Process Optimization of the Extraction of Moringa oleifera Seed Polyphenols by Ultrasound-Assisted Cellulase and Its in Vitro Activity
-
摘要: 本实验以辣木籽为原料,研究纤维素酶添加量、乙醇体积分数、纤维素酶解时间、超声时间对辣木籽多酚提取量的影响,并采用响应面法优化超声辅助纤维素酶法提取辣木籽多酚工艺。此外,研究辣木籽多酚的体外抗氧化和降糖降脂活性。结果表明,超声辅助纤维素酶法提取辣木籽多酚最佳工艺为:酶添加量0.30%、乙醇体积分数53.00%、酶解时间31.00 min、超声时间33.00 min,在此条件下,所得辣木籽多酚的提取量为6.90 mg/g,与预测值无显著性差异。辣木籽多酚提取物具有较好的抗氧化活性,对ABTS自由基和DPPH自由基的清除能力的IC50分别为0.76和0.61 mg/mL。同时,辣木籽多酚提取物具有较好的胰脂肪酶和α-淀粉酶抑制活性,其对胰脂肪酶和α-淀粉酶抑制率的IC50分别为1.35和6.55 mg/mL。该研究为辣木籽多酚提取物的提取和应用提供理论依据。Abstract: In this study, the effects of cellulase addition, ethanol volume fraction, cellulase digestion time and ultrasound time on the extraction rate of Moringa oleifera seeds polyphenols were investigated. At the same time, the extraction process of Moringa oleifera seeds polyphenols by ultrasound-assisted cellulase method was optimized using response surface methodology. In addition, the in vitro antioxidant and hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic activities of Moringa oleifera seeds polyphenols were also investigated. The results showed that the optimal process for the extraction of Moringa oleifera seed polyphenols by ultrasound-assisted cellulase was 0.30% enzyme addition, 53.00% volume fraction of ethanol, 31.00 min enzymatic digestion time, and 31.00 min ultrasound time. Under this process condition, the amount of Moringa oleifera seed polyphenols extracted obtained was 6.90 mg/g, which was not significantly different from the predicted value. In addition, the study found that Moringa oleifera seed polyphenols had good antioxidant activity, and its IC50 for scavenging ABTS radicals and DPPH radicals were 0.76 and 0.61 mg/mL, respectively. Meanwhile, Moringa oleifera seed polyphenols had some pancreatic lipase and α-amylase inhibitory activities, and theirs IC50 for pancreatic lipase and α-amylase inhibition rate were 1.35 and 6.55 mg/mL, respectively. This study provides a theoretical basis for the extraction and application of Moringa oleifera seed polyphenols.
-
Keywords:
- Moringa oleifera seed /
- polyphenols /
- cellulase /
- ultrasound /
- antioxidant /
- pancreatic lipase /
- α-amylase
-
辣木(Moringa oleifera Lam.)为辣木科辣木属多年生热带落叶乔木,在我国的热带和亚热带地区,如云南、福建、广东等地被广泛种植。研究表明,辣木营养价值丰富,并具有多种药理活性,如抗氧化[1]、抗癌[2]、抗菌[3]和降血糖[4]等多种生理活性。
辣木籽富含蛋白质、油脂、维生素等营养成分[5],同时还含有黄酮、多酚[6]、多糖[7]等多种生物活性物质,其中多酚是辣木籽的重要生物活性成分。研究表明,辣木籽多酚具有降血糖[8]、降血脂[9]、抗炎[10]、抗癌[11]、护肝[12]、抗菌[13]等生理功能。在之前的研究中,人们用水提法[14]、醇提法[15]、超声提取法[16]提取辣木籽多酚,但提取效率有限,因此,探索一种更优的方法提取辣木籽多酚尤为必要。
超声辅助酶法提取是一种新兴的提取技术,具有高效、环保、操作简单等优点。近年来,超声辅助酶法已被广泛用于从多种植物材料中提取多酚[17-18]。植物细胞壁可直接阻断细胞内容物的释放,影响植物多酚的提取,纤维素酶可水解纤维素,破坏植物的细胞壁[19],提高多酚提取量[20]。但是,目前仍未见有研究采用超声辅助酶法提取辣木籽多酚。因此,本实验采用超声辅助纤维素酶法提取辣木籽中的多酚类物质,以多酚提取量为评价指标,通过单因素和响应面设计试验,优化辣木籽多酚提取工艺。此外,研究了辣木籽多酚提取物的体外抗氧化、胰脂肪酶和α-淀粉酶抑制活性,为辣木籽多酚提取物的高效提取及开发利用提供了基础数据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
辣木籽 购于云南天佑科技开发有限公司。在60 ℃条件下,将辣木籽烘干至恒重。用粉碎机粉碎,过40目筛,用石油醚脱脂,反复脱脂3次直至石油醚不变黄,抽滤后留下滤渣,放入通风橱,待石油醚挥发完全,再次过40目筛,密封避光保存于4 ℃冰箱备用。无水乙醇、三氯乙酸 成都市隆科化学品有限公司;没食子酸标准品、福林酚、2,2'-联氮-双-3-乙基苯并噻唑啉-6-磺酸(2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid),ABTS)、1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl,DPPH)、α-淀粉酶(50 U/mg) 上海源叶生物技术有限公司;过硫酸钾、铁氰化钾、棕榈酸对硝基苯酯(PNPP) Aladdin公司;可溶性淀粉、AB-8大孔吸附树脂 Solarbio公司;无水碳酸钠 Macklin公司;磷酸二氢钠、磷酸氢二钠 天津市风船化学试剂科技有限公司;胰脂肪酶(100~500 U/mg) Sigma公司;所有有机试剂均为分析纯。
FA1004 电子天平 上海舜宇恒平科学仪器有限公司;800Y 高速多功能粉碎机 武义海纳电器有限公司;HH-11-2 恒温水浴锅 常州诺基仪器有限公司;CR-100S 超声清洗机 深圳市春霖超声波科技有限公司;LC-4014 低速离心机 安徽中科中佳科学仪器有限公司;RV 10 D S25 旋转蒸发仪 巩义市予华仪器有限责任公司;756PC 紫外分光光度计 上海菁华科技仪器有限公司;
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 辣木籽多酚的提取纯化
参考文献[21]提取辣木籽多酚,称取辣木籽粉末2.0 g,按照一定比例加入纤维素酶,再按照料液比为1:15(g/mL)加入一定体积分数的乙醇,在45 ℃水浴锅中,使纤维素酶与辣木籽反应一定时间,立即放入80 ℃水浴锅,高温水浴5 min使纤维素酶失活,取出冷却至室温后置于600 W、40 ℃条件下超声处理一段时间。浸提液经冷却后在3000 r/min转速条件下离心10 min,收集上清液,用乙醇定容至30 mL。采用响应面法优化条件提取多酚。
根据朱延胜等[22]的方法,提取液经AB-8大孔树脂纯化,并经过不同体积分数乙醇溶液洗脱后,旋蒸出乙醇溶剂并回收,冷冻干燥得到辣木籽多酚提取物冻干粉末。
1.2.2 辣木籽多酚含量测定
1.2.2.1 标准曲线的绘制
采用Folin-Ciocalteus比色法[23]测定辣木籽多酚含量。取20 mg没食子酸标准品,用20 mL蒸馏水溶解,配制成1 mg/mL的没食子酸储备液。分别取0、1、2、3、4、5 mL没食子酸储备液到100 mL容量瓶中,用蒸馏水定容至刻度,配制成10、20、30、40、50 μg/mL的没食子酸标准溶液。将1.0 mL不同浓度的没食子酸溶液与5.0 mL 10%的福林酚溶液混合,摇匀,室温下反应5 min后加入4.0 mL 7.5%碳酸钠溶液,避光反应放置60 min,在760 nm波长下测其吸光度。以没食子酸浓度为横坐标,吸光度为纵坐标,绘制没食子酸标准曲线,得到的没食子酸标准曲线为:Y=0.0098X+0.0479,R2=0.9999。
1.2.2.2 辣木籽多酚含量测定
取1.0 mL辣木籽多酚提取液加入5.0 mL 10%的福林酚溶液,摇匀,反应5 min,加入4.0 mL 7.5%的碳酸钠溶液,避光静置60 min,以空白对照作为参比液,在760 nm波长下测定吸光度,并以没食子酸标准曲线方程计算多酚含量。公式如(1)所示:
多酚提取量(mg/g)=(C×V×N)/M (1) 式中:C为多酚的质量浓度,mg/mL;V为提取液体积,mL;N为稀释倍数;M为样品质量,g。
1.2.3 单因素实验
固定料液比为1:15(g/mL),超声功率为600 W,乙醇体积分数60%,纤维素酶添加量0.6%,酶解时间30 min,超声时间30 min。分别考察不同纤维素酶添加量(0.2%、0.4%、0.6%、0.8%、1.0%)、不同乙醇体积分数(40%、50%、60%、70%、80%)、不同酶解时间(10、20、30、40、50 min)、不同超声时间(10、20、30、40、50 min)对辣木籽多酚提取量的影响,根据结果确定适宜的提取条件。
1.2.4 响应面试验设计
在单因素实验的基础上,以辣木籽多酚提取量(mg/g)为响应值,利用Design-Expert.V8.0.6软件进行Box-Behnken设计试验,响应面试验设计见表1。
表 1 响应面试验的因素与水平Table 1. Factors and levels of response surface experiments因素 水平 −1 0 1 酶添加量A(%) 0.2 0.4 0.6 乙醇体积分数B(%) 50 60 70 酶解时间C(min) 20 30 40 超声时间D(min) 20 30 40 1.2.5 体外抗氧化实验
将纯化后的冻干的样品用DMSO溶解,配制成质量浓度为100 mg/mL的母液,用蒸馏水稀释成质量浓度分别为0.02、0.04、0.08、0.16、0.32、0.64、1.28、2.56 mg/mL的辣木籽溶液,对其进行抗氧化指标的测定。
1.2.5.1 ABTS自由基清除率测定
参照Du等[24]的方法略作修改,取7.00 mmol/L ABTS与2.45 mmol/L过硫酸钾等体积混合,4 ℃避光反应12~16 h后获得ABTS+·溶液。用蒸馏水稀释ABTS+·溶液使其在734 nm处的吸光值为(0.7±0.05)。分别吸取20 μL不同质量浓度的辣木籽多酚提取物溶液于96孔板中,取180 μL ABTS+·工作液与样品液混匀。在室温下避光放置6 min,测其在734 nm波长处的吸光度,每个样品做三个平行,结果取平均值。以VC为阳性对照,用蒸馏水代替样品做空白对照。以下公式计算ABTS自由基清除率:
ABTS自由基清除率(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 式中:A0为蒸馏水与ABTS混合溶液吸光值;A1为样品液与ABTS混合溶液吸光值;A2为样品液吸光值。
1.2.5.2 DPPH自由基清除率测定
参照Hong等[25]的方法略作修改,分别吸取100 μL不同质量浓度的辣木籽多酚提取物溶液于96孔板中,取100 μL 0.2 mg/mL DPPH的无水乙醇溶液与样品液混匀。室温下避光静置反应30 min,于517 nm波长处测定其吸光值,每个样品做三个平行,结果取平均值。以VC为阳性对照,用蒸馏水代替样品做空白对照。以下公式计算DPPH自由基清除率:
DPPH自由基清除率(%)=(1−A1−A2A0)×100 式中:A0为纯水与DPPH混合溶液吸光值;A1为样品液与DPPH混合溶液吸光值;A2为样品液与无水乙醇混合溶液吸光值。
1.2.6 辣木籽多酚提取物体外酶抑制活性研究
1.2.6.1 辣木籽多酚提取物对胰脂肪酶抑制活性研究
参照Les等[26]的方法略作修改,取0.2 mL(0.64、1.28、2.56、5.12、10.24 mg/mL)纯化后冻干的辣木籽多酚提取物样品或0.2 mL的PBS于2 mL离心管中,再向试管中加入0.2 mL 2.5 mg/mL胰脂肪酶溶液,37 ℃孵育15 min后加入0.2 mL 0.01 mol/mL pNPP,继续在37 ℃反应15 min,反应结束后加入0.5 mL无水乙醇终止反应,在405 nm处测吸光度。
胰脂肪酶抑制率(%)=(1−Ai1−A1Ai0−A0)×100 式中:Ai1为实验组的吸光值;A1为实验空白组吸光值(PBS替代酶液);Ai0为对照组(PBS替代样品);A0为空白组。
1.2.6.2 辣木籽多酚提取物对α-淀粉酶抑制活性研究
参考Guo等[27]的方法并略作修改,先取0.2 mL(0.64、1.28、2.56、5.12、10.24 mg/mL)的辣木籽多酚提取物样品或0.2 mL的PBS于2 mL离心管中,向试管中加入0.2 mL 13 U/mL α-淀粉酶溶液,37 ℃孵育10 min,加入0.2 mL 1%可溶性淀粉溶液,继续在37 ℃反应10 min,加入0.4 mL DNS指示剂。将离心管放入沸水中水浴5 min,取出后用冰水迅速降温,在540 nm处测吸光度。
α-淀粉酶抑制率(%)=(1−Ai1−A1Ai0−A0)×100 式中:Ai1为实验组的吸光值;A1为实验空白组吸光值(PBS替代酶液);Ai0为对照组(PBS替代样品);A0为空白组。
1.3 数据处理
用Design-Expert.V8.0.6.1进行响应面试验设计,用IBM SPSS Statistics 26进行显著性分析,用Origin2021绘制图片,P<0.05表示差异显著。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验
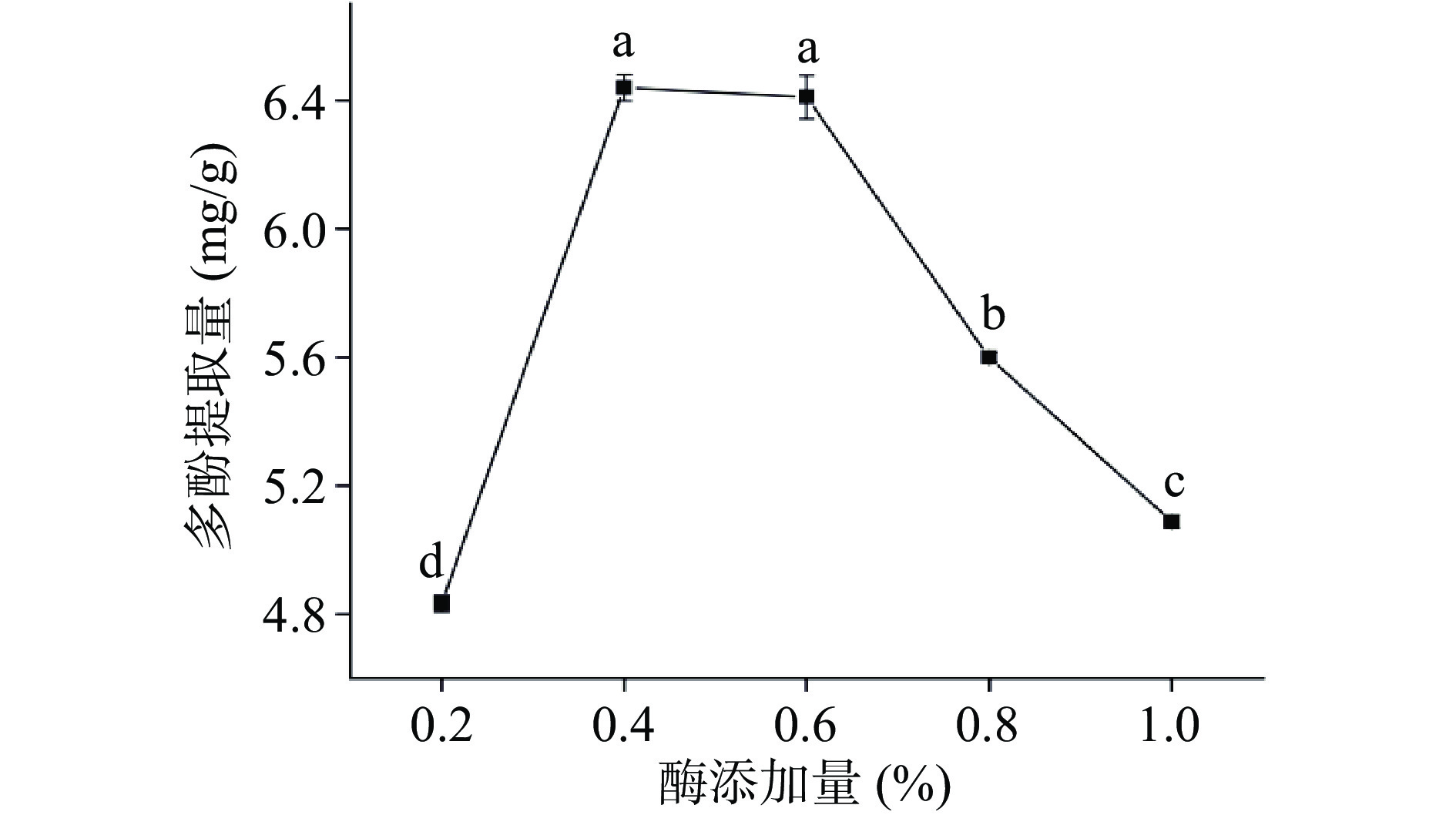
由图1所示,随着纤维素酶添加量的增加,多酚提取量呈先升高后降低的趋势。当纤维素酶添加量为0.2%~0.4%,随着纤维素酶添加量的增加,辣木籽多酚提取量显著增加(P<0.05),纤维素酶添加量为0.4%和0.6%时,辣木籽多酚提取量无显著性差异(P>0.05),当酶添加量大于0.6%时,多酚提取量显著降低(P<0.05)。这是由于一部分酚酸通过酯键和细胞壁中的纤维素和半纤维素结合,纤维素酶将与细胞壁结合的酚类物质释放了出来[28],使得多酚的提取量大大增加。当多酚的提取量达到最大值时,增加酶添加量酚类物质的提取量却显著性下降,这是由于纤维素酶本身是一种蛋白质,而多酚易与蛋白形成复合物,过量的纤维素酶与多酚结合,从而降低多酚的提取量[29]。因此,选择0.2%、0.4%和0.6%三个水平的纤维素酶添加量进行后续响应面优化试验。
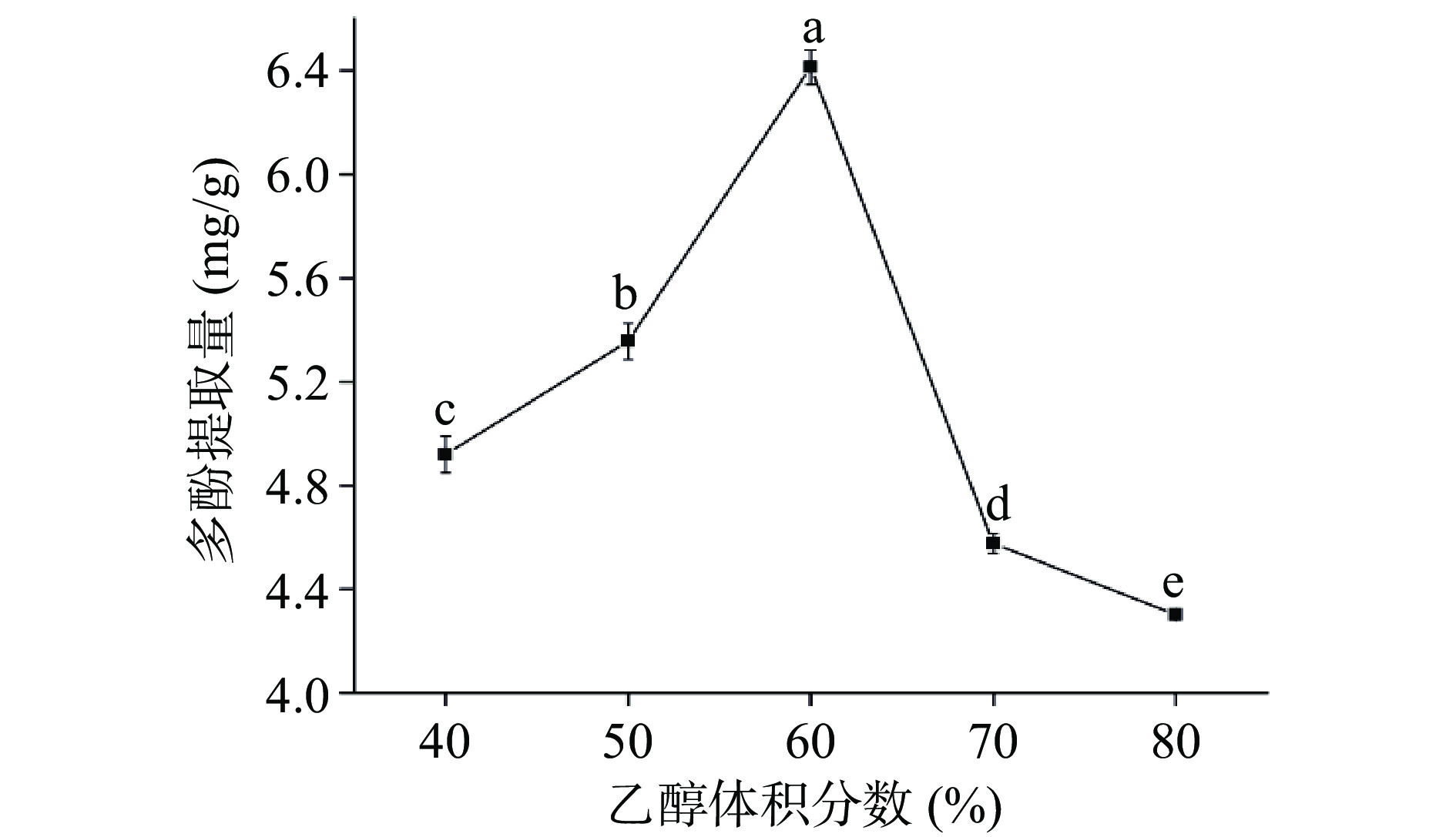
由图2所示,随着乙醇体积分数的增加,多酚提取量呈先升高后降低的趋势,在乙醇体积分数为60%时,多酚提取量达到最大值,且显著高于其它水平的提取量(P<0.05)。乙醇体积分数在60%以下时,随着体积分数的增加,多酚提取量增加,这是由于多酚受到氢键作用力的影响,易于溶出[30]。当乙醇体积分数高于60%时,溶剂极性减小,导致一些醇溶性杂质,如色素、油脂等被溶出,影响多酚的溶出[31]。综合考虑,选取乙醇体积分数分别为50%、60%和70%三个水平进行后续响应面优化试验。
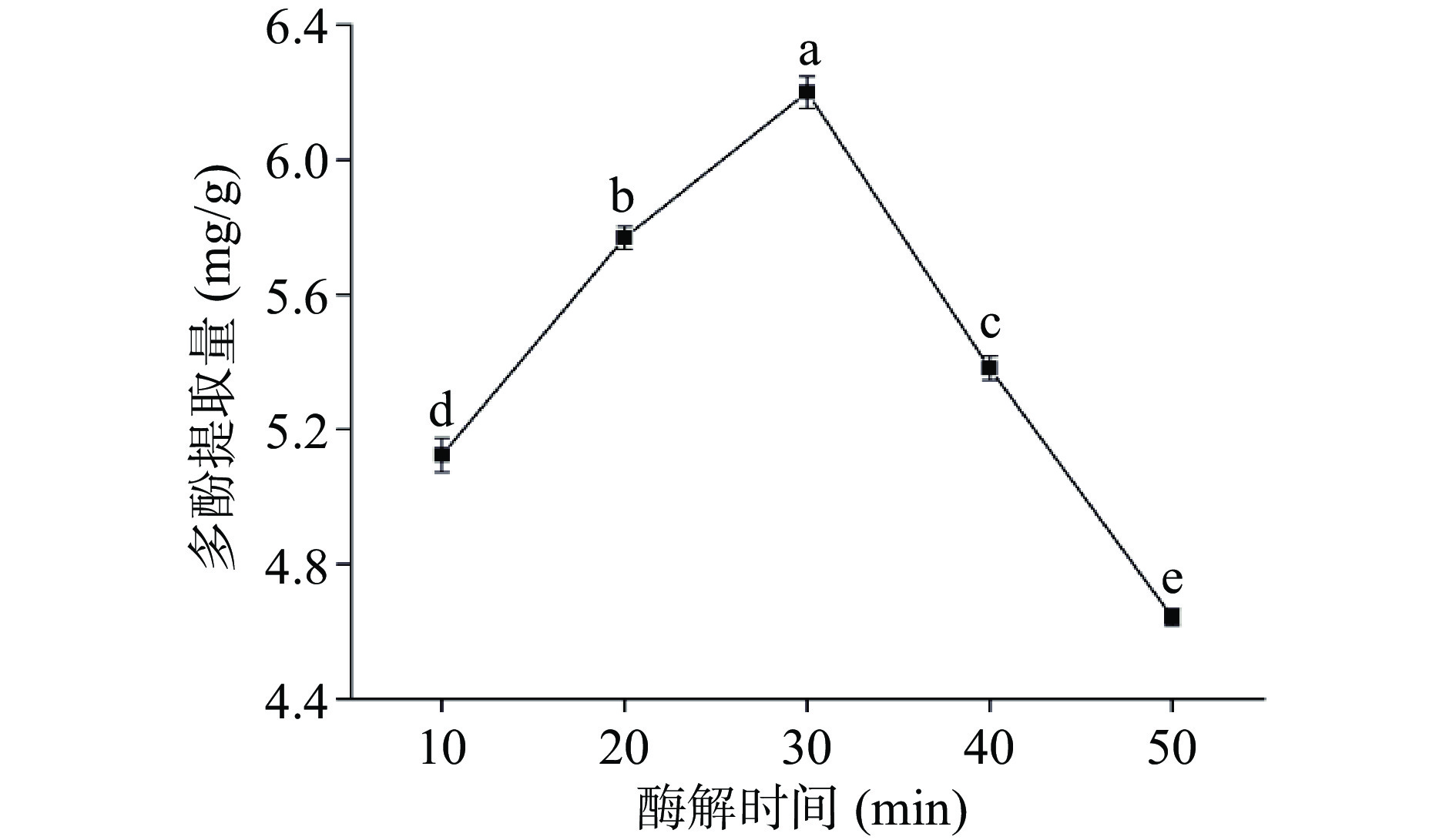
如图3所示,多酚提取量随着酶解时间的增加而增加,当酶解时间达到30 min时,多酚提取量达到最大值,且显著高于其它水平的提取量(P<0.05)。这是由于随着酶解时间增加,酶会破坏细胞壁的结构,使多酚溶出;但是酶解时间过长,多酚长时间暴露在空气中,导致其被氧化分解,使得提取量降低[32]。综合考虑,选取20、30和40 min 三个水平的酶解时间进行响应面试验。
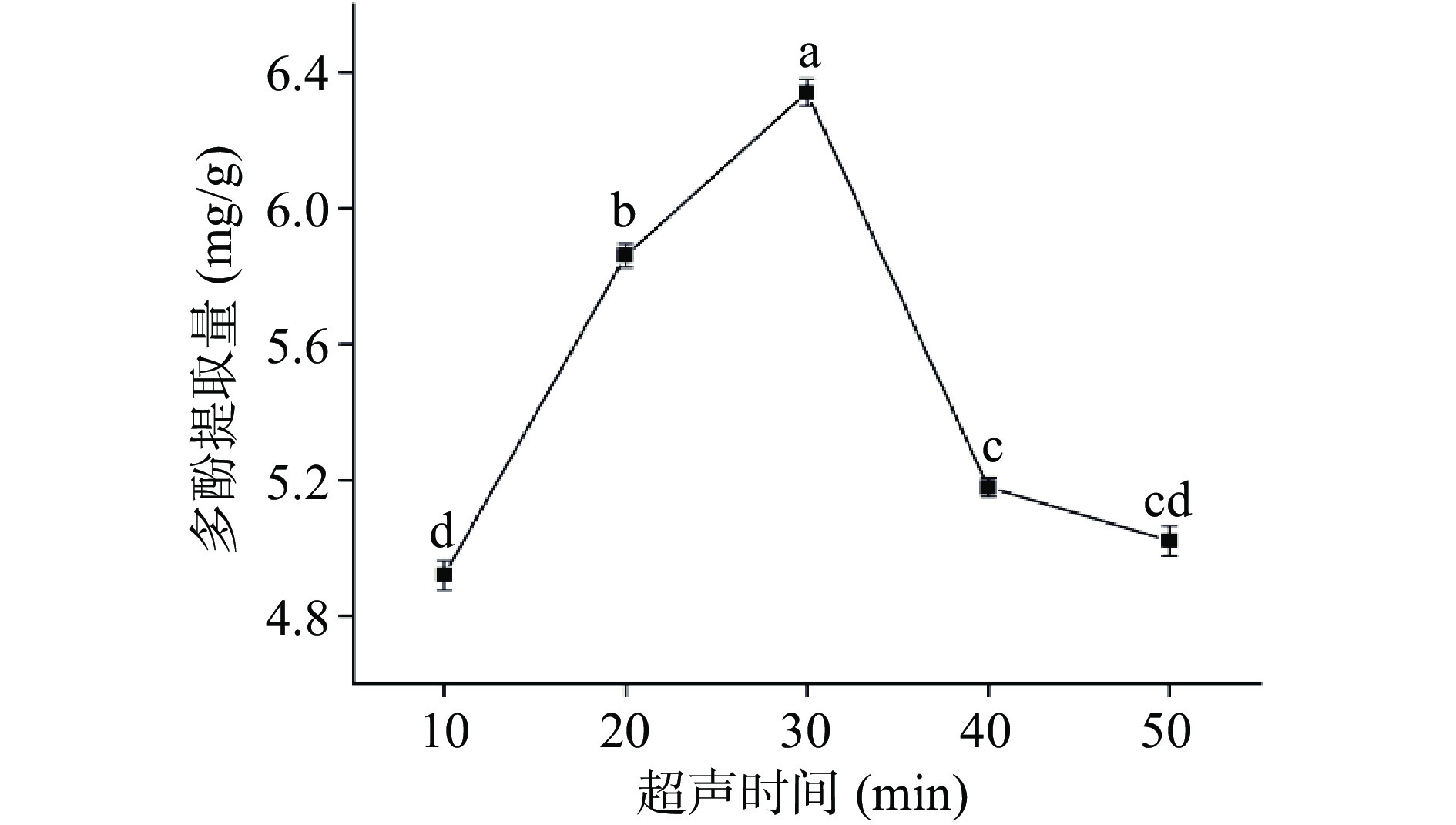
如图4所示,随着超声时间的增加,多酚提取量呈先上升后下降的趋势。多酚提取量在超声时间为30 min时达到最大值,且显著高于其他水平的提取量(P<0.05)。之后随着超声时间的增加,多酚提取量逐渐下降。这是由于超声强烈的机械剪切作用可以破坏细胞壁的结构,加速多酚的溶出[33]。但超声时间过长,会导致已经溶出的多酚结构受到破坏[34],且多酚暴露在空气中的时间过长,会发生氧化分解,造成提取量降低。综合考虑,选取时间20、30、40 min三个水平的超声时间进行响应面试验。
2.2 响应面法优化试验的设计与结果
根据单因素实验结果,以纤维素酶添加量(A)、乙醇体积分数(B)、酶解时间(C)、超声时间(D)为自变量,辣木籽多酚提取量为响应值,设计四因素三水平Box-Behnken响应面优化试验,共29个试验组合,试验设计及结果如表2所示。
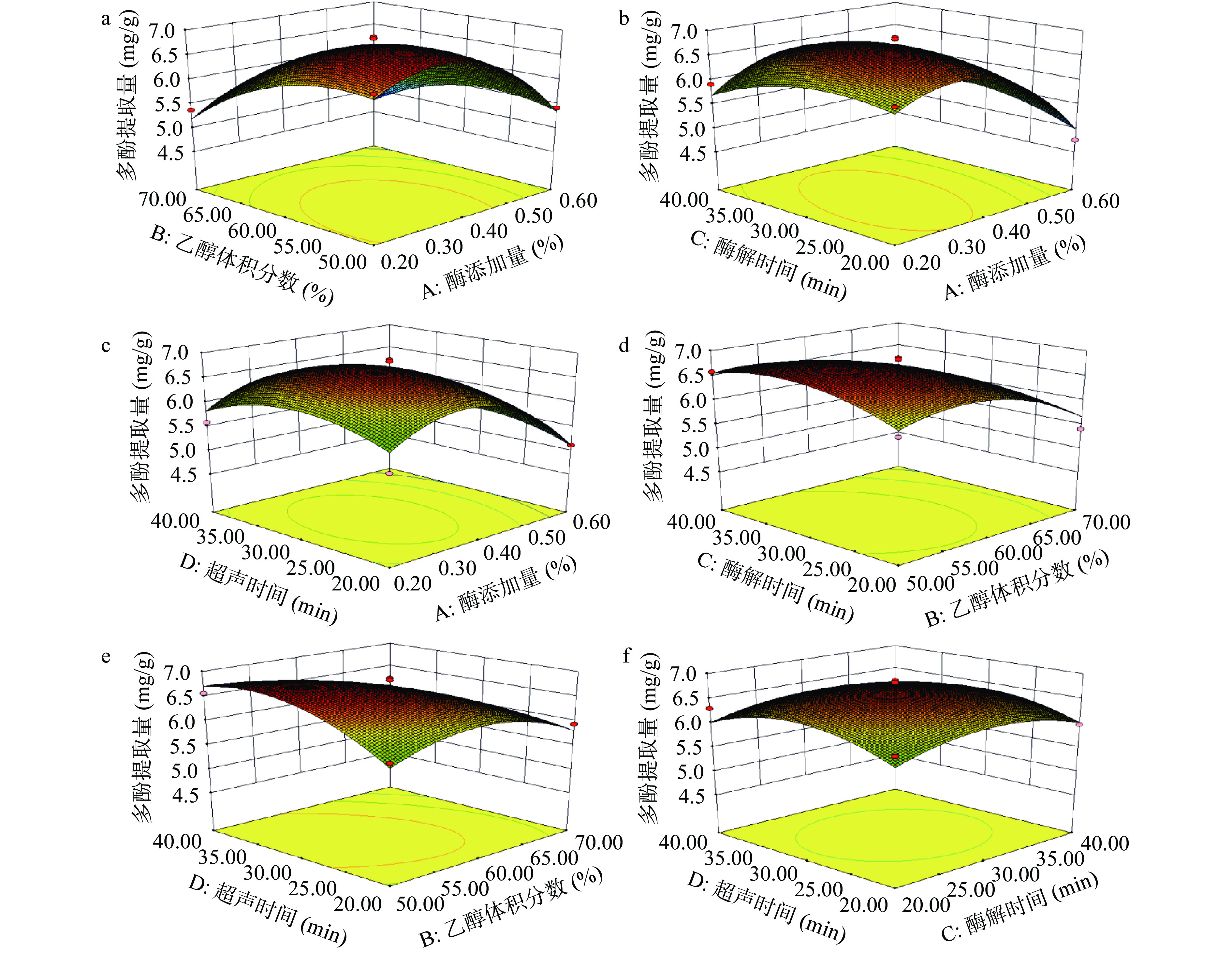
表 2 Box-Behnken试验设计和试验结果Table 2. Box-Behnken design matrix and response values试验号 A B C D Y 提取量(mg/g) 1 0 0 −1 −1 6.18 2 0 −1 0 −1 6.01 3 −1 0 0 −1 5.48 4 1 0 0 −1 5.12 5 0 1 0 −1 5.94 6 0 0 1 −1 5.98 7 0 −1 −1 0 6.11 8 −1 0 −1 0 6.30 9 1 0 −1 0 4.75 10 0 1 −1 0 5.41 11 −1 −1 0 0 6.51 12 1 −1 0 0 5.42 13 0 0 0 0 6.66 14 0 0 0 0 6.86 15 0 0 0 0 6.68 16 0 0 0 0 6.53 17 0 0 0 0 6.83 18 −1 1 0 0 5.38 19 1 1 0 0 4.93 20 0 −1 1 0 6.58 21 −1 0 1 0 5.92 22 1 0 1 0 5.26 23 0 1 1 0 5.19 24 0 0 −1 1 6.30 25 0 −1 0 1 6.56 26 −1 0 0 1 5.59 27 1 0 0 1 5.26 28 0 1 0 1 4.89 29 0 0 1 1 5.98 采用Design-Expert V8.0.6.1对表2响应面优化试验进行二次多项式拟合,从而得到辣木籽多酚提取量(Y)对纤维素酶添加量(A)、乙醇体积分数(B)、酶解时间(C)、超声时间(D)的回归模型方程:
Y=6.71−0.37A−0.45B−0.012C−0.010D+0.16AB+0.22AC+8.772−3AD−0.17BC−0.40BD−0.032CD−0.83A2−0.45B2−0.32C2−0.40D2
由表3可知,该回归模型具有较高显著性(P<0.0001),失拟项不显著(P=0.0955>0.05)。此外,分析结果中R2=0.9305,表明预测值和实测值之间有高度的相关性;R2Adj=0.8610,说明模型能够在86.10%的程度上解释实验结果;CV值为4.03%,说明模型方程能够很好地反映真实的实验值。由表3所示,A、B、A2、B2、C2、D2对响应值的影响达到极显著水平(P<0.01),四因素两两交互BD对辣木籽多酚提取量的影响极显著(P<0.01)。根据F值大小可知,各因素对辣木籽多酚提取量影响大小顺序为:乙醇体积分数(B)>纤维素酶添加量(A)>酶解时间(C)>超声时间(D)。
表 3 辣木籽多酚回归模型方差分析表Table 3. Analysis of variance table for the regression model of Moringa oleifera Lam. seed polyphenols来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 10.53 14 0.75 13.38 < 0.0001 ** A 1.64 1 1.64 29.16 < 0.0001 ** B 2.48 1 2.48 44.14 < 0.0001 ** C 0.0018 1 0.0018 0.032 0.8602 D 0.0013 1 0.0013 0.022 0.8833 AB 0.10 1 0.10 1.81 0.1994 AC 0.20 1 0.20 3.53 0.0811 AD 0.00031 1 0.00031 0.0054 0.9421 BC 0.12 1 0.12 2.10 0.1690 BD 0.64 1 0.64 11.34 0.0046 ** CD 0.0041 1 0.0041 0.071 0.7938 A2 4.43 1 4.43 78.82 < 0.0001 ** B2 1.31 1 1.31 23.33 0.0003 ** C2 0.67 1 0.67 11.97 0.0038 ** D2 1.06 1 1.06 18.92 0.0007 ** 残差 0.79 14 0.056 失拟项 0.72 10 0.072 4.03 0.0955 纯误差 0.071 4 0.018 总方差 11.32 28 注:*表示差异显著(0.01<P<0.05);**表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。 2.3 响应面优化分析
2.3.1 各因素之间的交互作用
响应面图能够形象地描述回归方程,通过等高线的椭圆程度可以表示变量之间的交互作用是否显著。椭圆表示两因素之间交互作用显著,而圆形表示两因素之间交互不显著。各因素之间的交互作用见图5,如图5e的等高线呈椭圆形,说明乙醇体积分数和超声时间之间的交互作用影响显著,而其他图等高线呈现偏圆形,说明对应的两因素交互作用不显著。响应面图和方差分析结果一致。
2.3.2 最优提取条件验证试验
由Design-Expert. V8.0.6.1软件得出的辣木籽多酚的最佳提取条件为:酶添加量0.34%、乙醇体积分数52.84%、酶解时间30.58 min、超声时间33.35 min。此条件下模型预测的最大提取量为6.92 mg/g。为验证响应面试验优化结果,考虑实际操作的可行性,调整最佳工艺为:酶添加量0.30%、乙醇体积分数53.00%、酶解时间31.00 min、超声时间33.00 min,在此条件下做验证实验,所得的多酚提取量为6.90 mg/g,验证结果与预测值接近,P=0.787>0.05,无显著性,说明该模型能较好地预测实际提取量。
杨迎等[15]采用溶剂提取法提取辣木籽多酚并对其抗氧化能力进行初步的研究,在最优条件下,辣木籽多酚提取量为4.12 mg/g,且具有较强的体外抗氧化能力;张超等[35]采用超声法辅助提取辣木籽多酚,所得辣木籽多酚的平均提取量为4.87 mg/g。本文采用超声辅助纤维素酶提取辣木籽多酚,所得提取量为6.90 mg/g,分别是溶剂提取法的1.67倍和超声提取法的1.42倍。因此,纤维素酶辅助超声法提取辣木籽多酚可以一定程度上增加辣木籽多酚的提取量。
2.4 体外抗氧化活性测定结果
经AB-8大孔树脂纯化后,辣木籽多酚纯度达到20.79%,用纯化后的辣木籽提取物进行体外活性研究。
2.4.1 ABTS自由基清除能力
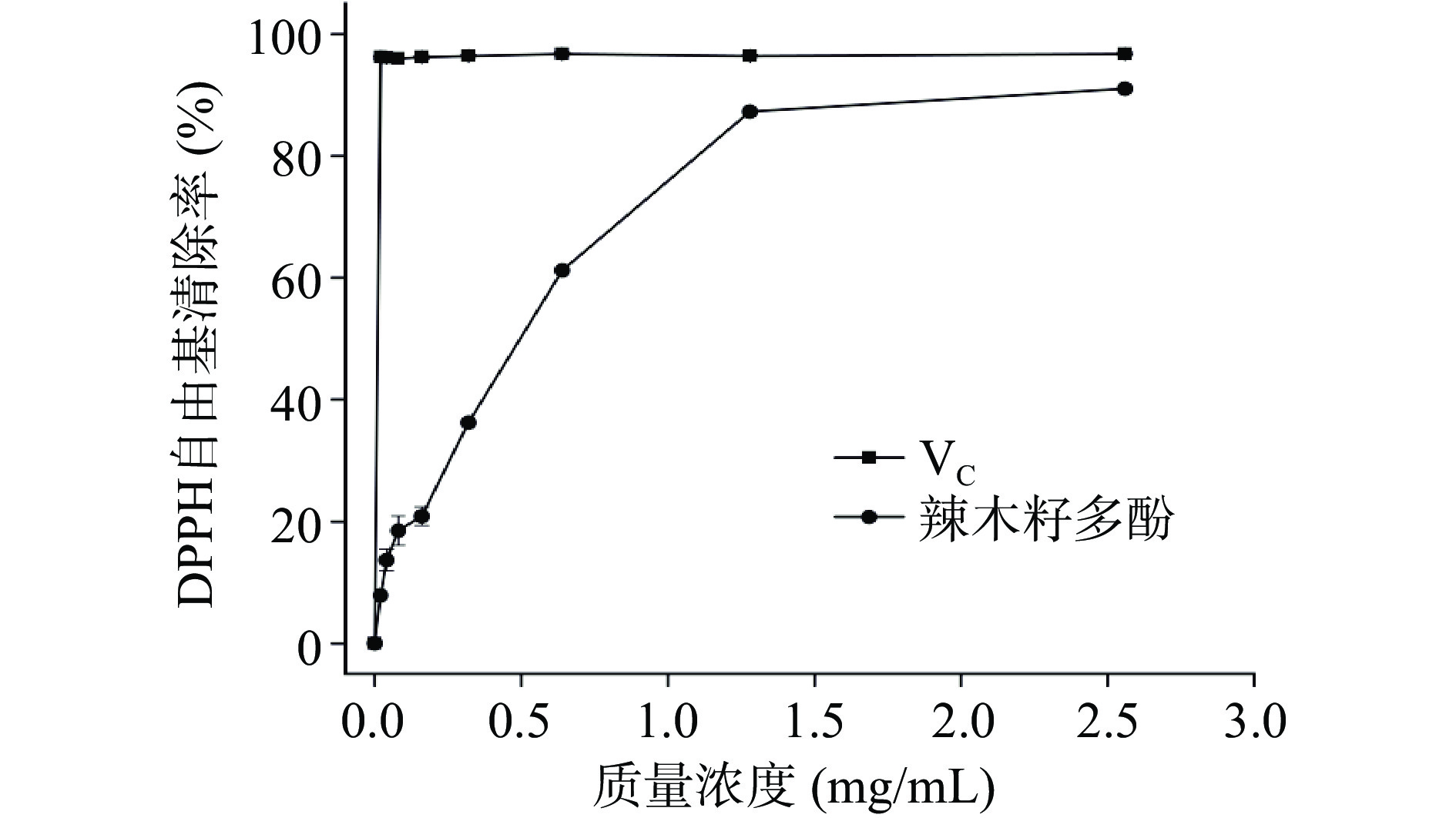
辣木籽多酚提取物清除ABTS自由基能力如图6所示。结果表明,随着辣木籽多酚提取物质量浓度的增加,其抗氧化能力明显增加,对ABTS自由基清除率的IC50为0.76 mg/mL。在剂量范围为0.02~2.56 mg/mL时,辣木籽多酚提取物对DPPH自由基的清除能力低于VC,但当辣木籽多酚提取物质量浓度处于最高点(2.56 mg/mL)时,辣木籽多酚提取物对ABTS自由基的清除能力可达到同等质量浓度VC的92.9%,说明辣木籽多酚提取物具有一定的ABTS自由基清除能力。
2.4.2 DPPH自由基清除能力
辣木籽多酚提取物清除DPPH自由基的能力如图7所示。结果表明,辣木籽多酚提取物和VC对DPPH自由基有清除作用,辣木籽多酚提取物清除DPPH自由基的IC50为0.61 mg/mL。在剂量范围为0.02~2.56 mg/mL时,辣木籽多酚提取物对DPPH自由基的清除能力低于VC,但当辣木籽多酚提取物质量浓度处于最高点(2.56 mg/mL)时,辣木籽多酚提取物对DPPH自由基的清除能力可达到同等质量浓度VC的93.0%,说明辣木籽多酚提取物具有一定的DPPH自由基清除能力。
2.5 辣木籽多酚提取物体外降糖降脂活性测定结果
胰脂肪酶是与肥胖相关的关键酶[36],可将三酰甘油分解为脂肪酸、甘油一酯和甘油。以棕榈酸对硝基苯酯(pNPP)为底物,经脂肪酶水解得到对硝基酚(pNP),通过吸光度的变化可测定样品溶液对脂肪酶的抑制作用。α-淀粉酶是一种碳水化合物水解酶,能够增加餐后血糖[37]。复杂的碳水化合物通过α-淀粉酶分解成葡萄糖,导致葡萄糖被快速吸收到血液中,从而导致高血糖[38]。
由图8所示,不同质量浓度的辣木籽多酚提取物对胰脂肪酶和α-淀粉酶具有一定的抑制作用,且抑制作用随质量浓度的增加而增加,其对胰脂肪酶和α-淀粉酶抑制率的IC50分别为1.35 mg/mL和6.55 mg/mL。相同质量浓度下,辣木籽多酚提取物对胰脂肪酶的抑制率要高于α-淀粉酶,在质量浓度为5.12 mg/mL时,其对胰脂肪酶的抑制率就达到了92%,说明辣木籽多酚提取物对胰脂肪酶的抑制作用相对较好。
3. 结论
辣木籽多酚提取的最佳工艺为酶添加量0.30%、乙醇体积分数53.00%、酶解时间31.00 min、超声时间33.00 min,此条件下得到辣木籽多酚提取量为6.90 mg/g,理论与实际值无显著性差异。辣木籽多酚提取物具有一定的抗氧化活性,对ABTS自由基和DPPH自由基的清除能力IC50分别为0.76 mg/mL和0.61 mg/mL。同时,辣木籽多酚提取物具有较好的胰脂肪酶和α-淀粉酶抑制活性,其对胰脂肪酶和α-淀粉酶抑制率的IC50分别为1.35 mg/mL和6.55 mg/mL,并且辣木籽多酚提取物对胰脂肪酶的抑制率要高于α-淀粉酶,说明辣木籽多酚提取物具有潜在的降脂活性。
-
表 1 响应面试验的因素与水平
Table 1 Factors and levels of response surface experiments
因素 水平 −1 0 1 酶添加量A(%) 0.2 0.4 0.6 乙醇体积分数B(%) 50 60 70 酶解时间C(min) 20 30 40 超声时间D(min) 20 30 40 表 2 Box-Behnken试验设计和试验结果
Table 2 Box-Behnken design matrix and response values
试验号 A B C D Y 提取量(mg/g) 1 0 0 −1 −1 6.18 2 0 −1 0 −1 6.01 3 −1 0 0 −1 5.48 4 1 0 0 −1 5.12 5 0 1 0 −1 5.94 6 0 0 1 −1 5.98 7 0 −1 −1 0 6.11 8 −1 0 −1 0 6.30 9 1 0 −1 0 4.75 10 0 1 −1 0 5.41 11 −1 −1 0 0 6.51 12 1 −1 0 0 5.42 13 0 0 0 0 6.66 14 0 0 0 0 6.86 15 0 0 0 0 6.68 16 0 0 0 0 6.53 17 0 0 0 0 6.83 18 −1 1 0 0 5.38 19 1 1 0 0 4.93 20 0 −1 1 0 6.58 21 −1 0 1 0 5.92 22 1 0 1 0 5.26 23 0 1 1 0 5.19 24 0 0 −1 1 6.30 25 0 −1 0 1 6.56 26 −1 0 0 1 5.59 27 1 0 0 1 5.26 28 0 1 0 1 4.89 29 0 0 1 1 5.98 表 3 辣木籽多酚回归模型方差分析表
Table 3 Analysis of variance table for the regression model of Moringa oleifera Lam. seed polyphenols
来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F值 P值 显著性 模型 10.53 14 0.75 13.38 < 0.0001 ** A 1.64 1 1.64 29.16 < 0.0001 ** B 2.48 1 2.48 44.14 < 0.0001 ** C 0.0018 1 0.0018 0.032 0.8602 D 0.0013 1 0.0013 0.022 0.8833 AB 0.10 1 0.10 1.81 0.1994 AC 0.20 1 0.20 3.53 0.0811 AD 0.00031 1 0.00031 0.0054 0.9421 BC 0.12 1 0.12 2.10 0.1690 BD 0.64 1 0.64 11.34 0.0046 ** CD 0.0041 1 0.0041 0.071 0.7938 A2 4.43 1 4.43 78.82 < 0.0001 ** B2 1.31 1 1.31 23.33 0.0003 ** C2 0.67 1 0.67 11.97 0.0038 ** D2 1.06 1 1.06 18.92 0.0007 ** 残差 0.79 14 0.056 失拟项 0.72 10 0.072 4.03 0.0955 纯误差 0.071 4 0.018 总方差 11.32 28 注:*表示差异显著(0.01<P<0.05);**表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。 -
[1] VERMA A R, VIJAYAKUMAR M, MATHELA C S, et al. In vitro and in vivo antioxidant properties of different fractions of Moringa oleifera leaves[J]. Food and Chemical Toxicology: An International Journal Published for the British Industrial Biological Research Association,2009,47(9):2196−2201. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2009.06.005
[2] AL-ASMARI A K, ALBALAWI S M, ATHAR M T, et al. Moringa oleifera as ananti-cancer agent against breast and colorectal cancer cell lines[J]. Plos One,2015,10:e0135814. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0135814
[3] PEIXOTO J R O, SILVA G C, COSTA R A, et al. In vitro antibacterial effect of aqueous and ethanolic Moringa leaf extracts[J]. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Medicine,2011,4(3):201−204. doi: 10.1016/S1995-7645(11)60069-2
[4] BEHESHTIPOUR J. Comment on "Anion gap toxicity in alloxan induced type 2 diabetic rats treated with antidiabetic noncytotoxic bioactive compounds of ethanolic extract of Moringa oleifera"[J]. Journal of Toxicology,2019,2019:3930587−3930587.
[5] 樊建麟, 邵金良, 叶艳萍, 杨东顺. 辣木籽营养成分含量测定[J]. 中国食物与营养,2016,22(5):69−72. [FAN J L, SHAO J L, YE Y P, et al. Determination of nutrient content of Moringa oleifera seeds[J]. Chinese Food and Nutrition,2016,22(5):69−72. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9577.2016.05.017 [6] LEONE A, SPADA A, BATTEZZATI A, et al. Moringa oleifera seeds and oil: Characteristics and uses for human health[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2016,17(12):2141−2155. doi: 10.3390/ijms17122141
[7] 董成国, 程大友, 崔杰, 等. 响应面法优化辣木籽水溶性多糖的提取工艺研究[J]. 中国甜菜糖业,2016,57(2):4−8. [DONG C G, CHENG D Y, CUI J, et al. Optimization of extraction process of water-soluble polysaccharides from Moringa oleifera seeds by response surface methodology[J]. China Beet Sugar Industry,2016,57(2):4−8. [8] AL-MALKI A L, EL R. The antidiabetic effect of low doses of Moringa oleifera Lam. seeds on streptozotocin induced diabetes and diabetic nephropathy in male rats[J]. Biomed Res Int,2015,2015:381040.
[9] 李丽, 张莉, 齐刚. 辣木果实对正常和高胆固醇血症家兔血脂的影响[J]. 现代药物与临床,2004,19(4):170−170. [LI L, ZHANG L, QI G. Effects of Moringa oleifera fruit on blood lipids in normal and hypercholesterolemic rabbits[J]. Modern Medicine and Clinical,2004,19(4):170−170. [10] ARAUJO L C, AGUIAR J S, NAPOLEO T H, et al. Evaluation of cytotoxic and anti-inflammatory activities of extracts and lectins from Moringa oleifera seeds[J]. PLoS One,2013,8(12):1−15.
[11] SHUA X S, WANG D D, ZHAO Y Y, et al. Extract from Moringa oleifera seeds suppresses the epithelial-mesenchymal transition-mediated metastasis of gastric cancer by targeting the metastatic suppressor ND R G1[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2018,50(2018):93−103.
[12] CHATTOPADHYAY S, MAITI S, MAJI G, et al. Protective role of Moringa oleifera seed on arsenic-induced hepatocellular degeneration in female albino rats[J]. Biological Trace Element Research,2011,142(2):200−212. doi: 10.1007/s12011-010-8761-7
[13] COELHO L, MOURA M. Water-soluble Moringa oleifera lectin interferes with growth, survival and cell permeability of corrosive and pathogenic bacteria[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology,2015,119(3):666−676. doi: 10.1111/jam.12882
[14] 黄颖, 谭书明, 陈小敏, 等. 辣木籽多酚提取工艺优化及解酒功效研究[J]. 食品科技,2019,44(6):248−255. [HUANG U, TAN S M, CHEN X M, et al. Optimization of extraction process of polyphenols from Moringa oleifera seeds and research on the efficacy of alcohol detoxification[J]. Food Science and Technology,2019,44(6):248−255. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2019.06.042 [15] 杨迎, 谢凡, 龚胜祥, 等. 响应面法优化辣木籽多酚提取工艺及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(3):172−178. [YANG Y, XIE F, GONG S X, et al. Optimization of extraction process and antioxidant activity of Moringa oleifera seed polyphenols by response surface methodology[J]. Food Industry Technology,2018,39(3):172−178. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2018.03.034 [16] 谭飔, 夏国灯, 韩杨, 等. 辣木籽多酚提取工艺优化及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品科技,2019,44(1):280−285. [TAN S, XIA G D, HAN Y, WANG X X. Optimization of extraction process of polyphenols from Moringa oleifera seeds and study on their antioxidant activity[J]. Food Technology,2019,44(1):280−285. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2019.01.048 [17] WANG J, LAN T, LEI Y, et al. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted enzymatic extraction of kiwi starch and evaluation of its structural, physicochemical, and functional characteristics[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2021,81:105866. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105866
[18] RAN J J, FAN M T, LI Y H, et al. Optimisation of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of polyphenols from apple peel employing cellulase enzymolysis[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2013,48(5):910−917.
[19] GAO Yuan, SHI Yutong, MIAO Na, et al. A green ultrasound-assisted enzymatic extraction method for efficient extraction of total polyphenols from Empetrum nigrum and determination of its bioactivities[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry,2022,109:559−576. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2022.02.041
[20] KAPASAKALIDIS P G, RASTALL R A, GORDON M H. Effect of a cellulase treatment on extraction of antioxidant phenols from black currant (Ribes nigrum L.) Pomace[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2009,57(10):4342−4351. doi: 10.1021/jf8029176
[21] 孟永海, 孟祥瑛, 付敬菊, 等. 超声波协同酶解法对山药总多酚提取及抗氧化活性影响研究[J]. 辽宁中医药大学学报,2020,22(4):63−66. [MENG Y H, MENG X Y, FU J J, et al. Effect of ultrasonic synergistic enzymatic digestion on the extraction and antioxidant activity of total polyphenols from yam[J]. Journal of Liaoning University of Chinese Medicine,2020,22(4):63−66. doi: 10.13194/j.issn.1673-842x.2020.04.016 [22] 朱延胜, 魏明, 钱森和, 等. 紫山药多酚分离纯化及其对α-葡萄糖苷酶活性的抑制作用[J/OL]. 食品与发酵工业: 1−10 [2022-06-29]. DOI: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.030252. ZHU Y S, WEI M, QIAN S H, et al. Isolation and purification of purple yam polyphenols and their inhibitory effect on α-glucosidase activity[J/OL]. Food and Fermentation Industry: 1−10[2022-06-29]. DOI: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.030252.
[23] MARVIBAIGI M, HOSSEINI S M, AMINI N. Launaea acanthodes (Boiss) O. Kuntze mediates hepatic glucose metabolism and ameliorates impaired pancreatic function in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2020,268(3):113577.
[24] DU Z, LIU J, ZHANG D, et al. Individual and synergistic antioxidant effects of dipeptides in in vitro antioxidant evaluation systems[J]. International Journal of Peptide Research & Therapeutics,2018,25:391−399.
[25] HONG M S, HAI Z Z, JUN Y Y, et al. In vitro and in vivo antioxidant activities of inulin[J]. PloS One,2018,13(2):e0192273. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0192273
[26] LES F, ARBONÉS-MAINAR J M, VALERO M S, et al. Pomegranate polyphenols and urolithin A inhibit α-glucosidase, dipeptidyl peptidase-4, lipase, triglyceride accumulation and adipogenesis related genes in 3T3-L1 adipocyte-like cells[J]. Journal of Ethnopharmacology,2018,220:67−74. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2018.03.029
[27] GUO X, LONG P, MENG Q, et al. An emerging strategy for evaluating the grades of Keemun black tea by combinatory liquid chromatography-Orbitrap mass spectrometry-based untargeted metabolomics and inhibition effects on α-glucosidase and α-amylase[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,246:74−81. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.10.148
[28] CHEN D, SHI J, HU X. Enhancement of polyphenol content and antioxidant capacity of oat (Avena nuda L.) bran by cellulase treatment[J]. Applied Biological Chemistry,2016,59(3):397−403. doi: 10.1007/s13765-016-0171-x
[29] LI C Y, TIAN Y, YANG Y X, et al. Characterization methods for investigating interaction mechanisms between plant polyphenols and proteins: A review[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(13):262−268.
[30] 李泉岑, 蔡雯雯, 李娜, 等. 响应面法优化香菇多酚提取工艺及稳定性研究[J]. 食品科技,2022,47(5):230−237. [LI Q C, CAI W W, LI N, et al. Optimization of extraction process and stability of lentinan polyphenols by response surface methodology[J]. Food Technology,2022,47(5):230−237. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9989.2022.5.spkj202205035 [31] RAHMAWATI I, FACHIR B A, MANURUNG Y H, et al. Application of response surface methodology in optimization condition of anthocyanin extraction process of cocoa peel waste with microwave assisted extraction method (MAE)[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science,2021,743(1):12091. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/743/1/012091
[32] 清源, 赵燕, 张万明. 油橄榄叶多酚的酶法提取及稳定性研究[J]. 中国调味品,2020,45(3):48−52, 61. [QING Y, ZHAO Y, ZHANG W M. Enzymatic extraction and stability study of polyphenols from olive leaves[J]. Chinese Condiments,2020,45(3):48−52, 61. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2020.03.011 [33] 王若兰, 郭亚鹏. 响应面法优化超声波辅助提取藜麦多酚的工艺条件[J]. 粮食与油脂,2020,33(9):1−7. [WANG R L, GUO Y P. Optimization of ultrasonic-assisted extraction of quinoa polyphenols by response surface methodology[J]. Grain and Oil,2020,33(9):1−7. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-9578.2020.09.001 [34] WU W, JIANG S, LIU M, et al. Simultaneous process optimization of ultrasound-assisted extraction of polyphenols and ellagic acid from pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) flowers and its biological activities[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2021,80:105833. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2021.105833
[35] 张超, 曹新志, 冯泉, 等. 超声波辅助提取辣木籽多酚工艺研究[J]. 化学研究与应用,2017,29(06):865−872. [ZHANG C, CAO X Z, FENG Q, et al. Ultrasonic-assisted extraction process of polyphenols from Moringa oleifera seeds[J]. Chemical Research and Applications,2017,29(06):865−872. [36] ZHU W, JIA Y, PENG J, et al. Inhibitory effect of persimmon tannin on pancreatic lipase and the underlying mechanism in vitro[J]. J Agric Food Chem,2018,66:8b00850.
[37] JIRAWAT R, CHIEN-HUNG J, SHIAN-REN L, et al. Hypoglycemic efficacy of docking selected natural compounds against α-glucosidase and α-amylase[J]. Molecules,2018,23(9):2260. doi: 10.3390/molecules23092260
[38] HUANG Doudou, DU Zenan, CHEN Yanhong, et al. Bio-guided isolation of two new hypoglycemic triterpenoid saponins from Polygonum capitatum drug design[J]. Development and Therapy,2021,15:5001−5010. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S341354
-
期刊类型引用(11)
1. 姜坤,李玉国,张道志,徐恒伟,冯丹萍,孟小茜,郑春英. 微生物发酵对刺五加叶黄酮类成分生物合成的影响. 中国农学通报. 2024(03): 145-151 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陆少君,蔡肇栩,郭瑞雪,谢群巧,罗力,唐春萍,陈文健,江涛. 基于TLR-4/NF-κB信号通路探究金花茶提取物对非酒精性脂肪肝的作用. 食品工业科技. 2024(20): 349-360 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 周月,王一珈,臧健,高英旭,潘丰,郭志富,李胤之. 刺五加活性成分及药用价值研究进展. 辽宁林业科技. 2024(06): 48-50+71 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 何嘉伟,江汉美,黄振阳,曾格格,戴全武,刘天琪,韩蔓. HS-SPME-GC-MS结合化学计量法分析刺五加不同部位的挥发性成分. 南京中医药大学学报. 2023(02): 146-156 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 李强,袁勇,李玉,于建海. 刺五加多糖对奶牛生产性能、抗氧化指标及免疫功能的影响. 中国饲料. 2023(12): 28-31 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 丁思宇,张道涵,韩丽琴. 星点-响应面法优化刺五加根黄酮闪式提取工艺研究. 吉林医药学院学报. 2023(04): 269-271 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 孙琳,井长欣,邹睿,辛宇,张晓旭,邱智东,王伟楠. 刺五加-灵芝双向固体发酵工艺优化及抗氧化活性评价. 科学技术与工程. 2023(21): 9004-9014 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 李强,张若冰,杨玉赫,田冰,李文兰,李陈雪. 刺五加叶化学成分及药理作用研究进展. 药学研究. 2023(07): 495-501 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 石玉璞,牛思思,韩璐瑶,李莞颖,余君伟,武冰辉,徐波,张艳萍,曹艳,乔长晟. 枸杞刺梨复合饮料的工艺优化及其降血糖性能. 食品研究与开发. 2023(18): 149-157 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 茆鑫,郑剑斌,李广耀,曲敏,郑心琪. 响应曲面法优化刺五加-五味子混菌发酵工艺的研究. 食品科技. 2023(09): 57-64 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 戴丛书,柴晶美,林长青. 金银花黄酮提取物的降血糖作用. 食品工业科技. 2022(24): 386-393 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(5)






 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:



