Effect of Salt Concentration on Muscle Quality of Ready-to-eat Shrimp (Solenocera crassicornis) During Chilled Storage
-
摘要: 以中华管鞭虾为研究对象,探究NaCl浓度(0%、2%、4%和6%)对即食中华管鞭虾仁冷藏期间肌肉品质变化的影响。在冷藏0、10、20、30、40和50 d时,比较不同组别中华管鞭虾肌肉色差、质构特性、水分含量、持水力、pH、挥发性盐基氮含量(TVB-N)、菌落总数、TBA值及组织微观结构的变化情况。结果表明,在冷藏过程中,相比于0% NaCl处理组(对照组),4%和6% NaCl可以显著(P<0.05)抑制虾仁肌肉色泽和质构特性的劣化,延缓肌肉TVB-N含量和TBA值的增加及微生物的快速生长。冷藏期间,各NaCl处理组虾仁肌肉持水力随贮藏时间延长而显著上升(P<0.05),且NaCl浓度越高虾仁肌肉持水力保持效果越好。随冷藏时间延长,各组虾仁肌肉水分含量呈先上升后下降趋势,而肌肉pH则先下降后上升,但添加NaCl使得虾仁肌肉水分含量和pH均显著低于对照组(P<0.05)。冷藏第40 d时,与对照组相比,NaCl浓度增加抑制了虾仁肌纤维组织的劣化,其中以4% NaCl处理虾仁肌肉组织结构保持较为完整,肌纤维组织排列较为紧密。综上,选用4% NaCl浸泡处理可以改善保持中华管鞭虾虾仁冷藏期间的肌肉品质。研究结果可为即食虾类产品开发及货架期控制提供理论依据与技术支撑。Abstract: The effects of NaCl concentrations (0%, 2%, 4% and 6%) on the changes in muscle quality of ready-to-eat shrimp (Solenocera crassicornis) were investigated during 50 days of chilled storage. During 0~50 day of chilled storage, the color, texture, moisture content, water-holding capacity, pH, total volatile base nitrogen (TVB-N) content, total bacterial count, TBA values, and histological changes were determined in the shrimp muscle tissues pre-treated with different NaCl solutions. The results showed that 4% and 6% NaCl treatments significant (P<0.05) inhibited the deterioration changes in the color and texture properties of shrimp muscle and retarded the increased in the TVB-N content, TBA value, and the total bacterial count, when they were compared with the control samples (0% NaCl) during chilled storage. The water-holding capacity of shrimp muscle soaked with NaCl solution increased significantly (P<0.05) during the storage, and the higher concentrations of NaCl treatments maintained the better water-holding capacity of shrimp muscle. As the storage period increased, the water content of shrimp samples increased firstly and then decreased, when the pH values decreased firstly and then increased. While, the shrimp samples soaked with NaCl solutions showed the lower water content and pH than those in the control samples (P<0.05). After 40 days of chilled storage, the higher NaCl concentrations greatly inhibited the deterioration of myofibrils in the shrimp muscle tissues compared with the control samples. The histological structure of the muscle tissues soaked in 4% NaCl solutions was relatively well maintained, and the tighter muscle fibers could be observed in the tissues compared with the control and other NaCl soaked samples. In summary, 4% NaCl soaking treatment could efficiently maintain the muscle quality of ready-to-eat shrimp during chilled storage. The results of this study would provide a theoretical basis and technical support for the development and shelf-life control of ready-to-eat shrimp products.
-
Keywords:
- Solenocera crassicornis /
- NaCl concentration /
- chilled storage /
- muscle /
- quality change
-
中华管鞭虾(Solenocera crassicornis)俗称红虾,是我国重要的经济海捕虾类之一,其肉质鲜美,深受消费者喜爱。中华管鞭虾肌肉中必需氨基酸含量高且种类齐全,是一种较为理想的蛋白质摄入源[1]。除此之外,中华管鞭虾中含有大量的不饱和脂肪酸,在预防心脑血管病、抗癌、促进人体发育等方面具有一定的功效[2]。近年来,随着人们生活节奏的加快,即食虾类食品因其方便携带、开袋即食的特点,越来越受到人们的青睐[3]。目前,市面上消费较多的即食虾类制品,多数为风干虾仁、烤虾或者其它方式加工的低水分虾仁制品,而高水分含量的即食虾仁制品在市面上还鲜有见到。
罐藏即食中华管鞭虾的加工主要包含清洗、水煮、制备虾仁、罐装、煮沸杀菌及密封等。其中,高温蒸煮会造成虾仁肌肉中蛋白质变性,致使虾仁肌肉中部分水溶性成分流失。同时可以使虾仁中微生物含量降至可接受水平,从而保障即食虾仁食用安全[4-5]。NaCl在即食虾类食品生产中是提供咸味的主要来源,同时其具有良好的提鲜作用[6]。有研究表明,在肉制品中添加一定量NaCl,可以有效改善肉制品的肌肉品质[7]。除此之外,由于NaCl具有抑菌作用,其在食品保鲜过程中也具有一定的效果[8]。关睿等[9]研究发现,在草鱼中添加NaCl可以抑制微生物的生长,同时降低鱼肌肉pH和TVB-N含量的快速增加,还可以减缓草鱼肌肉蛋白质的氧化作用,减少肌肉中丙二醛的生成。瞿丞等[10]分析了不同NaCl添加量腌制对于鸡肉质构特性的影响。结果表明,随着NaCl添加量的增加,造成肌肉收缩和水分流失,进而促使鸡肉的硬度、弹性显著上升。目前,关于NaCl浓度对即食虾类产品品质的影响,在贮藏期间是否会降低肌肉品质、延长贮藏货架期等方面还存在较多不明确的地方,关于盐水轻微加工高水分即食中华管鞭虾类产品的开发还未见报道。
本研究以蒸馏水处理为对照组,研究了NaCl浓度(2%,4%和6%)对冷藏即食中华管鞭虾理化特性、脂肪氧化及肌肉品质特性的影响,结果将为高水分即食中华管鞭虾虾仁的产品开发及品质保障提供理论依据。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
中华管鞭虾 购于舟山市国际水产城,平均体质量为(13±2)g。购买后将其放入带有冰袋的泡沫箱内,30 min内运送至实验室;冰醋酸、氧化镁、无水乙醇、硼酸、甲基红-溴甲酚绿指示剂等 分析纯,国药集团化学试剂有限公司;0.1 mol/L盐酸标准滴定液 广州和为医药科技有限公司;丙二醛测定试剂盒 南京建成生物工程研究所。
751UVGD型紫外-可见光分光光度计 上海第三分析仪器厂;CR-10型便携式色差仪 日本柯尼卡美能达公司;MS-Pro型物性测试仪 美国FTC公司;全自动凯氏定氮仪 山东海能仪器科学仪器有限公司;CF-16RN高速冷冻离心机 日本日立公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 样品处理
选取个体大小相似的中华管鞭虾,蒸馏水清洗后,采用沸水蒸煮3 min;蒸馏水冷却至室温,去头去壳制备成虾仁;将虾仁分别置于装有0%、2%、4%和6% NaCl溶液的玻璃罐中,虾仁与溶液质量比为1:3[11],煮沸5 min,密封;待冷却至室温后,4 ℃保存。冷藏第0、10、20、30、40和50 d取样测定。
1.2.2 色差测定
色差采用手持式色差仪进行测定,测试点为中华管鞭虾第二节肌肉,记录虾仁L*、a*和b*值。
1.2.3 质构特性测定
质构测定参考刘欣荣等[12]方法,并略作修改。采用质地剖面分析模型(TPA),测定虾仁硬度、弹性。测试探头选用P/50,测试速度为60 mm/min,样品形变量为30%,测试点选取虾仁第二节肌肉。
1.2.4 水分含量和持水力测定
水分含量测定参考《食品安全国家标准—食品中水分的测定》(GB 5009.3-2016)[13];持水力测定:参照李志鹏等[14]方法,并稍作改进。选取3只虾仁的第二节肌肉,切碎混合后,准确称取2 g样品称重记作W1,使用定性滤纸包裹,1600×g离心10 min(4 ℃),样品再次称重记为W2。
持水力(%)=[1−(W1−W2)/W1]×100 1.2.5 pH和 TVB-N含量测定
pH测定参考《食品安全国家标准—食品pH值的测定》(GB 5009.237-2016)[15];TVB-N含量测定参考《食品安全国家标准—食品中挥发性盐基氮的测定》(GB 5009.228-2016)[16]。
1.2.6 TBA值测定
采用丙二醛试剂盒测定虾仁肌肉TBA值,操作方法依据试剂盒使用说明书进行。
1.2.7 菌落总数测定
菌落总数测定参考《食品微生物学检验—菌落总数的测定》(GB 4789.2-2016)[17]。
1.2.8 苏木精-伊红染色观察分析
肌肉微观结构观察,参考祁雪儿等[18]方法。选取中华管鞭虾仁第二节肌肉,切成1 cm×1 cm×0.5 cm小块,使用4%多聚甲醛固定液浸泡固定,室温下过夜,苏木精-伊红常规染色后,显微镜下观察肌肉微观结构。
1.3 数据处理
上述指标测定进行三次平行实验。使用Excel进行数据统计,采用IBM SPSS软件进行数据分析(采用Ducan法分析差异显著性,P < 0.05),Origin 2019进行图形的绘制。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 NaCl浓度对中华管鞭虾肌肉色差的影响
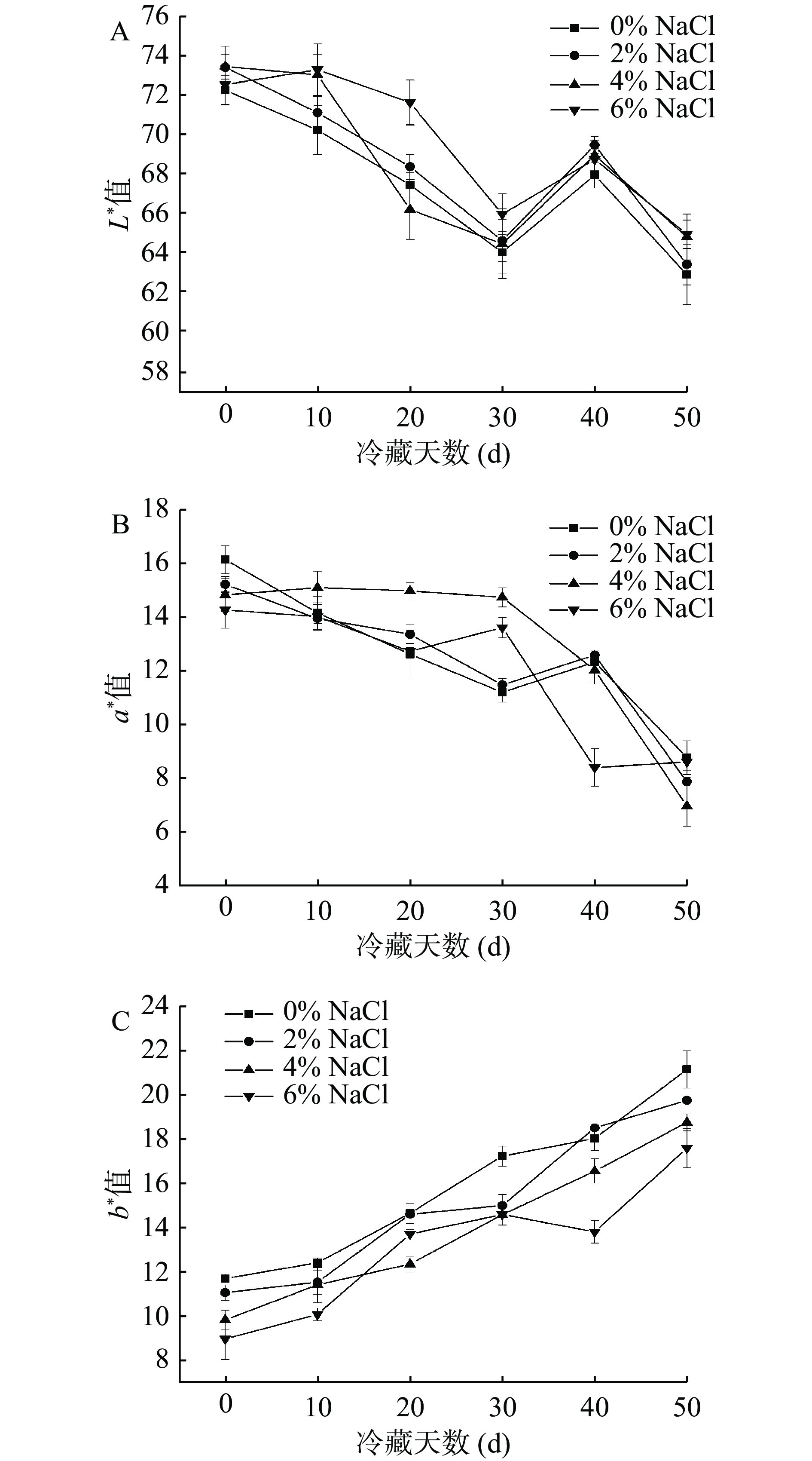
在冷藏期间即食中华管鞭虾虾仁肌肉色差变化,会直接影响消费者的可接受性[19]。L*值反映虾仁肌肉明亮度,正数为肌肉偏白;a*值反映虾仁肌肉红绿值,正数为肌肉偏红;b*值反映虾仁肌肉黄蓝值,正数为肌肉偏黄[20]。如图1A所示,冷藏期间,各组虾仁肌肉L*值整体呈下降趋势,可能是因为虾肉在残留内源酶的作用下生成有色醌类物质,从而导致肌肉透明度降低所致[21]。随着NaCl浓度的升高,虾仁肌肉L*值增加,NaCl组虾仁肌肉L*值显著高于对照组(P<0.05)。可能是因为添加NaCl降低了虾仁肌肉中水分含量导致虾仁肌肉密度提升,从而使得虾仁肌肉L*值上升[5]。4% NaCl组和6% NaCl组虾仁肌肉L*值在冷藏期价无显著性差异。此外,在冷藏第30~40 d时,虾仁肌肉L*值出现一定的波动,可能与虾仁肌肉持水性、组织结构及肌肉色素变化等有关,从而影响虾仁肌肉表面的光反射所致[9],其发生原因有待进一步探索;如图1B所示,随着冷藏时间延长,各组虾仁肌肉a*值均呈下降趋势,这可能是因为虾仁中的虾青素在冷藏过程中逐渐氧化,导致虾仁肌肉红色逐渐减淡[22]。冷藏期间,各组虾仁肌肉a*值之间无显著性差异,表明虾仁肌肉a*值变化受NaCl浓度影响较小;图1C显示,各组虾仁肌肉b*值随冷藏时间延长呈逐渐上升趋势,可能是因为虾仁肌肉中部分蛋白质及脂质发生氧化,品质逐渐劣化,致使虾体逐渐发黄[23-24]。其中,相同冷藏时间下,随着NaCl的升高,虾仁肌肉b*值显著降低(P<0.05),可能是因为NaCl的添加抑制了肌肉中脂质氧化的发生,从而有效抑制了虾仁肌肉冷藏期间b*值的上升。Yarnpakdee等[25]在研究中也发现,肌肉b*值变化被认为与脂肪氧化产物的产生存在密切的相关性。
2.2 NaCl浓度对中华管鞭虾肌肉质构特性的影响
硬度、弹性是影响即食中华管鞭虾虾仁质构特性的重要因素[26]。基于消费者的感官需求,即食虾仁肌肉硬度、弹性较高,其感官评分也较高[10]。由表1结果可以看出,冷藏期间各组虾仁肌肉的硬度、弹性随着冷藏时间的延长,呈先上升后下降的趋势。高浓度NaCl(4%、6% NaCl)组虾仁肌肉的硬度、弹性均显著高于对照组(P<0.05),表明添加NaCl能够提高虾仁肌肉的硬度和弹性。可能是因为NaCl可降低虾仁肌肉中自由水含量,引起虾仁肌肉的收缩,同时Na+离子诱导了肌球蛋白分子交联,从而提升了虾仁肌肉的硬度、弹性[5,27]。研究中,对照组虾仁肌肉质构特性同样呈现上升趋势,Chen等[28]在针对班节对虾肌肉质构研究中对照组同样出现相似变化趋势,其原因有待进一步探索。随着冷藏时间延长,虾仁在微生物作用下肌肉品质出现劣化,导致肌肉硬度、弹性逐渐降低,该结果与陶文斌[29]针对大黄鱼肌肉质构研究结论相似。在冷藏过程中,4%和6% NaCl组虾仁肌肉弹性、黏粘性和咀嚼性均显著高于对照组(P<0.05),该结果表明NaCl的添加在一定程度上有利于虾仁肌肉质构特性的保持。
表 1 NaCl浓度对冷藏中华管鞭虾肌肉质构特性的影响Table 1. Effects of NaCl concentrations on the texture characteristics of Solenocera crassicornis muscle during chilled storage冷藏时间(d) 0% NaCl 2% NaCl 4% NaCl 6% NaCl 硬度 0 3.60±0.15Bc 3.79±0.13ABc 3.77±0.06ABe 3.83±0.11Ad 10 4.25±0.10Ca 4.04±0.12Cb 4.53±0.07Aa 4.42±0.16ABbc 20 4.22±0.08Ca 4.57±0.09Ba 4.46±0.11Bab 5.13±0.18Aa 30 4.04±0.19Cb 4.24±0.08Bb 4.35±0.05Bbc 4.57±0.06Ab 40 3.87±0.08Cb 4.16±0.06Bb 4.27±0.10ABc 4.26±0.14Abc 50 3.49±0.33Bc 3.64±0.19Bc 4.03±0.07Ad 4.25±0.13Ac 弹性 0 1.51±0.05Bd 1.57±0.06Ac 1.57±0.08Ad 1.59±0.04Ad 10 1.97±0.06Aa 2.09±0.10Aa 2.13±0.04Aa 2.26±0.07Aa 20 1.98±0.05Aa 1.80±0.04Bb 2.01±0.06Ab 2.03±0.06Ab 30 1.80±0.02Bb 1.83±0.06Bb 1.94±0.05Ac 1.90±0.06Ac 40 1.67±0.06Bc 1.75±0.05Bb 1.85±0.04Ac 1.87±0.02Ac 50 1.50±0.04Bd 1.59±0.06Bc 1.80±0.04Ac 1.80±0.04Ac 注:同一行中不同大写字母表示相同指标数据存在显著性差异(P<0.05);同一列中不同小写字母表示同一指标不同NaCl浓度数据存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。 2.3 NaCl浓度对中华管鞭虾肌肉水分含量和持水力的影响
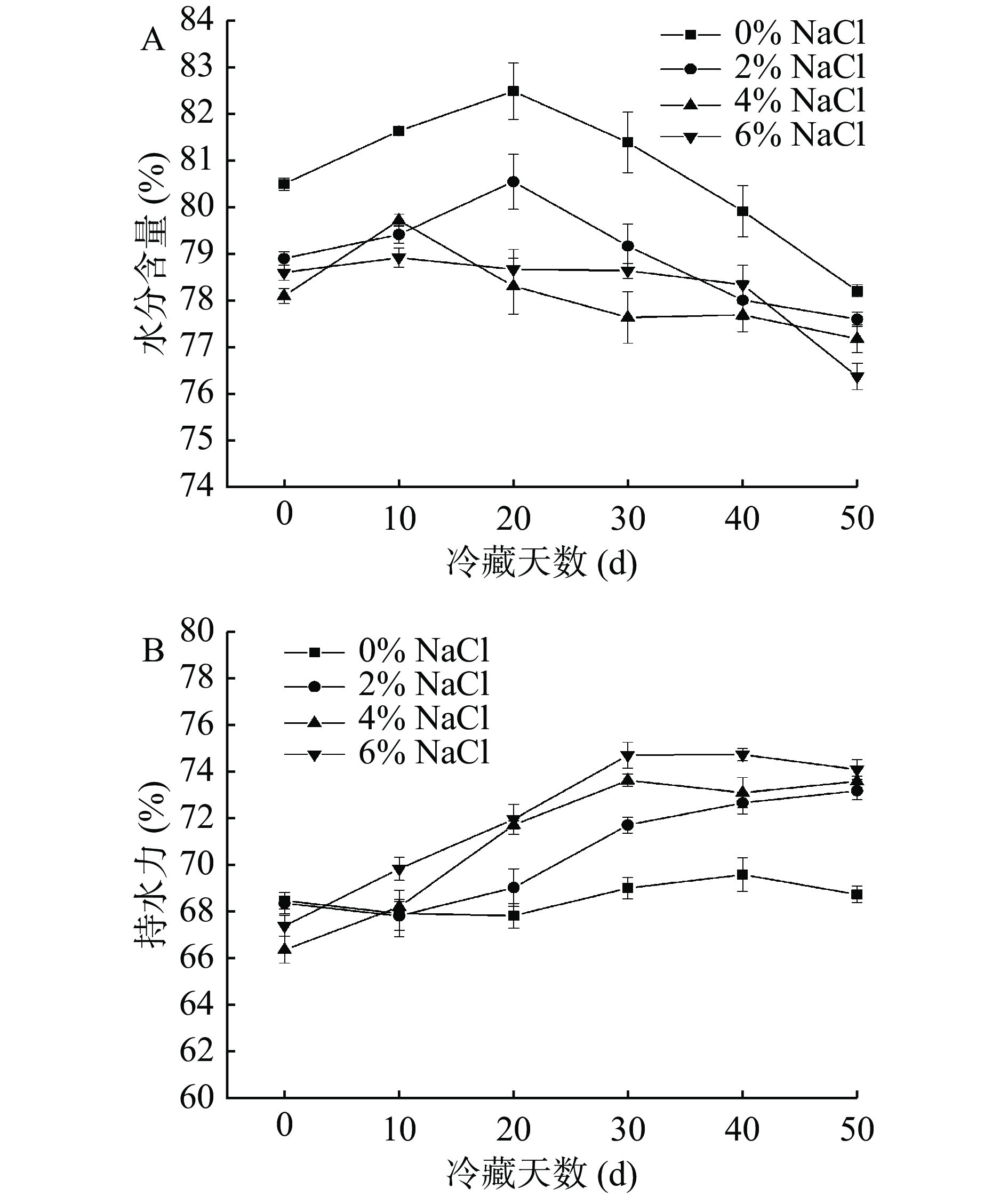
冷藏期间即食中华管鞭虾仁肌肉中水分含量变化,如图2A所示。各组虾仁肌肉中水分含量呈先上升后下降的趋势。可能是因为受加热蒸煮的影响,虾仁肌肉细胞流失部分水分。冷藏期间,浸渍液中水分在渗透压影响下又进入到虾仁肌肉细胞中,致使虾仁肌肉中水分含量有所增加。随着冷藏时间的延长,虾仁肌肉中NaCl含量增加、虾仁品质劣化,虾仁肌肉细胞中的水分被逐渐析出[10,30]。冷藏期间,随着NaCl浓度增加,虾仁肌肉中水分含量显著降低(P<0.05)。可能是因为NaCl浓度的升高引起了虾仁肌肉纤维组织的收缩以及肌原纤维结构的疏水区域的暴露。致使虾仁肌肉细胞中的部分水分被挤压出去,导致水分含量降低[5,31]。
持水力指虾仁肌肉冷藏过程中保持水分的能力,能够较好的反映虾仁的食用品质[32]。如图2B所示,冷藏期间,对照组虾仁肌肉持水力无明显变化,NaCl组虾仁肌肉持水力呈上升趋势,且显著高于对照组虾仁(P<0.05)。冷藏第50 d时,2%、4%和6% NaCl浸泡虾仁肌肉持水力分别上升了4.83%、7.23%和6.80%。结果表明,在冷藏期间,即食中华管鞭虾仁肌肉中NaCl含量的增加,可以提高虾仁肌肉中蛋白质的持水能力。可能是因为NaCl是一种亲水性离子物质,可使中华管鞭虾虾仁肌肉中部分自由水转化成结合水,同时不断促进盐溶性蛋白的溶出,从而导致持水力增加[33]。
2.4 NaCl浓度对中华管鞭虾肌肉pH和TVB-N含量的影响
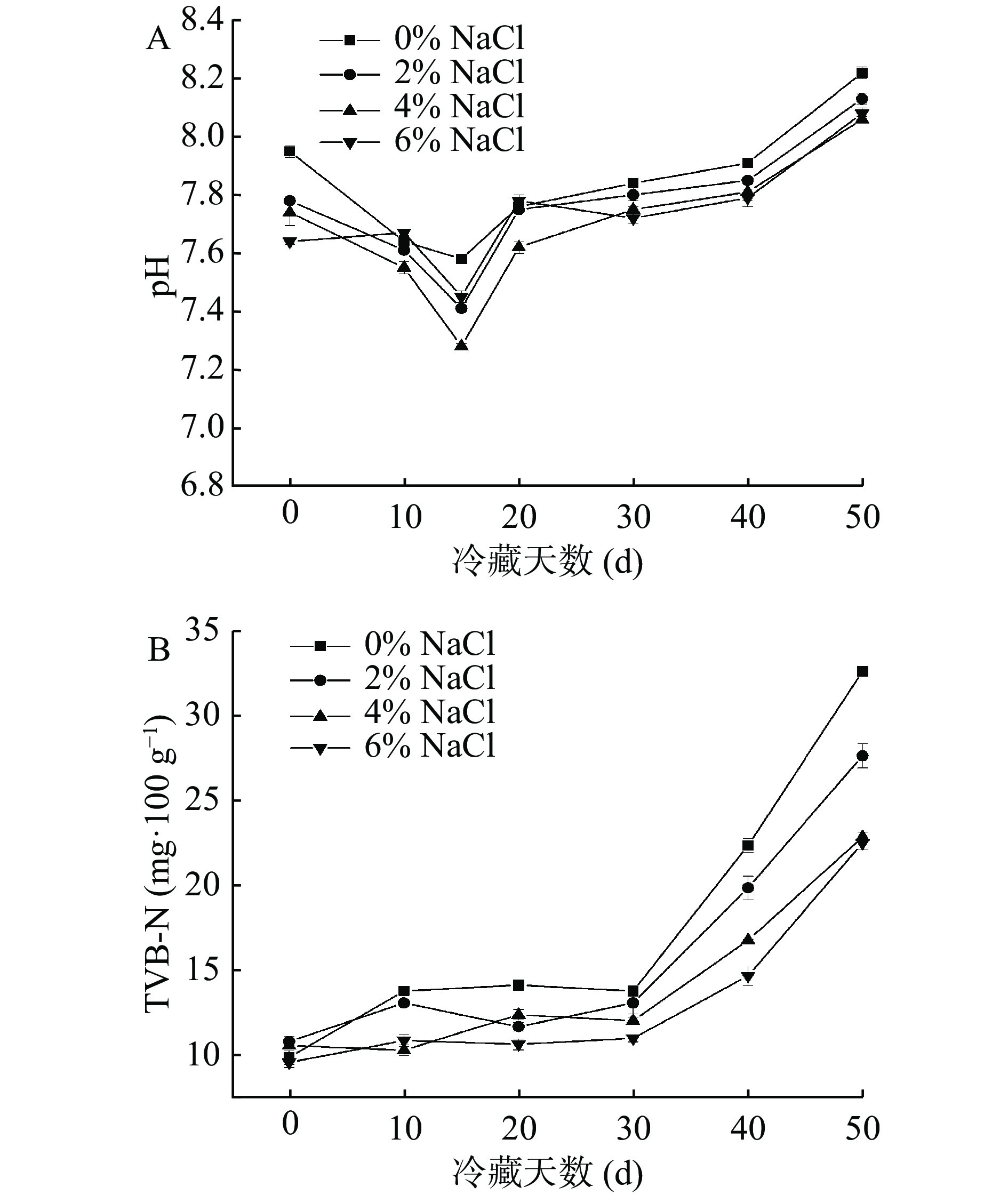
图3A为NaCl浓度对即食中华管鞭虾虾仁肌肉pH的影响结果。在冷藏期间,各组虾仁肌肉pH随时间延长呈先下降后上升的趋势。可能是因为冷藏前期,虾仁肌肉中的糖原被分解成酸性物质,导致虾仁pH下降[11]。随着冷藏时间延长,中华管鞭虾虾仁肌肉中部分蛋白质在微生物和内源酶作用下被分解产生胺类等碱性物质[34],因此冷藏第15d,各处理组虾仁肌肉pH逐渐上升。在冷藏过程中,对照组中华管鞭虾虾仁肌肉pH>2% NaCl组>4%和6% NaCl组,而4%和6% NaCl两组肌肉pH并无显著性差异。可能是因为NaCl可通过抑制微生物的生长,影响到肌肉中碱性物质的生成。NaCl浓度升高,可以提高对微生物的抑制效果,影响虾仁肌肉中碱性物质生成量。该结果与关睿等[9]对冷藏草鱼肌肉pH的研究结果相一致。
TVB-N反映肌肉中蛋白质在冷藏期间被分解成氨和胺类物质的量,可用来反映即食中华管鞭虾虾仁的腐败情况[35]。根据国标要求,海水虾类肌肉TVB-N含量不得超过30 mg/100 g[36]。由图3B可知,在贮藏期间不同NaCl浓度浸渍的虾仁肌肉TVB-N含量均呈上升趋势,冷藏30 d以后各组肌肉中TVB-N含量上升较快,可能是由于贮藏后期微生物生长繁殖速度较快所致[37]。冷藏第50 d时,对照组虾仁肌肉中TVB-N含量超出国家标准,达到32.62 mg/100 g,NaCl组虾仁肌肉中TVB-N含量显著低于对照组(P<0.05)。2% NaCl浸泡虾仁肌肉中TVB-N含量为27.62 mg/100 g,已经接近国标限量标准。4%和6% NaCl浸泡虾仁肌肉中TVB-N含量分别为22.82和22.47 mg/100 g,新鲜度相对较好。以上结果表明,添加一定浓度的NaCl可以有效抑制冷藏期间即食中华管鞭虾肌肉中TVB-N含量的生成。
2.5 NaCl浓度对中华管鞭虾肌肉TBA值的影响
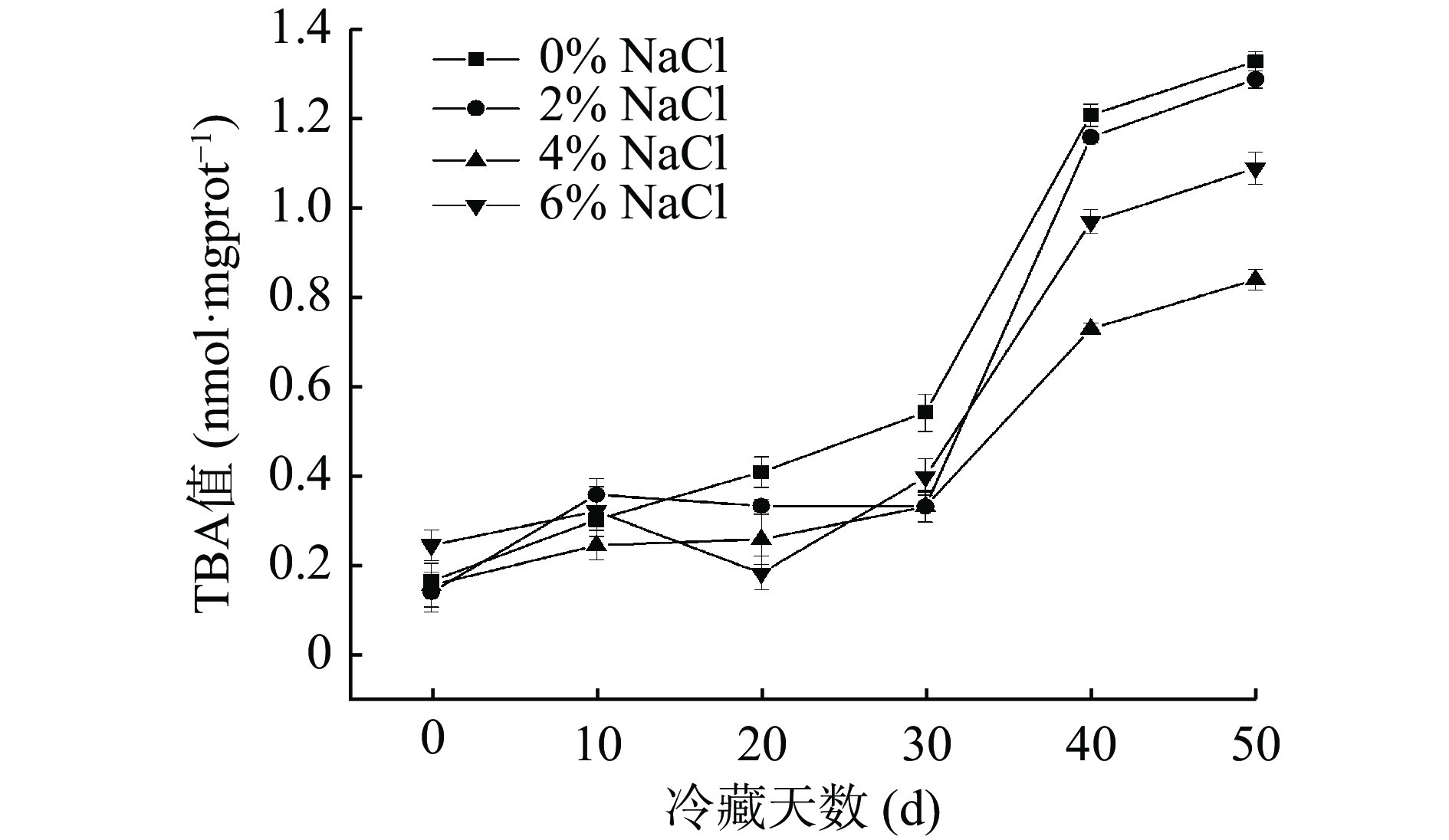
中华管鞭虾中含有的不饱和脂肪酸,在冷藏过程中易发生氧化,从而导致肌肉中丙二醛含量升高,因此TBA值可用来反映即食中华管鞭虾虾仁冷藏期间脂质氧化情况[38]。如图4所示,随着贮藏时间的延长,不同NaCl组虾仁肌肉中TBA值均呈上升趋势。冷藏前期,各NaCl组虾仁TBA值无显著性差异。冷藏第20 d时,对照组虾仁肌肉中TBA值显著高于NaCl组(P < 0.05),表明NaCl添加量对即食中华管鞭虾虾仁丙二醛生成有较大影响。冷藏第30 d时,各组虾仁肌肉中TBA值均呈现出较快的上升趋势,可能是因为冷藏后期虾仁肌肉品质劣化加剧导致[37];冷藏至50 d时,4%和6% NaCl组虾仁肌肉中TBA值均显著低于对照组(P < 0.05),表明4%和6% NaCl可以抑制脂肪的氧化,延缓TBA值的上升趋势。分析其原因可能是因为NaCl浓度的增加可以引起虾仁细胞质的浓缩,降低脂肪酶和脂肪氧化酶活性,从而抑制丙二醛的生成[39]。
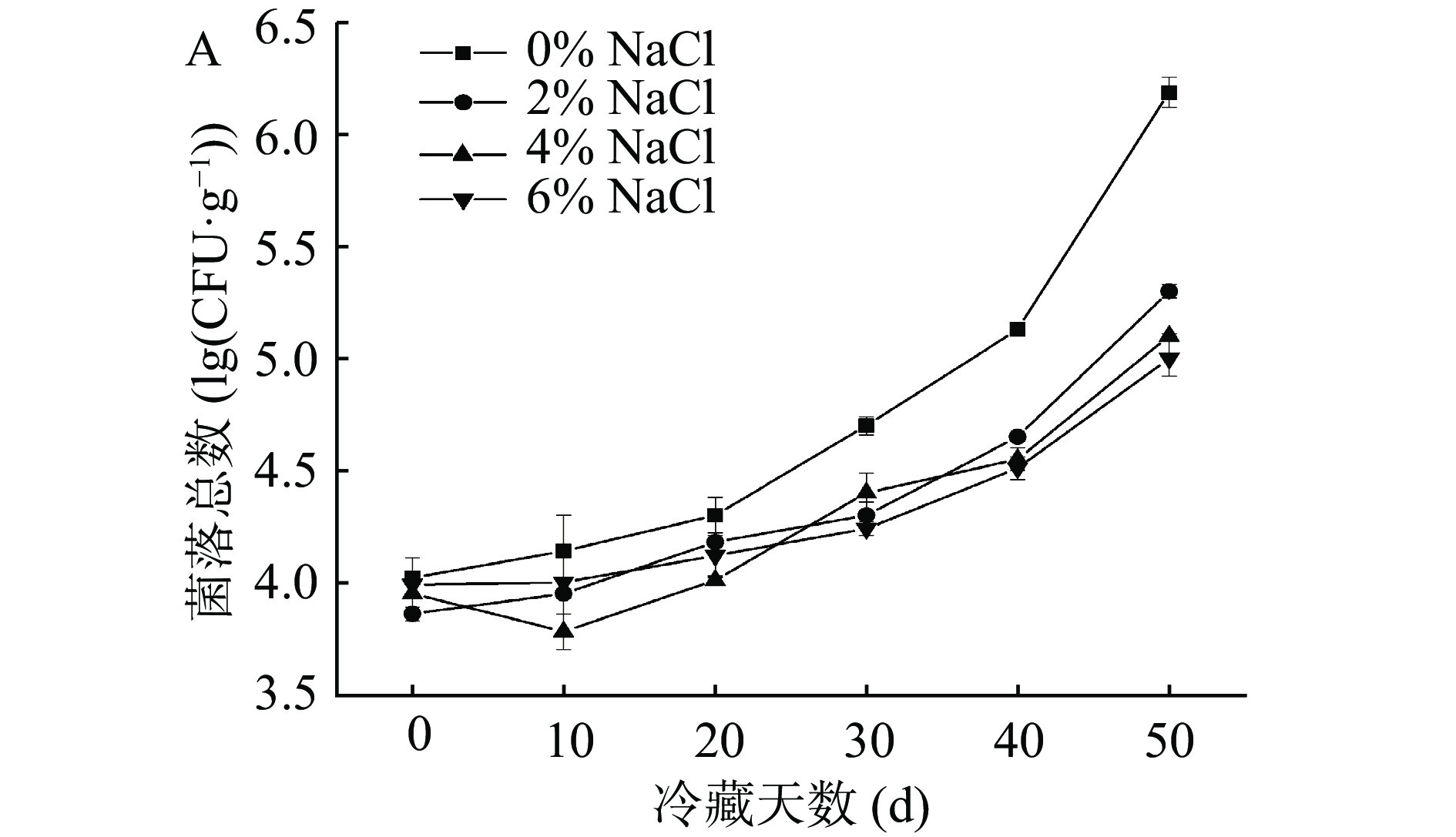
2.6 NaCl浓度对中华管鞭虾菌落总数影响
冷藏期间,在微生物生长与繁殖作用下,即食中华管鞭虾肌肉会不断劣化[40]。从图5中可以看出,随着冷藏时间的延长,各组虾仁菌落总数持续上升。各测定点NaCl浓度越高,菌落总数越低,且NaCl组菌落总数显著低于对照组(P<0.05)。在冷藏第50 d时,0%、2%、4%和6% NaCl组浸泡虾仁肌肉中菌落总数分别为6.19、5.3、5.1和5.0 lg(CFU·g−1)。根据GB 10136-2015《食品安全国家标准—动物性水产品制品》限定,动物性水产品中菌落总数不得超过6 lg(CFU·g−1)[41]。冷藏第50 d时,对照组虾仁菌落总数含量已超出国标规定的最大限值,NaCl组均未超出最大限值。结果表明NaCl浸泡可抑制即食虾仁中微生物的增长速度,且NaCl浓度越高对于虾仁中微生物的抑制效果越好。
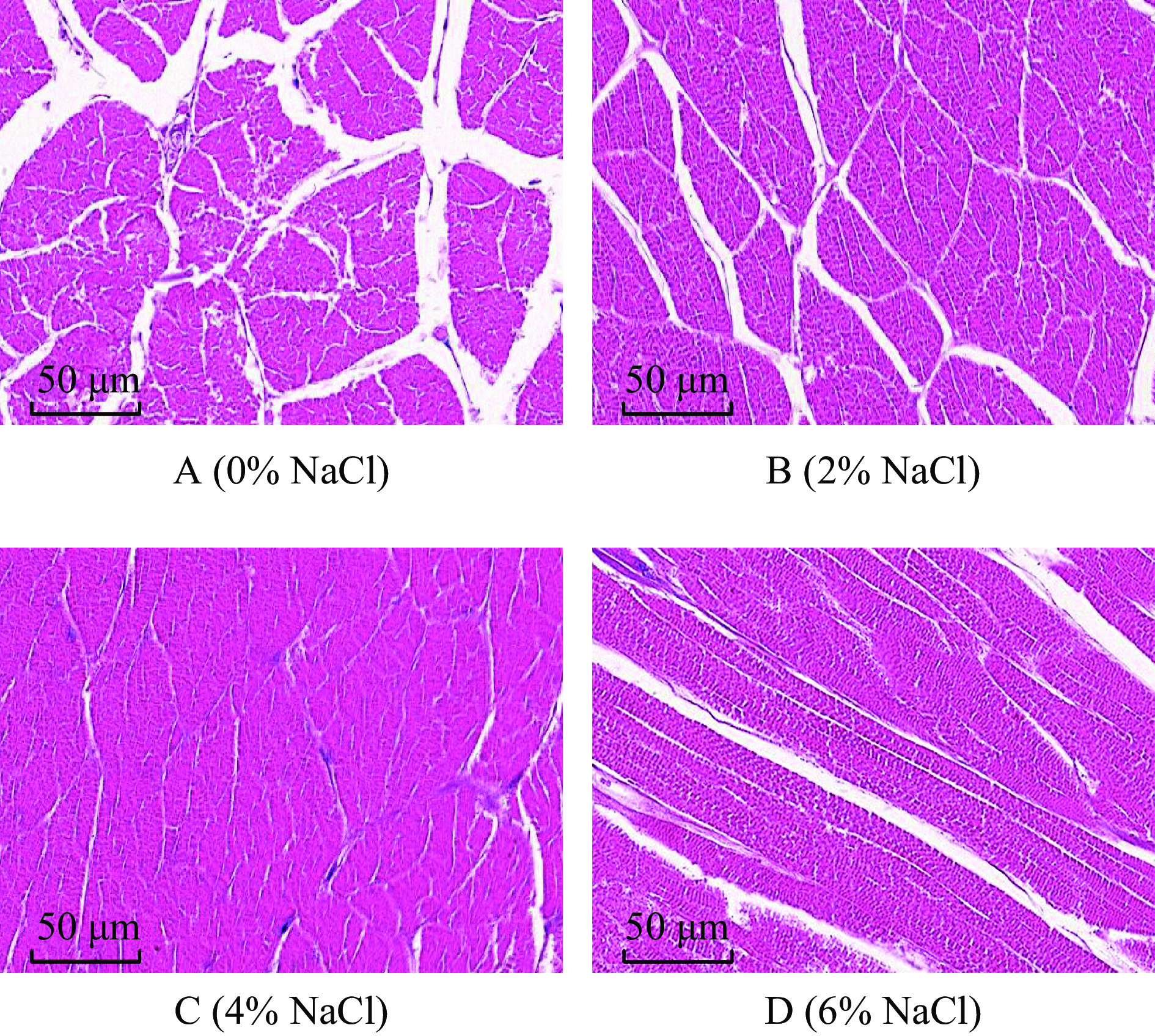
2.7 NaCl浓度对中华管鞭虾肌肉结构的影响
本研究中,冷藏第50 d时,对照组虾仁样品已经腐败,不具有食用价值和经济价值,故选取冷藏第40 d时各组虾仁肌肉进行微观结构的观察。前期研究表明,新鲜虾仁蒸煮后肌肉组织结构较完整,肌纤维排列较紧密,几乎没有白色间隙[42]。40 d时虾仁肌肉微观结构如图6所示,对照组虾仁肌肉组织明显比较松散,其肌原纤维之间的缝隙较大,部分组织出现破裂。相较于对照组,2% NaCl浸泡虾仁肌肉肌纤维间隙较小,肌肉组织完整性保持较好,4% NaCl浸泡虾仁肌肉结缔组织排列相对较为整齐、紧致,肌原纤维之间的间隙较小。在冷藏过程中,即食中华管鞭虾虾仁肌肉品质逐渐劣化,可能是因为虾仁肌肉中蛋白质降解[43]、脂质氧化以及微生物生长繁殖所致,导致虾仁肌肉结构遭到严重破坏[44]。Fulladosa等[45]研究发现,肉制品肌肉中含有一定量的NaCl,能够较好的保持肌肉结构的稳定性,在贮藏过程中NaCl含量较低,肉制品纹理结构容易发生劣化,NaCl含量增加到一定程度,肉制品的质地相对会增强。6% NaCl组虾仁肌肉纤维空隙相较于4% NaCl组增大,可能是因为NaCl浓度过高,会加速蛋白质氧化,促进蛋白质降解,导致肌肉组织完整性被破坏[46]。
3. 结论
通过NaCl浸泡处理对冷藏即食中华管鞭虾虾仁肌肉品质的影响研究发现,NaCl添加量对即食中华管鞭虾虾仁肌肉品质具有显著作用。在冷藏期间,各组虾仁肌肉中的水分含量呈先上升后下降趋势,pH呈先下降后上升趋势,且NaCl处理组虾仁肌肉中水分含量和pH显著低于对照组(P < 0.05)。高浓度NaCl较好的抑制了虾仁肌肉中TVB-N含量、TBA值及菌落总数的增加。在冷藏期间,4%和6% NaCl处理对于虾仁肌肉色泽、硬度、弹性及持水力的保持效果优于对照组。通过显微镜观察可以发现,冷藏40 d时与其他组相比,4% NaCl浸泡处理的虾仁肌肉结构完整性较好,肌纤维排列较为紧密。综合考虑,选用4% NaCl用于浸泡处理即食中华管鞭虾虾仁最为适合。本研究为高水分即食虾类食品的开发及探究NaCl浓度对于即食中华管鞭虾虾仁肌肉品质影响的相关研究提供了一定的理论依据。
-
表 1 NaCl浓度对冷藏中华管鞭虾肌肉质构特性的影响
Table 1 Effects of NaCl concentrations on the texture characteristics of Solenocera crassicornis muscle during chilled storage
冷藏时间(d) 0% NaCl 2% NaCl 4% NaCl 6% NaCl 硬度 0 3.60±0.15Bc 3.79±0.13ABc 3.77±0.06ABe 3.83±0.11Ad 10 4.25±0.10Ca 4.04±0.12Cb 4.53±0.07Aa 4.42±0.16ABbc 20 4.22±0.08Ca 4.57±0.09Ba 4.46±0.11Bab 5.13±0.18Aa 30 4.04±0.19Cb 4.24±0.08Bb 4.35±0.05Bbc 4.57±0.06Ab 40 3.87±0.08Cb 4.16±0.06Bb 4.27±0.10ABc 4.26±0.14Abc 50 3.49±0.33Bc 3.64±0.19Bc 4.03±0.07Ad 4.25±0.13Ac 弹性 0 1.51±0.05Bd 1.57±0.06Ac 1.57±0.08Ad 1.59±0.04Ad 10 1.97±0.06Aa 2.09±0.10Aa 2.13±0.04Aa 2.26±0.07Aa 20 1.98±0.05Aa 1.80±0.04Bb 2.01±0.06Ab 2.03±0.06Ab 30 1.80±0.02Bb 1.83±0.06Bb 1.94±0.05Ac 1.90±0.06Ac 40 1.67±0.06Bc 1.75±0.05Bb 1.85±0.04Ac 1.87±0.02Ac 50 1.50±0.04Bd 1.59±0.06Bc 1.80±0.04Ac 1.80±0.04Ac 注:同一行中不同大写字母表示相同指标数据存在显著性差异(P<0.05);同一列中不同小写字母表示同一指标不同NaCl浓度数据存在显著性差异(P<0.05)。 -
[1] 王潇, 张继光, 徐坤华, 等. 3种海捕虾肌肉营养成分分析与品质评价[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2014,40(8):209−214. [WANG X, ZHANG J G, XU K H, et al. Analysis and quality evaluation of nutrition in the muscle of three kinds of marine shrimps[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2014,40(8):209−214. [2] 李思敏. 低温物流中海捕虾的品质变化与货架期预测[D]. 杭州: 浙江工商大学, 2020: 2−4. LI S M. Quality change and shelf life forecast of sea shrimp in low temperature logistics[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Gongshang University, 2020: 2−4 .
[3] PAOLO B M, CLAUDIA P, NICOLA M, et al. Assessment of microbial populations in the manufacture of vacuum-packaged ready-to-eat roast beef and in a related production plant[J]. Journal of Food Protection,2019,82(1):58−64. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X.JFP-18-147
[4] NIAMNUY C, DEVAHASTIN S, SOPONRONNARIT S. Changes in protein compositions and their effects on physical changes of shrimp during boiling in salt solution[J]. Food Chemistry,2007,108(1):165−175.
[5] NIAMNUY C, DEVAHASTIN S, SOPONRONNARIT S. Quality changes of shrimp during boiling in salt solution[J]. Journal of Food Science,2007,72(5):S289−97. doi: 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2007.00349.x
[6] RENATA S, MARIESZ R, MARIAN G, et al. The effect of citric acid, NaCl, and CaCl2 on qualitative changes of horse meat in cold storage[J]. Processes,2020,8(9):1099. doi: 10.3390/pr8091099
[7] RIOS-MERA J D, SALDAÑA E, CRUZADO-BRAVO M L M, et al. Impact of the content and size of NaCl on dynamic sensory profile and instrumental texture of beef burgers[J]. Meat Science,2020,161(C):107992.
[8] DIMAKOPOULOU-PAPAZOGLOU D, KATSANIDIS E. Effect of maltodextrin, sodium chloride, and liquid smoke on the mass transfer kinetics and storage stability of osmotically dehydrated beef meat[J]. Food and Bioprocess Technology,2017,10(11):2034−2045. doi: 10.1007/s11947-017-1973-5
[9] 关睿, 李琳, 王建辉, 等. 不同食盐添加量对冷藏草鱼品质的影响[J]. 食品科学技术学报,2020,38(5):100−108,126. [GUAN R, LI L, WANG J H, et al. Effects of different levels of salt addition on quality of grass carp during cold storage[J]. Journal of Food Science and Technology,2020,38(5):100−108,126. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-6002.2020.05.013 [10] 瞿丞, 贺稚非, 王兆明, 等. 不同食盐添加量腌制对鸡肉脂质氧化、蛋白质氧化及食用品质的影响[J]. 食品科学,2020,41(16):77−85. [QU C, HE Z F, WANG Z M, et al. Effects of different salt concentrations on lipid oxidation, protein oxidation and eating quality of cured chicken meat[J]. Food Science,2020,41(16):77−85. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-20190504-012 [11] 李心悦. 南美白对虾即食虾仁加工关键技术研究[D]. 保定: 河北农业大学, 2014: 33−34. LI X Y. Research on the key technologies of Litopenaeus vannamei instant shrimp processing[D]. Baoding: Hebei Agricultural University, 2014: 33−34.
[12] 刘欣荣, 申亮, 齐凤生, 等. 微冻保鲜对红鳍东方鲀贮藏品质的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(18):128−135. [LIU X R, SHEN L, QI F S, et al. Effects of micro-frozen storage on the quality of Takifugu rubripes[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(18):128−135. [13] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.3-2016 食品中水分的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016: 9. National Health and Family Planning. GB 5009.3-2016 Determination of moisture in foods[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2016: 9.
[14] 李志鹏, 周晓娇, 水珊珊, 等. 低温贮藏中华管鞭虾肌肉品质及组织蛋白酶H活性变化[J]. 食品工业科技,2021,42(22):306−313. [LI Z P, ZHOU X J, SHUI S S, et al. Influence of cold storage on the quality of muscle and the activity of cathepsin H in red shrimp (Solenocera crassicornis)[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2021,42(22):306−313. [15] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB/T 5009.237-2016 食品pH值的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016: 3. National Health and Family Planning. GB/T 5009.237-2016 Determination of pH in foods[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2016: 9.
[16] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 5009.228-2016食品中挥发性盐基氮的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016: 3. National Health and Family Planning. GB 5009.228-2016 Determination of volatile basic nitrogen in foods[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2016: 3.
[17] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 4789.2-2016食品中菌落总数的测定[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016: 3. National Health and Family Planning. GB 4789.2-2016 Determination of total bacterial counts in foods [S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2016: 3.
[18] 祁雪儿, 毛俊龙, 姚慧, 等. 蛋白质氧化对中华管鞭虾肌肉品质特性的影响[J]. 食品科学,2021,42(18):15−21. [QI X E, MAO J L, YAO H, et al. Effect of protein oxidation on the quality attributes of Solenocera crassicornis muscle[J]. Food Science,2021,42(18):15−21. [19] 瞿桂香, 马文慧, 钱文霞, 等. 不同剂量电子束辐照即食小龙虾的品质分析[J]. 食品科技,2020,45(10):155−161. [QU G X, MA W H, QIAN W X, et al. Quality changes of instant crayfish irradiated by different electron-bean[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,45(10):155−161. [20] 于亚文, 田童童, 张建. 不同冷藏温度对白斑狗鱼品质变化的影响[J]. 食品研究与开发,2016,37(21):176−182. [YU Y W, TIAN T T, ZHANG J. The quality change of fresh Esox lucius under the different temperatures during cold storage[J]. Food Research and Development,2016,37(21):176−182. [21] 胡晓梦. 低温等离子体对中华管鞭虾品质影响及保鲜机理的研究[D]. 舟山: 浙江海洋大学, 2021: 20−23. HU X M. Study on the effect of cold plasma on the quality and fresh-keeping mechanism of Solenocera crassicornis[D]. Zhoushan: Zhejiang Ocean University, 2021: 20−23.
[22] NIAMNUY C, DEVAHASTIN S, SOPONRONNARIT S, et al. Kinetics of astaxanthin degradation and color changes of dried shrimp during storage[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2008,87(4):591−600. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2008.01.013
[23] 石径. 中华管鞭虾冻藏过程中品质变化规律及机理研究[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2018: 22−23. SHI J. Studies on quality changes and mechanism of mud shrimp (Solenocera crassicornis) during frozen storage[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2018: 22−23.
[24] ZHANG X, LAN W Q, XIE J. Combined citric acid and rosemary extract to maintain the quality of chilled Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) [J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation, 2021, 45(7).
[25] YARNPAKDEE S, BENJAKUL S, KRISTINSSON H G, et al. Effect of pretreatment on lipid oxidation and fishy odour development in protein hydrolysates from the muscle of Indian mackerel[J]. Food Chemistry,2012,135(4):2474−2482. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.07.037
[26] CEN S J, FANG Q, TONG L, et al. Effects of chitosan-sodium alginate-nisin preservatives on the quality and spoilage microbiota of Penaeus vannamei shrimp during cold storage[J]. International Journal of Food Microbiology,2021,349:109227. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2021.109227
[27] 任章睿, 熊善柏, 胡杨, 等. 真空浸渍处理对调理草鱼片品质的影响[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2020,11(12):3831−3839. [REN Z R, XIONG S B, HU Y, et al. Effect of vacuum impregnation on quality of seasoned grass carp fillets[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2020,11(12):3831−3839. [28] CHEN L H, JIAO D X, LIU H M, et al. Effects of water distribution and protein degradation on the texture of high pressure-treated shrimp (Penaeus monodon) during chilled storage[J]. Food Control,2022:132.
[29] 陶文斌. 低钠盐轻腌对养殖大黄鱼品质及风味影响研究[D]. 上海: 上海海洋大学, 2019: 28−31. TAO W B. Study on the effects of low-sodium salt on the quality and flavor of Larimichthys crocea during salting[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Ocean University, 2019: 28−31.
[30] 刘广娟, 徐泽权, 邢世均, 等. 磷酸盐对PSE猪肉食用品质和微观结构的影响[J]. 中国农业科技导报,2021,23(3):114−121. [LIU G J, XU Z Q, XING S J, et al. Effects of phosphate on eating quality and micro structure of PSE pork[J]. Journal of Agricultural Science and Technology,2021,23(3):114−121. [31] NGUYEN M V, ARASOON S, THORARINSDOTTIR K A, et al. Influence of salt concentration on the salting kinetics of cod loin (Gadus morhua) during brine salting[J]. Journal of Food Engineering,2010,100(2):225−231. doi: 10.1016/j.jfoodeng.2010.04.003
[32] 吴健锋, 张立彦. 食盐对猪肉脱水过程中物理特性及微观结构的影响[J]. 食品科学,2018,39(14):67−72. [WU J F, ZHANG L Y. Effect of sodium chloride on physical properties and microstructure of pork during dehydration[J]. Food Science,2018,39(14):67−72. doi: 10.7506/spkx1002-6630-201814010 [33] ZHANG Y W, WU J J, JAMALI M A, et al. Heat-induced gel properties of porcine myosin in a sodium chloride solution containing L-lysine an d L-histidine[J]. LWT-Food Science and Technology,2017,85:16−21. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2017.06.059
[34] 张珊, 林慧敏, 邓尚贵. 低压静电场对凡纳滨对虾保鲜效果的研究[J]. 食品科技,2020,45(10):141−147. [ZHANG S, LIN H M, DENG S G. Effect of low voltage electrostatic field on fresh-keeping of Litopenaeus vannamei[J]. Food Science and Technology,2020,45(10):141−147. doi: 10.13684/j.cnki.spkj.2020.10.024 [35] 徐慧倩, 严金红, 缪文华, 等. 低温等离子体对南美白对虾冷藏期间品质保持的效果[J]. 现代食品科技,2021,37(4):116−123,138. [XU H Q, YAN J H, MIAO W H, et al. Effect of cold atmospheric plasma on quality maintenance of Penaeus vannamei during cold storage[J]. Modern Food Science and Technology,2021,37(4):116−123,138. [36] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 2733-2015 鲜、冻动物性水产品[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016: 3. National Health and Family Planning. GB 2733-2015 Fresh and frozen animal aquatic products [S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2016: 3.
[37] 吴晨燕, 王晓艳, 王洋, 等. 熟制麻辣小龙虾冷藏和冻藏条件下的品质变化[J]. 肉类研究,2018,32(5):52−56. [WU Y C, WANG X Y, WANG Y, et al. Quality change of cooked spicy crayfish during refrigerated and frozen storage[J]. Meat Research,2018,32(5):52−56. [38] 张溪, 蓝蔚青, 谢晶, 等. 不同减菌预处理对鲜南美白对虾虾仁冷藏期间品质变化的影响[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2020,46(12):158−165. [ZHANG X, LAN W Q, XIA J, et al. Effects of different sterilization pretreatments on the quality of freshly peeled shrimps (Litopenaeus vannamei) during refrigerated storage[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2020,46(12):158−165. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.023557 [39] 顾赛麒, 郑皓铭, 戴王力, 等. 不同食盐添加量对腌制草鱼品质和风味的影响[J]. 浙江工业大学学报,2020,48(4):455−465. [GU S L, ZHENG H M, DAI W L, et al. Effects of salt content on the quality and flavor of salted grass carp[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University of Technology,2020,48(4):455−465. [40] 王静玉, 曲映红, 刘志东, 等. 不同贮藏条件下南美白对虾中生物胺的变化[J]. 食品与发酵工业,2021,47(6):42−48. [WANG J Y, QU Y H, LIU Z D, et al. Changes of biogenic amines in white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) at different storage conditions[J]. Food and Fermentation Industries,2021,47(6):42−48. doi: 10.13995/j.cnki.11-1802/ts.025637 [41] 国家卫生和计划生育委员会. GB 10136-2015动物性水产制品[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2016: 3. National Health and Family Planning. GB 10136-2015 Animal aquatic products [S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 2016: 3.
[42] XIE C, ZHANG B, MA L K, et al. Cryoprotective effects of trehalose, alginate, and its oligosaccharide on quality of cooked-shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) during frozen storage[J]. Journal of Food Processing and Preservation,2017,41(2):1745−4549.
[43] 崔宏博, 薛勇, 宿玮, 等. 即食南美白对虾贮藏过程中水分状态的变化研究[J]. 中国食品学报,2012,12(6):198−203. [CUI H B, XUE Y, SU W, et al. Study on moisture status change of ready-to-eat shrimp during storage[J]. Journal of Chinese Institute of Food Science and Technology,2012,12(6):198−203. [44] HSU W H, LAI Y G, WU S C. Effects of the anti-microbial peptide pardaxin plus sodiumerythorbate dissolved in different gels on the quality of Pacific white shrimp under refrigerated storage[J]. Food Control,2013(73):712−719.
[45] FULLADOSA E, GUERRERO L, ILLANA A, et al. Instrumental texture analysis on the surface of dry-cured ham to define the end of the process[J]. Meat Science,2020,172:108334−108334.
[46] 瞿丞. 食盐添加量和干燥温度对风鸡加工过程中理化特性的影响[D]. 重庆: 西南大学, 2020: 36-38. QU C. Effect of salt content and drying temperature on physicochemical properties of dry-cured chicken during processing[D]. Chongqing: Southwest University, 2020: 36-38.






 下载:
下载:
 下载:
下载:
