Effect of Caragana korshinskii Kom. on Meat Quality of Adipose Tissue, Volatile Fatty Acids and the Microbiota in Gastrointestinal Tract for Tan Sheep
-
摘要: 为探索日粮中添加柠条影响瘤胃、结肠内微生物生成的挥发性脂肪酸水平,进而调节滩羊肉品质、脂肪组织中主要脂肪酸含量的作用,本研究选取12只四月龄滩羊母羔随机分为两组,NC组饲喂30%精料及70%苜蓿颗粒,CK组为10%柠条替代等量苜蓿。预饲期10 d,正试期60 d。饲喂期结束屠宰时取其背最长肌、股四头肌、皮下脂肪,瘤胃、结肠内容物,利用16S rRNA测序技术、气相色谱-质谱联用技术等对滩羊瘤胃、结肠内菌群、脂肪组织的脂肪酸含量及肌肉理化特性进行测定。结果表明,饲喂柠条可导致滩羊股四头肌的压榨损失有提高的趋势,系水力和熟肉率有所下降;但饱和脂肪酸有降低的趋势,不饱和脂肪酸有提高的趋势;皮下脂肪中的软脂酸含量显著降低(P<0.05);瘤胃内丁酸和结肠内乙酸的浓度显著降低(P<0.05),结肠内异丁酸和异戊酸等支链脂肪酸水平极显著提高(P<0.01)。斯皮尔曼相关性分析显示,瘤胃内5-7N15菌属和YRC22菌属均与丁酸含量趋向正相关,而结肠内密螺旋体属与乙酸含量趋向正相关,但与异丁酸含量趋向负相关(0.05<P<0.1);结肠内异丁酸含量与股四头肌的熟肉率、系水力和压榨损失分别呈高度负相关和正相关,乙酸亦与背最长肌pH呈负相关关系。综上,柠条部分替代苜蓿饲喂滩羊,可以提高脂肪组织中不饱和脂肪酸含量,可作为反刍动物的粗饲料加以开发利用。Abstract: To explore the effect of Caragana korshinskii Kom. (CK) on meat quality and the main fatty acids of adipose tissue, which were supposed to be modulated by the level of volatile fatty acids from the microbiota of rumen and colon in sheep, twelve Tan ewe lambs (4-month-old) were randomly divided into two groups, NC was fed with 30% concentrate and 70% alfalfa, while CK with 10% CK instead of equivalent alfalfa. After 10 days of pre-trial and 60 days of feeding trial, the lambs were slaughtered and sampled with M. longissimus dorsi, quadriceps femoris, subcutaneous fat, and the contents of rumen and colon collection. Then the analyzing was carried out aimed to determine the characters of meat physical and chemical properties as usual method, the microbiota of gastrointestinal tract by 16S rRNA sequencing, and fatty acid contents either from subcutaneous adipose tissue or from rumen and colon by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. The results showed that feeding CK to Tan sheep could tend to increase mill loss, decrease water holding capacity and cooked meat percentage of quadriceps femoris. It also had the tendency effect to decrease saturated fatty acid and increase unsaturated fatty acid content in the meat. Furthermore, feeding CK could decrease the content of palmitic acid in subcutaneous adipose tissue significantly (P<0.05). Besides, the concentrations of butyric acid in rumen and acetic acid in colon decreased significantly (P<0.05), while the levels of branched chain fatty acids such as iso-butyric acid and iso-valeric acid in colon increased significantly (P<0.01). Through correlation analysis by Spearman method, both 5-7N15 and YRC22 in rumen genera tended to positively correlated with butyric acid concentration, while Treponema in colon genera tended to positively correlated with acetic acid content, but negatively correlated with the level of iso-butyric acid (0.05<P<0.1). In colon, iso-butyric acid was high inversely and positively correlated with the cooked meat percentage, water holding capacity and mill loss of quadriceps femoris, and acetic acid was negatively correlated with the pH value of M. longissimus dorsi. In conclusion, feeding CK to Tan sheep with partly instead of alfalfa could improve unsaturated fatty acid contents of adipose tissue, and then it could be developed as ruminant forage for utilization.
-
Keywords:
- Caragana korshinskii Kom. /
- microbiota /
- amplicon sequencing /
- fatty acid metabolism /
- Tan sheep
-
随着我国经济发展,居民对膳食品质要求的逐步提高,牛羊肉需求量呈连年递增状态。近十年来,尽管饲养牛羊的存栏量、牛羊肉产量持续升高,仍无法完全满足牛羊肉的消费需求,牛羊肉进口量不断攀升[1]。西北地区是我国牛羊肉的主要生产基地,其农业结构主要包含灌溉农业、绿洲农业和畜牧业。但西北地区降水稀少、气候干旱、草原多为荒漠类型,饲草资源不足是制约家畜产业发展的主要因素之一。
自上世纪九十年代我国提出“粮食作物-经济作物-饲料作物”的三元种植结构并进行较大规模推广后,饲用玉米和苜蓿已占总饲草数量的90%以上,部分缓解了饲草资源的紧缺,促进了草食家畜产业的发展。但囿于土地资源和生产力限制,进一步提高饲草产量的潜力有限,而非常规饲草在我国西北地区种类繁多,如三叶草、苏丹草、沙葱、百脉根、柠条等,分布较广且具有地区特性,极具开发利用价值。柠条(Caragana korshinskii Kom.)是豆科锦鸡儿属灌木,主要生长于我国西北地区。由于具有耐寒、抗高温、保持深层土壤水分等较高的生态价值,通常被用作水土保持和植被恢复作物予以种植利用[2-3]。虽然柠条中粗蛋白、必需氨基酸和多酚化合物含量较高[4],当地农牧民也偶尔将其作为饲料使用,但关于柠条饲用价值的研究还相对较少。为数不多的研究表明,饲粮中含有10%的柠条可以显著提高滩羊肌肉中肌内脂肪含量[5];日粮中添加柠条,可以不同程度地提高肉猪、肉兔和白绒山羊的生长性能以及奶牛的乳脂肪含量[6]。本实验室研究显示,饲粮中的柠条可以通过调节瘤胃微生物群落影响瘤胃蛋白合成和挥发性脂肪酸(volatile fatty acids,VFAs)的含量,进而有效提高滩羊的饲料转化效率[7]。
在鲜肉供应中,肉品质是消费者最为关注的评价指标。随着营养科学的不断进步,对肉品质的评价除了肉色、系水力、熟肉率、肌内脂肪含量和pH等[8]传统指标之外,脂肪酸的健康价值不断受到重视,羊肉脂肪酸的组成情况也日益受到消费者的关注。摄入过高的饱和脂肪酸会导致人体胆固醇、甘油三酯等血脂升高[9],而不饱和脂肪酸则有利于人体健康[10]。反刍动物的瘤胃和肠道是产生和吸收VFAs的重要器官,产生的VFAs被血液运输至肌肉、脂肪等组织,合成不同的长链脂肪酸(long chain fatty acids,LCFAs)[11]。有报道显示,胃肠道微生物及其代谢产物影响畜禽的肉品质和脂肪酸的合成代谢[12]。因此,本研究拟通过添加10%的柠条替代日粮中苜蓿饲喂滩羊,对其肌肉、脂肪的理化特性,瘤胃、结肠微生物组成以及与VFAs含量进行评估和相关性分析,对柠条改善滩羊肌肉、脂肪品质的情况予以评估,为柠条作为反刍动物饲草的开发利用提供数据支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
12只四月龄滩羊母羔 购自宁夏自治区盐池县滩羊繁育中心;饲喂滩羊的精料 正大预制料(中国);苜蓿颗粒 甘肃民祥牧草有限公司(中国);柠条 宁夏当地柠条种植户(中国);实验所用乙醚 购自GENERAL-REAGENT(中国);无水乙醇 购自上海麦克林(中国);石油醚、实验用海砂、乙酰氯、甲醇、正己烷、碳酸钠 来源于国药集团化学试剂有限公司(中国);磷酸 购自德国CNW Technologies GmbH公司;氦气、乙酸、丙酸、丁酸、戊酸、异丁酸、异戊酸标准品 购自美国Sigma公司;粪便微生物DNA提取试剂盒(DP328) 购自北京天根生化科技有限公司(中国)。
CR400柯尼卡色度计 柯尼卡美能达(日本)、Testo 205 pH计 深圳德图仪表(中国);RH100系水力测定仪 广州润湖仪器(中国);BYSXT-06索氏提取器 上海秉越电子(中国);C-LM3B嫩度仪 东北农业大学(中国);7890A-7000B气相色谱-质谱联用仪、HP-INNOWAX毛细管柱(30 m×0.25 mm×0.25 μm) 安捷伦(美国)。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品采集
12只四月龄滩羊母羔(27.5±3.3 kg),随机分为数量相等的两组:NC组和CK组。NC组饲喂30%精料及70%苜蓿颗粒;CK组用10%柠条替代等量苜蓿。预饲期10 d,正试期60 d,每只羊单圈单栏饲养,每天07:00和16:00定时饲喂,自由采食和饮水。屠宰前24 h禁食禁水,测定个体空腹宰前活重;采用颈动脉放血方式屠宰,去皮、去除头蹄、内脏,留肾脏及周围脂肪与胴体一起称重,记为胴体重;胴体重与宰前活重的比值为屠宰率。胴体沿脊柱左右劈半,完整采集右侧胴体背最长肌和股四头肌,装入塑封袋后4 ℃保存,用于肉品质检测;于胴体背部12~13肋骨处采集皮下脂肪50 g,−20 ℃保存,用于脂肪组织中LCFAs的检测。采集瘤胃液并经四层纱布过滤后装入5 mL冻存管,−80 ℃保存;屠宰后使用无菌采样器取结肠内容物3 g,立即放入液氮,30 min后,转移至−80 ℃保存。
1.2.2 肉品质检测
依据本实验室之前文章描述的方法[13]对采集的背最长肌和股四头肌样品进行肉色、压榨损失率、系水力、滴水损失、含水量、肌内脂肪含量、剪切力、熟肉率和pH检测测定。
1.2.2.1 色度
根据色度计使用说明检测样品的亮度(L*)、红度(a*)和黄度(b*),每个样品检测5次,记录均值。
1.2.2.2 压榨损失率和系水力
用直径2.523 cm的圆形取样器对1 cm厚肉样取样并称重计为m1,将圆形肉样放于两组吸水滤纸(18层/组)间,使用系水力测定仪施加350 N(5 min)后,再次称重计为m2。
压榨损失(%)=m1−m2m1×100 (1) 系水力(%)=总含水量−(m1−m2)m1×100 (2) 1.2.2.3 滴水损失
采用吊袋法检测。将肉样于4℃贮存24 h,贮存前后分别称量样品重量,记为m3和m4。
滴水损失(%)=m3−m4m3×100 (3) 1.2.2.4 含水量和肌内脂肪含量
取5 g(m5)肉样切碎后和海砂、无水乙醇混合放入铝容器,105 ℃干燥4 h,冷却后称重计为m6。干燥后的样品移至索氏提取器,使用石油醚60 ℃提取6 h,溶剂蒸发后烧瓶继续在100 ℃干燥器中干燥1 h,冷却并称重计为m7,烧瓶称重计m8。
含水量(%)=m5−m6m5×100 (4) 肌内脂肪(%)=m7−m8m5×100 (5) 1.2.2.5 剪切力
沿肌纤维方向将肉样切成2 cm×2 cm×1 cm小块,依据说明使用嫩度仪对每个样品检测6次,记录均值。
1.2.2.6 熟肉率
取肉样50 g计m9,将温度计插至肉样中心,80 ℃水浴,当温度计显示70 ℃时取出冷却至室温并称重计m10。
熟肉率(%)=m10m9×100 (6) 1.2.2.7 pH
肉样于4 ℃静置排酸24 h后测定。
1.2.3 皮下脂肪组织中主要脂肪酸检测
利用气相色谱-质谱联用仪,对采集到的皮下脂肪组织进行硬脂酸、软脂酸、油酸、亚油酸和棕榈油酸含量的测定[13]。约0.1 g皮下脂肪,剪碎后放入20 mL容量的顶空瓶,加入正己烷2 mL、体积比1:10的乙酰氯-甲醇溶液4 mL。80 ℃水浴2 h,20 min平摇一次。冷却至室温后,加入7%的碳酸钠溶液5 mL并摇匀,3000×g离心5 min,吸取有机相,剩余的水相再重复以上步骤萃取一次。使用有机相滤纸(0.22 μmol/L)对得到的有机相进行过滤后,注入安捷伦HP-INNOWAX毛细管色谱柱检测其中的硬脂酸、软脂酸、油酸、亚油酸和棕榈油酸含量。使用氦气为载气(流速1.5 mL/min,不分流模式),保持60 ℃ 2 min后,5 ℃/min升至260 ℃,再升至300 ℃并保持5 min;质谱使用条件为电子轰击电离(EI)源,电子能量为70 eV,温度230 ℃;全幅扫描模式(扫描范围30~400 m/z)。
1.2.4 瘤胃液、结肠内容物中挥发性脂肪酸检测
用乙醚配制乙酸、丙酸、丁酸、戊酸、异丁酸、异戊酸标准品,制作12个浓度梯度标准品曲线。采集的瘤胃液、结肠内容物样品过滤稀释,稀释液1 mL加15%磷酸50 μL、75 μg/mL的内标溶液(异己酸)10 μL和乙醚140 μL,涡旋振荡1 min,4 ℃ 12000 r/min离心10 min,取上清[14]。以1.2.3相同条件进行气相色谱-质谱联用技术检测。
1.2.5 瘤胃液、结肠内容物中微生物检测
使用粪便微生物DNA提取试剂盒,依据使用说明提取瘤胃液、结肠内容物中微生物基因组DNA,利用细菌16S rRNA V3-V4区通用引物组(341F/805R)进行扩增。PCR扩增体系为:5×反应缓冲液、5×GC缓冲液各5 μL,2.5 mmol/L的dNTP 2 μL,10 μmol/L上下游引物各1 μL,Q5 DNA聚合酶0.25 μL,ddH2O 8.75 μL,提取的基因组DNA 2 μL(20 ng/μL),反应总量为25 μL。PCR扩增条件为:94 ℃ 3 min;94 ℃ 20 s、55 ℃ 30 s、72 ℃ 30 s 6个循环;94 ℃ 15 s、68 ℃ 15 s、72 ℃ 30 s反应30个循环;72 ℃ 5 min。终产物用Illumina HiSeq2500测序平台进行双端测序。
1.3 数据处理
所有数值均以平均数±标准差表示。利用IBM SPSS21对各检测指标等进行t-检验,P<0.05为存在显著差异,0.05<P<0.1认为两组间具有显著性差异趋向。使用R4.0.3的ropls软件包对挥发性脂肪酸含量进行正交偏最小二乘判别分析(OPLS-DA)。用QIIME1.9.1分析16S rRNA测序数据,使用LEfSe分析确定两组间具有统计学差异的胃肠道菌属。通过R4.0.3的psych软件包对肉品质与胃肠道内挥发性脂肪酸、皮下脂肪组织的脂肪酸与胃肠道内挥发性脂肪酸、胃肠道内挥发性脂肪酸与其中主要差异菌属进行斯皮尔曼(Spearman)相关性分析。
2. 结果与分析
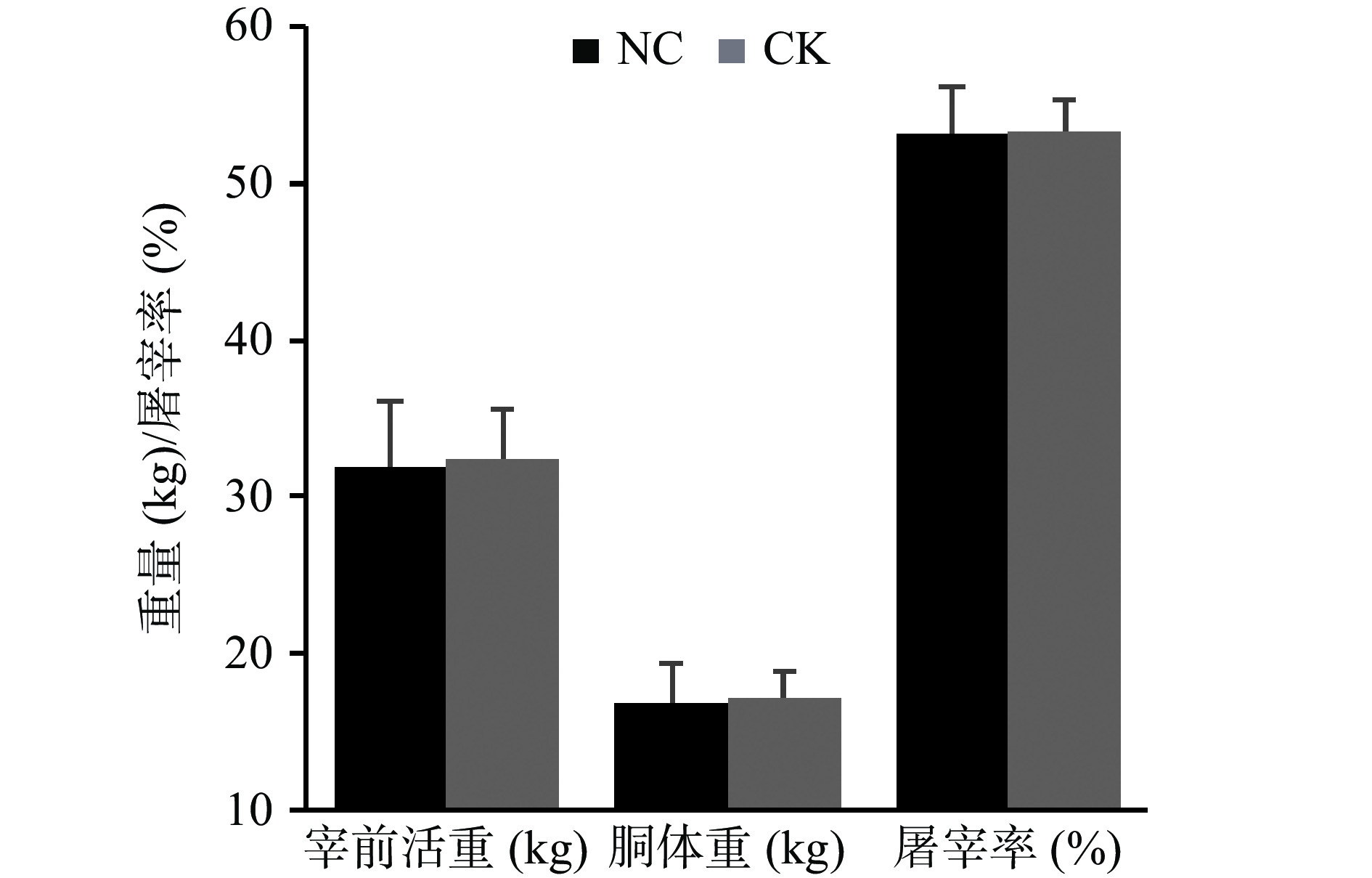
2.1 饲料中添加柠条对滩羊屠宰性状的影响
胴体的屠宰性状可以直观反映出家畜个体的生长性能。由图1可以看出,60 d正试期结束后,CK组滩羊的宰前活重、胴体重、屠宰率均略高于NC组,但未达到统计学差异显著水平(P>0.05)。该现象也出现在先前一些报道中,不论是6%、10%还是40%的柠条添加量对滩羊的生长性能均影响不大[15-16]。使用柠条部分替代苜蓿饲料,虽不能显著提高其生长性能,但由于柠条相比于苜蓿的售价低约34%~45%,有助于降低饲料的成本。
2.2 饲料中添加柠条对滩羊肉品质的影响
肉色的亮度(L*)、红度(a*)和黄度(b*)在两组滩羊的背最长肌和股四头肌间均无显著变化(P>0.05,表1)。压榨损失、系水力和熟肉率均是检测肌肉保水能力的指标,CK组的股四头肌压榨损失有提高的趋势,且CK组股四头肌的系水力和熟肉率也都有下降趋势,且背最长肌的含水量也略有提高的趋势。肌内脂肪是影响口感的重要因素之一,相比于NC组,CK组背最长肌和股四头肌的肌内脂肪含量均有所增加,但未达到显著水平(P>0.05)。从整体来看,柠条对股四头肌的影响高于背最长肌。
表 1 柠条对滩羊肉品质的影响Table 1. Effects of Caragana korshinskii Kom. on the meat quality of Tan sheep指标 背最长肌 股四头肌 对照组(NC组) 实验组(CK组) P值 对照组(NC组) 实验组(CK组) P值 亮度(L*) 40.11±1.94 39.80±1.42 0.78 42.42±1.71 42.35±2.03 0.96 红度(a*) 20.56±1.09 21.19±1.30 0.44 23.69±0.94 23.56±1.05 0.84 黄度(b*) 7.47±0.82 7.71±1.29 0.73 10.04±0.83 10.16±0.97 0.85 压榨损失(%) 32.96±2.02 34.28±2.81 0.42 25.90±2.43 29.51±2.99 0.07 系水力(%) 55.55±2.65 54.20±3.89 0.54 66.11±3.16 61.53±3.86 0.07 滴水损失(%) 1.09±0.11 1.12±0.30 0.84 0.78±0.21 0.93±0.14 0.22 含水量(%) 74.16±0.60 74.87±0.45 0.07 76.42±0.33 76.70±0.44 0.29 剪切力(N) 52.84±15.33 46.48±19.03 0.58 55.06±5.77 56.26±13.38 0.86 熟肉率(%) 86.25±1.63 84.31±1.98 0.13 84.76±0.98 80.70±2.80 0.02 肌内脂肪(%) 3.67±1.06 3.73±0.91 0.93 2.87±0.43 3.19±0.94 0.51 pH 5.73±0.04 5.78±0.07 0.20 5.84±0.03 5.91±0.06 0.03 由于营养水平、饲料配比、检测方法的不同,肉品质检测指标在柠条饲喂动物实验中的结果并不完全统一[17-18]。屠宰后的胴体因肌肉无氧糖酵解将导致乳酸积累而降低肌肉的pH,排酸则可以提升肉的嫩度和口感。24 h排酸后,CK组背最长肌和股四头肌的pH都高于NC组。也有研究表明,日粮中添加15%柠条或者柠条水提取物,可以降低绵羊背最长肌熟肉率,并显著提高24 h排酸后的背最长肌pH;此外,检测到柠条水提取物中多酚类化合物多达12种,含量高达40%[18]。日料中添加少量多酚(栗木单宁)饲喂湖羊公羔,也得到了相似的结果[19]。由此可见,柠条中的多酚可能是本实验中影响滩羊肉品质的主要化合物。
2.3 添加柠条对滩羊皮下脂肪组织中主要脂肪酸的影响
饱和脂肪酸包括硬脂酸、软脂酸等,过高的饱和脂肪酸摄入会导致机体胆固醇、甘油三酯等血脂的升高。不饱和脂肪酸包括油酸、亚油酸和棕榈油酸等,饮食中的不饱和脂肪酸对人体有重要的生理和保健功能。本研究表明,日粮中添加柠条,可以显著降低滩羊皮下脂肪中的软脂酸(P<0.05),并使饱和脂肪酸有降低的趋势。相较于NC组,CK组滩羊皮下脂肪中不饱和脂肪酸有提高趋势,其中,CK组中的油酸、亚油酸含量均有所升高,但未达到显著水平(P>0.05,表2)。
表 2 柠条对滩羊皮下脂肪中脂肪酸含量的影响Table 2. Effects of Caragana korshinskii Kom. on fatty acid content of subcutaneous fat in Tan sheep指标 对照组(NC组) 实验组(CK组) P值 饱和脂肪酸(%) 61.07±2.09 58.46±2.07 0.08 不饱和脂肪酸(%) 37.95±2.25 40.50±2.01 0.09 硬脂酸C18:0(%) 22.54±0.82 22.11±1.87 0.65 软脂酸C16:0(%) 27.80±1.28 25.14±1.23 0.01 油酸C18:1(%) 33.54±1.98 35.66±2.36 0.16 亚油酸C18:2(%) 2.59±0.74 3.09±0.66 0.29 棕榈油酸C16:1(%) 1.55±0.09 1.44±0.30 0.46 通常,硬脂酸在硬脂酰辅酶A脱氢酶(stearoyl-CoA desaturase,SCD)的作用下生成油酸,但在反刍动物中,则生成共轭亚油酸[20];而软脂酸则可以在SCD的作用下生成棕榈油酸[21]。同时,不饱和脂肪酸也可以经过催化加氢转化为饱和脂肪酸。研究表明反刍动物摄取多酚化合物可以保护肌肉、脂肪组织中的不饱和脂肪酸被氢化,增加不饱和脂肪酸的含量[22-24]。本研究显示的结果很可能是柠条中的多酚化合物促使了滩羊皮下脂肪组织中不饱和脂肪酸的增加、饱和脂肪酸的减少。
2.4 饲料中添加柠条对滩羊瘤胃、结肠内VFAs含量的影响
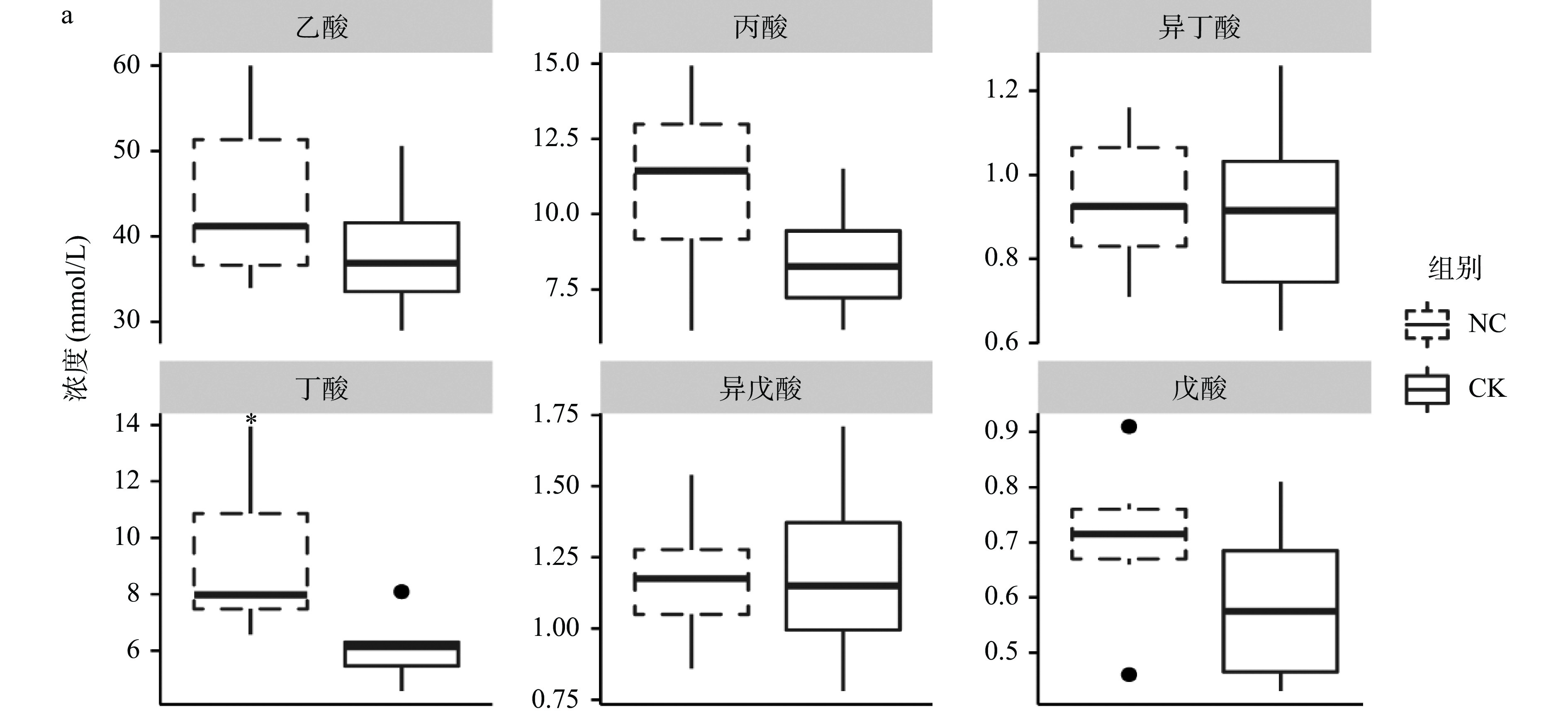
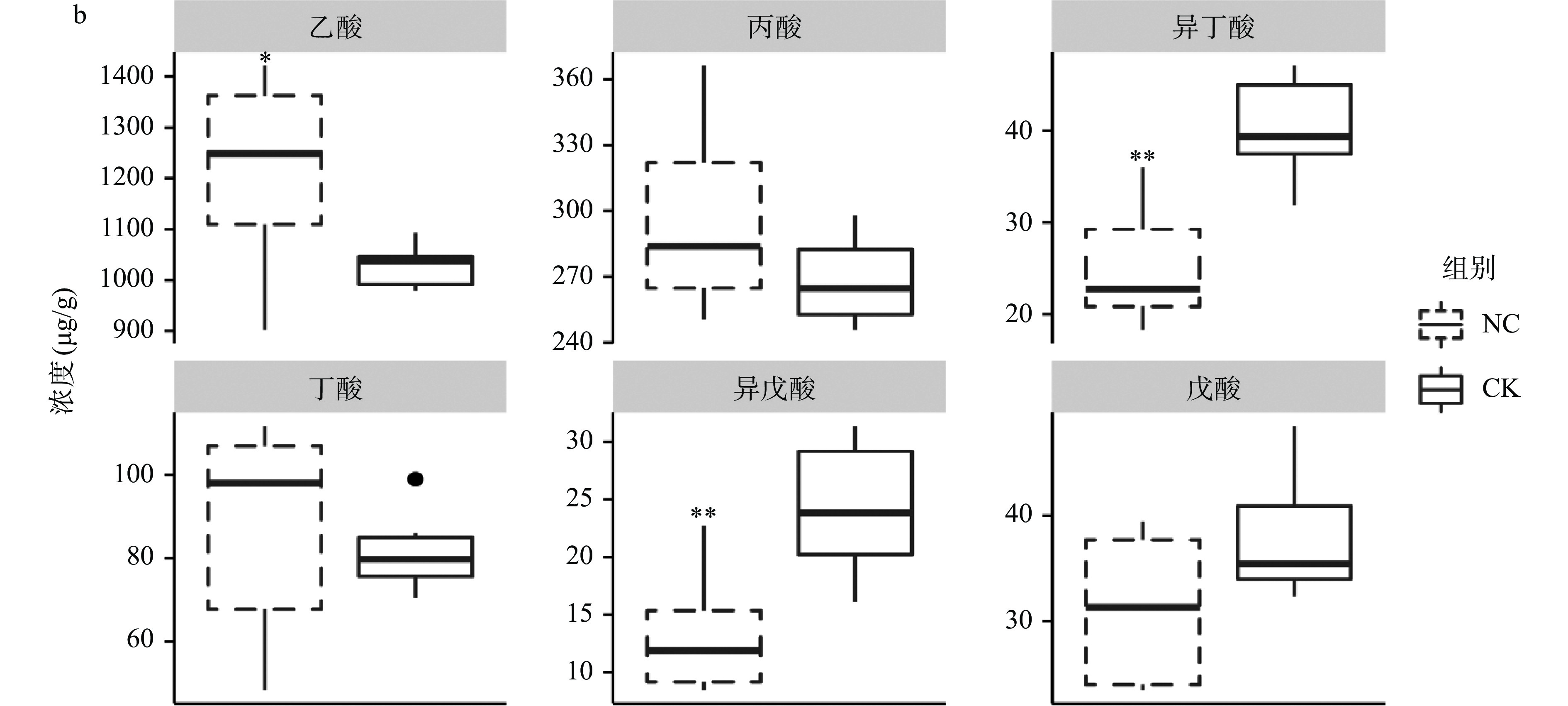
用OPLS-DA得分图可以最大程度展示各组间的差异。NC组和CK组滩羊瘤胃(图2a)、结肠(图2b)内VFAs的区分明显;通过比较瘤胃(图3a)和结肠(图3b)中VFAs的水平,饲喂柠条可以显著降低滩羊瘤胃内丁酸和结肠内乙酸的浓度(P<0.05);同时极显著地提高结肠内支链脂肪酸(异丁酸和异戊酸)的水平(P<0.01)。此外,饲喂柠条,不论对于滩羊瘤胃还是结肠,丙酸的含量都有所下降,但未达到显著水平(P>0.05)。
反刍动物的瘤胃是饲料发酵供能的器官。瘤胃微生物产生的VFAs,超过70%被瘤胃或瓣胃吸收并运输至宿主肝脏合成脂肪酸和葡萄糖等供给宿主的能量需求[25]。结肠中的微生物可发酵膳食纤维产生短链脂肪酸,即VFAs,除了用于结肠细胞供能,少量也会运输至宿主肝脏[26]。在本研究中,添加柠条会降低瘤胃和结肠微生物产生的VFAs,以及乙酸、丙酸和丁酸的含量,与Zhang等[16]使用含40%的柠条日粮饲喂滩羊,葛翠翠等[27]进行的100%柠条在滩羊瘤胃体外实验的结果一致;但与马宁等[15]使用6%柠条和4%菊花粕的颗粒日粮饲喂滩羊的结果相反。由于饲料中精料比例增加会直接导致瘤胃中VFAs总量上升,这一现象可能是饲料组成中精粗比的不同导致了上述相反的结果[28]。
在精粗比一致或相似的条件下,柠条降低瘤胃和结肠微生物VFAs的产量,可能与柠条中富含单宁、类黄酮等多酚化合物有关。易水解的单宁会直接影响产VFAs的瘤胃微生物丰度,而不易水解的单宁可以到达结肠后被结肠细菌降解,对结肠中产VFAs的细菌造成影响[6, 29]。
2.5 滩羊瘤胃、结肠内VFAs与肉品质和皮下脂肪组织中主要脂肪酸的相关性
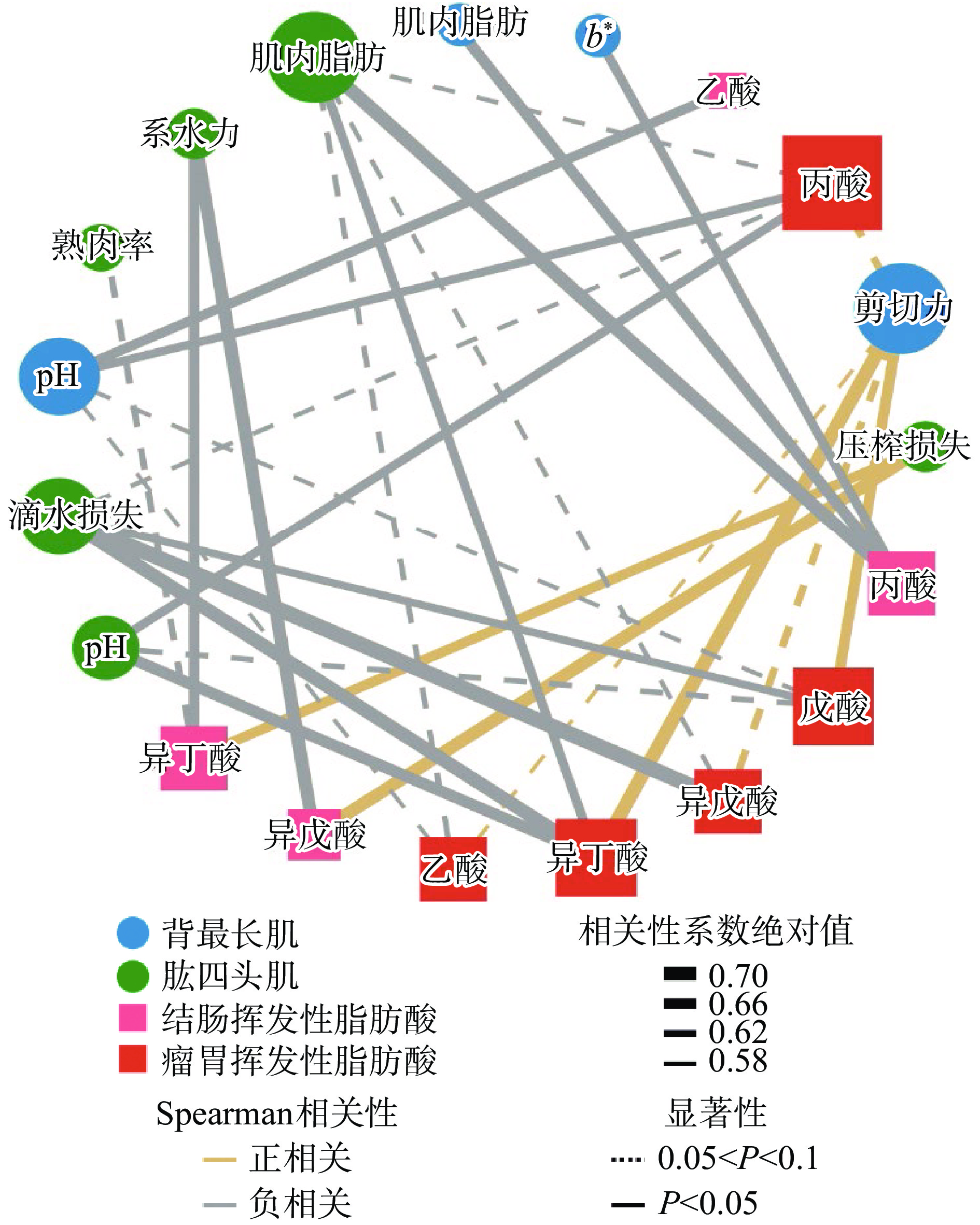
为进一步了解滩羊肉质特性和皮下脂肪组织中LCFAs与胃肠道中VFAs的关系,本文通过Spearman相关性系数对滩羊肉品质与胃肠道VFAs(图4)、皮下脂肪组织的LCFAs与胃肠道内VFAs进行了关联分析(图5),列出的相关性网络图仅展示了具有统计学意义的高相关性(|R|>0.5,P<0.05或0.05<P<0.1)关联结果。
图4所示,背最长肌的剪切力主要和瘤胃内VFAs呈正相关,而股四头肌的压榨损失主要与结肠中的VFAs呈正相关。股四头肌的系水力、滴水损失分别与结肠中的VFAs、瘤胃内VFAs呈负相关。肌肉的pH和瘤胃丙酸含量呈负相关,同时,肌内脂肪和胃肠道内丙酸含量密切相关(负相关)。
从图5可以看出,皮下脂肪中棕榈油酸含量与瘤胃内VFAs呈正相关,而软脂酸则与结肠中的异丁酸趋向负相关性。现有报道也表明,乙酸、丙酸和丁酸可以增加猪胴体的眼肌和胴体重量,减少背最长肌的滴水损失;丁酸可以减少肉鸡胸肌的滴水损失[30-31]。由此推论,饲喂柠条后,滩羊肉嫩度下降的原因可能是乙酸、丙酸和丁酸含量的下降,以及异丁酸和异戊酸含量的上升所致。
2.6 滩羊瘤胃、结肠内VFAs与胃肠道菌属的相关性
瘤胃、结肠内VFAs主要是由其中的胃肠道微生物产生,由此,本文还对胃肠道主要差异菌属与VFAs进行了关联分析(Spearman)。本文所指的主要差异菌属是指由LEfSe计算得到的两组间差异显著的菌属(P<0.05,图未作展示):两组间瘤胃内主要差异菌属是5-7N15菌属和YRC22菌属,结肠内主要差异菌属是颤螺旋菌属(Oscillospira)和密螺旋体属(Treponema)。图6仅展示具有统计学意义的高相关性(|R|>0.5,0.05<P<0.1)关联。
由图6可知,瘤胃内属于拟杆菌门的5-7N15菌属和YRC22菌属均与瘤胃内丁酸含量关联度较高,且趋向正相关。结肠内,密螺旋体属丰度在CK组滩羊中显著下降,且与乙酸含量趋向正相关,但与异丁酸含量则趋向负相关(0.05<P<0.1)。目前,5-7N15菌属和YRC22菌属都属于未鉴定细菌,对它们的研究基本停留在测序层面。密螺旋体属已被证明包含很多种致病菌[32],饲喂柠条显著降低密螺旋体属的丰度,说明柠条可以减少滩羊胃肠道内的有害菌数量。在荷斯坦母牛瘤胃中,密螺旋体属也被证实与乙酸含量呈正比[33],但尚未有与异丁酸相关的报道。因而,密螺旋体属和异丁酸有可能成为改善滩羊及肉品质和脂肪不饱和脂肪酸含量的作用靶点。
3. 结论
本研究发现,日粮中使用10%柠条等量替代苜蓿饲喂滩羊,虽然对滩羊的生长、屠宰性能没有显著提高,但从饲草成本角度,本研究使用的日粮配方降低了饲料成本;饲喂柠条虽然对滩羊股四头肌的嫩度有所降低,但是通过降低脂肪组织中饱和脂肪酸的含量和提高脂肪中不饱和脂肪酸的含量,滩羊肉的健康性能得以明显提高。
综合分析研究数据和目前的相关进展,可能是柠条中的多酚化合物直接影响了滩羊的肌肉和脂肪的生长代谢,也可能是通过降低胃肠道内密螺旋体属丰度,提高异丁酸含量、降低乙酸含量而影响了肌肉和脂肪组织的脂肪酸组成。
-
表 1 柠条对滩羊肉品质的影响
Table 1 Effects of Caragana korshinskii Kom. on the meat quality of Tan sheep
指标 背最长肌 股四头肌 对照组(NC组) 实验组(CK组) P值 对照组(NC组) 实验组(CK组) P值 亮度(L*) 40.11±1.94 39.80±1.42 0.78 42.42±1.71 42.35±2.03 0.96 红度(a*) 20.56±1.09 21.19±1.30 0.44 23.69±0.94 23.56±1.05 0.84 黄度(b*) 7.47±0.82 7.71±1.29 0.73 10.04±0.83 10.16±0.97 0.85 压榨损失(%) 32.96±2.02 34.28±2.81 0.42 25.90±2.43 29.51±2.99 0.07 系水力(%) 55.55±2.65 54.20±3.89 0.54 66.11±3.16 61.53±3.86 0.07 滴水损失(%) 1.09±0.11 1.12±0.30 0.84 0.78±0.21 0.93±0.14 0.22 含水量(%) 74.16±0.60 74.87±0.45 0.07 76.42±0.33 76.70±0.44 0.29 剪切力(N) 52.84±15.33 46.48±19.03 0.58 55.06±5.77 56.26±13.38 0.86 熟肉率(%) 86.25±1.63 84.31±1.98 0.13 84.76±0.98 80.70±2.80 0.02 肌内脂肪(%) 3.67±1.06 3.73±0.91 0.93 2.87±0.43 3.19±0.94 0.51 pH 5.73±0.04 5.78±0.07 0.20 5.84±0.03 5.91±0.06 0.03 表 2 柠条对滩羊皮下脂肪中脂肪酸含量的影响
Table 2 Effects of Caragana korshinskii Kom. on fatty acid content of subcutaneous fat in Tan sheep
指标 对照组(NC组) 实验组(CK组) P值 饱和脂肪酸(%) 61.07±2.09 58.46±2.07 0.08 不饱和脂肪酸(%) 37.95±2.25 40.50±2.01 0.09 硬脂酸C18:0(%) 22.54±0.82 22.11±1.87 0.65 软脂酸C16:0(%) 27.80±1.28 25.14±1.23 0.01 油酸C18:1(%) 33.54±1.98 35.66±2.36 0.16 亚油酸C18:2(%) 2.59±0.74 3.09±0.66 0.29 棕榈油酸C16:1(%) 1.55±0.09 1.44±0.30 0.46 -
[1] 袁圣钧. 基于国际视角的中国肉羊产业发展现状分析及肉羊企业发展策略研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2020 YUAN S J. Based on the international perspective of investigation on the status of mutton industry in China and its future development strategy[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2020.
[2] FU X, SHAO M A, WEI X, et al. Effects of two perennials, fallow and millet on distribution of phosphorous in soil and biomass on Sloping Loess Land, China[J]. Catena,2009,77(3):200−206. doi: 10.1016/j.catena.2008.12.017
[3] FU X, SHAO M, WEI X, et al. Effects of monovegetation restoration types on soil water distribution and balance on a hillslope in Northern Loess Plateau of China[J]. Journal of Hydrologic Engineering,2013,18(4):413−421. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)HE.1943-5584.0000628
[4] ZHONG C, SUN Z, ZHOU Z, et al. Chemical characterization and nutritional analysis of protein isolates from Caragana korshinskii Kom[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2014,62(14):3217−3222. doi: 10.1021/jf500349s
[5] XU X C, LIU T D, FAN S S, et al. Effects of fermented Caragana korshinskii on the intramuscular fat content and expression of FABP3, UBE3C, ADRB3, LIPE, and SCD in different muscles of Tan sheep[J]. Czech Journal of Animal Science,2020,65(4):145−152. doi: 10.17221/231/2019-CJAS
[6] 王丁. 柠条饲料化开发利用试验研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2007 WANG D. Study on the exploitation and utilization of peashrub feed stuff[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2007.
[7] WANG X, HUANG X, ZHANG Z, et al. Effect of Caragana korshinskii Kom. as a partial substitution for sheep forage on intake, digestibility, growth, carcass features, and the rumen bacterial community[J]. Tropical Animal Health and Production,2022,54(3):190. doi: 10.1007/s11250-022-03186-8
[8] PLEASANTS A B, THOMPSON J M, PETHICK D W. A model relating a function of tenderness, juiciness, flavour and overall liking to the eating quality of sheep meat[J]. Australian Journal of Experimental Agriculture,2005,45(5):483−489. doi: 10.1071/EA04106
[9] ERKKILÄ A, de MELLO V D, RISÉRUS U, et al. Dietary fatty acids and cardiovascular disease: An epidemiological approach[J]. Progress in Lipid Research,2008,47(3):172−187. doi: 10.1016/j.plipres.2008.01.004
[10] KUHNT K, DEGEN C, JAHREIS G. Evaluation of the impact of ruminant trans fatty acids on human health: Important aspects to consider[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2016,56(12):1964−1980. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2013.808605
[11] BRZOZOWSKA A M, OPRZADEK J. Metabolism of fatty acids in tissues and organs of the ruminants-A review[J]. Animal Science Papers and Reports,2016,34(3):211−219.
[12] 周敏, 汪凯歌, 张濂, 等. 微生物-肠-肌轴调节骨骼肌代谢和功能的研究进展[J]. 畜牧兽医学报,2022,53(9):1−13. [ZHOU M, WANG K G, ZHANG L, et al. Advances in microbiota-gut-muscle axis regulating skeletal muscle metabolism and function[J]. Acta Veterinaria et Zootechnica Sinica,2022,53(9):1−13. doi: 10.11843/j.issn.0366-6964.2022.01.001 [13] 张志超, 王小琪, 包琦, 等. 澳洲白羊与小尾寒羊杂交F1代背最长肌肉品质与皮下脂肪组织膻味物质分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(14):272−277. [ZHANG Z C, WANG X Q, BAO Q, et al. Analysis of the longissimus dorsi meat quality and the content of mutton flavor substances of F1 hybrid sheep between Australian white sheep and native small-tail han sheep[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(14):272−277. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020100127 [14] ZHANG S, WANG H, ZHU M J. A sensitive GC/MS detection method for analyzing microbial metabolites short chain fatty acids in fecal and serum samples[J]. Talanta,2019,196(2):49−54.
[15] 马宁, 许迟, 李涛, 等. 颗粒日粮中添加柠条对滩羊生长性能、血液生化指标、瘤胃发酵及羊肉品质的影响[J]. 畜牧与饲料科学,2021,42(3):14−20, 38. [MA N, XU C, LI T, et al. Effects of adding Caragana korshinskii in pelleted diet on growth performance, blood biochemical indicators, ruminal fermentation and mutton quality of Tan sheep[J]. Animal Husbandry and Feed Science,2021,42(3):14−20, 38. doi: 10.12160/j.issn.1672-5190.2021.03.003 [16] ZHANG K, QIAN Q, MAO Y, et al. Characterization of growth phenotypes and gastrointestinal tract microbiota in sheep fed with caragana[J]. Journal of Applied Microbiology,2021,131(6):2763−2779. doi: 10.1111/jam.15138
[17] 毛云睿. 饲草类型对滩羊生长性能、肉品质及胃肠道微生物区系的影响[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2021 MAO Y R. Effects of forage types on growth performance, meat quality and gastrointestinal microbiota in Tan sheep[D]. Yangling: Northwest A&F University, 2021.
[18] 张粟子. 柠条水提物对寒冷环境中绵羊生长、抗氧化及抗炎性能的影响[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2021 ZHANG S Z. Effects of aqueous extract of Caragana korshinskii on growth, antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of sheep in cold environment[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2021.
[19] 丁鑫. 不同栗木单宁水平日粮对湖羊公羔生产性能和肉品质的影响[D]. 兰州: 兰州大学, 2019 DING X. Effects of different chestnut tannin levels on the production performance and meat quality of Hu lambs[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University, 2019.
[20] WOOD J D, ENSER M, FISHER A V, et al. Fat deposition, fatty acid composition and meat quality: A review[J]. Meat Science,2008,78(4):343−358. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2007.07.019
[21] NTAMBI J M, MIYAZAKI M. Regulation of stearoyl-CoA desaturases and role in metabolism[J]. Progress in Lipid Research,2004,43(2):91−104. doi: 10.1016/S0163-7827(03)00039-0
[22] AGUSTINHO B C, ZEOULA L M, SANTOS N W, et al. Effects of flaxseed oil and vitamin E supplementation on digestibility and milk fatty composition and antioxidant capacity in water Buffaloes[J]. Animals,2020,10(8):1294. doi: 10.3390/ani10081294
[23] CIMMINO R, BARONE C M A, CLAPS S, et al. Effects of dietary supplementation with polyphenols on meat quality in Saanen goat kids[J]. BMC Veterinary Research,2018,14(1):181. doi: 10.1186/s12917-018-1513-1
[24] GESTEIRA S M, OLIVEIRA R L, SILVA T M, et al. Physicochemical quality, fatty acid composition, and sensory analysis of Nellore Steers meat fed with inclusion of condensed tannin in the diet[J]. Journal of Food Science,2018,83(5):1366−1372. doi: 10.1111/1750-3841.14136
[25] BIONAZ M, VARGAS-BELLO-PÉREZ E, BUSATO S. Advances in fatty acids nutrition in dairy cows: From gut to cells and effects on performance[J]. Journal of Animal Science and Biotechnology,2020,11(1):110. doi: 10.1186/s40104-020-00512-8
[26] DALILE B, VAN OUDENHOVE L, VERVLIET B, et al. The role of short-chain fatty acids in microbiota-gut-brain communication[J]. Nature Reviews Gastroenterology & Hepatology,2019,16(8):461−478.
[27] 葛翠翠, 梁戈, 李昊, 等. 玉米秸秆、柠条及葵花盘在滩羊瘤胃体外的消化及发酵性能[J]. 草业科学,2018,35(8):2009−2015. [GE C C, LIANG G, LI H, et al. Digestion and fermentation performance of corn straw, Caragana korshinskii, and sunflower calathide in Tan sheep in vitro[J]. Pratacultural Science,2018,35(8):2009−2015. doi: 10.11829/j.issn.1001-0629.2018-0596 [28] PITT R E, CROSS T L, PELL A N, et al. Use of in vitro gas production models in ruminal kinetics[J]. Mathematical Biosciences,1999,159(2):145−163. doi: 10.1016/S0025-5564(99)00020-6
[29] CHIVA-BLANCH G, VISIOLI F. Polyphenols and health: Moving beyond antioxidants[J]. Journal of Berry Research,2012,2(2):63−71. doi: 10.3233/JBR-2012-028
[30] JIAO A, DIAO H, YU B, et al. Infusion of short chain fatty acids in the ileum improves the carcass traits, meat quality and lipid metabolism of growing pigs[J]. Animal Nutrition,2021,7(1):94−100. doi: 10.1016/j.aninu.2020.05.009
[31] ZHANG W H, GAO F, ZHU Q F, et al. Dietary sodium butyrate alleviates the oxidative stress induced by corticosterone exposure and improves meat quality in broiler chickens[J]. Poultry Science,2011,90(11):2592−2599. doi: 10.3382/ps.2011-01446
[32] HAAKE D A, YANG X F. In Encyclopedia of microbiology[M]. 4th.: Amsterdam: Elsevier, 2019: 283-298.
[33] GAOWA N, PANKE-BUISSE K, WANG S, et al. Brisket disease is associated with lower volatile fatty acid production and altered rumen microbiome in Holstein Heifers[J]. Animals,2020,10(9):1712. doi: 10.3390/ani10091712
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 王喜庆,李成凤,郭丽,赵洪波,马雪,李杨,苏适,郭齐. 创新创业背景下“食品营养学”课程思政教学改革与实践. 食品与发酵科技. 2025(01): 188-192 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 隋晓楠,张妍,黄国,付昳丹,梁香玉,赵尚清,王思琦,杨爱峥,霍俊伟,江连洲. 省一流专业引领下“粮油加工副产物综合利用”课程创新创业元素的设计与实践. 食品工业科技. 2024(13): 308-314 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 李晓东,刘璐,李嘉钰,张秀秀,郑冬梅,崔立雪,张宏伟. 《乳品工艺学》课程思政教育的改革与实践. 食品工业科技. 2024(19): 376-382 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 罗港. 高职院校思政元素融入Premiere课程的研究与探索. 辽宁师专学报(社会科学版). 2023(02): 70-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 桂亚,马栎,李逸鹤,田林双. 高职院校粮食工程专业劳动教育的实践探究. 现代面粉工业. 2023(05): 36-39 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 贺光祖,叶惠慧,李逢振,王治昕,魏莎,李静. 食品类专业实践教学体系化微课的创新路径. 现代畜牧科技. 2023(11): 157-159 .  百度学术
百度学术
1. 杨攀平,李惠侠,胡亚美. 盐池滩羊肉品质特性及其潜在调控机理探讨. 草业学报. 2025(04): 223-232 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 吕玲燕,胡湘云,刘明君,顾国才,汪燕玲,韦明松,刘庆友,王献伟. 茉莉花渣对隆林黑山羊养分表观消化率、生长性能、屠宰性能、肉品质及血清生化指标的影响. 饲料研究. 2025(03): 12-17 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘嘉东,韩晓娟,张桂杰,黄帅. 柠条青贮替代全株玉米青贮对滩羊生长性能、脂肪沉积和肉品质的影响. 动物营养学报. 2023(09): 5827-5836 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)











 下载:
下载:


 下载:
下载:



