Effects of Sealed Yellowing on Aroma Characteristic and Key Aroma Compounds of Yellow Tea
-
摘要: 为明确闷黄对黄茶香气品质的影响,通过感官审评、顶空固相微萃取结合气相色谱-质谱联用技术和多元统计分析对3个茶树品种所制黄茶(有闷黄)和对照样(无闷黄)的香气特征和挥发性化合物组成开展研究。结果表明,与对照样相比,黄茶具有甜香风味。同时,黄茶中挥发性组分总含量是对照样的1.09~1.44倍,且醇类和烃类占比达到65.88%~76.93%。对挥发性化合物的主成分分析和层次聚类分析结果显示化合物组成体现了香气特征差异,进而可筛选出35种特征香气化合物(P<0.01)。正交偏最小二乘法判别分析进一步明确了闷黄影响的关键香气化合物14种(VIP≥1),其中具有花香、果香和甜香的α-松油醇、芳樟醇、γ-松油烯、柠檬烯、松油烯、苯乙酸甲酯、2,2,6-三甲基环己酮、4-氧代异佛尔酮和邻-异丙基苯在闷黄所制黄茶中含量明显高于对照样,这些化合物对黄茶呈现甜香的香气特征起到关键作用。Abstract: To illustrate effects of sealed yellowing on the aroma quality of tea samples, sensory evaluation, headspace solid-phase microextraction combined with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and multivariate statistical analysis were used to study the aroma characteristics and volatile compounds of yellow teas (with sealed yellowing) and control samples (without sealed yellowing) manufactured from three tea varieties. The result showed that yellow teas had sweet flavor compared with control samples. Meanwhile, the total content of volatile components in the yellow tea was 1.09~1.44 times that of the control sample, and the proportion of alcohols and hydrocarbons accounted for 65.88%~76.93%. The result of principal component analysis and hierarchical cluster analysis of volatile compounds indicated that the composition of compounds reflected the difference of aroma characteristics, and then 35 characteristic aroma compounds were screened (P<0.01). Furthermore, orthogonal partial least squares discriminant analysis identified 14 key aroma compounds affected by sealed yellowing (VIP≥1). Among them, the contents of α-terpineol, linalool, γ-terpinene, limonene, terpinene, methyl phenylacetate, 2,2,6-trimethylcycloheptane, 4-oxoisophorone and o-cymene, with floral, fruity and sweet aroma, were significantly higher in yellow teas than in control samples. These compounds were considered to be responsible for the sweet aroma characteristic of yellow tea.
-
茶是世界上最受欢迎的饮料之一,由茶树鲜嫩芽叶加工而成[1]。根据加工工艺和品质特征的不同,茶叶分为六大类。香气是茶叶的重要品质之一,不同茶类具有不同的香气特征[2-3],其感官表现由挥发性化合物的组成与含量决定[4],主要受茶树品种、栽培环境和加工工艺的影响[5-7]。目前已分离鉴定出了700多种与茶叶香气有关的成分,包括烃类、醇类、醛类和酯类等[8],这为茶叶香气特征的研究奠定了坚实的基础。
黄茶是六大茶类之一,特有的闷黄工序赋予了黄茶三黄(干茶黄、汤色黄、叶底黄)的特征[9-10]。闷黄使得茶叶内含物质在高温高湿条件下发生化学变化,经过干燥后,形成独特的黄茶香气品质[11]。雷玉萍等[12]取“御金香”鲜叶为原料,发现与不闷黄对照样相比,闷黄加工后的茶叶呈嫩栗香,甜香浓郁。文帅等[13]报道以金萱品种所制黄茶呈现锅巴香(干坯闷黄)和花香(湿坯闷黄)。张厅等[14]发现随着闷黄时间的增加,蒙顶黄芽的香型由清香转为甜香、火功香。张娇等[9]对比闷黄工序前后的茶叶样品,结果表明闷黄前样品清香较低,闷黄结束后清香带甜香。可见闷黄对黄茶香气品质的形成至关重要。
近年来,随着气相色谱—质谱联用(gas chromatography-mass spectrometry,GC-MS)技术的发展[15],利用顶空固相微萃取结合GC-MS已从黄小茶中检测出100多种挥发性化合物[16]。Shi等[17]通过搅拌棒吸附萃取结合GC-MS从15种市售黄茶中检测到74种化合物,其中醇类和酯类占比52.44%。宋玉欣等[18]从3个茶树品种黄茶中检测出42种香气物质,且均以醇类和醛类为主,共有的香气成分包括芳樟醇、正戊醇、庚醛等。然而现有研究集中在闷黄对黄茶香气特征的影响以及成品黄茶挥发性化合物分析方面,有关闷黄工序对挥发性化合物的影响尚不清楚。闷黄-香气特征-挥发性化合物之间的关系未被完全揭示,限制了对黄茶香气品质的完整认知。
为深入分析闷黄对黄茶香气特征及关键香气化合物的影响,本研究选取英红九号、茶树新品系YPX和金萱3个茶树品种为研究对象,按照有无闷黄工序分别加工黄茶和对照样,通过感官审评确定其香气特征;采用GC-MS技术进行挥发性有机化合物检测,结合多元统计分析,筛选黄茶呈香特征的关键香气化合物,分析闷黄工序对黄茶香气化合物组成的影响,明确闷黄-香气特征-挥发性香气化合物之间的相关性,为黄茶的工艺改进和品质定向调控提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
茶树鲜叶一芽二叶 广东省农业科学院茶叶研究所英德基地,茶树品种为英红九号(YJ)、金萱(JX)和茶树新品系(YPX),采摘时间为2019年6月;C7~C30饱和正构烷烃、癸酸乙酯 色谱纯,德国Meker公司。
YS-6CST-90I型燃气茶叶杀青机、YS-6CRT-40型茶叶揉捻机 福建省泉州裕盛机械有限公司;XS-6CHZ-9B型茶叶烘焙机 福建省安溪祥山机械有限公司;DVB/CarbonWR/PDMS Smart SPME Arrow萃取头(1.1 mm,120/20 μm)、多功能自动进样系统RTC120 瑞士CTC Analytics AG公司;DB-5MS毛细管色谱柱(60 m×0.32 mm,0.25 μm)、8890-5977 B气相色谱-质谱联用仪 美国Agilent公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 黄茶和对照样加工工艺
根据前期制茶研究基础形成黄茶加工工艺,并将同一品种茶树鲜叶分别制成黄茶(YT)和对照样(CK)。
黄茶工艺流程:摊青14 h(摊青叶含水量67%~70%)→260 ℃杀青6~7 min→摊凉30 min→揉捻→80 ℃闷堆6 h→90 ℃烘干2 h;
对照样品工艺流程:摊青14 h(摊青叶含水量67%~70%)→260 ℃杀青6~7 min→摊凉30 min→揉捻→90 ℃烘干2 h。
黄茶的闷黄采用湿坯闷黄,将揉捻后的在制叶完全密封置于80 ℃烘焙机中闷堆6 h;摊青、杀青、摊凉、揉捻和烘干加工的参数和环境条件与对照样相同。英红九号、YPX和金萱加工的黄茶分别记为YJ_YT、YPX_YT和JX_YT,英红九号、YPX和金萱加工的对照样分别记为YJ_CK、YPX_CK和JX_CK。
1.2.2 香气感官审评
参照国标GB/T 23776-2018《茶叶感官审评方法》进行茶叶香气感官审评。
1.2.3 挥发性物质提取
采用顶空固相微萃取的方法对茶叶挥发性物质进行提取。常温下将加工的6种茶叶样品磨成粉末,称取1.000±0.005 g样品于20 mL顶空瓶中,测定前加入2 μL浓度为100 μg/mL的癸酸乙酯正己烷溶液作为内标。萃取时将顶空瓶置于加热振荡器中,于60 ℃下平衡5 min;随后使用萃取头于60 ℃下萃取40 min。进样时萃取头在GC-MS进样口处解吸附2 min。
1.2.4 挥发性物质检测
气相色谱条件:进样口温度为250 ℃;采用不分流进样模式;氦气(99.999%)作为载气,流量为1 mL/min;升温程序设置为初始柱温35 ℃,保持2 min,以5 ℃/min升温至250 ℃,不保持。质谱条件:采用电子轰击离子源,电子能量为70 eV;传输线温度和离子源温度为230 ℃,四极杆温度为150 ℃;运行全扫描模式,扫描质荷比范围m/z 35~450;溶剂延迟8 min。
1.2.5 定性定量分析
由气相色谱-质谱联用仪检测所得的原始数据利用Masshunter工作站中的未知物分析软件(Unknowns Analysis,Version 10.0,美国Agilent公司)进行处理。定性分析是将原始数据与NIST17库中数据比对,以质谱结果匹配度得分大于70.0且线性保留指数(linear retention index,LRI)偏差在10个单位内为依据确定化合物。化合物的LRI根据Babushok等报道的公式计算,具体如公式(1):
LRI=100×n+100×tx−tntn+1−tn (1) 式中:
tx、tn和tn+1 分别为待测物质、含有n个碳原子正构烷烃和含有n+1个碳原子正构烷烃的保留时间(min)。化合物的相对含量,则通过公式(2)由癸酸乙酯内标校正求得:
相对含量(ng/g)=化合物峰面积内标峰面积×内标质量(ng)样品质量(g) (2) 1.3 数据处理
每个样品的重复取样3次检测挥发性有机物,数据定性定量,利用Excel计算相对含量、平均值和标准差,并做表格。采用TBtools绘制Venn图和聚类热图,Origin软件绘制柱形图[19]。利用Metaboanalyst 5.0和R语言对数据进行分析并作图[20-21]。前处理包括:a.以每组化合物最小值的1/5填充数据组中的缺失值;b.将数据进行对数变换和归一化。通过主成分分析(principle component analysis,PCA)和层次聚类分析(hierarchical cluster analysis,HCA)明确化合物和香气特征之间的关联,层次聚类分析中选用欧氏距离(euclidian distance)函数确定样品间距,以全连接(complete-linkage)算法测量类间距离。单因素方差分析(one-way analysis of variance,one-way ANOVA)结合最小显著差数,以校正P值小于0.01为标准,筛选差异极显著的特征香气化合物。正交偏最小二乘法判别分析(orthogonal partial least squares-discriminant analysis,OPLS-DA)筛选组间差异化合物。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 闷黄对黄茶香气特征的影响
为明确闷黄对黄茶香气特征的影响,对不同茶树品种所制的黄茶和对照样进行了感官审评,香气感官品质如表1所示。结果显示,同一茶树品种所制黄茶比对照样甜香特征更突出,表明闷黄工序有利于甜香品质的形成;不同茶树品种所制黄茶甜香程度不同,表明甜香特征不仅受闷黄的影响,还受茶树品种的影响。3个茶树品种所制黄茶均具甜香香气,与蒙顶黄芽和福鼎大白所制黄茶的甜香香型相似[22-24],而无闷黄的对照样与已报道的清香型绿茶特征相近[25-27],这表明闷黄可以使3个茶树品种黄茶带有甜香的香气特征。
表 1 不同茶树品种所制黄茶和对照样的香气感官品质Table 1. The aroma sensory quality of yellow tea and control sample manufactured from different tea varieties序号 茶样名称 香气特征 1 YJ_YT 甜香明显 2 YPX_YT 甜香明显 3 JX_YT 甜香 4 YJ_CK 清香带甜 5 YPX_CK 清香带微甜 6 JX_CK 清香带微甜 2.2 闷黄对黄茶香气组分的影响
为进一步研究闷黄对黄茶香气组分的影响,采用顶空固相微萃取结合GC-MS技术分析了黄茶和对照样的挥发性化合物。结果表明,YJ、YPX和JX这3个品种茶样中共检测到50种香气化合物(表2),包含醇类13种,醛类11种,烃类10种,酮类8种,酯类4种,以及其他类型化合物4种。
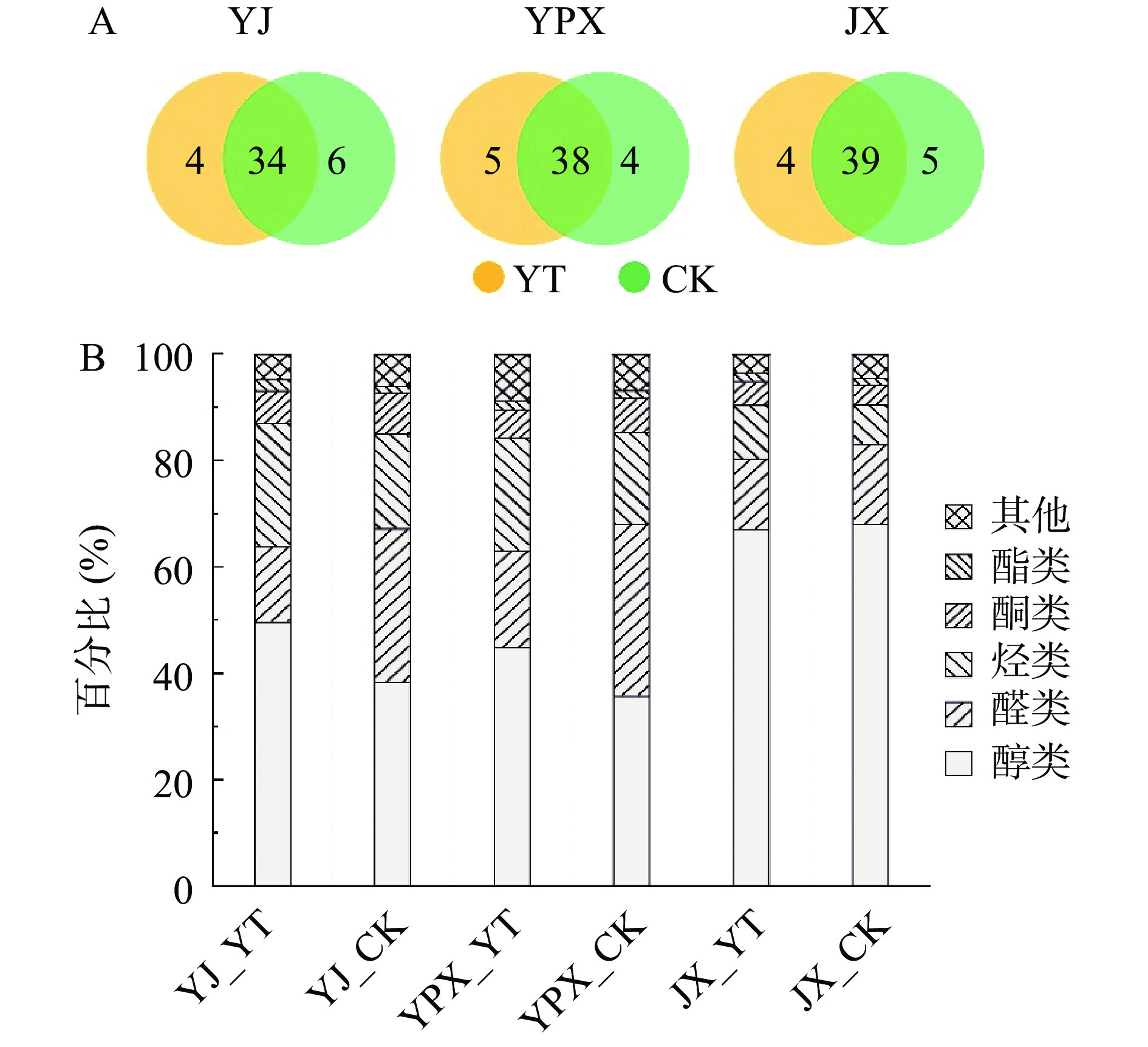
表 2 不同茶树品种所制黄茶和对照样的香气组分Table 2. The aroma components contained in yellow tea and control sample manufactured from different tea varieties编号 化合物 保留指数 匹配度 相对含量(ng/g) 谱库数值 实验数值 YJ_YT YPX_YT JX_YT YJ_CK YPX_CK JX_CK 醇类 1 1-戊醇 765 763 83 49.07±17.86 69.87±16.40 155.20±28.71 79.63±12.65 108.40±14.99 109.37±25.72 2 芳樟醇氧化物Ⅰ 1074 1072 92 31.33±1.27 37.73±5.05 453.13±38.57 27.67±3.52 37.80±2.81 358.47±27.22 3 芳樟醇氧化物Ⅱ 1086 1088 89 − − 352.55±34.01 − − 246.63±21.77 4 芳樟醇 1099 1098 97 614.60±18.33 415.17±41.23 818.03±38.27 393.63±36.35 205.10±10.15 341.53±18.46 5 脱氢芳樟醇 1108 1102 95 74.03±2.32 301.87±20.67 1190.93±29.99 55.80±4.33 297.23±13.45 842.93±25.65 6 苯乙醇 1121 1112 92 − 63.50±6.68 145.43±14.63 − 65.20±1.44 98.77±2.40 7 二氢芳樟醇 1136 1133 84 2.23±0.12 − − − − − 8 芳樟醇氧化物Ⅲ 1173 1171 93 5.57±0.15 16.07±1.14 139.40±5.80 6.53±0.71 24.70±0.69 135.70±4.03 9 芳樟醇氧化物Ⅳ 1174 1174 95 16.13±0.76 25.13±1.68 133.33±4.23 19.83±1.57 36.93±1.33 140.40±3.85 10 4-萜烯醇 1175 1184 88 21.13±0.49 23.63±1.60 − 12.67±1.81 − − 11 2,6-二甲基-3,7-辛二烯-2,6-二醇 1189 1185 96 − − 101.00±2.72 − 32.10±0.44 181.37±0.64 12 α-松油醇 1190 1197 89 159.73±4.85 120.83±6.30 141.87±4.20 34.63±1.63 29.33±2.05 18.63±2.00 13 香叶醇 1255 1246 79 37.83±1.88 26.77±0.67 − 8.05±0.64 − 8.97±5.77 该类化合物总量 1011.67±43.11 1100.57±90.18 3513.37±66.63 635.77±44.36 800.67±52.56 2482.77±116.85 醛类 14 正己醛 801 799 92 − 39.83±4.83 77.90±30.35 17.85±8.41 52.23±3.48 33.30±0.57 15 3-糠醛 832 829 85 − − 40.90±25.03 27.33±4.65 37.80±0.26 32.57±6.75 16 庚醛 901 900 80 − 12.50±3.08 25.87±7.26 5.50±1.99 21.17±0.71 12.47±0.47 17 (E)-2-庚烯醛 964 955 90 11.13±0.81 20.77±5.03 39.40±12.42 19.90±8.96 26.83±1.81 23.37±2.35 18 5-甲基呋喃醛 962 959 81 − − − 4.33±0.35 7.93±0.50 10.27±0.57 19 苯甲醛 961 963 97 114.23±5.17 134.90±8.92 156.23±10.10 195.97±20.21 278.43±5.01 194.43±11.32 20 (E,E)-2,4-庚二烯醛 1012 1010 91 28.20±0.46 81.97±5.00 113.40±5.34 52.03±4.55 102.63±1.44 70.33±5.21 21 苯乙醛 1044 1044 95 55.47±4.40 65.87±7.50 102.87±3.86 69.97±11.57 95.43±3.55 76.70±14.44 22 藏红花醛 1201 1201 95 17.40±0.62 17.90±1.85 41.60±3.39 24.50±2.27 20.73±1.20 28.30±1.25 23 β-环柠檬醛 1221 1222 94 62.97±4.38 62.43±2.73 103.63±1.12 61.17±6.07 66.33±1.69 64.40±2.41 24 β-环高柠檬醛 1254 1259 81 − 11.50±4.61 13.10±3.29 6.33±1.72 13.00±1.71 11.67±0.59 该类化合物总量 289.40±6.19 447.67±40.13 701.27±91.24 478.93±73.10 722.53±19.37 546.70±13.49 烃类 25 月桂烯 991 989 90 84.67±2.53 60.53±10.46 69.93±18.66 54.13±12.33 42.07±3.32 − 26 松油烯 1018 1019 89 17.37±1.06 14.57±4.55 9.20±0.52 9.73±1.04 10.47±0.76 6.03±0.76 27 邻-异丙基苯 1023 1027 94 33.87±1.19 53.37±10.16 60.97±7.00 23.60±6.01 36.43±2.55 33.67±2.41 28 柠檬烯 1030 1032 82 268.83±20.86 232.07±55.42 221.87±34.96 165.03±33.34 150.03±17.99 106.97±15.63 29 γ-松油烯 1061 1060 89 38.90±2.54 40.70±8.91 51.37±9.11 24.33±5.26 29.03±2.84 24.20±2.40 30 别罗勒烯 1131 1127 90 17.23±1.44 11.80±2.52 13.43±0.98 9.37±1.61 11.33±4.90 11.40±0.36 31 β-波旁烯 1384 1391 86 5.27±0.12 7.60±0.20 10.40±0.20 4.33±0.15 19.17±3.61 18.23±1.30 32 δ-杜松烯 1524 1522 93 5.77±0.35 63.37±1.55 62.17±0.78 5.03±0.25 64.70±2.65 50.73±2.56 33 (E)-菖蒲烯 1529 1526 87 1.25±0.07 23.20±1.08 17.50±0.69 − 18.60±0.70 13.87±0.81 34 α-二去氢菖蒲烯 1542 1548 85 − 10.37±0.57 8.53±0.15 − 4.47±0.15 3.67±0.12 该类化合物总量 472.73±28.36 517.57±89.77 525.37±63.58 295.57±59.72 386.30±31.86 268.77±21.27 酮类 35 2,2,6-三甲基环己酮 1035 1037 86 49.60±3.47 35.03±9.58 71.33±10.13 33.93±6.81 27.87±1.36 29.43±3.04 36 3,5-辛二烯-2-酮 1073 1067 87 35.43±3.45 51.07±5.27 74.73±3.93 42.27±8.06 57.23±3.26 50.70±5.12 37 异佛尔酮 1119 1123 83 − − 11.87±0.78 − − − 38 4-氧代异佛尔酮 1145 1144 79 4.83±0.25 8.90±0.57 14.70±1.20 3.95±0.21 − − 39 α-紫罗酮 1427 1422 78 4.87±0.32 4.63±0.15 − 5.47±0.32 5.70±0.20 4.37±0.32 40 橙花基丙酮 1435 1443 93 9.90±0.40 11.63±0.76 14.17±0.50 13.03±0.12 14.93±0.49 14.77±0.74 41 β-紫罗酮 1485 1479 91 15.47±0.98 21.50±1.31 35.87±1.50 20.93±0.70 29.43±1.72 27.80±0.82 42 5,6-环氧-β-紫罗酮 1488 1482 74 5.35±0.07 − 12.60±0.46 9.33±0.32 11.27±0.75 10.83±0.15 该类化合物总量 123.67±7.40 129.80±17.91 235.27±12.33 127.60±13.72 146.43±6.40 137.90±8.52 酯类 43 苯乙酸甲酯 1178 1174 90 22.63±0.97 11.27±2.35 13.15±0.49 − − − 44 水杨酸甲酯 1192 1194 89 − 4.20±0.42 22.97±0.74 − 3.37±0.35 13.37±0.45 45 2-甲氨基苯甲酸甲酯 1405 1408 77 1.60±0.10 2.47±0.15 − 1.27±0.12 2.40±0.10 2.35±0.07 46 二氢猕猴桃内酯 1530 1536 97 20.87±0.23 26.30±1.57 57.30±4.60 19.97±4.45 25.57±1.15 28.97±2.73 该类化合物总量 45.10±1.11 42.83±2.22 89.03±9.63 21.23±4.45 31.33±1.54 43.90±1.40 其他 47 2-戊基呋喃 993 990 85 − 33.23±5.49 − 34.90±3.26 59.77±5.35 44.23±2.84 48 2-乙酰基吡咯 1063 1058 92 57.80±1.15 48.43±2.54 72.00±3.83 52.03±4.25 22.83±0.97 56.33±1.89 49 苯乙腈 1143 1137 98 35.77±1.21 133.53±5.71 99.70±4.00 14.83±0.78 73.67±2.42 63.43±1.90 50 茶螺烷 1302 1305 80 3.63±0.15 3.80±0.57 13.97±0.57 − − 6.23±0.23 该类化合物总量 97.20±2.25 217.73±14.27 185.67±7.88 101.77±7.48 156.27±7.50 170.23±5.36 香气化合物总量 2039.77±65.27 2456.17±243.91 5249.97±123.07 1660.87±201.45 2243.53±86.83 3650.27±165.09 注:“−”表示化合物在此样品中检出频次≤1/3。 由Venn图(图1A)可以看出同一品种加工的黄茶和对照样,其香气组成存在差异。YJ_YT和YJ_CK各检出38和40种香气物质,黄茶特有组分4种(二氢芳樟醇、(E)-菖蒲烯、苯乙酸甲酯和茶螺烷),对照样特有组分6种(正己醛、3-糠醛、庚醛、5-甲基呋喃醛、β-环高柠檬醛和2-戊基呋喃)。YPX_YT和YPX_CK各检出香气物质43和42种,黄茶特有香气物质5种(4-萜烯醇、香叶醇、4-氧代异佛尔酮、苯乙酸甲酯和茶螺烷),对照样特有香气物质4种(2,6-二甲基-3,7-辛二烯-2,6-二醇、3-糠醛、5-甲基呋喃醛和5,6-环氧-β-紫罗兰酮)。JX_YT和JX_CK各检出香气物质43和44种,黄茶特有香气物质4种(月桂烯、异佛尔酮、4-氧代异佛尔酮和苯乙酸甲酯),对照样特有香气5种(香叶醇、5-甲基呋喃醛、α-紫罗兰酮、2-甲氨基苯甲酸甲酯和2-戊基呋喃)。苯乙酸甲酯是3个品种黄茶特有组分的共性化合物,YJ_YT和YPX_YT特有组分均包含茶螺烷,YPX_YT和JX_YT特有组分均包含4-氧代异佛尔酮,表明闷黄会形成黄茶特有的香气共性物质。同时闷黄导致的特有组分的形成也会受到茶树品种的影响。
除了特有组分上的差异,黄茶香气组分总含量均高于同一品种所制对照样,是对照样的1.09~1.44倍(表2),其中JX_YT所含的香气组分总含量最高(5249.97±123.07 ng/g),是JX_CK的1.44倍。与此发现一致的是,龙井、梅占两个茶树品种加工的黄茶所含挥发性化合物总含量高于其在同一品种无闷黄工序的绿茶中的总含量[28-29]。各类型香气物质的含量占比也有所不同,尤其是醇类、醛类和烃类物质的含量占比(图1B)。YJ_YT中醇类、醛类和烃类占比分别为49.60%、14.19%和23.18%,YJ_CK中则为38.28%、28.84%和17.80%;YPX_YT中醇类、醛类和烃类占比分别为44.81%、18.23%和21.07%,YPX_CK中则为35.69%、32.21%和17.22%;JX_YT中醇类、醛类和烃类的占比分别为66.92%、13.36%和10.01%,在JX_CK中则分别为68.02%、14.98%和7.36%。可见6种成品茶香气化合物均以醇类为主,烃类化合物占比在黄茶中高于同一品种对照样,醛类物质占比在黄茶中低于同一品种对照样。JX_YT与其他两种黄茶的香气组分分布略有差异,可能与茶树品种有关。张厅等[14]发现中茶302号加工的蒙顶黄芽茶香气组成以醇类为主,占比47.35%~52.13%,其次是烃类化合物,与本研究结果吻合。速晓娟等[30]对福鼎大白等茶树品种加工的蒙顶黄芽香气组分分析表明其中醇类最为丰富,占总挥发性物质的31.69%。蒋容港等[31]对不同原料等级黄茶香气的分析表明,芽型黄茶中醇类和烃类含量相近,且为最高;芽叶型黄茶中醇类含量最高,烃类次之,醇类含量约为烃类的两倍。可见,有闷黄工序的芽叶型黄茶香气组分中醇类和烃类贡献较大,但实际占比会受茶树品种的影响。
此外,从表2可以看出黄茶中含量较高的醇类主要为萜烯醇,烃类多为含碳数10的同分异构体和含碳数15的萜烯类。现有研究报道,加工过程中香气的形成主要有四种途径:类胡萝卜素的氧化降解、脂肪酸降解、糖苷水解和美拉德反应[32]。萜烯醇和萜烯类化合物与糖苷物质的水解相关,醛类物质源于脂肪酸和氨基酸等物质的代谢,酮类化合物主要来自类胡萝卜素的降解[32-35]。本研究的结果从侧面反映出闷黄工序有利于糖苷类水解释放萜烯醇和萜烯类化合物[11,17,36]。
2.3 闷黄影响的特征香气化合物
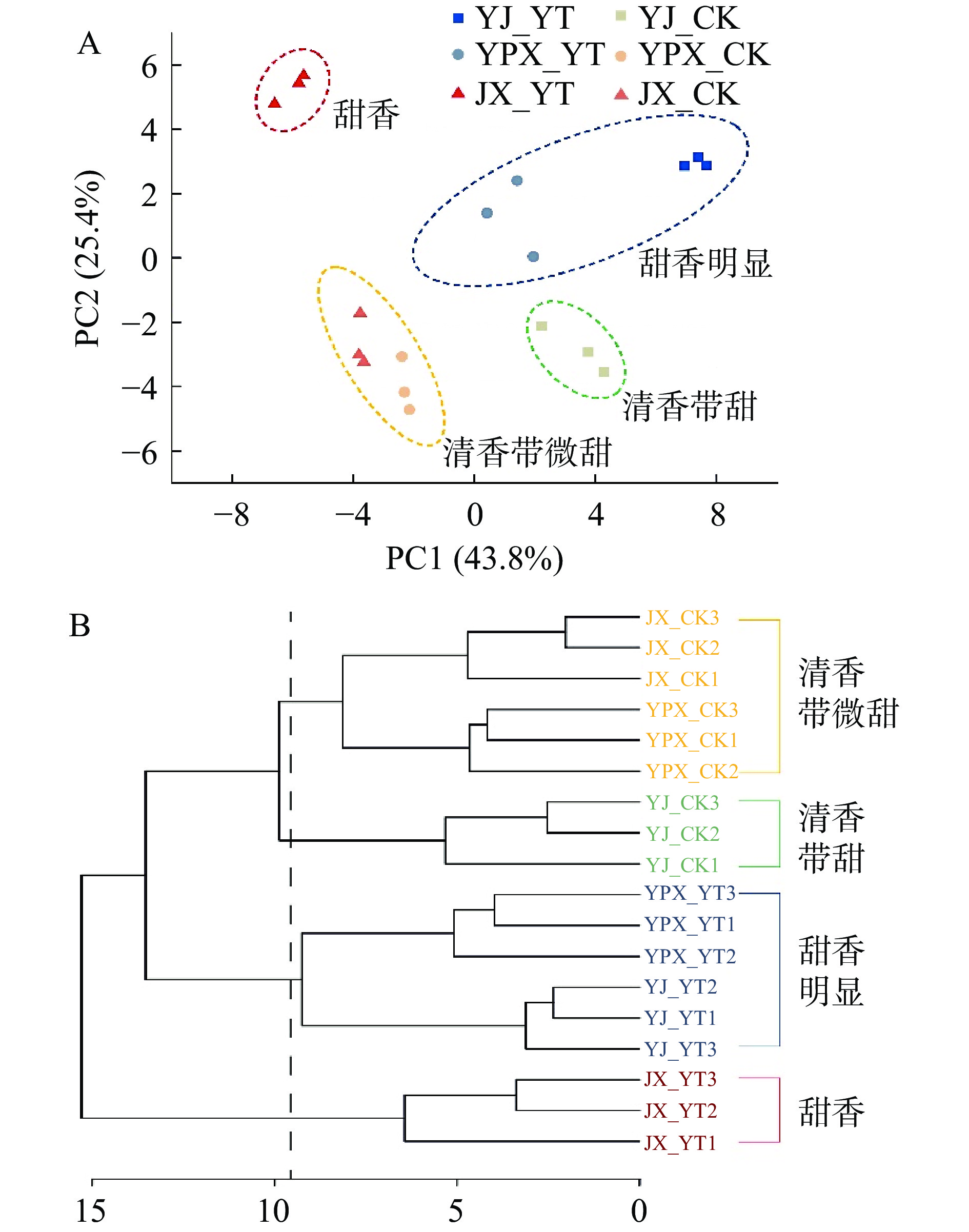
感官审评结果表明有无闷黄工序所制成品茶之间香气特征存在明显差异,为检验挥发性化合物组成能否体现香气特征差异,采用无监督的主成分分析和层次聚类分析对成品茶进行分类,并将结果与香气感官审评分类结果进行对比。将50种挥发性有机物的相对含量水平作为变量进行主成分分析,发现当选取2个主成分时,6种样品在PCA得分图的分布已有明显区别,累计方差贡献率为69.2%。由图2A可知,6种样品分布在PCA得分图的4个区域,YPX_YT和YJ_YT在PC1和PC2轴的正向,JX_YT在PC1轴的负向和PC2轴的正向,YJ_CK在PC1轴的正向和PC2轴的负向,JX_CK和YPX_CK在PC1和PC2轴的负向,这与感官审评香气特征分类一致。
以香气化合物为变量,对茶叶样品进行层次聚类分析。如图2B所示,当聚类距离为9.5左右时,这些样品可以被分为4类,分别为:JX_CK和YPX_CK、YJ_CK、YPX_YT和YJ_YT、JX_YT,与感官审评的分组一致。按照距离从近到远来看,JX_CK和YPX_CK首先聚成一类,说明其化合物信息的相似度高,与它们在PCA的集中分布一致,同时与感官审评上表现为同一香气类型相对应。在15的距离水平上,只有JX_YT被分为一组,说明与其他样品化合物组成差异大,与PCA图中结论相同。基于香气化合物的PCA和HCA分析得到的成品茶分类结果与香气感官审评分组结果一致,说明这些香气化合物组成代表了香气特征的差异。
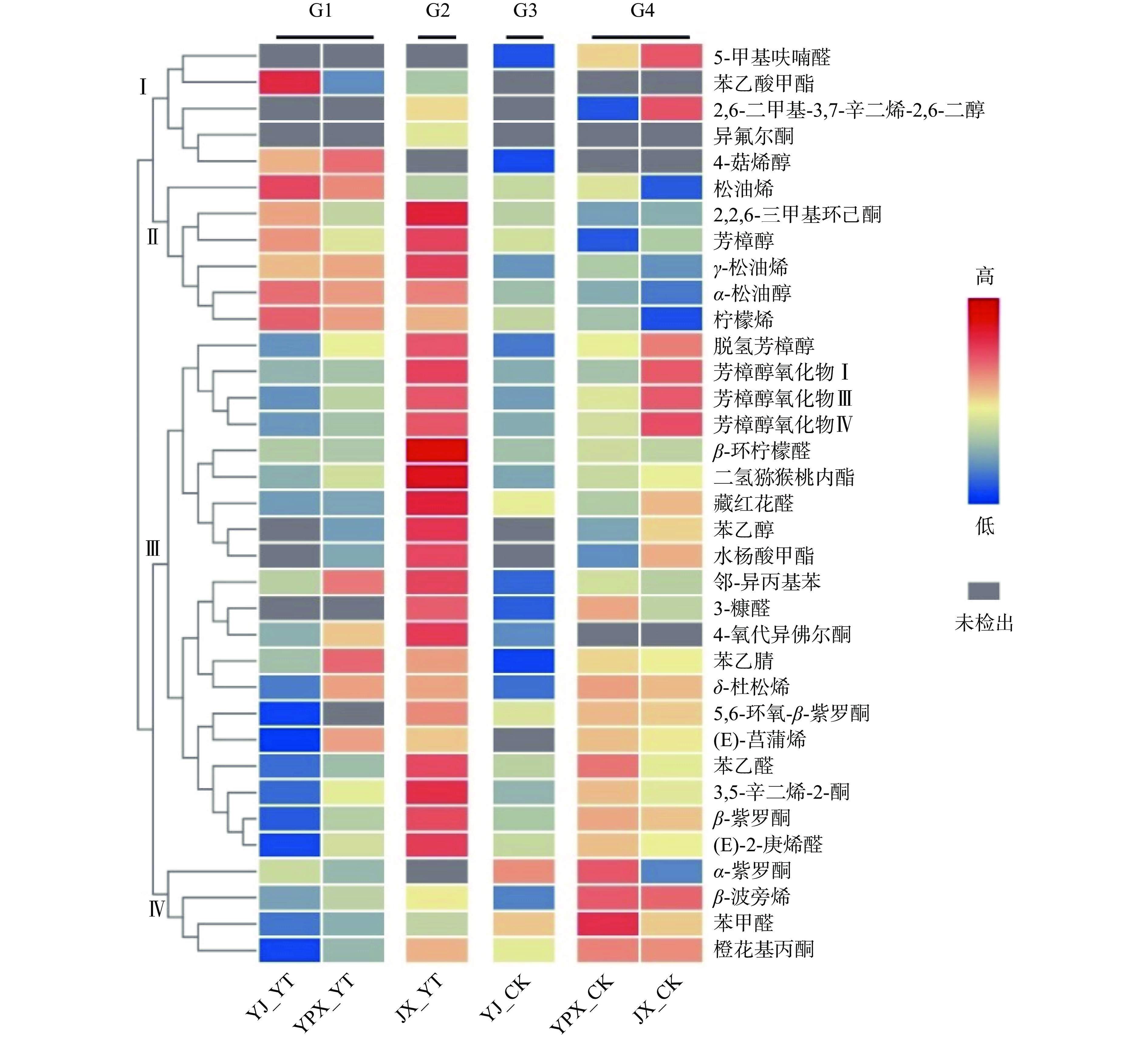
基于挥发性化合物与香气特征的关系,可筛选代表不同香气特征的特征香气化合物。将成品茶以香气特征分为4组,对所含的50种挥发性化合物进行单因素方差分析,以极显著性差异水平0.01(P<0.01)为标准,筛选出35种组间差异性极显著的化合物。基于其相对含量(对数变换和归一化后值)绘制聚类热图,结果如图3所示。特征香气化合物被分为4类,相对含量的高低以不同颜色显示,灰色表示该化合物未在茶样中检出;4组呈现不同香气特征的样品记为G1(甜香明显)、G2(甜香)、G3(清香带甜)和G4(清香带微甜)。
第Ⅰ类化合物仅在部分茶样中检出,代表了不同香气特征茶样中的特有组分。如5-甲基呋喃醛仅在G3、G4样品组中检出;苯乙酸甲酯具有甜香[37],仅在G1、G2样品组中检出,这2种化合物可能是导致茶样在有无闷黄加工后香气不同的关键化合物。
第Ⅱ类化合物是4种香气特征茶样共有的化合物,包括松油烯(柠檬香)、2,2,6-三甲基环己酮(辛辣、蜂蜜和柑橘香)、芳樟醇(花香)、γ-松油烯(柠檬和松脂香)、α-松油醇(花香和木香)和柠檬烯(柠檬香)[38-39]。除松油烯的相对含量在G1样品组中高于G2、G3、G4,其他化合物的相对含量均表现为在G1、G2茶样中高于G3、G4,并且这些化合物在霍山黄大茶、君山银针和蒙顶黄芽茶等黄茶中都被检测到,说明可能是影响香型转变的重要化合物[17,22,40]。Shi等[17]通过气相色谱-嗅闻法鉴定了黄茶中的关键香气化合物,结果显示芳樟醇促进了黄茶良好香气的形成。柠檬烯被报道是蒙顶黄芽茶甜香的代表物质[14,39],吴函殷等[41]的研究表明随着单丛茶蜜香香型的增强,柠檬烯的相对含量也明显增加,这些结果证实了柠檬烯和甜香之间的关联。
第Ⅲ类化合物在4组香气特征的茶样中含量高低差距大,大部分化合物的含量在G2样品组中最高,其次为G4,而在G1和G3样品组中含量低。例如脱氢芳樟醇、芳樟醇氧化物Ⅰ、芳樟醇氧化物Ⅲ和芳樟醇氧化物Ⅳ的含量在不同香型茶样中表现为G2>G4>G1>G3;苯乙醛(风信子香)、3,5-辛二烯-2-酮(果香、油脂气味)、β-紫罗酮(紫罗兰香)和(E)-2-庚烯醛(脂肪气味)的含量表现为G2>G4>G3>G1。
第Ⅳ类化合物在G4样品组中含量最高,而在G1样品组中含量最低。
可见有无闷黄工序显著影响了成品茶中特征香气化合物的分布,使黄茶形成了不同于对照样的香型。
2.4 闷黄影响的关键香气化合物
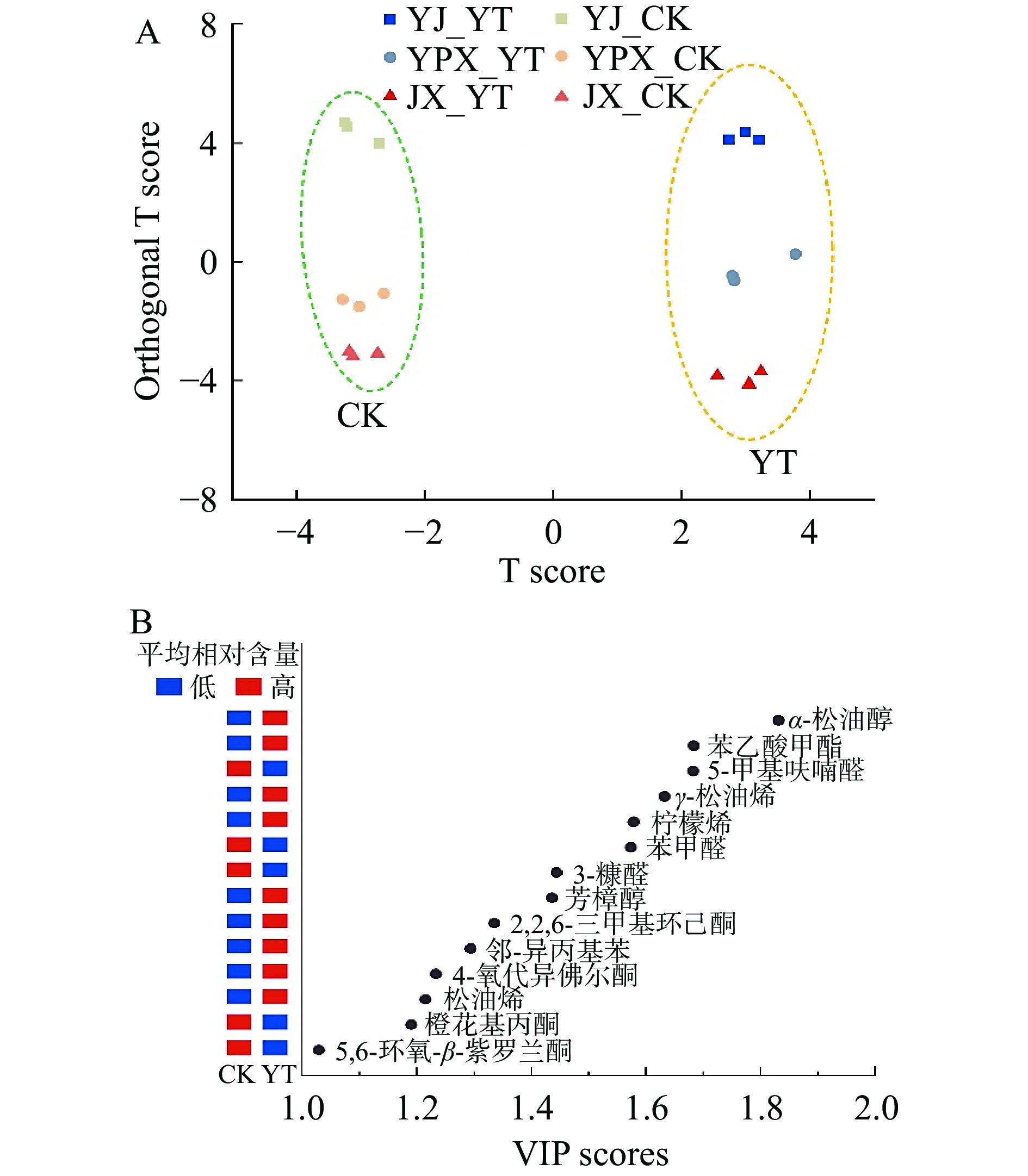
为了深入研究闷黄影响的关键香气物质,采用有监督判别方法——OPLS-DA,对有无闷黄工序所制黄茶和对照样的35种特征香气化合物进行分析。图4A为OPLS-DA得分图,2个类别在横坐标(主要成分)方向上被明显分开,没有分散,说明差异性显著。对模型进行交叉验证得到的R2Y为0.954,Q2为0.872,两者均接近1且差距较小,同时1000次置换检验的P值小于0.001,说明拟合模型的准确性好,预测能力强。因此可依据各香气组分在模型中的变量投影重要度(variable importance for the projection,VIP)筛选对组间差异贡献高的物质。以VIP≥1为条件共选出14种化合物,各个化合物的VIP得分和在对照样与黄茶中的平均相对含量如图4B所示。其中差异贡献度排在前三的化合物是α-松油醇、苯乙酸甲酯和5-甲基呋喃醛,VIP值分别为1.83、1.68和1.68,是闷黄影响的重要化合物。
从图4B中可以看出,这些关键化合物在黄茶中平均相对含量较高的有9种,分别为α-松油醇、苯乙酸甲酯、γ-松油烯、柠檬烯、芳樟醇、2,2,6-三甲基环己酮、邻-异丙基苯、4-氧代异佛尔酮和松油烯,推测闷黄过程可促进这些化合物的形成。α-松油醇和芳樟醇属于萜烯醇类,前体物质以樱草糖苷和葡萄糖苷为主,在加工过程中因水解而释放出来[33]。本研究中α-松油醇和芳樟醇在黄茶中含量显著高于对照样,这一方面可能是因为闷黄过程中高温高湿条件促进糖苷类水解[14];另一方面可能是因为湿热条件下产生的微生物所分泌的胞外酶有助于糖苷的转化[11,42]。γ-松油烯、柠檬烯和松油烯都是单环单萜类化合物,互为同分异构体。已有报道柠檬烯含量会随着闷黄时间的增长而明显增加[14]。然而几种单萜类物质在闷黄过程中的具体转化路径仍未可知,需要进一步研究。苯乙酸甲酯(蜂蜜香和甜香)在黄茶中检出而对照样中未检出。苯乙酸甲酯的产生被认为与高温过程相关[43-44],考虑到闷堆过程温度较高,推测闷黄有利于苯乙酸甲酯的形成。2,2,6-三甲基环己酮和4-氧代异佛尔酮为环己酮衍生物,主要来源于类胡萝卜素的氧化降解[32,35,45]。研究发现湿热作用是类胡萝卜素降解为香气组分的主要途径之一[35,45],而闷黄工序提供了湿热条件,因此推测湿热化学作用是促进类胡萝卜素形成黄茶关键香气化合物的主要因素。邻-异丙基苯有芳香气味,也是黄大茶和蒙顶黄芽茶的呈香组分[17]。前人对红茶香气成分的研究表明邻-异丙基苯主要以键合态存在于茶叶中[46],并会随着发酵时间的延长而增多[47]。推测黄茶中邻-异丙基苯的形成与长时间湿热环境下的闷堆有关。
此外,在闷黄所制黄茶中平均含量低于对照样的化合物有5种,包括5-甲基呋喃醛、苯甲醛、3-糠醛、橙花基丙酮和5,6-环氧-β-紫罗酮,推测闷黄过程可能会消耗或阻碍这几种化合物的形成。
总体来说,闷黄影响的关键香气化合物包括萜类和萜烯醇类化合物5种,芳香烃和芳香族酯类2种,醛类3种,酮类4种。其中9种在黄茶中平均相对含量较高,为黄茶中关键香气化合物,它们的形成可能与香气前体物质在闷黄过程的高温高湿条件下发生的反应相关。
3. 结论
闷黄是黄茶香气品质形成的关键工序,本研究发现闷黄促使黄茶香气品质具有甜香特征。对挥发性化合物的分析表明黄茶中香气组分与对照样存在明显差异,醇类和烃类占比达65.88%~76.93%,萜烯醇和萜烯类化合物为主要成分。借助多元统计分析筛选出35种特征香气化合物,例如具铃兰花香的芳樟醇和柠檬香的柠檬烯等在呈甜香茶样中占优势,而苦杏仁味的苯甲醛则在清香型茶样中贡献较大。进一步根据VIP≥1筛选出闷黄影响的关键香气化合物14种,其中α-松油醇、芳樟醇、γ-松油烯、柠檬烯、松油烯、苯乙酸甲酯、2,2,6-三甲基环己酮、4-氧代异佛尔酮和邻-异丙基苯在黄茶中的含量高于对照样,分别具有花香、果香和甜香,对塑造黄茶甜香风味至关重要。这些化合物的形成可能与闷黄过程密切相关,具体的转化和生成路径值得后续系统研究。本研究剖析了闷黄对黄茶香气特征和挥发性化合物的影响,明确了黄茶呈现甜香品质的关键香气化合物,为深入理解闷黄-香气特征-挥发性香气化合物之间的关联提供了理论基础。
-
表 1 不同茶树品种所制黄茶和对照样的香气感官品质
Table 1 The aroma sensory quality of yellow tea and control sample manufactured from different tea varieties
序号 茶样名称 香气特征 1 YJ_YT 甜香明显 2 YPX_YT 甜香明显 3 JX_YT 甜香 4 YJ_CK 清香带甜 5 YPX_CK 清香带微甜 6 JX_CK 清香带微甜 表 2 不同茶树品种所制黄茶和对照样的香气组分
Table 2 The aroma components contained in yellow tea and control sample manufactured from different tea varieties
编号 化合物 保留指数 匹配度 相对含量(ng/g) 谱库数值 实验数值 YJ_YT YPX_YT JX_YT YJ_CK YPX_CK JX_CK 醇类 1 1-戊醇 765 763 83 49.07±17.86 69.87±16.40 155.20±28.71 79.63±12.65 108.40±14.99 109.37±25.72 2 芳樟醇氧化物Ⅰ 1074 1072 92 31.33±1.27 37.73±5.05 453.13±38.57 27.67±3.52 37.80±2.81 358.47±27.22 3 芳樟醇氧化物Ⅱ 1086 1088 89 − − 352.55±34.01 − − 246.63±21.77 4 芳樟醇 1099 1098 97 614.60±18.33 415.17±41.23 818.03±38.27 393.63±36.35 205.10±10.15 341.53±18.46 5 脱氢芳樟醇 1108 1102 95 74.03±2.32 301.87±20.67 1190.93±29.99 55.80±4.33 297.23±13.45 842.93±25.65 6 苯乙醇 1121 1112 92 − 63.50±6.68 145.43±14.63 − 65.20±1.44 98.77±2.40 7 二氢芳樟醇 1136 1133 84 2.23±0.12 − − − − − 8 芳樟醇氧化物Ⅲ 1173 1171 93 5.57±0.15 16.07±1.14 139.40±5.80 6.53±0.71 24.70±0.69 135.70±4.03 9 芳樟醇氧化物Ⅳ 1174 1174 95 16.13±0.76 25.13±1.68 133.33±4.23 19.83±1.57 36.93±1.33 140.40±3.85 10 4-萜烯醇 1175 1184 88 21.13±0.49 23.63±1.60 − 12.67±1.81 − − 11 2,6-二甲基-3,7-辛二烯-2,6-二醇 1189 1185 96 − − 101.00±2.72 − 32.10±0.44 181.37±0.64 12 α-松油醇 1190 1197 89 159.73±4.85 120.83±6.30 141.87±4.20 34.63±1.63 29.33±2.05 18.63±2.00 13 香叶醇 1255 1246 79 37.83±1.88 26.77±0.67 − 8.05±0.64 − 8.97±5.77 该类化合物总量 1011.67±43.11 1100.57±90.18 3513.37±66.63 635.77±44.36 800.67±52.56 2482.77±116.85 醛类 14 正己醛 801 799 92 − 39.83±4.83 77.90±30.35 17.85±8.41 52.23±3.48 33.30±0.57 15 3-糠醛 832 829 85 − − 40.90±25.03 27.33±4.65 37.80±0.26 32.57±6.75 16 庚醛 901 900 80 − 12.50±3.08 25.87±7.26 5.50±1.99 21.17±0.71 12.47±0.47 17 (E)-2-庚烯醛 964 955 90 11.13±0.81 20.77±5.03 39.40±12.42 19.90±8.96 26.83±1.81 23.37±2.35 18 5-甲基呋喃醛 962 959 81 − − − 4.33±0.35 7.93±0.50 10.27±0.57 19 苯甲醛 961 963 97 114.23±5.17 134.90±8.92 156.23±10.10 195.97±20.21 278.43±5.01 194.43±11.32 20 (E,E)-2,4-庚二烯醛 1012 1010 91 28.20±0.46 81.97±5.00 113.40±5.34 52.03±4.55 102.63±1.44 70.33±5.21 21 苯乙醛 1044 1044 95 55.47±4.40 65.87±7.50 102.87±3.86 69.97±11.57 95.43±3.55 76.70±14.44 22 藏红花醛 1201 1201 95 17.40±0.62 17.90±1.85 41.60±3.39 24.50±2.27 20.73±1.20 28.30±1.25 23 β-环柠檬醛 1221 1222 94 62.97±4.38 62.43±2.73 103.63±1.12 61.17±6.07 66.33±1.69 64.40±2.41 24 β-环高柠檬醛 1254 1259 81 − 11.50±4.61 13.10±3.29 6.33±1.72 13.00±1.71 11.67±0.59 该类化合物总量 289.40±6.19 447.67±40.13 701.27±91.24 478.93±73.10 722.53±19.37 546.70±13.49 烃类 25 月桂烯 991 989 90 84.67±2.53 60.53±10.46 69.93±18.66 54.13±12.33 42.07±3.32 − 26 松油烯 1018 1019 89 17.37±1.06 14.57±4.55 9.20±0.52 9.73±1.04 10.47±0.76 6.03±0.76 27 邻-异丙基苯 1023 1027 94 33.87±1.19 53.37±10.16 60.97±7.00 23.60±6.01 36.43±2.55 33.67±2.41 28 柠檬烯 1030 1032 82 268.83±20.86 232.07±55.42 221.87±34.96 165.03±33.34 150.03±17.99 106.97±15.63 29 γ-松油烯 1061 1060 89 38.90±2.54 40.70±8.91 51.37±9.11 24.33±5.26 29.03±2.84 24.20±2.40 30 别罗勒烯 1131 1127 90 17.23±1.44 11.80±2.52 13.43±0.98 9.37±1.61 11.33±4.90 11.40±0.36 31 β-波旁烯 1384 1391 86 5.27±0.12 7.60±0.20 10.40±0.20 4.33±0.15 19.17±3.61 18.23±1.30 32 δ-杜松烯 1524 1522 93 5.77±0.35 63.37±1.55 62.17±0.78 5.03±0.25 64.70±2.65 50.73±2.56 33 (E)-菖蒲烯 1529 1526 87 1.25±0.07 23.20±1.08 17.50±0.69 − 18.60±0.70 13.87±0.81 34 α-二去氢菖蒲烯 1542 1548 85 − 10.37±0.57 8.53±0.15 − 4.47±0.15 3.67±0.12 该类化合物总量 472.73±28.36 517.57±89.77 525.37±63.58 295.57±59.72 386.30±31.86 268.77±21.27 酮类 35 2,2,6-三甲基环己酮 1035 1037 86 49.60±3.47 35.03±9.58 71.33±10.13 33.93±6.81 27.87±1.36 29.43±3.04 36 3,5-辛二烯-2-酮 1073 1067 87 35.43±3.45 51.07±5.27 74.73±3.93 42.27±8.06 57.23±3.26 50.70±5.12 37 异佛尔酮 1119 1123 83 − − 11.87±0.78 − − − 38 4-氧代异佛尔酮 1145 1144 79 4.83±0.25 8.90±0.57 14.70±1.20 3.95±0.21 − − 39 α-紫罗酮 1427 1422 78 4.87±0.32 4.63±0.15 − 5.47±0.32 5.70±0.20 4.37±0.32 40 橙花基丙酮 1435 1443 93 9.90±0.40 11.63±0.76 14.17±0.50 13.03±0.12 14.93±0.49 14.77±0.74 41 β-紫罗酮 1485 1479 91 15.47±0.98 21.50±1.31 35.87±1.50 20.93±0.70 29.43±1.72 27.80±0.82 42 5,6-环氧-β-紫罗酮 1488 1482 74 5.35±0.07 − 12.60±0.46 9.33±0.32 11.27±0.75 10.83±0.15 该类化合物总量 123.67±7.40 129.80±17.91 235.27±12.33 127.60±13.72 146.43±6.40 137.90±8.52 酯类 43 苯乙酸甲酯 1178 1174 90 22.63±0.97 11.27±2.35 13.15±0.49 − − − 44 水杨酸甲酯 1192 1194 89 − 4.20±0.42 22.97±0.74 − 3.37±0.35 13.37±0.45 45 2-甲氨基苯甲酸甲酯 1405 1408 77 1.60±0.10 2.47±0.15 − 1.27±0.12 2.40±0.10 2.35±0.07 46 二氢猕猴桃内酯 1530 1536 97 20.87±0.23 26.30±1.57 57.30±4.60 19.97±4.45 25.57±1.15 28.97±2.73 该类化合物总量 45.10±1.11 42.83±2.22 89.03±9.63 21.23±4.45 31.33±1.54 43.90±1.40 其他 47 2-戊基呋喃 993 990 85 − 33.23±5.49 − 34.90±3.26 59.77±5.35 44.23±2.84 48 2-乙酰基吡咯 1063 1058 92 57.80±1.15 48.43±2.54 72.00±3.83 52.03±4.25 22.83±0.97 56.33±1.89 49 苯乙腈 1143 1137 98 35.77±1.21 133.53±5.71 99.70±4.00 14.83±0.78 73.67±2.42 63.43±1.90 50 茶螺烷 1302 1305 80 3.63±0.15 3.80±0.57 13.97±0.57 − − 6.23±0.23 该类化合物总量 97.20±2.25 217.73±14.27 185.67±7.88 101.77±7.48 156.27±7.50 170.23±5.36 香气化合物总量 2039.77±65.27 2456.17±243.91 5249.97±123.07 1660.87±201.45 2243.53±86.83 3650.27±165.09 注:“−”表示化合物在此样品中检出频次≤1/3。 -
[1] KHAN N, MUKHTAR H. Tea polyphenols for health promotion[J]. Life Sciences,2007,81(7):519−533. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2007.06.011
[2] WANG Y, KAN Z, THOMPSON H J, et al. Impact of six typical processing methods on the chemical composition of tea leaves using a single Camellia sinensis cultivar, Longjing 43[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2019,67(19):5423−5436. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b05140
[3] BALDERMANN S, YANG Z, KATSUNO T, et al. Discrimination of green, oolong, and black teas by GC-MS analysis of characteristic volatile flavor compounds[J]. American Journal of Analytical Chemistry,2014,5(9):620−632. doi: 10.4236/ajac.2014.59070
[4] 夏涛. 制茶学[M]. 第三版. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2016 XIA T. Manufacture of tea[M]. The Third Edition. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2016.
[5] 王梦琪, 朱荫, 张悦, 等. 茶叶挥发性成分中关键呈香成分研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(23):341−349. [WANG M Q, ZHU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. A review of recent research on key aroma compounds in tea[J]. Food Science,2019,40(23):341−349. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181015-132 [6] 汪琦, 赵贵福, 张续周, 等. 4个茶树品种与季节对绿茶香气成分特征的影响[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(20):102−107. [WANG Q, ZHAO G F, ZHANG X Z, et al. Effects of four different tea varieties and harvesting seasons on aroma characteristics of green tea[J]. Food Science,2016,37(20):102−107. [7] ZHU B, ZHANG J, LI J, et al. Aroma profile of Jinmudan tea produced using Camellia sinensis, cultivar Jinmudan using solid-phase microextraction, gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, and chemometrics[J]. European Food Research and Technology,2021,247(5):1061−1082. doi: 10.1007/s00217-021-03687-0
[8] ZENG L, WATANABE N, YANG Z. Understanding the biosyntheses and stress response mechanisms of aroma compounds in tea (Camellia sinensis) to safely and effectively improve tea aroma[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2019,59(14):2321−2334. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1506907
[9] 张娇, 梁壮仙, 张拓, 等. 黄茶加工中主要品质成分的动态变化[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(16):200−205. [ZHANG J, LIANG Z X, ZHANG T, et al. Dynamic changes of main quality components during yellow tea processing[J]. Food Science,2019,40(16):200−205. [10] 戴前颖, 安琪, 郑芳玲, 等. 基于QDA法和CATA法的黄大茶的香气感官特性及喜好度分析[J/OL]. 食品科学: 1−16[2022-03-10]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2206.TS.20211108.2055.016.html DAI Q Y, AN Q, ZHENG F L, et al. Analysis of aroma sensory characteristics and preference degree of large yellow tea based on quantitative descriptive analysis and check-all-that-apply[J/OL]. Food Science: 1−16[2022-03-10]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/11.2206.TS.20211108.2055.016.html.
[11] XU J, WANG M, ZHAO J, et al. Yellow tea (Camellia sinensis L.), a promising Chinese tea: Processing, chemical constituents and health benefits[J]. Food Research International,2018,107:567−577. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.01.063
[12] 雷玉萍, 吴根玲, 梁慧玲, 等. 闷黄工艺对“御金香”夏暑茶品质及理化成分的影响[J]. 中国茶叶,2018,40(12):20−23. [LEI Y P, WU G L, LIANG H L, et al. Effect of smoking yellow process on quality and physicochemical components of “Yujinxiang” summer tea[J]. China Tea,2018,40(12):20−23. [13] 文帅, 安然, 李冬利, 等. 不同闷黄工艺对黄茶品质及其抑制HepG2细胞增殖的影响[J]. 茶叶通讯,2020,47(1):75−81. [WEN S, AN R, LI D L, et al. Effects of different yellowing process on the quality of yellow tea and the inhibition of HepG2 cell proliferation[J]. Tea Communication,2020,47(1):75−81. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-525X.2020.01.014 [14] 张厅, 刘晓, 王小萍, 等. 闷黄新工艺对蒙顶黄芽品质及香气的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(22):276−282. [ZHANG T, LIU X, WANG X P, et al. Effects of new piling technology on quality and aroma of Mengding yellow bud[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(22):276−282. [15] MA C, LI J, CHEN W, et al. Study of the aroma formation and transformation during the manufacturing process of oolong tea by solid-phase micro-extraction and gas chromatography–mass spectrometry combined with chemometrics[J]. Food Research International,2018,108:413−422. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2018.03.052
[16] 刘晓慧, 张丽霞, 王日为, 等. 顶空固相微萃取-气相色谱-质谱联用法分析黄茶香气成分[J]. 食品科学,2010,31(16):239−243. [LIU X H, ZHANG L X, WANG R W, et al. Analysis of volatile components of yellow tea by HS-SPME/GC-MS[J]. Food Science,2010,31(16):239−243. [17] SHI Y, WANG M, DONG Z, et al. Volatile components and key odorants of Chinese yellow tea (Camellia sinensis)[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2021,146(33):111512.
[18] 宋玉欣, 朱静静, 张拓, 等. 不同茶树品种茶鲜叶加工黄茶的适制性研究[J]. 食品与机械,2019,35(9):193−198. [SONG Y X, ZHU J J, ZHANG T, et al. Study on the suitability of fresh tea leaves from different tea varieties for yellow tea processing[J]. Food & Machinery,2019,35(9):193−198. [19] CHEN C, CHEN H, ZHANG Y, et al. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data[J]. Molecular Plant,2020,13(8):1194−1202. doi: 10.1016/j.molp.2020.06.009
[20] STIGLIC G, WATSON R, CILAR L. Are you ready? Using the R programme for statistical analysis and graphics[J]. Research in Nursing & Health,2019,42(6):494−499.
[21] PANG Z, CHONG J, ZHOU G, et al. Metabo analyst 5.0: Narrowing the gap between raw spectra and functional insights[J]. Nucleic Acids Research,2021,49(1):388−396.
[22] 孟爱丽, 庞晓莉, 温顺位, 等. 蒙顶黄芽香气特征及香气成分分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2014,35(18):106−112,117. [MENG A L, PANG X L, WEN S W, et al. Analysis of aroma characteristics and aroma components from Mengding yellow tea[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2014,35(18):106−112,117. [23] 李伟, 齐桂年, 刘晓, 等. 蒙顶黄芽加工过程感官品质及化学成分变化的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2015,36(16):95−99. [LI W, QI G N, LIU X, et al. Changes in organoleptic quality and chemical composition of Mengdinghuangya during processing[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2015,36(16):95−99. [24] 张明露, 彭玙舒, 尹杰. 不同闷黄时间和温度对黄茶品质的影响[J]. 耕作与栽培,2018(3):12−14. [ZHANG M L, PENG Y S, YIN J. Effects of different piling time and temperature during processing on the quality of yellow tea[J]. Tillage and Cultivation,2018(3):12−14. [25] 王梦琪, 朱荫, 张悦, 等. “清香”绿茶的挥发性成分及其关键香气成分分析[J]. 食品科学,2019,40(22):219−228. [WANG M Q, ZHU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Analysis of volatile composition and key aroma compounds of green teas with fresh scent flavor[J]. Food Science,2019,40(22):219−228. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20181229-349 [26] 王梦琪, 朱荫, 张悦, 等. “清香”与“栗香”绿茶中非挥发性化学成分的差异分析[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(14):151−158. [WANG M Q, ZHU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. Analysis of differential non-volatile chemical compounds between green teas with refreshing aroma and chestnut-like aroma[J]. Food Science,2021,42(14):151−158. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200629-373 [27] 黄海涛, 敖存, 郭敏明, 等. 花香与清香绿茶的香气组分及品种相关性分析[J]. 浙江农业科学,2018,59(5):738−741, 771. [HUANG H T, AO C, GUO M M, et al. Aroma components of flower-scent and fresh-scent green tea and correlation analysis with varieties[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Agricultural Sciences,2018,59(5):738−741, 771. [28] FENG Z, LI Y, LI M, et al. Tea aroma formation from six model manufacturing processes[J]. Food Chemistry,2019,285:347−354. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2019.01.174
[29] 谢关华, 陆安霞, 欧阳珂, 等. GC-MS结合化学计量学用于探究六大茶类香气形成的差异[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(20):260−270. [XIE G H, LU A X, OUYANG K, et al. Analysis of the aroma formation in six categories of teas by GC-MS combined with chemometrics[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(20):260−270. [30] 速晓娟, 郑晓娟, 杜晓, 等. 蒙顶黄芽主要成分含量及组分分析[J]. 食品科学,2014,35(12):108−114. [SU X J, ZHENG X J, DU X, et al. Analysis of main chemical components of Mengding yellow bud[J]. Food Science,2014,35(12):108−114. [31] 蒋容港, 黄燕, 金友兰, 等. 不同原料等级黄茶特征香气成分分析[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(16):89−98. [JIANG R G, HUANG Y, JIN Y L, et al. Analysis of characteristic aroma components of different grades of yellow tea[J]. Food Science,2021,42(16):89−98. [32] HO C T, ZHENG X, LI S. Tea aroma formation[J]. Food Science and Human Wellness,2015,4(1):9−27. doi: 10.1016/j.fshw.2015.04.001
[33] 张冬桃, 孙君, 叶乃兴, 等. 茶树萜烯类香气物质合成相关酶研究进展[J]. 茶叶学报,2015,56(2):68−79. [ZHANG D T, SUN J, YE N X, et al. Research progress of enzymes associated with terpene synthesis in Camellia sinensis[J]. Acta Tea Sinica,2015,56(2):68−79. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-4872.2015.02.002 [34] 马超龙, 李小嫄, 岳翠男, 等. 茶叶中脂肪酸及其对香气的影响研究进展[J]. 食品研究与开发,2017,38(4):220−224. [MA C L, LI X Y, YUE C N, et al. Progress on fatty acids in tea and their influences on tea aroma[J]. Food Research and Development,2017,38(4):220−224. [35] 陈丽, 叶玉龙, 王春燕, 等. 茶叶中类胡萝卜素香气前体研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(5):266−273. [CHEN L, YE Y L, WANG C Y, et al. Research progress on carotenoid aroma precursors in tea[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(5):266−273. [36] FAN F Y, ZHOU S J, QIAN H, et al. Effect of yellowing duration on the chemical profile of yellow tea and the associations with sensory traits[J]. Molecules,2022,27(3):940. doi: 10.3390/molecules27030940
[37] 岳翠男, 秦丹丹, 李文金, 等. 基于HS-SPME-GC-MS和OAV鉴定浮梁红茶关键呈香物质[J]. 食品工业科技,2022,43(9):251−258. [YUE C N, QIN D D, LI W J, et al. Identification of key aroma components in Fuliang black tea based on HS-SPME-GC-MS and OAV[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2022,43(9):251−258. [38] 杜红, 李艳, 贾翼, 等. 湿热后处理改善红茶风味品质的工艺优化及效果评价[J]. 湖南农业大学学报(自然科学版),2017,43(3):340−346. [DU H, LI Y, JIA Y, et al. Technical study and effectiveness evaluation of heat-moisture post-treatment on improving the flavor quality of black tea[J]. Journal of Hunan Agricultural University (Natural Sciences),2017,43(3):340−346. [39] GUO X, HO C T, SCHWAB W, et al. Effect of the roasting degree on flavor quality of large-leaf yellow tea[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,347(3):129016.
[40] 朱晓凤, 刘政权, 宛晓春, 等. SDE和HS-SPME结合GC-MS分析霍山黄大茶香气成分的比较[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(4):214−221. [ZHU X F, LIU Z Q, WAN X C, et al. Comparison of simultaneous distillation and extraction and headspace-solid phase microextraction for analysis of aroma components of Huoshan large-leaf yellow tea by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Food Science,2020,41(4):214−221. [41] 吴函殷, 刘晓辉, 罗龙新, 等. 12种单丛茶香气成分研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(19):234−239. [WU H Y, LIU X H, LUO L X, et al. Study on aroma components in twelve kinds of Dancong teas[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(19):234−239. [42] 刘晓, 张厅, 刘飞, 等. 蒙顶黄茶闷堆过程中主要品质成分及酶活性变化研究[J]. 中国农学通报,2017,33(27):97−101. [LIU X, ZHANG T, LIU F, et al. Variations of quality ingredients and primary enzymes activities of Mengding yellow tea during the piling process[J]. Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2017,33(27):97−101. doi: 10.11924/j.issn.1000-6850.casb16080075 [43] 曾亮, 王杰, 柳岩, 等. 小种红茶与工夫红茶品质特性的比较分析[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(20):51−56. [ZENG L, WANG J, LIU Y, et al. Comparative analysis of quality characteristics of Souchong and Congou[J]. Food Science,2016,37(20):51−56. [44] 詹宝珍, 吴志锋, 马春华, 等. 焙火时间对武夷岩茶肉桂香气品质的影响[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2022,13(3):811−819. [ZHAN B Z, WU Z F, MA C H, et al. Effects of roasting time on the aroma quality of Wuyi rock tea Rougui[J]. Journal of Food Safety & Quality,2022,13(3):811−819. [45] 刘飞, 叶阳, 李春华, 等. 工夫红茶加工过程中类胡萝卜素成分的动态变化[J]. 食品科学,2022,43(4):231−240. [LIU F, YE Y, LI C H, et al. Dynamic change of carotenoid compounds during Congou black tea manufacturing process[J]. Food Science,2022,43(4):231−240. [46] 杨旖旎, 杨桂秋, 杨小洪, 等. 老鹰茶游离和键合态挥发性成分的分析[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2019,45(3):254−260. [YANG Y N, YANG G Q, YANG X H, et al. Characterization of free and bound volatile compounds in Hawk tea (Litsea coreana L.)[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2019,45(3):254−260. [47] 潘科, 冯林, 陈娟, 等. HS-SPME-GC-MS联用法分析不同通氧发酵加工工艺红茶香气成分[J]. 食品科学,2015,36(8):181−186. [PAN K, FENG L, CHEN J, et al. Analysis of aroma compounds in black tea ventilated with oxygen for different durations during the fermentation process by head space-solid-phase micro-extraction and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry[J]. Food Science,2015,36(8):181−186. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201508033 -
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 潘冠均,段淋渊,赵嘉科,帅平,戴国礼,田维素,王金源,黄佳鹏,闭晓彤,林恩照,秦垦,郝志龙,张波. 摊放程度对枸杞芽叶茶风味品质的影响. 食品工业科技. 2025(04): 117-126 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 吴宗杰,欧晓西,林宏政,余欣茹,程守悦,吴晴阳,李鑫磊,孙云. 武夷肉桂加工中挥发性成分糖苷结合物和香气品质形成研究. 茶叶科学. 2024(01): 84-100 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 潘冠均,封娇,段淋渊,张炫鹂,戴国礼,帅平,秦垦,郝志龙,张波. 不同单株枸杞芽叶茶风味品质分析. 食品工业科技. 2024(15): 264-273 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 徐晓俞,李程勋,李爱萍,郑开斌,潘键,侯明香. 肉桂茶纯露挥发性成分分析. 福建农业科技. 2024(06): 49-55 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 占鑫怡,杨云,陈彬,黄慧清,赵梦莹,李鑫磊,孙云. 不同摇青程度春闺闽北乌龙茶品质差异分析. 食品工业科技. 2023(11): 271-279 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)








 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



