Effects of Different Drying Methods on Lipid Oxidation and Volatile Flavor Components of Spanish Mackerel (Scomberomorus niphonius)
-
摘要: 为探究不同干制方式对水产品脂肪氧化与挥发性风味物质组成的影响,以蓝点马鲛(Scomberomorus niphonius)为原料,采用热风干制、冷风干制和传统自然晾晒法制得对应实验组样品。测定了原料和不同实验组样品的水分质量分数、pH、脂肪含量、酸价(Acid value,AV)、过氧化值(Peroxide value,POV)、丙二醛(Malondialdehyde,MDA)、脂肪酸组成和挥发性风味物质等指标。结果显示:三种干制方式制得的样品的水分质量分数均在30%左右;pH始终保持在6以上;冷风干制组的AV、POV和MDA含量整体较低(P<0.05);热风干制组中脂肪含量下降最多,AV含量最高,POV和MDA含量显著低于自然晾晒组(P<0.05);自然晾晒组中AV含量最低,POV和MDA含量显著高于其他组别(P<0.05)。干制样品中不饱和脂肪酸尤其是ω-3多不饱和脂肪酸含量下降显著(P<0.05),其中自然晾晒组下降最为明显。原料和干制样品中共检出了8大类120种挥发性风味成分,主要由醛类、醇类和酯类构成。经主成分分析3个主成分对风味的累计贡献率达99.9%,其中自然晾晒组的总体评分最高。结果表明干制方式对蓝点马鲛的脂肪氧化程度和风味均有较大的影响,其中自然晾晒组风味更佳。本研究为传统的水产品加工行业的技术转型提供有效的数据支撑和发展方向。Abstract: To explore the effects of different drying methods on lipid oxidation and volatile flavor components of fishery products, the corresponding experimental groups were prepared by hot-air drying, cold-air drying and traditional natural drying using fresh Spanish mackerel (Scomberomorus niphonius) as raw material. The moisture content, pH value, lipid content, acid value (AV), peroxide value (POV), malondialdehyde (MDA), fatty acid composition and volatile flavor components of raw materials and different dried samples were measured. The results showed that the moisture content of dried samples prepared by three drying methods was about 30% with the pH value above 6. The AV, POV and the contents of MDA in the cold-air drying group were lower than the other groups (P<0.05). In the hot-air drying group, the lipid content decreased the most, and the AV was the highest, the POV and the content of MDA were significantly lower than those of natural drying group (P<0.05). The AV of the natural drying group represented the lowest, the POV and the content of MDA were significantly higher than those of other groups (P<0.05). The content of unsaturated fatty acid, especially the ω-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids decreased significantly (P<0.05), especially in the natural drying group. A total of 120 volatile flavor substances in 8 categories were detected from raw materials and drying samples, mainly composed of aldehydes, alcohols and esters. Principal component analysis revealed that the cumulative contribution rate of the 3 principal components to flavor was 99.9%, and the score of the natural drying group was the highest. The results indicated that the different drying methods had a great influence on the degree of lipid oxidation and flavor of Spanish mackerel, and the natural drying group had the best flavor. This research provides effective data support and development direction for the technological transformation of the traditional aquatic product processing industry.
-
蓝点马鲛俗称鲅鱼,属鲈形目(Perciformes)鲭科(Scombridae)马鲛属(Scomberomorus)[1],是一种暖温性大型中上层鱼类,广泛分布于太平洋西北部和中国渤海、黄海、东海等海域[2]。由于新鲜鲅鱼容易腐败变质[3],因此人们通常将其加盐腌制后进行晾晒制成咸干鲅鱼,脂肪经日晒后降解与氧化会产生挥发性风味物质,形成咸干鲅鱼独特的风味。这种传统的加工方式相对简单,因风味独特且能长期保存,深受消费者欢迎。但传统的日晒干制法由于没有标准化加工方式,可能存在生产流程不规范不完善等问题;且鲅鱼的不饱和脂肪酸(Unsaturated fatty acid,UFA)含量较高[4],日晒过程中UFA易发生氧化分解,对品质可能造成一定的影响。因此,需要开发针对鲅鱼的热风干燥和冷风干燥等现代干制技术。随着现代加工技术发展,尤其是热风干燥和冷风干燥等干制技术的应用,能否在保证风味的同时又能缓解脂质过氧化成为咸干鲅鱼的研究热点。
目前,国内外已有研究鉴定分析了传统咸干鲅鱼的挥发性风味物质,发现咸干鲅鱼的特征风味主要由醛、醇、酮及烃类化合物构成[5-6]。也有研究对市售咸干鲅鱼的安全性进行了研究分析,明确需要对其脂肪氧化情况需要给予一定的重视[7]。目前鲜有研究比较不同的加工方式对脂质氧化和特征风味物质产生的影响,解析脂肪氧化程度对咸干鲅鱼香气形成的影响机制。
本研究以蓝点马鲛为原材料,采用冷风干制、热风干制和传统自然晾晒工艺制得咸干鲅鱼,探讨不同干制工艺对制得的咸干鲅鱼中脂肪氧化及对挥发性风味物质形成的影响,初步解析其独特风味的形成机制,旨在探究咸干鲅鱼的现代化加工技术,并为改善咸干鲅鱼的品质提供理论参考和依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
鲜鲅鱼 体重1~1.5 kg,购于青岛市黄岛区胶南琅琊码头;食盐 中盐上海市盐业公司;三氯甲烷、焦性没食子酸、重铬酸钾 均为分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;甲醇 色谱纯,瑞典Oceanpak公司;质量分数15%三氟化硼-甲醇溶液、正庚烷(色谱纯)、异辛烷(色谱纯) 美国Sigma公司。
T18DS25高速均质机 德国IKA仪器公司;Ncofuge 15R高速冷冻离心机 上海力申科学仪器有限公司;UV-9000紫外可见分光光度计 上海元析仪器有限公司;Agilent 1260 Infinity高效液相色谱仪、7980A/5975C气相色谱-质谱联用仪 美国Agilent公司;PAL System三合一进样器 瑞士CTC公司;CAR/PDMS/DVB固相微萃取装置(75 μm) 美国SUPELCO公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品制备
预处理:新鲜鲅鱼沿脊骨剖开后去除内脏,洗净表面血污,沥干。
腌制:根据前期预实验效果,采取湿腌法,将经过预处理的鲅鱼整齐堆码于不锈钢盘中,准确称取鱼肉质量10%的食盐均匀涂抹于鱼片周身后加水没过鱼片,置于4 ℃(±1 ℃)冷风库中腌制12 h后用流水冲洗脱盐,腌制脱盐结束后将鱼置于晒网上沥干表面水分。
干制:采用热风干制(温度50 ℃,相对湿度30%,连续干制20 h);冷风干制(温度10 ℃,相对湿度30%,连续干制60 h);自然晾晒(冬季晴日自然风干5 d)三种干制方式。
取样:原料(新鲜鲅鱼)、腌制后未干制半成品、热风干制成品、冷风干制成品、自然晾晒成品。每种成品取5条鱼,去头、去尾、去刺、去骨后绞碎,置于−20 ℃冷藏备用。
1.2.2 水分质量分数测定
参照《GB 5009.3-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中水分的测定》中的直接干燥法进行样品水分质量分数的测定[8]。
1.2.3 pH测定
参考VIDAL等[9]的方法。准确称取5 g(0.01 g)样品绞碎,加入45 mL 超纯水后振荡30 s使其充分混匀,使用双层定量滤纸浸提30 min,弃去初滤液,使用pH计测定样品pH。
1.2.4 脂肪氧化情况测定
1.2.4.1 脂肪测定
参照《GB 5009.6-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中脂肪的测定》中的酸水解法进行样品脂肪测定[10]。
1.2.4.2 酸价测定
酸价(Acid value,AV)的测定参考PHUNG等[11]的方法,准确称取5 g(0.01 g)样品于50 mL聚丙烯离心管中,加入15 mL乙醚-乙醇(V:V=2:1)混合,涡旋振荡后超声(45 ℃,360 W)提取15 min后离心(4500 r/min,3 min),上清液移入锥形瓶中,残渣用上述方法再提取2次,合并上清液。以KOH标准溶液(含酚酞指示剂)滴定,滴定终点为出现粉红色且10 s内不褪色,此时记录下所需的KOH确切体积,计算公式如下。
式中:V为所用的KOH标准溶液的体积(mL);C为KOH标准溶液的准确浓度(mol/L);56.1为KOH的摩尔质量;m为试样的质量(g)。酸价以mg KOH/g表示。
1.2.4.3 过氧化值测定
参照《GB 5009.227-2016食品安全国家标准 食品中过氧化值的测定》中的滴定法进行过氧化值(Peroxide value,POV)的测定[12]。
1.2.4.4 丙二醛测定
参照《GB 5009.181-2016食品安全国家标准 食品中丙二醛的测定》中的高效液相色谱法进行丙二醛(MDA)的测定[13]。
1.2.4.5 脂肪酸组成测定
参照《GB 5009.168-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中脂肪酸的测定》中的归一化法进行脂肪酸组成的测定[14]。
1.2.5 挥发性风味物质测定
参照YU等[15]的方法并稍作修改。采用固相微萃取-气相色谱-质谱(SPME-GC-MS)的方法进行测定。取5 g(精确至0.01 g)样品于20 mL顶空瓶中,水浴60 ℃下平衡5 min,用SPME萃取针插入顶空瓶中萃取30 min,然后于进样口解吸5 min。
1.2.5.1 色谱条件
色谱柱:HP-INNOWAX毛细管柱(30 m×0.25 mm,0.25 µm);升温程序:40 ℃保持5 min,以8 ℃/min升至250 ℃,保持5 min;载气(He)流速1 mL/min,压力2.4 kPa;分流比:5:1。
1.2.5.2 质谱条件
电子轰击离子源;电子能量70 eV;离子源温度230 ℃;四极杆温度150 ℃,接口温度250 ℃,质量扫描范围m/z 30~400。
1.2.5.3 定性定量方法
将检测得到的挥发物质谱图与NIST 08.L和Wiley(Version 9.0)谱库中标准物质的质谱图进行比对,相似指数大于80(最大值100),与质谱图库中的标准谱图进行比较,且与其他文献相互比对分析后作为确认化合物。利用数据处理软件,扣除非嗅感物质杂峰和硅氧烷类杂峰后计算挥发性风味物质的总峰面积,采用面积归一化法计算各化合物的相对含量。
1.3 数据处理
以上测定每组重复3次。采用IBM SPSS Statistics 26.0软件进行数据分析,差异显著性分析由单因素方差分析(One-way ANOVA)法完成,P<0.05表示差异显著。对挥发性风味物质进行PCA主成分分析,利用Origin Pro 2021软件作图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 不同干制方式对咸干鲅鱼水分质量分数和pH的影响
如表1所示,经热风干制和冷风干制得到的咸干鲅鱼水分质量分数从原料的68%显著下降至30%左右(P<0.05),经过传统方式自然晾晒后得到的咸干鲅鱼水分质量分数略低,为26%。所有组别的pH始终保持在6以上,热风干制组的pH最高的原因可能是脂肪热降解导致脂肪酸氧化加剧,而在自然晾晒过程中,脂肪酸积累致使pH有小幅度的下降,这与余静等[16]的实验结果一致。
表 1 新鲜鲅鱼和不同咸干鲅鱼的水分质量分数和pHTable 1. Moisture content and pH of fresh and cured Spanish mackerel products by different drying methods2.2 不同干制方式对咸干鲅鱼脂肪氧化情况的影响
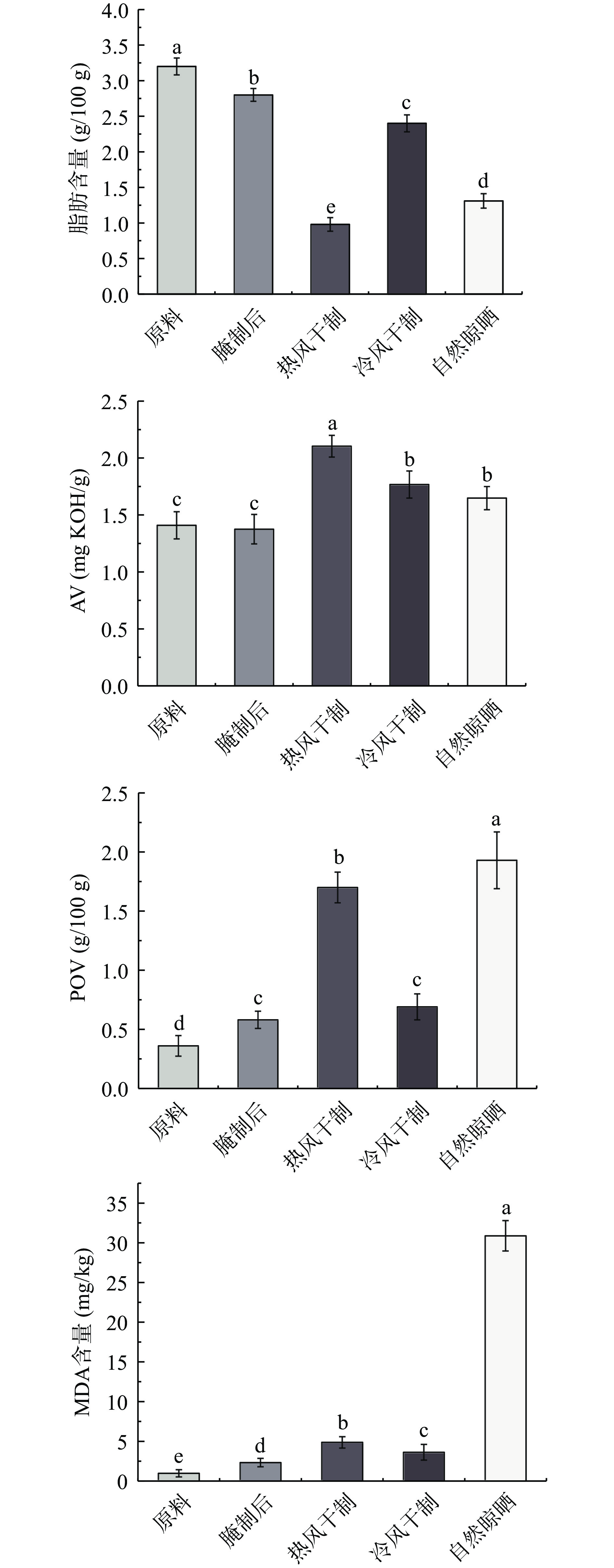
如图1所示,与原料组相比(3.20 g/100 g),腌制后的鱼肉脂肪含量下降,为2.80 g/100 g,说明食盐在一定程度上促进脂肪的氧化分解。在干制后的三组中,热风干制组的脂肪含量下降最多,为0.98 g/100 g;自然晾晒组脂肪含量略高于热风干制组,为1.31 g/100 g;冷风干制组的脂肪含量下降最少,为2.40 g/100 g。以腌制组为对照,热风干制组的脂肪含量下降了1.82 g/100 g,说明热风干制过程中脂肪发生了强烈分解[17]。高盐、光照、热处理等因素会促进脂肪氧化分解,从而导致脂肪含量的显著下降(P<0.05)。
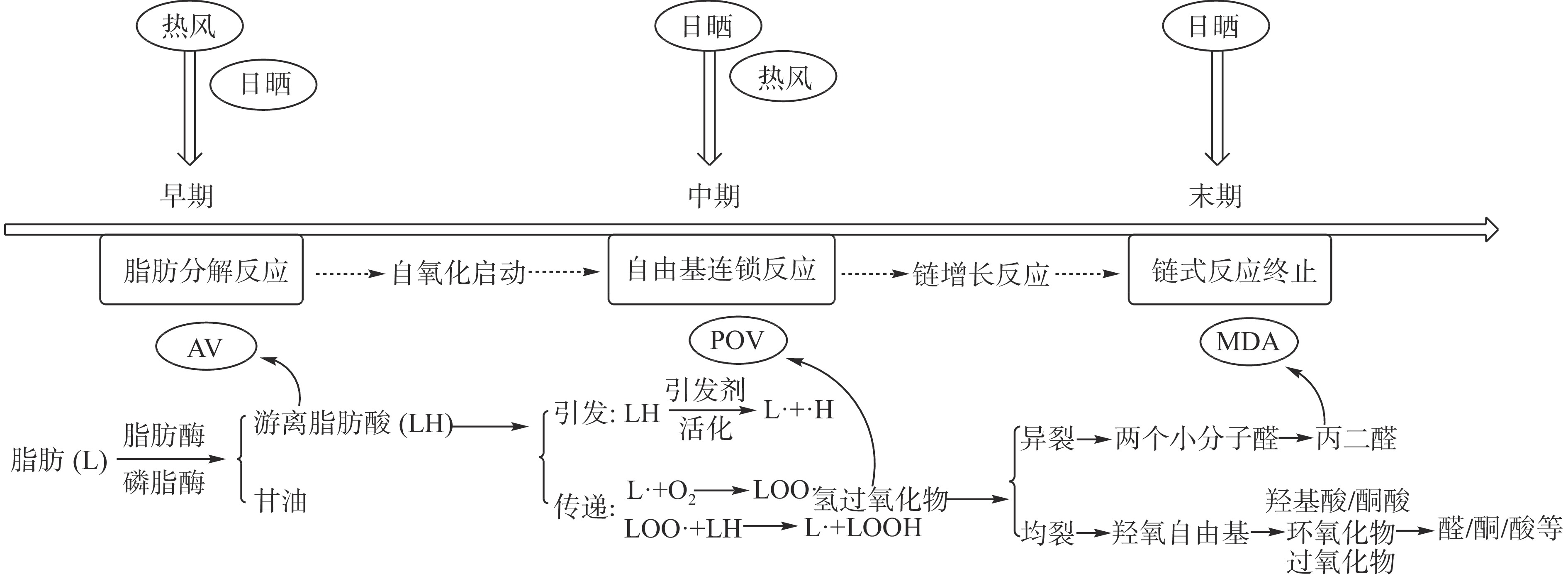
脂肪含量的下降反映了脂肪的氧化分解,但是脂肪氧化是不断变化的过程,其中AV、POV、MDA值的变化显示了其在不同阶段的氧化程度。由图1可见,经过三种加工方式处理的样品中的AV和MDA值均高于原料组和腌制组,且存在显著差异(P<0.05)。热风干制组的AV值最高,由于热风干制过程中较高的起始温度提高了鱼体肌肉内部脂肪酶的活力,脂肪氧化最早开始,从而水解累积了大量的游离脂肪酸(Free fat acid,FFA)[16],因此热风干制组的AV值显著高于冷风干制组和自然晾晒组(P<0.05)。冷风干制过程中由于鱼体在较低温度下氧化速率减缓,仅有少量的FFA发生氧化,累积的氢过氧化物(ROOH•)含量低,因此POV值与腌制组相比没有显著性差异(P>0.05);且脂肪酶的活力受到低温的影响,减缓了后续的脂质过氧化过程,所以MDA也保持较低的水平[18]。自然晾晒组由于冬季室外温度较低,鱼体初期的脂肪氧化速率较低,但由于户外光照的影响,大量的FFA被氧化为ROOH•,因此该组的AV值较低而POV值最高。日晒条件下会激活肌红蛋白等介导的光氧化反应[19],氧化速率大幅增加,大量的ROOH•进一步分解或热裂,所以自然晾晒组累积的MDA含量显著高于其他组(P<0.05)[20-21]。由此可以推断,温度会明显促进脂肪氧化初期的速率,日晒则会明显促进干制末期的脂肪过氧化情况,此结果与图1脂肪含量的变化规律互为印证。同时图2所示,高温和日晒都会促进脂肪氧化初期的速率,但高温对脂肪氧化初期的影响更为显著;高温和日晒都会促进脂肪自氧化进程,相比高温,日晒对链式反应的影响更为显著;而脂肪氧化终末期主要受日晒的影响。
2.3 不同干制方式对咸干鲅鱼脂肪酸含量的影响
UFA是水产品中非常重要的营养物质,由单不饱和脂肪酸(Monounsaturated fatty acid,MUFA)和多不饱和脂肪酸(Polyunsaturated fatty acid,PUFA)构成[22]。由表2可知,咸干鲅鱼中UFA含量很高,共占总脂肪酸的65%左右。在PUFA中,DHA(C22:6)和EPA(C20:5)含量最高,约占PUFA含量的89%,DHA和EPA属于ω-3 PUFA,是水产品中非常重要的营养物质,具有促进大脑发育、预防心脑血管疾病和防癌抗衰老的作用。咸干鲅鱼中饱和脂肪酸(Saturated fatty acid,SFA)含量较低,仅占总脂肪酸的35%左右,主要以软脂酸(C16:0)、硬脂酸(C18:0)和肉豆蔻酸(C14:0)为主,其中软脂酸含量最高,约占SFA含量的62.5%。
表 2 新鲜鲅鱼和不同咸干鲅鱼中各类脂质的脂肪酸相对含量Table 2. Fatty acid composition of fresh and cured Spanish mackerel products by different drying methods脂肪酸
类别
脂肪酸脂肪酸相对含量(%) 原料组 腌制组 热风干制组 冷风干制组 自然晾晒组 C14:0 3.9±0.9c 3.3±0.1e 3.6±0.8d 4.6±0.1b 4.8±0.5a C15:0 0.5±0.0a 0.6±0.0a 0.6±0.1a 0.5±0.0a 0.5±0.0a C16:0 20.9±2.0e 23.1±0.4a 22.7±1.0b 21.3±1.9d 22.1±1.0c C17:0 0.5±0.1a 0.5±0.0a 0.6±0.1a 0.5±0.0a 0.5±0.1a SFA C18:0 5.3±0.3b 5.8±0.2a 5.7±0.3a 5.5±0.7ab 5.8±0.8a C20:0 0.6±0.0bc 0.5±0.0c 0.5±0.0c 0.7±0.1ab 0.8±0.0a C22:0 0.2±0.0a 0.2±0.0a 0.2±0.0a 0.2±0.0a 0.2±0.0a C24:0 0.2±0.0a 0.2±0.0a 0.3±0.0a 0.3±0.0a 0.3±0.0a C16:1(n-9) 6.0±0.5b 5.5±0.3c 5.6±0.4c 6.6±0.4a 6.9±0.7a C18:1(n-9) 28.2±2.0d 30.7±0.5a 28.6±2.4c 27.9±0.7e 29.2±2.9b MUFA C20:1(n-9) 1.9±0.2a 1.6±0.1b 1.8±0.2ab 1.9±0.1a 1.6±0.5b C22:1(n-9) 0.4±0.0a 0.3±0.0a 0.4±0.0a 0.4±0.0a 0.4±0.0a C24:1(n-9) 0.8±0.1a 0.7±0.0a 0.8±0.0a 0.7±0.0a 0.7±0.0a C18:2(n-6) 0.9±0.0b 0.8±0.0c 1.0±0.1a 0.9±0.0b 0.9±0.0b C18:3(n-6) 0.1±0.0a ND ND 0.1±0.0a 0.1±0.0a C18:3(n-3) 0.9±0.1ab 0.8±0.0b 1.0±0.0a 0.9±0.0ab 0.7±0.0bc PUFA C20:2(n-6) 0.2±0.0a 0.2±0.0a 0.2±0.0a 0.2±0.0a 0.2±0.0a C20:4(n-6) 1.1±0.1ab 1.2±0.1a 1.1±0.1ab 1.0±0.1b 1.1±0.1ab C20:5(n-3) 7.9±0.7a 5.9±0.2e 6.2±0.7d 7.7±1.0b 7.4±0.9c C22:6(n-3) 17.8±1.0a 16.9±0.4ab 17.9±1.4a 16.7±0.9b 14.4±1.1c ƩSFA 32.1±2.0b 34.2±0.9a 34.2±2.0a 33.6±2.3ab 35.0±3.2a ƩMUFA 37.3±2.7b 38.8±1.2a 37.2±1.6b 37.5±2.0b 38.8±2.1a 合计 ƩPUFA 28.9±1.7a 25.8±0.8c 27.4±1.5b 27.5±1.4b 24.8±1.8d ƩPUFA(n-3) 26.6±2.0a 23.6±0.5c 25.1±2.0b 25.3±3.0b 22.5±2.1d ƩPUFA(n-6) 2.3±0.3a 2.2±0.2a 2.3±0.2a 2.2±0.2a 2.3±0.3a 注: ND表示相关数值未检出。 与新鲜鲅鱼样品相比,热风干制组中SFA含量增加的同时伴随着PUFA含量降低,这是由于DHA、EPA等PUFA极易氧化[23],不饱和键在加热时会发生氧化降解,SFA累积的含量升高,这与刘梦等[24]的研究结果一致。冷风干制组中以DHA、EPA为代表的PUFA含量下降幅度最小,且只含有一个不饱和键的MUFA基本未发生显著的变化(P>0.05),因为不饱和键在10 ℃的低温条件下相对稳定。冷风干制组的SFA中的豆蔻酸(C14:0)和花生酸(C20:0)含量均显著升高(P<0.05),从而使SFA的含量也明显升高,但上升幅度小于热风干制组。而在自然晾晒过程中,由于日晒和温度等因素的影响,相比腌制组,以豆蔻酸为代表的SFA含量均显著升高(P<0.05),这说明UFA中不饱和键氧化程度较高,因此PUFA的含量显著降低(P<0.05),且下降幅度最大。以DHA和α-亚麻酸为代表的ω-3 PUFA含量发生了显著下降(P<0.05),这表明在传统的自然晾晒法会在一定程度上造成鲅鱼重要营养物质的损失。但有研究表明,日晒条件下的光氧化可能是对水产制品香气的形成有显著贡献的氧化途径[25]。PUFA因为具有电子高密度区(C=C),因此在光照条件下容易发生光氧化降解[26],生成ROOH•,易分解成醛、酮、醇、酸、烷烃、呋喃和酯类等具有香气的小分子挥发物质。
2.4 不同干制方式对咸干鲅鱼挥发性风味物质的影响
本研究共检出了8大类120种挥发性风味成分,原料组、热风干制组、冷风干制和自然晾晒组样品中共分别检出了32、57、47、53种化合物,表明脂肪氧化程度对咸干鲅鱼的挥发性风味成分影响较大。前文提到,UFA经过LPO形成ROOH•的过程会产生重要的气味活性物质[27],如油酸、亚油酸、α-亚麻酸,生成13-,11-,10-,9-,8-ROOH,这些物质随后断裂不饱和键水解生成醛[28]。如研究发现辛醛由8-ROOH•裂解产生[29],己醛来源于亚油酸13-ROOH•[30]。通常认为,在风味形成中最重要的物质是醛类,因其阈值相对较低。己醛、辛醛、苯甲醛和苯乙醛这几种干制鱼制品中的特征香气贡献物质都在本实验中被检测到。热风干制组的己醛含量最高,而冷风干制组和自然晾晒组没有己醛检出。
醇类化合物是醛类在还原酶的作用下部分还原生成的,原料组中含量较高的乙醇、1-己醇、1-辛烯-3-醇、3,6-二甲氧基-9-芴-9-醇等在干制结束后相对含量明显下降或未检出,可能是参与了后续的分解反应。热风干制组中检出的1-戊烯-3-醇含量最高,它是EPA的代表氧化产物[30],此结果与表2中热风干制组EPA含量最低互为印证,表明温度较高时十分有利于该物质的生成。苯乙醇具有特殊玫瑰香气[31],在自然晾晒组中相对含量最高,推断该物质的生成可能与日晒条件有关。
醇类物质继续氧化产生会产生酮类,但本研究中检出的酮类化合物种类较少且相对含量较低,研究大都认为其阈值较高,所以酮类物质在本研究中对产品的整体香气贡献程度较低。本研究中酮类物质主要集中在冷风干制组中,2-丁酮、3-羟基-2-丁酮、2-壬酮、2-十一酮、7-辛烯-2-酮的相对含量较高;其中3-羟基-2-丁酮由乳酸菌的糖类物质发酵产生,该反应主要在温度相对较低时发生,因此该物质在本研究中仅在冷风干制组被检出,一些研究者认为这种物质对风干成熟产品的特征风味有一定的贡献[31-32]。
烷烃类物质主要来源于脂肪酸烷氧自由基的氧化裂解[33],热风干制组的相对含量最高。芳香类化合物在本研究中检出种类较少,该物质主要来源于苯丙氨酸的分解代谢或者来源于外界污染物,在鱼体富集后被检出[28]。烷烃类物质和芳香类物质因阈值普遍较大,因此对咸干鲅鱼的整体香气贡献较小。含硫和含氮化合物可能与微生物的繁殖有关,对风味贡献不高,在冷风干制组中相对含量最高[34]。酯类物质是由酸和醇之间的酯化作用产生的,会赋予咸干鲅鱼独特的酯香味[31],自然晾晒组中相对含量最高,推断原因是日晒条件下更易发生酯化反应[35]。杂环类物质大多来源于美拉德反应后期,在高温下较易生成,因此检出的杂环类物质主要集中在热风干制组[17]。
有研究表明,咸干鲅鱼中最典型的气味活性物质主要为醛类(己醛、辛醛、苯甲醛、苯乙醛)和醇类(3-甲基-1-丁醇、苯乙醇、(Z)-2-戊烯-1-醇、2-乙基-1-己醇)[26]。在本研究中,上述几种物质均有一定程度的检出,表明这些物质是咸干鲅鱼中常见的特征风味化合物,其共同作用赋予了咸干鲅鱼特殊的风味。在三种干制方式中,感觉阈值较低的醛醇类物质相对含量占比最大的是自然晾晒组,表明传统的自然晾晒组脂肪氧化程度最深,这对咸干鲅鱼整体香气的形成有很大贡献。
2.5 咸干鲅鱼挥发性风味物质的主成分分析
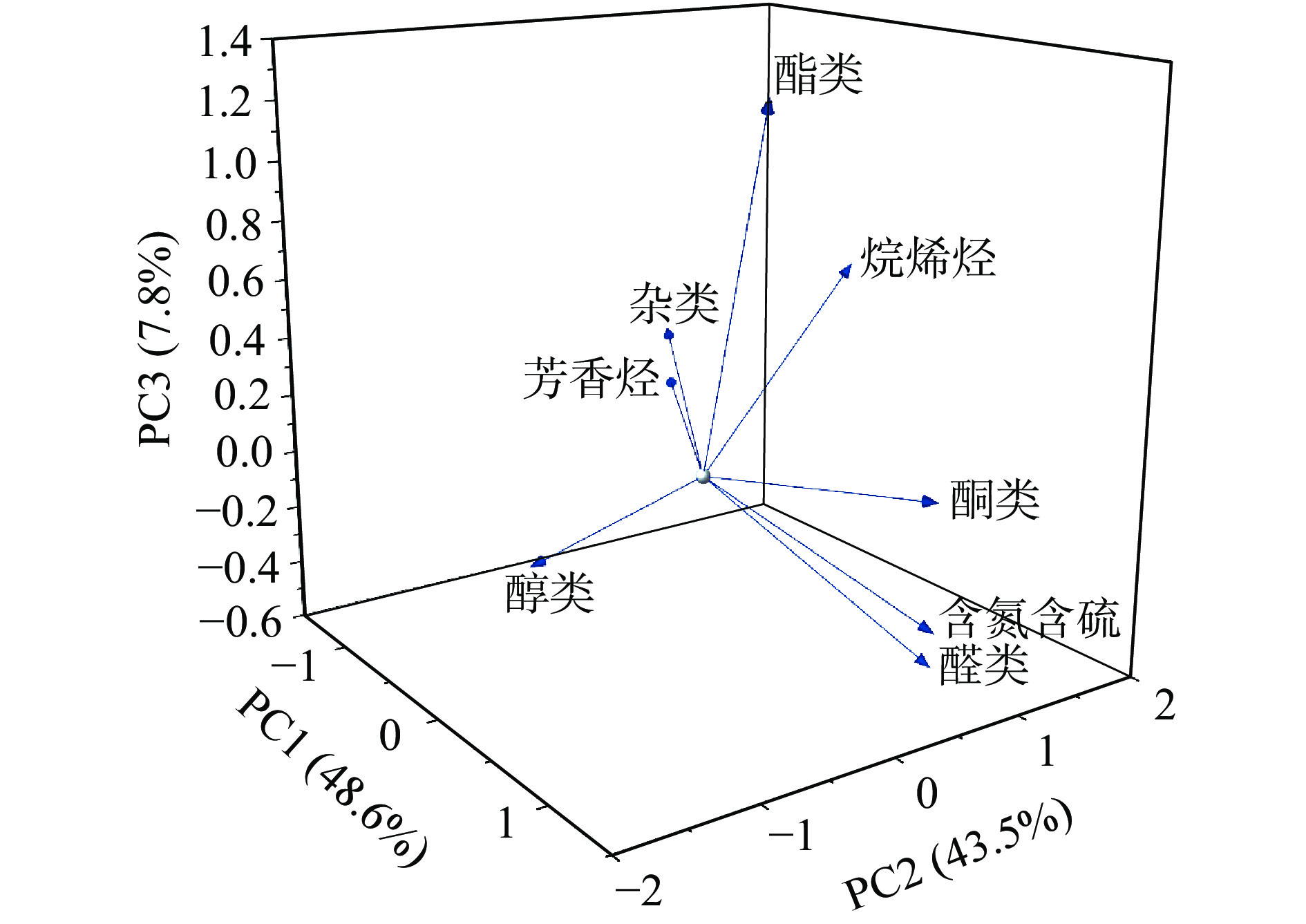
使用Origin Pro 2021中的Principal Component Analysis软件,采用降维的方式对表3中的8大类挥发性风味物质进行主成分分析,共发现3个主成分,第一主成分(PC1)的特征值为3.9,贡献率为48.6%;第二主成分(PC2)的特征值为3.5,贡献率为43.5%;第三主成分(PC3)的特征值为0.6,贡献率为7.8%,累计贡献率达到99.9%,因此这3个主成分能很好地反映各样品中挥发性风味物质的变化。由图3所示,各物质在载荷图上的绝对值越大,对该主成分的贡献率越大,其中PC1由酮类、芳香烃、含氮含硫类和杂类物质组成;PC2由醇类、醛类和烷烯烃类物质组成;PC3由酯类物质组成。
表 3 新鲜鲅鱼和不同咸干鲅鱼的挥发性风味成分及其相对含量Table 3. Volatile compounds and their relative contents of fresh and cured Spanish mackerel products by different drying methods化合物名称
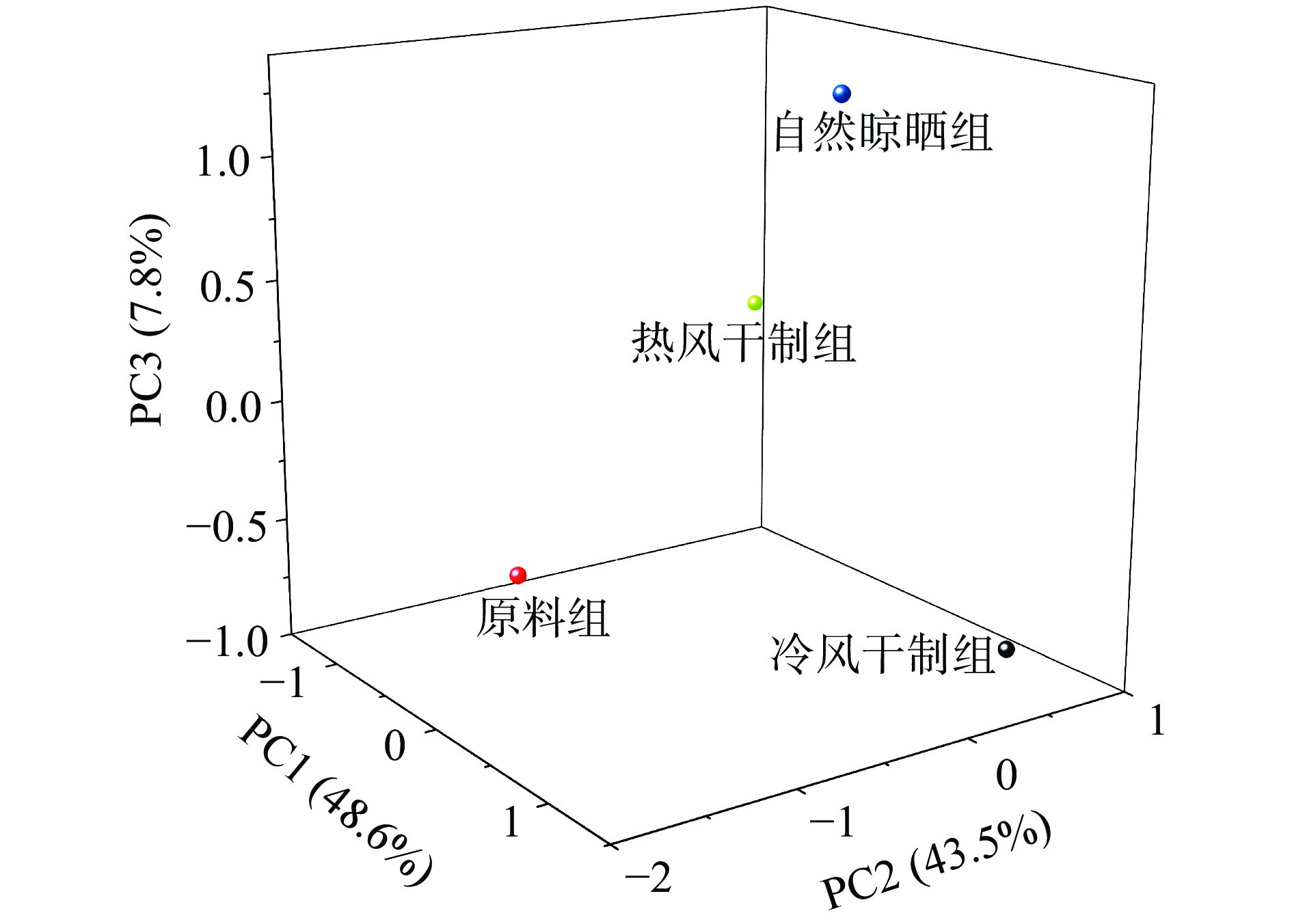
保留时间(min)相对含量(%) 原料组 热风干制组 冷风干制组 自然晾晒组 醛类 3-甲基-丁醛 2.967 − 2.08±0.18b 6.86±0.97a 2.55±0.87b 己醛 6.678 0.37±0.02a 0.44±0.07a − − 辛醛 11.523 0.32±0.01 − − − 苯甲醛 15.894 0.32±0.02c 0.85±0.09a 0.53±0.06b 0.19±0.01d 苯乙醛 17.784 − 0.43±0.23b 3.85±0.99a 2.35±0.72a 合计 1.01±0.17d 3.80±0.31c 11.24±0.37a 5.09±0.76b 醇类 乙醇 3.253 82.59±17.87a 1.74±0.43b − 1.07±0.22b 3,3-二甲基-2-戊醇 7.704 − − − 0.29±0.03 3,4-二甲基-2-己醇 7.137 − 0.31±0.06 − − 3,6,9,12-四氧十四烷-1-醇 7.229 − − 0.30±0.08a 0.05±0.01a α,β-二甲基-苯乙醇 7.785 − 0.39±0.07 − − 1-戊烯-3-醇 9.076 − 2.05±0.69a − 0.60±0.08b 4-甲基-环己醇 9.217 − 0.28±0.03 − − 3-甲基-1-丁醇 10.135 0.18±0.02c 0.55±0.07c 4.60±0.37b 19.71±1.87a (R)-2-辛醇 11.68 − 0.28±0.06 − − (Z)-2-戊烯-1-醇 12.366 0.30±0.02b 0.47±0.06a − 0.32±0.08b 2-甲基-3-戊醇 12.766 − − 0.21±0.02 − 1-己醇 12.966 0.40±0.01 − − − 1,4-环己二醇 13.603 − 0.41±0.03 − − 1-辛烯-3-醇 14.667 0.25±0.01 − − − 2-十三烷醇 14.878 − − 0.47±0.05 − 2,6-二甲基-4-庚醇 15.078 − 0.25±0.01 − − 2-乙基-1-己醇 15.332 0.24±0.01c 0.88±0.06a 0.69±0.09ab − 2-丙基-1-戊醇 15.337 − − − 0.35±0.04 2-十二烷醇 15.856 − − − 0.14±0.01 3,6-二甲氧基-9-芴-9-醇 16.812 0.26±0.02 − − − 双醚十八烷基-1,2-二醇 18.038 0.13±0.00 − − − 3-(甲硫基)-1-丙醇 18.848 − − − 1.08±0.11 1-庚糖醇 19 − 0.25±0.04 − − 苯乙醇 21.522 1.25±0.76c 0.38±0.04d 8.63±1.78b 15.68±2.87a 合计 85.59±18.99a 8.21±0.98cd 14.91±1.98c 39.29±3.53b 酮类 2-丁酮 2.772 − − 0.96±0.06 − 2-庚酮 9.227 − − − 0.68±0.04 3-羟基-2-丁酮 11.696 0.48±0.02a − 0.78±0.02a − 7-辛烯-2-酮 12.463 − − 1.60±0.14a 1.15±0.23a 2-壬酮 13.538 − − 1.38±0.43a 0.39±0.06b 3-庚酮 14.678 − − − 0.82±0.05 双醚2',6'-二羟基苯乙酮 15.629 − − − 1.09±0.04 2--1-苯基-乙酮 15.975 0.55±0.00 7-氯-1,3-二氢-5-苯基-1-2H-1,4-苄二氮杂-2-酮 16.806 − − 0.59±0.03 − 2-十一酮 17.131 − 0.47±0.01bc 0.83±0.03a 0.53±0.01b 合计 0.48±0.02c 1.02±0.01c 6.14±0.84a 4.65±0.38ab 烷烯烃 辛烷 1.983 − 0.25±0.03bc 2.42±0.98a 0.63±0.09b 壬烷 2.745 − − − 0.56±0.07 2,4-辛二烯 3.118 − − 0.64±0.03 − 正丁基醚 3.723 − 0.35±0.02 − − 乙基-1-丙烯醚 3.971 − − 1.47±0.17a 0.84±0.03a 八甲基环四硅氧烷 4.749 0.20±0.03b 0.15±0.01b 0.38±0.01a − 二甲基二硫醚 6.327 − 0.38±0.02a 0.28±0.01a − 1,4,7,10,13,16-六氧杂环十八烷 7.137 − 0.28±0.01a − 0.10±0.00b 双环-1-烯 9.941 − − − 0.14±0.00 亚芳基环己烷 9.978 − 0.32±0.02a 0.27±0.02a − 庚烷 10.2 − 0.69±0.06a 1.93±0.98a − 苯乙烯 10.816 − 6.16±0.87 − − 2-亚甲基双环己烷 10.848 − − − 0.55±0.03 1,3-环庚二烯 11.124 − − 0.24±0.01 − 1-乙基-1,4-环己二烯 11.134 − 0.64±0.08 − − 4-甲氧基-1-丁烯 11.718 − − − 0.85±0.06 1α,2β,3α,4β-四甲基环戊烷 12.242 − − − 0.14±0.01 1,22-二溴-十二烷 12.436 − 0.16±0.00 − − 1,2,4-三甲基环己烷 12.274 − 0.13±0.01 − − 十四烷 13.592 0.43±0.07c 0.54±0.02b 0.72±0.03a 0.42±0.03c 5-丙基癸烷 14.505 − − 0.26±0.01 − 3,5,5-三甲基-2-己烯 15.267 0.37±0.02c 0.98±0.02a − 0.74±0.04b 十五烷 15.505 0.76±0.05d 1.97±0.11c 2.40±0.56b 2.96±0.67a 2,6,10,14-四甲基-十五烷 18.238 0.82±0.09c 7.30±0.99ab 4.59±0.95b 9.41±1.09a (Z,Z)-1,3-环辛二烯 18.357 0.42±0.07 − − − 十七烷 18.659 1.38±0.76c 2.16±0.17b 3.46±0.65a 1.34±0.06c 苷菊环烃 19.232 − − 0.34±0.02 − 十八烷基甲基-环硅氧烷 20.323 − 0.41±0.03a 0.33±0.01ab 0.30±0.01b 六甲基-环三硅氧烷 20.523 − 0.89±0.05a 0.36±0.02b − 十甲基四硅氧烷 20.804 − 0.38±0.05a − 0.25±0.01a 十八烷 21.431 − 0.18±0.03 − − 十六碳-八硅氧烷 22.279 0.02±0.00a − 0.20±0.00a 0.01±0.00b 十二甲基五硅氧烷 22.284 − 0.11±0.02 − − 十二烷基甲基-六硅氧烷 24.915 0.06±0.01 − − − 1,4,7,10,13,16-六氧杂环十八烷 29.042 0.10±0.02 − − − 合计 4.55±0.65c 24.43±2.32a 20.30±3.77b 19.21±1.98b 芳香烃 − − − − 甲苯 5.452 0.14±0.02b 7.30±0.88a 0.27±0.04b 0.18±0.02b 乙苯 7.596 − 0.59±0.04 − − 对二甲苯 7.926 − 0.92±0.08a 0.19±0.02b − 甲氧基-苯基-肟 19.642 2.65±0.88a 1.93±0.80b 2.57±0.74a 2.63±0.86a 1-甲基萘 20.804 − − 0.36±0.04 − 2,6-二甲基苯酚 24.764 − − 0.14±0.01 − 合计 2.79±0.90c 10.74±1.8a 3.53±0.85b 2.81±0.88c 含氮含硫化合物 4-(二甲基氨基)-3-羟基-丁酸 1.465 − 0.71±0.07a − 0.99±0.07a 三甲胺 1.465 3.30±0.86d 5.79±0.15c 35.58±5.48a 21.85±2.27b 甲硫醇 1.595 1.35±0.06a 1.35±0.03a − − 三硫化二甲酯 13.257 − − 0.62±0.06 − N-苄基-N-乙基-对-异丙基苯甲酰胺 15.629 − 0.80±0.06 − − 氨基甲酸N-(3-氯-4-甲氧基苯基)-癸酯 16.709 − − 0.69±0.07 − 1H-1,2-二硫代喹啉 16.72 0.28±0.06 − − − 2-氨基-6-甲基苯甲酸 19.734 − − 2.87±0.32 − N-(3-甲基苯基)-2-氧-乙酰胺 23.64 − − 0.53±0.06 − 2-4-苯氧基-乙酰胺 24.926 − 0.42±0.06 − − 吲哚 27.745 − 2.40±0.67 − − 合计 4.93±0.98d 11.47±0.95c 40.28±5.99a 22.84±2.34b 酯类 L-丙氨酸甲酯 1.892 − − − 0.22±0.03 乙酸乙酯 2.626 − − − 0.30±0.02 2-戊醇甲酸酯 7.218 0.15±0.00 丁酸戊酯 11.032 − − − 0.10±0.03 三硫化二甲酯 13.257 − 0.12±0.01 − − 甲酸庚酯 14.77 0.41±0.02 − − − 戊酸2-羟基-4-甲基-甲酯 15.083 − − − 1.12±0.11 4-甲基-1-庚-4-醇乙酸酯 15.089 − − 0.17±0.02 − 2-戊醇丙酸酯 15.278 − − 0.59±0.10 − 2,3,5-三苄基阿拉伯内酯 18.038 − − − 0.48±0.09 苯甲酸三甲基甲硅烷基酯 18.124 − − − 0.36±0.06 戊酸2,4,6-三氯苯酯 23.683 − − − 0.35±0.06 硅酸二乙基双酯 24.899 − − 0.43±0.06 − 1,2-肼二甲酸二乙酯 25.828 − − − 0.16±0.02 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯 26.211 0.16±0.03 − − − 邻苯二甲酸异丁基壬基酯 28.837 0.60±0.08 − − − 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯 30.371 0.13±0.02 − − − 合计 1.29±0.15b 0.27±0.01c 1.20±0.18b 3.09±0.42a 杂类 2-乙啶 2.345 − − 1.26±0.21 − 苯并环丁烯 11.242 0.32±0.00 4,5-二甲基-嘧啶 12.355 − − 0.34±0.02 − 醋酸 14.7 − 15.84±1.39a − 1.13±0.05b 丙酸 16.185 − 1.68±0.36 − − 2-甲基-丙酸 16.682 − 1.71±0.47a − 1.02±0.13a 6-甲基-3-吡啶-1,5-对甲苯基-2-吡唑啉 16.79 − 0.31±0.03 − − 4-氯苯基-2,6-二苯基吡啶 16.806 − − − 0.23±0.02 丁酸 17.584 − 0.21±0.01a − 0.27±0.02a 2-甲基-丁酸 18.184 − 6.52±1.37 − − 2,3-二氢-2-甲基-5-乙基呋喃 19.313 − − − 0.26±0.03 4-甲基-戊酸 20.075 − 13.58±2.24 − − 2-甲基-2-苯基-1,3-二氧戊环 24.774 − − − 0.12±0.01 合计 − 40.17±5.87a 1.60±0.23c 3.03±0.26b 注:−表示未检出。 图4所示的是新鲜鲅鱼和各组咸干鲅鱼在3种主成分的得分情况。原料组作为对照,在PC1上得分最高(PC1:−0.29;PC2:−1.36;PC3:−0.56),其风味物质主要由酮类、芳香烃、含氮含硫类和杂类物质组成。热风组在PC2上得分最高(PC1:−1.28;PC2:0.78;PC3:0.13),风味物质主要由醇醛类和烷烯烃类物质构成,这与醇醛类的前体物质PUFA有关,在50 ℃的高温下,鲅鱼中较高含量的亚油酸、亚麻酸和EPA等物质更易发生裂解产生醇醛类风味物质,说明温度对咸干鲅鱼制品的风味影响较大,此结果与前文中不同组脂肪氧化各指标的变化互为印证。与原料组相似,冷风干制组也在PC1上得分最高(PC1:0.94;PC2:0.73;PC3:−0.92),风味物质主要由感觉阈值较低的酮类、芳香烃、含氮含硫类和杂类物质组成,由于冷风干制组的干制温度较低,前期脂肪氧化的相关指标也表明较低的温度下脂肪氧化程度不高。而自然晾晒组由于日晒的原因,脂肪氧化程度最深,光照会使脂肪氧化后产生特殊的酯香味,因此在风味物质中酯类物质贡献最大,在PC3上得分最高,在PC1和PC2上的总体得分也较高(PC1:0.64;PC2:−0.14;PC3:1.35)。综上所述,温度和光照是咸干鲅鱼加工时最重要的因素,冷风干制组的整体风味更接近原料组,整体风味没有得到很好地提高,自然晾晒组中特殊的酯类物质使得其风味更加丰富,得到了明显地改善。
3. 结论
比较3种不同干制方式(热风干制、冷风干制、自然晾晒)咸干鲅鱼制品的各测定指标可以得出,高温和日晒均对脂肪水解、氧化有显著影响。热风干制组的脂肪含量最低而AV值最高,表明高温显著促进脂肪的水解过程。自然晾晒组POV值和MDA含量显著高于其他组,则表明自然晾晒的咸干鲅鱼存在脂肪过度氧化的情况。鲅鱼的DHA和EPA含量较高,约占PUFA含量的89%,自然晾晒ω-3 PUFA的含量有显著影响,存在一定的营养物质流失情况。从咸干鲅鱼中检出了120种挥发性风味成分,得到醇、醛、酮、酯、烯、酸等八大类成分,采用主成分分析得到3个成分,累积贡献率达到99.9%,PCA表明,自然晾晒组检出的因脂肪氧化生成的物质相对含量更多,物质种类更丰富,风味得到明显的改善。本试验对咸干鲅鱼脂肪氧化的指标进行了较为全面的测定,且各组别脂肪氧化程度和生成风味物质的结果较为一致,说明传统的自然晾晒法能够使脂肪氧化程度更高且风味更佳,但存在营养价值流失或脂肪过氧化可能造成的安全性问题。本研究尚未涉及不同盐浓度腌制及不同晾晒时间对产品的影响,因此在后续的研究中,可以深入讨论自然晾晒条件下,不同工艺参数对咸干鲅鱼品质及风味的影响,旨在保留传统加工方法的同时,在一定程度上避免咸干鲅鱼营养价值流失并保留其原有的特色风味,开发可供实际生产的标准工艺流程,开发更多具有特色的腌干鱼类加工制品。
-
表 1 新鲜鲅鱼和不同咸干鲅鱼的水分质量分数和pH
Table 1 Moisture content and pH of fresh and cured Spanish mackerel products by different drying methods
表 2 新鲜鲅鱼和不同咸干鲅鱼中各类脂质的脂肪酸相对含量
Table 2 Fatty acid composition of fresh and cured Spanish mackerel products by different drying methods
脂肪酸
类别
脂肪酸脂肪酸相对含量(%) 原料组 腌制组 热风干制组 冷风干制组 自然晾晒组 C14:0 3.9±0.9c 3.3±0.1e 3.6±0.8d 4.6±0.1b 4.8±0.5a C15:0 0.5±0.0a 0.6±0.0a 0.6±0.1a 0.5±0.0a 0.5±0.0a C16:0 20.9±2.0e 23.1±0.4a 22.7±1.0b 21.3±1.9d 22.1±1.0c C17:0 0.5±0.1a 0.5±0.0a 0.6±0.1a 0.5±0.0a 0.5±0.1a SFA C18:0 5.3±0.3b 5.8±0.2a 5.7±0.3a 5.5±0.7ab 5.8±0.8a C20:0 0.6±0.0bc 0.5±0.0c 0.5±0.0c 0.7±0.1ab 0.8±0.0a C22:0 0.2±0.0a 0.2±0.0a 0.2±0.0a 0.2±0.0a 0.2±0.0a C24:0 0.2±0.0a 0.2±0.0a 0.3±0.0a 0.3±0.0a 0.3±0.0a C16:1(n-9) 6.0±0.5b 5.5±0.3c 5.6±0.4c 6.6±0.4a 6.9±0.7a C18:1(n-9) 28.2±2.0d 30.7±0.5a 28.6±2.4c 27.9±0.7e 29.2±2.9b MUFA C20:1(n-9) 1.9±0.2a 1.6±0.1b 1.8±0.2ab 1.9±0.1a 1.6±0.5b C22:1(n-9) 0.4±0.0a 0.3±0.0a 0.4±0.0a 0.4±0.0a 0.4±0.0a C24:1(n-9) 0.8±0.1a 0.7±0.0a 0.8±0.0a 0.7±0.0a 0.7±0.0a C18:2(n-6) 0.9±0.0b 0.8±0.0c 1.0±0.1a 0.9±0.0b 0.9±0.0b C18:3(n-6) 0.1±0.0a ND ND 0.1±0.0a 0.1±0.0a C18:3(n-3) 0.9±0.1ab 0.8±0.0b 1.0±0.0a 0.9±0.0ab 0.7±0.0bc PUFA C20:2(n-6) 0.2±0.0a 0.2±0.0a 0.2±0.0a 0.2±0.0a 0.2±0.0a C20:4(n-6) 1.1±0.1ab 1.2±0.1a 1.1±0.1ab 1.0±0.1b 1.1±0.1ab C20:5(n-3) 7.9±0.7a 5.9±0.2e 6.2±0.7d 7.7±1.0b 7.4±0.9c C22:6(n-3) 17.8±1.0a 16.9±0.4ab 17.9±1.4a 16.7±0.9b 14.4±1.1c ƩSFA 32.1±2.0b 34.2±0.9a 34.2±2.0a 33.6±2.3ab 35.0±3.2a ƩMUFA 37.3±2.7b 38.8±1.2a 37.2±1.6b 37.5±2.0b 38.8±2.1a 合计 ƩPUFA 28.9±1.7a 25.8±0.8c 27.4±1.5b 27.5±1.4b 24.8±1.8d ƩPUFA(n-3) 26.6±2.0a 23.6±0.5c 25.1±2.0b 25.3±3.0b 22.5±2.1d ƩPUFA(n-6) 2.3±0.3a 2.2±0.2a 2.3±0.2a 2.2±0.2a 2.3±0.3a 注: ND表示相关数值未检出。 表 3 新鲜鲅鱼和不同咸干鲅鱼的挥发性风味成分及其相对含量
Table 3 Volatile compounds and their relative contents of fresh and cured Spanish mackerel products by different drying methods
化合物名称
保留时间(min)相对含量(%) 原料组 热风干制组 冷风干制组 自然晾晒组 醛类 3-甲基-丁醛 2.967 − 2.08±0.18b 6.86±0.97a 2.55±0.87b 己醛 6.678 0.37±0.02a 0.44±0.07a − − 辛醛 11.523 0.32±0.01 − − − 苯甲醛 15.894 0.32±0.02c 0.85±0.09a 0.53±0.06b 0.19±0.01d 苯乙醛 17.784 − 0.43±0.23b 3.85±0.99a 2.35±0.72a 合计 1.01±0.17d 3.80±0.31c 11.24±0.37a 5.09±0.76b 醇类 乙醇 3.253 82.59±17.87a 1.74±0.43b − 1.07±0.22b 3,3-二甲基-2-戊醇 7.704 − − − 0.29±0.03 3,4-二甲基-2-己醇 7.137 − 0.31±0.06 − − 3,6,9,12-四氧十四烷-1-醇 7.229 − − 0.30±0.08a 0.05±0.01a α,β-二甲基-苯乙醇 7.785 − 0.39±0.07 − − 1-戊烯-3-醇 9.076 − 2.05±0.69a − 0.60±0.08b 4-甲基-环己醇 9.217 − 0.28±0.03 − − 3-甲基-1-丁醇 10.135 0.18±0.02c 0.55±0.07c 4.60±0.37b 19.71±1.87a (R)-2-辛醇 11.68 − 0.28±0.06 − − (Z)-2-戊烯-1-醇 12.366 0.30±0.02b 0.47±0.06a − 0.32±0.08b 2-甲基-3-戊醇 12.766 − − 0.21±0.02 − 1-己醇 12.966 0.40±0.01 − − − 1,4-环己二醇 13.603 − 0.41±0.03 − − 1-辛烯-3-醇 14.667 0.25±0.01 − − − 2-十三烷醇 14.878 − − 0.47±0.05 − 2,6-二甲基-4-庚醇 15.078 − 0.25±0.01 − − 2-乙基-1-己醇 15.332 0.24±0.01c 0.88±0.06a 0.69±0.09ab − 2-丙基-1-戊醇 15.337 − − − 0.35±0.04 2-十二烷醇 15.856 − − − 0.14±0.01 3,6-二甲氧基-9-芴-9-醇 16.812 0.26±0.02 − − − 双醚十八烷基-1,2-二醇 18.038 0.13±0.00 − − − 3-(甲硫基)-1-丙醇 18.848 − − − 1.08±0.11 1-庚糖醇 19 − 0.25±0.04 − − 苯乙醇 21.522 1.25±0.76c 0.38±0.04d 8.63±1.78b 15.68±2.87a 合计 85.59±18.99a 8.21±0.98cd 14.91±1.98c 39.29±3.53b 酮类 2-丁酮 2.772 − − 0.96±0.06 − 2-庚酮 9.227 − − − 0.68±0.04 3-羟基-2-丁酮 11.696 0.48±0.02a − 0.78±0.02a − 7-辛烯-2-酮 12.463 − − 1.60±0.14a 1.15±0.23a 2-壬酮 13.538 − − 1.38±0.43a 0.39±0.06b 3-庚酮 14.678 − − − 0.82±0.05 双醚2',6'-二羟基苯乙酮 15.629 − − − 1.09±0.04 2--1-苯基-乙酮 15.975 0.55±0.00 7-氯-1,3-二氢-5-苯基-1-2H-1,4-苄二氮杂-2-酮 16.806 − − 0.59±0.03 − 2-十一酮 17.131 − 0.47±0.01bc 0.83±0.03a 0.53±0.01b 合计 0.48±0.02c 1.02±0.01c 6.14±0.84a 4.65±0.38ab 烷烯烃 辛烷 1.983 − 0.25±0.03bc 2.42±0.98a 0.63±0.09b 壬烷 2.745 − − − 0.56±0.07 2,4-辛二烯 3.118 − − 0.64±0.03 − 正丁基醚 3.723 − 0.35±0.02 − − 乙基-1-丙烯醚 3.971 − − 1.47±0.17a 0.84±0.03a 八甲基环四硅氧烷 4.749 0.20±0.03b 0.15±0.01b 0.38±0.01a − 二甲基二硫醚 6.327 − 0.38±0.02a 0.28±0.01a − 1,4,7,10,13,16-六氧杂环十八烷 7.137 − 0.28±0.01a − 0.10±0.00b 双环-1-烯 9.941 − − − 0.14±0.00 亚芳基环己烷 9.978 − 0.32±0.02a 0.27±0.02a − 庚烷 10.2 − 0.69±0.06a 1.93±0.98a − 苯乙烯 10.816 − 6.16±0.87 − − 2-亚甲基双环己烷 10.848 − − − 0.55±0.03 1,3-环庚二烯 11.124 − − 0.24±0.01 − 1-乙基-1,4-环己二烯 11.134 − 0.64±0.08 − − 4-甲氧基-1-丁烯 11.718 − − − 0.85±0.06 1α,2β,3α,4β-四甲基环戊烷 12.242 − − − 0.14±0.01 1,22-二溴-十二烷 12.436 − 0.16±0.00 − − 1,2,4-三甲基环己烷 12.274 − 0.13±0.01 − − 十四烷 13.592 0.43±0.07c 0.54±0.02b 0.72±0.03a 0.42±0.03c 5-丙基癸烷 14.505 − − 0.26±0.01 − 3,5,5-三甲基-2-己烯 15.267 0.37±0.02c 0.98±0.02a − 0.74±0.04b 十五烷 15.505 0.76±0.05d 1.97±0.11c 2.40±0.56b 2.96±0.67a 2,6,10,14-四甲基-十五烷 18.238 0.82±0.09c 7.30±0.99ab 4.59±0.95b 9.41±1.09a (Z,Z)-1,3-环辛二烯 18.357 0.42±0.07 − − − 十七烷 18.659 1.38±0.76c 2.16±0.17b 3.46±0.65a 1.34±0.06c 苷菊环烃 19.232 − − 0.34±0.02 − 十八烷基甲基-环硅氧烷 20.323 − 0.41±0.03a 0.33±0.01ab 0.30±0.01b 六甲基-环三硅氧烷 20.523 − 0.89±0.05a 0.36±0.02b − 十甲基四硅氧烷 20.804 − 0.38±0.05a − 0.25±0.01a 十八烷 21.431 − 0.18±0.03 − − 十六碳-八硅氧烷 22.279 0.02±0.00a − 0.20±0.00a 0.01±0.00b 十二甲基五硅氧烷 22.284 − 0.11±0.02 − − 十二烷基甲基-六硅氧烷 24.915 0.06±0.01 − − − 1,4,7,10,13,16-六氧杂环十八烷 29.042 0.10±0.02 − − − 合计 4.55±0.65c 24.43±2.32a 20.30±3.77b 19.21±1.98b 芳香烃 − − − − 甲苯 5.452 0.14±0.02b 7.30±0.88a 0.27±0.04b 0.18±0.02b 乙苯 7.596 − 0.59±0.04 − − 对二甲苯 7.926 − 0.92±0.08a 0.19±0.02b − 甲氧基-苯基-肟 19.642 2.65±0.88a 1.93±0.80b 2.57±0.74a 2.63±0.86a 1-甲基萘 20.804 − − 0.36±0.04 − 2,6-二甲基苯酚 24.764 − − 0.14±0.01 − 合计 2.79±0.90c 10.74±1.8a 3.53±0.85b 2.81±0.88c 含氮含硫化合物 4-(二甲基氨基)-3-羟基-丁酸 1.465 − 0.71±0.07a − 0.99±0.07a 三甲胺 1.465 3.30±0.86d 5.79±0.15c 35.58±5.48a 21.85±2.27b 甲硫醇 1.595 1.35±0.06a 1.35±0.03a − − 三硫化二甲酯 13.257 − − 0.62±0.06 − N-苄基-N-乙基-对-异丙基苯甲酰胺 15.629 − 0.80±0.06 − − 氨基甲酸N-(3-氯-4-甲氧基苯基)-癸酯 16.709 − − 0.69±0.07 − 1H-1,2-二硫代喹啉 16.72 0.28±0.06 − − − 2-氨基-6-甲基苯甲酸 19.734 − − 2.87±0.32 − N-(3-甲基苯基)-2-氧-乙酰胺 23.64 − − 0.53±0.06 − 2-4-苯氧基-乙酰胺 24.926 − 0.42±0.06 − − 吲哚 27.745 − 2.40±0.67 − − 合计 4.93±0.98d 11.47±0.95c 40.28±5.99a 22.84±2.34b 酯类 L-丙氨酸甲酯 1.892 − − − 0.22±0.03 乙酸乙酯 2.626 − − − 0.30±0.02 2-戊醇甲酸酯 7.218 0.15±0.00 丁酸戊酯 11.032 − − − 0.10±0.03 三硫化二甲酯 13.257 − 0.12±0.01 − − 甲酸庚酯 14.77 0.41±0.02 − − − 戊酸2-羟基-4-甲基-甲酯 15.083 − − − 1.12±0.11 4-甲基-1-庚-4-醇乙酸酯 15.089 − − 0.17±0.02 − 2-戊醇丙酸酯 15.278 − − 0.59±0.10 − 2,3,5-三苄基阿拉伯内酯 18.038 − − − 0.48±0.09 苯甲酸三甲基甲硅烷基酯 18.124 − − − 0.36±0.06 戊酸2,4,6-三氯苯酯 23.683 − − − 0.35±0.06 硅酸二乙基双酯 24.899 − − 0.43±0.06 − 1,2-肼二甲酸二乙酯 25.828 − − − 0.16±0.02 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯 26.211 0.16±0.03 − − − 邻苯二甲酸异丁基壬基酯 28.837 0.60±0.08 − − − 邻苯二甲酸二丁酯 30.371 0.13±0.02 − − − 合计 1.29±0.15b 0.27±0.01c 1.20±0.18b 3.09±0.42a 杂类 2-乙啶 2.345 − − 1.26±0.21 − 苯并环丁烯 11.242 0.32±0.00 4,5-二甲基-嘧啶 12.355 − − 0.34±0.02 − 醋酸 14.7 − 15.84±1.39a − 1.13±0.05b 丙酸 16.185 − 1.68±0.36 − − 2-甲基-丙酸 16.682 − 1.71±0.47a − 1.02±0.13a 6-甲基-3-吡啶-1,5-对甲苯基-2-吡唑啉 16.79 − 0.31±0.03 − − 4-氯苯基-2,6-二苯基吡啶 16.806 − − − 0.23±0.02 丁酸 17.584 − 0.21±0.01a − 0.27±0.02a 2-甲基-丁酸 18.184 − 6.52±1.37 − − 2,3-二氢-2-甲基-5-乙基呋喃 19.313 − − − 0.26±0.03 4-甲基-戊酸 20.075 − 13.58±2.24 − − 2-甲基-2-苯基-1,3-二氧戊环 24.774 − − − 0.12±0.01 合计 − 40.17±5.87a 1.60±0.23c 3.03±0.26b 注:−表示未检出。 -
[1] WAN R, SONG P B, LI Z G, et al. Distribution and environmental characteristics of the spawning grounds of Scomberomorus niphonius in the coastal waters of Yellow Sea, China[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology,2020,31(1):275−281.
[2] 祖凯伟, 程家骅, 刘阳, 等. 产卵期及越冬期蓝点马鲛渔场分布变化及其与海表温度的关系[J]. 海洋湖沼通报,2019(6):48−57. [ZU K W, CHENG J Y, LIU Y, et al. Distribution of fishing grounds of Japanese Spanish mackerel (Scomberomorus niphonius) during spawning and overwintering period and its relation with sea surface temperature in China sea[J]. Transactions of Oceanology and Limnology,2019(6):48−57. [3] HUANG Y Z, LIU Y, JIN Z, et al. Sensory evaluation of fresh/frozen mackerel products: A review[J]. Comprehensive Reviews in Food Science and Food Safety,2021,20(4):3504−3530. doi: 10.1111/1541-4337.12776
[4] SVEINSDÓTTIR H I, KARLSDÓTTIR M G, ARASON S, et al. Effect of antioxidants on the sensory quality and physicochemical stability of Atlantic mackerel (Scomber scombrus) fillets during frozen storage[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,321:126744. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.126744
[5] 王玉, 赵延宁, 薛勇, 等. 基于电子鼻与SPME-GC-MS法分析咸鲅鱼加工过程挥发性风味成分变化[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(24):266−272. [WANG Y, ZHAO Y N, XUE Y, et al. Analysis of volatile flavor compounds changes during salted Spanish mackerel processing by electronic nose and SPME-GC-MS[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(24):266−272. [6] 王玉, 王睿迪, 薛勇, 等. 传统加工咸鲅鱼的挥发性风味成分[J]. 现代食品科技,2018,34(9):268−276. [WANG Y, WANG Y D, XUE Y, et al. Analysis of volatile flavor compounds changes during traditional processing of salted Spanish mackerel[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2018,34(9):268−276. [7] 赵延宁, 王玉, 王睿迪, 等. 市售咸干鲅鱼的安全性分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(14):215−220. [ZHAO Y N, WANG Y, WANG R D, et al. Safety analysis of commercially available salted and dried Spanish markerel[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(14):215−220. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.019258 [8] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. GB 5009.3-2016 食品安全国家标准 食品中水分的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016: 1−4 National Health and Wellness Commission of the People's Republic of China. GB 5009.3-201 National standard for food safety determination of moisture in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016: 1−4.
[9] VIDAL V A S, SANTANA J B, PAGLARINI C S, et al. Adding lysine and yeast extract improves sensory properties of low sodium salted meat[J]. Meat Science,2020:159. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2019.107911
[10] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. GB 5009.6-2016食品安全国家标准 食品中脂肪的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016: 3−5 National health and Wellness Commission of the People's Republic of China. GB 5009.6-2016 National standard for food safety determination of fat in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016: 3−5.
[11] PHUNG A S, BANNENBERG G, VIGOR C, et al. Chemical compositional changes in over-oxidized fish oils[J]. Foods,2020,9(10):1501−1532. doi: 10.3390/foods9101501
[12] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. GB 5009.227-2016食品安全国家标准 食品中过氧化值的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016: 1−4 National Health and Wellness Commission of the People's Republic of China. GB 5009.227-2016 National standard for food safety determination of peroxide value in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016: 1−4.
[13] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. GB 5009.181-2016食品安全国家标准 食品中丙二醛的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016: 1−3 National Health and Wellness Commission of the People's Republic of China. GB 5009.168-2016 National standard for food safety determination of malonaldehyde in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016: 1−3.
[14] 中华人民共和国国家卫生健康委员会. GB 5009.168-2016食品安全国家标准 食品中脂肪酸的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016: 10-11 National Health and Wellness Commission of the People's Republic of China. GB 5009.168-2016 National standard for food safety determination of fatty acids in food[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2016: 10-11.
[15] YU H, XIE T, XIE J, et al. Characterization of key aroma compounds in Chinese rice wine using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and gas chromatography-olfactometry[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,293:8−14. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.03.071
[16] 余静, 张佳敏, 王卫, 等. 干燥工艺对腌腊鱼品质特性的影响[J]. 食品研究与开发,2019,40(12):95−102. [YU J, ZHANG J M, WANG W, et al. Effect of drying process on quality characteristics of salted fish[J]. Food Research and Development,2019,40(12):95−102. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2019.12.016 [17] 顾赛麒, 周洪鑫, 郑皓铭, 等. 干制方式对腌腊草鱼脂肪氧化和挥发性风味成分的影响[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(21):1−10. [GU S Q, ZHOU H X, ZHENG H M, et al. Effects of different drying methods on lipid oxidation and volatile flavor components of cured grass carp[J]. Food Science,2018,39(21):1−10. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201821001 [18] WANG Z, HE Z, GAN X, et al. Interrelationship among ferrous myoglobin, lipid and protein oxidations in rabbit meat during refrigerated and super chilled storage[J]. Meat Science,2018,146:131−139. doi: 10.1016/j.meatsci.2018.08.006
[19] 顾赛麒, 鲍嵘斌, 冯媛, 等. 肉类和水产制品脂质光氧化机制及其影响因素[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(24):271−278. [GU S Q, BAO R B, FENG Y, et al. Mechanism and influencing factors of lipid photooxidation in meat and aquatic products[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(24):271−278. [20] 顾赛麒, 唐锦晶, 周绪霞, 等. 腌腊鱼传统日晒干制过程中品质变化与香气形成[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(17):36−44. [GU S Q, TANG J J, ZHOU X X, et al. Quality change and aroma formation in cured fish during traditional sun drying processing[J]. Food Science,2019,40(17):36−44. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20180716-201 [21] 高海, 蔡欢欢, 朱志伟. 光照和温度对草鱼和三文鱼鱼肉贮藏品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(15):244−249. [GAO H, CAI H H, ZHU Z W. Comparative study of effects of light exposure and storage temperature on the quality of grass carp fillets and salmon fillets[J]. Food Science,2017,38(15):244−249. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201715039 [22] CHEN J, LI J, LIU X, et al. Effects of dietary fat saturation level on growth performance, carcass traits, blood lipid parameters, tissue fatty acid composition and meat quality of finishing pigs[J]. Animal Bioscience,2021,34(5):895−903. doi: 10.5713/ajas.20.0247
[23] NAIN C W, BERDAL G, THAO P T P, et al. Green tea extract enhances the oxidative stability of DHA-rich oil[J]. Antioxidants (Basel),2021,10(6):982. doi: 10.3390/antiox10060982
[24] 刘梦, 史智佳, 杨震. 不同热加工温度对牛肉干脂肪酸及脂肪氧化的影响[J]. 肉类研究,2019,33(2):1−6. [LIU M, SHI Z J, YANG Z. Effects of different thermal processing temperatures on fatty acid composition and fat oxidation of beef jerky[J]. Meat Research,2019,33(2):1−6. doi: 10.7506/rlyj1001-8123-20181228-242 [25] 刘昌华. 鲈鱼风干成熟工艺及其脂质分解氧化和风味品质特性研究[D]. 南京: 南京农业大学, 2012. LIU C H. Study on drying-raping process of perches, lipolysis-lipid oxidation and flavor character during processing[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing Agricultural University, 2012.
[26] BATEN M A, WON N E, MOHIBBULLAH M, et al. Effect of hot smoking treatment in improving sensory and physicochemical properties of processed Japanese Spanish mackerel Scomberomorus niphonius[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2020,8(7):3957−3968.
[27] WU S, YANG J, DONG H, et al. Key aroma compounds of Chinese dry-cured Spanish mackerel (Scomberomorus niphonius) and their potential metabolic mechanisms[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,342:128381. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2020.128381
[28] CAO J, JIANG X, CHEN Q, et al. Oxidative stabilities of olive and camellia oils: Possible mechanism of aldehydes formation in oleic acid triglyceride at high temperature[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2020,118:108858. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108858
[29] 雷乙, 陈竟豪, 涂金金, 等. 鱼肉加工过程特征气味物质变化研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(15):201−210. [LEI Y, CHEN J H, TU J J, et al. Research progress on changes of characteristic odor substances in fish processing[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(15):201−210. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2020.15.034 [30] KIM J Y, KIM M J, LEE J. Role of moisture on the lipid oxidation determined by D(2)O in a linoleic acid model system[J]. Food Chemistry,2014,146:134−40. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.09.025
[31] GIMÉNEZ B, GÓMEZ-GUILLÉN M C, PÉREZ-MATEOS M, et al. Evaluation of lipid oxidation in horse mackerel patties covered with borage-containing film during frozen storage[J]. Food Chemistry,2011,124(4):1393−1403. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2010.07.097
[32] 李松林, 蒋长兴, 聂凌鸿, 等. 风鸡腌制和风干过程中挥发性成分的变化[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2015,41(3):191−198. [LI S L, JIANG C X, NIE L H, et al. Changes of volatile compounds during curing and drying of air-dried chicken[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2015,41(3):191−198. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.201503034 [33] LIU Y, WAN Z, YOHANNES K W, et al. Functional characteristics of lactobacillus and yeast single starter cultures in the ripening process of dry fermented sausage[J]. Frontier Microbiology,2021,11:611260. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2020.611260
[34] WANG M Q, MA W J, SHI J, et al. Characterization of the key aroma compounds in Longjing tea using stir bar sorptive extraction (SBSE) combined with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS), gas chromatography-olfactometry (GC-O), odor activity value (OAV), and aroma recombination[J]. Food Research International,2020,130:108908. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.108908
[35] GUO H, CHEN C, LEE D J. Nitrogen and sulfur metabolisms of Pseudomonas sp. C27 under mixotrophic growth condition[J]. Bioresource Technology,2019,293:122169. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2019.122169
-
期刊类型引用(9)
1. 向芳. 食品减盐策略研究进展. 食品与发酵工业. 2024(06): 350-358 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 赵亚丽,张香美,卢涵,杨贝,文港. 传统腌腊肉制品质量安全管理研究. 食品与机械. 2023(01): 55-60+156 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 刘东,夏金龙. 低钠酱鹿肉的配方优化及贮藏期特性研究. 中国调味品. 2023(03): 67-74 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李智,牛超杰,邹爱军,常超. 肉制品加工减盐技术及其应用. 武汉轻工大学学报. 2023(04): 31-38 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张彦慧,郑红霞,刘楠,高彦祥,毛立科. 胶体结构设计在减盐食品中的应用. 食品科学. 2022(01): 213-222 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 吕广英,孔君,郑润愽. 一种低钠休闲香肠的加工技术研究. 肉类工业. 2022(05): 16-19 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 芮李彤,李海静,张婷婷,郭琦,李子豪,夏秀芳. 食盐对肉制品品质形成的作用及减盐技术研究进展. 肉类研究. 2022(07): 61-67 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 孙悦,李震,王鹏,徐幸莲. 响应面优化减盐鸡肉松热加工工艺及品质测定. 食品工业科技. 2022(20): 263-273 .  本站查看
本站查看
9. 周平萍. 咸味剂咸度分析研究方法进展. 现代食品. 2022(17): 23-26+37 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)






 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



