Molecular Mechanism of Phedimus aizoon (Linnaeus)'t Hart. on Anti-inflammatory Effect Based on Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking and Experiment Research
-
摘要: 目的:本文基于网络药理学技术与分子对接和实验验证探讨费菜抗炎作用机制。方法:利用TCMSP、HERB等数据库,以口服生物利用度≥30%为筛选条件,得到费菜药效成分及其潜在靶点。利用GeneCards、OMIM等数据库查找炎症相关靶点,通过STRING数据库和Cytoscape3.8.0软件绘制PPI蛋白互作图,分析费菜中抗炎的关键药效成分和潜在作用靶点。利用David数据库对潜在作用靶点进行GO富集和KEGG信号通路富集,并进行可视化分析。应用AutoDock软件将药效成分与核心靶点进行分子对接,并进行可视化分析。利用高效液相色谱法分析药效成分。采用LPS诱导的RAW264.7细胞炎症模型,验证药效成分的抗炎作用。结果:筛选得到5个药效成分及相关靶点130个,抗炎靶点421个,两者取交集后获得费菜潜在抗炎靶点22个,其中关键靶点有PPARG、EGFR、TP53等,发挥关键作用的主要成分为β-谷甾醇和没食子酸。GO及KEGG富集分析结果表明,β-谷甾醇和没食子酸主要通过调控聚合酶II启动子的转录正调控、神经元凋亡过程的正调控和脂多糖反应等生物过程,通过癌症通路、乙型肝炎、TNF信号通路、MAPK信号通路等信号通路发挥抗炎作用。分子对接结果显示抗炎药效成分均与靶点蛋白分子对接结果良好。高效液相色谱法证明费菜中含有药效成分β-谷甾醇和没食子酸。实验验证结果表明,β-谷甾醇和没食子酸可显著降低促炎因子NO含量,提高抗炎因子IL-10含量(P<0.05),发挥抗炎作用。结论:本研究揭示了费菜通过调控多靶点、多途径发挥抗炎作用,为费菜的研究和应用奠定了基础。Abstract: Objective: To study the molecular mechanism of Phedimus aizoon (Linnaeus)'t Hart. on anti-inflammatory effect by network pharmacology, molecular docking, and experiment research. Methods: The potential anti-inflammatory effect ingredients and targets were acquired from TCMSP, HERB, and other databases under the screening condition of oral bioavailability ≥30%. The inflammation-related targets were collected from GeneCards, OMIM, and other databases, and the protein-protein interaction (PPI) analysis to obtain the key anti-inflammatory effect targets. Meanwhile, GO annotation and KEGG signal pathway enrichment analysis of the key targets was analyzed using the David database. Moreover, this study verified the key targets predicted by AutoDock molecular docking. The key anti-inflammatory effect ingredients of Phedimus aizoon (Linnaeus)'t Hart. were analyzed using high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC). The anti-inflammatory effect of the key ingredients was verified on the LPS-induced RAW264.7 cell model. Results: The results showed that there were five potent components corresponding to 130 related targets, and 421 inflammation-related targets, with 22 intersection anti-inflammatory targets, among which the key targets were PPARG, EGFR, TP53, etc. β-sitosterol and gallic acid (3,4,5-trihydroxy benzoic acid) were the main ingredients that can be anti-inflammatory. GO annotation and KEGG signal pathway enrichment analysis indicated that β-sitosterol and gallic acid played an anti-inflammatory role through multiple pathways such as transcription from RNA polymerase II promoter, positive regulation of neuron apoptotic process, and response to lipopolysaccharide, etc., as well as signal pathways including pathways in cancer, hepatitis B, TNF signaling pathway, MAPK signaling pathway, and other signaling pathways. Furthermore, the molecular docking analysis revealed that the key targets had good binding affinities with the key active ingredients. β-sitosterol and gallic acid as active ingredients in Phedimus aizoon (Linnaeus)'t Hart. were analyzed by HPLC. The experimental results showed that β-sitosterol and gallic acid could significantly reduce NO content, increase the content of IL-10 (P<0.05), and play an anti-inflammatory effect. Conclusion: This study revealed that Sedum aizoon L. would play an anti-inflammatory role by regulating multiple targets and multiple pathways, which laid a foundation for the research and application of Phedimus aizoon (Linnaeus)'t, Hart.
-
费菜是景天科景天属多年生草本[1],拉丁名为Phedimus aizoon (Linnaeus)'t Hart.,全草或根为药材的主要来源[2-3]。在中国四川、湖北、江苏、宁夏、内蒙古等多省地均有栽种,目前国内总产量已达到500万吨以上[4]。费菜作为一种食疗保健作用的蔬菜,不仅具有食用及饮用价值,与其他中草药配伍开发药用保健产品,而且已被用于鸡、鱼和奶牛的养殖中。据现代药理学研究发现,费菜中含有黄酮类、生物碱、酚酸类及挥发性成分等物质[3,5-6],具有保肝、止血、扩张血管和兴奋心脏、调脂、抑菌、抗氧化和增强免疫力等功效[5,7-9],且有报道表明,景天科景天属植物的黄酮类和酚酸类成分具有抗炎作用[10-11]。
黄安玉[11]在筛选养心草抗炎活性单体时,通过建立细菌脂多糖(Lipopolysaccharides,LPS)诱导RAW264.7巨噬细胞建立炎症模型,检测养心草水提乙酸乙酯部位分离的单体对巨噬细胞分泌的炎性细胞因子时发现,RAW264.7细胞经过LPS诱导后促进细胞因子一氧化氮(Nitric Oxide,NO)、肿瘤坏死因子-α(Tumor Necrosis Factor α,TNF-α)、白细胞介素-1β(Interleukin-1β,IL-1β)、白细胞介素-6(Interleukin-6,IL-6)的产生,而在养心草中发现的化合物单体中的原儿茶酸、香草酸、咖啡酸、槲皮素和木犀草素具有抑制这些炎性细胞因子产生的作用,没食子酸、槲皮素咖啡酸等对巨噬细胞有免疫调节作用,表明养心草可能通过减低炎症介质的分泌而发挥抗炎作用。而林珠灿等[12]在探讨景天三七不同部位的提取物在炎症细胞模型的抗炎活性时也发现,景天三七醋酸乙酯部位提取物富有酚酸类和黄酮类,能够显著抑制LSP诱导的炎性细胞中NO、TNF-α、IL-6的释放。另有研究[13]发现,横根费菜乙酸乙酯萃取部位对急性致炎剂二甲苯引起的小鼠耳廓肿胀有最优抑制作用,因其总黄酮含量最高,止痒抗炎效果亦最优。而且对相关炎症介质检测显示,横根费菜水部位对TNF-β、IL-6和NO表达水平具有最明显的抑制效果。然而近年来,利用大数据进行系统而深度挖掘和探讨费菜抗炎作用机制的研究甚少。
本文基于中草药“多成分-多靶点-多途径”的作用特点,结合网络药理学整体性与系统性的特征,通过网络数据库分析基因、蛋白、疾病以及药物之间的关联,从数据网络角度系统性揭示药物成分、疾病和生物系统之间的复杂关系[14-15]。采用分子对接技术将网络药理学得到的药效成分与靶蛋白进行结合探索,根据分析结果,对有效活性成分的抗炎作用进行实验验证,初步探讨费菜的抗炎作用及其分子机制。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 资料数据库
本文主要依据网络数据库平台及在线作图网站进行网络药理学研究,所用数据库、在线作图网站及其网址见表1。
表 1 文章所用数据库、在线作图网站及网址Table 1. Websites of the databases and drawing websites used for the article数据库、在线作
图网站名称网址 TCMSP https://tcmsp-e.com/ HERB http://drug.ac.cn/Search/ PubChem https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ SwissTargetPrediction http://www.swisstargetprediction.ch/predict.php Uniprot https://www.uniprot.org/ GeneCards https://www.genecards.org/ OMIM https://omim.org/ Venny 2.1.0 https://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/
index.htmlSTRING https://cn.string-db.org/ David https://david.ncifcrf.gov/home.jsp PDB数据库 https://www.rcsb.org/ 微生信 http://www.bioinformatics.com.cn/ 1.2 材料与仪器
小鼠巨噬细胞系RAW246.7 American Type Culture Collection (ATCC);β-谷甾醇(纯度≥98%) 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;没食子酸(纯度99%) 上海麦克林生化科技有限公司;脂多糖(Lipopolysaccharides,LPS)来源于大肠杆菌 美国Sigma公司;DMEM培养、胎牛血清和青霉素-链霉素 Gibco公司;一氧化氮检测试剂盒、小鼠IL-10 ELISA检测试剂盒 碧云天生物技术有限公司;色谱级甲醇、色谱级乙腈 北京迈瑞达科技有限公司;乙酸乙酯(分析纯)、磷酸 福晨化学试剂有限公司;娃哈哈纯净水 杭州娃哈哈百立食品有限公司;费菜 青海乐殊园农业科技有限公司。
全波长酶标仪 MultiskanTM Skyhigh Thermo fisher Scientific公司;CO2细胞培养箱 新加坡艺思科技有限公司;低温高速离心机 Tokyo公司;高效液相色谱仪 日本岛津;超声波清洗机 山东新华医疗器械股份有限公司;RE-3000旋转蒸发器 上海亚荣生化仪器厂。
1.3 实验方法
1.3.1 费菜药效成分与靶点的获取
在中药系统药理学数据库与分析平台(TCMSP,Traditional Chinese Medicine Systems Pharmacology Database and Analysis Platform)中以“景天三七”中文名进行搜索,根据口服生物利用度(oral bioavailability, OB)≥30%筛选费菜潜在的药效成分,并进行去重合并。根据药效成分的“Mod ID”在TCMSP数据库药效成分的“Related Targets”收集靶点;根据药效成分的“Molecule Name”在HERB数据库的“Ingredient”收集靶点;通过PubChem数据库下载药效成分2D 结构的SDF格式,用于SwissTargetPrediction数据库进行靶点预测。汇集所有药效成分相关靶点后,经Uniprot数据库标准化后,去重汇总。
1.3.2 筛选炎症靶点
通过GeneCards数据库、OMIM数据库以“inflammation”名称进行检索,去重汇总后,得到与炎症相关基因。将药物靶点与疾病靶点经Venny 2.1.0在线作图后,数据取交集即费菜潜在的抗炎靶点基因。
1.3.3 构建蛋白互作网络图
将费菜潜在的抗炎靶点基因导入STRING数据库,设置“Minimum required interaction score”为“high confidence (0.700)”,获得靶点蛋白-蛋白相互作用(Protein-Protein Interaction,PPI)网络分析。将.tsv格式的数据结果上传至Cytoscape 3.8.0软件,构建网络图,同时利用Degree值筛选网络中关键基因。
1.3.4 构建“药物-药效成分-靶点”网络分析
将1.3.2得到的交集靶蛋白与费菜相对应的药效成分上传至Cytoscape 3.8.0软件,构建“费菜-药效成分-靶点”的网络图。
1.3.5 功能富集和KEGG信号通路分析
将1.3.2项下的交集靶蛋白导入David数据库里面“Shortcut to DAVID Tools”选项下的“Gene Functional Classification Tool”中,以“Homo sapiens”为物种选择,进行GO功能富集和KEGG通路分析。获得的数据利用微生信在线作图软件绘制GO气泡图和KEGG信号通路气泡图。并利用Cytoscape 3.8.0软件构建“药效成分-核心靶点-通路”网络图。
1.3.6 分子对接
根据Degree值大小,选择PPI中前三的关键靶点与关键药效成分进行分子对接。通过TCMSP数据库及PubChem数据库检索下载得到药效成分的3D结构信息,并通过Uniprot数据库和PDB数据库得到靶蛋白的.pdb格式结构,使用Openbable2.4.1、PyMOL2.2.0软件对药效分子和靶蛋白进行加氢、去水及去电荷等前处理,进而通过Autodock4.2.6软件将处理后的药效分子与靶蛋白进行分子对接,最后利用PyMOL2.2.0软件进行可视化处理。
1.3.7 费菜中药效成分的鉴定
1.3.7.1 费菜药效成分的提取
准确称取粉碎过筛后的费菜样品2 g于锥形瓶中,加入60 mL蒸馏水,浸泡1 h后,超声30 min,取上清后残渣加蒸馏水40 mL,继续超声30 min,取上清。混合两次上清提取液,旋蒸浓缩,0.22 µm微孔滤膜过滤,4 ℃冰箱保存,用于没食子酸的检测。
称取粉碎过筛后的费菜样品200 g,加10倍水浸泡过夜后煎煮1 h,8层纱布过滤后取滤液;滤渣再次加入8倍水后煎煮1 h,8层纱布过滤后取滤液。合并两次滤液,浓缩至一定体积,加入乙酸乙酯进行萃取(80 mL×5),浓缩回收,0.22 µm微孔滤膜过滤,4 ℃冰箱内保存,用于β-谷甾醇的检测。
1.3.7.2 费菜药效成分检测的色谱条件
选用Agilent ZORBAX SB-C18(4.6×250 mm, 5 µm),流动相为甲醇-0.2%磷酸水溶液(90:10),柱温30 ℃,检测波长280 nm,流速0.8 mL/min,进样量10 µL,检测分析1.3.7.1中制备的没食子酸。
选用Agilent ZORBAX SB-C18(4.6×250 mm, 5 µm),流动相为乙腈(A)-0.1%磷酸水溶液(B),洗脱程序:0~5 min,90%~80%(A),5~30 min,80%~70%(A),30~35 min,70%~90%(A),柱温35 ℃;检测波长203 nm,流速1.0 mL/min,进样量10 µL,检测分析1.3.7.1中萃取的β-谷甾醇。
1.3.8 β-谷甾醇、没食子酸溶液配制
称取4 mg的β-谷甾醇,在2 mL离心管中溶解于2 mL无水乙醇,过0.22 µm针头式无菌过滤器,配制β-谷甾醇初始浓度为2 mg/mL。称取4 mg的没食子酸,在2 mL离心管中溶解于1 mL无水乙醇,过0.22 µm针头式无菌过滤器,配制没食子酸初始浓度为4 mg/mL。
1.3.9 药效成分抗炎作用实验验证
1.3.9.1 细胞培养
RAW264.7细胞于完全DMEM培养基(DMEM培养基+10%胎牛血清+1%青霉素-链霉素)中,置于CO2细胞培养箱中,37 ℃培养[16]。
1.3.9.2 实验处理及分组
接种5×105细胞/孔,细胞被培养在6孔板中12 h,弃掉原培养基,PBS冲洗3遍,加入含有终浓度为2、4、8 µg/mL的β-谷甾醇或10、20、40 µg/L没食子酸的DMEM完全培养基,处理2 h后,加入终浓度为1 µg/mL LPS共培养24 h,收集细胞上清和蛋白用于后续检测[17-18]。分组为空白对照CON组(不作处理)、LPS处理组(1 µg/mL LPS)、药物处理组(2、4、8 µg/mL β-谷甾醇+LPS或10、20、40 µg/L没食子酸+LPS)。
1.3.9.3 NO、IL-10含量检测
用碧云天NO检测试剂盒测定细胞上清中NO含量。碧云天Mouse IL-10 ELISA Kit试剂盒检测细胞上清中IL-10含量变化。
1.4 数据处理
应用Excel及GraphPad prism 9软件对数据进行统计处理,所有数据以均数±标准差(
ˉx ±SD)表示。组间比较采用单因素方差分析(one-way ANOVA),以P<0.05为差异统计学意义。2. 结果与分析
2.1 费菜药效成分与靶点
经TCMSP数据库检索获得19种费菜化学成分,根据口服利用度(Oral bioavailability, OB)≥30%筛选得到的费菜药效成分仅为6个,去除无靶点化合物后,得到5个主要的费菜药效成分,具体信息见表2。以“Homo sapiens”为物种筛选条件,去重汇总后获得的费菜药效成分潜在相关靶点130个。
表 2 费菜中主要药效成分Table 2. Main pharmacodynamic components in Sedum aizoon L.ID 分子名称 中文名称 口服利用度 (%)≥30% MOL002075 1-[(2S)-1-methyl-2-piperidyl]acetone 甲基异石榴皮碱 49.09 MOL002930 Tyrosol 对羟基苯乙醇 33.81 MOL000358 beta-sitosterol β-谷甾醇 36.91 MOL000359 sitosterol β-谷甾醇乙酸酯 36.91 MOL000513 3,4,5-trihydroxy benzoic acid 没食子酸 31.69 2.2 炎症靶点
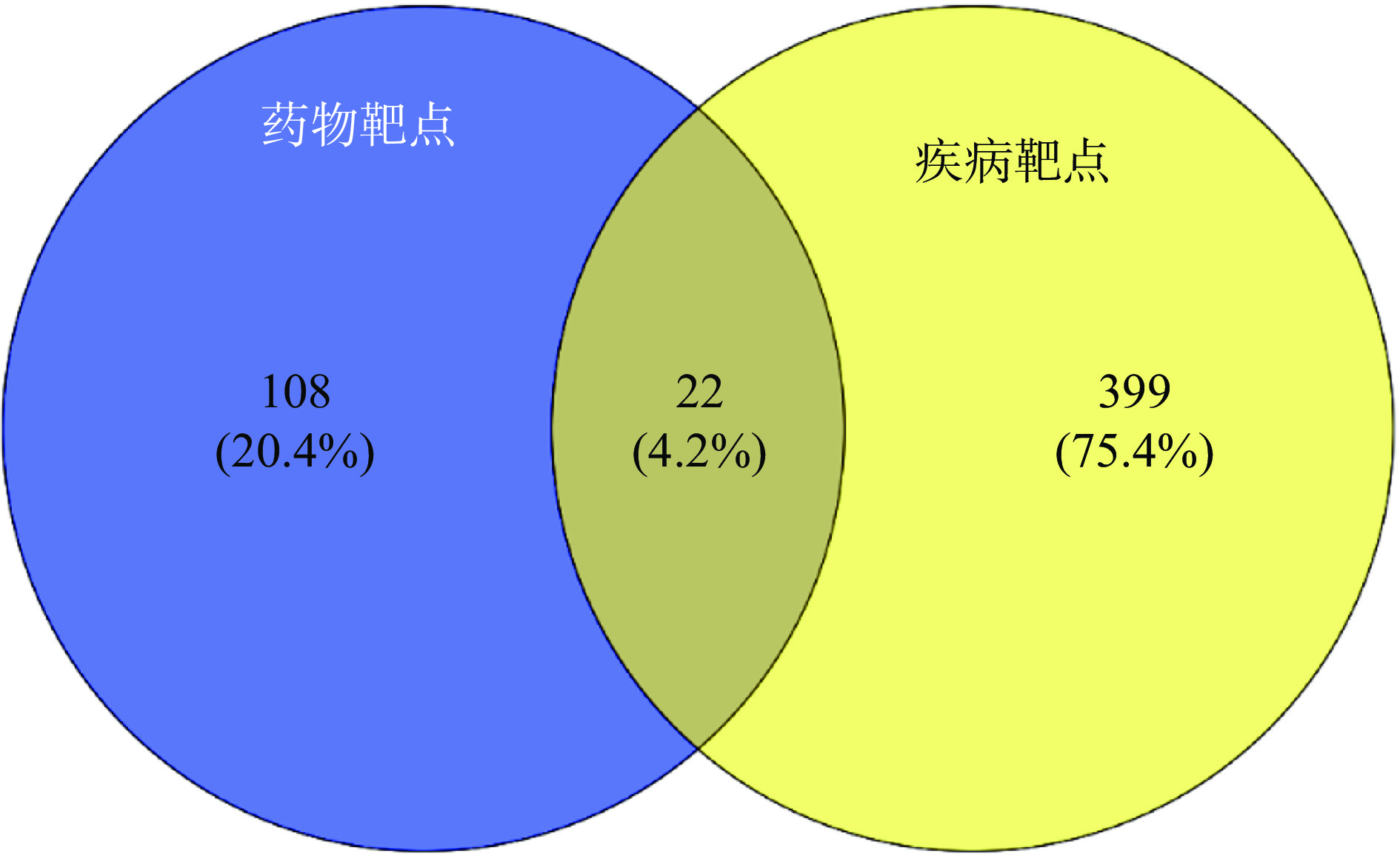
以“inflammation”在GeneCards数据库、OMIM数据库中检索炎症相关靶点,去重汇总后,得到421个靶点基因。将2.1获得的130个费菜药效成分靶点基因与炎症靶点基因通过Venny 2.1.0映射后,得到药物与疾病共同靶点22个(见图1),即费菜药效成分发挥抗炎作用的与潜在靶点ADRB2、CASP3、CASP8、JUN、MAPK1、MAPK14、NOS2、NR3C1、PIK3CG、PON1、PPARG、PRSS1、PTGS1、PTGS2、TGFB1、EGFR、FASLG、GPR35、NFE2L2、SERPINE1、TP53、TTR相关。
2.3 蛋白互作网络图
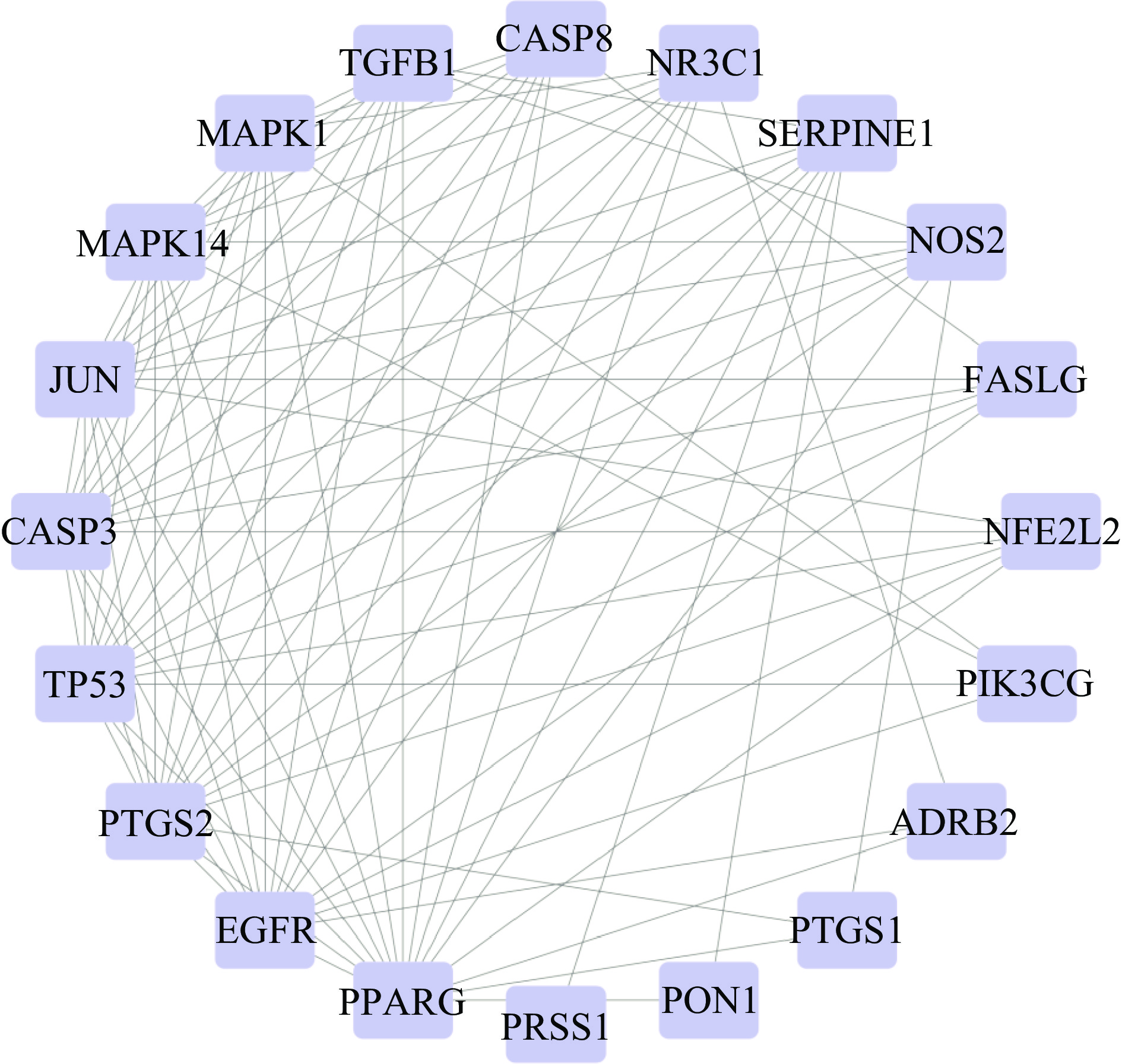
将上述22个共同靶点导入STRING数据库进行蛋白互作,以“高置信度(0.700)”为条件筛选的数据结果上传至Cytoscape 3.8.0软件进行分析,去除游离靶点,得到蛋白互作图,如图2,共获得20个节点,91条边。靶点连接的线越多,表明该靶点Degree值越高,是关键靶点。按照Degree值≥10筛选条件,获得费菜抗炎的关键靶点有:PPARG、EGFR、p53、PTGS2、CASP3、JUN、MAPK14、MAPK1、TGFB1,表明这些靶点与费菜抗炎作用有着更为直接的关系。
PPARG作为配体激活的转录因子,属于过氧化物酶体增殖物激活受体(PPAR)家族,参与多种肿瘤细胞的发生发展、转移、耐药过程[19]。PPARG表达的激活可能通过调节肺鳞状细胞癌(LSCC)上游调节因子和下游标记基因来抑制LSCC的发展和进展[20]。表皮生长因子受体(EGFR)整合了多条信号通路的输入来控制细胞生长、增殖和分化,可以与高尔基体相关高尔基体膜蛋白1(GOLM1)发生物理相互作用,EGFR是GOLM1介导的AKT/S6K下游激活和细胞迁移的增强所必需的,且表皮生长因子(EGF)与EGFR结合后,发挥EGF促进粘膜上皮细胞合成的作用,有助于胃肠道粘膜上皮细胞的再生与修复[21-22]。TP53是细胞周期相关的基因,主要通过合成细胞周期相关蛋白,在细胞增殖和凋亡的调控方面发挥重要作用,50%的肿瘤中存在TP53突变,突变型TP53破坏正常细胞结构,促进肿瘤细胞的代谢[23]。丝裂原活化蛋白激酶(MAPK)能够被多种炎症因子激活,增加组织细胞炎症发生几率,还可以通过不同的底物磷酸化,在基因水平和蛋白质水平对转录因子AP-l(JUN)活性进行调控,在炎症发生发展过程中起着重要作用[24-25]。
2.4 “药物-药效成分-靶点”网络分析
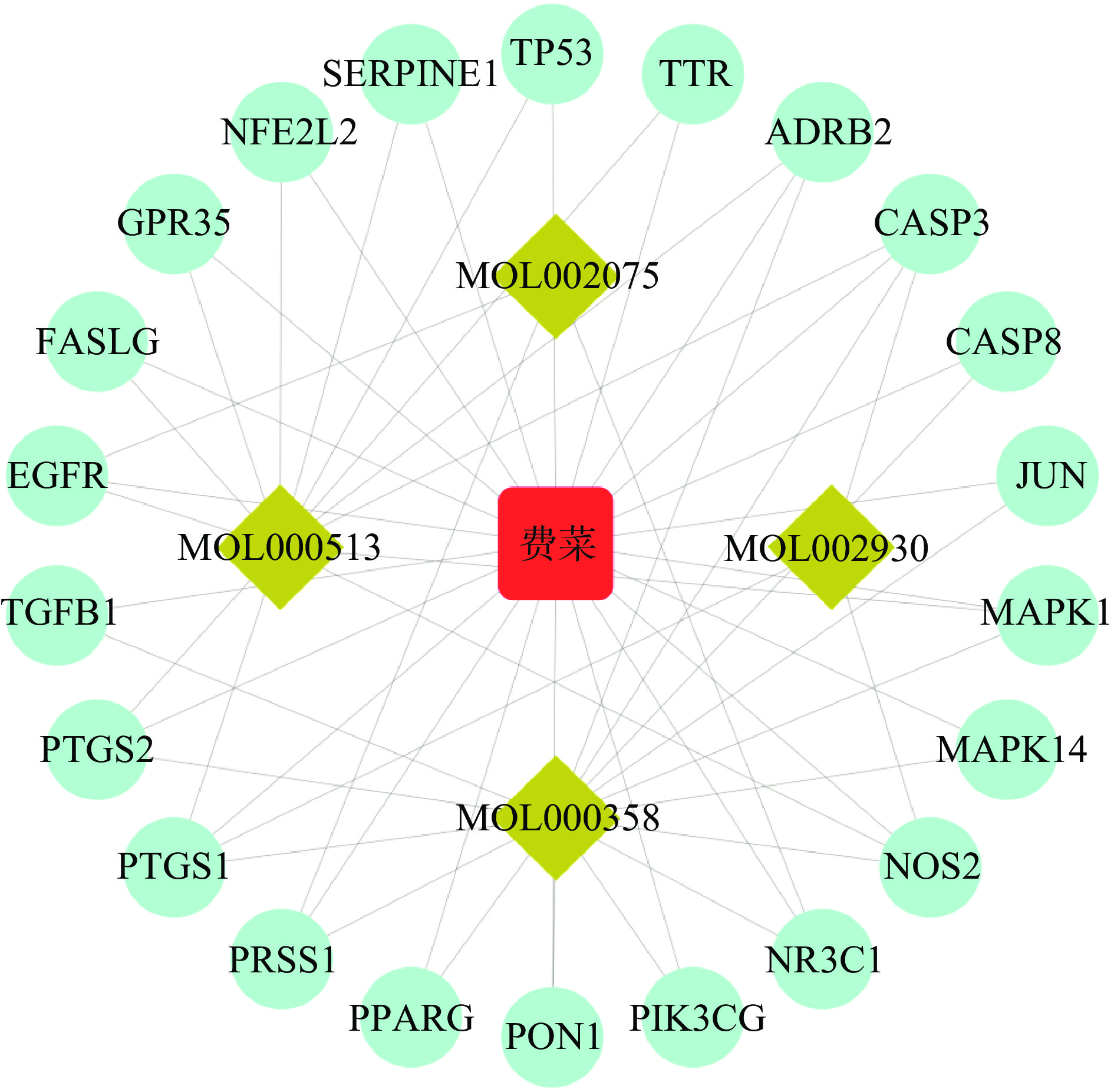
将费菜及其药效成分甲基异石榴皮碱、对羟基苯乙醇、β-谷甾醇和没食子酸的ID号与相对应的炎症靶点蛋白导入Cytoscape3.8.0软件,构建“药物-药效成分-靶点”网络图。去除游离靶点后,结果如图3所示,共获得25个节点,50条边,证明费菜通过4个药效成分调控多个靶点发挥抗炎作用。另外,Degree值越高,药效成分越能代表药材的药效。β-谷甾醇(Degree=15)和没食子酸(Degree=13)与费菜(Degree=22)的Degree值最接近,说明β-谷甾醇和没食子酸最能代表费菜的抗炎作用,因此,确定β-谷甾醇和没食子酸为费菜抗炎的药效成分。
据报道没食子酸具有强大的抗炎作用,可以抑制炎症诱导的促炎细胞因子和趋化因子以及细胞外基质降解和基质重塑酶的表达,还能显著抑制炎症诱导的肌层激活[26-27]。β-谷甾醇可以通过调节PPARy/NF-κB信号通路对心肌缺血/再灌注损伤具有保护作用[28],在研究辣木中分离的β-谷甾醇(BSS)的抗炎活性时发现,在7.5到30 µmol/L的剂量范围内,抑制PGN、TNF-α或LPS诱导的角质形成细胞和巨噬细胞中炎症因子的分泌[29]。大鼠的动脉瘤模型中,经β-谷甾醇给药降低了趋化因子和炎性细胞因子的表达,显著减小动脉瘤[30]。综上所述,本文将选择β-谷甾醇和没食子酸2个主要有效抗炎成分进行下一步研究。
2.5 GO功能富集和KEGG信号通路分析
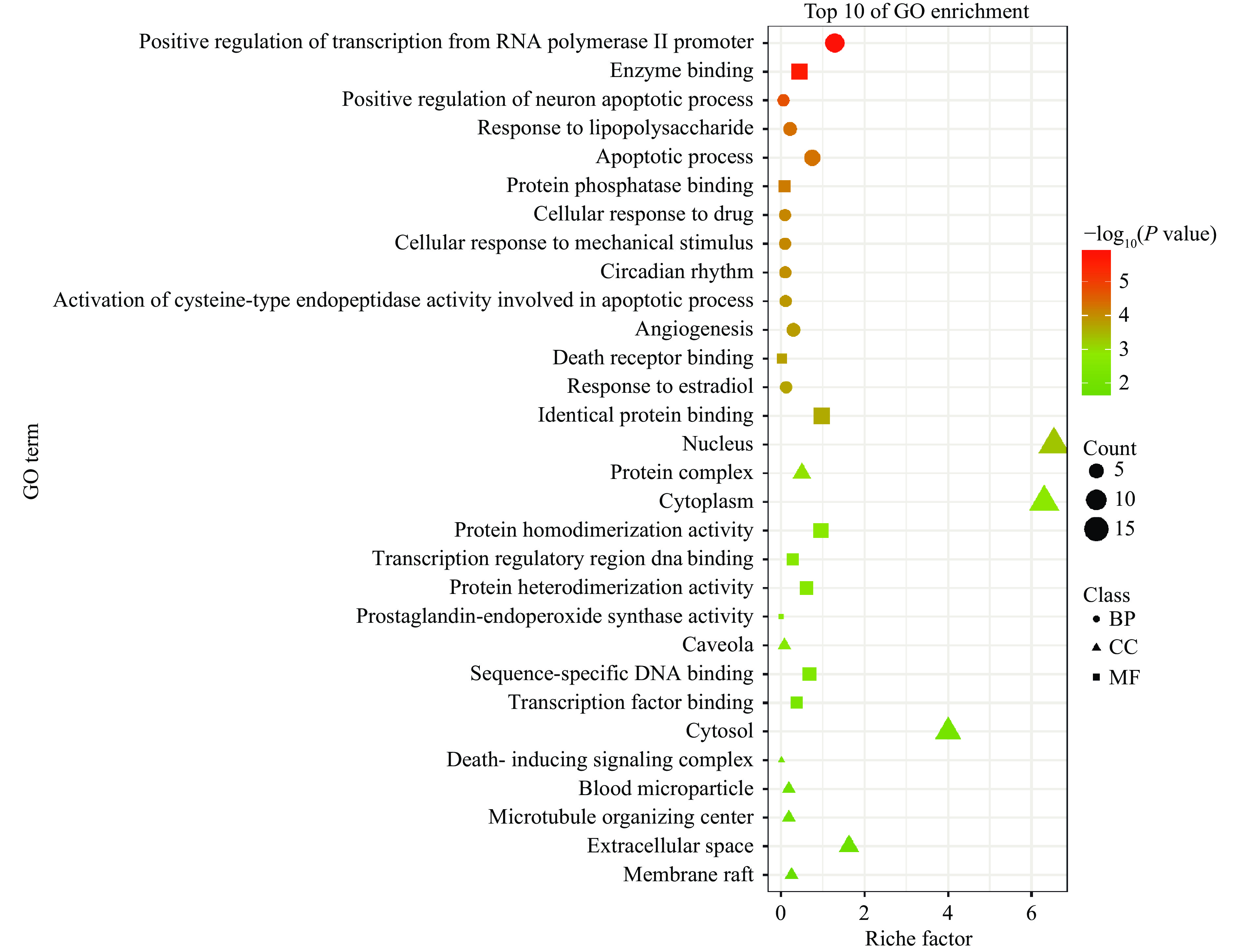
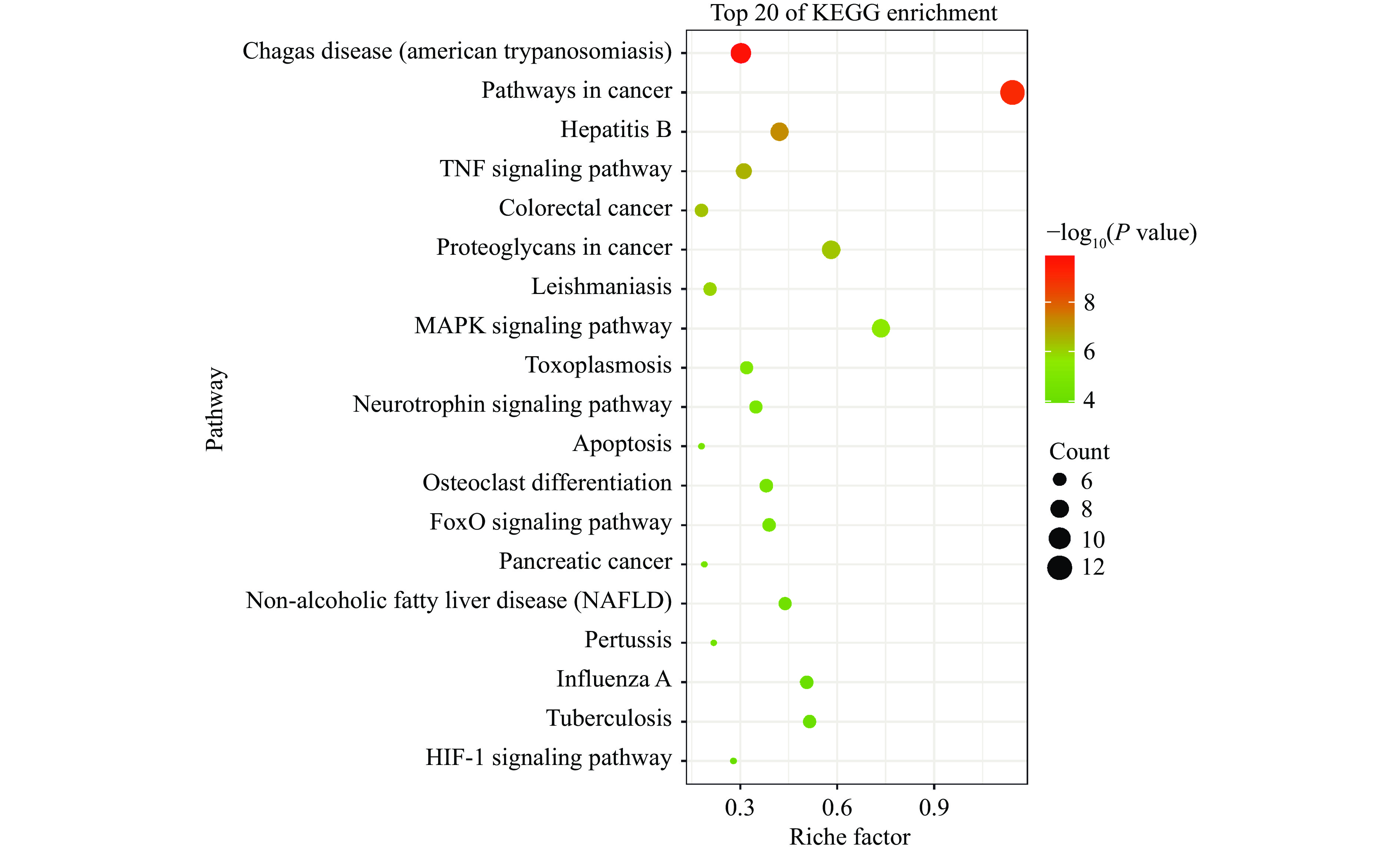
利用David数据库将获得的22个费菜抗炎的潜在靶点,以P<0.05、FDR<0.05为筛选条件,进行GO功能富集和KEGG分析,结果如图4~图5所示。生物过程主要包括RNA聚合酶II启动子的转录正调控、神经元凋亡过程的正调控和脂多糖反应等。分子成分主要为细胞核、蛋白复合物和细胞质等。主要涉及的分子功能是酶结合、蛋白磷酸酶结合和死亡受体结合等。KEGG信号通路分析发现,费菜药效成分发挥抗炎作用通路主要涉及美洲锥虫病、癌症通路、乙型肝炎、TNF信号通路、结肠直肠癌、MAPK信号通路、神经营养因子信号通路等信号通路。炎症与肿瘤的发生、发展密切相关[31],炎症反应不仅诱导肿瘤的发生,并且促进肿瘤的发展及转移,而且肿瘤微环境中存在的大量炎症细胞和炎症因子会诱导多种细胞因子以及趋化因子的表达,促使细胞增殖并诱导血管生成,从而促进肿瘤的发展及转移。在经典炎症信号通路中,PPARG、TNF、MAPK、p53等靶蛋白起着至关重要的作用,可以中和抑制炎症并减轻炎症病理[25,32],促进细胞分化、细胞生长和凋亡,激活氧化应激和炎症反应等[33]。β-谷甾醇和没食子酸抗炎靶点富集分析涉及大量炎症通路,表明费菜药效成分可以通过作用于信号通路中靶蛋白,降低细胞因子及趋化因子的产生与释放,抑制炎症反应过程中重要蛋白产生过程,逆转炎症反应,从而发挥抗炎作用[34-35]。
2.6 分子对接
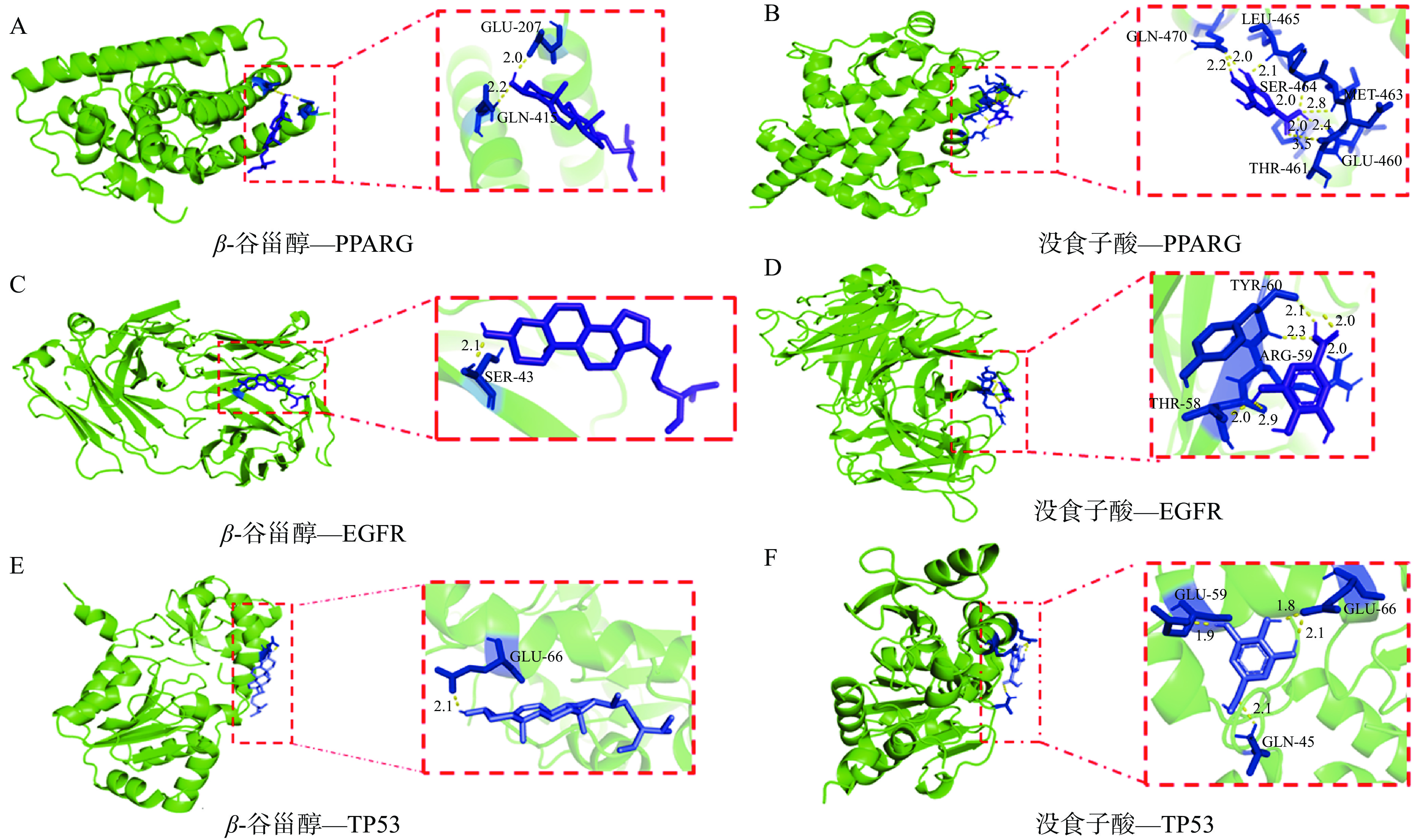
分子对接结果小于0时,配体小分子与受体蛋白可以自由结合,结合能越小,配体小分子与受体蛋白之间的亲和力越大,两者发生相互作用的可能性越高,进而发挥作用越大[36-38]。本研究利用分子对接技术,将β-谷甾醇和没食子酸与PPI预测结果中度值前三的靶蛋白PPARG、EGFR、TP53进行对接,结果表明(表3),β-谷甾醇和没食子酸与蛋白分子之间的结合能均小于0,β-谷甾醇和没食子酸与靶蛋白PPARG、EGFR、TP53均能较好地结合。另外,从分子对接示意图结(图6)可以看出β-谷甾醇与靶蛋白的结合能更低,表明β-谷甾醇与靶蛋白的结合更稳定。不同靶蛋白与小分子之间的相互结合位点不同,β-谷甾醇与PPARG通过Glu207、Gln415位点形成氢键相互作用,而β-谷甾醇与EGFR则是通过Ser43位点形成氢键相互作用。不同小分子与相同靶蛋白之间的相互结合位点亦不同,同一个TP53靶蛋白,β-谷甾醇通过Glu66位点形成氢键,而没食子酸不仅与Glu66位点,还与Glu59、Gln45位点形成氢键。结合位点多不代表结合能更低,β-谷甾醇仅通过Glu66结合位点即能发挥更稳定的结合作用,这表明它与配体分子有强烈的静电力作用,是关键位点。
表 3 核心靶点与药效成分分子对接结果Table 3. Molecular docking results of targets and pharmacodynamic components分子名称 结合能(kcal·mol−1) PPARG EGFR TP53 β-谷甾醇 −6.25 −6.75 −7.71 没食子酸 −4.57 −3.88 −4.11 2.7 费菜中药效成分的鉴定
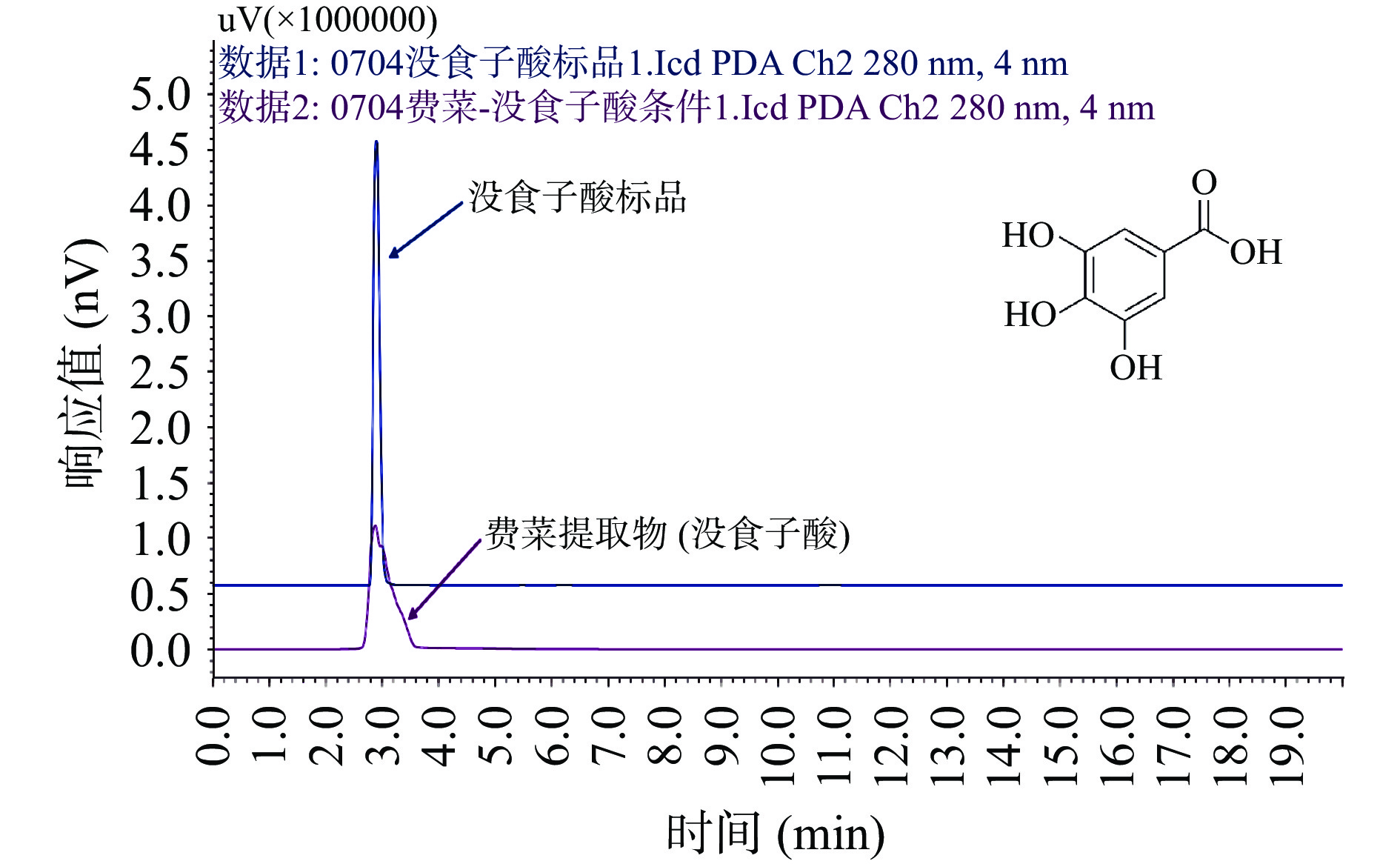
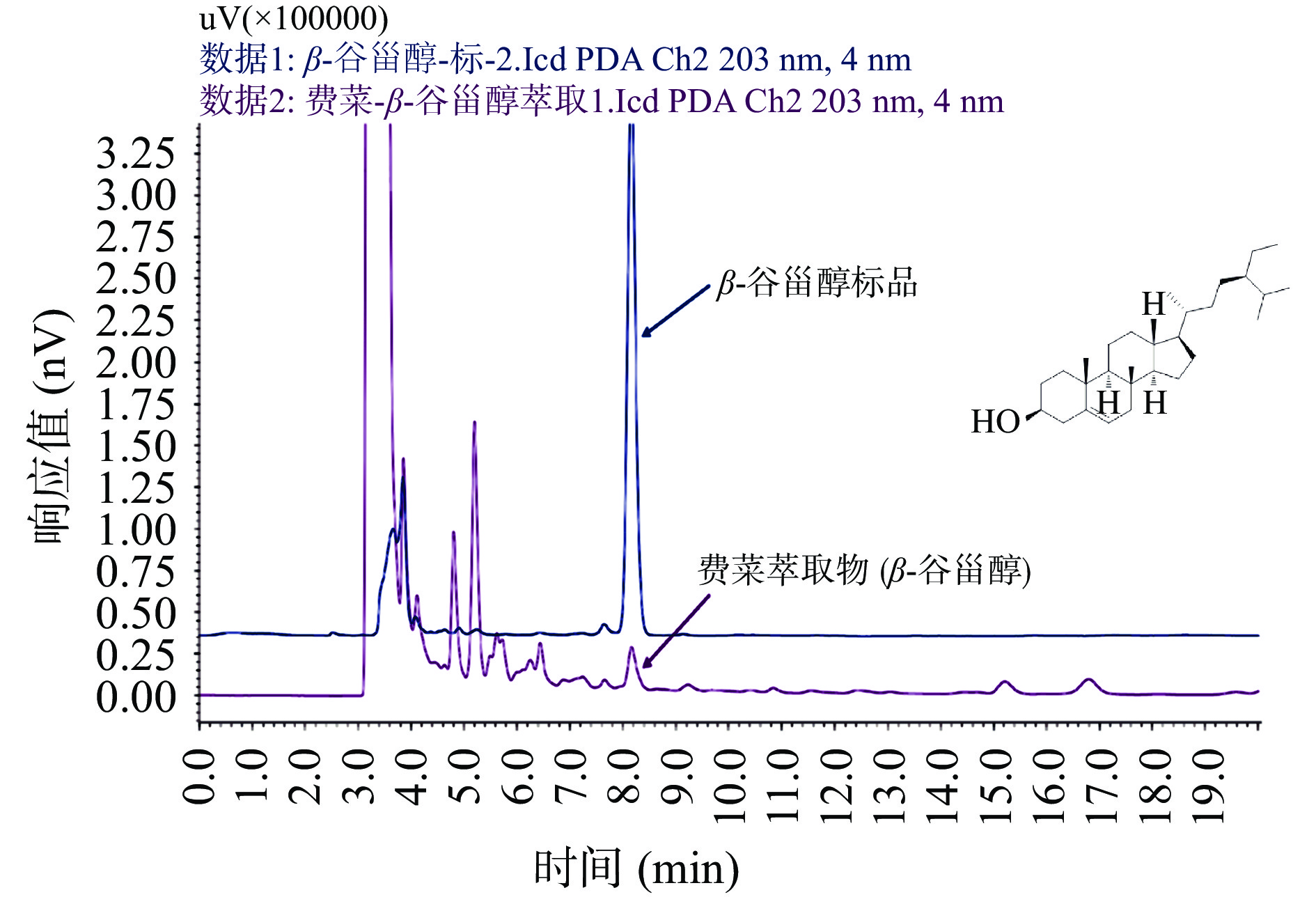
为确定没食子酸和β-谷甾醇是费菜中药效成分,本研究从费菜中提取没食子酸和β-谷甾醇[39-40],利用高效液相色谱法检测费菜提取物中没食子酸和β-谷甾醇,并与没食子酸和β-谷甾醇标准品进行比对,结果见图7~图8,保留时间在2.832的色谱峰可与没食子酸标品对比上,保留时间在8.165 min的色谱峰可与β-谷甾醇标品比对上,表明费菜中存在没食子酸和β-谷甾醇。在费菜抗炎作用的其他研究[11,13,41]中同样证明了没食子酸和β-谷甾醇的存在。
2.8 费菜主要有效抗炎药效成分抗炎效果验证
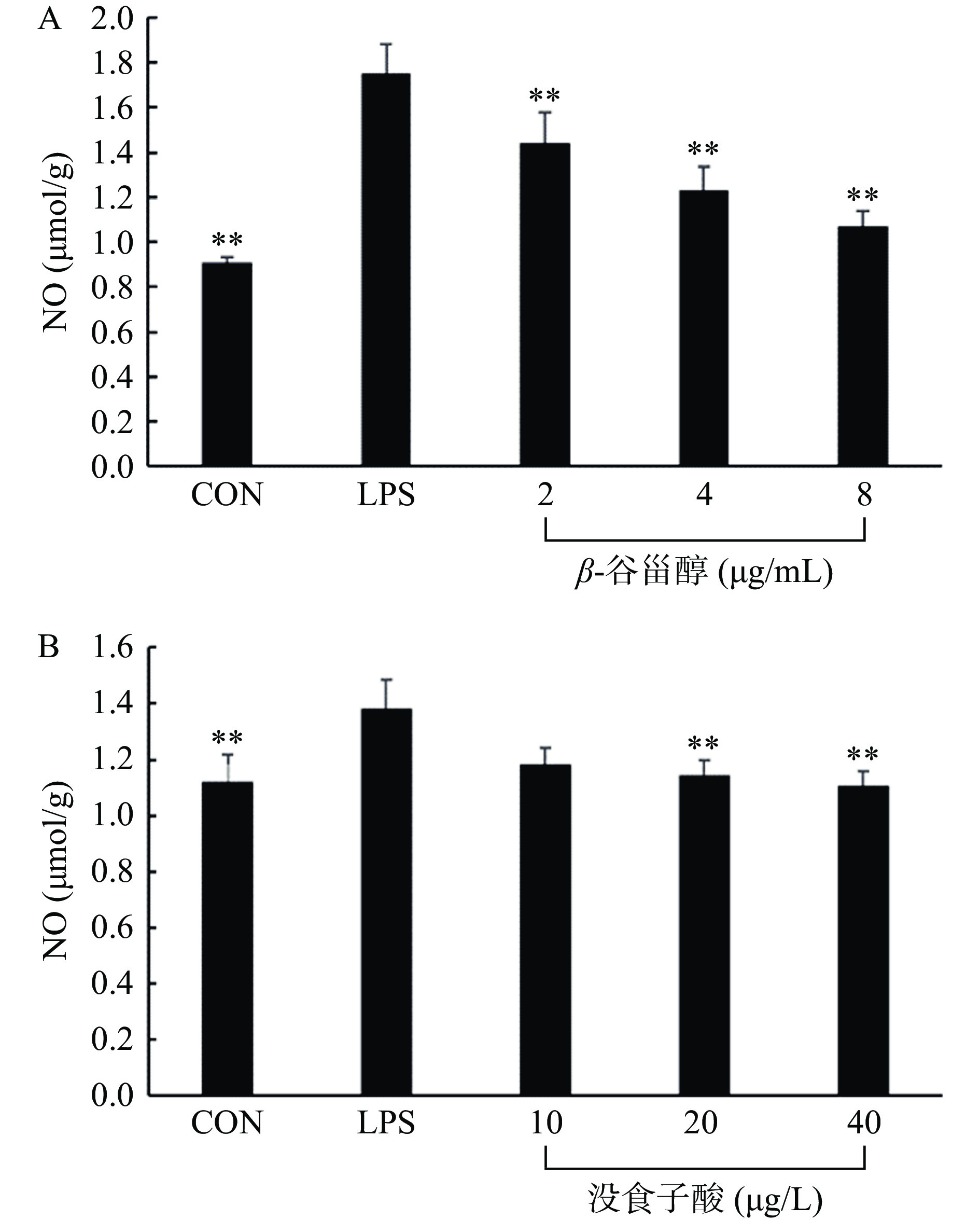
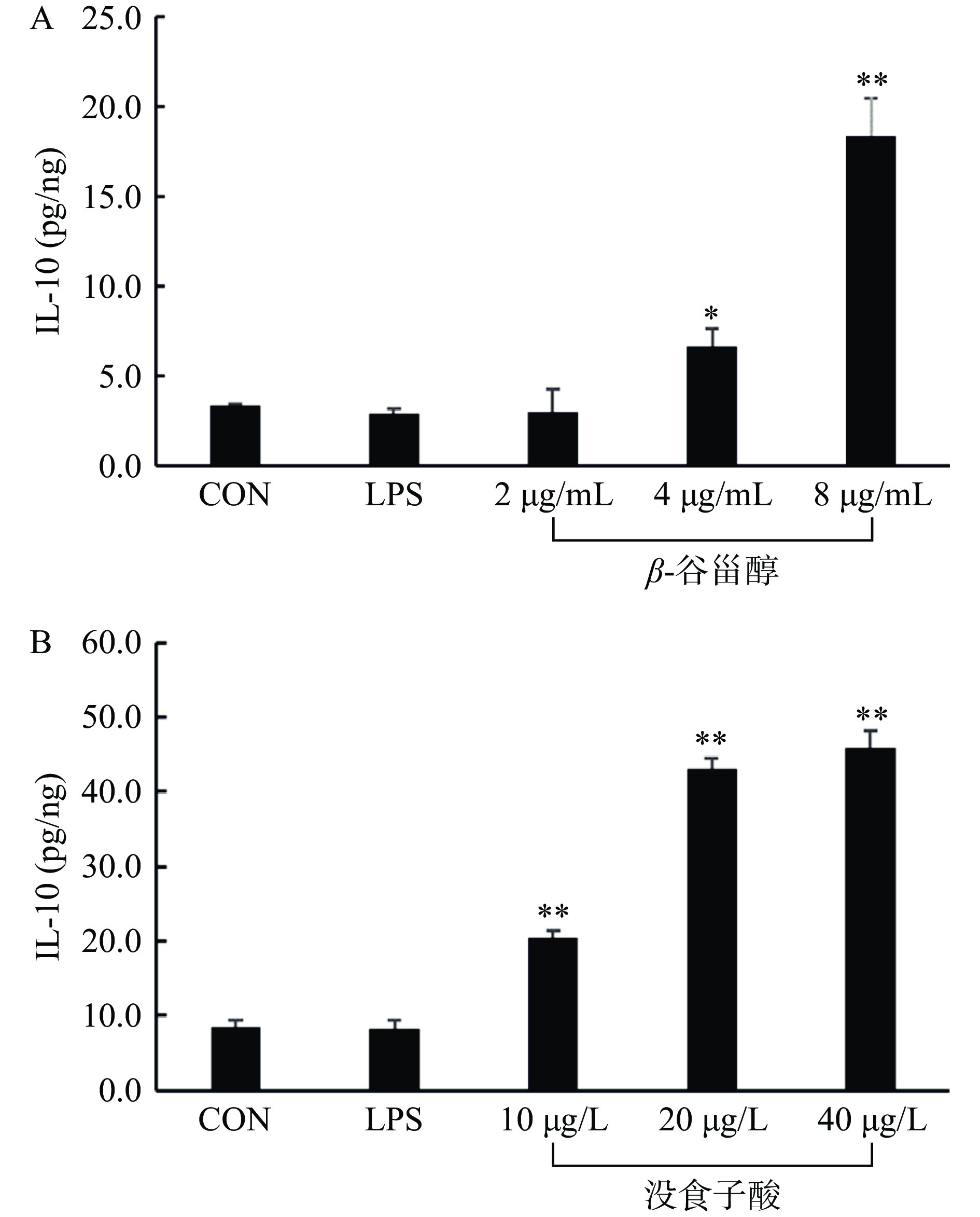
本研究利用LPS诱导的RAW264.7细胞模型,考察费菜的抗炎作用,结果如图9~图10所示,与LPS处理组相比,随着β-谷甾醇和没食子酸药物浓度的升高,细胞上清液中的NO含量降低,抗炎因子IL-10含量升高,呈剂量依赖性关系,当β-谷甾醇浓度≥2 µg/mL和没食子酸浓度≥20 µg/L时,两种药物能显著降低NO含量(P<0.01)。当β-谷甾醇浓度≥4 µg/mL和没食子酸浓度≥10 µg/L时,两种药物能显著提高IL-10含量(P<0.01)。
![]() 图 9 不同剂量的β-谷甾醇和没食子酸对上清中NO含量的影响注:与LPS组相比,*表示差异显著,P<0.05;**表示差异极显著,P<0.01;图10同。Figure 9. Effects of different doses of β-sitosterol and 3,4,5-trihydroxy benzoic acid on NO contents in the supernatant
图 9 不同剂量的β-谷甾醇和没食子酸对上清中NO含量的影响注:与LPS组相比,*表示差异显著,P<0.05;**表示差异极显著,P<0.01;图10同。Figure 9. Effects of different doses of β-sitosterol and 3,4,5-trihydroxy benzoic acid on NO contents in the supernatant这可能与药效成分的化学结构有关,即药物与抗炎作用之间的构效关系。没食子酸(3,4,5 -三羟基苯甲酸)是一种天然存在的多酚化合物,其发挥抗炎作用的机理之一可能是由于其不饱和双键的存在,对花生四烯酸(AA)的环氧酶(COX)和5-脱氧酶(5-LOX)起到抑制作用,且作为抗炎的活性基团更有利于化合物与蛋白的结合,抑制炎症发生[42];而β-谷甾醇以甾核为骨架,在它的C-5位有一个环内双键,双键位置决定抗炎作用,具有环内双键的化合物抗炎作用强于具有环外双键的化合物[43],β-谷甾醇的环内双键决定了其具有抗炎效果。根据分子对接结果表明β-谷甾醇较之没食子酸具有更低的结合能,可发挥更稳定的结合力,这可能与羟基位点个数有关, 羟基的酰化修饰不能增加抗炎活性[43],β-谷甾醇C-3位有一个羟基(-OH),而没食子酸C-3、C-4、C-5位均含有羟基。
3. 结论
综上所述,本研究应用网络药理学方法预测了费菜药效成分及作用靶点,其中关键抗炎药效成分为β-谷甾醇和没食子酸,关键靶点为PPARG、EGFR、TP53,通过正调控RNA聚合酶II启动子的转录,神经元凋亡以及参与脂多糖反应等多种生物过程,经由肿瘤途径、乙型肝炎和经典炎症信号通路等10条关键信号通路发挥抗炎作用。利用高效液相色谱法证明了费菜中含有药效成分β-谷甾醇和没食子酸。进一步通过细胞实验验证证明,费菜抗炎药效成分可通过降低促炎因子NO的含量,提高抗炎因子IL-10的含量发挥抗炎作用,呈剂量依赖关系。没食子酸发挥抗炎作用可能是由于其结构中的不饱和双键作为抗炎的活性基团可有效促进药物与蛋白作用,降低炎症反应;β-谷甾醇发挥抗炎作用可能是由于其结构中的环内双键使其具有强抗炎作用,且分子对接结果显示两者均能很好地与蛋白结合。本研究为进一步深入研究费菜抗炎作用及其作用机理提供理论依据。
-
图 9 不同剂量的β-谷甾醇和没食子酸对上清中NO含量的影响
注:与LPS组相比,*表示差异显著,P<0.05;**表示差异极显著,P<0.01;图10同。
Figure 9. Effects of different doses of β-sitosterol and 3,4,5-trihydroxy benzoic acid on NO contents in the supernatant
表 1 文章所用数据库、在线作图网站及网址
Table 1 Websites of the databases and drawing websites used for the article
数据库、在线作
图网站名称网址 TCMSP https://tcmsp-e.com/ HERB http://drug.ac.cn/Search/ PubChem https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/ SwissTargetPrediction http://www.swisstargetprediction.ch/predict.php Uniprot https://www.uniprot.org/ GeneCards https://www.genecards.org/ OMIM https://omim.org/ Venny 2.1.0 https://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/
index.htmlSTRING https://cn.string-db.org/ David https://david.ncifcrf.gov/home.jsp PDB数据库 https://www.rcsb.org/ 微生信 http://www.bioinformatics.com.cn/ 表 2 费菜中主要药效成分
Table 2 Main pharmacodynamic components in Sedum aizoon L.
ID 分子名称 中文名称 口服利用度 (%)≥30% MOL002075 1-[(2S)-1-methyl-2-piperidyl]acetone 甲基异石榴皮碱 49.09 MOL002930 Tyrosol 对羟基苯乙醇 33.81 MOL000358 beta-sitosterol β-谷甾醇 36.91 MOL000359 sitosterol β-谷甾醇乙酸酯 36.91 MOL000513 3,4,5-trihydroxy benzoic acid 没食子酸 31.69 表 3 核心靶点与药效成分分子对接结果
Table 3 Molecular docking results of targets and pharmacodynamic components
分子名称 结合能(kcal·mol−1) PPARG EGFR TP53 β-谷甾醇 −6.25 −6.75 −7.71 没食子酸 −4.57 −3.88 −4.11 -
[1] LI M, QI Z, HAO Y, et al. New adducts of iriflophene and flavonoids isolated from Sedum aizoon L. with potential antitumor activity[J]. Molecules,2017,22:1859. doi: 10.3390/molecules22111859
[2] 南京中医药大学. 中药大辞典[M]. 上海: 上海科学技术出版社, 2006. 在线查询版:http://www.zhongyaocai360.com/zhongyaodacidian/ The Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine. Dictionary of traditional Chinese medicine[M]. Shanghai: Shanghai Science and Technology Press, 2006. Online query version: http://www.zhongyaocai360.com/zhongyaodacidian/.
[3] 谭波, 何席呈, 李婷, 等. 景天三七化学成分及药理作用研究进展[J]. 中国民族民间医药,2018,27(17):49−52. [TAN B, HE X C, LI T, et al. Research progress on chemical constituents and medical functions of Sedum aizoon L J]. Chinese Journal of Ethnomedicine and Ethnopharmacy,2018,27(17):49−52.
[4] 中国科学院中国植物志委员会. 中国植物志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1984: 128 Editorial Committee of Chinese Flora. Chinese academy of sciences[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1984: 128.
[5] GONG J, QIU S, WENG Q, et al. Effect of different drying methods on phenolic compounds and antioxidant capacity in different fractions of Sedum aizoon L.[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 2020, 44(9): e14723.
[6] XU T, WANG Z, LEI T, et al. New flavonoid glycosides from Sedum aizoon L.[J]. Fitoterapia,2015,101:125−132. doi: 10.1016/j.fitote.2014.12.014
[7] LIN Z, FANG Y, HUANG A, et al. Chemical constituents from Sedum aizoon and their hemostatic activity[J]. Pharmaceutical Biology,2014,52:1429−1434. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2014.895019
[8] XIONG Y, YI P, DU C, et al. A new adduct of iriflophene and flavonoid from Sedum aizoon L.[J]. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology,2020,92:104119. doi: 10.1016/j.bse.2020.104119
[9] XU F, CAO S, WANG C, et al. Antimicrobial activity of flavonoids from Sedum aizoon L. against Aeromonas in culture medium and in frozen pork[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2019,7:3224−3232.
[10] LIU Z, MIN C, DONG H, et al. Improvement of adventitious root formation in Sedum aizoon L. and the production of flavonoids[J]. South African Journal of Botany,2021,137:483−491. doi: 10.1016/j.sajb.2020.10.024
[11] 黄安玉. 养心草水提乙酸乙酯部位止血和抗炎活性的筛选[D]. 福州: 福建中医药大学, 2014 HUANG A Y. Study on ethyl acetate parts of hemostatic and anti-inflammatory effect of Sedum aizoon L. activity screening [D]. Fuzhou: Fujian University of Traditional Chinese Medicine, 2014.
[12] 林珠灿, 张龙, 张睿卓, 等. 基于炎症细胞模型的景天三七醋酸乙酯部位抗炎活性及其HPLC指纹图谱的研究[J]. 中国药学(英文版),2015,24(10):647−653. [LIN Z C, ZHANG L, ZHANG R Z, et al. Anti-inflammatory effect of ethyl acetate extract of Sedum aizoon L. in LPS-stimulated RAW 264.7 macrophages and its HPLC fingerprint[J]. Journal of Chinese Pharmaceutical Sciences,2015,24(10):647−653. [13] 韩宁娟, 方欢乐, 牛睿, 等. 横根费菜不同溶剂萃取部位止痒抗炎作用研究[J]. 西北药学杂志,2018,33(4):496−499. [HAN N J, FANG H L, NIU R, et al. Study on the antipruritic and anti-inflammatory effects of different polar fractions of Sedum kamtschaticum fish[J]. Northwest Pharmaceutical Journal,2018,33(4):496−499. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-2407.2018.04.018 [14] 黄美雯, 杨华杰, 周晓春, 等. 网络药理学在民族药研究中的应用与展望[J]. 中国中药杂志,2019,44:3187−3194. [HUANG M W, YANG H J, ZHOU X C, et al. Advances on network pharmacology in ethnomedicine research[J]. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica,2019,44:3187−3194. doi: 10.19540/j.cnki.cjcmm.20190711.201 [15] 解静, 高杉, 李琳, 等. 网络药理学在中药领域中的研究进展与应用策略[J]. 中草药,2019,50:2257−2265. [XIE J, GAO S, LI L, et al. Research progress and application strategy on network pharmacology in Chinese materia medica[J]. Chinese Traditional Herbal Drugs,2019,50:2257−2265. doi: 10.7501/j.issn.0253-2670.2019.10.001 [16] 姚凤, 周清燕, 熊瑛, 等. β-谷甾醇对脂多糖诱导的小鼠急性肺损伤的保护作用研究[J]. 中国农学通报,2015,31(2):55−61. [YAO F, ZHOU Q Y, XIONG Y, et al. Protective effects of β-sitosterol on acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide in mice[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2015,31(2):55−61. [17] BUI TTHL, BUI HT, NGUYEN PT, et al. A new phenolic component from Triticum aestivum sprouts and its effects on LPS-stimulated production of nitric oxide and TNF-α in RAW 264.7 cells[J]. Phytotherapy Research,2014,28:1064−1070. doi: 10.1002/ptr.5097
[18] 黄丽华, 侯林, 薛海南, 等. 没食子酸通过拮抗脂多糖诱导的TLR4/NF-κB活化抑制RAW264.7巨噬细胞炎性反应[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志,2016,12(12):1610−1614. [HUANG L H, HOU L, XUE H N, et al. Gallic acid inhibits inflammatory response of RAW264.7 macrophages by blocking the activation of TLR4/NF-κB induced by LPS[J]. Chinese Journal of Cellular and Molecular Immunolo,2016,12(12):1610−1614. doi: 10.13423/j.cnki.cjcmi.007974 [19] 杨宇钦. PPARG/FABP4信号通路介导乳腺癌增殖侵袭能力的体外研究[D]. 广州: 南方医科大学, 2020 YANG Y Q. In vitro study on proliferation and invasion of breast cancer mediated by PPARG/FABP4 signal pathway [D]. Guangzhou: Southern Medical University, 2020.
[20] SHI S, YU G, HUANG B, et al. PPARG could work as a valid therapeutic strategy for the treatment of lung squamous cell carcinoma[J]. PPAR Research,2020,2020:2510951.
[21] ZHU W, QIN L. GOLM1-regulated EGFR/RTK recycling is a novel target for combating HCC metastasis[J]. Science China Life Science,2017,60:98−101. doi: 10.1007/s11427-016-0311-x
[22] 袁奕清, 胡小军. 芍药甘草汤加减对急性胃溃疡患者血清炎症因子、胃黏膜表皮生长因子及受体表达的影响[J]. 世界中西医结合杂志,2021,16(1):92−95, 99. [YUAN Y Q, HU X J. Effect of modified Shaoyao Gancao decoction on the expression of serum inflammatory factors, gastric mucosal epidermal growth factor, and receptor in patients with acute gastric ulcer[J]. World Journal of Integrated Traditional and Western Medicine,2021,16(1):92−95, 99. [23] 贺小威, 徐玲. 细胞周期相关基因CDKN2A、TP53、RB1和BRCA2在恶性肿瘤中的研究进展[J]. 现代肿瘤医学,2018,26(1):153−157. [HE X W, XU L. Advances on the role of cell cycle-related genes CDKN2A, TP53, RB1 and RBCA2 in malignancies[J]. Journal of Modern Oncology,2018,26(1):153−157. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-4992.2018.01.040 [24] 何庆南. 转录因子AP-1的研究进展[J]. 国外医学: 儿科学分册,1999,26:152−155. [HE Q N. Advances in the study of activator protein-1[J]. Foreign Medical Sciences (Section of Pediatrics),1999,26:152−155. [25] FARKHONDEH T, MEHRPOUR O, BUHRMANN C, et al. Organophosphorus compounds and MAPK signaling pathways[J]. International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2020,21:4258. doi: 10.3390/ijms21124258
[26] CAITLYN NGUYEN-NGO C S, ANDREW LAI, JANE C WILLCOX, et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of gallic acid in human gestational tissues in vitro[J]. Reproduction,2020,160:561−578. doi: 10.1530/REP-20-0249
[27] DEHGHANI M A, SHANKIBA MARAM N, MOGHIMIPOUR E, et al. Protective effect of gallic acid and gallic acid-loaded Eudragit-RS 100 nanoparticles on cisplatin-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and inflammation in rat kidney[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta Molecular Basis of Disease,2020,1866:165911. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2020.165911
[28] LIN F, XU L, HUANG M, et al. Beta-sitosterol protects against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury via targeting PPARγ/NF-κB signalling[J]. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine,2020,2020:2679409.
[29] LIAO P, LAI M, HSU K, et al. Identification of β-sitosterol as in vitro anti-inflammatory constituent in Moringa oleifera[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2018,66:10748−10759. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b04555
[30] YANG Q, YU D, ZHANG Y. β-sitosterol attenuates the intracranial aneurysm growth by suppressing TNF-α-mediated mechanism[J]. Pharmacology,2019,104:303−311. doi: 10.1159/000502221
[31] 李晓宇, 何兴祥. 炎症与肿瘤的关系研究进展[J]. 广东医学,2006,27(9):1427−1428. [LI X Y, HE X X. Research progress on the relationship between inflammation and tumor[J]. Guangdong Medical Journal,2006,27(9):1427−1428. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9448.2006.09.074 [32] 辛剑, 陈辉兵, 尚艺泰. p38MAPK信号通路抑制剂对TNF-α诱导的乳腺癌细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 中国妇幼保健, 2019, 34: 1375-1379 XIN J, CHEN H B, SHANG Y T. Effects of p38MAPK signaling pathway inhibitors on TNF-α-induced apoptosis of breast cancer cells[J]. Maternal and Child Health Care of China, 2019, 34: 1375-1379.
[33] 万星, 李相国, 李修贤, 等. Beta-谷甾醇通过抑制TNF-α-NF-κB和TβR1-Smad2/3信号通路抗小鼠肝纤维化损伤[J]. 中国药理学同胞, 2020, 36: 75-80 WAN X, LI X G, LI X X, et al. Beta-sitosterol inhibits hepatic fibrosis in mice by inhibiting TNF-α-NF-κB and Tβ R1-SMad2/3 signaling pathways[J]. Chinese Pharmacology Compatriots, 2020, 36: 75-80.
[34] SHI Y X, HUANG C, YANG Z, et al. Impact of hepatitis B virus infection on hepatic metabolic signaling pathway[J]. World J Gastroenterol,2016,22:8161−8167. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i36.8161
[35] CHEN L, DENG H, CUI H, et al. Inflammatory responses and inflammation-associated diseases in organs[J]. Oncotarget,2018,9(6):7204−7218. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.23208
[36] 刘明. 蛋白质与配体相互作用机理的分子模拟研究[D]. 北京: 北京工业大学, 2010 LIU M. Protein and ligand with molecular modeling approaches[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Technology, 2010.
[37] 牟艳芳, 陈文璐, 周冰, 等. 基于网络药理学与分子对接技术探讨川蛭通络胶囊干预微循环障碍的机制研究[J]. 中草药,2021,52(24):7550−7560. [MOU Y F, CHEN W L, ZHOU B, et al. Mechanism of Chuan Zhi Tongluo capsules on microcirculation disturbance based on network pharmacology and molecular docking[J]. Chinese Traditional Herbal Drugs,2021,52(24):7550−7560. [38] 雷欢, 邓琴, 刘子源, 等. 基于网络药理学和分子对接方法探讨香叶木素治疗高尿酸血症肾病的分子机制[J]. 山东医药,2022,62(14):9−13,24. [LEI H, DENG Q, LIU Z Y, et al. To explore the molecular mechanism of German lignin in the treatment of hyperuricemia nephropathy based on network pharmacology and molecular docking method[J]. Shandong Medical Journal,2022,62(14):9−13,24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-266X.2022.14.003 [39] 林珠灿. 景天三七止血、抗炎物质基础与质量评价的研究[D]. 南京: 南京中医药大学, 2014 LIN Z C. Studies on hemostatic and anti-inflammatory effective substances of Phedimus aizoon (Linnaeus)'t Hart. and its quality evaluation[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, 2014.
[40] 付煜荣, 王至宝, 田嘉铭. 景天三七中没食子酸的提取[J]. 陕西中医,2006,27(9):1138−1139. [FU Y R, WANG Z B, TIAN J M. Extraction of gallic acid from Phedimus aizoon (Linnaeus)'t Hart doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7369.2006.09.081 J]. Shaanxi Journal of Traditional Chinese Medicine,2006,27(9):1138−1139. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-7369.2006.09.081
[41] 李乔, 于洋, 李明晓, 等. 费菜根茎化学成分的分离与鉴定[J]. 中国现代中药,2020,22(3):353−357. [LI Q, YU Y, LI M X, et al. Isolation and identification of the chemical constituents from the rhizome of Phedimus aizoon (Linnaeus)'t Hart doi: 10.13313/j.issn.1673-4890.20191203001 J]. Modern Chinese Medicine,2020,22(3):353−357. doi: 10.13313/j.issn.1673-4890.20191203001
[42] 余虹, 李逐波. 不饱和双键化合物与药物活性研究进展[J]. 解放军药学学报,2008(3):234−238. [YU H, LI Z B. Research progress in intestinal unsaturated double-bond compounds and drug activity[J]. Pharmaceutical Journal of Chinese People's Liberation Army,2008(3):234−238. [43] 刘艳红, 冯锋, 谢宁, 等. 穿心莲内酯衍生物抗肿瘤、解热抗炎构效关系研究进展[J]. 西北药学杂志,2013,28(1):95−98. [LIU Y H, FENG F, XIE N, et al. Advances in research on the anti-tumor, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory activity of andrographolide derivatives[J]. Northwest Pharmaceutical Journal,2013,28(1):95−98. -
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 黄潇漪,贾利蓉,孙玉鼎,曹月刚,冉旭. 天然香辛料对烘炒花生仁货架期品质的影响. 食品工业科技. 2024(12): 285-293 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 魏甜甜,魏勃,王承,李凯,谢彩锋,杭方学. 黄冰糖低温浸渍茉莉花制备风味糖浆工艺优化. 食品工业科技. 2022(12): 181-187 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 邹林武,姜福全,戚智胜. 白冰糖提取玫瑰花风味的工艺研究. 现代食品. 2022(15): 94-96+117 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 宣晓婷,陈思媛,乐耀元,尚海涛,曾昊溟,凌建刚,张文媛. 高水分南美白对虾虾干货架期预测模型的构建. 农产品加工. 2022(19): 78-82+90 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)





 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:
