Optimization of Ethanol Extraction Process for Active Components from Broussonetia papyrifera Root Bark and Its Antioxidant Activity
-
摘要: 以构树根皮为原料,通过单因素实验考察不同因素对构树根皮总黄酮和多酚提取量的影响。运用Design-Expert 11软件设计响应面法优化构树根皮乙醇回流提取工艺,并进行工艺验证。最后对提取得到的构树根皮乙醇提取物进行DPPH·、ABTS+·、羟自由基清除能力和总还原能力的测定,评价其抗氧化活性。响应面分析表明,构树根皮总黄酮和多酚的最佳提取工艺为提取温度75 ℃、提取时间117 min、料液比1:16 g/mL、乙醇浓度70%。此条件下,构树根皮总黄酮和多酚提取量分别为23.93±0.30 mg/g和14.69±0.56 mg/g,与预测理论值接近。抗氧化实验表明,构树根皮乙醇提取物对DPPH·、ABTS+·和羟自由基的半数清除浓度(IC50)分别为5.256 μg/mL、0.259 mg/mL和0.310 mg/mL,且清除能力与其浓度呈现一定的量效关系。当提取物浓度为1.0 mg/mL时,总还原能力达到1.484±0.062。此优化实验有效可行,构树根皮乙醇提取物具有较强的抗氧化活性。本研究为构树资源的综合利用提供了一定的理论依据。Abstract: In this study, single factor experiments were employed to determine the effects of various factors on yields of total flavonoids and polyphenols from Broussonetia papyrifera root bark. Then Box-Behnken design and response surface methodology were used to optimize the ethanol reflux extraction process using the Design-Expert 11 software. Moreover, the antioxidant activity of the ethanol extract of Broussonetia papyrifera root bark was evaluated by determining the scavenging capacity of DPPH·, ABTS+·, and the hydroxyl free radical, as well as the total reducing power. Results showed that the optimal conditions were as follows: Extraction temperature 75 ℃, extraction time 117 min, solid-liquid ratio 1:16 g/mL, and ethanol concentration 70%. Under these conditions, the experimental extraction yield values of total flavonoids and polyphenols from Broussonetia papyrifera root bark were 23.93±0.30 mg/g and 14.69±0.56 mg/g, respectively, which was not significantly different in comparison to predicted values. The IC50 values of scavenging rates on DPPH·, ABTS+·, and the hydroxyl free radical were 5.256 μg/mL, 0.259 mg/mL, and 0.310 mg/mL, respectively, and the scavenging rates showed a certain dose-effect relationship with the sample concentration. In addition, the total reducing power of 1.0 mg/mL ethanol extract of the root bark was 1.484±0.062. These results indicated that this optimization test was effective and feasible, and the ethanol extract of Broussonetia papyrifera root bark had good antioxidant activity in vitro. The present study provides supplement information for the comprehensive utilization of Broussonetia papyrifera in food and medicine ingredients.
-
构树(Broussonetia papyrifera (L.) vent)别名楮树、谷浆树,为桑科(Moraceae)构属多年生落叶乔木,生长于我国华南、华北、西南等地区[1]。凭借树叶和树皮在牲畜饲料和造纸行业得到广泛的应用,构树扶贫已成为国家“精准扶贫十大工程”之一[2-3]。丰富的营养价值[4]和抗氧化[5-6]、降血糖[7]、抗炎[8]等多种生物活性赋予了构树叶、果实、根皮等不同部位在药食领域的开发价值和潜力,使其被视为不可多得的天然保健品来源。
构树根系浅,侧根分布广泛,萌芽力和分蘖力强,生长快,耐修剪[9]。近年来,构树根皮活性成分的提取和分离引起国内外学者的广泛关注。杨晨悦等[10]从构树根皮中分离并鉴定出咖啡酸甲酯、黑立脂素苷、槲皮素等11个酚类化合物;Son等[11]从构树根皮中分离得到巴比黄酮醇A,其结构为5,7,3',4'-四羟基-6,5'-二-(γ,γ-二甲基烯丙基)-黄酮醇;Ryu等[12]从构树根皮中分离出构树芴酮A和构树芴酮B,随后又从根皮提取物中分离鉴定出9种酚类物质[13]。丰富的多酚类化合物赋予构树根皮及其提取物多种生物学活性[14-15]。张意笠等[16]发现,构树根皮总黄酮具有抗氧化活性,且两者存在一定量效关系。Lee等[17]发现,从构树根皮中提取的黄酮醇B可提高机体对胰岛素的敏感性,具有开发成降糖相关功能性食品的潜力。
构树根皮富含黄酮类和多酚类化合物,且这两类物质主要存在于根皮的乙醇提取物中[10,14,16]。相关研究结果表明,这两类物质具有多种活性,有望成为相关保健食品开发的重要来源[15-17]。然而,针对构树叶[18]或根皮[16,19]提取工艺的研究均以黄酮的得率为指标,无法兼顾多种活性成分的提取效果。因此,本研究以总黄酮和多酚的提取量为指标,采用乙醇回流提取法,通过Box-Behnken法优化构树根皮多酚类物质的提取工艺,以期促进构树资源的高效开发利用。同时,通过测定提取物对DPPH自由基(DPPH·)、ABTS阳离子自由基(ABTS+·)、羟基自由基(·OH)的清除能力及对二价铁的还原能力,分析构树根皮的抗氧化活性,为开发天然抗氧化剂和相关功能食品提供依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
构树根皮 购于安徽亳州中药材交易中心,由广东药科大学中药学院程轩轩教授鉴定为构树嫩根皮;芦丁标准品、没食子酸标准品 生物制品,BR,纯度≥98%,上海麦克林有限公司;福林酚试剂 分析纯,北京索莱宝科技有限公司;1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(DPPH)、2,2'-联氮-双-3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸(ABTS) 分析纯,Sigma公司;其他试剂 均为分析纯。
SS-1022高速粉碎机 武义海纳电器有限公司;UV-1700紫外分光光度计 日本岛津公司;Multiskan酶标仪 赛默飞世尔科技公司;HH-2恒温水浴锅 常州亿通分析仪器制造有限公司;ALX13M07型高速离心机 贝克曼库尔特商贸有限公司;RE-5299型旋转蒸发仪 广州市星烁仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 原材料预处理
将新鲜构树嫩根皮洗净晾晒,切成碎块,60 ℃烘干至恒重,粉碎后过60目筛,−20 ℃保存备用。
1.2.2 提取工艺
准确称取2.0 g构树根皮粉末,按照设定条件连续回流提取两次,抽滤后将提取液45 °C旋蒸浓缩,定容备用。
1.2.3 单因素实验
设定提取时间60 min、料液比1:10 g/mL,乙醇浓度65%,探究提取温度(55、65、75、85、95 ℃)对总黄酮、多酚提取量的影响;设定提取温度65 ℃ 、料液比1:10 g/mL,乙醇浓度65%,探究提取时间(30、60、90、120、150 min)对总黄酮、多酚提取量的影响;设定提取温度65 ℃ 、提取时间60 min、乙醇浓度65%,探究料液比(1:5、1:10、1:15、1:20、1:25 g/mL)对总黄酮及多酚提取量的影响;设定提取温度65 ℃ 、提取时间60 min、料液比1:10 g/mL,探究乙醇浓度(55%、65%、75%、85%、95%)对总黄酮及多酚提取量的影响。以上实验每组平行3次。
1.2.4 响应面试验方法设计
采用Box-Behnken试验设计原则,以构树根皮总黄酮、多酚的提取量为指标,对提取温度、提取时间、料液比、乙醇浓度进行试验设计,具体因素水平见表1。
表 1 Box-Behnken试验因素和水平Table 1. Test factors and levels of Box-Behnken水平 因素 A温度(°C ) B时间(min) C料液比(g/mL) D乙醇浓度(%) −1 65 60 1:10 65 0 75 90 1:15 75 1 85 120 1:20 85 1.2.5 总黄酮提取量测定
配制浓度为0、5、10、20、30、40、50 μg/mL的芦丁溶液。参考张富坤等[20]的方法进行总黄酮测定,并以芦丁浓度为横坐标(x),以吸光值为纵坐标(y),绘制标准曲线,得回归方程y=0.417x+0.0058(R2=0.9985)。通过方程得出构树根皮提取液中总黄酮浓度,按照公式(1)计算构树根皮提取液中总黄酮含量。
(1) 式中:W1为总黄酮提取量,mg/g;C为构树根皮提取液中总黄酮浓度,mg/mL;V为提取液体积,mL;N为稀释倍数;M为构树根皮原料质量,g。
1.2.6 多酚提取量测定
配制浓度为0、10、20、40、60、80、100 μg/mL的没食子酸溶液。参考Yap等[21]的方法进行多酚含量测定,并以没食子酸浓度为横坐标(x),以吸光值为纵坐标(y),绘制标准曲线,得回归方程y=4.1052x−0.0091(R2=0.9901)。通过方程得出构树根皮提取液中多酚的浓度,按照公式(2)计算构树根皮提取液中多酚含量。
(2) 式中:W2为多酚提取量,mg/g;C为构树根皮提取液中多酚的浓度,mg/mL;V为提取液体积,mL;N为稀释倍数;M为构树根皮原料质量,g。
1.2.7 抗氧化活性测定
1.2.7.1 DPPH自由基清除能力测定
参考Cheung等[22]的方法,将构树根皮乙醇提取物干燥后,用无水乙醇配成提取物浓度为4、8、12、16、20 μg/mL的样品溶液,各吸取100 μL,分别加入100 μL 0.1 mmol/L DPPH溶液,混匀,室温避光静置30 min,在517 nm处测定各样品吸光值Ai,用无水乙醇代替DPPH测定吸光值Aj,用无水乙醇代替样品测定吸光值Ao。相同浓度的抗坏血酸溶液用作阳性对照。
(3) 1.2.7.2 ABTS阳离子自由基清除能力测定
参照Soong等[23]的方法配制ABTS储备液,并用无水乙醇调整使其在734 nm处吸光值处在0.70±0.02,即得ABTS工作液。分别取0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8、1.0 mg/mL的提取物溶液各1 mL,分别加入4 mL ABTS,混匀,避光静置6 min,在734 nm处测量吸光值Ai,无水乙醇替代ABTS,测量吸光值Aj;用无水乙醇替代样品溶液,测量吸光值Ao。相同浓度的抗坏血酸溶液用作阳性对照。
(4) 1.2.7.3 羟自由基清除率测定
参考Li等[24]的方法,分别取0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8、1.0 mg/mL的提取物溶液各2 mL,加入2 mL 6 mmol/mL FeSO4溶液及2 mL 6 mmol/mL H2O2溶液,摇匀放置10 min后,加入2 mL 6 mmol/mL水杨酸溶液,37 °C 水浴30 min,3700 r/min离心10 min,取上清液,测量510 nm处吸光值Ai,用蒸馏水代替水杨酸,用同样方法测量吸光值Aj;另用无水乙醇作空白,测定吸光值Ao。相同浓度的抗坏血酸溶液用作阳性对照。
(5) 1.2.7.4 总还原能力测定
分别取0.2、0.4、0.6、0.8、1.0 mg/mL的提取物溶液各1 mL,加入1%(w/v)铁氰化钾溶液及pH6.6磷酸缓冲液各1 mL,混匀,50 °C水浴20 min,加入2 mL 10%(w/v)三氯乙酸溶液,3000 r/min离心10 min,取2 mL上清液,加入2 mL蒸馏水和0.4 mL 0.1%(w/v)FeCl3,50 °C水浴10 min,测量700 nm处吸光值。以无水乙醇作空白,相同浓度的抗坏血酸溶液用作阳性对照。
1.3 数据处理
所有试验重复3次,数据以平均值±标准差表示,采用Graphpad prism 8进行作图及差异性分析;采用Design-Expert 11完成响应面设计并进行方差分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验结果
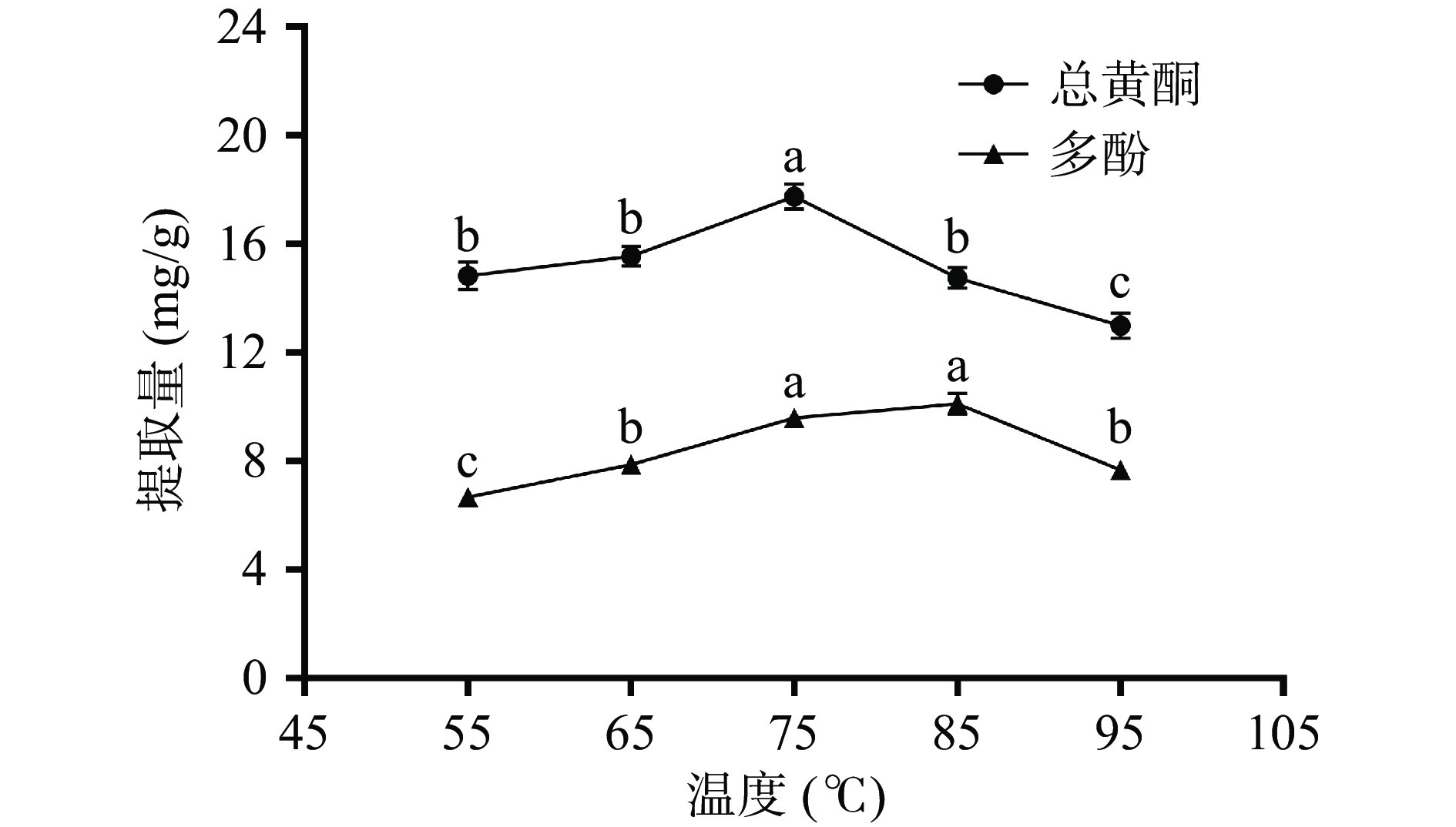
2.1.1 提取温度对提取构树根皮总黄酮和多酚的影响
由图1可知,总黄酮和多酚提取量呈现先增加后减少。在75 ℃条件下,总黄酮提取量达到最大值17.74±0.47 mg/g;此后,随温度增加,提取量明显下降。这可能是温度升高导致脂溶性杂质溶出增加、消耗溶剂所致。在85 ℃条件下,多酚提取量达到最大值10.11±0.38 mg/g,此后随温度升高,提取量有所下降。这可能是高温环境下,多酚容易发生分解,导致提取物中多酚含量下降[25]。综合考虑节能及成本效益,选择65、75和85 ℃为优化工艺的提取温度。
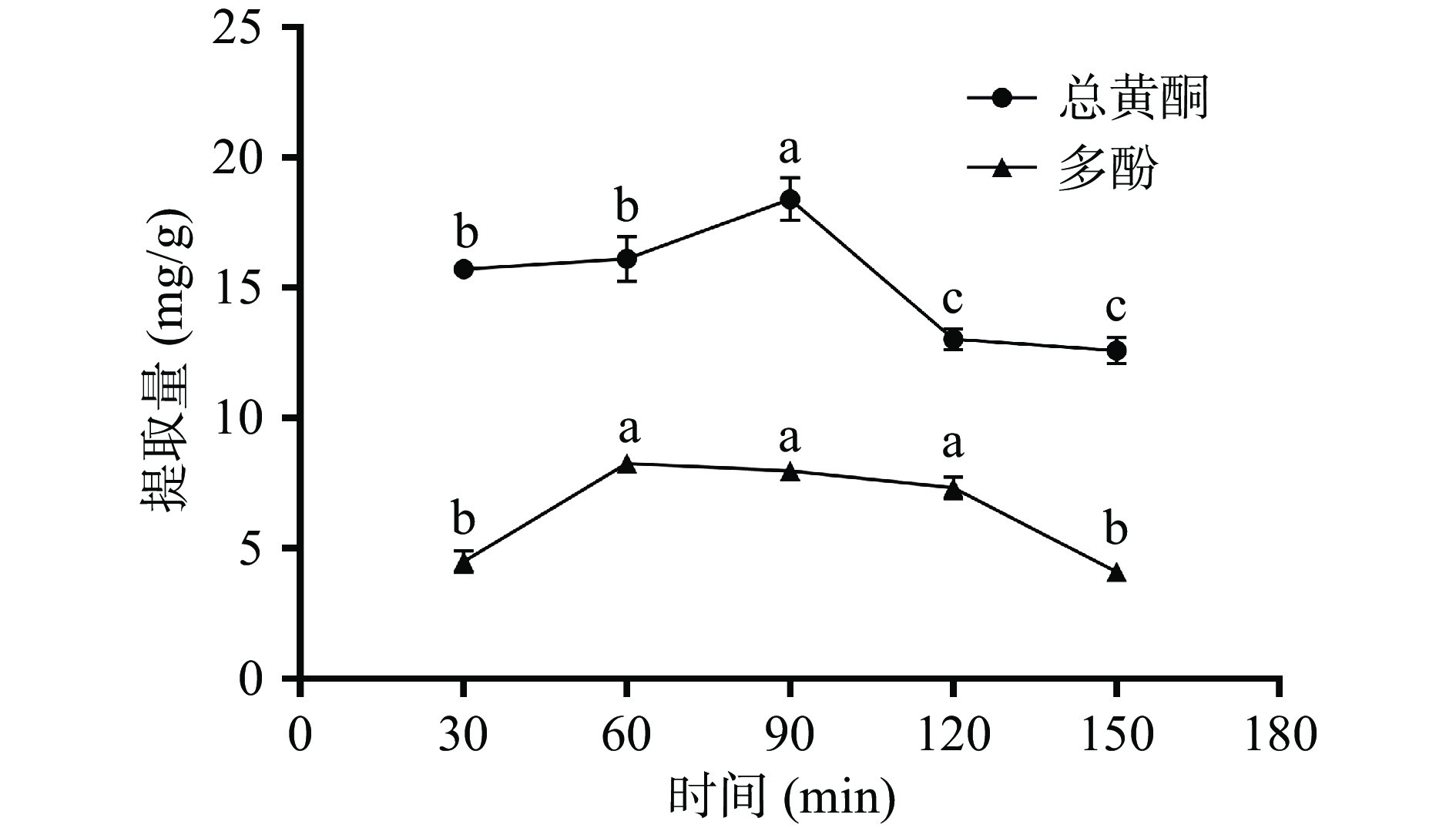
2.1.2 提取时间对提取构树根皮总黄酮和多酚的影响
由图2可知,连续提取90 min后,总黄酮达到最大提取量18.41±0.80 mg/g;连续提取60 min,多酚达到最大提取量8.26±0.15 mg/g。然而,时间继续延长,总黄酮、多酚提取量开始减少。这可能是经过一段时间提取后,总黄酮、多酚已基本被提出,提取时间过长会导致酚类物质发生氧化、降解,致使其含量下降[26]。因此,选取60、90和120 min为优化工艺的提取时间。
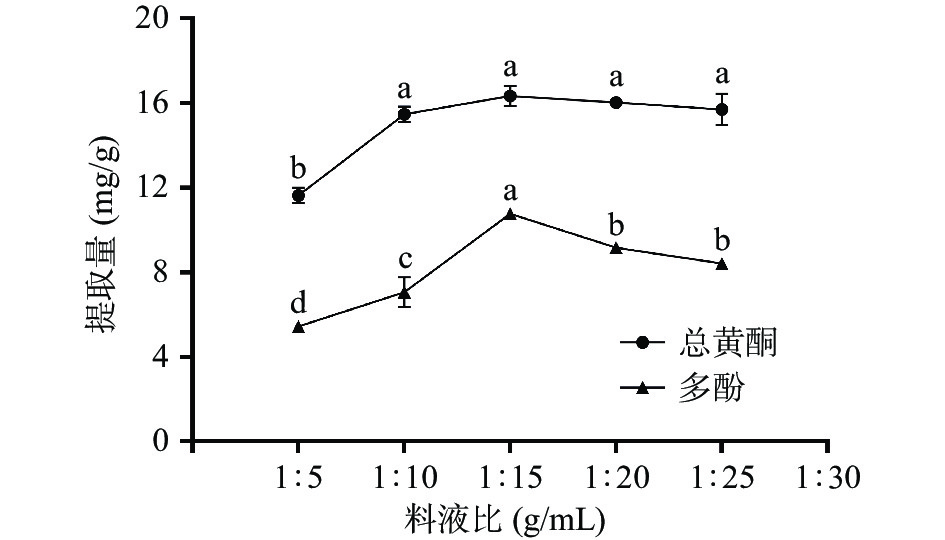
2.1.3 料液比对提取构树根皮总黄酮和多酚的影响
结合图3,当料液比为1:15 g/mL时,总黄酮和多酚提取量分别达到最大值,分别为16.35±0.479 mg/g和10.77±0.18 mg/g,继续增大乙醇用量,总黄酮和多酚的提取量下降。这可能是料液比为1:15 g/mL时,构树根皮中总黄酮和多酚已全部溶出,再增大料液比可能使其他醇溶性杂质析出,与活性成分共同竞争溶出空间,从而导致含量下降[27]。综合考虑总黄酮与多酚以及提取成本,选择1:10、1:15和1:20 g/mL作为优化工艺的料液比。
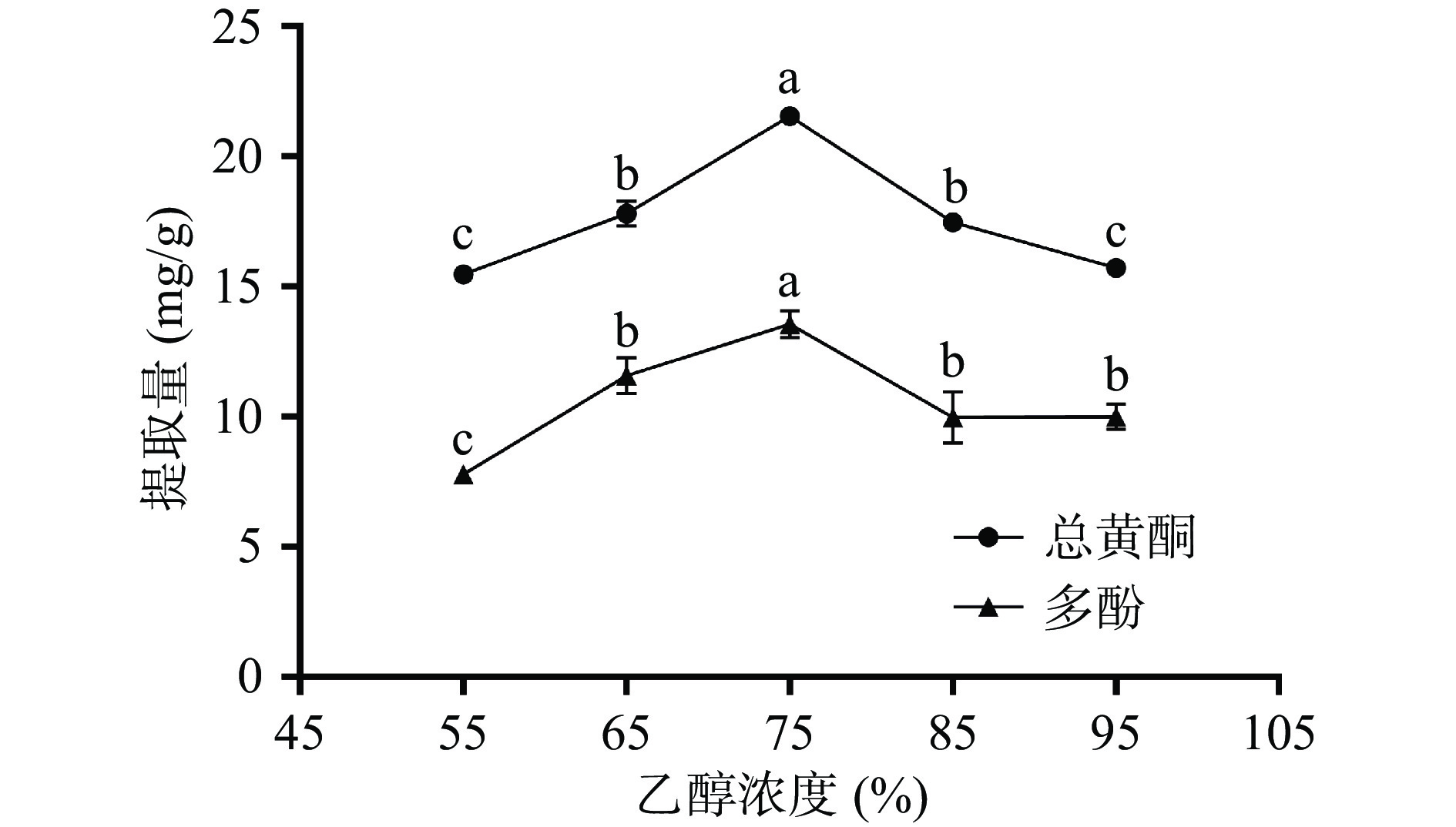
2.1.4 乙醇浓度对提取构树根皮总黄酮和多酚的影响
从图4可以看出,随着乙醇浓度的增加,总黄酮和多酚的提取量先增加后减少。采用75%乙醇进行提取时,两者的提取量最大,分别为21.55±0.28 mg/g和13.55±0.52 mg/g。在乙醇浓度为55%~75%的条件下,提取体系促进酚类物质与蛋白质、多糖等物质之间的氢键及疏水作用力破坏,有助于提取总黄酮和多酚;相反,高浓度乙醇与总黄酮、多酚之间极性差异大,不利于相关物质的提取[28]。因此,选取65%、75%和85%为优化工艺的乙醇浓度。
2.2 响应面试验优化提取工艺
2.2.1 响应面试验设计
运用Design-Expert 11软件对构树根皮中总黄酮和多酚的提取工艺进行优化,共产生29组实验(包括5组零点实验进行误差校正),具体结果见表2。
表 2 响应面试验设计与结果Table 2. Design and results of response surface experiment试验号 因素 总黄酮提取量(mg/g) 多酚提取量(mg/g) A温度 B时间 C料液比 D乙醇浓度 1 −1 −1 0 0 13.72 13.50 2 1 −1 0 0 17.00 12.86 3 −1 1 0 0 19.95 12.82 4 1 1 0 0 17.27 13.34 5 0 0 −1 −1 13.83 11.66 6 0 0 1 −1 19.63 12.29 7 0 0 −1 1 14.89 12.28 8 0 0 1 1 14.96 13.69 9 −1 0 0 −1 14.20 12.23 10 1 0 0 −1 19.24 12.85 11 −1 0 0 1 18.07 13.42 12 1 0 0 1 17.79 13.31 13 0 −1 −1 0 11.50 11.54 14 0 1 −1 0 17.22 12.77 15 0 −1 1 0 16.24 12.61 16 0 1 1 0 17.27 13.48 17 −1 0 −1 0 12.11 11.88 18 1 0 −1 0 11.96 11.34 19 −1 0 1 0 13.88 13.26 20 1 0 1 0 14.99 12.29 21 0 −1 0 −1 19.87 11.29 22 0 1 0 −1 23.55 14.64 23 0 −1 0 1 20.51 14.21 24 0 1 0 1 23.58 13.02 25 0 0 0 0 22.35 14.23 26 0 0 0 0 23.65 14.70 27 0 0 0 0 22.67 14.64 28 0 0 0 0 21.67 14.07 29 0 0 0 0 22.51 14.43 2.2.2 回归模型建立及方差分析
采用Design-Expert 11软件进行回归拟合及方差分析,结果见表3和表4。
表 3 总黄酮回归模型方差分析Table 3. Analysis of variance of the regression model of flavonoids方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 382.75 14 27.34 23.06 <0.0001 ** A温度 3.33 1 3.33 2.81 0.1158 B时间 33.33 1 33.33 28.12 0.0001 ** C料液比 19.88 1 19.88 16.77 0.0011 ** D乙醇浓度 0.0222 1 0.0222 0.0187 0.8931 AB 8.88 1 8.88 7.49 0.0160 * AC 0.4013 1 0.4013 0.3386 0.5699 AD 7.07 1 7.07 5.96 0.0285 * BC 5.48 1 5.48 4.62 0.0496 * BD 0.0929 1 0.0929 0.0783 0.7836 CD 8.22 1 8.22 6.93 0.0197 * A² 120.75 1 120.75 101.87 <0.001 ** B² 4.98 1 4.98 4.2 0.0597 C² 216.4 1 216.4 182.57 <0.001 ** D² 2.11 1 2.11 1.78 0.2033 残差 16.59 14 1.19 失拟项 14.55 10 1.46 2.85 0.1621 不显著 纯误差 2.04 4 0.5102 总方差 399.34 28 注:** P<0.01,表示差异性极显著;* P<0.05,表示差异性显著,表4同。 表 4 多酚回归模型方差分析Table 4. Analysis of variance of the regression model of polyphenols方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 27.24 14 1.95 14.74 <0.0001 ** A温度 0.1051 1 0.1051 0.7962 0.3873 B时间 1.37 1 1.37 10.42 0.0061 ** C料液比 3.15 1 3.15 23.9 0.0002 ** D乙醇浓度 2.06 1 2.06 15.64 0.0014 ** AB 0.3381 1 0.3381 2.56 0.1318 AC 0.0466 1 0.0466 0.3529 0.5620 AD 0.1357 1 0.1357 1.03 0.3278 BC 0.0339 1 0.0339 0.257 0.6201 BD 5.17 1 5.17 39.21 <0.0001 ** CD 0.1542 1 0.1542 1.17 0.2981 A² 4.61 1 4.61 34.94 <0.0001 ** B² 1.44 1 1.44 10.92 0.0052 C² 11.77 1 11.77 89.14 <0.0001 ** D² 2.5 1 2.5 18.93 0.0007 ** 残差 1.85 14 0.132 失拟项 1.57 10 0.1567 2.23 0.2283 不显著 纯误差 0.2809 4 0.0702 总方差 29.09 28 2.2.2.1 总黄酮提取量回归模型方差分析
构树根皮总黄酮提取量的回归模型方差分析结果见表3。经回归拟合后,得到总黄酮提取量的回归方程为:Y1=22.57+0.5269A+1.67B+1.29C−0.043D−1.49AB+0.3168AC−1.33AD−1.17BC−0.1524BD−1.43CD−4.31A2−0.8760B2−5.78C2−0.5705D2。
由表3可知,模型F值为23.06,且P<0.0001,说明模型极显著;失拟项P=0.1621,影响不显著,说明其他因素对试验结果影响不大,所选模型适宜;决定系数R2=0.9584,表明此模型能解释95.84%响应值的变化,模型可靠,可用于构树根皮总黄酮提取量的分析和预测。从F值大小可知,各因素对总黄酮提取量影响的主次顺序为:时间(B)>料液比(C)>温度(A)>乙醇浓度(D)。
2.2.2.2 多酚提取量回归模型方差分析
构树根皮多酚提取量的回归模型方差分析结果见表4。经回归拟合后,得到多酚提取量回归方程为: Y2=14.41−0.0936A+0.3385B+0.5127C+0.4147D+0.2908AB−0.1079AC−0.1842AD−0.0921BC−1.14BD+0.1963CD−0.8432A2−0.4715B2−1.35C²−0.6206D2。
由表4可知,模型F值为14.74,且P<0.0001,说明模型极显著;失拟项P=0.2283,影响不显著,说明其他因素对试验结果影响较小,所选模型适宜;决定系数R2=0.9365表明方程有良好的拟合度,此模型能解释93.65%响应值的变化,适用于构树根皮多酚提取量的分析和预测。从F值大小可知,各因素对多酚提取量影响的主次顺序为:料液比(C)>乙醇浓度(D)>时间(B)>温度(A)。
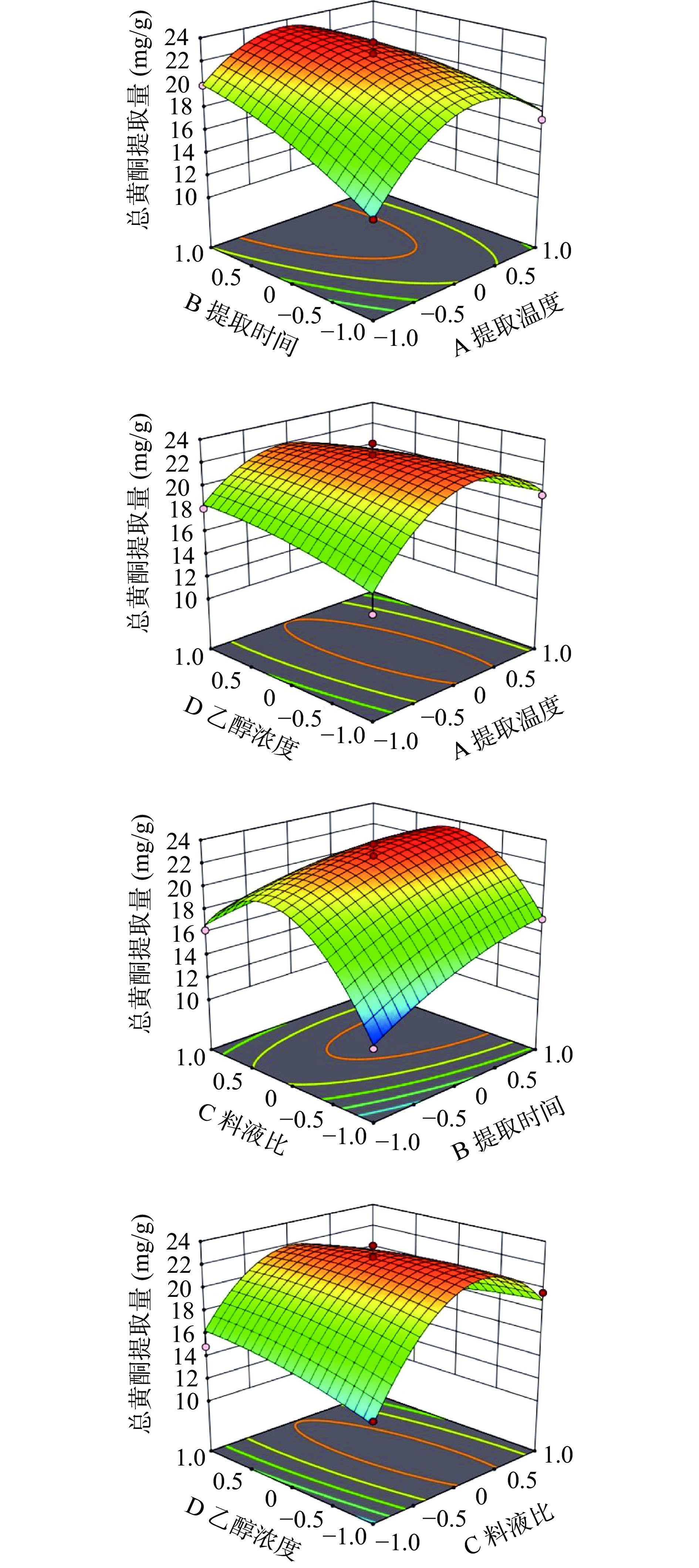
2.2.3 各因素交互作用分析
采用Design-Expert 11软件,绘制各因素之间交互作用的3D响应面图,结果见图5和图6。响应面曲面的陡缓变化情况和等高线的形状可反映出各交互作用对响应值的影响,响应面曲面越陡峭、等高线呈现椭圆形表明两因素交互作用显著,反之则说明交互作用对响应值的影响不显著[29]。
2.2.3.1 总黄酮提取量交互作用分析
从图5可以看出,AB、AD、BC、CD所形成的响应面曲面坡度较陡峭,其等高线呈椭圆形,表明AB、AD、BC、CD各自交互作用明显,对总黄酮提取量的影响显著。对比可知,与表3模型方差分析结果一致。
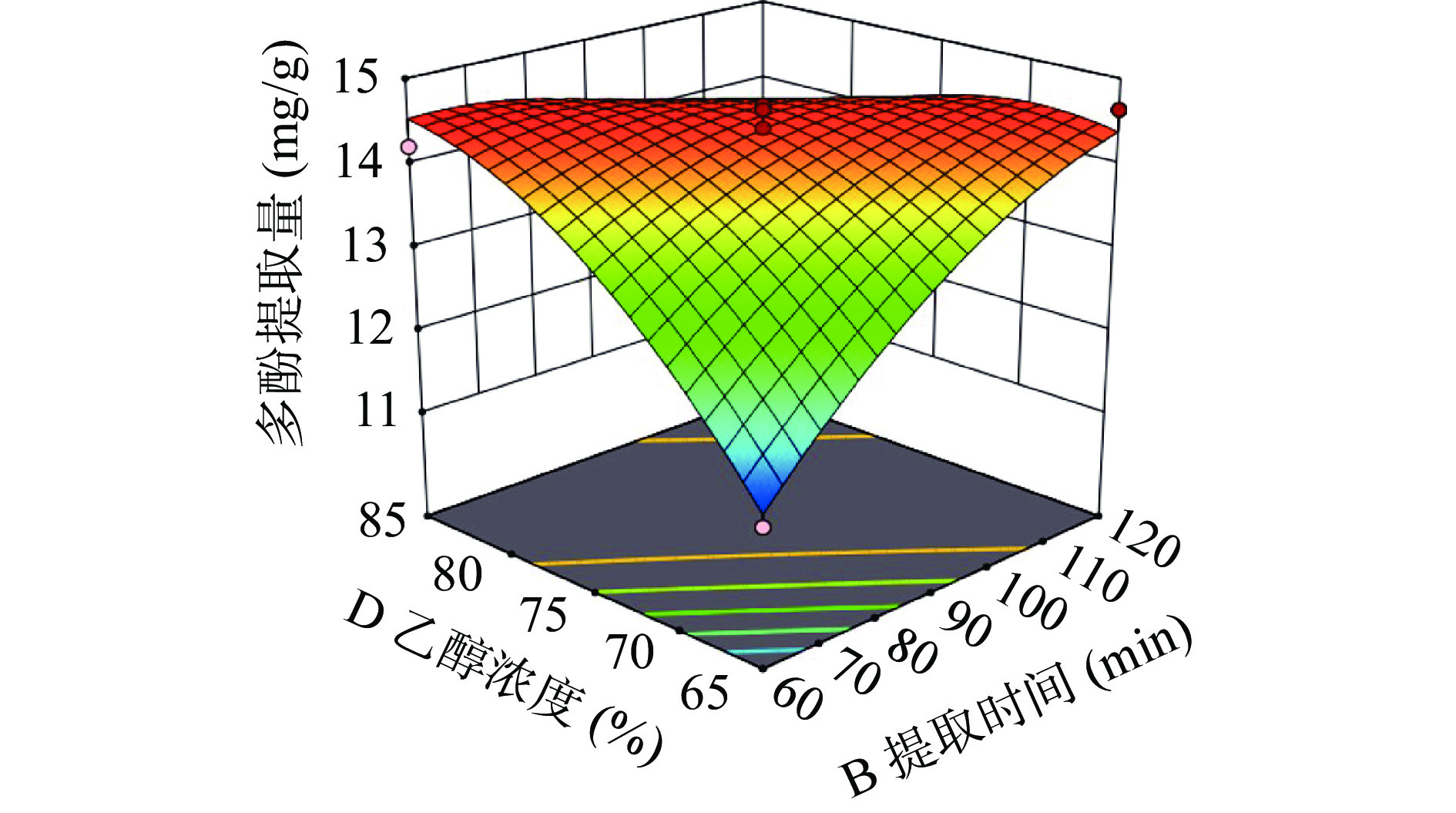
2.2.3.2 多酚提取量交互作用分析
从图6可以看出,BD所形成的响应面曲面坡度较陡峭,等高线呈椭圆形,表明BD的交互作用明显且对多酚提取量的影响极显著;而其他交互作用均不显著。对比可知,与表4模型方差分析结果一致。
2.2.4 最优条件的确定及验证试验
模型和方差分析结果表明,提取时间、料液比和乙醇浓度对总黄酮和多酚提取量的影响显著。在上述基础上,将总黄酮和多酚提取量的同时最大化设为优化的最终目标,通过Design-Expert 11.0软件分析表明,构树根皮最优提取条件为:提取温度75.48 ℃、提取时间117.16 min、料液比1:15.5 g/mL、乙醇浓度70.42%。在最佳工艺下,总黄酮、多酚提取量的预测值分别为23.34 mg/g和14.52 mg/g。为方便操作,将相关参数调整为提取温度75 ℃、提取时间117 min、料液比1:16 g/mL、乙醇浓度70%,并进行3次独立验证。经测定,总黄酮、多酚的实际提取量分别为23.93±0.30 mg/g和14.69±0.56 mg/g,与预测理论值的相对误差分别为2.53%和1.03%,说明响应面试验和回归方程的预测值基本吻合,优化所得提取工艺参数具有实用价值。
2.3 抗氧化活性测定结果
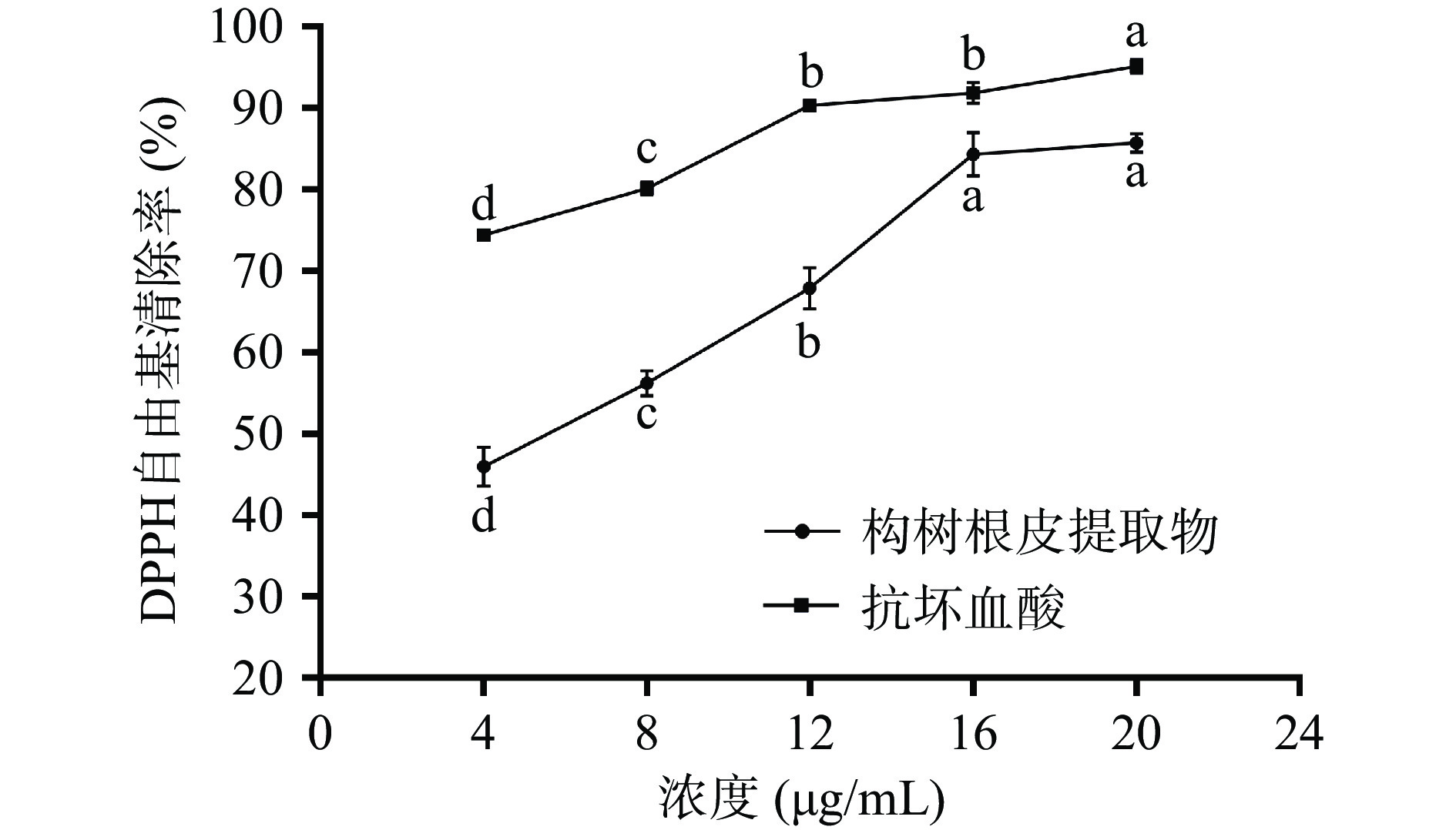
2.3.1 DPPH自由基清除率测定
由图7可知,构树根皮提取物清除DPPH自由基的能力随浓度增大而提高。当浓度从4 μg/mL增加到20 μg/mL时,清除率呈现快速增长。当浓度为16 μg/mL时,提取物和抗坏血酸的清除率分别达到84.34%和91.92%,两者十分接近,说明构树根皮提取物在较低浓度就具有较强的DPPH自由基清除能力。经计算,其IC50值为5.256 μg/mL,显著小于构树根总黄酮对DPPH自由基的IC50值[16],这可能与提取物中含有较多的多酚类物质有关。
2.3.2 ABTS阳离子自由基清除率测定
结合图8,构树根皮提取物对ABTS+·的清除率呈现一定的量效关系,其IC50值为0.259 mg/mL。在浓度为0.2~1 mg/mL时,随提取物浓度增加,ABTS+·的清除率明显上升。当浓度为1 mg/mL时,清除率达到94.81%,与抗坏血酸的清除效果非常接近,且高于同为桑科的无花果的总黄酮提取物对ABTS+·的清除作用[30]。说明构树根皮提取物有较强的抗氧化活性。
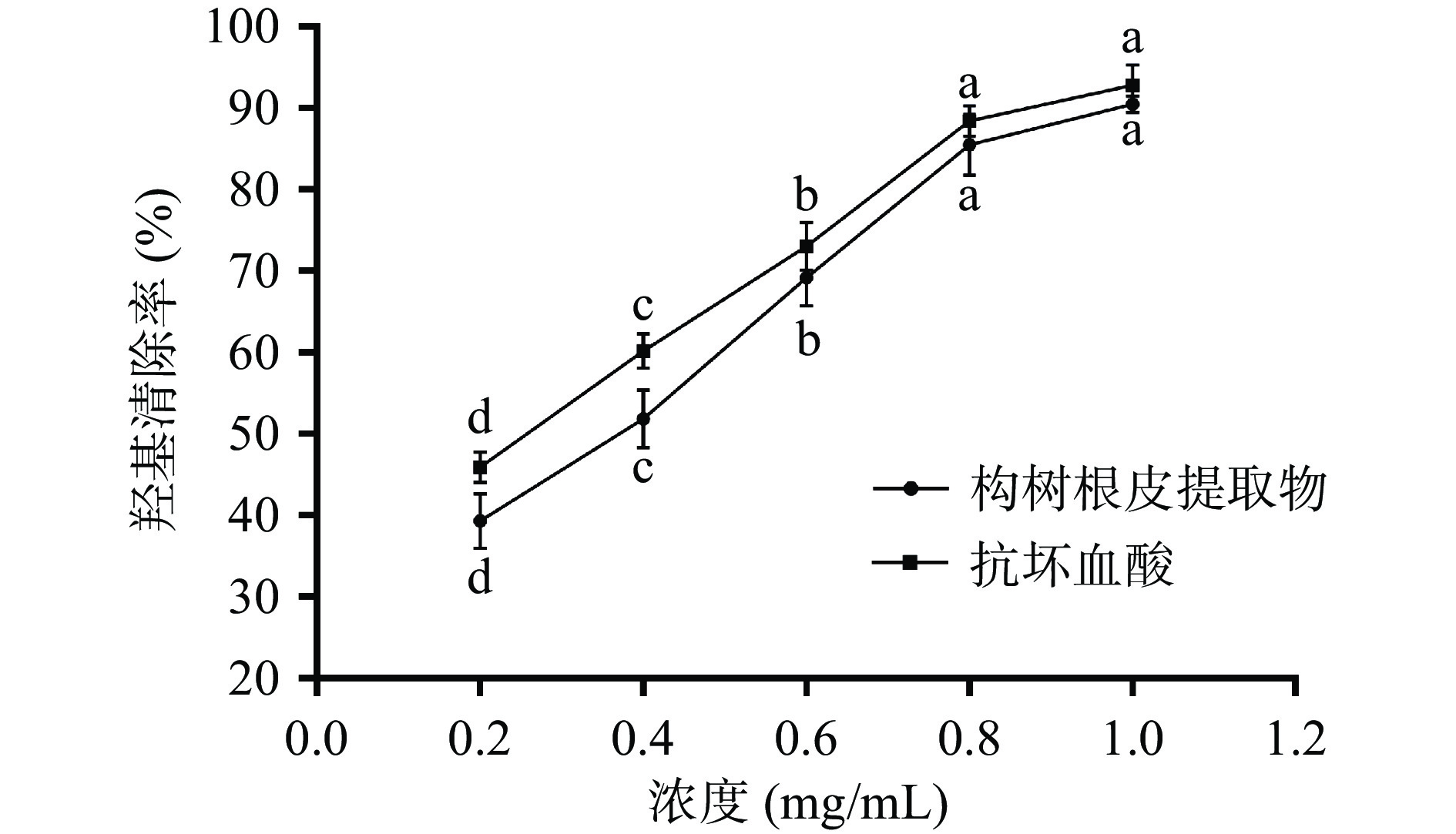
2.3.3 羟基清除能力测定
图9表明,构树根皮提取物具有清除·OH的能力,且具有较好的量效关系,其IC50值为0.310 mg/mL。当浓度从0.2 mg/mL增大到0.8 mg/mL时,清除率由39.29%增加到85.52%;当浓度为1.0 mg/mL时,提取物的·OH清除率高达90.49%,略低于抗坏血酸的清除率,显著高于同为桑科植物的薛荔藤多酚提取物的清除能力[31]。这可能是由于构树根皮醇提物中具有抗氧化功效的物质较多[32]。
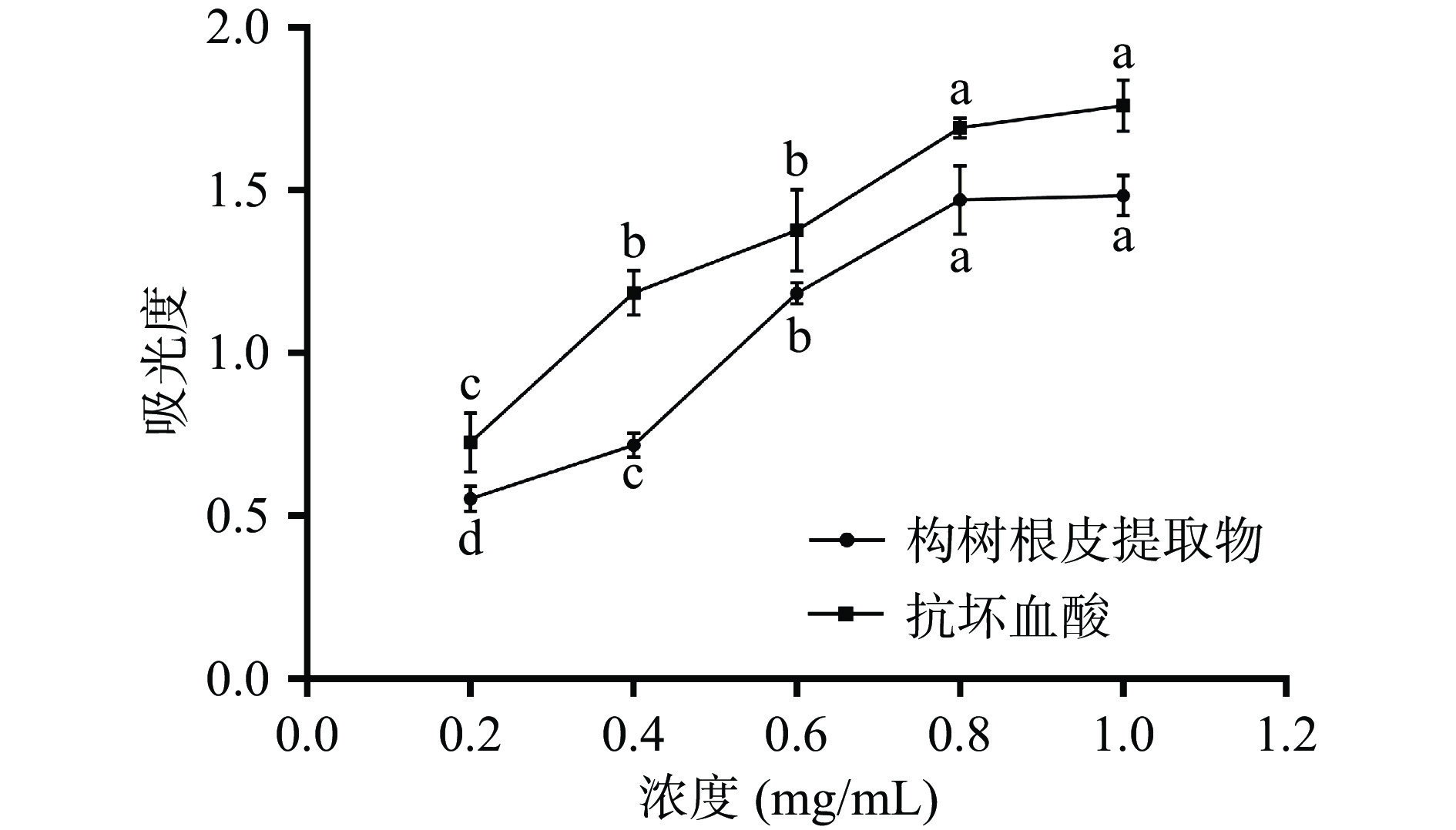
2.3.4 总还原能力测定
如图10所示,提取物的总还原能力整体低于同浓度的抗坏血酸溶液。当浓度为0.6 mg/mL时,提取物的总还原能力接近抗坏血酸;当浓度为1.0 mg/mL,提取物的总还原能力为1.484±0.062,显著高于同为乙醇提取的小麦麸皮总黄酮提取物的总还原力[33]。
从上述结果可以看出,构树根皮提取物有清除各种自由基(DPPH·、ABTS+·、·OH)的能力,其抗氧化活性和总还原能力均较好,具有应用于天然抗氧化剂的潜力。
3. 结论
本研究以构树根皮为原料,以总黄酮和多酚提取量为指标,通过响应面法优化获得最佳提取工艺:提取温度75 ℃、提取时间117 min、料液比1:16 g/mL、乙醇浓度70%。在该条件下,总黄酮和多酚的提取量分别为23.93±0.30 mg/g和14.69±0.56 mg/g,与理论值相近,说明响应面法优化所得提取工艺是可靠的,对于今后实际生产具有指导意义。此外,DPPH·、ABTS+·和·OH的体外清除试验表明,构树根皮提取物具有较好的抗氧化活性,且总还原能力较强。因此,本研究为今后构树资源的综合开发利用奠定了基础,也为开发天然抗氧化剂和功能食品提供了科学依据。
-
表 1 Box-Behnken试验因素和水平
Table 1 Test factors and levels of Box-Behnken
水平 因素 A温度(°C ) B时间(min) C料液比(g/mL) D乙醇浓度(%) −1 65 60 1:10 65 0 75 90 1:15 75 1 85 120 1:20 85 表 2 响应面试验设计与结果
Table 2 Design and results of response surface experiment
试验号 因素 总黄酮提取量(mg/g) 多酚提取量(mg/g) A温度 B时间 C料液比 D乙醇浓度 1 −1 −1 0 0 13.72 13.50 2 1 −1 0 0 17.00 12.86 3 −1 1 0 0 19.95 12.82 4 1 1 0 0 17.27 13.34 5 0 0 −1 −1 13.83 11.66 6 0 0 1 −1 19.63 12.29 7 0 0 −1 1 14.89 12.28 8 0 0 1 1 14.96 13.69 9 −1 0 0 −1 14.20 12.23 10 1 0 0 −1 19.24 12.85 11 −1 0 0 1 18.07 13.42 12 1 0 0 1 17.79 13.31 13 0 −1 −1 0 11.50 11.54 14 0 1 −1 0 17.22 12.77 15 0 −1 1 0 16.24 12.61 16 0 1 1 0 17.27 13.48 17 −1 0 −1 0 12.11 11.88 18 1 0 −1 0 11.96 11.34 19 −1 0 1 0 13.88 13.26 20 1 0 1 0 14.99 12.29 21 0 −1 0 −1 19.87 11.29 22 0 1 0 −1 23.55 14.64 23 0 −1 0 1 20.51 14.21 24 0 1 0 1 23.58 13.02 25 0 0 0 0 22.35 14.23 26 0 0 0 0 23.65 14.70 27 0 0 0 0 22.67 14.64 28 0 0 0 0 21.67 14.07 29 0 0 0 0 22.51 14.43 表 3 总黄酮回归模型方差分析
Table 3 Analysis of variance of the regression model of flavonoids
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 382.75 14 27.34 23.06 <0.0001 ** A温度 3.33 1 3.33 2.81 0.1158 B时间 33.33 1 33.33 28.12 0.0001 ** C料液比 19.88 1 19.88 16.77 0.0011 ** D乙醇浓度 0.0222 1 0.0222 0.0187 0.8931 AB 8.88 1 8.88 7.49 0.0160 * AC 0.4013 1 0.4013 0.3386 0.5699 AD 7.07 1 7.07 5.96 0.0285 * BC 5.48 1 5.48 4.62 0.0496 * BD 0.0929 1 0.0929 0.0783 0.7836 CD 8.22 1 8.22 6.93 0.0197 * A² 120.75 1 120.75 101.87 <0.001 ** B² 4.98 1 4.98 4.2 0.0597 C² 216.4 1 216.4 182.57 <0.001 ** D² 2.11 1 2.11 1.78 0.2033 残差 16.59 14 1.19 失拟项 14.55 10 1.46 2.85 0.1621 不显著 纯误差 2.04 4 0.5102 总方差 399.34 28 注:** P<0.01,表示差异性极显著;* P<0.05,表示差异性显著,表4同。 表 4 多酚回归模型方差分析
Table 4 Analysis of variance of the regression model of polyphenols
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 27.24 14 1.95 14.74 <0.0001 ** A温度 0.1051 1 0.1051 0.7962 0.3873 B时间 1.37 1 1.37 10.42 0.0061 ** C料液比 3.15 1 3.15 23.9 0.0002 ** D乙醇浓度 2.06 1 2.06 15.64 0.0014 ** AB 0.3381 1 0.3381 2.56 0.1318 AC 0.0466 1 0.0466 0.3529 0.5620 AD 0.1357 1 0.1357 1.03 0.3278 BC 0.0339 1 0.0339 0.257 0.6201 BD 5.17 1 5.17 39.21 <0.0001 ** CD 0.1542 1 0.1542 1.17 0.2981 A² 4.61 1 4.61 34.94 <0.0001 ** B² 1.44 1 1.44 10.92 0.0052 C² 11.77 1 11.77 89.14 <0.0001 ** D² 2.5 1 2.5 18.93 0.0007 ** 残差 1.85 14 0.132 失拟项 1.57 10 0.1567 2.23 0.2283 不显著 纯误差 0.2809 4 0.0702 总方差 29.09 28 -
[1] 彭献军, 沈世华. 构树: 一种新型木本模式植物[J]. 植物学报,2018,53(3):372−381. [PENG Xianjun, SHEN Shihua. The paper mulberry: A novel model system for woody plant research[J]. Chinese Bulletin of Botany,2018,53(3):372−381. [2] 路博文, 姜雯, 申文强, 等. 构树的营养价值及其饲用技术研究进展[J]. 饲料研究,2021,44(17):109−113. [LU Bowen, JIANG Wen, SHEN Wenqiang, et al. Nutritional value of paper mulberry and its progress on forage technology[J]. Feed Research,2021,44(17):109−113. doi: 10.13557/j.cnki.issn1002-2813.2021.17.026 [3] 何连芳, 白淑云, 刘秉钺. 不同树龄杂交构树的纤维特性及制浆性能研究[J]. 中国造纸学报,2009,24(1):1−5. [HE Lianfang, BAI Shuyun, LIU Bingyu. Study on the fiber characteristics and pilping properties of hybrid paper mulberry at different ages[J]. Transactions of China Pulp and Paper,2009,24(1):1−5. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6842.2009.01.001 [4] 陈谭星, 孙慧军, 曹力凡, 等. 不同植物生长调节剂对构树营养品质的影响[J]. 饲料研究,2022(11):97−101. [CHEN Tanxing, SUN Huijun, CAO Lifan, et al. Effect of different plant growth regulators on nutritional quality of paper mulberry[J]. Feed Research,2022(11):97−101. doi: 10.13557/j.cnki.issn1002-2813.2022.11.021 [5] KO H H, CHANG W L, LU T M. Antityrosinase and antioxidant effects of ent-kaurane diterpenes from leaves of Broussonetia papyrifera[J]. Journal of Natural Products,2008,71(11):1930−1933. doi: 10.1021/np800564z
[6] HAN Q, WU Z, HUANG B, et al. Extraction, antioxidant and antibacterial activities of Broussonetia papyrifera fruits polysaccharides[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2016,92:116−124. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.06.087
[7] LEE H, LI H, JEONG J H, et al. Kazinol B from Broussonetia kazinoki improves insulin sensitivity via Akt and AMPK activation in 3T3-L1 adipocytes[J]. Fitoterapia,2016,112:90−96. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2016.05.006
[8] GUO Fujiang, LI Feng, HUANG Cheng, et al. Prenylflavone derivatives from Broussonetia papyrifera inhibit the growth of breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo[J]. Phytochemistry Letters,2013,6(3):331−336. doi: 10.1016/j.phytol.2013.03.017
[9] YANG Xinrong, FU Bingyi, SUN Fang, et al. Encyclopedic reference of traditional Chinese medicine, [M]. Springer-Verlag, Berlin Heidelberg, 2003.
[10] 杨晨悦, 王晓玲. 构树皮中的酚性化合物研究[J]. 中药材,2018,41(1):111−114. [YANG Chenyue, WANG Xiaoling. Phenolic constituents from the barks of Broussonetia papyrifera[J]. Journal of Chinese Medicinal Materials,2018,41(1):111−114. doi: 10.13863/j.issn1001-4454.2018.01.023 [11] SON K H, KWON S J, CHANG H W, et al. Papyriflavonol A, a new prenylated flavonol from Broussonetia papyrifera[J]. Fitoterapia,2001,72(4):456−458. doi: 10.1016/S0367-326X(00)00329-4
[12] RYU H W, LEE B W, CURTIS-LONG M J, et al. Polyphenols from Broussonetia papyrifera displaying potent alpha-glucosidase inhibition[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2010, 58: 202–208.
[13] RYU H W, LEE J H, KANG J E, et al. Inhibition of xanthine oxidase by phenolic phytochemicals from Broussonetia papyrifera[J]. Journal of the Korean Society for Applied Biological Chemistry,2012,55:587−594. doi: 10.1007/s13765-012-2143-0
[14] TIAN J L, LIU T L, XUE J J, et al. Flavanoids derivatives from the root bark of Broussonetia papyrifera as a tyrosinase inhibitor[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2019,138:111445. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.06.008
[15] PARK M H, JUNG S, YUK H J, et al. Rapid identification of isoprenylated flavonoids constituents with inhibitory activity on bacterial neuraminidase from root barks of paper mulberry (Broussonetia papyrifera)[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,174:61−68. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.01.140
[16] 张意笠, 胡培豪, 黄真, 等. 小构树总黄酮提取工艺优化及其抗氧化、美白活性[J]. 中成药,2020,42(4):842−848. [ZHANG Yili, HU Peihao, HUANG Zhen, et al. Extraction process optimization and anti-oxidant, whitening activities of total flavonoids from Broussonetia kazinoki[J]. Chinese Traditional Patent Medicine,2020,42(4):842−848. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1528.2020.04.004 [17] LEE J M, CHOI S S, PARK M H, et al. Broussonetia papyrifera root bark extract exhibits anti-inflammatory effects on adipose tissue and improves insulin sensitivity potentially via AMPK activation[J]. Nutrients,2020,12(3):773. doi: 10.3390/nu12030773
[18] 张兴荣, 张学林, 贺连智, 等. 构树叶总黄酮提取工艺优化及成分分析[J]. 现代食品科技,2021,37(2):213−220. [ZHANG Xingrong, ZHANG Xuelin, HE Lianzhi, et al. Optimization of extraction process and component analysis of the flavonoids from Broussonetia papyrifera leaves[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2021,37(2):213−220. [19] 徐梦宇, 咸淑慧, 王荣镇, 等. 杂交枸树根黄酮类物质的提取及其抑菌活性研究[J]. 食品科技,2011,36(4):194−196. [XU Mengyu, XIAN Shuhui, WANG Rongzhen, et al. Extraction and antibacterial activity of flavonoids in roots of the Broussonetia papyrifera (L.) vent[J]. Food Science and Technology,2011,36(4):194−196. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2011.04.011 [20] 张富坤, 孙媛, 高艺菲, 等. 表面活性剂辅助超声提取柿叶总黄酮工艺优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(5):224−229. [ZHANG Fukun, SUN Yuan, GAO Yifei, et al. Optimization of surfactant-assisted ultrasonic extraction of flavonoids from Persimmon leaves[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(5):224−229. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2021070146 [21] YAP J Y, HII C L, ONG S P, et al. Effects of drying on total polyphenols content and antioxidant properties of Carica papaya leaves[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2020,100(7):2932−2937. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10320
[22] CHEUNG L M, CHEUNG P C K, OOI V E C. Antioxidant activity and total phenolics of edible mushroom extracts[J]. Food Chemistry,2003,81(2):249−255. doi: 10.1016/S0308-8146(02)00419-3
[23] SOONG Y Y, BARLOW P J. Antioxidant activity and phenolic content of selected fruit seeds[J]. Food Chemistry,2004,88(3):411−417. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2004.02.003
[24] LI L, THAKUR K, LIAO B Y, et al. Antioxidant and antimicrobial potential of polysaccharides sequentially extracted from Polygonatum cyrtonema Hua[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,114:317−323. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.03.121
[25] 磨正遵, 商飞飞, 潘中田, 等. 响应面法优化超声波辅助提取广西大果山楂叶总黄酮工艺[J]. 南方农业学报,2018,49(5):986−992. [MO Zhengzun, SHANG Feifei, PAN Zhongtian, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of total flavonoids from Guangxi hawthorn leaves with response surface methodology[J]. Journal of Southern Agricultural Sciences,2018,49(5):986−992. [26] WANG Q Z, LIU Y Y, CUI J, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction for herbicidal activity of chicory root extracts[J]. Industrial Crops & Products,2011,34(3):1429−1438.
[27] 时羽杰, 肖徐, 李晶晶, 等. 核桃内种皮总黄酮的提取工艺优化及抗氧化性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(2):192−198,209. [SHI Yujie, XIAO Xu, LI Jingjing, et al. Optimization of extraction process and antioxidant activity of total flavonoids in walnut inner seed coat[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(2):192−198,209. [28] 张静, 陶俊葓, 刘银, 等. 响应曲面法优化超声辅助提取芒果叶中多酚和黄酮工艺及抗氧化活性研究[J]. 云南民族大学学报(自然科学版),2020,29(6):527−534. [ZHANG Jing, TAO Junping, LIU Yin, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction process and antioxidant activity of total polyphenols and total flavonoids from mango leaves using response surface methodology[J]. Journal of Yunnan University for Nationalities (Natural Science Edition),2020,29(6):527−534. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8513.2020.06.001 [29] 殷海洋, 刘振春, 张世康, 等. 响应面优化超声波辅助酶法提取油莎豆ACE抑制肽的工艺[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(14):182−187. [YIN Haiyang, LIU Zhenchun, ZHANG Shikang, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic extraction of ACE inhibitory peptides from Cyperus esculentus by response surface method[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(14):182−187. [30] 莫一凡, 姚凌云, 冯涛, 等. 无花果总黄酮闪式提取工艺优化及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(12):186−191, 220. [MO Yifan, YAO Lingyun, FENG Tao, et al. Optimization of flash extraction process of total flavonoids from fig( Ficus carica L.) and its antioxidant activities[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(12):186−191, 220. [31] 黄秋萍, 郑燕菲, 赵汉民, 等. 薛荔藤多酚提取工艺优化及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品研究与开发,2022,43(4):70−75. [HUANG Qiuping, ZHENG Yanfei, ZHAO Hanmin, et al. Optimized extraction technology and antioxidant activities of polyphenols from Ficus pumila Cane[J]. Food Research and Development,2022,43(4):70−75. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2022.04.011 [32] SOUHILA M, MUSTAPHA K, ABDERAHIM B, et al. Phenolic and flavonoid contents, antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of leaf extracts from ten Algerian Ficus carica L. varieties[J]. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine,2016,6(3):239−245. doi: 10.1016/j.apjtb.2015.12.010
[33] 冯艳钰, 臧延青. 三种小麦麸皮总黄酮的体外抗氧化活性[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(9):16−24. [FENG Yanyu, ZANG Yanqing. Study on the antioxidant activity of total flavonoids from three wheat brans in vitro[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(9):16−24. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.025886 -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 王宏,王丽阳,周杰伦,曾晓房,姜浩,梁一柱,陈学桥,白卫东. 化橘红活性成分及功效研究进展. 农产品加工. 2024(23): 85-91 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 任晨汐,卞灿锋,李宁,高雅,张玉霞,胡钦,肖丽霞,关天竺. 基于网络药理学和分子对接探究药膳“枸杞-桑椹-覆盆子汤”治疗糖尿病肾病的分子机制. 保鲜与加工. 2023(11): 51-61 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:



