Effect of Fatty Acid Unsaturation on Gel Properties of Hairtail Myosin
-
摘要: 为了研究脂肪酸不饱和度对肌球蛋白凝胶特性的影响,分析了添加四种不同饱和度的脂肪酸(硬脂酸、油酸、亚油酸和α-亚麻酸)后,带鱼肌球蛋白凝胶强度、持水性、化学作用力、流变特性、凝胶电泳、蛋白质二级结构等指标的变化规律。结果表明,肌球蛋白的凝胶强度和持水性会随着脂肪酸不饱和度的增加,呈先升高后降低的趋势,其中肌球蛋白-亚油酸复合体系的凝胶强度和持水性最高,与对照组相比分别提高了59.73%和15.73%。流变和电泳图谱结果显示,添加脂肪酸后肌球蛋白的储能模量(G')和耗能模量(G'')均高于对照组,且随着脂肪酸不饱和度的增加呈先增加后降低的趋势,并在肌球蛋白-亚油酸组达到最大值,而蛋白组成无显著性变化。红外光谱结果显示,脂肪酸不饱和度对肌球蛋白分子骨架没有明显影响,但硬脂酸、油酸和亚油酸会促使肌球蛋白构象朝不规则方向转变。综上,脂肪酸不饱和度对肌球蛋白的凝胶特性具有显著性影响,其中亚油酸改善带鱼肌球蛋白凝胶性能的效果最好。Abstract: In order to investigate effects of fatty acid unsaturation on the gel properties of myosin, four kinds of fatty acids (stearic acid, oleic acid, linoleic acid, and α-linolenic acid) with different saturation was added into hairtail myosin. The changes of gel strength, water holding capacity, chemical forces, rheological properties, gel electrophoresis and protein secondary structure of myosin were analyzed. The results showed that gel strength and water holding capacity of myosin increased first and then decreased with the increasing of fatty acid unsaturation. The gel strength and water holding capacity of myosin-linoleic acid composite system were the highest, increasing by 59.73% and 15.73% compared with control group, respectively. The results of the rheological and electropherogram indicated that the storage modulus (G') and loss modulus (G'') of myosin containing fatty acids were higher than that of control group. The G' and G'' increased first and then decreased with the increasing of fatty acid unsaturation, and reached the maximum value in the myosin-linoleic acid group. However, there was no significant change in protein composition among all the groups. Infrared spectroscopy showed that the unsaturation of fatty acid had no obvious effect on the molecular backbone of myosin, but stearic acid, oleic acid, and linoleic acid promoted the conformation transform of myosin to irregular direction. In summary, fatty acid unsaturation had a significant effect on the gel properties of myosin, and linoleic acid was the best at improving the gel properties of hairtail myosin.
-
Keywords:
- fatty acid /
- myosin /
- gel properties /
- protein structure /
- linoleic acid
-
鱼体经过采肉、漂洗、精滤、脱水,搅拌之后得到的肌原纤维蛋白浓缩物称为鱼糜,可进一步加工成各种各样风味独特、富有弹性的鱼糜制品[1]。鱼糜制品具有独特的质构和丰富的营养价值,已成为我国水产品资源利用中重要的产品之一。然而,在鱼糜加工的漂洗环节,鱼肉本身富含的多不饱和脂肪酸将被去除,造成鱼肉营养价值的流失[2]。添加外源油脂可提升鱼糜制品的营养价值,改善其感官特性,为提升鱼糜制品的经济价值、进行鱼糜产品创新和开拓更大的鱼糜制品市场提供一定的理论依据。
不同脂质对鱼糜制品凝胶特性的影响不尽相同。例如,添加猪油可提升鱼糜制品的质构和风味[3]。亚麻籽油、海藻油、鲱鱼油、磷虾油可改善鱼糜蛋白的流变特性,但对鱼糜凝胶强度无提升作用[4]。添加油茶籽油可提高白菇鱼鱼糜的凝胶品质[5-6]。Mi等[7]研究也发现紫苏油可显著提高草鱼鱼糜凝胶的白度,但对鱼糜凝胶特性有负面影响。目前的研究主要集中在油脂添加量和种类对鱼糜凝胶特性、流变特性和微观结构等方面的影响。然而,不同脂质中脂肪酸的含量和种类千差万别,脂肪酸不饱和度对鱼糜凝胶特性的影响尚未见报道,影响机理也有待于进一步研究。
肌球蛋白(myosin,MS)是鱼糜凝胶形成过程中最为关键的蛋白,其在加热过程中发生变性后,暴露的活性基团间发生交联作用进而形成凝胶网络结构[8-9]。研究表明,脂质的加入破坏了鱼糜蛋白质的构象,使得疏水残基暴露出来,而疏水残基的暴露和脂质的添加会促进蛋白之间的相互作用,使蛋白之间形成更加致密的凝胶网络结构[5]。脂肪酸的不饱和度会对脂肪酸分子结构、稳定性和功能特性有显著影响。因此,比较脂肪酸不饱和度对鱼肌球蛋白凝胶特性的影响对新型鱼糜制品的开发具有重要意义。
带鱼(Trichiurus haumela)分布广泛,是我国主要的海产经济鱼类,其年捕捞量正逐年增加[10]。目前带鱼捕捞后大多直接销售或加工成冷冻品,而少部分的带鱼用于制备鱼糜,以提高带鱼的加工利用率,但是研究表明带鱼鱼糜的色泽、凝胶特性等品质均有待改善[11]。因此,本文以带鱼肌球蛋白为研究对象,分析不同不饱和度的脂肪酸对带鱼肌球蛋白凝胶强度、持水性、流变学特性、化学作用力、蛋白质二级结构及分子量分布的影响,探讨脂肪酸不饱和度对肌球蛋白凝胶特性的影响机制,以期为带鱼深加工提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
冰鲜带鱼 锦州市科技路市场;硬脂酸(stearic acid,SA,C18:0)、油酸(oleic acid,OA,C18:1)、亚油酸(linoleic acid,LA,C18:2)、α-亚麻酸(α-linolenic acid,ALA,C18:3) 西格玛奥德里奇(上海)贸易有限公司,纯度≥98%;盐酸、醋酸镁、尿素、三磷酸腺苷二纳(ATP-Na2)、三羟甲基氨基甲烷(Tris)、十二烷基硫酸钠(SDS)等 均为分析纯。
UV-2550紫外可见光分光光度计 岛津仪器(苏州)有限公司;TA.XT Plus质构仪 Stable micro systems公司;Mini protean 3凝胶电泳仪 美国Bio-Rad公司;Discovery DHR-1流变仪 美国TA公司;Varian640-IR红外光谱仪 德国瓦瑞安公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 肌球蛋白的提取
参考Cao等[12]的方法并稍作修改。带鱼背部肌肉经绞肉机破碎后,与8倍体积含0.1 mol/L KCl和20 mmol/L的Tris-HCl缓冲液(pH7.5)混合,9000 r/min下均质1 min。均质混合物于4 ℃下静置15 min,离心10 min(8000 r/min,4 ℃),取沉淀物,加入3倍体积的Tris-HCl缓冲液(pH6.8,含0.45 mol/L KCl、5 mmol/L β-巯基乙醇、0.2 mol/L Mg(CH3COO)2、1 mmol/L乙二醇(2-氨基乙基醚)双四乙酸和20 mmol/L Tris),加入ATP-Na2,控制最终浓度为10 mmol/L。4 ℃静置90 min,保持同样温度下11000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液,加入3倍体积的1 mmol/L KHCO3。4 ℃放置15 min,离心20 min(11000 r/min,4 ℃),取沉淀物,加入2.5倍体积的Tris-HCl缓冲液(pH7.5,含0.5 mol/L KCl、5 mmol/L β-巯基乙醇和20 mmol/l Tris)。4 ℃放置10 min,再加入3倍体积的1 mmol/L KHCO3并加入MgCl2调整最终浓度为10 mmol/L。置于4 ℃下过夜后,离心20 min(10000 r/min,4 ℃),沉淀物加入Tris-HCl缓冲液(pH7.5,0.6 mol/L NaCl和20 mmol/L)中,即为肌球蛋白溶液,采用Lowry法[13]确定该肌球蛋白质量浓度。
1.2.2 肌球蛋白-脂肪酸混合凝胶的制备
将提取的肌球蛋白用Tris-HCl缓冲液(pH7.5)调整至40 mg/mL,以溶液中蛋白质量为标准分别添加0.5%的硬脂酸、油酸、亚油酸和α-亚麻酸,制成肌球蛋白-脂肪酸溶胶。再分装至高度为25 mm凝胶小瓶中,40 ℃水浴加热30 min,90 ℃加热20 min,降温后于4 ℃下放置过夜,制备成肌球蛋白-脂肪酸凝胶[14]。凝胶样品分别标记为MS、MS+SA、MS+OA、MS+LA和MS+ALA。
1.2.3 凝胶强度的测定
将凝胶样品放在室温下(25~30 ℃)平衡30 min,从凝胶小瓶中取出,用质构仪测定凝胶样品的破断力和凹陷距离。选用P/5S球形金属探头,测试速度:1 mm/s,形变量:30%,触发力:7.5 g[15]。
1.2.4 持水性的测定
称取小块(3 g)凝胶样品(W1),用双层滤纸包好后,置于50 mL离心管中,4 ℃,5000 r/min下离心15 min,离心结束后立即称量样品(W2)。凝胶持水性按下式计算[16]:
持水性(%)=W2W1×100 1.2.5 流变学特性的测定
参考姜帅等[17]的方法并稍做修改。取适量肌球蛋白-脂肪酸溶胶置于载物台上,测试平行板直径为40 mm,设置狭缝间距0.55 mm,石蜡液封边。温度扫描条件:升温范围为20~80 ℃,升温速率为2 ℃/min,扫描频率为0.1 Hz,应变为2%,降温速率设置为4 ℃/min,降温范围为80~20 ℃。
1.2.6 化学作用力的测定
称取3 g的凝胶样品,分别加入15 mL的0.05 mol/L NaCl(A)、0.6 mol/L NaCl(B)、0.6 mol/L NaCl+1.5 mol/L尿素(C)、0.6 mol/L NaCl+8 mol/L尿素(D),高速匀浆1 min,4 ℃静置1 h,10000 r/min离心15 min,取上清液,用双缩脲法测定蛋白浓度。以各溶液(A液、B液、C液、D液)蛋白含量差值计算得到化学作用力[18]。
1.2.7 蛋白质二级结构的测定
将冷冻干燥后的凝胶样品与溴化钾粉末以质量比1:50混合,置于玛瑙研钵中研磨均匀,使用红外光谱仪进行扫描,扫描波数范围为400~4000 cm−1。
1.2.8 SDS-PAGE分析
参考Mi等[19]的方法并稍做修改。称取凝胶样品3 g,与27 mL 5% SDS溶液混合,高速均质1 min,经85 ℃水浴加热1 h后自然冷却。10000 r/min离心8 min,取上清液。调节蛋白浓度,按照1:1比例添加上样缓冲液,煮沸5 min。其中浓缩胶浓度为4%,分离胶浓度为12%。上样量10 μL,先将电压设定为80 V,待样品进入浓缩胶后,调整电压为120 V。电泳结束后用质量分数0.25%的考马斯亮蓝R-250染色40 min,立即使用脱色液(50%甲醇和10%冰乙酸)脱色至背景基本无色。使用Quantity One软件进行扫描拍照后分析。
1.3 数据处理
实验中所有分析重复两次,每次做3个平行测定(n=2×3),结果以平均值±标准差表示。数据使用SPSS 19.0软件进行分析,采用Duncan法多重比较,P<0.05表示差异显著,并用Origin 8.0作图。
2. 结果与分析
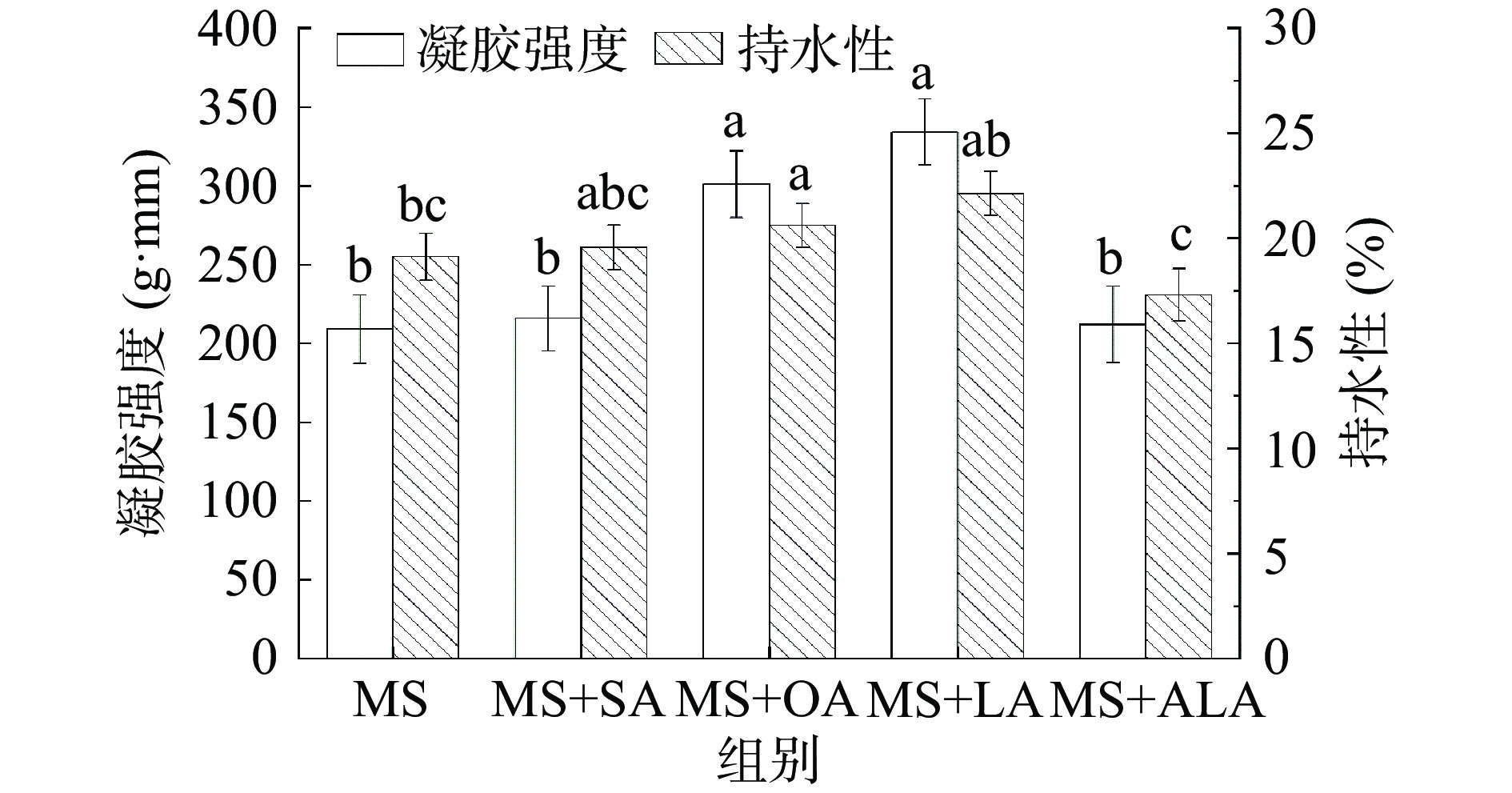
2.1 脂肪酸不饱和度对肌球蛋白凝胶强度和持水性的影响
脂肪酸不饱和度对带鱼肌球蛋白凝胶强度的影响如图1所示。随着脂肪酸不饱和度的增加,肌球蛋白的凝胶强度呈先升高后降低的趋势,添加亚油酸时,肌球蛋白的凝胶强度值最大,与肌球蛋白组相比提高了59.73%。脂肪酸颗粒可填充在肌原纤维蛋白凝胶结构的网络空隙中从而提高其凝胶强度[20]。贾丽娜等[21]对比猪油和玉米油对肌原纤维蛋白凝胶特性的影响时发现玉米油可以更好地填充于肌原纤维蛋白的凝胶网络结构中,从而提高蛋白-脂质复合体系的凝胶强度,这是因为玉米油中不饱和脂肪酸含量较高。高不饱和脂肪酸含量的玉米油在高速剪切下,能形成较小的乳液颗粒。添加α-亚麻酸时,肌球蛋白的凝胶强度显著降低(P<0.05,图1),这是由于α-亚麻酸的不饱和度大于硬脂酸、油酸和亚油酸,脂肪酸的不饱和度增加会使得其热稳定性降低,更易被氧化,而氧化后的脂肪酸会影响蛋白的凝胶特性[22]。李保玲等[23]研究表明氧化亚油酸浓度的增加会减少肌原纤维蛋白凝胶内部的疏水相互作用和氢键含量,从而降低肌原纤维蛋白的凝胶性能。
由图1可知,随着脂肪酸不饱和度的增加,肌球蛋白凝胶的持水性也随之升高,在肌球蛋白-亚油酸实验组达到最高,与对照组相比提升了15.73%。随着不饱和度的继续增加,肌球蛋白-α-亚麻酸组的持水性显著降低(P<0.05)。在热诱导凝胶形成过程中,部分变性蛋白的疏水区域可与分散的脂肪球结合,形成界面蛋白膜[24]。凝胶形成后,脂肪球被界面蛋白膜固定在凝胶网络内部,蛋白质凝胶网络基质的聚集度提高,脂肪和水分受限于物理屏障,流动性降低[23]。而α-亚麻酸由于不饱和度较高,过度的氧化可能影响了蛋白分子间二硫键的形成,从而使持水性下降[25]。
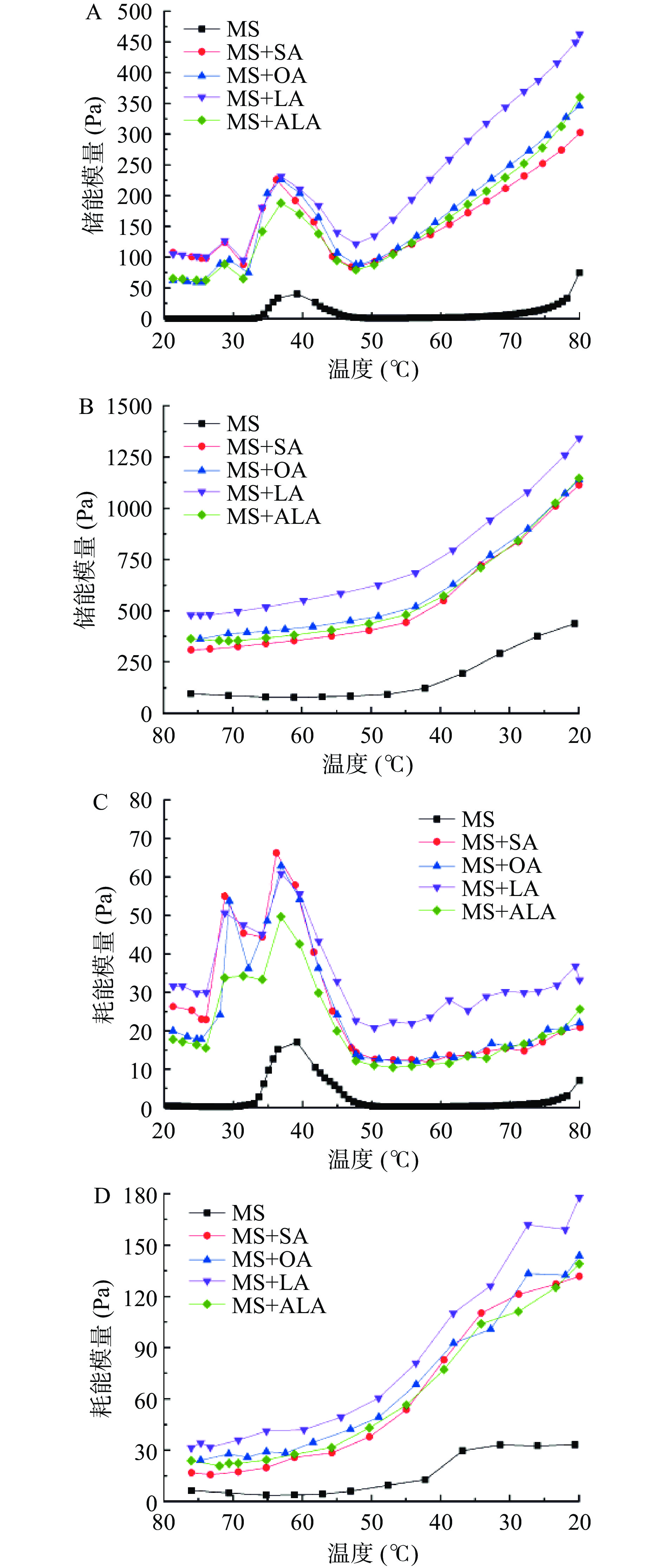
2.2 脂肪酸不饱和度对肌球蛋白流变学特性的影响
图2显示不同种类的脂肪酸对带鱼肌球蛋白凝胶形成和冷却过程中储能模量(G')和耗能模量(G'')的影响。由图2A和图2C可知,加热到33 ℃时,肌球蛋白头部通过氢键发生交联形成简单的凝胶网络,G'和G''开始上升。41 ℃后肌球蛋白G'和G''逐渐下降,这是因为肌球蛋白分子轻链解离使分子流动性增强或温度升高,蛋白网络结构被暂时破坏[8,26]。65 ℃后肌球蛋白发生变性,疏水相互作用、二硫键等化学键的生成使蛋白凝胶形成稳定的网络结构,G'和G''才稍微升高[8,16]。添加脂肪酸后,复合体系在加热过程中的G'和G''显著高于肌球蛋白组(P<0.05),尤其在加热后期,肌球蛋白-亚油酸复合体系的G'和G''明显高于其他组。另外,脂肪酸的加入使G'第一次上升的温度提前,说明脂肪酸参与到了凝胶网络的形成。Zhou等[6]也发现山茶籽油的添加可明显提高鲢鱼肌原纤维蛋白的G'和G''。在热诱导凝胶形成过程中,肌球蛋白受热变性,蛋白结构遭到破坏,疏水基团暴露,脂肪酸通过与肌球蛋白间的疏水相互作用填充到凝胶基质的网络空隙中[4]。
从图2B和图2D中可以看出,随着温度的降低,肌球蛋白-脂肪酸复合体系的G'和G''逐渐增加,说明降温过程中肌球蛋白凝胶的网络结构变得更加坚固,凝胶强度更高。与纯肌球蛋白组相比,不同不饱和度的脂肪酸均可提高肌球蛋白降温过程中的G'和G'',使肌球蛋白产生更高弹性的凝胶,其中肌球蛋白-亚油酸复合体系的G'和G''显著高于其他组(P<0.05),这与凝胶强度的结果相一致(图1)。
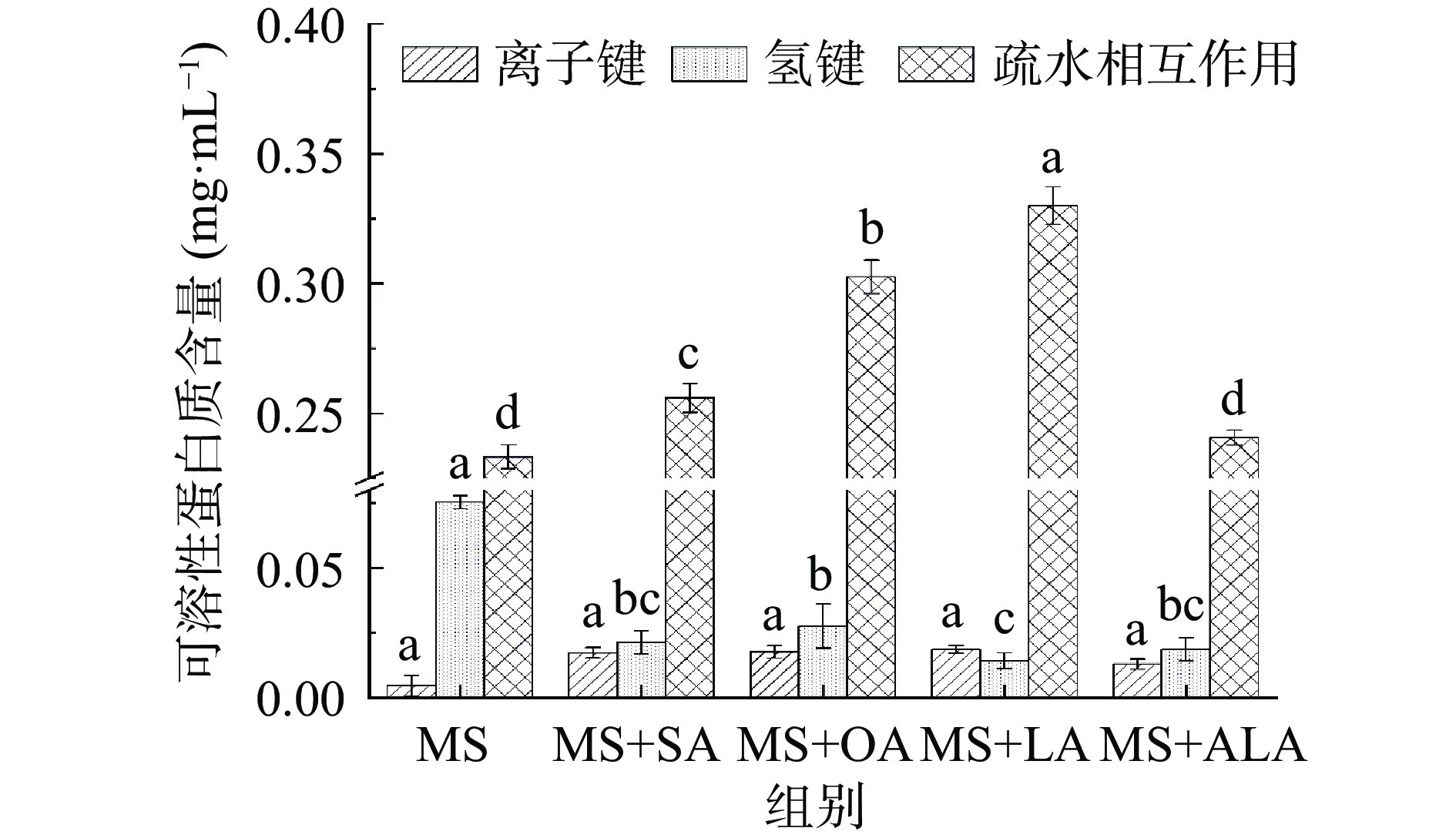
2.3 脂肪酸不饱和度对肌球蛋白凝胶化学作用力的影响
如图3所示,脂肪酸的添加可以提高肌球蛋白凝胶中离子键的含量,显著降低氢键的含量(P<0.05)。然而,脂肪酸的不饱和度对肌球蛋白凝胶中离子键和氢键含量影响不显著(P>0.05)。疏水相互作用在肌球蛋白凝胶中的贡献更大,且随着脂肪酸不饱和度的增加,疏水相互作用的含量呈先升高后降低的趋势。与肌球蛋白组相比,肌球蛋白-亚油酸复合体系中疏水相互作用的含量提高了41.45%。推测添加一定不饱和度的脂肪酸可以增强蛋白质分子间的疏水相互作用,而不饱和度过高会导致氧化程度更高,可能会影响蛋白质疏水基团的暴露,不利于蛋白质间的交联,从而影响肌球蛋白的凝胶强度。这也与凝胶强度的变化趋势相同(图1)。Zhou等[6]研究表明添加山茶籽油可以提高鱼糜凝胶中离子键的含量,增强疏水相互作用。然而,Yan等[27]发现随着鱼油浓度的升高,鱼糜凝胶中的疏水相互作用呈现下降的趋势,说明油滴的添加阻碍蛋白质的重排和展开,影响蛋白质的水合作用。这种矛盾的结果可能是由于添加的脂质中脂肪酸类型不同导致的,山茶籽油中富含亚油酸,而鱼油中富含多不饱和脂肪酸,可见脂肪酸不饱和度对鱼糜凝胶中的化学作用力的形成具有重要影响。
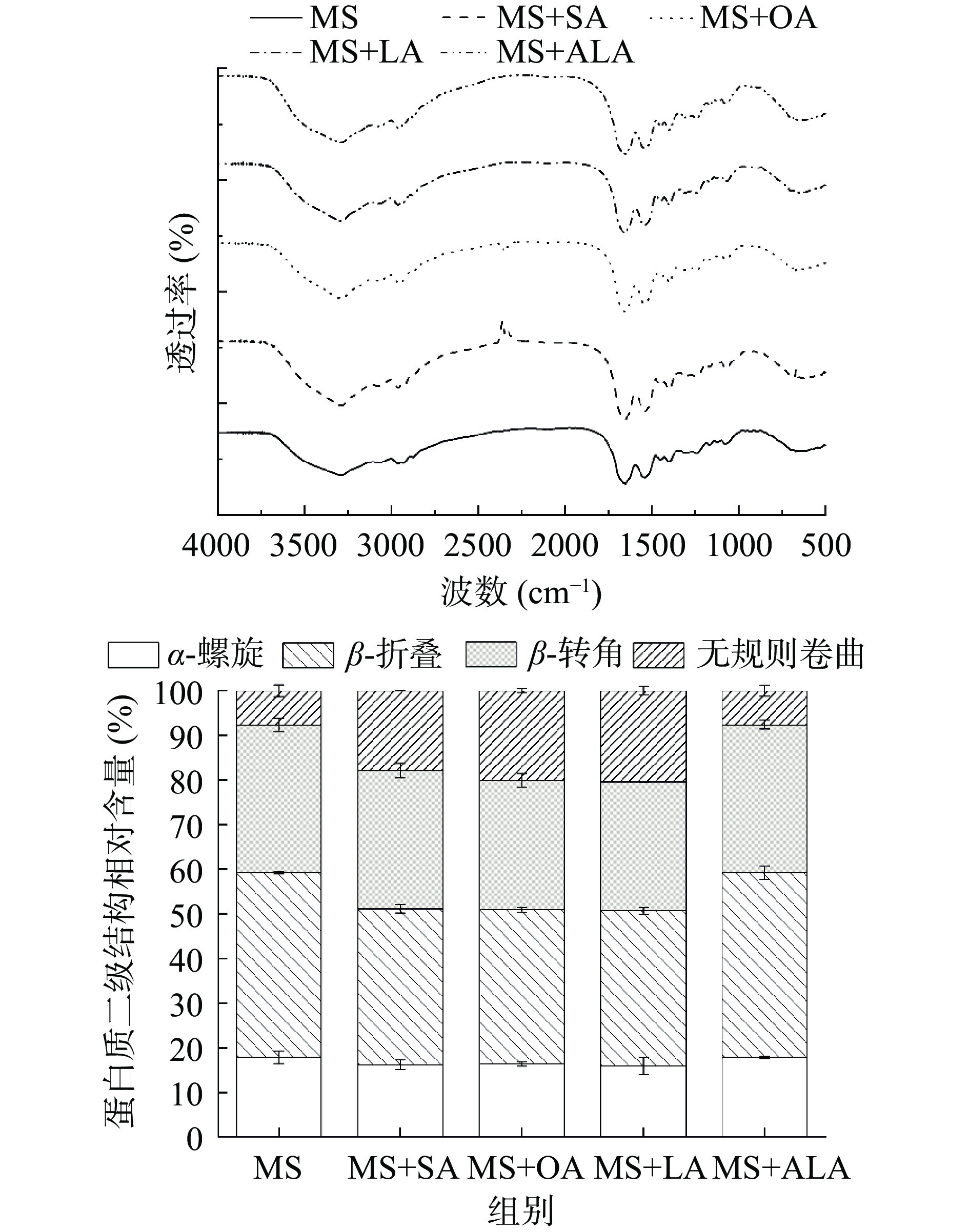
2.4 脂肪酸不饱和度对肌球蛋白凝胶蛋白二级结构的影响
傅里叶红外光谱是分析蛋白质二级结构的重要技术。由图4A可知,添加脂肪酸的肌球蛋白凝胶的特征吸收峰酰胺A带、酰胺Ⅰ、Ⅱ和Ⅲ带均没有明显变化,说明脂肪酸的加入没有改变肌球蛋白凝胶的功能基团。3290 cm−1处的峰随脂肪酸不饱和度的增加而逐渐变大,但与纯肌球蛋白相比,峰值变小,说明脂肪酸的添加降低了肌球蛋白凝胶间的氢键作用,这可能是由于脂肪酸液滴在肌球蛋白凝胶网络结构间隙中起到了填充作用,使结构更紧密,水分子以更小的状态分散在蛋白质-脂肪酸凝胶网络结构中,限制了水分的流动,降低水分子之间氢键的形成能力[5]。但随着脂肪酸不饱和度的增加,分子间氢键作用加强。
肌球蛋白二级结构的相对含量可由酰胺Ⅰ带计算得到,如图4B所示。添加硬脂酸、油酸和亚油酸后,肌球蛋白的α-螺旋、β-折叠和β-转角结构的相对含量均显著降低(P<0.05),而无规则卷曲结构的相对含量显著升高(P<0.05),说明脂肪酸的加入使肌球蛋白朝更加不规则的方向转变,有利于疏水集团的暴露,能够更好地与脂肪酸相互作用,从而增加其凝胶强度。Zhou等[6]指出鱼糜的凝胶强度与α-螺旋结构的含量呈负相关,与本实验结果一致。α-亚麻酸对肌球蛋白二级结构的相对含量无显著性影响(P>0.05,图4B),这说明不饱和度过高的脂肪酸可能由于其氧化程度的提高,影响了蛋白凝胶中α-螺旋结构的解旋,因此抑制了由于脂肪酸的添加引起的蛋白质去折叠、构象重排和交联,导致肌球蛋白-α-亚麻酸复合体系中蛋白二级结构的变化不显著[28]。
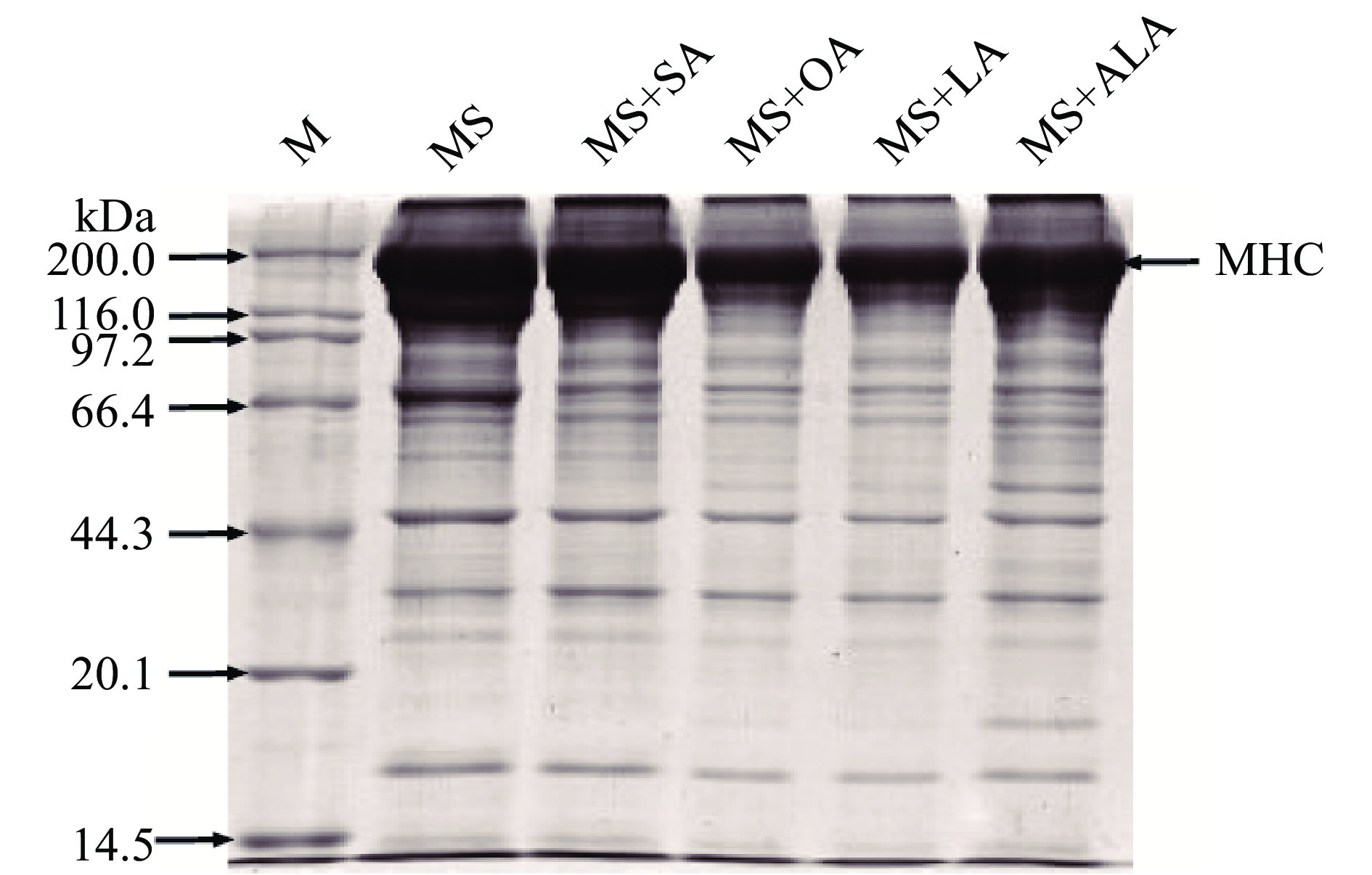
2.5 脂肪酸不饱和度对肌球蛋白凝胶SDS-PAGE的影响
图5表示肌球蛋白和肌球蛋白-脂肪酸复合凝胶的电泳图谱。可以看出,各组样品的条带组成基本相同,说明脂肪酸没有参与蛋白分子的交联,而是以被包埋的油滴形式参与到凝胶网络的形成当中,这与之前的研究报道一致[29]。Gani等[30]证明天然椰子油的添加对鱼糜蛋白的分子组成没有明显的影响。而肌球蛋白-亚麻酸复合凝聚的肌球蛋白重链(MHC)条带较浅,可能与其不饱和度较高,氧化程度高有一定程度的关系。鱼油在微波加热过程中易被氧化,脂质氧化产物通过非二硫共价键造成鱼糜中的MHC聚集[24,27]。
3. 结论
带鱼肌球蛋白的凝胶特性与所添加的脂肪酸的不饱和度密切相关。结果显示肌球蛋白的凝胶强度和持水性均随着脂肪酸不饱和度的增加先升高后降低,其中肌球蛋白-亚油酸复合体系的凝胶强度和持水性最高。脂肪酸的添加可显著改善肌球蛋白的流变特性,肌球蛋白-亚油酸组的G'和G''达到最大值。带鱼肌球蛋白凝胶的分子间作用力以疏水相互作用为主,脂肪酸的加入可提高疏水相互作用和离子键的含量,降低氢键的含量。脂肪酸以油滴形式包埋在凝胶网络结构中,对蛋白分子骨架没有明显影响,但硬脂酸、油酸和亚油酸的添加会促进肌球蛋白的α-螺旋、β-折叠和β-转角结构向无规则卷曲结构的转变。综合考虑亚油酸对带鱼肌球蛋白凝胶特性的改善效果最佳。以上结果为新型带鱼鱼糜制品的开发提供了理论依据。
-
-
[1] 张玉洁, 张金闯, 陈琼玲, 等. 鱼糜蛋白制品及其加工技术[J]. 中国食品学报,2022,22(1):389−400. [ZHANG Y J, ZHANG J C, CHEN Q L, et al. Surimi protein products and its processing technology[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2022,22(1):389−400. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2022.01.042 [2] 米红波, 王聪, 赵博, 等. 大豆油、亚麻籽油和紫苏籽油对草鱼鱼糜品质的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(18):60−64. [MI H B, WANG C, ZHAO B, et al. Effects of soybean flaxseed and perilla seed oils on the quality of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) surimi gels[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(18):60−64. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2017.18.012 [3] 仪淑敏, 李强, 张畅, 等. 油脂对鱼糜及畜禽肉糜制品的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(11):359−367. [YI S M, LI Q, ZHANG C, et al. The effect of oil on surimi and minced meat products of livestock and poultry[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2021,21(11):359−367. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2021.11.039 [4] PIETROWSKI B N, TAHERGORABI R, JACZYNSKI J. Dynamic rheology and thermal transitions of surimi seafood enhanced with ω-3-rich oils[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2011,27(2):384−389.
[5] 周绪霞, 姜珊, 顾赛麒, 等. 油茶籽油对鱼糜凝胶特性及凝胶结构的影响[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(9):27−33. [ZHOU X X, JIANG S, GU S Q, et al. Effect of camellia tea oil on properties and structure of surimi gel[J]. Food Science,2017,38(9):27−33. [6] ZHOU X X, JIANG S, ZHAO D D, et al. Changes in physicochemical properties and protein structure of surimi enhanced with camellia tea oil[J]. LWT - Food Science and Technology,2017,84:562−571. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2017.03.026
[7] MI H B, ZHAO B, WANG C, et al. Effect of 6-gingerol on physicochemical properties of grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) surimi fortified with perilla oil during refrigerated storage[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2017,97:4807−4814. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.8350
[8] 时浩楠, 张梦玲, 张晋, 等. 纳米鱼骨对鲢鱼肌球蛋白凝胶性能的影响[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(3):71−76. [SHI H N, ZHANG M L, ZHANG J, et al. Effect of nano-scaled fish bone on gel properties of silver carp myosin[J]. Food Science,2021,42(3):71−76. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200125-270 [9] MI H B, LIANG S Y, LI Z H, et al. Effect of corn starch on the structure, physicochemical and gel properties of hairtail (Trichiurus haumela) myosin[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2021,56(6):2843−2852.
[10] 农业部渔业局. 中国渔业统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2020. Ministry of Agriculture and Rural Affairs of the People's Republic of China. China fisheries statistics yearbook[M]. Beijing: China Agricultural Press, 2020.
[11] 陈燕婷, 林露, 高星, 等. 超高压对带鱼鱼糜凝胶特性及其肌原纤维蛋白结构的影响[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(21):115−120. [CHEN Y T, LIN L, GAO X, et al. Effect of ultra-high pressure on the myofibrillar protein structure and gel properties of hairtail surimi[J]. Food Science,2019,40(21):115−120. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181021-223 [12] CAO H, JIAO X, FAN D, et al. Microwave irradiation promotes aggregation behavior of myosin through conformation changes[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,96:11−19. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.05.002
[13] LOWRY O H, ROSEBROUGH N J, FARR A L, et al. Protein measurement with the Folinphenol reagent[J]. Journal of Biological Chemistry,1951,193(1):265−275. doi: 10.1016/S0021-9258(19)52451-6
[14] XU Y X, LV Y N, YIN Y M, et al. Improvement of the gel properties and flavor adsorption capacity of fish myosin upon yeast β-glucan incorporation[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,397:133766. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.133766
[15] 米红波, 李岩, 李政翰, 等. 木薯淀粉对栉孔扇贝闭壳肌凝胶特性的改善作用[J]. 食品科学技术学报,2020,38(3):102−110. [Mi H B, LI Y, LI Z H, et al. Improvement of cassava starch on gel properties of adductor muscle puree from Chlamys farreri[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2020,38(3):102−110. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6002.2020.03.013 [16] 米红波, 王聪, 苏情, 等. 变性淀粉对白鲢鱼鱼糜凝胶特性和蛋白构象的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2021,21(1):72−80. [MI H B, WANG C, SU Q, et al. Effect of modified starch on gel properties and protein conformation of surimi from silver carp[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2021,21(1):72−80. [17] 姜帅, 曹传爱, 康辉, 等. 燕麦β-葡聚糖对肌原纤维蛋白乳化和凝胶特性的影响[J]. 食品科学技术学报,2019,37(5):32−41. [JIANG S, CAO C A, KANG H, et al. Effects of oat β-glucan on emulsifying and gel properties of myofibrillar protein[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2019,37(5):32−41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6002.2019.05.005 [18] MI H B, LI Y, WANG C, et al. The interaction of starch-gums and their effect on gel properties and protein conformation of silver carp surimi[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2021,112:106290. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.106290
[19] MI H B, ZHAO Y M, LI Y, et al. Combining effect of soybean protein isolate and transglutaminase on the gel properties of Zhikong scallop (Chlamys farreri) adductor muscle[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2021,138:110727. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2020.110727
[20] 许帅强. 脂肪酸饱和度对猪肉盐溶性蛋白乳化特性及凝胶特性的影响[D]. 锦州: 渤海大学, 2019. XU S Q. Effect of fatty acid saturation on emulsifying properties and gel properties of salt-soluble protein in pork[D]. Jinzhou: Bohai University, 2019.
[21] 贾丽娜, 庞杰, 吴云辉, 等. 乳化油脂与罗非鱼肌原纤维蛋白复合凝胶质构性质的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2015,36(2):121−125. [JIA L N, PANG J, WU Y H, et al. Textural properties of lipid-tilapia myofibrillar protein composite gels[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2015,36(2):121−125. [22] 陆健, 黄卫宁, 冀聪伟, 等. 煎炸油热稳定性及氧化稳定性影响因素分析[J]. 农业机械,2012(9):47−50. [LU J, HUANG W N, JI C W, et al. Analysis of influencing factors of thermal stability and oxidation stability of frying oil[J]. Farm Machinery,2012(9):47−50. [23] 李保玲, 李颖, 朱振宝, 等. 氧化亚油酸对肌原纤维蛋白胶凝行为及热诱导凝胶体外消化率的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业, 2021, 47(19): 1-12. LI B L, LI Y, ZHU Z H, et al. Effect of oxidized linoleic acid on gelling behavior of myofibrillar protein and in vitro digestibility of the heat-induced gel[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries, 2021, 47(19): 1-12.
[24] ZHOU X X, CHEN H, LYU F, et al. Physicochemical properties and microstructure of fish myofibrillar protein-lipid composite gels: Effects of fat type and concentration[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2018,90:433−442.
[25] LIN W L, HAN Y X, LIU F F, et al. Effect of lipid on surimi gelation properties of the three major Chinese carp[J]. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2020,100(13):4671−4677. doi: 10.1002/jsfa.10414
[26] 梁雯雯, 杨天, 郭建, 等. 升温方式对鲢鱼肌球蛋白结构和理化性质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(21):24−31. [LIANG W W, YANG T, GUO T, et al. Effects of heating methods on the structure and physicochemical properties of silver carp myosin[J]. Food Science,2021,42(21):24−31. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20201012-086 [27] YAN B W, JIAO X D, ZHU H P, et al. Chemical interactions involved in microwave heat-induced surimi gel fortified with fish oil and its formation mechanism[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,105:105779. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.105779
[28] HAN Z Y, XU S Q, SUN J X, et al. Effects of fatty acid saturation degree on salt-soluble pork protein conformation and interfacial adsorption characteristics at the oil/water interface[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,113(4):106472.
[29] 王莉莎. 植物油与肌原纤维蛋白乳化复合凝胶的结构特性[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2019. WANG L S. Structural properties of vegetable oil and myofibrillar emulsified composite gel[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2019.
[30] GANI A, BENJAKUL S, NUTHONG P. Effect of virgin coconut oil on properties of surimi gel[J]. Journal of Food Science & Technology,2018,55(2):496−505.






 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



