Determination of Hydrogen Concentration in Hydrogen-rich Water by Headspace Gas Chromatography and Hydrogen Microelectrode
-
摘要: 氢气含量为富氢水的关键指标之一,但目前尚无标准检测方法。本文将超饱和富氢水稀释后采用顶空-气相色谱法与氢气微电极法测定了氢气含量,对检测方法进行了条件优化、方法学评价,并对市售富氢水产品进行了氢气含量检测。结果显示,顶空-气相色谱法优化后的顶空进样平衡温度为70 ℃、平衡时间为20 min。在0~1.61 mg/L氢气含量范围内决定系数(R2)为0.9976,在0.161、0.805、1.449 mg/L添加水平,回收率分别为104.90%、102.22%和97.78%,相对标准偏差(RSD)分别为3.87%、2.29%和1.69%。氢气微电极法在0~1.61 mg/L氢气含量范围内R2为0.9978,在0.161、0.805、1.449 mg/L添加水平,回收率分别为96.75%、95.78%和98.00%,RSD分别为1.84%、0.98%和2.80%。对7种市售罐装富氢水的检测发现,不同产品中氢气含量相差较大,从0.8~6.2 mg/L不等,但均达到现有团体标准的要求。开盖后超饱和富氢水中氢气存留量在30 min内降低约10%,6 h内降低约50%。本研究建立了富氢水中氢气含量的检测方法,顶空-气相色谱法与氢气微电极法均可用于实际样品的测定。Abstract: The hydrogen concentration is one of the key indicators of hydrogen-rich water, but there is no standard detection method at present. In this paper, the concentration of hydrogen in hydrogen-rich water was determined by headspace gas chromatography and hydrogen microelectrode followed by sample dilution. The detection method was optimized, the methodological evaluations were performed, and the hydrogen concentrations of hydrogen-rich water products were tested. Results showed that for headspace gas chromatography method, the optimized headspace sampling equilibrium temperature was 70 ℃ and the time was 20 min. The determination coefficient (R2) was 0.9976 in the range of 0~1.61 mg/L hydrogen content. The recoveries were 104.90%, 102.22%, 97.78%, and the relative standard deviations (RSD) were 3.87%, 2.29%, 1.69% at the spiked levels of 0.161, 0.805 and 1.449 mg/L. For hydrogen microelectrode method, the R2 was 0.9978 in the range of 0~1.61 mg/L hydrogen content. The recoveries were 96.75%, 95.78%, 98.00%, and the RSD were 1.84%, 0.98%, 2.80% at the spiked levels of 0.161, 0.805 and 1.449 mg/L. For the detection of seven commercial hydrogen-rich water products, it showed that hydrogen content varies greatly, ranging from 0.8~6.2 mg/L, although they all met the requirements of the existing group standard. The hydrogen concentration decreased by 10% in 30 min and 50% in 6 h after the cover was opened. The present study would develop the methods for hydrogen concentration detection in hydrogen-rich water, and both of the headspace gas chromatography and hydrogen microelectrode methods were reliable and can be used in actual samples.
-
氢气在常温常压下为无色无味气体,其分子量小,在体内可无障碍地透过各种屏障进入细胞内部[1-2]。2007年,有学者发现吸入低浓度的氢气在体内可中和毒性自由基,减少缺血再灌注损伤[3]。之后,氢气的生物医学效应得到了广泛关注。从基础研究到临床治疗,氢气在呼吸系统疾病、代谢性疾病、衰老相关疾病等多个领域崭露头角[4-8]。氢气用于人体的安全性体现在多个方面:首先,氢气是人体肠道菌群的正常代谢产物[9-10]。同时,在潜水医学领域氢气早已应用于人体,没有发现任何的毒性反应及不良后果[11]。在氢气医学迅速发展的近十几年中,大量的临床试验也未发现氢气的毒副作用[12-14]。更多高质量的氢气安全性和有效性数据有待科学家们进一步收集分析。在我国,氢气已被认可作为食品添加剂,出现在正式颁布的国家标准中[15],在日本[16]、欧盟[17]、美国[18],氢气也被列为安全的食品添加剂。作用于人体的氢气供体多种多样,主要包括吸入不同浓度氢气、饮用富氢水、氢水沐浴等[12,19-20],其中饮用富氢水是较为常见的一种方式[21]。
富氢水即含有氢气的水,其制备及储存方式有多种,氢气含量为评价富氢水的最关键指标之一[22-23]。在常温常压下饱和氢气水溶液中氢气含量约为1.61 mg/L,通过微气泡等技术,可以使水中不仅有溶解状态的氢气,也有微气泡状态的氢气,从而提高了富氢水中的氢气含量[24]。目前水中氢气含量的检测方法有气相色谱法、氢气微电极法、亚甲蓝氧化还原滴定法等[25-27]。文献中已有相关检测方法的报道,但检测对象均为实验室中充入氢气的水,对市面上的富氢水产品或超饱和富氢水中氢气含量检测尚无报道。这些方法是否适合目前富氢水产品中氢气含量的检测尚无系统研究。气相色谱法检测从富氢水中释放出来的氢气,对于含微气泡的超饱和富氢水,可以通过加热等方式促进氢气的释放。氢电极法适用于检测溶解于水中的氢气,其测量范围为饱和浓度以下,目前市面上很多富氢水为超饱和的微气泡富氢水,本文通过稀释的方式使氢气浓度至饱和以下并完全溶解。亚甲蓝氧化还原滴定法通过纳米铂催化氢气还原亚甲蓝,根据亚甲基蓝的用量得到水溶液中氢气的含量[28]。此法方便快捷,但较为粗略,无法准确定量。
在我国,富氢水产品尚未制订国家标准和行业标准,目前仅有团体标准T/NAHIEM 16-2019《含氢包装饮用水》[29],其中提到“产品保质期内,氢气含量不低于0.6 mg/L”,在氢气含量检验中提到“氢气的含量使用气相色谱法进行测定(对氢浓度的检测也可采用与气相色谱法精度相当的检测方法)”,但具体检测流程尚未制定。为规范相关市场,推进行业发展,建立标准的富氢水中氢气含量检测方法刻不容缓。可以定量检测富氢水中氢气含量的方法主要为顶空-气相色谱法和氢气微电极法。本文对两种检测方法进行了方法学验证,建立了可用于实际富氢水产品中氢气含量的检测方法,并检测了市面罐装富氢水中氢气含量,可以为相关应用提供参考。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
20 mL顶空瓶 美国Agilent公司;超纯水 密理博Milli-Q超纯水机;7种市售罐装富氢水 (产品1,生产日期:2022-02-25,1.5 mg/L<标注浓度<2 mg/L;产品2,生产日期:2022-02-26,2.5 mg/L<标注浓度≤3 mg/L;产品3,生产日期:2022-01-25,1.5 mg/L<标注浓度<2 mg/L;产品4,生产日期:2021-11-24,2.5 mg/L<标注浓度≤3 mg/L;产品5,生产日期:2021-11-23,2 mg/L≤标注浓度≤2.5 mg/L;产品6,生产日期:2022-01-19,2 mg/L≤标注浓度≤2.5 mg/L;产品7,生产日期:2022-01-19,1.5 mg/L<标注浓度<2 mg/L)。
8890气相色谱仪配热导检测器、7697A顶空进样器、GS-CarbonPLOT毛细管柱(30 m×3 μm,0.32 mm) 美国Agilent公司;微电极系统(配有H2-50氢气微电极) 丹麦Unisense公司;SPE-300纯水氢气发生器 济南浩伟实验仪器有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 氢气标准水溶液的制备
在20 ℃,标准大气压(101 kPa)下将氢气发生器制备的高纯度氢气(>99.99%)经分散器充入超纯水中直到饱和。查阅文献可知此时水中氢气浓度约为805 μmol/L[30],即1.61 mg/L。将此溶液用超纯水稀释,配制成浓度为0、0.161、0.322、0.805、0.966、1.449、1.610 mg/L的标准工作溶液。
1.2.2 顶空-气相色谱检测
色谱柱:GS-CarbonPLOT毛细管柱(30 m×3 μm,0.32 mm);载气(N2)流速3.0 mL/min;进样口温度200℃,分流比20:1;柱温35 ℃,检测器温度: 200 ℃。顶空条件:样品平衡时间20 min;顶空瓶温度70 ℃;定量环温度80 ℃;传输线温度80 ℃;进样时间0.5 min。取5 mL标准工作液置于20 mL顶空瓶中,立即封闭后检测,得到标准曲线。将待测富氢水用超纯水稀释至标准曲线范围内(氢气浓度<1.61 mg/L),取5 mL稀释后样本置于20 mL顶空瓶中检测。根据标准曲线计算稀释后样本中氢气含量,并乘以稀释倍数得到原始样本中氢气含量。
1.2.3 氢气微电极检测
氢气微电极极化电压为100 mV,将氢气微电极插入超纯水中,待电极信号稳定后开始进行检测。极化时间约为2 h。取10 mL标准工作液于50 mL离心管中,立即将氢气微电极插入液面以下待信号稳定,得到标准曲线。将待测富氢水用超纯水稀释至标准曲线范围内(氢气浓度<1.61 mg/L),取10 mL稀释后样本检测,根据标准曲线计算稀释后样本中氢气含量,并乘以稀释倍数得到原始样本中氢气含量。
1.2.4 罐装富氢水产品中氢气含量检测
开盖后立即取适量体积富氢水用超纯水稀释至标准曲线范围内(氢气浓度<1.61 mg/L),根据1.2.2和1.2.3中的方法分别检测罐装富氢水产品中氢气含量。检测日期均为2022年3月,各产品均在保质期内。对于产品1和产品2,采用氢气微电极法检测开盖后8.3 h内定时取样,检测氢气含量随时间变化情况。
1.3 数据处理
相关实验重复3次,数据用均值±标准差表示。2组之间检测结果使用独立样本t检验分析显著性差异。采用使用SPSS 20 及 Origin 8.5 软件进行数据分析及图形绘制。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 顶空-气相色谱法
2.1.1 顶空进样平衡温度与时间的优化
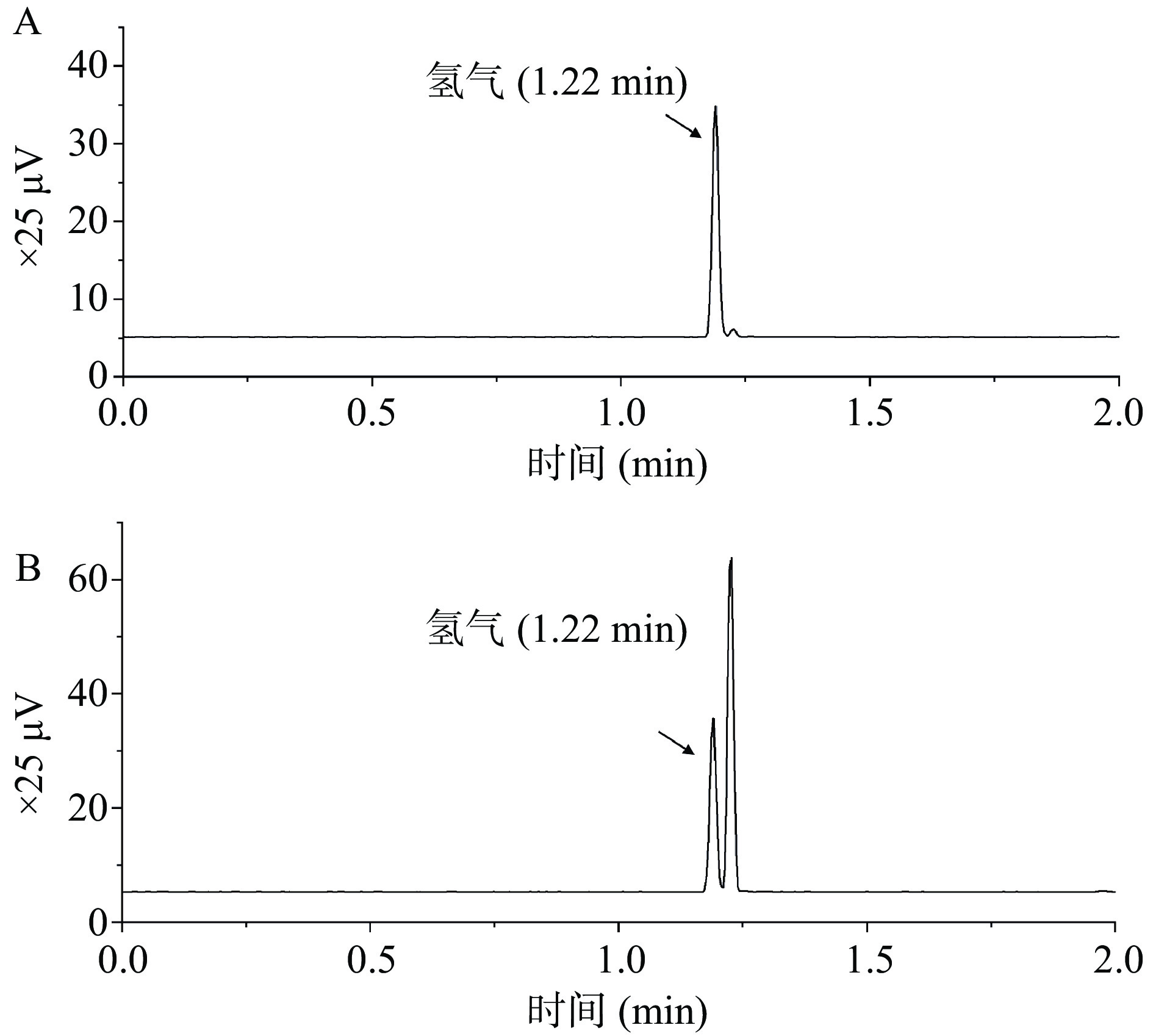
对于水中氢气的检测,分子筛毛细管柱会受到水蒸气的影响,本研究采用GS-CarbonPLOT毛细管柱。图1A为单纯氢气进样色谱图,图1B为富氢水样本检测色谱图。可知氢气出峰时间为1.22 min。在该色谱条件下,色谱图基线稳定,氢气峰能够分离,并且无拖尾等现象。
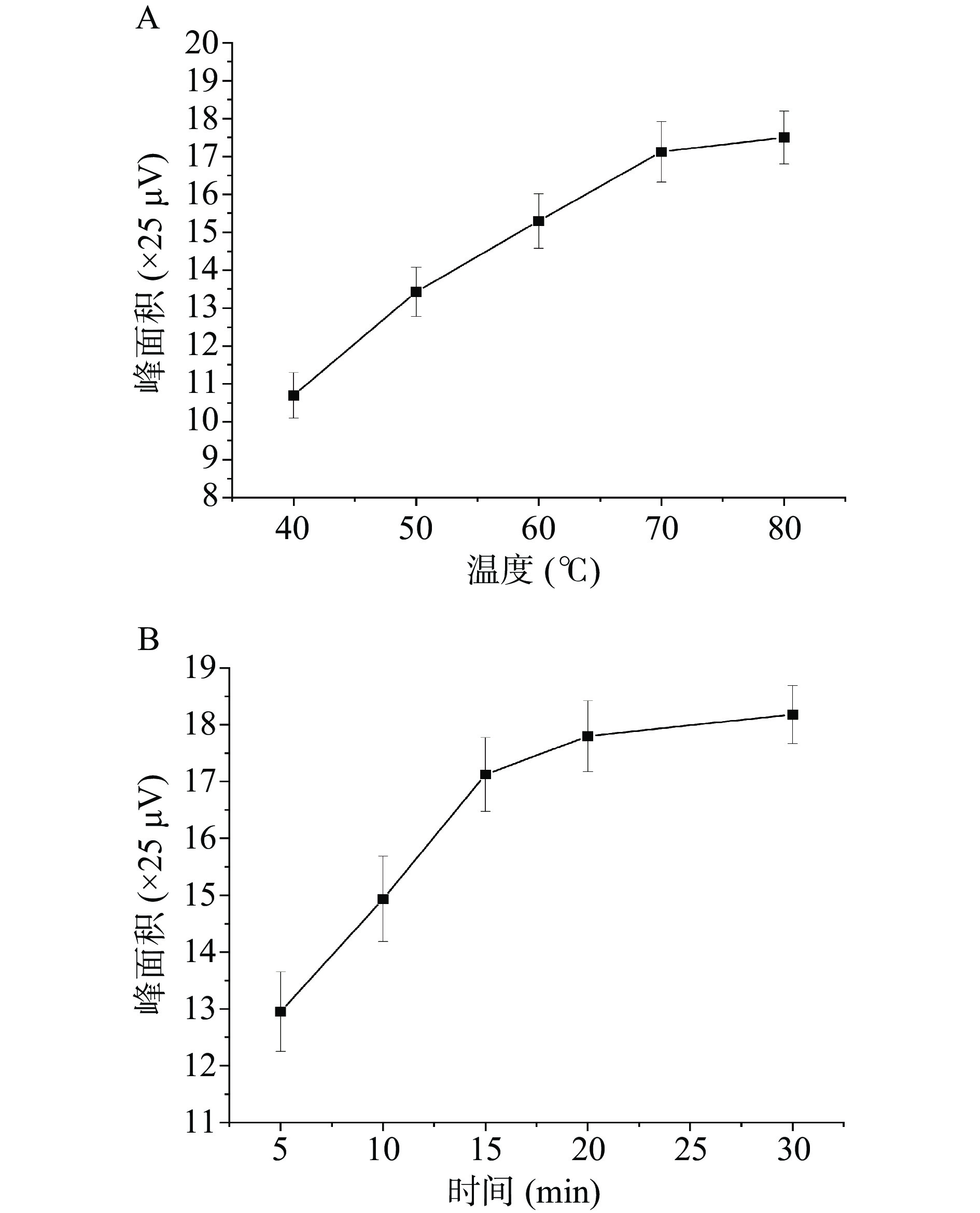
气相色谱法检测的前提是将水中的氢气释放出来,这就需要采用顶空的前处理方法。选取同一浓度(氢气0.805 mg/L)样品,考察了顶空进样的不同平衡温度(40、50、60、70、80 ℃)和不同平衡时间(5、10、15、20、30 min)对测定结果的影响。结果表明:平衡时间为15 min时,随着平衡温度的升高,氢气峰面积相应递增,当温度超过70 ℃,目标物的峰面积增加缓慢,且温度过高会影响顶空瓶气密性,故实验选择70 ℃作为平衡温度(图2A);平衡温度为70 ℃时,随着平衡时间增加,5~20 min目标物的峰面积逐级递增并趋于平稳,之后峰面积才基本不再增加(图2B)。故实验选择顶空进样的平衡温度和平衡时间分别为70 ℃和20 min。
2.1.2 线性关系、检出限和定量限
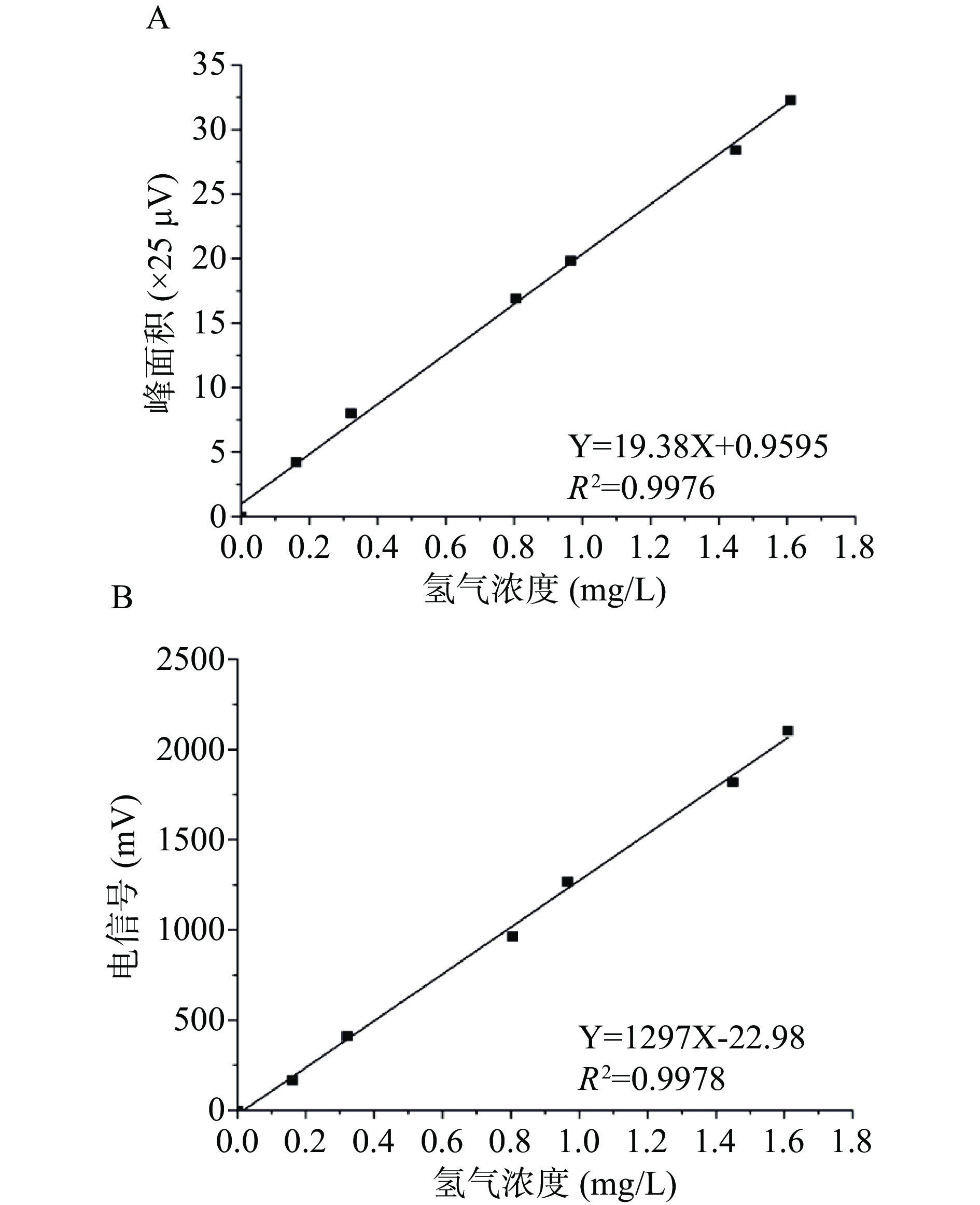
在优化后的条件下,将0、0.161、0.322、0.805、0.966、1.449、1.610 mg/L梯度标准工作溶液使用顶空-气相色谱法进行检测,以峰面积(Y)为纵坐标,氢气浓度(X,mg/L)为横坐标进行回归运算,得到顶空-气相色谱法回归方程为Y=19.38X+0.9595,R2=0.9976。在0~1.610 mg/L范围内本方法具有良好的线性关系(图3A)。以3倍信噪比为检出限,10倍信噪比为定量限,得检出限为0.0036 mg/L,定量限为0.012 mg/L。
2.1.3 准确度和精密度
配制氢气浓度为0.1613、0.805、1.449 mg/L的标准溶液进行检测,每个浓度在优化后条件下平行测定6次,通过回收率来考察方法的准确度,通过相对标准偏差(RSD)来考察方法的精密度,测定结果如表1所示。实验结果表明,在0.161、0.805、1.449 mg/L添加水平,回收率分别为104.90%、102.22%和97.78%,说明准确度良好。RSD分别为3.87%、2.29%和1.69%,均小于5%,说明精密度良好(表1)。
表 1 顶空-气相色谱法的准确度及精密度Table 1. Accuracy and precision of the detection by headspace gas chromatography方法 氢气浓度
(mg/L)实际检测值 (mg/L) 平均回收率(%) RSD (%) 顶空-气相色谱法 0.161 0.179 0.162 0.161 0.172 0.178 0.163 104.90 3.87 0.805 0.830 0.827 0.843 0.785 0.833 0.819 102.22 2.29 1.449 1.454 1.413 1.377 1.426 1.421 1.410 97.78 1.69 2.2 氢气微电极法
2.2.1 线性关系、检出限和定量限
将0、0.161、0.322、0.805、0.966、1.449、1.610 mg/L梯度标准工作溶液使用氢气微电极法进行检测,以信号强度(Y)为纵坐标,氢气浓度(X,mg/L)为横坐标进行回归运算,得到氢气微电极法回归方程为Y=1297X−22.98,R2=0.9978。在0~1.610 mg/L范围内本方法均具有良好的线性关系(图3B)。以3倍信噪比为检出限,10倍信噪比为定量限,得检出限为0.00023 mg/L,定量限为0.00077 mg/L。
2.2.2 准确度和精密度
对氢气浓度为0.1613、0.805 、1.449 mg/L标准溶液使用氢气微电极法进行检测,平行测定6次。如表2所示,在0.161、0.805、1.449 mg/L添加水平,回收率分别为96.75%、95.78%和98.00%,说明准确度良好。相对标准偏差(RSD)分别为1.84%、0.98%和2.80%,均小于5%,说明精密度良好(表2)。
表 2 氢气微电极法的准确度及精密度Table 2. Accuracy and precision of the detection by hydrogen microsensor方法 氢气浓度
(mg/L)实际检测值 (mg/L) 平均回收率(%) RSD (%) 氢气微电极法 0.161 0.155 0.154 0.153 0.159 0.154 0.159 96.75 1.84 0.805 0.763 0.766 0.779 0.765 0.782 0.775 95.78 0.98 1.449 1.409 1.389 1.380 1.408 1.483 1.450 98.00 2.80 2.3 实际样品检测
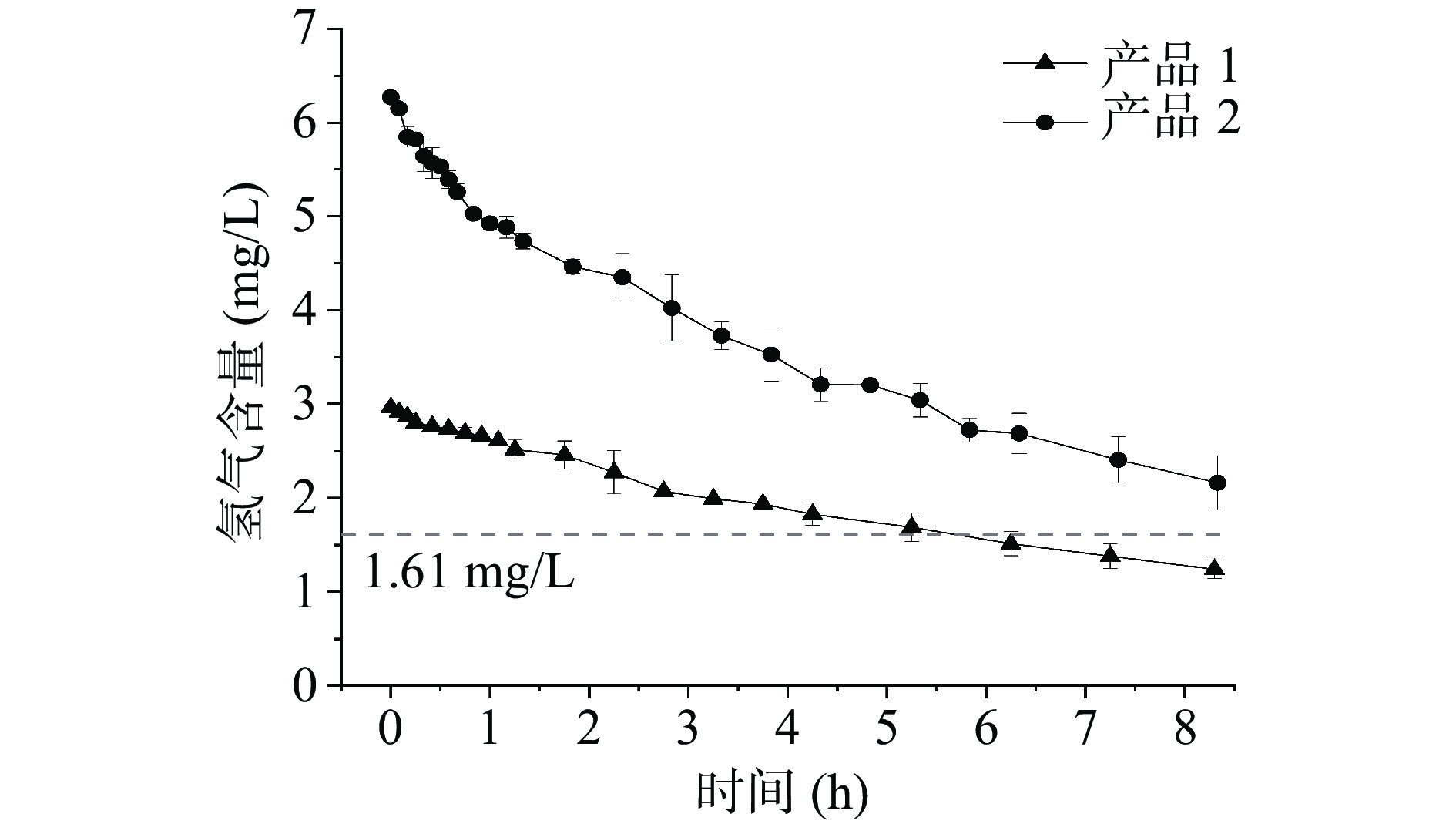
对市售7种罐装富氢水(编号1~7),每种3个样品(01~03),使用2种方法进行测试。结果见表3。可以看出,市面上罐装富氢水氢气含量均达到了团体标准T/NAHIEM 16-2019《含氢包装饮用水》中规定的0.6 mg/L,但不同品牌产品氢气含量相差很大,从0.8至6.2 mg/L不等。富氢水中的氢气在暴露于空气之中后易于散发[31],在产品开盖后氢气存留情况如何,也是一个值得关注的指标。本实验以氢气含量最高的产品(产品1和产品2)为代表,得到了在开盖后富氢水氢气含量随时间变化情况。由图4可知,在开始阶段氢气散失速度较快,之后逐渐减缓。对于初始浓度约为3 mg/L的富氢水产品,开盖后5 h内仍然在氢气水溶液饱和浓度之上;对于初始浓度约为6 mg/L的富氢水产品,开盖后8 h内仍然可达到2.2 mg/L以上,远超过饱和氢气浓度。总体来说,开盖后超饱和富氢水中氢气存留量在30 min内降低约10%,6 h内约降低一半。
表 3 样品检测结果Table 3. Measurement result of the sample编号 标注氢气浓度范围(mg/L) 氢气浓度(mg/L) 顶空-气相色谱法 氢气微电极法 1-01 1.5<浓度<2 3.30 3.22 1-02 2.91 2.88 1-03 2.72 3.02 2-01 2.5<浓度≤3 6.01 6.14 2-02 6.22 6.21 2-03 6.15 6.26 3-01 1.5<浓度<2 0.78 0.82 3-02 0.82 0.83 3-03 0.86 0.88 4-01 2.5<浓度≤3 1.03 1.13 4-02 1.06 1.21 4-03 1.00 1.12 5-01 2≤浓度≤2.5 1.02 1.20 5-02 1.12 1.12 5-03 1.10 1.06 6-01 2≤浓度≤2.5 3.15 3.27 6-02 3.00 3.13 6-03 3.10 3.27 7-01 1.5<浓度<2 3.12 3.40 7-02 3.23 3.13 7-03 3.39 3.41 3. 讨论与结论
随着氢气的生物医学效应和机制研究的深入,氢气相关健康产品也越来越多,富氢水是其中重要的产品之一,氢气含量是富氢水的关键指标。本文建立了富氢水中氢气含量的检测方法,并对市面上的罐装富氢水进行了检测。在样本的前处理方面,对于超饱和的富氢水,需通过稀释的方式使氢气含量在标准曲线范围之内,即氢气的饱和浓度1.61 mg/L以下。此外,气相色谱法需通过顶空进样的方式,使溶解于水中的氢气释放出来,因此增加了前处理的步骤。在检测成本方面,氢气微电极法设备和耗材的成本低于气相色谱法。方法学考察结果表明,顶空-气相色谱法与氢气微电极法在0~1.61 mg/L氢气含量范围内均有良好线性关系,在低、中、高三个添加水平下,回收率分别为97.78%~104.90%、95.78%~98.00%,相对标准偏差分别为1.69%~3.87%、0.98%~2.80%,均能够满足检测要求。目前市面上罐装富氢水产品标注的氢气含量从1.6 ppm(约1.6 mg/L)到3 ppm(约3 mg/L)不等。通过对市面上7种罐装富氢水进行检测表明这些产品均达到团体标准规定的0.6 mg/L,但氢气含量相差较大,不同产品甚至能相差近8倍。本文通过顶空-气相色谱法和氢气微电极法对富氢水中氢气含量进行检测,可以为相关应用及标准的制定提供参考。
-
表 1 顶空-气相色谱法的准确度及精密度
Table 1 Accuracy and precision of the detection by headspace gas chromatography
方法 氢气浓度
(mg/L)实际检测值 (mg/L) 平均回收率(%) RSD (%) 顶空-气相色谱法 0.161 0.179 0.162 0.161 0.172 0.178 0.163 104.90 3.87 0.805 0.830 0.827 0.843 0.785 0.833 0.819 102.22 2.29 1.449 1.454 1.413 1.377 1.426 1.421 1.410 97.78 1.69 表 2 氢气微电极法的准确度及精密度
Table 2 Accuracy and precision of the detection by hydrogen microsensor
方法 氢气浓度
(mg/L)实际检测值 (mg/L) 平均回收率(%) RSD (%) 氢气微电极法 0.161 0.155 0.154 0.153 0.159 0.154 0.159 96.75 1.84 0.805 0.763 0.766 0.779 0.765 0.782 0.775 95.78 0.98 1.449 1.409 1.389 1.380 1.408 1.483 1.450 98.00 2.80 表 3 样品检测结果
Table 3 Measurement result of the sample
编号 标注氢气浓度范围(mg/L) 氢气浓度(mg/L) 顶空-气相色谱法 氢气微电极法 1-01 1.5<浓度<2 3.30 3.22 1-02 2.91 2.88 1-03 2.72 3.02 2-01 2.5<浓度≤3 6.01 6.14 2-02 6.22 6.21 2-03 6.15 6.26 3-01 1.5<浓度<2 0.78 0.82 3-02 0.82 0.83 3-03 0.86 0.88 4-01 2.5<浓度≤3 1.03 1.13 4-02 1.06 1.21 4-03 1.00 1.12 5-01 2≤浓度≤2.5 1.02 1.20 5-02 1.12 1.12 5-03 1.10 1.06 6-01 2≤浓度≤2.5 3.15 3.27 6-02 3.00 3.13 6-03 3.10 3.27 7-01 1.5<浓度<2 3.12 3.40 7-02 3.23 3.13 7-03 3.39 3.41 -
[1] OHTA S. Molecular hydrogen as a preventive and therapeutic medical gas: Initiation, development and potential of hydrogen medicine[J]. Pharmacol Ther,2014,144(1):1−11. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2014.04.006
[2] GONG W J, JIANG L D, ZHU Y X, et al. An activity-based ratiometric fluorescent probe for In vivo real-time imaging of hydrogen molecules[J]. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl,2022,61(9):e202114594.
[3] OHSAWA I, ISHIKAWA M, TAKAHASHI K, et al. Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing cytotoxic oxygen radicals[J]. Nat Med,2007,13(6):688−694. doi: 10.1038/nm1577
[4] 赵敏, 秦树存. 氢气生物医学效应的发现, 研究与应用[J]. 山东第一医科大学(山东省医学科学院)学报,2021,42(5):339−346. [ZHAO M, QIN S C. Discovery, research and application of hydrogen biomedical effects[J]. Journal of Shandong First Medical University & Shandong Academy of Medical Sciences,2021,42(5):339−346. [5] CHEN W, ZHANG H T, QIN S C. Neuroprotective effects of molecular hydrogen: A critical review[J]. Neurosci Bull,2021,37(3):389−404. doi: 10.1007/s12264-020-00597-1
[6] RUSSELL G, NENOV A, KISHER H, et al. Molecular hydrogen as medicine: An assessment of administration methods[J]. Hydrogen,2021,2(4):444−460. doi: 10.3390/hydrogen2040025
[7] TAO G R, SONG G H, QIN S C. Molecular hydrogen: Current knowledge on mechanism in alleviating free radical damage and diseases[J]. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai),2019,51(12):1189−1197. doi: 10.1093/abbs/gmz121
[8] LIU B Y, XUE J L, GU Q Q, et al. In vivo microelectrode monitoring of real-time hydrogen concentration in different tissues of rats after inhaling hydrogen gas[J]. Medical Gas Research,2022,12(3):107−112. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.330694
[9] WOLF P G, BISWAS A, MORALES S E, et al. H2 metabolism is widespread and diverse among human colonic microbes[J]. Gut Microbes,2016,7(3):235−245. doi: 10.1080/19490976.2016.1182288
[10] HYLEMON P B, HARRIS S C, RIDLON J M. Metabolism of hydrogen gases and bile acids in the gut microbiome[J]. FEBS Lett,2018,592(12):2070−2082. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.13064
[11] SUN X J, OHTA S, NAKAO A. Hydrogen molecular biology and medicine [M]. Springer, 2015.
[12] NICOLSON G L, DE MATTOS G F, SETTINERI R, et al. Clinical effects of hydrogen administration: From animal and human diseases to exercise medicine[J]. International Journal of Clinical Medicine,2016,7(1):32. doi: 10.4236/ijcm.2016.71005
[13] 秦树存, 李璞. 氢气医学人群试验(漫画版)[M]. 天津: 天津科技翻译出版有限公司, 2021 QIN S C, LI P. Hydrogen medical population trial cartoon version [M]. Tianjin: Tianjin Science & Technology Translation & Publishing Co., Ltd., 2021.
[14] CHEN J B, KONG X F, LV Y Y, et al. ''Real world survey'' of hydrogen-controlled cancer: A follow-up report of 82 advanced cancer patients[J]. Medical Gas Research,2019,9(3):115−121. doi: 10.4103/2045-9912.266985
[15] 中华人民共和国国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 31633-2014. 食品国家安全标准 食品添加剂 氢气[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2014 National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People's Republic of China. GB 31633-2014. National food safety standards. Food additives. Hydrogen [S]. Beijing Standards Press of China, 2014.
[16] Ministry of Health and Welfare. List of existing food additives[S/OL].https://www.ffcr.or.jp/en/tenka/list-of-existing-food-additives/list-of-existing-food-additives.html. Accessed by January 30, 2014.
[17] The European Parliament and the Council of the European Union[S/OL]. Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European parliament and of the Council of 16 December 2008 on food additives. https://eur-lex.europa.eu/eli/reg/2011/1129/oj. Accessed by November 11, 2011.
[18] Food and Drug Administration USA[S/OL]. AgeNCY RESPONSE LET-TEr GRAS Notice No.520.https://www.cfsanappsexternal.fda. gov/scripts/fdcc/?set=GRASNotices&id=520&sort=GRN_No&or der=DESC&startrow=1&type=basic&search=hydrogen. Accessed by October 28, 2016.
[19] FU Z L, ZHANG J, ZHANG Y. Role of molecular hydrogen in ageing and ageing-related diseases[J]. Oxid Med Cell Longev,2022,2022:2249749.
[20] OSTOJIC S M. Molecular hydrogen: An inert gas turns clinically effective[J]. Ann Med,2015,47(4):301−304. doi: 10.3109/07853890.2015.1034765
[21] OHTA S. Molecular hydrogen as a novel antioxidant: Overview of the advantages of hydrogen for medical applications[J]. Methods in enzymology,2015,555:289−317.
[22] OSTOJIC S M. Hydrogen-rich water as a modulator of gut microbiota?[J]. Journal of Functional Foods,2021,78:104360. doi: 10.1016/j.jff.2021.104360
[23] 刘伯言, 秦树存. 氢分子供体种类及其在体内代谢动力学特点[J]. 生理学报,2019,71(2):371−377. [LIU B Y, QIN S C. Different types of molecular hydrogen donors and their pharmacokinetics in vivo[J]. Acta Physiologica Sinica,2019,71(2):371−377. doi: 10.13294/j.aps.2018.0083 [24] LIU S, OSHITA S, THUYET D Q, et al. Antioxidant activity of hydrogen nanobubbles in water with different reactive oxygen species both in vivo and in vitro[J]. Langmuir,2018,34(39):11878−11885. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b02440
[25] 张昭, 魏娅楠, 仪杨, 等. 水相中氢气浓度检测方法的建立[J]. 生物技术进展,2020,10(2):158−163. [ZHANG Z, WEI Y N, YI Y, et al. Establishment of a detection method of hydrogen concentration in aqueous phase[J]. Current Biotechnology,2020,10(2):158−163. [26] 龙庆云, 杨品, 韦桂欢. 顶空气相色谱法测定富氢水中的氢气[J]. 化学分析计量,2017,26(5):71−73. [LONG Q Y, YANG P, WEI G H. Determination of hydrogen in hydrogen-rich water by headspace gas chromatography[J]. Chemical Analysis and Meterage,2017,26(5):71−73. [27] 黄建军, 顾平, 陆彩霞. 气相色谱法测定水相中微量氢气[J]. 分析试验室,2008,27(B12):369−372. [HUANG J J, GU P, LU C X. Determination of trace hydrogen in aqueous phase by gas chromatography[J]. Chinese Journal of Analysis Laboratory,2008,27(B12):369−372. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0720.2008.z2.111 [28] SEO T, KUROKAWA R, SATO B. A convenient method for determining the concentration of hydrogen in water: Use of methylene blue with colloidal platinum[J]. Medical gas research,2012,2(1):1−6. doi: 10.1186/2045-9912-2-1
[29] 孙学军, 秦树存, 马雪梅, 等. T/NAHIEM 16-2019. 全国卫生产业企业管理协会团体标准 含氢包装饮用水[S]. 2019 SUN X J, QIN S C, MA X M, et al. T/NAHIEM 16-2019. Group standards of national association of health industry and enterprise management. Packaged drinking hydrogen water[S]. 2019.
[30] WIESENBURG D A, GUINASSO JR N L. Equilibrium solubilities of methane, carbon monoxide, and hydrogen in water and sea water[J]. Journal of Chemical and Engineering Data,1979,24(4):356−360. doi: 10.1021/je60083a006
[31] OHTA S. Recent progress toward hydrogen medicine: Potential of molecular hydrogen for preventive and therapeutic applications[J]. Curr Pharm Des,2011,17(22):2241−2252. doi: 10.2174/138161211797052664
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 张全通,郑尧,杨柳,张帅帅,郭全友. 计算机视觉结合卷积神经网络快速检测南极磷虾粉中的虾青素含量. 食品工业科技. 2025(03): 11-18 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 刘鑫,马本学,李玉洁,陈金成,喻国威. 基于改进YOLOv7-ByteTrack的干制哈密大枣缺陷检测与计数系统. 农业工程学报. 2024(03): 303-312 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 贾雅欣,李传峰,罗华平,吴明清. 基于边缘轮廓定积分测量红枣体积的研究. 塔里木大学学报. 2024(01): 75-83 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 朱丽娟. 基于机器视觉的红枣裂纹特征提取. 科技风. 2024(10): 17-19 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 吴思,诸定莲,鲁梦瑶,万以磊,高亮亮,陈龙,汤卫荣,吴文彪. 基于机器视觉的大闸蟹自动分级分选设备研究与开发. 扬州大学学报(农业与生命科学版). 2024(04): 137-146 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 汤文祺,曹玉华,李应果. 基于机器视觉的一品红自动分级方法研究. 现代农业装备. 2024(05): 53-58 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 赵晓梅,李洪港. 基于X射线图像的金属腐蚀深度估计方法. 山东冶金. 2023(05): 25-27 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 蒋平. 一种快速红枣表面缺陷识别方法. 大众标准化. 2023(23): 55-57 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(13)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



