Protective Effect of Aloe Polysaccharide on Oxidative Stress Injury of HepG2 Cells Induced by D-galactose
-
摘要: 目的:探讨芦荟多糖对HepG2细胞氧化损伤的保护作用,分析其体外抗氧化能力。方法:以HepG2细胞为研究对象,建立D-半乳糖诱导细胞氧化损伤模型,以不同浓度芦荟多糖进行预保护处理。采用细胞增殖与毒性检测试剂盒测定HepG2细胞存活率,生物化学法检测细胞超氧化物歧化酶、过氧化氢酶、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶活力,酶联免疫吸附法测定细胞总抗氧化能力及丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)含量,实时荧光定量PCR检测细胞Keap1、Nrf2、NQO1和HO-1基因表达水平。结果:与D-半乳糖模型组比较,25、50、100 μg/mL的芦荟多糖预保护处理能不同程度地提高HepG2细胞存活率;芦荟多糖能显著增强细胞中抗氧化酶的活性,降低细胞MDA的生成量(P<0.05),且作用效果与芦荟多糖浓度成正比;细胞中Keap1基因表达显著降低,Nrf2、NQO1、HO-1 mRNA表达显著提高(P<0.05)。结论:芦荟多糖可以减轻HepG2细胞的氧化应激损伤,激活Nrf2表达并抑制其泛素化降解,提高下游NQO1、HO-1的转录水平,增强细胞抗氧化酶系活性并调控细胞氧化还原系统,以达到减轻细胞氧化损伤程度、提高细胞抗氧化应激损伤的效果。Abstract: Objective: To investigate the protective effect of aloe polysaccharide on oxidative damage in HepG2 cells, and analyze its antioxidant capacity in vitro. Methods: HepG2 cells were used as the study target, to establish D-galactose-induced cell oxidation damage model and pre-protected with different concentrations of aloe polysaccharide. Cell Counting Kit-8 was used to determine the survival rate of HepG2 cells, biochemical assays were performed to detect the cellular superoxide dismutase, catalase and glutathione peroxidase activities, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay was used to determine the total antioxidant capacity and malondialdehyde content. Quantitative real-time PCR was used to detect the cellular Keap1, Nrf2, NQO1 and HO-1 gene expression levels. Results: Compared with the D-galactose model group, the pre-protection with 25, 50, 100 μg/mL of aloe polysaccharide increased the survival rate of HepG2 cells to different degrees. Aloe polysaccharide significantly enhanced the activity of antioxidant enzymes in cells and reduced the production of malondialdehyde in cells (P<0.05), and the effect was proportional to the concentration of aloe polysaccharide. The expression of Keap1 in cells was significantly reduced, and the expression of Nrf2, NQO1 and HO-1 in cells was significantly increased (P<0.05). Conclusion: Aloe polysaccharide can reduce oxidative stress damage in HepG2 cells, activate Nrf2 expression and inhibit its ubiquitination degradation, increase the transcription level of downstream NQO1 and HO-1, enhance the activity of cellular antioxidant enzymes and regulate the cellular redox system, to reduce the degree of oxidative damage and improve the effectiveness of cellular resistance to oxidative stress damage.
-
Keywords:
- aloe polysaccharide /
- D-galactose /
- oxidative stress /
- HepG2 cells /
- Nrf2
-
近代以来大量研究发现,生物体有着应对细胞正常代谢活动产生的活性氧(reactive oxygen species,ROS)、活性氮等自由基的一套调节系统,且涉及到多种信号通路间的协同作用。当外界刺激导致ROS过度积累至超过机体的调节能力时,有害物质引起抗氧化通路上的某些蛋白表达下调,导致细胞内抗氧化防御系统失衡,此时即表现为氧化应激状态[1]。氧化应激与多种疾病的形成有关,如缺血性脑卒中[2]、阿尔茨海默病[3]、糖尿病[4]等,并在引起人体炎症反应和衰老中起重要作用[5]。因此,保护机体免受氧化应激损伤依旧是当下研究的热点。
芦荟多糖(aloe polysaccharide,AP)是从芦荟中提取的天然多糖类化合物,具有增强免疫[6]、促进癌细胞自噬[7]、抗炎[8]等多种药理作用。已有研究显示,芦荟多糖能下调黄曲霉毒素B1代谢活化酶细胞色素P4501A2和3A的表达,减轻黄曲霉毒素B1造成的肝脏损伤[9];通过下调结肠组织中OX40、OX40L蛋白表达水平,减弱炎症性肠病小鼠免疫功能过度激活而实现对炎症性肠病的治疗作用[10]。
刘泽鑫等[11]通过测定芦荟多糖清除1,1-二苯基-2-三硝基苯肼(1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl,DPPH)、2,2-联氮-二(3-乙基-苯并噻唑-6-磺酸)二铵盐[2,2-azinobis-(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulphonate),ABTS]和超氧阴离子等的能力,得出芦荟多糖具有体外抗氧化活性的结论;张晓林等[12]通过腹腔注射四氯化碳构建小鼠肝损伤模型,中华芦荟多糖能起到提高血清丙氨酸氨基转移酶等相关酶活力,减轻小鼠急性肝损伤程度的作用。但有关芦荟多糖对细胞抗氧化作用的具体机制尚缺乏深入系统性的研究,本研究通过测定氧化应激损伤的HepG2细胞存活率、抗氧化酶活力、丙二醛(malondialdehyde,MDA)含量和相关基因的表达水平,探讨芦荟多糖对D-半乳糖致细胞氧化损伤的保护作用,为芦荟多糖的应用提供理论和实验依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
芦荟多糖、维生素C(Vitamin C,VC) UV≥98%,源叶生物科技有限公司;D-半乳糖(D-galactose,D-gal) 生物技术级,麦克林生化科技有限公司;人肝癌细胞株HepG2 锦州医科大学生命科学院保存;DMEM(dulbecco’s modified eagle medium)高糖培养基、磷酸盐缓冲液(phosphate buffered solution,PBS)、胰蛋白酶消化液、青-链霉素混合液、二甲基亚砜(dimethyl sulfoxide,DMSO) 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;胎牛血清(fetal bovine serum,FBS) 赛默飞世尔科技有限公司;细胞增殖与毒性检测(Cell Counting Kit-8,CCK-8)试剂盒、总RNA抽提试剂(Trizol) 碧云天生物技术研究所;人丙二醛酶联免疫吸附(enzyme linked immunosorbent assay,ELISA)试剂盒、人总抗氧化能力(total antioxidant capacity,T-AOC)ELISA试剂盒 上海酶联生物科技有限公司;超氧化物歧化酶(superoxide dismutase,SOD)试剂盒、过氧化氢酶(catalase,CAT)试剂盒、谷胱甘肽过氧化物酶(glutathione peroxidase,GPx)试剂盒 上海碧云天生物技术有限公司;TaKaRa逆转录试剂盒、TB Green™ Premix Ex Taq™ II试剂盒 大连宝生物工程有限公司。
HR40-B2型生物安全柜 青岛海尔特种电器有限公司;Read Max1500型光吸收全波长酶标仪 上海闪谱生物科技有限公司;Olympus BX53倒置光学显微镜 日本Olympus公司;3H12RI智能高速冷冻离心机 湖南赫西仪器装备有限公司;CB-S 170二氧化碳恒温培养箱 德国Binder公司;JY88-IIN超声波细胞粉碎仪 宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司;Mastercyler ep realplex4型实时荧光定量PCR仪、BioPhotometer plus型蛋白核酸分析仪 德国Eppendorf公司;Tanon 2500全自动凝胶成像系统 中国天能科技有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 HepG2细胞培养
根据Juan等[13]的实验方法,以含10% FBS、1%青-链霉素双抗混合液的DMEM高糖培养基为完全培养基,37 ℃、5% CO2为常规条件培养HepG2细胞。当细胞密度达到85%时,PBS洗去破碎的细胞与代谢产物,胰酶收集细胞并按1:3比例传代。剩余细胞均匀混合至含10% DMSO的FBS中,−80 ℃或液氮条件下冻存。
1.2.2 CCK-8法测定芦荟多糖安全浓度范围
CCK-8溶液可以通过与活细胞线粒体中的脱氢酶发生还原反应生成橙黄色物质,使细胞数目与颜色呈线性关系[14]。选择处于对数生长期的HepG2细胞,以密度为5×104个/mL接种于96孔细胞培养板中,每孔100 μL。在37 ℃、5% CO2条件下培养24 h,倒置显微镜下观察细胞充分贴壁后,弃去培养基,用pH调节至7.2~7.4,浓度为0.01 mol/L的PBS漂洗1~2次,并进行分组:芦荟多糖组加入100 μL含芦荟多糖(终浓度分别为12.5、25、50、100、200、400 μg/mL)的DMEM完全培养基;对照组予以等体积完全培养基。于37 ℃、5% CO2条件下与细胞共培养20 h后,每孔加入10 μL CCK-8溶液,常规孵育2 h,按说明书检测各孔在波长为450 nm时的吸光度(OD)值,并计算细胞存活率。每浓度组设五个复孔。
细胞存活率(%)=实验组OD值对照组OD值×100 1.2.3 HepG2细胞氧化应激模型的建立
以含1%青-链霉素双抗混合液的DMEM高糖培养基为无血清培养基,按1.2.2的方法,将细胞以5×104个/mL接种到96孔板中,每孔100 μL。常规培养24 h后,更换为100 μL含D-gal(终浓度为50、100、200、400 mmol/L)的无血清培养基,对照组予以等体积无血清培养基,分别诱导12、24、36 h,CCK-8法检测细胞存活率。每浓度组设五个复孔。
1.2.4 芦荟多糖对氧化应激损伤细胞存活率的影响
按1.2.2的方法,将细胞以5×104个/mL接种于96孔板中,每孔100 μL。实验分组为:对照组、D-gal模型组、VC阳性组、芦荟多糖低、中、高浓度保护组,每组设五个复孔。
细胞常规培养24 h至完全贴壁后弃去培养基,VC阳性组加入终浓度为100 μg/mL的含VC完全培养基,芦荟多糖保护组每孔加入100 μL终浓度为25、50、100 μg/mL的含芦荟多糖完全培养基;对照组与模型组予以等体积完全培养基,常规条件下与细胞共培养20 h。弃去培养基,除对照组外,每孔各加入D-gal浓度为200 mmol/L的无血清培养基100 μL,诱导24 h;对照组加入等体积的无血清培养基,CCK-8法检测细胞存活率。
1.2.5 细胞抗氧化酶活力、T-AOC水平及MDA含量测定
酶联免疫分析(ELISA)法是通过抗原-抗体-酶标抗体复合物在辣根过氧化物酶的催化下发生显色反应的免疫学分析方法,相比传统方法灵敏度更高。采用ELISA法检测细胞中T-AOC、MDA含量,能更好地排除其他条件干扰,较真实地反映出待测值水平。
SOD活性检测采用WST-8比色法[15],基于甲臢染料的显色反应检测细胞中SOD酶活性;CAT酶可以催化过氧化氢产生水和氧气,通过计算其在单位时间内催化产物生成量,可确定细胞中CAT活力[16];GPx能特异性催化有机过氧化物试剂与还原型谷胱甘肽反应生成黄色产物TNB,定量检测GPx酶活力。
参考Wang等[17]的方法,将细胞以1×106个/mL浓度接种于6孔板中,每孔1 mL。铺板后十字摇匀,常规培养细胞24 h。镜下观察细胞充分贴壁后,移除旧培养基,PBS漂洗2次,按照1.2.4的方法进行分组和给药,每孔1 mL。D-gal诱导结束后,收集每孔培养上清液,4000 r/min条件下离心10 min,弃去沉淀,按说明书操作测定细胞培养上清液中MDA水平。
取出上清液后,每孔加适量PBS洗1~2次。用无菌刮刀轻柔刮下孔板底部的细胞,加入1 mL预冷的PBS,混匀后置于超声波细胞粉碎仪中,超声功率200 W,超声时间5 s,间隔10 s,重复30次。镜下观察细胞破碎效果,取充分裂解后的细胞匀浆,4000 r/min条件下离心10 min,收集上清液,分别按说明书操作检测细胞中SOD、CAT、GPx、T-AOC水平。实验设五组平行。
1.2.6 实时荧光定量PCR检测细胞Keap1、Nrf2、NQO1和HO-1的mRNA表达量
将细胞以1×106个/mL接种于6孔板中,每孔1 mL。十字摇匀后,常规培养细胞24 h,按照1.2.4的方法进行分组与给药,每孔1 mL。D-gal造模结束后弃去培养基,胰酶消化、收集细胞于无RNA酶EP管中,加入PBS吹匀,离心1~2次洗净胰酶。采用Trizol法提取细胞总RNA,核酸蛋白分析仪测定RNA纯度和浓度。RNA纯度A260/280在1.8~2.1之间,浓度用无RNA酶水调整至400~600 ng/μL。
按照TaKaRa逆转录试剂盒与TB Green嵌合荧光法实时荧光定量PCR(Quantitative Real-time PCR,qRT-PCR)试剂盒说明书配制反应体系。逆转录体系为20 μL,37 ℃,15 min;85 ℃,5 s。PCR体系为25 μL,95 ℃,30 s;95 ℃,5 s,60 ℃,30 s,循环40次。参考潘聪等[18]的引物设计(见表1),GAPDH作为内参,2-ΔΔCt法计算mRNA的相对表达水平,琼脂糖凝胶电泳检测扩增产物[19]。
表 1 引物序列Table 1. Primer sequence基因名称 引物序列(5’-3’) NM编号 GAPDH F
RCGACCACTTTGTCAAGCTCA
AGGGGTCTACATGGCAACTGNM_001357943 KEAP1 F
RAGAGCGGGATGAGTGGCA
GCTGAATTAAGGCGGTTTGTCNM_012289 NRF2 F
RCAGTCAGCGACGGAAAGAGT
AAGTGACTGAAACGTAGCCGANM_006164 NQO1 F
RCCCCAGGATTCAGGCGTTG
ATCAGTGCTCTTCTGCCGACNM_001025434 HO-1 F
RATGACACCAAGGACCAGAG
TAAGGACCCATCGGAGAAGNM_002133 1.3 数据处理
实验结果采用SPSS 26.0进行统计与分析,数值以
ˉx ±s表示。单因素方差分析进行组间比较,LSD法做两两比较检验显著性,以不同字母标注不同组别间的差异具有统计学意义,小写字母表示差异显著(P<0.05),大写字母表示差异极显著(P<0.01)。2. 结果与分析
2.1 芦荟多糖的安全浓度范围
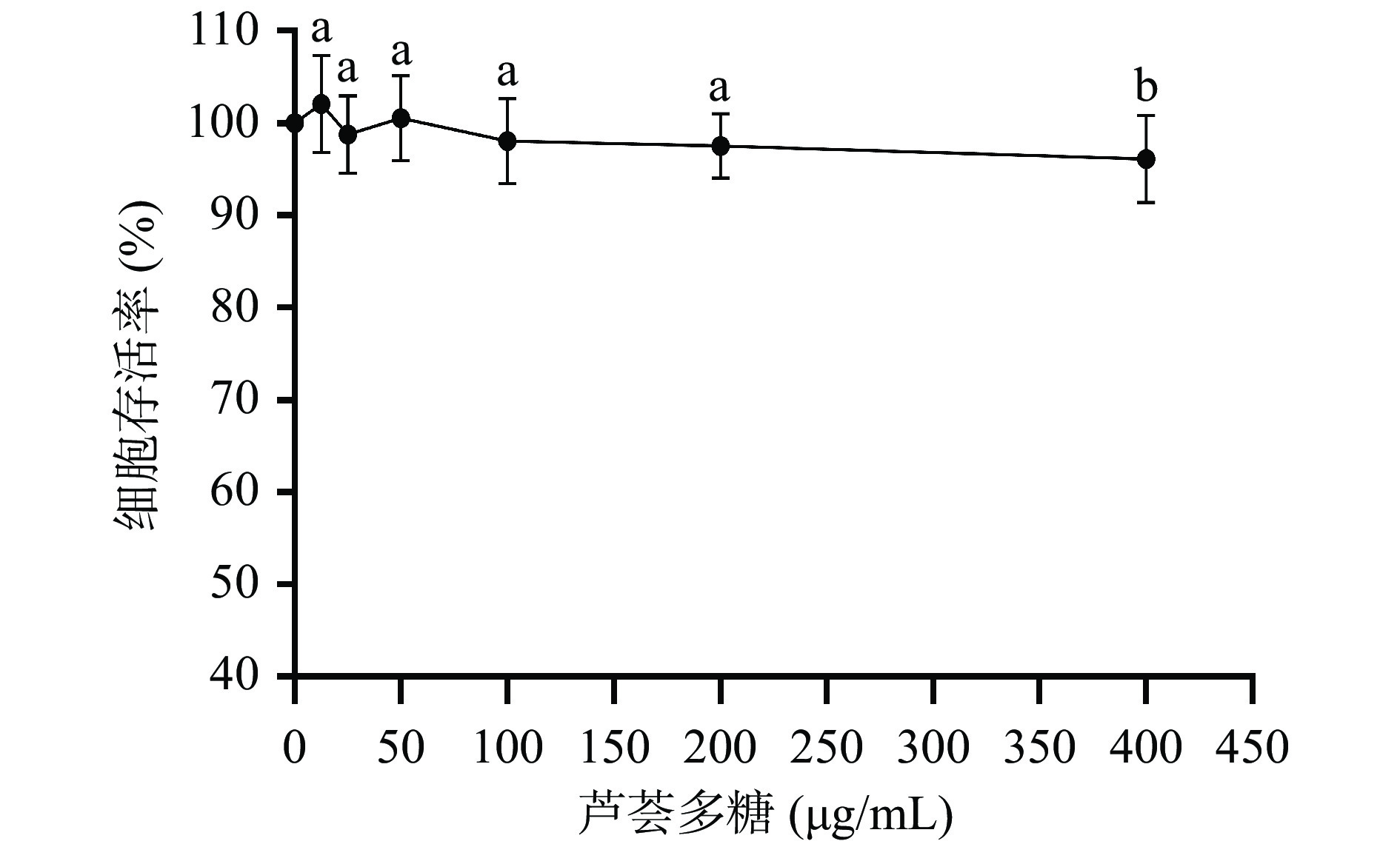
细胞存活率是衡量细胞损伤程度的直观指标之一。实验通过CCK-8法测定不同浓度芦荟多糖共培养条件下HepG2细胞的存活率,从而分析药物对细胞的毒性作用,确定芦荟多糖对HepG2细胞的安全浓度范围。实验结果如图1所示,在12.5~400 μg/mL范围内,HepG2细胞的存活率均≥90%;当质量浓度小于400 μg/mL时,芦荟多糖处理组与对照组之间的差异不显著(P>0.05),即此时芦荟多糖对细胞无明显毒性作用。综合考虑,选择质量浓度为25、50、100 μg/mL的芦荟多糖作为低、中、高浓度组来进行后续实验。
2.2 HepG2细胞氧化应激模型的建立
D-半乳糖(D-galactose,D-gal)是一种稳定性较高的六碳醛糖,在机体中通过半乳糖氧化酶进行代谢。当D-gal大量堆积于细胞时,会导致细胞糖代谢异常[20],进而引起细胞肿胀、坏死,破坏机体抗氧化防御系统,致使细胞产生氧化应激现象。
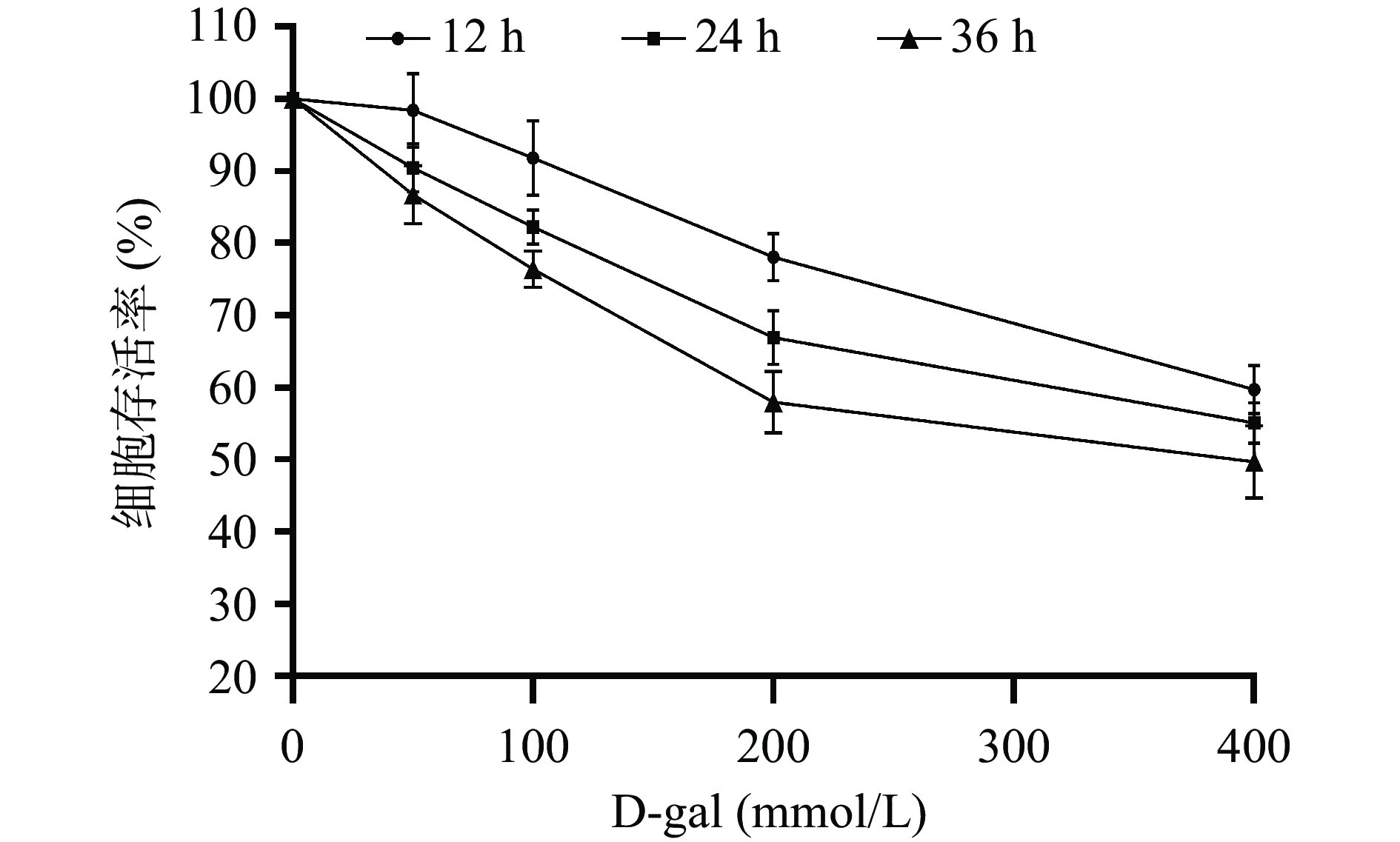
HepG2细胞存活率与D-gal浓度、诱导时间的关系如图2所示。随着D-gal浓度增大和诱导时间延长,细胞存活率表现出下降趋势,其中,400 mmol/L浓度组的细胞存活率均在60%以下,表明通过D-gal诱导细胞建立氧化应激模型的方法具有可行性。通常情况下,细胞用作构建损伤模型时的存活率应在50%~70%之间,此时既达到损伤要求,又不会对细胞造成不可逆伤害[21]。结果表明,当D-gal浓度为200 mmol/L、诱导时间为24 h时,细胞存活率降至66.92%±3.70%,处于构建模型的适宜范围之内。由此选择D-gal诱导条件为200 mmol/L,24 h。
2.3 芦荟多糖对氧化应激损伤细胞存活率的影响
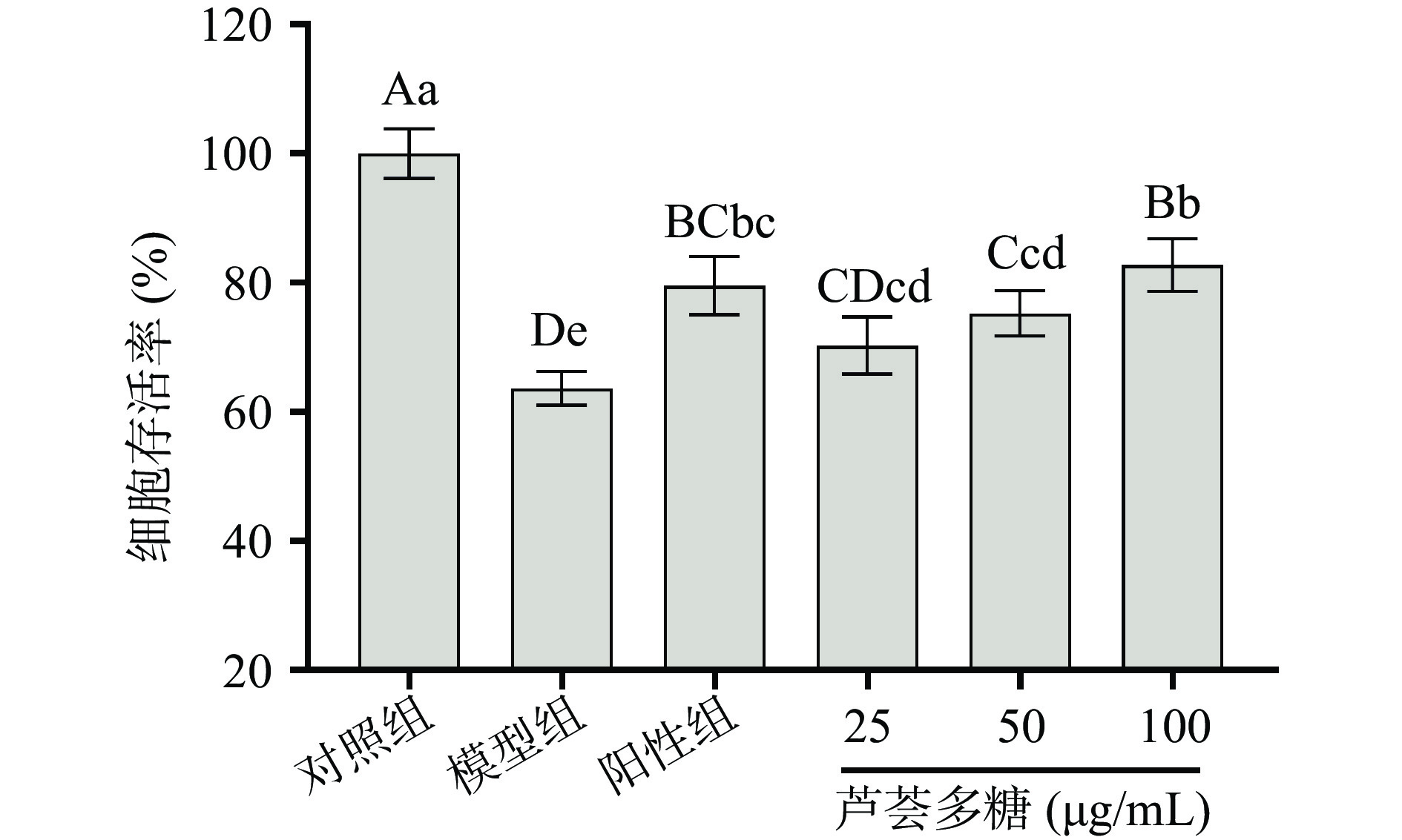
实验结果如图3所示。D-gal诱导后的细胞存活率降至63.68%±2.64%,与对照组相比有极显著差异(P<0.01),且处于构建损伤模型的存活率范围内,可视为造模成功。芦荟多糖低、中、高浓度组细胞存活率分别为70.27%±4.43%、75.26%±3.49%、82.74%±4.06%,与模型组相比均有显著提高(P<0.05),且细胞存活率与芦荟多糖浓度呈正相关,其中终浓度50、100 μg/mL的芦荟多糖处理组表现为极显著(P<0.01)。维生素C作为天然抗氧化剂,可以清除人体内过氧化自由基、猝灭单线态氧,减轻机体氧化损伤,并参与修复受损的组织细胞[22]。以VC为阳性参照组,中、高浓度的芦荟多糖组细胞存活率与其没有显著性差异(P>0.05),体现了相近的保护作用。实验结果表明,三个浓度组的芦荟多糖预保护处理均能显著提高氧化应激损伤的细胞存活率(P<0.05)。
2.4 芦荟多糖对HepG2细胞抗氧化能力的影响
2.4.1 细胞上清液MDA含量测定
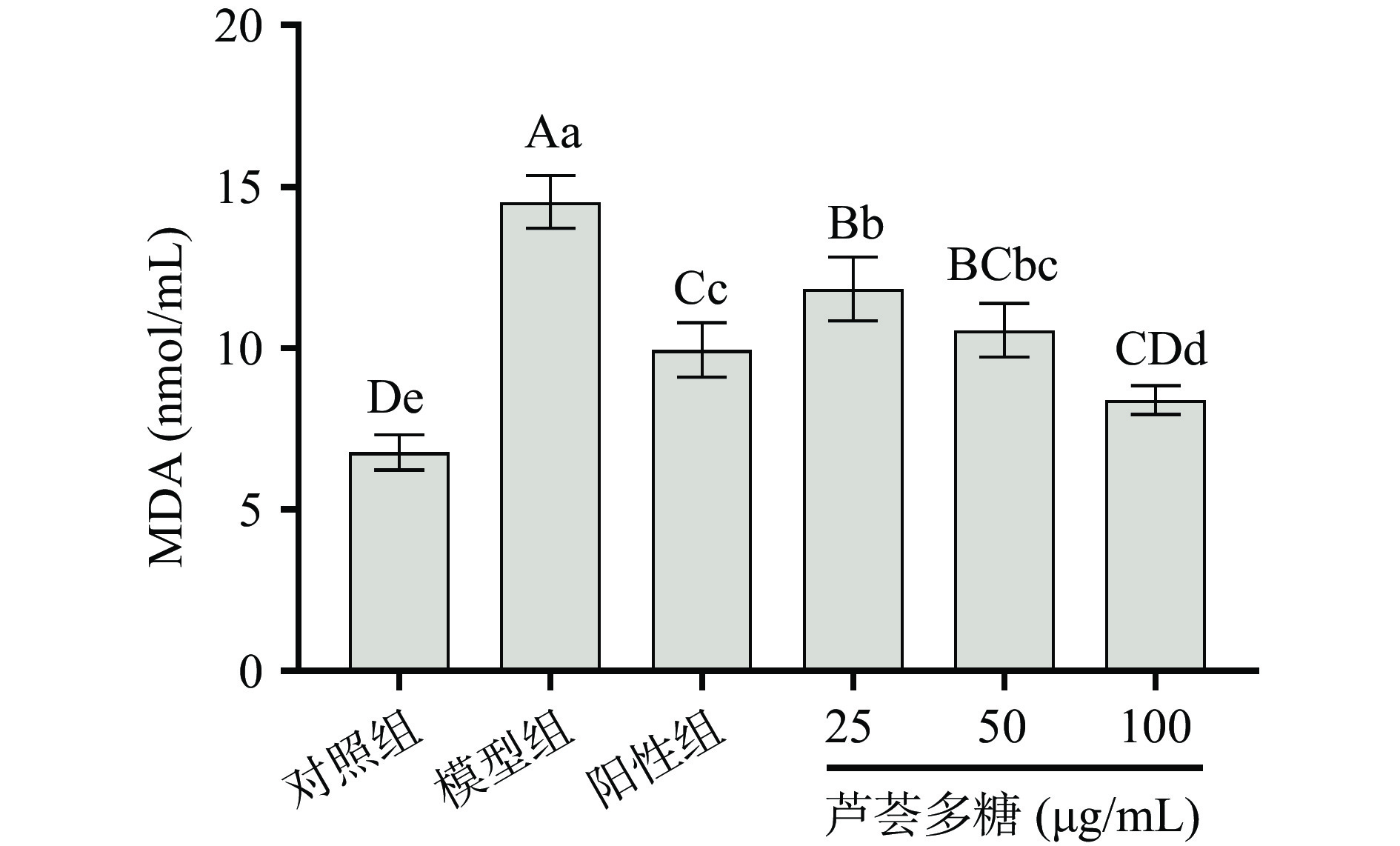
MDA是由ROS作用于细胞膜发生链式反应,引起脂质过氧化而产生的有毒物质,其过量积累会破坏细胞膜结构导致细胞质溢出,损害细胞功能[23]。因此,可通过MDA含量检测细胞受氧化损伤程度[24]。如图4所示,D-gal模型组细胞培养上清液中MDA含量为(14.53±0.82)nmol/mL,与对照组(6.78±0.55)nmol/mL相比有极显著增加(P<0.01)。在实验组中,细胞经过25~100 μg/mL芦荟多糖的预保护处理,MDA的含量均较模型组显著降低(P<0.05),分别为(11.83±0.99)、(10.56±0.82)、(8.39±0.45)nmol/mL,表明芦荟多糖可以在一定程度上缓解ROS对细胞造成的损伤,且其保护作用随浓度的增高而逐渐加大,其中高浓度组的芦荟多糖处理较VC组(9.95±0.84 nmol/mL)效果更显著(P<0.05)。
2.4.2 细胞抗氧化酶系活力测定
ROS由过氧化氢、超氧阴离子、羟基自由基、单线态氧等组成,炎症反应、冷热应激、衰老、紫外线、过量摄入酒精等内外界因素都会导致细胞内ROS大量积累。清除ROS是保护生物体减轻氧化应激损伤的重要途径,在人体中主要靠抗氧化酶系来实现。SOD、CAT、GPx属于常见的抗氧化酶类,参与组成生物对氧化损伤的防御体系,降低ROS对细胞的侵害[25-26]。实验通过检测HepG2细胞中三种酶活力的变化,来初步评价芦荟多糖的抗氧化能力。结果见表2。
表 2 HepG2细胞中SOD、CAT、GPx、T-AOC水平Table 2. SOD, CAT, GPx, T-AOC levels in HepG2 cells组别 剂量(μg/mL) SOD
(U/mL)CAT
(U/mL)GPx
(U/mL)T-AOC
(U/mL)对照组 56.91±4.33Aa 13.93±1.22Aa 30.22±3.42Aa 82.32±2.66Aa 模型组 27.42±2.35Cd 5.59±0.41Cd 14.46±1.67Dd 48.73±1.42De VC阳性组 38.28±1.49Bc 9.67±0.81Bbc 26.13±1.69ABab 72.68±2.23Bb AP低浓度组 25 34.08±3.43BCcd 7.61±0.95BCcd 18.70±2.31Cc 56.50±1.89Cd AP中浓度组 50 37.56±2.81Bc 11.01±1.65ABb 22.09±1.68BCb 66.91±2.47Bc AP高浓度组 100 45.34±5.12Bb 9.61±2.03Bbc 24.72±1.10Bb 72.74±3.26Bb 注:不同小写字母代表差异显著(P<0.05),不同大写字母代表差异极显著(P<0.01);表3同。 D-gal造模后,三种酶活力均较正常细胞极显著降低(P<0.01),D-gal对细胞抗氧化酶活性起明显抑制作用。与模型组相比,中、高浓度芦荟多糖处理组细胞中三种酶的活力水平均显著增强(P<0.05),其中,SOD、GPx活力上升趋势与芦荟多糖呈浓度依赖关系。在25 μg/mL的芦荟多糖处理组中,GPx活力与模型组相比显著升高(P<0.05),SOD、CAT活性虽有所提高但差异不显著(P>0.05)。当芦荟多糖浓度为100 μg/mL时,细胞中SOD的活性显著高于VC阳性组(P<0.05)。以上结果表明,芦荟多糖能增强氧化应激条件下HepG2细胞中SOD、CAT、GPx的活性,作用效果与其浓度呈正相关。
2.4.3 细胞总抗氧化能力
总抗氧化能力(T-AOC)代表能够平衡细胞内氧化还原状态的各种抗氧化活性物质和酶系的总体水平,通常用来综合评价生物抵御氧化应激损伤的能力[27]。由表2可知,D-gal诱导的HepG2细胞总抗氧化能力极显著降低(P<0.01)。经过芦荟多糖三个浓度组的预保护处理后,细胞中T-AOC显著提高,与模型组相比表现为极显著(P<0.01),其中,100 μg/mL的芦荟多糖组总抗氧化能力提升幅度最大,和VC组得到了近似结果。
结合2.3结果分析,各组细胞存活率的变化趋势与2.4.2实验结果一致,其原理可能为芦荟多糖在一定程度上提高了细胞中SOD、CAT、GPx等抗氧化酶活力,从而起到增强细胞应对外界氧化损伤的能力,减少细胞的死亡数量。
2.5 芦荟多糖对细胞Keap1、Nrf2、NQO1和HO-1的mRNA表达水平的影响
核因子E2相关因子2(Nuclear factor E2 related factor 2,Nrf2)是在机体抵御氧化应激损伤时起重要作用的一种转录调节因子,对位于其下游靶基因的表达起活化作用。在机体内氧化还原处于平衡状态时,Nrf2在胞浆中被Kelch样ECH相关蛋白1(Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1,Keap1)的相互作用所结合,与cullin 3(CUL3)/RBX E3泛素连接酶形成复合体,最终导致Nrf2蛋白酶体降解[28]。当平衡被打破后,氧化应激导致Keap1构象发生变化,Nrf2泛素化中止的同时半衰期延长,转移至细胞核中与抗氧化反应原件(antioxident responsed element,ARE)结合[29],并激活下游醌氧化还原酶1(Quinone oxidoreductase 1,NQO1)、血红素加氧酶-1(Hemeoxygenase1,HO-1)、谷胱甘肽S-转移酶[30]等Ⅱ相解毒酶基因的表达。
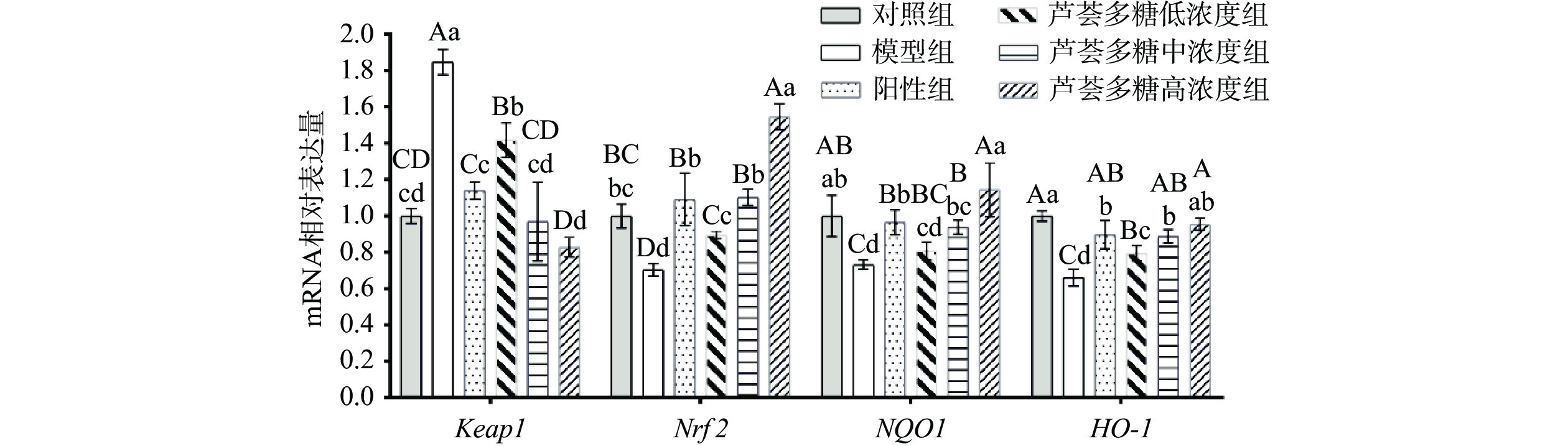
Keap1/Nrf2是调节人体氧化失衡、降低炎症反应、提高线粒体功能[31]的重要通路,在细胞抗氧化损伤、维持内环境稳态的过程中起着必不可少的作用。通过qRT-PCR测定HepG2细胞中Keap1、Nrf2、NQO1和HO-1基因的表达量,可以进一步明确芦荟多糖对HepG2细胞氧化应激损伤的保护作用途径。实验结果见表3及图5。
表 3 HepG2细胞Keap1、Nrf2、NQO1、HO-1的相对表达量Table 3. Relative expression of Keap1, Nrf2, NQO1 and HO-1 in HepG2 cells组别 剂量
(μg/mL)Keap1 Nrf2 NQO1 HO-1 对照组 1.000±0.041CDcd 1.000±0.067BCbc 1.000±0.113ABab 1.000±0.028Aa 模型组 1.848±0.071Aa 0.703±0.034Dd 0.732±0.026Cd 0.661±0.045Cd VC阳性组 1.140±0.048Cc 1.092±0.145Bb 0.965±0.069Bb 0.897±0.078ABb AP低浓度组 25 1.419±0.095Bb 0.896±0.018Cc 0.807±0.048BCcd 0.794±0.041Bc AP中浓度组 50 0.969±0.216CDcd 1.103±0.044Bb 0.938±0.039Bbc 0.889±0.037ABb AP高浓度组 100 0.827±0.055Dd 1.546±0.071Aa 1.145±0.147Aa 0.954±0.033Aab D-gal处理后,HepG2细胞Nrf2、NQO1、HO-1 mRNA表达水平显著降低(P<0.05)。与D-gal模型组相比,芦荟多糖处理后的细胞Keap1基因表达水平极显著降低(P<0.01),当芦荟多糖的质量浓度为50、100 μg/mL时,Keap1表达与对照组间无显著差异(P>0.05);细胞中Nrf2、NQO1和HO-1的mRNA表达水平与模型组相比均显著提高(P<0.05),并与芦荟多糖浓度呈正相关,其中,芦荟多糖高浓度组的Nrf2和NQO1表达水平显著高于VC阳性组(P<0.05)。结果表明,D-gal会抑制Nrf2及下游蛋白的mRNA表达,而芦荟多糖可以有效缓解D-gal造成的Nrf2抑制作用,减轻细胞氧化损伤程度。
3. 讨论与结论
实验结果表明:芦荟多糖在12.5~400 μg/mL范围内对HepG2细胞无毒性作用;在D-gal浓度为200 mmol/L,诱导时间24 h条件下,通过25、50、100 μg/mL三个浓度的芦荟多糖预保护处理,可以不同程度地提高氧化损伤细胞的存活率,减少细胞MDA的生成量,提高细胞SOD、CAT、GPx活力和T-AOC水平,浓度依赖性地上调Nrf2、NQO1、HO-1基因的表达并降低Keap1的表达。由此可以推断,芦荟多糖能负向调节Keap1的表达以抑制Nrf2泛素化降解,提高NQO1、HO-1的转录水平,增强细胞抗氧化酶系活性并调控细胞氧化还原系统,以达到减轻细胞氧化损伤程度、提高细胞抗氧化能力的效果。
本研究通过构建D-gal诱导的体外损伤模型,证明了芦荟多糖对氧化应激损伤的HepG2细胞有保护作用,其机制可能与降低Keap1的表达水平从而抑制Keap1-CUL3/RBX E3复合体间的相互作用,激活Nrf2在细胞质的合成和核积累,启动下游ARE调控的抗氧化代谢途径中NQO1、HO-1等Ⅱ相解毒酶和包括SOD、CAT、GPx在内的抗氧化酶系基因转录有关。Nrf2作为生物体抵御外源性刺激的核心转录因子,除了Keap1蛋白发挥主要调控功能外,其磷酸化活化与蛋白激酶C(protein Kinase C,PKC)、胞内磷脂酰肌醇-3-激酶(phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase,PI3K)等多种信号通路分子也存在相关性[32]。李建学[33]的研究结果表明,芦荟多糖能促进PKC蛋白的表达及磷酸化,引起丝裂原活化蛋白激酶反应以促进创面愈合。在细胞应对氧化应激损伤的调节过程中,PKC介导的Nrf2磷酸化修饰在Nrf2核易位过程中起重要作用[34],由此可以猜测,芦荟多糖对Nrf2的激活效应不仅体现在Keap1/Nrf2通路上,可能还涉及到PKC/Nrf2/HO-1等信号通路间的级联调控作用。
目前关于芦荟多糖的提取方式正不断优化,分离纯化水平进一步提升,芦荟多糖在食品行业中的应用有广阔前景。本研究对于将芦荟多糖作为功能性成分进行食品新产品的研发,提供了一定的理论依据和参考价值。然而,功能因子在生物体内的调节途径较为复杂,影响因素更多,因此对于芦荟多糖在体内发挥抗氧化作用的机制以及与信号通路间的调控关系,还需进行更深入的研究。
-
表 1 引物序列
Table 1 Primer sequence
基因名称 引物序列(5’-3’) NM编号 GAPDH F
RCGACCACTTTGTCAAGCTCA
AGGGGTCTACATGGCAACTGNM_001357943 KEAP1 F
RAGAGCGGGATGAGTGGCA
GCTGAATTAAGGCGGTTTGTCNM_012289 NRF2 F
RCAGTCAGCGACGGAAAGAGT
AAGTGACTGAAACGTAGCCGANM_006164 NQO1 F
RCCCCAGGATTCAGGCGTTG
ATCAGTGCTCTTCTGCCGACNM_001025434 HO-1 F
RATGACACCAAGGACCAGAG
TAAGGACCCATCGGAGAAGNM_002133 表 2 HepG2细胞中SOD、CAT、GPx、T-AOC水平
Table 2 SOD, CAT, GPx, T-AOC levels in HepG2 cells
组别 剂量(μg/mL) SOD
(U/mL)CAT
(U/mL)GPx
(U/mL)T-AOC
(U/mL)对照组 56.91±4.33Aa 13.93±1.22Aa 30.22±3.42Aa 82.32±2.66Aa 模型组 27.42±2.35Cd 5.59±0.41Cd 14.46±1.67Dd 48.73±1.42De VC阳性组 38.28±1.49Bc 9.67±0.81Bbc 26.13±1.69ABab 72.68±2.23Bb AP低浓度组 25 34.08±3.43BCcd 7.61±0.95BCcd 18.70±2.31Cc 56.50±1.89Cd AP中浓度组 50 37.56±2.81Bc 11.01±1.65ABb 22.09±1.68BCb 66.91±2.47Bc AP高浓度组 100 45.34±5.12Bb 9.61±2.03Bbc 24.72±1.10Bb 72.74±3.26Bb 注:不同小写字母代表差异显著(P<0.05),不同大写字母代表差异极显著(P<0.01);表3同。 表 3 HepG2细胞Keap1、Nrf2、NQO1、HO-1的相对表达量
Table 3 Relative expression of Keap1, Nrf2, NQO1 and HO-1 in HepG2 cells
组别 剂量
(μg/mL)Keap1 Nrf2 NQO1 HO-1 对照组 1.000±0.041CDcd 1.000±0.067BCbc 1.000±0.113ABab 1.000±0.028Aa 模型组 1.848±0.071Aa 0.703±0.034Dd 0.732±0.026Cd 0.661±0.045Cd VC阳性组 1.140±0.048Cc 1.092±0.145Bb 0.965±0.069Bb 0.897±0.078ABb AP低浓度组 25 1.419±0.095Bb 0.896±0.018Cc 0.807±0.048BCcd 0.794±0.041Bc AP中浓度组 50 0.969±0.216CDcd 1.103±0.044Bb 0.938±0.039Bbc 0.889±0.037ABb AP高浓度组 100 0.827±0.055Dd 1.546±0.071Aa 1.145±0.147Aa 0.954±0.033Aab -
[1] HU Y Y, WANG S P, WANG A Q, et al. Antioxidant and hepatoprotective effect of Penthorum chinense Pursh extract against t-BHP-induced liver damage in L02 cells[J]. Molecules,2015,20(4):6443−6453. doi: 10.3390/molecules20046443
[2] ZHANG D, FENG Y, PAN H, et al. 9-Methylfascaplysin exerts anti-ischemic stroke neuroprotective effects via the inhibition of neuroinflammation and oxidativestress in rats[J]. Int Immunopharmacol,2021,97:107656. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107656
[3] 邵思迈, 史洺, 余姊阳, 等. 阿尔茨海默病中的β淀粉样肽与氧化应激[J]. 中国比较医学杂志,2021,31(10):131−135. [SHAO S M, SHI M, YU Z Y, et al. Amyloid-β protein and oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease[J]. Chinese Journal of Comparative Medicine,2021,31(10):131−135. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7856.2021.10.020 [4] TAKANO K, KOARASHI K, KAWABE K, et al. Insulin expression in cultured astrocytes and the decrease by amyloid β[J]. Neurochem Int,2018,119:171−177. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2017.10.017
[5] PRABU S M, MUTHUMANI M. Retraction note to: Silibinin ameliorates arsenic induced nephrotoxicity by abrogation of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis in rats[J]. Molecular biology reports,2021,48(6):1.
[6] SUN Z H, WEI K, YAN Z G, et al. Effect of immunological enhancement of aloe polysaccharide on chickens immunized with Bordetella avium inactivated vaccine[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2011,86(2):684−690. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2011.05.012
[7] XU C, XU F. Radio sensitizing effect of aloe polysaccharide on pancreatic cancer bxpc-3 cells[J]. Pakistan Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences,2016,29(4):1123.
[8] 张文志, 欧水平, 吴会超, 等. 芦荟多糖对实验性结肠炎大鼠肠黏膜的保护作用及其机制研究[J]. 实用医学杂志,2016,32(3):352−355. [ZHANG W Z, OU S P, WU H C, et al. The protection effect and mechanism of aloe polysaccharide on experimental colitis mucosa[J]. The Journal of Practical Medicine,2016,32(3):352−355. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-5725.2016.03.004 [9] 崔燕. 芦荟对黄曲霉毒素B1致大鼠肝损伤的干预及其作用机制研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2015 CUI Y. Hepatoprotective activity and mechanism of Aloe vera on aflatoxin B1-induced liver injury in rats[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2015.
[10] 刘达, 诸凡凡, 向正国. 芦荟多糖对炎症性肠病小鼠免疫功能及OX40、OX40L表达的影响[J]. 中国中医急症,2018,27(6):1015−1018,1029. [LIU D, ZHU F F, XIANG Z G. Influences of aloe polysaccharide on immunologic function and expressions of OX40 and OX40L in mice with inflammatory bowel disease[J]. Journal of Emergency in Traditional Chinese Medicine,2018,27(6):1015−1018,1029. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-745X.2018.06.021 [11] 刘泽鑫, 刘畅, 钱和. 芦荟多糖复方体外抗氧化及预防小鼠酒精性肝损伤作用[J]. 食品科技,2020,45(2):211−218. [LIU Z X, LIU C, QIAN H. Aloe polysaccharide compound in vitro antioxidant and prevention of alcoholic liver injury in mice[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,45(2):211−218. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2020.02.035 [12] 张晓林, 杨安平. 中华芦荟多糖对小鼠急性肝损伤保护作用[J]. 中国公共卫生,2007(3):339−340. [ZHANG X L, YANG A P. Protective effect of polysaccharide from Aloe vera L. var Chinensis on acute liver injury in mice[J]. Chinese Journal of Public Health,2007(3):339−340. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-0580.2007.03.040 [13] JUAN B. Ergothioneine rich Agaricus bisporus extracts decreases lipid accumulation induced by oleic acid in HepG2 cells: Possible implications in the treatment of nonalcoholic liver fatty disease[J]. Food Science & Nutrition,2019,5(2):1−7.
[14] ZHOU X, WANG W M, LI Z F, et al. Rosmarinic acid decreases the malignancy of pancreatic cancer through inhibiting Gli1 signaling[J]. Phytomedicine,2022,95:153861. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2021.153861
[15] GUO W J, LIU J X, SUN J X, et al. Butyrate alleviates oxidative stress by regulating NRF2 nuclear accumulation and H3K9/14 acetylation via GPR109A in bovine mammary epithelial cells and mammary glands[J]. Free Radic Biol Med,2020,152:728−742. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.01.016
[16] PAN X, SONG X, WANG C, et al. H2Se induces reductive stress in HepG2 cells and activates cell autophagy by regulating the redox of HMGB1 protein under hypoxia[J]. Theranostics,2019,9(6):1794−1808. doi: 10.7150/thno.31841
[17] WANG Y D, LI J Y, QIN Y, et al. Exogenous hydrogen sulfide alleviates-induced intracellular inflammation in HepG2 cells[J]. Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology & Diabetes,2020,128(3):137−143.
[18] 潘聪, 张大力, 段盛林, 等. 高核苷酸酵母水解物调控HepG2细胞氧化损伤作用[J]. 中国食品学报,2020,20(9):10−18. [PAN C, ZHANG D L, DUAN S L, et al. High-nucleotide yeast hydrolysate regulates oxidative damage of HepG2 cells[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2020,20(9):10−18. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2020.09.002 [19] 金鑫, 李敬双, 王一伦, 等. 银杏多糖对小鼠淋巴细胞免疫调节作用的研究[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(4):301−306. [JIN X, LI J S, WANG Y L, et al. Effects of Ginkgo biloba polysaccharides on immune regulation of lymphocyte in mice[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(4):301−306. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020040312 [20] 张佳婵, 程琳, 化璟琳, 等. 沙棘粕醇提取物对小鼠氧化应激损伤的保护作用及机制[J]. 中国食品学报,2019,19(7):11−19. [ZHANG J C, CHENG L, HUA J L, et al. The protective effect and mechanism of ethanol extract from seabuckthorn meal on oxidative stress injury in mice[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2019,19(7):11−19. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2019.07.002 [21] 张业尼, 钱磊, 陈雪, 等. 过氧化氢诱导HepG2细胞氧化应激模型的建立[J]. 食品研究与开发,2018,39(5):160−164. [ZHANG Y N, QIAN L, CHEN X, et al. Establishment of hydrogen peroxide induced oxidative stress model in HepG2 cells[J]. Food Research and Development,2018,39(5):160−164. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2018.05.029 [22] 匡逸静, 谢安琪, 田鹏, 等. 维生素C对酒精性肝损伤大鼠肠道菌群的影响[J]. 现代食品,2021(10):192−195,202. [KUANG Y J, XIE A Q, TIAN P. et al. Effect of vitamin C on intestinal flora in rats with alcoholic liver injury[J]. Modern Food,2021(10):192−195,202. doi: 10.16736/j.cnki.cn41-1434/ts.2021.10.051 [23] BUSH C J, BINDER C J. Malondialdehyde epitopes as mediators of sterile inflammation[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta. Molecular and Cell Biology of Lipids,2016,1862(4):398−406.
[24] ISLAMIANA D, PRABOWO R, PRAMANINGTYAS M D. The effect of orange water kefir on malondialdehyde (MDA) level and superoxide dismutase (SOD) inhibition rate in kidney tissue of the hyperlipidemic rat (Rattus norvegicus)[J]. Atherosclerosis,2020,315:e264.
[25] GAO Y, LIU Y J, MA F L, et al. Lactobacillus plantarum Y44 alleviates oxidative stress by regulating gut microbiota and colonic barrier function in Balb/C mice with subcutaneous d-galactose injection[J]. Food & Functin,2021,12:373−386.
[26] JAIKUA W, KUEAKHAI P, CHAITHIRAYANON K, et al. Cytosolic superoxide dismutase can provide protection against Fasciocla gigantica[J]. Acta Tropi-ca,2016,162:75−82. doi: 10.1016/j.actatropica.2016.06.020
[27] JIA R, DU J L, CAO L P, et al. Effects of dietary baicalin supplementation on growth performance, antioxidative status and protection against oxidative stress-induced liver injury in GIFT tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus)[J]. Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology,2021,240:108914.
[28] ZHANG L L, KAN M, ZHANG M M, et al. Multiregion sequencing reveals the intratumor heterogeneity of driver mutations in TP53-driven non-small cell lung cancer[J]. Int J Cancer,2017,140(1):103−108. doi: 10.1002/ijc.30437
[29] 李燕, 龚美玲, 叶小萍, 等. KEAP1基因及其突变位点对非小细胞肺癌细胞株作用的实验初步研究[J]. 现代生物医学进展,2021,21(7):1201−1207. [LI Y, GONG M L, YE X P, et al. The functional study of KEAP1 gene and its mutation in NSCLC cell line: a preliminary experimental study[J]. Progress in Modern Biomedicine,2021,21(7):1201−1207. [30] RUOTSALAINEN A K, LAPPALAINEN J P, HEISKANEN E, et al. Nuclear factor E2-related factor 2 deficiency impairs atherosclerotic lesion development but promotes features of plaque instability in hypercholesterolaemic mice[J]. Cardiovasc Res,2019,115(1):243−254. doi: 10.1093/cvr/cvy143
[31] LU M C, JI J A, JIANG Z Y, et al. The Keap1-Nrf2-ARE pathway as a potential preventive and therapeutic target: an update[J]. Medicinal Research Reviews,2016,36(5):924−963. doi: 10.1002/med.21396
[32] 王丹. PI3K/Akt/JNK信号级联调控Nrf2/HO-1在三氯生致神经元氧化损伤中的作用研究[D]. 沈阳: 中国医科大学, 2021 WANG D. Triclosan regulates Nrf2/HO-1 pathway through the PI3K/Akt/JNK[D]. Shenyang: China Medical University, 2021.
[33] 李建学. 芦荟多糖通过VEGFR-2介导的PKC信号通路调控血管内皮细胞增殖和促进创面愈合的作用机制[D]. 福州: 福建医科大学, 2016 LI J X. The mechanism of aloe vera polysaccharides regulates proliferation in vascular endothelial cell mediated by PKC signaling pathways of VEGFR-2 and improves wound healing in mice[D]. Fuzhou: Fujian Medical University, 2016.
[34] 董文珠, 曹晓倩, 王璐, 等. AngⅡ-ROS-PKC/Nrf2/HO-1通路调控LX-2细胞增殖的机制研究[J]. 浙江中医药大学学报,2018,42(4):319−325. [DONG W Z, CAO X Q, WANG L, et al. Mechanism of AngⅡ-ROS-PKC/Nrf2/HO-1 pathway regulating proliferation of LX-2 cells[J]. Journal of Zhejiang Chinese Medical University,2018,42(4):319−325. doi: 10.16466/j.issn1005-5509.2018.04.017






 下载:
下载:

 下载:
下载:



