Analysis of Protein Structure and Functional Properties of Hemp Seeds of Different Varieties
-
摘要: 本文通过碱溶酸沉法提取了四个品种汉麻籽分离蛋白(Hemp protein isolate,HPI),测定了其分子量,并通过圆二色谱,游离巯基和二硫键含量以及表面疏水性表征其结构,最后测定了其功能特性并进行了功能特性和空间结构间的相关性分析。结果表明:HPI主要由含有两个亚基的麻仁球蛋白(约为50 kDa)和白蛋白(10~15 kDa)组成。四种HPI的二级结构中自由卷曲约占50%。东北的HPI二硫键含量为(5.20±0.32)μmol/g,拥有更稳定的结构;山西的HPI游离巯基为(15.18±0.32)μmol/g,更容易形成聚集体。在pH为4~6时,HPI的溶解度仅为4.85%~31.48%;其持水性和持油性分别为3.26~4.24和4.36~6.03 g/g,优于大部分植物蛋白;乳化能力和起泡能力较差。α-螺旋和表面疏水性与乳化性呈显著正相关性(r=0.70,0.65,P<0.05);乳化稳定性与自由卷曲呈极显著正相关性(r=0.74,P<0.01),与二硫键呈极显著负相关性(r=−0.72,P<0.01)。综上,不同品种HPI的功能特性和空间结构有较大差异,研究结果可为汉麻籽分离蛋白的精深加工及其在不同食品及配方中的应用提供一定的理论依据。Abstract: In this paper, hemp protein isolate (HPI) of four different varieties was extracted by alkali dissolution and acid precipitation. The molecular weight of HPI was determined and its structures were characterized by circular dichroism, free sulfhydryl and disulfide bond content and surface hydrophobicity. Finally, its functional properties were determined and the correlation analysis between functional properties and spatial structure was conducted. The results showed that HPI was mainly composed of edestin (~50 kDa) and albumin (10~15 kDa), and the former had two subunits. Random coil accounted for about 50% of the secondary structure. The content of disulfide bond in HPI from Dongbei was (5.20±0.32) μmol/g which means a more stable structure, and the content of free sulfhydryl groups HPI from Shanxi was (15.18±0.32) μmol/g that means it was easier to form aggregates. At pH4~6, the solubility of HPI was only 4.85%~31.48%. The water holding capacity and oil holding capacity of HPI were 3.26~4.24 and 4.36~6.03 g/g, respectively, superior to most plant proteins. Compared with other plant proteins, HPI had poor emulsifying and foaming capacity. Alpha-helix and surface hydrophobicity were significantly positive in correlation with emulsifying ability (r=0.70, 0.65, P<0.05). There was highly significant positive correlation between emulsifying stability and random coil (r=0.74, P<0.01), and distinct negative correlation between emulsifying stability and disulfide bond (r=−0.72, P<0.01). Overall, the functional properties and spatial structure of different varieties of HPI were quite different. The research results could provide a theoretical basis for the intensive processing of HPI and its application in different foods and formulas.
-
汉麻(Cannabis sativa L.)也称工业大麻、火麻、线麻等,是一种一年生草本植物,隶属于大麻科[1]。汉麻为无毒品种,四氢大麻酚含量低于0.3%[2]。据联合国粮农组织的统计资料显示,中国是汉麻种植面积最大的国家,约占全世界的50%,原麻产量占全球的25%[2-3]。汉麻籽,即汉麻植物产生的种子,富含蛋白质(20%~40%)、脂肪(28%~40%)及其它活性组分[2],具有抗氧化[4]、抗高血压[5]、神经保护[6]、降血糖[7]等多种生理活性,已成为一种极具开发价值与应用前景的食品原料。在欧、美、日、韩等发达地区和国家,汉麻籽作为食品和保健品原料,越来越受消费者的欢迎[8]。2001年汉麻籽被我国卫生部列为药食同源名录,为汉麻籽的开发提供大力支持[9]。但当前我国对汉麻籽的开发仍处于初级阶段,开发利用也主要集中在军用服装纤维原料和优质食用油上,对汉麻籽蛋白的研究开发较少。
汉麻籽蛋白主要由麻仁球蛋白和白蛋白组成,氨基酸种类齐全且组成均衡,包括8种必需氨基酸,其中精氨酸含量最为丰富,营养价值高,致敏性低,易消化,是一种极具开发前景的新兴的优质植物蛋白源[10-13]。目前,国内外对汉麻籽蛋白的开发主要集中在分离蛋白(Hemp protein isolate,HPI)的提取制备、氨基酸组成、功能的改性和蛋白类食品制作等方面。何锦凤等[14]测定了我国主要几种汉麻籽的基本组分、氨基酸和脂肪酸组成以及汉麻籽油的各项指标,表明其营养价值以及作为食品原料应用的可能性。Vonapartis等[15]对比了加拿大境内种植的十种汉麻籽中蛋白质和脂肪含量、脂肪酸组成以及酚类含量,证明其作为膳食来源的巨大潜能。Corrado等[16]测定了六种汉麻籽中常量和微量的矿物质元素,发现其微量元素差异显著且可以将其作为钾、钙、铁、锌的良好来源。
综上,目前的研究主要聚焦于汉麻籽基本组分、氨基酸和脂肪酸组成及微量元素的差异分析,但对不同品种汉麻籽分离蛋白的结构表征、功能特性及其相关性进行分析鲜有报道。因此,本研究对四个不同品种汉麻籽分离蛋白的分子量、结构以及溶解度、持水性、持油性、乳化性、起泡性等进行系统检测和数据分析,并探讨HPI结构差异和功能特性之间的相关性,为HPI的加工适宜性和相关食品及保健品的开发提供理论支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
汉麻籽 分别购自黑龙江省汉麻科技发展有限公司(火麻1号)、广西巴马常春藤生命科技发展有限公司(巴马火麻种)、内蒙古汉麻农业发展有限责任公司(内蒙包头种)、山西长治平顺潞麻农业科技有限公司(汾麻3号);玉米油 食品级,金龙鱼粮油食品股份有限公司;BCA法蛋白质浓度测定试剂盒 生工生物工程(上海)有限公司;所有试剂 均为分析纯。
Z-326K离心机 德国Hermle labortechnik GmbH公司;THM-2875恒温水浴锅 美国赛默飞世尔科技公司;Triad冷冻干燥机 美国Labconoco公司;S10手持式高速均质机 上海微弥科技有限公司;J-1500圆二色谱仪 日本分光公司;Infinite M200 Pro多功能酶标仪 瑞士帝肯公司;ChemiDoc XRS+System高灵敏度化学发光成像系统 美国Bio-Rad公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 汉麻籽分离蛋白的制备
采用碱溶酸沉法制备汉麻籽分离蛋白,参考Jiang等[17]的方法并稍作修改。将磨碎的汉麻籽粉过80目筛并与正己烷混合(1:3,w/v),在超声水浴中(360 W,40 ℃)处理60 min,抽滤后收集残留物。该过程重复三次以获得脱脂汉麻籽粕。脱脂后的粉末与去离子水以1:10的料液比混合后,用1 mol/L NaOH调节pH至11.0,在40 ℃水浴中连续搅拌2 h,并以6000×g离心10 min。取上清液用1 mol/L HCl调节pH至4.0使汉麻籽蛋白沉淀,并在4 ℃下过夜。通过在6000×g下离心10 min回收沉淀物,然后添加去离子水调节pH至7.0,置于−80 ℃,5.0 Pa环境中冷冻干燥后获得汉麻籽分离蛋白粉,并储存在−20 ℃直至分析。
1.2.2 汉麻籽分离蛋白分子量的测定(SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳)
参考Nasrollahzadeh等[18]的方法并稍作修改。取40 μL 2 mg/mL蛋白液于离心管中,加入10 μL蛋白上样缓冲液,充分混匀后置于沸水浴10 min,然后在−20 ℃放置2 min,12000×g离心5 min,小心吸取5~10 μL上清液加样进行SDS-PAGE检测。电泳条件为:浓缩胶80 V,20 min;分离胶120 V,80 min。待电泳结束后,考马斯亮蓝R250快速染色20~30 min,清水脱色12 h,至胶块透明清晰。在凝胶成像仪上拍照保存并分析条带。
1.2.3 汉麻籽分离蛋白质结构测定
1.2.3.1 圆二色谱分析
参考张意锋等[19]的方法并稍作改动。在室温下进行测定,使用1 mm的石英皿。用磷酸盐缓冲液将蛋白样品稀释至0.1 mg/mL后上样,圆二色谱仪波长范围设置为190~240 nm,扫描速度为50 nm/min,扫描步长为1 nm。蛋白二级结构用K2D程序 (http://dichroweb.cryst.bbk.ac.uk) 分析。
1.2.3.2 游离巯基和二硫键
参考张意锋等[19]的方法并稍作改动。取20 mg分离蛋白溶于4 mL Tris-Glycine缓冲液(0.086 mol/L,pH8.0)后加入100 μL 4 mg/mL 5,5'-二硫代双(2-硝基苯甲酸)(DTNB),振荡混匀,在室温下避光放置30 min后,8000×g离心10 min,取上清液在412 nm处测定吸光度,未加蛋白的作为空白对照。测定总巯基含量的缓冲液中另含有8 mol/L尿素,游离巯基和二硫键含量使用下述公式计算:
游离巯基含量(μmol/g)=A×DC×73.53 (1) 二硫键含量(μmol/g)=总巯基含量−游离巯基含量2 (2) 式中:A表示吸光度;D表示稀释因子;C表示样品浓度。
1.2.3.3 表面疏水性
参考张意锋等[19]的方法并稍作改动。利用1-苯胺基-8-萘磺酸 (ANS) 作为荧光探针对蛋白质表面疏水性进行测定。使用10 mmol/L PBS溶液(pH7.0)配制0.05、0.10、0.15、0.20、0.25 mg/mL的蛋白溶液,取2 mL稀释液加入10 μL ANS溶液(8.0 mmol/L),设置激发波长为390 nm、发射波长470 nm,上样检测。表面疏水性表示为荧光强度随蛋白浓度变化的斜率。
1.2.4 汉麻籽分离蛋白功能特性的测定
1.2.4.1 溶解度
参考Jiang等[17]的方法进行溶解度的测定。配制1 mg/mL的汉麻籽分离蛋白液,用0.1 mol/L HCl或NaOH调节pH至2.0、4.0、6.0、8.0、10.0,室温下搅拌30 min后以8000×g 10 min,取上清液使用BCA试剂盒测定不同pH下的溶解度。
1.2.4.2 持水性和持油性
参考Ogunwolu等[20]的方法进行持水性和持油性的测定,结果表示为每克蛋白吸收的水/油质量。
1.2.4.3 乳化性及乳化稳定性
参考Jiang等[17]的方法进行乳化性及乳化稳定性的测定并稍作修改。取 10 mg/mL的蛋白液15 mL并向其中加入5 mL玉米油,在12000 r/min下均质2 min后,从底部取50 μL加入5 mL 0.1% SDS,混匀后在500 nm处测定吸光度。乳化活性指数(emulsifying activity index,EAI)用来表示乳化性能,使用下述公式计算得出:
乳化活性指数(m2/g)=2×2.303×A×DC×(1−ϕ)×104 (3) 式中:A表示吸光度;D表示稀释因子;C表示样品浓度;
ϕ 表示油在体系中的体积分数(0.25)。记录第0和30 min的EAI,其比值为乳化稳定指数(emulsifying stability index,ESI),用来衡量样品的乳化稳定性。1.2.4.4 起泡性及起泡稳定性
参考Jiang等[17]的方法进行起泡性及起泡稳定性的测定。以12000 r/min均质20 mL 10 mg/mL的蛋白溶液2 min后,测定起泡性及其稳定性,起泡性表示为悬浮体积增加百分比,起泡稳定性表示为静置30 min后剩余的发泡百分比。
1.3 数据处理
每项指标均做3次重复试验,所得数据采用SPSS Statistics 19进行分析,结果表示为平均值±标准差,P<0.05为显著性差异。
2. 结果与分析
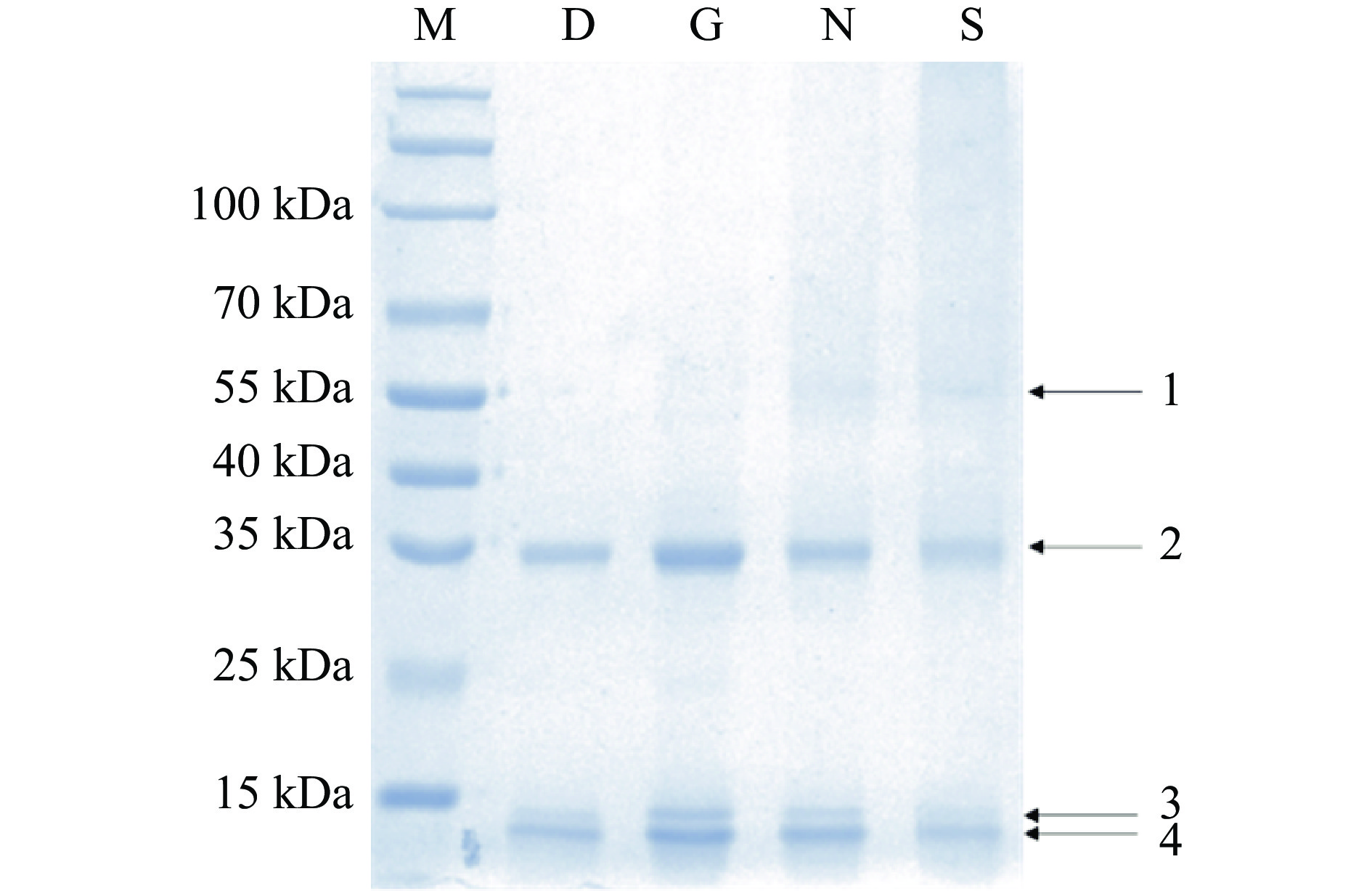
2.1 汉麻籽分离蛋白的分子量
由图1的凝胶电泳可知,HPI主要麻仁球蛋白和白蛋白组成。麻仁球蛋白分子量较大,约为50 kDa,只有山西和内蒙古的HPI检测到有少量该成分(条带1)。麻仁球蛋白的每个单体通常由一个酸性亚基和一个碱性亚基通过二硫键相连[21]。因此,条带2可能对应酸性亚基(分子量约为35 kDa),广西HPI在该条带呈现较深的颜色,可以认为其酸性亚基含量较高。此外,四种HPI中均未检测到碱性亚基。白蛋白分子量较小,一般为10~15 kDa,对应条带3和4,这与之前研究结果一致[10,21]。基于条带颜色,可以认为广西和内蒙古的HPI白蛋白含量较高。
2.2 汉麻籽分离蛋白质结构
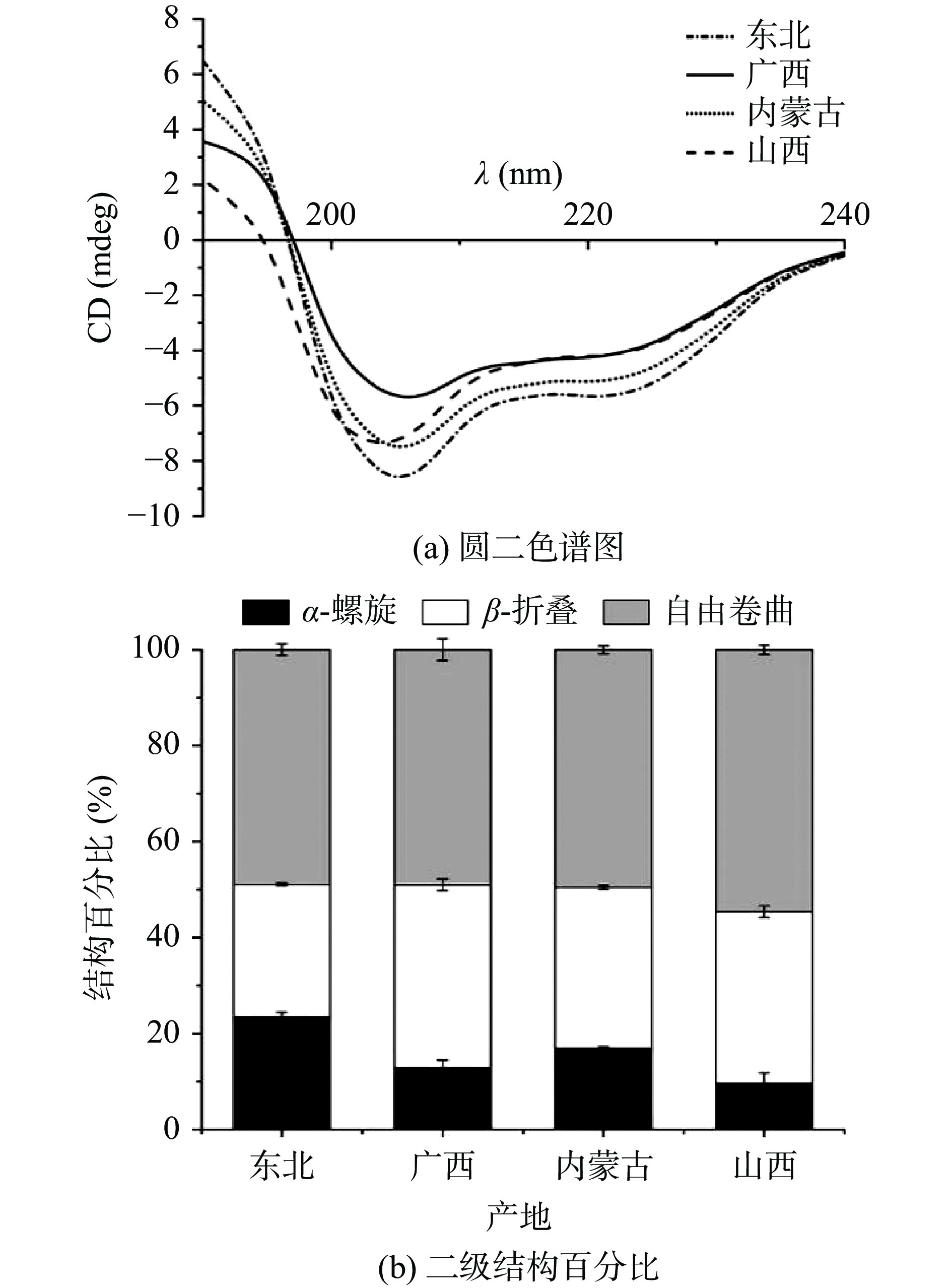
2.2.1 圆二色谱图和二级结构
HPI的圆二色谱结果和二级结构如图2所示。从图2a可以看出,四种HPI的圆二色谱曲线在206 nm处有明显负峰,东北的HPI在该点有最大绝对值,这与α-螺旋结构及其占比相关。经过计算得到α-螺旋、β-折叠和自由卷曲的占比结果如图2b所示。四种HPI中含量最高的均为自由卷曲,约占50%;其次是β-折叠(27.7%~38.1%),这与之前研究结果一致[22]。α-螺旋代表蛋白质空间结构的有序性,其稳定性主要靠氢键维持,而氢键的断裂会导致蛋白质空间结构由有序逐渐变为无序;同时,较低的α-螺旋含量会降低人体的利用效率[23]。有研究表明[24],缬氨酸、异亮氨酸和脯氨酸可以促进β-折叠结构的形成,而课题组之前对于四种汉麻籽氨基酸组成的测定(未在本文中展示)也验证了这一结果:广西HPI(β-折叠占比为38.13%)和山西HPI(β-折叠占比35.83%)中这三种氨基酸的含量均为四个品种中的前两位。综上,东北的HPI(α-螺旋占比为23.45%)更有利于人体的吸收利用。
2.2.2 游离巯基和二硫键
HPI的游离巯基和二硫键含量如图3a所示。游离巯基和二硫键含量分别为6.31~14.81 μmol/g和1.74~5.20 μmol/g,各品种间有显著差异(P<0.05)。其中,山西HPI含有较多的游离巯基(14.81±0.32) μmol/g,而相对应的二硫键含量(1.74±0.03) μmol/g为四个品种中最低。游离巯基和二硫键是蛋白质空间构象中重要的官能团,可以赋予蛋白质结构稳定性和刚性[25]。二硫键是共价键,与半胱氨酸残基相连,可以使得肽链的空间结构更紧密,而较低的含硫氨基酸含量会抑制二硫键的形成[26]。因此,高二硫键含量的蛋白质(东北HPI)在结构上更稳定,而高游离巯基含量的蛋白质(山西HPI)很有可能相互缔合形成聚集体。
2.2.3 表面疏水性
表面疏水性是蛋白质三级结构和疏水相互作用的另一个关键指标,与蛋白质的功能特性密切相关,HPI的表面疏水性如图3b所示。四种HPI的表面疏水性指数(H0)从993到4195不等,且各组间有显著差异(P<0.05)。较高的H0表明蛋白质内部的疏水基团暴露在分子表面,为荧光探针提供了更多的结合位点[27],这可能是由于极性氨基酸残基之间的相互作用所引起的静电排斥,使得蛋白质空间结构展开,从而使更多疏水性氨基酸暴露于表面[28]。此外,有研究表明[25,27],具有较高H0的蛋白质往往意味着溶液中存在大量为聚集的蛋白质,并可以迅速吸附到空气-水界面,从而带来更好的表面活性,这样的蛋白质往往也将有较好乳化和起泡能力。所以,可以合理推测内蒙古的HPI具有较好的乳化性。
2.3 汉麻籽分离蛋白的功能特性
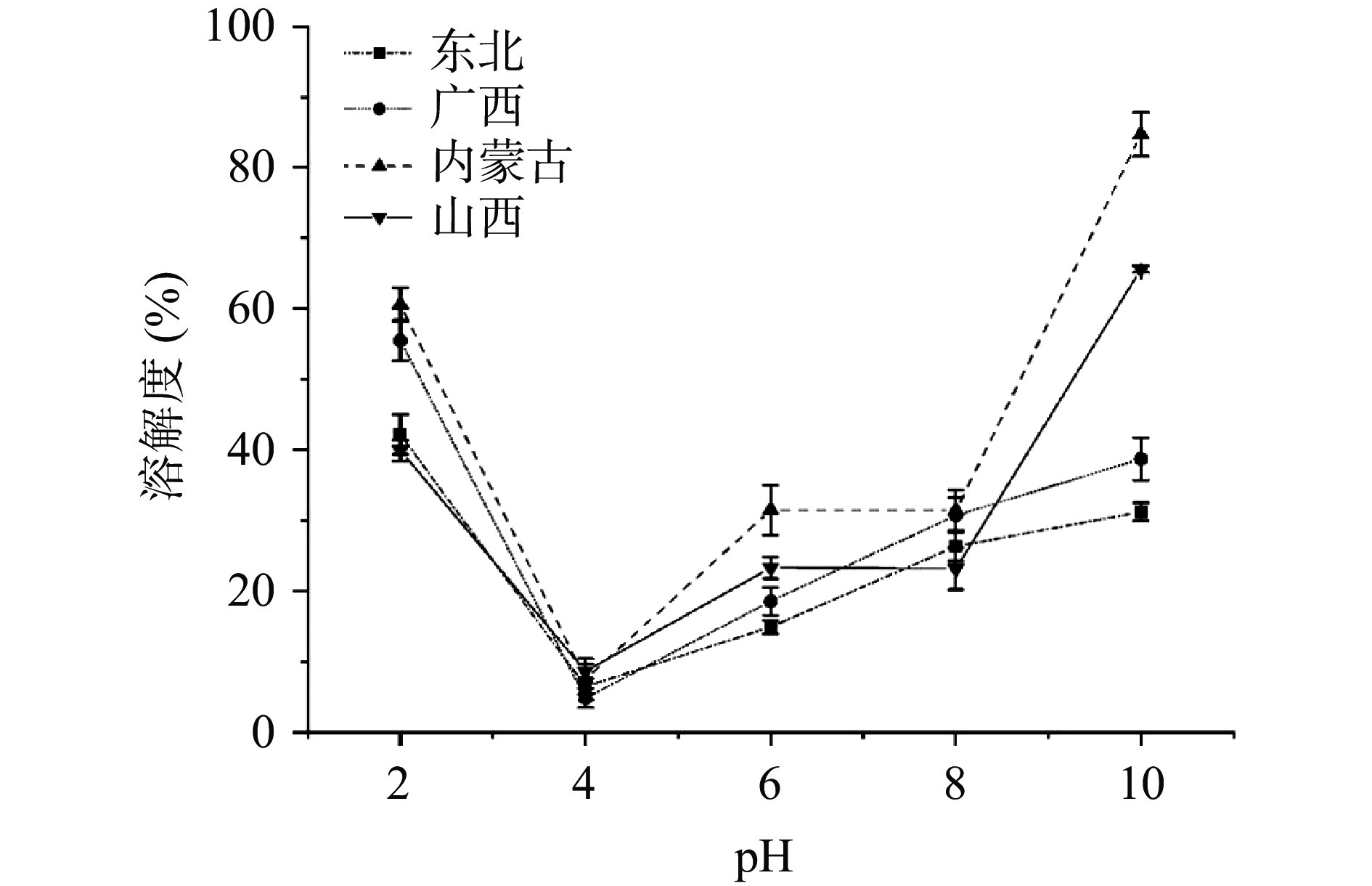
2.3.1 溶解度
不同pH条件下的HPI溶解度如图4所示。在测试的pH范围(2~10)内,HPI的溶解度呈现典型的“U”型曲线,表明其受pH变化影响显著,而HPI在碱性条件下溶解比酸性条件更充分,这与之前研究结果一致,可能的原因是球蛋白亚基在特定pH范围内结构和构象的变化[10]。HPI在pH约为4时溶解度最小,此pH处于等电点附近,蛋白分子间静电斥力较低,容易通过疏水键聚集沉淀[29],而在pH为10时,不同品种的HPI溶解度变化很大,从31.23%(东北)到84.71%(内蒙古)。当pH小于8时,HPI的溶解度低于大豆分离蛋白(SPI),这主要是由于蛋白质组成和六聚体聚集的差异[10]。在一定pH范围内,提取和处理方法也会影响蛋白质的溶解度,本研究采用碱提取。该方法操作简便、蛋白质得率高,并能保留较多得酚类物质[22]。
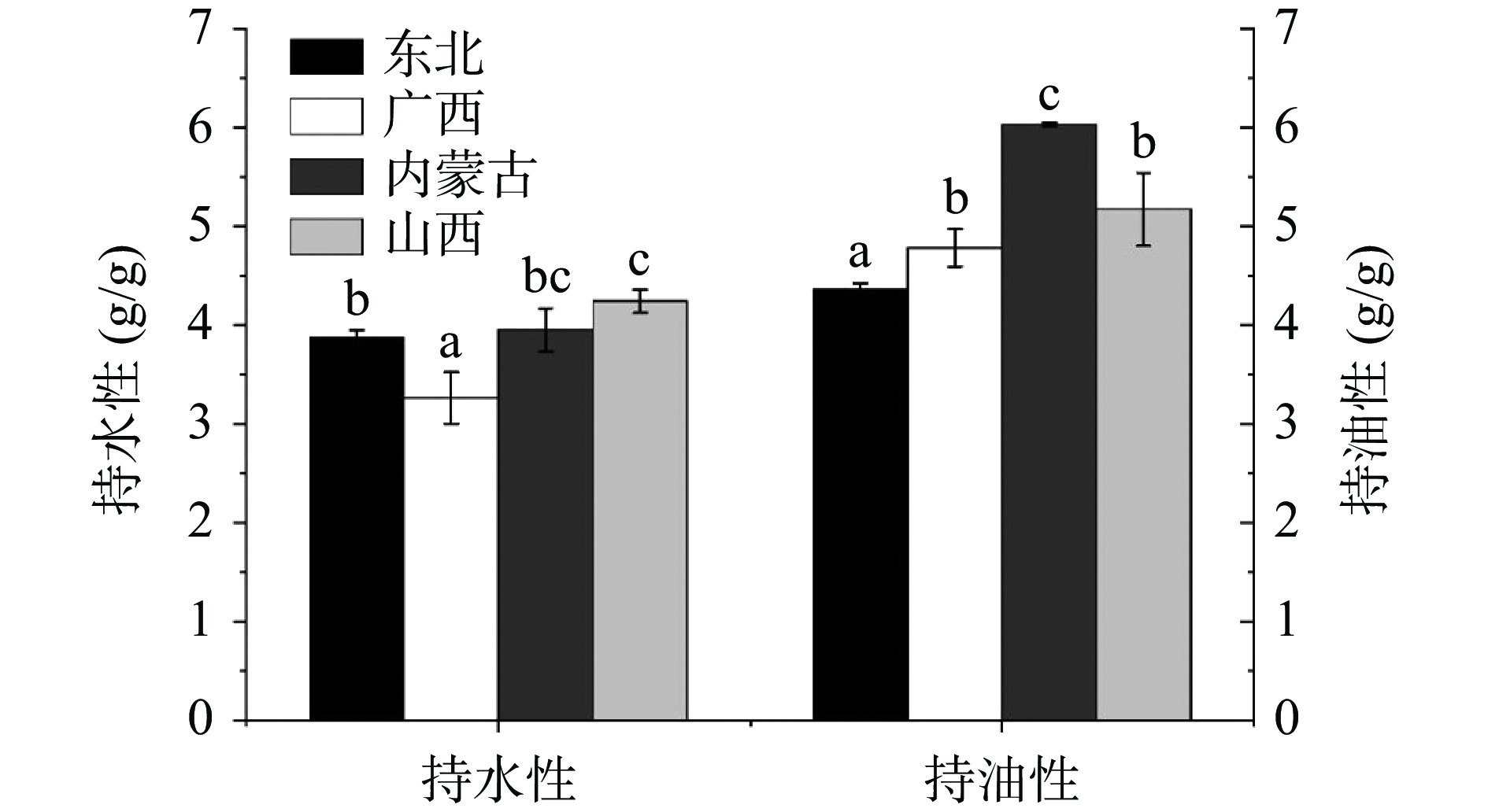
2.3.2 持水性和持油性
HPI的持水性和持油性如图5所示。不同品种HPI的持水性有较为明显的差异,从3.26至4.24 g/g不等,该指标和SPI(3.6 g/g)相当,而优于绿豆分离蛋白(2.1 g/g)、黑豆分离蛋白(2.9 g/g)和芸豆分离蛋白(1.6~3.6 g/g)[10,25,30]。东北、内蒙古和山西的HPI的持水性优于先前的研究结果[10],这可能是因为这三个品种汉麻籽中疏水性氨基酸占比较低所带来的。考虑蛋白质持水性推荐范围为1.49~4.72 g/g[10],HPI可能成为粘性食品的理想成分。HPI的持油性从4.36~6.03 g/g不等,与豌豆分离蛋白(6.4 g/g)和芸豆分离蛋白(5.9 g/g)相当[30]。HPI较好的持水性和持油性使其有潜力成为各种产品的理想成分。本研究中,内蒙古和山西的HPI可以作为基质或配料应用于粘性食品加工。
2.3.3 乳化性及其稳定性
HPI的乳化活性指数(EAI)和乳化稳定指数(ESI)如图6所示。HPI的EAI从4.10至6.78 m2/g,要低于豌豆分离蛋白(15.6~26.6 m2/g)和芸豆分离蛋白(11.8~14.1 m2/g)[30]。在四个品种中,内蒙古的HPI拥有更好的乳化能力,该结果也应证了2.2.3中的推论,其原因可能是在中性pH范围内较大的溶解度和较高的表面疏水性为其提供了.更快的界面扩散速率;而山西HPI的乳化稳定指数(70.71%)要明显优于其他品种,这是由于7S球蛋白(约50 kDa)的存在可以使其拥有更好的稳定性[21]。乳化能力取决于蛋白质在水-油界面的性质,蛋白质在该界面上引起构象重排并形成内聚膜,可以在蛋糕及其他产品的生产中发挥重要作用[2]。之前有项研究表明[10],HPI不同pH下EAI的变化与其溶解度曲线非常相似,故HPI较差的乳化性能可以归因于中性pH范围内较低的溶解度。
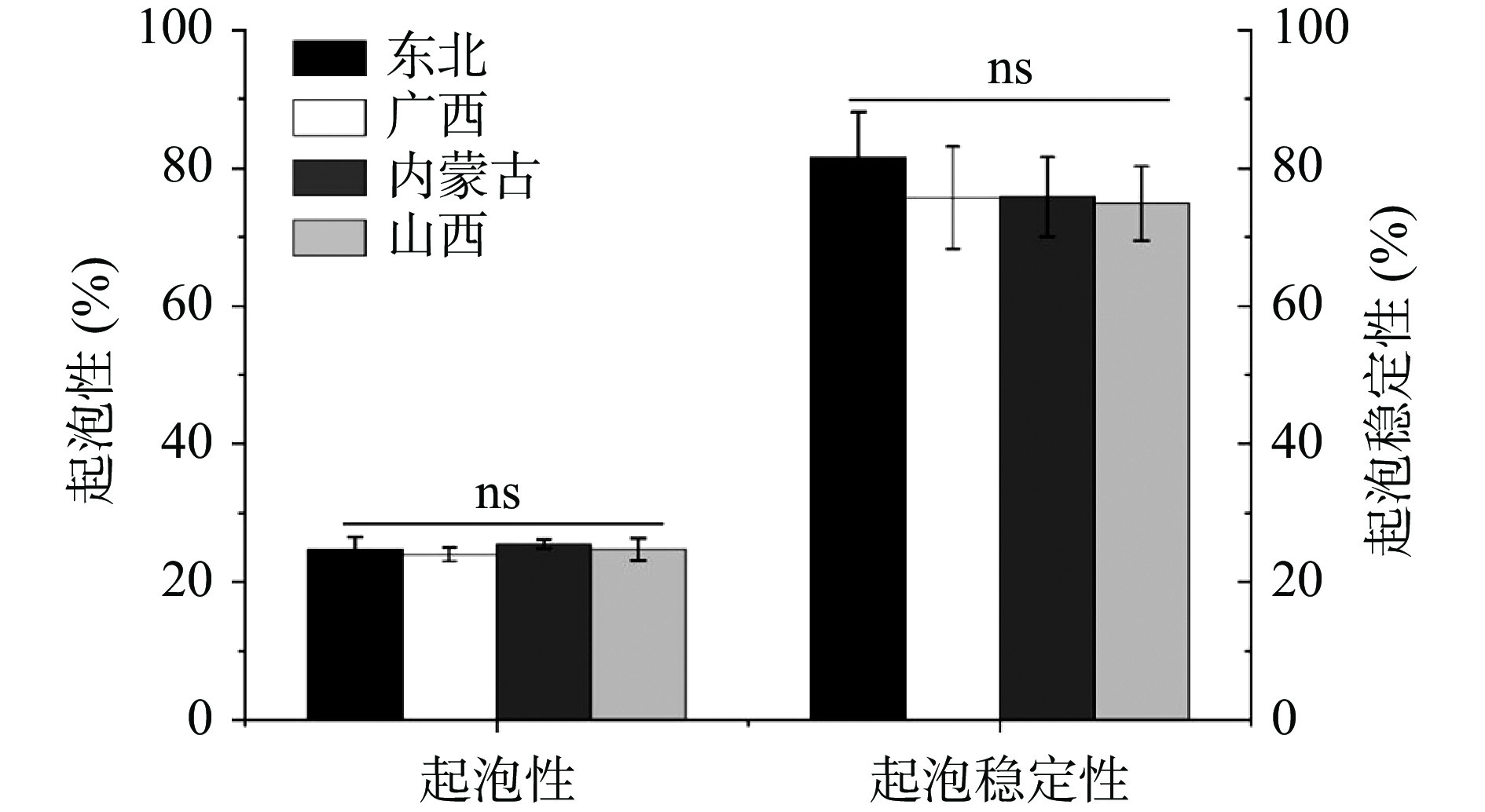
2.3.4 起泡性及其稳定性
HPI的起泡性及其稳定性如图7所示。HPI的起泡性及其稳定性分别为23.97%~25.54%和74.81%~81.49%,各组间无显著差异,其中,起泡稳定性明显优于之前的研究结果(58.8%)[31]。起泡能力与电荷密度、疏水性等固有因素有关,而蛋白质膜的流变特性影响泡沫稳定性[32]。虽然各组间没有显著差异,但东北的HPI的起泡稳定性(81.49%)要略优于其他三种,结合之前氨基酸组成的测定结果,可以合理推测是其较多的疏水性氨基酸使得有利于蛋白质-蛋白质疏水性结合,从而在分界面形成内聚性膜。通常,植物蛋白中球蛋白比例较高,而这种盐溶性蛋白不利于获得良好的功能特性,故需要通过特定的提取或处理方法进行改性。
2.4 汉麻籽分离蛋白功能特性和结构之间的相关性
为探究蛋白质空间结构与功能特性的关系,进行了两者间的相关性分析,结果如表1。研究表明,α-螺旋与乳化性、自由卷曲与乳化稳定性有显著的正相关性(P<0.05),说明降低β-折叠在二级结构中的占比可以有效提高乳化性能。起泡性能和其他所有指标都不存在显著的相关性。同时,二硫键对于乳化稳定性也有很明显的促进作用(P<0.01),说明当巯基被束缚在蛋白质疏水核心内时,乳化效果更好。表面疏水性与持油性(P<0.01)和乳化性(P<0.05)都有明显的正相关性,说明当疏水性基团或氨基酸释放到蛋白质表面时,表面活性将得到明显提升。值得一提的是,HPI的游离巯基和二硫键比二级结构与更多的功能特性指标存在相关性,这可能是改善其功能特性的关键。因此上述分析证明了功能特性和结构之间存在一定的相关性,为后续的改性提供了参考,同时也验证了测定结果的准确性。
表 1 汉麻籽分离蛋白功能特性和结构之间的相关性分析Table 1. Correlation analysis between functional properties and structure of hemp protein isolate功能特性 结构特性 持水性 持油性 乳化性 乳化稳定性 起泡性 起泡稳定性 α-螺旋 β-折叠 自由卷曲 游离巯基 二硫键 表面疏水性 持水性 1.00 0.32 0.01 0.78** 0.26 0.10 −0.05 −0.30 0.55 0.18 −0.38 −0.21 持油性 1.00 0.32 0.26 0.46 −0.31 −0.26 0.30 0.08 0.15 −0.17 0.76** 乳化性 1.00 −0.42 0.31 0.30 0.701* −0.58* −0.54 −.086** 0.76** 0.65* 乳化稳定性 1.00 0.23 −0.06 −0.44 0.10 0.74** 0.60* −0.72** −0.29 起泡性 1.00 −0.28 0.27 −0.25 −0.16 −0.14 0.09 0.39 起泡稳定性 1.00 0.38 −0.33 −0.26 −0.39 0.38 −0.15 α-螺旋 1.00 −0.88** −0.70* −0.93** 0.89** 0.07 β-折叠 1.00 0.25 0.75** −0.61* 0.19 自由卷曲 1.00 0.74** −0.89** −0.42 游离巯基 1.00 −0.96** −0.31 二硫键 1.00 0.32 表面疏水性 1.00 注:显著性水平 *, P<0.05;**,P<0.01。 3. 结论
四个品种的HPI有相似的溶解度曲线:在pH为4~6时,溶解度仅为4.85%~31.48%;而pH为2或10时,四种HPI溶解度最高。内蒙古的HPI有较好的持油性和乳化性,山西的HPI有较好的持水性和乳化稳定性;而在起泡性能方面,四种HPI无明显差异。相较于其他植物蛋白,HPI的功能特性较差,主要是因为中性pH范围内的溶解度较差。HPI主要由含有两个亚基的麻仁球蛋白(约为50 kDa)和白蛋白(10~15 kDa)组成,其二级结构主要为自由卷曲(约占50%)。较高的二硫键含量(5.20±0.32) μmol/g使得东北的HPI有更稳定的空间结构,而较好的表面疏水性(H0=4195)给山西的HPI带来了更好的起泡和乳化能力。此外,HPI的功能特性与结构存在一定的相关性,可为改性处理提供一定的参考。
-
表 1 汉麻籽分离蛋白功能特性和结构之间的相关性分析
Table 1 Correlation analysis between functional properties and structure of hemp protein isolate
功能特性 结构特性 持水性 持油性 乳化性 乳化稳定性 起泡性 起泡稳定性 α-螺旋 β-折叠 自由卷曲 游离巯基 二硫键 表面疏水性 持水性 1.00 0.32 0.01 0.78** 0.26 0.10 −0.05 −0.30 0.55 0.18 −0.38 −0.21 持油性 1.00 0.32 0.26 0.46 −0.31 −0.26 0.30 0.08 0.15 −0.17 0.76** 乳化性 1.00 −0.42 0.31 0.30 0.701* −0.58* −0.54 −.086** 0.76** 0.65* 乳化稳定性 1.00 0.23 −0.06 −0.44 0.10 0.74** 0.60* −0.72** −0.29 起泡性 1.00 −0.28 0.27 −0.25 −0.16 −0.14 0.09 0.39 起泡稳定性 1.00 0.38 −0.33 −0.26 −0.39 0.38 −0.15 α-螺旋 1.00 −0.88** −0.70* −0.93** 0.89** 0.07 β-折叠 1.00 0.25 0.75** −0.61* 0.19 自由卷曲 1.00 0.74** −0.89** −0.42 游离巯基 1.00 −0.96** −0.31 二硫键 1.00 0.32 表面疏水性 1.00 注:显著性水平 *, P<0.05;**,P<0.01。 -
[1] ANDRE C M, HAUSMAN J F, GUERRIERO G. Cannabis sativa: The plant of the thousand and one molecules[J]. Frontiers in Plant Science,2016,7:19.
[2] SHEN P, GAO Z, FANG B, et al. Ferreting out the secrets of industrial hemp protein as emerging functional food ingredients[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2021,112:1−15.
[3] TANG K L, WANG J Y, YANG Y, et al. Fiber hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) yield and its response to fertilization and planting density in China[J]. Industrial Crops & Products,2022,177:114542.
[4] FRASSINETTI S, MOCCIA E, CALTAVUTURO L, et al. Nutraceutical potential of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) seeds and sprouts[J]. Food Chemistry,2018,262:56−66. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.04.078
[5] TEH S S, BEKHIT A E A, CARNE A, et al. Antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory activities of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) protein hydrolysates produced by the proteases AFP, HT, Pro-G, actinidin and zingibain[J]. Food Chemistry,2016,203:199−206. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.02.057
[6] NONGONIERMA A B, FITZGERALD R J. Investigation of the potential of hemp, pea, rice and soy protein hydrolysates as a source of dipeptidyl peptidase IV (DPP-IV) inhibitory peptides[J]. Food Digestion: Research and Current Opinion,2015,6:1−3. doi: 10.1007/s13228-015-0042-7
[7] YU Z, WU S, ZHAO W, et al. Anti-alzheimers activity and molecular mechanism of albumin-derived peptides against AChE and BChE[J]. Food & Function,2018,9(2):1173−1178.
[8] KING J W. The relationship between cannabis/hemp use in foods and processing methodology[J]. Current Opinion in Food Science,2019,28:32−40. doi: 10.1016/j.cofs.2019.04.007
[9] 予辑. 药食同源原料目录(2017版)[J]. 口腔护理用品工业,2017,27(6):24−28. [YU J. Medicinal and food ingredients directory (2017 version)[J]. Oral Care Industry,2017,27(6):24−28. [10] CHUAN-HE T, ZI T, XIAN-SHENG W, et al. Physicochemical and functional properties of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) protein isolate[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2006,54(23):8945−8950. doi: 10.1021/jf0619176
[11] WANG X S, TANG C H, YANG X Q, et al. Characterization, amino acid composition and in vitro digestibility of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) proteins[J]. Food Chemistry,2008,107(1):11−18. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.06.064
[12] WANG Q, JIANG J, XIONG Y L. High pressure homogenization combined with pH shift treatment: A process to produce physically and oxidatively stable hemp milk[J]. Food Research International,2018,106:487−494. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.01.021
[13] MALOMO S A, ALUKO R E. A comparative study of the structural and functional properties of isolated hemp seed (Cannabis sativa L.) albumin and globulin fractions[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2015,43:743−752. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2014.08.001
[14] 何锦风, 陈天鹏, 卢蓉蓉, 等. 汉麻籽的综合利用及产业化研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2010,10(3):98−112. [HE J F, CHEN T P, LU R R, et al. Study on the comprehensive utilization and industrialization of hempseed (Fructus cannabis)[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2010,10(3):98−112. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-7848.2010.03.016 [15] VONAPARTIS E, AUBIN M P, SEGUIN P, et al. Seed composition of ten industrial hemp cultivars approved for production in Canada[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2015,39:8−12. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2014.11.004
[16] CORRADO G, PANNICO A, ZARRELLI A, et al. Macro and trace element mineral composition of six hemp varieties grown as microgreens[J]. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis,2022,114:104750. doi: 10.1016/j.jfca.2022.104750
[17] JIANG Y, ZHOU X, ZHENG Y, et al. Impact of ultrasonication/shear emulsifying/microwave-assisted enzymatic extraction on rheological, structural, and functional properties of Akebia trifoliata (Thunb.) Koidz. seed protein isolates[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,112:106355. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106355
[18] NASROLLAHZADEH F, ROMAN L, SWARAJ V J S, et al. Hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) protein concentrates from wet and dry industrial fractionation: Molecular properties, nutritional composition, and anisotropic structuring[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2022,131:107755. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2022.107755
[19] 张意锋, 邓云, 赵艳云. 双循环高静压对鱿鱼原肌球蛋白二、三级结构的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2018,18(5):45−50. [ZHANG Y F, DENG Y, ZHAO Y Y. Effect of two-cycle high hydrostatic pressure on the secondary and tertiary structures of squid Tropomyosin Tod p1[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2018,18(5):45−50. [20] OGUNWOLU S O, HENSHAW F O, MOCK H P, et al. Functional properties of protein concentrates and isolates produced from cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) nut[J]. Food Chemistry,2009,115(3):852−858. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.01.011
[21] SHEN P, GAO Z, XU M, et al. The impact of hempseed dehulling on chemical composition, structure properties and aromatic profile of hemp protein isolate[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,106:105889. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.105889
[22] MALOMO S A, HE R, ALUKO R E. Structural and functional properties of hemp seed protein products[J]. Journal of Food Science,2014,79(8):C1512−C1521. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.12537
[23] FEVZIOGLU M, OZTURK O K, HAMAKER B R, et al. Quantitative approach to study secondary structure of proteins by FT-IR spectroscopy, using a model wheat gluten system[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,164:2753−2760. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.07.299
[24] 张永金, 胡艳红, 葛武鹏, 等. 母乳、牛乳与主要小品种乳蛋白质组成及乳清蛋白二级结构比较[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(15):4779−4786. [ZHANG Y J, HU Y H, GE W P, et al. Comparative study on the composition of protein and secondary structure of whey protein in human milk, milk and main small varieties of milk[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2022,13(15):4779−4786. [25] DENG Y, HUANG L, ZHANG C, et al. Physicochemical and functional properties of Chinese quince seed protein isolate[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,283:539−548. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.083
[26] YU M, ZENG M, QIN F, et al. Physicochemical and functional properties of protein extracts from Torreya grandis seeds[J]. Food Chemistry,2017,227:453−460. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.01.114
[27] TAN M, XU J, GAO H, et al. Effects of combined high hydrostatic pressure and pH-shifting pretreatment on the structure and emulsifying properties of soy protein isolates[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2021,306:110622. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2021.110622
[28] BAKWO BASSOGOG C B, NYOBE C E, NGUI S P, et al. Effect of heat treatment on the structure, functional properties and composition of Moringa oleifera seed proteins[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,384:132546. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132546
[29] WANG Q, XIONG Y L. Processing, nutrition, and functionality of hempseed protein: A review[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2019,18(4):936−952. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12450
[30] SHEVKANI K, SINGH N, KAUR A, et al. Structural and functional characterization of kidney bean and field pea protein isolates: A comparative study[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2015,43:679−689. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2014.07.024
[31] YIN S W, TANG C H, CAO J S, et al. Effects of limited enzymatic hydrolysis with trypsin on the functional properties of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) protein isolate[J]. Food Chemistry,2007,106(3):1004−1013.
[32] AMAGLIANI L, O'REGAN J, KELLY A L, et al. The composition, extraction, functionality and applications of rice proteins: A review[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2017,64:1−12.
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 何怀叶,孔令辉,裴迅,周望庭,吴慕慈,张瑞,何静仁. 不同制备方法对魔芋飞粉蛋白质结构及功能特性的影响. 食品工业科技. 2025(07): 49-59 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 沈祥皓,陈昌威,付靖雯,杨柳莺,王则程,杨金玉,盘赛昆. 响应面分析法优化女贞子蛋白质提取工艺及功能性研究. 中国调味品. 2024(07): 1-9 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘聪,尹乐斌,邹文广,罗雪韵,杨学为. 响应面法优化辣椒籽蛋白提取工艺及其功能性质研究. 邵阳学院学报(自然科学版). 2023(06): 78-87 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)









 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



