Analysis and Comparison on the Quality and Volatile Flavor Components of Crude Fish Oil from the Viscera of Three Freshwater Fishes
-
摘要: 为提高淡水鱼类加工副产物的高值化利用,本文以3种常见的淡水鱼(草鱼、青鱼和鲢鱼)内脏为原料提取粗鱼油,进行理化指标评价、脂肪酸组成及挥发性风味成分分析。结果表明,青鱼油的理化指标最佳,其过氧化值、酸价、水分及挥发物、茴香胺值、不皂化物等较低;鲢鱼油次之,草鱼油最差。青鱼油、鲢鱼油和草鱼油中分别检测出16、22、27种脂肪酸,均以棕榈酸(C16:0)、油酸(C18:1n-9c)、亚油酸(C18:2n-6c)为主,鲢鱼油的相对营养价值最高。3种粗鱼油共检测出66种挥发性物质,包括烃类17种,醇类7种,醛类15种,酮类3种,酯类8种,酸类10种,酚类3种,其他类3种。草鱼油中含量最高的是酚类物质(59.86%);青鱼油中挥发性物质以醇类为主,含量为53.23%;鲢鱼油中含量最高的是酸类物质(27.64%)。3种粗鱼油共得到10种关键风味成分,主要以醛类、醇类和酚类物质为主。反式-2,4-癸二烯醛、壬醛、反式-2,4-庚二烯醛、苯乙醛、1-辛烯-3-醇等是粗鱼油中主要的鱼腥味、油脂味风味物质。Abstract: In order to improve the high-value utilization of by-products from freshwater fish processing, crude fish oil was extracted from the viscera of three common freshwater fishes (grass carp, black carp and silver carp), and the physicochemical indexes, fatty acid composition as well as volatile flavor components were monitored. The findings indicated that a best quality was observed in black carp oil due to its lower peroxide value, acid value, moisture and volatile matter, anisidine value and unsaponifiable matter, followed by silver carp oil and grass carp oil. A total of 27 fatty acids were detected in silver carp oil accompanied by 22 and 16 fatty acids in black carp oil and grass carp oil. The most preponderant fatty acids in three crude fish oils were palmitic acid (C16:0), oleic acid (C18:1n-9c) as well as linoleic acid (C18:2n-6c), and a highest nutritional value was observed in silver carp oil. The 66 volatile compounds involving 17 hydrocarbons, 7 alcohols, 15 aldehydes, 3 ketones, 8 esters, 10 acids, 3 phenols and 3 other components were detected in three crude fish oils. The highest level of volatile substances in grass carp oil, black carp oil and silver carp oil were separately phenols (59.86%), alcohols (53.23%) and acids (27.64%). Additional, aldehydes, alcohols and phenols were found to be the prominence among the 10 key flavor components obtained from the three crude fish oils. Trans-2,4-decadienal, nonanal, trans-2,4-hepadienal, phenylacetaldehyde, 1-octanene-3-alcohol were the main fishy and oil flavor substances in crude fish oils.
-
Keywords:
- fish viscera /
- crude fish oil /
- basic indexes /
- fatty acid /
- key flavor components
-
我国作为全球淡水鱼生产消费大国,近年来淡水鱼养殖与加工业发展较快,根据中国渔业统计年鉴,2020年我国淡水养殖鱼类产量为2586.38万吨,淡水加工总量为411.51万吨[1]。但在淡水鱼生产加工中,原料利用率较低,会产生大量鱼头鱼骨、鱼鳞鱼皮、鱼内脏等副产物,约占原料总重的60%左右,造成资源浪费及环境污染[2]。目前副产物中对鱼头鱼骨、鱼鳞鱼皮加工利用比较多,开发利用形式有鱼骨钙、软骨素,蛋白肽、胶原蛋白和明胶等,而对鱼内脏加工利用较少,除少数加工为动物饲料,大多被丢弃浪费[3-6]。鱼内脏是鱼类主要加工副产物,占整鱼的12%~18%,油脂含量丰富,具有很高的开发利用价值[7]。
鱼内脏鱼油具有较高的营养价值和保健功能,含有丰富的n-3系多不饱和脂肪酸,如二十碳五烯酸(EPA)和二十二碳六烯酸(DHA),具有预防癌症和心脑血管疾病、缓解炎症、降低代谢综合症患者患糖尿病的风险等作用[8-9]。近年来,对海水鱼油的研究报道较多,淡水鱼油的报道相对较少。Zhang等[10]采用超临界CO2和乙醇的方式来提取秋刀鱼内脏磷脂,并使用蒸发散射光检测器的高效液相色谱法定量分析磷脂提取物的主要成分。相朝清等[11]采用皂化酸解工艺,对斑点叉尾鮰鱼内脏油中的脂肪酸进行提取,并对其提取工艺参数进行响应面优化。于淑池等[12]以金鲳鱼骨为原料,采用酶解法提取鱼油,并对金鲳鱼油的提取工艺及理化特性进行了研究。王正云等[13]以青鱼内脏为原料,采用微波辅助蛋白酶提取鱼油,通过单因素实验及响应面法确定了最佳的提取工艺,并对脂肪酸进行了分析。然而,海水鱼类资源有限,其提取成本昂贵,难以满足市场需求。我国淡水鱼养殖和加工产量巨大,因此,对淡水鱼类内脏进行鱼油的高值利用前景广阔。目前,淡水鱼油的研究大部分停留在上游提取领域,而对下游产品质量及风味领域的报道不多。
本文以市场上常见的3种淡水鱼(草鱼、青鱼和鲢鱼)内脏为研究对象,通过有机溶剂法萃取粗鱼油,并对其脂肪酸组成、基本理化指标及挥发性风味成分进行分析,以期为淡水鱼类加工副产物的高值化利用提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
草鱼、青鱼、鲢鱼 1.50±0.30kg,均购于南昌市长胜农贸大市场;37种脂肪酸甲酯混合标准品、平板计数琼脂培养基 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;乙酸、乙醇、氢氧化钾、无水硫酸钠、碘化钾、乙醚、环己烷、异丙醇、二氯甲烷 西陇科学股份有限公司;三氯甲烷 成都科隆化学品有限公司;正己烷 天津大茂化学试剂厂;异辛烷、韦氏(Wijs)试剂、P-4茴香胺、硫代硫酸钠标准液 上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司;以上试剂均为分析纯。
IKA T 25 digital ULTRA-TURRAX数显型分散机 德国IKA公司;Eppendorf 5430/5430R高速冷冻离心机 德国Eppendorf公司;DUG-914OA型电热恒温鼓风干燥箱 上海精宏实验设备有限公司;隔水式培养箱 上海一恒科学仪器有限公司;N-2000型紫外检测仪 上海嘉鹏科技有限公司;7890B气相色谱仪、75 μm碳分子筛/聚二甲基硅氧烷萃取头 美国Supelco公司;7890A/5975气相色谱-质谱联用仪 美国Agilent公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品预处理
草鱼、青鱼、鲢鱼分别用清水清洗干净,剖开取鱼全部内脏,沥干,粉碎机搅碎,自封袋封装,置于−18 ℃冰箱保存备用。
1.2.2 粗鱼油提取方法
参照付雪媛等[14]的方法,并稍作修改。称取鱼内脏64.00 g置于烧杯中,加入正己烷-蒸馏水混合液(2:1)150 mL,采用高速分散机以9600 r/min均质2 min,随后加入正己烷50 mL,继续均质1 min,加入50 mL蒸馏水,继续均质30 s。其后在低温高速离心机7000 r/min转速下离心10 min,离心后将正己烷层置于锥形瓶中,加入适量无水硫酸钠,中性滤纸过滤,旋转蒸发至干燥,得粗鱼油。
1.2.3 粗鱼油基本指标评价
过氧化值的测定参照GB 5009.227−2016中的滴定法;酸价的测定参照GB 5009.229−2016中的冷溶剂指示剂滴定法;水分及挥发物的测定参照GB 5009.236−2016中的电热干燥箱法;茴香胺值的测定参照GB/T 24304−2009;碘值的测定参照GB/T 5532−2008;不皂化物的测定参照GB/T 5535.2−2008中的己烷提取法;不溶性杂质含量的测定参照GB/T 15688−2008;菌落总数的测定参照GB 4789.2−2016。
1.2.4 粗鱼油脂肪酸组成测定
1.2.4.1 样品甲酯化
称取粗鱼油30.00 mg于试管中,加入2 mL正己烷,100 μL 4%的NaOH-甲醇溶液,振荡混匀,置于37 ℃水浴锅中反应35 min,取上层正己烷层1 mL,过0.22 μm有机膜,进样分析[15]。
1.2.4.2 气相色谱条件
色谱柱:CP-Si188熔融石英毛细管柱(100 m×0.25 mm×0.2 μm);进样口温度为250 ℃;压力为24.52 psi;总流速为29.4 mL/min;恒压不分流进样;进样量为1 μL;载气为氢气(99.99%);柱压为24.52 psi;程序升温:45 ℃(4 min)→13 ℃/min→175 ℃(27 min)→4 ℃/min→215 ℃(35 min)。FID检测器,250 ℃,燃气为氢气和空气,流速分别为30 mL/min和300 mL/min;氮气(99.99%)作为助燃气,流速为30 mL/min[15]。
1.2.5 粗鱼油挥发性风味成分测定
1.2.5.1 固相微萃取条件
称取粗鱼油5.00 g于20 mL样品瓶中,密封瓶口,60 ℃水浴加热平衡30 min后,插入老化好的萃取头,继续顶空吸附30 min后取出萃取头,并迅速插入气相色谱进样口中,于250 ℃下解析10 min。
1.2.5.2 气相质谱测定条件
气相条件[16]:色谱柱:DB-Wax毛细管柱(30 m×0.25 μm×0.25 mm);进样口温度250 ℃;载气He;流速1.0 mL/min;采用不分流模式;升温程序:40 ℃(3 min)→5 ℃/min→240 ℃(15 min)。质谱条件:EI电离源;电离电压70 eV;离子源温度230 ℃;四极杆温度150 ℃。
1.2.5.3 挥发性风味成分定性与定量分析
定性分析:通过NIST 14质谱库对未知化合物进行检索匹配,匹配度大于800(最大值为1000)的鉴定结果予以保留给出化合物名称。
定量分析:粗鱼油中各挥发性成分相对含量根据峰面积比求得。
1.2.6 粗鱼油关键风味成分评价方法
采用刘登勇等[17]提出的相对气味活度值法(ROAV)对3种内脏粗鱼油关键风味化合物进行分析。
1.3 数据处理
所有试验均做3次平行,结果以平均值±标准差表示,实验数据采用Origin 2021绘图,用SPSS16.0统计软件对数据进行单因素方差分析(ANOVA),显著性差异分析采用Duncan检验,P<0.05表示存在显著性差异。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 粗鱼油理化指标分析
3种淡水鱼内脏粗鱼油理化指标及SC/T 3502−2016粗鱼油标准见表1。
表 1 3种粗鱼油理化指标Table 1. Physicochemical indexes of the three crude fish oils指标 草鱼油 青鱼油 鲢鱼油 SC/T 3502−2016粗鱼油 一级 二级 过氧化值(mmol/kg) 0.43±0.03b 0.22±0.06b 1.99±0.27a ≤12.0 ≤20.0 酸价(mg KOH/g) 18.37±0.88a 6.36±0.07c 12.25±0.18b ≤8.0 ≤15.0 水分及挥发物(%) 0.38±0.07a 0.32±0.03a 0.36±0.02a ≤0.3 ≤0.5 茴香胺值 1.40±0.24a 1.33±0.32a 1.78±0.59a − 碘值(g/100 g) 97.63±5.08c 106.39±6.74b 118.71±13.03a ≥120 不皂化物(%) 0.59±0.04a 0.33±0.19a 0.29±0.06a − 不溶性杂质(%) 1.85±0.08a 1.40±0.58a 2.20±0.47a ≤0.5 菌落总数(CFU/mL) <1 <1 <1 ≤103 注:—为未做限定;同行不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 过氧化值主要反映氢过氧化物的含量,氢过氧化物可分解为醛酮类和氧化物等导致鱼油酸败变质,是判断鱼油是否酸败或酸败程度的重要指标[18]。由表1可知,草鱼油与青鱼油过氧化值无显著性差异(P>0.05),鲢鱼油过氧化值显著高于其他两种粗鱼油(P<0.05),为1.99 mmol/kg,3种粗鱼油均符合SC/T 3502−2016规定的粗鱼油一级标准。酸价可用于判断鱼油中的游离脂肪酸含量,是衡量油脂氧化酸败的重要指标,且与不良风味物质的存在有关[19]。3种粗鱼油酸价同样存在显著性差异(P<0.05),其中草鱼油酸价最高,为18.37 mg/g,未达到SC/T 3502−2016规定的粗鱼油二级标准,可能与羧基类酸性物质较高有关。Cozzolinoa等[20]发现水分含量与鱼油酸败有关,而残留的易挥发性物质较高会影响鱼油的品质及安全性。3种粗鱼油水分及挥发物含量无显著性差异(P>0.05),均小于0.5%,符合SC/T 3502−2016规定的粗鱼油二级标准。鱼油标准SC/T 3502−2016中未对粗鱼油的茴香胺值与不皂化物含量进行限量规定,3种粗鱼油茴香胺值与不皂化物均较低。碘值可反映鱼油的不饱和程度,不溶性杂质可反映鱼油中残留物含量[21]。3种粗鱼油碘值较低,均未达到SC/T 3502−2016规定的粗鱼油二级标准,可能与粗鱼油不溶性杂质含量较高有关。菌落总数是鱼油的卫生指标之一,微生物的存在会引起鱼油发生酸败,3种粗鱼油菌落总数均符合SC/T 3502−2016规定的粗鱼油标准。综合分析比较3种粗鱼油的基本指标可以得出:青鱼油的理化指标最佳,其过氧化值、酸价、水分及挥发物、茴香胺值、不皂化物等较低;鲢鱼油次之,草鱼油最差。
2.2 粗鱼油脂肪酸组成成分分析
采用气相色谱对3种淡水鱼内脏粗鱼油脂肪酸组成及相对含量进行分析(表2)。由表2可知,3种粗鱼油在脂肪酸组成与含量上差异显著(P<0.05),共检测出29种脂肪酸,草鱼油、青鱼油、鲢鱼油分别为16、22和27种,分布范围为C10~C23。3种粗鱼油均以棕榈酸(C16:0)、油酸(C18:1n-9c)、亚油酸(C18:2n-6c)为主。一般而言,鱼油不饱和脂肪酸含量越高,营养价值相对越高[22]。鲢鱼油不饱和脂肪酸含量较高,为64.18%,草鱼油与青鱼油不饱和脂肪酸含量无显著性差异(P>0.05),含量较低,分别为71.83%、75.49%。研究发现,单不饱和脂肪酸具降血糖、调节血脂、降胆固醇等生理功能特性[23];多不饱和脂肪酸具有预防心血管系统疾病、抗癌、调节免疫力等生理功能特性[24]。3种粗鱼油含有丰富的单不饱和脂肪酸,含量达42.20%~54.28%,主要有油酸(C18:1n-9c)、棕榈油酸(C16:1);多不饱和脂肪酸的含量为21.21%~27.17%,主要有亚油酸(C18:2n-6c)、α-亚麻酸(C18:3n-3)。EPA和DHA有“脑黄金”和“血管清道夫”之称,具有极大的保健价值。3种粗鱼油EPA和DHA含量差别较大(P<0.05),鲢鱼油含量最高,为3.97%,青鱼油含量次之,仅为0.09%,而EPA和DHA并未在草鱼油中检测出,这可能进一步佐证了鲢鱼油较青鱼油和草鱼油有更高的碘值。张立坚等[25]测定的鲢鱼油EPA和DHA总量为3.57%,EPA、DHA含量分别为1.27%、2.30%,与本文结果类似。涂宗财等[26]通过钾法提取草鱼不同部位鱼油,其中内脏鱼油EPA+DHA含量为0.29%;林婉玲等[27]测定了青鱼肌肉脂肪中EPA+DHA含量为1.70%,与本文结果存在差异,这可能是鱼油提取方法、提取部位等不同所致。3种粗鱼油中n-3PUFA含量最高的是鲢鱼油,为12.92%,显著高于其他两种粗鱼油(P<0.05);草鱼油与青鱼油n-6PUFA含量较高,分别为24.62%、18.94%,显著高于鲢鱼油(P<0.05)。有研究提出,n-6/n-3比值与人类疾病的炎症病理有关,当该比值低于4:1时可以降低心血管疾病的死亡率[28]。3种粗鱼油中鲢鱼油的n-6/n-3远低于4:1,草鱼、青鱼两种粗鱼油的n-6/n-3高于这一比值。综合分析比较3种粗鱼油的脂肪酸组成可以得出:鲢鱼油营养价值最高,其EPA和DHA含量最高,n-6/n-3比值最低,且不饱和脂肪酸含量较高。
表 2 3种粗鱼油各类脂肪酸占比Table 2. Proportion of various fatty acid in three crude fish oils脂肪酸 相对含量(%) 草鱼油 青鱼油 鲢鱼油 C10:0 − 0.13±0.12a − C12:0 1.16±0.08b 1.72±0.61a 0.25±0.04c C13:0 − − 0.28±0.04a C14:0 1.67±0.55c 2.14±0.29b 3.75±0.35a C15:0 0.18±0.01b 0.15±0.03b 1.63±0.10a C16:0 20.83±2.68ab 16.70±0.38b 23.52±0.44a C17:0 − 0.13±0.02b 0.91±0.02a C18:0 3.72±0.49a 3.23±0.13a 3.37±0.05a C20:0 0.17±0.05ab 0.14±0.04a 0.28±0.01a C21:0 − − 0.16±0.01a C22:0 0.44±0.08a 0.18±0.00b 0.28±0.01b C23:0 − − 1.39±0.03a ∑SFA 28.17±3.93b 24.51±1.61b 35.82±1.10a C16:1 4.08±0.33b 4.80±0.03b 9.66±0.27a C17:1 − 0.21±0.06b 1.27±0.02a C18:1n-9t 0.15±0.02b 0.38±0.00a C18:1n-9c 39.68±0.01b 47.96±0.89a 27.91±0.51c C20:1 0.89±0.32b 1.05±0.00b 2.87±0.08a C22:1n-9 − 0.11±0.01a 0.11±0.00a ∑MUFA 44.65±0.66b 54.28±1.01a 42.20±0.88c C18:2n-6t − − 1.32±0.04a C18:2n-6c 22.66±1.82a 17.45±0.28b 4.30±0.06c C18:3n-6 0.33±0.02b 0.35±0.03b 0.41±0.00a C18:3n-3 2.02±0.21b 1.79±0.06c 8.88±0.12a C20:2 0.54±0.15b 0.40±0.00c 0.85±0.37a C20:3n-6 0.68±0.16a 0.73±0.04a − C20:3n-3 − − 0.08±0.00a C20:4n-6 0.96±0.17a 0.41±0.03c 0.70±0.02b C22:2 − − 1.46±0.04a C20:5n-3(EPA) − − 2.53±0.08a C22:6n-3(DHA) − 0.09±0.01b 1.44±0.03a ∑PUFA 27.17±2.53a 21.21±0.45b 21.97±0.76b EPA+DHA − 0.09±0.01b 3.97±0.10a n-3∑PUFA 2.02±0.21b 1.87±0.07b 12.92±0.23a n-6∑PUFA 24.62±2.17a 18.94±0.38b 6.73±0.12c n-6/n-3 12.20 10.11 0.52 注:−为未检测到该物质;同行不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 2.3 粗鱼油挥发性风味成分
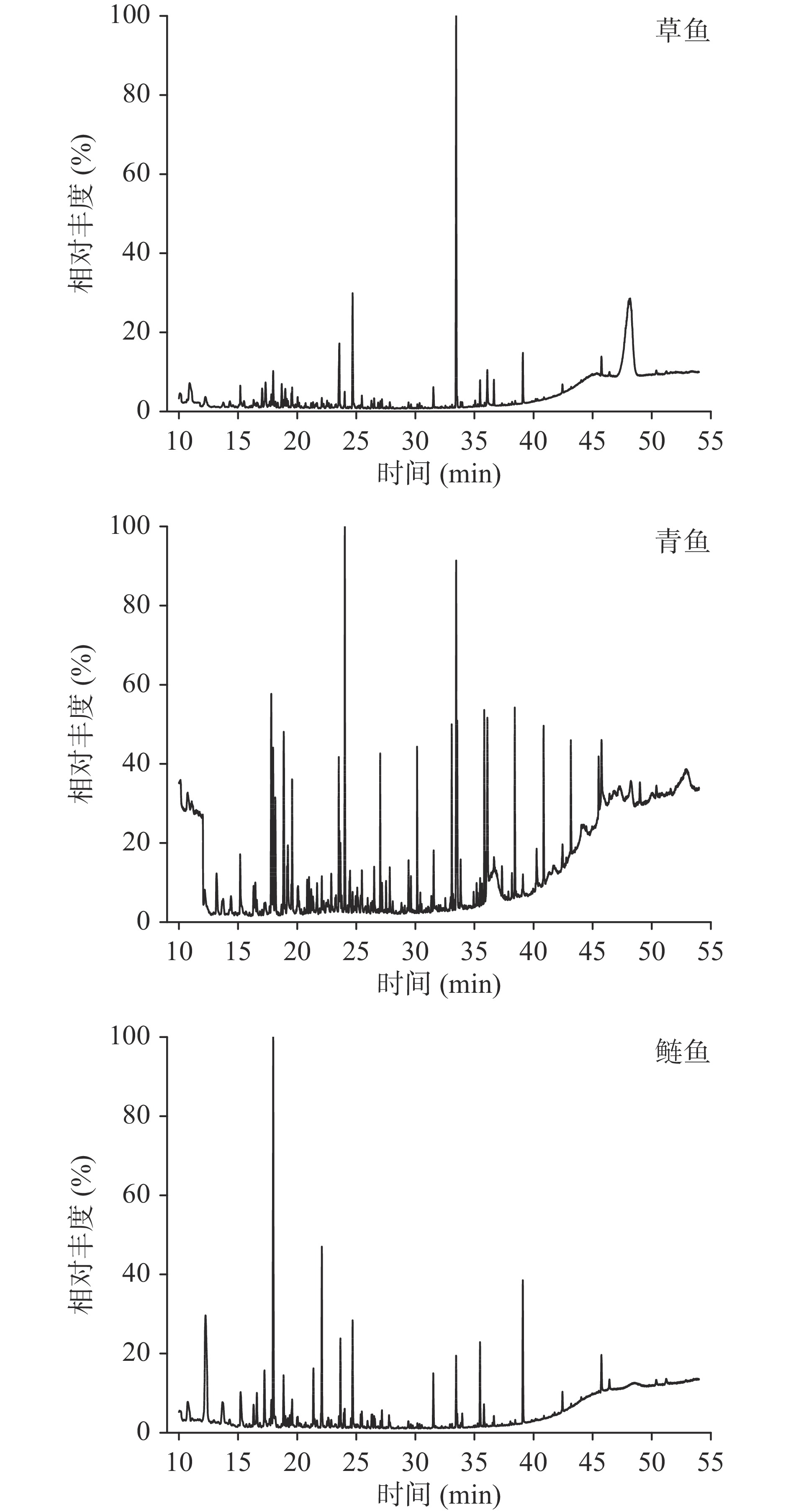
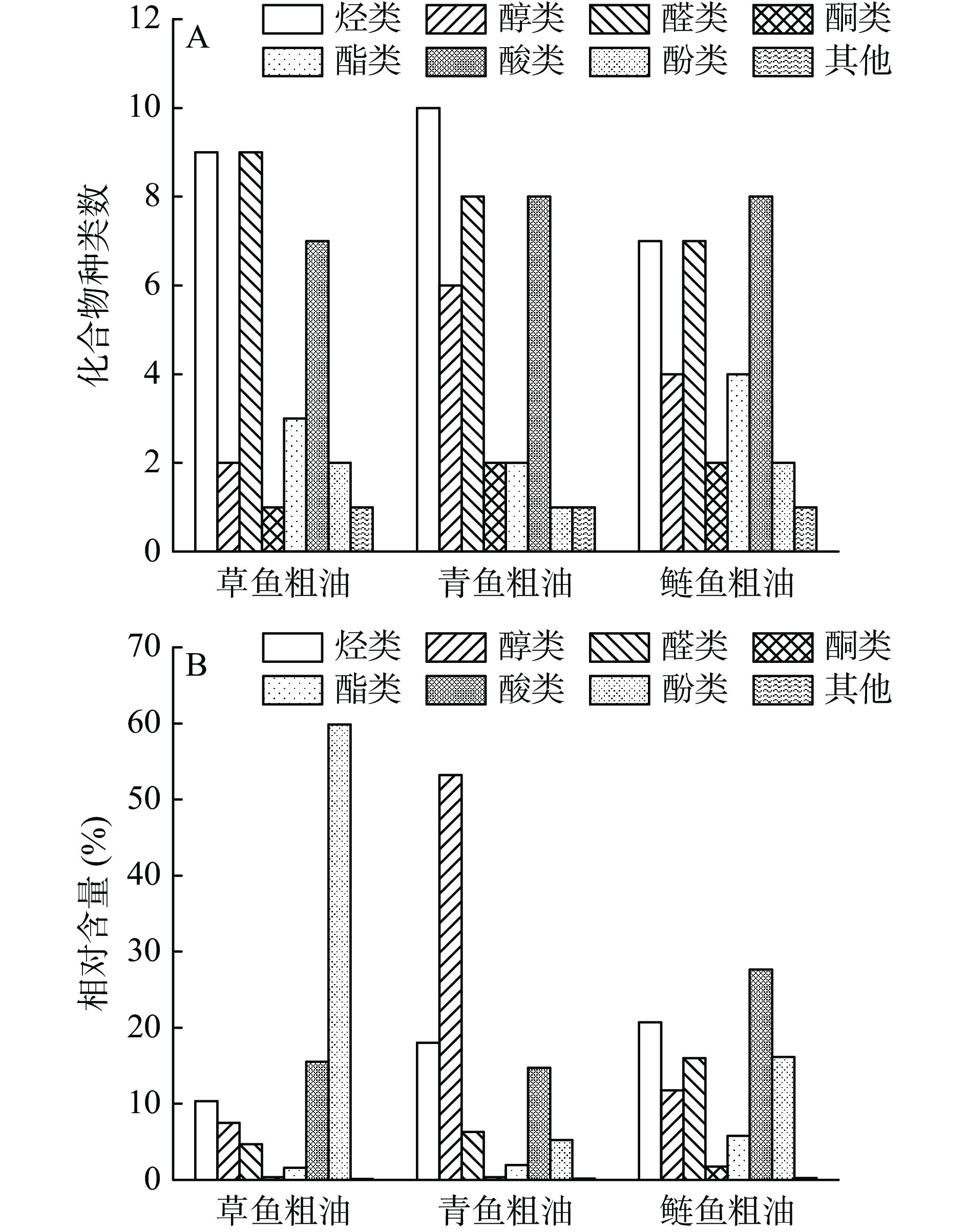
对3种淡水鱼内脏粗鱼油的挥发性风味成分进行对比分析,3种粗鱼油挥发性成分总离子流图如图1,分析结果见图2和表3。3种粗鱼油共检测出66种挥发性物质,根据它们的一般性质和化学结构将其分为8类,包括烃类17种,醛类15种,酸类10种,酯类8种,酚类3种,醇类7种,酮类3种,其他类3种。草鱼油、青鱼油和鲢鱼油中分别检测出34、38、35种挥发性物质。不同粗油中挥发物质的组成和相对含量存在较大差异,草鱼油中相对含量最高的是酚类物质(59.86%),而青鱼油中酚类物质只占5.24%;青鱼油中挥发性物质以醇类为主,相对含量为53.23%;鲢鱼油中相对含量最高的是酸类物质,占27.64%。1-辛烯-3-醇、壬醛、苯乙酮、癸酸等15种挥发性物质在3种粗油中均有检测到,而有些挥发性物质仅在某种鱼油中检出,如(-)-异喇叭烯、反-2-辛烯醛、十二酸甲酯仅在草鱼油中检出,苯乙烯、2-乙基-1-己醇、2(5H)-呋喃酮、邻苯二甲酸二甲酯仅在青鱼油中检出,1-烯丙基-2-甲苯、2-丁基-1-辛醇、乙醇酸乙酯仅在鲢鱼油中被检出。
表 3 3种粗鱼油风味成分及占比Table 3. Flavor components and their proportion in three crude fish oils序号 化合物名称 分子式 感觉阈值[38−39](μg/kg) 相对含量(%) 草鱼油 青鱼油 鲢鱼油 烃类 1 苯乙烯 C8H8 730 − 8.96 − 2 1,2,4-三甲基苯 C9H12 − 0.30 − 3 3,5,5-三甲基-2-己烯 C9H18 − 3.46 − 4 1-烯丙基-2-甲苯 C10H12 − − 0.11 5 2-乙基对二甲苯 C10H14 0.53 − 6 1,2,4,5-四甲苯 C10H14 4.35 − 0.29 7 2-甲基萘 C11H10 14 0.41 − − 8 1-甲基萘 C11H10 14 − 0.27 − 9 1-乙基-2,4,5-三甲基苯 C11H16 1.09 − − 10 五甲基苯 C11H16 − 0.24 − 11 十四烷 C14H30 1000 0.65 2.54 0.61 12 (-)-异喇叭烯 C15H24 0.24 − − 13 1-石竹烯 C15H24 64 − 0.44 − 14 十五烷 C15H32 0.78 0.47 1.97 15 十六烷 C16H34 3000 0.49 0.34 1.04 16 十七烷 C17H36 1.81 1.02 16.29 17 十八烷 C18H38 − − 0.38 总含量 10.34 18.03 20.69 醇类 18 苯甲醇 C7H8O 10000 − 0.82 − 19 2,7-辛二烯-1-醇 C8H14O − 5.98 2.63 20 1-辛烯-3-醇 C8H16O 1 6.58 32.95 7.47 21 (2Z)-2-辛烯-1-醇 C8H16O 40 0.92 12.80 1.53 22 2-乙基-1-己醇 C8H18O 270000 − 0.48 − 23 1-辛醇 C8H18O 110 − 0.20 − 24 2-丁基-1-辛醇 C12H26O − − 0.12 总含量 7.50 53.23 11.75 醛类 25 苯甲醛 C7H6O 350 − 1.23 − 26 反式-2,4-庚二烯醛 C7H10O 10 1.01 − 10.75 27 苯乙醛 C8H8O 4 0.50 − 0.64 28 反-2-辛烯醛 C8H14O 0.1 0.55 − − 29 2,4-二甲基苯甲醛 C9H10O − 0.74 − 30 (Z)-2-壬烯醛 C9H16O 8 − 0.63 − 31 反式-2-壬烯醛 C9H16O 3 0.28 − 0.15 32 壬醛 C9H18O 1 1.19 2.01 1.77 33 2,4-癸二烯醛 C10H16O 0.07 0.39 0.67 − 34 反式-2,4-癸二烯醛 C10H16O 0.1 0.40 0.72 0.42 35 3-甲氧基-4-羟基苯甲醛 C8H8O3 0.22 − − 36 3-羟基-4-甲氧基苯甲醛 C8H8O3 − − 0.35 37 2-十一烯醛 C11H20O − 0.12 − 38 E-14-十六烷烯醛 C16H30O − − 1.91 39 十六醛 C16H32O 0.11 0.17 − 总含量 4.66 6.29 16.00 酮类 40 2(5H)-呋喃酮 C4H4O2 − 0.12 − 41 苯乙酮 C8H8O 65 0.37 0.25 0.21 42 3,5-辛二烯-2-酮 C8H12O 150 − − 1.53 总含量 0.37 0.37 1.74 酯类 43 乙醇酸乙酯 C4H8O3 − − 3.19 44 己酸乙烯基酯 C8H14O2 − − 1.14 45 丁位癸内酯 C10H18O2 0.55 0.58 − 46 癸酸甲酯 C11H22O2 0.16 − − 47 十二酸甲酯 C13H26O2 0.89 − − 48 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯 C10H10O4 − 1.377 − 49 十四酸乙酯 C16H32O2 − − 0.60 50 十六酸乙酯 C18H36O2 2000 − − 0.86 总含量 1.60 1.95 5.79 酸类 51 乙酸 C2H4O2 180000 1.65 1.19 14.41 52 丙酸 C3H6O2 20000 − − 1.13 53 己酸 C6H12O2 10000 1.22 1.08 − 54 庚酸 C7H14O2 − 0.38 − 55 辛酸 C8H16O2 3000 3.07 3.71 0.42 56 壬酸 C9H18O2 1.31 0.73 7.50 57 癸酸 C10H20O2 4.35 4.68 0.97 58 十一酸 C11H22O2 − − 0.67 59 十四酸 C14H28O2 1.07 0.85 0.68 60 十六酸 C16H32O2 2.85 2.11 1.85 总含量 15.53 14.74 27.64 酚类 61 丁香酚 C10H12O2 7.1 59.20 5.24 − 62 (E)-2-甲氧基-4-(1-丙烯基苯酚) C10H12O2 0.66 − 0.31 63 2-甲氧基-3-(2-丙烯基)-苯酚 C10H12O2 − − 15.85 总含量 59.86 5.24 16.16 其他 64 甲酰胺 CH3NO − − 0.23 65 吲哚 C8H7N 140 0.13 − − 66 氨基蝶呤 C19H20N8O5 − 0.16 − 总含量 0.13 0.16 0.23 注:−为未检出或检索到该物质。 草鱼油、青鱼油、鲢鱼油中烃类物质相对含量均较高,分别为10.34%、18.03%、20.69%,包括烷烃、烯烃以及芳香烃。烃类物质由于阈值较高,对粗鱼油风味贡献较小,但烯烃类化合物在一定条件下可形成醛、酮类,是粗鱼油产生鱼腥味的潜在因素[29]。草鱼油和青鱼油中检出甲基萘,其通常被认为是环境污染造成的,会对粗鱼油带来不愉快的气息[30]。醇类物质主要来源于脂肪的氧化降解,其阈值一般较高,对于风味的贡献较小,但不饱和醇阈值较低,对风味的贡献较大,如1-辛烯-3-醇阈值较低,是亚油酸经氧化为为氢过氧化物裂解的产物,具油脂味和土腥味[31],在3种粗鱼油中均被检出。醛类物质一般来自于不饱和脂肪酸的氧化降解[32],阈值低,对粗鱼油的整体风味影响很大。3种粗鱼油醛类物质中壬醛的含量均较高,壬醛己被鉴定出广泛存在于淡水鱼及海水鱼中,具鱼腥味、脂香[33]。鲢鱼油中醛类含量最高的是反式-2,4-庚二烯醛,该物质具脂香、青草香、油脂味。宋恭帅等[34]在用蒸煮法制备的甲鱼油中检出壬醛、反式-2,4-庚二烯醛,并被认定为甲鱼油的主体特征风味物质。酮类物质阈值相对醛类较高,但对粗鱼油的整体风味具一定影响,有独特的果香和清香[35]。草鱼油、青鱼油、鲢鱼油中酮类物质不仅化合物种类少,其相对含量也低,分别为0.37%、0.37%、1.74%,这与张蒙娜等[36]对精制沙丁鱼油挥发性风味解析结果一致。酯类物质是通过酸和醇的酯化反应形成,在3种粗鱼油中酯类物质化合物种类与相对含量均较低,其中草鱼油与青鱼油分别只占1.60%、1.95%。在3种粗鱼油中共检测出10种酸类,相对含量较高,介于14.74%~27.64%,其阈值较高,对风味贡献不大。酚类物质同酸类物质一样,阈值较高。在草鱼油挥发性物质中丁香酚的相对含量最高(59.20%),对草鱼油整体风味影响较大,其可能是草鱼在运输过程中使用了丁香酚作为麻醉剂,最终残留在鱼油内[37]。此外,在3种粗油中还检测出相对含量较低的甲酰胺、吲哚及氨基蝶呤,这些物质对粗鱼油风味的形成有一定的辅助作用。
2.4 粗鱼油关键风味成分
风味贡献取决于挥发性化合物占比及其阈值[38]。由表4可知,3种内脏粗鱼油关键风味成分相似但也存在一定差异,草鱼油、青鱼油和鲢鱼油中分别得到9、5、5种关键风味成分,主要以醛类、醇类和酚类物质为主。
表 4 草鱼、青鱼及鲢鱼油关键风味成分Table 4. Key flavor components in grass carp oil, black carp oil and silver carp oil序号 化合物 ROAV 气味描述 草鱼油 青鱼油 鲢鱼油 烃类 1 苯乙烯 − 0.04 − 甜香、脂香、塑料味 2 2-甲基萘 0.35 − − 甜香、花香、木香 3 1-甲基萘 − 0.06 − 樟脑味 4 十四烷 0.01 0.01 0.01 微弱蜡香 5 1-石竹烯 − 0.02 − 甜香、木香、丁香味 6 十六烷 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 − 醇类 7 苯甲醇 − <0.01 − 玫瑰花香、酚醛香 8 1-辛烯-3-醇 78.92 100 100 蘑菇香、油脂味、土腥味 9 (2Z)-2-辛烯-1-醇 0.28 0.97 0.51 甜香、花香 10 2-乙基-1-己醇 − <0.01 − 柑橘香、油脂味、清香 11 1-辛醇 − 0.01 − 蜡香、青草香、香菇味 醛类 12 苯甲醛 − 0.01 − 苦杏仁味、坚果香 13 反式-2,4-庚二烯醛 1.21 − 14.39 脂香、青草香、油脂味 14 苯乙醛 1.50 − 2.14 青草香、花香、可可豆味 15 反-2-辛烯醛 69.96 − − 油脂味、青草香 16 (Z)-2-壬烯醛 − 0.24 − 脂香、蜡香、黄瓜味 17 反式-2-壬烯醛 1.12 − 0.67 油脂味、青草香、醛香 18 壬醛 14.27 6.10 23.69 鱼腥味、脂香、玫瑰香 19 2,4-癸二烯醛 66.82 29.05 − 脂香、油脂味、鱼腥味 20 反式-2,4-癸二烯醛 47.97 21.85 56.22 油脂味、坚果香、鱼腥味 酮类 21 苯乙酮 0.07 0.01 0.04 辛辣味、杏仁味、山楂香 22 3,5-辛二烯-2-酮 − − 0.14 水果香、清香、青草香 其他 23 十六酸乙酯 − − 0.01 蜡香、奶油香、脂香 24 乙酸 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 酸味、醋味 25 丙酸 − − <0.01 辛辣味、酸味、奶酪香 26 己酸 <0.01 <0.01 − 酸味、奶酪香 27 辛酸 0.01 <0.01 <0.01 腐臭味、油脂味、奶酪味 28 丁香酚 100 2.24 − 辛香、烟熏香、熏肉香 29 吲哚 0.01 − − 花香、樟脑味 注:−为未检出或检索到该物质无法计算ROAV和未查到气味描述;气味描述来源于http://www.perflavory.com/index.html。 醛类物质感官阈值低,ROAV较大,其风味特征随浓度发生变化[39],对粗鱼油整体风味的改善具有重要影响。壬醛和反式-2,4-癸二烯醛在3种粗鱼油中均被检出,ROAV较大,是粗鱼油的主要风味贡献物质,贡献鱼腥味、油脂味和脂香。草鱼油与青鱼油中分别单独检测出反-2-辛烯醛和(Z)-2-壬烯醛,反-2-辛烯醛具油脂味、青草香,ROAV大于1,对草鱼油风味起关键作用;(Z)-2-壬烯醛具脂香、蜡香、黄瓜味,对青鱼油风味有重要的修饰作用。此外,粗鱼油中还检测出ROAV较大的2,4-癸二烯醛、反式2,4-庚二烯醛、苯乙醛、反式-2-壬烯醛等醛类化合物,对粗鱼油的鱼腥味、油脂味等贡献较大。3种粗鱼油醇类物质中ROAV最大的均为1-辛烯-3-醇,在草鱼油中为78.92,在青鱼油与鲢鱼油中均为100,其对粗鱼油中蘑菇香、油脂味和土腥味等气味具有较大贡献。(2Z)-2-辛烯-1-醇对粗鱼油风味有重要的修饰作用,贡献甜香、花香。陈娜等[40]研究表明反式2,4-庚二烯醛是乙酯型鱼油的主要鱼腥味物质,可作为鱼油产品质量优劣的指标。张红燕等[41]研究表明1-辛烯-3-醇、反-2-辛烯醛、辛醛、己醛、庚醛等是金枪鱼油冬化前后的主体风味成分。窦鑫[42]研究表明(E,Z)- 2,4-癸二烯醛、反式-2-壬烯醛、壬醛、1-辛烯-3-醇、反式2,4-庚二烯醛、庚醛等是大黄鱼肝油的主要关键风味物质,经精制后除反式-2-壬烯醛的OAV上升,其余关键风味物质均下降,鱼腥味、油脂味等不良风味降低。因此可通过精制等方法控制反式-2,4-癸二烯醛、壬醛、1-辛烯-3-醇、反式-2,4-庚二烯醛、苯乙醛等的含量改善粗鱼油的整体风味。在草鱼油中丁香酚ROAV为100,其含量也相对最高,对草鱼油的整体风味贡献最大,贡献了辛香、烟熏香等气味,青鱼油中丁香酚ROAV为2.24,鲢鱼油中未检出,这可能是草鱼油与其他两种鱼油风味存在较大差异的原因。苯乙酮具辛辣味、杏仁味,在3种粗鱼油中ROAV均小于0.1,对粗鱼油风味影响不大。烃类、酯类、酸类等物质阈值较高,所以其ROAV极小,对粗鱼油的整体风味贡献不大。
3. 结论
本研究对3种常见的淡水鱼内脏粗鱼油理化指标、脂肪酸组成、挥发性风味成分进行分析比较。结果表明,除草鱼油过氧化值外,3种粗鱼油过氧化值、酸价、水分及挥发物、茴香胺值、不皂化物及菌落总数均达到SC/T 3502–2016规定的粗鱼油二级标准或以上,其中青鱼油理化指标最佳。3种粗鱼油均以棕榈酸、油酸、亚油酸为主,但在脂肪酸组成与含量上差异明显,其中鲢鱼油营养价值最高。3种粗鱼油共检测出66种挥发性物质,其中草鱼油挥发性物质种类最少,含量最高的是酚类物质,青鱼油、鲢鱼油中含量最高的分别是醇类和酸类物质。草鱼油、青鱼油和鲢鱼油中分别得到9、5、5种关键风味成分,主要以醛类、醇类和酚类物质为主,反式-2,4-癸二烯醛、壬醛、反式-2,4-庚二烯醛、苯乙醛、1-辛烯-3-醇等是粗鱼油中主要的鱼腥味、油脂味风味物质。因此,3种淡水鱼内脏油在营养成分组成、理化性质及挥发性风味成分上各有差异,我们在开发利用时应根据其相应的特点有区别对待,以获取成本更低、附加值更高的产品。本研究为淡水鱼内脏的进一步高值化利用提供了一定的理论依据。
-
表 1 3种粗鱼油理化指标
Table 1 Physicochemical indexes of the three crude fish oils
指标 草鱼油 青鱼油 鲢鱼油 SC/T 3502−2016粗鱼油 一级 二级 过氧化值(mmol/kg) 0.43±0.03b 0.22±0.06b 1.99±0.27a ≤12.0 ≤20.0 酸价(mg KOH/g) 18.37±0.88a 6.36±0.07c 12.25±0.18b ≤8.0 ≤15.0 水分及挥发物(%) 0.38±0.07a 0.32±0.03a 0.36±0.02a ≤0.3 ≤0.5 茴香胺值 1.40±0.24a 1.33±0.32a 1.78±0.59a − 碘值(g/100 g) 97.63±5.08c 106.39±6.74b 118.71±13.03a ≥120 不皂化物(%) 0.59±0.04a 0.33±0.19a 0.29±0.06a − 不溶性杂质(%) 1.85±0.08a 1.40±0.58a 2.20±0.47a ≤0.5 菌落总数(CFU/mL) <1 <1 <1 ≤103 注:—为未做限定;同行不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 2 3种粗鱼油各类脂肪酸占比
Table 2 Proportion of various fatty acid in three crude fish oils
脂肪酸 相对含量(%) 草鱼油 青鱼油 鲢鱼油 C10:0 − 0.13±0.12a − C12:0 1.16±0.08b 1.72±0.61a 0.25±0.04c C13:0 − − 0.28±0.04a C14:0 1.67±0.55c 2.14±0.29b 3.75±0.35a C15:0 0.18±0.01b 0.15±0.03b 1.63±0.10a C16:0 20.83±2.68ab 16.70±0.38b 23.52±0.44a C17:0 − 0.13±0.02b 0.91±0.02a C18:0 3.72±0.49a 3.23±0.13a 3.37±0.05a C20:0 0.17±0.05ab 0.14±0.04a 0.28±0.01a C21:0 − − 0.16±0.01a C22:0 0.44±0.08a 0.18±0.00b 0.28±0.01b C23:0 − − 1.39±0.03a ∑SFA 28.17±3.93b 24.51±1.61b 35.82±1.10a C16:1 4.08±0.33b 4.80±0.03b 9.66±0.27a C17:1 − 0.21±0.06b 1.27±0.02a C18:1n-9t 0.15±0.02b 0.38±0.00a C18:1n-9c 39.68±0.01b 47.96±0.89a 27.91±0.51c C20:1 0.89±0.32b 1.05±0.00b 2.87±0.08a C22:1n-9 − 0.11±0.01a 0.11±0.00a ∑MUFA 44.65±0.66b 54.28±1.01a 42.20±0.88c C18:2n-6t − − 1.32±0.04a C18:2n-6c 22.66±1.82a 17.45±0.28b 4.30±0.06c C18:3n-6 0.33±0.02b 0.35±0.03b 0.41±0.00a C18:3n-3 2.02±0.21b 1.79±0.06c 8.88±0.12a C20:2 0.54±0.15b 0.40±0.00c 0.85±0.37a C20:3n-6 0.68±0.16a 0.73±0.04a − C20:3n-3 − − 0.08±0.00a C20:4n-6 0.96±0.17a 0.41±0.03c 0.70±0.02b C22:2 − − 1.46±0.04a C20:5n-3(EPA) − − 2.53±0.08a C22:6n-3(DHA) − 0.09±0.01b 1.44±0.03a ∑PUFA 27.17±2.53a 21.21±0.45b 21.97±0.76b EPA+DHA − 0.09±0.01b 3.97±0.10a n-3∑PUFA 2.02±0.21b 1.87±0.07b 12.92±0.23a n-6∑PUFA 24.62±2.17a 18.94±0.38b 6.73±0.12c n-6/n-3 12.20 10.11 0.52 注:−为未检测到该物质;同行不同字母表示差异显著(P<0.05)。 表 3 3种粗鱼油风味成分及占比
Table 3 Flavor components and their proportion in three crude fish oils
序号 化合物名称 分子式 感觉阈值[38−39](μg/kg) 相对含量(%) 草鱼油 青鱼油 鲢鱼油 烃类 1 苯乙烯 C8H8 730 − 8.96 − 2 1,2,4-三甲基苯 C9H12 − 0.30 − 3 3,5,5-三甲基-2-己烯 C9H18 − 3.46 − 4 1-烯丙基-2-甲苯 C10H12 − − 0.11 5 2-乙基对二甲苯 C10H14 0.53 − 6 1,2,4,5-四甲苯 C10H14 4.35 − 0.29 7 2-甲基萘 C11H10 14 0.41 − − 8 1-甲基萘 C11H10 14 − 0.27 − 9 1-乙基-2,4,5-三甲基苯 C11H16 1.09 − − 10 五甲基苯 C11H16 − 0.24 − 11 十四烷 C14H30 1000 0.65 2.54 0.61 12 (-)-异喇叭烯 C15H24 0.24 − − 13 1-石竹烯 C15H24 64 − 0.44 − 14 十五烷 C15H32 0.78 0.47 1.97 15 十六烷 C16H34 3000 0.49 0.34 1.04 16 十七烷 C17H36 1.81 1.02 16.29 17 十八烷 C18H38 − − 0.38 总含量 10.34 18.03 20.69 醇类 18 苯甲醇 C7H8O 10000 − 0.82 − 19 2,7-辛二烯-1-醇 C8H14O − 5.98 2.63 20 1-辛烯-3-醇 C8H16O 1 6.58 32.95 7.47 21 (2Z)-2-辛烯-1-醇 C8H16O 40 0.92 12.80 1.53 22 2-乙基-1-己醇 C8H18O 270000 − 0.48 − 23 1-辛醇 C8H18O 110 − 0.20 − 24 2-丁基-1-辛醇 C12H26O − − 0.12 总含量 7.50 53.23 11.75 醛类 25 苯甲醛 C7H6O 350 − 1.23 − 26 反式-2,4-庚二烯醛 C7H10O 10 1.01 − 10.75 27 苯乙醛 C8H8O 4 0.50 − 0.64 28 反-2-辛烯醛 C8H14O 0.1 0.55 − − 29 2,4-二甲基苯甲醛 C9H10O − 0.74 − 30 (Z)-2-壬烯醛 C9H16O 8 − 0.63 − 31 反式-2-壬烯醛 C9H16O 3 0.28 − 0.15 32 壬醛 C9H18O 1 1.19 2.01 1.77 33 2,4-癸二烯醛 C10H16O 0.07 0.39 0.67 − 34 反式-2,4-癸二烯醛 C10H16O 0.1 0.40 0.72 0.42 35 3-甲氧基-4-羟基苯甲醛 C8H8O3 0.22 − − 36 3-羟基-4-甲氧基苯甲醛 C8H8O3 − − 0.35 37 2-十一烯醛 C11H20O − 0.12 − 38 E-14-十六烷烯醛 C16H30O − − 1.91 39 十六醛 C16H32O 0.11 0.17 − 总含量 4.66 6.29 16.00 酮类 40 2(5H)-呋喃酮 C4H4O2 − 0.12 − 41 苯乙酮 C8H8O 65 0.37 0.25 0.21 42 3,5-辛二烯-2-酮 C8H12O 150 − − 1.53 总含量 0.37 0.37 1.74 酯类 43 乙醇酸乙酯 C4H8O3 − − 3.19 44 己酸乙烯基酯 C8H14O2 − − 1.14 45 丁位癸内酯 C10H18O2 0.55 0.58 − 46 癸酸甲酯 C11H22O2 0.16 − − 47 十二酸甲酯 C13H26O2 0.89 − − 48 邻苯二甲酸二甲酯 C10H10O4 − 1.377 − 49 十四酸乙酯 C16H32O2 − − 0.60 50 十六酸乙酯 C18H36O2 2000 − − 0.86 总含量 1.60 1.95 5.79 酸类 51 乙酸 C2H4O2 180000 1.65 1.19 14.41 52 丙酸 C3H6O2 20000 − − 1.13 53 己酸 C6H12O2 10000 1.22 1.08 − 54 庚酸 C7H14O2 − 0.38 − 55 辛酸 C8H16O2 3000 3.07 3.71 0.42 56 壬酸 C9H18O2 1.31 0.73 7.50 57 癸酸 C10H20O2 4.35 4.68 0.97 58 十一酸 C11H22O2 − − 0.67 59 十四酸 C14H28O2 1.07 0.85 0.68 60 十六酸 C16H32O2 2.85 2.11 1.85 总含量 15.53 14.74 27.64 酚类 61 丁香酚 C10H12O2 7.1 59.20 5.24 − 62 (E)-2-甲氧基-4-(1-丙烯基苯酚) C10H12O2 0.66 − 0.31 63 2-甲氧基-3-(2-丙烯基)-苯酚 C10H12O2 − − 15.85 总含量 59.86 5.24 16.16 其他 64 甲酰胺 CH3NO − − 0.23 65 吲哚 C8H7N 140 0.13 − − 66 氨基蝶呤 C19H20N8O5 − 0.16 − 总含量 0.13 0.16 0.23 注:−为未检出或检索到该物质。 表 4 草鱼、青鱼及鲢鱼油关键风味成分
Table 4 Key flavor components in grass carp oil, black carp oil and silver carp oil
序号 化合物 ROAV 气味描述 草鱼油 青鱼油 鲢鱼油 烃类 1 苯乙烯 − 0.04 − 甜香、脂香、塑料味 2 2-甲基萘 0.35 − − 甜香、花香、木香 3 1-甲基萘 − 0.06 − 樟脑味 4 十四烷 0.01 0.01 0.01 微弱蜡香 5 1-石竹烯 − 0.02 − 甜香、木香、丁香味 6 十六烷 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 − 醇类 7 苯甲醇 − <0.01 − 玫瑰花香、酚醛香 8 1-辛烯-3-醇 78.92 100 100 蘑菇香、油脂味、土腥味 9 (2Z)-2-辛烯-1-醇 0.28 0.97 0.51 甜香、花香 10 2-乙基-1-己醇 − <0.01 − 柑橘香、油脂味、清香 11 1-辛醇 − 0.01 − 蜡香、青草香、香菇味 醛类 12 苯甲醛 − 0.01 − 苦杏仁味、坚果香 13 反式-2,4-庚二烯醛 1.21 − 14.39 脂香、青草香、油脂味 14 苯乙醛 1.50 − 2.14 青草香、花香、可可豆味 15 反-2-辛烯醛 69.96 − − 油脂味、青草香 16 (Z)-2-壬烯醛 − 0.24 − 脂香、蜡香、黄瓜味 17 反式-2-壬烯醛 1.12 − 0.67 油脂味、青草香、醛香 18 壬醛 14.27 6.10 23.69 鱼腥味、脂香、玫瑰香 19 2,4-癸二烯醛 66.82 29.05 − 脂香、油脂味、鱼腥味 20 反式-2,4-癸二烯醛 47.97 21.85 56.22 油脂味、坚果香、鱼腥味 酮类 21 苯乙酮 0.07 0.01 0.04 辛辣味、杏仁味、山楂香 22 3,5-辛二烯-2-酮 − − 0.14 水果香、清香、青草香 其他 23 十六酸乙酯 − − 0.01 蜡香、奶油香、脂香 24 乙酸 <0.01 <0.01 <0.01 酸味、醋味 25 丙酸 − − <0.01 辛辣味、酸味、奶酪香 26 己酸 <0.01 <0.01 − 酸味、奶酪香 27 辛酸 0.01 <0.01 <0.01 腐臭味、油脂味、奶酪味 28 丁香酚 100 2.24 − 辛香、烟熏香、熏肉香 29 吲哚 0.01 − − 花香、樟脑味 注:−为未检出或检索到该物质无法计算ROAV和未查到气味描述;气味描述来源于http://www.perflavory.com/index.html。 -
[1] 农业部渔业渔政管理局. 中国渔业统计年鉴[M]. 北京: 中国农业出版社, 2020 Ministry of Agriculture Fishery Administration. China fishery statistics yearbook [M]. Beijing: China Agriculture Press, 2020.
[2] 蔡路昀, 张滋慧, 李秀霞, 等. 鱼类下脚料在工业中应用的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2017,38(8):356−363. [CAI L Y, ZHANG Z H, LI X X, et al. Research progress of industrial applications of fish processing by-products[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2017,38(8):356−363. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2017.08.061 [3] 冯淳淞, 洪惠, 罗永康. 鱼骨综合利用的研究进展[J]. 中国水产,2021(11):85−87. [FENG C S, HONG H, LUO Y K. Research progress on comprehensive utilization of fishbone[J]. China Fisheries,2021(11):85−87. [4] 代昕冉, 刘焱, 陈力力. 淡水鱼鳞综合利用研究进展[J]. 农产品加工,2018(16):61−66. [DAI X R, LIU Y, CHEN L L. Research process in comprehensive utilization of freshwater fish scales[J]. Farm Products Processing,2018(16):61−66. doi: 10.16693/j.cnki.1671-9646(X).2018.08.047 [5] USMAN M, SAHAR A, INAM-UR-RAHEEM M, et al. Gelatin extraction from fish waste and potential applications in food sector[J]. International Journal of Food Science & Technology,2022,57(1):154−163.
[6] 窦鑫, 吴燕燕. 海水鱼内脏高值化利用的研究现状与发展趋势[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(13):372−378. [DOU X, WU Y Y. Research status and development trend of high-value utilization of marine fish offal[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(13):372−378. [7] ESTIASIH T, AHMADI K, ALI D Y, et al. Valorisation of viscera from fish processing for food industry utilizations[J]. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science,2021,924(1):12024. doi: 10.1088/1755-1315/924/1/012024
[8] SERHIYENKO V. Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, metabolic syndrome and diabetes mellitus[J]. Current Research in Diabetes & Obesity Journal,2018,5(4):1−4.
[9] GOH K K, CHEN C Y, CHEN C H, et al. Effects of omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids supplements on psychopathology and metabolic parameters in schizophrenia: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials[J]. Journal of Psychopharmacol,2021,35(3):221−235. doi: 10.1177/0269881120981392
[10] ZHANG J, TAO N, WANG M, et al. Characterization of phospholipids from Pacific saury (Cololabis saira) viscera and their neuroprotective activity[J]. Food Bioscience,2018,24:120−126. doi: 10.1016/j.fbio.2018.06.002
[11] 相朝清, 张波涛, 许瑞红, 等. 响应面法优化斑点叉尾鮰鱼内脏油脂肪酸提取工艺研究[J]. 肉类工业,2020(4):26−29. [XIANG C Q, ZHANG B T, XU R H, et al. Optimization of extraction technology of fatty acids in visceral oil from ietalurus punetaus by response surface method[J]. Meat Industry,2020(4):26−29. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-5467.2020.04.006 [12] 于淑池, 李晨晨, 徐云升, 等. 金鲳鱼骨中鱼油的提取工艺及脂肪酸成分分析[J]. 食品工业,2021,42(3):147−152. [YU S C, LI C C, XU Y S, et al. Extraction technology of oil from Trachinotus ovatus bone and analysis on its fatty acids composition[J]. The Food Industry,2021,42(3):147−152. [13] 王正云, 蒋慧亮, 周洁, 等. 微波辅助酶法提取青鱼内脏鱼油工艺优化及脂肪酸组成分析[J]. 食品工业科技,2020,41(3):182−187. [WANG Z Y, JIANG H L, ZHOU J, et al. Technological optimization of microwave-assisted enzymatic extraction of fish oil from black carp viscera and analysis of fatty acid composition[J]. Food Industry Science and Technology,2020,41(3):182−187. [14] 付雪媛, 钟宏, 宋文山, 等. 章鱼内脏鱼油的提取及品质分析[J]. 中国油脂,2020,45(5):17−22. [FU X Y, ZHONG H, SONG W S, et al. Extraction and quality analysis of octopus viscera fish oil[J]. China Oils and Fats,2020,45(5):17−22. doi: 10.12166/j.zgyz.1003-7969/2020.05.004 [15] 江鑫, 陈倩媛, 俞文韬, 等. LCMS-IT-TOF测定不同脂肪酸结构食用油中的羰基化合物[J]. 食品工业科技,2019,40(21):231−238. [JIANG X, CHEN Q Y, YU W T, et al. Determination of carbonyl compounds in edible oils with different fatty acid compositions by LCMS-IT-TOF[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(21):231−238. [16] 李金林, 涂宗财, 张露, 等. SPME-GC-MS法分析草鱼汤烹制过程中挥发性成分变化[J]. 食品科学,2016,37(22):149−154. [LIN J L, TU Z C, ZHANG L, et al. SPME-GC-MS analysis of changes in volatile compounds during preparation of grass carp soup[J]. Food Science,2016,37(22):149−154. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201622022 [17] 刘登勇, 周光宏, 徐幸莲. 确定食品关键风味化合物的一种新方法: “ROAV”法[J]. 食品科学,2008(7):370−374. [LIU D, ZHOU G H, XU X L, et al. ''ROAV'' method: A new method for determining key odor compounds of rugao ham[J]. Food Science,2008(7):370−374. [18] AIDOS I, SCHLVIS-SMIT R, VELDMAN M, et al. Chemical and sensory evaluation of crude oil extracted from herring byproducts from different processing operations[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2003,51(7):1897−1903. doi: 10.1021/jf020684p
[19] CREXI V T, MONTE M L, SOARES L A D S, et al. Production and refinement of oil from carp (Cyprinus carpio) viscera[J]. Food Chemistry,2010,119(3):945−950. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2009.07.050
[20] COZZOLINO D, MURRAY I, CHREE A, et al. Multivariate determination of free fatty acids and moisture in fish oils by partial least-squares regression and near-infrared spectroscopy[J]. LWT - Food Science and Technology,2005,38(8):821−828. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2004.10.007
[21] 代志凯, 李祥清, 陈子杰, 等. 国产与进口鱼油品质分析比较[J]. 中国油脂,2018,43(6):51−55. [DAI Z K, LI X Q, CHEN Z Z, et al. Analysis and comparison of quality of domestic and imported fish oil[J]. China Oils and Fats,2018,43(6):51−55. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7969.2018.06.012 [22] 刘迪, 谭北平, 迟淑艳, 等. 不同储存时间和抗氧化剂添加量对鱼油质量影响的研究[J]. 中国油脂,2018,43(1):80−84. [LIU D, TAN B P, CHI S X, et al. Effects of different storage time and dosage of antioxidant on quality of fish oil[J]. China Oils and Fats,2018,43(1):80−84. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7969.2018.01.021 [23] 王炜, 张伟敏. 单不饱和脂肪酸的功能特性[J]. 中国食物与营养,2005(4):44−46. [WANG W, ZHANG W M. Functional properties of monounsaturated fatty acids[J]. Food and Nutrition in China,2005(4):44−46. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-9577.2005.04.014 [24] 李琪, 张娴. 多不饱和脂肪酸的生理功能概述[J]. 食品安全导刊,2019(18):55. [LI Q, ZHANG X. Overview of physiological functions of polyunsaturated fatty acids[J]. Chian Food Safety Magazine,2019(18):55. doi: 10.16043/j.cnki.cfs.2019.18.044 [25] 张立坚, 杨会邦, 蔡春. 3种淡水鱼油脂肪酸的含量分析[J]. 食品研究与开发,2011,32(4):115−117. [ZHANG L J, YANG H B, CAI C. The profile of fatty acids in the fish oil of three kind of freshwater[J]. Food Research and Development,2011,32(4):115−117. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-6521.2011.04.034 [26] 涂宗财, 张朋, 王辉, 等. 草鱼鱼油钾法提取及其脂肪酸组成分析[J]. 南昌大学学报(理科版),2012,36(4):367−372. [TU Z C, ZHANG P, WANG H, et al. Extraction of fish oil from grass carp using KOH hydrolysis and composition of the fatty acids[J]. Journal of Nanchang University (Natural Science),2012,36(4):367−372. [27] 林婉玲, 韩迎雪, 李来好, 等. 6种鲤科鱼肌肉脂肪的脂肪酸组成比较及相关性分析[J]. 中国油脂,2019,44(10):29−34. [LIN W L, HAN Y X, LI L H, et al. Comparison and correlation analysis on fatty acid composition in muscle fat of six species of Cyprinid fishes[J]. China Oil and Fats,2019,44(10):29−34. [28] CALDER P C, ALBERS R, ANTOINE J M, et al. Inflammatory disease processes and interactions with nutrition[J]. British Journal of Nutrition,2009,101(S1):1−45. doi: 10.1017/S0007114509377867
[29] 吴丽香, 张雯, 童秋霞, 等. 即食秋刀鱼加工过程中挥发性成分变化规律[J]. 食品与机械,2021,37(9):29−36. [WU L X, ZHANG W, TONG Q X, et al. Study on the variation components of ready-to-eat Pacific saury (Coloabis saira) duying processing[J]. Food & Machinery,2021,37(9):29−36. doi: 10.13652/j.issn.1003-5788.2021.09.005 [30] PERŠURIĆ Ž, SAFTIĆ L, MAŠEK T, et al. Comparison of triacylglycerol analysis by MALDI-TOF/MS, fatty acid analysis by GC-MS and non-selective analysis by NIRS in combination with chemometrics for determination of extra virgin olive oil geographical origin. A case study[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2018,95:326−332. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2018.04.072
[31] SUN Y, ZHANG Y, SONG H. Variation of aroma components during frozen storage of cooked beef balls by SPME and SAFE coupled with GC-O-MS[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2021,45(1):e15036.
[32] 魏育坤, 魏好程, 伍菱, 等. SPME/SDE-GC-MS分析宁德养殖大黄鱼挥发性化合物[J]. 食品研究与开发,2020,41(15):129−136. [WEI Y K, WEI H C, WU L, et al. Analysis of volatile compounds in framed Pseudosciaena crocea from Ningde district by SPME/SDE-GC-MS[J]. Food Research and Development,2020,41(15):129−136. doi: 10.12161/j.issn.1005-6521.2020.15.023 [33] 王玉, 赵延宁, 薛勇, 等. 基于电子鼻与SPME-GC-MS法分析咸鲅鱼加工过程挥发性风味成分变化[J]. 食品工业科技,2018,39(24):266−272. [WANG Y, ZHAO Y Y, XUE Y, et al. Analysis of volatile flavor compounds changes during salted spanish mackerel processing by electronic nose and SPME-GC-MS[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2018,39(24):266−272. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2018.24.045 [34] 宋恭帅, 张蒙娜, 俞喜娜, 等. 5种提取方法对甲鱼油品质的影响[J]. 核农学报,2019,33(9):1789−1799. [SONG G S, ZHANG M N, YU X N, et al. Effects of five extraction methods on the quality of turtle oil[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2019,33(9):1789−1799. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2019.09.1789 [35] LI J, TU Z, ZHANG L, et al. Characterization of volatile compounds in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idellus) soup cooked using a traditional chinese method by GC-MS[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preseration,2017,41(4):1−15.
[36] 张蒙娜, 宋恭帅, 彭茜, 等. 精制沙丁鱼油品质及挥发性风味成分分析[J]. 中国油脂,2018,43(4):48−52. [ZHANG M N, SONG G S, PENG X, et al. Quality and volatile flavor components of refined sardine oil[J]. China Oil and Fats,2018,43(4):48−52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-7969.2018.04.011 [37] XU J H, LIUY, ZHOU X W, et al. Anaesthetic effects of eugenol on preservation and transportation of yellow catfish (Pelteobagrus fulvidraco)[J]. Aquaculture Research,2021,52(8):3796−3803. doi: 10.1111/are.15225
[38] ZHU Y, CHEN J, CHEN X, et al. Use of relative odor activity value (ROAV) to link aroma profiles to volatile compounds: Application to fresh and dried eel (Muraenesox cinereus)[J]. International Journal of Food Properties,2020,23(1):2257−2270. doi: 10.1080/10942912.2020.1856133
[39] 丁浩宸, 李栋芳, 张燕平, 等. 南极磷虾虾仁与4种海虾虾仁挥发性风味成分对比[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2013,39(10):57−62. [DING H C, LI D F, ZHANG Y P, et al. Comparison of the volatile flavor composition of Euphausia superba and four kinds of sea shrimps[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2013,39(10):57−62. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.2013.10.003 [40] 陈娜, 陈小娥, 方旭波, 等. 基于电子鼻和气质联用技术分析鱼油挥发性成分[J]. 中国粮油学报,2017,32(10):179−184. [CHEN N, CHEN X E, FANG X B, et al. Analysis of the volatile components of fish oil based on the electronic nose and GC-MS[J]. Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils,2017,32(10):179−184. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-0174.2017.10.030 [41] 张红燕, 李晔, 袁贝, 等. 金枪鱼油冬化前后脂肪酸含量和主体风味的解[J]. 核农学报,2017,31(2):314−324. [ZHANG H Y, LI Y, YUANG B, et al. Analysis of fatty acid content and main flavor of Thunnus tuna oil winterization before and after[J]. Journal of Nuclear Agricultural Sciences,2017,31(2):314−324. doi: 10.11869/j.issn.100-8551.2017.02.0314 [42] 窦鑫. 大黄鱼鱼肝油的酶法制取与脱腥研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2021 DOU X. Enzymatic preparation and deodorization of large yellow croaker (Pseudosciaena crocea) liver oil [D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2021.
-
期刊类型引用(6)
1. 孟晓华. 超声波-微波辅助酶法提取花生红衣白藜芦醇的工艺研究. 粮食加工. 2024(02): 48-53 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 匡燕,罗跃中,姚琦. 响应面法优化超声辅助碱法提取米糠中膳食纤维. 武汉轻工大学学报. 2023(01): 26-32 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 张林威,贺便,黄亮,朱仁威,王雅怡. 超微粉碎-微波辅助提取洋蓟可溶性膳食纤维工艺优化. 食品研究与开发. 2023(16): 134-142 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 李颖,王长远. 小米谷糠多糖抗氧化及体外免疫活性. 食品研究与开发. 2023(20): 55-62 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 肖志刚,元沅,高岩,周廉舜,时家峰,王鹏,于小帅,段玉敏,李国德. 不同处理方式对豆渣可溶性膳食纤维得率及理化特性的影响. 食品安全质量检测学报. 2023(21): 35-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 张桐,胡益波,柳建良. 贡柑果皮黄酮类化合物组成及抗氧化活性研究. 浙江柑橘. 2023(04): 24-28 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(6)





 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:



