Process Optimization and Antioxidant Analysis of Enzymatic Preparation of Hemerocallis citrina Juice
-
摘要: 以黄花菜为原料,通过酶解工艺的优化,探究酶解前后所得黄花菜汁的抗氧化活性。本研究采用不同比例的纤维素酶和果胶酶进行酶解实验,以酶解黄花菜的出汁率为指标,通过响应面优化法确定最佳的黄花菜酶解工艺,并且利用高效液相色谱-三重四级杆质谱联用仪(High Performance Liquid Chromatography-triple Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry,HPLC-MS/MS)对样品中的多酚进行定性和定量分析,同时对样品的体外抗氧化活性进行测定。结果表明:按每100 g黄花菜汁(黄花菜与水料液比为1:1)计,酶解温度为50 ℃,酶解时间2 h,复合酶的添加总量为0.4%,其中纤维素酶:果胶酶=1:3时酶解效果较优,出汁率为78.54%。总酚含量提升1.3倍,DPPH自由基清除率提高了9.02%,ABTS+自由基清除率提高了6.15%,且总酚与DPPH自由基清除能力相关系数为0.929,与ABTS+自由基清除能力相关系数为0.968,说明黄花菜汁的体外抗氧化能力和总酚含量的变化密切相关。Abstract: The antioxidant activity of day lily juice before and after enzymatic digestion was investigated by the optimization of the enzymatic digestion process using day lily as raw material. In this study, the enzymatic hydrolysis experiments with different ratios of cellulase and pectinase were carried out, and the best enzymatic digestion process of day lily juice was determined by response surface optimization using the juice yield of day lily as an index. The polyphenols in the samples were analyzed qualitatively and quantitatively by high performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry, and the antioxidant activity of the samples in vitro was also evaluated. The optimal enzymolysis conditions were obtained as follows: Enzymatic digestion temperature at 50 ℃ and time of 2 h, the total enzyme addition of 0.4% per 100 g of day lily juice (1:1 ratio of day lily to water), and cellulase:pectinase=1:3 , and the juice yield was 78.54%. The total phenol content increased by 1.3 times, the DPPH free radical scavenging rate increased by 9.02%, and the ABTS+ free radical scavenging rate increased by 6.15%. The correlation coefficient between total phenol and DPPH free radical scavenging capacity was 0.929, and the correlation coefficient between total phenol and ABTS+ free radical scavenging capacity was 0.968, indicating that the antioxidant capacity in vitro of day lily juice was closely related to the change of total phenol content.
-
黄花菜(Hemerocallis citrina Braoni)又名金针菜、萱草、忘忧草,属百合目,目前主要产地在湖南祁东、山西大同、陕西大荔和甘肃庆阳,其中以大同黄花菜质量最好[1],获得“中国地理标志产品”标签。黄花菜是一种高蛋白、低热值、富含维生素的绿色保健蔬菜[2],相较于胡萝卜、番茄、木耳等常见蔬菜和食用菌[3],具有膳食纤维、蛋白质含量更丰富,钙、铁、锌、硒以及磷等矿物质元素含量较高的特点[4]。黄花菜的类黄酮类化合物[5-6]、蒽醌类化合物[7]、萜类化合物[8]、生物碱类化合物[9]和酚酸类化合物[10]等功能因子含量丰富,其中芦丁和橙皮苷等酚类物质具有较强的抗抑郁活性[11],黄酮类物质有很好的抗氧化效果[12]。
鲜黄花菜的营养品质高,但由于黄花菜花期短,再加上采后的蒸腾作用、呼吸作用、营养物质代谢等因素,导致鲜黄花菜采后保护酶系统遭到破坏[13],乙烯释放量上升,很容易腐烂变质,不耐贮藏,极大地制约了黄花菜鲜食品质的提升和产业发展。市场上常见的黄花菜消费方式主要包括干制、腌制和速冻等,这类粗加工方式相较于鲜黄花,干制容易造成黄花菜功能活性成分损失严重,极大降低了其功能价值[14];腌制不能使黄花菜中活性物质完全释放,容易造成不良风味的产生[15]。这制约了黄花菜消费模式的进一步拓展。同时,虽然黄花菜营养的研究报道较多,但针对黄花菜制汁的报道较少,因此针对目前的局限性,拓展黄花菜的精深加工势在必行,不仅可提升当地经济效益,更可满足市场和消费者的需求。
酶技术加工是现代食品工业生产的核心技术之一,可以增强果蔬细胞渗透率进而提高出汁率,同时增强果蔬汁浓缩加工时的稳定性,提高产品澄清度,保留产品营养成分[16]。黄花菜果胶、纤维素含量丰富,其彼此缠绕交联,使得细胞壁难以裂解[13]。而常规酶解技术大多使用单一酶,造成黄花菜出汁率低、酶解时间长,利用率低等问题。因此,本研究拟以复合蔬菜汁为载体,着眼于黄花菜“制汁”的关键问题,选用纤维素酶和果胶酶对打浆后黄花菜进行酶解,破坏黄花菜细胞壁[17],分解果胶,显著提升出汁率[18],进一步提升多酚物质的含量,充分利用黄花菜的营养价值,为黄花菜产品开发提供直接经验,黄花菜产业化拓展奠定基础。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
新鲜黄花菜 产自山西大同,大同云萱农业发展公司,采后黄花菜速冻保鲜,经冷链运输至实验室冷冻保存;纤维素酶FFG-0660(≥4400 U/mg)、果胶酶FFG-0658(≥5000 U/mg) 诺维信(中国)生物技术有限公司;甲醇、乙醇 色谱级,北京百灵威科技有限公司:没食子酸、绿原酸(纯度≥98%)、奎宁酸(纯度≥98%)、龙胆酸(纯度≥98%)、芦丁(纯度≥95%)、柚皮云香苷(纯度≥98%)、异槲皮素(纯度≥98%)、槲皮苷(纯度≥98%)、紫云英苷(纯度99%)、杨梅酮(纯度99%)、二氢槲皮素(纯度≥98%)、槲皮素(纯度≥95%)、异鼠李素(纯度≥99%)、橙皮素(纯度97%)、根皮素(纯度≥99%)、柚皮素(纯度≥95%)、高良姜素(纯度≥95%)、杨梅苷(纯度≥99%) 美国 Sigma-Aldrich 公司。
Agilent1260-6460型高效液相色谱-三重四级杆质谱(配以DB-5J&W毛细管柱,30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm) 美国安捷伦有限公司;T6新世纪紫外可见分光光度计 北京普析通用仪器有限责任公司;HH-4数显恒温水浴锅 国华电器有限公司;5L13-Y91S破壁机 九阳股份有限公司;GL-20G-Ⅱ高速离心机 上海安亭科学仪器厂;FD-1A-50冷冻干燥机 北京博医康实验仪器有限公司;KQ-400KDE高功率数控超声波清洗器 江苏昆山市超声仪器有限公司;R-100旋转蒸发仪 瑞士BUCHI有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 酶解法制备黄花菜汁的工艺
将新鲜黄花菜于100 ℃烫漂1 min后沥干,按照黄花菜:水=1:1的比例打浆,离心后(8000 r/min,15 min)取上清液做为酶解前黄花菜汁对照。取100 g离心前的黄花浆汁于三角瓶中,水浴加热至实验条件设定的酶解温度,按照一定浓度和比例加入果胶酶、纤维素酶或者两者复合,于不同温度酶解后,灭酶(95 ℃,3 min),冷却离心(8000 r/min,15 min),上清液作为酶解后黄花菜汁[19]。
黄花菜出汁率(%)=酶解后上清液质量黄花浆汁总质量×100 1.2.2 黄花菜浆汁酶解的单因素实验
黄花菜按照1.2.1的酶解条件处理,以出汁率作为指标,固定黄花菜浆汁100 g,酶解时间为2 h,酶解温度为40 ℃,酶的添加总量为0.4%,对单一酶制剂和复合酶制剂进行筛选,探讨纤维素酶与果胶酶的不同配比(1:0、5:1、3:1、1:1、1:3、5:1、0:1 w/w),确定两者的最适添加比例,然后分别考察酶解时间(1、2、3、4、5 h)时,酶解温度固定值为50 ℃,酶的添加总量为0.4%,对黄花菜出汁率的影响[20-22];考察酶解温度(30、40、50、60、70 ℃)时,酶解时间固定值为2 h,酶的添加总量为0.4%,对黄花菜出汁率的影响;考察酶的添加总量(0、0.1%、0.2%、0.3%、0.4%、0.5%,w/w)时,固定酶解时间为2 h,酶解温度为50 ℃,对黄花菜出汁率的影响。
1.2.3 响应面试验优化黄花菜浆汁酶解条件
以单因素实验结果为依据,以酶解时间(A)、酶解温度(B)、酶的添加总量(C)为影响因素,以出汁率为考察指标,应用Box-Behnken设计3因素3水平的响应面试验,对酶解工艺进行优化,试验因素与水平见表1。
表 1 响应面试验因素与水平Table 1. Factors and levels of response surface test因素 编码 水平 −1 0 1 酶解时间(h) A 1 2 3 酶解温度(℃) B 40 50 60 酶的添加总量(%) C 0.3 0.4 0.5 1.2.4 酶解前后黄花菜汁总酚的检测
1.2.1中的黄花浆汁上清液和黄花菜汁总多酚检测采用Folin-C方法[23]。具体检测操作参考 Li等[24]的方法并稍作修改。准确称量0.5000 g没食子酸于烧杯中,用乙醇溶解并定容至100 mL容量瓶中,分别取0、0.4、0.6、0.8、1.0、1.2、1.4、1.6 mL于10 mL具塞试管,用乙醇定容至10 mL,则没食子酸标品的浓度为0、200、300、400、500、600、700、800 mg/L。取0.1 mL不同浓度的标品溶液于具塞比色管,依次用蒸馏水定至6 mL,加入福林酚试剂0.5 mL,振荡,静置5 min后加入20% Na2CO3溶液,蒸馏水定容至10 mL,摇匀,避光静置2 h,765 nm下测吸光值,以试剂空白为参比,绘制标准曲线,所得回归方程为:y=0.001x+0.0219(R2=0.9992),在没食子酸 0~800 mg/L 浓度范围内,质量浓度与吸光度呈良好的线性关系。
取0.1 mL样品溶液于具塞比色管,依次用蒸馏水定至6 mL,加入福林酚试剂0.5 mL,振荡,静置5 min后加入20% Na2CO3溶液,蒸馏水定容至10 mL,摇匀,避光静置2 h,以试剂空白做参比,紫外分光光度计765 nm下测吸光值。根据测得的吸光度和标准曲线回归方程,计算样品中的多酚提取量,公式如下:
w=C×N×Vm×1000 式中,w 为总酚的提取量 (mg/kg);C 为样品溶液中总酚的浓度(mg/L);N 为样品溶液的稀释倍数;V 为黄花菜汁总体积 (mL);m 为黄花菜汁总质量(g)
1.2.5 酶解前后黄花菜体外抗氧化活性的变化
用1.2.1得到的酶解前黄花浆汁和酶解后的黄花菜汁分别进行体外抗氧化活性测定,具体方法如下:
1.2.5.1 ABTS+自由基清除能力的测定
用甲醇稀释ABTS溶液至吸光度为0.70±0.02,取0.04 mL样品加入到4 mL ABTS溶液中,避光反应10 min,使用分光光度计在734 nm处测定溶液的吸光度[25],公式如下:
ABTS+自由基清除能力(%)=[A0−(A2−A1)]/A0×100 式中,A0为ABTS溶液的吸光度值;A1为样品的吸光度值;A2为反应后的溶液的吸光度值。
1.2.5.2 DPPH自由基清除能力测定
取0.1 mL样品与3.9 mL 0.06 mmol/L DPPH溶液避光反应30 min,使用分光光度计在517 nm处测定溶液的吸光度[6],公式如下:
DPPH自由基清除能力(%)=[As−(A4−A3)]/As×100 式中,As为DPPH溶液的吸光度值;A3为样品的吸光度值;A4为反应后的溶液的吸光度值。
1.2.6 黄花菜汁多酚的提取
黄花菜汁多酚的提取方法参照Rouphael等[26]的方法并稍作修改。将1.2.1得到的酶解前后黄花菜汁冻干后,取1 g冻干粉于20 mL 70%甲醇中,冰水浴超声提取30 min,离心(8000 r/min,15 min,4 ℃),收集上清液,向下层沉淀物加入20 mL 70%甲醇,冰水浴超声提取30 min,离心并收集上清液,重复三次,将上清液合并后旋蒸以除去有机溶剂,用70%甲醇定容至25 mL。
1.2.7 酶解前后黄花菜汁单体多酚分析
多酚化合物的检测根据标准物质或文献中物质的质谱信息进行定性,通过标准物质进行定量分析,或采用结构相近的多酚化合物的标准物质进行定量分析[27]。将1.2.6的提取液过0.22 μm滤膜,利用高效液相色谱-三重四级杆质谱联用仪对样品中的多酚进行检测,色谱柱为Agilent proshell 120 EC-C18 (3 mm×100 mm,2.7 μm)。检测方法为:流动相A为水+0.1%甲酸,流动相B为甲醇。流动相洗脱程序为:0~1 min,5%B;1~5 min,30%~40% B;5~7 min,40%~80% B;7~10 min,80% B;10~10.10 min,80%~30% B;10.10~18 min,30% B;流速为0.3 mL/min,柱温为25 ℃,进样量2 μL。电离方式为电喷雾电离(Electrospray Ionization,ESI),负离子模式,雾化气压力为35 psi,干燥气流速为10 L/min,干燥气温度为330 ℃,毛细管电压为3500 V,喷嘴电压为500 V。定性定量通过标样在多反应检测MRM模式下的质谱信息、保留时间以及标准曲线确定[28]。
1.2.8 酶解前后黄花菜汁酚类物质与DPPH自由基清除能力、ABTS+自由基清除能力的相关性分析
用统计分析软件 SPSS 21.0 对数据进行数据统计、Pearson 进行黄花菜汁总酚含量及单体多酚物质与DPPH自由基清除能力、ABTS+自由基清除能力的相关性分析。
1.3 数据处理
所有实验重复3次,单因素实验结果采用ANOVA进行统计分析,P<0.05为差异显著标准,具有统计学意义,并以平均值±标准误差表示实验结果。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 黄花菜浆汁酶解工艺单因素实验结果
黄花菜浆汁酶解后以出汁率作为指标,对比分析不同纤维素酶与果胶酶的比例、酶解时间、酶解温度和酶的添加总量对出汁率的影响。
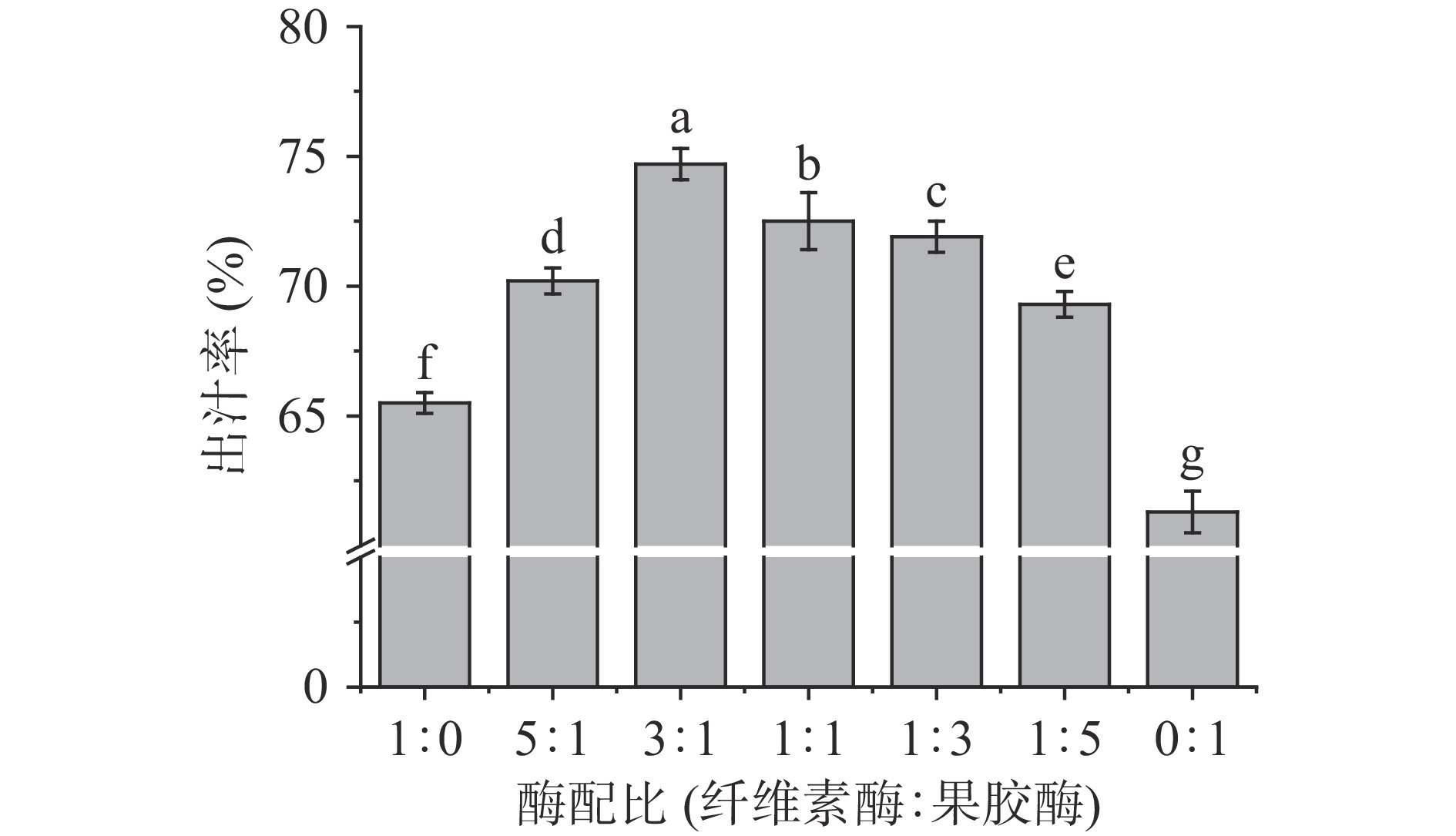
2.1.1 不同纤维素酶与果胶酶配比对出汁率的影响
从图1可以看出随着纤维素酶在酶添加总量的占比逐渐减少,出汁率呈先上升后下降的趋势,纤维素酶与果胶酶的添加比例为3:1时出汁率达到最高。随着果胶酶在酶添加总量的占比增加,出汁率下降的原因可能是大量果胶质类物质被水解,在沉淀过程中吸附了体系中的部分可溶性固形物,此外,酶解过程中黄花汁溶液体系被破坏,一些蛋白类物质容易凝聚形成沉淀,也会影响出汁率和可溶性固形物的溶解性[29]。因此,纤维素酶:果胶酶为3:1的复合酶制剂达到的酶解效果最好。
2.1.2 酶解时间对出汁率的影响
从图2可以看出,酶解2 h的出汁率与1 h的有显著性差异(P<0.05)。酶解2 h后,随着时间的增加,出汁率的变化不显著(P>0.05)。尽管酶解时间越长会呈现出汁率也随之增加的趋势,然而过长酶解时间,会造成影响营养成分损失以及影响风味物质[20],同时结合工业生产和成本控制来看,选择1、2、3 h开展响应面设计试验。
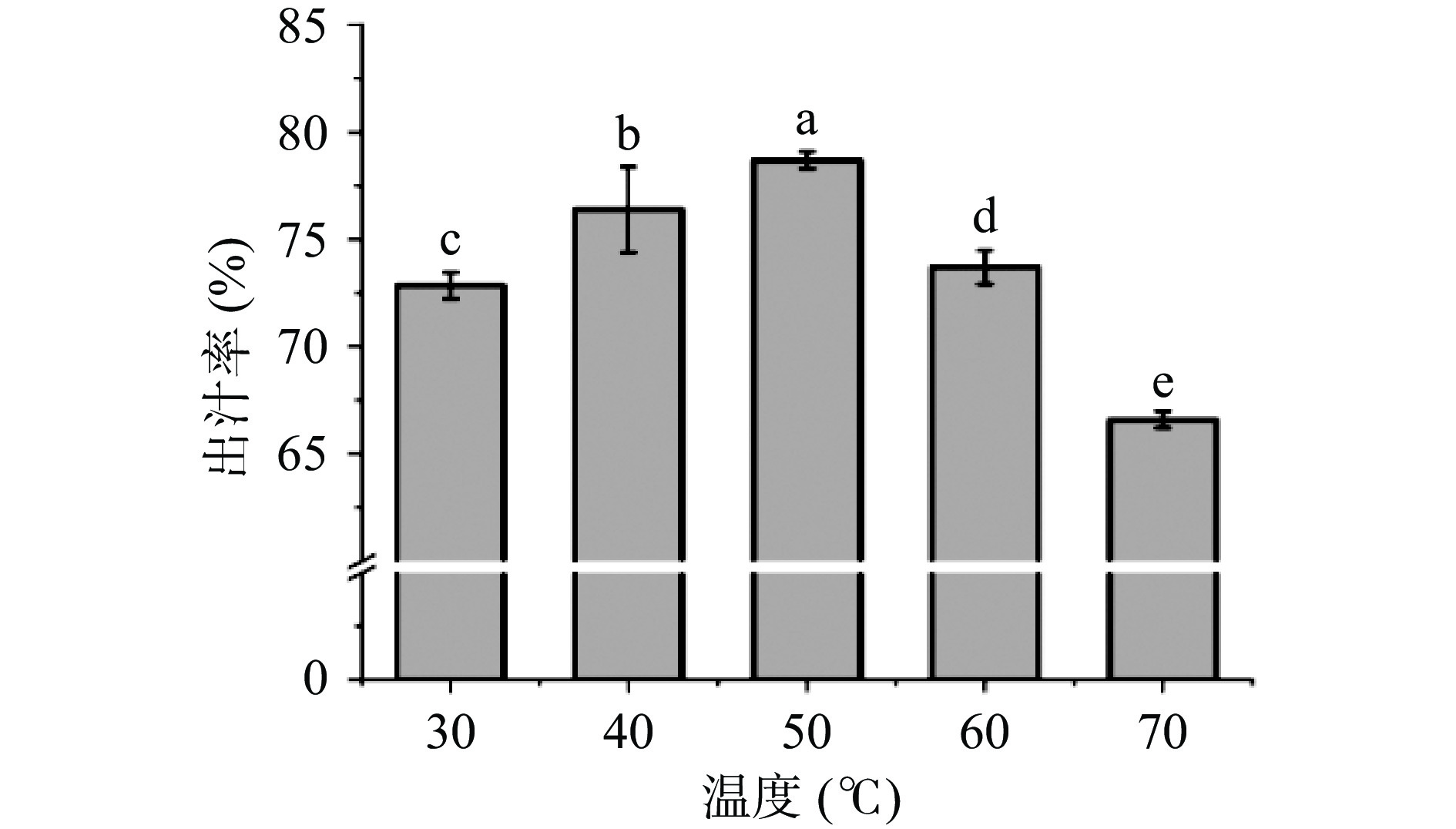
2.1.3 酶解温度对出汁率的影响
从图3可得,酶解温度在30~50 ℃时黄花出汁率随温度的升高而升高,而50 ℃之后出汁率随着酶解温度而下降。当温度高于50 ℃后,酶分子结构发生变化,酶的生物活性被破坏,无法发挥作用,导致出汁率反而下降[21]。综上所述,选择酶解温度为40、50、60 ℃设计响应面设计试验。
2.1.4 酶的添加总量对出汁率的影响
由图4得出,出汁率随酶的添加总量先升高后趋于平稳,未添加酶的对照组与添加酶的处理组的出汁率差异显著(P<0.05)。当酶的添加总量在0~0.3%时,显著提高了出汁率(P<0.05),当酶的添加总量大于0.4%时,出汁率变化不明显。当酶添加量继续增加时,可能因为底物已经充分酶解,酶的作用效果不显著,黄花菜的出汁率不再随着添加量的增多而升高,这说明适当的酶添加量,可增加黄花菜的出汁率[22]。因此,选择0.3%、0.4%、0.5%进行响应面设计试验。
2.2 黄花菜浆汁酶解实验最优条件选择
以单因素实验结果为依据,选择纤维素酶与果胶酶的比例(3:1)为固定因素,酶解时间(A)、酶解温度(B)、酶的添加总量(C)为自变量,以出汁率为响应值,通过Design Expert 12.0.3对优化因素进行Box-Benhnken试验设计,得到表2响应面优化试验结果。
表 2 Box-Behnken试验设计结果Table 2. Box-Behnken experiment design results实验号 A B C Y:出汁率
(%)1 −1 −1 0 74.41 2 1 −1 0 75.93 3 −1 1 0 73.11 4 1 1 0 75.32 5 −1 0 0 74.32 6 1 0 −1 75.62 7 −1 0 1 73.53 8 1 0 1 76.27 9 0 −1 −1 76.22 10 0 1 −1 75.16 11 0 −1 1 76.74 12 0 1 1 75.27 13 0 0 0 78.71 14 0 0 0 78.71 15 0 0 0 78.43 16 0 0 0 78.71 17 0 0 0 78.43 通过 Design-Expert-V8.0.6.1 软件进行响应面分析,得到回归拟合方程:
Y(%)=+78.60+0.97A−0.55B+0.061C+0.17AB+0.36AC−0.10BC−2.41A2−1.50B2−1.25C2
通过对此回归方程进行方差分析,由表3可知,总模型P<0.0001,具有高度显著性。实验模型的决定系数R2=0.9959,证明该实验结果可靠。而失拟项中P=0.2707>0.05,说明失拟项差异不显著,此方程对实验拟合度较好,能够充分反映该实验实际情况。酶解时间A的一次项和二次项,酶解温度B的一次项和二次项对黄花出汁率均有极显著影响(P<0.01),酶解时间和酶解温度、酶解温度和酶的添加总量之间的交互作用对黄花出汁率的影响不显著(P>0.05),无统计学差异。通过此模型发现各影响因素对出汁率的影响顺序为A>B>C,所以对黄花菜浆汁酶解效果影响最大的因素是酶解时间,其次是酶解温度。
表 3 回归模型方差分析Table 3. Variance analysis of regression equation方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 模型 55.45 9 6.16 188.93 <0.0001 A-酶解时间 7.55 1 7.55 231.44 <0.0001 B-酶解温度 2.46 1 2.46 75.57 <0.0001 C-酶的添加总量 0.03 1 0.03 0.92 0.3693 AB 0.12 1 0.12 3.65 0.0977 AC 0.52 1 0.52 15.9 0.0053 BC 0.042 1 0.042 1.29 0.2936 A2 24.43 1 24.43 749.36 <0.0001 B2 9.43 1 9.43 289.18 <0.0001 C2 6.62 1 6.62 203.05 <0.0001 残差 0.23 7 0.033 失拟项 0.13 3 0.045 1.9 0.2707 净误差 0.094 4 0.024 总和 55.67 16 利用响应面软件 Design-Expert-V8.0.6.1 处理,得到酶解时间、酶解温度、酶的添加总量交互作用的响应面图(如图5~图7)。酶解时间和酶的添加总量交互作用对黄花菜出汁率影响显著(P<0.05),酶的添加总量和酶解温度交互作用对黄花菜出汁率影响不显著(P>0.05)。根据得到的响应面模型确定酶解黄花菜的最佳工艺为:酶解温度为48.25 ℃,酶解时间2.20 h,酶的添加总量为0.41%,预测此条件下黄花菜出汁率为 78.60%。在实际操作过程中,将预测值转化为具体参数:酶解温度为50 ℃,酶解时间2 h,酶的添加总量为0.4%,其中纤维素酶:果胶酶=3:1 ,进行验证实验,并重复三次,出汁率为78.54%±0.31%,结果与模型预测值的相对标准偏差小于1%。说明采用响应面优化得到的黄花菜酶解工艺参数具有可行性。
2.3 酶解前后黄花菜汁总酚和体外抗氧化活性的变化
多酚是黄花菜中主要的功能活性成分之一[14],本文通过对比酶解前后黄花菜汁中多酚的浓度,以体外抗氧化活性为指标,进一步验证酶解工艺对黄花菜汁抗氧化活性的提高。
使用福林酚法完成对黄花菜汁总酚的检测,结果如图8所示,酶解后黄花菜汁中的总酚浓度比酶解前的总酚浓度提升1.3倍。纤维素酶和果胶酶通过水解细胞壁相关组织成分使细胞内活性物质溶出从而提高了黄花汁中的总酚含量,与Rodrigues等 [30]的研究一致。
从图9可以看出酶解后DPPH和ABTS+自由基清除能力都有不同程度的提高,DPPH自由基清除率提高了9.02%,ABTS+自由基清除率提高了6.15%。综合酶解前后总酚含量变化与对DPPH和ABTS+自由基清除率的提升效果来看,酶解前后黄花菜汁的体外抗氧化能力与总酚含量密切相关,同时,Prior等[31]的研究表示,酚类物质含量与抗氧化活性有直接联系,多酚含量越高,食品的抗氧化活性越强。综上,可以得出结论,酶解工艺可显著提升黄花菜汁中多酚含量,增强其抗氧化性。
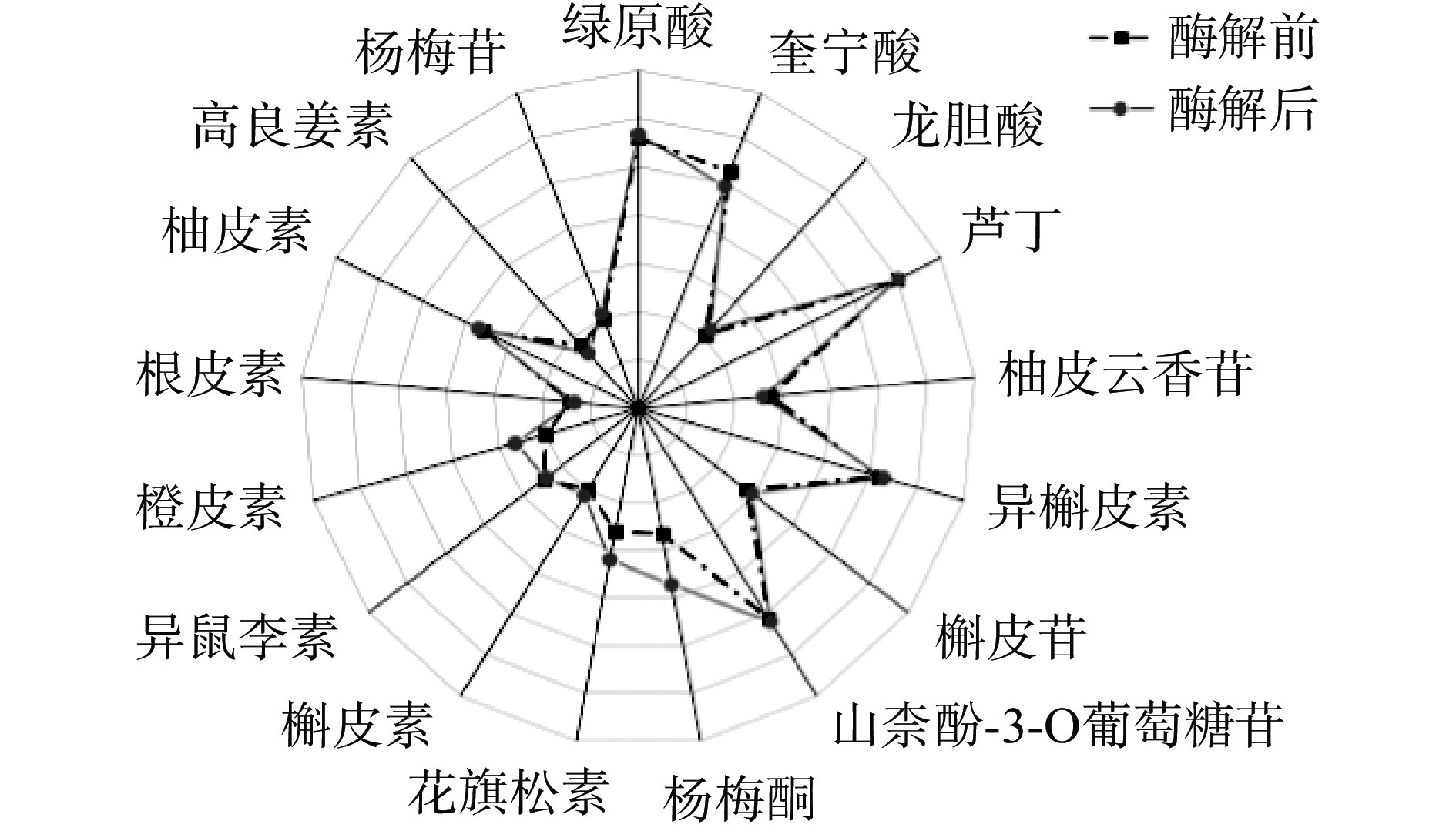
2.4 酶解前后黄花菜汁中多酚单体含量的变化
本研究共检测到17种多酚类物质,其中12种多酚类物质在酶解后含量增加,通过对多酚单体的具体分析,进一步解析黄花菜汁当中的功能活性成分,验证酶解工艺对黄花菜汁抗氧化活性的提升。
从图10可知,酶解前后黄花菜中酚酸类物质含量变化显著,其中奎宁酸含量减少,绿原酸含量增长到原来的1.17倍。推测其原因是纤维素酶破坏细胞壁,促进奎宁酸、绿原酸最大限度溶出,同时,奎宁酸通过与其他物质反应合成绿原酸,使得奎宁酸含量反而下降[32]。绿原酸具有广泛的生物活性,抗菌、抗病毒、抗氧化等效果显著[33]。龙胆酸是水杨酸经肾脏代谢后的次级产物,其含量经酶解后增加了1.4倍。龙胆酸不仅抗氧化作用明显,自身也易于被人体吸收[34]。
检测黄花菜汁中杨梅酮、花旗松素、异槲皮素、槲皮素、橙皮素、柚皮素、杨梅苷等14种黄酮类物质含量在酶解后都升高。杨梅酮含量增加了8倍,这种黄酮醇类化合物除具有抗氧化性外,还有保护神经系统[35]、降低血糖、抗癌[36]、预防心血管疾病的作用[37-38]。花旗松素是一种活性较强的抗氧化物,具有抗炎[39]、抗肿瘤作用[40],其含量相较于酶解前增加至3.4倍。异槲皮素属于天然黄酮醇糖苷形式的化合物,具有抗氧化、抗菌、调节免疫等活性[41],而且相较于其他天然黄酮物质,吸收率和生物利用度良好[42]。酶解后异槲皮素含量增加至1.21倍。此外,槲皮苷、芦丁的含量也有提升(槲皮苷含量增加至1.35倍,芦丁增加了0.06倍),这些物质也有较强的药理活性[43-44]。综合来看,多酚单体的含量变化符合总酚的变化趋势,进一步验证了本研究的酶解工艺可以显著提升黄花菜汁的活性物质含量。
2.5 相关性分析
酶解前后黄花菜汁的DPPH自由基清除率和ABTS+自由基清除率与部分酚类活性物质单体的相关性分析见表4。黄花菜酶解过程中的龙胆酸含量与黄花菜汁的ABTS+自由基清除能力表现极显著相关性(P<0.01),绿原酸、异槲皮素、山柰酚-3-O葡萄糖苷、杨梅酮、花旗松素、槲皮素、橙皮素、柚皮素、杨梅苷含量与黄花菜汁的DPPH自由基清除能力、ABTS+自由基清除能力表现出极显著的相关性(P<0.01)。其中花旗松素、槲皮素、柚皮素含量与DPPH自由基清除能力有最大相关性,均为0.997,且橙皮素含量与ABTS+自由基清除能力相关性最大,为0.998。花旗松素、槲皮素、橙皮素是黄花菜汁抗氧化能力的主要贡献者。此外,奎宁酸与DPPH自由基清除能力、ABTS+自由基清除能力呈一定负相关性(P<0.05),分析原因可能是奎宁酸通过与其他物质反应合成绿原酸[32],进而出现了奎宁酸含量下降,而黄花菜汁DPPH自由基清除能力、ABTS+自由基清除能力提升的现象。综上所述,总酚含量与黄花菜汁的DPPH自由基清除能力、ABTS+自由基清除能力表现出极显著的相关性(P<0.01),说明酶解工艺显著提升了黄花菜汁的抗氧化能力,与Prior等[31]的研究一致。
表 4 黄花菜酶解前后抗氧化活性与其多酚成分含量的相关性分析Table 4. Correlation analysis of antioxidant activity and polyphenol content of day lily before and after enzymatic hydrolysis种类 相关系数(r) 显著性(P) ABTS+· DPPH· ABTS+· DPPH· 绿原酸 0.970 0.961 0.001 0.002 奎宁酸 −0.889 −0.844 0.018 0.035 龙胆酸 0.938 0.896 0.006 0.016 芦丁 0.690 0.657 0.129 0.157 柚皮云香苷 −0.727 −0.66 0.102 0.154 异槲皮素 0.936 0.915 0.006 0.010 槲皮苷 0.792 0.765 0.060 0.076 山柰酚-3-O葡萄糖苷 0.973 0.963 0.001 0.002 杨梅酮 0.969 0.937 0.001 0.006 花旗松素 0.985 0.997 0.001 0.001 槲皮素 0.985 0.997 0.001 0.001 异鼠李素 0.143 0.152 0.787 0.774 橙皮素 0.998 0.990 0.001 0.001 根皮素 −0.542 −0.445 0.267 0.377 柚皮素 0.991 0.997 0.001 0.001 高良姜素 −0.745 −0.702 0.089 0.120 杨梅苷 0.946 0.917 0.004 0.010 总酚 0.968 0.929 0.001 0.007 注:表中P<0.01表示相关性极显著,P<0.05表示相关性显著,P>0.05表示相关性不显著。 3. 结论
黄花菜含有丰富的多酚类物质,本研究通过响应面设计确定了黄花菜的最佳酶解工艺,并通过分析得出该酶解工艺条件下,出汁率可达78.54%,总酚含量提升1.3倍,其中绿原酸、杨梅酮、花旗松素、异槲皮素、槲皮素、柚皮素等多酚单体的含量升高,显著提升黄花菜汁的抗氧化活性。此酶解工艺不仅为黄花菜原料的取汁问题有直接贡献,同时为后续扩大黄花菜消费模式,开发复合果蔬饮料提供奠定了研究基础。但本研究对黄花菜的主要营养和风味变化尚有不足,酶解前后其他类黄酮物质、萜类物质对抗氧化性的作用有待进一步探究,接下来的研究内容将围绕营养和风味建立更加完善、多元的评价指标,构建出更完善、更适用于黄花菜产业化的生产工艺体系。
-
表 1 响应面试验因素与水平
Table 1 Factors and levels of response surface test
因素 编码 水平 −1 0 1 酶解时间(h) A 1 2 3 酶解温度(℃) B 40 50 60 酶的添加总量(%) C 0.3 0.4 0.5 表 2 Box-Behnken试验设计结果
Table 2 Box-Behnken experiment design results
实验号 A B C Y:出汁率
(%)1 −1 −1 0 74.41 2 1 −1 0 75.93 3 −1 1 0 73.11 4 1 1 0 75.32 5 −1 0 0 74.32 6 1 0 −1 75.62 7 −1 0 1 73.53 8 1 0 1 76.27 9 0 −1 −1 76.22 10 0 1 −1 75.16 11 0 −1 1 76.74 12 0 1 1 75.27 13 0 0 0 78.71 14 0 0 0 78.71 15 0 0 0 78.43 16 0 0 0 78.71 17 0 0 0 78.43 表 3 回归模型方差分析
Table 3 Variance analysis of regression equation
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 模型 55.45 9 6.16 188.93 <0.0001 A-酶解时间 7.55 1 7.55 231.44 <0.0001 B-酶解温度 2.46 1 2.46 75.57 <0.0001 C-酶的添加总量 0.03 1 0.03 0.92 0.3693 AB 0.12 1 0.12 3.65 0.0977 AC 0.52 1 0.52 15.9 0.0053 BC 0.042 1 0.042 1.29 0.2936 A2 24.43 1 24.43 749.36 <0.0001 B2 9.43 1 9.43 289.18 <0.0001 C2 6.62 1 6.62 203.05 <0.0001 残差 0.23 7 0.033 失拟项 0.13 3 0.045 1.9 0.2707 净误差 0.094 4 0.024 总和 55.67 16 表 4 黄花菜酶解前后抗氧化活性与其多酚成分含量的相关性分析
Table 4 Correlation analysis of antioxidant activity and polyphenol content of day lily before and after enzymatic hydrolysis
种类 相关系数(r) 显著性(P) ABTS+· DPPH· ABTS+· DPPH· 绿原酸 0.970 0.961 0.001 0.002 奎宁酸 −0.889 −0.844 0.018 0.035 龙胆酸 0.938 0.896 0.006 0.016 芦丁 0.690 0.657 0.129 0.157 柚皮云香苷 −0.727 −0.66 0.102 0.154 异槲皮素 0.936 0.915 0.006 0.010 槲皮苷 0.792 0.765 0.060 0.076 山柰酚-3-O葡萄糖苷 0.973 0.963 0.001 0.002 杨梅酮 0.969 0.937 0.001 0.006 花旗松素 0.985 0.997 0.001 0.001 槲皮素 0.985 0.997 0.001 0.001 异鼠李素 0.143 0.152 0.787 0.774 橙皮素 0.998 0.990 0.001 0.001 根皮素 −0.542 −0.445 0.267 0.377 柚皮素 0.991 0.997 0.001 0.001 高良姜素 −0.745 −0.702 0.089 0.120 杨梅苷 0.946 0.917 0.004 0.010 总酚 0.968 0.929 0.001 0.007 注:表中P<0.01表示相关性极显著,P<0.05表示相关性显著,P>0.05表示相关性不显著。 -
[1] 张德纯. 山西大同黄花菜[J]. 中国蔬菜,2020(9):1. [ZHANG D C. Hemerocallis in Datong, Shanxi[J]. Chinese Vegetables,2020(9):1. ZHANG D C. Hemerocallis in Datong, Shanxi[J]. Chinese Vegetables, 2020(9): 30.
[2] 秦喜悦, 张雷, 温艳斌, 等. 黄花菜营养活性研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2022,43(5):204−209. [QIN X Y, ZHANG L, WEN Y B, et al. Research progress on nutritional activity of Hemerocallis[J]. Food Research and Development,2022,43(5):204−209. QIN X Y, ZHANG L, WEN Y B, et al. Research progress on nutritional activity of Hemerocallis[J]. Food Research and Development, 2022, 43(5): 204-209.
[3] 韩志平, 张春业, 张海霞, 等. 黄花菜和3种食用菌营养价值的研究[J]. 山西大同大学学报(自然科学版),2013,29(5):63−65. [HAN Z P, ZHANG C Y, WEN H X, et al. Study on nutritional value of Hemerocallis and three edible fungi[J]. Journal of Shanxi Datong University (Natural Science Edition),2013,29(5):63−65. HAN Z P, ZHANG C Y, WEN H X, et al. Study on nutritional value of Hemerocallis and three edible fungi[J]. Journal of Shanxi Datong University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 29(5): 63-65.
[4] 米智, 刘荔贞, 李慧. 响应面法优化黄花菜多酚提取工艺及抗氧化活性的研究[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2022,33(3):139−147. [MI Z, LIU L Z, LI H. Optimization of polyphenol extraction process and antioxidant activity of Hemerocallis by response surface methodology[J]. Chinese Food Additives,2022,33(3):139−147. doi: 10.19804/j.issn1006-2513.2022.03.019 MI Z, LIU L Z, LI H. Optimization of polyphenol extraction process and antioxidant Activity of Hemerocallis by response surface methodology[J]. Chinese Food Additives, 2022, 33(3): 139-147. DOI: 10.19804/j.issn1006-2513.2022.03.019.
[5] DU B J, TANG X S, LIU F, et al. Antidepressant-like effects of the hydroalcoholic extracts of Hemerocallis citrina and its potential active components[J]. BMC Complementary & Alternative Medicine,2014,14:326.
[6] LIN Y L, LU C K, HUANG Y J, et al. Antioxidative caffeoylquinic acids and flavonoids from Hemerocallis fulva flowers[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2011,59(16):8789−8795.
[7] CICHEWICZ R H, LIM K C, MCKERROW J H, et al. Kwanzoquinones A-G and other constituents of Hemerocallis fulva ‘Kwanzo’ roots and their activity against the human pathogenic trematode Schistosoma mansoni[J]. Tetrahedron,2002,58(42):8597−8606.
[8] SZEWCZYK K, KALEMBA D, MIAZGA-KARSKA M, et al. The essential oil composition of selectedHemerocallis cultivars and their biological activity[J]. Open Chemistry,2019,17(1):1412−1422.
[9] ZHANG Y, ZHAO X C, XIE Y G, et al. Eight new γ-lactam alkaloids from the roots of the Hemerocallis minor Mill[J]. Fitoterapia,2017,118:80−86.
[10] CLIFFORD M N, WU W G, KUHNERT N. The chlorogenic acids of Hemerocallis[J]. Food Chemistry,2006,95(4):574−578.
[11] GU L, LIU Y J, WANG Y B, et al. Role for monoaminergic systems in the antidepressant-like effect of ethanol extracts from Hemerocallis citrina[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2012,139(3):780−787. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.11.059
[12] 蔡建勤, 土小宁, 殷丽强. 黄河流域黄花菜产业高质量发展的对策及建议[J]. 中国水土保持,2022(1):5−7. [CAI J L, TU X N, YIN L Q. Countermeasures and suggestions for the high-quality development of cauliflower industry in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Soil and Water Conservation in China,2022(1):5−7. CAI J L, TU X N, YIN L Q. Countermeasures and suggestions for the high-quality development of cauliflower industry in the Yellow River Basin[J]. Soil and Water Conservation in China, 2022(1): 5-7.
[13] 龚吉军. 黄花菜贮藏保鲜研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南农业大学, 2003. GONG J J. Study on storage and fresh keeping of Hemerocallis citrina[D]. Changsha: Hunan Agricultural University, 2003.
[14] CHEN Q, FU M, QU Q, et al. Effect of blanching pretreatment on antioxidant activities and involved compounds in fresh day lily (Hemerocallis fulva L.) flowers[J]. Quality Assurance and Safety of Crops & Foods,2014,7(3):287−293.
[15] 杨富民, 张丽, 严晓娟. 干制黄花菜工业化生产工艺技术[J]. 农业工程学报,2008,24(11):264−267. [YANG F M, ZHANG L, YAN X J. Technology for drying Hemerocallis for industrialized production[J]. Transactions of the CSAE,2008,24(11):264−267. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2008.11.054 YANG F M, ZHANG L, YAN X J. Technology for drying Hemerocallis for industrialized production[J]. Transactions of the CSAE, 2008, 24(11): 264-267. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1002-6819.2008.11.054
[16] KUL A, SAGIRLI O. Determination of enzymatic hydrolysis efficiency in detection of cannabis use by UPLC-MS-MS[J]. Journal of Analytical Toxicology,2022,46(3):257−263.
[17] 余兴莲. 纤维素酶降解纤维素机理的研究进展[J]. 宁波大学学报(理工版),2007,20(1):78−82. [YU X L. Research progress of cellulose degradation mechanism by cellulase[J]. Journal of Ningbo University (Science and Engineering Edition),2007,20(1):78−82. YU X L. Research progress of cellulose degradation mechanism by Cellulase[J]. Journal of Ningbo University (Science and Engineering Edition), 2007, 20(1): 78-82.
[18] 陈娟, 阚健全, 杜木英, 等. 果胶酶制剂及其在果浆出汁和果汁澄清方面的应用[J]. 中国食品添加剂,2006(3):103−108. [CHEN J, KAN J Q, DU M Y, et al. Pectinase preparation and its application in juice production and clarification of fruit juice[J]. Chinese Food Additives,2006(3):103−108. CHEN J, KAN J Q, DU M Y, et al. Pectinase preparation and its application in juice production and clarification of fruit juice[J]. Chinese Food Additives, 2006(3): 103-108.
[19] 曹熙, 杨大伟. 黄花菜多酚类化合物的鉴定及漂烫与贮藏对其稳定性的影响研究[J]. 核农学报,2021,35(12):2787−2798. [CAO X, YANG D W. Identification of polyphenols in cauliflower and sudy on the effect of blanching and storage on its stability[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agriculture,2021,35(12):2787−2798. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2021.12.2787 CAO X, YANG D W. Identification of polyphenols in cauliflower and sudy on the effect of blanching and storage on its stability[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agriculture, , 2021, 35(12): 2787-2798. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2021.12.2787
[20] 叶勒生·托合达别克, 涂振东, 李斌斌, 等. 响应面优化甜高粱汁酶解工艺分析[J]. 新疆农业科学,2022,59(7):1632−1641. [YELSON T B, TU Z D, LI B B, et al. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of sweet sorghum juice by response surface methodology[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences,2022,59(7):1632−1641. YELSON T B, TU Z D, LI B B, et al. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis of sweet sorghum juice by response surface methodology[J]. Xinjiang Agricultural Sciences, 2022, 59(7): 1632-1641.
[21] SZASZ G. The effect of temperature on enzyme activity and on the affinity of enzymes to their substrates[J]. Zeitschrift fur klinische Chemie und klinische Biochemie,1974,12(4):166−70.
[22] 廖慧琦, 曹少谦, 杨华, 等. 鲐鱼免疫活性肽的酶解工艺优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(14):163−170. [PANG H Q, CAO S Q, YANG H, et al. Optimization of enzymatic Hydrolysis of mackerel immunoactive peptides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(14):163−170. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021090087 PANG H Q, CAO S Q, YANG H, et al. Optimization of enzymatic Hydrolysis of mackerel immunoactive peptides[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry, 2022, 43(14): 163-170. DOI: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021090087.
[23] XU J, YE A Y, DING J M. Determination of total phenolic content using the Folin-C assay: Single-laboratory validation, first action 2017.13[J]. Journal of AOAC International,2018,101(5):1466−1472.
[24] LI N, SHI J L, WANG K. Profile and antioxidant activity of phenolic extracts from 10 crabapples (Malus wild species)[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2014,62(3):574−581. doi: 10.1021/jf404542d
[25] 全国生化检测标准化技术委员会(SAC/TC 387). GB/T 39100-2020 多肽抗氧化性测定 DPPH和ABTS+法[S].北京: 中国标准出版社, 2020. National Technical Committee for Standardization of Biochemical Testing(SAC/TC 387). GB/T 39100-2020 Determination of antioxidant activity of polypeptides DPPH and ABTS+ method[S].Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2020.
[26] ROUPHAEL Y, COLLA G, GRAZIANI G, et al. Phenolic composition, antioxidant activity and mineral profile in two seed-propagated artichoke cultivars as affected by microbial inoculants and planting time[J]. Food Chemistry, 2017: S030881461730763X.
[27] 班龄尹. 朝鲜蓟副产物青贮过程中功能性成分的变化[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2020. BAN L Y. Changes in functional components of artichoke by-products during silage[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2020.
[28] 毛瑜. 不同发酵工艺对刺梨酒香气及多酚物质的影响[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2020. MAO Y. Effects of different fermentation processes on aroma and polyphenols of Rosa roxburghii Tratt wine[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2020.
[29] KASHAP D R, VOHRA P K, CHOPRA S, et al. Applications of pectinases in the commercial sector: A review[J]. Bioresource Technol,2001,77(3):215−227. doi: 10.1016/S0960-8524(00)00118-8
[30] RODRIGUES D, SOUSA S, SILVA A, et al. Impact of enzyme and ultrasound-assisted extraction methods on biological propeties of red, brown and green seaweeds from the central west coat of Portugal[J]. J Agric Food Chem,2015(63):3177−3188.
[31] PRIOR R L, WU X L, SCHAICH K. Standardized methods for the determination of antioxidant capacity and phenolics in foods and dietary supplements[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food and Food Chemistry,2005,53(10):4290−4302. doi: 10.1021/jf0502698
[32] RESE E T. Enzymatic hydrolysis of the walls of yeasts cells and germinated fungal spores[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta,1997,499(1):10−23.
[33] 万凡, 侯扶江, 伊宝, 等. 绿原酸的生理功能及其在畜禽生产中的应用[J]. 动物营养学报,2021,33(5):2416−2427. [WAN F, HOU F J, YIN B, et al. Physiological function of chlorogenic acid and its application in livestock and poultry production[J]. Journal of Animal Nutrition,2021,33(5):2416−2427. WAN F, HOU F J, YIN B, et al. Physiological function of chlorogenic acid and its application in livestock and poultry production[J]. Journal of Animal Nutrition, 2021, 33(5): 2416-2427.
[34] 巩红云. Pseudomonas putida XL501和Haloferax vocalnii WFD11降解芳烃化合物的龙胆酸代谢途径关键酶的研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2017. GONG H Y. Pseudomonas putida XL501 and Haloferax vocalnii WFD11 study on the key enzymes of gentian acid metabolic pathway in the degradation of aromatic compounds[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2017
[35] TIAN H, YANG F, LIU C, et al. Effects of phenolic constituents of daylily flowers on corticosterone and glutamate-treated PC12 cells[J]. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine,2017,17(1):1−12. doi: 10.1186/s12906-016-1505-2
[36] 姬赐玉, 田欢, 杨飞飞, 等. 黄花菜中酚类成分对过氧化氢诱导大鼠嗜铬细胞瘤 PC12 细胞损伤的保护作用研究[J]. 世界最新医学信息文摘,2019,19(30):220−222,224. [JI C Y, TIAN H, YANG F F, et al. Protective effects of phenolic components in Hemerocallis citrina Baroni on hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced damage of rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells[J]. World Latest Medicine Information,2019,19(30):220−222,224. JI C Y, TIAN H, YANG F F, et al. Protective effects of phenolic components in Hemerocallis citrina Baroni on hydrogen peroxide (H2O2)-induced damage of rat pheochromocytoma (PC12) cells[J]. World Latest Medicine Information, 2019, 19(30): 220-222, 224.
[37] 房仙颖, 章祎唯, 萧伟, 等. 异槲皮素的制备及研究进展[J]. 天然产物研究与开发,2020,32(4):708−717. [FANG X Y, ZHANG Y W, XIAO W, et al. Preparation and research progress of isoquercetin[J]. Research and Development of Natural Products,2020,32(4):708−717. doi: 10.16333/j.1001-6880.2020.4.022 FANG X Y, ZHANG Y W, XIAO W, et al. Preparation and research progress of isoquercetin[J]. Research and Development of Natural Products, 2020, 32(4): 708-717. doi: 10.16333/j.1001-6880.2020.4.022
[38] DUDLEY E G, STEELE J L. Succinate production and citrate catabolism by Cheddar cheese nonstarter lactobacilli[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology,2005,98(1):14−23. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.2004.02440.X
[39] 刘合生, 戚向阳, 曹少谦, 等. 杨梅乙醇提取物对小鼠酒精性肝损伤的保护作用[J]. 中国食品学报,2014,14(8):34−40. [LIU H S, Qi X Y, CAO S Q, et al. Protective effect of Myrica rubra ethanol extract on alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Food,2014,14(8):34−40. LIU H S, Qi X Y, CAO S Q, et al. Protective effect of Myrica rubra ethanol extract on alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Chinese Journal of food, 2014, 14(8): 34- 40.
[40] ONG K C, KHOO H E. Biological effects of myricetin[J]. General Pharmacology,1997,29(2):121−126. doi: 10.1016/S0306-3623(96)00421-1
[41] MBIKAY M, CHRETIEN M. Isoquercetin as an anti-Covid-19 medication: A potential to realize[J]. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 2022, 13: 830205.
[42] MOHD S R, MOHD I M, TEH L K, et al. A Pharmacokinetic study by LC-MS/MS to quantify isoquercetin and astragalin in rat serum after oral administration of a combined extract of Moringa oleifera and Centella asiatica[J]. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia, 2020, 30: 804–809.
[43] ZHANG Y, CHEWIC R H, NAIR M G. Lipid peroxidation inhibitory compounds from daylily (Hemerocallis fulva) leaves[J]. Life Sciences,2004,75(6):753−763. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2004.03.002
[44] LIU X, LUO L, LIU B, et al. Ethanol extracts from Hemerocallis citrina attenuate the upregulation of proinflammatory cytokines and indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase in rats[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2014,153(2):484−490. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.03.001
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 朱碧芬,张若妍,尹浩,钟宇,王丹凤,邓云,章敏燕,赵芳. 四种食用菌糖蛋白粗提物体外抗氧化和抑菌活性比较. 食用菌学报. 2024(03): 59-65 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 李通,王晓巍,杨建杰,耿新军,伏晓辉. 西北地区大棚吊袋栽培黑木耳品种筛选及营养物质分析. 中国食用菌. 2024(03): 28-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 辛加敏,阮婧华,王聪,谭荣,查鑫,李广松,王海燕,韦利芬,胡小伟. 补骨脂糖蛋白提取工艺优化及成分测定. 食品研究与开发. 2024(19): 97-105 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 许梦粤,田鑫,王君可,武傲雪,邹芷怡,吴佳辉,王红波. 菜豆多糖与香菇多糖结构特征以及体外重要生物活性综合对比评价. 食品科学. 2024(23): 2318-2327 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李海霞,赵婉彤,郝兆然,王清鸽,屈佰锁,陈雅倩,张瑞,裴龙英,姜露熙. 黑木耳膨化脆片的研制. 发酵科技通讯. 2023(01): 28-34 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 王崇队,马敏,张明,王丽,吴茂玉,和法涛,张俊宇,马超. 牡丹籽蛋白的提取工艺优化及理化性质分析. 中国果菜. 2023(03): 24-30 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 张一平,薛璟,张辰,张蕾,季宏更,蒋益. 食(药)用菌糖蛋白的研究进展. 中国食用菌. 2023(02): 1-10 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)






 下载:
下载:










 下载:
下载:



