Development of Sandwich and Competitive ELISA Formats to Determine Soybean Allergen: Evaluation of Their Performance to Detect Soy in Processed Food
-
摘要: 本文以大豆混合过敏原为目标,建立了快速、便捷检测大豆过敏原的夹心酶联免疫吸附方法(sandwich-enzyme linked immunosorbent assay)和间接竞争酶联免疫吸附方法(indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay),通过实际加工样品的回收实验、加标食品回收实验以及对真实食物样本的检测,对这两种方法进行了比较,确定了各自的适用范围。结果表明,夹心ELISA方法标准品浓度在0.0078~30 μg/mL范围内呈现出良好的线性关系,曲线方程为y=0.2333x+0.0692,决定系数R2=0.995。竞争ELISA方法的检测范围为10~100000 ng/mL,最低检测限为10 ng/mL。对购入橙汁进行加标回收实验,夹心ELISA检测后的回收率要高于竞争ELISA检测后的回收率,达100%以上;而对成分和加工方式都比较复杂的巧克力、牛肉酱、面包或蛋糕来说,竞争ELISA检测后的回收率要高于夹心ELISA检测后的回收率。对发酵类食物进行检测,竞争ELISA方法检测到的浓度要高于夹心ELISA,而对成分比较简单的食物比如芝麻糊、豆奶等进行检测时,夹心ELISA的检测浓度要略高于竞争ELISA。综上,竞争ELISA方法更适用于食物基质复杂,经过深度加工的食品,而夹心ELISA方法更适用于食物成分简单,轻加工后的食品,两种方法在各自的适用范围内均能实现较准确的检测。Abstract: Taking soybean mixed allergens as the target, a sandwich-enzyme linked immunosorbent assay and an indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for the rapid and convenient detection of soybean allergens were established. The two methods were compared through the recovery experiment of actual processed samples, the recovery experiment of spiked food and the detection of real food samples, and their respective application scopes were determined. Sandwich ELISA method, the standard concentration was in the range of 0.0078~30 μg/mL, showing a good linear relationship, the curve equation was y=0.2333x+0.0692 with coefficient of determination R2=0.995. The detection range of the competitive ELISA method was 10~100000 ng/mL, and the lowest detection limit was 10 ng/mL. The recovery rate of orange juice after sandwich ELISA was higher than that after competitive ELISA, reaching more than 100%. For chocolate, beef sauce, bread and cake with complex ingredients and processing methods, the recovery rate after competitive ELISA was higher than that after double-antibody sandwich ELISA. In the detection of soybean allergens in fermented foods, the concentration detected by competitive ELISA was higher than that detected by sandwich ELISA, while in the detection of simple ingredients such as sesame paste and soy milk, the concentration detected by sandwich ELISA was slightly higher than that detected by competitive ELISA. In general, the competitive ELISA method was more suitable for the food with complex food matrix and deeply processed, while the sandwich ELISA method was more suitable for the food with simple food ingredients and lightly processed food, both of the two methods can achieve more accurate detection in their respective application scope.
-
Keywords:
- soybean /
- allergens /
- double-antibody sandwich ELISA /
- competitive ELISA /
- detection
-
大豆蛋白因其高营养价值和功能特性,成为食品工业中最重要的植物蛋白来源之一[1]。研究表明食用大豆有降低血浆胆固醇、甘油三酯和低密度脂蛋白等有益作用。因此大豆蛋白如今被广泛用于肉类、乳制品、烘焙产品和食用酱等原料中[2]。但是,大豆也是公认的八大食物过敏原之一,是人类常见的食物过敏原[3]。大豆过敏的患病率在一般人群中约为0.3%~0.4%,幼儿比成人更容易受到影响[4]。大豆过敏患者症状轻微时会出现嘴唇或面部肿胀、皮肤红肿、抽搐、呕吐、肚痛或肚泻等,严重时可能会导致过敏性休克,甚至死亡[5]。
一些研究已经证明至少有16种过敏原可以与大豆过敏患者血清的IgE结合,其中Gly m Bd 28K、Gly m Bd 30K和β-伴大豆球蛋白的α亚基(Gly m Bd 60K)是大豆中的主要过敏原[6]。众所周知,对食物过敏唯一有效的治疗方法就是避免食用这些食物,但是现在食物配料多种多样,食物的组成变得十分复杂,很难避免食用大豆成分[7]。因此,建立针对大豆过敏原的方便、快捷、灵敏、特异的检测方法,对于保护大豆过敏患者的消费安全和身体健康有重要的现实意义。
目前,针对大豆过敏原的检测主要有液相色谱技术、生物传感器、生物质谱技术等,其中酶联免疫吸附方法(Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay,ELISA)具有操作简便、快速、灵敏度高、特异性强、经济等特点[8-10]。但是在对大豆过敏原的ELISA检测方法的研究中,研究较多的过敏原是β-伴大豆球蛋白、Gly m 4、Gly m 8等单一过敏原,针对混合过敏原蛋白的ELISA研究报道较少[11-13]。混合过敏原蛋白可以制备出含有诸多抗体位点的抗体,这样抗体可最大程度上与抗原及待检样品结合,较准确地对潜在过敏原进行检测,不容易出现漏检的情况[14]。因此,本研究选择大豆多组分混合过敏原蛋白作为免疫原,建立双抗夹心ELISA方法和间接竞争ELISA方法[15-17],用这两种方法来检测加工条件下的样品,比较在实际加工样品和真实食物样品中的检测能力,并确定这两种方法各自适用的检测条件,从而为大豆过敏原便捷、准确、快速检测提供新的途径。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 材料与仪器
大豆 东北农业大学种植;羊多抗血清、兔多抗血清 北京华大蛋白公司制备;辣根过氧化物酶(horseradish peroxidase,HRP)标记的羊抗兔IgG、兔抗羊IgG、TMB单组份显色液、牛血清白蛋白(Bovine serum albumin,BSA) 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;吐温20、磷酸二氢钾、氯化钾、氯化钠、磷酸氢二钠、浓硫酸、丙酮 均为分析纯;BCA蛋白定量试剂盒 北京索莱宝科技有限公司;高筋小麦粉、低筋小麦粉、黄油 益海嘉里金龙鱼粮油食品股份有限公司;细砂糖 广州市华侨糖厂;豆奶、酱油、饼干、黄豆酱、芝麻糊、鸡蛋、牛奶等食品 均购自青岛利群超市。
800TS吸收光酶标仪 美国BioTek公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 大豆混合过敏原的提取
先将大豆研磨成细小粉末,过80目筛后,收集大豆粉,之后在4 ℃条件下,加入一定量的丙酮,脱脂、脱色;按照1:10(g/mL)比例加入细胞裂解液,在室温条件下充分混匀(约3 h),之后在12000 r/min,4 ℃条件下离心20 min,收集上清液,将上清液通过0.22 μm的滤膜过滤,得到大豆多组分混合过敏原溶液,于−20 ℃保存。
1.2.2 多克隆抗体的制备
羊多抗血清和兔多抗血清是由北京华大蛋白公司制备,具体操作步骤如下:用1.2.1提取得到的大豆混合过敏原溶液免疫羊和新西兰雄兔,用不含大豆蛋白的饲料喂养刚断奶的小羊和新西兰兔,待体重达到2 kg左右时进行免疫,每隔两周加强免疫一次,共免疫4次。在第三次免疫后,可对羊和兔进行少量血液的采集,之后利用间接ELISA法测定抗体效价,合格后,经过一次的冲击加强免疫,可大量采血。采血前这两种动物禁食24 h,以防血脂过高。得到的血液于37 ℃静置2 h,之后4 ℃过夜,次日9500 r/min,4 ℃条件下离心20 min,分装并于−80 ℃保存。
得到的血清采用Protein A/G亲和层析柱进行纯化。取少量的血清与等体积的1 mol/L Tris-HCl缓冲液(pH8.0)混合,上样于预先用0.15 mol/L NaCl(pH7.0)的缓冲液平衡好的Protein A/G Sepharose亲和层析柱。依次用0.15 mol/L NaCl、20 mmol/L Na2HPO4(pH7.0)的缓冲液流洗,0.1 mol/L甘氨酸(pH3.0)的缓冲液洗脱。最终获得纯化的IgG抗体,将纯化的多克隆抗体进行聚丙烯酰胺凝胶电泳(SDS-PAGE)分析[18],分装后置于−80 ℃保存备用。
1.2.3 夹心ELISA定量检测方法的建立
1.2.3.1 夹心ELISA基本检测程序
用碳酸盐缓冲液(0.1 mol/L,pH9.6)稀释多克隆抗体到一定质量浓度,加入96孔酶标板中,每孔100 μL,4 ℃过夜。然后用PBST(PBS含0.05%吐温-20,pH7.4)洗涤3次,每孔300 μL,每次5 min左右,弃去洗涤液,在吸水纸上将酶标板拍干,之后的洗涤步骤与此步骤完全相同。用1% BSA封闭,37 ℃温育120 min左右,洗涤拍干后,每孔加入100 μL标准溶液(大豆混合过敏原溶液、食物样本或者PBST作为对照),37 ℃孵育60 min后洗涤拍干,接着每孔加入100 μL一定浓度的另一株多克隆抗体,37 ℃孵育60 min后洗涤拍干;之后每孔加入100 μL稀释到一定倍数的酶标抗体溶液,在37 ℃反应30 min后洗涤拍干,TMB底物溶液避光显色10 min,最后以2 mol/L H2SO4溶液终止反应,测定OD450值,计算P/N值(其中P为阳性样品值,N为阴性对照值)[19-20]。
1.2.3.2 捕获抗体、检测抗体和酶标二抗工作浓度的选择
在相同的反应条件下,采用1.2.3.1节的步骤分别对羊多克隆抗体(捕获抗体)(1:3000、1:5000、1:8000、1:10000、1:12000)、兔多克隆抗体(检测抗体)(1:4000、1:6000、1:8000、1:10000、1:12000)和酶标二抗(1:5000、1:8000、1:10000、1:12000、1:15000)进行检测,将抗原浓度设置为阳性5 μg/mL,PBST代替抗原为阴性,测定OD450值,并计算P/N值,确定最佳稀释度。
1.2.3.3 检测时间的确定
在抗体最佳工作浓度条件下,采用1.2.3.1节的步骤分别对抗原孵育时间(30、60、90 min)、检测抗体孵育时间(30、60、90 min)、酶标二抗工作时间(30、60、90 min)、TMB显色时间(5、10、15 min)进行实验。将抗原浓度设置为阳性5 μg/mL,PBST代替抗原为阴性,测定OD450值,并计算P/N值,确定最佳检测条件。
1.2.3.4 标准曲线制作
按照确定好的实验条件,检测不同浓度抗原(0.0078~30 μg/mL),测定OD450值并绘制校准曲线,找出线性范围,确定最终的标准曲线。
1.2.4 竞争ELISA定量检测方法的建立
1.2.4.1 竞争ELISA基本检测程序
将大豆过敏原用0.05 mol/L pH9.6 CBS稀释液稀释后,各孔加100 μL于96孔酶标板中,4 ℃包被过夜后拍干,用PBST洗涤缓冲液重复洗涤三次,每次5 min,弃去洗涤液,在吸水纸上将酶标板拍干,之后的洗涤步骤与此步骤完全相同。用5%脱脂奶粉封闭液进行封闭,每孔加入300 μL,在37 ℃恒温培养箱中封闭120 min后,弃掉封闭液,用PBST洗涤缓冲液洗涤拍干;将50 μL一抗和50 μL不同浓度的蛋白溶液混合,在37 ℃预孵育10 min后加入孔内,每孔100 μL,37 ℃恒温孵育90 min后将液体倒出,洗涤拍干;将稀释到一定倍数的酶标二抗加入所有孔中,每孔100 μL,37 ℃恒温孵育60 min后将液体倒出,洗涤拍干,TMB底物溶液避光显色10 min,最后以2 mol/L H2SO4溶液终止反应,测定OD450值[21-22]。
1.2.4.2 最佳包被抗原浓度的优化
以制备得到的大豆过敏原(10 mg/mL)为标品,从蛋白浓度为10 μg/mL时开始进行梯度稀释,兔多克隆抗体以稀释倍数为2×104时开始往下稀释。选择吸光度值在1.3附近,且空白值低于0.1的参数为最终工作浓度。
1.2.4.3 最佳一抗、二抗工作浓度的优化
将抗原稀释至最佳浓度,进行包被,来优化兔多克隆抗体和羊抗兔酶标二抗的工作浓度。兔多克隆抗体的稀释倍数为1×104、2×104、4×104、8×104、1.6×105,分别在96孔板中纵向加入,羊抗兔酶标二抗的稀释倍数为2×104、4×104、8×104、1.6×105、3.2×105,分别在96孔板中横向加入。用棋盘法选择吸光度值在1.3附近,且空白值低于0.1的参数为最终工作浓度。
1.2.4.4 标准曲线制作
确定抗原、抗体最佳的工作浓度后,按照1.2.4.1的操作步骤测定不同大豆过敏原浓度下的吸光度值。以大豆过敏原作为竞争物,起始浓度为100 μg/mL,以4倍梯度稀释,共12个浓度,在最优条件下进行竞争ELISA实验。将标准品各浓度的OD值换算成B/B0(其中B为各蛋白浓度在450 nm下的OD值,B0是空白对照的平均值),以B/B0为纵坐标,相应标准品的浓度为横坐标,制作标准曲线。依据四参数拟合公式y=(A−D)/[1+(x/C)−B]+D对该曲线进行拟合(其中D表示吸光度下限值,代表着S型曲线的下渐近线;而A表示吸光度上限值,代表着S型曲线的上渐近线;C为吸光度增长速度开始发生变化的浓度值;B为吸光度增加速率参数,相当于曲线的斜率)。依据LOD=B0-3SD(SD为空白对照的标准偏差)计算检测限。
1.2.5 实际加工样品的制备
本研究中制备两种实际加工食品,分别是面包和蛋糕,进行实际样品回收率的测定,这种方法能够评估加工对提取和回收目标蛋白的实际影响以及检测效率。
制作面包的过程为:将5 g酵母加在125 g水中搅拌至酵母融化,再将250 g高筋小麦粉、50 g细砂糖、30 g黄油和50 g鸡蛋加入进行和面,直至面团能抻成很薄的薄膜,之后将面团静置醒发30 min,将成型好的面团放入烤盘中再次醒发,醒发至原体积的2~3倍,烤炉预热至上火180 ℃,下火200 ℃,烘烤15 min,取出冷却后即可。在本实验中需要两种面包,一种是未添加大豆的面包,一种是添加大豆的面包(在烘烤前将一定量的大豆粉均匀的铺在面团表面)。烘焙结束后,按照最佳前处理方法对两种面包进行蛋白提取,待用。
制作蛋糕的过程为:将5个鸡蛋蛋白用打蛋器打至粗泡状态,在蛋白里加入15 g细砂糖,继续打至细腻的泡沫,再加入15 g细砂糖,继续打至可呈现纹路的状态,最后再加入20 g的细砂糖,继续打至干性发泡的状态(当提起打蛋器的时候,蛋白能拉出一个短小直立的尖角),另外将5个蛋黄与30 g细砂糖搅拌均匀至蛋黄颜色变浅,再边搅拌边加入50 mL色拉油和50 mL牛奶,最后筛入90 g低筋小麦粉,慢慢地搅匀至光滑细腻无颗粒。蛋黄糊搅拌完成后,取蛋白霜入蛋黄糊中,翻拌均匀至光滑细腻无颗粒。把蛋糕放入预热好的烤箱中,上下火,170 ℃,烘烤40 min,取出即可。在本实验中需要两种蛋糕,一种是未添加大豆的蛋糕,一种是添加大豆的蛋糕(在烘烤前将一定量的大豆粉均匀的铺在面团表面)。烘焙结束后,按照最佳前处理方法对两种蛋糕进行蛋白提取,待用。
1.2.6 加标样品的制备
将三种不含大豆蛋白的食物(橙汁、巧克力、牛肉酱)打碎,然后将1 g食物碎加入总体积为5 mL的0.01 mol/L pH8.5 CBS(含0.05% SDS和0.05% DTT)中,用提取得到的大豆混合过敏原溶液进行加标,使终浓度为0.5、2、5 μg/mL。在4 ℃下涡旋振荡孵育1 h,然后10000 r/min离心10 min,取上清液,进行ELISA实验,每个梯度重复3次,根据下式计算回收率。
1.2.7 真实食物样品的制备
从超市购买豆奶、酱油、饼干、黄豆酱、芝麻糊5种经过剧烈加工过的食品,这些食品经过了发酵或高温烘焙等,采用双抗夹心ELISA和竞争ELISA分别检测其中是否含有大豆过敏原,对检测结果进行分析比较。提取步骤与上述相同。
1.3 数据处理
采用Microsoft Excel软件进行数据统计,所有数据为3次重复的平均值±标准差。并运用Origin软件进行作图,采用IBM SPSS Statistics 19.0(SPSS,Chicago,Illinois,USA)进行单因素方差分析等统计学分析,查看样本显著性(P<0.05)。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 大豆混合过敏原的制备
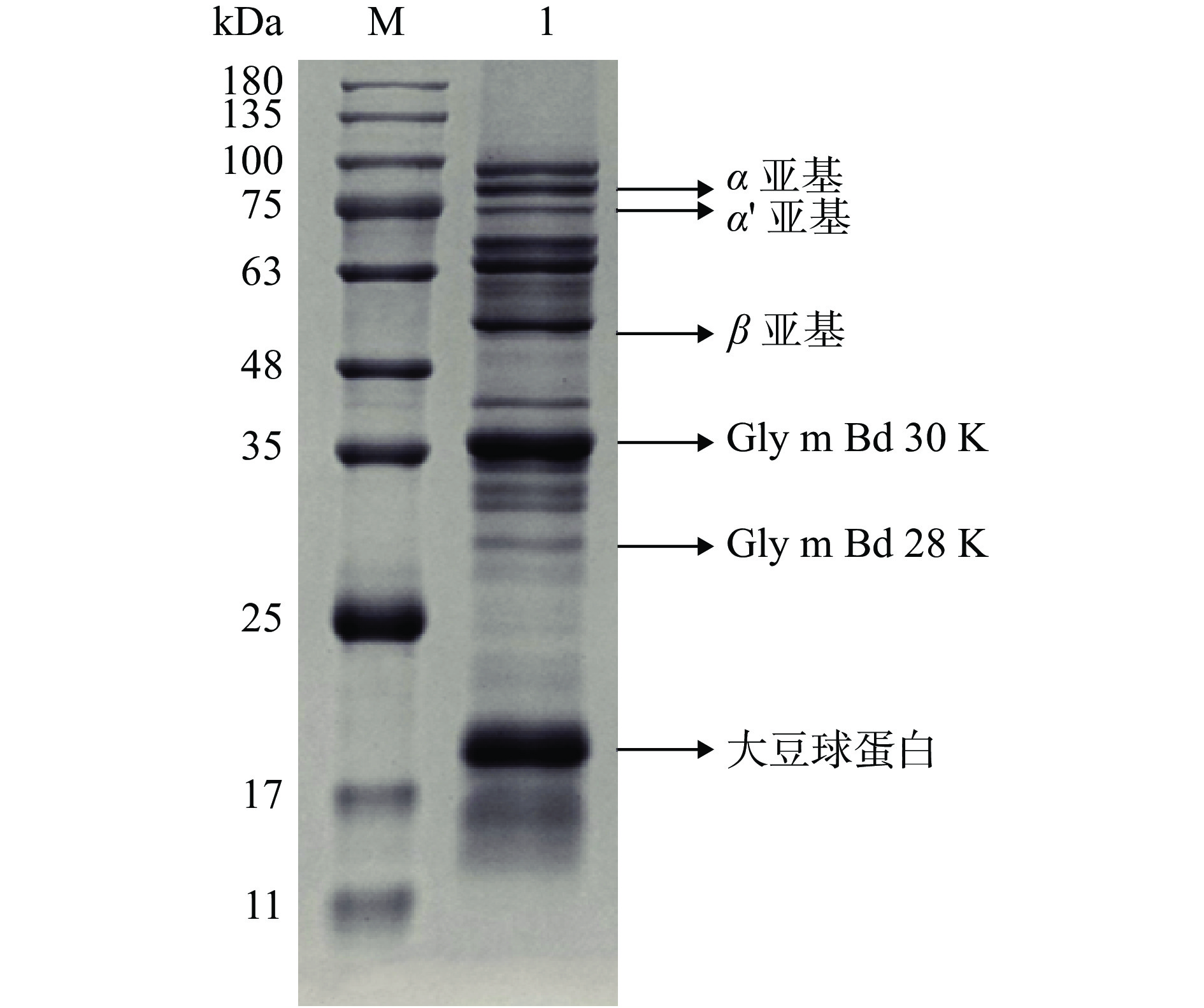
提取后的大豆混合过敏原溶液经BCA蛋白定量试剂盒定量后,通过SDS-PAGE电泳进行分析。如图1所示。
大豆中过敏原蛋白众多,致敏原数据库共收录38种,包括16种IgE介导的过敏原。但目前根据蛋白含量多少和致敏能力的大小,大豆球蛋白(22、52~55 kDa)、Gly m Bd 30K(30~35 kDa)、Gly m Bd 28K(28 kDa)和β-伴大豆球蛋白(50、63~67、75 kDa)被认为是大豆中最主要的过敏原。通过SDS-PAGE结果,可以看到主要的过敏原均已提取得到,与文献中所报道的情况基本一致[6]。
2.2 兔多抗和羊多抗纯化结果
将兔血清和羊血清进行Protein A/G亲和层析柱纯化后,得到的SDS-PAGE结果如图2所示。纯化的IgG抗体的分子量为150 kDa左右,本实验采用还原性电泳,泳道1和2显示,IgG在还原条件下主要显示为25 kDa的轻链和50 kDa的重链,说明经过Protein A/G亲和层析柱的纯化,得到了纯度较高的兔多克隆抗体和羊多克隆抗体。
2.3 夹心ELISA定量检测方法的建立
2.3.1 最佳捕获抗体、检测抗体和酶标二抗工作浓度的确定
如图3显示,当捕获抗体稀释5000倍时,P/N值最大;当检测抗体稀释8000倍时,P/N值最大;当酶标二抗稀释10000倍时,P/N值最大。最终考虑抗体等试剂的价格因素和食品安全风险因素等最终确定了如下实验条件,羊多克隆抗体用作捕获抗体以5000倍稀释;兔多克隆抗体作为检测抗体以8000倍稀释;酶标二抗以10000倍稀释。
2.3.2 最佳检测时间的确定
如图4所示,随着抗原孵育时间和TMB显色时间的增加,OD值也在增加,但由于整个反应过程阴性空白OD值非常低,故P/N值也在增加,当抗原孵育时间为60 min、TMB显色时间为10 min时,OD值已经超过1.0,满足实验要求,所以为了节省检测时间,提高检测效率,确定抗原孵育时间为60 min,TMB显色时间为10 min。当检测抗体孵育时间和酶标二抗工作时间增加到90 min时,P/N值均开始降低且OD值增加不多,故选择60 min作为检测抗体的孵育时间和酶标二抗的工作时间。
2.3.3 标准曲线的确立
在上述最适反应条件下制作标准曲线,将抗原设置为不同浓度(0.0078~30 μg/mL),并进行线性回归分析,选取其中具有线性关系的标准浓度范围(0.0625、0.25、1、2、3、4、6 μg/mL),绘制标准曲线。此曲线的回归方程为y=0.2333x+0.0692,R2为0.995,其中x表示抗原的浓度,y表示不同浓度抗原的吸光度,从结果来看,该标准曲线的线性关系良好。
2.4 竞争ELISA定量检测方法的建立
2.4.1 最佳抗原包被浓度的确定
结果如表1所示。从横向看,随着抗原浓度的降低,OD值也越来越低,当抗原浓度为2.5 μg/mL时,已经达到饱和,因此最终确定包被抗原的浓度为2.5 μg/mL。
表 1 棋盘法优化包被抗原的浓度Table 1. Results of chessboard method for optimination coating concentration一抗稀释倍数 大豆过敏原浓度(μg/mL) 10 5 2.5 1.25 0.63 0.31 0.16 0 2×104 1.80 1.55 1.50 1.13 0.92 0.47 0.23 0.01 4×104 1.06 1.06 0.98 0.86 0.51 0.25 0.13 0.01 8×104 0.82 0.66 0.58 0.49 0.39 0.14 0.07 0.01 1.6×105 0.47 0.38 0.36 0.29 0.21 0.08 0.04 0.01 3.2×105 0.28 0.22 0.20 0.16 0.09 0.05 0.03 0.01 0 0.06 0.05 0.04 0.03 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.01 2.4.2 最佳一抗、二抗工作浓度的优化
结果见表2。当兔多克隆抗体稀释倍数为20000倍时,已经达到饱和,当稀释倍数从2×104倍增加到4×104倍时,吸光度值有非常明显的降低,故可先将一抗稀释倍数定为20000倍,再观察二抗,当二抗稀释倍数为8×104倍时,OD值可达到1.3,且背景值很低,所以可将二抗稀释倍数定为80000倍。因此,确定包被抗原的最终浓度为2.5 μg/mL,兔多克隆抗体最佳稀释倍数为20000倍,HRP标记羊抗兔IgG的最佳稀释倍数为80000倍。
表 2 棋盘法优化一抗和二抗的工作浓度Table 2. Results of chessboard method for optimination of primary antibody and secondary antibody二抗稀释倍数 一抗稀释倍数 1×104 2×104 4×104 8×104 1.6×105 0 2×104 3.73 3.13 1.77 1.42 0.81 0.03 4×104 2.59 2.01 1.28 0.72 0.39 0.03 8×104 1.69 1.31 0.71 0.40 0.22 0.03 1.6×105 0.94 0.63 0.38 0.22 0.14 0.03 3.2×105 0.50 0.34 0.21 0.12 0.08 0.02 0 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.02 2.4.3 标准曲线的建立
确定抗原、抗体最佳的工作浓度后,按照1.2.4.1的操作步骤测定不同大豆过敏原浓度下的吸光度值。从结果来看(图5),检测范围为10~100000 ng/mL,最低检测限为10 ng/mL。
2.5 竞争ELISA方法和双抗夹心ELISA方法的分析比较
2.5.1 实际加工样品回收结果
在面包和蛋糕进行烘烤前,将3.0 g大豆粉揉搓在20.0 g面团中,进行烘焙。制作完成后,按照大豆过敏原的提取方法对自制的面包和蛋糕进行蛋白的提取,将提取的蛋白适度稀释后,用竞争ELISA方法和双抗夹心ELISA方法分别检测空白样品和加入大豆过敏原的加工样品。大豆中蛋白的含量约在40%~50%,可根据此数据进行回收率的计算。添加回收结果见表3。
表 3 竞争ELISA法和双抗夹心ELISA法添加回收结果Table 3. Results of actual processed samples by competitive ELISA and double-antibody sandwich ELISA检测方法 添加大豆的质量
(mg/g)蛋白的理论
添加量
(mg/g)ELISA测定值
(mg/g面包)回收率
(%)ELISA测定值
(mg/g蛋糕)回收率
(%)夹心
ELISA150 60 30.12±0.53 50.20±0.88 27.98±0.61 46.60±0.42 竞争
ELISA150 60 35.66±0.34 59.40±0.16 31.35±0.55 52.30±0.32 从结果来看,在经过高温烘烤等剧烈加工后的食物样品,竞争ELISA检测后的回收率要高于双抗夹心ELISA的回收率,该结果与De等[21]的研究结果一致。这可能都是因为在剧烈的加工条件下,某些过敏原上的多个抗原表位被破坏,两株抗体不能识别过敏原上的两个不同的表位,而竞争ELISA中抗体只需要识别单个表位,所以某些夹心ELISA方法检测不到的蛋白,竞争ELISA方法可以检测得到。
2.5.2 加标食品回收结果
将提取得到的大豆混合过敏原溶液加入三种不含大豆蛋白的食物(橙汁、巧克力、牛肉酱)中,使终浓度为0.5、2、5 μg/mL,用双抗夹心ELISA方法和竞争ELISA两种方法来进行加标实验,根据检测结果计算回收率。结果见表4。
表 4 竞争ELISA法和双抗夹心ELISA法加标回收结果Table 4. Results of competitive ELISA method and double-antibody sandwich ELISA method for the detection of labeled food基质
样品大豆过敏原
加标浓度
(μg/mL)夹心ELISA
检测浓度
(μg/mL)回收率
(%)竞争ELISA
检测浓度
(μg/mL)回收率
(%)橙汁 0.5 0.59±0.32 118.00±0.64 0.47±0.38 94.00±0.76 2 1.89±0.56 94.50±0.28 1.92±0.31 96.00±0.16 5 5.35±1.01 107.00±0.20 4.93±0.56 98.60±0.11 巧克力 0.5 ND ND 0.34±0.11 68.00±0.22 2 1.54±0.33 77.00±0.17 2.45±0.45 122.50±0.23 5 4.14±1.26 82.80±0.25 4.58±0.99 91.60±0.20 牛肉酱 0.5 ND ND 0.38±0.20 76.00±0.40 2 1.39±1.32 69.50±0.66 1.51±1.11 75.50±0.56 5 4.23±1.08 84.60±0.22 4.88±1.20 97.60±0.24 注:结果表示为平均值±标准差(n=3);ND表示未检出;表5同。 当基质样品为橙汁时,从结果中可以看出双抗夹心ELISA方法检测得到的回收率要高于竞争ELISA,橙汁中成分简单,加工不复杂,在这种环境中,夹心ELISA方法的准确性和灵敏度均是要由于竞争ELISA方法,这与Segura等[23]的研究一致。但是在巧克力和牛肉酱中,当大豆过敏原的加标浓度较低(0.5 μg/mL)时,双抗夹心ELISA中没有检测到大豆过敏原,而竞争ELISA方法中检测到了大豆过敏原的存在,回收率为68%和76%,回收率不高的原因可能是因为基质中成分的复杂,基质效应的影响,但整体上在这种基质中成分较多,加工较为复杂的食物样品检测中,竞争ELISA方法还是较为适用的。
2.5.3 真实样品检测结果
除了对实际样品进行加标回收实验,还购买了五种在售食品,分别是豆奶、酱油、饼干、黄豆酱、芝麻糊,在这几种食物的标签上,豆奶、酱油和黄豆酱这三种分别标注了大豆成分,饼干和芝麻糊这两种食物标签上未标注大豆成分。采用竞争ELISA和双抗夹心ELISA方法对这5种食物进行检测,结果如表5。
表 5 竞争ELISA法和双抗夹心ELISA法对真实食品的检测结果Table 5. Results of competitive ELISA and double-antibody sandwich ELISA on real food食物样品 竞争ELISA测得大豆过敏原含量
(mg/mL)夹心ELISA测得大豆过敏原含量
(mg/mL)酱油 3.28±0.99 2.56±0.67 饼干 ND ND 芝麻糊 0.18±0.36 0.35±0.13 黄豆酱 6.52±0.45 5.83±0.21 豆奶 1.53±0.52 1.89±0.23 结果显示,在对芝麻糊中大豆过敏原的检测中,夹心ELISA方法和竞争ELISA方法都检测到了微量大豆过敏原的存在,但是在芝麻糊食品标签上没有标注大豆过敏原成分,这可能是由于在食品的生产环节造成了交叉污染导致的。在饼干当中均未检测到大豆过敏原成分,这与标签和配料表上描述的一致,在对酱油和黄豆酱的检测中,竞争ELISA方法比夹心ELISA方法检测到的大豆过敏原含量要略高一些,这可能也是因为黄豆酱和酱油都属于发酵类食品,发酵对食物中的蛋白有影响,会导致某些蛋白过敏原性的降低,或者大分子蛋白的降解,或者对过敏原的表位造成破坏,进而导致夹心ELISA方法无法完全准确地测出其中所含过敏原的含量[24]。在对豆奶中大豆过敏原的检测中,夹心ELISA方法要比竞争ELISA方法的灵敏度和准确性更好一些,这与之前的研究结果是一致的,对于成分简单,轻加工的食品来说,更适用于夹心ELISA方法进行大豆过敏原的检测,而对于深度加工,加工条件比较剧烈的食品来说,更适用于竞争ELISA方法来检测其中大豆过敏原的含量。
3. 讨论
本研究初步建立了检测大豆过敏原的双抗夹心ELISA方法和竞争ELISA方法,通过实际加工样品的回收实验、加标食品回收实验以及对真实食物样本的检测,对竞争ELISA法和双抗夹心ELISA法的适用范围进行了比较,结果表明,竞争ELISA法更适用于食物基质复杂,经过深度加工的食品,而夹心ELISA法更适用于食物成分简单,轻加工后的食品,两种方法没有优劣之分,在各自的适用范围内均能实现较准确的检测。
在进行回收率的实验中,发现有基质效应的存在,越是复杂的食物体系,回收率会越低,可能是因为食品基质的复杂组分之间会产生相互作用来影响过敏原的检测,并且基质组分和加工时的相互作用等因素可能会加大对过敏原检测的影响[25-26]。所以在以后可增强对食品基质效应的影响以及食品加工对食物致敏性影响的研究。
综上,本研究初步建立了大豆过敏原的两种ELISA检测方法,并进行了比较。对之后食物样品中大豆蛋白的快速检测和筛选有积极的作用,使得可以通过检测尽可能低量的过敏原来最大程度的降低过敏反应的风险,具有一定的应用前景和应用价值。
-
表 1 棋盘法优化包被抗原的浓度
Table 1 Results of chessboard method for optimination coating concentration
一抗稀释倍数 大豆过敏原浓度(μg/mL) 10 5 2.5 1.25 0.63 0.31 0.16 0 2×104 1.80 1.55 1.50 1.13 0.92 0.47 0.23 0.01 4×104 1.06 1.06 0.98 0.86 0.51 0.25 0.13 0.01 8×104 0.82 0.66 0.58 0.49 0.39 0.14 0.07 0.01 1.6×105 0.47 0.38 0.36 0.29 0.21 0.08 0.04 0.01 3.2×105 0.28 0.22 0.20 0.16 0.09 0.05 0.03 0.01 0 0.06 0.05 0.04 0.03 0.02 0.01 0.01 0.01 表 2 棋盘法优化一抗和二抗的工作浓度
Table 2 Results of chessboard method for optimination of primary antibody and secondary antibody
二抗稀释倍数 一抗稀释倍数 1×104 2×104 4×104 8×104 1.6×105 0 2×104 3.73 3.13 1.77 1.42 0.81 0.03 4×104 2.59 2.01 1.28 0.72 0.39 0.03 8×104 1.69 1.31 0.71 0.40 0.22 0.03 1.6×105 0.94 0.63 0.38 0.22 0.14 0.03 3.2×105 0.50 0.34 0.21 0.12 0.08 0.02 0 0.03 0.02 0.03 0.03 0.02 0.02 表 3 竞争ELISA法和双抗夹心ELISA法添加回收结果
Table 3 Results of actual processed samples by competitive ELISA and double-antibody sandwich ELISA
检测方法 添加大豆的质量
(mg/g)蛋白的理论
添加量
(mg/g)ELISA测定值
(mg/g面包)回收率
(%)ELISA测定值
(mg/g蛋糕)回收率
(%)夹心
ELISA150 60 30.12±0.53 50.20±0.88 27.98±0.61 46.60±0.42 竞争
ELISA150 60 35.66±0.34 59.40±0.16 31.35±0.55 52.30±0.32 表 4 竞争ELISA法和双抗夹心ELISA法加标回收结果
Table 4 Results of competitive ELISA method and double-antibody sandwich ELISA method for the detection of labeled food
基质
样品大豆过敏原
加标浓度
(μg/mL)夹心ELISA
检测浓度
(μg/mL)回收率
(%)竞争ELISA
检测浓度
(μg/mL)回收率
(%)橙汁 0.5 0.59±0.32 118.00±0.64 0.47±0.38 94.00±0.76 2 1.89±0.56 94.50±0.28 1.92±0.31 96.00±0.16 5 5.35±1.01 107.00±0.20 4.93±0.56 98.60±0.11 巧克力 0.5 ND ND 0.34±0.11 68.00±0.22 2 1.54±0.33 77.00±0.17 2.45±0.45 122.50±0.23 5 4.14±1.26 82.80±0.25 4.58±0.99 91.60±0.20 牛肉酱 0.5 ND ND 0.38±0.20 76.00±0.40 2 1.39±1.32 69.50±0.66 1.51±1.11 75.50±0.56 5 4.23±1.08 84.60±0.22 4.88±1.20 97.60±0.24 注:结果表示为平均值±标准差(n=3);ND表示未检出;表5同。 表 5 竞争ELISA法和双抗夹心ELISA法对真实食品的检测结果
Table 5 Results of competitive ELISA and double-antibody sandwich ELISA on real food
食物样品 竞争ELISA测得大豆过敏原含量
(mg/mL)夹心ELISA测得大豆过敏原含量
(mg/mL)酱油 3.28±0.99 2.56±0.67 饼干 ND ND 芝麻糊 0.18±0.36 0.35±0.13 黄豆酱 6.52±0.45 5.83±0.21 豆奶 1.53±0.52 1.89±0.23 -
[1] 李堂昊, 布冠好, 陈复生. 大豆主要过敏原β-伴大豆球蛋白及其抗原表位的研究进展[J]. 大豆科学,2019,38(5):806−812. [LI T H, BU G H, CHEN F S. Development in major allergen β-conglycinin and its antigen epitopes of soybean[J]. Soybean Science,2019,38(5):806−812. [2] L'HOCINE L, BOYE J I. Allergenicity of soybean: New developments in identification of allergenic proteins, cross-reactivities and hypoallergenization technologies[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2007,47(2):127−143. doi: 10.1080/10408390600626487
[3] FRANKE A A, HALM B M, ASHBURN L A. Isoflavones in children and adults consuming soy[J]. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics,2008,476(2):161−170. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2008.02.009
[4] WANG T, QIN G, SUN Z, et al. Advances of research on glycinin and β-conglycinin: A review of two major soybean allergenic proteins[J]. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2014,54(7):850−862. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2011.613534
[5] SAEED H, GAGNON C, COBER E, et al. Using patient serum to epitope map soybean glycinins reveals common epitopes shared with many legumes and tree nuts[J]. Molecular Immunology,2016,70:125−133. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2015.12.008
[6] 朱婷伟, 陈复生, 布冠好, 等. 大豆蛋白过敏原结构与功能的研究进展[J]. 食品工业科技,2013,34(21):377−380. [ZHU T W, CHEN F S, BU G H, et al. Developments in the structure and function of soybean protein allergens[J]. Science and Technology of Food Industry,2013,34(21):377−380. doi: 10.13386/j.issn1002-0306.2013.21.034 [7] 杨慧, 陈红兵, 程伟, 等. 大豆主要过敏原及其脱敏方法的研究进展[J]. 食品科学,2011,32(21):273−277. [YANG H, CHEN H B, CHENG W, et al. Research progress of soybean allergens and its desensitization methods[J]. Food Science,2011,32(21):273−277. [8] TÖRÖK K, HAJAS L, BUGYI Z, et al. Investigation of the effects of food processing and matrix components on the analytical results of ELISA using an incurred gliadin reference material candidate[J]. Acta Alimentaria,2015,44(3):390−399. doi: 10.1556/AAlim.2014.0018
[9] LI Y S, MENG X Y, ZHOU Y, et al. Magnetic bead and gold nanoparticle probes based immunoassay for β-casein detection in bovine milk samples[J]. Biosensors & Bioelectronics,2015,66:559−564.
[10] TAN Y, HALSEY J F, TANG T, et al. Application of photonic crystal enhanced fluorescence to detection of low serum concentrations of human IgE antibodies specific for a purified cat allergen (Fel D1)[J]. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,2016,77:194−201. doi: 10.1016/j.bios.2015.08.071
[11] SEGURA G I, BLÁZQUEZ S A, GALÁN M P, et al. Development of sandwich and competitive ELISA formats to determine β-conglycinin: Evaluation of their performance to detect soy in processed food[J]. Food Control,2019,103:78−85. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2019.03.035
[12] GENG T, LIU K, FRAZIER R, et al. Development of a sandwich ELISA for quantification of Gly m 4, a soybean allergen[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2015,63(20):4947−4953. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b00792
[13] UEBERHAM E, SPIEGEL H, HAVENITH H, et al. Simplified tracking of a soy allergen in processed food using a monoclonal antibody-based sandwich ELISA targeting the soybean 2S albumin Gly m 8[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2019,67(31):8660−8667. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.9b02717
[14] ZENG L, SONG S, ZHENG Q, et al. Development of a sandwich ELISA and immunochromatographic strip for the detection of shrimp tropomyosin[J]. Food and Agricultural Immunology,2019,30(1):606−619. doi: 10.1080/09540105.2019.1609912
[15] KOIZUMI D, SHIROTA K, ODA H, et al. Development and evaluation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay using a nonpoisonous extraction system for the determination of crustacean protein in processed foods[J]. Journal of Aoac International,2017,101(3):798−804.
[16] WEI Y, SATHE S K, TEUBER S S, et al. A sensitive sandwich ELISA for the detection of trace amounts of cashew (Anacardium occidentale L.) nut in foods[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2003,51(11):3215−3221. doi: 10.1021/jf025977x
[17] 张洁琼. 杏仁过敏原ELISA方法的建立及加工方式对致敏性的影响[D]. 天津: 天津科技大学, 2013. ZHANG J Q. Development of enzyme-linked immunoassay and effects of processing for almond allergen, amandin[D]. Tianjin: Tianjin University of Science and Technology, 2013.
[18] 吕良涛, 林洪, 李振兴, 等. 菲律宾蛤仔过敏原原肌球蛋白的鉴定与分子克隆[J]. 食品安全质量检测学报,2015,6(11):4538−4544. [LÜ L T, LIN H, LI Z X, et al. Identification and molecular cloning of tropomyosin, an allergen of clams Philippines[J]. Journal of Food Safety and Quality,2015,6(11):4538−4544. doi: 10.19812/j.cnki.jfsq11-5956/ts.2015.11.049 [19] LIU C, CHHABRA G S, SATHE S K. Pistachio (Pistacia vera L.) detection and quantification using a murine monoclonal antibody-based direct sandwich enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay[J]. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry,2015,63(41):9139−9149. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.5b03066
[20] KIYOTA K, KAWATSU K, SAKATA J, et al. Development of sandwich ELISA for quantification of the orange allergen profilin (Cit s 2)[J]. Food and Agricultural Immunology,2016,27(1):128−137. doi: 10.1080/09540105.2015.1079599
[21] DE L R, MATA L, ESTOPAÑÁN G, et al. Evaluation of indirect competitive and double antibody sandwich ELISA tests to determine β-lactoglobulin and ovomucoid in model processed foods[J]. Food and Agricultural Immunology,2008,19(4):339−350. doi: 10.1080/09540100802520755
[22] DENG X, LIU L, MA W, et al. Development and validation of a sandwich ELISA for quantification of peanut agglutinin (PNA) in foods[J]. Food and Agricultural Immunology,2012,23(3):265−272. doi: 10.1080/09540105.2011.617358
[23] SEGURA G I, NICOLAU L I, GALÁN M P, et al. Development of two ELISA formats to determine glycinin. Application to detect soy in model and commercial processed food[J]. Food Control,2018,93:32−39. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2018.05.038
[24] 许倩. 不同加工处理对牛乳蛋白抗原性及过敏原性的影响[D]. 北京: 中国农业大学, 2017 XU Q. Effects of different processing treatments on antigenicity and allergenicity of milk protein[D]. Beijing: China Agricultural University, 2017.
[25] TAYLOR S L, NORDLEE J A, NIEMANN L M, et al. Allergen immunoassays-considerations for use of naturally incurred standards[J]. Analytical & Bioanalytical Chemistry,2009,395(1):83−92.
[26] 范祚舟, 徐加发, 沈萍萍. 酶联免疫分析技术研究进展[J]. 分析科学学报,2011,27(1):113−118. [FAN Z Z, XU J F, SHEN P P. Research progress of enzyme-linked immunoassay[J]. Journal of Analytical Science,2011,27(1):113−118.






 下载:
下载:




 下载:
下载:
