒径测定
采用激光纳米粒度分析仪测量样品的粒径大小,设定散射角为90°,折光指数1.330,测定温度25 ℃,保温2.0 min,每个样品均重复三次[21]。
1.2.2.7 核磁共振分析
将50 mg牛蒡中性多糖溶解在0.5 mL D2O中。样品在室温30 ℃下使用高分辨率核磁共振光谱仪进行结构分析,并用MestReNova处理数据。
1.2.3 牛蒡中性多糖的抗炎活性评价
1.2.3.1 对斑马鱼巨噬细胞移动的影响
将状态良好、发育3 d的斑马鱼胚胎置于荧光显微镜下进行观察,挑选出发绿色荧光(巨噬细胞)的幼鱼,移入24孔板,每孔12条幼鱼。设置空白对照组(胚胎培养用水)、阳性对照组(20 µmol/L布洛芬)、模型组(40 µmol/L硫酸铜)、牛蒡粗多糖(50、100、200 µg/mL)组和牛蒡中性多糖(50、100、200 µg/mL)组。首先,将空白对照组和模型组分别加入2 mL胚胎培养用水,其余各组加入2 mL设定浓度的培养溶液,置于光照培养箱作用3 h后,避光加入2 µL 4 mol/L的硫酸铜溶液(空白对照组除外),使硫酸铜终浓度为40 µmol/L,置于光照培养箱中避光作用1 h后,在荧光显微镜下观察不同组处理方法对斑马鱼巨噬细胞迁移的影响,统计泄殖腔后迁移至侧线的巨噬细胞数量,评价不同组处理方法对斑马鱼巨噬细胞的影响。
1.2.3.2 实时荧光定量PCR分析
收集斑马鱼约30只,加入裂解液,置于破碎仪中将组织彻底研磨均匀,采用RNA提取试剂盒提取RNA。在RNA free条件下,通过HiScript® Ⅲ RT SurperMix for qPCR(+gDNA wiper)试剂盒逆转录RNA,获得cDNA。使用实时定量PCR仪进行实时定量聚合酶链式反应(qRT-PCR),测定炎性因子IL-1β、COX-2、MyD88、AP-1、IKBα及IL-12α的表达水平。cDNA扩增包括一个循环95 ℃预变性30 s,40个循环95 ℃变性10 s和60 ℃退火10 s,然后是一个循环95 ℃ 15 s,60 ℃ 60 s,95 ℃ 15 s。每个反应体积包括2×ChamQ Universal SYBR qPCR Master(10.0 µL)、正向和反向引物(0.4 µL)、cDNA(1 µL)和ddH2O(8.2 µL)。使用溶解曲线进行相对定量以进行质量控制,通过Relative expression=2−△△Ct计算每个样品中基因表达的结果,以β-actin基因作为数据分析的参照。引物由济南博尚有限公司合成。引物序列如表1所示。
表 1 引物序列Table 1. Primer sequences名称 引物序列 β-actin Forward 5'-CTCCGGTATGTGCAAAGC-3' Reverse 5'-CCATCACTCCCTGATGTCT-3' IL-1β Forward 5'-CTCAGCCTGTGTGTTTGGGA-3' Reverse 5'-GGGACATTTGACGGACTCG-3' COX-2 Forward 5'-ATCCTGTTGTCAAGGTCCCA-3' Reverse 5'-CAAGGGTGCGGGTGTAAT-3' MyD88 Forward 5'-ACCATCGCCAGTGAGCTTAT-3' Reverse 5'-CAGATGGTCAGAAAGCGCAG-3' AP-1 Forward 5'-CCACCGCTCTCTCCTATC-3' Reverse 5'-ATCCTCTCCAGTTTCCTCTT-3' IKBα Forward 5'-GGTGGAAAGACTCCTGAAAGC-3' Reverse 5'-TGTAGTTAGGGAAGGTAAGAATG-3' IL-12α Forward 5'-ACTCCTACAAGCCCAGCAC-3' Reverse 5'-GGACACTCGGTCGTCAAAC-3' 1.3 数据处理
每组试验均重复3次,采用Origin 2017软件绘图,数据以平均值±标准偏差(Mean±SD)表示,使用SPSS 25.0统计软件进行单因素方差分析(One-Way ANOVA),使用Waller-Duncan(W)进行多重比较分析。P<0.05为有显著性差异,P<0.01为有极显著性差异。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 牛蒡粗多糖的提取和分离纯化
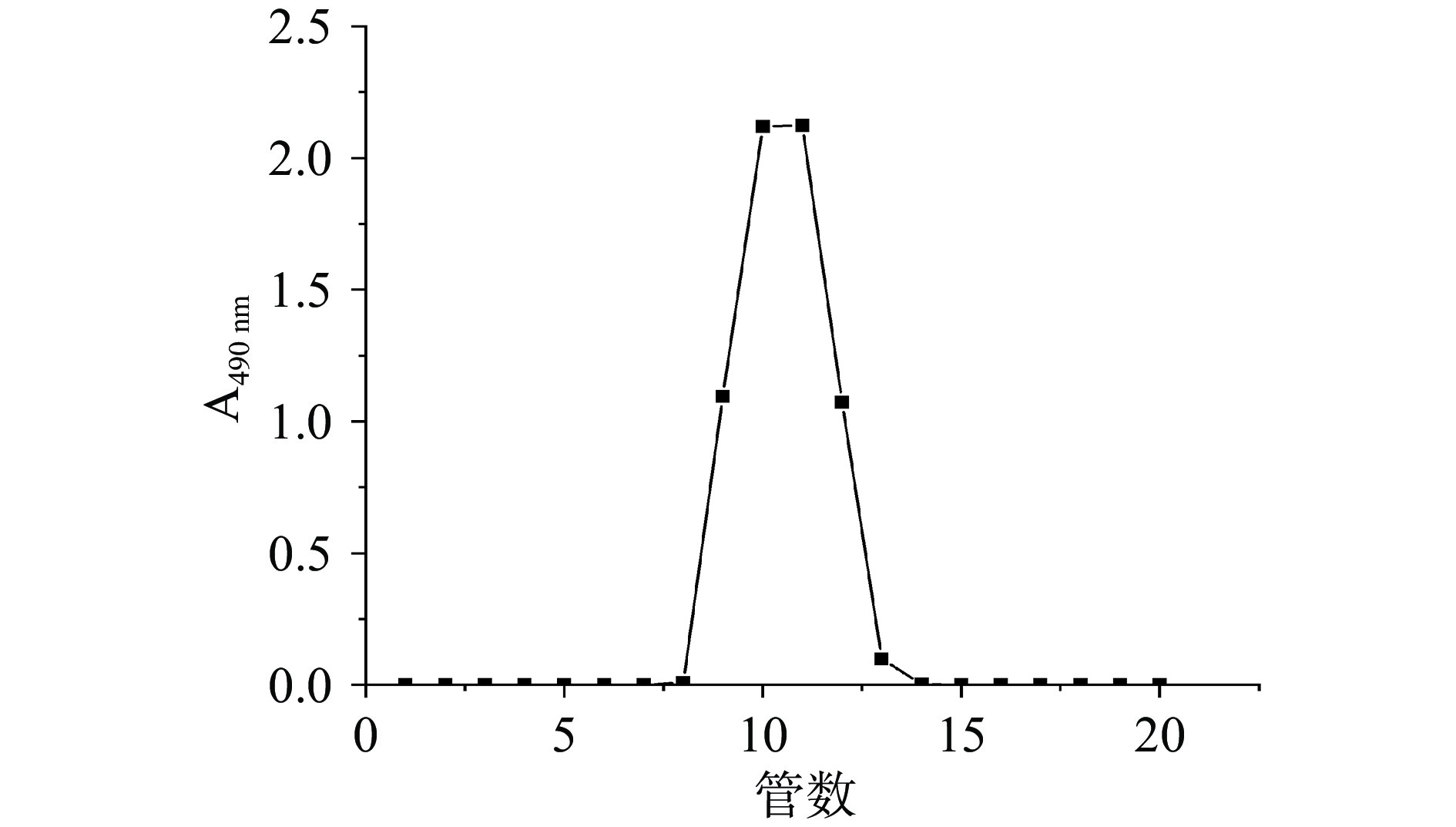
牛蒡粗多糖的DEAE-52纤维素柱洗脱曲线见图1。牛蒡粗多糖得率为12.23%,为棕色粉末,苯酚硫酸法测得糖含量约为70.48%。经DEAE-52纤维素柱纯化、冷冻干燥后,得到白色粉末状牛蒡中性多糖,回收率为56.59%,糖纯度为95.71%。
2.2 牛蒡中性多糖的结构表征
2.2.1 单糖组成
牛蒡粗多糖和牛蒡中性多糖的单糖组成色谱图见图2。牛蒡粗多糖中主要单糖组分及其摩尔比为果糖:葡萄糖:阿拉伯糖:半乳糖:鼠李糖=83.95:2.3:8.4:4.72:0.63。牛蒡中性多糖中主要单糖组分及其摩尔比为果糖:葡萄糖:阿拉伯糖:半乳糖=90.82:8.02:0.77:0.39。牛蒡粗多糖主要由果糖、葡萄糖、阿拉伯糖和半乳糖组成,牛蒡中性多糖主要由果糖和葡萄糖组成,摩尔比为11.32:1。果糖和葡萄糖均为牛蒡粗多糖和牛蒡中性多糖的主要成分,然而经DEAE-52纯化后牛蒡中性多糖中几乎不含有阿拉伯糖和半乳糖。这一结果与Li等[5]从白肌牛蒡中提取的菊粉型果聚糖有相似的单糖组成,果糖是牛蒡中性多糖中主要的单糖。
2.2.2 分子量
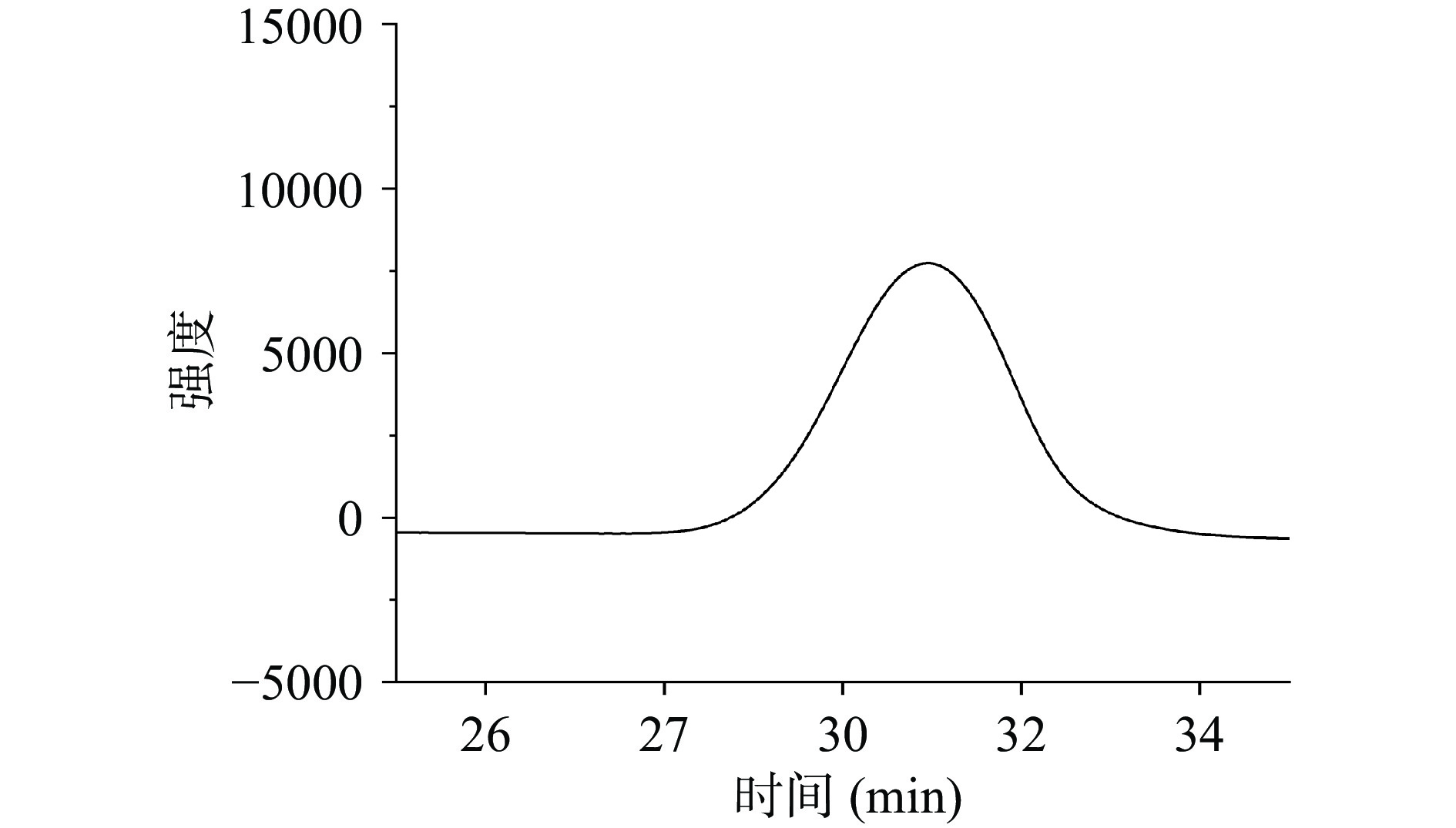
牛蒡中性多糖的分子量谱图如图3所示,表现出单一且相对对称的峰,表明牛蒡中性多糖纯度较高[22]。通过葡聚糖标准曲线:y=0.001359996x3−0.1188730x2+3.208289x−22.38322(R2=0.9999),将出峰时间代入标曲,得牛蒡中性多糖的重均分子量(Mw)为2682 Da,数均分子量(Mn)为2079 Da,Mw/Mn的比值(多分散系数)为1.2905。
2.2.3 紫外光谱分析
由图4可知,牛蒡中性多糖在260和280 nm处没有紫外吸收,说明经过纯化后的牛蒡中性多糖中不含核酸和蛋白质。
2.2.4 傅里叶变换红外光谱分析
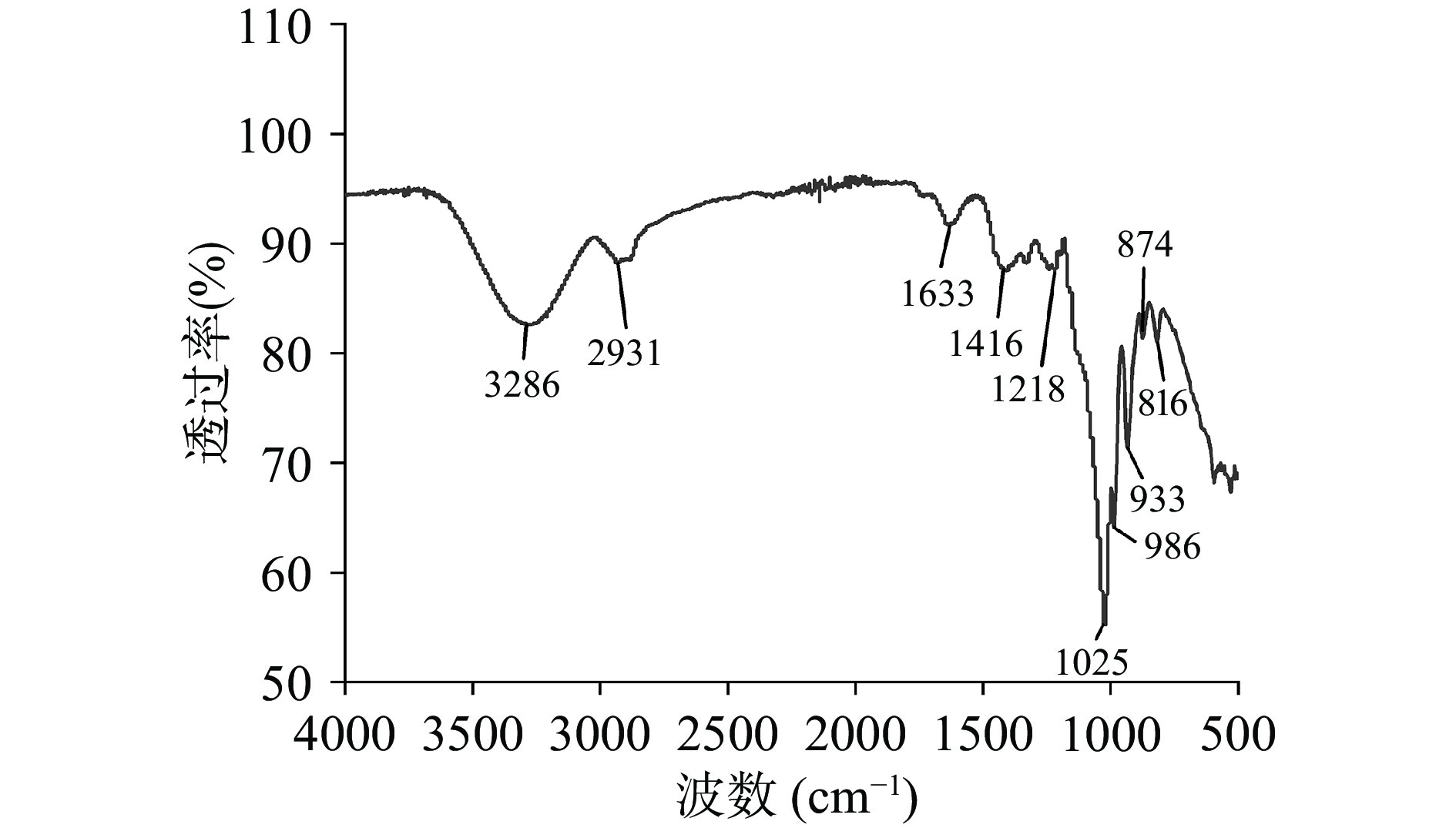
牛蒡中性多糖的傅里叶变换红外光谱如图5所示。在4000~500 cm−1范围内的吸收带为多糖的特征吸收峰[23]。在3286 cm−1处的宽拉伸峰属于O-H键伸缩振动;2931 cm−1附近的吸收峰对应于不对称C-H伸缩振动[24]。1633和1416 cm−1处的峰值分别属于对称C=O伸缩振动和不对称C=O伸缩振动耦合的C-H弯曲振动。1218 cm−1附近及1025 cm−1附近的吸收谱带是呋喃糖环中C-O-H和C-O-C伸缩振动的特征[25]。在933 cm−1处对应α-D-呋喃果糖基[26]。在816和874 cm−1处的吸收峰为长链菊粉的特征指纹区域,包括β(2→1)-D-糖苷键[27],表明存在带有β构型糖苷键的呋喃糖。红外光谱显示,牛蒡中性多糖属于菊粉型果聚糖。
2.2.5 XRD分析
牛蒡中性多糖的X-射线衍射图谱如图6所示。通常晶体表现为尖而窄的特征峰,而非晶态物质表现为宽而弥散的衍射峰。结果显示:多糖在2θ为12.16°、16.35°、17.85°和21.3°处出现了明显的尖而窄的晶体衍射峰,表明牛蒡中性多糖中不仅有微晶结构,也有晶体和非晶结构并存的多晶体系。这与Lou等[28]研究的天然长链菊粉晶体结构相似。
2.2.6 粒径测定
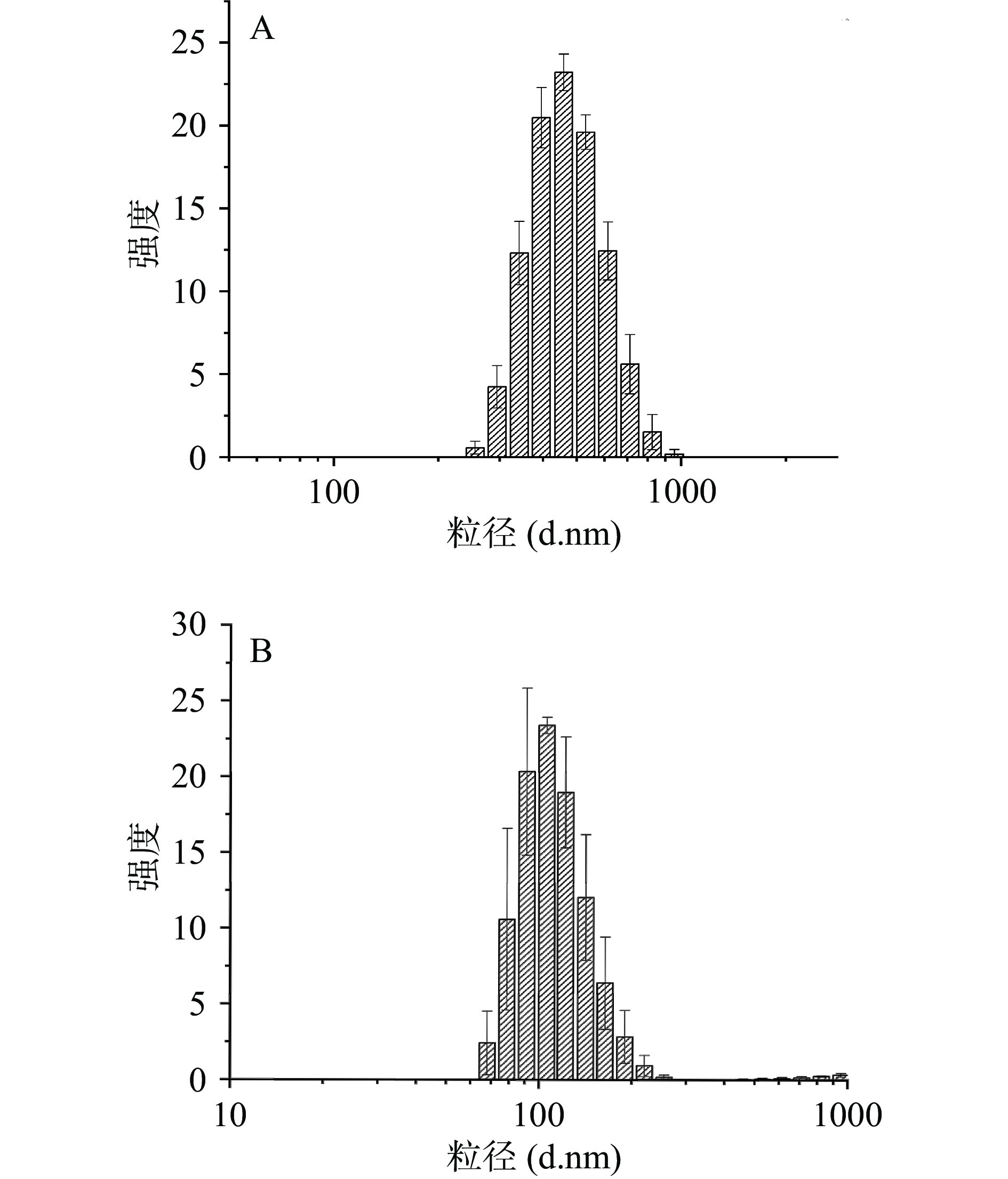
如图7,牛蒡粗多糖粒径主要分布在200~800 nm范围内,而经过DEAE-52纤维素柱分离后的牛蒡中性多糖粒径主要分布在80~110 nm范围内。与粗多糖相比,牛蒡中性多糖粒径明显减小,粒径的减小可能是由于在分离和纯化过程中多糖分子之间相互作用的减少[29]。
2.2.7 核磁共振波谱分析
在1H-NMR谱图(图8A)中,牛蒡中性多糖的化学位移(δ,ppm)在3.40~5.50 ppm之间,表现出多糖的典型特征。在δH 5.44 ppm处有一个低峰,这个信号的耦合常数(J)为2.4 Hz,是α-构型的糖苷异位质子;其余峰值在δH 4.21~4.29 ppm、δH 4.06~4.15 ppm和δH 3.66~3.96 ppm之间,其中δH 4.21~4.29 ppm为果糖的H-3。13C-NMR谱图(图8B)的δC (ppm)在103.3、81.1、77.1、74.4、62.2和61.0处显示了6个强信号,这些信号归因于果聚糖残基[30]。根据DEPT-135谱图(图8C),δC 103.3处的信号是由糖基残基C-1和C-2位置的异头碳共振引起的,δC 62.2和δC 61.0处的信号分别由糖基残基C-1和C-2位置的碳信号引起的。此外,δC 92.5的次要信号为葡萄糖基的异头碳共振,属于α-D构型[31]。
表2为二维核磁HSQC谱图(图8D)、1H-1H COSY谱图(图8E)和HMBC谱(图8F)中得到的主要糖残基的氢和碳的信号归属(δ)。δC 61.0/δH 3.71、3.92为果聚糖残基C-1的信号,而δC 77.1/δH 4.26、δC 74.4/δH 4.10、δC 81.1/δH 3.86和δC 62.2/δH 3.78、3.83分别为果聚糖残基C-3、C-4、C-5和C-6的信号[32]。此外,δC 92.5/δH 5.44处的次要信号归属为葡萄糖残基C-1信号,而δC 71.3/δH 3.55、δC 73.5/δH 3.74、δC 70.3/δH 3.49和δC −/δH 3.84为1H-1H COSY光谱中葡萄糖残基的C-2、C-3、C-4、C-5[32]。通过HMBC谱(图8F)进一步阐明牛蒡中性多糖中单糖的排布。葡萄糖基残基的异位质子H-1(δH 5.44 ppm)与果糖基残基的C-2 (δC 103.3 ppm)呈强交叉峰,表明葡萄糖和果糖之间存在1,2连接。果糖残基C-2(δC 103.3 ppm)与果糖残基H-1(δH 3.71 ppm,δH 3.92 ppm)的相关性较强,证明了果糖残基之间2,1连接的存在。由此可知,牛蒡中性多糖主要由α-D-吡喃葡萄糖基-(1→2)-[β-D-呋喃果糖基-(1→2)]10-β-D-呋喃果糖基组成,推测的牛蒡中性多糖结构如图9所示[33]。这与Li等[5]从白肌牛蒡中提取的菊粉型果聚糖结构类似,两个品种分子量略有不同,原因除了品种差异之外,推测还可能与地理环境、日照、降水等环境因素有关。
表 2 牛蒡中性多糖的1H和13C-NMR谱的化学位移Table 2. Chemical shift (ppm) of 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectra of neutral polysaccharide from Arctium lappa L.位置 果糖 葡萄糖 1H-NMR 13C-NMR 1H-NMR 13C-NMR 1 3.71,3.92 61.0 5.44(d,J=2.4 Hz) 92.5 2 / 103.3 3.55 71.3 3 4.26 77.1 3.74 73.5 4 4.10 74.4 3.49 70.3 5 3.86 81.1 3.84 / 6 3.78,3.83 62.2 / / 2.3 牛蒡中性多糖的抗炎活性评价
2.3.1 对斑马鱼巨噬细胞移动的影响
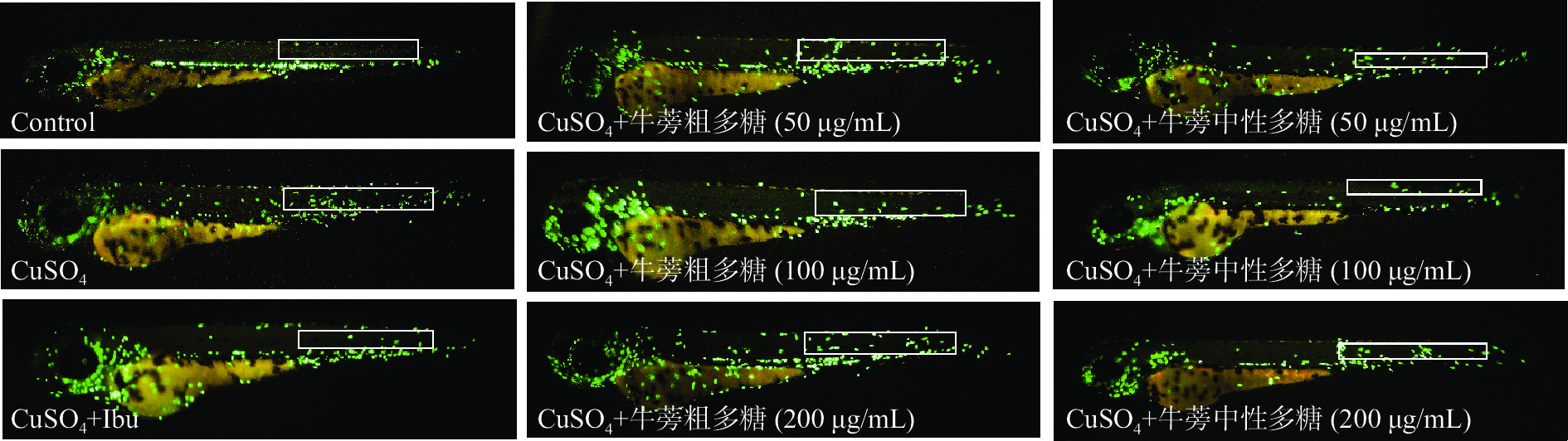
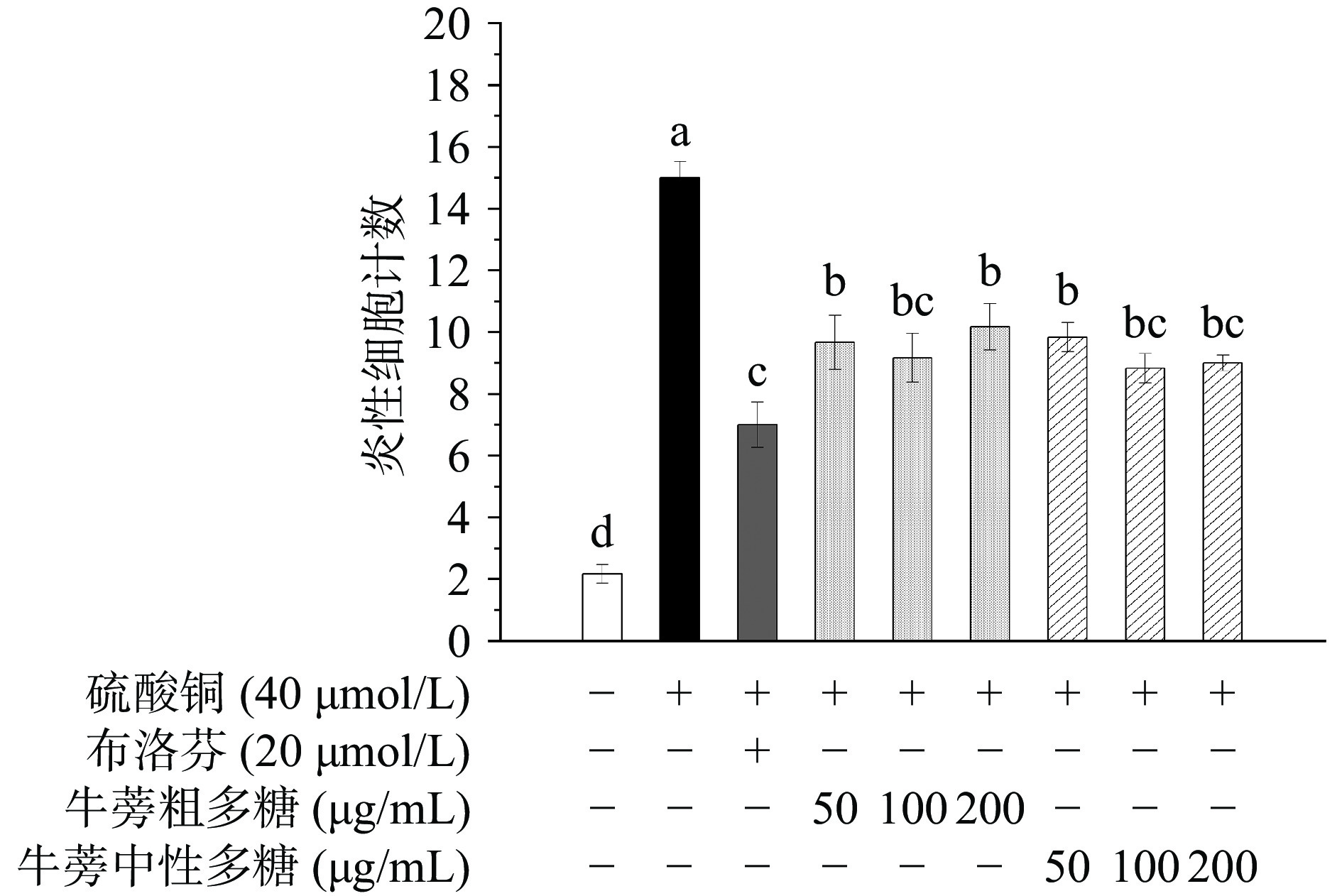
将空白对照组、阳性对照组、模型组、牛蒡粗多糖(50、100、200 µg/mL)组和牛蒡中性多糖(50、100、200 µg/mL)组处理后,于荧光显微镜下进行观察并拍照。结果见图10与图11。与空白对照组相比,模型组斑马鱼的巨噬细胞向其侧线处发生了迁移。与空白对照组相比,模型对照组斑马鱼炎症细胞数量显著(P<0.05)上升,表明成功建立了CuSO4诱导的斑马鱼炎症模型[12];使用阳性药物布洛芬处理后,斑马鱼巨噬细胞的迁移数目明显减少,且与模型组相比具有显著性差异(P<0.05),表明布洛芬对炎症反应具有较好的抑制效果。牛蒡粗多糖(50、100、200 µg/mL)组和牛蒡中性多糖(50、100、200 µg/mL)组巨噬细胞迁移数目较模型组显著减少,均表现出较好的抑制炎症作用。相比之下,牛蒡粗多糖为100 µg/mL时,巨噬细胞数量较模型组下降了38.89%,抗炎效果最佳;牛蒡中性多糖为100 µg/mL时,巨噬细胞数量较模型组下降了41.11%,抗炎效果最佳;且当浓度为200 µg/mL时,牛蒡中性多糖的抗炎效果略优于牛蒡粗多糖,表明经过DEAE-52分离纯化有助于提高牛蒡多糖的抗炎活性。
![]() 图 11 不同浓度多糖处理的斑马鱼巨噬细胞迁移数量图注:不同字母表示差异性显著(P<0.05,n=3),相同字母表示没有显著性差异(P>0.05);图12同。Figure 11. Migrating number of zebrafish macrophages with different polysaccharide concentrations
图 11 不同浓度多糖处理的斑马鱼巨噬细胞迁移数量图注:不同字母表示差异性显著(P<0.05,n=3),相同字母表示没有显著性差异(P>0.05);图12同。Figure 11. Migrating number of zebrafish macrophages with different polysaccharide concentrations2.3.2 对斑马鱼炎症因子表达量的影响
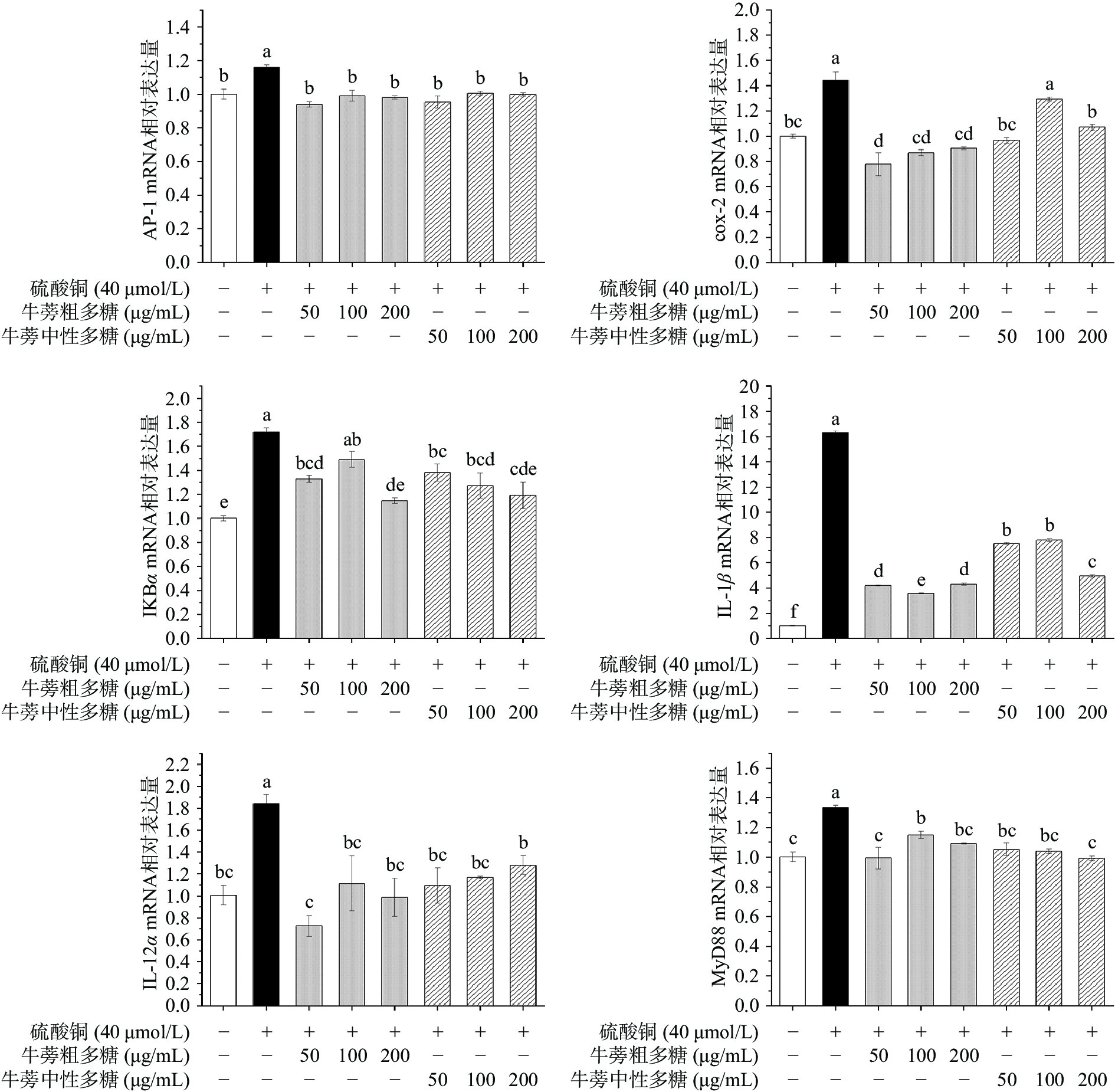
使用实时荧光定量PCR法检测不同组间斑马鱼炎症基因的变化情况,结果见图12所示。核转录因子激活蛋白-1(AP-1)是一种重要的真核转录因子,可以诱导细胞凋亡并诱导黏附因子和炎症因子的合成,AP-1表达的失调与炎症的发生和进展密切相关[34]。髓样分化因子MyD88是一种细胞质衔接分子,通过沉默MyD88依赖性TLR1/2信号传导可发挥抗炎作用[35]。Toll样受体(TLR)是参与非特异性免疫的重要蛋白质分子,配体刺激TLR4使其表达增加,通过MyD88依赖性或非依赖性信号通路诱导NF-κB的活性,导致NF-κB的激活,然后释放炎性细胞因子(IL-1、IL-6、IL-8、IL-12、TNF-α和IFN-γ等)、COX-2等,从而发挥早期免疫反应的作用[36-37]。通过测定不同炎性细胞因子mRNA的表达量,发现空白组中炎性细胞因子mRNA的表达量普遍较低;加入硫酸铜后的模型组炎性细胞因子mRNA的表达量明显上升,说明成功建立了炎症模型。同时,牛蒡粗多糖及牛蒡中性多糖的加入使炎性细胞因子mRNA的表达量显著下降,与模型组相比,牛蒡粗多糖处理组六种炎症因子mRNA表达量的最大下降率分别可达23.69%、38.01%、60.69%、39.71%、78.39%及25.53%;牛蒡中性多糖处理组六种炎症因子mRNA表达量的最大下降率分别可达24.74%、40.54%、49.63%、27.80%、69.64%及26.97%。表明牛蒡粗多糖及牛蒡中性多糖可以通过下调炎症因子表达量来发挥抗炎作用。因此,推测牛蒡中性多糖可能通过沉默炎症细胞因子信号传导,抑制TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB信号通路的过度激活,从而抑制炎症反应。Zhang等[12]研究发现炎症因子的失调可能与NF-κB信号通路有关,而牛蒡水溶性多糖可以显着降低TNF-α、IL-1β和IL-6炎性因子的表达水平,并抑制NO的释放,表明牛蒡多糖有良好的抗炎活性,有效调节促炎和抗炎细胞因子的水平,增强免疫活性,同时抑制病原菌的发育,促进有益微生物的生长。
3. 结论
本研究从柳川理想牛蒡中提取并制备获得牛蒡中性多糖,重均分子量为2682 Da,数均分子量为2079 Da,主要由果糖和葡萄糖组成,摩尔比为11.32:1,且不同品种的牛蒡多糖分子量会存在一定差异。牛蒡中性多糖粒径主要分布在80~110 nm,由β构型的呋喃糖组成,其结构可能为α-D-吡喃葡萄糖基-(1→2)-[β-D-呋喃果糖基-(1→2)]10-β-D-呋喃果糖基。斑马鱼体内抗炎活性表明,牛蒡中性多糖处理可使斑马鱼侧线巨噬细胞迁移数目较模型组显著(P<0.05)减少,通过检测炎症因子的mRNA表达量发现牛蒡中性多糖可以通过下调炎症因子表达量来发挥抗炎作用,表现出较好的抑制炎症作用。研究结果表明牛蒡中性多糖具有较好的抗炎活性,可为牛蒡中性多糖功能性食品的开发提供依据。
-
图 11 不同浓度多糖处理的斑马鱼巨噬细胞迁移数量图
注:不同字母表示差异性显著(P<0.05,n=3),相同字母表示没有显著性差异(P>0.05);图12同。
Figure 11. Migrating number of zebrafish macrophages with different polysaccharide concentrations
表 1 引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequences
名称 引物序列 β-actin Forward 5'-CTCCGGTATGTGCAAAGC-3' Reverse 5'-CCATCACTCCCTGATGTCT-3' IL-1β Forward 5'-CTCAGCCTGTGTGTTTGGGA-3' Reverse 5'-GGGACATTTGACGGACTCG-3' COX-2 Forward 5'-ATCCTGTTGTCAAGGTCCCA-3' Reverse 5'-CAAGGGTGCGGGTGTAAT-3' MyD88 Forward 5'-ACCATCGCCAGTGAGCTTAT-3' Reverse 5'-CAGATGGTCAGAAAGCGCAG-3' AP-1 Forward 5'-CCACCGCTCTCTCCTATC-3' Reverse 5'-ATCCTCTCCAGTTTCCTCTT-3' IKBα Forward 5'-GGTGGAAAGACTCCTGAAAGC-3' Reverse 5'-TGTAGTTAGGGAAGGTAAGAATG-3' IL-12α Forward 5'-ACTCCTACAAGCCCAGCAC-3' Reverse 5'-GGACACTCGGTCGTCAAAC-3' 表 2 牛蒡中性多糖的1H和13C-NMR谱的化学位移
Table 2 Chemical shift (ppm) of 1H-NMR and 13C-NMR spectra of neutral polysaccharide from Arctium lappa L.
位置 果糖 葡萄糖 1H-NMR 13C-NMR 1H-NMR 13C-NMR 1 3.71,3.92 61.0 5.44(d,J=2.4 Hz) 92.5 2 / 103.3 3.55 71.3 3 4.26 77.1 3.74 73.5 4 4.10 74.4 3.49 70.3 5 3.86 81.1 3.84 / 6 3.78,3.83 62.2 / / -
[1] 李玲玉, 邱志常, 朱姗姗, 等. 响应面法优化牛蒡多糖超声辅助提取工艺与抗氧化活性评价[J]. 食品科技,2020,45(11):197−204, 211. [LI L Y, QIU Z C, ZHU S S, et al. Optimization of polysaccharides from Arctium lappa L. by ultrasound-assisted extraction using response surface methodology and its antioxidant activities[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,45(11):197−204, 211. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2020.11.032 LI L Y, QIU Z C, ZHU S S, et al. Optimization of polysaccharides from Arctium lappa L. by ultrasound-assisted extraction using response surface methodology and its antioxidant activities[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2020, 45(11): 197-204, 211. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2020.11.032
[2] 朱姗姗, 张斌, 朱文卿, 等. 牛蒡多糖特性分析及对脂多糖诱导巨噬细胞炎症的调节作用[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(15):272−278. [ZHU S S, ZHANG B, ZHU W Q, et al. Analysis of properties of burdock polysaccharide and its regulatory effect on lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophage inflammation[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(15):272−278. ZHU S S, ZHANG B, ZHU W Q, et al. Analysis of properties of burdock polysaccharide and its regulatory effect on lipopolysaccharide-induced macrophage inflammation[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(15): 272-278.
[3] RODRIGUEZ J M F, DE SOUZA A R C, KRÜGER R L, et al. Kinetics, composition and antioxidant activity of burdock (Arctium lappa) root extracts obtained with supercritical CO2 and co-solvent[J]. The Journal of Supercritical Fluids,2018,135:25−33. doi: 10.1016/j.supflu.2017.12.034
[4] 王禹, 马维红. 牛蒡化学成分及其对心血管疾病保护作用的研究进展[J]. 华夏医学,2020,33(3):178−181. [WANG Y, MA W H. Research progress on the chemical constituents of Arctium lappa L. and its protective effects on cardiovascular disease[J]. Acta Medicinae Sinica,2020,33(3):178−181. doi: 10.19296/j.cnki.1008-2409.2020-03-051 WANG Y, MA W H. Research progress on the chemical constituents of Arctium lappa L. and its protective effects on cardiovascular disease[J]. Acta Medicinae Sinica, 2020, 33(3): 178-181. doi: 10.19296/j.cnki.1008-2409.2020-03-051
[5] LI L Y, QIU Z C, DONG H J, et al. Structural characterization and antioxidant activities of one neutral polysaccharide and three acid polysaccharides from the roots of Arctium lappa L.: A comparison[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,182:187−196. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.03.177
[6] WANG K P, TANG Z H, ZHENG Z M, et al. Protective effects of Angelica sinensis polysaccharide against hyperglycemia and liver injury in multiple low-dose streptozotocin-induced type 2 diabetic BALB/c mice[J]. Food & Function, 2016, 7: 4889−4897.
[7] WANG Y, ZHANG N F, KAN J, et al. Structural characterization of water-soluble polysaccharide from Arctium lappa and its effects on colitis mice[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2019,213:89−99. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.02.090
[8] ZHANG N F, WANG Y, KAN J, et al. In vivo and in vitro anti-inflammatory effects of water-soluble polysaccharide from Arctium lappa[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,135:717−724. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.171
[9] MAGHSOUMI-NOROUZABAD L, SHISHEHBOR F, ABED R, et al. Effect of Arctium lappa linne (Burdock) root tea consumption on lipid profile and blood pressure in patients with knee psteoarthritis[J]. Journal of Herbal Medicine, 2019, 17-18: 100266.
[10] YU J B, HU M Q, WANG Y Y, et al. Extraction, partial characterization and bioactivity of polysaccharides from Senecio scandens Buch.-Ham[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,109:535−543. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.12.119
[11] XIE Z L, WANG Y, HUANG J Q, et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of polysaccharides from Phellinus linteus by regulating the NF-κB translocation in LPS-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,129:61−67. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.02.023
[12] ZHANG X, ZHANG N F, KAN J, et al. Anti-inflammatory activity of alkali-soluble polysaccharides from Arctium lappa L. and its effect on gut microbiota of mice with inflammation[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,154:773−787. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.03.111
[13] ZHU S S, QIU Z C, QIAO X G, et al. Creating burdock polysaccharide-oleanolic acid-ursolic acid nanoparticles to deliver enhanced effects: Fabrication, structural characterization and property evaluation[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness,2023,12(2):454−466. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2022.07.047
[14] CHEN S D, GUAN X Y, YONG T Q, et al. Structural characterization and hepatoprotective activity of an acidic polysaccharide from Ganoderma lucidum[J]. Food Chemistry: X,2022,13:100204. doi: 10.1016/j.fochx.2022.100204
[15] LIU M, GONG Z, LIU H, et al. Structural characterization and anti-tumor activity in vitro of a water-soluble polysaccharide from dark brick tea[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2022,205:615−625. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2022.02.089
[16] ZHU Z P, CHEN J, CHEN Y, et al. Extraction, structural characterization and antioxidant activity of turmeric polysaccharides[J]. LWT,2022,154:112805. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112805
[17] MA L Y, XU R, LIN H F, et al. Structural characterization and antioxidant activities of polysaccharides from okra (Abelmoschus esculentus (L.) Moench) pericarp[J]. Bioactive Carbohydrates and Dietary Fibre,2021,26:100277. doi: 10.1016/j.bcdf.2021.100277
[18] 汤陈鹏, 吕峰, 王蓉琳. 孔石莼多糖锌结构表征与体外降血糖活性[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(7):52−58. [TANG C P, LÜ F, WANG R L. Structural characterization and hypoglycemic activity in vitro of Ulva pertusa polysaccharides-zinc complex[J]. Food Science,2020,41(7):52−58. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190320-263 TANG C P, LV F, WANG R L. Structural characterization and hypoglycemic activity in vitro of Ulva pertusa polysaccharides-zinc complex[J]. Food Science, 2020, 41(07): 52-58. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190320-263
[19] ROMANO N, ARAUJO-ANDRADE C, LECOT J, et al. Infrared spectroscopy as an alternative methodology to evaluate the effect of structural features on the physical-chemical properties of inulins[J]. Food Research International,2018,109:223−231. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.04.032
[20] PATEL M K, TANNA B, MISHRA A, et al. Physicochemical characterization, antioxidant and anti-proliferative activities of a polysaccharide extracted from psyllium (P. ovata) leaves[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,118:976−987. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.06.139
[21] 朱文卿, 朱姗姗, 何秋霞, 等. 牛蒡多糖与绿原酸对斑马鱼氧化损伤的协同抗氧化作用[J]. 中国食品学报,2022,22(4):95−103. [ZHU W Q, ZHU S S, HE Q X, et al. Synergistic antioxidant effect of burdock polysaccharide and chlorogenic acid on zebrafish oxidative damage[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2022,22(4):95−103. ZHU W Q, ZHU S S, HE Q X, et al. Synergistic antioxidant effect of burdock polysaccharide and chlorogenic acid on zebrafish oxidative damage[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology, 2022, 22(4): 95-103.
[22] 郝林华, 陈靠山, 李光友. 牛蒡菊糖及其制备方法的研究[J]. 中国海洋大学学报(自然科学版),2004(3):423−428. [HAO L H, CHEN K S, LI G Y. Study on great burdock inulin and its extraction technique[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China (Natural Science Edition),2004(3):423−428. HAO L H, CHEN K S, LI G Y. Study on great burdock inulin and its extraction technique[J]. Periodical of Ocean University of China(Natural Science Edition), 2004, (3): 423-428.
[23] LIU W, WANG J J, ZHANG Z Z, et al. In vitro and in vivo antioxidant activity of a fructan from the roots of Arctium lappa L.[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2014,65:446−453. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2014.01.062
[24] ZHANG J J, TAN W Q, ZHAO P Z, et al. Facile synthesis, characterization, antioxidant activity, and antibacterial activity of carboxymethyl inulin salt derivatives[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2022,199:138−149. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.12.140
[25] EL-KHOLY W M, AAMER R A, ALI A N A. Utilization of inulin extracted from chicory (Cichorium intybus L.) roots to improve the properties of low-fat synbiotic yoghurt[J]. Annals of Agricultural Sciences,2020,65(1):59−67. doi: 10.1016/j.aoas.2020.02.002
[26] 胡彦波, 翟丽媛, 刘扬, 等. 薇菜多糖的分离纯化及体外抗氧化活性[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(1):59−66. [HU Y B, ZHAI L Y, LIU Y, et al. Isolation, purification and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Osmunda japonica[J]. Food Science,2022,43(1):59−66. HU Y B, ZHAI L Y, LIU Y, et al. Isolation, purification and antioxidant activity of polysaccharides from Osmunda japonica[J]. Food Science, 2022, 43(1): 59-66.
[27] PETKOVA N T, SHEROVA G, DENEV P P. Characterization of inulin from dahlia tubers isolated by microwave and ultrasound-assisted extractions[J]. International Food Research Journal,2018,25(5):1876−1884.
[28] LOU X Q, LUO D L, YUE C H, et al. Effect of ultrasound treatment on the physicochemical and structural properties of long-chain inulins[J]. LWT,2022,154:112578. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2021.112578
[29] REN Y P, LIU S X. Effects of separation and purification on structural characteristics of polysaccharide from quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa willd)[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2022,552(2):286−291.
[30] SHAO T L, YUAN P C, ZHANG W Z, et al. Preparation and characterization of sulfated inulin-type fructans from Jerusalem artichoke tubers and their antitumor activity[J]. Carbohydrate Research,2021,509:108422. doi: 10.1016/j.carres.2021.108422
[31] SUN Q L, ZHU L X, LI Y X, et al. A novel inulin-type fructan from Asparagus cochinchinensis and its beneficial impact on human intestinal microbiota[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,247:116761. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116761
[32] MENG Y, XU Y J, CHANG C, et al. Extraction, characterization and anti-inflammatory activities of an inulin-type fructan from Codonopsis pilosula[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,163:1677−1686. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.09.117
[33] CALEFFI E R, KRAUSOVÁ G, HYRŠLOVÁ I, et al. Isolation and prebiotic activity of inulin-type fructan extracted from Pfaffia glomerata (Spreng) Pedersen roots[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2015,80:392−399. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.06.053
[34] ZHANG Y, WANG C, JIA Z L, et al. Isoniazid promotes the anti-inflammatory response in zebrafish associated with regulation of the PPARγ/NF-κB/AP-1 pathway[J]. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 2020, 316: 108928.
[35] ZHAN H Y, CHEN H X, TANG Z Z, et al. SIX1 attenuates inflammation and rheumatoid arthritis by silencing MyD88-dependent TLR1/2 signaling[J]. International Immunopharmacology,2022,106:108613. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108613
[36] LIU Y, SHI W D, XIE Q Q, et al. Induction of COX-2 by feline calicivirus via activation of the MEK1-ERK1/2 pathway, and attenuation of feline lung inflammation and injury by MEK1 inhibitor AZD6244 (selumetinib)[J]. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications,2022,604:8−13. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.02.060
[37] WANG L, SHI H, ZHAO C C, et al. Astragaloside IV protects diabetic cardiomyopathy against inflammation and apoptosis via regulating TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway[J]. Journal of Functional Foods, 2022, 88: 104905.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 汪吉鹏,朱滕滕,刘璐,马铖,魏晓博,刘慧燕,方海田. λ-Red重组技术结合复合诱变提高大肠杆菌L-异亮氨酸合成能力. 食品工业科技. 2025(02): 167-174 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 戴一佳,赵亮. 益生菌对发酵乳品质影响的研究进展. 食品工业科技. 2024(08): 388-396 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)







 下载:
下载:





 下载:
下载:



