Effects of Rosa roxburghii Tratt Aqueous Extract on Protein and Lipid Oxidation of Minced Yak Meat during Storage
-
摘要: 本研究旨在探讨刺梨水提物(Rosa roxburghii Tratt Aqueous Extract,RRTAE)对牦牛肉糜在贮藏过程蛋白质和脂质氧化的影响规律。与空白对照、0.02%二丁基羟基甲苯(Butylated Hydroxy Toluene,BHT)进行比较,添加0.02%、0.10%、0.20% RRTAE到牦牛肉糜中,测定贮藏1、3、6、9 d各组牦牛肉糜的色泽、pH、硫代巴比妥酸(Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances,TBARS)值、荧光化合物(有机相δ For、水相δ Faq)、共轭二烯(Conjugated Diolefins,CD)值、羰基含量、表面疏水性、色氨酸含量、二聚酪氨酸含量、感官品质。结果表明,与空白对照、阳性对照(0.02%BHT)相比,0.10%、0.20%RRTAE可显著降低牦牛肉糜的pH(P<0.05),0.02%RRTAE与阳性对照组效果接近,且RRTAE可改善其感官品质,显著抑制a*、b*值的降低(P<0.05),但对L*值有一定的负面作用;0.02% RRTAE可显著降低其TBARS值、二聚酪氨酸含量(P<0.05),且抑制效果随RRTAE添加量的增加而提高;添加0.20% RRTAE可显著降低其δ Faq、羰基含量、表面疏水性、色氨酸荧光值(P<0.05)。本研究认为,RRTAE具有改善牦牛肉糜贮藏过程理化特性的作用,可以作为肉糜保鲜中有潜力的抗氧化剂。Abstract: The objective of this study was to investigate the effect of Rosa roxburghii Tratt aqueous extract (RRTAE) on protein and lipid oxidation of minced yak meat during storage. Compared with the blank control and positive control of 0.02% butylated hydroxy toluene (BHT), 0.02%, 0.10%, and 0.20% RRTAE were added to minced yak meat. The color, pH, thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) value, fluorescent compounds (organic phase δ For, aqueous phase δ Faq), conjugated diolefins (CD) value, carbonyl content, surface hydrophobicity, tryptophan content, dimertyrosine content, and sensory quality of minced yak meat in each group were evaluated on the day 1, 3, 6 and 9 during the storage. The results showed that added 0.10% or 0.20% RRTAE in the minced yak meat could significantly reduce the pH (P<0.05), and 0.02% RRTAE had similar effectiveness comparing with the positive control. RRTAE improved sensory quality, significantly inhibited the decrease of a* and b* values (P<0.05), but impaired to the L* value. Addition of 0.02% RRTAE significantly lowered the TBARS value and dimertyrosine content (P<0.05), and this effect strengthened with the elevation of RRTAE level. Adding 0.20% RRTAE in minced yak meat also significantly reduced the δ Faq, carbonyl content, surface hydrophobicity, and tryptophan fluorescence value (P<0.05). The results suggest that RRTAE can improve the physico-chemical properties of minced yak meat during storage, and may be a potential antioxidant in minced meat storage.
-
牦牛肉具有蛋白质含量高、脂肪含量低和营养丰富等特点,受到消费者的广泛关注。牦牛肉在加工贮藏过程暴露在空气中容易被氧化,导致腐败变质,产生不良风味,添加抗氧化剂可以适当延长其产品货架期,但合成类抗氧化剂存在一定毒性和致癌作用[1]。天然抗氧化剂主要是从野生植物果实中提取制备而成,具有较高的安全性和抗氧化作用,现已成为食品加工多个领域新的研究热点。
常见的几种天然活性抗氧化剂[2]主要分为以下四种,酚类化合物、天然色素类、维生素及其衍生物、含氮化合物。刺梨水提物(Rosa roxburghii Tratt Aqueous Extract,RRTAE)是以蔷薇科植物缫丝花的果实刺梨为生产原料,经过粉碎、提取、浓缩、干燥等生产工艺流程所制得的一种粉状物[3]。付阳洋等[4]研究发现,刺梨富含黄酮、维生素C、多酚、多糖、超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)及三萜等活性成分,其中维生素C、黄酮及多酚含量较高,均可显现出较强的抗氧化能力[5]。梁梦琳等[6]通过鉴定刺梨果的各种化学成分,发现刺梨果实含有近6种三萜类化合物,其中的野蔷薇苷、刺梨苷等对肠炎沙门氏菌、致病性金黄色葡萄球菌、枯草芽孢杆菌等均有抑制作用,而刺梨水提物能抑制大肠杆菌、沙门氏菌等的生长,可作为潜在的天然食品防腐剂加以利用。
目前关于刺梨的营养价值、生物学功能及其在畜禽生产中的应用的研究报告较多,集中在刺梨果实、刺梨醇提物、刺梨水提物、刺梨果渣副产物等的饲用化研究[7],也有致力于刺梨果实中水溶性多糖调节小鼠肠道菌群、降低其体重,以及降血糖、抗炎、抗氧化和抗肿瘤等生物功效的研究[8]。过去的体内外实验研究已证实刺梨水提物具有较强的自由基清除能力,对蛋白质损伤有很强的抑制作用,对肝匀浆体系内蛋白质和脂质的氧化损伤具有保护作用[9],但尚未见有关刺梨水提物作为天然抗氧化剂添加到肉质产品中的研究报道。本研究旨在探讨添加不同量(0.02%、0.10%、0.20%)的RRTAE对牦牛肉糜在4 ℃贮藏条件下,1、3、6、9 d时的色泽、pH、硫代巴比妥酸(Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances,TBARS)值、荧光化合物含量(δ For、δ Faq)、共轭二烯(Conjugated Diolefins,CD)值、羰基含量、表面疏水性、二聚酪氨酸含量、色氨酸含量、感官品质的变化,揭示RRTAE在牦牛肉糜中的抗氧化作用,为 RRTAE作为新型天然抗氧化剂在食品保鲜研究领域里的应用提供新的理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
牦牛肉 红原县国中食品有限责任公司;刺梨水提物(20 g浓缩为1 g) 陕西艾特生物科技有限公司;牛血清白蛋白(BR级) 上海如吉生物科技发展有限公司;二丁基羟基甲苯 上海源叶生物科技有限公司;三氯乙酸(TCA)、没食子酸、2-硫代巴比妥酸(TBA)、浓硫酸、硫酸奎宁、正已烷、异丙醇、磷酸氢二钠、磷酸二氢钠、氯化钠、氧化镁、氢氧化钠、硫酸铜、酒石酸钾钠、碘化钾、浓盐酸、乙酸乙酯、无水乙醇、盐酸胍、溴酚蓝、乙二胺四乙酸-二钠、乙二醇双(2-氨基乙基醚)四乙酸(EGTA)、2,4-二硝基苯肼(DNPH) 成都市科隆化学品有限公司,试剂均为分析纯。
UV1810S紫外分光光度计 龙尼柯仪器有限公司;F-4700 荧光分光光度计 日本株式会所日立高新技术科学那珂事业所;九阳 JYL-D05 绞肉机 九阳股份有限公司;PL303 分析天平 METTLER TOLEDO公司;pH 直测仪 德国 Matthaus 公司;CR-400色彩色差仪 日本Konica Minolta公司;5804R冷冻离心机 德国 Eppendorf 公司;T-25 高速匀浆机 德国 IKA 公司;LD510 电子天平 沈阳龙腾电子有限公司;HH-6数显恒温水浴锅 国华电器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 牦牛肉糜制作
参考李琼帅等[10]的制作方法,牦牛肉在4 ℃下解冻,去除可见脂肪和结缔组织,用6 mm孔板绞肉机绞碎,分为5组,如表1所示。各成分充分混合后,将牦牛肉糜制成70 g的肉饼(直径约6 cm,厚约1 cm),分别放入自封袋中,置于冰箱冷藏保存(4 ℃),所有指标分别在第1、3、6、9 d(9 d后牦牛肉糜有严重异味,组织状态差,研究意义不大)测定,每次测定重复3次。表中NaCl是肉品加工中一种常见的腌制剂,成本较低,常与合成类抗氧化剂或天然抗氧化剂复配使用[11],试验组中添加1.5%NaCl可适当延长牦牛肉糜贮藏期并为生产加工提供参考依据,因此以添加1.5%NaCl为空白对照组;表中BHT是常用的合成类抗氧化剂,以添加0.02%BHT(国标允许最大添加量)为阳性对照,可为RRTAE是否可作为天然抗氧化剂更好地代替合成类抗氧化剂使用提供参考依据;表中RRTAE中多酚含量较高,其浓度过高影响色氨酸指标测定的正确性,而通过前期预实验可知牦牛肉糜中添加0.20%RRTAE可对色氨酸产生屏障作用,并且多酚含量较高时影响蛋白质的乳化特性[12]。因此设立添加量为0.02%、0.10%、0.20%的RRTAE为试验组。
表 1 牦牛肉糜处理组Table 1. Minced yak meat treatment group组号 组别 处理 1 空白对照 1.5%NaCl 2 0.02% BHT 1.5%NaCl、0.02% BHT 3 0.02% RRTAE 1.5%NaCl、0.02% RRTAE 4 0.10% RRTAE 1.5%NaCl、0.10% RRTAE 5 0.20% RRTAE 1.5%NaCl、0.20% RRTAE 注:NaCl、BHT和RRTAE添加量均以牦牛肉糜质量为基准,且1.5%、0.02%、0.10%、0.20%均为质量分数。 1.2.2 色泽测定
使用色差仪测定所有试验组样品的L*值、a*值和b*值。
1.2.3 pH测定
参考顾苑婷等[13]的测定方法,取10 g牦牛肉糜样品,放入锥形瓶中,向瓶中加入100 mL蒸馏水,振荡锥形瓶使肉糜分散开,浸泡0.5 h后用漏斗(或纱布)过滤,测定滤液pH。
1.2.4 TBARS值测定
参考阮一凡等[14]的测定方法,取样品10 g,加入30 mL 7.5%三氯乙酸(含0.1%乙二胺四乙酸-二钠、0.1%没食子酸),70 ℃水浴中浸泡30 min。经滤纸过滤后。吸取5 mL上清液,加入5 mL 0.02 mol/L 硫代巴比妥酸溶液,沸水浴中反应40 min,快速冷却后,分别测定532和600 nm波长处的吸光值。TBARS值按下式计算:
式中:A532、A600分别为待测液在532 nm、600 nm处的吸光值;V为5 mL(上清液体积);m为肉样质量(kg);l为1 cm(光程);ε为摩尔吸光系数,156000 L/(mol·cm)。
1.2.5 荧光化合物含量测定
参考李锦锦等[15]的方法,准确称取2 g牦牛肉糜,加入20 mL去离子水,匀浆30 s(12000 r/min),取匀浆液2 mL,加入提取溶剂20 mL(正己烷:异丙醇=3:1),混匀后离心 5 min (3000×g,4 ℃),吸取上层有机相和下层水相,分别测定有机相和水相在393/463和327/415 nm处、狭缝均为5 nm时的荧光值。
荧光转化(δ F)用Fr的比值表示,δ F = Fr(393/463 nm)/Fr(327/415 nm)。水相的荧光转化为δ Faq,有机相的荧光转化为δ For,其中Fr(相对荧光值)=F/Fst,F为样品在激发/发射最大值时的荧光值,Fst用1 µg/mL硫酸奎宁溶液(用 0.05 mol/L硫酸溶解)对应的荧光值表示。
1.2.6 CD值测定
参考GEORGANTELIS等[16]的方法,准确称取2 g牦牛肉糜,加入20 mL去离子水,匀浆30 s(12 000 r/min),取匀浆液2 mL,加入提取溶剂20 mL(正己烷:异丙醇=3:1),混匀后离心 5 min(3000×g,4 ℃),于233 nm处测定上层清液吸光值。按下式计算CD 值:
式中:
1.2.7 肌原纤维蛋白(Myofibrillar Protein,MP)提取
参考郑娇等[17]的方法,稍作修改。称取牦牛肉糜约40 g,加入4倍体积的缓冲液(0.1 mol/L NaCl, 2 mmol/L MgCl2,1 mmol/L EGTA,20 mmol/L PBS,pH7.0)匀浆15 s,均质液离心 15 min(2500×g,4 ℃) ,弃上清液,取沉淀重复上述操作2次。三次提取后,沉淀加入4倍体积的缓冲液(50 mmol/L NaCl,50 mmol/L PBS,pH6.4),匀浆15 s,离心15 min ( 2500×g,4 ℃) ,弃上清液。向沉淀中加入4倍体积的缓冲液(20 mmol/L PB,pH6.0),均质15 s,4层纱布过滤,离心15 min(2500×g,4 ℃) ,弃上清液,将沉淀置于密封容器中冷藏(4 ℃),用双缩脲法测定蛋白质浓度,并在一天内完成蛋白质氧化指标的测定。
1.2.8 羰基含量测定
参考贾娜等[18]的方法,用缓冲液(0.6 mol/L NaCl,20 mmol/L PBS,pH6.0)调蛋白浓度至 5 mg/mL,分别吸取1 mL蛋白溶液与1 mL 10 mmol/L DNPH溶液于10 mL离心管中,室温静置60 min(每15 min振摇一次),加入1 mL 20% TCA溶液,冷冻离心5 min(12000×g,4 ℃)。去除上清液后,沉淀用乙酸乙酯-乙醇(体积比1:1)洗涤至上清液澄清,加入3 mL 6 mol/L盐酸胍溶液。为溶解蛋白沉淀,可将其置于37 ℃水浴15 min,离心5 min(10000 r/min,4 ℃),吸取上清液在370 nm波长下测定溶液的吸光度。蛋白质的羰基含量采用分子吸光系数22000 L/(mol·cm)计算。
1.2.9 表面疏水性测定
参考李琼帅等[10]的方法,吸取2 mL 2 mg/mL蛋白质溶液于10 mL离心管中,加入400 µL 1 mg/mL的溴酚蓝并摇匀,离心15 min(6000 r/min,4 ℃)。将上清液稀释10倍,在595 nm处测定溶液吸光值。以溴酚蓝结合量表示所有样品的表面疏水性,计算公式如下:
式中:A样品,在595 nm测定的吸光值;A空白,以缓冲液(0.6 mol/L NaCl,20 mmol/L PBS,pH6.0)代替蛋白溶液进行相同操作测定的吸光度。
1.2.10 二聚酪氨酸含量测定
参考邓思杨等[19]的方法,荧光比色皿中加入4 mL 2 mg/mL的蛋白溶液测定其荧光强度。激发波长为325 nm,发射波长为420 nm,狭缝宽度均为5 nm,电压400 V。待测样品的二聚酪氨酸含量用下式表示,单位为AU。
式中:A样品为利用F-4700荧光分光光度计测定的蛋白溶液的吸光度;p为蛋白溶液质量浓度,即2 mg/mL。
1.2.11 色氨酸荧光值测定
参考李玲等[20]的方法,荧光比色皿中加入4 mL 1 mg/mL的蛋白溶液,激发波长为283 nm,起始波长为295 nm,终止波长为400 nm,狭缝宽度均设置为 5 nm,电压为400 V,记录发射光谱。
1.2.12 感官品质评价
参考盘艳梅等[21]的测定方法,稍作修改。选20名感官评定人员,分别对不同试验组的牦牛肉糜进行感官分析,并按表2进行评定。
表 2 牦牛肉糜感官评定标准Table 2. Sensory evaluation standard of minced yak meat等级 分值 表观色彩 组织状态 气味 一级鲜牦牛肉 4 鲜红 有弹性,不粘手 牦牛肉风味浓郁 二级鲜牦牛肉 3 鲜( 褐) 红 弹性不足,
有少量汁液流出牦牛肉风味不浓郁 轻度变质牦牛肉 2 褐红 松弛粘手,
汁液流失较多稍有异味 变质牦牛肉 1 褐红发白 粘手,汁液流失多 腐败牦牛肉味 1.3 数据处理
每次测定重复3次,结果用平均值±标准差表示;利用SPSS 22.0和Excel 2019软件处理数据,用ANOVA进行差异显著性和数据方差分析,并采用Duncan’s法进行多重比较,P<0.05表示差异显著,利用 Origin 2018软件作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 RRTAE对牦牛肉糜色泽的影响
不同处理组对贮藏期间牦牛肉糜色泽的影响如表3所示。贮藏第1 d,空白对照组的L*值高于各RRTAE处理组,且随着RRTAE添加量的增加,L*值不断减小,这可能是因为RRTAE本身为深黄色粉末所致。随着贮藏时间的延长,空白对照组、0.02% BHT处理组L*值不断降低,这主要是由于肉糜表面水分蒸发,其表面亮度变暗[22]。贮藏第3 d开始,各 RRTAE处理组的L*值均显著高于空白对照组(P<0.05),其中0.20% RRTAE处理组的L*值在贮藏第6~9 d时显著高于0.02% BHT、0.02% RRTAE、0.10% RRTAE处理组(P<0.05),说明在牦牛肉糜中添加RRTAE可以有效延缓L*值的降低。
表 3 RRTAE对牦牛肉糜色泽的影响Table 3. Effect of RRTAE on the color of minced yak meat贮藏时间(d) 组别 L* a* b* 1 空白对照 32.02±0.55Aa 8.93±0.89Ab 9.55±0.84Ac BHT(0.02%) 32.29±1.85Aa 10.18±1.80Aab 10.47±0.86BCbc RRTAE(0.02%) 31.85±0.95Ca 11.70±1.17Aa 12.06±0.85Aa RRTAE(0.10%) 31.53±1.05Ca 10.48±1.60Bab 11.77±2.37Aab RRTAE(0.20%) 31.20±0.60Da 11.57±1.46ABa 12.99±0.48ABa 3 空白对照 29.52±0.42Bc 8.63±0.79Ab 9.64±0.65Ab BHT(0.02%) 32.08±1.49Ab 8.26±1.65Bb 10.27±1.62Cb RRTAE(0.02%) 33.38±1.60Bab 10.23±1.27Aab 10.97±1.52Bab RRTAE(0.10%) 33.04±1.53Bab 11.13±0.96ABa 11.38±1.08Aa RRTAE(0.20%) 34.15±0.90Ca 10.76±2.71Ba 10.39±1.09Cab 6 空白对照 28.73±0.43BCd 5.75±0.24Bd 9.25±0.89Ab BHT(0.02%) 32.01±0.65Ac 8.02±0.72Bc 11.75±0.62ABa RRTAE(0.02%) 34.98±0.82Ab 10.64±1.13Ab 12.45±1.02Aa RRTAE(0.10%) 35.22±0.75Ab 11.66±0.66ABb 12.36±0.87Aa RRTAE(0.20%) 36.36±0.90Ba 13.38±1.68Aa 12.57±0.75Ba 9 空白对照 28.31±1.30Cd 5.62±0.49Bb 9.07±0.31Ac BHT(0.02%) 29.71±1.03Bc 6.35±1.05Cb 12.02±0.96Ab RRTAE(0.02%) 35.39±1.10Ab 11.82±1.42Aa 12.84±0.48Aab RRTAE(0.10%) 35.55±0.98Ab 12.34±1.53Aa 12.97±1.93Aab RRTAE(0.20%) 38.55±0.81Aa 13.38±1.92Aa 13.89±0.98Aa 注:贮藏时间相同但处理组不同的差异显著性用同列小写字母表示;处理组相同但贮藏时间不同的差异显著性用同列大写字母表示;表4同。 牦牛肉糜在氧化过程中,可产生大量的高铁肌红蛋白(Metmyoglobin,Met Mb),肉色变暗,这是消费者所不期望的[23]。贮藏过程中空白对照组a*值不断下降。贮藏第1 d,0.02% RRTAE、0.20% RRTAE与空白对照组的a*值差异显著(P<0.05)。贮藏第6 d开始,各RRTAE处理组的a*值显著高于空白对照组、0.02% BHT处理组,且RRTAE添加量越大,a*值越高,说明牦牛肉糜中添加RRTAE可以抑制Fe3+的产生,从而减少Met Mb的形成,延缓a*值下降。
脂质氧化产物与蛋白质氨基反应可产生脂褐素,引起牦牛肉糜的b*发生变化。在整个贮藏期结束,空白对照组的b*值下降,这与李琼帅等[22]的研究结果类似。贮藏第 9 d,各 RRTAE 处理组相比第 1 d的b*值无显著上升或下降的趋势(P>0.05)。综上,添加0.20% RRTAE对改善牦牛肉糜色泽的效果最佳。
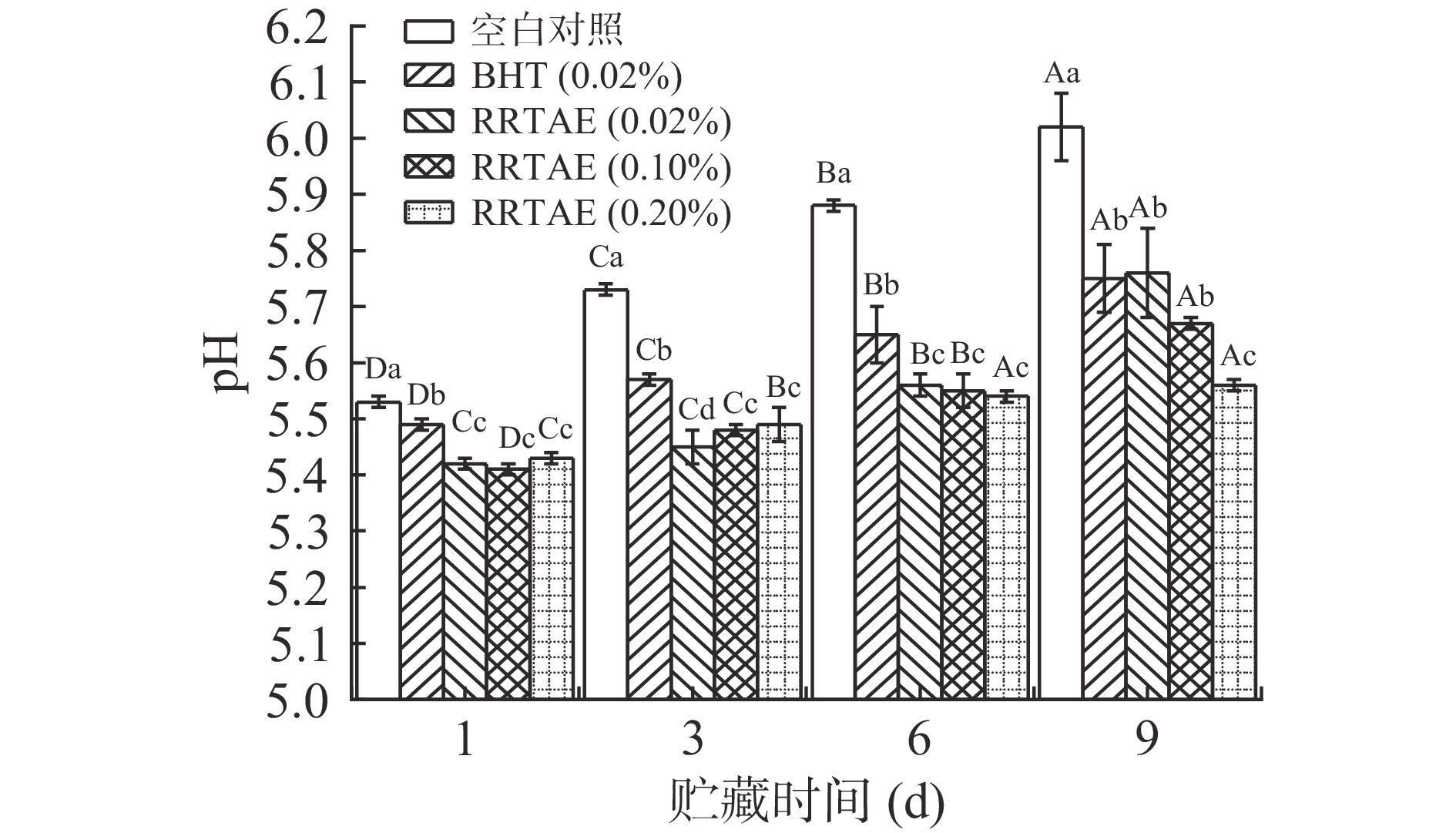
2.2 RRTAE对牦牛肉糜pH的影响
肉样的酸度值是反映肉样新鲜度和微生物污染程度的重要指标之一,可以反映肉质的好坏[22]。RRTAE对牦牛肉糜pH的影响如图1所示,贮藏时间越长,各处理组的pH越大,这可能与贮藏过程中牦牛肉糜含有的氨基酸分解产生的氨有关[22]。贮藏第1 d,各 RRTAE 处理组之间的 pH 无显著区别(P>0.05),且均低于空白对照组和0.02% BHT处理组,这可能与RRTAE含有没食子酸、原儿茶酸等酸性成分有关[22]。贮藏第9 d,0.20% RRTAE处理组的pH显著低于其他处理组(P<0.05)。一般情况下,肉的pH越高,保水性越好,但颜色较暗,保存性差且易被微生物污染[21],说明0.20% RRTAE处理组的效果最好,这可能与RRTAE降低了牦牛肉糜中蛋白质转化成碱性和氨类物质的速度有关,说明在牦牛肉糜中添加RRTAE可有效延缓牦牛肉糜pH的增加,这与李伟等[24]的研究结果相似。
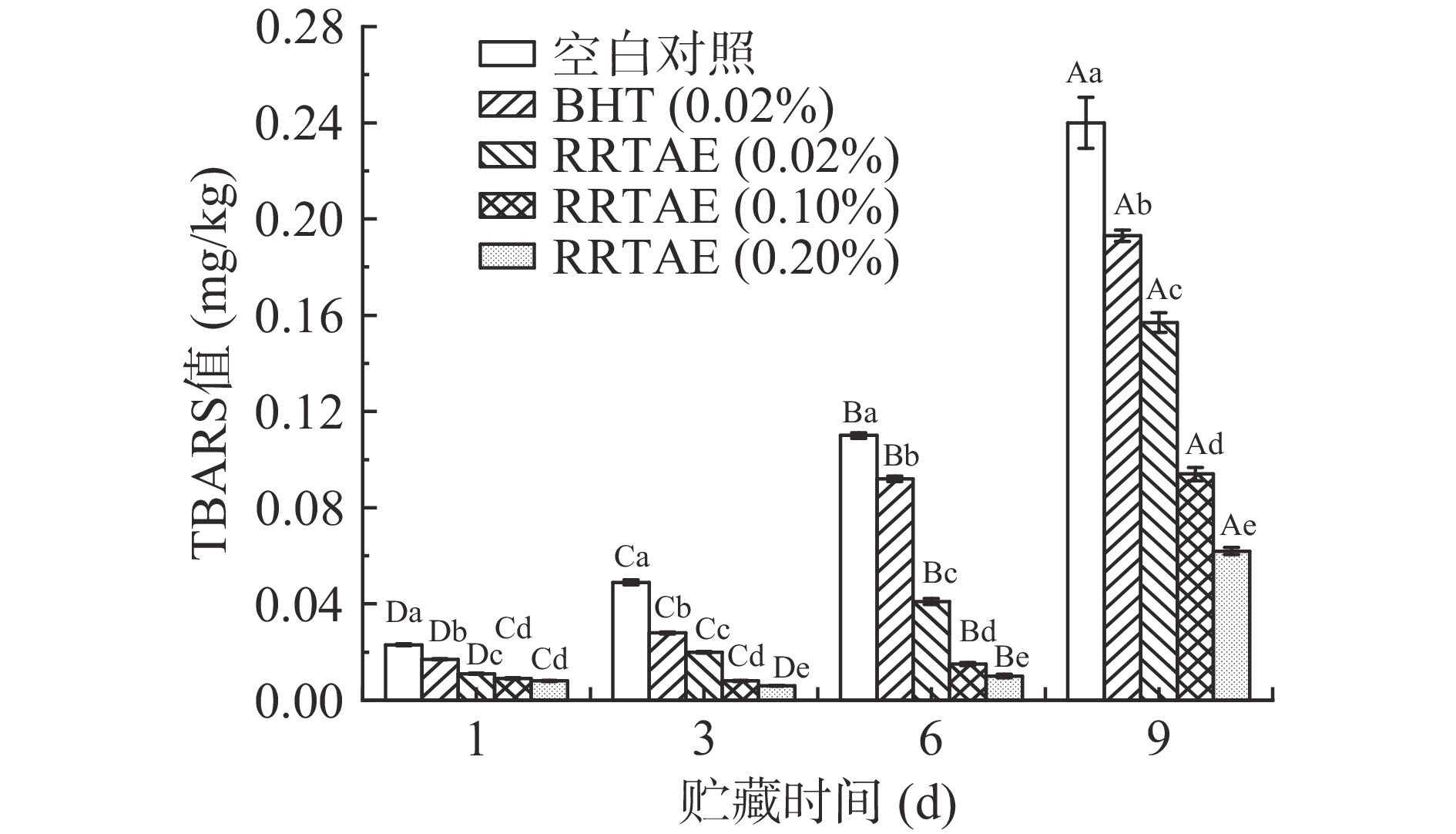
2.3 RRTAE对牦牛肉糜TBARS值的影响
脂质氧化可以导致肉样产生异味,降低牦牛肉糜的品质特性。RRTAE对牦牛肉糜TBARS值的影响如图2所示,贮藏过程中,不用处理方式的牦牛肉糜TBARS值均在升高。贮藏9 d内,各RRTAE处理组TBARS值显著低于空白对照组、0.02%BHT处理组(P<0.05),说明RRTAE可以有效抑制牦牛肉糜的脂质氧化现象,这可能与RRTAE含有的酚羟基与自由基作用,延缓脂质氧化过程中氢过氧化物的分解形成醛、酮等物质有关[21]。贮藏第3~9 d,0.20% RRTAE处理组TBARS值显著低于其他试验组(P<0.05),说明0.20% RRTAE处理组的效果最好。刺梨提取物中酚类物质含量较高,其可作为还原剂、氢供体、自由基清除剂等抑制脂质氧化[25]。张煊等[26]发现在冷藏素肉丸中添加藤茶提取物可有效抑制TBARS值的增加,与本实验结果相似。
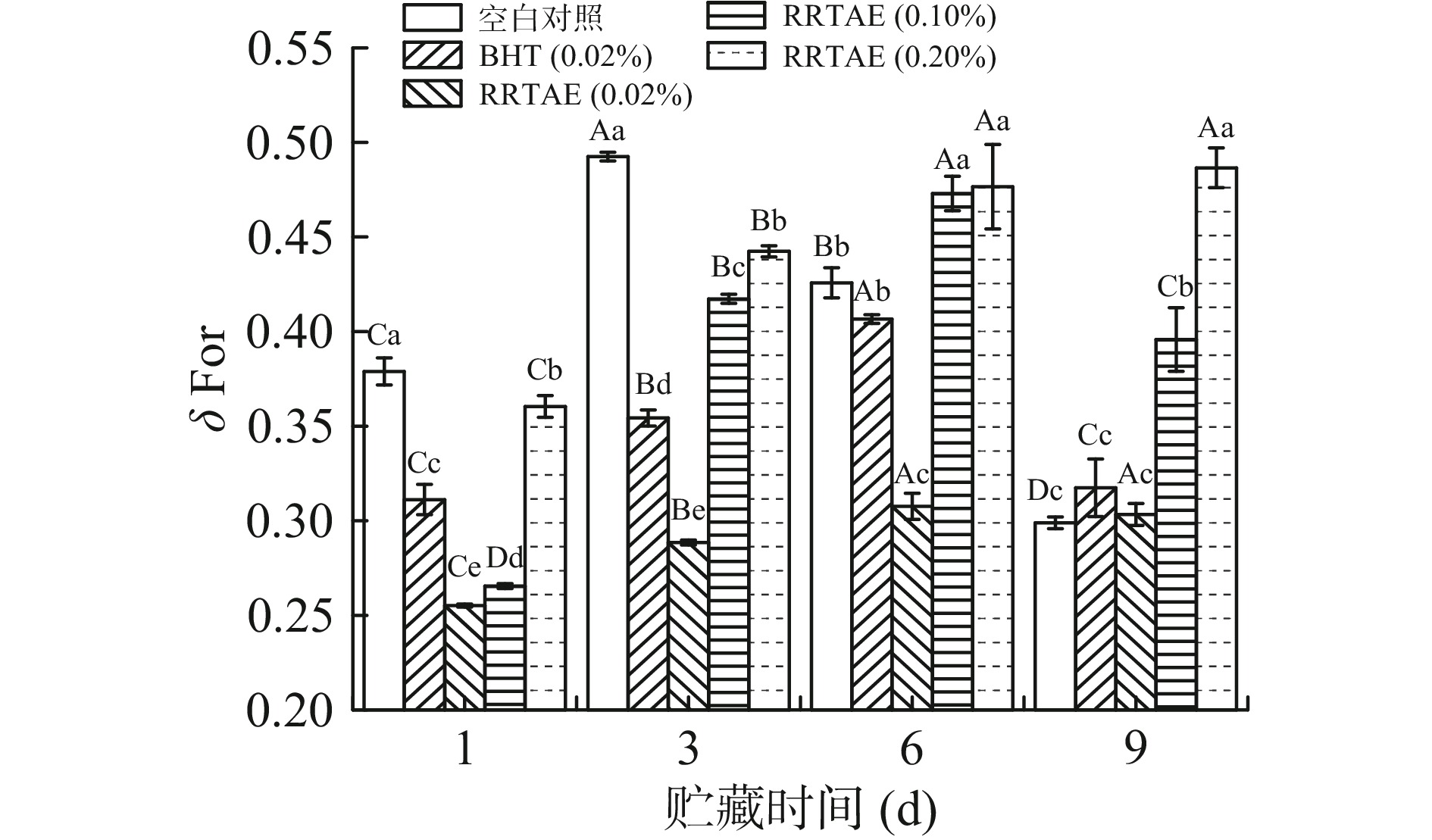
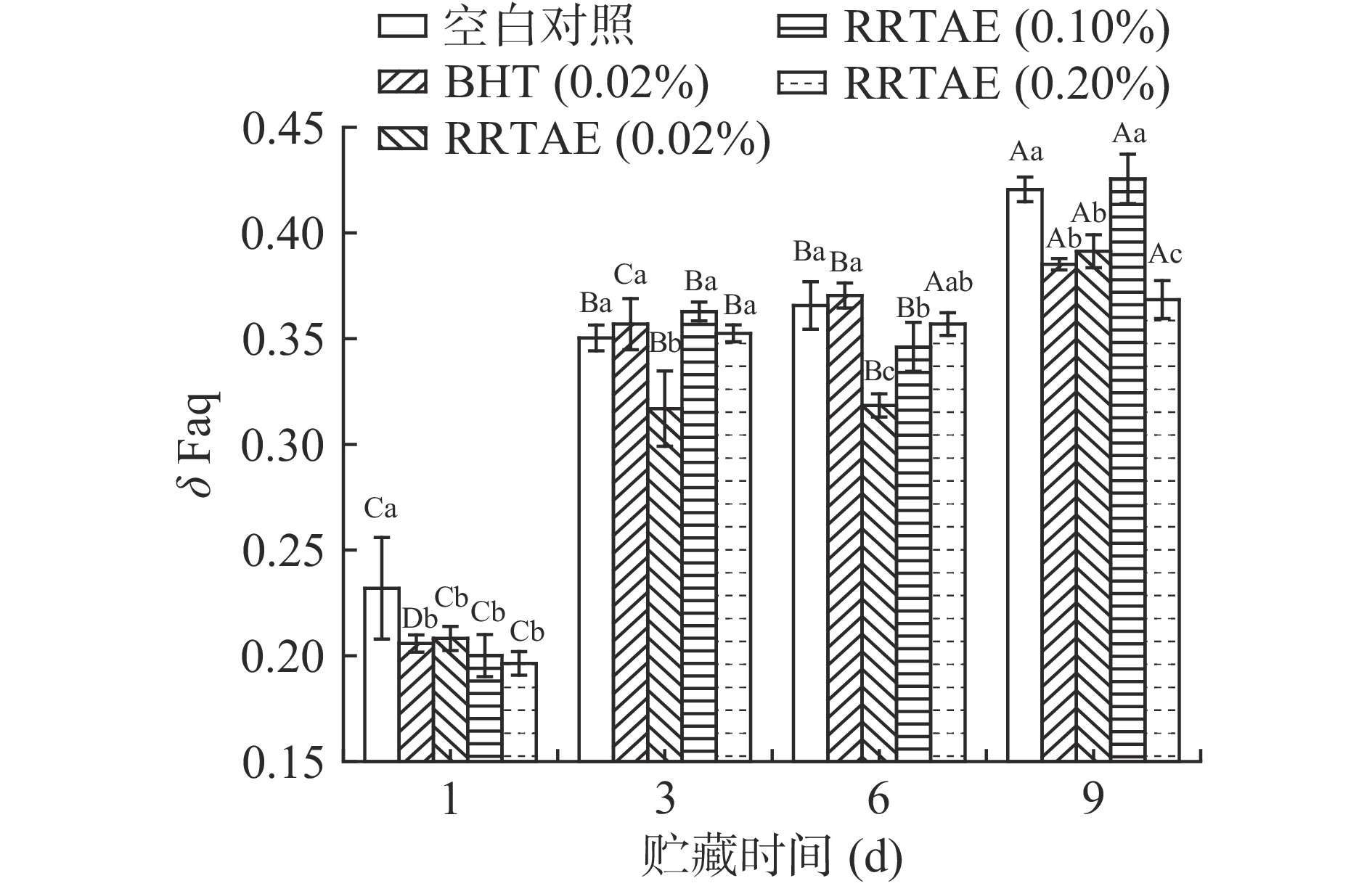
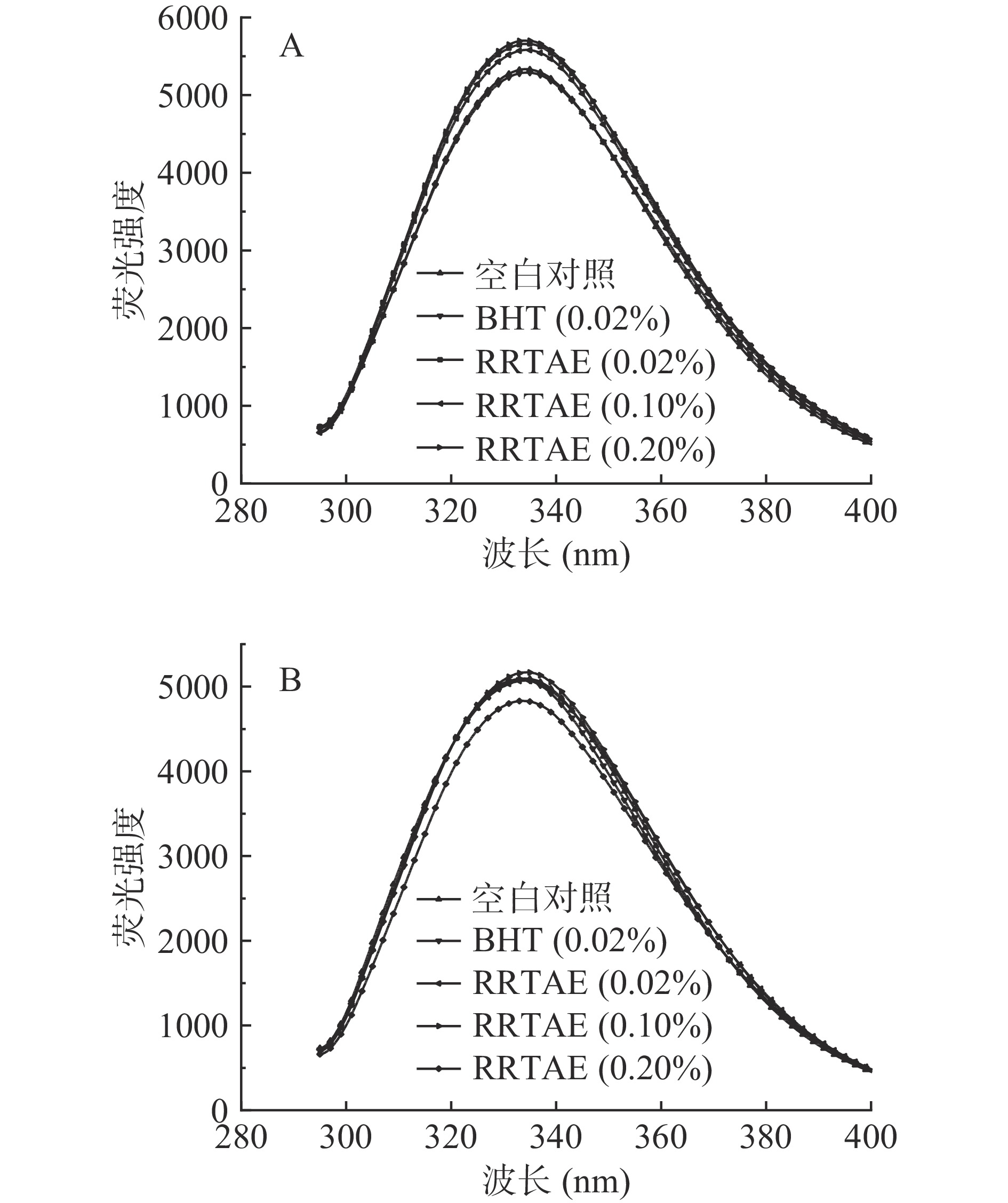
2.4 RRTAE对牦牛肉糜荧光化合物的影响
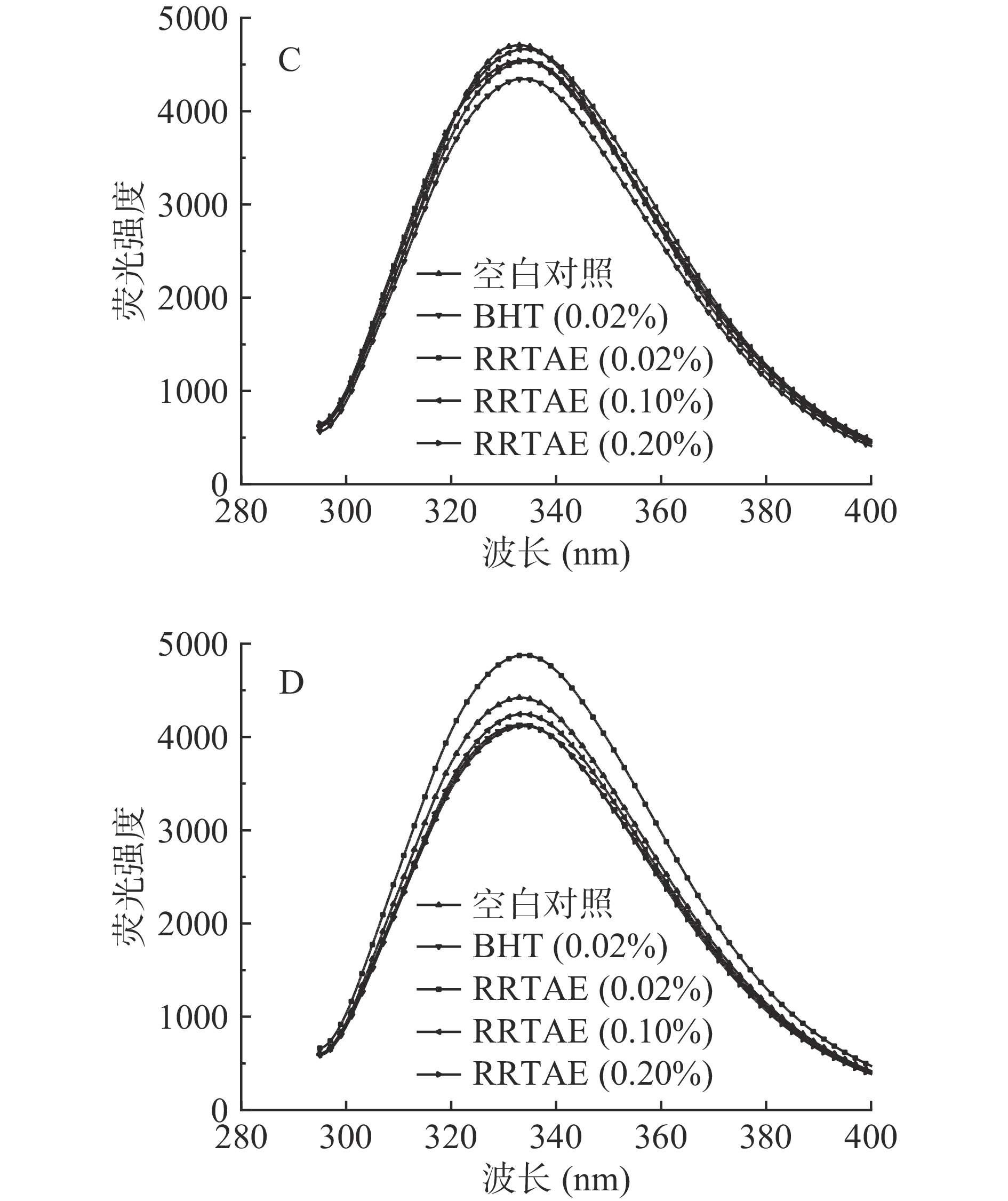
荧光化合物的含量可间接反应脂质的过氧化水平,脂质过氧化可产生丙二醛等羰基化合物,其可与蛋白质、氨基酸反应生成能产生荧光的席夫碱[15]。不同处理方式下,牦牛肉糜在有机相(δ For)中的荧光位移如图3所示,在水相(δ Faq)中的荧光位移如图4所示。荧光在有机相中的位移显示,贮藏第1 d,各RRTAE处理组的δ For显著低于空白对照(P<0.05)。贮藏9 d内,除0.20% RRTAE处理组以外的所有试验组的 δ For均呈现先增大后减小的趋势,0.20% RRTAE处理组的δ For持续增加。AUBOUG等[27]发现沙丁鱼的δ For会随着贮藏时间的延长而增大,而脂质进一步氧化可能导致荧光物质附着在氨基成分上,使其不溶于有机溶剂,引起δ For下降,说明0.20% RRTAE处理组可能未发生进一步氧化。
荧光在水相中的位移显示,贮藏第1 d,各RRTAE处理组的δ Faq显著低于空白对照组(P<0.05),但与0.02% BHT处理组接近。贮藏第9 d,0.20% RRTAE处理组的δ Faq显著低于其他试验组(P<0.05)。贮藏时间越长,脂溶性化合物在水相中的溶解性越强,各试验组的δ Faq越大[15],这与卢亭等[28]的研究结果相似。综上,牦牛肉糜中添加RRTAE可有效抑制水相中荧光位移的增加,同时减缓脂质进一步氧化的速度,且0.20% RRTAE处理组抑制脂质氧化的效果最好。
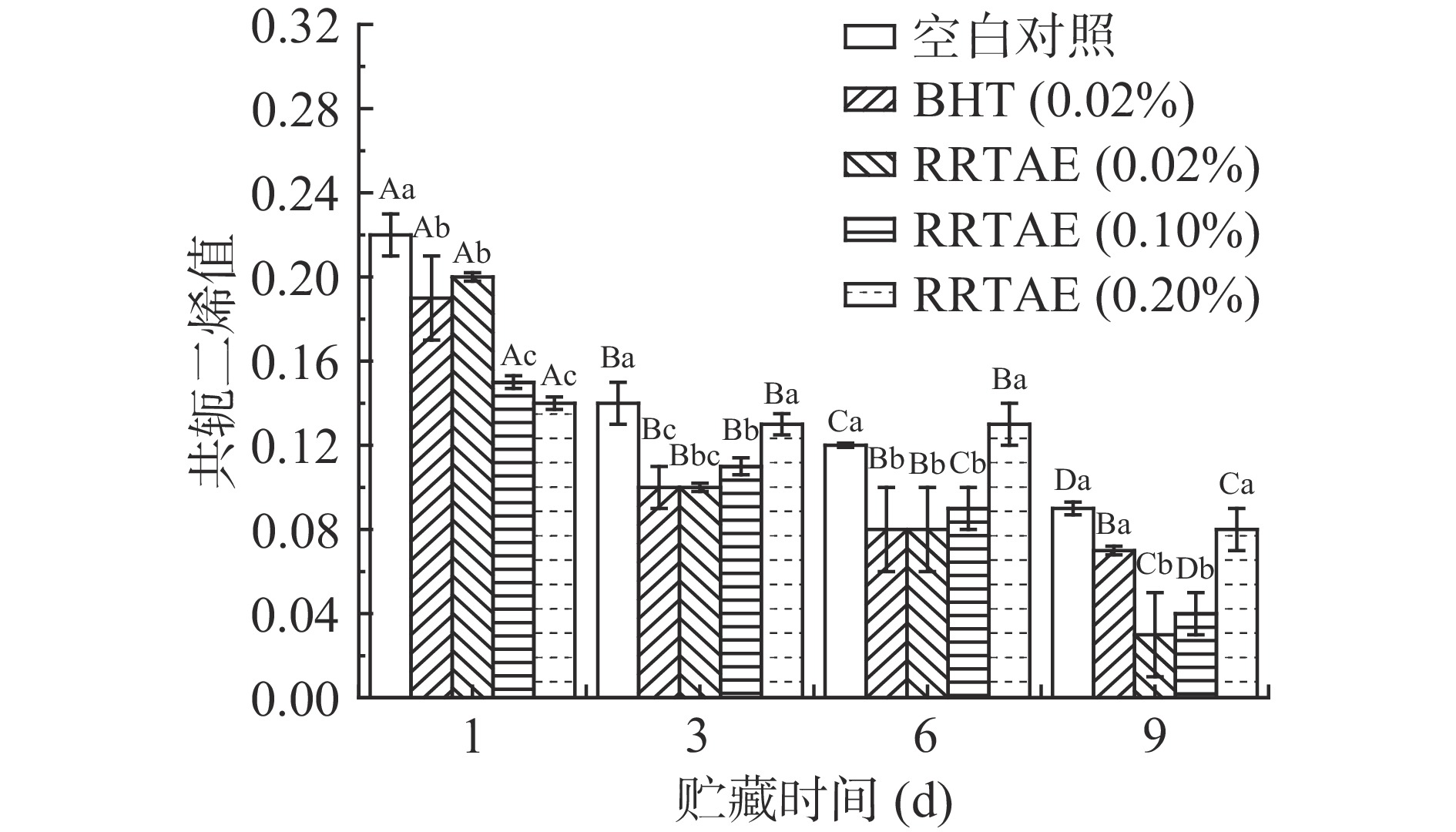
2.5 RRTAE对牦牛肉糜CD值的影响
共轭二烯是脂质氧化过程的中间产物,其极不稳定,可进一步分解生成次级氧化产物,可以用来反映脂质的氧化程度[29]。牦牛肉糜初级氧化产物CD值如图5所示,贮藏第1 d,空白对照组的CD值显著高于其他试验组(P<0.05),且RRTAE添加量越大,CD值越小,这可能与RRTAE中含有的抗氧化物质有关,例如维生素C、黄酮、多酚等[5],其可清除牦牛肉糜贮藏过程中产生的自由基,使多不饱和脂肪免受一定程度的损伤,从而减少双键和共轭二烯的排列。贮藏期间,空白对照组、0.02% BHT、0.02% RRTAE、0.10%RRTAE、0.20%RRTAE处理组的CD值分别下降0.13、0.12、0.17、0.11、0.06,说明牦牛肉糜中添加RRTAE可有效减缓脂质进一步氧化的速度,且0.20% RRTAE 处理组的抑制效果最好。整个贮藏期间,所有处理组的CD值均下降,这可能是由于脂质二级氧化产物共轭二烯进一步分解成其他小分子挥发性物质[29]。
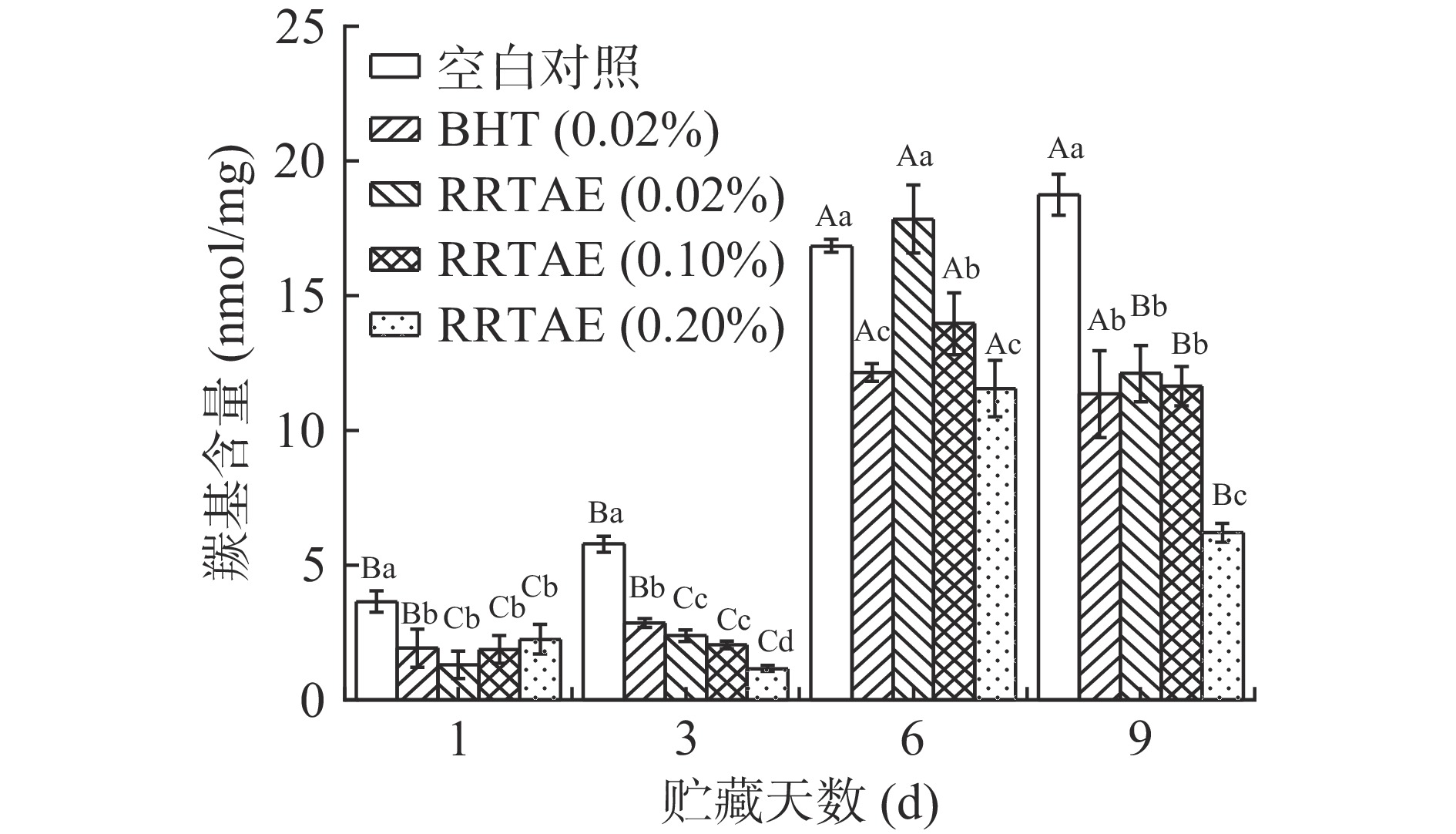
2.6 RRTAE对牦牛肉糜羰基含量的影响
氨基酸侧链NH2基团的直接氧化、肽链骨架的断裂、与还原糖发生反应等与羰基含量的变化密切相关[18]。因此,羰基含量可作为判断肉样中蛋白质氧化程度的重要依据。如图6所示,贮藏期间,所有试验组的羰基含量整体上是增大的,其中空白对照组的羰基含量由第1 d的3.65 nmol/mg显著增加到第9 d的18.75 nmol/mg(P<0.05),说明蛋白质的氧化程度越大,羰基含量越高,这与贾娜等[18]研究冷藏猪肉糜中添加儿茶素的结果相似。贮藏第1 d,各RRTAE处理组的羰基含量显著低于空白对照组(P<0.05),RRTAE各组之间与0.02% BHT处理组差异不显著(P>0.05),说明在一定时间内,RRTAE的浓度对蛋白质的氧化抑制速率影响不大。贮藏第9 d,0.02% BHT处理组与0.02% RRTAE、0.10% RRTAE处理组差异不显著(P>0.05),但0.20% RRTAE处理组显著低于0.02% BHT处理组(P<0.05),这可能与0.20% RRTAE处理组含有的酚类物质浓度较高有关。UTRERA等[30]发现酚类物质的抗氧化效果与其自身浓度、种类等密切相关。
2.7 RRTAE对牦牛肉糜表面疏水性的影响
表面疏水性可作为评判蛋白质分子内部疏水性氨基酸残基暴露程度地主要指标之一,其常用溴酚蓝结合量表示[10]。牦牛肉糜的表面疏水性如图7所示,随贮藏时间的延长,所有处理组的表面疏水性呈不同程度地增长,其中空白对照组第9 d的溴酚蓝结合量约为第1 d的1.51倍,说明贮藏时间越长,MP内部的非极性氨基酸暴露的程度越大,蛋白质的不稳定性也逐渐增加。贮藏第1 d,所有RRTAE处理组的溴酚蓝结合量均显著低于空白对照组(P<0.05),0.10% RRTAE、0.20% RRTAE处理组高于0.02% BHT处理组(P<0.05),说明贮藏初期RRTAE对蛋白质氧化的抑制作用明显,但效果没有BHT好。贮藏第6~9 d,所有RRTAE处理组的溴酚蓝结合量均显著低于空白对照组、0.02% BHT处理组(P<0.05),其中0.20% RRTAE处理组的溴酚蓝结合量最小,说明随着氧化程度的加剧,RRTAE充分抑制了蛋白结构的暴露程度,可以有效降低牦牛肉糜的表面疏水性,且0.20% RRTAE处理组的效果最好。吕卫金等[31]发现通过抑制冷藏大黄鱼的蛋白质氧化损伤可有效改善肉品腐败变质的程度。因此,牦牛肉糜中加入RRTAE可通过抑制蛋白质氧化在一定程度上提高肉品的品质特性。
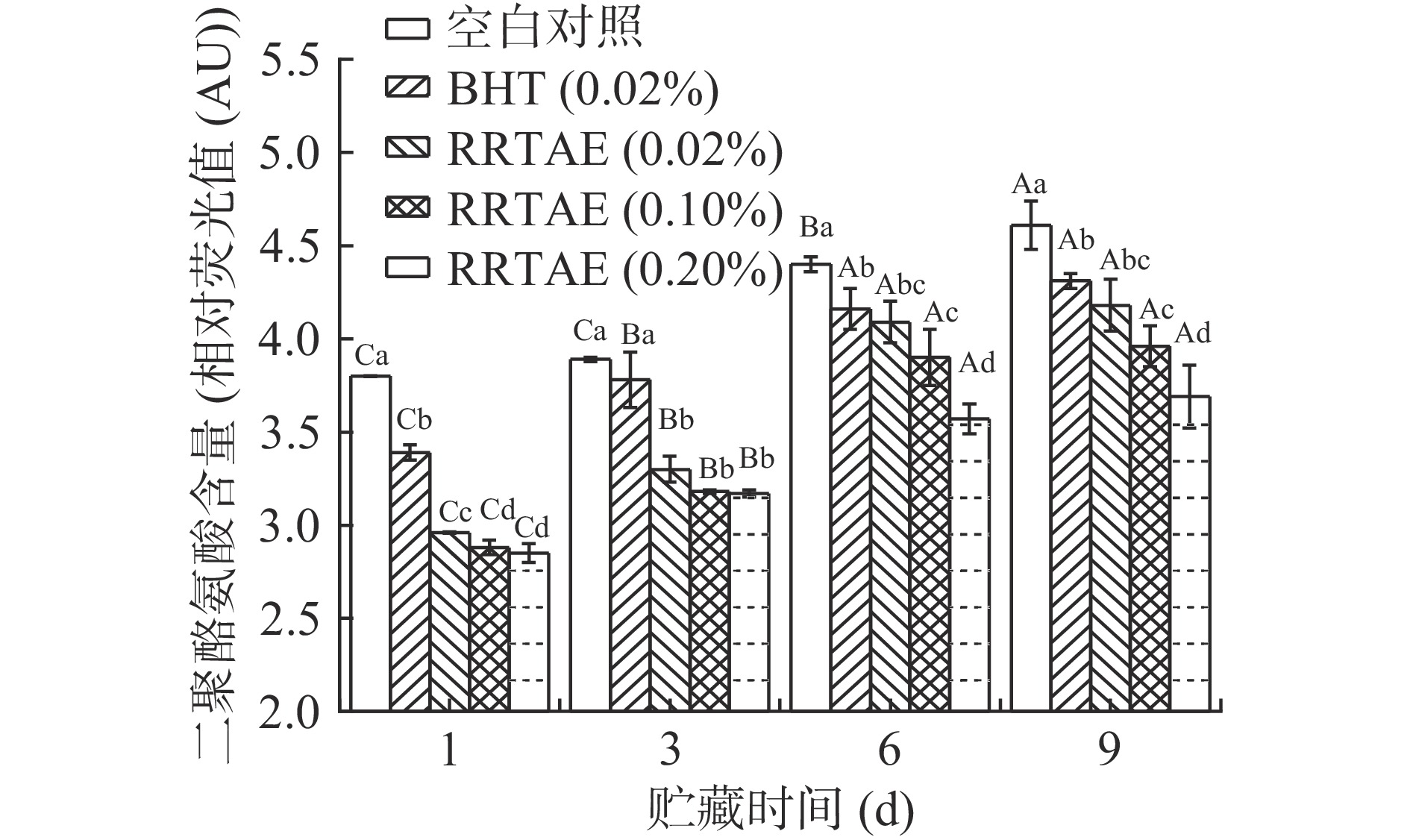
2.8 RRTAE对牦牛肉糜二聚酪氨酸含量的影响
二聚酪氨酸由酪氨酸受到自由基攻击后产生的酪氨酸自由基和酪氨酸残基通过共价键和非共价键相互作用形成,其可在一定程度上反映蛋白质结构的变化[32],且二聚酪氨酸含量越高,蛋白质结构变化越严重,氧化程度越大。如图8所示,随着贮藏时间的延长,各试验组的二聚酪氨酸含量呈上升趋势,其中空白对照组的二聚酪氨酸含量从第1 d的3.802 AU增加到了第9 d的4.610 AU,其原因可能是牦牛肉糜所含的蛋白质发生氧化作用产生大量的酪氨酸残基,从而相互聚合产生大量的二聚酪氨酸所致。贮藏第1~3 d,各RRTAE处理组的二聚酪氨酸含量均显著低于空白对照组、0.02% BHT处理组(P<0.05)。贮藏 6~9 d,各RRTAE处理组的二聚酪氨酸含量均显著低于空白对照组(P<0.05),0.20% RRTAE处理组的二聚酪氨酸含量显著低于其他试验组(P<0.05),说明RRTAE具有良好的抗氧化性能,且0.20% RRTAE抗氧化效果最好,这可能与RRTAE含有较高浓度的抗氧化活性物质有关,其可有效清除氧化过程中产生的自由基,从而有效抑制二聚酪氨酸含量的增加[32]。
2.9 RRTAE对牦牛肉糜色氨酸的影响
色氨酸是芳香族氨基酸的一种,其对色氨酸残基周边的微环境特别敏感,可作为评判蛋白质结构变化程度的指标之一[10]。牦牛肉糜色氨酸荧光强度如图9所示,随着时间的延长,所有处理组的色氨酸荧光强度均不断下降,荧光强度降低的主要原因可能是贮藏期间蛋白质的空间结构发生改变导致色氨酸被暴露在极性环境中,使牦牛肉糜的荧光强度降低[19]。贮藏第9 d,各RRTAE处理组的色氨酸荧光强度随添加量的增加而逐渐降低,可能是由于0.20% RRTAE处理组中多酚物质占主导地位,增强了极性环境,且对色氨酸产生屏障作用,降低了色氨酸荧光强度,这与李锦锦等[12]研究结果相似。
2.10 RRTAE对牦牛肉糜感官品质的影响
不同处理对牦牛肉糜感官品质的影响如表4所示。“表观色彩”指标:贮藏第1 d,各试验组间无显著差异(P>0.05)。贮藏第3~9 d,各RRTAE处理组表观色彩评分值均显著高于空白对照组、0.02% BHT处理组(P<0.05),这可能是因为RRTAE可抑制Met Mb的形成,在一定程度上维持牦牛肉糜的颜色。
表 4 RRTAE对牦牛肉糜感官品质的影响Table 4. Effect of RRTAE on sensory quality of minced yak meat贮藏时间(d) 组别 表观色彩 组织状态 气味 1 空白对照 3.70±0.17Aa 3.80±0.10Aa 3.82±0.06Aa BHT(0.02%) 3.83±0.15Aa 3.83±0.06Aa 3.92±0.06Aa RRTAE(0.02%) 3.80±0.10Aa 3.90±0.10Aa 3.90±0.07Aa RRTAE(0.10%) 3.87±0.06Aa 3.90±0.01Aa 3.92±0.12Aa RRTAE(0.20%) 3.90±0.10Aa 3.92±0.05Aa 3.92±0.06Aa 3 空白对照 2.30±0.26Bb 3.03±0.06Bc 3.00±0.10Bc BHT(0.02%) 2.37±0.32Bb 3.10±0.10Bc 3.10±0.10Bc RRTAE(0.02%) 3.10±0.10Ba 3.50±0.10Bb 3.50±0.10Bb RRTAE(0.10%) 3.30±0.26Ba 3.83±0.15Aa 3.83±0.15Aa RRTAE(0.20%) 3.37±0.32Ba 3.90±0.10Aa 3.70±0.10Bab 6 空白对照 2.00±0.10Bb 2.07±0.06Cc 2.20±0.20Cc BHT(0.02%) 2.10±0.10Bb 2.13±0.06Cc 2.17±0.06Cc RRTAE(0.02%) 3.13±0.15Ba 3.20±0.20Cb 3.07±0.06Cb RRTAE(0.10%) 3.30±0.10Ba 3.23±0.15Bb 3.17±0.06Bb RRTAE(0.20%) 3.30±0.10Ba 3.47±0.06Ba 3.70±0.10Ba 9 空白对照 1.10±0.10Cd 1.03±0.15Dc 2.00±0.10Cc BHT(0.02%) 1.30±0.10Cc 0.87±0.06Dc 1.87±0.06Dc RRTAE(0.02%) 2.73±0.06Cb 2.73±0.06Db 2.73±0.06Db RRTAE(0.10%) 3.07±0.06Ba 3.13±0.06Ba 3.10±0.10Ba RRTAE(0.20%) 3.20±0.10Ba 3.30±0.10Ca 3.07±0.06Ca “组织状态”指标:随着贮藏时间的延长,所有试验组的牦牛肉糜组织状态呈下降趋势,可能是因为肉糜表面的水分减少使弹性下降。贮藏第1 d,各试验组组织状态无显著差异(P>0.05)。贮藏第3~9 d,各RRTAE处理组的组织状态显著优于空白对照组、0.02% BHT处理组(P<0.05),且0.20% RRTAE处理组的效果最好。
“气味”指标:整个贮藏期,所有试验组的气味评分值均出现显著下降(P<0.05),且贮藏第9 d的空白对照组相比第一天的气味指标值减少了1.82。贮藏第1 d,各试验组气味评分值无显著差异(P>0.05)。贮藏第3 d开始,各RRTAE处理组的气味评分值显著高于空白对照组、0.02%BHT处理组(P<0.05)。贮藏结束时,0.10% RRTAE、0.20% RRTAE处理组相比于第1 d的气味评分值分别减少了0.82、0.85,说明牦牛肉糜中加入RRTAE可在一定程度上抑制气味的变化。综上,添加0.20% RRTAE对贮藏期间牦牛肉糜感官品质的改善效果最好。
3. 结论
RRTAE富含维生素C、黄酮、多酚等抗氧化物质,具有很强的抗氧化作用,可抑制贮藏过程中牦牛肉糜pH的增加,并改善牦牛肉糜的a*、b*值;在抑制蛋白质氧化方面,当RRTAE添加量为0.20%时,可降低牦牛肉糜的羰基含量,其抑制效果可能随RRTAE所含酚类物质浓度的增加而提高;RRTAE可降低牦牛肉糜的表面疏水性、二聚酪氨酸含量,且二聚酪氨酸的抑制效果随添加量的增多而递增;在抑制脂质氧化方面,RRTAE的添加量为0.02%即可显著抑制TBARS值的增加,且RRTAE的添加量越大,抑制效果越好。综上,RRTAE可显著改善贮藏过程中牦牛肉糜感官品质的变化,对贮藏期间牦牛肉糜的理化性质也具有良好的改善效果。
-
表 1 牦牛肉糜处理组
Table 1 Minced yak meat treatment group
组号 组别 处理 1 空白对照 1.5%NaCl 2 0.02% BHT 1.5%NaCl、0.02% BHT 3 0.02% RRTAE 1.5%NaCl、0.02% RRTAE 4 0.10% RRTAE 1.5%NaCl、0.10% RRTAE 5 0.20% RRTAE 1.5%NaCl、0.20% RRTAE 注:NaCl、BHT和RRTAE添加量均以牦牛肉糜质量为基准,且1.5%、0.02%、0.10%、0.20%均为质量分数。 表 2 牦牛肉糜感官评定标准
Table 2 Sensory evaluation standard of minced yak meat
等级 分值 表观色彩 组织状态 气味 一级鲜牦牛肉 4 鲜红 有弹性,不粘手 牦牛肉风味浓郁 二级鲜牦牛肉 3 鲜( 褐) 红 弹性不足,
有少量汁液流出牦牛肉风味不浓郁 轻度变质牦牛肉 2 褐红 松弛粘手,
汁液流失较多稍有异味 变质牦牛肉 1 褐红发白 粘手,汁液流失多 腐败牦牛肉味 表 3 RRTAE对牦牛肉糜色泽的影响
Table 3 Effect of RRTAE on the color of minced yak meat
贮藏时间(d) 组别 L* a* b* 1 空白对照 32.02±0.55Aa 8.93±0.89Ab 9.55±0.84Ac BHT(0.02%) 32.29±1.85Aa 10.18±1.80Aab 10.47±0.86BCbc RRTAE(0.02%) 31.85±0.95Ca 11.70±1.17Aa 12.06±0.85Aa RRTAE(0.10%) 31.53±1.05Ca 10.48±1.60Bab 11.77±2.37Aab RRTAE(0.20%) 31.20±0.60Da 11.57±1.46ABa 12.99±0.48ABa 3 空白对照 29.52±0.42Bc 8.63±0.79Ab 9.64±0.65Ab BHT(0.02%) 32.08±1.49Ab 8.26±1.65Bb 10.27±1.62Cb RRTAE(0.02%) 33.38±1.60Bab 10.23±1.27Aab 10.97±1.52Bab RRTAE(0.10%) 33.04±1.53Bab 11.13±0.96ABa 11.38±1.08Aa RRTAE(0.20%) 34.15±0.90Ca 10.76±2.71Ba 10.39±1.09Cab 6 空白对照 28.73±0.43BCd 5.75±0.24Bd 9.25±0.89Ab BHT(0.02%) 32.01±0.65Ac 8.02±0.72Bc 11.75±0.62ABa RRTAE(0.02%) 34.98±0.82Ab 10.64±1.13Ab 12.45±1.02Aa RRTAE(0.10%) 35.22±0.75Ab 11.66±0.66ABb 12.36±0.87Aa RRTAE(0.20%) 36.36±0.90Ba 13.38±1.68Aa 12.57±0.75Ba 9 空白对照 28.31±1.30Cd 5.62±0.49Bb 9.07±0.31Ac BHT(0.02%) 29.71±1.03Bc 6.35±1.05Cb 12.02±0.96Ab RRTAE(0.02%) 35.39±1.10Ab 11.82±1.42Aa 12.84±0.48Aab RRTAE(0.10%) 35.55±0.98Ab 12.34±1.53Aa 12.97±1.93Aab RRTAE(0.20%) 38.55±0.81Aa 13.38±1.92Aa 13.89±0.98Aa 注:贮藏时间相同但处理组不同的差异显著性用同列小写字母表示;处理组相同但贮藏时间不同的差异显著性用同列大写字母表示;表4同。 表 4 RRTAE对牦牛肉糜感官品质的影响
Table 4 Effect of RRTAE on sensory quality of minced yak meat
贮藏时间(d) 组别 表观色彩 组织状态 气味 1 空白对照 3.70±0.17Aa 3.80±0.10Aa 3.82±0.06Aa BHT(0.02%) 3.83±0.15Aa 3.83±0.06Aa 3.92±0.06Aa RRTAE(0.02%) 3.80±0.10Aa 3.90±0.10Aa 3.90±0.07Aa RRTAE(0.10%) 3.87±0.06Aa 3.90±0.01Aa 3.92±0.12Aa RRTAE(0.20%) 3.90±0.10Aa 3.92±0.05Aa 3.92±0.06Aa 3 空白对照 2.30±0.26Bb 3.03±0.06Bc 3.00±0.10Bc BHT(0.02%) 2.37±0.32Bb 3.10±0.10Bc 3.10±0.10Bc RRTAE(0.02%) 3.10±0.10Ba 3.50±0.10Bb 3.50±0.10Bb RRTAE(0.10%) 3.30±0.26Ba 3.83±0.15Aa 3.83±0.15Aa RRTAE(0.20%) 3.37±0.32Ba 3.90±0.10Aa 3.70±0.10Bab 6 空白对照 2.00±0.10Bb 2.07±0.06Cc 2.20±0.20Cc BHT(0.02%) 2.10±0.10Bb 2.13±0.06Cc 2.17±0.06Cc RRTAE(0.02%) 3.13±0.15Ba 3.20±0.20Cb 3.07±0.06Cb RRTAE(0.10%) 3.30±0.10Ba 3.23±0.15Bb 3.17±0.06Bb RRTAE(0.20%) 3.30±0.10Ba 3.47±0.06Ba 3.70±0.10Ba 9 空白对照 1.10±0.10Cd 1.03±0.15Dc 2.00±0.10Cc BHT(0.02%) 1.30±0.10Cc 0.87±0.06Dc 1.87±0.06Dc RRTAE(0.02%) 2.73±0.06Cb 2.73±0.06Db 2.73±0.06Db RRTAE(0.10%) 3.07±0.06Ba 3.13±0.06Ba 3.10±0.10Ba RRTAE(0.20%) 3.20±0.10Ba 3.30±0.10Ca 3.07±0.06Ca -
[1] 陈晓迪, 刘飞, 徐虹. 脂溶性天然抗氧化剂的研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(3):299−304. [CHEN X D, LIU F, XU H. State of the art of the study of natural liposoluble antioxidants[J]. Food Science,2017,38(3):299−304. [2] 类红梅, 罗欣, 毛衍伟, 等. 天然抗氧化剂的功能及其在肉与肉制品中的应用研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(21):267−277. [LEI H M, LUO X, MAO Y W, et al. Research progress on the function of natural antioxidants and their application in meat and meat products[J]. Food Science,2020,41(21):267−277. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20191025-286 [3] 邱光明, 谭兰兰, 汪长国, 等. 刺梨提取物的制备及其在卷烟中的应用研究[J]. 安徽农业科学,2014,42(13):4046−4049. [QIU G M, TAN L L, WANG C G, et al. Preparation of Rosa roxburghii extract and its application in cigarette[J]. Anhui Agricultural Science,2014,42(13):4046−4049. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2014.13.101 [4] 付阳洋, 刘佳敏, 卢小鸾, 等. 刺梨主要活性成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(13):328−335, 342. [FU Y Y, LIU J M, LU X L, et al. Research progress on main active components and pharmacological effects of Rosa roxburghii Tratt[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(13):328−335, 342. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.13.052 [5] 范春雪, 邓玉林, 张亚玺, 等. 刺梨药理活性研究进展[J]. 生命科学仪器,2021,19(2):14−21. [FAN C X, DENG Y L, ZHANG Y X, et al. Research progress on pharmacological activity of Rosa roxburghii Tratt[J]. Life Science Instruments,2021,19(2):14−21. [6] 梁梦琳, 李清, 龙勇兵, 等. 刺梨的化学成分鉴定及其抗菌活性[J]. 贵州农业科学,2019,47(5):10−13. [LIANG M L, LI Q, LONG Y B, et al. Identification of chemical constituents of Rosa roxburghii and their antibacterial activitiesies[J]. Guizhou Agricultural Sciences,2019,47(5):10−13. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3601.2019.05.003 [7] 贺琴, 尚含乐. 刺梨的营养价值、生物学功能及其在畜禽生产中的应用[J]. 动物营养学报,2022,34(8):4776−4784. [HE Q, SHANG H L. Nutritional value and biological function of Rosa roxburghii Tratt and its application in livestock and poultry production[J]. Chinese Journal of Animal Nutrition,2022,34(8):4776−4784. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-267x.2022.08.003 [8] 张潘, 汪磊, 陈洁, 许飞. 刺梨多糖对非酒精性脂肪肝小鼠回肠粘膜屏障功能的影响[J/OL]. 食品科学: 1−20[2022-07-11]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2206.TS.2022062. ZHANG P, WANG L, CHEN J, et al. Effects of Rosa roxburghii Tratt polysaccharide on ileal mucosal barrier function in mice with non-alcoholic fatty liver[J/OL]. Food Science: 1−20[2022-07-11]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2206.TS.2022062.
[9] 董玉雪. 刺梨水提物抗氧化损伤作用研究[D]. 杨凌: 西北农林科技大学, 2011. DONG Y X. The effect on oxidative damage of aqueous extract from Rose roxburghii Tratt[D]. Yangling: Northwest Agriculture and Forestry University, 2011.
[10] 李琼帅, 唐善虎, 李思宁, 等. 石榴皮提取物对贮藏期间牦牛肉糜蛋白质氧化及挥发性风味物质影响的研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(10):93−100. [LI Q S, TANG S H, LI S N, et al. Effects of pomegranate peel extract on protein oxidation and volatile flavor substances of yak meat during storage[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2022,48(10):93−100. [11] 孟嘉珺, 许树荣, 邓莎, 等. 食盐腌制对鸡肉品质、肌原纤维蛋白结构和功能特性的影响[J/OL]. 食品工业科技: 1−16[2022-07-11]. DOI: 10.13386/j. issn1002-0306.2022020270. MENG J J. XU S R, DENG S, et al. Effects of salt marinating on chicken quality and structure characteristics, function characteristics of chicken myofibrillar protein[J/OL]. Science and Technology of Food Industry: 1−16[2022-07-11]. DOI: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2022020270.
[12] 李锦锦, 唐善虎, 李思宁, 等. 大蒜粉对牦牛肉肌原纤维蛋白体外氧化保护作用的研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(14):145−152. [LI J J, TANG S H, LI S N, et al. Oxidative protection effect of garlic powder on yak myofibrillar protein in vitro[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2022,48(14):145−152. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.028625 [13] 顾苑婷, 牟琴, 黄燕, 等. 迷迭香和百里香提取物对冷藏猪肉丸品质的影响[J]. 食品科技,2021,46(4):103−109. [GU Y T, MOU Q, HUANG Y, et al. Effects of rosemary and thyme extracts on the quality of chilled pork balls[J]. Food Science and Technology,2021,46(4):103−109. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2021.04.016 [14] 阮一凡, 潘道东, 孙杨赢, 等. 混菌发酵鸭腿工艺优化及其贮藏品质特性[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(10):101−109. [RUAN Y F, PAN D D, SUN Y Y, et al. Optimization of production of fermented duck thigh with a mixed starter culture of Lactobacillus plantarum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae and changes in its quality characteristics during storage[J]. Food Science,2020,41(10):101−109. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190408-068 [15] 李锦锦, 莫然, 李琼帅, 等. 超声波解冻功率对猪肝品质及脂质氧化特性的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(8):113−119, 127. [LI J J, MO R, LI Q S, et al. Effects of ultrasonic thawing power on quality and lipid oxidation properties of porcine liver[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2022,48(8):113−119, 127. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.027680 [16] GEORGANTELIS D, BLEKAS G, KATIKOU P, et al. Effect of rosemary extract, chitosan and α-tocopherol on lipid oxidation and colour stability during frozen storage of beef burgers[J]. Meat Science,2007,75(2):256−264. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2006.07.018
[17] 郑娇, 唐善虎, 李思宁, 等. 有机酸前处理对风干牦牛肉理化性质及挥发性风味物质的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(7):97−104. [ZHENG J, TANG S H, LI S N, et al. Effects of pre-treatments with organic acid on the physicochemical properties and volatile flavor substances of air-dried yak jerky[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2020,46(7):97−104. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.022727 [18] 贾娜, 刘丹, 王乐田, 等. 儿茶素对冷藏猪肉糜脂肪和蛋白氧化及品质特性的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2018,18(12):210−218. [JIA N, LIU D, WANG L T, et al. Effect of catechin on lipid/protein oxidation and quality of minced pork during chilled storage[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2018,18(12):210−218. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2018.12.027 [19] 邓思杨, 王博, 李海静, 等. 冻融次数对镜鲤鱼肌原纤维蛋白功能和结构特性变化的影响[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(11):95−101. [DENG S Y, WANG B, LI H J, et al. Effect of freeze-thaw cycles on changes in functional and structural properties of myofibrillar protein from mirror carp (Cyprinus carpio var. specularis)[J]. Food Science,2019,40(11):95−101. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180606-079 [20] 李玲, 季慧, 康大成, 等. 氧化条件下茶多酚对猪肉肌原纤维蛋白理化和凝胶特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(2):12−17. [LI L, JI H, KANG D C, et al. Effect of tea polyphenols on physicochemical and gel properties of pork myofibrillar protein under oxidative conditions[J]. Food Science,2019,40(2):12−17. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180606-064 [21] 盘艳梅, 吴海铃, 刘啸, 等. 海藻酸钠/迷迭香涂膜对冷却猪肉品质的影响[J]. 安徽农业科学,2021,49(14):166−168, 171. [PAN Y M, WU H L, LIU X, et al. Effect of sodium alginate/rosemary coating on quality of chilled pork[J]. Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2021,49(14):166−168, 171. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0517-6611.2021.14.044 [22] 李琼帅, 唐善虎, 李思宁, 等. 石榴皮提取物对牦牛肉糜制品贮藏期间理化特性及流变特性影响的研究[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022,48(6):90−97. [LI Q S, TANG S H, LI S N, et al. Effects of pomegranate peel extract on the physico-chemical properties and rheological properties of yak minced meat products during storage[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2022,48(6):90−97. [23] FAUSTMAN C, SUN Q, MANCINI R, et al. Myoglobin and lipid oxidation interactions: Mechanistic bases and control[J]. Meat Science,2010,86(1):86−94. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2010.04.025
[24] 李伟, 张小英, 陈熔, 等. 桉叶多酚对冷却猪肉的保鲜效果[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(11):252−257. [LI W, ZHANG X Y, CHEN R, et al. Preservative effects of eucalyptus robusta leaves polyphenols extact on chilled pork[J]. Food and Fermentation Industry,2020,46(11):252−257. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.022781 [25] VILLALOBOS-DELGADO L H, EG GONZÁLEZ-MONDRAGÓN, J RAMÍREZ-ANDRADE, et al. Oxidative stability in raw, cooked, and frozen ground beef using epazote (Chenopodium ambrosioides L.)[J]. Meat Science,2020,168:108−187.
[26] 张煊, 徐玉, 薛海, 等. 藤茶提取物对素肉丸冷藏期间脂质和蛋白质氧化的抗氧化活性影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(3):212−217. [ZHANG X, XU Y, XUE H, et al. Antioxidant activity of vine tea (Ampelopsis grossedentata) extract on lipid and protein oxidation in vegetarian meatballs during refrigerated storage[J]. Food Science,2020,41(3):212−217. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190207-024 [27] AUBOURG S P, SOTELO C G, R PÉREZ-MARTÍN. Assessment of quality changes in frozen sardine (Sardina pilchardus) by fluorescence detection[J]. Journal of the American Oil Chemists Society,1998,75(5):575−580. doi: 10.1007/s11746-998-0068-x
[28] 卢亭, 邱继善, 徐玲萍, 等. 不同保鲜技术对大黄鱼品质的影响[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2021,12(23):9198−9202. [LU T, QIU J S, XU L P, et al. Effects of different preservation techniques on the quality of Pseudosciaena crocea[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2021,12(23):9198−9202. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-0381.2021.23.spaqzljcjs202123031 [29] 潘娜, 屈文娇, 君睿红, 等. 不同品种葵花籽油氧化稳定性研究[J]. 中国油脂,2014,39(12):42−45. [PAN N, QU W J, JUN R H, et al. Oxidative stability of oils extracted from different sunflower varieties[J]. China Oil and Fats,2014,39(12):42−45. [30] UTRERA M, M ESTÉVEZ. Analysis of tryptophan oxidation by fluorescence spectroscopy: Effect of metal-catalyzed oxidation and selected phenolic compounds[J]. Food Chemistry,2012,135(1):88−93. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.04.101
[31] 吕卫金, 赵进, 汪金林, 等. 茶多酚延缓冷藏大黄鱼肌原纤维蛋白变性降解机理研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2014,14(1):60−67. [LÜ W J, ZHAO J, WANG J L, et al. Effects of tea polyphenols on preservation mechanism of myofibrillar protein from large yellow croaker[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2014,14(1):60−67. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2014.01.017 [32] 方海砚, 苑歆, 刘友明, 等. 羟自由基氧化对鲢鱼肌原纤维蛋白结构的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(4):6−12. [FANG H Y, YUAN X, LIU Y M, et al. Effect of hydroxyl radical oxidation on the structure of silver carp myofibrillar protein[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(4):6−12. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.04.002 -
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 王馨,吴孟仙,陈媛媛,王林峰,杨生玉,李星科. 杜仲叶固态混菌发酵工艺优化及其体外活性研究. 中国食品添加剂. 2025(03): 29-37 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:






 下载:
下载:



