Effects of Solid Frmented Bran on the Quality of Dough and Noodles
-
摘要: 本文使用乳酸菌和酵母菌发酵麦麸,通过糊化特性、动态流变学、面条质构特性和体外消化等指标来探究固态发酵麦麸对面团以及面条品质的影响。结果表明,发酵麦麸的不溶性膳食纤维含量显著降低(P<0.05),可溶性膳食纤维、可溶性阿拉伯木聚糖(WEAX)和多酚含量显著提高(P<0.05)。与未发酵麦麸组相比,发酵麦麸组面团的峰值粘度和谷值粘度增加;弹性模量(G')和粘性模量(G")增大,tanδ和蠕变柔量(J)减小,面团的粘弹性和结构强度增加;水分分布得到改善,弱结合水的流动性提高,强结合水的含量增加;二级结构中的β-折叠和无规则卷曲的相对含量显著降低(P<0.05),而β-转角则显著增加(P<0.05),减弱了麦麸对面筋蛋白的解聚作用。与此同时,发酵麦麸显著降低(P<0.05)全麦面条的蒸煮损失率。发酵麦麸组全麦面条的硬度和咀嚼度减小,弹性和粘聚性有所增加。消化实验表明发酵麦麸面条的葡萄糖释放量均低于普通小麦粉面条以及未发酵麦麸面条,强化了全麦面条淀粉的抗消化性。Abstract: In this paper, the effect of solid fermented bran on dough as well as noodle quality was investigated by using lactic acid bacteria and yeast to ferment bran, through paste characteristics, dynamic rheology, noodle texture and in vitro digestion. The results showed that the insoluble dietary fibre content of the fermented bran was significantly lower (P<0.05) and the soluble dietary fibre, WEAX and polyphenol content were significantly higher (P<0.05). Compared to the unfermented bran group, the peak and grain viscosity of the dough increased in the fermented bran group. The elastic modulus (G') and viscous modulus (G") increased, tanδ and creep flexibility (J) decreased, and the viscoelasticity and structural strength of the dough increased. The moisture distribution was improved, the mobility of weakly bound water increased and the content of strongly bound water increased. The relative content of β-sheet and random-coil in the secondary structure was significantly reduced (P<0.05), while the β-turn was significantly increased (P<0.05), weakening the depolymerising effect of bran on gluten proteins. At the same time, fermented bran significantly reduced (P<0.05) the cooking loss rate of wholemeal noodles. The hardness and chewiness of the wholemeal noodles in the fermented bran group were reduced and the elasticity and cohesiveness were increased. The final digestion experiments showed that the glucose release from the fermented bran noodles was lower than that of both the plain wheat flour noodles and the unfermented bran noodles, which enhanced the digestibility of the whole wheat noodles starch.
-
随着人们对健康产品需求的提高,能够有效克服高血压、糖尿病和结肠癌等健康问题的全麦食品被人们所重视[1]。小麦麸皮富含膳食纤维、维生素以及多酚类活性成分,其营养和功能特性使麦麸成为全麦食品优异的添加选择[2],Fardet等[3]的报道称麦麸中多酚等活性成分在全麦食品中发挥重要作用,使全麦食品在抗衰老、癌症预防等方面具备潜在的功效。面条作为传统面食,在人们日常饮食中占据重要地位,但是因为肥胖症的增加和追求健康饮食,添加麦麸制成的低GI、高纤维的全麦面条受到人们的青睐[4]。但是添加高吸水性的麦麸会对面团的面筋蛋白有一定的破坏作用,削弱全麦面团的筋力和粘弹性,使面团可塑性变差[5-6]。麦麸对面团的弱化作用使全麦面条出现变硬、粘聚性降低以及干物质损失率变大等食用品质降低的现象[7]。
为了提高麦麸的利用率,人们对麦麸进行改性,减弱其不利影响。Li等[8]利用微波处理全麦粉,发现微波处理后淀粉的峰值和最终粘度增加,全麦鲜面条的微生物生长和变暗率明显受到抑制。Xing等[9]研究了超声静置对全麦面条特性的影响,与对照组相比,超声处理可以加速面团中水分重新分布,面筋大分子聚合物增加,改善了全麦面条的质地特性。Zhang等[10]的研究发现,添加预水合处理麦麸的全麦馒头质地以及内部结构得到有效改善,且提高了全麦面条的加工质量。相比于物理化学等改性方法,微生物发酵改性成本低,条件温和且能显著提高活性成分的含量[11]。Banu等[12]研究发现酵母发酵燕麦麸皮改善了全麦面包的比容和硬度,且提高了总酚含量。Tu等[13]发现添加松生拟层孔菌发酵麦麸的面团的结构性得到了显著改善,植酸含量显著降低。杨文丹等[14]利用马克斯克鲁维酵母发酵麦麸并制得发酵麦麸面包,结果表明面包面团的发酵特性提高,面包的质构特性和比容得到显著提升。
目前,对固态发酵麦麸应用于全麦面条的报道较少,因此,本研究采用乳酸菌、酵母菌以及乳酸酵母协同对麦麸进行固态发酵,并探讨固态发酵麦麸的添加对面团以及面条的品质特性影响,旨在为发酵麦麸应用到在面条制品中提供理论依据和科学支撑。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
小麦麸皮 山东德州夏津发达面粉有限公司;小麦粉 河北金沙河面业有限公司;鼠李糖乳杆菌(Lactobacillus rhamnosus,LGG)、植物乳杆菌(Lactobacillus plantarum,LP)、酿酒酵母(Saccharomyces cerevisiae,SC) 大学微生物实验室保藏菌种;唾液淀粉酶(500 U/mL)、胃蛋白酶(2500 U/mg)、糖化酶(10万U/mL)、中温a-淀粉酶(2000 U/mL) 阿拉丁试剂(上海)有限公司;葡萄糖试剂盒 长春汇力生物技术有限公司。
TecMaster快速黏度仪(Rapid Visco Analyzer,RVA) Newport Scientific公司;Model Hake 60哈克红外流变联用仪(Thermal Fisher Scientific)、Micro MR-25低场核磁 赛默飞世尔科技(中国)有限公司;IS50傅里叶红外光谱仪 美国尼高利公司;Epoch2多功能酶标仪 美国Thermo公司;TA.XT.Plus质构分析仪 英国Stable Micro Symstems公司;JYN-YM1面条机 杭州九阳生活电器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 麦麸固态发酵
将100 g小麦麸皮分别置于烧杯中密封,121 ℃高温灭菌20 min,冷却至室温。鼠李糖乳杆菌发酵组(GFB):在灭菌麦麸中接入5%(v/w)浓度为108 CFU/mL的LGG;植物乳杆菌发酵组(PFB):在灭菌麦麸中接入5%(v/w)浓度为108 CFU/mL的LP;酿酒酵母菌发酵组(SFB):在灭菌麦麸中接入5%(v/w)浓度为108 CFU/mL的SC;鼠李糖乳杆菌和酿酒酵母菌协同发酵组(GSFB):将浓度为108 CFU/mL的LGG和SC按照(1:1)(v/v)的比例混合,在灭菌麦麸中接入5%(v/w)的混合菌;植物乳杆菌和酿酒酵母菌协同发酵组(PSFB):将浓度为108 CFU/mL的LP和SC按照(1:1)(v/v)的比例混合,在灭菌麦麸中接入5%(v/w)的混合菌。
将上述接种后的麦麸与无菌水以1:1(w/v)的比例充分混和,在37 ℃恒温和真空条件下发酵48 h后,干燥粉碎并过60目筛。同时以未发酵麦麸作为对照组(WB)。
1.2.2 麦麸膳食纤维含量的测定
酶水解法进行测定,参照GB 5009.88-2014《食品中膳食纤维的测定》。
1.2.3 麦麸可溶性阿拉伯木聚糖(WEAX)含量的测定
准确称取0.5 g样品,加入20 mL去离子水,于室温下用磁力搅拌提取30 min后,5000 r/min离心10 min,取1 mL上清液于20 mL具塞试管中,同时加入等体积去离子水,然后加入10 mL反应液(5 mL 20%间苯三酚-乙醇溶液、110 mL冰醋酸、2 mL浓盐酸、1 mL 17.5 g/L葡萄糖溶液,现用现配),沸水浴反应25 min,冰浴终止反应,冷却至室温,立即在552和510 nm处测定其吸光值。同时以D-木糖标准溶液作为标准品绘制标准曲线,计算552和510 nm(对应己糖干扰)处吸光度的差值并与标准曲线y=0.0014x+0.0362(R2=0.9985)进行比较,计算可溶性阿拉伯木聚糖的含量[15]。
1.2.4 麦麸多酚含量的测定
准确称取样品1 g,加入4 mL体积分数为70%乙醇溶液,在0 ℃条件下,150 W超声提取30 min,然后将浸提液4000 r/min离心20 min,取上清液,残渣重复提取2次。收集三次提取液用乙醇定容到刻度。取多酚提取上清液200 μL,加入200 μL的福林酚试剂,混匀氧化5 min后,用400 μL 15%(w/v)的Na2CO3溶液中和反应,在25 ℃培养箱中避光孵育30 min后,将混合物于10000 r/min离心5 min,使用酶标仪在760 nm处测量吸光值。同时以没食子酸标准溶液作为标准品,制作标准曲线,根据标准曲线y=0.0167x+0.0689(R2=0.9988)计算多酚含量[13]。
1.2.5 全麦面团制备
未发酵麦麸和发酵麦麸各组分别以10%的比例加入小麦粉中,过60目筛使其混合均匀,然后将100 g混合粉和蒸馏水按照质量比2:1(w/w) 的比例和成面团,静置20 min待测。BF:添加未发酵麦麸的面团;GF:添加LGG发酵麦麸的面团;PF:添加LP发酵麦麸的面团;SF:添加SC发酵麦麸的面团;GSF:添加LGG和SC协同发酵麦麸的面团;PSF:添加LP和SC协同发酵麦麸的面团。小麦粉制成空白面团作为对照组。
1.2.6 面团糊化特性的测定
参考郑排云[16]的方法使用快速粘度分析仪(RVA)测定样品的糊化特性。称取3 g样品置于RVA专用样品桶中,加入25 mL蒸馏水,置于仪器中测定。
1.2.7 面团动态流变学特性的测定
1.2.7.1 粘弹特性的测定
参考肖悦等[17]的方法使用动态流变仪测定面团的粘弹特性。测量参数:模式为振荡频率扫描,温度25 ℃,间隔距离1 mm,扫描频率范围0.1~10 Hz,应变1%。
1.2.7.2 蠕变-回复特性的测定
参考谢岩黎等[18]的方法使用旋转流变仪测定面团的蠕变特性。测量参数:模式为Step-Creep,温度25 ℃,蠕变应变力为50 Pa。
1.2.8 面团水分分布的测定
使用低场核磁共振(LF-NMR)测定面团的水分分布。先以FID 实验调节至合适TW,然后使用CPMG脉冲序列测定横向弛豫时间(T2)。采样参数:采样频率(SW):100 kHz,采样点数(TD):36008,间隔时间(TW):1500 ms,回波个数(NECH):2000,重复扫描次数(NS):8。
1.2.9 面团蛋白质二级结构的测定
使用傅利叶变换红外光谱仪(FI-IR)分析面团蛋白二级结构相对含量。在波数400~4000 cm−1的范围内,样品用FI-IR进行全波段扫描,得到傅里叶红外光谱图,然后使用Omnic 8.0和Peakfit v 4.12软件处理分析1600~1700 cm−1段的光图谱,β-折叠、无规则卷曲、α-螺旋和β-转角对应的波数分别为1610~1640、1640~1650、1650~1660和1665~1700 cm−1。根据所得图中各子峰的面积占比,计算二级结构的相对含量[19]。
1.2.10 面条蒸煮特性的测定
将1.2.2制得面团通过小型面条机压成宽度约0.5 cm、长度约20 cm的面条。取30根20 cm的面条称重后放入装有500 mL沸水的烧杯中,煮至最佳蒸煮时间(面条白芯消失时),然后将熟面条捞出,在滤纸上沥干5 min,称量并记录。将蒸煮面条的面汤继续加热蒸至约50 mL,移至105 ℃烘箱烘至恒重。按下列公式计算吸水率和蒸煮损失率:
(1) (2) 式中:A表示吸水率,%;P表示蒸煮损失率,%;m1表示生面条质量,g;m2表示熟面条质量,g;m3表示空烧杯的质量,g;m4表示烧杯和干物质质量,g;w表示生面条水分含量,%。
1.2.11 面条质构特性的测定
参考罗云[20]的方法,面条煮至最佳蒸煮时间(面条白芯消失),沥干后使用质构分析(TPA)测定熟面条的质构特性。探头型号:P36;测前速度:2 mm/s;测中速度:1 mm/s;测后速度:1 mm/s;压缩量:50%;触发力:5 g;压缩间隔时间:1 s。
1.2.12 面条消化特性的测定
参照Englyst等[21]的方法并稍作修改。准确称取200 mg样品,加入300 μL的唾液淀粉酶溶液(60 μL的唾液淀粉酶溶于5 mL的醋酸-醋酸钠缓冲液),将样品置于水浴摇床(37 ℃,100 r/min)中酶解反应5 min后,加入15 mL胃蛋白酶(250 mg的猪源胃蛋白酶溶于250 mL浓度为0.02 mol/L的盐酸溶液)酶解反应30 min,然后向酶解液中加入15 mL 0.02 mol/L的NaOH溶液和25 mL醋酸-醋酸钠缓冲液以及10 mL复合酶溶液(1200 μL的中温a-淀粉酶和200 μL的糖化酶溶于100 mL pH为5.0的醋酸-醋酸钠缓冲液),在37 ℃条件下继续酶解反应,分别在0、0.5、1.0、1.5、2.0、2.5、3.0、6.0、9.0和12.0 h取1 mL酶解液,沸水浴进行灭酶10 min后,1000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液冷却至室温,上清液中的葡萄糖含量用葡萄糖试剂盒测定,每次均取样测量三次,取平均值。
1.3 数据处理
使用SPSS Statistix 26对以上所得数据进行分析,邓肯氏多重比较法分析数据的差异性显著,P<0.05代表差异性显著。采用Origin 2019和Prism 9软件进行做图。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 固态发酵对麦麸化学成分的影响
如表1所示,乳酸菌和酵母菌代谢过程中会产生多种不同类型的解聚酶,如糖苷水解酶、纤维素或木聚糖降解酶和酯酶,同时产生有机酸,降低pH,在酶解和酸解的作用下,麦麸的细胞壁被降解,不可溶性膳食纤维(IDF)转化为可溶性膳食纤维(SDF),所以发酵麦麸的IDF显著降低(P<0.05),SDF显著增加(P<0.05),其中,GSFB和PSFB分别增加2.03和1.94倍。不同解聚酶打断多酚与细胞璧纤维素间的酯键或醚键,束缚型多酚转化为游离型多酚,不溶性阿拉伯木聚糖(WUAX)转化为可溶性阿拉伯木聚糖(WEAX)[22],发酵麦麸的WEAX和多酚的含量显著增加(P<0.05),其中WEAX提高了207%~310%,多酚提高了49%~94%。
表 1 固态发酵前后麦麸化学成分的变化Table 1. Chemical composition of wheat bran before and after solid state fermentation指标 WB GFB PFB SFB GSFB PSFB 不可溶性膳食纤维(%) 53.69±0.76a 47.97±0.54bc 48.23±0.29b 48.5±0.56b 45.06±1.23c 46.98±0.96c 可溶性膳食纤维(%) 5.93±0.15c 8.27±0.13b 7.81±0.25b 8.58±0.07b 12.06±0.42a 11.49±0.12a WEAX(mg/g) 8.20±0.29d 26.85±0.33c 25.16±0.25c 28.84±0.32bc 33.63±0.18a 30.76±0.75b 多酚(mgGAE/g) 2.64±0.06d 4.14±0.04c 3.93±0.05c 4.52±0.15b 4.96±0.12a 5.12±0.08a 注:不同上标字母表示相同指标不同样品间存在显著性差异,P<0.05。 2.2 发酵麦麸对面团糊化特性的影响
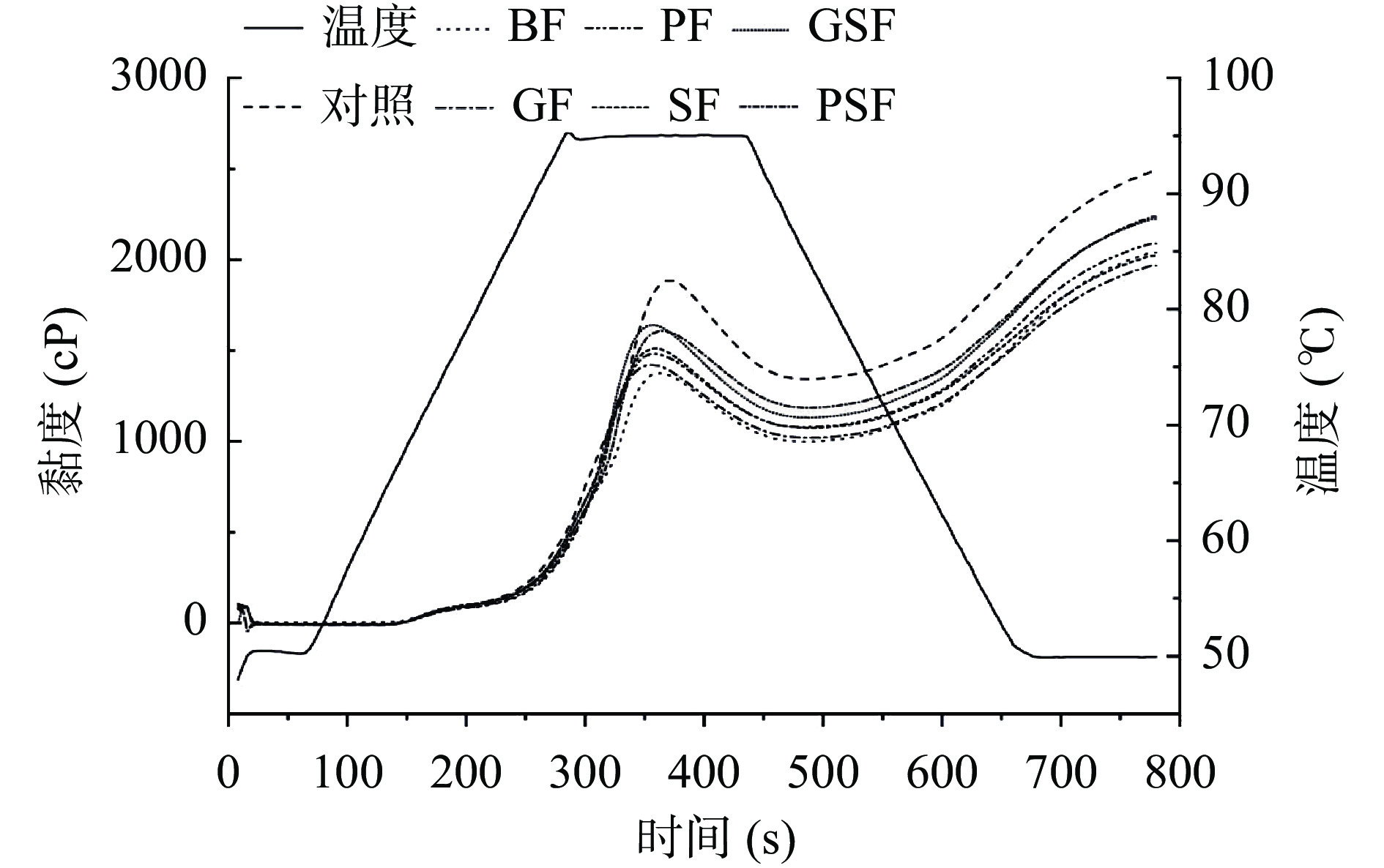
由图1可以看出,麦麸的添加降低了体系的淀粉相对含量并限制了淀粉糊化可利用水,使体系的糊化程度降低[23],全麦面团的峰值粘度、谷值粘度和最终粘度均低于对照组。发酵麦麸组的峰值粘度较BF(1375 cP)相比有所升高,其中GSF和PSF的峰值粘度分别达到1642和1609 cP,可能是由于麦麸经发酵后WEAX含量的增加使其吸水能力减弱[24],淀粉在吸水糊化过程中可利用水相对增加,更容易糊化,糊化黏度增加。谷值粘度呈现相同的规律,而且PF、GSF和PSF的最终黏度也高于BF。结果表明发酵麦麸有助于改善全麦面团的糊化特性,协同发酵能加强改善效果。而淀粉的糊化特性和面条的质构特性密切相关[25]。
2.3 发酵麦麸对面团流变特性的影响
2.3.1 发酵麦麸对面团粘弹特性的影响
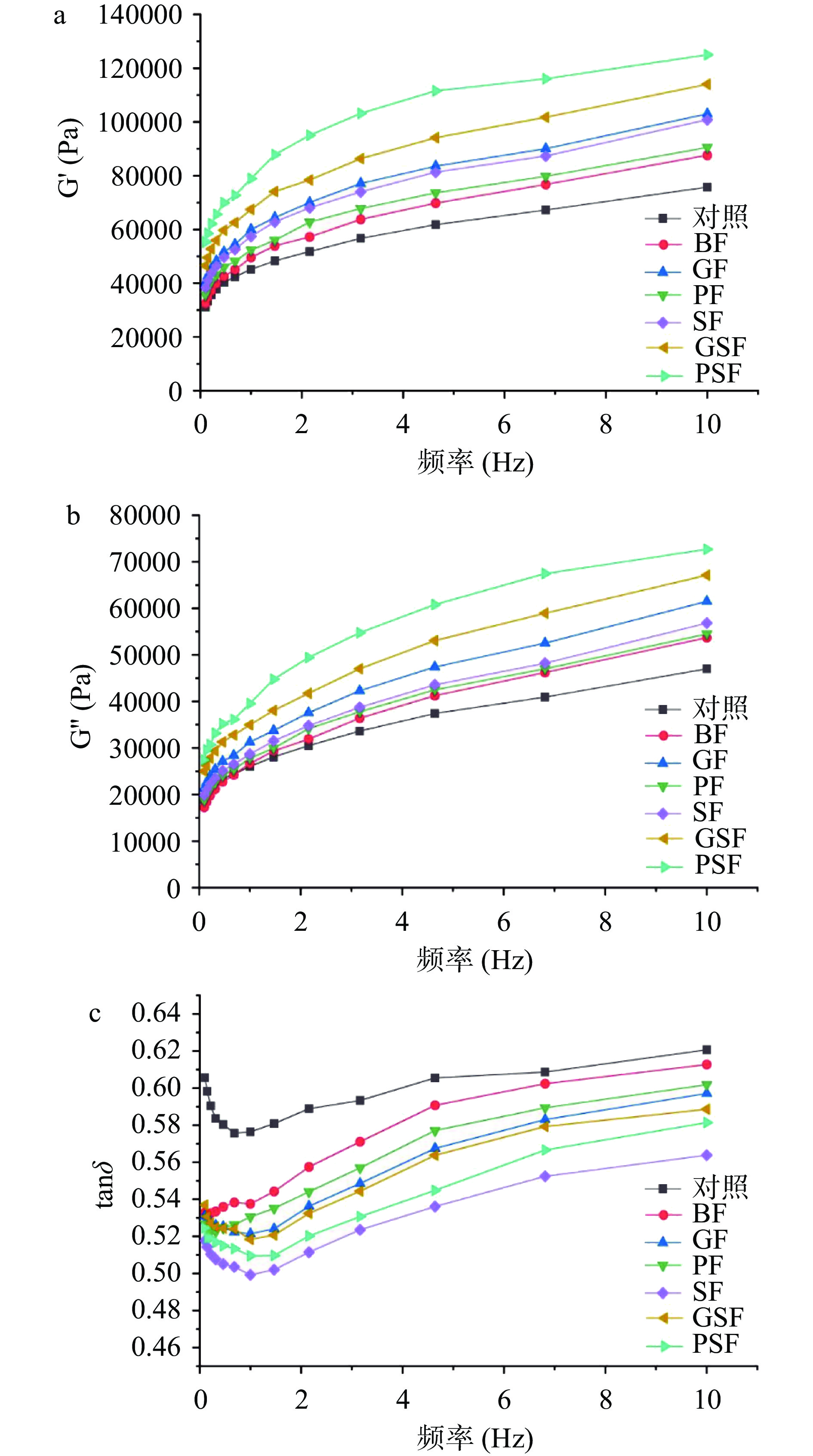
面团的动态频率扫描实验可以表征面团的粘弹特性,而面团粘弹性则可以反映面团的结构强度。弹性模量(G' )、粘性模量(G")和tanδ(G"/G' )是反应面团粘弹性的三个指标。不同面团的频率扫描结果如图2所示。结果表明,随着频率的增加,所有面团的G' 和G"均不断增加。且G'大于G"。在相同频率下,弹性模量G' 的大小为:PSF>GSF>GF>SF>PF>BF>对照,粘性模量G"有着相同的规律。表明乳酸菌和酵母菌协同发酵麦麸能有效的提高面团的粘弹性,Li等[26]的研究也得到了相似的结果。此外,所有面团的tanδ值随频率的增加先降低后升高,且tanδ < 1,这符合面团的类固体性质且弹性特征明显。发酵麦麸组的面团的tanδ均小于BF,tanδ值越小表明发酵麦麸面团体系中的高聚物更多,网络结构更强[27]。原因可能是发酵使麦麸的可溶性膳食纤维比如WEAX充分释放,其在面团形成的过程中与面筋蛋白交联形成新的网状结构,提高了面团弹性[28],结合水分分布分析,发酵麦麸使面团的水分在膳食纤维、面筋和淀粉中重新分配,更有利于面筋蛋白的形成,从而加强面团的网络结构[29]。对于乳酸酵母协同发酵组,微生物对麦麸的作用更强,释放更多的可溶性膳食纤维,所以粘弹性提高的最明显。
2.3.2 发酵麦麸对面团蠕变-回复特性的影响
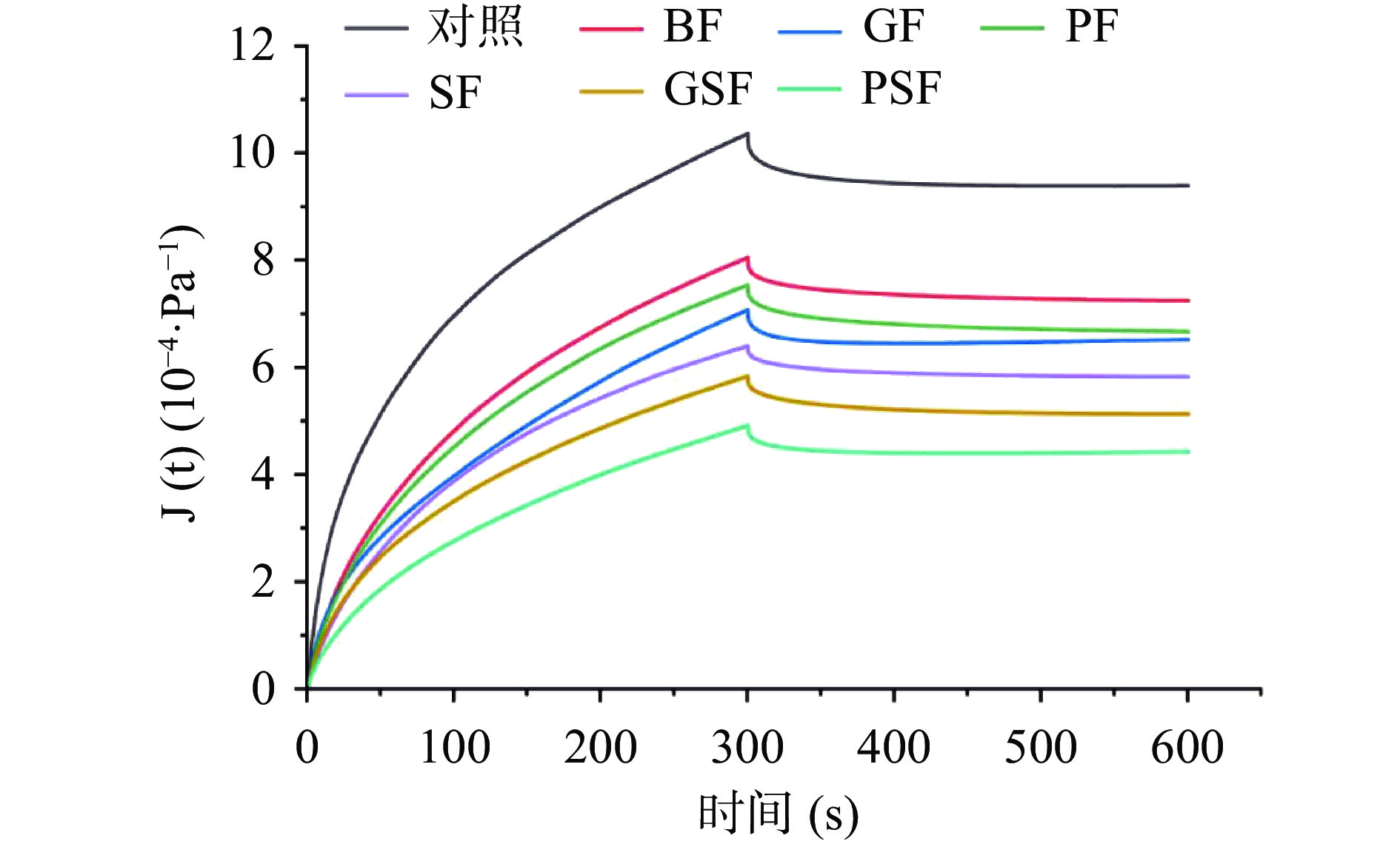
蠕变-回复实验的蠕变阶段反应面团内部结构强度,回复阶段反应面团内部结构抵抗外力形变的能力。这种方法可以从侧面表征面团阶段时间的粘弹性[30]。图3表示不同面团蠕变-回复特性曲线。发酵麦麸的加入,使全麦面团的最大蠕变柔量(Jmax)呈现明显降低的趋势,且低于BF,瞬时蠕变柔量(J0)和迟滞蠕变柔量(J1)也有相同的趋势。蠕变柔量(J)与样品的内部结构相关,柔量小的面团表明其内部结构比较强大,有更高的抵抗形变能力,反之柔量大的面团其内部结构更脆弱[31]。所以发酵麦麸添加使面团的内部结构增强,能更加有效抵御面团形变。这可能是因为发酵麦麸增加了面团的高聚物含量,使其机械强度更强[28]。
2.4 发酵麦麸对全麦面团水分分布的影响
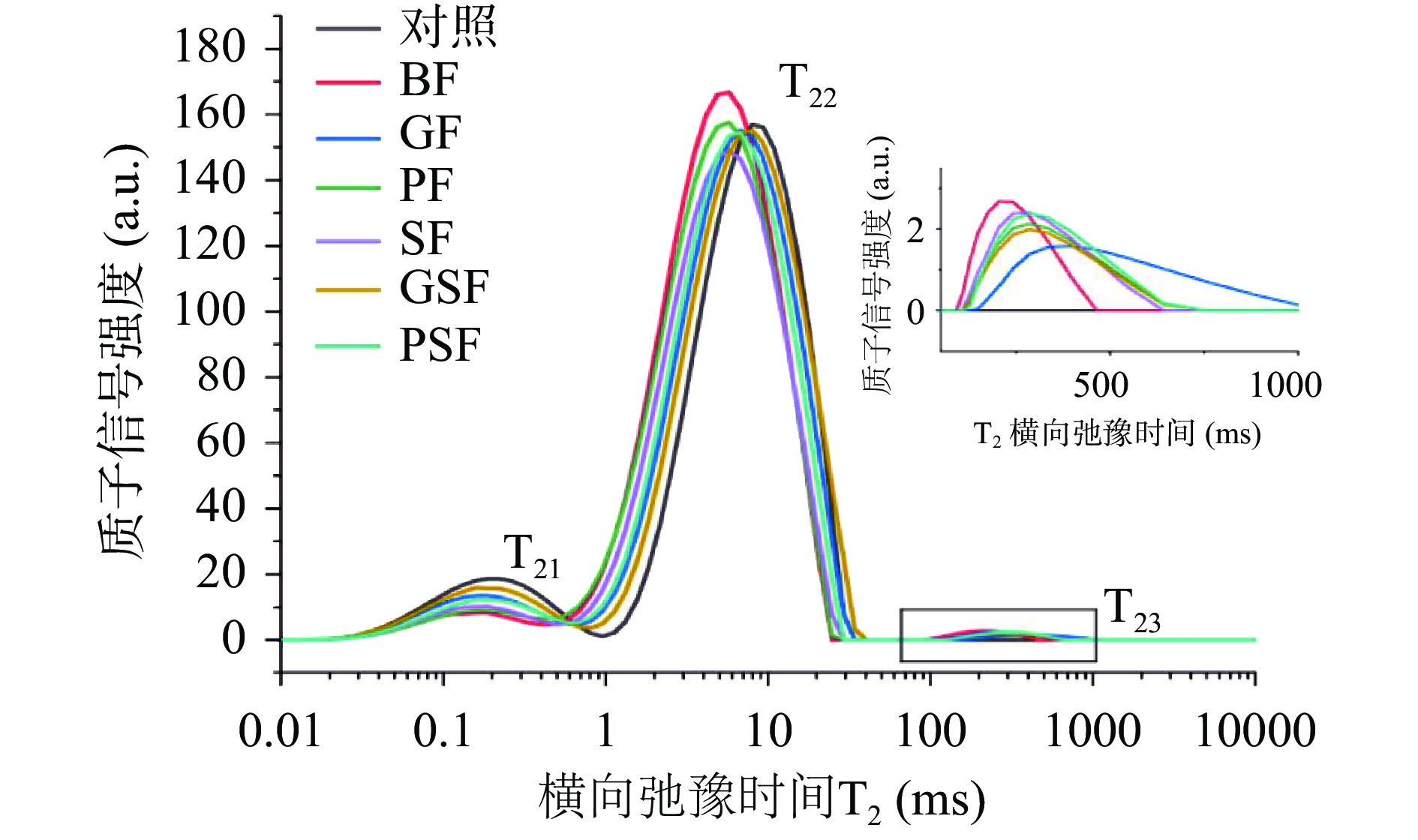
低场核磁共振仪对面团扫描的结果用T2弛豫时间分布曲线显示。实验结果如图4和表2所示,全麦面团的T2弛豫时间曲线中出现了三个峰区,分别为T21、T22和T23,T21表示与蛋白质、淀粉等大分子物质紧密结合的强结合水,T22表示被面筋网络结构所包裹不易流动的弱结合水,T23表示可以自由流动的自由水,A21、A22和A23分别表示T21、T22和T23的峰占比,即面团中强结合水、弱结合水和自由水的相对含量[32]。与BF相比,GF、PF和SF的T21和T22无明显变化,GSF和PSF的T21减小,T22增加,另外麦麸经发酵后的T23都增加,可能是因为发酵麦麸组面团中与麦麸结合的水流动性增加[33],同时,发酵麦麸组中,除了PF,其他组面团的A21与BF相比,显著增加(P<0.05),其中GSF和PSF的A21相比于BF(4.35%)增加到9.45%和8.10%,而A22和A23有所下降,表明面团中部分弱结合水和自由水迁移至强结合水,使强结合水的含量增加,面团水分子与蛋白质和淀粉等物质的结合程度增加[34]。实验结果表明发酵麦麸使全麦面团水分重新分布,降低了麦麸的竞争吸水作用,减弱麦麸对全麦面团的负面影响。
表 2 不同面团的水分分布(%)Table 2. Moisture distribution of different varieties of dough (%)样品 A21 A22 A23 对照 10.81±0.25a 89.14±1.45b 0.05±0.00d BF 4.35±0.18d 94.92±0.56a 0.75±0.04ab GF 8.14±0.07b 91.30±2.07b 0.55±0.10c PF 4.93±0.15d 94.42±1.24a 0.67±0.08b SF 6.02±0.21c 93.20±2.58a 0.78±0.13a GSF 9.45±0.08ab 89.94±0.82b 0.61±0.07bc PSF 8.10±0.12b 91.20±1.83b 0.71±0.05ab 注:同列不同上标字母表示样品间存在显著性差异,P<0.05;表3同。 2.5 发酵麦麸对全麦面团蛋白质二级结构的影响
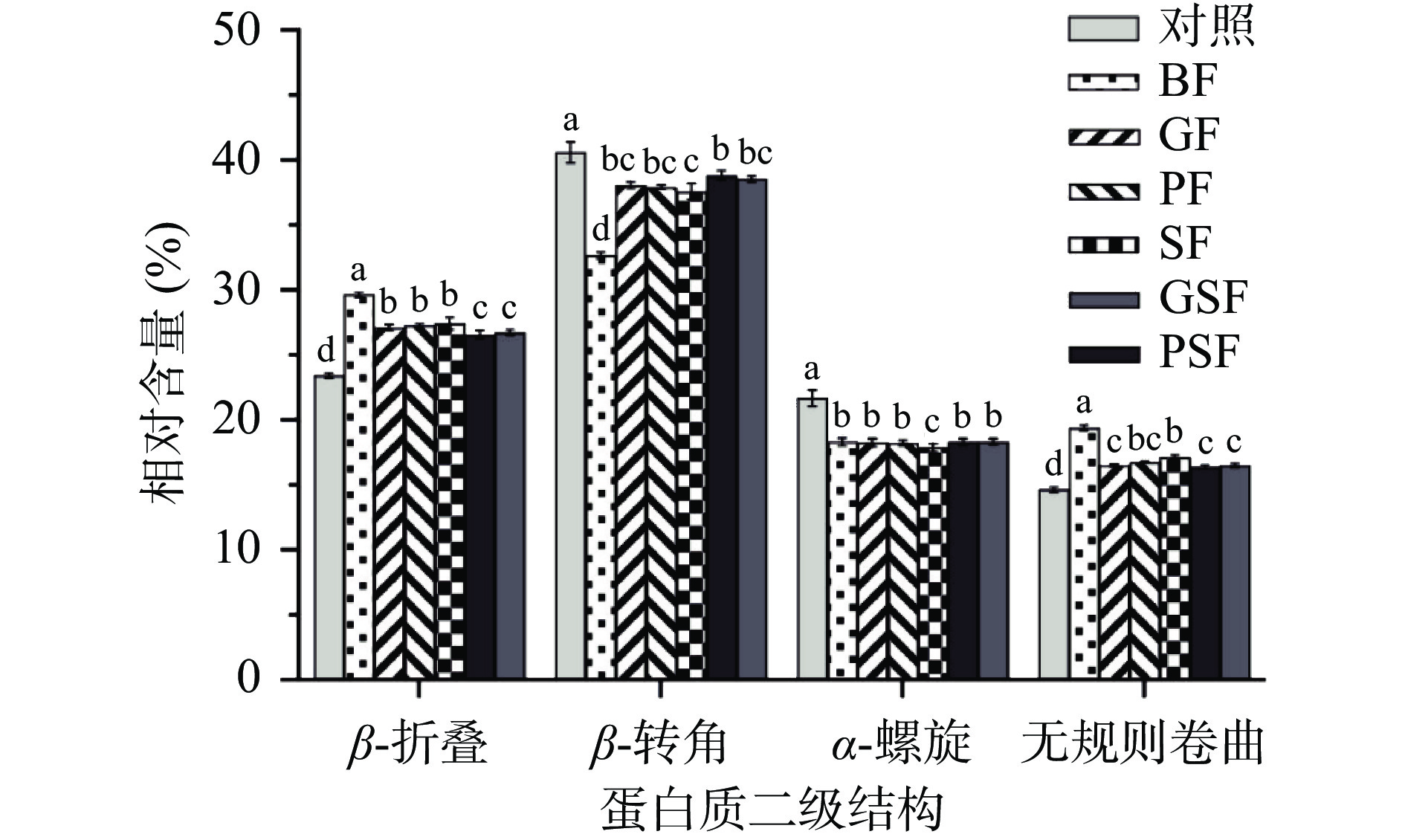
蛋白质二级结构的变化,会影响以二硫键、氢键等作用力维持的蛋白质高级结构,从而对面筋网络结构的形成造成影响。由图5可知,加入麦麸后,面团的β-折叠和无规则卷曲显著增加(P<0.05),而β-转角显著减少(P<0.05),有研究称β-转角的减少提高了肽链的延伸程度,不利于面筋蛋白聚合物的形成[35]。稳定的α-螺旋结构减少表明面团有序的二级结构趋于无序结构,这与黄莲燕等[5]的研究相一致。对于发酵麦麸组,面团中β-折叠和无规则卷曲的相对含量均显著低于BF(P<0.05),而β-转角则显著高于BF(P<0.05),乳酸酵母协同发酵后,面团的β-转角结构增加更显著,其中GSF由BF的32.68%增加到38.82%。α-螺旋则没有明显影响。二级结构的变化可能与发酵麦麸改善体系水分分布有关,Bock[36]的研究证明,蛋白二级结构在充分水合条件下,二级结构更趋向于β-转角。有报道称面团中的β-转角可能是谷蛋白多肽链中β-螺旋区域(β-spiraldomains),连续的β-转角组成β-螺旋结构,可以为面团提供良好的粘弹性[37]。结果表明发酵麦麸能减弱麦麸对面筋蛋白的解聚作用,更有利于高粘弹性面筋蛋白的形成。乳酸酵母协同发酵组对面团体系的水分分布影响更明显,因此二级结构有更显著的变化。
2.6 发酵麦麸对全麦面条蒸煮特性和质构特性的影响
面条的吸水率和蒸煮损失率是评价面条蒸煮品质的重要参数。由表3可以得知,麦麸的加入提高了面条的吸水率,蒸煮损失率则降低,这与姬翔[38]的研究发现一致。在吸水率方面,PSF相比于BF显著增加(P<0.05),而其他组没有显著变化。相比于未发酵麦麸,发酵麦麸可以显著减小(P<0.05)全麦面条的蒸煮损失率,GSF和PSF由BF的12.299%降为9.381%和10.14%,GSF的蒸煮损失率趋近于空白面条的8.014%。说明发酵麦麸提高了面条中淀粉与面筋蛋白的结合程度,原因可能是发酵麦麸能够减少麦麸对面筋蛋白的弱化程度且强化蛋白-淀粉-纤维的网络结构,阻碍淀粉聚合物在蒸煮过程中的扩散[39]。
表 3 不同面条的蒸煮特性和质构特性Table 3. Cooking and texture properties of different varieties of cooked noodles样品 蒸煮品质 质构特性 吸水率(%) 蒸煮损失率(%) 硬度(g) 弹性(%) 粘聚性(g·sec) 咀嚼度 对照 104.69±2.76d 8.014±0.200e 4880.915±75.327d 0.830±0.012a 0.679±0.006a 2750.829±69.390c BF 118.74±4.57bc 12.299±0.170a 6130.121±58.762a 0.726±0.007bc 0.668±0.005b 2975.571±19.197a GF 119.49±1.82bc 11.681±0.130b 5946.111±129.039ab 0.732±0.011bc 0.671±0.005ab 2921.300±13.573ab PF 121.18±1.05abc 11.477±0.400b 6024.193±96.163a 0.735±0.004bc 0.672±0.003ab 2973.903±42.829a SF 115.67±2.81c 11.683±0.170b 5866.924±52.165abc 0.732±0.005bc 0.670±0.003ab 2877.413±20.902abc GSF 125.05±2.02ab 9.381±0.190d 5541.118±38.595c 0.742±0.003b 0.674±0.005ab 2771.218±18.787c PSF 127.87±2.03a 10.140±0.140c 5624.590±18.252bc 0.738±0.005bc 0.675±0.004ab 2799.350±40.654bc 如表3所示,相比于对照组,麦麸的加入会导致面条硬度显著增大(P<0.05),弹性显著降低(P<0.05),晁慧梅[7]的研究表明全麦面团的硬度与麦麸的不溶性膳食纤维呈正比,其与蛋白质形成高分子聚合物并填充于面筋间隙,提高硬度。发酵能够使麦麸的不溶性膳食纤维的含量降低,提高具有高粘度性的可溶性膳食纤维的含量,从而使发酵麦麸组的全麦面条硬度降低,其中GSF显著降低(P<0.05),由BF的6130.121 g降为5541.118 g,而弹性和粘聚性有所增加,但并不显著,咀嚼度与硬度成正相关,所以咀嚼度有所降低。
2.7 发酵麦麸对全麦面条消化特性的影响
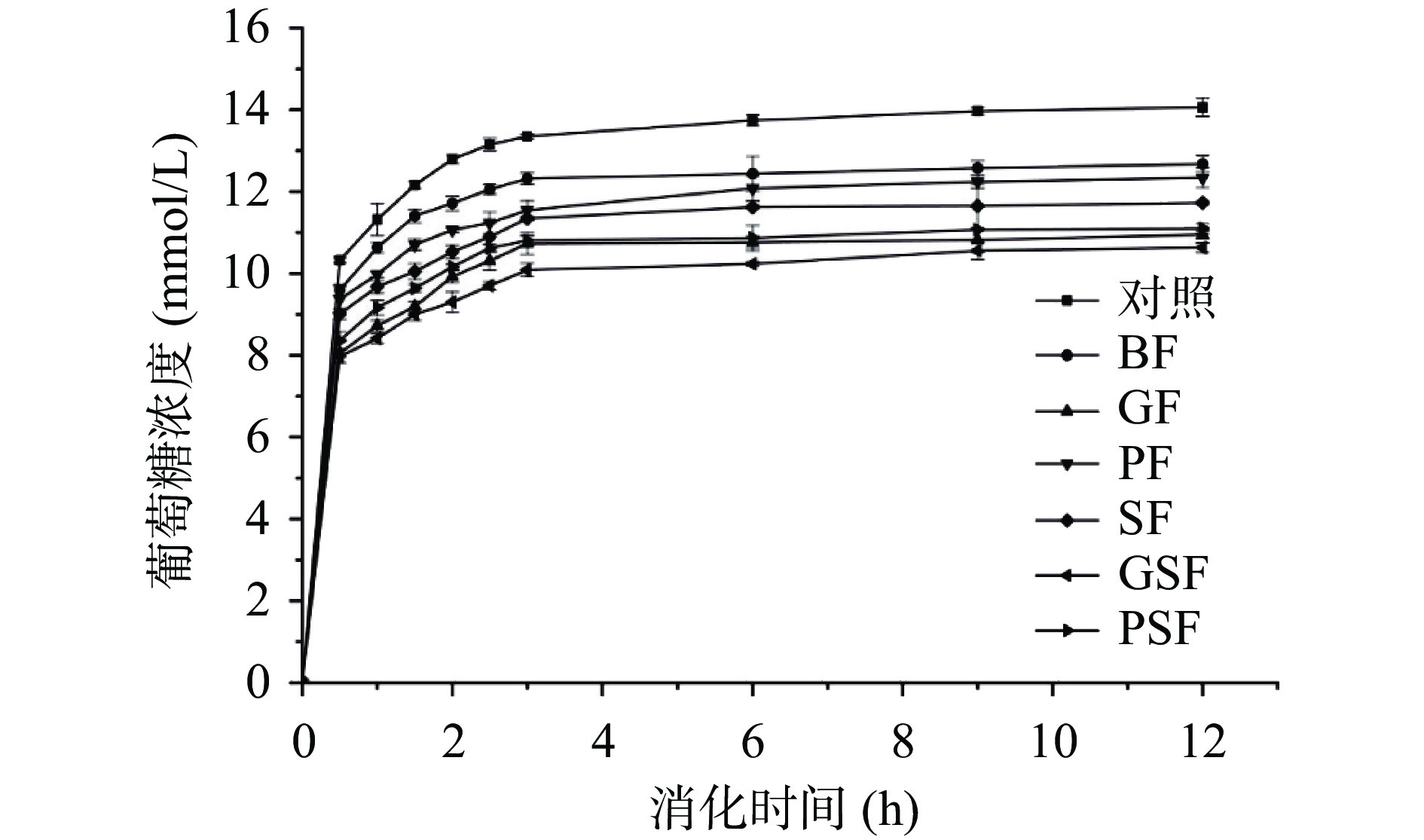
由图6可以看出,样品经过消化后,葡萄糖浓度随着时间的延长,总体趋势是在3 h前逐渐升高然后趋于稳定。在整个消化过程中,对照面条的葡萄糖释放量最高,麦麸的加入使得葡萄糖释放量显著降低。在消化终点12 h,BF的葡萄糖浓度为11.62 mmol/L,而发酵麦麸组面条的葡萄糖释放量要低于BF,其中PSF的最终葡萄糖浓度最低,为10.63 mmol/L。表明添加发酵麦麸一定程度上增加了全麦面条的抗消化性。肖志刚等[40]对改性麦麸面包研究中也得到了相似的消化结果,发酵麦麸组面条消化率的降低可能是SDF-蛋白质-淀粉凝胶结构和多酚类等活性物质对相关酶抑制活性的协同作用的结果[24,41]。
3. 结论
本研究表明,通过乳酸菌和酵母菌的发酵,麦麸的IDF含量显著降低(P<0.05)而SDF显著增加(P<0.05),各发酵组麦麸的WEAX含量提高了207%~310%,多酚含量提高了49%~94%。相比于未发酵麦麸,发酵麦麸提高了全麦面团的糊化特性和黏弹性,增强了面团的内部结构;使全麦面团弱结合水和自由水流动性增加,强结合水含量增加而自由水含量减少,其中GSF和PSF的A21相比于BF(4.35%)增加到9.45%和8.10%;蛋白质二级结构β-转角占比显著增加(P<0.05),β-折叠和无规则卷曲显著降低(P<0.05),减弱了麦麸对面团面筋蛋白结构的破坏。对于全麦面条,发酵麦麸显著降低(P<0.05)全麦面条的蒸煮损失率;改善了面条的质构特性,其中乳酸酵母协同发酵组的硬度显著降低(P<0.05),粘聚性和弹性有所增加,同时还抑制了全麦面条的淀粉消化。研究表明固态发酵能够减弱麦麸对面团以及面条的弱化,且乳酸菌和酵母菌协同发酵在降低弱化程度方面表现有更突出的优势。对于酵母菌和乳酸菌发酵对麦麸的改性效果以及对面条的影响有待进一步的探究,提高麦麸的利用率。
-
表 1 固态发酵前后麦麸化学成分的变化
Table 1 Chemical composition of wheat bran before and after solid state fermentation
指标 WB GFB PFB SFB GSFB PSFB 不可溶性膳食纤维(%) 53.69±0.76a 47.97±0.54bc 48.23±0.29b 48.5±0.56b 45.06±1.23c 46.98±0.96c 可溶性膳食纤维(%) 5.93±0.15c 8.27±0.13b 7.81±0.25b 8.58±0.07b 12.06±0.42a 11.49±0.12a WEAX(mg/g) 8.20±0.29d 26.85±0.33c 25.16±0.25c 28.84±0.32bc 33.63±0.18a 30.76±0.75b 多酚(mgGAE/g) 2.64±0.06d 4.14±0.04c 3.93±0.05c 4.52±0.15b 4.96±0.12a 5.12±0.08a 注:不同上标字母表示相同指标不同样品间存在显著性差异,P<0.05。 表 2 不同面团的水分分布(%)
Table 2 Moisture distribution of different varieties of dough (%)
样品 A21 A22 A23 对照 10.81±0.25a 89.14±1.45b 0.05±0.00d BF 4.35±0.18d 94.92±0.56a 0.75±0.04ab GF 8.14±0.07b 91.30±2.07b 0.55±0.10c PF 4.93±0.15d 94.42±1.24a 0.67±0.08b SF 6.02±0.21c 93.20±2.58a 0.78±0.13a GSF 9.45±0.08ab 89.94±0.82b 0.61±0.07bc PSF 8.10±0.12b 91.20±1.83b 0.71±0.05ab 注:同列不同上标字母表示样品间存在显著性差异,P<0.05;表3同。 表 3 不同面条的蒸煮特性和质构特性
Table 3 Cooking and texture properties of different varieties of cooked noodles
样品 蒸煮品质 质构特性 吸水率(%) 蒸煮损失率(%) 硬度(g) 弹性(%) 粘聚性(g·sec) 咀嚼度 对照 104.69±2.76d 8.014±0.200e 4880.915±75.327d 0.830±0.012a 0.679±0.006a 2750.829±69.390c BF 118.74±4.57bc 12.299±0.170a 6130.121±58.762a 0.726±0.007bc 0.668±0.005b 2975.571±19.197a GF 119.49±1.82bc 11.681±0.130b 5946.111±129.039ab 0.732±0.011bc 0.671±0.005ab 2921.300±13.573ab PF 121.18±1.05abc 11.477±0.400b 6024.193±96.163a 0.735±0.004bc 0.672±0.003ab 2973.903±42.829a SF 115.67±2.81c 11.683±0.170b 5866.924±52.165abc 0.732±0.005bc 0.670±0.003ab 2877.413±20.902abc GSF 125.05±2.02ab 9.381±0.190d 5541.118±38.595c 0.742±0.003b 0.674±0.005ab 2771.218±18.787c PSF 127.87±2.03a 10.140±0.140c 5624.590±18.252bc 0.738±0.005bc 0.675±0.004ab 2799.350±40.654bc -
[1] KIRWAN J P, MALIN S K, SCELSI A R, et al. A whole-grain diet reduces cardiovascular risk factors in overweight and obese adults: A randomized controlled trial[J]. Journal of Nutrition,2016,146(11):2244−2251. doi: 10.3945/jn.116.230508
[2] MARTINDIANA A B, GARCIACASAC M J, MARTINEZVILLALUENGA C, et al. Wheat and oat brans as sources of polyphenol compounds for development of antioxidant nutraceutical ingredients[J]. Foods,2021,10(1):115. doi: 10.3390/foods10010115
[3] FARDET, ANTHONY. New hypotheses for the health-protective mechanisms of whole-grain cereals: What is beyond fibre?[J]. Nutrition Research Reviews,2010,23(1):65−134.
[4] MENG N, GARY G H. Whole wheat noodle: Processing, quality improvement, and nutritional and health benefits[J]. Cereal Chemistry,2019,96(1):23−33. doi: 10.1002/cche.10095
[5] 黄莲燕, 张小爽, 张君慧, 等. 不同谷物麸皮对面团流变学特性及面筋蛋白结构的影响[J]. 食品科学,2017,38(23):1−7. [HUANG L Y, ZHANG X S, ZHANG H J, et al. Effect of different cereal brans on the rheological properties and gluten protein structure of dough[J]. Food Science,2017,38(23):1−7. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201723001 [6] YAMINA D E B, WISSE H, PAULA M, et al. Selective modification of wheat bran affects its impact on gluten-starch dough rheology, microstructure and bread volume[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,113:106348.
[7] 晁慧梅. 小麦麸皮特性与全麦面条品质关系研究[D]. 合肥: 安徽农业大学, 2019 CHAO H M. Study on the relationship between wheat bran characteristics and wholemeal pasta quality[D]. Hefei: Anhui Agricultural University, 2019.
[8] LI M, SUN Q J, ZHU K X. Delineating the quality and component changes of whole-wheat flour and storage stability of fresh noodles induced by microwave treatment[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2017,84:378−384. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2017.06.001
[9] XING J J, QIAO J Y, YANG Z, et al. Effects of ultrasound-assisted resting on the qualities of whole wheat dough sheets and noodles[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology, 2021, 5(3): 5609−5618.
[10] ZHANG Y, GAO F, HE Z. Effects of bran hydration and autoclaving on processing quality of Chinese steamed bread and noodles produced from whole grain wheat flour[J]. Cereal Chemistry,2019,96(1):104−114. doi: 10.1002/cche.10113
[11] 陈蒙慧, 刘远晓, 关二旗, 等. 生物处理对麦麸品质及全麦制品品质改善的研究进展[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2022(4):1−7. [CHEN M H, LIU Y X, GUAN E Q, et al. Research progress on improving the quality of wheat bran and whole wheat products by biological treatment[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2022(4):1−7. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.030761 [12] BANU I, MACELARU I, APRODU I. Bioprocessing for improving the rheological properties of dough and quality of the wheat bread supplemented with oat bran[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2017,41(5):e13112. doi: 10.1111/jfpp.13112
[13] TU J, ZHAO J, LIU G, et al. Solid state fermentation by fomitopsis pinicola improves physicochemical and functional properties of wheat bran and the bran-containing products[J]. Food Chemistry,2020,328(1):127046.
[14] 杨文丹, 张宾乐, 庄靓, 等. 发酵麦麸对面包面团生化特征及烘焙学特性的影响[J]. 食品与机械,2018,34(3):6−11. [YNAG W D, ZHANG B L, ZHUANG J, et al. Effects of fermented wheat bran on biochemical and baking characteristics of bread dough[J]. Food & Machinery,2018,34(3):6−11. doi: 10.13652/j.issn.1003-5788.2018.03.002 [15] MARCO S, ANNALISA R, LUCA C, et al. Solid state lactic acid fermentation: A strategy to improve wheat bran functionality-science direct[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2020,118:108668. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2019.108668
[16] 郑排云. 壳聚糖与淀粉干热交联对复合物性质影响研究[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2015 ZHENG P Y. Study on the effect of dry thermal cross-linking of chitosan and starch on the properties of complexes[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2015.
[17] 肖悦, 刘敏, 刘金光, 等. 黄变对大米流变特性以及内部结构的影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(11):22−27. [XIAO Y, LIU M, LIU J G, et al. Influence of rheological changes on the rheological properties and internal structure of rice[J]. Food Science,2020,41(11):22−27. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190611-118 [18] 谢岩黎, 王晨, 郝振宇. 抗性淀粉与小麦粉共混体系黏弹性的研究[J]. 中国粮油学报,2018,33(2):25−30. [XIE Y L, WANG Y, HAO Z Y. Study on the viscoelasticity of the blending system of resistant starch and wheat flour[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2018,33(2):25−30. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2018.02.005 [19] BOCK J E, CONNELLY R K, DAMODARAN S. Impact of bran addition on water properties and gluten secondary structure in wheat flour doughs studied by attenuated total reflectance Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy[J]. Cereal Chemistry,2013,90(4):377−386. doi: 10.1094/CCHEM-01-13-0008-FI
[20] 罗云. 蛋清粉对挂面品质的影响及其机理研究[D]. 无锡: 江南大学, 2015 LUO Y. Study on the effect of egg white powder on the quality of hanging noodles and its mechanism[D]. Wuxi: Jiangnan University, 2015.
[21] ENGLYST H N, KINGMAN S M, CUMMINGS J H. Classification and measurement of nutritionally important starch fractions[J]. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition,1992,46(2):S33−50.
[22] WU H, LI H, XUE Y, et al. High efficiency co-production of ferulic acid and xylooligosaccharides from wheat bran by recombinant xy-lanase and feruloyl esterase[J]. Biochemical Engineering Journal,2017,120:41−48. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2017.01.001
[23] MA S, WANG Z, TIAN X L, et al. Effect of synergistic fermentation of Lactobacillus plantarum and Saccharomyces cerevisiae on thermal properties of wheat bran dietary fiber-wheat starch system[J]. Food Chemistry,2022,373(PA):131417.
[24] LIU Y, WANG S W, KANG J, et al. Arabinoxylan from wheat bran: Molecular degradation and functional investigation[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,107:105914. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2020.105914
[25] 张慧娟, 冯钰琳, 段雅文, 等. 谷物麸皮对面团及中式面条品质的影响[J]. 中国食品学报,2019,19(2):71−79. [ZHANG H J, FNEG Y L, DUAN Y W, et al. Effects of grain bran on quality of dough and Chinese noodle[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2019,19(2):71−79. doi: 10.16429/j.1009-7848.2019.02.010 [26] LI L, WANG Z, LI L M, et al. Effects of fermented wheat bran on flour, dough, and steamed bread characteristics[J]. Journal of Chemistry,2018(201):1−7.
[27] 陈前, 李娜, 贺晓光, 等. 瓜尔豆胶对马铃薯-小麦混合粉面团质构和流变特性的影响[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(6):198−203. [CHEN Q, LI N, HE X G, et al. Effect of guar gum on the textural and rheological properties of potato-wheat flour dough mixtures[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2020,41(6):198−203. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2020.06.033 [28] WANG P, ZHAO X, YANG R, et al. Water-extractable arabinoxylan-induced changes in the conformation and polymerization behavior of gluten upon thermal treatment[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2020,68(13):4005−4016. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b08122
[29] GUO X N, YANG S, ZHU K X. Impact of arabinoxylan with different molecular weight on the thermo-mechanical, rheological, water mobility and microstructural characteristics of wheat dough[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2018,53(9):2150−2158.
[30] SUN X, KOLSEL F, NICKERSON M T, et al. Modeling the viscoelastic behavior of wheat flour dough prepared from a wide range of formulations[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2020,98(C):105129.
[31] LIU N, MA S, LI L, et al. Study on the effect of wheat bran dietary fiber on the rheological properties of dough[J]. Grain & Oil Sci and Technol,2019,2(1):1−5.
[32] 范玲, 马森, 王晓曦, 等. 麦麸添加量和粒度对发酵面团特性的影响[J]. 中国粮油学报,2016,31(7):19−24. [FAN L, MA S, WANG X X, et al. The effect of bran addition and particle size on the characteristics of fermented dough[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2016,31(7):19−24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2016.07.004 [33] LI J, KANG J, WANG L, et al. Effect of water migration between arabinoxylans and gluten on baking quality of whole wheat bread detected by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)[J]. Journal of Agricultural & Food Chemistry,2012,60(26):6507.
[34] 周玉瑾, 李梦琴, 李超然, 等. 麦麸水溶性膳食纤维和水不溶性膳食纤维对面条性状指标的影响及其扫描电镜的观察[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2015,41(6):128−133. [ZHOU Y J, LI M Q, LI C R, et al. Effect of water-soluble dietary fibre and water-insoluble dietary fibre of wheat bran on the trait index of noodles and its observation by scanning electron microscopy[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2015,41(6):128−133. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.201506024 [35] HAN W, MA S, LI L, et al. Gluten aggregation behavior in gluten and gluten-starch doughs after wheat bran dietary fiber addition[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2019,106(1):1−6.
[36] BOCK J E, DAMODARAN S. Bran-induced changes in water structure and gluten conformation in model gluten dough studied by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy[J]. Food Hydrocolloids,2013,31(2):146−155. doi: 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2012.10.014
[37] WELLNER N, MILLS E, BROWNSEY G, et al. Changes in protein secondary structure during gluten deformation studied by dynamic fourier transform infrared spectroscopy[J]. Biomacromolecules,2005,6(1):255−261. doi: 10.1021/bm049584d
[38] 姬翔. 全麦粉对面粉及面条品质的影响[D]. 郑州: 河南工业大学, 2019 JI X. Effects of whole wheat flour on flour and noodle quality[D]. Zhengzhou: Henan University of Technology, 2019.
[39] LEI M, HUANG J, TIAN X, et al. Effects of insoluble dietary fiber from wheat bran on noodle quality[J]. Grain & Oil Science and Technology,2021,4(1):1−9.
[40] 肖志刚, 李芮芷, 罗志刚, 等. 添加改性麸皮对含麸皮面包结构及消化特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2021(6):39−45. [XIAO Z G, LI Z R, LUO Z G, et al. Effect of modified bran addition on the structure and digestive characteristics of bread containing bran[J]. Food Science,2021(6):39−45. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20200223-267 [41] 梁雅琪, 徐文静, 李晨. 苦荞面包中生物活性物质体外淀粉消化特性及感官评价[J]. 农产品加工,2021(20):16−19. [LIANG Y Q, XU W J, LI C. In vitro starch digestion characteristics and sensory evaluation of bioactive substances from Tartary buckwheat bread[J]. Academic Periodical of Farm Products Processing,2021(20):16−19. -
期刊类型引用(5)
1. 陈聪,薛桥丽,胡永金,魏美娟,陈中爱. 云南木姜子醇提物抑菌活性及其稳定性研究. 食品工业科技. 2023(16): 147-154 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 段雪娟,黄煜强,张潼,韩雅莉,吴克刚,黄庶识. 肉桂醛熏蒸对金黄色葡萄球菌胞内生物大分子的影响. 中国食品学报. 2023(10): 90-100 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张文艳,李俊杰,艾玲松,李茂东,赵仲霞,师睿. 青花椒总生物碱对金黄色葡萄球菌抑菌活性研究. 工业微生物. 2023(06): 50-54 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 王建梅,王国盼,陆安静,秦琳,鲁艳柳,白朝钧,何芋岐,谭道鹏. 金钗石斛提取物对5种耐药菌的体外抑菌活性评价. 遵义医科大学学报. 2022(03): 334-338 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 黄藩,王迎春,叶玉龙,龚雪蛟,黄颖博,熊元元. 变温萎凋技术对贡眉白茶品质的影响. 中国农学通报. 2022(19): 159-164 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(6)







 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



