Optimization of Expression Conditions, Purification and Identification of the Recombinant Cowpea Hemoglobin Lb Ⅱ in Escherichia coli
-
摘要: 豇豆根瘤中含有大量豆血红蛋白。该蛋白是良好的天然色素,可用于人造肉的着色,本文将携带豇豆血红蛋白Lb II基因的质粒pET-15b转化进入大肠杆菌BL21中表达,并对表达条件进行优化。通过查找NCBI数据库得到一条全长456 bp的豇豆血红蛋白Lb II的序列,以pET-15b作为表达载体,大肠杆菌BL21-CodonPlus (DE3)-R-IL作为重组工程菌进行表达,成功表达出豇豆血红蛋白Lb II,并使用镍柱层析对蛋白进行初步纯化,同时添加抗坏血酸为抗氧化剂。以IPTG浓度、温度、时间为自变量,Lb II表达量为因变量进行单因素实验。结果表明,在IPTG终浓度为1.0 mmol/L、诱导温度为25 ℃,时间为14 h时,重组豆血红蛋白Lb II的表达量最高,经SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳和可见光光谱分析法鉴定为目的蛋白Lb II。经响应面试验优化后,表达量可以达到7.30 μg/mL。本研究为后续使用工程菌发酵生产豆血红蛋白奠定了基础。Abstract: Cowpea has a red nodule containing large amounts of bean hemoglobin. The protein is a good natural pigment and can be used as color agent in artificial meat. In this study, a 456 bp sequence of cowpea leghemoglobin Ⅱ (Lb II) was obtained from the NCBI database. Using the pET-15b as the expression vector and E. coli BL21-CodonPlus (DE3)-R-IL as the recombinant expression host, the cowpea Lb Ⅱ was successfully expressed, then preliminarily purified this protein by using the nickel column chromatography and added ascorbic acid as the antioxidant simultaneously. IPTG concentration, temperature and time were used as the independent variables and Lb Ⅱ expression as the dependent variable to univariate experiments. The results showed that the highest yield of recombinant Lb Ⅱ protein was obtained at a final IPTG concentration of 1.0 mmol/L and 25 ℃ for 14 h. The recombinant protein was identified as Lb Ⅱ by SDS-PAGE and visible spectrophotometry methods. After the response surface experiment, the titer could reach 7.30 μg/mL in recombinant expression. This study would lay a basis for the subsequent fermentation and production of cowpea hemoglobin in other gene engineering strains.
-
Keywords:
- cowpea /
- hemoglobin /
- response surface method optimization /
- recombinant expression
-
近年来,植物基食品大量涌入市场,市场份额占比不断增加[1]。2019年美国食品药品监督管理局(Food and Drug Administration,FDA)首次批准了大豆血红蛋白作为人造肉的着色剂。研究发现,豆血红蛋白的结构和基因序列与牛珠蛋白相似,以豆血红蛋白作为色素添加剂,在赋予植物肉类似牛肉的颜色质地的同时,还具有较高的营养价值[2]。血红素是铁卟啉化合物,机体中约有70%的铁以血红素的形式存在[3],且血红素作为合成胆红素的必备前体,是制备人工牛黄的重要原料[4]。随着人们对血红蛋白功效的深入研究,血红素和血红蛋白肽作为一种良好的补铁剂已被广泛应用于功能性食品中[5]。
豆血红蛋白(Leghemoglobin,Lb)是一类在与根瘤菌共生的植物结节根部中发现的植物血红蛋白。1931年豆血红蛋白首次被发现存在于豆科植物根瘤中[6],该蛋白质中含有的血红素可以使根瘤呈现粉红色,含量约占根瘤细胞内可溶性蛋白的30%左右[7]。豆血红蛋白由一个血红素和一条肽链组成,经分级提取可以得到两个主要成分和两个次要成分[8]。与哺乳动物血红蛋白相同,豆血红蛋白中的辅基血红素有与氧气可逆结合的功能,通过调节根瘤细胞周围的氧气浓度,维持固氮酶所需的低自由氧浓度,并起到氧缓冲剂的作用。豆血红蛋白还可通过氧化磷酸化提供固氮作用所需能量,同时保护对氧气较敏感的固氮酶,由此保证根瘤固氮作用的正常运行[9],且研究表明根瘤中固氮酶活性与豆血红蛋白的含量呈正相关[10-11]。豇豆(Vigna unguiculata)属双子叶植物纲、蔷薇目,又称为饭豆和长豆[12]。豇豆中含有丰富的维生素、微量元素和易于消化吸收的优质蛋白质、多糖等营养物质,且豆荚、豆粒味道鲜美,在中国被广泛栽培。豇豆根瘤中含有三种豆血红蛋白(Lb Ⅰ、Lb Ⅱ和Lb Ⅲ),其中以Lb Ⅱ为主。
目前已经在包括豆科植物在内的多种植物中分离出了血红蛋白,但由于根瘤中血红蛋白的含量有限,提取成本较高,无法实现理想的产业化生产。微生物发酵成本低、产量大,是高效生产血红蛋白的重要方法之一[13],目前已实现多种血红蛋白的异源表达[14]。随着基因组测序技术的发展,许多植物血红蛋白的基因序列已被阐明,为后期通过基因工程和微生物发酵生产植物血红蛋白提供了基础,并已经实现了大豆[15-18]、黄羽扇豆[19-20]、小麦[21]等植物血红蛋白的异源表达。但是豆血红蛋白在大肠杆菌中的表达量仍然低,且豇豆血红蛋白表达和条件优化相关研究较少。
本研究将Lb Ⅱ的基因序列经过密码子优化,连接到表达载体pET-15b上,并转化进入大肠杆菌中进行诱导表达,以Lb Ⅱ表达量为指标,IPTG浓度、诱导温度和诱导时间为变量优化表达条件,以期提高其表达量并为进一步在其他工程菌中的异源表达提供理论和技术参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
大肠杆菌Escherichia coli BL21-CodonPlus (DE3)-R-IL、大肠杆菌(Escherichia coli)DH5α、质粒pET-15b 本实验室−80 ℃保存;蛋白胨、酵母浸粉、氯化钠、琼脂粉等培养基 北京奥博星生物技术有限公司;预染标准蛋白质分子量 诺维赞生物技术有限公司;蛋白上样缓冲液 碧云天生物技术有限公司;抗坏血酸、抗生素、牛血清蛋白及SDS-PAGE电泳缓冲液、咪唑、磷酸钠缓冲液、氯化钠等药品 上海生物生工生物工程有限公司;His TrapTMHP亲和层析柱 美国GE公司。
TGL-16M型高速冷冻离心机 长沙湘仪离心机设备有限公司;ZWY-240恒温培养振荡器 上海精宏设备有限公司;DYY-6C电泳仪 北京六一仪器厂;SPX型智能生化培养箱 宁波江南仪器厂;JY92-ⅡDN超声细胞粉碎机 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司;721型紫外可见光光度计 上海舜宇恒平科学仪器有限公司;Infinite F200 Pro型酶标仪 瑞士Tecan生物有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 重组质粒pET-15b-Lb Ⅱ构建
豇豆Lb Ⅱ基因序列(GenBank编号:U33205.1)经在线密码子优化(Codon adaptation tool)软件(http://www.jcat.de/)优化后,由南京金斯瑞生物科技公司合成。将合成的基因序列经N末端Nde I和C末端BamH I双酶切后,通过DNA连接酶克隆入pET-15b质粒,得到重组质粒pET-15b-Lb Ⅱ,转化进入大肠杆菌DH5α,经LB固体培养基(含100 mg/L氨苄青霉素)筛选后获得重组菌DH5α-pET-15b-Lb Ⅱ,并经DNA测序验证重组质粒构建正确。
1.2.2 重组质粒在大肠杆菌中的表达
1.2.2.1 大肠杆菌的转化
将构建成功重组质粒pET15b-Lb Ⅱ转化大肠杆菌Escherichia coli BL21-CodonPlus (DE3)-R-IL,使用添加终浓度为100 mg/L氨苄青霉素和100 mg/L氯霉素的LB固体培养基筛选阳性克隆。然后挑取单克隆在终浓度为100 mg/L氨苄青霉素和34 mg/L氯霉素的LB液体培养基(胰蛋白胨10.0 g/L,酵母提取物5.0 g/L,氧化钠10.0 g/L,pH7.0)中在37 ℃、180 r/min条件下培养过夜,获得重组成功的大肠杆菌。
1.2.2.2 表达条件的优化
将培养过夜的含重组pET-15b-Lb Ⅱ的大肠杆菌按1:100接种至新的含上述抗生素的LB培养基(1 L)中。上述培养基继续培养2~3 h,OD600达到约0.8后,分别探究IPTG浓度、诱导温度、诱导时间对Lb Ⅱ表达量的影响。
1.2.3 重组Lb Ⅱ的收集
将诱导过的菌液加入离心管中,4 ℃,8000 r/min,离心15 min,收集菌体沉淀,沉淀可见明显红色。加入破壁缓冲液(含有20 mmol/L磷酸钠缓冲液、50 mmol/L氯化钠、20 mmol/L咪唑),用枪尖将菌体重悬,于涡旋混合器上充分的均匀混合。冰上超声工作5 s,间歇5 s,时间15 min,功率120 W破壁菌体。将裂解溶液于4 ℃、10000 r/min离心15 min,保留上清液,即为重组诱导表达的总蛋白溶液。
1.2.4 重组血红蛋白的纯化
蛋白镍柱亲和层析首先用10 mL的蒸馏水对层析柱冲洗排气,之后加入10 mL Binging buffer(20 mmol/L咪唑,20 mmol/L磷酸钠缓冲液,0.5 mol/L氯化钠,pH7.4)平衡镍柱,然后加入经0.22 μL微孔滤膜过滤后的总蛋白溶液(含有3 mmol/L抗坏血酸)。待蛋白溶液与镍柱充分结合后,在镍柱上可见明显的红色柱层。加入10 mL含有终浓度为3 mmol/L抗坏血酸的Binging buffer冲洗,随后加入10 mL Washing buffer(50 mmol/L咪唑,20 mmol/L磷酸钠缓冲液,0.5 mol/L氯化钠,3 mmol/L抗坏血酸,pH7.4)洗去杂蛋白,再加入6 mL Elution buffer(200 mmol/L咪唑,20 mmol/L磷酸钠缓冲液,0.5 mol/L氯化钠,3 mmol/L抗坏血酸,pH7.4)收集目的蛋白。
1.2.5 Lb Ⅱ的鉴定与表达量的测定
对得到的重组豇豆血红蛋白进行SDS-PAGE电泳鉴定,并在500~600 nm条件下,对纯化后的重组蛋白进行可见光吸收光谱测定。以牛血清蛋白为标准蛋白,利用BSA定量法对纯化后不同诱导表达条件下的重组蛋白表达量测定。以牛血清蛋白浓度为横坐标(X),吸光度为纵坐标(Y),在595nm波长下测得标准曲线为y=0.00622x+0.49624。
1.2.6 表达条件的单因素实验
1.2.6.1 IPTG浓度对Lb Ⅱ表达量的影响
加入终浓度为0.05、0.07、0.10、0.15、0.20、0.30 mmol/L的IPTG(isopropyl-β-D-1-thiogalactoside,异丙基-β-D-硫代半乳糖苷),25 ℃诱导16 h。每个实验重复3次并计算实验结果的平均值。
1.2.6.2 诱导温度对Lb Ⅱ表达量的影响
加入终浓度为0.1 mmol/L的IPTG,于16、20、25、30、37 ℃,诱导16 h。每个实验重复3次并计算实验结果平均值。
1.2.6.3 诱导时间对Lb Ⅱ表达量的影响
加入终浓度为0.1 mmol/L的IPTG,25 ℃培养10、12、14、16 h。每个实验重复3次并计算实验结果的平均值。
1.2.7 响应面优化试验设计
在单因素实验的基础上,以IPTG浓度(mmol/L)、诱导温度(℃)、诱导时间(h)为自变量,Lb Ⅱ表达量为响应值,利用Box-Behnken进行试验设计,通过三因素三水平实验对发酵条件进行优化,确定摇瓶发酵的最佳条件。实验因素与水平编码见表1。
表 1 响应面试验因素与水平编码Table 1. Experimental factors and level coding of the response surface水平 因素 A IPTG浓度(mmol/L) B 诱导温度(℃) C 诱导时间(h) 1 0.07 20 12 0 0.11 25 14 −1 0.15 30 16 1.3 数据处理
每组实验数据均重复3次取平均值,采用Origin 2021软件对单因素实验结果进行分析;采用Design-Expert 11软件进行响应面试验设计及优化。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 重组质粒pET-15b-Lb II的表达
2.1.1 Lb II的重组表达
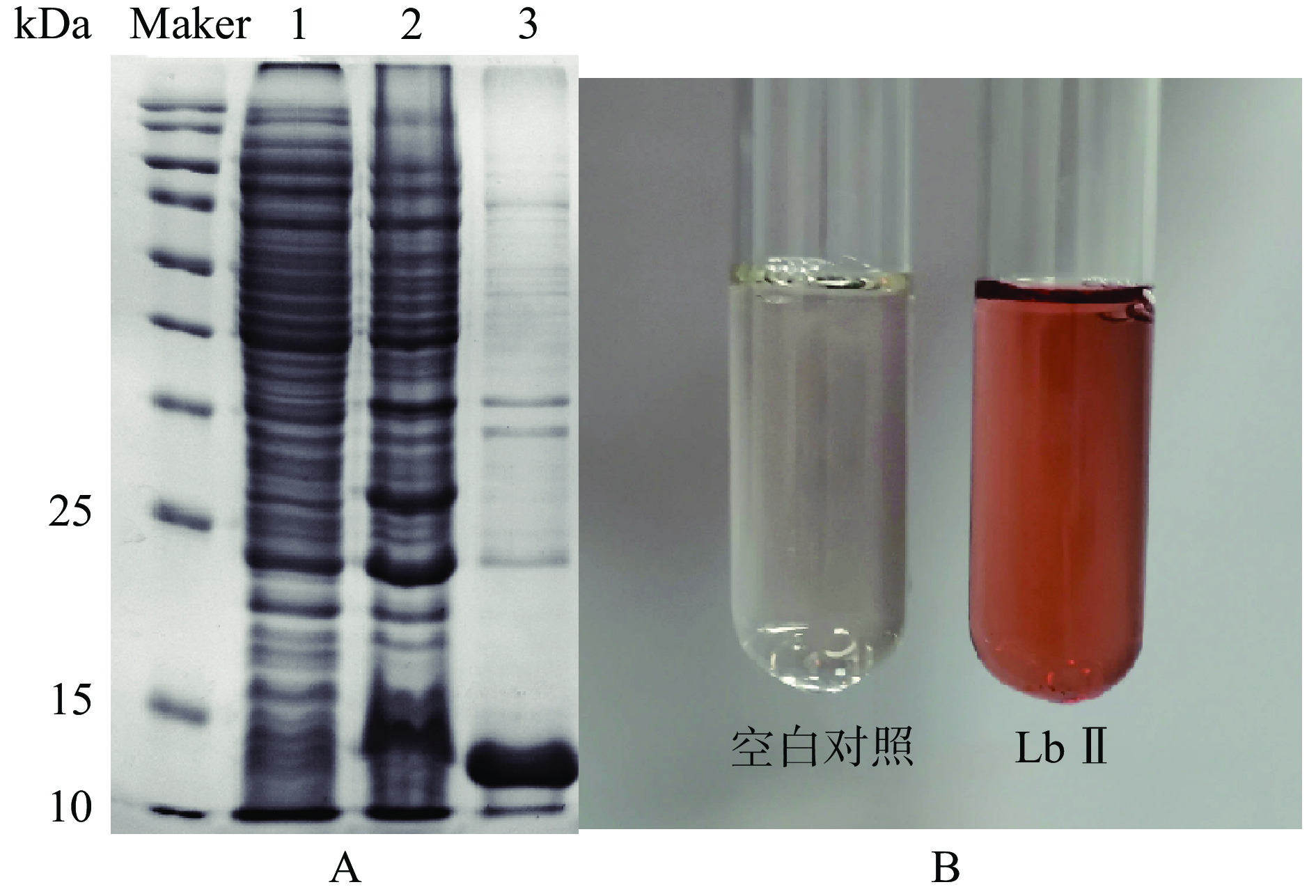
SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳分析结果表明,目的蛋白溶液在约14 kDa出现了明显的目的条带,如图1A所示,与通过其氨基酸序列所预测的蛋白质分子量一致(https://web.expasy.org/compute_pi/)。重组蛋白溶液与对照即未转化重组质粒的大肠杆菌表达的蛋白溶液相比,呈现明显的红色,如图1B所示,表明豆血红蛋白在大肠杆菌中成功表达。
2.1.2 重组Lb Ⅱ的纯化
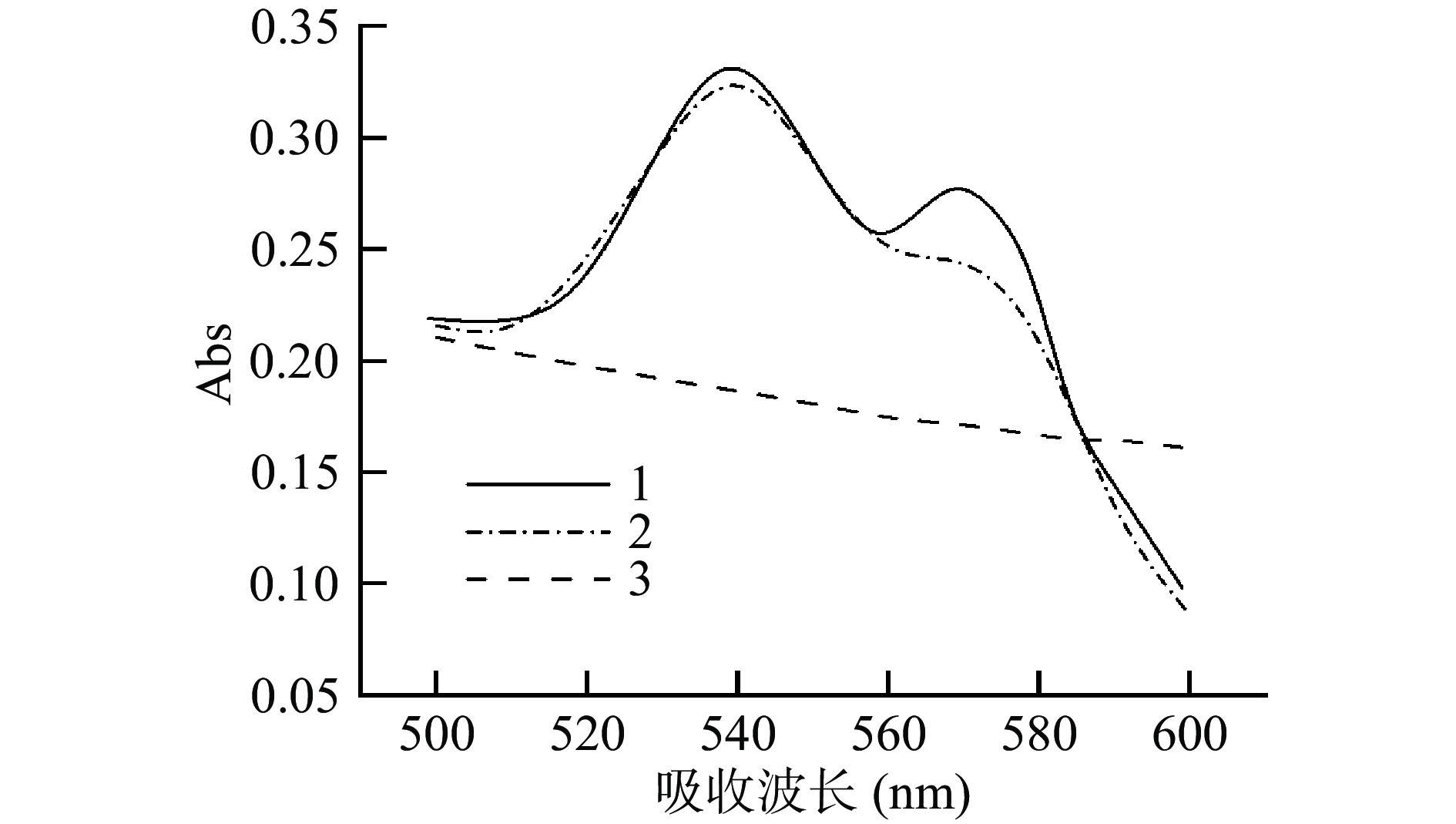
前期研究证明,由于血红蛋白中包含铁卟啉结构,可以与氧结合形成氧合血红蛋白,所以在540和570 nm左右有特征峰[22],因此通过可见光吸收光谱进一步确认Lb Ⅱ的成功表达。豆血红蛋白中的亚铁离子作为还原剂易被氧化为高铁离子,从而失去活性,且镍柱中含有大量金属离子,还原性较强,可能会对二价铁离子产生破坏。抗坏血酸是一种抗氧化剂,有还原高铁血红蛋白的作用[23-26],未加入抗坏血酸时(图2,曲线2),在570 nm处出现了肩峰,表明在镍柱层析的过程中可能破坏了二价铁或铁卟啉的结构,使二价铁被改变价态[27],失去了可逆结合氧气的活性。加入抗坏血酸进行纯化后,在540和570 nm处出现明显的吸收峰(图2,曲线1),而未转化重组质粒的蛋白溶液无吸收峰(曲线3),表明转化大肠杆菌后成功表达出重组Lb Ⅱ蛋白。
2.2 重组Lb Ⅱ表达条件的优化
2.2.1 IPTG浓度对重组Lb Ⅱ在大肠杆菌BL21中表达的影响
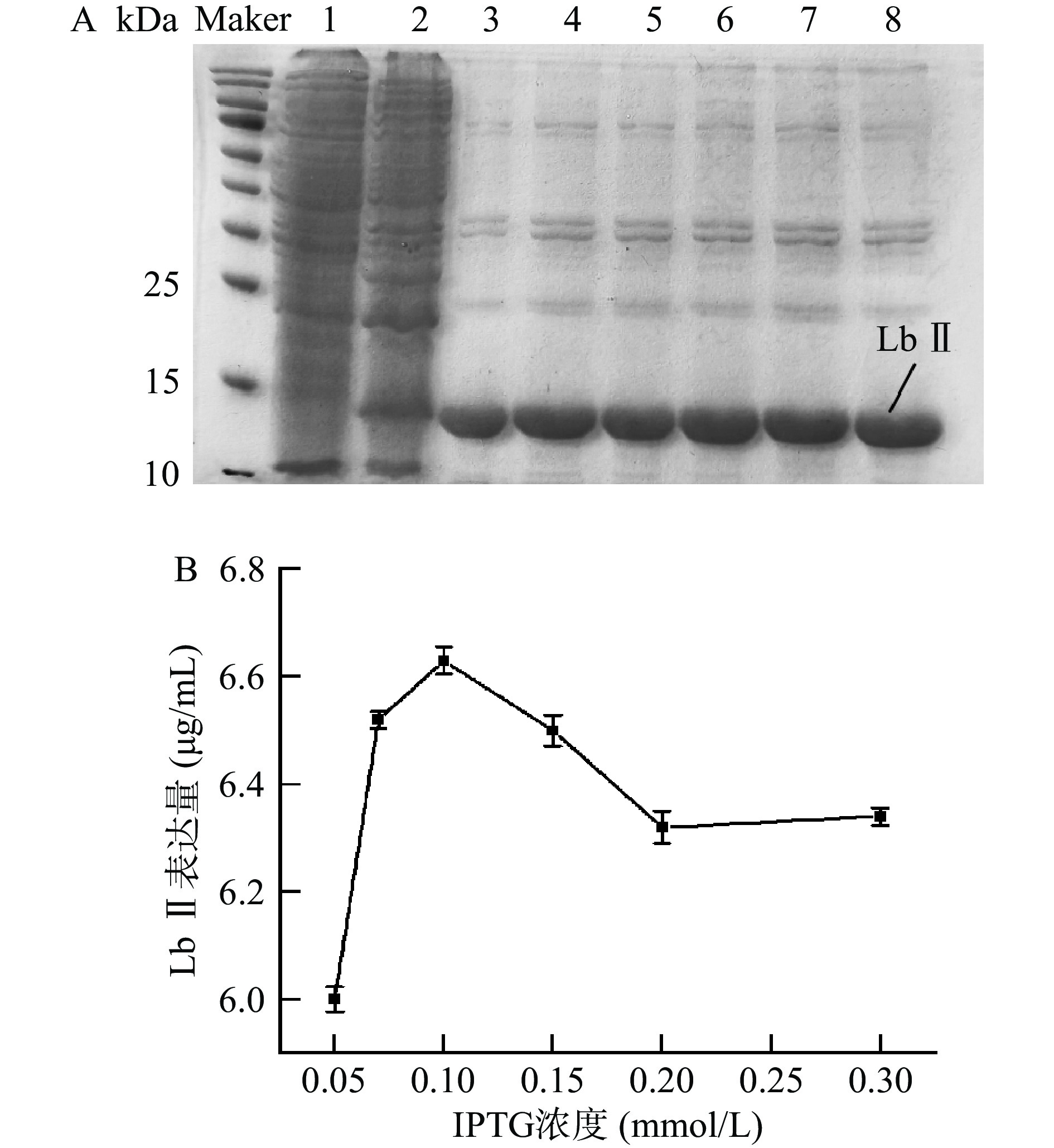
如图3所示,当诱导剂浓度在0.05~0.1 mmol/L范围内时,Lb Ⅱ的表达量逐渐上升,在诱导剂浓度为0.1 mmol/L时达到最大,之后随着诱导剂浓度的上升表达量开始下降。其原因可能是IPTG具有一定的细胞毒性,浓度越高,对细胞活性越不利[28-30]。采用较低浓度的IPTG可以适当地降低表达速度,避免因表达速度过快或表达量过多而产生包涵体。
![]() 图 3 不同IPTG浓度的重组蛋白Lb Ⅱ的电泳图(A)和重组蛋白表达量变化曲线(B)注:1:不携带重组质粒的BL21总蛋白;2:IPTG浓度为0.05 mmol/L时重组菌总蛋白;3~8:IPTG浓度分别为0.05、0.07、0.10、0.15、0.20、0.30 mmol/L的纯化蛋白。Figure 3. Electrophoresis diagram (A) and changing curves of the recombinant protein expression (B) of the recombinant protein Lb Ⅱ at different IPTG concentrations
图 3 不同IPTG浓度的重组蛋白Lb Ⅱ的电泳图(A)和重组蛋白表达量变化曲线(B)注:1:不携带重组质粒的BL21总蛋白;2:IPTG浓度为0.05 mmol/L时重组菌总蛋白;3~8:IPTG浓度分别为0.05、0.07、0.10、0.15、0.20、0.30 mmol/L的纯化蛋白。Figure 3. Electrophoresis diagram (A) and changing curves of the recombinant protein expression (B) of the recombinant protein Lb Ⅱ at different IPTG concentrations2.2.2 诱导温度对重组Lb Ⅱ在大肠杆菌BL21中表达的影响
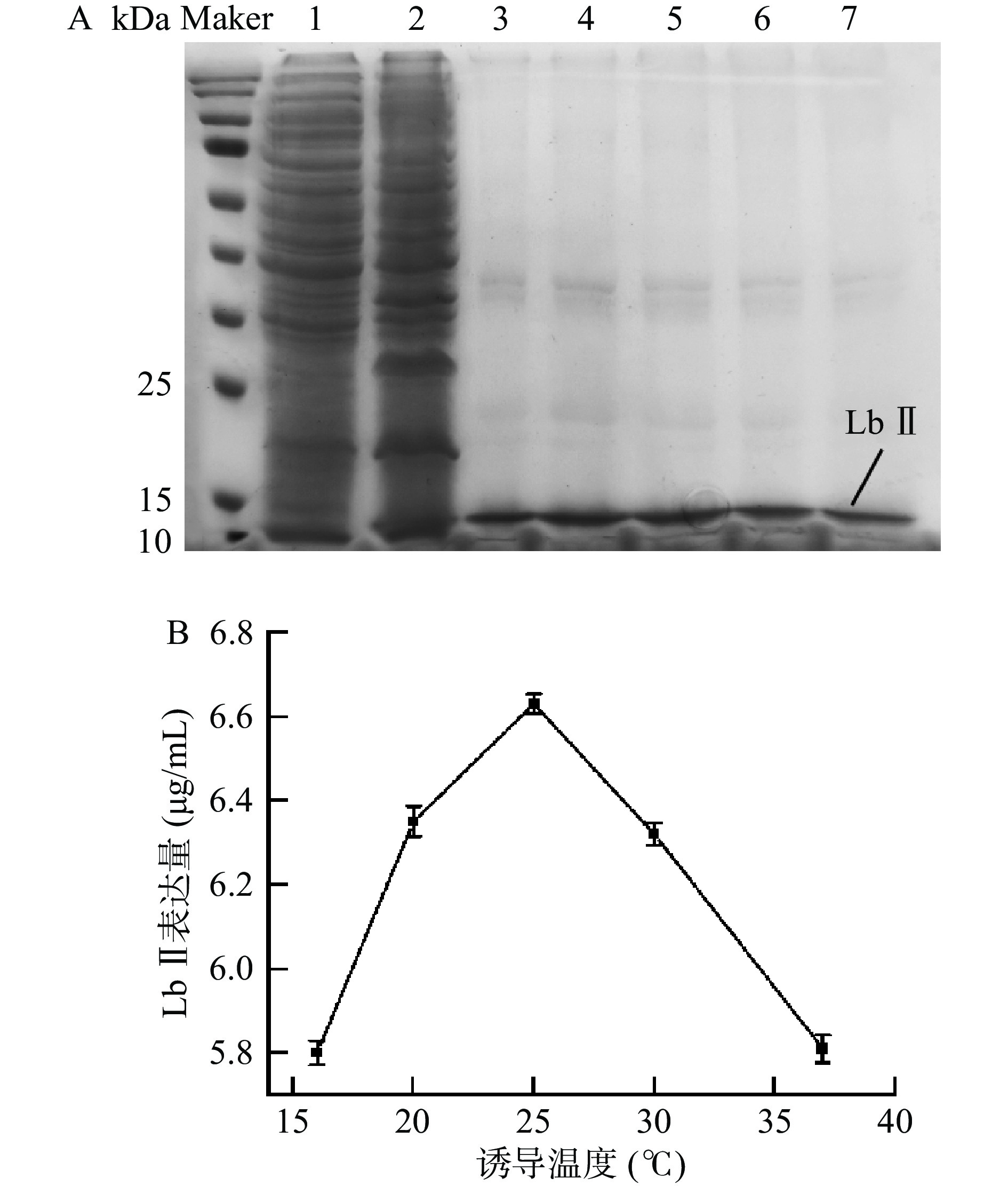
如图4所示,当温度不断上升至25 ℃时,蛋白表达量也在不断增加;当温度大于25 ℃时,蛋白表达量随着温度的升高开始下降。这可能是因为温度影响着细胞活性和可溶性蛋白的表达。外源基因的表达产物可能因过量表达,无法及时正确折叠而产生包涵体,低温诱导可以控制表达速度,增加可溶性蛋白的表达量,同时还可以减少较高温度可能导致的重组蛋白降解[31-32]。
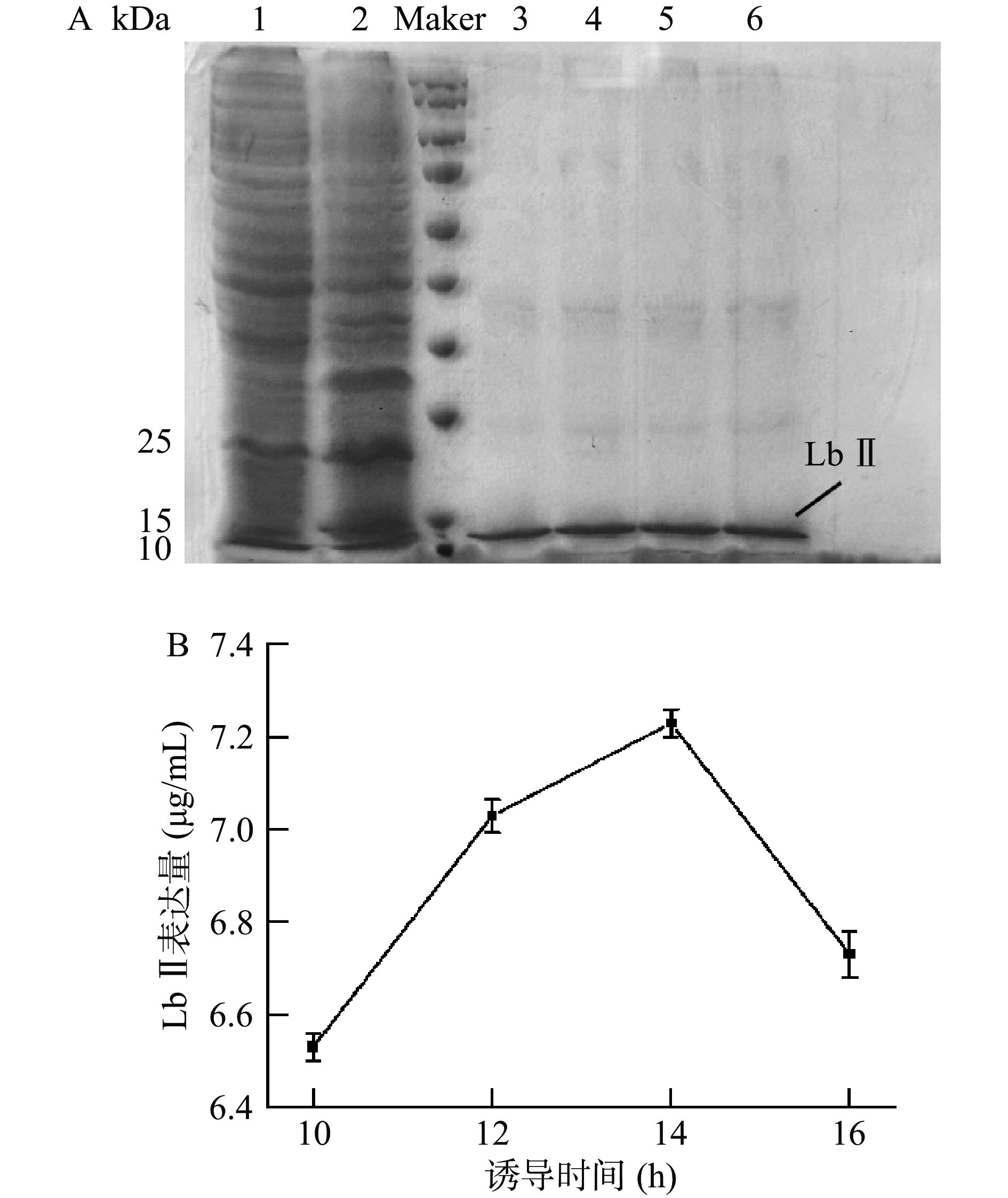
2.2.3 诱导时间对重组Lb Ⅱ在大肠杆菌BL21中表达的影响
结果如图5所示。研究显示随着诱导时间的延长,表达量不断增加,在诱导时间达到14 h后,表达量最多;随后随着时间的延长表达量不断减少。可能是由于随着表达时间增长,目的蛋白在被表达的同时被大量降解,同时诱导时间过长也会对细胞活性产生消极影响,出现菌体老化从而使表达效率降低。
2.3 响应面试验结果
2.3.1 响应面试验设计及结果
在单因素实验的基础上可以确定最佳的摇瓶发酵条件为:IPTG浓度为0.1 mmol/L,诱导温度为25 ℃,诱导时间为14 h,在此基础上对表达条件进行响应面试验优化[33]。该研究以IPTG浓度(A)、诱导温度(B)、诱导时间(C)为自变量,Lb Ⅱ表达量为响应值,利用Box-Behnken进行试验设计,实验方案与结果如表2所示。
表 2 响应面试验设计及结果Table 2. Design and results of the response surface experiment实验号 因素 Y: Lb Ⅱ表达量(μg/mL) A B C 1 0 1 −1 5.70 2 0 0 0 7.36 3 1 0 1 6.50 4 1 0 −1 6.43 5 0 0 0 7.20 6 −1 0 1 6.67 7 −1 −1 −1 5.83 8 1 −1 −1 5.86 9 0 0 0 7.10 10 −1 1 −1 5.80 11 1 1 0 5.90 12 0 0 0 7.23 13 −1 0 −1 5.63 14 0 1 1 6.32 15 0 −1 1 6.35 16 0 −1 −1 5.72 17 0 0 0 7.26 2.3.2 回归模型的建立与方差分析
利用Design-Expert 11软件对表2结果进行分析,得到了二次多项回归方程。
Y=−42.89+118.08A+1.66B+3.10C+0.09AB−3.03AC−0.0002BC−342.97A2−0.03B2−0.09C2
由表3可知,模型P<0.0001,表明该模型差异极显著;失拟项P=0.3951>0.05,表明该模型失拟项极不显著,说明该模型拟合程度好;模型决定系数R2=0.9890,校正决定系数R2Adj=0.9749,说明实验结果与模型预测结果一致性好,误差小。模型可用于豇豆血红蛋白Lb Ⅱ表达量的分析。方程中的一次项A(P<0.05)显著,一次项C(P<0.01)极显著,说明IPTG浓度对Lb Ⅱ表达量影响较为明显,诱导时间对Lb Ⅱ表达量的影响极明显。根据F值大小可以判断本实验采用的三个因素对Lb Ⅱ表达量的影响的主次顺序为:B(诱导温度)<A(IPTG浓度)<C(诱导时间);二次项A2、B2和C2极显著(P<0.01)。
表 3 回归模型方差分析Table 3. Analysis of variance of the regression model方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F P 模型 6.27 9 0.6972 69.97 <0.0001** A 0.0722 1 0.0722 7.25 0.0310* B 0.0002 1 0.0002 0.0201 0.8913 C 0.6962 1 0.6962 69.87 <0.0001** AB 0.0012 1 0.0012 0.1229 0.7362 AC 0.2352 1 0.2352 0.2352 0.0018** BC 0 1 0 0.0025 0.9615 A2 1.27 1 1.27 127.24 <0.0001** B2 2.93 1 2.93 293.74 <0.0001** C2 0.5882 1 0.5882 59.03 0.0001* 残差 0.0697 7 0.0100 失拟项 0.0341 3 0.0114 1.28 0.3951 纯误差 0.0356 4 0.0089 总和 6.34 16 注:R2=0.9890,R2Adj=0.9749。*表示差异显著(P<0.05),**表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。 2.3.3 各因素相互作用结果与分析
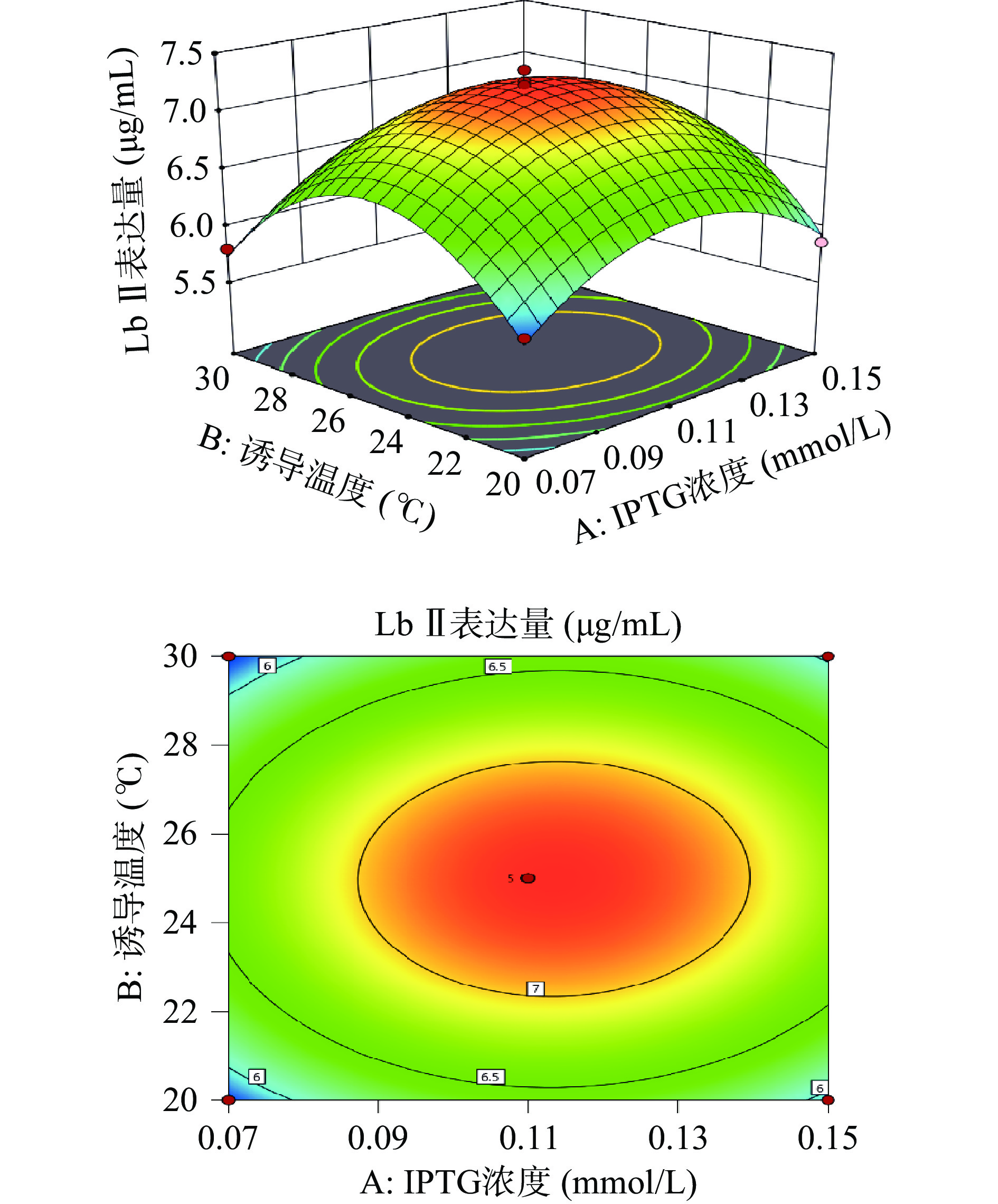
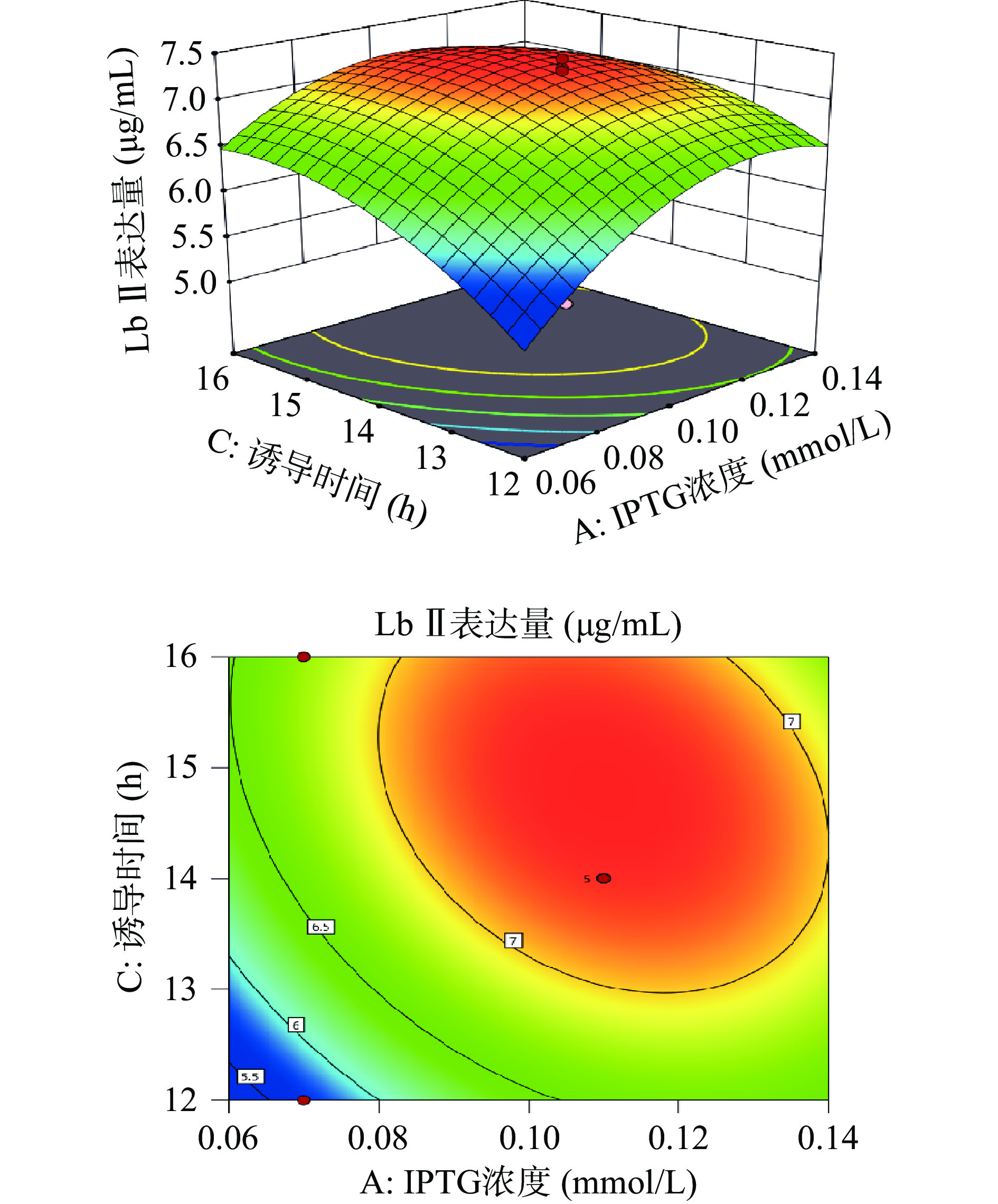
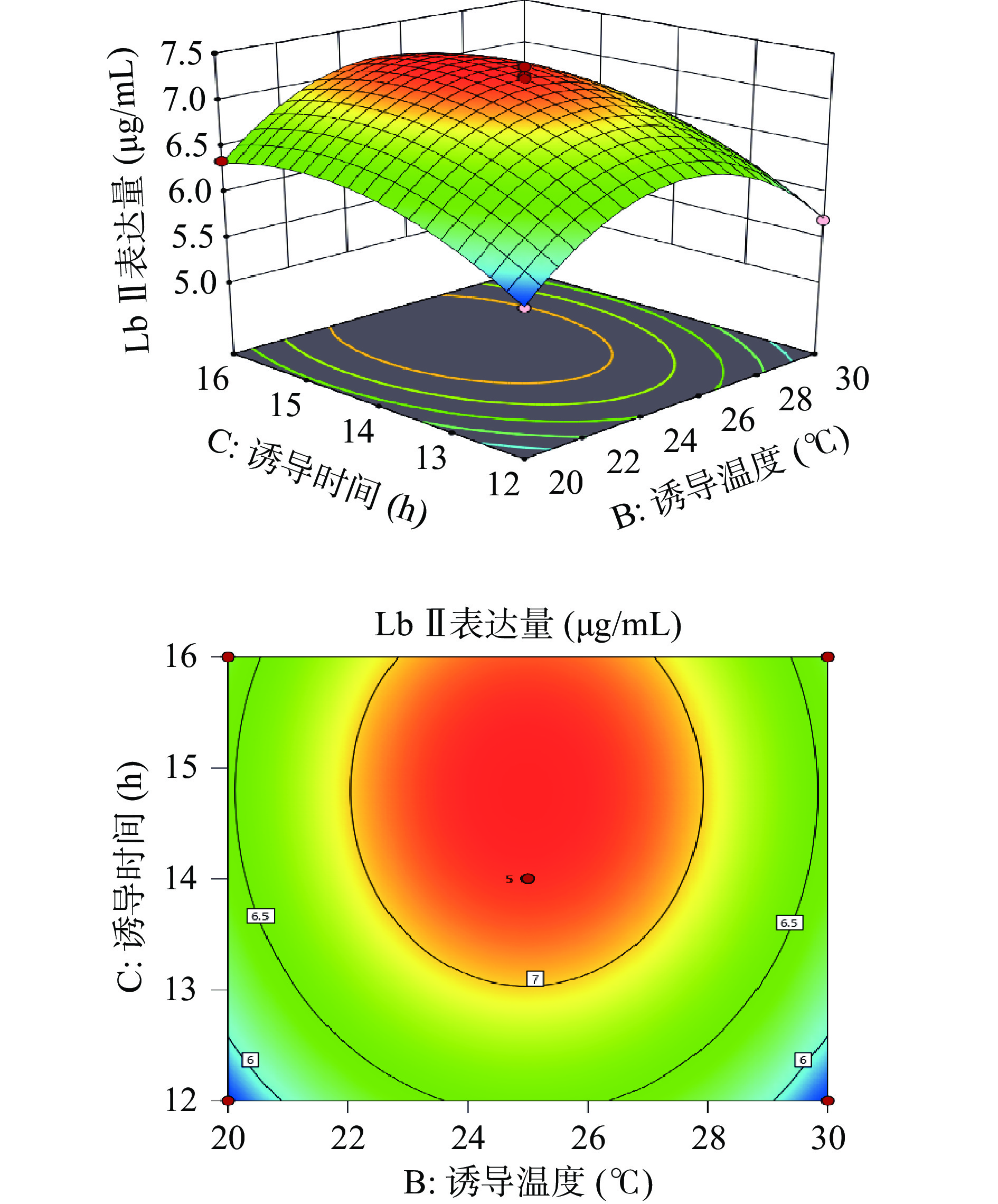
利用Design-Expert 11绘制出各因素之间交互作用的三维响应面图和等高线图。响应面的陡峭程度和等高线的形状可以反映出两两因素交互作用是否显著和因素对实验结果的影响程度。响应面越陡峭表明因素对结果影响越大,交互作用更显著。等高线呈现椭圆形表明两个因素之间交互作用显著,呈现圆形则表示不显著。
由图6所示,Lb Ⅱ表达量随着诱导温度和IPTG浓度的上升而呈先增加后下降的趋势,等高线呈圆形,表示诱导温度和IPTG浓度的相互作用不显著。由图7可知,Lb Ⅱ表达量随着IPTG浓度和诱导时间的增大呈现出先增大后减小的趋势。响应面曲面坡度相对陡峭,说明IPTG浓度和诱导时间交互作用对Lb Ⅱ表达量的影响较大。等高线呈椭圆形,说明IPTG浓度和诱导时间交互作用较显著。由图8可知,当诱导时间和诱导温度逐渐增大时Lb Ⅱ表达量呈现出先增大后减小的趋势,且等高线呈圆形,表示诱导温度和诱导时间之间的交互作用不显著。
2.3.4 验证试验
根据二次多项回归方程可以预测得出最佳的表达条件为:IPTG浓度为0.110 mmol/L;诱导温度为24.983 ℃;诱导时间为14.791 h。在此条件下Lb Ⅱ的表达量可以达到7.29 μg/mL。根据实际情况,将条件设定为IPTG浓度:0.11 mmol/L;诱导温度:25 ℃;诱导时间:15 h。在此条件下进行试验,表达量达到7.30 ±0.03μg/mL。实验结果与预测值较接近,拟合性较好,验证了该模型的有效性。
3. 结论
豆血红蛋白是一类在豆科植物根瘤中广泛存在的蛋白质,对维持根瘤菌进行正常的固氮活动有着十分重要的作用。天然的豆血红蛋白含量少且不易提取,因此可通过基因工程方法进行重组高效表达,为其作为植物肉的着色剂等应用领域提供来源。迄今,尚未有豇豆来源血红蛋白在基因工程菌中重组表达、条件优化及其表达量的报道。本实验成功克隆并构建了含有豇豆血红蛋白Lb Ⅱ基因的pET-15b重组质粒,并在大肠杆菌BL21-CodonPlus (DE3)-R-IL中经过单因素实验,对诱导温度、诱导时间、IPTG浓度进行优化后得到高效表达。结果表明,最优表达条件为在OD600达到0.8时,加入终浓度为0.1 mmol/L的IPTG,25 ℃诱导14 h。
在设计重组质粒时,在经过密码子优化后的目的序列前端加入His标签,在后期处理粗蛋白提取物时,可使用操作较简单的镍柱层析进行纯化。由于血红蛋白中含有血红素的特点,易被镍柱中的金属离子氧化从而失去活性,故选择在纯化时加入终浓度为3 mmol/L的抗坏血酸作为抗氧化剂,镍柱层析得到Lb Ⅱ,并通过SDS-PAGE凝胶电泳和紫外可见光分析法对产物进行定性,确定在大肠杆菌中成功表达出了豇豆血红蛋白,最后使用BSA定量法对纯化后的目的蛋白进行定量,可知在最佳诱导条件(IPTG浓度0.11 mmol/L、诱导温度25 ℃、诱导时间15 h)下,表达量为7.23 μg/mL。对单因素实验结果进行响应面优化,根据优化后条件进行诱导,表达量达到7.30 μg/mL。本研究为今后使用酵母菌、乳酸菌等其他工程菌表达豆科血红蛋白提供了理论参考。
-
图 3 不同IPTG浓度的重组蛋白Lb Ⅱ的电泳图(A)和重组蛋白表达量变化曲线(B)
注:1:不携带重组质粒的BL21总蛋白;2:IPTG浓度为0.05 mmol/L时重组菌总蛋白;3~8:IPTG浓度分别为0.05、0.07、0.10、0.15、0.20、0.30 mmol/L的纯化蛋白。
Figure 3. Electrophoresis diagram (A) and changing curves of the recombinant protein expression (B) of the recombinant protein Lb Ⅱ at different IPTG concentrations
表 1 响应面试验因素与水平编码
Table 1 Experimental factors and level coding of the response surface
水平 因素 A IPTG浓度(mmol/L) B 诱导温度(℃) C 诱导时间(h) 1 0.07 20 12 0 0.11 25 14 −1 0.15 30 16 表 2 响应面试验设计及结果
Table 2 Design and results of the response surface experiment
实验号 因素 Y: Lb Ⅱ表达量(μg/mL) A B C 1 0 1 −1 5.70 2 0 0 0 7.36 3 1 0 1 6.50 4 1 0 −1 6.43 5 0 0 0 7.20 6 −1 0 1 6.67 7 −1 −1 −1 5.83 8 1 −1 −1 5.86 9 0 0 0 7.10 10 −1 1 −1 5.80 11 1 1 0 5.90 12 0 0 0 7.23 13 −1 0 −1 5.63 14 0 1 1 6.32 15 0 −1 1 6.35 16 0 −1 −1 5.72 17 0 0 0 7.26 表 3 回归模型方差分析
Table 3 Analysis of variance of the regression model
方差来源 平方和 自由度 均方 F P 模型 6.27 9 0.6972 69.97 <0.0001** A 0.0722 1 0.0722 7.25 0.0310* B 0.0002 1 0.0002 0.0201 0.8913 C 0.6962 1 0.6962 69.87 <0.0001** AB 0.0012 1 0.0012 0.1229 0.7362 AC 0.2352 1 0.2352 0.2352 0.0018** BC 0 1 0 0.0025 0.9615 A2 1.27 1 1.27 127.24 <0.0001** B2 2.93 1 2.93 293.74 <0.0001** C2 0.5882 1 0.5882 59.03 0.0001* 残差 0.0697 7 0.0100 失拟项 0.0341 3 0.0114 1.28 0.3951 纯误差 0.0356 4 0.0089 总和 6.34 16 注:R2=0.9890,R2Adj=0.9749。*表示差异显著(P<0.05),**表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。 -
[1] 曾艳, 郝学财, 董婷, 等. 植物蛋白肉的原料开发、加工工艺与质构营养特性研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(3):338−345,350. [ZENG Y, HAO X C, DONG T, et al. Research progress on raw material development, processing technology and nutritional properties of plant based meat[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(3):338−345,350. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020030365 [2] KATELYN S, KARINA N, SARA A, et al. The molecular magic of “meatless” meats: Structural and sequence similarities between soy leghemoglobin and bovine globins[J]. The FASEB Journal,2020,34(S1):1.
[3] 卫乐红, 时亚文, 陈石良, 等. 血红素铁的制备及应用研究进展[J]. 食品与药品,2013(5):357−359,360. [WEI L H, SHI Y W, CHEN S L, et al. Progress on preparation and application of heme iron[J]. Food and Drug,2013(5):357−359,360. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-979X.2013.05.021 [4] 张旭, 王卫, 汪正熙, 等. 畜禽血食用产品及1其研究进展[J]. 中国调味品,2020,45(4):194−196. [ZHANG X, WANG W, WANG Z X, et al. Research progress of livestock and poultry blood edible products[J]. China Condiment,2020,45(4):194−196. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-9973.2020.04.041 [5] 武汉医学院. 营养与食品卫生学[M]. 北京: 人民卫生出版社, 1982, 29 Wuhan University School of Medcine. Nutrition and food hygiene[M]. Beijing: People's Health Publishing House, 1982, 29.
[6] 郭荫杰, 冯献忠, 杨素欣. 植物血红蛋白基因功能研究进展[J]. 土壤与作物,2018,7(2):160−167. [GUO Y J, FENG X Z, YANG S X. Research progress on the function of plant hemoglobin gene[J]. Soils and Crops,2018,7(2):160−167. doi: 10.11689/j.issn.2095-2961.2018.02.008 [7] ALAIN P, JEAN R. Separation of soybean leghemoglobin components by isoelectric focusing in immobilized pH gradients[J]. Electrophoresis,1987,8(4):212−214. doi: 10.1002/elps.1150080408
[8] PÄIVI L, NILS E. The primary structure of kidney bean leghemoglobin[J]. FEBS Letters,1974,43(2):239−240.
[9] 耿挺. 上海科学家发现豆科植物生物固氮新调控机制[N]. 上海科技报, 2021-11-03(006) GENG T. Shanghai scientists discover a new regulatory mechanism of biological nitrogen fixation in legumes[N]. Shanghai Science and Technology News, 2021-11-03(006).
[10] 柯丹霞, 彭昆鹏. 利用酵母双杂交系统筛选大豆结瘤因子受体NFR1α的互作蛋白[J]. 作物学报,2020,46(1):31−39. [KE D X, PENG K P. The interaction protein of soybean nodulation factor receptor NFR1α was screened by yeast two-hybrid system[J]. Acta Agronomica Sinica,2020,46(1):31−39. [11] 王田, 王志杰, 张云鹤, 等. 大豆根瘤豆血红蛋白含量与产量关系研究[J]. 大豆科学,2020,39(1):45−51. [WANG T, WANG Z J, ZHANG Y H, et al. Study on relationship between soybean leghemoglobin content and yield[J]. Soybean Science,2020,39(1):45−51. [12] 中国植物志编委. 中国植物志[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 1995 Flora of China Editorial Committee. Flora reipublicae popularis sinicae[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 1995.
[13] 周景文, 张国强, 赵鑫锐, 等. 未来食品的发展: 植物蛋白肉与细胞培养肉[J]. 食品与生物技术学报,2020,39(10):1−8. [ZHOU J W, ZHANG G Q, ZHAO X R, et al. Future of food: Plant-based and cell-cultured meat[J]. Journal of Food Science and Biotechnology,2020,39(10):1−8. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-1689.2020.10.001 [14] ZHAO X, ZHOU J, DU G, et al. Recent advances in the microbial synthesis of hemoglobin[J]. Trends in Biotechnology,2021,39(3):286−297.
[15] STOUGAARD J, PETERSEN T E, MARCKER KA. Expression of a complete soybean leghemoglobin gene in root nodules of transgenic Lotus corniculatus[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,1987,84(16):5754−5757.
[16] JONES DK, ROSELL FI, LLOYD E, et al. Bacterial expression and spectroscopic characterization of soybean leghaemoglobin A[J]. The Biochemical Journal,1998,330(Pt.2):983−988.
[17] ZHANG B, ZHAO X, WANG Z, et al. Efficient secretory expression and purification of food-grade porcine myoglobin in Komagataella phaffii[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2021,69(35):10235−10245.
[18] 陈林杰, 薛常鲁, 苏悦, 等. 豆血红蛋白在毕赤酵母中的表达条件优化[J]. 微生物学通报,2022,49(6):2050−2061. [CHEN L J, XUE C L, SU Y, et al. Optimization of leghemoglobin expression conditions in Pichia pastoris[J]. Microbiology China,2022,49(6):2050−2061. [19] SIKORSKI M M, STROZYCKI P M, VORGIAS C E, et al. Cloning and expression of plant leghemoglobin cDNA of Lupinus luteus in Escherichia coli and purification of the recombinant protein[J]. Plant Science,1995,108(1):109−117. doi: 10.1016/0168-9452(95)04125-E
[20] STRÓŻYCKI P M, KARŁOWSKI W M, DESSAUX Y, et al. Lupine leghemoglobin I : Expression in transgenic lotus and tobacco tissues[J]. Molecular and General Genetics MGG,2000,263(2):173−182. doi: 10.1007/s004380051158
[21] DUFF S M, WITTENBERG J B, HILL R D. Expression, purification, and properties of recombinant barley (Hordeum sp.) hemoglobin. Optical spectra and reactions with gaseous ligands[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry,1997,272(27):16746−16752. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.27.16746
[22] 丘家杵, 阮萍, 雍军光, 等. 健康人血红蛋白紫外可见吸收光谱和FTIR光谱[J]. 光谱学与光谱分析,2020,40(5):1425−1430. [QIU J C, LUAN P, YONG J G, et al. UV-Visible absorption spectra and FTIR of hemoglobin of healthy people and it spectroscopic analysis[J]. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis,2020,40(5):1425−1430. [23] GIULIVI C, CADENAS E. The reaction of ascorbic acid with different heme iron redox states of myoglobin. Antioxidant and prooxidant aspects[J]. FEBS Letters,1993,332(3):287−290. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(93)80651-A
[24] TOMODA A, TAKESHITA M, YONEYAMA Y. Characterization of intermediate hemoglobin produced during methemoglobin reduction by ascorbic acid[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry,1978,253(20):7415−7419.
[25] GEBICKA L, BANASIAK E. Flavonoids as reductants of ferryl hemoglobin[J]. Acta Biochimica Polonica,2009,56(3):509−513.
[26] 苏秀兰, 王翔. 脐血血红蛋白体外氧化还原研究[J]. 四川理工学院学报(自然科学版),2016,29(2):9−13. [SU X L, WANG X. The redox reaction of placenta hemoglobin in vitro[J]. Journal of University of Science & Engineering (Natural Science Edition),2016,29(2):9−13. [27] MENG F, ALAYASH A I. Determination of extinction coefficients of human hemoglobin in various redox states[J]. Analytical Biochemistry,2017,521:11−19. doi: 10.1016/j.ab.2017.01.002
[28] 张叶明, 付正豪, 陈云雨. 重组泛素样特异性蛋白酶1在大肠杆菌中的表达条件优化与分离纯化[J]. 锦州医科大学学报,2020,41(6):1−4. [ZHANG Y M, FU Z H, CHEN Y Y. Optimization of expression conditions and isolation and purification of recombinant ubiquitin-like specific protease 1 in Escherichia coli[J]. Journal of Liaoning Medical University,2020,41(6):1−4. [29] 王娟, 王建勇, 苏平, 等. 藻胆蛋白表达条件优化的研究[J]. 湖北师范学院学报(自然科学版),2012,32(4):50−55. [WANG J, WANG J Y, SU P, et al. Research on the optimization expression conditions of recombinant phycobiliprotein[J]. Journal of Hubei Normal University (Natural Science),2012,32(4):50−55. [30] 左泽红, 魏韬, 郭丽琼, 等. 平菇高丝氨酸乙酰基转移酶基因的克隆及异源表达优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(13):64−70,77. [ZUO Z H, WEI T, GUO L Q, et al. Cloning and heterologous expression optimization of homoserine acetyltransferase gene from Pleurotus ostreatus[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(13):64−70,77. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2019.13.011 [31] 唐玮, 杨敏, 于源, 等. 乳糖诱导大肠杆菌产褐藻胶裂解酶的条件优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(15):134−139. [TANG W, YANG M, YU Y, et al. Expression and optimization of alginate lyase in recombinant Escherichia coli induced by lactose[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(15):134−139. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2017.15.026 [32] 叶姣, 陈长华, 夏杰, 等. 温度对重组大肠杆菌生长及外源蛋白表达的影响[J]. 华东理工大学学报,2002(4):364−367. [YE J, CHEN C H, XIA J, et al. Effect of temperature on the growth of recombinant E. coli and on the expression of recombinant protein[J]. Journal of East China University of Science and Technology,2002(4):364−367. [33] 田艳杰, 宋兆祥, 马振武, 等. 木聚糖酶xynZF-318在枯草芽孢杆菌WB600中的表达及发酵条件优化[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(22):120−125,133. [TIAN Y J, SONG Z X, MA Z W, et al. Expression and fermentation condition optimization of xylanase xynZF-318 in Bacillus subtilis WB600[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(22):120−125,133. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020010071 -
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 汪吉鹏,朱滕滕,刘璐,马铖,魏晓博,刘慧燕,方海田. λ-Red重组技术结合复合诱变提高大肠杆菌L-异亮氨酸合成能力. 食品工业科技. 2025(02): 167-174 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 戴一佳,赵亮. 益生菌对发酵乳品质影响的研究进展. 食品工业科技. 2024(08): 388-396 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



