Sulfation Modification and Properties Analysis of Soluble Dietary Fiber from Rosa sterilis Pomace
-
摘要: 以无籽刺梨渣可溶性膳食纤维(Rosa sterilis Soluble Dietary Fiber,RSDF)为原料,取代度为评价指标,对RSDF进行硫酸酯化改性(氨基磺酸-N,N二甲基甲酰胺法),制取硫酸酯化无籽刺梨渣可溶性膳食纤维(Sulfated Soluble Dietary Fiber,SSDF)。探究料液比(g/mL)、氨基磺酸比(g/g)、反应时间(min)以及反应温度(℃)对取代度影响,并进行4因素3水平正交试验,获取最佳酯化工艺,最后采用红外光谱与差示扫描量热对比分析RSDF与SSDF差异。结果表明,硫酸酯化最佳条件为料液比1:80 g/mL、氨基磺酸比1:4 g/g、反应时间195 min和反应温度80 ℃,此条件下SSDF的取代度为1.84±0.19。红外光谱表明经硫酸酯化改性后SSDF在1254 cm−1与893 cm−1处出现了硫酸酯化物的特征峰,表明硫酸酯化成功。差示扫描量热分析表明经改性后SSDF的熔融温度为140 ℃,热稳定性略低于RSDF。Abstract: In this paper, the Rosa sterilis soluble dietary fiber (RSDF) was used as raw material. The degree of substitution was used as the evaluation index, the RSDF was modified by sulfate esterification (Sulfamic acid-N,N-dimethylformamide method) and prepared sulfated soluble dietary fiber (SSDF). The influence of RSDF and N,N-dimethylformamide solid-liquid ratio (g/mL), RSDF and sulfamic acid ratio (g/g), reaction time (min) and reaction temperature (℃) on the degree of substitution were investigated, and three levels of the four single factors were selected for orthogonal test to obtain the best esterification process. Finally, the difference between RSDF and SSDF was analyzed by infrared spectroscopy and differential scanning calorimetry. The results showed that the optimal conditions were solid-liquid ratio of 1:80 g/mL, sulfamic acid ratio of 1:4 g/g, reaction time of 195 min and reaction temperature of 80 ℃. Under these conditions, the substitution degree of SSDF was 1.84±0.19. Infrared spectrum showed that the characteristic peak of SSDF at 1254 cm−1 and 893 cm−1 appeared after the sulfated modification, indicated that the sulfated was successful. Differential scanning calorimetry analysis showed that the melting temperature of SSDF was 140 ℃ and its thermal stability was slightly lower than RSDF.
-
Keywords:
- sulfated /
- soluble dietary fiber /
- Rosa sterilis pomace /
- process optimization
-
无籽刺梨(Rosa sterilis)属贵州特有种系[1],富含黄酮、维生素C、膳食纤维[2-3]等功能性成分,具有广阔的药用和食品资源开发前景[4-5]。但其加工后的果渣被当成废料丢弃或填埋处理,造成资源浪费和环境污染,且无籽刺梨果渣易发霉腐烂等特点使其资源再利用过程中面临诸多问题[6],如何将无籽刺梨渣高值化利用成为了一个重要的研究课题。
膳食纤维分为可溶性膳食纤维(Soluble Dietary Fiber,SDF)和不溶性膳食纤维[7](Insoluble Dietary Fiber,IDF)。采用传统方法[8](热水法、化学法、酶法)提取的SDF活性不强,而化学修饰后可使SDF具备更强的活性与应用价值[9]。硫酸酯化可溶性膳食纤维(Sulfation Soluble Dietary Fiber,SSDF)是结构中的羟基被硫酸基团取代而形成的一类多功能生理活性物质[10],经硫酸化修饰后,原有构象被改变,生物活性功能改变。研究发现经硫酸酯化改性后,增加或强化了抗氧化、抗凝血、抗癌等多种活性,张虽栓等[11]研究表明经过硫酸酯化修饰后能大幅增加硫酸酯化裂褶菌多糖(SSGP)羟自由基清除率,相较于改性前的羟自由基清除率是未改性裂褶菌多糖(SGP)的2.6倍,LIANG等[12]研究表明海藻多糖经硫酸酯化后能增强抗凝血活性,且在脱硫酸基团后抗凝血活性消失,CHEN等[13]研究表明南瓜多糖硫酸基团引入后能提高对超氧阴离子的清除力。硫酸酯化常用的氯磺酸-吡啶法[13]和浓硫酸法[14]酯化过程反应剧烈,需要在冰浴条件下进行[10],且试剂危险性高。氨基磺酸-N,N二甲基甲酰胺法是以氨基磺酸为酯化剂,N,N二甲基甲酰胺为溶剂进行硫酸酯化的方法。沈洁等[15]研究氨基磺酸-N,N二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)法硫酸酯化灵芝多糖,结果表明其酯化物色泽较浅且反应过程更温和,且N,N二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)对酯化剂与酯化物有较好溶解性。
目前尚未见无籽刺梨渣可溶性膳食纤维的硫酸酯化研究,且氨基磺酸-N,N二甲基甲酰胺法为不常用的硫酸酯化方法,对于无籽刺梨渣可溶性膳食纤维的硫酸酯化效果未知。因此本文以氨基磺酸为酯化剂,N,N二甲基甲酰胺为溶剂,取代度为指标,采用氨基磺酸-N,N二甲基甲酰胺法硫酸酯化无籽刺梨可溶性膳食纤维,通过单因素与正交试验获取最佳酯化方法,分析无籽刺梨渣可溶性膳食纤维(Rosa sterilis Pomace Soluble Dietary Fiber,RSDF)和SSDF红外光谱与热稳定性,以期为无籽刺梨渣再加工利用与RSDF的硫酸酯化提供理论参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
无籽刺梨 产自昆明阿子营;氨基磺酸、N,N二甲基甲酰胺、氢氧化钠、三氯乙酸、氯化钡、硫酸钾 广东光华科技股份有限公司,以上试剂均为分析纯;耐高温α-淀粉酶(CAS 9001-19-8,4000 U/g)、碱性蛋白酶(CAS9014-01-1,200 U/mg)、纤维素酶(CAS9012-54-8,35 U/mg) 南京都莱生物技术有限公司;95%乙醇、石油醚(60~90 ℃) 天津市致远化学试剂有限公司。
SB25-12DTDS超声波清洗器 宁波新艺超声设备有限公司;IKA-RV10立式旋转蒸发仪 南京荣华科学器材有限公司;UV-2600紫外可见分光光度计 岛津仪器有限公司;DSC-204F1差示扫描量热仪 德国耐驰仪器制造有限公司;IR Prestige-21型傅立叶变换红外光谱仪 岛津仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品处理
无籽刺梨渣50 ℃烘干至含水量3%后,除杂,粉碎,过60目筛,取筛下物按料液比1:15 g/mL加入石油醚,室温下400 r/min搅拌4 h脱脂,抽滤,取残渣。将残渣重复上述步骤2次,50 ℃烘干得脱脂无籽刺梨粉,4 ℃密封保存备用。
1.2.2 无籽刺梨渣可溶性膳食纤维制备
参考李晗等[2]方法制备无籽刺梨渣可溶性膳食纤维(Rosa sterilis Soluble Dietary Fiber,RSDF),略有修改。称取一定量脱脂无籽刺梨粉,1:25 g/mL料液比加入蒸馏水,2 mol/L NaOH调pH至9.0,加入6%碱性蛋白酶(酶添加量按脱脂无籽刺梨渣粉质量计,下同)。55 ℃水浴30 min后以1 mol/L盐酸调pH至4.8,加入8%高温α-淀粉酶,90 ℃水浴45 min后沸水浴10 min灭酶,冷却至室温,加入9%纤维素酶,超声(250 W,50 ℃,45 min),沸水浴灭酶10 min,冷却至室温后,离心(5500 r/min,10 min)取上清液。70 ℃蒸馏水清洗沉淀至中性,重复上述步骤,合并沉淀洗涤液与上清液,真空浓缩至原体积1/3,醇沉1 h(预热至60 ℃,4倍体积的95%乙醇),离心(5500 r/min,5 min),收集沉淀,50 ℃干燥,4 ℃密封保存备用。
1.2.3 无籽刺梨渣可溶性膳食纤维的硫酸酯化
参照文献[15-17]制备SSDF,略有修改。称取1 g RSDF与N,N二甲基甲酰胺按一定料液比混合后置入水浴锅,达到反应温度后加入适量氨基磺酸,200 r/min水浴搅拌反应一段时间。反应结束后迅速放入冰水浴中,以3 mol/L NaOH调节反应液pH至7.0,4倍体积95%乙醇醇沉12 h,无水乙醇清洗2遍沉淀后5500 r/min离心10 min,收集沉淀。去离子水复溶后蒸馏水透析(8000~14000 Da)3 d,每8 h换1次水,夜间12 h换1次水。收集透析袋内液体,浓缩至原体积1/3,4倍体积95%乙醇醇沉12 h,离心(5500 r/min,5 min)收集沉淀,50 ℃烘干即得SSDF,4 ℃密封保存备用。
1.2.4 单因素实验
1.2.4.1 料液比对取代度的影响
固定氨基磺酸比1:3 g/g、反应温度65 ℃、反应时间60 min,研究RSDF与N,N二甲基甲酰胺料液比(1:60、1:70、1:80、1:90、1:100 g/mL)对SSDF取代度影响。
1.2.4.2 氨基磺酸比对取代度的影响
固定料液比1:70 g/mL、反应温度65 ℃、反应时间60 min,研究RSDF与氨基磺酸比(1:1、1:2、1:3、1:4、1:5 g/g)对SSDF取代度影响。
1.2.4.3 反应时间对取代度的影响
固定料液比1:70 g/mL、氨基磺酸比1:3 g/g、反应温度65 ℃,研究反应时间(15、60、105、150、195 min)对SSDF取代度影响。
1.2.4.4 反应温度对取代度的影响
固定料液比1:70 g/mL、氨基磺酸比1:3 g/g、反应时间60 min,研究反应温度(35、50、65、80、95 ℃)对SSDF取代影响。
1.2.5 正交试验
选取料液比、氨基磺酸比、反应温度、反应时间作为正交试验因素,以SSDF取代度为参考指标,采用正交试验进行工艺优化,正交试验因素水平见表1。
表 1 正交因素水平设计Table 1. Level of orthogonal factors水平 A料液比
(g/mL)B氨基磺酸比
(g/g)C反应温度
(℃)D反应时间
(min)1 1:60 1:2 65 105 2 1:70 1:3 80 150 3 1:80 1:4 95 195 1.2.6 取代度测定
1.2.6.1 标准曲线绘制
参照文献[18]绘制标准曲线。吸取1 mg/mL K2SO4标准溶液(溶剂为1 mol/mL HCl)0.02、0.04、0.08、0.12、0.16、0.20 mL,加入1 mol/L HCl使其总体积达0.20 mL,加入3.8 mL 3%三氯乙酸(w/v)及1 mL 0.5%氯化钡-明胶溶液(w/v),混合均匀后室温下反应20 min,360 nm波长下测吸光度值A1,以1 mL 0.5%明胶溶液(w/v)代替氯化钡-明胶溶液重复上述操作,测吸光度A2,以硫酸根毫克数为横坐标,(A1-A2)为纵坐标绘制硫酸根标准曲线,得y=0.9353x−0.0271,R2=0.9957。
1.2.6.2 样品测定
采用氯化钡-明胶比浊法[19-20]测定取代度。称取100 mg SSDF置于25 mL具塞刻度管中,加入10 mL 1 mol/L HCl,沸水浴水解4 h,1 mol/L HCl补至10 mL,冷却至室温并收集水解液。准确吸取0.2 mL水解液,后续步骤参照1.2.6.1进行,按式(1)和(2)计算取代度。
S(% )=CVW (1) DS=1.62×S32−1.62×S (2) 式中:S为样品中含硫占比,%;C为测试样品浓度g/mL;V为测试样品体积,mL;W为称量样品质量,g;DS为样品取代度。
1.2.7 傅里叶红外光谱(Fourier Transform Infrared,FTIR)分析
采用溴化钾压片法[21],取少量样品与溴化钾粉末混匀并充分研磨。于压片机内压成薄片后取出,放入红外光谱仪中扫描,扫描范围500~4000 cm−1。
1.2.8 差示扫描热(Differential Scanning Calorimetry,DSC)分析
称取5~10 mg样品于铝制坩埚中,以空坩埚为空白对照,扫描温度范围35~250 ℃,升温速度10 ℃/min,氮气流速20 mL/min。
1.3 数据处理
每组试验重复3次,结果以(平均值±标准差)表示。采用软件SPSS 20.0对单因素进行Tukey显著性检验,软件Origin 2018作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验
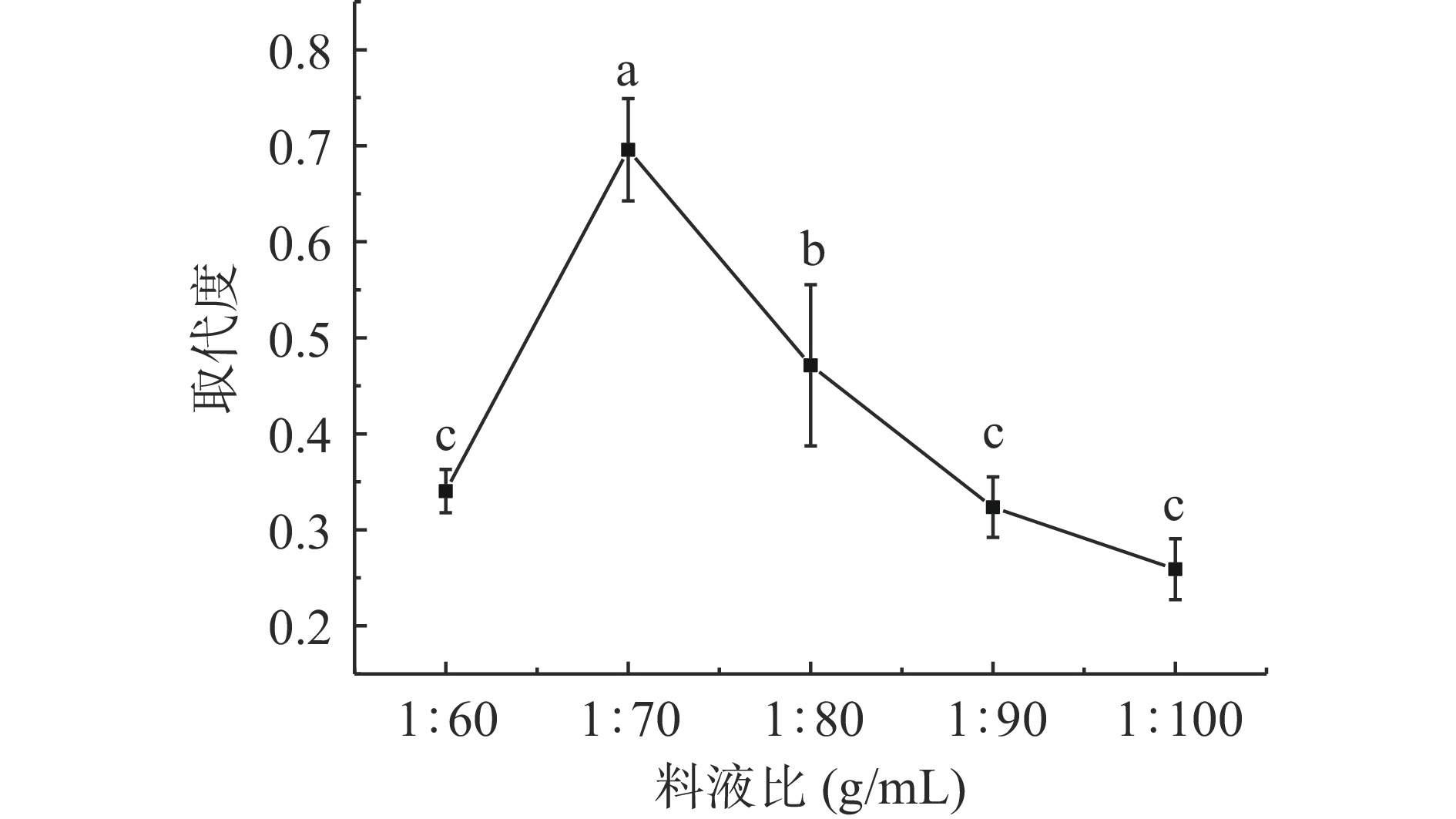
2.1.1 料液比对SSDF取代度影响
N,N二甲基甲酰胺是一种优良的有机溶剂,对无机化合物与有机化合物都有良好溶解性,与其它硫酸酯化方法中溶剂相比较,N,N二甲基甲酰胺对氨基磺酸展现出较好的亲核力[22]。图1为料液比对SSDF取代度的影响。图1可知,取代度随料液比的增加呈先增大后下降趋势,RSDF与N,N二甲基甲酰胺料液比为1:70 g/mL时达最大取代度0.69±0.05,相较于1:60 g/mL取代度0.34±0.02提升了102.9%。料液比超过1:70 g/mL后取代度显著下降(P<0.05),这与沈洁等[15]的研究结果相似,适宜的料液比能促进硫酸酯化反应的进行,料液比的大小会影响反应底物的浓度与溶解度,当料液比小于1:70 g/mL时多糖与氨基磺酸都不能较好的溶于DMF中,两者在体系中分散不均匀且反应物之间接触不充分导致取代度降低。当料液比由1:70 g/mL增至1:100 g/mL时,取代度逐渐降低,这是因为高过最适料液比时,加入RSDF与氨基磺酸量为定值造成了底物/溶剂整体数值降低,虽然在此过程中RSDF与氨基磺酸溶解度增大但反应物之间相互接触概率降低进而导致SSDF取代度下降。
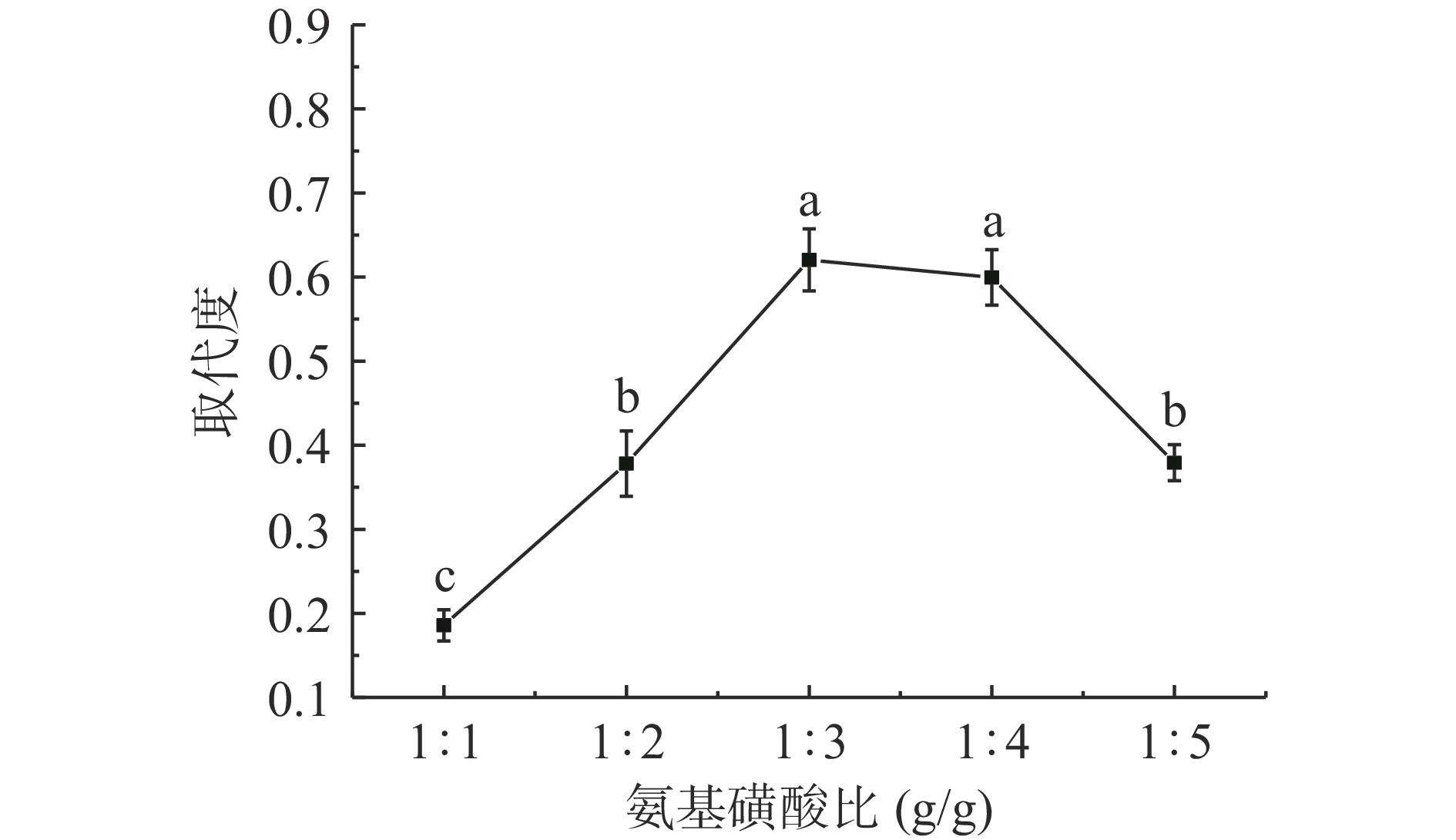
2.1.2 氨基磺酸比对SSDF取代度影响
氨基磺酸又称“固体硫酸”,具有高电离度,酸性强的特点,溶解后酸性与硫酸、盐酸、硝酸相似,在硫酸酯化反应中与氯磺酸、三氧化硫和浓硫酸三种酯化剂相比更温和且硫酸酯化物色泽更浅,但氨基磺酸反应活性低,需要在高温条件下才能完全反应。图2为不同氨基磺酸比对SSDF取代度的影响。由图2可知,SSDF取代度随氨基磺酸比的增加呈先增加后下降趋势,与刘昱均[22]的研究结果相似,氨基磺酸比为1:1~1:3 g/g时,取代度逐渐增大(P<0.05),在1:3 g/g时取代度达到最大值0.62±0.04。推测此现象产生的原因是氨基磺酸比较低时,反应体系中氨基磺酸浓度小,提供的磺化基团-SO3H不足,与RSDF糖苷键结合少,酯化反应未能完全进行,进而取代度较低。氨基磺酸比超过1:3 g/g,SSDF取代度逐渐下降,当氨基磺酸比为1:5 g/g时取代度为0.38±0.02,较氨基磺酸比1:3 g/g时显著下降38.7%(P<0.05),推测此现象产生是因为氨基磺酸增加,反应体系酸度随之提高,造成反应物部分降解与不完全硫酸酯化,王文侠等[23]研究也表明除了上述因素以外,体系酸度过高造成的反应物板结也会影响取代度。
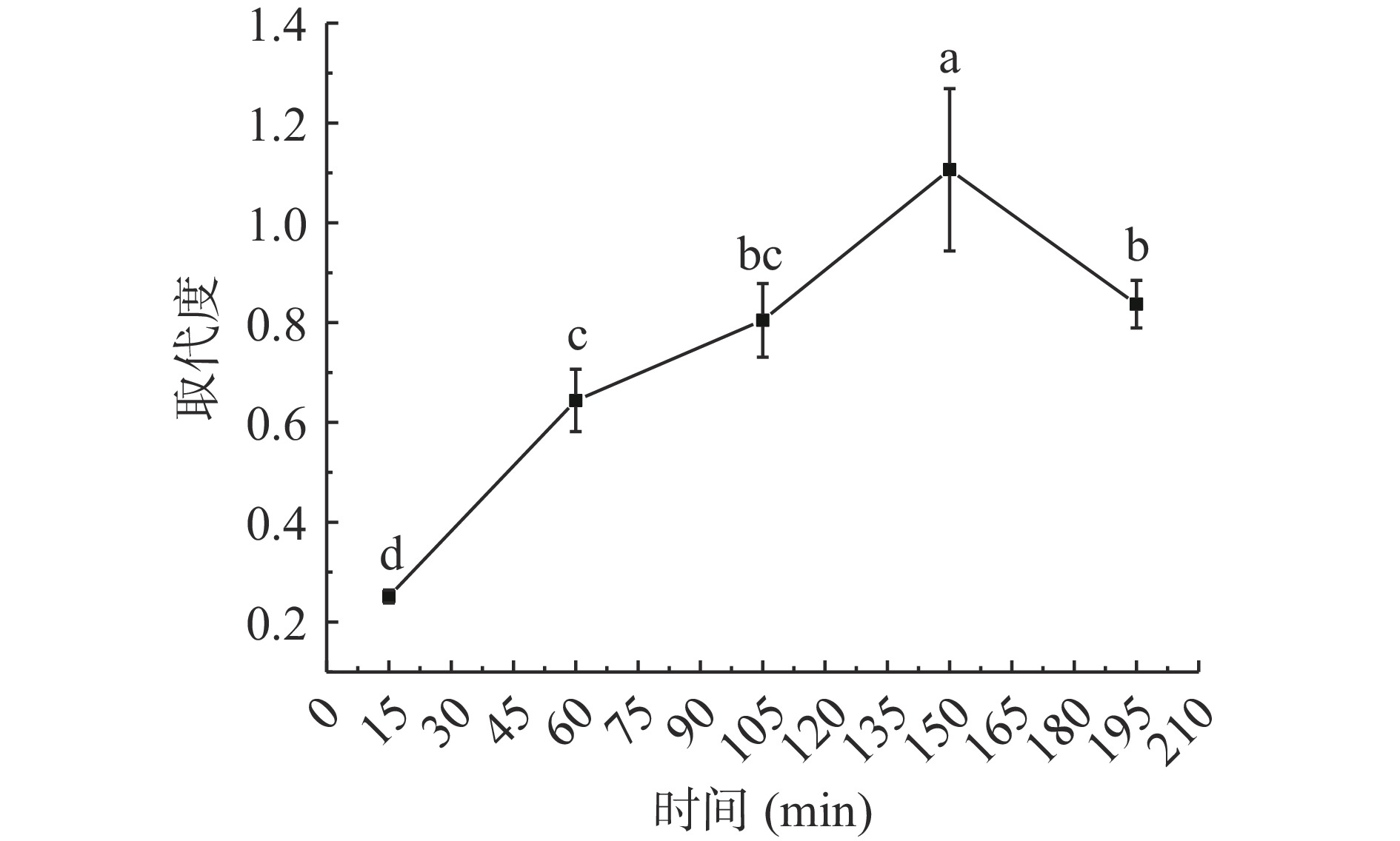
2.1.3 反应时间对SSDF取代度影响
图3为不同反应时间对取代度影响。图3可知,反应时间15~150 min取代度呈现上升趋势,且15~60 min取代度随时间增长由0.25±0.01增至0.64±0.06,可能是反应时间小于15 min时,氨基磺酸与RSDF接触时间不足,酯化反应进行不充分导致。反应时间超过15 min时酯化反应加快SSDF取代度显著增加(P<0.05),150 min时达到最大值1.11±0.16,再次说明了适当的反应时长将促进酯化反应的进行,氨基磺酸与RSDF硫酸酯化的最佳时间为150 min。与150 min相比,195 min时取代度为0.84±0.05,显著降低了24.32%(P<0.05),因为随着反应时间延长,氨基磺酸在DMF中逐渐溶解,增加了溶液酸性,过酸条件下酯化时间过长会导致RSDF部分降解以及多糖酯键与糖苷键断裂[24],最终取代度下降。
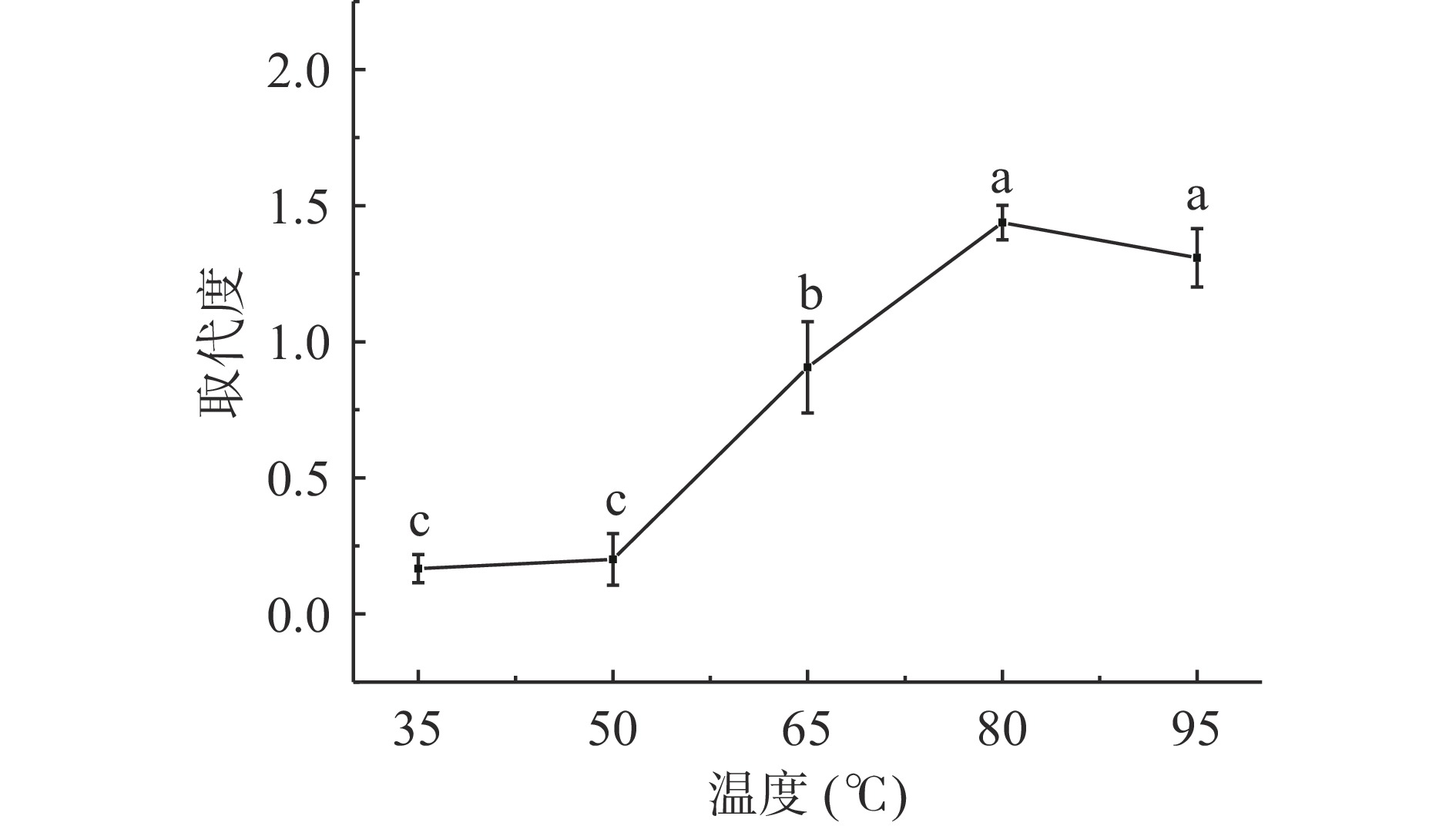
2.1.4 反应温度对SSDF取代度影响
图4可知,取代度随反应温度的增加呈现出先增后减趋势。反应温度35~80 ℃,取代度逐渐增加,但35~50 ℃区间增加不显著(P>0.05),因为温度造成的热效应影响了分子运动,高温时分子运动加快,分子间碰撞概率增加,低温时分子运动速度缓慢,碰撞概率下降,较低温度下导致酯化不完全;反应温度50~80 ℃时,取代度显著增加(P<0.05);当温度到达80 ℃时存在最大取代度1.43±0.06,侧面反映出酯化反应的进行需要适当温度来加快分子运动,增加反应几率。反应温度为95 ℃时,取代度为1.3±0.11,较80 ℃最大取代度小幅下降(P>0.05),这是因为高温提高了降解速率,反应温度过高易导致膳食纤维在酸度体系中降解。
不同反应条件下的取代度不同,温度与时间影响对取代度影响最大,硫酸酯化过程中,降解和硫酸酯化是一组相互竞争的反应[25]。从图3和图4反映出取代度达到最大值后,随着反应时间的延长和反应温度的升高,取代度下降。这可能是因为高硫酸盐的糖残基在反应中降解,如果需要高取代度的产物,关键反应条件的控制是一个主要方面。
2.2 正交试验
在单因素实验基础上,将料液比、氨基磺酸比、反应时间、反应温度作为正交试验因素,以取代度为指标,利用4因素3水平正交试验设计进行分析,分析结果见表2。正交表可知,影响硫酸酯化的因素依次为:C>D>A>B,即反应温度>反应时间>料液比>氨基磺酸比,该结果与单因素试验结果相符。根据K值知,SSDF最佳酯化条件为A3B3C2D3,对应料液比1:80 g/mL、氨基磺酸比1:4 g/g、反应温度80 ℃和反应时间195 min。根据此条件进行验证试验,取代度为1.84±0.19。
表 2 正交试验设计及结果Table 2. Design and results of orthogonal experiment试验号 A B C D 取代度 1 1 1 1 1 0.55±0.07 2 1 2 2 2 1.80±0.10 3 1 3 3 3 1.44±0.05 4 2 1 2 3 1.72±0.51 5 2 2 3 1 0.59±0.21 6 2 3 1 2 0.92±0.02 7 3 1 3 2 1.58±0.46 8 3 2 1 3 1.23±0.31 9 3 3 2 1 1.75±0.40 K1 3.79 3.85 2.7 2.89 K2 3.23 3.62 5.27 4.30 K3 4.56 4.11 3.61 4.39 k1 1.26 1.28 0.90 0.96 k2 1.08 1.21 1.76 1.43 k3 1.52 1.37 1.20 1.46 R 1.33 0.49 2.57 1.50 C>D>A>B A3B3C2D3 2.3 红外光谱分析
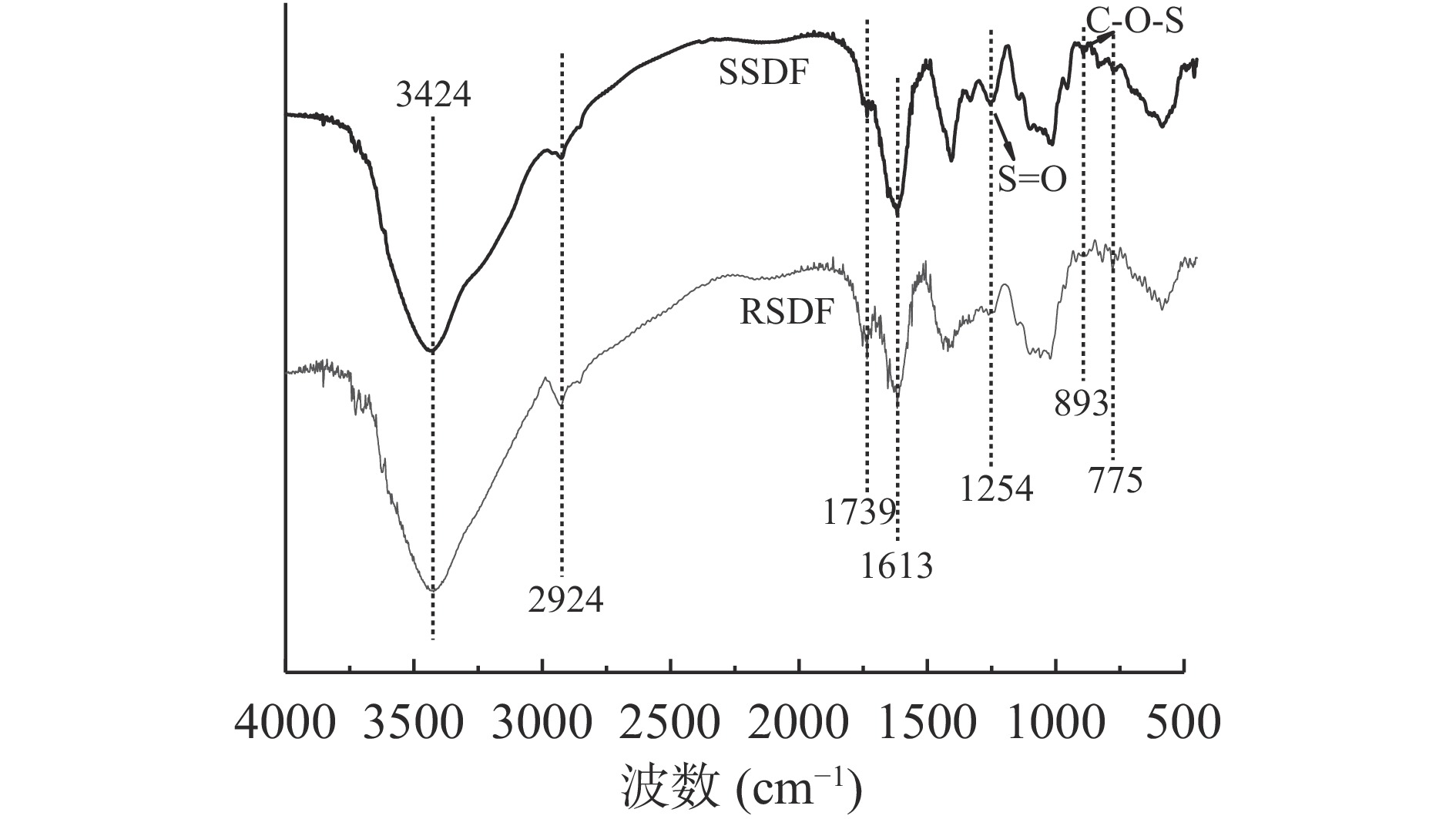
红外光谱图中吸收峰的变化可反映出物质化学键的组成及变化[26]。RSDF与SSDF的红外光谱如图5所示,3424 cm−1存在一处强而宽的吸收峰,该吸收峰归因于RSDF与SSDF分子中O-H伸缩振动,该峰以宽型型式出现是由于分子内或者分子间的氢键缔合作用导致,由峰值强度可知RSDF与SSDF中存在大量的羟基基团,能够加强各自分子间的作用力。与RSDF相比,SSDF的宽型吸收峰出现小幅度收缩,表明氢键的减少[27-28]。2924 cm−1处的峰是因为C-H对称和非对称伸缩振动引起的吸收峰,属于多糖类物质的特征峰,表明了可溶性膳食纤维属于多糖中的一种。1739 cm−1处的吸收峰是由C=O伸缩振动引起,该基团主要来源于葡萄糖糠醛[29]。1613 cm−1处窄而强的吸收峰出现对应了O-H的弯曲振动。SSDF在1254 cm−1出现一处尖锐的吸收峰归因于不对称的硫酸基团S=O伸缩振动,893 cm−1处出现的弱吸收峰对应C-O-S键的伸缩振动特征吸收峰,因此硫酸酯化是成功的。775 cm−1处RSDF出现相对弱峰值是由吡喃糖对称环伸缩振动所致,反映了RSDF的吡喃型糖环[27]。
2.4 热稳定性分析
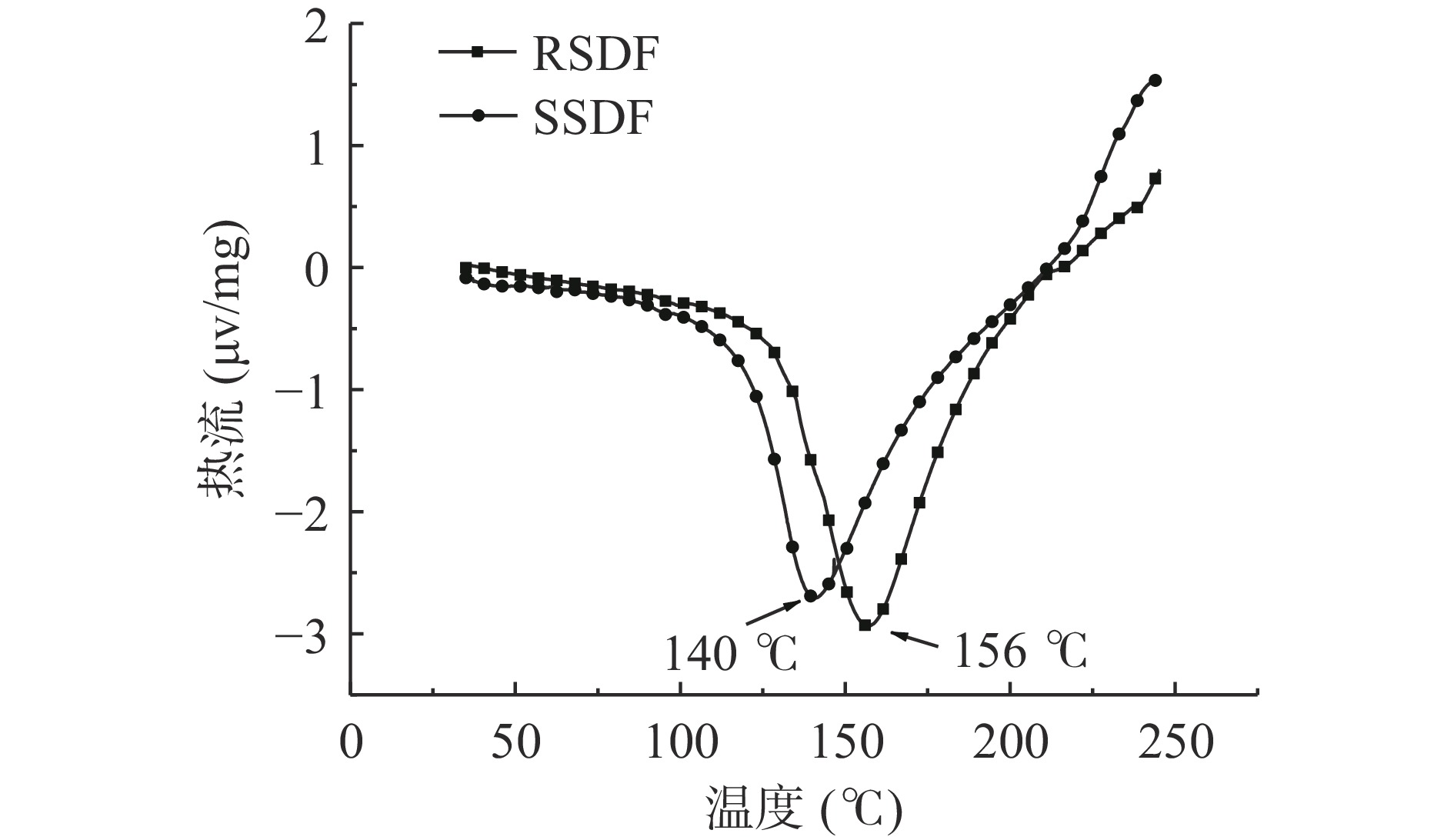
差示扫描量热仪可研究物质的热稳定性,获取物质转变构象过程中热力学信息,膳食纤维在后续加工应用范围广,热稳定性是其中的影响因素之一[30]。RSDF 与 SSDF 的 DSC 曲线如图6所示。RSDF 与SSDF 在 35~250 ℃ 范围内,波峰随温度的上升展现出凹陷的吸热峰,表明二者升温后熔融吸热,产生吸热峰。RSDF 的吸热峰值为 156 ℃,SSDF 的吸热峰值出现在 140 ℃,硫酸酯化后 SSDF 的热稳定性下降了 16 ℃,推测是硫酸酯化后 SSDF 中引入了新的基团,且在酸性环境下改性结构变得更为疏松导致了 SSDF 内部孔隙增大所以热稳定性低于 RSDF。而 SSDF 的吸热峰弱于 RSDF,是因为改性过程中加热与化学物质共同作用下,结合水的部分损失造成。
3. 结论
采用氨基磺酸为酯化剂,N,N二甲基甲酰胺(DMF)为溶剂硫酸酯化RSDF。得最佳酯化条件:料液比1:80 g/mL、氨基磺酸比1:4 g/g、反应时间195 min和反应温度80 ℃,此条件下验证了SSDF取代度为1.84±0.19。傅里叶红外光谱表明SSDF的氢键含量减少,且1254 cm−1处与893 cm−1处出现新特征峰,分别对应硫酸基团S=O伸缩振动吸收峰与C-O-S键的伸缩振动特征吸收峰,这两个峰的出现表明硫酸酯化成功。差示扫描量热分析表明,SSDF熔融温度为140 ℃,热稳定性低于RSDF。试验说明了氨基磺酸-N,N二甲基甲酰胺法为一种可行的硫酸酯化膳食纤维方法,该方法简单有效具备低毒的特点能够更好的适用于制备硫酸酯化无籽刺梨渣可溶性膳食纤维。
-
表 1 正交因素水平设计
Table 1 Level of orthogonal factors
水平 A料液比
(g/mL)B氨基磺酸比
(g/g)C反应温度
(℃)D反应时间
(min)1 1:60 1:2 65 105 2 1:70 1:3 80 150 3 1:80 1:4 95 195 表 2 正交试验设计及结果
Table 2 Design and results of orthogonal experiment
试验号 A B C D 取代度 1 1 1 1 1 0.55±0.07 2 1 2 2 2 1.80±0.10 3 1 3 3 3 1.44±0.05 4 2 1 2 3 1.72±0.51 5 2 2 3 1 0.59±0.21 6 2 3 1 2 0.92±0.02 7 3 1 3 2 1.58±0.46 8 3 2 1 3 1.23±0.31 9 3 3 2 1 1.75±0.40 K1 3.79 3.85 2.7 2.89 K2 3.23 3.62 5.27 4.30 K3 4.56 4.11 3.61 4.39 k1 1.26 1.28 0.90 0.96 k2 1.08 1.21 1.76 1.43 k3 1.52 1.37 1.20 1.46 R 1.33 0.49 2.57 1.50 C>D>A>B A3B3C2D3 -
[1] 郑元, 吴月圆, 辛培尧, 等. 环境因子对无籽刺梨光合生理日变化进程的影响研究[J]. 西部林业科学,2013,42(3):21−27. [ZHENG Y, WU Y Y, XIN P Y, et al. Relationship between photosynthetic physiology diurnal dynamics of Rosa sterilis and environmental factors[J]. Journal of West China Forestry Science,2013,42(3):21−27. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8246.2013.03.005 [2] 李晗, 范方宇, 戚建华, 等. 超声辅助酶法提取无籽刺梨渣膳食纤维及理化性质评价[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(4):194−201. [LI H, FAN F Y, QI J H, et al. Ultrasonic assisted enzymatic extraction of dietary fiber from Rosa sterilis pomace and its physicochemical properties[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(4):194−201. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2021.04.030 [3] YANG Q Q, ZHANG D, FARHA A K, et al. Phytochemicals, essential oils, and bioactivities of an underutilized wild fruit Cili (Rosa roxburghii)[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2020,143:111928. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2019.111928
[4] YANG H, HU J W, HUANG X F, et al. Risk assessment of heavy metals pollution for Rosa sterilis and soil from planting bases located in karst areas of Guizhou Province[J]. Applied Mechanics and Materials,2014,700:475−481. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.700.475
[5] ZHU J Z, ZHANG B, WANG B X, et al. In-vitro inhibitory effects of flavonoids in Rosa roxburghii and R. sterilis fruits on α-glucosidase: Effect of stomach digestion on flavonoids alone and in combination with acarbose[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2019,54:13−21. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2019.01.009
[6] 刘晓燕, 谢丹, 马立志, 等. 刺梨果渣发酵前后活性成分及抗氧化能力的比较研究[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(2):16−24. [LIU X Y, XIE D, MA L Z, et al. Comparative study on active components and antioxidant capacity of Rosa roxburghii Tratt. fruit residue before and after fermentation[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(2):16−24. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2021.02.003 [7] ALBA K, MAC N W, LAWS A P, et al. Fractionation and characterization of dietary fibre from blackcurrant pomace[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,81:398−408. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2018.03.023
[8] WANG Z J, XIE JIAN H, SHEN M Y, et al. Sulfated modification of polysaccharides: Synthesis, characterization and bioactivities[J]. Trends in Food Science & Technology,2018,74:147−157.
[9] XU Y Q, GAO Y K, LIU F, et al. Sulfated modification of the polysaccharides from blackcurrant and their antioxidant and α-amylase inhibitory activities[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,109:1344−1354. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.11.164
[10] 杨波, 杨光, 陈远娇, 等. 纳豆多糖的硫酸化改性工艺[J]. 上海理工大学学报,2020,42(5):497−503. [YANG B, YANG G, CHEN Y J, et al. Sulfuration modification of natto polysaccharides[J]. University of Shanghai for Science and Technology,2020,42(5):497−503. doi: 10.13255/j.cnki.jusst.20191112001 [11] 张虽栓, 蔡花真. 硫酸酯化裂褶菌多糖的制备及其抗氧化活性研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2017,38(8):17−21. [ZHANG S S, CAI H Z. Preparation and antioxidative activities of the sulfated Schizophyllan polysaccharide[J]. Food Research and Development,2017,38(8):17−21. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2017.08.004 [12] LIANG W A, MAO X, PENG X H, et al. Effects of sulfate group in red seaweed polysaccharides on anticoagulant activity and cytotoxicity[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2014,101:776−785. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.10.010
[13] CHEN L, HUNG G. Antioxidant activities of sulfated pumpkin polysaccharides[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,126:743−746. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.261
[14] 巩晓佩. 硫酸化修饰红枣多糖的结构表征及生物活性的研究[D]. 石河子: 石河子大学, 2021 GONG X P. Study on the structure characterization and biological activity of sulfated modified Jujube polysaccharide[D]. Shihezi: Shihezi University, 2021.
[15] 沈洁, 刘昱均, 张珏. 发酵灵芝胞外多糖硫酸化修饰[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2015,34(6):666−671. [SHEN J, LIU Y J, ZHANG J. Sulfated modification of extracellular polysaccharide from submerged fermentation of Ganoderma lucidum[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2015,34(6):666−671. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2015.06.023 [16] 侯令. 硫酸酯化苹果渣水溶性多糖结构表征和生物活性研究[D]. 西安: 陕西科技大学, 2017 HOU L. Primary structural characterization and biological activity study of sulfated apple pomace polysaccharides[D]. Xi'an: Shaanxi University of Science and Technology, 2017.
[17] 周本宏, 谭珺, 张婵, 等. 硫酸酯化天麻多糖的制备及其抗氧化活性[J]. 中国医院药学杂志,2017,37(17):1685−1691. [ZHOU B H, TAN J, ZHANG C, et al. Preparation of sulfated polysaccharides from Gastrodia elata Blume and its antioxidant activity[J]. Chinese Hospital Pharmacy Journal,2017,37(17):1685−1691. doi: 10.13286/j.cnki.chinhosppharmacyj.2017.17.07 [18] CHEN Y, ZHANG H, WANG Y, et al. Sulfated modification of the polysaccharides from Ganoderma atrum and their antioxidant and immunomodulating activities[J]. Food Chemistry,2015,186:231−238. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.10.032
[19] HE L, YAN X T, LIANG J, et al. Comparison of different extraction methods for polysaccharides from Dendrobium officinale stem[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,198:101−108. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.06.073
[20] WANG J, BAO A, MENG X, et al. An efficient approach to prepare sulfated polysaccharide and evaluation of anti-tumor activities in vitro[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,184:366−375. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.12.065
[21] 朱玉婷, 谭姚, 莫开菊. 硫酸酯化修饰葛仙米多糖工艺研究[J]. 食品科学,2011,32(24):46−49. [ZHU Y T, TAN Y, MO K J. Sulfation modification of polysaccharide extracted from Nostoc sphaeroides Kützing[J]. Food Science,2011,32(24):46−49. [22] 刘昱均. 发酵灵芝多糖的硫酸酯化及其生物活性的研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2013 LIU Y J. Studies of fermented Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides modified by sulfuric acid and their biological activity[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2013.
[23] 王文侠, 王龙艳, 宋春丽, 等. 豆渣多糖硫酸酯化工艺条件优化及其抗氧化活性[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2013,39(1):103−107. [WANG W X, WANG L Y, SONG C L et al. Optimization on sulfuric acid esterification process conditions of bean dregs polysaccharide and antioxidant activity[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2013,39(1):103−107. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.2013.01.023 [24] SI X, ZHOU Z K, BU D D, et al. Effect of sulfation on the antioxidant properties and in vitro cell proliferation characteristics of polysaccharides isolated from corn bran[J]. Cyta-Journal of Food,2016,14(4):555−564. doi: 10.1080/19476337.2016.1176074
[25] YANG J H, DU Y M, WEN Y, et al. Sulfation of Chinese lacquer polysaccharides in different solvents[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2003,52(4):397−403. doi: 10.1016/S0144-8617(02)00330-2
[26] 吴海波, 于静雯, 吴长玲, 等. 空化微射流对豆渣膳食纤维结构及功能特性影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(1):94−99. [WU H B, YU J W, WU C L et al. Cavitation microjet effects on structural and functional properties of okara dietary fiber[J]. Food Science,2020,41(1):94−99. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181119-215 [27] 陈放. 苦瓜多糖及其衍生物的制备和抗氧化活性研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆师范大学, 2020 CHENG F. Study on preparation and antioxidant activity of Momordica charantia polysaccharide and its derivatives[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Normal University, 2020.
[28] 黄诗雨. 米糠多糖及衍生物的制备与抗氧化活性研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆师范大学, 2021 HUANG S Y. Preparation and antioxidant activity of rice bran polysaccharide and its derivatives[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing Normal University, 2021.
[29] ZHANG C, CHEN H M, BAI W Q. Characterization of Momordica charantia L. polysaccharide and its protective effect on pancreatic cells injury in STZ-induced diabetic mice[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,115:45−52. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.04.039
[30] 王中华, 蔡同强, 杨丛远, 等. 鸡血藤多糖的硫酸化修饰、表征及活性研究[J]. 广西大学学报(自然科学版),2018,43(5):2041−2046. [WANG Z H, CAI T Q, YANG C Y et al. Sulfated modification, characterization and activities of polysaccharides from Millettia dielsiana[J]. Journal of Guangxi University (Natural Science Edition),2018,43(5):2041−2046. -
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 张敏杰,杨武德,代叶,李玮,魏晴,梁珊珊. 黔产不同商品规格金钗石斛质量评价研究. 亚太传统医药. 2024(04): 39-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 林鑫静,张明,李鑫,周春阳,蒲跃,袁斌,范艺缤,范润勇,夏天琴,尤俊,杨晓曦,胥正敏. 调脏舒秘合剂小鼠急性毒性实验研究. 现代中医药. 2023(02): 91-95 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 杨吉容,石京山. 金钗石斛破壁粉对自发性高血压大鼠血压及心功能的影响. 遵义医科大学学报. 2022(06): 699-705 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)





 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:
