Formation of Volatile Flavor Compounds and Changes in Fat Oxidation in Blunt-snout Bream by Traditional Sun-drying and Shade-drying
-
摘要: 为探究传统干腌鱼的挥发性风味物质,本研究以新鲜武昌鱼为原料,采用日晒、阴干两种传统干制方式对腌制武昌鱼进行加工,并通过测定过氧化值、酸价、茴香胺值、共轭二稀与共轭三稀、羰基价、脂肪酸含量,结合挥发性化合物测定、电子鼻及感官评价来探究传统干腌武昌鱼特征风味物质的形成和风味差异。结果显示:日晒干制的武昌鱼,其过氧化值、酸价、茴香胺值、多烯指数、羰基价均高于阴干和未干制组。日晒武昌鱼的不饱和脂肪酸相对含量要低于阴干和未干制的武昌鱼,尤其是油酸(C18:1n9)、亚油酸(C18:2n9)、亚麻酸(C18:3n3)。日晒对武昌鱼整体气味和挥发性风味物质影响较大。日晒武昌鱼挥发性物质有28种,阴干武昌鱼有23种,未干制组为20种。日晒干制武昌鱼具有更强的哈喇味和肉香味,阴干武昌鱼有更显著的鱼腥味和哈喇味。相关性结果表明:武昌鱼的香气物质与脂肪氧化呈显著正相关,与典型的单不饱和脂肪酸和多不饱和脂肪酸呈负相关。脂肪氧化是干腌鱼香气形成的重要途径,日晒促进了脂肪氧化、干腌武昌鱼风味的形成和香气积累。
-
关键词:
- 干腌武昌鱼 /
- 日晒 /
- 挥发性风味物质 /
- 香气活性值(OAV) /
- 脂肪氧化
Abstract: In this experiment, blunt-snout bream was used as raw material, and the pickled blunt-snout bream was processed by two traditional drying methods, sun-drying and shade-drying, and by measuring peroxide value, acid value, anisidine value, polydilute index, carbonyl value, fatty acid content combined with the determination of volatile compounds, electronic nose and sensory evaluation to explore the characteristic flavor compounds of dried fish in different traditional drying methods and overall flavor differences. The results showed that the oxidation value, acid value, anisidine value, polydilute index and carbonyl value of blunt-snout bream dried in sunlight were higher than those in the shade-drying and undried groups. The relative content of unsaturated fatty acids in sun-dried blunt-snout bream was lower than that of shade-dried and undried blunt-snout bream, especially oleic acid (C18:1n9), linoleic acid (C18:2n9), and linolenic acid (C18:3n3) were significantly lower. Different drying methods had a greater impact on the overall odor and volatile flavor compounds of blunt-snout bream. The main types of volatile substances produced by the two drying methods were 28 and 23, respectively, and 20 in the wet group. Most of the characteristic flavor substances in sun dried fish were aldehydes and alcohols. Sun-dried blunt-snout bream had stronger halal flavor and meat flavor, shade-dried blunt-snout bream has more pronounced fishy smell and rancidity, and undried blunt-snout bream had a strong fishy smell and fragrance. The correlation results showed that the aroma compounds of blunt-snout bream were positively correlated with fat oxidation, and significantly negatively correlated with typical monounsaturated fat plugs and polyunsaturated fatty acids. Fat oxidation was an important pathway for the formation of aroma in blunt-snout bream, and sunlight promoted fat oxidation, the formation of flavor and aroma accumulation in blunt-snout bream.-
Keywords:
- blunt-snout bream /
- sunlight /
- volatile flavor compounds /
- odor activity value(OAV) /
- fat oxidation
-
武昌鱼(Megalobrama amblycephala),学名团头鲂,俗称鳊鱼等。武昌鱼作为我国所特有的优良淡水鱼类,是易伯鲁教授在1955年确定的新物种。一代伟人毛主席在畅游长江后,留下了“才饮长沙水,又食武昌鱼”这样的佳句,让武昌鱼闻名海内外[1]。干腌鱼制品咸香适宜、风味独特,是我国传统的水产加工食品之一。我国各个地区都有食用干腌鱼制品的饮食习惯。不同地区的制作工艺不同,形成了各具地方特色的干腌鱼产品[2],武昌鱼常用来制作干腌鱼类产品。日晒是传统常见的干制方法。起初干腌制品的制作是为了使食物得到更好、更久地保存,之后其独特的风味受到人们的喜爱和长久的亲睐。
干腌鱼的特殊香气形成机理复杂,但此前已有大量研究表明这些香气物质来源于脂肪氧化、蛋白质和硫胺素的降解、美拉德反应等[3]。由于鱼类含有大量的不饱和脂肪酸,在干制过程中极易发生氧化分解,生成醛、醇、酮等小分子物质。目前现在工业技术已经可以加快干腌制品的干制和腌制,但张进杰[4]研究表明,工业化风干干制的鱼肉风味没有传统干制的气味丰富,传统干腌鱼风味较丰富可能是由于复杂的干制条件与环境,如日晒、风速、湿度等因素。顾赛麒[5]的研究表明,不同干制方式下的干腌鱼脂肪氧化程度和挥发性化合物存在显著差异,光照组的干腌鱼挥发性风味物质均高于避光组,冷风与热风干燥的氧化反应类型不同导致主要挥发性化合物也存在差别。Wang等[6]的结果表明,菜籽油的挥发性化合物在光照后发生变化,特别是醛挥发性化合物的含量显著增加。Zhao等[7]的研究还表明,在阳光下酿造的蚕豆酱比在阴凉下酿造的香气更浓郁,阳光照射有利于挥发性化合物的积累。传统干腌鱼常见的干制方式有日晒干制和阴干,不同干燥方式造成鱼肉发生的主要反应和反应程度存在差异,导致产生的挥发性化合物也存在差异。目前日晒对干腌制品香气和脂肪氧化影响的相关报道较少。
本研究以新鲜腌制后的武昌鱼为原料,通过两种传统干制方式得到干腌武昌鱼成品,研究日晒和阴干的传统干腌鱼风味及脂肪氧化的变化,同时对比有无日晒的传统干腌鱼风味差异,阐明传统干制武昌鱼的主要风味物质,为干腌鱼风味加工及调控提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
新鲜武昌鱼、食盐、白糖、白酒 湖北省武汉市悦联商业悦活里超市;正构烷烃外标(C7~C30) Sigma-Aldrich Chemical Co. (St. Louis, MO, USA);甲醇、盐酸、焦性没食子酸、石油醚(沸程:30~60 ℃)、氢氧化钠、三氟化硼甲醇溶液、甲醇三氯甲烷、冰乙酸、碘化钾、可溶性淀粉、硫代硫酸钠、乙醚、异丙醇、酚酞、氢氧化钾、茴香胺、冰醋酸、异辛烷、环己烷、苯、2,4-二硝基苯肼、乙醇、三氯乙酸试剂 均为分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;仲辛醇 为色谱纯,上海化成工业发展有限公司。
GL-25MS型台式高速冷冻离心机 上海卢湘仪离心机仪器有限公司;722N型可见分光光度计 上海仪电分析仪器有限公司;PEN3型德国AIRSENSE电子鼻 北京盈盛恒泰科技有限责任公司;GL244-1SCN型分析天平 德国赛多利斯仪器有限公司;DZD-400/S型真空包装机 江苏腾通包装机械有限公司;HH-S2型电热恒温水浴锅 上海力衡仪器仪表有限公司;LGJ-25C型冷冻干燥机 北京四环科学仪器厂有限公司;7890A-5975C型 GC-MS气相色谱质谱联用仪、DB-WAX型色谱柱 美国安捷伦科技公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品处理
1.2.1.1 原料处理
鲜活武昌鱼(长34±2 cm,重约1.6 kg)带水活体运输至实验室宰杀,去鳞,将鱼从背部剖开,除去内脏,用无菌水洗去血、残留的内脏组织和黑膜,然后沥干水进行腌制。
腌制:准确地称取整鱼质量2%的食盐、1%的糖和0.5%的白酒(酒精度:42%vol)均匀地涂在鱼的全身。将鱼整齐地平铺在不锈钢盆中,放入4 ℃的冰箱中腌制。每24 h上下翻动一次,总共2 d。
干制:腌制后,洗去鱼表面的盐份及液体,取其中一批鱼不进行干制作为对照。用不锈钢钩横向刺穿鱼体使其展平悬挂。将日晒处理组的鱼暴露在室外自然环境中并保证有充足的阳光照射,阴干处理组的鱼悬挂至室外自然环境的遮阴处避免日晒。干制时长为每日8:00~17:00共计4 d,其余时间放置于4 ℃的冰箱中直至干制结束。干燥时间和气候参数如下:2021年3月21~24日4 d,连续晴天。气候条件:根据武汉市洪山区气象数据显示,3.21日8:00~17:00平均气温为12.38 ℃,风速3.13 m/s,湿度45.18%;3.22日8:00~17:00的平均气温为10.71 ℃,风速为1.27 m/s,相对湿度为63.4%;3.23日8:00~17:00的平均气温为11.37 ℃,风速为2.24 m/s,相对湿度为59.3%;3.24日8:00~17:00的平均气温为12.24 ℃,平均风速为2.88 m/s,相对湿度为43.4%。干制4 d的平均日晒强度为84282 lux,阴干处日晒强度始终低于270 lux。干制结束日晒干制武昌鱼的水分含量为47.6%,阴干武昌鱼水分含量为52.1%。将所有干腌鱼样品真空包装并储存在−80 ℃且基于干基样品分析。
1.2.2 指标测定方法
1.2.2.1 脂肪的提取及脂含量测定
参考Folch等[8]的方法并稍作修改。准确称取5.0 g切碎后鱼肉装入烧杯,加入40 mL氯仿-甲醇溶液(V/V,2:1),冰浴匀浆60 s后液转至具塞比色管并用氯仿-甲醇溶液定容至100 mL,静置1 h后过滤,去除蛋白和结缔组织,滤液中加入0.2倍体积的生理盐水,3500 r/min离心15 min,吸出多余上层液体,将下层溶液放置水浴氮吹仪中,氮气吹扫浓缩除去下层有机溶剂,得到脂质并称取其质量,除去事前称取干燥离心管质量得到其脂肪含量。
1.2.2.2 过氧化值的测定
测定方法参考GB5009.227-2016[9],取1.3.1油脂试样进行测定。
1.2.2.3 酸价的测定
测定方法参考GB5009.229-2016[10],取1.3 1油样进行测定。
1.2.2.4 茴香胺值的测定
测定方法参考GB 24304-2009[11],取1.3.1油样进行测定。
1.2.2.5 多烯指数的测定
测定方法参考GB 22500-2008[12],取1.3.1油样进行测定。
1.2.2.6 羰基价的测定
参考韩瑞阳等[13]方法,称取0.05~1.00 g 1.3.1中油样,置于10 mL容量瓶中,加正丁醇溶解试样并稀释至刻度取出1 mL放入15 mL离心试管中,加入1 mL 2,4-二硝基苯肼溶液,盖上塞子,摇匀。在40 ℃水浴中加热20 min。反应后取出用流水冷却至室温,加入8 mL氢氧化钾-正丁醇溶液。涡旋剧烈振荡混匀后,在室温下于3000 r/min离心5 min。以1 cm比色杯,用试剂空白调节零点,于420 nm处测定吸光度。
1.2.2.7 脂肪酸相对含量的测定
脂肪水解方法参考GB5009.168-2016[14],脂肪酸甲酯化方法参照王未君和Kaluzny等[15-16]的方法并稍作修改。水解后提取的总脂油样0.5 g于10 mL离心管中,加入0.5 mL 0.5 mol/L氢氧化钠-甲醇溶液,再加入2.5 mL正己烷溶液,旋涡混合5 min,于5000 r/min条件下离心10 min,取上层液体,通过0.22 μm有机微孔滤膜过滤,加入25 μL十九烷酸甲酯作为内标,正己烷定容至1 mL,进行气相色谱分析。气相色谱条件:色谱柱:HP-FFAP(60 m,0.25 mm,0.25 μm);升温程序为初温90 ℃,保持2 min,以10 ℃/min的速率升温至180 ℃,再以5 ℃/min的温度升温至240 ℃,保持10 min;载气为高纯氦气,流量为1.0 mL/min,进样量1 μL,分流比1:30,进样口温度为230 ℃;火焰离子化检测器温度为240 ℃。根据37种脂肪酸甲酯混标来确定各脂肪酸的保留时间,以十九烷酸甲酯为内标物质进行定量分析。
1.2.2.8 电子鼻仪器测定
参考陈方雪等[17]的方法进行测定,取2.0 g 1.3.1搅碎的样品,置于20 mL电子鼻进样瓶中,密封后于40 ℃水浴平衡30 min进行测定。PEN3电子鼻测定参数:清洗时间100 s,测定时间120 s,气体流量150 mL/min,每个样品重复3次,特征值提取时间点118~119 s。
1.2.2.9 挥发性化合物含量测定
参考顾赛麒等[18]的方法并稍做修改。取2.0 g 1.3.1搅碎样品于20 mL顶空瓶中,放入磁力搅拌器在40 ℃下平衡15 min,萃取40 min。
定性分析:将检测到的挥发物质谱图与NIST 17谱库中的标准物质谱图进行对比,同时计算各物质的线性保留指数(linear retention index,LRI),并与文献与网站[19]中的LRI值进行比对,LRI计算公式:
式中:tn和tn+1分别为碳数为n、n+1的正构烷烃的保留时间,t是在tn和tn+1之间的某个化合物的保留时间。
定量分析:将50 μL质量浓度为0.8×10−6 g/mL的内标物仲辛醇加入到2 g充分绞碎的鱼肉样品中,通过计算待测挥发物与仲辛醇峰面积的比值得到各挥发性化合物的含量。
仪器参数:GC-MS分析在配至5975C质谱仪的Agilent 7890A气相色谱仪上进行。在DB-WAX色谱柱(60 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm)上进行分离。载气氦气的恒定流速为1.0 mL/min。进样器温度为250 ℃,离子源温度为230 ℃。温度程序如下:烘箱温度保持在40 ℃,以2 ℃/min的速度升至100 ℃,然后以5 ℃/min的速度升至180 ℃,最后在8 ℃升至250 ℃/min,保持5 min。涂层纤维在进样口在250 ℃下解吸5 min。MS扫描在30~400 amu的范围内进行。全扫描模式,不分流。
1.2.2.10 气味活性值分析
气味活性值(odor activi-ty value,OAV)可用于表征风味化合物贡献大小的物理量,从而反映风味物质对样品整体风味的贡献度,OAV大于1的风味物质被认为具有气味活性是对样品风味有贡献的物质,OAV大于1的组分对风味主体物实际作用;OAV值越大说明该组分对样品总体的风味贡献度越大。OAV计算公式如下:
式中:OAV为某个香气化合物的气味活性值,Ci为香气化合物的质量浓度(ng/g),OTi为特征香气化合物在水中的气味阈值。
1.2.2.11 风味轮廓分析
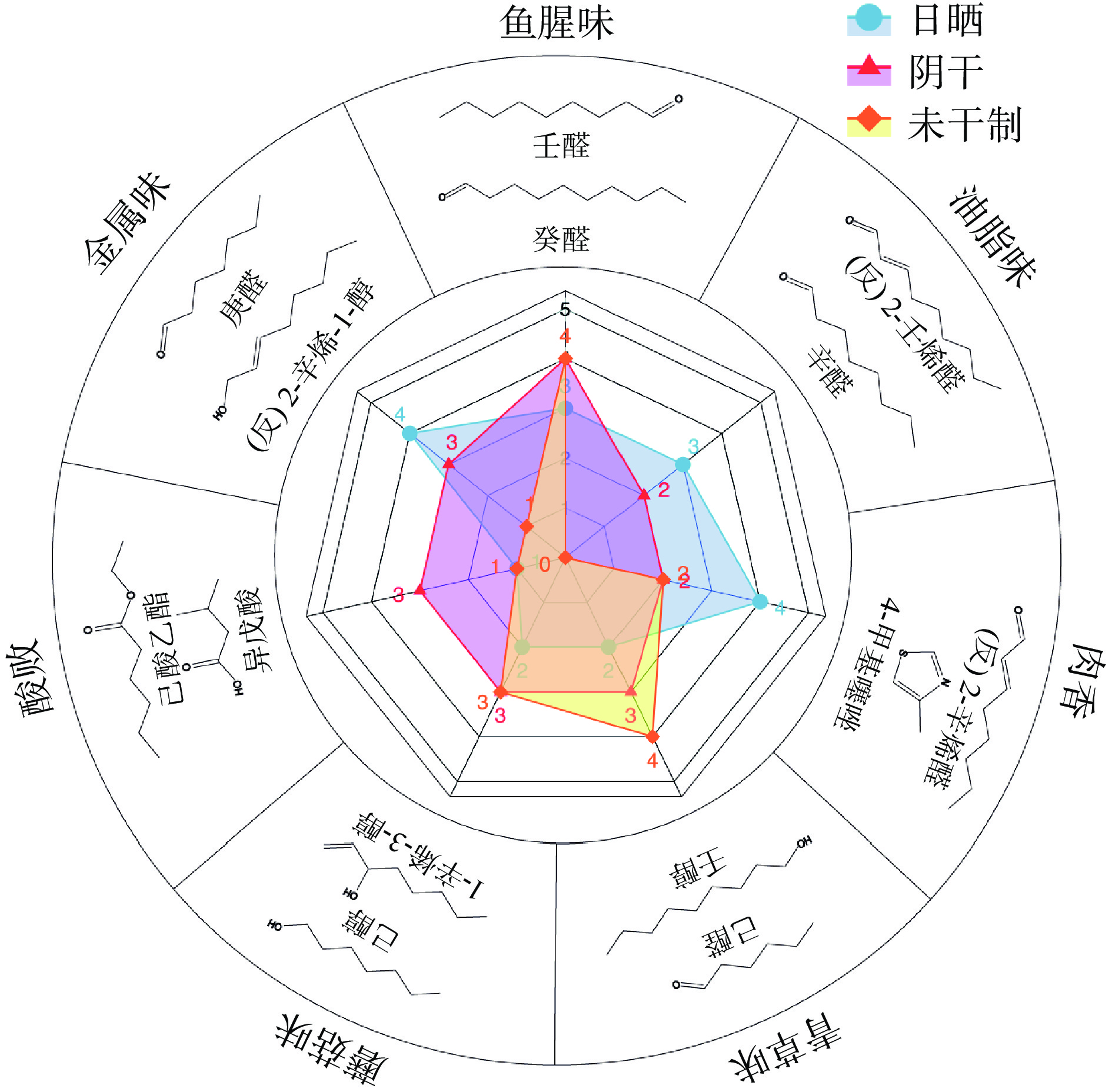
参考Tan等[20]的方法对干腌武昌鱼进行感官评定。15名感官评价成员都接受了三天的干腌鱼评估培训和实践。选取七个气味描述性词汇用于区分样本分别为鱼腥味、脂肪味、肉味、青草味、土壤味、花果味和金属味。七个描述词汇以下列香气为参考:壬醛、癸醛用于描述“鱼腥味”、反式-2-壬烯醛、辛醛用于描述“脂肪味”、2-辛醛、4-甲基噻唑用于描述“肉味”、己醛、壬醇描述“青草味”、己醇、1-辛烯-3-醇描述“土壤味”、异戊酸、己酸乙酯描述“花果香”特性以及庚醛、2-辛烯-1-醇的用于描述“金属”。评估标准为(0=难以察觉,1=弱,3=显著,5=非常强)。将获得的七维风味轮廓绘制在蜘蛛网图中。
1.3 数据处理
使用SPASS、Graphpad Prism9软件进行数据处理及图表绘制,数据以平均值±标准差表示,使用R studio 4.1.0 (RStudio Inc, USA)进行相关性分析。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 传统干腌武昌鱼脂肪氧化的变化
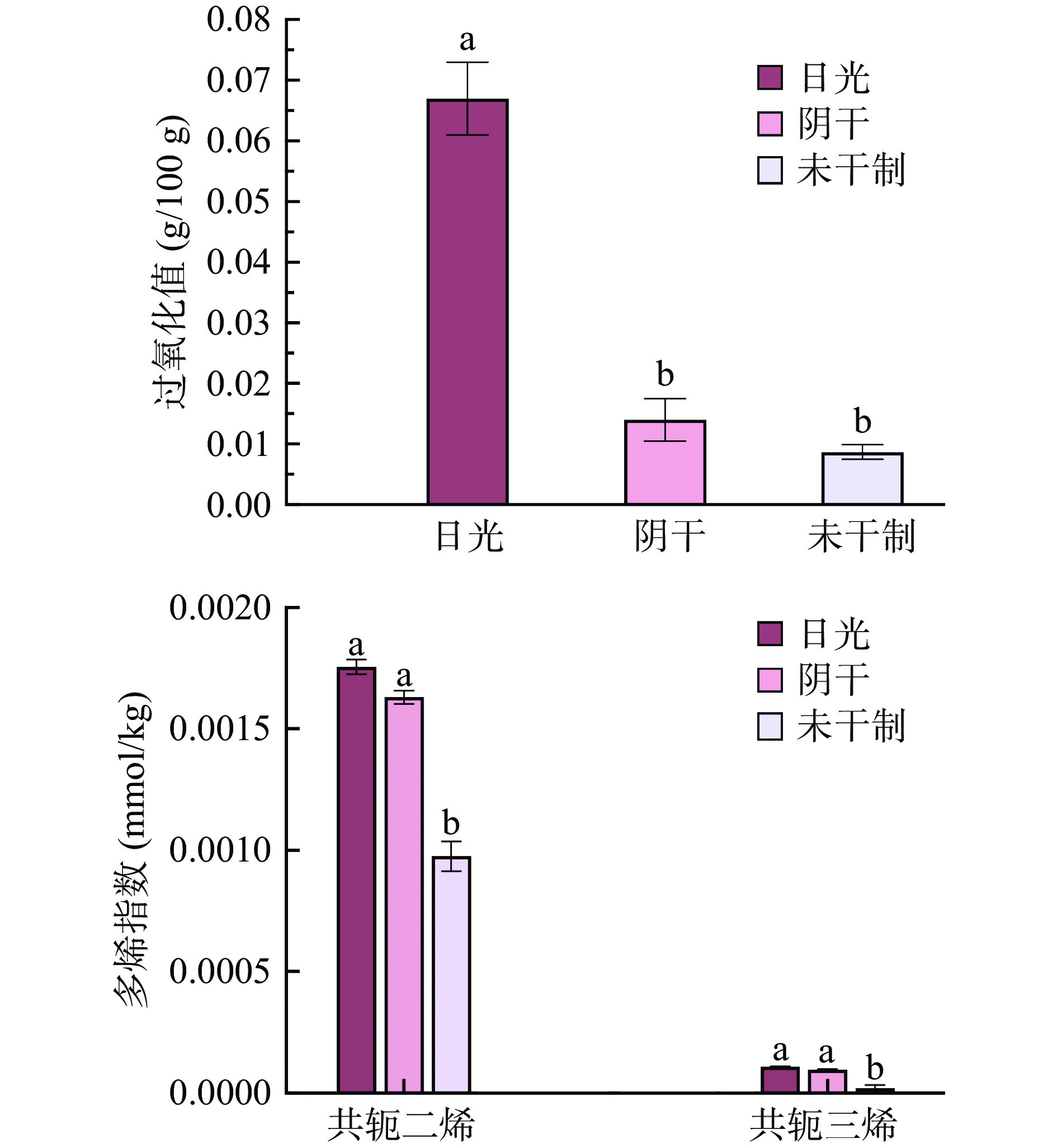
实验结果表明两种传统干制方式干制武昌鱼在脂肪氧化程度上有显著性差异,过氧化值(POV,peroxide value)主要用于表征样品中的初级氧化产物——氢过氧化物。如图1所示,传统日晒的武昌鱼POV值为0.069 g/100 g是阴干武昌鱼的6倍。共轭烯烃(conjugated diene,CD;conjugate triene,CT)主要是由于多不饱和脂肪酸氧化产生的化合物,同时也表征鱼肉中的初级氧化产物[21]。传统日晒武昌鱼的共轭二烯含量为0.00178 mmol/kg,高于传统阴干武昌鱼0.00161 mmol/kg,这与测定的过氧化值结果一致,但共轭三烯含量两种干制方式无显著差异,日晒干制为0.000108 mmol/kg,阴干武昌鱼为0.0000997 mmol/kg。
![]() 图 1 传统干腌武昌鱼初级氧化产物的变化注:不同字母表示同一指标不同干腌方法具有显著性差异,P<0.05,图2同。Figure 1. Changes in primary oxidation products of traditional dried blunt-snout bream
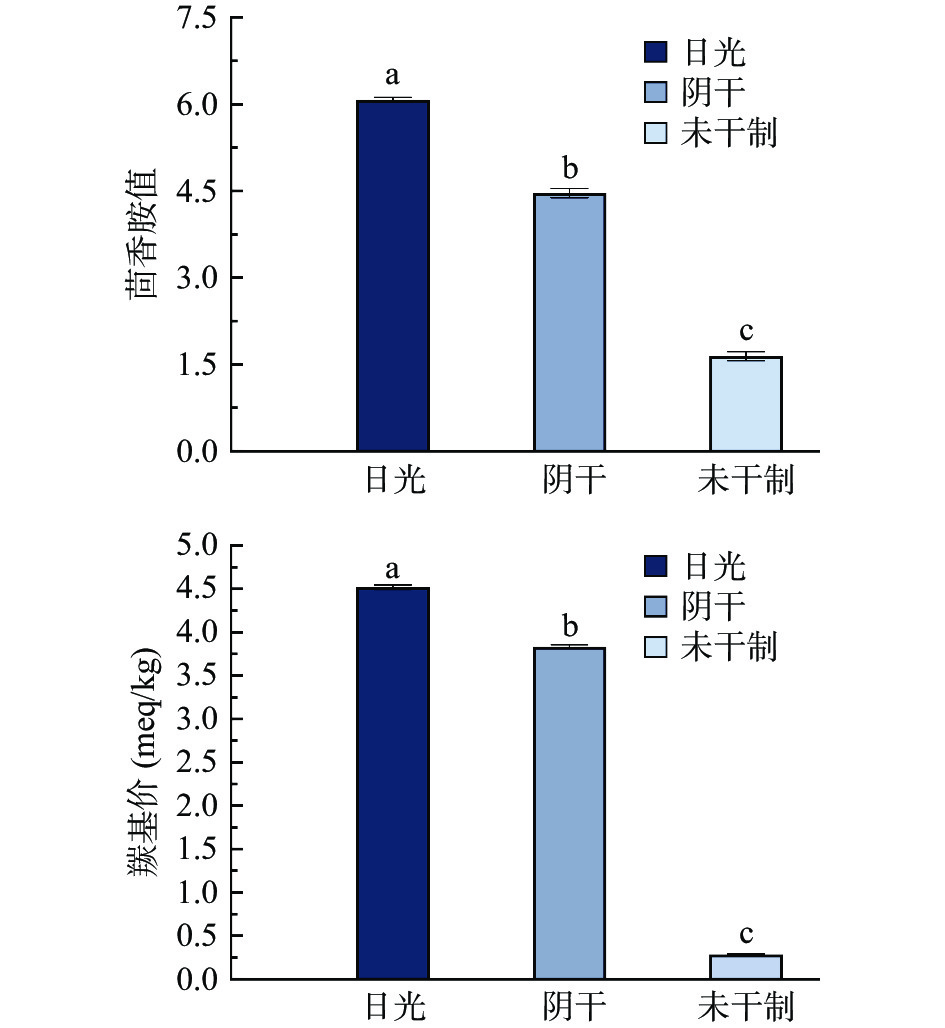
图 1 传统干腌武昌鱼初级氧化产物的变化注:不同字母表示同一指标不同干腌方法具有显著性差异,P<0.05,图2同。Figure 1. Changes in primary oxidation products of traditional dried blunt-snout bream茴香胺(p-anisidine value,p-AnV)值主要由p-AnV表征,p-AnV反映油脂中次级氧化产物醛类总含量(主要指a-p-不饱和醛)[22],传统日晒武昌鱼的茴香胺值显著高于阴干武昌鱼的茴香胺值。羰基价(carbonyl value,CV)是油脂酸败时产生含有醛基和酮基的脂肪酸或甘油酸及聚合物的总量,用来表征油脂氧化程度。由图2可知,次级氧化指标茴香胺值和羰基价传统日晒均显著高于传统阴干武昌鱼(P<0.05)。这可能是因为日晒促进了脂肪氧化,加快氧化速率,氢过氧化物继续反应生成次级氧化产物[5]。
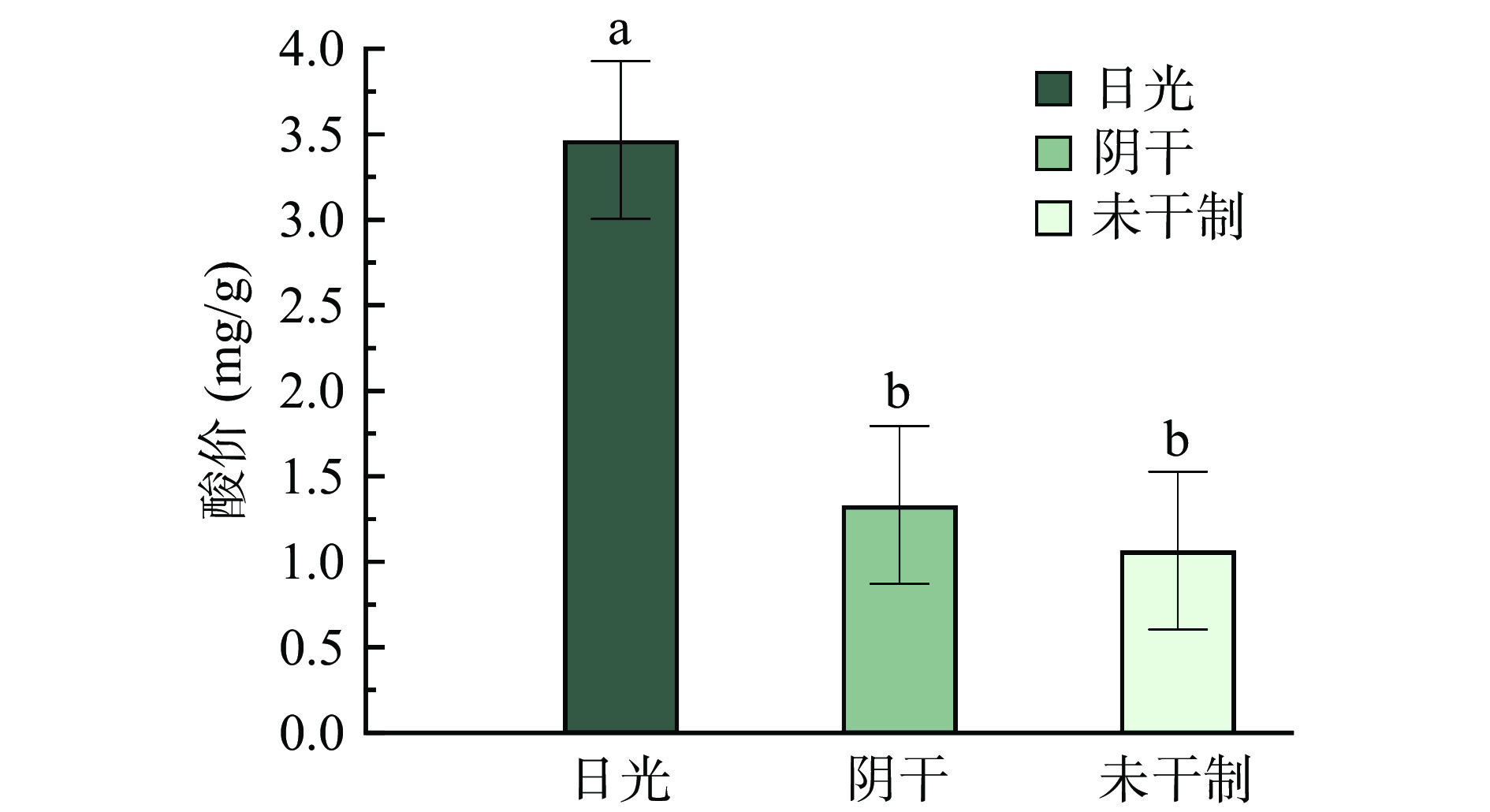
酸价(acid value,AV)主要用于表征脂质样品中的游离脂肪酸的总量(包括脂质氧化的三级氧化产表物——因醛类氧化而获得的游离中短链羧酸和高级脂肪酸甘油酯水解产生的游离长链脂肪酸)。由图3可知,传统日晒武昌鱼AV为3.5 mg/g,阴干武昌鱼的AV为1.3 mg/g,脂肪水解程度显著低于传统日晒武昌鱼(P<0.05),但阴干武昌鱼的酸价与腌制未干制的武昌鱼无显著差异,这可能是由于光照促进和加深了氧化的发生,使脂肪酸加速降解,同时由于游离脂肪酸更易氧化,使得日晒武昌鱼产生更多的氧化产物[5]。
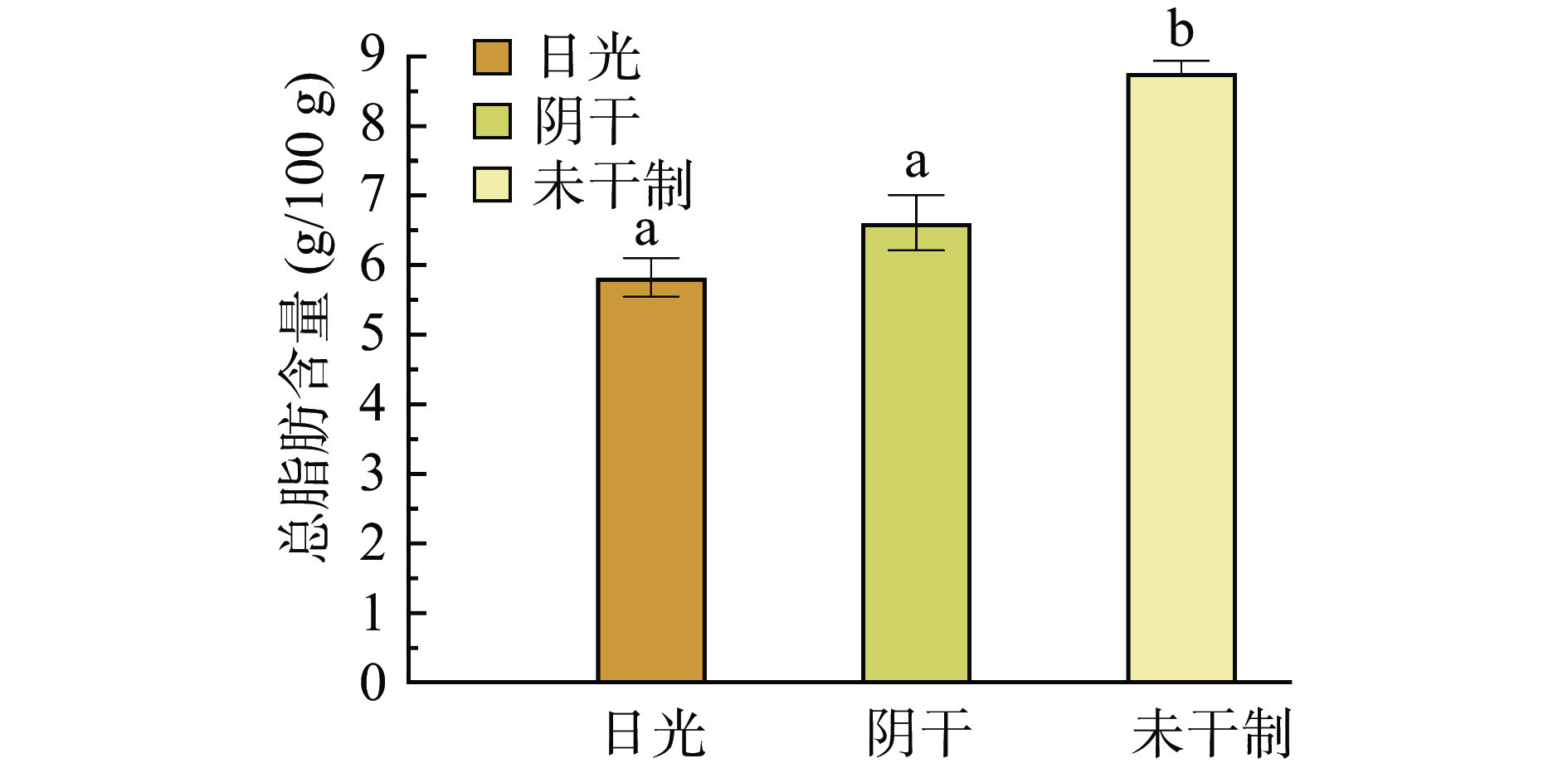
由图4可知,两种干制方式下的武昌鱼脂肪含量均下降,但日晒干制和阴干武昌鱼的脂肪含量显著小于未干制的武昌鱼(P<0.05)。日晒是常用的传统干制方式,日晒也是干制制品脂肪氧化降解的主要途径,且日晒可引发光氧化,其速率是自氧化的上千倍[23]。这些现象可能是由于日晒加速了脂肪氧化的速率,脂肪降解的脂肪酸作为氧化底物,在自氧化的同时,日晒使光敏剂将激态氧转变为激发态氧,直接与基态含烯底物的双键结合生成氢过氧化物,再分解或聚合生成醛、酮、酸等化合物或聚物及多聚物。同时部分氢过氧化物也可能分解生成自由基再进入氧化链循环[24]。不饱和脂肪酸暴露在日晒下便会增加其氧化及酸败,所以日晒干制的武昌鱼脂肪氧化程度高于阴干武昌鱼的脂肪氧化程度。
2.2 传统干腌武昌鱼的脂肪酸含量
脂肪酸根据其不饱和度可分为:饱和脂肪酸(saturated fatty acids,SFA)、单不饱和脂肪酸(monounsaturated fatty acids,MUFA)和多不饱和脂肪酸(polyunsaturated fatty acids,PUFA)[24-25]。在腌制过程中脂肪酸被内源酶水解,在干制过程中又作为底物反应降解为醛、酮、酸等小分子物质,并生成有香气的挥发性化合物等。由表1可知,MUFA和PUFA是腌腊鱼脂肪酸的重要构成组分,研究表明日晒干制和阴干两种干制方式下武昌鱼的MUFA和PUFA的相对含量均有下降,SFA的相对含量升高。油酸(C18:1n9c)和亚油酸(C18:2n6c)是腌制武昌鱼中相对含量最高的UFA。两种干制方式的武昌鱼样品的UFA在相对含量上均存在差异。传统日晒武昌鱼的ΣUFA相对含量占总脂肪酸的71%,阴干武昌鱼的ΣUFA相对含量占总脂肪酸的80%。UFA由PUFA和MUFA组成,传统日晒武昌鱼的PUFA相对含量低于传统阴干武昌鱼,这些现象是因为脂肪氧化大多发生在不饱和脂肪酸上,饱和脂肪酸结构稳定不易发生氧化,不饱和脂肪酸含有双键,其中多不饱和脂肪酸所含双键更多,更易氧化与自由基及激发态氧反应,从而导致脂肪氧化[26]。在风干武昌鱼中,油酸(C18:1n9c)、亚油酸(C18:2n6c)、(C18:3n6)、亚麻酸(C20:3n3)和花生四烯酸(C20:4n6)是有较大变化的不饱和脂肪酸,其中亚油酸是多数线性醛的前体物质如己醛、庚醛等。2-辛烯醛主要来源于亚油酸,而2-己烯醛主要来源于亚麻酸。2-庚烯醛可能源自α-亚麻酸[18]。花生四烯酸是1-辛烯-3-醇的前体物质,EPA是1-戊烯-3-醇的前体物质[27]。综上,这些脂肪酸降解生成的挥发性化合物可能对风干武昌鱼的风味提供了很大的贡献。n-3系PUFA因具有预防心脑血管疾病、促进大脑和视神经发育、防癌抗衰老等生理功效,其种类包括:亚麻酸(C20:3n3)、二十二碳六烯酸(DHA,C22:6n3)、二十碳五烯酸(EPA,C20:5n3)等[28],在以上两种干制方式武昌鱼中均检出。日晒因素对亚油酸、亚麻酸、DHA等PUFA相对含量影响显著,印证了不饱和程度越高、电子密度越大,在日晒条件下就越容易受到单线态氧的攻击而发生氧化降解[24]。
表 1 传统干腌武昌鱼脂肪酸含量的变化Table 1. Changes of the fatty acid content of traditional dried blunt-snout bream脂肪酸类别 脂肪酸 相对含量(%) 日晒 阴干 未干制
SFAC4:0 0.94±0.07 0.43±0.04 N.D C12:0 0.10±0.06 0.01±0.01 0.02±0.01 C14:0 0.84±0.03 0.86±0.08 0.16±0.03 C15:0 5.01±1.31 0.14±0.05 0.04±0.01 C16:0 10.89±1.77 11.57±2.01 N.D C17:0 4.25±1.12 0.18±0.06 0.02±0.01 C18:0 0.17±0.12 0.19±0.06 N.D C20:0 N.D 0.80±0.16 N.D C21:0 2.74±0.31 0.13±0.07 N.D C22:0 0.73±0.05 1.15±0.05 0.08±0.01 C23:0 0.63±0.08 0.17±0.02 0.01±0.01 C24:0 0.73±0.17 0.29±0.03 0.13±0.02
MUFAC14:1 0.05±0.01 0.04±0.01 0.21±0.13 C15:1 0.03±0.01 N.D N.D C16:1 1.09±0.02 2.08±0.13 2.33±1.07 C17:1 0.46±0.08 0.20±0.03 0.50±0.06 C20:1 0.87±0.11 2.02±1.05 3.18±1.37 C24:1 0.46±0.02 0.37±0.04 0.53±0.32 C18:1n9t 0.24±0.07 0.26±0.08 0.26±0.18 C18:1n9c 35.59±2.03 39.34±2.79 44.54±3.39
PUFAC18:2n6c 14.84±1.72 19.01±2.63 21.37±3.21 C18:2n6t 4.73±0.67 1.39±0.07 1.31±0.83 C18:3n6 3.78±0.21 6.71±1.34 7.21±2.35 C18:3n3 1.75±0.06 2.51±0.32 3.15±1.77 C20:2 0.06±0.01 0.56±0.08 1.27±0.84 C20:3n6 2.37±0.21 0.01±0.01 3.23±2.15 C20:4n6 2.26±0.09 3.91±0.03 5.16±2.78 C20:3n3 0.94±0.11 1.53±0.09 N.D C22:1n9 N.D 1.68±0.15 1.92±0.32 C22:2 N.D 0.52±0.02 N.D C20:5n3 0.61±0.03 0.87±0.04 1.57±0.77 C22:6n3 0.73±0.02 1.08±0.36 2.10±1.12 ΣMUFA 38.79±3.83 44.31±1.78 44.49±2.64 ΣPUFA 32.07±1.11 39.77±1.37 48.29±2.73 ΣSFA 29.14±2.77 15.92±2.01 0.46±0.31 2.3 传统干腌武昌鱼挥发性风味物质的含量及OAV值
采用气相色谱-质谱法从刚腌制结束的鱼肉块和两种干制方式的腌腊鱼中共检出了38种挥发性风味成分,并根据保留指数再次定性,仅有5种物质未查阅到对应的参考指数[19]。其中传统日晒鱼肉28种、阴干鱼肉23种、腌制结束时的鱼肉20种。所有挥发物中OAV大于1的气味活性物质有15种,主要以醛类、醇类和杂环类为主,其中己醛、辛醛、癸醛、壬醛、2-辛烯醛、3-甲基丁醛、1-辛烯-3-醇、乙醇、己醇、庚醇、2-戊基呋喃、乙酸己酯、D-柠檬烯13种物质的OAV大于1,可认为其是传统腌腊鱼中主要的气味活性物质。由表2可知,日晒干制武昌鱼和阴干武昌鱼的挥发物总含量分别是2922.98和1935.44 ng/g,OAV总和分别是924.87和183.75,挥发物总含量分别是刚腌制结束的5.9倍和4.0倍,表明传统日晒工艺有利于腌腊鱼整体香气的形成。醛类因其较低的阈值,通常对腌腊鱼整体香气具有着重要贡献。由表2可知,按传统工艺日制作的腌腊鱼日晒品中,醛类OAV总和为502.78,占所有挥发性风味成分OAV总和的54.36%,6种醛类物质OAV>1,是对干腌鱼整体风味有贡献的香气物质。此前已有研究表明,腌腊鱼中C6~C10饱和醛的风味前体物质是由于油酸、亚油酸、亚麻酸及花生四烯酸等不饱和脂肪酸氧化形成的[29],其中己醛、庚醛、辛醛、壬醛分别呈现青草味、哈喇味、鱼腥味及油脂味,而烯醛主要源自亚油酸酯和亚麻酸酯的氢过氧化物的降解[30],3-甲基丁醛是Strecker降解氨基酸生成的具有花香味的物质[31]。干腌鱼特征性风味被描述为咸香味、脂香味和鱼香味等多种复杂香味融合的气味。上述3种饱和醛(壬醛、辛醛、己醛)以及1种烯醛(2-壬烯醛)与传统腌腊鱼风味特征相符,可能对其整体香气贡献显著。
表 2 传统干腌武昌鱼风味物质含量及OAV值Table 2. Flavor substance content and OAV value of traditional dried blunt-snout bream中文名 英文名称 ID LRI 香气阈值
(ng/g)[18]含量(ng/g) OAV 计算值 参考值[19] 日晒 阴干 未干制 日晒 阴干 未干制
醛类己醛 Hexanal MS、LRI 1079.70 1081 4.5 362.67±17.38 42.50±6.93 5.97±2.22 80.59 9.4 1.31 庚醛 Heptanal MS、LRI 1181.59 1183 2.8 20.53±3.76 7.32 壬醛 Nonanal MS、LRI 1388.90 1392 1.1 249.6±7.44 25.30±5.36 110.45±13.87 226.91 23 100.4 癸醛 Decanal MS、LRI 1459.34 1447 0.1 7.93±0.81 79.3 正辛醛 Octanal MS、LRI 1286.34 1287 0.5 38.52±2.24 65.62 反-2-辛烯醛 2-Octenal, (E)- MS、LRI 1346.30 1345 3 54.98±6.92 18.32 反-2-己烯醛 2-Hexenal, (E)- MS、LRI 1211.37 1212 19.2 8.93±4.13 <1 顺-2-庚烯醛 (E)-2-heptenal MS、LRI 1242.37 1243 13.5 2.37±0.17 3-甲基丁醛 Butanal, 3-methyl- MS、LRI − 906 1.1 114.43±7.03 28.25±2.47 104.02 25.68 苯甲醛 Benzaldehyde MS、LRI 1531.21 1530 41.7 5.94 0.21±0.13 2.09±1.05 <1 <1 <1 2-戊基呋喃 Furan, 2-pentyl- MS、LRI 1230.74 1231 5.8 53.12±7.21 6.10±0.48 9.16 1.05 乙醇 Ethanol MS、LRI 930 256.72±10.71 51.344
醇类正戊醇 1-Pentanol MS、LRI 1245.73 1247 42 67.16±2.63 20.76±1.93 0.76±0.03 <1 <1 <1 正己醇 1-Hexanol MS、LRI 1350.14 1361 5.6 110.15±8.71 48.94±2.54 38.21±2.09 19.67 8.74 6.82 正辛醇 1-Octanol MS、LRI 1553.62 1557 9.98±1.11 4.18±1.37 <1 <1 <1 壬醇 1-Nonanol MS、LRI 41 10.23±0.21 4.17±0.16 <1- <1 <1 庚醇 1-Heptanol MS、LRI 1449.36 1457 1.1 9.56±0.34 2.09±0.85 8.69 1.9 2,3-丁二醇 2,3-Butanediol, [R-(R*,R*)]- MS、LRI 1612.34 1607 95.1 87.47±3.38 145.45±9.92 <1 <1 <1 3-辛醇 3-Octanol MS、LRI 1391.48 1394 110 2.85±0.84 <1 1-烯-3-辛醇 1-Octen-3-ol MS、 LRI 1393.28 1394- 1 555.98±21.75 162.51±4.67 33.42±5.26 373.05 108.34 22.28 1-戊烯-3-醇 1-Penten-3-ol MS、LRI 1160.55 1163 64.83±3.77 12.44±2.12 <1 <1 反-2-辛烯-1-醇 2-Octen-1-ol, (E)- MS 1627.76 − 20 6.12±1.45 <1 3-甲基-1-丁醇 1-Butanol, 3-methyl- MS、LRI 1204.76 1206 1000 97.44±2.21 59.34±7.32 2-乙基己醇 2-Ethylhexanol MS、LRI 300 7.46±1.02 <1 3-辛酮 3-Octanone MS、LRI 1253.72 1251 50.2 1.79±0.66 <1 酮类 3-羟基-2-丁酮 2-Butanone, 3-hydroxy- MS、LRI 1292.39 1286 800 362.49±12.54 326.96±8.29 <1 <1 2-甲基-3-辛酮 Acetoin MS、LRI 1321.71 1323 850 362.49±3.25 4.77±1.04 <1 <1 3,5-辛二烯酮 3,5-Octadien-2-one MS、LRI 1511.36 1517 150 38.80±3.74 813.22±11.86 <1 <1 2,3-辛二酮 2,3-Octanedione MS、LRI 1319.91 1323 32.65±0.87 2.09±0.96 <1 <1 <1 苯乙醇 Phenethyl alcohol MS、LRI 5.60±1.59 <1 乙酸 Acetic acid MS、LRI 1441.33 1442 60 119.97±3.74 7.76±1.19 <1 <1 己酸乙酯 Ethyl caproate MS、LRI 1232.22 1232 5 18.78 9.77±1.85 6.95 3.60 其他 己酸甲酯 Methyl caproate MS、LRI 1186.25 1187 70 107.16±2.04 0.73±0.18 1.54 <1 辛酸甲酯 Methyl octanoate MS、LRI 1390.84 1392 20.41±1.21 3.55±1.57 0.89±0.13 <1 <1 <1 异戊酸 Butanoic acid, 3-methyl- MS、LRI 1669.40 1671 60 9.73±1.22 32.24±2.70 <1 <1 己酸 Hexanoic acid MS、LRI 1855 3.5/60 16.22±2.34 <1 <1 柠檬烯 D-Limonene MS、LRI 1193.7 1198 10 45.71±4.57 24.02±3.32 2.68±0.93 4.57 2.4 <1 4-甲基噻唑 4-Methylthiazole MS 1277.65 1279 20.23±1.08 6.13±0.77 1.80±0.02 <1 <1 <1 醇类主要源自脂肪酸的二级氢过氧化物的分解、脂肪氧化酶作用或由羰基化合物还原生成。由表2可知,干制后的鱼肉醇类物质含量增大,并且不饱和醇的种类增多。其中己醇、1-辛烯-3-醇是气味贡献较高的香气物质。己醇是油酸氧化的产物也具有青草味,1-辛烯-3-醇具有鱼腥味和蘑菇味的特点,有研究表明1-辛烯-3-醇是花生四烯酸氧化分解的产物。吴燕燕等[32]在腌红牙䱛中也检测出这两种醇类,并指出1-辛烯-3-醇是一种具有浓郁蘑菇味的成分,能产生清淡的香气,使腌制加工后的鱼肉更加柔和。
酮类主要由脂肪酸的氧化降解以及醇类物质的氧化生成[33]。干制结束后,鱼肉中酮类物的OAV总和小于1,但酮类化合物的含量占比并不低。酮作为脂肪最终氧化降解的底物之一在干制后含量升高,但由于其阈值较高,对干腌鱼的整体风味贡献不大,其气味贡献度远不如醛类和醇类等。然而,有研究指出,酮类对腥味减退具有一定的贡献[34]。
杂环类、酸类和酯类多数来源于蛋白质和硫胺素的热氧化降解、二羰基化合物的斯特克雷降解和脂肪氧化[26]。其中对干腌鱼整体气味贡献较大的挥发性物质为2-戊基呋喃和乙酸己酯。其中2-戊基呋喃有焦糖香味是脂肪氧化的产物[35],而己酸乙酯具有水果香气和酸味[36],是对阴干武昌鱼整体风味贡献较大的香气物质。
在传统日晒武昌鱼中,醛类醇类挥发性化合物在总挥发性化合物中占比较高,醛类和醇类含有较低的感官阈值,因此它们可能赋予了日晒武昌鱼强烈的油脂味、金属味和青草味。而在阴干武昌鱼中,醇类、酯类和酸类的含量占比较高,所以我们推断它们可能赋予了阴干武昌鱼强烈的鱼腥味和酸味,从而导致了两种干制武昌鱼整体风味差异较大。
2.4 传统干腌武昌鱼风味的电子鼻结果
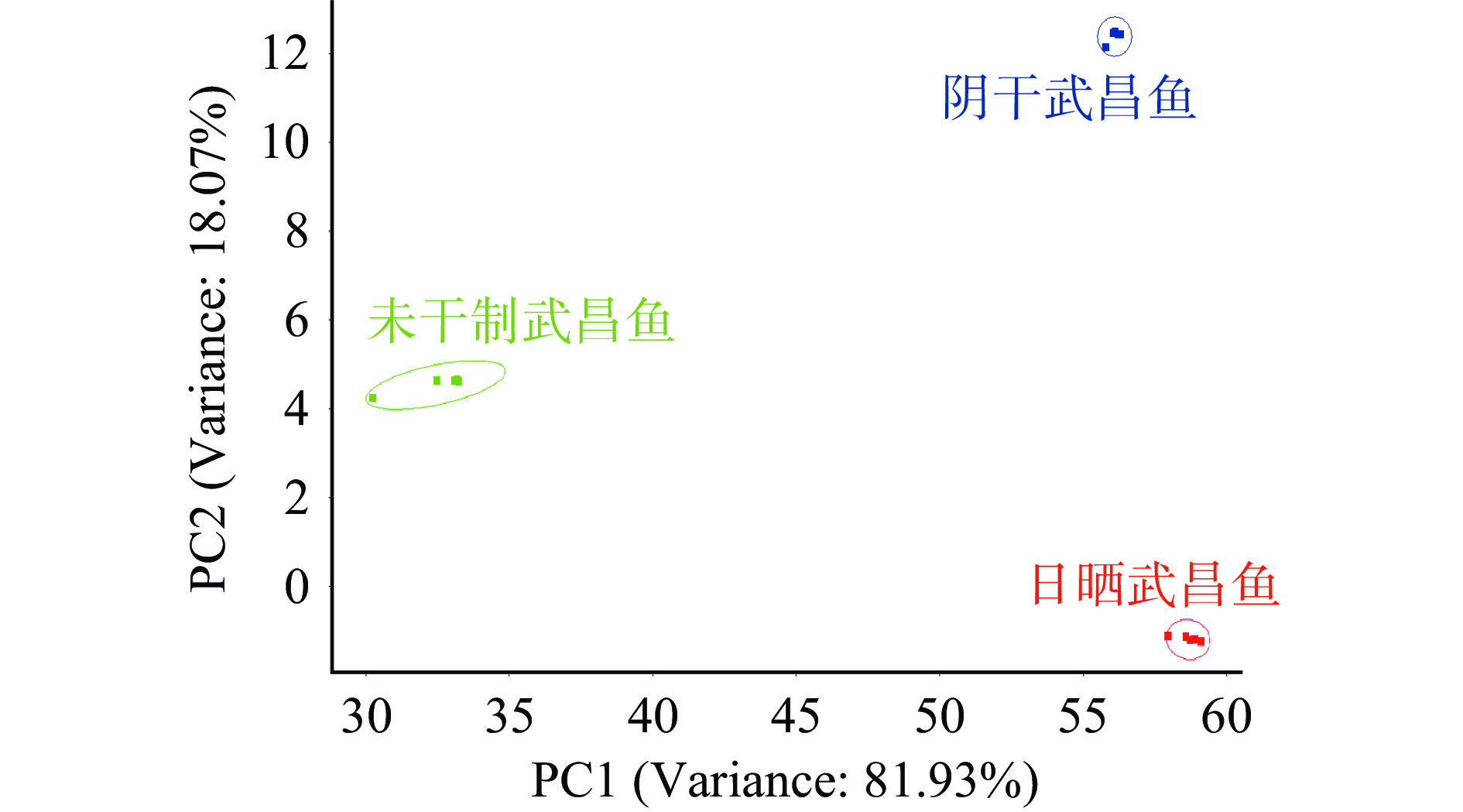
样品均远离原点且具有其独立的气味区域,说明日晒干制、阴干干制的武昌鱼和未干制的武昌鱼总体气味差异显著。由图5可知,电子鼻主成分分析的横纵坐标可以看出,第一主成分和第二主成分的贡献率分别为81.93%、18.07%,累计贡献率达到100%,说明样品整体差异性信息在该主成分平面上有较为充分的展示[37]。电子鼻PCA结果显示三种鱼肉的整体气味有显著差异。这与GC-MS相似的结果,这三类成分的含量在日晒鱼、阴干鱼、未干制鱼中依次变低。干腌鱼的风味被描述为鱼腥味、油脂味、肉香、青草味、土壤味、酸味、金属味。日晒鱼有强烈的脂肪味,这是因为日晒鱼中含有OAV值较高的辛醛、壬醛和反2-壬烯醛等油脂香的物质。日晒鱼独有的庚醛赋予了其试剂味、金属味。壬醛、1-辛烯-3-醇和己醛在阴干武昌鱼中是OAV值最高的3个化合物,它们赋予了阴干武昌鱼较强的鱼腥味、青草味和土壤味。干制后的鱼肉相比未干制的鱼肉,有着丰富的风味轮廓,未干制的鱼肉几乎没有脂肪的香气。鱼腥味和酸味是未干制鱼肉的主要风味(图6)。根据之前GC-MS的结果,日晒干制的鱼肉与阴干的鱼肉有显著差异是因为醛醇酮小分子化合物种类和含量的差异造成的。可能是日晒加速了氧化,给日晒干制的鱼肉带来了强烈的油脂香和肉香味。而无日晒的环境可能更适合微生物的生长,有利于分解鱼肉中的蛋白质等物质,使阴干的鱼肉有较明显的鱼腥味和酸味。
2.5 干腌武昌鱼的脂肪酸、特征性风味物质及氧化指标的相关性分析
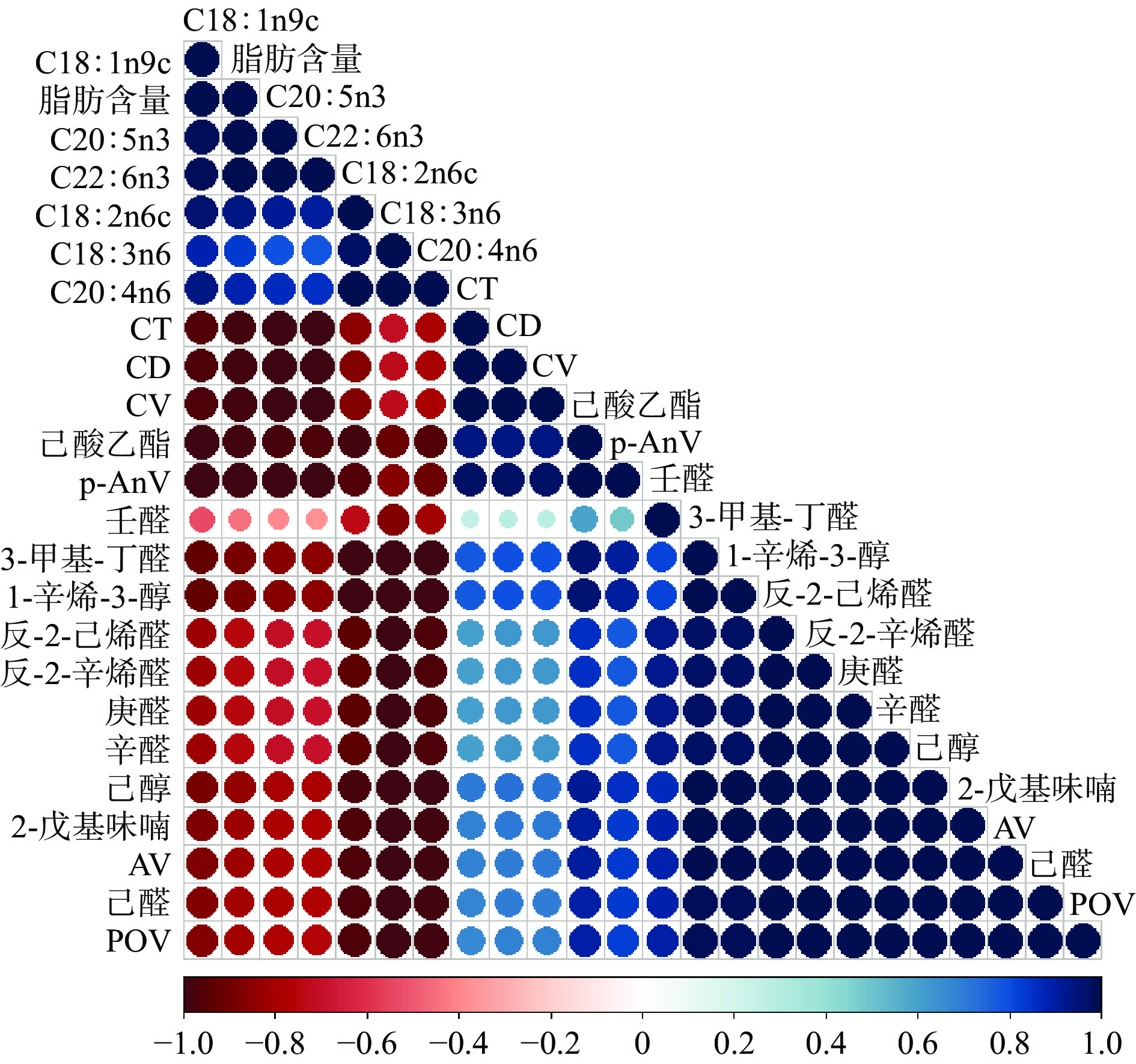
从风干武昌鱼的脂肪酸、特征风味物质及脂肪氧化指标的相关性分析(图7)可以看出,风干武昌鱼的特征风味物质均与脂肪酸呈负相关,尤其是亚油酸、亚麻酸与花生四烯酸与己醛、庚醛、辛醛、1-辛烯-3-醇、2-戊基呋喃、反-2-辛烯醛和己醇呈负相关,说明这类不饱和脂肪酸的含量直接影响这类挥发性化合物的生成,这与线性醛、不饱和醇等挥发性化合物是由多数不饱和脂肪酸降解形成的结果一致。同时,这些脂肪酸正是这些醛类的风味前体物质。p-AV、AV、POV与挥发性化合物呈正相关,即氧化的程度越深,此类风味物质的含量越高。其中POV与AV呈正相关,这是因为脂肪水解为游离脂肪酸发生氧化生成氧化初级产物氢过氧化物是氧化的初步阶段,部分氢过氧化物会产生新的自由基继续与底物反应,再发生氧化反应,还有部分氢过氧化物再降解,生成次级氧化产物,产生这些挥发性化合物[38]。
3. 结论
两种传统干制方式的武昌鱼在整体气味上有显著差异,日晒干制的武昌鱼有更强的哈喇味和肉香味,阴干武昌鱼有更显著的鱼腥味和花果香,这是由于两种干制方式的特征风味物质辛醛、庚醛、2-辛烯醛、3-甲基-1-丁醛、庚醇具有鱼腥味和油脂味,而1-辛烯-3-醇、乙酸己酯、D-柠檬烯具有鱼腥味和水果香气。同时,因为日晒加速了脂肪的氧化,使得日晒干制的鱼肉醛、醇类物质较多且含量高。醛、醇多为低阈值的香气物质,表明了日晒干制的武昌鱼整体气味更加丰富。在香气形成的过程中两种干制方式下,鱼肉的不饱和脂肪酸含量也在降低,多不饱和双键的脂肪酸变化越显著,因光氧化的速率比自氧化快速,所以日晒干制武昌鱼的脂肪酸含量变化比阴干更为显著。日晒加速了氧化赋予了鱼肉更丰富的气味,阴干的武昌鱼的气味更清香。风干武昌鱼的香气物质源于脂肪氧化,与不饱和脂肪酸中亚油酸(C18:2n6c)、(C18:3n6)、亚麻酸(C20:3(n-3))和花生四烯酸(C20:4n6)相关。现代工业化干制方法可以加速干制时间,但是整体风味不如传统干制干腌鱼风味丰富。本实验为干腌鱼的风味加工与调控提供了一定的参考,但光氧化对干腌产品香气的影响值得进一步探索,因此光的控制和利用对干腌鱼特征香气物质的形成尤为重要。
-
图 1 传统干腌武昌鱼初级氧化产物的变化
注:不同字母表示同一指标不同干腌方法具有显著性差异,P<0.05,图2同。
Figure 1. Changes in primary oxidation products of traditional dried blunt-snout bream
表 1 传统干腌武昌鱼脂肪酸含量的变化
Table 1 Changes of the fatty acid content of traditional dried blunt-snout bream
脂肪酸类别 脂肪酸 相对含量(%) 日晒 阴干 未干制
SFAC4:0 0.94±0.07 0.43±0.04 N.D C12:0 0.10±0.06 0.01±0.01 0.02±0.01 C14:0 0.84±0.03 0.86±0.08 0.16±0.03 C15:0 5.01±1.31 0.14±0.05 0.04±0.01 C16:0 10.89±1.77 11.57±2.01 N.D C17:0 4.25±1.12 0.18±0.06 0.02±0.01 C18:0 0.17±0.12 0.19±0.06 N.D C20:0 N.D 0.80±0.16 N.D C21:0 2.74±0.31 0.13±0.07 N.D C22:0 0.73±0.05 1.15±0.05 0.08±0.01 C23:0 0.63±0.08 0.17±0.02 0.01±0.01 C24:0 0.73±0.17 0.29±0.03 0.13±0.02
MUFAC14:1 0.05±0.01 0.04±0.01 0.21±0.13 C15:1 0.03±0.01 N.D N.D C16:1 1.09±0.02 2.08±0.13 2.33±1.07 C17:1 0.46±0.08 0.20±0.03 0.50±0.06 C20:1 0.87±0.11 2.02±1.05 3.18±1.37 C24:1 0.46±0.02 0.37±0.04 0.53±0.32 C18:1n9t 0.24±0.07 0.26±0.08 0.26±0.18 C18:1n9c 35.59±2.03 39.34±2.79 44.54±3.39
PUFAC18:2n6c 14.84±1.72 19.01±2.63 21.37±3.21 C18:2n6t 4.73±0.67 1.39±0.07 1.31±0.83 C18:3n6 3.78±0.21 6.71±1.34 7.21±2.35 C18:3n3 1.75±0.06 2.51±0.32 3.15±1.77 C20:2 0.06±0.01 0.56±0.08 1.27±0.84 C20:3n6 2.37±0.21 0.01±0.01 3.23±2.15 C20:4n6 2.26±0.09 3.91±0.03 5.16±2.78 C20:3n3 0.94±0.11 1.53±0.09 N.D C22:1n9 N.D 1.68±0.15 1.92±0.32 C22:2 N.D 0.52±0.02 N.D C20:5n3 0.61±0.03 0.87±0.04 1.57±0.77 C22:6n3 0.73±0.02 1.08±0.36 2.10±1.12 ΣMUFA 38.79±3.83 44.31±1.78 44.49±2.64 ΣPUFA 32.07±1.11 39.77±1.37 48.29±2.73 ΣSFA 29.14±2.77 15.92±2.01 0.46±0.31 表 2 传统干腌武昌鱼风味物质含量及OAV值
Table 2 Flavor substance content and OAV value of traditional dried blunt-snout bream
中文名 英文名称 ID LRI 香气阈值
(ng/g)[18]含量(ng/g) OAV 计算值 参考值[19] 日晒 阴干 未干制 日晒 阴干 未干制
醛类己醛 Hexanal MS、LRI 1079.70 1081 4.5 362.67±17.38 42.50±6.93 5.97±2.22 80.59 9.4 1.31 庚醛 Heptanal MS、LRI 1181.59 1183 2.8 20.53±3.76 7.32 壬醛 Nonanal MS、LRI 1388.90 1392 1.1 249.6±7.44 25.30±5.36 110.45±13.87 226.91 23 100.4 癸醛 Decanal MS、LRI 1459.34 1447 0.1 7.93±0.81 79.3 正辛醛 Octanal MS、LRI 1286.34 1287 0.5 38.52±2.24 65.62 反-2-辛烯醛 2-Octenal, (E)- MS、LRI 1346.30 1345 3 54.98±6.92 18.32 反-2-己烯醛 2-Hexenal, (E)- MS、LRI 1211.37 1212 19.2 8.93±4.13 <1 顺-2-庚烯醛 (E)-2-heptenal MS、LRI 1242.37 1243 13.5 2.37±0.17 3-甲基丁醛 Butanal, 3-methyl- MS、LRI − 906 1.1 114.43±7.03 28.25±2.47 104.02 25.68 苯甲醛 Benzaldehyde MS、LRI 1531.21 1530 41.7 5.94 0.21±0.13 2.09±1.05 <1 <1 <1 2-戊基呋喃 Furan, 2-pentyl- MS、LRI 1230.74 1231 5.8 53.12±7.21 6.10±0.48 9.16 1.05 乙醇 Ethanol MS、LRI 930 256.72±10.71 51.344
醇类正戊醇 1-Pentanol MS、LRI 1245.73 1247 42 67.16±2.63 20.76±1.93 0.76±0.03 <1 <1 <1 正己醇 1-Hexanol MS、LRI 1350.14 1361 5.6 110.15±8.71 48.94±2.54 38.21±2.09 19.67 8.74 6.82 正辛醇 1-Octanol MS、LRI 1553.62 1557 9.98±1.11 4.18±1.37 <1 <1 <1 壬醇 1-Nonanol MS、LRI 41 10.23±0.21 4.17±0.16 <1- <1 <1 庚醇 1-Heptanol MS、LRI 1449.36 1457 1.1 9.56±0.34 2.09±0.85 8.69 1.9 2,3-丁二醇 2,3-Butanediol, [R-(R*,R*)]- MS、LRI 1612.34 1607 95.1 87.47±3.38 145.45±9.92 <1 <1 <1 3-辛醇 3-Octanol MS、LRI 1391.48 1394 110 2.85±0.84 <1 1-烯-3-辛醇 1-Octen-3-ol MS、 LRI 1393.28 1394- 1 555.98±21.75 162.51±4.67 33.42±5.26 373.05 108.34 22.28 1-戊烯-3-醇 1-Penten-3-ol MS、LRI 1160.55 1163 64.83±3.77 12.44±2.12 <1 <1 反-2-辛烯-1-醇 2-Octen-1-ol, (E)- MS 1627.76 − 20 6.12±1.45 <1 3-甲基-1-丁醇 1-Butanol, 3-methyl- MS、LRI 1204.76 1206 1000 97.44±2.21 59.34±7.32 2-乙基己醇 2-Ethylhexanol MS、LRI 300 7.46±1.02 <1 3-辛酮 3-Octanone MS、LRI 1253.72 1251 50.2 1.79±0.66 <1 酮类 3-羟基-2-丁酮 2-Butanone, 3-hydroxy- MS、LRI 1292.39 1286 800 362.49±12.54 326.96±8.29 <1 <1 2-甲基-3-辛酮 Acetoin MS、LRI 1321.71 1323 850 362.49±3.25 4.77±1.04 <1 <1 3,5-辛二烯酮 3,5-Octadien-2-one MS、LRI 1511.36 1517 150 38.80±3.74 813.22±11.86 <1 <1 2,3-辛二酮 2,3-Octanedione MS、LRI 1319.91 1323 32.65±0.87 2.09±0.96 <1 <1 <1 苯乙醇 Phenethyl alcohol MS、LRI 5.60±1.59 <1 乙酸 Acetic acid MS、LRI 1441.33 1442 60 119.97±3.74 7.76±1.19 <1 <1 己酸乙酯 Ethyl caproate MS、LRI 1232.22 1232 5 18.78 9.77±1.85 6.95 3.60 其他 己酸甲酯 Methyl caproate MS、LRI 1186.25 1187 70 107.16±2.04 0.73±0.18 1.54 <1 辛酸甲酯 Methyl octanoate MS、LRI 1390.84 1392 20.41±1.21 3.55±1.57 0.89±0.13 <1 <1 <1 异戊酸 Butanoic acid, 3-methyl- MS、LRI 1669.40 1671 60 9.73±1.22 32.24±2.70 <1 <1 己酸 Hexanoic acid MS、LRI 1855 3.5/60 16.22±2.34 <1 <1 柠檬烯 D-Limonene MS、LRI 1193.7 1198 10 45.71±4.57 24.02±3.32 2.68±0.93 4.57 2.4 <1 4-甲基噻唑 4-Methylthiazole MS 1277.65 1279 20.23±1.08 6.13±0.77 1.80±0.02 <1 <1 <1 -
[1] 叶元土, 郭建林, 萧培珍, 等. 养殖武昌鱼体色与鳞片黑色素细胞初步观察[J]. 饲料工业,2006(22):25−27. [YE Y T, GUO J L, XIAO P Z, et al. Preliminary observation on body color and scale melanocytes of cultured Wuchang fish[J]. Feed Industry,2006(22):25−27. YE Y T, GUO J L, XIAO P Z, et al. Preliminary observation on body color and scale melanocytes of cultured Wuchang fish[J]. Feed Industry, 2006(22): 25-27.
[2] 林剑军, 赵文红, 刘巧瑜, 等. 脂质水解氧化对干腌鱼制品风味影响的研究进展[J]. 食品工业,2021,42(9):206−210. [LIN J J, ZHAO W H, LIU Q Y, et al. Research progress on the effect of lipid hydrolysis and oxidation on the flavor of dried salted fish products[J]. Food Industry,2021,42(9):206−210. LIN J J, ZHAO W H, LIU Q Y, et al. Research progress on the effect of lipid hydrolysis and oxidation on the flavor of dried salted fish products [J]. Food Industry, 2021, 42(9): 206-210.
[3] 郭雅. 不同腌制工艺对风干鳊鱼品质影响研究[D]. 南京: 南京师范大学, 2016 GUO Y. Study on the effect of different pickling techniques on the quality of air-dried bream[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Normal University, 2016.
[4] 张进杰. 中国南方传统腊鱼加工、品质及安全性研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2012 ZHANG J J. Research on processing, quality and safety of traditional cured fish in southern China[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2012.
[5] 顾赛麒, 周洪鑫, 郑皓铭, 等. 干制方式对腌腊草鱼脂肪氧化和挥发性风味成分的影响[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(21):1−10. [GU S Q, ZHOU H X, ZHENG H M, et al. Effects of drying methods on fat oxidation and volatile flavor components of pickled grass carp[J]. Food Science,2018,39(21):1−10. GU S Q, ZHOU H X, ZHENG H M, et al. Effects of drying methods on fat oxidation and volatile flavor components of pickled grass carp [J]. Food Science, 2018, 39(21): 1-10.
[6] WANG M, WANG M, HUYAN Z, et al. Investigation of the effects of lights, temperatures and packaging materials on the virgin rapeseed oil flavors during storage[J]. Food Science and Technology, 2022, 157.
[7] ZHAO S, NIU C, YANG X, et al. Roles of sunlight exposure on chemosensory characteristic of broad bean paste by untargeted profiling of volatile flavors and multivariate statistical analysis[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,381:132115. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132115
[8] FOLCH J, LEES M, STANL S G H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,1957,226(1):497−509. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(18)64849-5
[9] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.227-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中过氧化值的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. The National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China GB 5009.227-2016 National Food Safety Standard-Determination of peroxide value in foods[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016.
[10] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.229-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中酸价的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. The National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China GB 5009.229-2016 National Food Safety Standard-Determination of acid value in foods[S]. Beijing: China Standards Publishing House, 2016.
[11] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 24304-2009 食品安全国家标准 动物油脂 茴香胺值的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009. The National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China GB 24304-2009 National Food Safety Standard for Animal Fats-Determination of anisidine value[S]. Beijing: China Standards Publishing House, 2009.
[12] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GBT 22500-2008 食品安全国家标准 动物油脂吸光度的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. The National Health and Family Planning Com-mission of the People's Republic of China GBT 22500-2008 National Food Safety Standard-Determination of absorbance of animal fat[S]. Beijing: China Standards Publishing House, 2008.
[13] 韩瑞阳, 蓝芳, 梁宏, 等. 正丁醇常数法快速测定煎炸油脂中羰基价[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2014,5(11):3501−3508. [HAN R Y, LAN F, LIANG H, et al. Rapid determination of carbonyl valence in frying oil by n-butanol constant method[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection,2014,5(11):3501−3508. HAN R Y, LAN F, LIANG H, et al. Rapid determination of carbonyl valence in frying oil by n-butanol constant method[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality Inspection, 2014, 5(11): 3501-3508. .
[14] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.168-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中脂肪酸的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016. The National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China GB 5009.168-2016 National Food Safety Standard-Determination of fatty acids in foods[S] Beijing: China Standards Publishing House, 2016.
[15] KALUZNY M A, DUNCAN L A, MERRITT M V, et al. Rapid separation of lipid classes in high yield and purity using bonded phase columns[J]. Journal of Lipid Research,1985,26(1):135−140. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2275(20)34412-6
[16] 王未君, 郑畅, 杨博, 等. 膨爆预处理对三种菜籽油品质及挥发性风味成分的影响[J]. 中国油料作物学报, 2022, 443): 659−666. DOI: 10.19802/j.issn.1007-9084.2021122. WANG W J, ZHENG C, YANG B, et al. Effects of expansion pretreatment on the quality and volatile flavor components of three kinds of rapeseed oils [J]. Chinese Journal of Oil Crops, 2022, 44(3): 659−666. DOI: 10.19802/j.issn.1007-9084.2021122.
[17] 陈方雪, 周明珠, 邓祎, 等. 电子束辐照处理对鮰鱼冷藏期间品质的影响[J]. 肉类研究,2021,35(6):57−62. [CHEN F X, ZHOU M Z, DENG Y, et al. Effects of electron beam irradiation on the quality of channel catfish during refrigeration[J]. Meat Research,2021,35(6):57−62. CHEN F X, ZHOU M Z, DENG Y, et al. Effects of electron beam irradiation on the quality of channel catfish during refrigeration [J]. Meat Research, 2021, 35(6): 57-62.
[18] 顾赛麒, 唐锦晶, 周绪霞, 等. 腌腊鱼传统日晒干制过程中品质变化与香气形成[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(17):36−44. [GU S Q, TANG J J, ZHOU X X, et al. Quality change and aroma formation of cured fish during traditional sun drying[J]. Food Science,2019,40(17):36−44. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180716-201 GU S Q, TANG J J, ZHOU X X, et al. Quality change and aroma formation of cured fish during traditional sun drying[J]. Food Science, 2019, 40(17): 36-44. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180716-201
[19] The LRI and odor database[DB/OL]. ( 2004-11-19) . http: / /www. odour. org. uk/.
[20] TAN F L, WANG P, TIAN H L, et al. Characterization of key aroma compounds in flat peach juice based on gas chromatography-mass spectrometry-olfactometry (GC-MS-O), odor activity value (OAV), aroma recombination, and omission experiments[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,366(PP):130604−130604.
[21] CZERNER M, MABEL C T, MARIAI Y. Ripening of salted anchovy (Engraulis anchoita): development of lipid oxidation, colour and other sensorial characteristics[J]. Journal of the Science of Food & Agriculture,2011,91(4):609−615.
[22] WANG X Y, XIE J, CHEN X J. Differences in lipid composition of Bigeye tuna (Thunnus obesus) during storage at 0 ℃ and 4 ℃[J]. Food Research International,2021,143:110233. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110233
[23] 周胜强. 油脂氧化酸败的主要诱因——光氧化[J]. 四川粮油科技,2003(2):28−30. [ZHOU Shengqiang. The main cause of oxidative rancidity of fats and oils——photooxidation[J]. Sichuan Cereals and Oils Science and Technology,2003(2):28−30. ZHOU Shengqiang. The main cause of oxidative rancidity of fats and oils——photooxidation[J]. Sichuan Cereals and Oils Science and Technology, 2003(2): 28-30.
[24] 顾赛麒, 鲍嵘斌, 冯媛, 等. 肉类和水产制品脂质光氧化机制及其影响因素[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(24):271−278. [GU S Q, BAO R B, FENG Y, et al. Mechanism and influencing factors of lipid photooxidation in meat and aquatic products[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2021,47(24):271−278. GU S Q, BAO R B, FENG Y, et al. Mechanism and influencing factors of lipid photooxidation in meat and aquatic products[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry, 2021, 47(24): 271-278.
[25] GUO X, WANG Y, LU S, et al. Changes in proteolysis, protein oxidation, flavor, color and texture of dry-cured mutton ham during storage[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021(8):111860.
[26] TONGNUANCHAN P, BENJAKUL S, PRODPRAN T. Roles of lipid oxidation and pH on properties and yellow discolouration during storage of film from red tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus) muscle protein[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2011,25(3):426−433. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2010.07.013
[27] ZHAO D, HU J, CHEN W. Analysis of the relationship between microorganisms and flavor development in dry-cured grass carp by high-throughput sequencing, volatile flavor analysis and metabolomics[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,368:130889. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130889
[28] WONG K W. Clinical efficacy of n-3 fatty acid supplementation in patients with asthma[J]. Journal of the American Dietetic Association,2005,105(1):98−105. doi: 10.1016/j.jada.2004.10.009
[29] QI Z, YDA B, SGA B, et al. Identification of changes in volatile compounds in dry-cured fish during storage using HS-GC-IMS[J]. Food Research International,2020,137:107339.
[30] LOPEZ P M, PEREZ S C, FRANCO D, et al. Molecular insight into taste and aroma of sliced dry-cured ham induced by protein degradation undergone high-pressure conditions[J]. Food Research International,2019,122(Aug.):635−642.
[31] MORETTI V M, VASCONI M, CAPRINO F, et al. Fatty acid profiles and volatile compounds formation during processing and ripening of a traditional salted dry fish product[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2016,41(5):13133.
[32] 吴燕燕, 游刚, 李来好, 等. 低盐乳酸菌法与传统法腌干鱼制品的风味比较[J]. 水产学报,2014,38(4):600−611. [WU Y Y, YOU G, LI L H, et al. Comparison of flavor of dried fish products cured by low-salt lactic acid bacteria method and traditional method[J]. Journal of Fisheries,2014,38(4):600−611. WU Y Y, YOU G, LI L H, et al. Comparison of flavor of dried fish products cured by low-salt lactic acid bacteria method and traditional method[J]. Journal of Fisheries, 2014, 38(4): 600-611.
[33] MAZHAR S, KILCAWLEY K N, HILL C, et al. A systems-wide analysis of proteolytic and lipolytic pathways uncovers the flavor-forming potential of the gram-positive bacterium Macrococcus caseolyticus subsp. caseolyticus[J]. Frontiers in Microbiology,2020(11):1533. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.01533
[34] FLORES M. Understanding the implications of current health trends on the aroma of wet and dry cured meat products[J]. Meat Science,2018,144:53−61. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2018.04.016
[35] XU Y, LI L, REGENSTEIN J M, et al. The contribution of autochthonous microflora on free fatty acids release and flavor development in low-salt fermented fish[J]. Food Chemistry, 2018: S030881461830390X.
[36] MANTANA B, KANOK O I, KEITH R C. Characterization of potent odorants in Thai chempedak fruit (Artocarpus integer Merr. ), an exotic fruit of Southeast Asia[J]. Food Research International,2014,66:388−395. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2014.10.004
[37] 李璇, 邓尚贵, 张宾, 等. 基于电子鼻的竹荚鱼肉鲜度及品质的评价[J]. 浙江海洋学院学报(自然科学版),2012,31(5):384−388. [LI X, DENG S G, ZHANG B, et al. Evaluation of freshness and quality of horse mackerel meat based on electronic nose[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science Edition),2012,31(5):384−388. LI X, DENG S G, ZHANG B, et al. Evaluation of freshness and quality of horse mackerel meat based on electronic nose [J]. Journal of Zhejiang Ocean University (Natural Science Edition), 2012, 31(5): 384-388.
[38] LOVE J D, PEARSON A M. Lipid oxidation in meat and meat products—A review[J]. Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society,1971,48(10):547−549. doi: 10.1007/BF02544559
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 汪吉鹏,朱滕滕,刘璐,马铖,魏晓博,刘慧燕,方海田. λ-Red重组技术结合复合诱变提高大肠杆菌L-异亮氨酸合成能力. 食品工业科技. 2025(02): 167-174 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 戴一佳,赵亮. 益生菌对发酵乳品质影响的研究进展. 食品工业科技. 2024(08): 388-396 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



