Preparation and Characterization of Modified Corn Bract Cellulose/Nano Talcum Powder/Pea Starch Composite Film
-
摘要: 为开发绿色可降解的食品包装材料,本文以豌豆淀粉(pea starch,PS)为主要成膜基质,改性玉米苞叶纤维素(modified corn bract cellulose,MCBC)、纳米滑石粉(nano talcum powder,NTP)为增强材料,甘油为增塑剂,共混流延制备复合膜,测定其膜性能,并用扫描电子显微镜、傅里叶红外光谱对复合膜进行表征,最后对其进行热重分析与降解性分析。结果表明,经单因素实验及正交试验得到最佳复合膜制备工艺为PS 8%,甘油2.5%,MCBC 0.8%,NTP 0.15%,在此条件下制得的复合膜厚度为0.042 mm,透光率32.58%,抗拉强度32.48 MPa,断裂伸长率33.61%,水蒸气透过率0.19×10−10 g/(m·s·Pa),透油系数0.006 g·mm/m2d,吸水率55.79%,溶解度18.04%。扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscopy,SEM)结果显示,复合膜表面光滑均匀,结构致密;傅里叶红外光谱(Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy,FTIR)结果显示,MCBC、NTP、PS三者之间相容性良好,分子间氢键作用增强;热重分析(thermal gravimetric analyzer,TGA)结果显示,复合膜热分解温度为318.12 ℃,热稳定性提高;降解性分析表明土壤掩埋8 d时自然降解率为96.47%,可完全生物降解,本研究为MCBC/NTP/PS复合膜在食品工业中的应用提供了参考。Abstract: The study aimed to develop green degradable food packaging materials. Here, the composite film was prepared by tape casting method, which pea starch (PS) was used as the main film-forming matrix, modified corn bract cellulose (MCBC) and nano talcum powder (NTP) were used as reinforcing material and glycerin was used as plasticizer. The properties of the composite membrane were determined, and the composite membrane was characterized by scanning electron microscope and Fourier infrared spectroscopy. Finally, the thermogravimetric analysis and degradation analysis were carried out. Results showed that, the optimal preparation conditions of composite film including PS 8%, glycerol 2.5%, MCBC 0.8%, NTP 0.15% by using the method of single factor experiments and orthogonal experiment. Under these conditions, the thickness of composite film was 0.042 mm, the transmittance was 32.58%, the tensile strength was 32.48 MPa, the elongation at break was 33.61%, the water vapor transmission was 0.19×10−10 g/(m·s·Pa), the oil permeability coefficient was 0.006 g·mm/m2d, the water absorption rate was 55.79% and the solubility was 18.04%. The results of scanning electron microscopy (SEM) showed that the surface of the composite film was smooth and uniform, and the structure was compact. The results of fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR) showed that MCBC, NTP and PS were compatible well, and the intermolecular hydrogen bond of them were enhanced. Moreover, the results of thermal gravimetric analyzer (TGA) showed that the decomposition temperature of composite film was 318.12 ℃, and the heat stability of composite film was improved. Degradation analysis also showed that the natural degradation rate of composite film was 96.47% after being buried in soil for 8 days, therefore, the composite film could be biodegraded completely. The study would provide a reference for the application of MCBC/NTP/PS composite film in food industry.
-
石油原料合成塑料包装膜因轻薄耐用、成本低等性能在食品包装行业得到广泛应用,但难降解性使其无法被妥善处理。时至今日,焚烧产生的大量颗粒、一氧化碳、二噁英和多环芳烃等物质仍被认为是空气污染主要来源之一[1];同时,塑料垃圾进入环境后的自毒效应会污染土壤和地下水,可凭借风和水流运输形成世界性“海洋垃圾带”,严重破坏海洋生态系统,甚至产生不可逆影响[2-3]。此外,塑料垃圾还可成为化学品、有机污染物和病原体借助食物链进入人体的载体,给健康带来极大威胁[4]。因此,开发安全、经济、环境友好型包装材料是当前人们关注的热点。淀粉是一种无毒、多功能、可再生、可降解、价格低廉的天然多糖,特别是豌豆淀粉(pea starch,PS)因含较高直链淀粉(35%~65%)而表现出良好的成膜性,是潜在包装候选物[5-6]。但是单一的淀粉薄膜在力学结构、阻隔性能等方面存在一定缺陷,无法满足应用要求。随着研究的深入,已经开发出了多层技术、交联技术和共混复合技术来增强薄膜的稳定性和延展性,最大限度地提高耐水性、内聚力、刚性、机械强度和阻隔性能[7]。
玉米是我国第一大粮食作物,年产量高达2.25亿吨,居世界第二位[8]。玉米苞叶作为玉米果实采摘后的农业废弃物,利用率极低。玉米苞叶中含有54%~58%的纤维素,具有比强度及比模量高、比表面积大、机械性能优异、生物相容性好、可降解等一系列优点,非常适合作为增强材料[9]。但是由于纤维素的分子链中含有亲水性羟基,导致其不能够在大多数非极性聚合物中均匀分散,从而影响在复合材料方面的应用[10]。硬脂酸是一种源自动植物油脂的饱和脂肪酸,具有低表面能,富含长疏水性烃链,其中的-COOH能够与纤维素中的-OH发生酯化反应,可提高纤维素的疏水性及与其他材料的界面相容性[11]。史颖涵[12]使用硬脂酸对纳米α-纤维素进行表面疏水改性,并将它们加入到木薯淀粉中共混流延制备复合膜,当添加量为0.5%时,膜的机械性能和弹性模量得到增强,疏水性能提升,但是热稳定性下降。而纳米滑石粉(nano talcum powder,NTP)是一种耐热、润滑、防水、化学惰性、可吸附油脂且具有高纵横比的层状矿物,其粒度越小,表面积越大,分散性和吸附性就越强[13]。Castillo等[14]研究证实纳米滑石粒子可提高淀粉膜的阻隔性、抗弹性变形能力、机械性能和热稳定性,而不影响其生物降解特性。
因此,本文将PS、改性玉米苞叶纤维素(modified corn bract cellulose,MCBC)和NTP三者进行复配,制备具有良好柔韧性、耐水性及热稳定性的可降解型复合膜,在其最佳制备工艺基础上,通过扫描电子显微镜(scanning electron microscopy,SEM)、傅里叶红外光谱(Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy,FTIR)、热重分析(thermal gravimetric analyzer,TGA)对其进行表征,并分析其自然降解性能,以期为促进绿色环保新型包装材料在食品工业中的应用提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
玉米苞叶纤维素 实验室自制;PS(食品级) 新乡良润全谷物食品有限公司;NTP(食品级) 桂林桂广滑石开发有限公司;甘油、溴化钾、无水乙醇、硬脂酸、硫酸钾、无水氯化钙(分析纯) 天津市科密欧化学试剂有限公司;聚乙烯板、大豆油 市购。
DK-S24数显恒温水浴锅 常州市金坛友联仪器研究所;DQANT450扫描电子显微镜 美国FEI;Z-36HK高速低温离心机 德国HERMLE;JB-3A磁力恒温定时搅拌器 上海理达仪器厂;VERTEX70傅里叶红外光谱 德国Bruker;GZX-9240MBE电热恒温鼓风干燥箱 上海博讯实业有限公司医疗设备厂;XM-P30H无极调功超声波清洗机 小美超声仪器有限公司;Uvmini-1240紫外可见分光光度计 日本SHIMADZU;WSD8101恒温恒湿箱 昆山威胜德检测设备有限公司;FA1004A电子天平 上海精天电子仪器有限公司;TA-XT质构仪 英国Stable Microsystems;QFC-25 mm螺旋测微尺 深圳新德亚精密仪器有限公司;STA409PC热重分析仪 德国耐驰。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 MCBC的制备
取5 g玉米苞叶纤维素加蒸馏水至40 mL,与60 mL无水乙醇混匀超声30 min,加5 g硬脂酸继续超声30 min,80 ℃恒温磁力搅拌8 h后4 ℃ 10000 r/min离心10 min,沉淀物用无水乙醇洗涤,50 ℃干燥24 h,得到MCBC。
1.2.2 复合膜的制备
PS中加入25 ℃蒸馏水、甘油、MCBC和NTP混匀,90 ℃热水浴中搅拌30 min,静置10 min。每100 mL该溶液倾倒在聚乙烯板上流延成膜,40℃干燥形成复合膜,恒温恒湿箱(温度25 ℃±2 ℃,湿度55%±5%)中平衡24 h以进行指标测定。
1.2.2.1 复合膜制备单因素实验
按照1.2.2中所述步骤进行,固定添加量为:PS 7%、甘油2.5%、MCBC 1.2%、NTP 0.15%,分别考察PS 5%、6%、7%、8%、9%,甘油1.5%、2%、2.5%、3%、3.5%,MCBC 0、0.4%、0.8%、1.2%、1.6%、2%,NTP 0、0.05%、0.1%、0.15%、0.2%、0.25%对复合膜性能的影响。
1.2.2.2 复合膜制备正交试验
如表1,以抗拉强度、断裂伸长率、水蒸气透过率和透油系数为指标,L9(34)正交试验优化复合膜的制备工艺。
表 1 正交试验因素水平设计Table 1. Orthogonal test factor level水平 因素 A PS添加量(%) B 甘油添加量(%) C MCBC添加量(%) D NTP添加量(%) 1 7 2 0.8 0.1 2 8 2.5 1.2 0.15 3 9 3 1.6 0.2 1.2.3 膜性能的测定
1.2.3.1 厚度的测定
在待测膜四角各取1点,中心位置取1点,共5点,测量膜厚度,取平均值[15]。
1.2.3.2 透明度的测定
参照高凌云等[16]的方法并稍作修改。按照比色皿形状大小裁剪膜,波长600 nm测定透光率。
1.2.3.3 机械性能的测定
参照GB/T 1040.3-2006[17]。膜裁剪为2 cm×9 cm的条状固定于仪器上,设置有效拉伸强度5 cm,行走速度20 mm/min。
抗拉强度(MPa)=Fb×d (1) 式中:F为最大负荷,N;b为宽度,mm;d为厚度,mm。
断裂伸长率(%)=LL0×100 (2) 式中:L为试样拉伸后位移,mm;L0为试样原始长度,mm。
1.2.3.4 水蒸气透过率的测定
参照董增等[18]的方法并稍作修改。用膜将装有5 g无水氯化钙的称量杯封严称重,置于装有饱和硫酸钾溶液的密闭容器中,保持水分蒸汽压差△P(25 ℃下,△P约为3168 Pa)不变,记录24 h后质量变化。计算公式如下:
水蒸气透过率[×10−10g/(m⋅s⋅Pa)]=m×DA×t×ΔP (3) 式中:m为质量变化,g;D为膜厚度,m;A为杯口面积,m2;t为时间,s;△P为水分蒸气压差,Pa。
1.2.3.5 透油系数的测定
参照李鸿梅等[19]的方法并稍作修改。用6 cm×6 cm的膜将直径为1.5 cm装有5 mL大豆油的试管口封住,倒立于恒重滤纸上,称量滤纸质量,测试时间为7 d,计算公式如下:
透油系数(g⋅mm/m2d)=Δm×YS×P (4) 式中:△m为滤纸质量变化,g;S为试管口面积,m2;Y为膜厚度,mm;P为测试时间,d。
1.2.3.6 吸水率的测定
参照GB/T 1034-2008[20]。将3 cm×5 cm的膜80 ℃烘干至恒重,浸入25±2℃的蒸馏水中24 h,用滤纸吸去多余水分,快速称重。
吸水率(%)=A1−A0A0×100 (5) 式中:A0为样品原始质量,g;A1为样品吸水后质量,g。
1.2.3.7 溶解度的测定
参照田冰释等[21]的方法并稍作修改。将3 cm×5 cm的膜80 ℃烘干至恒重,25±2℃的300 mL蒸馏水中浸泡24 h,再次干燥至恒重后称重,计算溶解度。
溶解度(%)=m1−m2m1×100 (6) 式中:m1为样品原始质量,g;m2为样品浸泡后烘干的质量,g。
1.2.4 复合膜表面形貌观测
SEM观测,样品喷金,加速电压15 kV。
1.2.5 复合膜红外光谱分析
称取2 mg样品粉末与溴化钾粉末按1:100混匀后一同压成透明薄片,于仪器中测量。
1.2.6 复合膜热重分析
称取10 mg样品粉末于坩埚中,氮气做保护气,升温速率10 ℃/min,进气量20 mL/min,加热到500 ℃。
1.2.7 复合膜降解性测定
参照鲁亚楠[22]的方法,采用自然土埋法。将80 ℃烘干至恒重的4 cm×6 cm的复合膜夹在塑料网纱间,埋于花圃中,深度为15 cm,每天取出反复冲洗,50 ℃下烘干称重,计算公式如下:
降解率(%)=W1−W2W1×100 (7) 式中:W1为初始质量,g;W2为降解后的质量,g。
1.3 数据处理
所有试验做三次平行,试验结果以“平均值±标准差”表示;采用Excel软件对数据进行整理与分析;利用Origin 2018进行绘图,SPSS 23.0软件进行方差分析(ANOVA),差异显著性水平表示方法:显著(P<0.05),极显著(P<0.01)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 单因素实验结果
2.1.1 PS添加量对复合膜性能的影响
结果如表2。随PS含量增加,膜厚度从0.037 mm增加至0.125 mm,透光率由49.77%下降至27.05%,这是由于淀粉含量越多,成膜溶液中干物质越多,膜越厚,而膜厚度的增加进而会阻碍光线的通过,所以透光率降低[23]。
表 2 PS添加量对膜性能的影响Table 2. Effects of the level of PS on film propertiesPS添加量
(%)厚度
(mm)透光率
(%)抗拉强度
(Mpa)断裂伸长率
(%)水蒸气透过率
[×10−10g/(m·s·Pa)]透油系数
(g·mm/m2d)吸水率
(%)溶解度
(%)5 0.037±0.006c 49.77±2.28a 16.39±0.76d 36.48±0.83a 1.18±0.055a 0.305±0.024a 32.08±2.39d 23.91±0.26a 6 0.046±0.012c 43.36±1.05b 24.72±0.63c 34.75±1.22b 0.75±0.036b 0.128±0.013b 43.11±2.73c 19.28±0.52b 7 0.052±0.009c 35.18±0.93c 28.31±1.01b 32.16±0.94c 0.51±0.046c 0.024±0.006c 57.62±4.23b 18.54±0.18c 8 0.083±0.014b 30.29±0.70d 31.05±1.12a 31.47±0.52c 0.24±0.082d 0.000±0.000c 62.44±2.12b 17.63±0.31d 9 0.125±0.016a 27.05±0.82e 32.46±0.92a 27.83±0.56d 0.21±0.031d 0.000±0.000c 80.79±5.57a 14.37±0.47e 注:同列不同字母标记的数据表示显著性差异,P<0.05;表3~表5同。 抗拉强度随着PS含量的增加呈上升趋势,断裂伸长率呈下降趋势,当PS添加量为9%和5%时,抗拉强度和断裂伸长率最高,分别为32.46 MPa和36.48%,这是因为更高浓度的固体增强了淀粉分子间氢键作用,使得膜致密性良好,因此需要更大的强度来破坏它,但是淀粉含量增加会相对降低膜的含水量,减小分子链的活动性,导致断裂伸长率降低[24]。
水蒸气透过率和透油系数均呈降低趋势,当PS添加量为9%时,水蒸气透过率达到最低,为0.21×10−10 g/(m·s·Pa),在8%和9%时透油系数最低,均为0,这是由于PS含量增加,其相容作用增强,减少了薄膜骨架间的孔隙,且PS含有疏油性羟基,可以阻挡部分油分子在淀粉膜表面的吸附,所以阻隔性增强[25]。
随PS添加量增加,薄膜吸水率逐渐升高,溶解度逐渐下降,在添加量为5%和9%时,吸水率和溶解度最低,分别为32.08%和14.37%,这是因为PS含有亲水性羟基,PS含量越多,薄膜吸水性越强,同时薄膜分子间氢键作用也会随着PS的增加而增强,所以溶解度降低。
作为理想的食品包装膜,最重要的就是机械性能和阻隔性能,要同时满足抗拉强度高、断裂伸长率高、水蒸气透过率低、透油系数低的要求。因此,以机械性能和阻隔性能作为主要考察指标,选择PS添加量8%左右开展正交试验。
2.1.2 甘油添加量对复合膜性能的影响
结果如表3。随甘油含量增加,膜厚度由0.058 mm增加至0.079 mm,变化趋势较为平缓,透光率先上升后下降,在添加量为2.5%时透光性最好,为35.94%,这是因为甘油的-OH与生物聚合物的-OH形成氢键,使膜的透光性增大,而继续添加甘油时,直链淀粉的相对含量下降使得膜的致密度下降,从而引起透光率降低[26]。
表 3 甘油添加量对膜性能的影响Table 3. Effects of the level of glycerol on film properties甘油添加量
(%)厚度
(mm)透光率
(%)抗拉强度
(MPa)断裂伸长率
(%)水蒸气透过率
[×10−10g/(m·s·Pa)]透油系数
(g·mm/m2d)吸水率
(%)溶解度
(%)1.5 0.058±0.012b 30.71±0.75c 22.79±0.29d 20.16±0.21e 0.87±0.053b 0.201±0.007a 68.41±3.01a 9.27±0.63c 2 0.062±0.006ab 32.88±0.46b 23.54±0.52cd 24.35±1.22d 0.52±0.035cd 0.057±0.016b 57.66±2.53b 10.94±0.82b 2.5 0.065±0.004ab 35.94±0.89a 26.92±0.33b 32.55±1.15c 0.43±0.047d 0.013±0.009c 55.37±3.28b 12.08±0.25b 3 0.061±0.008b 35.01±1.28a 28.14±0.67a 38.09±0.99b 0.56±0.015c 0.008±0.002c 54.26±1.42b 17.52±1.13a 3.5 0.079±0.010a 31.22±1.03bc 24.26±0.87c 45.13±1.09a 1.19±0.087a 0.046±0.014b 56.19±2.19b 18.33±0.74a 薄膜的抗拉强度先升高后降低,在甘油添加量为3%时最高,为28.14 MPa,这是由于各分子之间氢键的形成使其他更强的键的互作用力受阻,导致薄膜的抗拉强度降低;而随着甘油含量增加,断裂伸长率逐渐升高,在添加量为3.5%时达到最高值,为45.13%,这是由于薄膜的结晶区遭到甘油破坏,非结晶区占比增加,增加了薄膜基质的自由体积,使淀粉链之间的接近度降低,在张力的作用下促进了淀粉链的运动,增强了薄膜的柔韧性[27]。
水蒸气透过率、透油系数和吸水率先降低后升高,当甘油添加量在2.5%、3%和3%时,三者达到最低,分别为0.43×10−10g/(m·s·Pa)、0.008 g·mm/m2d和54.26%,这是因为一个甘油分子中含有三个亲水醇羟基,甘油越多,吸水性越强,溶解度持续增大,就会导致薄膜阻隔性能下降[28]。
因此,以机械性能和阻隔性能作为主要考察指标,选择甘油添加量2.5%左右开展正交试验。
2.1.3 MCBC添加量对复合膜性能的影响
结果如表4。随MCBC含量增加,膜厚度由0.027 mm增加至0.174 mm,透光率从43.88%降低至16.64%,这是由于MCBC含量过多和厚度过大均会阻碍光线的通过,所以透光率显著(P<0.05)下降。
表 4 MCBC添加量对膜性能的影响Table 4. Effects of the level of MCBC on film propertiesMCBC添加量
(%)厚度
(mm)透光率
(%)抗拉强度
(Mpa)断裂伸长率
(%)水蒸气透过率
[×10−10g/(m·s·Pa)]透油系数
(g·mm/m2d)吸水率
(%)溶解度
(%)0 0.027±0.005d 43.88±2.76a 19.24±0.53c 30.11±0.96b 1.05±0.040a 0.143±0.003a 59.51±0.85ab 22.57±0.43b 0.4 0.048±0.014cd 37.16±2.05b 22.15±0.71b 32.46±2.15ab 0.72±0.090b 0.056±0.023b 57.23±2.51ab 20.28±0.79c 0.8 0.055±0.012c 28.95±0.61c 29.07±1.32a 34.07±1.47a 0.33±0.026d 0.000±0.000c 54.77±2.34b 17.83±0.52de 1.2 0.061±0.003c 26.57±1.24c 27.86±0.96a 32.35±0.63ab 0.46±0.021c 0.000±0.000c 55.39±3.86b 17.55±0.36e 1.6 0.093±0.011b 19.33±0.58d 21.49±0.38b 25.88±0.85c 0.49±0.036c 0.000±0.000b 56.41±1.09b 19.04±0.84cd 2 0.174±0.025a 16.64±0.32d 18.63±0.66c 17.26±0.42d 0.68±0.057b 0.038±0.010b 62.06±2.67a 25.62±1.18a 抗拉强度和断裂伸长率均先升高后下降,在MCBC为0.8%时达到最高值,分别为29.07 MPa和34.07%,与不添加MCBC相比高出51.09%和13.15%,这是因为当纤维素添加量适宜时能够与基质以及增塑剂等之间形成良好的相互作用,但是一旦过多非常容易发生团聚现象,导致结构变得不均匀,进而影响其机械性能[29]。
水蒸气透过率、吸水率、溶解度以及透油系数均先降低后升高,在MCBC 为0.8%、0.8%、1.2%时,水蒸气透过率、吸水率、溶解度分别达到最低值0.33×10−10 g/(m·s·Pa)、54.77%和17.55%,与不添加MCBC相比分别降低了68.57%、7.97%和22.24%;当MCBC添加量在0.8%~1.6%之间时,透油系数均为0。这是因为当添加适量的MCBC时能促使聚合物更好地缔合,且经硬脂酸改性处理的纤维素中-OH与硬脂酸中的-COOH的长疏水性烃链反应生成酯键,提高了纤维素的疏水性[30]。此外,根据Kristo等[31]的说法,MCBC的存在可能导致水分子通过路径曲折,限制了水分渗透,所以能够在一定程度上提高机械性能和阻隔性能,但添加量过多时,易发生团聚现象,导致复合膜结构不均匀,进而使分子间作用变小,孔隙增大,最终影响其力学性能和阻隔性能。
因此,以机械性能和阻隔性能作为主要考察指标,选择MCBC添加量1.2%左右开展正交试验。
2.1.4 NTP添加量对复合膜性能的影响
结果如表5。随NTP含量增加,厚度从0.058 mm增至0.119 mm,透光率从33.68%降低至18.43%,抗拉强度和断裂伸长率先升高后降低,在NTP为0.15%时达到最高值,分别为26.97 MPa和32.35%,与不添加NTP相比分别提高了43.92%和38.90%。这是因为NTP能够在淀粉基质中良好分散,导致从淀粉基质到填料的优异应力转移,纳米颗粒的高比面积使填料-聚合物基质界面相互作用变得更强,因此复合膜的强度能在一定范围内呈现增强趋势[32]。但是当NTP添加量超过0.15%后,膜的抗拉强度跌落的十分明显,这可能是过多的纳米粒子致使PS与填料之间的相互作用减弱的缘故。断裂伸长率先上升是由于NTP具有良好的润滑性和助流性,使得膜的延展性得到增强,同样,当NTP加入量过多时,断裂伸长率下降,这是因为大量的纳米粒子在淀粉基质中的流动性变差,增加了膜的刚性和脆性[33]。
表 5 NTP添加量对膜性能的影响Table 5. Effects of the level of NTP on film propertiesNTP添加量
(%)厚度
(mm)透光率
(%)抗拉强度
(Mpa)断裂伸长率
(%)水蒸气透过率
[×10−10g/(m·s·Pa)]透油系数
(g·mm/m2d)吸水率
(%)溶解度
(%)0 0.058±0.014d 33.68±0.73a 18.74±0.96c 23.29±1.07c 0.99±0.035a 0.164±0.022a 68.35±1.84a 20.62±0.92b 0.05 0.063±0.006d 32.57±1.34a 23.58±0.48b 27.49±0.96b 0.78±0.017b 0.105±0.010b 65.48±3.47a 18.83±0.79c 0.1 0.074±0.011cd 29.26±0.97b 25.72±0.73a 32.05±1.25a 0.65±0.059c 0.073±0.008c 58.19±2.96b 17.95±0.53c 0.15 0.095±0.018bc 27.67±1.59b 26.97±0.79a 32.35±0.64a 0.42±0.012e 0.031±0.004d 56.29±0.85b 17.50±0.55c 0.2 0.102±0.005ab 24.89±0.62c 24.16±0.42b 26.18±0.85b 0.35±0.040f 0.028±0.005d 43.78±1.61c 18.26±0.87c 0.25 0.119±0.012a 18.43±0.58d 16.62±0.35d 13.97±0.43d 0.56±0.031d 0.049±0.011d 27.62±0.62d 25.49±1.04a 透油系数、水蒸气透过率和溶解度先降低后升高,NTP为0.2%时,水蒸气透过率和透油系数达最低值0.35×10−10 g/(m·s·Pa)和0.028 g·mm/m2d,NTP为0.15%时,溶解度达最低值17.50%,与不添加NTP相比分别降低64.65%、82.93%和15.13%,而吸水率则是从68.35%下降至27.62%。这是由于NTP不亲水,适量的NTP能够形成曲折的路径,阻碍游离水通过淀粉基质的扩散,所以吸水率和溶解度降低,但当NTP添加过多时,膜渐渐变为白色而透明度大幅度降低,尤其超过0.2%以后,MCBC、NTP和PS不能紧密相容,溶解度上升非常明显,在水中能够看到脱落的少量白色物质。
因此,以机械性能和阻隔性能作为主要考察指标,选择NTP添加量0.15%左右开展正交试验。
2.2 正交试验结果
采用加权综合评分法对指标进行评分,极差及方差对结果进行分析。根据膜的应用特性,四个指标权重相同,权值λ1=λ2=λ3=λ4=0.25,λ1+λ2+λ3+λ4=1[34]。设每个指标最好值对应100分,最差值对应0分,其中抗拉强度和断裂伸长率越高越好,水蒸气透过率和透油系数越低越好,计算综合评分值。
结果见表6和表7。根据直观分析,各因素影响主次顺序为A>C>D>B,即PS添加量>MCBC添加量>NTP添加量>甘油添加量。方差分析结果显示A、B、C、D的影响均显著(P<0.05)。最优组合为A2B2C1D2,即PS 8%、甘油2.5%、MCBC 0.8%、NTP 0.15%。对此条件进行三次验证试验,所得复合膜抗拉强度32.48 MPa,透油系数0.006 g·mm/m2d,水蒸气透过率0.19×10−10 g/(m·s·Pa),断裂伸长率33.61%,综合评分93.502,高于正交试验最高评分值。最佳复合膜的其他指标为厚度0.042 mm,透光率32.58%,吸水率55.79%,溶解度18.04%,复合膜的综合性能相对较好。
表 6 正交试验设计及结果Table 6. Results of orthogonal array design tests实验号 因素 抗拉强度
(MPa)断裂伸长率
(%)水蒸气透过率
[×10−10g/(m·s·Pa)]透油系数
(g·mm/m2d)综合评分值 A B C D 1 1 1 1 1 24.22 34.13 0.48 0.114 29.702 2 1 2 2 2 27.73 35.18 0.45 0.033 62.733 3 1 3 3 3 26.32 25.32 0.61 0.105 11.051 4 2 1 2 3 31.90 27.21 0.27 0.015 70.969 5 2 2 3 1 25.11 26.17 0.23 0.037 45.810 6 2 3 1 2 32.75 31.43 0.18 0.041 81.829 7 3 1 3 2 26.45 24.07 0.39 0.072 28.215 8 3 2 1 3 28.24 26.55 0.15 0.006 67.363 9 3 3 2 1 29.47 25.72 0.46 0.089 33.039 K1 103.486 128.886 178.894 108.552 K2 198.609 175.906 166.741 172.777 K3 128.616 114.868 85.076 149.383 k1 34.495 42.962 59.631 36.184 k2 66.203 58.635 55.580 57.592 k3 42.872 38.289 28.359 49.794 R 31.708 20.346 31.272 21.408 优水平 A2 B2 C1 D2 表 7 方差分析表Table 7. Variance analysis of orthogonal tests方差来源 Ⅲ类平方和 自由度 均方 F 显著性 A 3948.107 2 1974.054 24.452 P<0.05 B 879.540 2 439.770 5.447 P<0.05 C 5145.223 2 2572.612 31.867 P<0.05 D 1380.646 2 690.323 8.551 P<0.05 误差 1453.152 18 80.731 2.3 复合膜扫描电镜分析
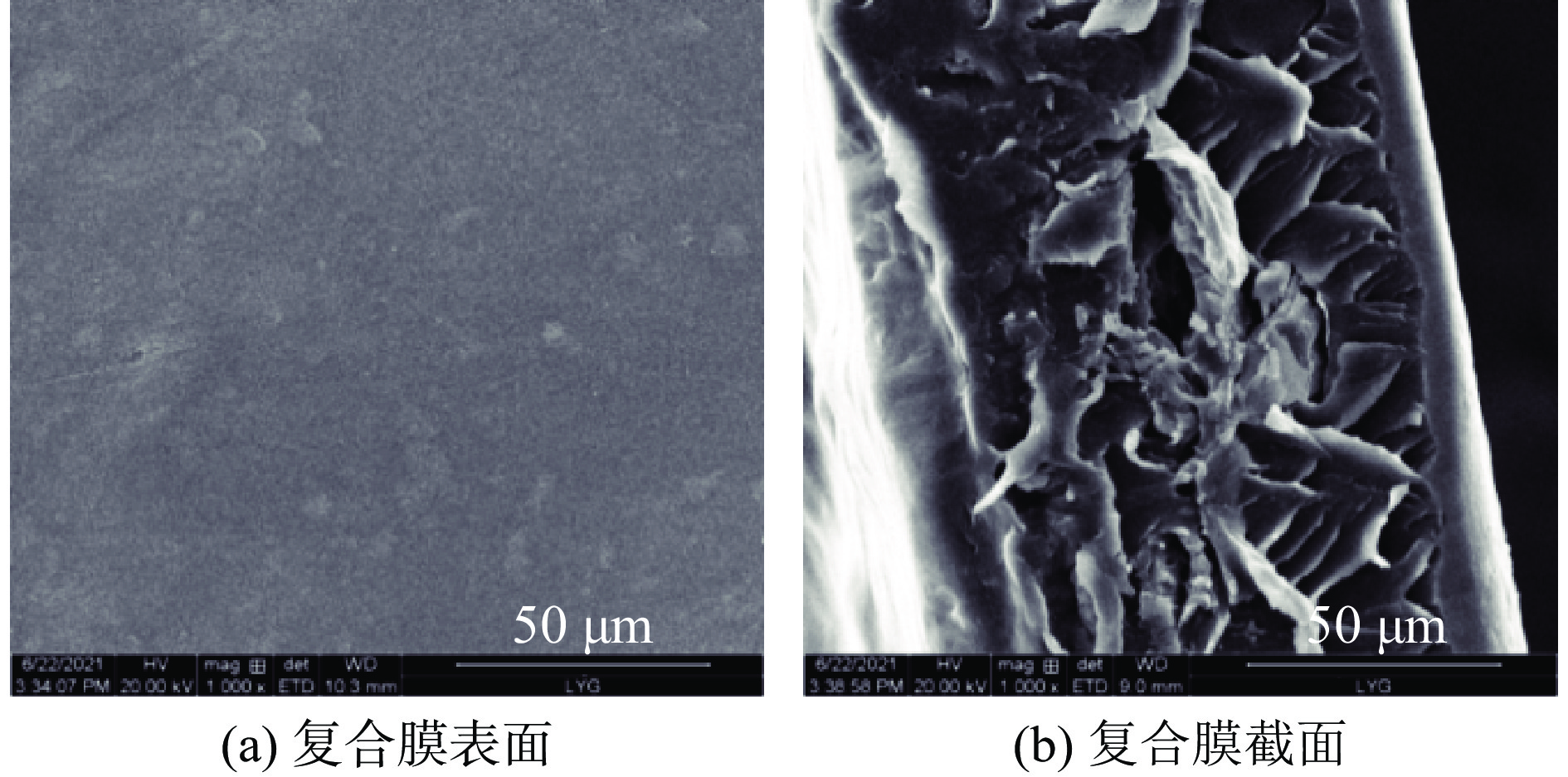
复合膜表面和截面的扫描电镜结果如图1(a)。由图1(a)可知,复合膜整体光滑均一,无淀粉颗粒存在,无裂纹和孔隙,说明PS、MCBC和NTP三者相容性较好,天然填料在基质中的均匀分散和强附着力能在提高生物复合膜(高弹性)的机械效率方面发挥重要作用[35]。由于纤维表面质地粗糙,所以能够观察到图1(b)中横截面较粗糙,但无间隙存在,进一步证明三种材料之间连接紧密。
2.4 复合膜傅里叶红外光谱分析
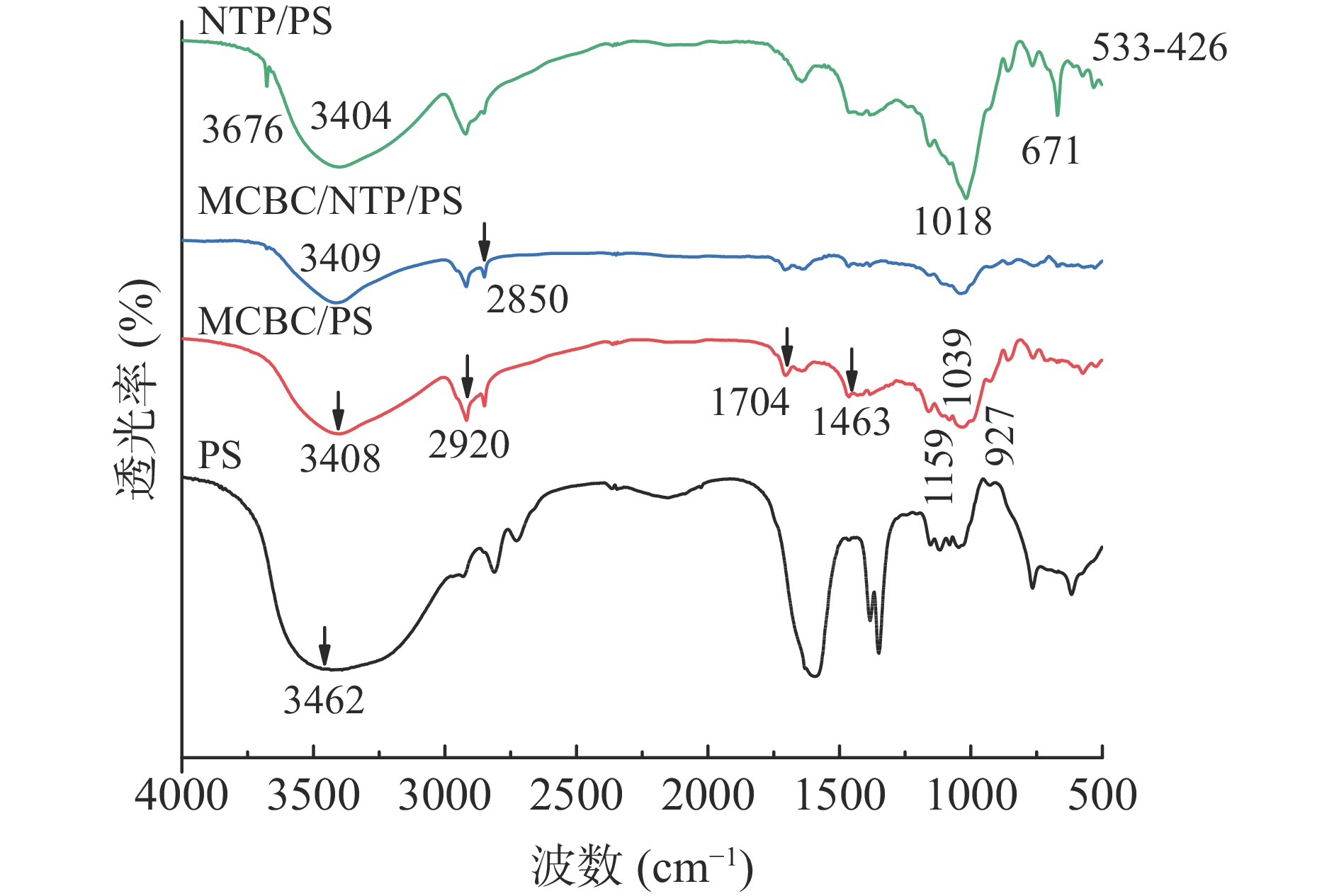
红外光谱如图2所示。MCBC/PS、MCBC/NTP/PS和NTP/PS这3种膜在3408 cm−1处左右都有1个峰出现,这与淀粉中-OH基团的伸缩振动有关;与PS膜中3462 cm−1处的谱带相比,3种复合膜的光谱分别移至3408、3409和3404 cm−1,这种转变表明分子间氢键作用增强[36]。927、1039和1159 cm−1是C-O拉伸,1641 cm−1处是结合水,2920 cm−1是C-H拉伸,1463 cm−1是甘油;在621、574和524 cm−1的波段归因于葡萄糖环的骨架引起的复杂振动[37]。关于NTP,在3676 cm−1处是Mg3-OH,1018 cm−1是Si-O-Si拉伸,671cm−1是-OH变形,536和452 cm−1是Si-O-Mg,466 cm−1是Mg-O,426 cm−1是Si-O [38]。最佳复合膜光谱显示对应于MCBC/PS的信号及对应于NTP/PS的信号,由于NTP浓度低,最佳复合膜中的滑石带强度相对较弱。
2.5 复合膜热重分析
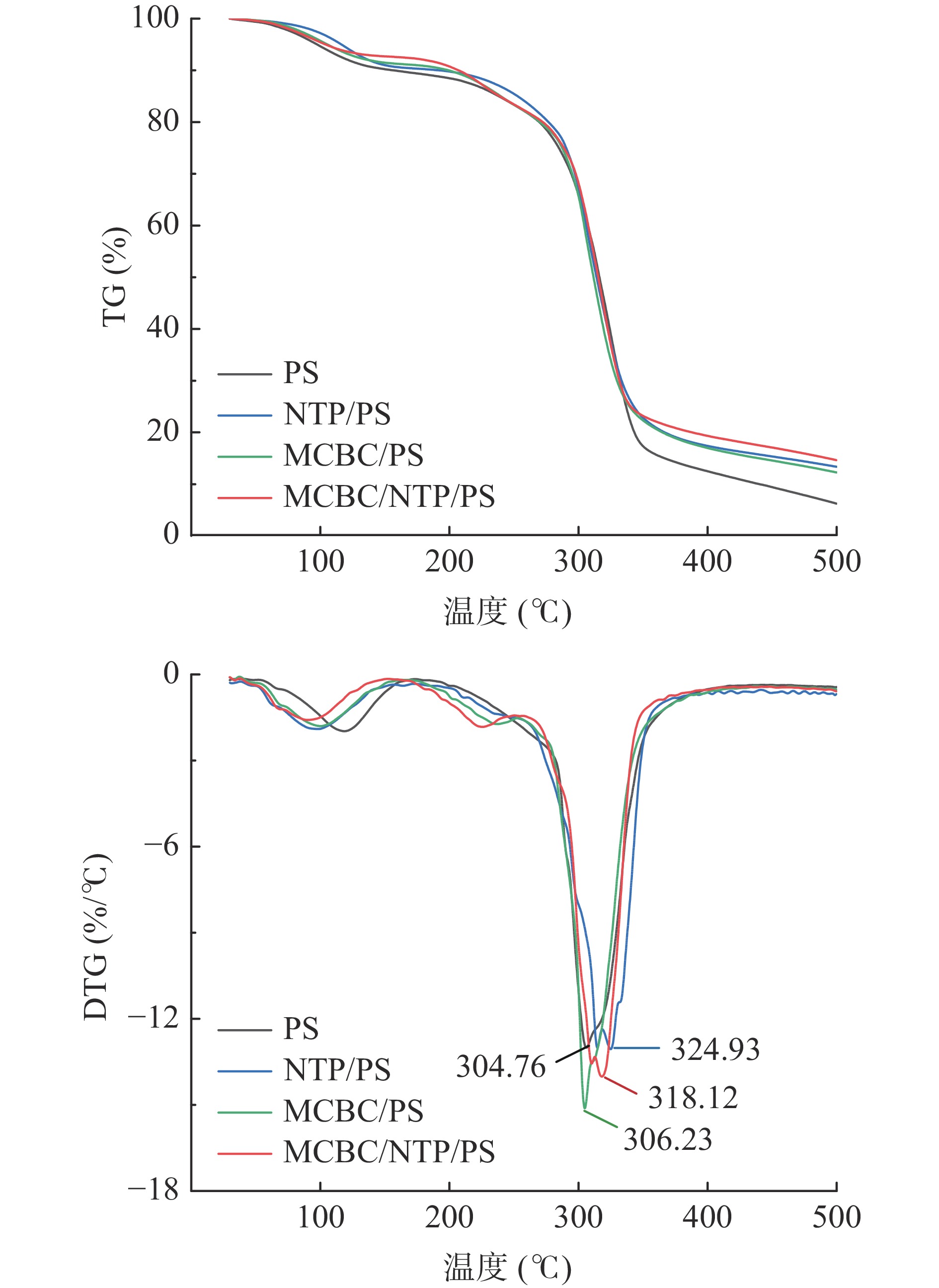
复合膜的TG和DTG结果如图3。PS、NTP/PS、MCBC/PS和MCBC/NTP/PS薄膜的失重主要体现在4个不同的区域。在50~250 ℃下,膜内甘油和水分发生蒸发现象,导致重量损失;第3个区域主要描述主聚合物链在300~350 ℃下的脱水,这导致低分子量不饱和碳和脂肪族碳物质的形成;在高于400 ℃温度下,发生进一步分解,并留下残留物[39]。与纯PS薄膜相比,加入NTP、MCBC和MCBC/NTP的薄膜的热稳定性更高。从DTG曲线来看,PS、NTP/PS、MCBC/PS和MCBC/NTP/PS薄膜的第3阶段热分解温度分别为304.76、324.93、306.23和318.12 ℃。结果表明,NTP/PS薄膜表现出最高的耐热性,其次是MCBC/NTP/PS薄膜,虽然MCBC/NTP/PS薄膜的热稳定性不是最佳的,但仍高于PS和MCBC/PS薄膜。
2.6 复合膜降解性分析
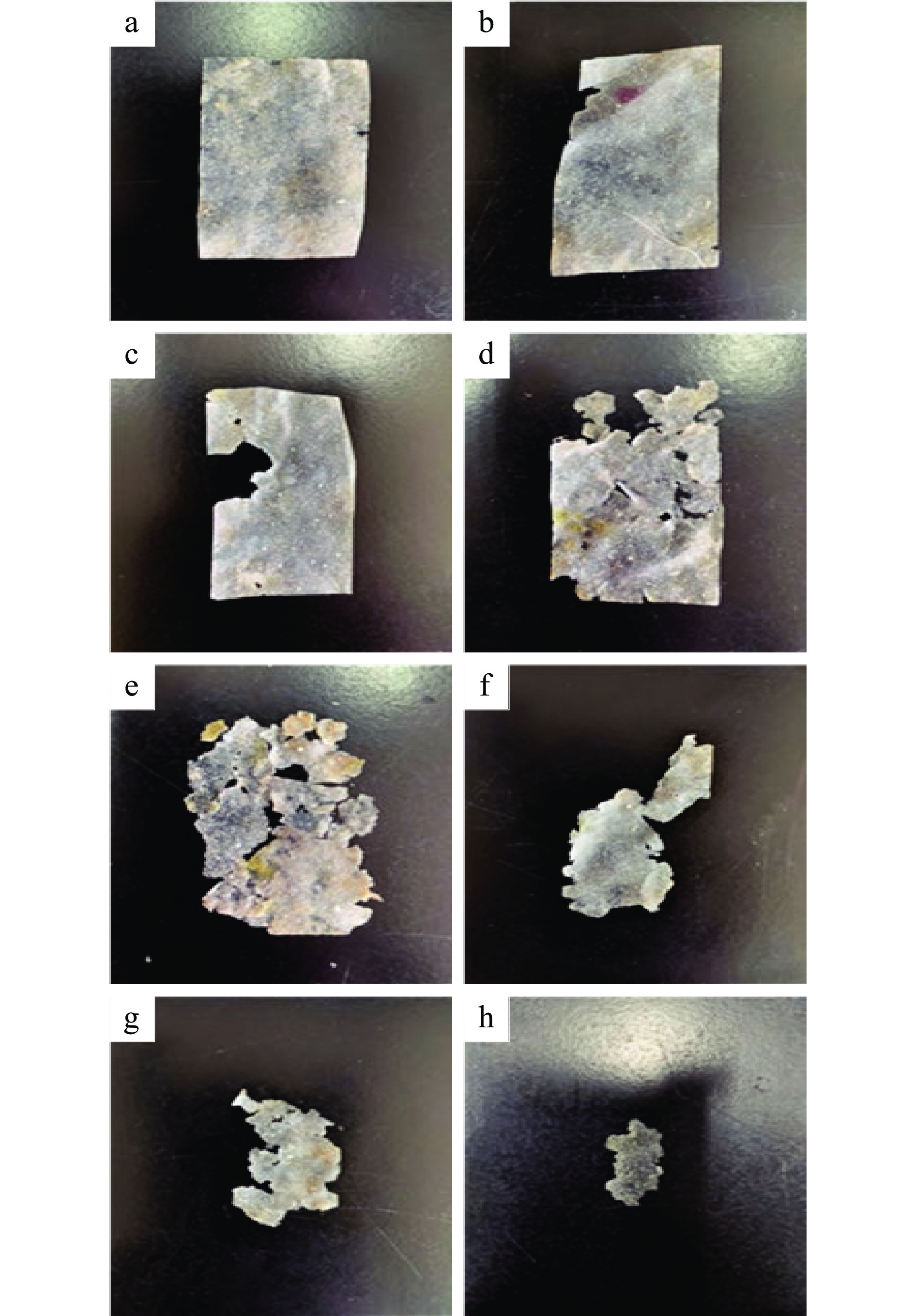
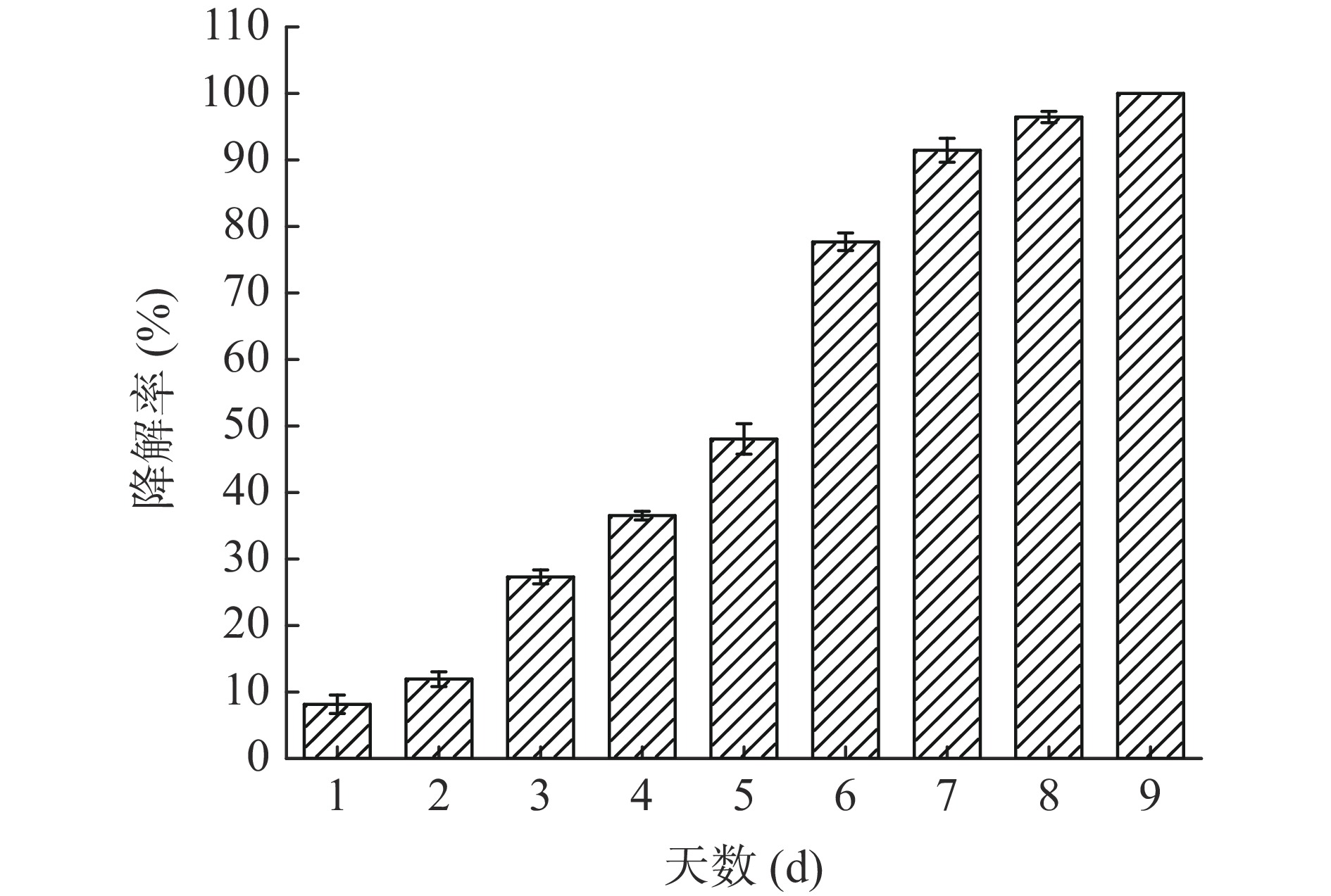
复合膜的降解过程和对应的降解率如图4和图5,第1 d复合膜表面无明显变化,降解率为8.16%;第2~4 d,膜表面开始出现不规则缺口,这是由于土壤内生物的作用导致开始发生明显降解,这3 d的降解率分别为11.94%、27.32%和36.52%;第5 d可明显观察到膜被分解成大小不一的碎片,此时的降解率为48.04%;自第6 d开始降解率增幅明显,膜也仅剩一小部分没有被降解,第6~8 d的降解率分别为77.69%、86.60%和96.47%,第9 d复合膜完全消失,降解率达100%。复合膜的降解速度如此之快是由PS具有吸水的物理特性,导致复合膜对微生物攻击的敏感性更高,而尺寸较大或纤维含量较高的薄膜有更大的生物降解趋势,更易受到微生物的攻击[40]。这些研究结果表明,试验制备的复合膜不会对环境产生影响,为完全可生物降解。
3. 结论
本文以PS为成膜基质、MCBC和NTP为增强材料、甘油为增塑剂进行MCBC/NTP/PS复合膜的制备与性能研究,探明了PS、MCBC、NTP及甘油添加量对膜性能的影响。研究表明复合膜的最佳制备工艺为:MCBC 0.8%、PS 8%、NTP 0.15%、甘油2.5%,此条件下获得的复合膜表面光滑平整、结构致密,NTP、MCBC和PS之间相容性良好,氢键作用加强,具有良好的机械性能、阻隔性能和热稳定性,并且可完全生物降解。本研究为MCBC/NTP/PS复合膜的在绿色食品工业的实际开发应用提供了理论指导,在后续工作中应进一步深入研究该复合膜的贮存性能和实际应用性能。
-
表 1 正交试验因素水平设计
Table 1 Orthogonal test factor level
水平 因素 A PS添加量(%) B 甘油添加量(%) C MCBC添加量(%) D NTP添加量(%) 1 7 2 0.8 0.1 2 8 2.5 1.2 0.15 3 9 3 1.6 0.2 表 2 PS添加量对膜性能的影响
Table 2 Effects of the level of PS on film properties
PS添加量
(%)厚度
(mm)透光率
(%)抗拉强度
(Mpa)断裂伸长率
(%)水蒸气透过率
[×10−10g/(m·s·Pa)]透油系数
(g·mm/m2d)吸水率
(%)溶解度
(%)5 0.037±0.006c 49.77±2.28a 16.39±0.76d 36.48±0.83a 1.18±0.055a 0.305±0.024a 32.08±2.39d 23.91±0.26a 6 0.046±0.012c 43.36±1.05b 24.72±0.63c 34.75±1.22b 0.75±0.036b 0.128±0.013b 43.11±2.73c 19.28±0.52b 7 0.052±0.009c 35.18±0.93c 28.31±1.01b 32.16±0.94c 0.51±0.046c 0.024±0.006c 57.62±4.23b 18.54±0.18c 8 0.083±0.014b 30.29±0.70d 31.05±1.12a 31.47±0.52c 0.24±0.082d 0.000±0.000c 62.44±2.12b 17.63±0.31d 9 0.125±0.016a 27.05±0.82e 32.46±0.92a 27.83±0.56d 0.21±0.031d 0.000±0.000c 80.79±5.57a 14.37±0.47e 注:同列不同字母标记的数据表示显著性差异,P<0.05;表3~表5同。 表 3 甘油添加量对膜性能的影响
Table 3 Effects of the level of glycerol on film properties
甘油添加量
(%)厚度
(mm)透光率
(%)抗拉强度
(MPa)断裂伸长率
(%)水蒸气透过率
[×10−10g/(m·s·Pa)]透油系数
(g·mm/m2d)吸水率
(%)溶解度
(%)1.5 0.058±0.012b 30.71±0.75c 22.79±0.29d 20.16±0.21e 0.87±0.053b 0.201±0.007a 68.41±3.01a 9.27±0.63c 2 0.062±0.006ab 32.88±0.46b 23.54±0.52cd 24.35±1.22d 0.52±0.035cd 0.057±0.016b 57.66±2.53b 10.94±0.82b 2.5 0.065±0.004ab 35.94±0.89a 26.92±0.33b 32.55±1.15c 0.43±0.047d 0.013±0.009c 55.37±3.28b 12.08±0.25b 3 0.061±0.008b 35.01±1.28a 28.14±0.67a 38.09±0.99b 0.56±0.015c 0.008±0.002c 54.26±1.42b 17.52±1.13a 3.5 0.079±0.010a 31.22±1.03bc 24.26±0.87c 45.13±1.09a 1.19±0.087a 0.046±0.014b 56.19±2.19b 18.33±0.74a 表 4 MCBC添加量对膜性能的影响
Table 4 Effects of the level of MCBC on film properties
MCBC添加量
(%)厚度
(mm)透光率
(%)抗拉强度
(Mpa)断裂伸长率
(%)水蒸气透过率
[×10−10g/(m·s·Pa)]透油系数
(g·mm/m2d)吸水率
(%)溶解度
(%)0 0.027±0.005d 43.88±2.76a 19.24±0.53c 30.11±0.96b 1.05±0.040a 0.143±0.003a 59.51±0.85ab 22.57±0.43b 0.4 0.048±0.014cd 37.16±2.05b 22.15±0.71b 32.46±2.15ab 0.72±0.090b 0.056±0.023b 57.23±2.51ab 20.28±0.79c 0.8 0.055±0.012c 28.95±0.61c 29.07±1.32a 34.07±1.47a 0.33±0.026d 0.000±0.000c 54.77±2.34b 17.83±0.52de 1.2 0.061±0.003c 26.57±1.24c 27.86±0.96a 32.35±0.63ab 0.46±0.021c 0.000±0.000c 55.39±3.86b 17.55±0.36e 1.6 0.093±0.011b 19.33±0.58d 21.49±0.38b 25.88±0.85c 0.49±0.036c 0.000±0.000b 56.41±1.09b 19.04±0.84cd 2 0.174±0.025a 16.64±0.32d 18.63±0.66c 17.26±0.42d 0.68±0.057b 0.038±0.010b 62.06±2.67a 25.62±1.18a 表 5 NTP添加量对膜性能的影响
Table 5 Effects of the level of NTP on film properties
NTP添加量
(%)厚度
(mm)透光率
(%)抗拉强度
(Mpa)断裂伸长率
(%)水蒸气透过率
[×10−10g/(m·s·Pa)]透油系数
(g·mm/m2d)吸水率
(%)溶解度
(%)0 0.058±0.014d 33.68±0.73a 18.74±0.96c 23.29±1.07c 0.99±0.035a 0.164±0.022a 68.35±1.84a 20.62±0.92b 0.05 0.063±0.006d 32.57±1.34a 23.58±0.48b 27.49±0.96b 0.78±0.017b 0.105±0.010b 65.48±3.47a 18.83±0.79c 0.1 0.074±0.011cd 29.26±0.97b 25.72±0.73a 32.05±1.25a 0.65±0.059c 0.073±0.008c 58.19±2.96b 17.95±0.53c 0.15 0.095±0.018bc 27.67±1.59b 26.97±0.79a 32.35±0.64a 0.42±0.012e 0.031±0.004d 56.29±0.85b 17.50±0.55c 0.2 0.102±0.005ab 24.89±0.62c 24.16±0.42b 26.18±0.85b 0.35±0.040f 0.028±0.005d 43.78±1.61c 18.26±0.87c 0.25 0.119±0.012a 18.43±0.58d 16.62±0.35d 13.97±0.43d 0.56±0.031d 0.049±0.011d 27.62±0.62d 25.49±1.04a 表 6 正交试验设计及结果
Table 6 Results of orthogonal array design tests
实验号 因素 抗拉强度
(MPa)断裂伸长率
(%)水蒸气透过率
[×10−10g/(m·s·Pa)]透油系数
(g·mm/m2d)综合评分值 A B C D 1 1 1 1 1 24.22 34.13 0.48 0.114 29.702 2 1 2 2 2 27.73 35.18 0.45 0.033 62.733 3 1 3 3 3 26.32 25.32 0.61 0.105 11.051 4 2 1 2 3 31.90 27.21 0.27 0.015 70.969 5 2 2 3 1 25.11 26.17 0.23 0.037 45.810 6 2 3 1 2 32.75 31.43 0.18 0.041 81.829 7 3 1 3 2 26.45 24.07 0.39 0.072 28.215 8 3 2 1 3 28.24 26.55 0.15 0.006 67.363 9 3 3 2 1 29.47 25.72 0.46 0.089 33.039 K1 103.486 128.886 178.894 108.552 K2 198.609 175.906 166.741 172.777 K3 128.616 114.868 85.076 149.383 k1 34.495 42.962 59.631 36.184 k2 66.203 58.635 55.580 57.592 k3 42.872 38.289 28.359 49.794 R 31.708 20.346 31.272 21.408 优水平 A2 B2 C1 D2 表 7 方差分析表
Table 7 Variance analysis of orthogonal tests
方差来源 Ⅲ类平方和 自由度 均方 F 显著性 A 3948.107 2 1974.054 24.452 P<0.05 B 879.540 2 439.770 5.447 P<0.05 C 5145.223 2 2572.612 31.867 P<0.05 D 1380.646 2 690.323 8.551 P<0.05 误差 1453.152 18 80.731 -
[1] 王东利, 徐晓白, 储少岗. 塑料废物焚烧与持久性有机物环境污染[J]. 环境与健康杂志,2003(4):250−252. [WANG Dongli, XU Xiaobai, CHU Shaogang. Waste plastics incineration and environmental pollution caused by persistent organic pollutants[J]. Journal of Environment and Health,2003(4):250−252. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5914.2003.04.040 [2] KASAVAN S, YUSOFF S, FAKRI M F R, et al. Plastic pollution in water ecosystems: A bibliometric analysis from 2000 to 2020[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2021,313:127946. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127946
[3] ZHANG K, HAMIDIAN A H, TUBIĆ A, et al. Understanding plastic degradation and microplastic formation in the environment: A review[J]. Environmental Pollution,2021,274:116554. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2021.116554
[4] 朱永官, 朱冬, 许通, 等. (微)塑料污染对土壤生态系统的影响: 进展与思考[J]. 农业环境科学学报,2019,38(1):1−6. [ZHU Yongguan, ZHU Dong, XU Tong, et al. Impacts of (micro) plastics on soil ecosystem: Progress and perspective[J]. Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2019,38(1):1−6. doi: 10.11654/jaes.2018-1427 [5] ZHOU X, YANG R, WANG B, et al. Development and characterization of bilayer films based on pea starch/polylactic acid and use in the cherry tomatoes packaging[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2019,222:114912. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.05.042
[6] ZHOU D, MA Z, YIN X, et al. Structural characteristics and physicochemical properties of field pea starch modified by physical, enzymatic, and acid treatments[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2019,93:386−394. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2019.02.048
[7] ALIAS A R, WAN M K, SARBON N M. Emerging materials and technologies of multi-layer film for food packaging application: A review[J]. Food Control,2022:108875.
[8] 陈印军, 王琦琪, 向雁. 我国玉米生产地位、优势与自给率分析[J]. 中国农业资源与区划,2019,40(1):7−16. [CHEN Yinjun, WANG Qiqi, XIANG Yan. Analysis on the status, superiority and self-sufficiency ratio of maize in China[J]. Chinese Journal of Agricultural Resources and Regional Planning,2019,40(1):7−16. [9] BANGAR S P, WHITESIDE W S. Nano-cellulose reinforced starch bio composite films-A review on green composites[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,185:849−860. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.07.017
[10] 程书平, 范廷玉, 彭丹. 纳米纤维素的化学改性及应用进展[J]. 广东化工,2020,47(20):230−231. [CHENG Shuping, FAN Tingyu, PENG Dan. Research on chemical modification and application of nanocellulose[J]. Guangdong Chemical Industry,2020,47(20):230−231. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-1865.2020.20.116 [11] 曹坤丽, 吴燕, 吴兆旭, 等. 硬脂酸改性纳米纤丝化纤维素的制备与表征[J]. 科技创新与应用,2016(28):32−33. [CAO Kunli, WU Yan, WU Zhaoxu, et al. Preparation and characterization of nanofibrillated cellulose modified by stearic acid[J]. Technology Innovation and Application,2016(28):32−33. [12] 史颖涵. 基于苹果渣多酚-硬脂酸改性微纳米级纤维素的可食复合淀粉包装膜的研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2020 SHI Yinghan. Study on edible composite starch packaging film based on apple pomace polyphenol-stearic acid modified micro-nano cellulose [D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2020.
[13] CASTILLO L, LÓPEZ O, LÓPEZ C, et al. Thermoplastic starch films reinforced with talc nanoparticles[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2013,95(2):664−674. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.03.026
[14] CASTILLO L A, LÓPEZ O V, GHILARDI J, et al. Thermoplastic starch/talc bionanocomposites. Influence of particle morphology on final properties[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2015,51:432−440. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.05.030
[15] 李悦, 李晓娇, 张云娟, 等. 葛根淀粉可食膜的制备及其性能研究[J]. 食品研究与开发,2021,42(12):108−115. [LI Yue, LI Xiaojiao, ZHANG Yunjuan, et al. Preparation and physical properties of pueraria lobata starch edible film[J]. Food Research and Development,2021,42(12):108−115. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2021.12.018 [16] 高凌云, 张本山. 木薯氧化淀粉-壳聚糖复合膜的成膜特性研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2010,31(10):322−324, 337. [GAO Lingyun, ZHANG Benshan. Study on film forming characteristics of oxidized cassava starch-chitosan blend film[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2010,31(10):322−324, 337. [17] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 1040.3-2006塑料 拉伸性能的测定 第3部分: 薄膜和薄片的试验条件[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006 General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, China National Standardization Administration. GB/T 1040.3-2006 Plastics-Determination of tensile properties-Part 3: Test conditions for films and sheets[S].Beijing: China Standard Press, 2006.
[18] 董增, 宋也好, 余明, 等. 纳米SiO2/壳聚糖/淀粉复合包装膜的制备及性能[J]. 塑料工业,2017,45(9):135−139. [DONG Zeng, SONG Yehao, YU Ming, et al. Preparation and performances of starch/chitosan/nano silica composite packaging film[J]. China Plastics Industry,2017,45(9):135−139. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5770.2017.09.030 [19] 李鸿梅, 盖彦红, 闵伟红, 等. 响应面试验优化拉伸法制备低成本玉米蛋白粉源膜工艺[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(12):76−82. [LI Hongmei, GAI Yanhong, MIN Weihong, et al. Response surface optimization of preparation of low-cost film from corn gluten meal by stretching method[J]. Food Science,2016,37(12):76−82. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201612013 [20] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. GB/T 1034-2008塑料 吸水性的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008 General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, China National Standardization Administration. GB/T 1034-2008 Plastics-Determination of water absorption[S].Beijing: China Standard Press, 2008.
[21] 田冰释, 王利强, 郄冰玉, 等. 马铃薯淀粉/海藻酸钠复合交联可食膜阻湿性影响因素研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(5):285−288, 328. [TIAN Bingshi, WANG Liqiang, QIE Bingyu, et al. Study on influencing factors water resistant properties of PS/SA composite cross-linked edible films[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(5):285−288, 328. [22] 鲁亚楠. 可食性玉米醇溶蛋白复合膜性能的研究[D]. 郑州: 河南工业大学, 2013 LU Yanan. Research on the properties of edible zein composite films [D]. Zhengzhou: Henan University of Technology, 2013.
[23] MARAN J P, SIVAKUMAR V, THIRUGNANASAMBANDHAM K, et al. Response surface modeling and analysis of barrier and optical properties of maize starch edible films[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2013,60:412−421. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2013.06.029
[24] NARVÁEZ-GÓMEZ G, FIGUEROA-FLÓREZ J, SALCEDO-MENDOZA J, et al. Development and characterization of dual-modified yam (Dioscorea rotundata) starch-based films[J]. Heliyon,2021,7(4):e06644. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e06644
[25] 周悦, 吴雪辉, 谢家星, 等. 可食性肉桂精油复合膜的制备及其缓释性能[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(15):170−176. [ZHOU Yue, WU Xuehui, XIE Jiaxing, et al. Preparation and sustained release properties of cinnamon edible essential oil composite film[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(15):170−176. [26] 谢玮, 崔少宁, 肖川, 等. 姜渣-玉米淀粉膜的制备及研究[J]. 包装工程,2018,39(23):93−99. [XIE Wei, CUI Shaoning, XIAO Chuan, et al. Preparation and study of ginger residue-corn starch film[J]. Packaging Engineering,2018,39(23):93−99. [27] 马璟, 李蔚然, 王丽杰, 等. 柠檬汁纳米银抗菌复合膜的制备工艺优化及性能研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(8):31−40. [MA Jing, LI Weiran, WANG Lijie, et al. Preparation process optimization and performance research of lemon juice nano silver antimicrobial composite membrane[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(8):31−40. [28] 成淑君, 李秋铮, 曾瑶英, 等. 肉桂精油抗菌膜的制备及应用[J]. 食品工业,2020,41(6):19−23. [CHENG Shujun, LI Qiuzheng, ZENG Yaoying, et al. Preparation and application of antibacterial film of cinnamon essential oil[J]. The Food Industry,2020,41(6):19−23. [29] VERSINO F, GARCÍA M A. Cassava (Manihot esculenta) starch films reinforced with natural fibrous filler[J]. Industrial Crops and Products,2014,58:305−314. doi: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2014.04.040
[30] 朱文凯, 张洋, 吴燕. 硬脂酸改性纳米纤维素晶体/纳米ZnO复合材料的制备与表征[J]. 纤维素科学与技术,2019,27(2):39−45. [ZHU Wenkai, ZHANG Yang, WU Yan. Preparation and characterization of stearic acid modified CNC/nano ZnO composites[J]. Joural of Cellulose Science and Technology,2019,27(2):39−45. [31] KRISTO E, BILIADERIS C G. Physical properties of starch nanocrystal-reinforced pullulan films[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2007,68(1):146−158. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2006.07.021
[32] RAMMAK T, BOONSUK P, KAEWTATIP K. Mechanical and barrier properties of starch blend films enhanced with kaolin for application in food packaging[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,192:1013−1020. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.10.081
[33] LÓPEZ O V, CASTILLO L A, GARCIA M A, et al. Food packaging bags based on thermoplastic corn starch reinforced with talc nanoparticles[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2015,43:18−24. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2014.04.021
[34] 张帆. 干热变性莲子淀粉制备工艺及其成膜特性的研究与应用[D]. 福州: 福建农林大学, 2012 ZHANG Fan. Research and application on preparation technology and edible film's forming property of lotus-seed starches modified by dry heating[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Agriculture and Forestry University, 2012.
[35] HAZRATI K Z, SAPUAN S M, ZUHRI M Y M, et al. Preparation and characterization of starch-based biocomposite films reinforced by Dioscorea hispida fibers[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology,2021,15:1342−1355. doi: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2021.09.003
[36] 朱洁. 纳米ZnO和纳米SiO2在甘油-水复合塑化体系中对淀粉膜性能的影响[D]. 济南: 齐鲁工业大学, 2021 ZHU Jie. Effect of Nano ZnO and Nano SiO2 on performance of starch film in glycerol-water compound plastic system [D]. Jinan: Qilu University of Techology, 2021.
[37] ZHANG Y, HAN J H. Mechanical and thermal characteristics of pea starch films plasticized with monosaccharides and polyols[J]. Journal of Food Science,2006,71(2):E109−E118. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2621.2006.tb08891.x
[38] CASTILLO L A, BARBOSA S E, MAIZA P, et al. Surface modifications of talcs effects of inorganic and organic acid treatments[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2011,46(8):2578−2586. doi: 10.1007/s10853-010-5110-3
[39] KUMAR P, TANWAR R, GUPTA V, et al. Pineapple peel extract incorporated poly (vinyl alcohol)-corn starch film for active food packaging: Preparation, characterization and antioxidant activity[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,187:223−231. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.07.136
[40] EDHIREJ A, SAPUAN S M, JAWAID M, et al. Preparation and characterization of cassava bagasse reinforced thermoplastic cassava starch[J]. Fibers and Polymers,2017,18(1):162−171. doi: 10.1007/s12221-017-6251-7
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 李羽佳,王喜明,姚利宏,胡建鹏. 无机质增强植物纤维高分子复合材料研究进展. 化工新型材料. 2025(01): 15-20 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 王雅荭,谢京颖,高彦祥. 生物基材料及其在食品包装中的研究进展. 中国食品添加剂. 2024(11): 238-248 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 陈龙,周舟,杨雪杰,王清,邢淑婕,李建芳. 茶末-纳米纤维素-硼砂复合膜的制备、优化及性能表征. 食品科技. 2024(12): 27-35 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)





 下载:
下载:







 下载:
下载:



